Contents. Preface xiii
|
|
|
- Evangeline Ray
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Contents Preface xiii 1. Introduction to Microcontrollers Computer System Central Processing Unit 2 CPU Components Memory I/O Unit System Bus How does the CPU Read Data from the Memory Chip? What can a Computer do? How does Computer Execute Program Instructions? Microprocessor, Microcomputer and Microcontroller Microprocessor Microcomputer Microcontroller Comparison between Microprocessor and Microcontroller Classification of Microcontrollers Word Length: 4, 8, 16, 32, 64-bit Microcontrollers Memory Architecture: Von Neumann and Harvard Architectures Core Architecture: Microcoded and Hardwired Designs Instruction Set Architectures: CISC and RISC Choosing a Microcontroller Applications of Microcontrollers History and Introduction to The 8051 Microcontroller Family Overview of The 8051 Family Features of the 8051 (MCS 51) Family Variants and Enhancements Comparison between MCS 51, PIC, AVR and HCS11/12 Families Advantages of using 8051 Family of Microcontrollers Embedded Systems 15 Embedded Microcontrollers 15 Points to Remember 15 Objective Questions 16 Review Questions with Answers 17 Exercise Programming Model and Architecture of the The 8051 Architecture 20 ALU 21 Memory 21 Peripherals 21 Timing and Control Unit 21 Oscillator Programming Model of The On-Chip Memory Organization 22 Special Function Registers (SFRs) 22 Internal RAM 23 Internal ROM Special Function Registers (SFRs) 23 Accumulator: A 23 B 23 PSW 23 Program Counter: PC 24 Data Pointer: DPTR 24 Stack Pointer: SP 25 I/O Port Registers (latches): P0, P1, P2 and P3 25 Peripheral Data Registers: TL0, TH0, TL1, TH1, and SBUF 25 Peripheral Control Registers: IP, IE, TMOD, TCON, SCON, and PCON Internal RAM 25 Register Banks 25 Bit Addressable Memory 27 General-Purpose RAM Internal ROM External Memory Organization 29 Points to Remember 30 Objective Questions 31 Review Questions with Answers 32 Exercise Program Development Process and Tools Programming Language Machine Language Assembly Language High-Level Language Comparison between Programming Languages Why Assembly Language? Assembly Language Structure Label 37
2 vi Instructions 37 Instruction Size Comments Assembly-Language-Program Example Program Execution Process Software and Hardware Development Tools Design and Documentation Tools 39 Flowcharts 40 Pseudo-codes Software Development Tools 40 Editor 40 Assembler 41 Cross Assembler 42 Compiler 42 Linker 42 Simulator 42 Debugger Hardware Development Tools 43 Emulator or In Circuit Emulator (ICE) 43 Logic Analyzer 43 Target System Integrated Development Environments (IDE) Assembler Directives 43 Originate-ORG 43 Define Byte-DB 44 Define Word-DW 44 Equate-EQU 44 END Program Development Process 45 Create Source Code 45 Assemble all Source Code Files 45 Link all the Object Code Files 45 Test the Program for Correctness Loading Program into Microcontroller 47 Parallel Programming 47 Serial Programming The Intel Hex File Format 48 Introduction to the Instruction Set 54 Points to Remember 49 Objective Questions 50 Review Questions with Answers 51 Exercise Addressing Modes and Data Movement Instructions Why Data Movement Instructions First? Addressing Modes 54 Acronyms used in the Instructions Immediate Addressing Mode 55 Notations for Numbers of Different Number Systems 56 Use of Expressions 56 Contents Register Addressing Mode Direct Addressing Mode Indirect Addressing Mode 58 Register Indirect Addressing Mode 58 Indexed Addressing Mode Operand Modifiers: # External Memory Data Movements Data Memory Access Program Memory Access Data Exchange Push and Pop Instructions 63 Points to Remember 65 Objective Questions 67 Review Questions with Answers 68 Exercise Arithmetic and Logical Instructions Arithmetic Instructions Addition 71 Addition of Multi-Byte Numbers Subtraction Signed Arithmetic 75 Positive Numbers 75 Negative Numbers 75 Overflow 77 Addition of Unlike Signed Numbers 77 Addition of Like Signed Numbers 78 Subtraction of Unlike Signed Numbers 80 Subtraction of Like Signed Numbers 81 Recovering a Result from Overflow Decimal (Binary Coded Decimal BCD) Arithmetic 83 DA A Decimal Adjust Accumulator for Addition Multiplication 85 Use of OV in Multiplication Division 86 Use of OV in Division Increment and Decrement Logical Instructions Byte Operations 89 AND Operation 89 OR Operation 90 EX-OR Operation 90 Logical Operations with Ports Unary Operations 92 Summary of Arithmetic and Logical Instructions 94 Points to Remember 95 Objective Questions 96 Review Questions with Answers 97 Exercise 98
