MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
- Jewel Carter
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The owner withdraws cash from the business. How does this withdrawal affect the accounting 1) equation? A) No effect on the assets, liabilities, or owner's equity B) Assets decrease; owner's equity decreases C) Assets increase; liabilities decrease D) Assets decrease; owner's equity increases 2) Beginning Owner's equity is $20, 000. Cash withdrawals by the owner were $7, 000. Ending 2) owner's equity is $37, 000. What was net income? A) $24, 000 B) $10, 000 C) $27, 000 D) $13, 000 3) A proprietorship possesses which of the following characteristics? 3) A) A proprietorship joins two or more individuals as co-owners. B) If a proprietorship cannot pay its debts, lenders cannot take the owners' personal assets to satisfy the obligations. C) A proprietorship has a single owner. D) None of the above is a characteristic of a partnership. 4) There are relatively few types of revenue. Which of the following in NOT a type of revenue? 4) A) owner withdrawals B) service C) sales D) interest 5) Wayne Tate purchased a building for his grocery store for $30, 000 in Based on inflation 5) estimates, he has adjusted the amount of this asset in his accounting records. The building in now reported at $75, 000. Which of the following concepts or principles of accounting is being violated? A) stable monetary unit concept B) going-concern concept C) entity concept D) reliability concept 6) Land is purchased with a $20, 000 down payment and the execution of an $80, 000 promissory 6) note. How does this purchase affect the accounting equation? A) assets increase $80, 000; liabilities decrease $20, 000 B) assets increase $80, 000; owner's equity increases $80, 000 C) assets increase $20, 000; liabilities decrease $80, 000 D) assets increase $80, 000; liabilities increase $80, 000 1
2 7) Accounting information may be generated for a variety of purposes. The key product(s) of 7) accounting is (are) which of the following documents? A) Financial statements B) Spreadsheets C) Workpapers D) Remittance advices Case 1.3 The following is a list of account balances (all except owner's equity) of Wilson Mowing Company as of December 31 of the first year of operation: Accounts receivable $ 2, 500 Accounts payable 3, 500 Salary expense 4, 500 Repairs expense 800 Truck 8, 500 Equipment 6, 300 Notes payable 8, 200 Cash 6, 800 Supplies expense 1, 600 Service revenue 31, 900 Gasoline expense 3, 800 Salary payable 200 The owner, J.D. Wilson, invested $3, 000 at the beginning of the year and withdrew $12, 000 during the year for his personal use. 8) Refer to Case 1.3. At the end of the year, what is the amount of total assets? 8) A) $11, 900 B) $12, 200 C) $24, 100 D) $21, 200 Case 1.1 Scott Camera Shop started the year with total assets $80, 000 and total liabilities of $40, 000. During the year, the business earned revenues of $120, 000 and incurred expenses of $70, 000. Scott withdrew $60, ) Refer to Case 1.1. What is the amount of the net change in Scott's capital balance for the year? 9) A) $10, 000 decrease B) $50, 000 increase C) $40, 000 increase D) $30, 000 decrease 10) Many organizations have contributed to the process of creating and/or using generally accepted 10) accounting principles. Which of the following organizations has the primary responsibility for formulating accounting standards? A) CMA B) AICPA C) FASB D) SEC 2
3 11) A partnership possesses which of the following characteristics? 11) A) A partnership joins two or more individuals as co-owners. B) A partnership is owned by shareholders or stockholders. C) If a partnership cannot pay its debts, lenders cannot take the owners' personal assets to satisfy the obligations. D) None of the above is a characteristic of a partnership 12) Which of the following financial statements lists the entity's assets, liabilities, and owner's equity as 12) of a specific date? A) statement of owner's equity B) income statement C) statement of cash flows D) balance sheet 13) Which of the following types of decision makers use accounting information to make business 13) decisions? A) creditors B) business owners C) investors D) all of the above 14) A $5, 000 account receivable is collected. How is the accounting equation affected? 14) A) assets increase $5, 000; liabilities decrease $5, 000 B) assets increase $5, 000; assets decrease $5, 000 C) assets increase $5, 000; liabilities increase $5, 000 D) assets increase $5, 000; owner's equity increases $5, ) Assets are $150, 000 and total liabilities are $90, 000. What would total owner's equity be? 15) A) $300, 000 B) $60, 000 C) $180, 000 D) $240, ) Accounting is the information system that provides information to various users. What process(es) 16) does this include? A) processing the data into reports B) communicating the results to decisions makers C) measuring business activity D) all of the above 17) Which of the following statements best describes managerial accounting? 17) A) Managerial accounting provides information for people outside the company. B) Managerial accounting focuses on outside investors and lenders that are not part of day-to-day management. C) Managerial accounting focuses on information for internal decision making. D) None of these statements is true of managerial accounting. 3
4 18) Which of the following is a correct accounting equation? 18) A) Assets + Revenue = Owner's equity B) Assets = Liabilities + Owner's equity C) Assets + Revenue = Liabilities + Expenses D) Assets + Liabilities = Owner's equity Case 1.2 Sharon Samson starts a plumbing service, Reliable Waterworks. Selected transactions are described as follows: a. Sharon deposits $7, 000 into a new checking account for the company. b. Sharon pays $4, 000 cash for equipment to be used for plumbing repairs. c. Sharon borrows $15, 000 from a local bank and deposits the money in the checking account. d. Sharon pays $600 rent for the first month. e. Sharon pays $400 cash for plumbing supplies to be used on various jobs in the future. f. Sharon completes a plumbing repair project for a local lawyer and receives $1, 300 cash. g. Sharon withdraws $2, 500 for personal use. 19) Refer to Case 1.2. After all of the transactions, what is the amount of total liabilities? 19) A) $4, 000 B) $4, 400 C) $19, 000 D) $15, ) Which of the following financial statements reports an increase or decrease in net cash during the 20) time period covered? A) statement of owner's equity B) statement of cash flows C) income statement D) balance sheet 21) Land was originally purchased for $20, 000. It is sold for $65, 000 in cash. How does the sale affect 21) the accounting equation? A) assets increase $45, 000; owner's equity increases $45, 000 B) assets increase $65, 000; owner's equity increases $65, 000 C) assets increase $65, 000; liabilities decrease $20, 000; owner's equity increases $45, 000 D) assets increase $20, 000; no change for liabilities; owner's equity increases $55, ) Which of the following financial statements reports cash receipts and cash payments during a 22) period of time? A) balance sheet B) statement of owner's equity C) income statement D) statement of cash flows 4
5 23) Phillip and Reed have developed a new technology for home computer systems. However, they 23) need to raise a large amount of capital to build the production and support facilities to market their product successfully. Which of the following business types would be the most likely to attract enough investors to provide the company with the necessary capital to begin production? A) Partnership B) Limited liability partnership C) Corporation D) Proprietorship 24) Each financial statement has a heading giving three pieces of data. Which of the following items is 24) NOT included in these headings? A) name of the financial statement B) date or time period covered C) name of the preparer of the statement D) name of the business 25) Accountants often refer to GAAP. What do the letters GAAP stand for when discussing 25) accounting? A) Global accommodation accounting principles. B) Generally accepted accounting principles. C) Generate accurate accounting policies. D) Grandma's awesome apple pie. 26) A limited liability company possesses which of the following characteristics? 26) A) A limited liability company is an "artificial person" in the eyes of the law. B) A limited liability company joins one or more individuals as co-owners. C) If a limited liability company cannot pay its debts, lenders cannot take the owners' personal assets to satisfy the obligations. D) All of the above are characteristics of a limited liability company. 27) Total liabilities increase by $7, 000. How is the accounting equation affected? 27) A) Assets must have increased by $7000 or owner's equity must have decreased by $7000. B) Owner's equity must have increased by $7, 000. C) Assets and owner's equity must have each decreased by $3, 500. D) Assets must have decreased by $7, ) Net income is $34, 000. Beginning owner's equity is $29, 000. Ending owner's equity is $55, ) What were owners' cash withdrawals? A) $8, 000 B) $18, 000 C) $5, 000 D) $60, 000 5
