MIM. No. Locus Gene Protein. AD p16.3 FGFR3 FGFR3. AD p16.3 FGFR3 FGFR3
|
|
|
- Ursula Alexander
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1. Achondrodysplasia group Thanatophoric dysplasia type 1 AD p16.3 FGFR3 FGFR3 (TD1) Thanatophoric dysplasia type 2 AD p16.3 FGFR3 FGFR3 (TD2) Severe achondroplasia with AD see 4p16.3 FGFR3 FGFR3 developmental delay and acanthosis nigricans (SADDAN) Achondroplasia AD p16.3 FGFR3 FGFR3 Hypochondroplasia AD p16.3 FGFR3 FGFR3 Camptodactyly, tall stature and AD p16.3 FGFR3 FGFR3 hearing loss syndrome (CATSHL) Hypochondroplasia like AD, SP dysplasia(s)
2 See also group 33 for craniosynostoses syndromes linked to FGFR3 mutations, as well as LADD syndrome in group 39 for another FGFR3-related phenotype 2. Type 2 collagen group and similar disorders Achondrogenesis type 2 (ACG2; AD q13.1 COL2A1 Type 2 collagen Langer-Saldino) Platyspondylic dysplasia, AD q13.1 COL2A1 Type 2 collagen Torra type Hypochondrogenesis AD q13.1 COL2A1 Type 2 collagen Spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia AD q13.1 COL2A1 Type 2 collagen congenital (SEDC) Spondyloepimetaphyseal AD q13.1 COL2A1 Type 2 collagen dysplasia (SEMD) Strudwick type
3 Kniest dysplasia AD q13.1 COL2A1 Type 2 collagen Spondyloperipheral dysplasia AD q13.1 COL2A1 Type 2 collagen Mild SED with premature onset AD 12q13.1 COL2A1 Type 2 collagen arthrosis SED with metatarsal shortening AD q13.1 COL2A1 Type 2 collagen (formerly Czech dysplasia) Stickler syndrome type 1 AD q13.1 COL2A1 Type 2 collagen Stickler-like syndrome(s) 3. Type 11 collagen group Stickler syndrome type 2 AD p21 COL11A1 Type 11 collagen alpha-1 chain Marshall syndrome AD p21 COL11A1 Type 11 collagen alpha-1 chain
4 Fibrochondrogenesis AR p21 COL11A1 Type 11 collagen alpha-1 chain Otospondylomegaepiphyseal dysplasia (OSMED), recessive AR p21.3 COL11A2 Type 11 collagen alpha-2 chain type Otospondylomegaepiphyseal dysplasia (OSMED), dominant AD p21.3 COL11A2 Type 11 collagen alpha-2 chain type (Weissenbacher- Zweymüller syndrome, Stickler syndrome type 3) See also Stickler syndrome type 1 in group 2 4. Sulphation disorders group Achondrogenesis type 1B (ACG1B) AR q32-33 DTDST SLC26A2 sulfate transporter Atelosteogenesis type 2 (AO2) AR q32-33 DTDST SLC26A2 sulfate transporter
5 Diastrophic dysplasia (DTD) AR q32-33 DTDST SLC26A2 sulfate transporter MED, autosomal recessive type (rmed; EDM4) AR q32-33 DTDST SLC26A2 sulfate transporter SEMD, PAPSS2 type AR q23- PAPSS2 PAPS-Synthetase 2 q24 Chondrodysplasia with congenital joint dislocations, CHST3 type (recessive Larsen syndrome) AR q22.1 CHST3 Carbohydrate sulfotransferase 3; chondroitin 6- sulfotransferase Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, CHST14 type ( musculo-skeletal variant ) AR q14 CHST14 Carbohydrate sulfotransferase 14; dermatan 4- sulfotransferase See also group 7 and group 26 for other conditions with multiple dislocations. 5. Perlecan group
6 Dyssegmental dysplasia, Silverman-Handmaker type AR q36-34 PLC (HSPG2) Perlecan Dyssegmental dysplasia, Rolland-Desbuquois type AR q36-34 PLC (HSPG2) Perlecan Schwartz-Jampel syndrome (myotonic chondrodystrophy) AR q36-34 PLC (HSPG2) Perlecan 6. Aggrecan group SED, Kimberley type AD q26 AGC1 Aggrecan SEMD, Aggrecan type AR q26 AGC1 Aggrecan Familial osteochondritis AD q26 AGC1 Aggrecan dissecans 7. Filamin group and related disorders Frontometaphyseal dysplasia XLD Xq28 FLNA Filamin A
7 Osteodysplasty Melnick-Needles XLD Xq28 FLNA Filamin A Otopalatodigital syndrome type 1 XLD Xq28 FLNA Filamin A (OPD1) Otopalatodigital syndrome type XLD Xq28 FLNA Filamin A 2 (OPD2) Terminal osseous dysplasia with XLD Xq28 FLNA Filamin A pigmentary defects (TODPD) Atelosteogenesis type 1 (AO1) AD p14.3 FLNB Filamin B Atelosteogenesis type 3 (AO3) AD p14.3 FLNB Filamin B Larsen syndrome (dominant) AD p14.3 FLNB Filamin B Spondylo-carpal-tarsal dysplasia AR p14.3 FLNB Filamin B Spondylo-carpal-tarsal dysplasia AR
8 Franck - ter Haar syndrome AR q35.1 SH3PXD2B TKS4 Serpentine fibula - polycystic AD? kidney syndrome (see also group 4 for recessive Larsen syndrome and group 26 for conditions with multiple dislocations) 8. TRPV4 group Metatropic dysplasia AD q24.1 TRPV4 Transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily V, member 4 Spondyloepimetaphyseal dysplasia, Maroteaux type (Pseudo-Morquio syndrome type AD q24.1 TRPV4 Transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily V, member 4 2) Spondylometaphyseal dysplasia, Kozlowski type AD q24.1 TRPV4 Transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily V, member 4
9 Brachyolmia, autosomal dominant type AD q24.1 TRPV4 Transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily V, member 4 Familial digital arthropathy with brachydactyly AD q24.1 TRPV4 Transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily V, member 4 9. Short-ribs dysplasias (with or without polydactyly) group Chondroectodermal dysplasia AR p16 EVC1 EvC gene 1 (Ellis-van Creveld) 4p16 EVC2 EvC gene 2 Short ribs polydactyly syndrome (SRPS) type 1/3 AR q22.3 DYNC2H1 Dynein, cytoplasmic 2, heavy chain 1 (Saldino-Noonan/Verma- Naumoff) SRPS type 1/3 (Saldino- Noonan/Verma-Naumoff) AR q25.33 IFT80 Intraflagellar transport 80 (homolog of)
10 SRPS type 1/3 (Saldino- AR Noonan/Verma-Naumoff) SRPS type 2 (Majewski) AR SRPS type 4 (Beemer) AR Oral-facial-digital syndrome type AR (Mohr-Majewski) Asphyxiating thoracic dysplasia (ATD; Jeune) AR q25.33 IFT80 intraflagellar transport 80 (homolog of) Asphyxiating thoracic dysplasia (ATD; Jeune) AR q22.3 DYNC2H1 Dynein, cytoplasmic 2, heavy chain 1 Asphyxiating thoracic dysplasia AR (ATD; Jeune) Thoracolaryngopelvic dysplasia AD (Barnes) See also paternal UPD14 and
11 cerebro-costo-mandibular syndrome 10. Multiple epiphyseal dysplasia and pseudoachondroplasia group Pseudoachondroplasia (PSACH) AD p COMP COMP Multiple epiphyseal dysplasia AD p13.1 COMP COMP (MED) type 1 (EDM1) Multiple epiphyseal dysplasia AD p COL9A2 Collagen 9 alpha-2 chain (MED) type 2 (EDM2) Multiple epiphyseal dysplasia AD q13.3 COL9A3 Collagen 9 alpha-3 chain (MED) type 3 (EDM3) Multiple epiphyseal dysplasia AD p23-24 MATN3 Matrilin 3 (MED) type 5 (EDM5) Multiple epiphyseal dysplasia AD q13 COL9A1 Collagen 9 alpha-1 chain
12 (MED) type 6 (EDM6) Multiple epiphyseal dysplasia (MED), other types Stickler syndrome, recessive type AR q13 COL9A1 Collagen 9 alpha-1 chain Familial hip dysplasia (Beukes) AD q35 Multiple epiphyseal dysplasia AR with microcephaly and nystagmus (Lowry-Wood) See also Multiple Epiphyseal Dysplasia, recessive type (rmed; EDM4) in sulphation disorders (group 4), Familial osteochondritis dissecans in the Aggrecan group, as well as ASPED in the Acromelic group 11. Metaphyseal dysplasias Metaphyseal dysplasia, Schmid AD q COL10A1 Collagen 10 alpha-1 chain
13 type (MCS) Cartilage-hair hypoplasia (CHH; metaphyseal dysplasia, AR p13 RMRP RNA component of RNAse H McKusick type) Metaphyseal dysplasia, Jansen AD p PTHR1 PTH/PTHrP receptor 1 type Eiken dysplasia AR p PTHR1 PTH/PTHrP receptor 1 Metaphyseal dysplasia with AR q11 SBDS SBDS protein pancreatic insufficiency and cyclic neutropenia (Shwachman- Bodian-Diamond syndrome, SBDS) Metaphyseal anadysplasia type 1 AD, AR q22.2 MMP13 Matrix metalloproteinase 13 Metaphyseal anadysplasia type 2 AR 20q13.12 MMP9 Matrix metalloproteinase 9 Metaphyseal dysplasia, Spahr AR type
14 Metaphyseal AR acroscyphodysplasia (various types) Genochondromatosis (type AD/SP /type 2) Metaphyseal chondromatosis with D-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria AR/SP see Spondylometaphyseal dysplasias (SMD) Spondyloenchondrodysplasia (SPENCD) AR p13.2 ACP5 Tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) Odontochondrodysplasia AR (ODCD) Spondylometaphyseal dysplasia, AD Sutcliffe type or corner fractures type
15 SMD with severe genu valgum AD SMD with cone-rod dystrophy AR SMD with retinal degeneration, AR axial type Dysspondyloenchondromatosis SP SP Cheirospondyloenchondromatosis See also SMD Kozlowski (group TRPV4) disorders in group 11 as well as SMD Sedaghatian type in group 12; there are many individual reports of SMD variants. 13. Spondylo-epi-(meta)- physeal dysplasias (SE(M)D)
16 Dyggve-Melchior-Clausen AR q12- DYM Dymeclin dysplasia (DMC) 21.1 Immuno-osseous dysplasia (Schimke) AR q34-36 SMARCAL1 SWI/SNF-related regulator of chromatin subfamily A- like protein 1 SED, Wolcott-Rallison type AR p12 EIF2AK3 Translation initiation factor 2-alpha kinase-3 SEMD, Matrilin type AR p23-p24 MATN3 Matrilin 3 SEMD, short limb abnormal calcification type AR q23 DDR2 Discoidin domain receptor family, member 2 SED tarda, X-linked (SED-XL) XLR Xp22 SEDL Sedlin AR p16.1 NKX3-2 NK3 Homeobox 2 Spondylo-megaepiphysealmetaphyseal dysplasia (SMMD) Spondylodysplastic Ehlers- AR p11.2 SLC39A13 Zinc transporter ZIP13 Danlos syndrome
17 SPONASTRIME dysplasia AR SEMD with joint laxity (SEMD- AD JL) leptodactylic or Hall type SEMD with joint laxity (SEMD- AR JL) Beighton type Platyspondyly (brachyolmia) AR with amelogenesis imperfecta Late onset SED, autosomal AR recessive type Brachyolmia, Hobaek and Toledo types AR , See also: Brachyolmia (group 8), Opsismodysplasia (group 14), SEMDs (group 11), mucopolysaccharidosis type 4 (Morquio syndrome) and other conditions in group 26, as well as PPRD (SED with progressive
18 arthropathy) in group Severe spondylodysplastic dysplasias Achondrogenesis type 1A (ACG1A) AR q32.12 TRIP11 Golgi-microtubuleassociated protein, 210-KD; GMAP210 Schneckenbecken dysplasia AR p31.3 SLC35D1 solute carrier family 35 member D1; UDPglucuronic acid/udp-nacetylgalactosamine dual transporter Spondylometaphyseal dysplasia, AR Sedaghatian type Severe spondylometaphyseal AR 7q11 SBDS SBDS gene, function still unclear dysplasia (SMD Sedaghatianlike) Opsismodysplasia AR