3 Contents vii 6. Bit-Processing Instructions Bit Addressability Bit-Addressable Memories Bit-Addressable Internal RAM Bit-Addressable Special Function Registers Bit-Processing Instructions Instruction using Carry Other Instructions Conditional Jump Instructions 107 Summary of Bit-Processing Instructions 108 Points to Remember 108 Objective Questions 109 Review Questions with Answers 109 Exercise Program-Flow Control Instructions Jump Instructions Unconditional Jumps 112 Short Jump 112 Absolute Jump 114 Long Jump Conditional Jumps 117 Bit Jumps 117 Byte Jumps Loops 119 Nested Loops Calls and Subroutines 122 Relation of Calls and Stack 122 Cautions while Developing Subroutines Stack Initialization and Overflow Time-Delay Generation using Software 127 NOP (No Operation) 127 Summary of Program-Flow Control Instructions 129 Points to Remember 130 Objective Questions 130 Review Questions with Answers 131 Exercise Look-Up Tables and Jump Tables Look-Up Tables and their Usage Faster Evaluation of Functions Miscellaneous Conversions The 8051 and Look-Up Tables Jump Tables 140 Points to Remember 141 Objective Questions 141 Exercise Code Conversions, Array Processing and 16 Bit Arithmetic Code Conversions Array Processing Bit Operations Other Programs 155 Points to Remember 158 Exercise Timing and Instruction Execution The Clock Pulse Machine Cycle Instructions Timing Byte 1 Machine Cycle Instructions Byte 1 Machine Cycle Instructions Byte 2 Machine Cycle Instructions Byte 2 Machine Cycle Instructions External Memory Access External RAM (Data Memory) Access Data Memory Read/Write Cycle External ROM (Code Memory) Access Instruction Execution MOV A, Operand ADD A, Operand LCALL Label MOVX DPTR 169 Points to Remember 169 Objective Questions 171 Review Questions with Answers 171 Exercise The 8051 Hardware, System Design and Troubleshooting The 8051 Pin Diagram The 8051 Pin Description Power Consumption Control of The Idle Mode 178 Power Down Mode 178 Tip for Power Saving Design of The 8051 based System 179 Reset Circuit 179 Clock Circuit 179 Pull-up Resistors 179 Demultiplexer Troubleshooting 8051 based Systems Program Memory Protection 180 Points to Remember 180 Objective Questions 181 Review Questions with Answers 181 Exercise The 8051 Programming in C Data Types for The 8051 Supported by Cx51 Compiler Native Word Size: char 184
4 viii Contents Additional Data Types for the Bit 185 sfr 185 sbit Implementing Infinite Loops in a C Program Bit Addressing in the C Language Accessing Memory Areas of The Internal RAM (Data Memory) External RAM (Data Memory) Program/Code Memory Bit Addressable Variables Interrupt-Service Routines 197 using attribute Operators Data Serialization using Port Pins Rotate Operations in C Left Rotation Right Rotation Pointers Pointers to Absolute Addresses Time Delays in C Increasing the Code Efficiency Variable Size Use of Unsigned Data Types Use of Bit Variables Inline Functions Use of Internal RAM Inline Assembly/Hand-Coded Assembly Avoid Standard Library Routines Use of Intrinsic Functions Performance Comparison between Assembly and C Programs 207 Points to Remember 212 Objective Questions 212 Review Questions with Answers 213 Exercise Input/Output Ports The 8051 Ports Port Configuring the Port as an Input 217 Configuring the Port as an Output Port Port 0 as an Address/Data Bus Port Port Reading Latch Versus Reading Port Pin 225 Logical Operation with Ports Port Current Capabilities 227 Points to Remember 227 Objective Questions 227 Review Questions with Answers 228 Exercise Timers Need of Timers How Does a Timer Operate? Timers in The TMOD (Timer Mode Control) Register 232 Gate 232 C/T 233 M1 and M TCON Register Timer Circuits as an Interval Timer Timer Mode Timer Mode Operation of the Timer in Mode Initial Value to be Loaded in Timer Registers 237 Square-Wave Generation using