6 29) A corporation possesses all but one of the following characteristics. Which of the following is NOT 29) a characteristic of a corporation? A) If a corporation cannot pay its debts, lenders can take the owners' personal assets to satisfy the obligations. B) A corporation is owned by shareholders or stockholders. C) A corporation is an "artificial person" in the eyes of the law. D) Ownership is divided into individual shares. Case 1.2 Sharon Samson starts a plumbing service, Reliable Waterworks. Selected transactions are described as follows: a. Sharon deposits $7, 000 into a new checking account for the company. b. Sharon pays $4, 000 cash for equipment to be used for plumbing repairs. c. Sharon borrows $15, 000 from a local bank and deposits the money in the checking account. d. Sharon pays $600 rent for the first month. e. Sharon pays $400 cash for plumbing supplies to be used on various jobs in the future. f. Sharon completes a plumbing repair project for a local lawyer and receives $1, 300 cash. g. Sharon withdraws $2, 500 for personal use. 30) Refer to Case 1.2. After all of the transactions, what is the amount of total assets? 30) A) $20, 200 B) $25, 700 C) $24, 200 D) $5, ) The primary objective of financial reporting is to provide information useful for making 31) investment and lending decisions. To be useful, information must possess certain characteristics. Which of the following is NOT one of the basic characteristics that accounting information must possess to be useful. A) reliability B) comparability C) relevance D) an owner's equity section 32) The financial statements should be prepared in which of the following orders? 32) A) income statement, statement of owner's equity, balance sheet B) balance sheet, income statement, statement of owner's equity C) balance sheet, statement of owner's equity, income statement D) statement of owner's equity, balance sheet, income statement 6
7 Case 1.3 The following is a list of account balances (all except owner's equity) of Wilson Mowing Company as of December 31 of the first year of operation: Accounts receivable $ 2, 500 Accounts payable 3, 500 Salary expense 4, 500 Repairs expense 800 Truck 8, 500 Equipment 6, 300 Notes payable 8, 200 Cash 6, 800 Supplies expense 1, 600 Service revenue 31, 900 Gasoline expense 3, 800 Salary payable 200 The owner, J.D. Wilson, invested $3, 000 at the beginning of the year and withdrew $12, 000 during the year for his personal use. 33) Refer to Case 1.3. At the end of the year, what is the amount of total owner's equity? 33) A) $21, 200 B) $24, 100 C) $12, 200 D) $11, ) The owner withdraws cash for personal use. Which of the following would be true? 34) A) Total assets would increase. B) Owner's equity would decrease. C) Net income would decrease. D) There would be no effect on total assets. 35) A $250 payment on account was posted as a debit to Accounts Receivable and a credit to Accounts 35) Payable. Which of the following conditions will exist? A) Owner's equity will be overstated. B) Accounts Payable will be understated. C) Accounts Receivable will be overstated. D) Cash will be overstated. 36) Which of the following is the book (or printout) holding all the accounts? 36) A) Trial balance B) Ledger C) Account D) Journal 37) Which of the following statements about expenses is correct? 37) A) Expenses increase owner's equity, so an expense account's normal balance is a debit balance. B) Expenses decrease owner's equity, so an expense account's normal balance is a credit balance. C) Expenses decrease owner's equity, so an expense account's normal balance is a debit balance. D) Expenses increase owner's equity, so an expense account's normal balance is a credit balance. 7
8 38) Which of the following statements about revenue is correct? 38) A) Revenues increase owner's equity, so a revenue account's normal balance is a credit balance. B) Revenues decrease owner's equity, so a revenue account's normal balance is a credit balance. C) Revenues decrease owner's equity, so a revenue account's normal balance is a debit balance. D) Revenues increase owner's equity, so a revenue account's normal balance is a debit balance. 39) A business makes a principal payment of cash on a note payable. The note payable was originally 39) issued for the purchase of equipment. Which of the following occurs? A) An asset is debited and a liability is credited. B) An asset is debited and an asset is credited. C) A liability is debited and a liability is credited. D) An asset is credited and a liability is debited. 40) Which of the following accounts decrease due to a debit? 40) A) Interest Payable B) Prepaid Insurance C) Cash D) Both A and B decrease when debited. 41) Accountants record transactions first in which of the following? 41) A) Journal B) Trial balance C) Ledger D) Chart of accounts 42) Which of the following accounts is NOT an example of an asset? 42) A) Cash B) Building C) Accounts Receivable D) Notes Payable 43) A business receives cash in payment of accounts receivable. Which of the following occurs? 43) A) An asset is credited and a liability is debited. B) An asset is debited and a liability is credited. C) A liability is debited and a liability is credited. D) An asset is debited and an asset is credited. 8
9 44) Which of the following journal entries would be recorded if a business performed services for $400 44) cash and $1,000 on account? A) Service Revenue 1,000 Cash 400 Accounts Receivable 1,400 B) Cash 400 Accounts Receivable 1,000 Service Revenue 1,400 C) Service revenue 1,400 Cash 1,000 Accounts Payable 400 D) Cash 1,400 Accounts Receivable 1,000 Service Revenue ) Which of the following is the last step of journalizing an entry? 45) A) Determine whether each account is increased or decreased. B) Post the accounts to the ledger. C) Identify each account affected and its type. D) Record the transaction in the journal, including a brief explanation. 46) The following entries were made by the accountant of Patel Pastries during its first month of 46) operations. a. James Patel,the owner,deposited $3,000 in the company's new checking account. b. Mr. Patel paid the first month's rent of $400. c. Mr. Patel purchased equipment by signing a note payable of $11,000. d. Cash sales for the month were $4,500. e. Mr. Patel purchased cooking supplies for $1,400. After the accountant posts these entries to the general ledger, what is the balance in the James Patel, Capital account? A) $5,700 B) $7,100 C) $3,000 D) $14,000 47) Which of the following accounts increase due to a credit? 47) A) Cash B) Owner's Capital C) Accounts Receivable D) Both A and B increase when credited. 48) Which of the following accounts is a liability? 48) A) Accounts Payable B) Prepaid Expenses C) Salary Expense D) Service Revenue 9
10 49) A business receives a cash payment for services rendered. Which of the following occurs? 49) A) An asset is debited and a liability is credited. B) An asset is debited and a revenue account is credited. C) An asset is credited and a liability is debited. D) An asset is debited and a revenue account is debited. Case 2.1 The following transactions have been journalized and posted to the proper accounts. 1. Mark Call invested $7,000 cash in his new design services business. 2. Mark paid the first month's rent with $ Mark purchased equipment by paying $2,000 down and executing a note payable for $4, Mark purchased supplies for $850 cash. 5. Mark billed a client for $4,000 of design services completed 6. Mark received $3,000 of the account for the completed services. 50) Refer to Case 2.1. What is the balance in Accounts Receivable? 50) A) $1,000 B) $8,500 C) $4,000 D) $7,000 51) Which of the following accounts is an example of a liability? 51) A) Service revenue B) Building C) Accounts receivable D) Notes payable Case 2.1 The following transactions have been journalized and posted to the proper accounts. 1. Mark Call invested $7,000 cash in his new design services business. 2. Mark paid the first month's rent with $ Mark purchased equipment by paying $2,000 down and executing a note payable for $4, Mark purchased supplies for $850 cash. 5. Mark billed a client for $4,000 of design services completed 6. Mark received $3,000 of the account for the completed services. 52) Refer to Case 2.1. What is the balance in Notes Payable? 52) A) $4,500 B) $1,000 C) $4,000 D) $7,000 10
11 53) Which of the following journal entries would be recorded if a business purchased equipment for 53) $3, 000 cash? A) Equipment 3,000 Accounts Payable 3,000 B) Equipment 3,000 Cash 3,000 C) Cash 3,000 Equipment 3,000 D) Cash 3,000 Accounts Payable 3,000 54) Which of the following journal entries would be recorded if a business paid cash of $600 on 54) account? Supplies had been purchased on account last month. A) Accounts Payable 600 Cash 600 B) Cash 600 Supplies 600 C) Accounts Payable 600 Supplies 600 D) Cash 600 Accounts Payable ) A utility bill is received. It will be paid in the following accounting period. Which of the following 55) would be true as a result of the receipt of the utility bill? A) Net income will increase. B) Owner's equity will decrease. C) Total liabilities will decrease. D) There will be no effect on total liabilities. 56) Which of the following are differences in the accrual method and cash-basis method of 56) accounting? A) Accrual accounting is required by generally accepted accounting principles because it provides more information than cash-basis accounting. B) Accrual accounting records revenue when services are rendered. Cash-basis accounting records revenue when cash is received. C) Accrual accounting records expenses when incurred. Cash-basis accounting records expenses when cash is paid. D) All of the above are true. 57) The adjusting process has two purposes. Which of the following represents these two purposes? 57) A) 1) Measure net income or loss and 2) Update the balance sheet B) 1) Compute ending capital and 2) Journalize the period's activity C) Both A and B are correct D) None of the above 11