19 See also: Thanatophoric dysplasia, types 1 and 2 (group 1); ACG2 and Torra dysplasia (group 2); Fibrochondrogenesis (group 3); Achondrogenesis type 1B (ACG1B, group 4); and Metatropic Dysplasia (TRPV4 group) 15. Acromelic dysplasias Trichorhinophalangeal dysplasia types 1/3 AD q24 TRPS1 Zinc finger transcription factor Trichorhinophalangeal dysplasia type 2 (Langer-Giedion) AD q24 TRPS1 and EXT1 Zinc finger transcription factor and Exostosin 1 Acrocapitofemoral dysplasia AR q33-q35 IHH Indian hedgehog Cranioectodermal dysplasia (Levin-Sensenbrenner) type 1 AR q21 IFT122 Intraflagellar transport 122 (Chlamydomonas, homolog of) Cranioectodermal dysplasia AR p24.1 WDR35 WD repeat-containing
20 (Levin-Sensenbrenner) type 2 protein 35 Geleophysic dysplasia AR q34.2 ADAMTSL ADAMTS-like protein 2 2 Geleophysic dysplasia, other AR types Acromicric dysplasia AD Acrodysostosis AD AD Angel-shaped phalangoepiphyseal dysplasia (ASPED) Saldino-Mainzer dysplasia AR See also: Short rib dysplasias group 16. Acromesomelic dysplasias
21 Acromesomelic dysplasia type Maroteaux (AMDM) AR p13-12 NPR2 Natriuretic peptide receptor 2 Grebe dysplasia AR q11.2 GDF5 Growth and Differentiation Factor 5 Fibular hypoplasia and complex brachydactyly (Du Pan) AR q11.2 GDF5 Growth and Differentiation Factor 5 Acromesomelic dysplasia with genital anomalies AR q23-24 BMPR1B Bone morphogenetic protein receptor 1B Acromesomelic dysplasia, AD Osebold-Remondini type 17. Mesomelic and rhizomesomelic dysplasias Dyschondrosteosis (Leri-Weill) Pseudo Xpter- SHOX Short stature homeobox AD p22.32 gene Langer type (homozygous Pseudo Xpter- SHOX Short stature homeobox dyschondrosteosis) AR p22.32 gene
22 Omodysplasia AR q31- GPC6 Glypican 6 q32 Robinow syndrome, recessive type AR q22 ROR2 Receptor tyrosine kinaselike orphan receptor 2 Robinow syndrome, dominant AD type Mesomelic dysplasia, Korean type AD 2q24-32 Duplication in HOXD gene cluster Mesomelic dysplasia, Kantaputra type AD q24-32 Duplications in HOXD gene cluster Mesomelic dysplasia, Nievergelt AD type Mesomelic dysplasia, Kozlowski- AR Reardon type Mesomelic dysplasia with acral synostoses (Verloes-David- AD q13 SULF1 and SLCO5A1 Heparan sulfate 6-Oendosulfatase 1 and solute carrier organic anion
23 Pfeiffer type) transporter family member 5A1 Mesomelic dysplasia, SP Savarirayan type (Triangular Tibia-Fibular Aplasia) 18. Bent bones dysplasias Campomelic dysplasia (CD) AD q24.3- SOX9 SRY-box Stüve-Wiedemann dysplasia AR p13.1 LIFR Leukemia Inhibitory Factor Receptor Kyphomelic dysplasia, several forms Bent bones at birth can be seen in a variety of conditions, including osteogenesis imperfecta, Antley-Bixler syndrome, cartilage-hair hypoplasia, Cummings syndrome, hypophosphatasia, dyssegmental dysplasia, TD,
24 ATD, and others 19. Slender bone dysplasia group 3-M syndrome (3M1) AR p21.1 CUL7 Cullin 7 3-M syndrome (3M2) AR q35 OBSL1 Obscurin-like 1 Kenny-Caffey dysplasia type 1 AR q42-q43 TBCE Tubulin-specific chaperone E Kenny-Caffey dysplasia type 2 AD Microcephalic osteodysplastic AR q primordial dwarfism type 1/3 (MOPD1) Microcephalic osteodysplastic AR q PCNT2 Pericentrin 2 primordial dwarfism type 2 (MOPD2; Majewski type) IMAGE syndrome (intrauterine XL/AD growth retardation, metaphyseal
25 dysplasia, adrenal hypoplasia, and genital anomalies) Osteocraniostenosis SP Hallermann-Streiff syndrome AR See also Cerebro-arthro-digital dysplasia 20. Dysplasias with multiple joint dislocations Desbuquois dysplasia (with AR q25.3 CANT1 accessory ossification centre in digit 2) Desbuquois dysplasia with short AR q25.3 CANT1 metacarpals and elongated phalanges (Kim type) Desbuquois dysplasia (other AR variants with or without accessory ossification centre)
26 Pseudodiastrophic dysplasia AR See also: SED with congenital dislocations, CHST3 type (group 4); Atelosteogenesis type 3 and Larsen syndrome (group 6); SEMDs with joint laxity (group 11) 21. Chondrodysplasia punctata (CDP) group CDP, X-linked dominant, XLD Xp11 EBP Emopamil-binding protein Conradi-Hünermann type (CDPX2) CDP, X-linked recessive, XLR Xp22.3 ARSE Arylsulfatase E brachytelephalangic type (CDPX1) CHILD (congenital hemidysplasia, ichthyosis, limb XLD Xp11 NSDHL NAD(P)H steroid dehydrogenase-like protein defects)
27 CHILD (congenital XLD Xq28 EBP Emopamil-binding protein hemidysplasia, ichthyosis, limb defects) Greenberg dysplasia AR q42.1 LBR Lamin B receptor, 3-betahydroxysterol delta (14)- reductase Rhizomelic CDP type 1 AR q22-24 PEX7 Peroxisomal PTS2 receptor Rhizomelic CDP type 2 AR q42 DHPAT Dihydroxyacetonephosphat e acyltransferase (DHAPAT) Rhizomelic CDP type 3 AR q31 AGPS Alkylglycerone-phosphate synthase (AGPS) CDP tibial-metacarpal type AD/AR Astley-Kendall dysplasia AR? Note that stippling can occur in several syndromes such as Zellweger, Smith-Lemli-Opitz
28 and others. See also desmosterolosis as well as SEMD short limb - abnormal calcification type in group Neonatal osteosclerotic dysplasias Blomstrand dysplasia AR p PTHR1 PTH/PTHrP receptor 1 Desmosterolosis AR p DHCR24 3-beta-hydroxysterol delta- 24-reductase Caffey disease (including AD q21-22 COL1A1 Collagen 1, alpha-1 chain infantile and attenuated forms) Caffey disease (severe variants AR with prenatal onset) AR p22 FAM20C Raine dysplasia (lethal and nonlethal forms) See also Astley-Kendall dysplasia and CDPs in group 21
29 23. Increased bone density group (without modification of bone shape) Osteopetrosis, severe neonatal or infantile forms (OPTB1) AR q13 TCIRG1 Subunit of ATPase proton pump Osteopetrosis, severe neonatal or AR p13 CLCN7 Chloride channel 7 infantile forms (OPTB4) Osteopetrosis, infantile form, with nervous system involvement (OPTB5) AR q21 OSTM1 Grey lethal/osteopetrosis associated transmembrane protein Osteopetrosis, intermediate form, osteoclast-poor (OPTB2) AR q14.11 RANKL (TNFSF11) Receptor activator of NFkappa-B ligand (Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily, member 11) Osteopetrosis, infantile form, osteoclast-poor with immunoglobulin deficiency (OPTB7) AR q21.33 RANK (TNFRSF11 A) Receptor activator of NFkappa-B
30 Osteopetrosis, intermediate form (OPTB6) AR q21.3 PLEKHM1 Pleckstrin homology domain-containing protein, family M, member 1 Osteopetrosis, intermediate form AR p13 CLCN7 Chloride channel pump (OPTA2) Osteopetrosis with renal tubular AR q22 CA2 Carbonic anhydrase 2 acidosis (OPTB3) Osteopetrosis, late-onset form type 1 (OPTA1) AD q13.4 LRP5 Low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5 Osteopetrosis, late-onset form AD p13 CLCN7 Chloride channel 7 type 2 (OPTA2) Osteopetrosis with ectodermal dysplasia and immune defect (OLEDAID) XL Xq28 IKBKG (NEMO) Inhibitor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhar, kinase of Osteopetrosis, moderate form with defective leucocyte adhesion (LAD3) AR q12 FERMT3 (KIND3) Fermitin 3 (Kindlin 3)
31 Osteopetrosis, moderate form with defective leucocyte adhesion AR q13 RASGRP2 (CalDAG- GEF1) Ras guanyl nucleotidereleasing protein 2 Pyknodysostosis AR q21 CTSK Cathepsin K Osteopoikilosis AD q14 LEMD3 LEM domain-containing 3 Melorheostosis with AD q14 LEMD3 LEM domain-containing 3 osteopoikilosis Osteopathia striata with cranial XLD Xq11.1 WTX FAM123B sclerosis (OSCS) Melorheostosis SP Dysosteosclerosis AR Osteomesopyknosis AD Osteopetrosis with infantile AR? neuroaxonal dysplasia
32 24. Increased bone density group with metaphyseal and/or diaphyseal involvement Craniometaphyseal dysplasia, AD p15.2- ANKH Homolog of mouse ANK autosomal dominant type 14.2 (ankylosis) gene Diaphyseal dysplasia Camurati- Engelmann AD q13 TGFbeta1 Transforming growth factor beta 1 Hematodiaphyseal dysplasia AR q34 TBXAS1 Thromboxane A synthase 1 Ghosal Hypertrophic osteoarthropathy AR q34-35 HPGD 15-alphahydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase Pachydermoperiostosis AD (hypertrophic osteoarthropathy, primary, autosomal dominant) Oculodentoosseous dysplasia (ODOD) mild type AD q22-23 GJA1 Gap junction protein alpha- 1
33 Oculodentoosseous dysplasia AR (ODOD) severe type Osteoectasia with AR q24 OPG Osteoprotegerin hyperphosphatasia (juvenile Paget disease) Sclerosteosis AR q12-21 SOST Sclerostin Endosteal hyperostosis, van AR q12-21 SOST Sclerostin Buchem type Trichodentoosseous dysplasia AD q21 DLX3 Distal-less homeobox 3 Craniometaphyseal dysplasia, AR q21-22 autosomal recessive type Diaphyseal medullary stenosis AD p21-p22 with bone malignancy Craniodiaphyseal dysplasia AD
34 Craniometadiaphyseal dysplasia, AR -- Wormian bone type Endosteal sclerosis with AR cerebellar hypoplasia Lenz-Majewski hyperostotic SP dysplasia Metaphyseal dysplasia, Braun- XL Tinschert type Pyle disease AR Osteogenesis Imperfecta and decreased bone density group For comments the classification of Osteogenesis Imperfecta, please refer to the text
35 Osteogenesis imperfecta, non- AD COL1A1, COL1A1: Collagen 1 alpha-1 deforming form (OI type 1) COL1A2 chain, COL1A2: Collagen 1 alpha- Osteogenesis imperfecta, AD, AR COL1A1, perinatal lethal form (OI type 2) COL1A2, CRTAP, LEPRE1, PPIB Osteogenesis imperfecta, AD, AR COL1A1, progressively deforming type (OI COL1A2, type 3) CRTAP, LEPRE1, PPIB, FKBP10, SERPINH1 Osteogenesis imperfecta, AD, AR COL1A1, moderate form (OI type 4) COL1A2, CRTAP, FKBP10, SP7 Osteogenesis imperfecta with AD calcification of the interosseous membranes and/or hypertrophic
36 callus (OI type 5) Osteogenesis imperfecta, other types Bruck syndrome type 1 (BS1) AR p12 FKBP10 FK506 binding protein 10 Bruck syndrome type 2 (BS2) AR q23-24 PLOD2 Procollagen lysyl hydroxylase 2 Osteoporosis-pseudoglioma syndrome AR q12-13 LRP5 LDL-receptor related protein 5 Calvarial doughnut lesions with AD bone fragility Idiopathic juvenile osteoporosis SP Cole-Carpenter dysplasia (bone SP fragility with craniosynostosis) Spondylo-ocular dysplasia AR
37 Osteopenia with radiolucent AD lesions of the mandible Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, progeroid form AR q35 B4GALT7 Xylosylprotein 4-beta- galactosyltransferase deficiency Geroderma osteodysplasticum AR q24.2 GORAB SCYL1-binding protein 1 Cutis laxa, autosomal recessive form, type 2B (ARCL2B) AR q25.3 PYCR1 Pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase 1 Cutis laxa, autosomal recessive form, type 2A (ARCL2A) (Wrinkly skin syndrome) AR , q24.3 ATP6VOA2 ATPase, H+ transporting, lysosomal, V0 subunit A2 Singleton-Merten dysplasia AD Abnormal mineralization group Hypophosphatasia, perinatal AR p36.1- ALPL Alkaline phosphatase, lethal and infantile forms p34 tissue non-specific