Timers 238 Timer Mode Timer Mode Operation of Mode Generating Larger Delays Timer Mode Reading the Value of a Timer Timer as an Event Counter 252 Simulation Procedure Frequency Measurement using Timers 254 Points to Remember 256 Objective Questions 256 Review Questions with Answers 257 Exercise Serial Communications Need for the Serial Communication Synchronous and Asynchronous Serial Communications Format of Asynchronous Serial Data Frame Rate of Data Transfer RS 232 : Serial Data Transmission Standard Hand-shaking Process between DTE and DCE RS232 to TTL Interfacing UART UART Features SBUF (Serial Data Buffer) Register One Name Two Registers 265 SCON Serial Control Register 265
5 Contents ix Serial Port Control (SCON) Register Modes of Operation Mode 0 8 bit Shift Register Mode 266 Transmission 266 Reception 266 Baud Rate for Mode Mode 1 Standard 8-bit UART Mode 269 Transmission 269 Reception 270 Baud Rate for Mode Software Development to Transmit and Receive Data Serially 272 Simulation Result 274 Simulation Procedure Mode 2 Multiprocessor Communication 280 Transmission 281 Reception 281 Multiprocessor Communication 281 Baud Rate for Mode Mode Second Serial Port in The DS89C4x0 283 Points to Remember 285 Objective Questions 285 Review Questions with Answers 287 Exercise Interrupts Need of Interrupts How are Interrupts Useful? Interrupts in The Reset as a Special Interrupt Interrupt Handling and Execution Programming the Interrupts Interrupt Enable (IE) Register Interrupt Priority (IP) Register Timer Interrupts Programming of Timer Interrupts Simultaneous and Independent use of both the Timers External Interrupts Level-Triggered External Interrupts Transition (Edge) Triggered External Interrupts 304 Simulation Procedure Pulse Generation using External Interrupt Sampling of Edge-Triggered Interrupts Serial Port Interrupts 307 Simulation Procedure 308 Simulation Result Interrupt Priorities Nested and Multiple Interrupts Blocking Conditions Interrupt Latency Generating Interrupts using Instructions Cautions While Developing Interrupt Service Routines Dilemma: Use Interrupt or Polling? Project: Full-Duplex System 316 Problem Statement 316 Program Development 317 Suggested Modification 318 Points to Remember 318 Objective Questions 318 Review Questions with Answers 320 Exercise Interfacing Keyboards Keyboard Design Considerations Mechanical Properties of the Switches Key Debouncing using Hardware Key Debouncing using Software Keyboard Configurations Simple Keyboard Configuration (Using I/O Pins directly) 324 Advantages of a Simple Keyboard 324 Disadvantages of Simple Keyboard 325 Key-Press Detection and the Code Generation 325 Algorithm 325 Program for a Simple Keyboard 325 Key Identification using the Hardware Technique 327 Advantage of Hardware Technique Matrix Keyboard Configuration 328 Key-Code Generation 328 Key Identification and Key Code Generation using Counters 329 Key Identification and Key-Code Generation using the Look-Up Table 331 Points to Remember 331 Objective Questions 332 Review Questions with Answers 332 Exercise Interfacing Display Devices: LED, Seven Segment Display and LCD Light Emitting Diodes 334 Applications of LEDs Seven-Segment Display 337
6 x Contents Segment Multiplexing within one Seven-Segment Display Digit Multiplexing Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) Pin Description for LCD LCD Commands Initialization of the LCD using the Internal Reset Circuit Software Initialization of the LCD LCD Timing Modes of operation bit Mode 344 Importance of Monitoring Busy Flag bit Mode Project: Simple Burglar Alarm System 350 Program Development 351 Suggested Modifications 353 Points to Remember 353 Objective Questions 353 Review Questions with Answers 354 Exercise Interfacing ADC, DAC and Sensors Analog to Digital Converters Need for Analog-to-Digital Converters Methods of Conversion ADC Parameters Common ADC Chips ADC 0801/02/03/04/05 Chips 358 Analog inputs 358 Analog Input Voltage Range 358 Digital Output 359 Clock Source Handshaking Process between the Microcontroller and ADC 0804 Chip ADC 0808/0809 Chips Serial ADC Chips 364 Serial ADC Chip MAX1112/ MAX Pin Description of MAX1112/ Control Byte of MAX1112/ MAX Sending Control Byte