12 58) Under the cash-basis method of accounting, service revenue is recorded at which of the following 58) times? A) When the services are completed B) When payment for the services is received C) At the end of the accounting period D) Both A and B 59) Employees of Robert Rogers, CPA, worked during the last two weeks of December. They received 59) their paychecks on January 2. The matching principle would require that which of the following accounts appear on the income statement for the year ended December 31? A) Salary Expense B) Accounts Receivable C) Salaries Payable D) Accounting Expense 60) Which of the following is the time-period concept? 60) A) The concept that determines when to record revenue. B) The concept that determines when to record expenses. C) The concept that ensures that information is reported at regular intervals. D) None of the above. 61) Unearned revenue is which of the following? 61) A) Revenue that the business has collected but not yet earned B) Revenue that will be collected and earned in the future C) Revenue that the business has earned but not collected D) Revenue that has been collected and earned 62) Which of the following entries would be made as the result of the matching principle? 62) A) Salary Expense 1,000 Accounts Payable 1,000 B) Accounts Receivable 1,000 Service Revenue 1,000 C) Cash 1,000 Service Revenue 1,000 D) Both A and B 63) Salaries payable is an example of which of the following? 63) A) Accrued revenue B) Unearned revenue C) An accrued expense D) A prepaid expense 12
13 64) What debit is required as part of an adjusting entry when unearned income is initially recorded as 64) revenue? A) A debit to an asset account B) A debit to an unearned expense account C) A debit to a contra account D) A debit to a deferred revenue account 65) The accountant for Noble Jewelry Repair Company failed to make an adjusting entry for 65) depreciation expense for the current year. What is the effect of this error on total liabilities? A) Total liabilities are overstated. B) Total liabilities are not affected. C) Total liabilities are understated. D) There is not enough information presented to determine the effect on total liabilities. 66) Which of the following entries would be recorded if a company is using the cash-basis method of 66) accounting? A) Cash 1,000 Service Revenue 1,000 B) Cash 1,000 Accounts Receivable 1,000 C) Salary Expense 1,000 Cash 1,000 D) Both A and C 67) Accrued revenue is which of the following? 67) A) Revenue that the business has collected but not yet earned B) Revenue that will be collected and earned in the future C) Revenue that the business has earned but not collected D) Revenue that has been collected and earned 68) How do the adjusting entries differ from other journal entries? 68) A) Adjusting entries debit or credit at least one income statement account and at least one balance sheet account. B) Adjusting entries never affect cash. C) Adjusting entries are made only at the end of the period. D) All of the above. 69) Which of the following computes ending capital? 69) A) Statement of owner's equity B) Balance sheet C) Adjusted trial balance D) Income statement 13
14 70) The income statement should list expenses is what order? 70) A) Alphabetical order B) Order of importance to the company's primary mission C) Ascending order by amount D) Descending order by amount 71) Caleb Brown has owned and operated a bicycle sales and repair shop for many years. Which of the 71) following business types would provide the owner's personal assets with protection from product liability exposure? A) Limited liability company B) Limited liability partnership C) Proprietorship D) Partnership 72) Which of the following financial statements reports that total assets equal total liabilities plus total 72) owner's equity? A) statement of cash flows. B) balance sheet. C) statement of owner's equity D) income statement. 73) Which of the following amounts appears on both the statement of owner's equity and the balance 73) sheet? A) total revenues B) ending owner's equity C) net income D) total assets 74) The assets and liabilities of Matt Wesley, Contractor, are as follows: Cash, $10, 000; Accounts 74) Receivable, $8, 200; Supplies, $1, 050; Land, $25, 000; Accounts Payable, $6, 530. What is the amount of owner's equity? A) $50, 780 B) $21, 500 C) $37, 720 D) $44, ) Assets are $270, 000 and owner's equity is $90, 000. What would liabilities be? 75) A) $270, 000 B) $60, 000 C) $360, 000 D) $180, 000 Case 1.2 Sharon Samson starts a plumbing service, Reliable Waterworks. Selected transactions are described as follows: a. Sharon deposits $7, 000 into a new checking account for the company. b. Sharon pays $4, 000 cash for equipment to be used for plumbing repairs. c. Sharon borrows $15, 000 from a local bank and deposits the money in the checking account. d. Sharon pays $600 rent for the first month. e. Sharon pays $400 cash for plumbing supplies to be used on various jobs in the future. f. Sharon completes a plumbing repair project for a local lawyer and receives $1, 300 cash. g. Sharon withdraws $2, 500 for personal use. 76) Refer to Case 1.2. After all of the transactions, what is the amount of total owner's equity? 76) A) $5, 200 B) $7, 700 C) $3, 900 D) $20,
15 77) Which of the following concepts (or principles) would be most likely to require that a person with 77) three different businesses keep three different checking accounts? A) entity concept B) going-concern concept C) cost principle D) reliability concept 78) Dylan Chase is a CPA and is one of the tax partners in a CPA practice. One of Dylan's partners 78) sometimes takes very aggressive positions when auditing their clients. Which of the following business types would provide Dylan's personal assets with protection from malpractice liability for his partners' aggressive auditing tactics? A) Limited liability company B) Proprietorship C) Partnership D) Limited liability partnership 79) Which of the following statements best defines accounting financial statements? 79) A) Financial statements process information into reports. B) Financial statements are the verbal statements made to business news organizations by chief financial officers. C) Financial statements are the information system that measures business activities. D) Financial statements are documents that report on a business in monetary terms, providing information to help people make informed business decisions. Case 1.3 The following is a list of account balances (all except owner's equity) of Wilson Mowing Company as of December 31 of the first year of operation: Accounts receivable $ 2, 500 Accounts payable 3, 500 Salary expense 4, 500 Repairs expense 800 Truck 8, 500 Equipment 6, 300 Notes payable 8, 200 Cash 6, 800 Supplies expense 1, 600 Service revenue 31, 900 Gasoline expense 3, 800 Salary payable 200 The owner, J.D. Wilson, invested $3, 000 at the beginning of the year and withdrew $12, 000 during the year for his personal use. 80) Refer to Case 1.3. At the end of the year, what is net income? 80) A) $21, 200 B) $12, 200 C) $24, 100 D) $11,
16 81) A trial balance is prepared and the sum of the debits equals the sum of the credits. Which of the 81) following conclusions is correct? A) The accounting equation is mathematically correct. B) All of the transactions have been correctly posted. C) All errors have been found and corrected. D) All of the account balances are correct. 82) A bill is sent to a client for services rendered. It will be paid in the following accounting period. 82) Which of the following would be true as a result of mailing the bill to the client? A) There will be no effect on total assets. B) Net income will increase. C) Total liabilities will decrease. D) Owner's equity will decrease. 83) A business makes a cash payment of $12, 000 to a creditor. Which of the following occurs? 83) A) Cash is credited for $12, 000. B) Cash is debited for $12, 000. C) Accounts payable is credited for $12, 000. D) Both A and C. 84) A business completes services for $16,000 on account. Which of the following occurs? 84) A) Cash is debited for $16,000. B) Accounts receivable is debited for $16,000. C) Service revenue is credited for $16,000. D) Both B and C. Case 2.1 The following transactions have been journalized and posted to the proper accounts. 1. Mark Call invested $7,000 cash in his new design services business. 2. Mark paid the first month's rent with $ Mark purchased equipment by paying $2,000 down and executing a note payable for $4, Mark purchased supplies for $850 cash. 5. Mark billed a client for $4,000 of design services completed 6. Mark received $3,000 of the account for the completed services. 85) Refer to Case 2.1. What is the balance in Cash? 85) A) $7,850 B) $6,450 C) $8,450 D) $8,150 16
17 86) A chart of accounts is which of the following? 86) A) A list of all the accounts with their balances. B) A chronological record of transactions. C) A list of all the accounts with their account numbers. D) A book (or printout) holding all the accounts. 87) Under which of the following methods of accounting is an expense recorded ONLY when cash is 87) paid? A) Receivable B) Deferral C) Cash D) Accrual 88) Robert Rogers, CPA, owns a computer used in his business. The matching principle would require 88) that which of the following accounts appear on the income statement for the year ended December 31? A) Accounts Receivable B) Service Revenue C) Depreciation Expense D) Accumulated Depreciation 89) Robert Rogers, CPA, completed accounting services in December. A bill was mailed on December 89) 30. A check arrived in the mail and was deposited on January 5. The revenue principle would require that which of the following accounts appear on the income statement for the year ended December 31? A) Accounts Payable B) Accounting Expense C) Service Revenue D) Accounts Receivable 90) The adjusting entry to record supplies expense accomplishes which of the following? 90) A) Decreases an asset and increases an expense B) Decreases a liability and increases a revenue C) Increases an asset and increases an expense D) Decreases a liability and increases an expense 91) Which of the following amounts appears on both the income statement and the balance sheet? 91) A) net income B) total assets C) ending owner's equity D) none of these amounts appear on both the income statement and the balance sheet. 92) Beginning owner's equity was $25, 000. Ending owner's equity is $37, 000. The owner's 92) withdrawals were $23, 000. What was net income or loss for the year: A) Net income of $35, 000 B) Net income of $16, 000 C) Net loss of $35, 000 D) Net loss of $14,