38 (TNSALP) Hypophosphatasia, adult form AD p36.1- p34 ALPL Alkaline phosphatase, tissue non-specific (TNSALP) Hypophosphatemic rickets, X- linked dominant XLD Xp22 PHEX X-linked hypophosphatemia membrane protease Hypophosphatemic rickets, AD p13.3 FGF23 Fibroblast growth factor 23 autosomal dominant Hypophosphatemic rickets, autosomal recessive, type 1 AR q21 DMP1 Dentin matrix acidic phosphoprotein 1 (ARHR1) Hypophosphatemic rickets, autosomal recessive, type 2 (ARHR2) AR q23 ENPP1 Ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phospho diesterase 1 Hypophosphatemic rickets with XLR Xp11.22 ClCN5 Chloride channel 5 hypercalciuria, X-linked recessive
39 Hypophosphatemic rickets with hypercalciuria, autosomal AR q34 SLC34A3 Sodium-phosphate cotransporter recessive (HHRH) Neonatal hyperparathyroidism, AR q CASR Calcium-sensing receptor severe form Familial hypocalciuric AD q CASR Calcium-sensing receptor hypercalcemia with transient neonatal hyperparathyroidism Calcium pyrophosphate AD p15.2- ANKH Homolog of mouse ANK deposition disease (familial 14.2 (ankylosis) gene chondrocalcisnosis) type 2 See also Jansen dysplasia and Eiken dysplasia 27. Lysosomal Storage Diseases with Skeletal Involvement (Dysostosis Multiplex group) Mucopolysaccharidosis type AR p16.3 IDA Alpha-1-Iduronidase
40 1H/1S Mucopolysaccharidosis type 2 XLR Xq IDS Iduronate-2-sulfatase Mucopolysaccharidosis type 3A AR q25.3 HSS Heparan sulfate sulfatase Mucopolysaccharidosis type 3B AR q21 NAGLU N-Ac-beta-Dglucosaminidase Mucopolysaccharidosis type 3C AR p11-q13 HSGNAT Ac-CoA: alphaglucosaminide N- acetyltransferase Mucopolysaccharidosis type 3D AR q14 GNS N-Acetylglucosamine 6- sulfatase Mucopolysaccharidosis type 4A AR q24.3 GALNS Galactosamine-6-sulfate sulfatase Mucopolysaccharidosis type 4B AR p21.33 GLBI beta-galactosidase Mucopolysaccharidosis type 6 AR q13.3 ARSB Arylsulfatase B
41 Mucopolysaccharidosis type 7 AR q21.11 GUSB beta-glucuronidase Fucosidosis AR p34 FUCA alpha-fucosidase alpha-mannosidosis AR p MANA alpha-mannosidase beta-mannosidosis AR q22-25 MANB beta-mannosidase Aspartylglucosaminuria AR q23-27 AGA Aspartyl-glucosaminidase GMI Gangliosidosis, several AR p GLB1 beta-galactosidase forms Sialidosis, several forms AR p21.3 NEU1 Neuraminidase (sialidase) Sialic acid storage disease (SIASD) AR q14-q15 SLC17A5 Sialin (sialic acid transporter) Galactosialidosis, several forms AR q13.1 PPGB beta-galactosidase protective protein
42 Multiple sulfatase deficiency AR p26 SUMF1 Sulfatase-modifying factor- 1 Mucolipidosis II (I-cell disease), alpha/beta type AR q21-23 GNPTAB N-Acetylglucosamine 1- phosphotransferase, alpha/beta subunits Mucolipidosis III (Pseudo- Hurler polydystrophy), alpha/beta type AR q21-23 GNPTAB N-Acetylglucosamine 1- phosphotransferase, alpha/beta subunits Mucolipidosis III (Pseudo- Hurler polydystrophy), gamma type AR q21-23 GNPTG N-Acetylglucosamine 1- phosphotransferase, gamma subunit 28. Osteolysis group Familial expansile osteolysis AD q22.1 RANK (TNFRSF11 A) Mandibuloacral dysplasia type A AD q21.2 LMNA Lamin A/C
43 Mandibuloacral dysplasia type B AR p34 ZMPSTE24 Zinc metalloproteinase Progeria, Hutchinson-Gilford AD q21.2 LMNA Lamin A/C type Torg-Winchester syndrome AR q13 MMP2 Matrix metalloproteinase 2 Hajdu-Cheney syndrome AD Multicentric carpal-tarsal AD osteolysis with and without nephropathy Lipomembraneous osteodystrophy with leukoephalopathy (presenile AR p21.2 TREM2 Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 dementia with bone cysts; Nasu- Hakola) Lipomembraneous osteodystrophy with AR q13.1 TYROBP Tyro protein tyrosine kinase-binding protein leukoephalopathy (presenile dementia with bone cysts; Nasu- Hakola)
44 See also Pycnodysostosis, cleidocranial dysplasia and Singleton-Merten syndrome. Note: several neurologic conditions may cause acroosteolysis 29. Disorganized development of skeletal components group Multiple cartilaginous exostoses AD q EXT1 Exostosin-1 1 Multiple cartilaginous exostoses AD p12-11 EXT2 Exostosin-2 2 Multiple cartilaginous exostoses AD p 3 Cherubism AD p16 SH3BP2 SH3 domain-binding protein 2 Fibrous dysplasia, polyostotic SP q13 GNAS1 Guanine nucleotidebinding protein, alpha-
45 form stimulating activity subunit 1 Progressive osseous heteroplasia AD q13 GNAS1 Guanine nucleotidebinding protein, alphastimulating activity subunit 1 Gnathodiaphyseal dysplasia AD p TMEM16E Transmembrane protein 16E Metachondromatosis AD q24 PTPN11 Protein-tyrosine phosphatase nonreceptortype 11 Osteoglophonic dysplasia AD p11 FGFR1 Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva (FOP) AD, SP q23-24 ACVR1 Activin A (BMP type 1) receptor Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) AD q11.2 NF1 Neurofibromin Carpotarsal AD
46 osteochondromatosis Cherubism with gingival AR fibromatosis (Ramon syndrome) Dysplasia epiphysealis SP hemimelica (Trevor) Enchondromatosis (Ollier) SP Enchondromatosis with SP hemangiomata (Maffucci) See also: Proteus syndrome in group Overgrowth syndromes with skeletal involvement Weaver syndrome SP/AD Sotos syndrome AD q35 NSD1 Nuclear receptor-binding su-var, enhar of zeste, and trithorax domain
47 protein 1 Marshall-Smith syndrome SP p13.3 NFIX nuclear factor I/X Proteus syndrome SP Marfan syndrome AD q21.1 FBN1 Fibrillin 1 Congenital contractural AD q23.3 FBN2 Fibrillin 2 arachnodactyly Loeys-Dietz syndrome types 1A and 2A AD , , 9q22 TGFBR1, TGFbeta receptor subunit 1 Loeys-Dietz syndrome types 1B and 2B AD , p22 TGFBR2 TGFbeta receptor subunit 2 Overgrowth syndrome with 2q37 translocations SP -- 2q37 NPPC Natriuretic peptide precursor C Overgrowth syndrome with SP? skeletal dysplasia (Nishimura- Schmidt, endochondral
48 gigantism) See also: Shprintzen-Goldberg syndrome in Craniosynostosis group 31. Genetic inflammatory/rheumatoidlike osteoarthropathies Progressive pseudorheumatoid dysplasia (PPRD; SED with AR q22-23 WISP3 WNT1-inducible signaling pathway protein 3 progressive arthropathy) Chronic infantile neurologic AD q44 CIAS1 Cryopyrin cutaneous articular syndrome (CINCA)/neonatal onset multisystem inflammatory disease (NOMID) Sterile multifocal osteomyelitis, periostitis, and pustulosis AR q14.2 IL1RN Interleukin 1 receptor antagonist (CINCA/NOMID-like) Chronic recurrent multifocal AR p11.3 LPIN2 Lipin 2 osteomyelitis with congenital
49 dyserythropoietic anemia (CRMO with CDA; Majeed syndrome) Hyperostosis/hyperphosphatemi a syndrome AR q24-q31; GALNT3 UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-Dgalactosamine:polypeptide N- acetylgalactosaminyltransfe rase 3 Infantile systemic AR q21 ANTXR2 Anthrax toxin receptor 2 hyalinosis/juvenile hyaline fibromatosis (ISH/JHF) 32. Cleidocranial dysplasia and isolated cranial ossification defects group Cleidocranial dysplasia AD p21 RUNX2 Runt related transcription factor 2 CDAGS syndrome (craniosynostosis, delayed AR q12- q13 fontanel closure, parietal foramina, imperforate anus, genital anomalies, skin eruption)
50 Yunis-Varon dysplasia AR Parietal foramina (isolated) AD q11.2 ALX4 Aristaless-like 4 Parietal foramina (isolated) AD q34-35 MSX2 Muscle segment homeobox 2 See also: pycnodysostosis, wrinkly skin syndrome, and several others 33. Craniosynostosis syndromes Pfeiffer syndrome (FGFR1- related) AD p12 FGFR1 Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 Pfeiffer syndrome (FGFR2- related) AD q26.12 FGFR2 Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 Apert syndrome AD q26.12 FGFR2 Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2
51 Craniosynostosis with cutis gyrata (Beare-Stevenson) AD q26.12 FGFR2 Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 Crouzon syndrome AD q26.12 FGFR2 Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 Crouzon-like craniosynostosis with acanthosis nigricans AD p16.3 FGFR3 Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (Crouzonodermoskeletal syndrome) Craniosynostosis, Muenke type AD p16.3 FGFR3 Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 Antley-Bixler syndrome AR q11.23 POR Cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase Craniosynostosis Boston type AD q35.2 MSX2 MSX2 Saethre-Chotzen syndrome AD p21.1 TWIST1 TWIST Shprintzen-Goldberg syndrome AD
52 Baller-Gerold syndrome AR q24.3 RECQL4 RECQ Protein-like 4 Carpenter syndrome AR RAB23 See also Cole-Carpenter syndrome in group 24, CDAGS syndrome in group 29, and Craniofrontonasal syndrome in group Dysostoses with predominant craniofacial involvement Mandibulo-facial dysostosis (Treacher Collins, Fraschetti- AD q32 TCOF1 Treacher Collins- Fraschetti syndrome 1 Klein) Mandibulo-facial dysostosis (Treacher-Collins, Fraschetti- AD q12.2 POLR1D Polymerase (RNA) I polypeptide D Klein) Mandibulo-facial dysostosis (Treacher-Collins, Fraschetti- AR p21.1 POLR1C Polymerase (RNA) I polypeptide C
53 Klein) Oral-facial-digital syndrome type XLR Xp22.3 CXORF5 chr. X open reading frame 5 I (OFD1) Weyer acrofacial (acrodental) AD p16 EVC1 Ellis-van Creveld 1 protein dysostosis AR p12.3 ICK Intestinal cell kinase Endocrine-cerebroosteodysplasia (ECO) Craniofrontonasal syndrome XLD Xq13.1 EFNB1 Ephrin B1 Frontonasal dysplasia, type 1 AR p13.3 ALX3 Aristaless-like-3 Frontonasal dysplasia, type 2 AR p11.2 ALX4 Aristaless-like-4 Frontonasal dysplasia, type 3 AR q21.3 ALX1 Aristaless-like 1 Hemifacial microsomia SP/AD Miller syndrome (postaxial AR q22 DHODH Dihydroorotate
54 acrofacial dysostosis) dehydrogenase Acrofacial dysostosis, Nager type AD/AR Acrofacial dysostosis, Rodriguez AR type See also Oral-facial-digital syndrome type IV in the Short Rib Dysplasias group 35. Dysostoses with predominant vertebral with and without costal involvement Currarino triad AD q36 HLXB9 Homeobox gene HB9 Spondylocostal dysostosis type 1 AR q13 Dll3 Delta-like 3 (SCD1) Spondylocostal dysostosis type 2 (SCD2) AR q26 MESP2 Mesoderm posterior (expressed in) 2