to MAX 1112/ MAX Reading Digital Output Data (Result) from the Serial ADC Chip 367 Common Serial ADC Chips On-chip ADCs 371 P89LPC Applications of ADCs Digital-to-Analog Converters DAC Parameters Common DAC chips DAC AD557 Chip DAC 0808 Chip 378 Operation of DAC Applications of DACs Temperature Sensor: LM LM35 Specifications Common Temperature Sensors Applications of Temperature Sensors Infrared (IR) Sensors TSOP 17xx IR Receivers Interfacing of TSOP 17xx with the Applications of IR Sensors 385 Project: Temperature Monitoring System 385 Project: Function Generator 389 Points to Remember 393 Objective Questions 394 Review Questions with Answers 395 Exercise Interfacing Relays, Opto-Couplers, Stepper and DC Motors Relays Relay Operation Relay Driver Circuits and Interfacing 397 Driver Circuit Operation 398 Advantages of using a Relay 399 Drawbacks of Electromechanical Relays Parameters of Relays 399 Input Coil Side (Low Power, Controlling Side) 399 Output Switch Side (High Power, Load Side) Opto-Coupler Opto-Coupler Operation Applications of Opto-Couplers Stepper Motors Permanent-Magnet Stepper Motors Unipolar and Bipolar Stepper Motors Direction and Speed Control Interfacing with the Circuit Operation Rotation of Motor for Specified Angle Applications of Stepper Motors DC Motors Analog Speed Control Digital Speed Control Direction Control 410
7 Contents xi Pulse-Width Modulation (PWM) DC Motor Driver Circuits Interfacing DC Motors with the Project: DC Motor-Speed-Control System 416 Project: Automatic Street Light Control System 420 Points to Remember 421 Objective Questions 422 Review Questions with Answers 422 Exercise Interfacing External Memory and Real-Time Clock Memory Interfacing and its Need Memory Chips Address Signals Data Signals Control Signals Semiconductor Memory Devices Volatile Memory 426 SRAM: Static RAM 427 DRAM: Dynamic RAM Nonvolatile Memory 427 ROM 427 PROM: Programmable ROM 428 EPROM: Erasable Programmable ROM 428 EEPROM: Electrically Erasable and Programmable ROM 428 Flash 428 NVRAM: Nonvolatile RAM Memory Map and Address Decoding Signals used in Memory Interfacing The 8051 and the Corresponding Memory Chip Signals 429 Address Lines (A 15 A 0 ) 429 Data Lines (D7 D0) Address Decoder using Logic Gates 430 Memory Read and Write Operations Address Decoder using Decoder Chip Program/Code Memory Interfacing Data/RAM Memory Interfacing Data Memory Using ROM ROM as Data as well as Program Memory RAM as Data as well as Program Memory On-Chip EEPROM Programming in AT89S Steps to Write (Program) a Byte in Data EEPROM 440 Steps to Write a Page (Maximum 32 Bytes) in Data EEPROM 441 Steps to Read a Byte(s) from Data EEPROM Real-Time Clock DS12887: Real-time Clock Chip 443 Main Features of the DS Address Map Interfacing DS12887 with the Programming the DS Oscillator Control Bits 444 Setting the Time and Date 445 Reading the Time and Date Square Wave Output Alarms Periodic Interrupts Update Cycles Interrupt Sources 450 Points to Remember 450 Objective Questions 450 Review Questions with Answers 451 Exercise I2C and SPI Protocols Inter Integrated Circuit (IIC or I 2 C) 454 I2C Bus Features I2C Bus Hardware Configuration V CC or V DD I2C Devices I2C Protocol START and STOP Conditions Data Validity Data Transfer Operations on I2C Bus Write Operation Read Operation Arbitration and the Clock Synchronization Clock Stretching Burst Read/Write Modes Driving The I2C Bus I2C Interface Module of P89C66x Microcontrollers Programming I2C Interface of P89C66x 463 Using I2C Interface as a Master 463 Initialization of I2C Module 463 Generate START Condition 463 Transmit Data 464 Read Data 464 Generate a STOP Condition Interfacing PCF8594C-2 Serial EEPROM 466 Addressing of PCF8594C Write Operation 467 Read Operation xxx and AT24Cxxxx Serial EEPROMs 467 Using I2C Device as a Slave 470