18 93) Corporate ownership is a very popular type of ownership in the United States. Which of the 93) following is a major reason that corporate ownership is popular? A) Corporate shareholders have limited liability for the debts of the corporation. B) The life of a corporation is limited by the death of an owner. C) Most corporations are small or medium-sized. D) A corporation is usually managed by the owners. 94) Which of the following accounts is an owner's equity account? 94) A) Accounts Payable B) Capital C) Accrued Liability D) Prepaid Expense 95) Which of the following arithmetic formulas is the expanded accounting equation? 95) A) Assets = Liabilities + Owner, capital - Owner, withdrawals + Revenues - Expenses B) Assets + Revenues - Expenses = Liabilities + Owner, capital - Owner, withdrawals C) Assets + Liabilities + Owner, capital = Owner, withdrawals + Revenues - Expenses D) Assets + Liabilities = Owner, capital - Owner, withdrawals + Revenues - Expenses 96) Under the accrual method of accounting, an expense is recorded at which of the following times? 96) A) When payment for the expense is made B) When the expense is incurred C) At the end of the accounting period D) Both A and C 97) Businesses can be organized in a variety of forms. The types of business forms found in the U.S. 97) include all of the following except one. Which one is NOT included? A) Proprietorship B) Partnership C) Tax shelter D) Corporation 98) Which of the following is a method used to detect errors when the two columns of the trial balance 98) are NOT equal? A) Compute the difference in the columns and search the trial balance for the missing amount. B) Compute the difference in the columns and search the trial balance for a transposition if the difference is evenly divisible by 9. C) Compute the difference in the columns, divide the difference between total debits and total credits by 2 and search for the amount in the trial balance. D) All of the above are suggested methods for detecting errors. 99) What debit is required as part of the entry that will eventually require an adjusting entry to 99) depreciation expense? A) A debit to an asset account B) A debit to a deferred revenue account C) A debit to a contra account D) A debit to an unearned expense account 18
19 100) A liability is paid with cash. How does paying this liability affect the accounting equation? 100) A) Liabilities decrease; owner's equity increases B) Assets decrease; liabilities decrease C) Assets increase; liabilities decrease D) Assets increase; liabilities increase 19
Accounting Notes. Cash - includes money and any medium of exchange that a bank accepts at face value
 Asset Accounts: Cash - includes money and any medium of exchange that a bank accepts at face value Accounts Receivable - a record of an oral or implied promise of future cash receipts in exchange for goods
Asset Accounts: Cash - includes money and any medium of exchange that a bank accepts at face value Accounts Receivable - a record of an oral or implied promise of future cash receipts in exchange for goods
Basic Accounting Principles
 Basic Accounting Principles Basic Accounting Model The basic accounting model represents the relationship between assets (what the company owns), liabilities (what the company owes), and owner s equity
Basic Accounting Principles Basic Accounting Model The basic accounting model represents the relationship between assets (what the company owns), liabilities (what the company owes), and owner s equity
Vol. 1, Chapter 3 - Accounting Adjustments
 Vol. 1, Chapter 3 - Accounting Adjustments Problem 1 1. ($20,000 2,000) 48 = $375 per month 2. Jan. 31 Depreciation Expense $375 Accumulated Depreciation Van $375 To record depreciation expense for January
Vol. 1, Chapter 3 - Accounting Adjustments Problem 1 1. ($20,000 2,000) 48 = $375 per month 2. Jan. 31 Depreciation Expense $375 Accumulated Depreciation Van $375 To record depreciation expense for January
Dr. M. D. Chase BA 201 Examination 1J
 Dr. M. D. Chase BA 201 Examination 1J Instructions: 1. Place your Name, Code Number of the Examination and the Examination Number on your Scantron form. Failure to follow these instructions will result
Dr. M. D. Chase BA 201 Examination 1J Instructions: 1. Place your Name, Code Number of the Examination and the Examination Number on your Scantron form. Failure to follow these instructions will result
Accounting II Second Semester Final
 Name: Class: Date: Accounting II Second Semester Final Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Profit is the difference between:
Name: Class: Date: Accounting II Second Semester Final Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Profit is the difference between:
Chapter 1. Introduction to Accounting and Business
 1 Chapter 1 Introduction to Accounting and Business Learning Objective 1 Describe the nature of a business, the role of accounting, and ethics in business. Nature of Business and Accounting A business
1 Chapter 1 Introduction to Accounting and Business Learning Objective 1 Describe the nature of a business, the role of accounting, and ethics in business. Nature of Business and Accounting A business
Time Period Assumption
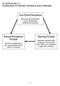 ILLUSTRATION 3-1 GUIDELINES TO REPORT REVENUE AND EXPENSES Time Period Assumption Economic life of business can be divided into artificial time periods Revenue Recognition Principle Revenue recognized
ILLUSTRATION 3-1 GUIDELINES TO REPORT REVENUE AND EXPENSES Time Period Assumption Economic life of business can be divided into artificial time periods Revenue Recognition Principle Revenue recognized
EXERCISES. Does not normally require adjustment. Normally requires adjustment (AE).
 EXERCISES Ex. 3 1 1. Prepaid expense 2. Accrued revenue 3. Unearned revenue 4. Accrued expense 5. Unearned revenue 6. Prepaid expense 7. Accrued expense 8. Accrued expense Ex. 3 2 Account Accounts Receivable...
EXERCISES Ex. 3 1 1. Prepaid expense 2. Accrued revenue 3. Unearned revenue 4. Accrued expense 5. Unearned revenue 6. Prepaid expense 7. Accrued expense 8. Accrued expense Ex. 3 2 Account Accounts Receivable...
CHAPTER 2 ACCOUNTING FOR TRANSACTIONS
 CHAPTER 2 ACCOUNTING FOR TRANSACTIONS Key Terms and Concepts to Know Double entry accounting: Debits and Credits Total debits must always equal total credits Accounting Books: Accounts General Journal
CHAPTER 2 ACCOUNTING FOR TRANSACTIONS Key Terms and Concepts to Know Double entry accounting: Debits and Credits Total debits must always equal total credits Accounting Books: Accounts General Journal
Accounting Cycle. Matching Principle
 CHAPTER 3 Accounting Cycle Analyze and record the transactions Post the transactions and prepare trial balance Adjust the accounts and prepare trial balance Prepare the financial statements Close the accounts
CHAPTER 3 Accounting Cycle Analyze and record the transactions Post the transactions and prepare trial balance Adjust the accounts and prepare trial balance Prepare the financial statements Close the accounts
ACCT1115. Review Package - Midterm SOLUTION Fall 2013
 ACCT1115 Review Package - Midterm SOLUTION Fall 2013 Part I Multiple Choice 1) How should you record the purchase of an expensive automobile? a) Decrease cash, increase assets b) Decrease cash, increase
ACCT1115 Review Package - Midterm SOLUTION Fall 2013 Part I Multiple Choice 1) How should you record the purchase of an expensive automobile? a) Decrease cash, increase assets b) Decrease cash, increase
PART 1. BASIC CONCEPTS AND ACCOUNTING MODEL
 CHAPTER 1 PART 1. BASIC CONCEPTS AND ACCOUNTING MODEL OBJECTIVES The objectives of this part are: To introduce a definition of accounting, the need for accounting information, and the various accounting
CHAPTER 1 PART 1. BASIC CONCEPTS AND ACCOUNTING MODEL OBJECTIVES The objectives of this part are: To introduce a definition of accounting, the need for accounting information, and the various accounting
> DO IT! Chapter 3 Adjusting the Accounts. Timing Concepts. Adjusting Entries for Deferrals D-12. Solution
 Chapter 3 Adjusting the Accounts Timing Concepts Review the glossary terms. Study carefully the revenue recognition principle, the expense recognition principle, and the time period assumption. Several
Chapter 3 Adjusting the Accounts Timing Concepts Review the glossary terms. Study carefully the revenue recognition principle, the expense recognition principle, and the time period assumption. Several
How To Calculate A Trial Balance For A Company
 THE BASIC MODEL The accounting information system is designed to collect and organize data into information that is useful for stakeholders. The Accounting Equation The basic accounting equation is what
THE BASIC MODEL The accounting information system is designed to collect and organize data into information that is useful for stakeholders. The Accounting Equation The basic accounting equation is what
The Work Sheet and the Closing Process
 C H A P T E R 4 The Work Sheet and the Closing Process A systematic approach is essential for efficient and accurate processing of large amounts of information. Whether work sheets are on paper or computerized,
C H A P T E R 4 The Work Sheet and the Closing Process A systematic approach is essential for efficient and accurate processing of large amounts of information. Whether work sheets are on paper or computerized,
THE ACCOUNTING INFORMATION SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 3 THE ACCOUNTING INFORMATION SYSTEM OVERVIEW Accounting information must be accumulated and summarized before it can be communicated and analysed. In this chapter, we will discuss the steps involved
CHAPTER 3 THE ACCOUNTING INFORMATION SYSTEM OVERVIEW Accounting information must be accumulated and summarized before it can be communicated and analysed. In this chapter, we will discuss the steps involved