55 Spondylocostal dysostosis type 3 AR? p22 LFNG Lunatic fringe (SCD3) Spondylocostal dysostosis type 4 (SCD4) AR 17p13.1 HES7 Hairy-and-enhar-of- split-7 Spondylothoracic dysostosis AR 15q26 MESP2 Mesoderm posterior (expressed in) 2 Klippel-Feil anomaly with laryngeal malformation AD q22.1 GDF6 Growth and differentiation factor 6 Spondylocostal/thoracic AD/AR dysostosis, other forms Cerebro-costo-mandibular AD/AR syndrome (rib gap syndrome) Cerebro-costo-mandibular-like syndrome with vertebral defects AR q25 COG1 Component of oligomeric Golgi complex 1 Diaphanospondylodysostosis AR p14 BMPER Bone morphogenetic protein-binding endothelial cell precursor-derived
56 regulator See also Spondylocarpotarsal dysplasia in group 7 and Spondylo-metaphysealmegaepiphyseal dysplasia in group Patellar dysostoses Ischiopatellar dysplasia (small patella syndrome) AD q21- q22 TBX4 T-box gene 4 Small patella - like syndrome with clubfoot AD 5q31 PITX1 Paired-like homeodomain transcription factor 1 (pituitary homeobox 1) Nail-patella syndrome AD q34.1 LMX1B LIM homeobox transcription factor 1 Genitopatellar syndrome AR? Ear-patella-short stature AR syndrome (Meier-Gorlin)
57 See also MED group for conditions with patellar changes as well as ischio-pubic-patellar dysplasia as mild expression of campomelic dysplasia 37. Brachydactylies (with or without extraskeletal manifestations) Brachydactyly type A1 AD q35-36 IHH Indian Hedgehog Brachydactyly type A1 AD 5p31 Brachydactyly type A2 AD q23 BMPR1B Bone Morphogenetic Protein Receptor, 1B Brachydactyly type A2 AD BMP2 Bone Morphogenetic Protein Type 2 Brachydactyly type A2 AD q11.2 GDF5 Growth and Differentiation Factor 5
58 Brachydactyly type A3 AD Brachydactyly type B AD q22 ROR2 Receptor Tyrosine Kinaselike Orphan Receptor 2 Brachydactyly type B2 AD q NOG Noggin Brachydactyly type C AD, AR q11.2 GDF5 Growth and Differentiation Factor 5 Brachydactyly type D AD q31 HOXD13 Homeobox D13 Brachydactyly type E AD p11.22 PTHLH Parathyroid hormone-like hormone (Parathyroid hormone related peptide, PTHRP) Brachydactyly type E AD q31 HOXD13 Homeobox D13 Brachydactyly - mental AD q37.3 HDAC4 Histone deacetylase 4 retardation syndrome
59 Hyperphosphatasia with mental retardation, brachytelephalangy, and distinct face AR 1p36.11 PIGV Phosphatidylinositol-glycan biosynthesis class V protein (GPI mannosyltransferase 2) Brachydactyly-hypertension syndrome (Bilginturian) 11.2 Brachydactyly with anonychia AD q24.3 SOX9 (Cooks syndrome) AD p24.1 MYCN nmyc oncogene AD p12.2- Microcephaly-oculo-digitoesophageal-duodenal syndrome (Feingold syndrome) Hand-foot-genital syndrome AD p14.2 HOXA13 Homeobox A13 Brachydactyly with elbow AD dysplasia (Liebenberg syndrome) Keutel syndrome AR p MGP Matrix Gla protein
60 Albright hereditary osteodystrophy (AHO) AD q13 GNAS1 Guanine nucleotide binding protein of adenylate cyclase subunit Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome AD p13.3 CREBBP CREB-Binding Protein Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome AD q13 EP300 E1A-Binding Protein, 300- KD Catel-Manzke syndrome XLR? Brachydactyly, Temtamy type AR Christian type brachydactyly AD Coffin-Siris syndrome AR Mononen type brachydactyly XLD? Poland anomaly SP See also group 20 for other
61 conditions with brachydactyly as well as brachytelephalangic CDP. 38. Limb hypoplasia reduction defects group Ulnar-mammary syndrome AD TBX3 T-box gene 3 de Lange syndrome AD p13.1 NIPBL Nipped-B-like Fanconi anemia (see note below) AR (several) (several) Thrombocytopenia-absent radius AR?/AD? q21.1 (several) (TAR) Thrombocythemia with distal AD 3q27 THPO Thrombopoietin limb defects Holt-Oram syndrome AD q24.1 TBX5 T-box gene 5 Okihiro syndrome (Duane AD q13 SALL4 SAL-like 4 radial ray anomaly)
62 Cousin syndrome AR p13 TBX15 T-box gene 15 Roberts syndrome AR p21.1 ESCO2 Homolog of Establishment of Cohesion - 2 Split-hand-foot malformation with long bone deficiency AD q42.2- q43 (SHFLD1) Split-hand-foot malformation AD q14.1 with long bone deficiency (SHFLD2) Split-hand-foot malformation AD p13.1 with long bone deficiency (SHFLD3) Tibial hemimelia AR AD Tibial hemimeliapolysyndactyly-triphalangeal thumb
63 Acheiropodia AR q36 LMBR1 Putative receptor protein Tetra-amelia XL Tetra-amelia AR q21 WNT3 Wingless-type MMTV integration site family, member 3 Ankyloblepharon-ectodermal AD q27 P63 (TP63) Tumor Protein p63 dysplasia-cleft lip/palate (AEC) Ectrodactyly-ectodermal AD q27 P63 (TP63) Tumor Protein p63 dysplasia cleft-palate syndrome Type 3 (EEC3) Ectrodactyly-ectodermal dysplasia cleft-palate syndrome AD q type 1 (EEC1) Ectrodactyly-ectodermal AR q22 CDH3 Cadherin 3 dysplasia-macular dystrophy syndrome (EEM)
64 Limb-mammary syndrome AD q27 P63 (TP63) Tumor Protein p63 (including ADULT syndrome) Split hand-foot malformation, AD q27 P63 (TP63) Tumor Protein p63 isolated form, type 4 (SHFM4) Split hand-foot malformation, isolated form, type 1 (SHFM1) AD q Split hand-foot Malformation, XL Xq26 isolated form, type 2 (SHFM2) Split hand-foot malformation, AD q24 FBXW4 Dactylin isolated form, type 3 (SHFM3) Split hand-foot malformation, AD q31 isolated form, type 5 (SHFM5) Al-Awadi Raas-Rothschild limbpelvis hypoplasia-aplasia AR p25 WNT7A Wingless-type MMTV integration site family, member 7A Fuhrmann syndrome AR p25 WNT7A Wingless-type MMTV integration site family,
65 member 7A RAPADILINO syndrome AR q24.3 RECQL4 RECQ Protein-like 4 Adams-Oliver syndrome AD/AR Femoral hypoplasia-unusual face SP/AD? syndrome (FHUFS) Femur-fibula-ulna syndrome SP? (FFU) Hanhart syndrome AD (Hypoglossia-hypodactylia) Scapulo-iliac dysplasia AD (Kosenow) Note: the particularly complex genetic basis of Fanconi anemia and its complementation groups is acknowledged but not further listed in this Nosology. The Reader is referred to or to specialized reviews. - See
66 also CHILD in group 20 and the mesomelic and acromesomelic dysplasias. 39. Polydactyly-Syndactyly- Triphalangism group Preaxial polydactyly type 1 AD q36 SHH Sonic Hedgehog (PPD1) Preaxial polydactyly type 1 AD (PPD1) Preaxial polydactyly type 2 AD q36 SHH Sonic Hedgehog (PPD2)/Triphalangeal thumb (TPT) Preaxial polydactyly type 3 AD (PPD3) Preaxial polydactyly type 4 (PPD4) AD p13 GLI3 Gli-Kruppel Family Member 3 Greig cephalopolysyndactyly AD p13 GLI3 Gli-Kruppel Family
67 syndrome Member 3 Pallister-Hall syndrome AD p13 GLI3 Gli-Kruppel Family Member 3 Synpolydactyly (complex, AD q13.3 FBLN1 Fibulin 1 fibulin1 - associated) Synpolydactyly AD q31 HOXD13 Homeobox D13 Townes-Brocks syndrome AD q12.1 SALL1 SAL-like 1 (Renal-Ear-Anal-Radial syndrome) Lacrimo-auriculo-dento-digital syndrome (LADD) AD q26.12 FGFR2 Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 Lacrimo-auriculo-dento-digital syndrome (LADD) AD p16.3 FGFR3 Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 Lacrimo-auriculo-dento-digital AD p13-p12 FGF10 Fibroblast growth factor 10 syndrome (LADD)
68 Acrocallosal syndrome AR p13 Acro-pectoral syndrome AD q36 Acro-pectoro-vertebral dysplasia AD q36 (F-syndrome) Mirror-image polydactyly of AD q36 SHH Sonic Hedgehog hands and feet (Laurin-Sandrow syndrome) Mirror-image polydactyly of hands and feet (Laurin-Sandrow syndrome) Cenani-Lenz syndactyly AR p11.2 LRP4 low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 4 Cenani-Lenz like syndactyly SP (AD?) 15q13-q14 GREM1, Gremlin 1, Formin 1 FMN1 Oligosyndactyly, radio-ulnar SP (AR?) 15q13-q14 FMN1 Formin 1 synostosis, hearing loss and
69 renal defects syndrome Syndactyly, Malik-Percin type AD p13.3 STAR syndrome (syndactyly of XL Xq28 FAM58A toes, telecanthus, ano- and renal malformations) Syndactyly type 1 (III IV) AD q34-36 Syndactyly type 3 (IV V) AD q21-23 GJA1 Syndactyly type 4 (I V) Haas AD q36 SHH Sonic Hedgehog type Syndactyly type 5 (syndactyly AD q31 HOXD13 with metacarpal and metatarsal fusion) Syndactyly with craniosynostosis (Philadelphia type) AD q Syndactyly with microcephaly AR and mental retardation (Filippi
70 syndrome) Meckel syndrome type 1 AR q23 MKS1 Meckel syndrome type 2 AR q Meckel syndrome type 3 AR q21 TMEM67 Meckel syndrome type 4 AR q CEP290 Meckel syndrome type 5 AR q12.1 RPGRIP1L Meckel syndrome type 6 AR p15 CC2D2A Note: the Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome can present with polydactyly and/or syndactyly. See also the SRPS group. 40. Defects in joint formation and synostoses
71 Multiple synostoses syndrome AD q22 NOG Noggin type 1 Multiple synostoses syndrome type 2 AD q11.2 GDF5 Growth and Differentiation Factor 5 Multiple synostoses syndrome AD q11-q12 FGF9 type 3 Proximal symphalangism type 1 AD q22 NOG Noggin Proximal symphalangism type 2 AD q11.2 GDF5 Growth and Differentiation Factor 5 Radio-ulnar synostosis with AD p HOXA11 Homeobox A11 amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia
Limb Development. Limb Development. Limb Axes. Limb Development. Clinical Terms
 Limb Development Overview of Limb Formation Initiation of Limb Development Limb Field Outgrowth of the Mesoderm Morphogenetic Signaling Development of Limb Tissues Skeleton Musculature Innervation Vasculature
Limb Development Overview of Limb Formation Initiation of Limb Development Limb Field Outgrowth of the Mesoderm Morphogenetic Signaling Development of Limb Tissues Skeleton Musculature Innervation Vasculature
Developmental Disorders
 Developmental Disorders General Principles Causes: Genetic Environmental (Maternal, Physical, Chemical) Mechanisms (Retinoic Acid) General Principles Teratology Study of Monsters Teratogen agent that produces
Developmental Disorders General Principles Causes: Genetic Environmental (Maternal, Physical, Chemical) Mechanisms (Retinoic Acid) General Principles Teratology Study of Monsters Teratogen agent that produces
Laboratory User Guides
 CLINICAL GENETIC SERVICE Laboratory User Guides (Website version) January 2016 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH GOVERNMENT OF HONG KONG SAR Page 1 of 10 Compared with the previous version of January 2015, several