8 xii Contents Initialization of I2C Module 470 Monitor the Bus Condition 470 Transmit Data 470 Read Data I2C Devices Serial Peripheral Interface SPI Operation Clock Polarity and Phase in SPI Device SPI Bus Configurations AT89S825x SPI Interface Module of AT89S825x Microcontrollers Interfacing MAX512/13 with SPI Bus 477 Serial-Input Data Format and Control Codes for MAX512/ Interfacing MAX512/13 with AT89S SPI Devices Comparison between I2C and SPI Protocols 479 Points to Remember 479 Objective Questions 480 Review Questions with Answers 481 Exercise The 8051 Variants, AVR and PIC Microcontrollers The 8051 Enhancements Additional 128 Bytes of On-Chip RAM Timer Maximum Clock Speed 485 Clocks/Machine Cycle Program Memory Identification Variants from NXP (Philips) Variants from Atmel Corporation Variants from Dallas Semiconductor Variants from Silicon Laboratories Common On-Chip Peripherals Watchdog Timer Controller Area Network (CAN) Analog Comparator Pulse-width Modulator ADC and DAC Real-Time Clock (RTC) Other Peripherals and Features 488 Multiple DPTRs 489 Four Levels of Interrupt Priorities 489 In-System Programming (ISP) 489 In-Application Programming (IAP) MCS 151/251 Microcontrollers MCS 96 Microcontrollers AVR Microcontrollers AVR ATmega Family Programming Model of ATmega16 Family of Microcontrollers 493 General-Purpose Registers: R0 R STATUS Register 494 Program Counter 495 Stack Pointer 495 Data Memory 495 Data EEPROM 495 Program Memory 496 I/O Ports and Peripherals PIC Microcontrollers PIC18 Family Programming Model of PIC18 Family of Microcontrollers 498 Working Register (WREG) 498 Bank Select Register (BSR) 499 File Select Registers (FSR) 499 STATUS Register 499 Table Pointer 500 Program Counter 500 Stack and Stack Pointer 500 Special Function Registers (SFRs) 500 Data Memory 500 Program Memory 501 Data EEPROM Memory 501 I/O Ports 502 Points to Remember 501 Objective Questions 501 Review Questions with Answers 502 Exercise 502 Appendix A: The 8051 Instruction Set Summary 503 Appendix B: Using Keil µvision 4.0 IDE 525 Appendix C: Instructions Arranged Functionally 540 Appendix D: ASCII Codes 549 Appendix E: Special Function Registers Quick View 551 Index 555
DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE & ENGINEERING Question Bank Subject Name: EC6504 - Microprocessor & Microcontroller Year/Sem : II/IV
 DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE & ENGINEERING Question Bank Subject Name: EC6504 - Microprocessor & Microcontroller Year/Sem : II/IV UNIT I THE 8086 MICROPROCESSOR 1. What is the purpose of segment registers
DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE & ENGINEERING Question Bank Subject Name: EC6504 - Microprocessor & Microcontroller Year/Sem : II/IV UNIT I THE 8086 MICROPROCESSOR 1. What is the purpose of segment registers
8051 MICROCONTROLLER COURSE
 8051 MICROCONTROLLER COURSE Objective: 1. Familiarization with different types of Microcontroller 2. To know 8051 microcontroller in detail 3. Programming and Interfacing 8051 microcontroller Prerequisites:
8051 MICROCONTROLLER COURSE Objective: 1. Familiarization with different types of Microcontroller 2. To know 8051 microcontroller in detail 3. Programming and Interfacing 8051 microcontroller Prerequisites:
8051 hardware summary
 8051 hardware summary 8051 block diagram 8051 pinouts + 5V ports port 0 port 1 port 2 port 3 : dual-purpose (general-purpose, external memory address and data) : dedicated (interfacing to external devices)
8051 hardware summary 8051 block diagram 8051 pinouts + 5V ports port 0 port 1 port 2 port 3 : dual-purpose (general-purpose, external memory address and data) : dedicated (interfacing to external devices)
PART B QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS UNIT I
 PART B QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS UNIT I 1. Explain the architecture of 8085 microprocessor? Logic pin out of 8085 microprocessor Address bus: unidirectional bus, used as high order bus Data bus: bi-directional
PART B QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS UNIT I 1. Explain the architecture of 8085 microprocessor? Logic pin out of 8085 microprocessor Address bus: unidirectional bus, used as high order bus Data bus: bi-directional
MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCOMPUTER BASICS
 Introduction MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCOMPUTER BASICS At present there are many types and sizes of computers available. These computers are designed and constructed based on digital and Integrated Circuit