1. If the assets owned by a business total $100,000 and liabilities total $70,000, stockholders' equity totals $30,000.
 Rallis Page 1 Name: _ Date: 1. If the assets owned by a business total $100,000 and liabilities total $70,000, stockholders' equity totals $30,000. A) True B) False 2. If total liabilities decreased by
Rallis Page 1 Name: _ Date: 1. If the assets owned by a business total $100,000 and liabilities total $70,000, stockholders' equity totals $30,000. A) True B) False 2. If total liabilities decreased by
Chapter 5 Accrual Adjustments and Financial Statement Preparation. Revenue recognition Matching expenses to revenues Expenses related to periods
 Chapter 5 Accrual Adjustments and Financial Statement Preparation Revenue recognition Matching expenses to revenues Expenses related to periods 1 The Measurement of Income major function of accounting
Chapter 5 Accrual Adjustments and Financial Statement Preparation Revenue recognition Matching expenses to revenues Expenses related to periods 1 The Measurement of Income major function of accounting
CHAPTER 2 REVIEW OF THE ACCOUNTING PROCESS. Lecture Outline
 CHAPTER 2 REVIEW OF THE ACCOUNTING PROCESS Overview Chapter 1 explained that the primary means of conveying financial information to investors, creditors, and other external users is through financial
CHAPTER 2 REVIEW OF THE ACCOUNTING PROCESS Overview Chapter 1 explained that the primary means of conveying financial information to investors, creditors, and other external users is through financial
CHAPTER 3 ADJUSTING THE ACCOUNTS
 CHAPTER 3 ADJUSTING THE ACCOUNTS TIME PERIOD ASSUMPTION The time period (or periodicity) assumption assumes that the economic life of a business can be divided into artificial time periods generally a
CHAPTER 3 ADJUSTING THE ACCOUNTS TIME PERIOD ASSUMPTION The time period (or periodicity) assumption assumes that the economic life of a business can be divided into artificial time periods generally a
Accounting Self Study Guide for Staff of Micro Finance Institutions
 Accounting Self Study Guide for Staff of Micro Finance Institutions LESSON 5 Summarizing Changes in Financial Position OBJECTIVES The purpose of this lesson is to show how to summarize the transactions
Accounting Self Study Guide for Staff of Micro Finance Institutions LESSON 5 Summarizing Changes in Financial Position OBJECTIVES The purpose of this lesson is to show how to summarize the transactions
CHAE Review. Capital Leases & Forms of Business
 CHAE Review Financial Statements, Capital Leases & Forms of Business This is a complete review of the two volume text book, Certified Hospitality Accountant Executive Study Guide, as published by The Educational
CHAE Review Financial Statements, Capital Leases & Forms of Business This is a complete review of the two volume text book, Certified Hospitality Accountant Executive Study Guide, as published by The Educational
Bookkeeping Tips & T Accounts Prepared by Accomp Services (www.accompservices.ca)
 Bookkeeping Tips & T Accounts Prepared by Accomp Services (www.accompservices.ca) Further valuable accounting and bookkeeping website resources are listed at the end of this document. A business is one
Bookkeeping Tips & T Accounts Prepared by Accomp Services (www.accompservices.ca) Further valuable accounting and bookkeeping website resources are listed at the end of this document. A business is one
Exam 1 chapters 1-4 Needles 10ed
 Exam 1 chapters 1-4 Needles 10ed Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is the most appropriate definition of accounting?
Exam 1 chapters 1-4 Needles 10ed Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is the most appropriate definition of accounting?
Definition of Accounting
 SOLUTIONS TO EXERCISES Lesson 1: Definition of Accounting 1. What is accounting? What are its main functions? Accounting is the process of financially measuring, recording, summarizing and communicating
SOLUTIONS TO EXERCISES Lesson 1: Definition of Accounting 1. What is accounting? What are its main functions? Accounting is the process of financially measuring, recording, summarizing and communicating
Transaction Analysis SPOTLIGHT. 2 Chapter 40878 Page 53 09/25/07 jhr APPLE COMPUTER, INC.
 2 Chapter 40878 9/25/07 3:18 PM Page 53 2 Transaction Analysis 2 Chapter 40878 Page 53 09/25/07 jhr SPOTLIGHT APPLE COMPUTER, INC. How do you manage your music library? You may use Apple Computer s itunes,
2 Chapter 40878 9/25/07 3:18 PM Page 53 2 Transaction Analysis 2 Chapter 40878 Page 53 09/25/07 jhr SPOTLIGHT APPLE COMPUTER, INC. How do you manage your music library? You may use Apple Computer s itunes,
In the event of a tie, the score on the last ten questions will be used as a tie-breaker.
 NEW YORK STATE ASSOCIATION FUTURE BUSINESS LEADERS OF AMERICA SPRING DISTRICT MEETING ACCOUNTING II 2010 TEST DIRECTIONS 1. Complete the information requested on the answer sheet. PRINT your name on the
NEW YORK STATE ASSOCIATION FUTURE BUSINESS LEADERS OF AMERICA SPRING DISTRICT MEETING ACCOUNTING II 2010 TEST DIRECTIONS 1. Complete the information requested on the answer sheet. PRINT your name on the
Accounting Skills Assessment Practice Exam Page 1 of 10
 NAU ACCOUNTING SKILLS ASSESSMENT PRACTICE EXAM & KEY 1. A company received cash and issued common stock. What was the effect on the accounting equation? Assets Liabilities Stockholders Equity A. + NE +
NAU ACCOUNTING SKILLS ASSESSMENT PRACTICE EXAM & KEY 1. A company received cash and issued common stock. What was the effect on the accounting equation? Assets Liabilities Stockholders Equity A. + NE +
STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS AND WORKING CAPITAL ANALYSIS
 C H A P T E R 1 0 STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS AND WORKING CAPITAL ANALYSIS I N T R O D U C T I O N Historically, profit-oriented businesses have used the accrual basis of accounting in which the income statement,
C H A P T E R 1 0 STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS AND WORKING CAPITAL ANALYSIS I N T R O D U C T I O N Historically, profit-oriented businesses have used the accrual basis of accounting in which the income statement,
Summary. Introduction to Accounting. Chapter
 1 Chapter Introduction to Accounting Summary 1. Accounting consists of five stages: (1) recording (bookkeeping), (2) summarizing, (3) analyzing, (4) interpreting and (5) reporting the financial information
1 Chapter Introduction to Accounting Summary 1. Accounting consists of five stages: (1) recording (bookkeeping), (2) summarizing, (3) analyzing, (4) interpreting and (5) reporting the financial information
Accrual vs Deferral Accrual vs Cash Basis
 1 - Accrual vs Deferral Accrual vs Cash Basis - understanding debits and credits a transaction either increases or decreases the balance of accounts. increases and decreases in accounts are based on the
1 - Accrual vs Deferral Accrual vs Cash Basis - understanding debits and credits a transaction either increases or decreases the balance of accounts. increases and decreases in accounts are based on the
Preparing Financial Statements
 Carroll_CH03_023-040.qxd 8/10/06 4:37 PM Page 23 CHAPTER 3 Preparing Financial Statements OBJECTIVES F After reading this chapter, the student should be able to: 1. Describe the general process by which
Carroll_CH03_023-040.qxd 8/10/06 4:37 PM Page 23 CHAPTER 3 Preparing Financial Statements OBJECTIVES F After reading this chapter, the student should be able to: 1. Describe the general process by which
2 Transaction Analysis
 29366_06_ch2_p053-110 12/12/07 5:50 PM Page 53 2 Transaction Analysis SPOTLIGHT A P P L E C O M P U T E R, I N C. How do you manage your music library? You may use Apple Computer s itunes, which along
29366_06_ch2_p053-110 12/12/07 5:50 PM Page 53 2 Transaction Analysis SPOTLIGHT A P P L E C O M P U T E R, I N C. How do you manage your music library? You may use Apple Computer s itunes, which along
TRANSACTIONS ANALYSIS EXAMPLE. Maxwell Partners Medical Diagnostic Services report the following information for 2011, their first year of operations:
 TRANSACTIONS ANALYSIS EXAMPLE Maxwell Partners Medical Diagnostic Services report the following information for 2011, their first year of operations: 1. Billings to clients for services provided: $350,000
TRANSACTIONS ANALYSIS EXAMPLE Maxwell Partners Medical Diagnostic Services report the following information for 2011, their first year of operations: 1. Billings to clients for services provided: $350,000
Chapter 3: Double-Entry Bookkeeping
 Chapter 3: Double-Entry Bookkeeping Double-entry bookkeeping underpins accounting A way of systematically recording the financial transactions of a company so that each transaction is recorded twice. Basic
Chapter 3: Double-Entry Bookkeeping Double-entry bookkeeping underpins accounting A way of systematically recording the financial transactions of a company so that each transaction is recorded twice. Basic
Financial Statements Tutorial
 Financial Statement Review: Financial Statements Tutorial There are four major financial statements used to communicate information to external users (creditors, investors, suppliers, etc.) - 1. Balance
Financial Statement Review: Financial Statements Tutorial There are four major financial statements used to communicate information to external users (creditors, investors, suppliers, etc.) - 1. Balance
Chapter 4. Completing the accounting cycle. Appendix 4A: Reversing entries
 1 Chapter 4 Completing the accounting cycle Appendix 4A: Reversing entries 2 Learning objective 1. Prepare reversing entries and describe their purpose 3 Reversing entries Reversing entries are optional
1 Chapter 4 Completing the accounting cycle Appendix 4A: Reversing entries 2 Learning objective 1. Prepare reversing entries and describe their purpose 3 Reversing entries Reversing entries are optional
Guide to Financial Statements Study Guide
 Guide to Financial Statements Study Guide Overview (Topic 1) Three major financial statements: The Income Statement The Balance Sheet The Cash Flow Statement Objectives: Explain the underlying equation
Guide to Financial Statements Study Guide Overview (Topic 1) Three major financial statements: The Income Statement The Balance Sheet The Cash Flow Statement Objectives: Explain the underlying equation
Analyzing the Statement of Cash Flows
 Analyzing the Statement of Cash Flows Operating Activities NACM Upstate New York Credit Conference 2015 By Ron Sereika, CCE,CEW NACM 1 Objectives of this Educational Session u Show how the statement of
Analyzing the Statement of Cash Flows Operating Activities NACM Upstate New York Credit Conference 2015 By Ron Sereika, CCE,CEW NACM 1 Objectives of this Educational Session u Show how the statement of
C02-Fundamentals of financial accounting
 Sample Exam Paper Question 1 The difference between an income statement and an income and expenditure account is that: A. An income and expenditure account is an international term for an Income statement.