CLINICAL GENETIC SERVICE Laboratory User Guides (Website version) January 2016 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH GOVERNMENT OF HONG KONG SAR Page 1 of 10 Compared with the previous version of January 2015, several
CHS 06-07 BONES AND SKELETAL TISSUES
 CHS 06-07 BONES AND SKELETAL TISSUES This chapter provides a review of bone and skeletal tissue. The human skeleton is composed primarily of two connective tissues: (1) cartilage and (2) bone. CHARACTERISTICS
CHS 06-07 BONES AND SKELETAL TISSUES This chapter provides a review of bone and skeletal tissue. The human skeleton is composed primarily of two connective tissues: (1) cartilage and (2) bone. CHARACTERISTICS
Skeletal Development Multiple Cellular Origins
 Skeletal Development Multiple Cellular Origins 1 - Paraxial Mesoderm Somite, Sclerotome Axial Skeleton (e.g. vertebra) 2 - Lateral Plate Mesoderm Appendicular Skeleton (e.g. limb) 3 - Neural Crest Head
Skeletal Development Multiple Cellular Origins 1 - Paraxial Mesoderm Somite, Sclerotome Axial Skeleton (e.g. vertebra) 2 - Lateral Plate Mesoderm Appendicular Skeleton (e.g. limb) 3 - Neural Crest Head
Child Abuse or Osteogenesis Imperfecta?
 Child Abuse or Osteogenesis Imperfecta? 804 W. Diamond Ave., Ste. 210 Gaithersburg, MD 20878 (800) 981-2663 (301) 947-0083 Fax: (301) 947-0456 Internet: www.oif.org Email: bonelink@oif.org The Osteogenesis
Child Abuse or Osteogenesis Imperfecta? 804 W. Diamond Ave., Ste. 210 Gaithersburg, MD 20878 (800) 981-2663 (301) 947-0083 Fax: (301) 947-0456 Internet: www.oif.org Email: bonelink@oif.org The Osteogenesis
Osseous Tissue & Structure. The skeletal system includes: Storage of minerals: calcium salts
 Chapter 15 Lecture The Skeletal System: Osseous Tissue & Skeletal Structure The Skeletal System The skeletal system includes: Bones, cartilages, ligaments Bone tissue = osseous tissue Includes living cells
Chapter 15 Lecture The Skeletal System: Osseous Tissue & Skeletal Structure The Skeletal System The skeletal system includes: Bones, cartilages, ligaments Bone tissue = osseous tissue Includes living cells
Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review
 Name: Period: Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review 1. List four functions of the skeletal system: a. b. c. d. 2. Define ossification and identify the roles of the osteoblasts, osteocytes, and
Name: Period: Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review 1. List four functions of the skeletal system: a. b. c. d. 2. Define ossification and identify the roles of the osteoblasts, osteocytes, and
Pseudohypoparathyroidism: A Variation on the Theme of Hypoparathyroidism
 Pseudohypoparathyroidism: A Variation on the Theme of Hypoparathyroidism Amanda Tencza MS IV 1 and Michael A. Levine, MD 2 1 Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine of Case Western Reserve University
Pseudohypoparathyroidism: A Variation on the Theme of Hypoparathyroidism Amanda Tencza MS IV 1 and Michael A. Levine, MD 2 1 Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine of Case Western Reserve University
7. Skeletal System: Bone Structure and Function
 7. Skeletal System: Bone Structure and Function For the next two chapters (7 and 9) we will study the skeletal system. Although the major feature of this system is the bones, the skeletal system also consists
7. Skeletal System: Bone Structure and Function For the next two chapters (7 and 9) we will study the skeletal system. Although the major feature of this system is the bones, the skeletal system also consists
LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT
 UNIT - HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY Chapter 18 LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT Movement is an important feature of living organism. Both the microbes and macrobes show wide range of movements. The movements results in change
UNIT - HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY Chapter 18 LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT Movement is an important feature of living organism. Both the microbes and macrobes show wide range of movements. The movements results in change
E. Blood cells production. Blood cells are produced within the cavities of bones.
 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 1. The skeletal system consists of bone, cartilage, ligaments (attach bone to another bone), and tendons (attach muscle to bone). 2. Functions. A. Support. Bone helps to
FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 1. The skeletal system consists of bone, cartilage, ligaments (attach bone to another bone), and tendons (attach muscle to bone). 2. Functions. A. Support. Bone helps to
SPONDYLOEPIPHYSEAL DYSPLASIA, CONGENITA NATURAL HISTORY INTRODUCTION:
 SPONDYLOEPIPHYSEAL DYSPLASIA, CONGENITA NATURAL HISTORY Richard M. Pauli, M.D., Ph.D., Midwest Regional Bone Dysplasia Clinics revised 8/2009 INTRODUCTION: The following summary of the medical expectations
SPONDYLOEPIPHYSEAL DYSPLASIA, CONGENITA NATURAL HISTORY Richard M. Pauli, M.D., Ph.D., Midwest Regional Bone Dysplasia Clinics revised 8/2009 INTRODUCTION: The following summary of the medical expectations
Chapter 6: The Skeletal System: Bone Tissue
 Chapter 6: The Skeletal System: Bone Tissue Chapter Objectives FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 1. Discuss the functions of support, protection, assistance in movement, mineral homeostasis, blood cell
Chapter 6: The Skeletal System: Bone Tissue Chapter Objectives FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 1. Discuss the functions of support, protection, assistance in movement, mineral homeostasis, blood cell
Causes of Birth Defects
 Causes of Birth Defects Some medical / genetic terms: congenital defects: visible defects present at birth (due to any cause (genetic, developmental error ). syndrome: the symptoms that characterize any
Causes of Birth Defects Some medical / genetic terms: congenital defects: visible defects present at birth (due to any cause (genetic, developmental error ). syndrome: the symptoms that characterize any
Control of Gene Expression
 Control of Gene Expression (Learning Objectives) Explain the role of gene expression is differentiation of function of cells which leads to the emergence of different tissues, organs, and organ systems
Control of Gene Expression (Learning Objectives) Explain the role of gene expression is differentiation of function of cells which leads to the emergence of different tissues, organs, and organ systems
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeleton is the body s bony framework which consists of 206 bones. The bones are made up of water(45%), calcium and phosphorous(35%) and other organic materials(20%). The calcium
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeleton is the body s bony framework which consists of 206 bones. The bones are made up of water(45%), calcium and phosphorous(35%) and other organic materials(20%). The calcium
10/12/2011. Classification of Bones Every adult skeleton contains 206 bones which can be arranged into six broad categories according to shape
 Primary Functions of Skeletal System 1. support 2. storage of minerals & lipids -calcium salts provide vital minerals -lipids are in stored yellow marrow 3. blood cell production -RBC s, WBC s, and other
Primary Functions of Skeletal System 1. support 2. storage of minerals & lipids -calcium salts provide vital minerals -lipids are in stored yellow marrow 3. blood cell production -RBC s, WBC s, and other
DIAGNOSING CHILDHOOD MUSCULAR DYSTROPHIES
 DIAGNOSING CHILDHOOD MUSCULAR DYSTROPHIES Extracts from a review article by KN North and KJ Jones: Recent advances in diagnosis of the childhood muscular dystrophies Journal of Paediatrics and Child Health
DIAGNOSING CHILDHOOD MUSCULAR DYSTROPHIES Extracts from a review article by KN North and KJ Jones: Recent advances in diagnosis of the childhood muscular dystrophies Journal of Paediatrics and Child Health
Chapter 11. What are the functions of the skeletal system? More detail on bone
 Skeletal System Chapter 11 11.1 Overview of the skeletal system What are the functions of the skeletal system? 1. Supports the body 2. Protects the soft body parts 3. Produces blood cells 4. Stores minerals
Skeletal System Chapter 11 11.1 Overview of the skeletal system What are the functions of the skeletal system? 1. Supports the body 2. Protects the soft body parts 3. Produces blood cells 4. Stores minerals
Genetic Bases of Hearing Loss: Future Treatment Implications
 Genetic Bases of Hearing Loss: Future Treatment Implications Luis F. Escobar, MD Medical Director Medical Genetics & Neurodevelopmental Pediatrics of Indiana Peyton Manning Children s Hospital St. Vincent
Genetic Bases of Hearing Loss: Future Treatment Implications Luis F. Escobar, MD Medical Director Medical Genetics & Neurodevelopmental Pediatrics of Indiana Peyton Manning Children s Hospital St. Vincent
OBJECTIVE: List and describe the functions of the skeletal system. D. Storage depot for minerals and homeostasis
 Text Reference: Chapters 6 and 7 Pages 1-6 are mostly a review from lab Know this material before you come to lecture. Lecture will begin on page 7 Read text and complete packet before lecture. I. Introduction
Text Reference: Chapters 6 and 7 Pages 1-6 are mostly a review from lab Know this material before you come to lecture. Lecture will begin on page 7 Read text and complete packet before lecture. I. Introduction
CHARACTERSTIC RADIOGRAPHIC APPEARANCE
 OSTEOLYTIC LESIONS APPROACH AGE Metastatic Neuroblastoma in infant and young child. Metastases and multiple myeloma in middle aged and elderly. Ewing s sarcoma and simple bone cyst in children and teens.
OSTEOLYTIC LESIONS APPROACH AGE Metastatic Neuroblastoma in infant and young child. Metastases and multiple myeloma in middle aged and elderly. Ewing s sarcoma and simple bone cyst in children and teens.