Introduction MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCOMPUTER BASICS At present there are many types and sizes of computers available. These computers are designed and constructed based on digital and Integrated Circuit
Flash Microcontroller. Memory Organization. Memory Organization
 The information presented in this chapter is collected from the Microcontroller Architectural Overview, AT89C51, AT89LV51, AT89C52, AT89LV52, AT89C2051, and AT89C1051 data sheets of this book. The material
The information presented in this chapter is collected from the Microcontroller Architectural Overview, AT89C51, AT89LV51, AT89C52, AT89LV52, AT89C2051, and AT89C1051 data sheets of this book. The material
MICROPROCESSOR. Exclusive for IACE Students www.iace.co.in iacehyd.blogspot.in Ph: 9700077455/422 Page 1
 MICROPROCESSOR A microprocessor incorporates the functions of a computer s central processing unit (CPU) on a single Integrated (IC), or at most a few integrated circuit. It is a multipurpose, programmable
MICROPROCESSOR A microprocessor incorporates the functions of a computer s central processing unit (CPU) on a single Integrated (IC), or at most a few integrated circuit. It is a multipurpose, programmable
Serial Communications
 Serial Communications 1 Serial Communication Introduction Serial communication buses Asynchronous and synchronous communication UART block diagram UART clock requirements Programming the UARTs Operation
Serial Communications 1 Serial Communication Introduction Serial communication buses Asynchronous and synchronous communication UART block diagram UART clock requirements Programming the UARTs Operation
Keil C51 Cross Compiler
 Keil C51 Cross Compiler ANSI C Compiler Generates fast compact code for the 8051 and it s derivatives Advantages of C over Assembler Do not need to know the microcontroller instruction set Register allocation
Keil C51 Cross Compiler ANSI C Compiler Generates fast compact code for the 8051 and it s derivatives Advantages of C over Assembler Do not need to know the microcontroller instruction set Register allocation
8051 Serial Port. Crystal TXD. I/O Device RXD. Embedded Systems 1 5-1 8051 Peripherals
 8051 Serial Port The 8051 contains a UART Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter The serial port is full-duplex It can transmit and receive simultaneously 2 Port 3 pins are used to provide the serial
8051 Serial Port The 8051 contains a UART Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter The serial port is full-duplex It can transmit and receive simultaneously 2 Port 3 pins are used to provide the serial
8-Bit Flash Microcontroller for Smart Cards. AT89SCXXXXA Summary. Features. Description. Complete datasheet available under NDA
 Features Compatible with MCS-51 products On-chip Flash Program Memory Endurance: 1,000 Write/Erase Cycles On-chip EEPROM Data Memory Endurance: 100,000 Write/Erase Cycles 512 x 8-bit RAM ISO 7816 I/O Port
Features Compatible with MCS-51 products On-chip Flash Program Memory Endurance: 1,000 Write/Erase Cycles On-chip EEPROM Data Memory Endurance: 100,000 Write/Erase Cycles 512 x 8-bit RAM ISO 7816 I/O Port
2.0 Command and Data Handling Subsystem
 2.0 Command and Data Handling Subsystem The Command and Data Handling Subsystem is the brain of the whole autonomous CubeSat. The C&DH system consists of an Onboard Computer, OBC, which controls the operation
2.0 Command and Data Handling Subsystem The Command and Data Handling Subsystem is the brain of the whole autonomous CubeSat. The C&DH system consists of an Onboard Computer, OBC, which controls the operation
Embedded Systems on ARM Cortex-M3 (4weeks/45hrs)
 Embedded Systems on ARM Cortex-M3 (4weeks/45hrs) Course & Kit Contents LEARN HOW TO: Use of Keil Real View for ARM Use ARM Cortex-M3 MCU for professional embedded application development Understanding
Embedded Systems on ARM Cortex-M3 (4weeks/45hrs) Course & Kit Contents LEARN HOW TO: Use of Keil Real View for ARM Use ARM Cortex-M3 MCU for professional embedded application development Understanding
Microtronics technologies Mobile: 99707 90092
 For more Project details visit: http://www.projectsof8051.com/rfid-based-attendance-management-system/ Code Project Title 1500 RFid Based Attendance System Synopsis for RFid Based Attendance System 1.