Sample Exam Paper Question 1 The difference between an income statement and an income and expenditure account is that: A. An income and expenditure account is an international term for an Income statement.
Accounting Norms and Principles January 7, 2003
 1 Accounting Norms and Principles January 7, 2003 The purpose of an accounting system is to provide credit union management with complete and accurate financial information that can be used to operate
1 Accounting Norms and Principles January 7, 2003 The purpose of an accounting system is to provide credit union management with complete and accurate financial information that can be used to operate
Learn Accounting Understand Business: Course Review Answers
 Learn Accounting Understand Business: Course Review Answers 1. What type of accounting measures the activity of the company by looking at economic events regardless of when cash transactions occur? A.
Learn Accounting Understand Business: Course Review Answers 1. What type of accounting measures the activity of the company by looking at economic events regardless of when cash transactions occur? A.
Basic Accounting. Supplement for Using Simply Accounting Version 8.0 for Windows by. M. Purbhoo and D. Purbhoo
 Basic Accounting Supplement for Using Simply Accounting Version 8.0 for Windows by M. Purbhoo and D. Purbhoo Basic Accounting Contents: Accounting Theory 3 Basic Accounting 3 Balance Sheet 3 Income Statement
Basic Accounting Supplement for Using Simply Accounting Version 8.0 for Windows by M. Purbhoo and D. Purbhoo Basic Accounting Contents: Accounting Theory 3 Basic Accounting 3 Balance Sheet 3 Income Statement
Module 3: Adjusting the accounts, preparing the statements, and completing the accounting cycle
 Page 1 of 27 Module 3: Adjusting the accounts, preparing the statements, and completing the accounting cycle Overview In Module 2 you studied the fundamental steps in recording accounting information by
Page 1 of 27 Module 3: Adjusting the accounts, preparing the statements, and completing the accounting cycle Overview In Module 2 you studied the fundamental steps in recording accounting information by
Fundamentals of Financial Accounting
 Fundamentals of Financial Accounting CHAPTER I Accounting in action. What is accounting? Accounting is the recording of financial transactions plus storing, sorting, retrieving, summarizing, and presenting
Fundamentals of Financial Accounting CHAPTER I Accounting in action. What is accounting? Accounting is the recording of financial transactions plus storing, sorting, retrieving, summarizing, and presenting
Assignment 6: Adjusting Journal Entries and
 Name: Due Date: December 12, 2011 Score: out of a possible 47 Course value: 7.5% Assignment 6: Adjusting Journal Entries and Worksheets A series of transactions are presented and their journal entries
Name: Due Date: December 12, 2011 Score: out of a possible 47 Course value: 7.5% Assignment 6: Adjusting Journal Entries and Worksheets A series of transactions are presented and their journal entries
CHAPTER 3 Solutions MEASURING BUSINESS INCOME
 CHAPTER 3 Solutions MEASURING BUSINESS INCOME Chapter 3, SE 1. 1. 2. 3. 4. c b d a Chapter 3, SE 2. Dec. 31 Insurance Expense 800 Prepaid Insurance To record insurance expired during the year $460 + $1,040
CHAPTER 3 Solutions MEASURING BUSINESS INCOME Chapter 3, SE 1. 1. 2. 3. 4. c b d a Chapter 3, SE 2. Dec. 31 Insurance Expense 800 Prepaid Insurance To record insurance expired during the year $460 + $1,040
Accrual Accounting Process
 Accrual Accounting Process 15.501 Accounting Spring 2004 Professor S. Roychowdhury Sloan School of Management Massachusetts Institute of Technology Feb 17/18, 2004 1 An accountant s functions include Classifying
Accrual Accounting Process 15.501 Accounting Spring 2004 Professor S. Roychowdhury Sloan School of Management Massachusetts Institute of Technology Feb 17/18, 2004 1 An accountant s functions include Classifying
How To Account For Revenue Under Accrual Accounting
 BAT 4M: Chapter 3 ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS 01. (a) Under the time period assumption, an accountant is required to determine the relevance of each business transaction to specific accounting periods, and its
BAT 4M: Chapter 3 ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS 01. (a) Under the time period assumption, an accountant is required to determine the relevance of each business transaction to specific accounting periods, and its
Financial Accounting. (Exam)
 Financial Accounting (Exam) Your AccountingCoach PRO membership includes lifetime access to all of our materials Take a quick tour by visiting wwwaccountingcoachcom/quicktour Table of Contents (click to
Financial Accounting (Exam) Your AccountingCoach PRO membership includes lifetime access to all of our materials Take a quick tour by visiting wwwaccountingcoachcom/quicktour Table of Contents (click to
SMART TOUCH LEARNING Balance Sheet May 31, 2013 $ 4,800. $ 48,700 Accounts receivable 2,600. 900 Inventory 30,500. 100 Supplies.
 3 The Adjusting Process Are these balances correctly showing everything the company OWNS? SMART TOUCH LEARNING ance Sheet May 31, 2013 Are these balances correctly showing everything the company OWES?
3 The Adjusting Process Are these balances correctly showing everything the company OWNS? SMART TOUCH LEARNING ance Sheet May 31, 2013 Are these balances correctly showing everything the company OWES?
Chapter 6 Statement of Cash Flows
 Chapter 6 Statement of Cash Flows The Statement of Cash Flows describes the cash inflows and outflows for the firm based upon three categories of activities. Operating Activities: Generally include transactions
Chapter 6 Statement of Cash Flows The Statement of Cash Flows describes the cash inflows and outflows for the firm based upon three categories of activities. Operating Activities: Generally include transactions
Chapter 4: Accounting Records
 Chapter 4: Accounting Records Structure and terminology of Double Entry Bookkeeping The T account records the effect of transactions under one accounting aspect two opposite effects possible, e.g. inflows
Chapter 4: Accounting Records Structure and terminology of Double Entry Bookkeeping The T account records the effect of transactions under one accounting aspect two opposite effects possible, e.g. inflows
Review of Accounting Principles
 Appendix A Review of Accounting Principles Appendix A is a review of basic accounting principles and procedures. Standard accounting procedures are based on the double-entry system. This means that each
Appendix A Review of Accounting Principles Appendix A is a review of basic accounting principles and procedures. Standard accounting procedures are based on the double-entry system. This means that each
Note that net income has no direct relationship to cash. This means that even though a business is producing net income, it may have no cash.
 Accounting 300A-1A Financial Statements and the Accounting Model Page 1 I FINANCIAL STATEMENTS and the ACCOUNTING MODEL A Review of Key Concepts and Terms: 1 Financial Accounting is the language of business
Accounting 300A-1A Financial Statements and the Accounting Model Page 1 I FINANCIAL STATEMENTS and the ACCOUNTING MODEL A Review of Key Concepts and Terms: 1 Financial Accounting is the language of business
CHAPTER 2 THE RECORDING PROCESS SUMMARY OF QUESTIONS BY STUDY OBJECTIVES AND BLOOM S TAXONOMY. True-False Statements. Multiple Choice Questions
 CHAPTER 2 THE RECORDING PROCESS sg st SUMMARY OF QUESTIONS BY STUDY OBJECTIVES AND BLOOM S TAXONOMY Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT True-False Statements 1. 1 K 9. 2 K 17. 3 K 25.
CHAPTER 2 THE RECORDING PROCESS sg st SUMMARY OF QUESTIONS BY STUDY OBJECTIVES AND BLOOM S TAXONOMY Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT True-False Statements 1. 1 K 9. 2 K 17. 3 K 25.