Skeletal system. 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 NURS1004 Week 6 Part I Prepared by Didy Button Skeletal system An Introduction to the Skeletal System The Skeletal System Includes: Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues 6-1
NURS1004 Week 6 Part I Prepared by Didy Button Skeletal system An Introduction to the Skeletal System The Skeletal System Includes: Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues 6-1
Chapter-21b: Hormones and Receptors
 1 hapter-21b: Hormones and Receptors Hormone classes Hormones are classified according to the distance over which they act. 1. Autocrine hormones --- act on the same cell that released them. Interleukin-2
1 hapter-21b: Hormones and Receptors Hormone classes Hormones are classified according to the distance over which they act. 1. Autocrine hormones --- act on the same cell that released them. Interleukin-2
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone
Louise Simmons Clinical Nurse Specialist Inherited Metabolic Disorders (IMD) Birmingham Children s Hospital
 Louise Simmons Clinical Nurse Specialist Inherited Metabolic Disorders (IMD) Birmingham Children s Hospital Individually rare Collectively not uncommon - 1:700 - Childhood cancer 1:500 Genetically inherited
Louise Simmons Clinical Nurse Specialist Inherited Metabolic Disorders (IMD) Birmingham Children s Hospital Individually rare Collectively not uncommon - 1:700 - Childhood cancer 1:500 Genetically inherited
Bone Tissue Chapter 7
 Bone Tissue Chapter 7 Tissues and organs of the skeletal system Histology of osseous tissue Bone development Physiology of osseous tissue Bone disorders Bone Tissue Bone is alive and continuously changing.
Bone Tissue Chapter 7 Tissues and organs of the skeletal system Histology of osseous tissue Bone development Physiology of osseous tissue Bone disorders Bone Tissue Bone is alive and continuously changing.
TERATOGENESIS ONTOGENESIS
 TERATOGENESIS ONTOGENESIS Inborn developmental defects Occured during prenatal development Are present by delivery At about 3-5 % newborns are affected. Inborn developmental defects 1. CHROMOSOMAL ABERRATIONS
TERATOGENESIS ONTOGENESIS Inborn developmental defects Occured during prenatal development Are present by delivery At about 3-5 % newborns are affected. Inborn developmental defects 1. CHROMOSOMAL ABERRATIONS
Mucolipidoses. U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health
 Mucolipidoses U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health Mucolipidoses What are the mucolipidoses? The mucolipidoses (ML) are a group of inherited metabolic diseases that
Mucolipidoses U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health Mucolipidoses What are the mucolipidoses? The mucolipidoses (ML) are a group of inherited metabolic diseases that
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM: BONE TISSUE. Chapter 6. Anatomy and Physiology Lecture
 Chapter 6 1 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM: BONE TISSUE Chapter 6 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Chapter 6 2 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM: BONE TISSUE Bone (Osseous) Tissue forms most of the skeleton: Skeletal System - the
Chapter 6 1 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM: BONE TISSUE Chapter 6 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Chapter 6 2 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM: BONE TISSUE Bone (Osseous) Tissue forms most of the skeleton: Skeletal System - the
DISEASES OF THE MUSKULOSKELETAL SYSTEM AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE
 DISEASES OF THE MUSKULOSKELETAL SYSTEM AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE ARTHROPATHIES AND RELATED DISORDERS (710 719.9) 710 DIFFUSE DISEASES OF CONNECTIVE TISSUE 710.0 SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS 710.1 SYSTEMIC
DISEASES OF THE MUSKULOSKELETAL SYSTEM AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE ARTHROPATHIES AND RELATED DISORDERS (710 719.9) 710 DIFFUSE DISEASES OF CONNECTIVE TISSUE 710.0 SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS 710.1 SYSTEMIC
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley. Practice Exam #2
 Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam #2 For questions 1 through 3, select your answers from the following responses: a. stratified squamous epithelium b. reticular connective tissue
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam #2 For questions 1 through 3, select your answers from the following responses: a. stratified squamous epithelium b. reticular connective tissue
BIOL 4260 Human Evolu3onary Anatomy Lecture 5: Bone Development & Trunk Anatomy. Lecture 2: Fossil Record
 BIOL 4260 Human Evolu3onary Anatomy Lecture 5: Bone Development & Trunk Anatomy Lecture 2: Fossil Record Segmentation Cyclic genescreate segme ntation clock for somite production Final #s 4 occipital 8
BIOL 4260 Human Evolu3onary Anatomy Lecture 5: Bone Development & Trunk Anatomy Lecture 2: Fossil Record Segmentation Cyclic genescreate segme ntation clock for somite production Final #s 4 occipital 8
Osteoporosis in childhood
 Postgraduate Medical Journal (August 1977) 53, 450-456. Osteoporosis in childhood C. E. DENT* Ph.D., F.R.C.P., F.R.S. Department of Human Metabolism, University College Hospital Medical School, London
Postgraduate Medical Journal (August 1977) 53, 450-456. Osteoporosis in childhood C. E. DENT* Ph.D., F.R.C.P., F.R.S. Department of Human Metabolism, University College Hospital Medical School, London
Chromosomal Abnormalities
 Chromosomal Abnormalities George E Tiller, MD, PhD Regional Chief, Dept. Genetics Southern California Permanente Medical Group Los Angeles, CA Objectives of Lecture list several indications for karyotyping
Chromosomal Abnormalities George E Tiller, MD, PhD Regional Chief, Dept. Genetics Southern California Permanente Medical Group Los Angeles, CA Objectives of Lecture list several indications for karyotyping
Congenital Anomalies In Diamond Blackfan Anemia (DBA)
 Congenital Anomalies In Diamond Blackfan Anemia (DBA) CS217857 National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities Division of Blood Disorders Congenital Anomalies In Diamond Blackfan Anemia
Congenital Anomalies In Diamond Blackfan Anemia (DBA) CS217857 National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities Division of Blood Disorders Congenital Anomalies In Diamond Blackfan Anemia
Chapter 9 Mitochondrial Structure and Function
 Chapter 9 Mitochondrial Structure and Function 1 2 3 Structure and function Oxidative phosphorylation and ATP Synthesis Peroxisome Overview 2 Mitochondria have characteristic morphologies despite variable
Chapter 9 Mitochondrial Structure and Function 1 2 3 Structure and function Oxidative phosphorylation and ATP Synthesis Peroxisome Overview 2 Mitochondria have characteristic morphologies despite variable
Osteogenesis Imperfecta
 Osteogenesis Imperfecta Abstract Osteogenesis imperfecta (OI) is a genetic disorder of connective tissue characterized by brittle bones. Other characteristics are poorly formed teeth, blue sclera of the
Osteogenesis Imperfecta Abstract Osteogenesis imperfecta (OI) is a genetic disorder of connective tissue characterized by brittle bones. Other characteristics are poorly formed teeth, blue sclera of the
Function of Bones. Bone Tissue and Bones BONE CLASSIFICATION. Long Bones Gross Anatomy. Lab Activity 1 - Gross Anatomy of a Long Bone
 Function of Bones Bone Tissue and Bones Bones form the framework of the skeleton. Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part
Function of Bones Bone Tissue and Bones Bones form the framework of the skeleton. Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part
3) There are different types of extracellular signaling molecules. 4) most signaling molecules are secreted by exocytosis
 XIV) Signaling. A) The need for Signaling in multicellular organisms B) yeast need to signal to respond to various factors C) Extracellular signaling molecules bind to receptors 1) most bind to receptors
XIV) Signaling. A) The need for Signaling in multicellular organisms B) yeast need to signal to respond to various factors C) Extracellular signaling molecules bind to receptors 1) most bind to receptors
BONES AND BONE TISSUE
 BIO 2401 BONES & BONE TISSUE page 1 BONES AND BONE TISSUE Organization of the Skeletal System components: 1) bone 2) skeletal cartilage: surrounded by dense irregular connective tissue which acts to girdle
BIO 2401 BONES & BONE TISSUE page 1 BONES AND BONE TISSUE Organization of the Skeletal System components: 1) bone 2) skeletal cartilage: surrounded by dense irregular connective tissue which acts to girdle
Mechanism of hormone action
 Mechanism of hormone action ผศ.ดร.พญ.ส ว ฒณ ค ปต ว ฒ ภาคว ชาสร รว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร ศ ร ราชพยาบาล Aims What is hormone receptor Type of hormone receptors - cell surface receptor - intracellular receptor
Mechanism of hormone action ผศ.ดร.พญ.ส ว ฒณ ค ปต ว ฒ ภาคว ชาสร รว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร ศ ร ราชพยาบาล Aims What is hormone receptor Type of hormone receptors - cell surface receptor - intracellular receptor
D. Vitamin D. 1. Two main forms; vitamin D2 and D3
 D. Vitamin D. Two main forms; vitamin D2 and D3 H H D3 - Cholecalciferol D2 - Ergocalciferol Technically, vitamin D is not a vitamin. It is the name given to a group of fat-soluble prohormones (substances
D. Vitamin D. Two main forms; vitamin D2 and D3 H H D3 - Cholecalciferol D2 - Ergocalciferol Technically, vitamin D is not a vitamin. It is the name given to a group of fat-soluble prohormones (substances
23. TERATOGENS AND THEIR EFFECTS
 23. TERATOGENS AND THEIR EFFECTS Wendy Chung, M.D. Ph.D. Telephone: 851-5313 e-mail: wkc15@columbia.edu SUMMARY A congenital malformation is an anatomical or structural abnormality present at birth. Congenital
23. TERATOGENS AND THEIR EFFECTS Wendy Chung, M.D. Ph.D. Telephone: 851-5313 e-mail: wkc15@columbia.edu SUMMARY A congenital malformation is an anatomical or structural abnormality present at birth. Congenital
GENETIC TESTING AND MARFAN SYNDROME
 GENETIC TESTING AND MARFAN SYNDROME Genetic testing for mutations in fibrillin-1 (FBN1) and other genes has become an important and reliable option to aid in the diagnosis of Marfan syndrome and related
GENETIC TESTING AND MARFAN SYNDROME Genetic testing for mutations in fibrillin-1 (FBN1) and other genes has become an important and reliable option to aid in the diagnosis of Marfan syndrome and related
Control of Gene Expression
 Control of Gene Expression What is Gene Expression? Gene expression is the process by which informa9on from a gene is used in the synthesis of a func9onal gene product. What is Gene Expression? Figure
Control of Gene Expression What is Gene Expression? Gene expression is the process by which informa9on from a gene is used in the synthesis of a func9onal gene product. What is Gene Expression? Figure
Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together.
 Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together. CLASSES OF JOINTS. 1. Joints are classified according to how the bones are held together. 2. The three types of
Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together. CLASSES OF JOINTS. 1. Joints are classified according to how the bones are held together. 2. The three types of
Actions of Hormones on Target Cells Page 1. Actions of Hormones on Target Cells Page 2. Goals/ What You Need to Know Goals What You Need to Know
 Actions of Hormones on Target Cells Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Actions of Hormones on Target Cells Hormones
Actions of Hormones on Target Cells Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Actions of Hormones on Target Cells Hormones
FDA Approved Indications
 Preferred Agents: Humatrope (somatropin) Nutropin (somatropin) Medication Nutropin AQ (somatropin) Nutropin AQ NuSpin (somatropin) Non-Preferred Agents: Genotropin (somatropin) Omnitrope (somatropin) Norditropin
Preferred Agents: Humatrope (somatropin) Nutropin (somatropin) Medication Nutropin AQ (somatropin) Nutropin AQ NuSpin (somatropin) Non-Preferred Agents: Genotropin (somatropin) Omnitrope (somatropin) Norditropin
Observing Vertebrate Skeletons
 Name Class Date Chapter 33 Comparing Chordates Observing Vertebrate Skeletons Introduction One characteristic common to all vertebrates is the presence of a skeleton. The endoskeleton provides support,
Name Class Date Chapter 33 Comparing Chordates Observing Vertebrate Skeletons Introduction One characteristic common to all vertebrates is the presence of a skeleton. The endoskeleton provides support,
Name Date Period. 2. When a molecule of double-stranded DNA undergoes replication, it results in
 DNA, RNA, Protein Synthesis Keystone 1. During the process shown above, the two strands of one DNA molecule are unwound. Then, DNA polymerases add complementary nucleotides to each strand which results
DNA, RNA, Protein Synthesis Keystone 1. During the process shown above, the two strands of one DNA molecule are unwound. Then, DNA polymerases add complementary nucleotides to each strand which results
Sickle cell anemia: Altered beta chain Single AA change (#6 Glu to Val) Consequence: Protein polymerizes Change in RBC shape ---> phenotypes
 Protein Structure Polypeptide: Protein: Therefore: Example: Single chain of amino acids 1 or more polypeptide chains All polypeptides are proteins Some proteins contain >1 polypeptide Hemoglobin (O 2 binding
Protein Structure Polypeptide: Protein: Therefore: Example: Single chain of amino acids 1 or more polypeptide chains All polypeptides are proteins Some proteins contain >1 polypeptide Hemoglobin (O 2 binding
Abnormalities of the Teeth. Abnomalities of teeth. Local factors associated with enamel defects. Environmental alterations
 Abnormalities of the Teeth Abnomalities of teeth Environmental alterations Developmental alterations Steven Chussid D.D.S. Director, Division of Pediatric Dentistry Environmental alterations Effects on
Abnormalities of the Teeth Abnomalities of teeth Environmental alterations Developmental alterations Steven Chussid D.D.S. Director, Division of Pediatric Dentistry Environmental alterations Effects on
Jennifer A. Defant, M.S., C.G.C. Certified Genetic Counselor Division of Genetics and Metabolism University of Florida
 Jennifer A. Defant, M.S., C.G.C. Certified Genetic Counselor Division of Genetics and Metabolism University of Florida 60% of childhood hearing loss is genetic Syndromic Nonsyndromic 40% of childhood hearing
Jennifer A. Defant, M.S., C.G.C. Certified Genetic Counselor Division of Genetics and Metabolism University of Florida 60% of childhood hearing loss is genetic Syndromic Nonsyndromic 40% of childhood hearing
CARTILAGE HAIR HYPOPLASIA NATURAL HISTORY INTRODUCTION:
 Richard M. Pauli, M.D., Ph.D., Midwest Regional Bone Dysplasia Clinic revised 7/2010 CARTILAGE HAIR HYPOPLASIA NATURAL HISTORY INTRODUCTION: The following summary of the medical expectations in Cartilage
Richard M. Pauli, M.D., Ph.D., Midwest Regional Bone Dysplasia Clinic revised 7/2010 CARTILAGE HAIR HYPOPLASIA NATURAL HISTORY INTRODUCTION: The following summary of the medical expectations in Cartilage
5 Localized Bone Lesions
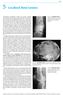 75 5 Localized Bone Lesions Conventional radiography remains the primary imaging modality for the evaluation of skeletal lesions. The combination of conventional radiography, which has a high specificity
75 5 Localized Bone Lesions Conventional radiography remains the primary imaging modality for the evaluation of skeletal lesions. The combination of conventional radiography, which has a high specificity
Arthritis of the Hands
 Arthritis of the Hands On the Agenda Normal Osteoarthitis Rheumatoid arthritis CPPD crystal deposition Gout Psoriatic arthritis Normal Hand X-ray Osteoarthritis (DJD) Gradual degeneration of articular
Arthritis of the Hands On the Agenda Normal Osteoarthitis Rheumatoid arthritis CPPD crystal deposition Gout Psoriatic arthritis Normal Hand X-ray Osteoarthritis (DJD) Gradual degeneration of articular
A RARE CASE OF FAILURE TO THRIVE IN INFANTS: MALIGNANT INFANTILE OSTEOPETROSIS
 A RARE CASE OF FAILURE TO THRIVE IN INFANTS: MALIGNANT INFANTILE OSTEOPETROSIS Ramona Stroescu 1,2, Teofana Bizerea 1, Elena Pop 1, Otilia Mărginean 1,2, Ioana Micle 1, Mihaela Dobre 1 Abstract Background:
A RARE CASE OF FAILURE TO THRIVE IN INFANTS: MALIGNANT INFANTILE OSTEOPETROSIS Ramona Stroescu 1,2, Teofana Bizerea 1, Elena Pop 1, Otilia Mărginean 1,2, Ioana Micle 1, Mihaela Dobre 1 Abstract Background:
ICD-10 Codes for Orthodontics
 Introduction Kirt E. Simmons, DDS, PhD This document is meant to provide general information on diagnostic coding, specifically coding using the ICD-10 code set. Proper and accurate diagnostic coding is
Introduction Kirt E. Simmons, DDS, PhD This document is meant to provide general information on diagnostic coding, specifically coding using the ICD-10 code set. Proper and accurate diagnostic coding is
treatments) worked by killing cancerous cells using chemo or radiotherapy. While these techniques can
 Shristi Pandey Genomics and Medicine Winter 2011 Prof. Doug Brutlag Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: A look into how genomics is changing the way we treat Cancer. Until the late 1990s, nearly all treatment methods
Shristi Pandey Genomics and Medicine Winter 2011 Prof. Doug Brutlag Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: A look into how genomics is changing the way we treat Cancer. Until the late 1990s, nearly all treatment methods
MRI of Bone Marrow Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation
 MRI of Bone Marrow Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel, M.D. Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology Washington University School of Medicine St. Louis, MO and Visiting Scientist, AFIP, Washington,
MRI of Bone Marrow Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel, M.D. Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology Washington University School of Medicine St. Louis, MO and Visiting Scientist, AFIP, Washington,
STEM CELL FELLOWSHIP
 Module I: The Basic Principles of Stem Cells 1. Basics of Stem Cells a. Understanding the development of embryonic stem cells i. Embryonic stem cells ii. Embryonic germ cells iii. Differentiated stem cell
Module I: The Basic Principles of Stem Cells 1. Basics of Stem Cells a. Understanding the development of embryonic stem cells i. Embryonic stem cells ii. Embryonic germ cells iii. Differentiated stem cell
Genetic Disorders in the United Arab Emirates
 Genetic Disorders in the United Arab Emirates Ghazi Omar Tadmouri Erol Baysal Mansour Al Zarooni Mohammed Naveed Najat Rashid Sarah Al-Haj Ali Mahmoud Taleb Al Ali The burgeoning research in medical and
Genetic Disorders in the United Arab Emirates Ghazi Omar Tadmouri Erol Baysal Mansour Al Zarooni Mohammed Naveed Najat Rashid Sarah Al-Haj Ali Mahmoud Taleb Al Ali The burgeoning research in medical and
Copyright 2000-2003 Mark Brandt, Ph.D. 54
 Pyruvate Oxidation Overview of pyruvate metabolism Pyruvate can be produced in a variety of ways. It is an end product of glycolysis, and can be derived from lactate taken up from the environment (or,
Pyruvate Oxidation Overview of pyruvate metabolism Pyruvate can be produced in a variety of ways. It is an end product of glycolysis, and can be derived from lactate taken up from the environment (or,
Molecular Cell Biology. Prof. D. Karunagaran. Department of Biotechnology. Indian Institute of Technology Madras. Module 7 Cell Signaling Mechanisms
 Molecular Cell Biology Prof. D. Karunagaran Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology Madras Module 7 Cell Signaling Mechanisms Lecture 2 GPCR Signaling Receptors - G protein coupled receptors
Molecular Cell Biology Prof. D. Karunagaran Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology Madras Module 7 Cell Signaling Mechanisms Lecture 2 GPCR Signaling Receptors - G protein coupled receptors
Genetic Mutations. Indicator 4.8: Compare the consequences of mutations in body cells with those in gametes.
 Genetic Mutations Indicator 4.8: Compare the consequences of mutations in body cells with those in gametes. Agenda Warm UP: What is a mutation? Body cell? Gamete? Notes on Mutations Karyotype Web Activity
Genetic Mutations Indicator 4.8: Compare the consequences of mutations in body cells with those in gametes. Agenda Warm UP: What is a mutation? Body cell? Gamete? Notes on Mutations Karyotype Web Activity
Classification of bones Any bone may be classified into one of the following groups:
 Skeletal system This system is made up of hard tissues like bone and cartilages. This system gives form and shape to animal body The skeleton of a living animal is made up living structures of bones. The
Skeletal system This system is made up of hard tissues like bone and cartilages. This system gives form and shape to animal body The skeleton of a living animal is made up living structures of bones. The
Mechanisms of Hormonal Action Bryant Miles
 Mechanisms of ormonal Action Bryant Miles Multicellular organisms need to coordinate metabolic activities. Complex signaling systems have evolved using chemicals called hormones to regulate cellular activities.
Mechanisms of ormonal Action Bryant Miles Multicellular organisms need to coordinate metabolic activities. Complex signaling systems have evolved using chemicals called hormones to regulate cellular activities.
Co-pay assistance organizations offering assistance
 Acromegaly Acute Exacerbations of Multiple Sclerosis Acute Porphyrias Advanced Idiopathic Parkinson' s Disease Age-Related Macular Degeneration www.theassistancefund.org Alcohol Dependence Alpha-1 Antitrypsin
Acromegaly Acute Exacerbations of Multiple Sclerosis Acute Porphyrias Advanced Idiopathic Parkinson' s Disease Age-Related Macular Degeneration www.theassistancefund.org Alcohol Dependence Alpha-1 Antitrypsin
Lecture 8. Protein Trafficking/Targeting. Protein targeting is necessary for proteins that are destined to work outside the cytoplasm.
 Protein Trafficking/Targeting (8.1) Lecture 8 Protein Trafficking/Targeting Protein targeting is necessary for proteins that are destined to work outside the cytoplasm. Protein targeting is more complex
Protein Trafficking/Targeting (8.1) Lecture 8 Protein Trafficking/Targeting Protein targeting is necessary for proteins that are destined to work outside the cytoplasm. Protein targeting is more complex
NURS 821 Alterations in the Musculoskeletal System. Rheumatoid Arthritis. Type III Hypersensitivity Response
 NURS 821 Alterations in the Musculoskeletal System Margaret H. Birney PhD, RN Lecture 12 Part 2 Joint Disorders (cont d) Rheumatoid Arthritis Definition: Autoimmune disorder occurring in genetically sensitive
NURS 821 Alterations in the Musculoskeletal System Margaret H. Birney PhD, RN Lecture 12 Part 2 Joint Disorders (cont d) Rheumatoid Arthritis Definition: Autoimmune disorder occurring in genetically sensitive
1. outer fibrous layer contains fibroblasts that secrete collagen
 I. cartilage A. perichondrium 1. outer fibrous layer contains fibroblasts that secrete collagen 2. inner chondrogenic layer contains cells that can proliferate and turn into chondroblasts B. cartilage
I. cartilage A. perichondrium 1. outer fibrous layer contains fibroblasts that secrete collagen 2. inner chondrogenic layer contains cells that can proliferate and turn into chondroblasts B. cartilage
Muscular Dystrophy. By. Tina Strauss
 Muscular Dystrophy By. Tina Strauss Story Outline for Presentation on Muscular Dystrophy What is Muscular Dystrophy? Signs & Symptoms Types When to seek medical attention? Screening and Diagnosis Treatment
Muscular Dystrophy By. Tina Strauss Story Outline for Presentation on Muscular Dystrophy What is Muscular Dystrophy? Signs & Symptoms Types When to seek medical attention? Screening and Diagnosis Treatment
DISCUSSION TOPICS. Embryology Etiology Presentation Associated Anomalies Classification Management
 MICROTIA Emily Tignor, MD Faculty Advisor: Shraddha Mukerji, MD The University of Texas Medical Branch Department of Otolaryngology Grand Rounds Presentation October 30, 2013 DISCUSSION TOPICS Embryology
MICROTIA Emily Tignor, MD Faculty Advisor: Shraddha Mukerji, MD The University of Texas Medical Branch Department of Otolaryngology Grand Rounds Presentation October 30, 2013 DISCUSSION TOPICS Embryology
Lecture 3: Mutations
 Lecture 3: Mutations Recall that the flow of information within a cell involves the transcription of DNA to mrna and the translation of mrna to protein. Recall also, that the flow of information between
Lecture 3: Mutations Recall that the flow of information within a cell involves the transcription of DNA to mrna and the translation of mrna to protein. Recall also, that the flow of information between
UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES
 UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 4.01 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A. Support 1. Provides a framework for the body. 2. Supports soft tissue. 3. Serves as a point of attachment for ligaments,
UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 4.01 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A. Support 1. Provides a framework for the body. 2. Supports soft tissue. 3. Serves as a point of attachment for ligaments,
NORD Guides for Physicians #1. Physician s Guide to. Tyrosinemia. Type 1
 NORD Guides for Physicians #1 The National Organization for Rare Disorders Physician s Guide to Tyrosinemia Type 1 The original version of this booklet was made possible by donations in honor of Danielle
NORD Guides for Physicians #1 The National Organization for Rare Disorders Physician s Guide to Tyrosinemia Type 1 The original version of this booklet was made possible by donations in honor of Danielle
Spine in Patients with Diastrophic Dysplasia - a clinical and radiological study
 Hospital for Children and Adolescents Paediatric Orthopaedics University of Helsinki and Orton Orthopaedic Hospital Helsinki Spine in Patients with Diastrophic Dysplasia - a clinical and radiological study
Hospital for Children and Adolescents Paediatric Orthopaedics University of Helsinki and Orton Orthopaedic Hospital Helsinki Spine in Patients with Diastrophic Dysplasia - a clinical and radiological study