ILLUSTRATION 3-1 DOUBLE-ENTRY ACCOUNTING SYSTEM
 ILLUSTRATION 3-1 DOUBLE-ENTRY ACCOUNTING SYSTEM ASSETS Increase Decrease + DOUBLE-ENTRY ACCOUNTING REAL (PERMANENT) ACCOUNTS = LIABILITIES + Rules of Thumb + If the "normal balance" for an account is a
ILLUSTRATION 3-1 DOUBLE-ENTRY ACCOUNTING SYSTEM ASSETS Increase Decrease + DOUBLE-ENTRY ACCOUNTING REAL (PERMANENT) ACCOUNTS = LIABILITIES + Rules of Thumb + If the "normal balance" for an account is a
Century 21 Accounting, 8e General Journal Chapter Outlines
 Century 21 Accounting, 8e General Journal Chapter Outlines PART 1 Chapter 1 ACCOUNTING FOR A SERVICE BUSINESS ORGANIZED AS A PROPRIETORSHIP Starting A Proprietorship: Changes that Affect the Accounting
Century 21 Accounting, 8e General Journal Chapter Outlines PART 1 Chapter 1 ACCOUNTING FOR A SERVICE BUSINESS ORGANIZED AS A PROPRIETORSHIP Starting A Proprietorship: Changes that Affect the Accounting
CHAPTER 4 The Mechanics of Financial Accounting
 CHAPTER 4 The Mechanics of Financial Accounting SYNOPSIS This chapter covers the mechanics underlying preparation of financial statements and how they help to ensure that a company s transactions are accurately
CHAPTER 4 The Mechanics of Financial Accounting SYNOPSIS This chapter covers the mechanics underlying preparation of financial statements and how they help to ensure that a company s transactions are accurately
The Accounting Process
 GAAP LITERATURE The Accounting Process Chapter 3 TRADITIONAL: Original pronouncements, issued by the FASB. SEPT. 2009 CHANGE: Codification issued by the FASB. DIFFERENCE: Codification is listed by topic
GAAP LITERATURE The Accounting Process Chapter 3 TRADITIONAL: Original pronouncements, issued by the FASB. SEPT. 2009 CHANGE: Codification issued by the FASB. DIFFERENCE: Codification is listed by topic
Chapter 21 The Statement of Cash Flows Revisited
 Chapter 21 The Statement of Cash Flows Revisited AACSB assurance of learning standards in accounting and business education require documentation of outcomes assessment. Although schools, departments,
Chapter 21 The Statement of Cash Flows Revisited AACSB assurance of learning standards in accounting and business education require documentation of outcomes assessment. Although schools, departments,
MIDTERM EXAMINATION. Afaaq_tariq@yahoo.com. Fall 2009
 MIDTERM EXAMINATION Afaaq_tariq@yahoo.com Fall 2009 FIN621- Financial Statement Analysis Asslam O Alikum FIN621- Financial Statement Analysis (Session 3) solved by Afaaq n Shani Bhai with reference n numerical
MIDTERM EXAMINATION Afaaq_tariq@yahoo.com Fall 2009 FIN621- Financial Statement Analysis Asslam O Alikum FIN621- Financial Statement Analysis (Session 3) solved by Afaaq n Shani Bhai with reference n numerical
UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO School of Accounting and Finance
 UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO School of Accounting and Finance AFM 101 Professor Duane Kennedy Mid-Term Examination Fall 2008 Date and Time: October 16, 2008, 7:15 8:45pm Pages: 16, including cover Name: Student
UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO School of Accounting and Finance AFM 101 Professor Duane Kennedy Mid-Term Examination Fall 2008 Date and Time: October 16, 2008, 7:15 8:45pm Pages: 16, including cover Name: Student
Student Solutions Manual to Accompany. Introduction to Financial Accounting. David Annand. Based on International Financial Reporting Standards
 Student Solutions Manual to Accompany Introduction to Financial Accounting Based on International Financial Reporting Standards David Annand Copyright 2014 David Annand Published by David Annand 4910C
Student Solutions Manual to Accompany Introduction to Financial Accounting Based on International Financial Reporting Standards David Annand Copyright 2014 David Annand Published by David Annand 4910C
Chapter 4. Completing the accounting cycle
 1 Chapter 4 Completing the accounting cycle 2 Learning objectives 1. Prepare an accounting worksheet and describe its purpose 2. Prepare a classified balance sheet and explain the major headings 3. Explain
1 Chapter 4 Completing the accounting cycle 2 Learning objectives 1. Prepare an accounting worksheet and describe its purpose 2. Prepare a classified balance sheet and explain the major headings 3. Explain
In the event of a tie, the score on the last ten questions will be used as a tie-breaker.
 NEW YORK STATE ASSOCIATION FUTURE BUSINESS LEADERS OF AMERICA SPRING DISTRICT MEETING ACCOUNTING I 2010 TEST DIRECTIONS 1. Complete the information requested on the answer sheet. PRINT your name on the
NEW YORK STATE ASSOCIATION FUTURE BUSINESS LEADERS OF AMERICA SPRING DISTRICT MEETING ACCOUNTING I 2010 TEST DIRECTIONS 1. Complete the information requested on the answer sheet. PRINT your name on the
b. Do not recognize revenue until steel is shipped. c. Do not recognize revenue until next year after the games are played.
 CHAPTER FOUR SE4-2 Revenue recognition a. Recognize revenue from car sales for 12,000. Notes receivable $12,000 Sales revenue $12,000 b. Do not recognize revenue until steel is shipped. c. Do not recognize
CHAPTER FOUR SE4-2 Revenue recognition a. Recognize revenue from car sales for 12,000. Notes receivable $12,000 Sales revenue $12,000 b. Do not recognize revenue until steel is shipped. c. Do not recognize
CHAPTER 3 THE ADJUSTING PROCESS
 1. a. Under cash-basis accounting, revenues are reported in the period in which cash is received and expenses are reported in the period in which cash is paid. b. Under accrual-basis accounting, revenues
1. a. Under cash-basis accounting, revenues are reported in the period in which cash is received and expenses are reported in the period in which cash is paid. b. Under accrual-basis accounting, revenues
revenue/ Accounts receivable/ Cash/Service revenue) account.
 The correct answer is shown. On December 27, a business completed a $400 service that had not yet been billed or recorded as of December 31. Demonstrate the required adjusting entry of the business by
The correct answer is shown. On December 27, a business completed a $400 service that had not yet been billed or recorded as of December 31. Demonstrate the required adjusting entry of the business by
The General Journal and the General Ledger
 4-1 McGraw-Hill 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter 4 The General Journal and the General Ledger Section 1: The General Journal Section Objectives 1. Record transactions in
4-1 McGraw-Hill 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter 4 The General Journal and the General Ledger Section 1: The General Journal Section Objectives 1. Record transactions in
CHAPTER 3 The Accounting Information System
 CHAPTER 3 The Accounting Information System 3-1 LECTURE OUTLINE Chapter 3 provides a review of accounting procedures throughout the accounting cycle. Depending on time constraints and students accounting
CHAPTER 3 The Accounting Information System 3-1 LECTURE OUTLINE Chapter 3 provides a review of accounting procedures throughout the accounting cycle. Depending on time constraints and students accounting
GBA 521 Midterm Review Dr. Markelevich
 GBA 521 Midterm Review Dr. Markelevich Multiple Choice (3 points for each question) Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Wynn Corp. Wynn Corp. reported
GBA 521 Midterm Review Dr. Markelevich Multiple Choice (3 points for each question) Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Wynn Corp. Wynn Corp. reported
Score: Pass/Fail. Purchase Returns and Allowances. Sales Returns and Allowances. Journal entries The accounting equation Treasury Stock
 Walsh College Fundamental Financial Accounting Student Name: Practice Evaluation Exam Phone/Email: Date: This evaluation exam will be used to determine your knowledge of Financial Accounting and to assist
Walsh College Fundamental Financial Accounting Student Name: Practice Evaluation Exam Phone/Email: Date: This evaluation exam will be used to determine your knowledge of Financial Accounting and to assist
CHAPTER 5 THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE: REPORTING FINANCIAL RESULTS
 CHAPTER 5 THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE: REPORTING FINANCIAL RESULTS OVERVIEW OF BRIEF EXERCISES, EXERCISES, PROBLEMS AND CRITICAL THINKING CASES Brief Exercises Topic Learning Objectives Skills B. Ex. 5.1 B. Ex.
CHAPTER 5 THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE: REPORTING FINANCIAL RESULTS OVERVIEW OF BRIEF EXERCISES, EXERCISES, PROBLEMS AND CRITICAL THINKING CASES Brief Exercises Topic Learning Objectives Skills B. Ex. 5.1 B. Ex.
Completing the Accounting Cycle
 C H A P T E R 4 Completing the Accounting Cycle Financial Accounting 14e Warren Reeve Duchac human/istock/360/getty Images Flow of Accounting Information (slide 1 of 5) End-of-Period Spreadsheet (Work
C H A P T E R 4 Completing the Accounting Cycle Financial Accounting 14e Warren Reeve Duchac human/istock/360/getty Images Flow of Accounting Information (slide 1 of 5) End-of-Period Spreadsheet (Work
Self-test Comprehensive Problems II 综 合 自 测 题 II
 Self-test Comprehensive Problems II 综 合 自 测 题 II Part One (30%) 1. Give the Chinese/English of the following terms: (5%) subsidiary ledger 统 制 账 户 purchase requisition 现 金 溢 缺 petty cash fund 永 续 盘 存 制
Self-test Comprehensive Problems II 综 合 自 测 题 II Part One (30%) 1. Give the Chinese/English of the following terms: (5%) subsidiary ledger 统 制 账 户 purchase requisition 现 金 溢 缺 petty cash fund 永 续 盘 存 制
Chapter 4 Adjustments, Financial Statements, and the Quality of Earnings
 Chapter 4 Adjustments, Financial Statements, and the Quality of Earnings ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS 1. Adjusting entries are made at the end of the accounting period to record all revenues and expenses that
Chapter 4 Adjustments, Financial Statements, and the Quality of Earnings ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS 1. Adjusting entries are made at the end of the accounting period to record all revenues and expenses that
In this chapter, we build on the basic knowledge of how businesses
 03-Seidman.qxd 5/15/04 11:52 AM Page 41 3 An Introduction to Business Financial Statements In this chapter, we build on the basic knowledge of how businesses are financed by looking at how firms organize
03-Seidman.qxd 5/15/04 11:52 AM Page 41 3 An Introduction to Business Financial Statements In this chapter, we build on the basic knowledge of how businesses are financed by looking at how firms organize
CHAPTER 3. BE3-2 Advertising. Dec. 31 Advertising Supplies Expense 7200 Advertising Supplies 7200 to adjust. BE3-3 Bere Co.
 CHAPTER 3 BE3-2 Advertising Advertising Supplies Supplies Expense 8700 7200 7200 1500 7200 Dec. Advertising Supplies Expense 7200 Advertising Supplies 7200 BE3-3 Bere Co. Prepaid Insurance Insurance Expense
CHAPTER 3 BE3-2 Advertising Advertising Supplies Supplies Expense 8700 7200 7200 1500 7200 Dec. Advertising Supplies Expense 7200 Advertising Supplies 7200 BE3-3 Bere Co. Prepaid Insurance Insurance Expense
RECORDING OF TRANSACTIONS (JOURNAL ENTRIES, LEDGER AND TRIAL BALANCE)
 Source Document : RECORDING OF TRANSACTIONS (JOURNAL ENTRIES, LEDGER AND TRIAL BALANCE) A document which provides evidence of the transactions is called the Source Document such as Cash memo, Invoice etc.
Source Document : RECORDING OF TRANSACTIONS (JOURNAL ENTRIES, LEDGER AND TRIAL BALANCE) A document which provides evidence of the transactions is called the Source Document such as Cash memo, Invoice etc.
E2-2: Identifying Financing, Investing and Operating Transactions?
 E2-2: Identifying Financing, Investing and Operating Transactions? Listed below are eight transactions. In each case, identify whether the transaction is an example of financing, investing or operating
E2-2: Identifying Financing, Investing and Operating Transactions? Listed below are eight transactions. In each case, identify whether the transaction is an example of financing, investing or operating
RAPID REVIEW Chapter Content
 RAPID REVIEW BASIC ACCOUNTING EQUATION (Chapter 2) INVENTORY (Chapters 5 and 6) Basic Equation Assets Owner s Equity Expanded Owner s Owner s Assets Equation = Liabilities Capital Drawing Revenues Debit
RAPID REVIEW BASIC ACCOUNTING EQUATION (Chapter 2) INVENTORY (Chapters 5 and 6) Basic Equation Assets Owner s Equity Expanded Owner s Owner s Assets Equation = Liabilities Capital Drawing Revenues Debit
Accounting Basics, Part 1
 Accounting Basics, Part 1 Accrual, Double-Entry Accounting, Debits & Credits, Chart of Accounts, Journals and, Ledger Part 1 What s Here Introduction Business Types Business Organization Professional Advice
Accounting Basics, Part 1 Accrual, Double-Entry Accounting, Debits & Credits, Chart of Accounts, Journals and, Ledger Part 1 What s Here Introduction Business Types Business Organization Professional Advice
Paper 2 Accounting (Syllabus 2008)
 Section A- FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING 1. Which of the following is not a Fixed Asset? (a) Building (b) Bank balance (c) Plant (d) Goodwill [Hints: (b) Fixed asset is an asset held with the intention of being
Section A- FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING 1. Which of the following is not a Fixed Asset? (a) Building (b) Bank balance (c) Plant (d) Goodwill [Hints: (b) Fixed asset is an asset held with the intention of being
Course 1: Evaluating Financial Performance
 Excellence in Financial Management Course 1: Evaluating Financial Performance Prepared by: Matt H. Evans, CPA, CMA, CFM This course provides a basic understanding of how to use ratio analysis for evaluating
Excellence in Financial Management Course 1: Evaluating Financial Performance Prepared by: Matt H. Evans, CPA, CMA, CFM This course provides a basic understanding of how to use ratio analysis for evaluating
When to Debit and Credit in Accounting
 When to Debit and Credit in Accounting Journal entries show a firm s transactions throughout a period of time; for example, when a company purchases supplies a journal entry will show the amount of supplies
When to Debit and Credit in Accounting Journal entries show a firm s transactions throughout a period of time; for example, when a company purchases supplies a journal entry will show the amount of supplies
CENTURY 21 ACCOUNTING, 8e General Journal Chapter Objectives
 CENTURY 21 ACCOUNTING, 8e General Journal Chapter Objectives Chapter 1 Starting A Proprietorship: Changes that Affect the Accounting Equation After studying Chapter 1, you will be able to: 1. Define accounting
CENTURY 21 ACCOUNTING, 8e General Journal Chapter Objectives Chapter 1 Starting A Proprietorship: Changes that Affect the Accounting Equation After studying Chapter 1, you will be able to: 1. Define accounting
ACCOUNTING COMPETENCY EXAM SAMPLE EXAM. 2. The financial statement or statements that pertain to a stated period of time is (are) the:
 ACCOUNTING COMPETENCY EXAM SAMPLE EXAM 1. The accounting process does not include: a. interpreting d. observing b. reporting e. classifying c. purchasing 2. The financial statement or statements that pertain
ACCOUNTING COMPETENCY EXAM SAMPLE EXAM 1. The accounting process does not include: a. interpreting d. observing b. reporting e. classifying c. purchasing 2. The financial statement or statements that pertain
CHAPTER 14: THE ROLE OF ACCOUNTANTS AND ACCOUNTING INFORMATION
 CHAPTER 14: THE ROLE OF ACCOUNTANTS AND ACCOUNTING INFORMATION I. What Is Accounting and Who Uses Accounting Information? Accounting is a comprehensive system for collecting, analyzing, and communicating
CHAPTER 14: THE ROLE OF ACCOUNTANTS AND ACCOUNTING INFORMATION I. What Is Accounting and Who Uses Accounting Information? Accounting is a comprehensive system for collecting, analyzing, and communicating
CHAPTER 3 ADJUSTING THE ACCOUNTS SUMMARY OF QUESTIONS BY STUDY OBJECTIVES AND BLOOM S TAXONOMY. Multiple Choice Questions
 sg st a CHAPTER 3 ADJUSTING THE ACCOUNTS SUMMARY OF QUESTIONS BY STUDY OBJECTIVES AND BLOOM S TAXONOMY Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT True-False Statements 1. 1 C 9. 2 C 17. 5 C
sg st a CHAPTER 3 ADJUSTING THE ACCOUNTS SUMMARY OF QUESTIONS BY STUDY OBJECTIVES AND BLOOM S TAXONOMY Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT Item SO BT True-False Statements 1. 1 C 9. 2 C 17. 5 C
Chapter 16 Accounting for Income Taxes
 DEFERRED TAX ASSETS AND DEFERRED TAX LIABILITIES Fundamental Concepts There are fundamental differences in the amount of income and expenses reported for GAAP and income tax purposes. The objective for
DEFERRED TAX ASSETS AND DEFERRED TAX LIABILITIES Fundamental Concepts There are fundamental differences in the amount of income and expenses reported for GAAP and income tax purposes. The objective for
Chapter 1 Accounting in action
 Chapter 1 Accounting in action What is Accounting Accounting is the financial information system that consists of three basic activities-it identifies, records, and communicates the economic events of
Chapter 1 Accounting in action What is Accounting Accounting is the financial information system that consists of three basic activities-it identifies, records, and communicates the economic events of
ACCOUNTING 105 CONCEPTS REVIEW
 ACCOUNTING 105 CONCEPTS REVIEW A note from the tutors: This handout is designed to help you review important information as you study for your cumulative final exam. While it does cover many important
ACCOUNTING 105 CONCEPTS REVIEW A note from the tutors: This handout is designed to help you review important information as you study for your cumulative final exam. While it does cover many important
The Double-Entry System EFFECTS OF TRANSACTIONS ON THE BALANCE SHEET. Initial Paid-in Capital. An Example Entity. Transaction 2.
 The Double-Entry System EFFECTS OF TRANSACTIONS ON THE BALANCE SHEET 2001 Richard S. Barr Transaction: Any event that affects the entity's financial position and requires recording Every accounting transaction
The Double-Entry System EFFECTS OF TRANSACTIONS ON THE BALANCE SHEET 2001 Richard S. Barr Transaction: Any event that affects the entity's financial position and requires recording Every accounting transaction
Adjusting the Accounts
 HOSP 1210 (Financial Acct) Learning Centre Adjusting the Accounts Anytime we prepare financial statements or reach the end of an accounting period, there are account adjustments that need to be made to
HOSP 1210 (Financial Acct) Learning Centre Adjusting the Accounts Anytime we prepare financial statements or reach the end of an accounting period, there are account adjustments that need to be made to
Accg100 Accounting 1A. Lecture Notes
 Accg100 Accounting 1A Lecture Notes Semester 2, 2012 1 Table of Contents Lecture Notes Page Week 1: Introduction to Accounting, Ethics, 3 Business Entities, Financial Statements Week 2: Accounting for
Accg100 Accounting 1A Lecture Notes Semester 2, 2012 1 Table of Contents Lecture Notes Page Week 1: Introduction to Accounting, Ethics, 3 Business Entities, Financial Statements Week 2: Accounting for
The Nature of Accounting Systems
 Basic Accounting & Budgeting February 4, 2009 The Nature of Accounting Systems Accounting is the process of recording, classifying, summarizing, reporting and interpreting information about the economic
Basic Accounting & Budgeting February 4, 2009 The Nature of Accounting Systems Accounting is the process of recording, classifying, summarizing, reporting and interpreting information about the economic