# Circuits relevant to cancer, related to known TFs.
 # Circuits relevant to cancer, related to known TFs. # Final dataset of circuits where at least one gene has been annotated as relevant to cancer. # Circuits correspond to blocks separated by a symbol.
# Circuits relevant to cancer, related to known TFs. # Final dataset of circuits where at least one gene has been annotated as relevant to cancer. # Circuits correspond to blocks separated by a symbol.
LABORATORY EXERCISE 12 BONE STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATION
 LABORATORY EXERCISE 12 BONE STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATION FIG. 12.1 1. Articular cartilage (hyaline cartilage) 6. Periosteum 2. Spongy bone (red marrow) 7. Proximal epiphysis 3. Medullary cavity 8. Diaphysis
LABORATORY EXERCISE 12 BONE STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATION FIG. 12.1 1. Articular cartilage (hyaline cartilage) 6. Periosteum 2. Spongy bone (red marrow) 7. Proximal epiphysis 3. Medullary cavity 8. Diaphysis
USEFULNESS OF BONE AGE IN PAEDIATRIC ENDOCRINOLOGY. Rina Balducci Center of Pediatric Endocrinology, Department of Public Health and Cell Biology
 USEFULNESS OF BONE AGE IN PAEDIATRIC ENDOCRINOLOGY Gian Luigi Spadoni and Stefano Cianfarani Rina Balducci Center of Pediatric Endocrinology, Department of Public Health and Cell Biology Tor Vergata University,
USEFULNESS OF BONE AGE IN PAEDIATRIC ENDOCRINOLOGY Gian Luigi Spadoni and Stefano Cianfarani Rina Balducci Center of Pediatric Endocrinology, Department of Public Health and Cell Biology Tor Vergata University,
WHEN TO BE CONCERNED: Leg Bowing, Intoeing and Flat Feet.
 WHEN TO BE CONCERNED: Leg Bowing, Intoeing and Flat Feet. Understanding normal childhood development and recognizing signs of pathology WHAT IS NORMAL? Very important: the average and normal are not the
WHEN TO BE CONCERNED: Leg Bowing, Intoeing and Flat Feet. Understanding normal childhood development and recognizing signs of pathology WHAT IS NORMAL? Very important: the average and normal are not the
Brunswick School Department: Grades 11-12. Essential Understandings
 Understandings Questions Knowledge Vocabulary Skills Bones provide invaluable structure and support for the body. There are a variety of bone shapes. Joints connect bones. The skeletal system is divided
Understandings Questions Knowledge Vocabulary Skills Bones provide invaluable structure and support for the body. There are a variety of bone shapes. Joints connect bones. The skeletal system is divided
ACMG Practice Guideline
 June 2007 Vol. 9 No. 6 ACMG Practice Guideline Indications for genetic referral: a guide for healthcare providers Beth A. Pletcher, MD 1, Helga V. Toriello, PhD 2, Sarah J. Noblin, MS, CGC 3, Laurie H.
June 2007 Vol. 9 No. 6 ACMG Practice Guideline Indications for genetic referral: a guide for healthcare providers Beth A. Pletcher, MD 1, Helga V. Toriello, PhD 2, Sarah J. Noblin, MS, CGC 3, Laurie H.
Module F SKELETAL SYSTEM & ARTICULATIONS
 Module F SKELETAL SYSTEM & ARTICULATIONS Topic from General functions of bone & the skeletal system Structural components microscopic anatomy Structural components gross anatomy Physiology of embryonic
Module F SKELETAL SYSTEM & ARTICULATIONS Topic from General functions of bone & the skeletal system Structural components microscopic anatomy Structural components gross anatomy Physiology of embryonic
Objectives Role of Medical Genetics in Hearing Loss Evaluation. 5 y.o. boy with severe SNHL
 Objectives Role of Medical Genetics in Hearing Loss Evaluation Millan Patel, MD UBC Dept. of Medical Genetics October 22, 2010 Case presentation to illustrate importance of defining syndromic hearing loss
Objectives Role of Medical Genetics in Hearing Loss Evaluation Millan Patel, MD UBC Dept. of Medical Genetics October 22, 2010 Case presentation to illustrate importance of defining syndromic hearing loss
CMS Limitations Guide Mammograms and Bone Density Radiology Services
 CMS Limitations Guide Mammograms and Bone Density Radiology Services Starting July 1, 2008, CMS has placed numerous medical necessity limits on tests and procedures. This reference guide provides you with
CMS Limitations Guide Mammograms and Bone Density Radiology Services Starting July 1, 2008, CMS has placed numerous medical necessity limits on tests and procedures. This reference guide provides you with
Topic #4: Legg Calve Perthes Disease (LCP) (Aseptic femoral head necrosis)
 Topic #4: Legg Calve Perthes Disease (LCP) (Aseptic femoral head necrosis) Young Westies, and other breeds of purebred dogs, can develop a debilitating condition in which the bones that form the top of
Topic #4: Legg Calve Perthes Disease (LCP) (Aseptic femoral head necrosis) Young Westies, and other breeds of purebred dogs, can develop a debilitating condition in which the bones that form the top of
Gene mutation and molecular medicine Chapter 15
 Gene mutation and molecular medicine Chapter 15 Lecture Objectives What Are Mutations? How Are DNA Molecules and Mutations Analyzed? How Do Defective Proteins Lead to Diseases? What DNA Changes Lead to
Gene mutation and molecular medicine Chapter 15 Lecture Objectives What Are Mutations? How Are DNA Molecules and Mutations Analyzed? How Do Defective Proteins Lead to Diseases? What DNA Changes Lead to
Human Bones BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN ACTIVITY ASSESSMENT OPPORTUNITIES. Grade 4 Quarter 3 Activity 21
 activity 21 Human Bones BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN Grade 4 Quarter 3 Activity 21 SC.F.1.2.1 The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structures and functions
activity 21 Human Bones BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN Grade 4 Quarter 3 Activity 21 SC.F.1.2.1 The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structures and functions
Prior Authorization Form
 Prior Authorization Form Growth Hormone This fax machine is located in a secure location as required by HIPAA regulations. Complete/review information, sign and date. Fax signed forms to CVS/Caremark at
Prior Authorization Form Growth Hormone This fax machine is located in a secure location as required by HIPAA regulations. Complete/review information, sign and date. Fax signed forms to CVS/Caremark at
2007 7.013 Problem Set 1 KEY
 2007 7.013 Problem Set 1 KEY Due before 5 PM on FRIDAY, February 16, 2007. Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YOUR ANSWERS ON THIS PRINTOUT. 1. Where in a eukaryotic cell do you
2007 7.013 Problem Set 1 KEY Due before 5 PM on FRIDAY, February 16, 2007. Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YOUR ANSWERS ON THIS PRINTOUT. 1. Where in a eukaryotic cell do you
Human Body Vocabulary Words Week 1
 Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
9 Miscellaneous QUESTIONS. 1 Which of the following is the most common tumor complication associated with the disorder depicted by the radiograph?
 9 Miscellaneous QUESTIONS 1 Which of the following is the most common tumor complication associated with the disorder depicted by the radiograph? A. Lymphoma B. Sarcoma C. Giant cell tumor D. Enchondroma
9 Miscellaneous QUESTIONS 1 Which of the following is the most common tumor complication associated with the disorder depicted by the radiograph? A. Lymphoma B. Sarcoma C. Giant cell tumor D. Enchondroma
ENDOCRINE, NUTRITIONAL AND METABOLIC DISEASES AND IMMUNITY DISORDERS
 ENDOCRINE, NUTRITIONAL AND METABOLIC DISEASES AND IMMUNITY DISORDERS DISORDERS OF THYROID GLAND (240 246.9) 240 SIMPLE AND UNSPECIFIED GOITRE 240.0 GOITRE, SPECIFIED AS SIMPLE 240.9 GOITRE, UNSPECIFIED
ENDOCRINE, NUTRITIONAL AND METABOLIC DISEASES AND IMMUNITY DISORDERS DISORDERS OF THYROID GLAND (240 246.9) 240 SIMPLE AND UNSPECIFIED GOITRE 240.0 GOITRE, SPECIFIED AS SIMPLE 240.9 GOITRE, UNSPECIFIED
chronic leukemia lymphoma myeloma differentiated 14 September 1999 Pre- Transformed Ig Surface Surface Secreted Myeloma Major malignant counterpart
 Disease Usual phenotype acute leukemia precursor chronic leukemia lymphoma myeloma differentiated Pre- B-cell B-cell Transformed B-cell Plasma cell Ig Surface Surface Secreted Major malignant counterpart
Disease Usual phenotype acute leukemia precursor chronic leukemia lymphoma myeloma differentiated Pre- B-cell B-cell Transformed B-cell Plasma cell Ig Surface Surface Secreted Major malignant counterpart
G. Shashidhar Pai, MD MUSC Children s Hospital Department of Pediatrics Division of Genetics
 G. Shashidhar Pai, MD MUSC Children s Hospital Department of Pediatrics Division of Genetics One of every 500 newborns has bilateral permanent sensorineural hearing loss 40 db which makes it the most common
G. Shashidhar Pai, MD MUSC Children s Hospital Department of Pediatrics Division of Genetics One of every 500 newborns has bilateral permanent sensorineural hearing loss 40 db which makes it the most common
19. Drug Treatment Trials
 1 9. D R U G T R E A T M E N T T R I A L S 19. Drug Treatment Trials The science behind the Progeria clinical drug trials Trial medications at a glance Progeria clinical drug trials The science behind
1 9. D R U G T R E A T M E N T T R I A L S 19. Drug Treatment Trials The science behind the Progeria clinical drug trials Trial medications at a glance Progeria clinical drug trials The science behind
Lecture Series 7. From DNA to Protein. Genotype to Phenotype. Reading Assignments. A. Genes and the Synthesis of Polypeptides
 Lecture Series 7 From DNA to Protein: Genotype to Phenotype Reading Assignments Read Chapter 7 From DNA to Protein A. Genes and the Synthesis of Polypeptides Genes are made up of DNA and are expressed
Lecture Series 7 From DNA to Protein: Genotype to Phenotype Reading Assignments Read Chapter 7 From DNA to Protein A. Genes and the Synthesis of Polypeptides Genes are made up of DNA and are expressed