For more Project details visit: http://www.projectsof8051.com/rfid-based-attendance-management-system/ Code Project Title 1500 RFid Based Attendance System Synopsis for RFid Based Attendance System 1.
Microcontroller Basics A microcontroller is a small, low-cost computer-on-a-chip which usually includes:
 Microcontroller Basics A microcontroller is a small, low-cost computer-on-a-chip which usually includes: An 8 or 16 bit microprocessor (CPU). A small amount of RAM. Programmable ROM and/or flash memory.
Microcontroller Basics A microcontroller is a small, low-cost computer-on-a-chip which usually includes: An 8 or 16 bit microprocessor (CPU). A small amount of RAM. Programmable ROM and/or flash memory.
AUTOMATIC NIGHT LAMP WITH MORNING ALARM USING MICROPROCESSOR
 AUTOMATIC NIGHT LAMP WITH MORNING ALARM USING MICROPROCESSOR INTRODUCTION This Project "Automatic Night Lamp with Morning Alarm" was developed using Microprocessor. It is the Heart of the system. The sensors
AUTOMATIC NIGHT LAMP WITH MORNING ALARM USING MICROPROCESSOR INTRODUCTION This Project "Automatic Night Lamp with Morning Alarm" was developed using Microprocessor. It is the Heart of the system. The sensors
Microcontrollers in Practice
 M. Mitescu I. Susnea Microcontrollers in Practice With 117 Figures, 34 Tables and CD-Rom 4y Springer Contents Resources of Microcontrollers, 1 1.1 In this Chapter 1 1.2 Microcontroller Architectures 1
M. Mitescu I. Susnea Microcontrollers in Practice With 117 Figures, 34 Tables and CD-Rom 4y Springer Contents Resources of Microcontrollers, 1 1.1 In this Chapter 1 1.2 Microcontroller Architectures 1
CHAPTER 7: The CPU and Memory
 CHAPTER 7: The CPU and Memory The Architecture of Computer Hardware, Systems Software & Networking: An Information Technology Approach 4th Edition, Irv Englander John Wiley and Sons 2010 PowerPoint slides
CHAPTER 7: The CPU and Memory The Architecture of Computer Hardware, Systems Software & Networking: An Information Technology Approach 4th Edition, Irv Englander John Wiley and Sons 2010 PowerPoint slides
Hardware and Software Requirements
 C Compiler Real-Time OS Simulator Training Evaluation Boards Installing and Using the Keil Monitor-51 Application Note 152 May 31, 2000, Munich, Germany by Keil Support, Keil Elektronik GmbH support.intl@keil.com
C Compiler Real-Time OS Simulator Training Evaluation Boards Installing and Using the Keil Monitor-51 Application Note 152 May 31, 2000, Munich, Germany by Keil Support, Keil Elektronik GmbH support.intl@keil.com
150127-Microprocessor & Assembly Language
 Chapter 3 Z80 Microprocessor Architecture The Z 80 is one of the most talented 8 bit microprocessors, and many microprocessor-based systems are designed around the Z80. The Z80 microprocessor needs an
Chapter 3 Z80 Microprocessor Architecture The Z 80 is one of the most talented 8 bit microprocessors, and many microprocessor-based systems are designed around the Z80. The Z80 microprocessor needs an
Chapter 1 Lesson 3 Hardware Elements in the Embedded Systems. 2008 Chapter-1L03: "Embedded Systems - ", Raj Kamal, Publs.: McGraw-Hill Education
 Chapter 1 Lesson 3 Hardware Elements in the Embedded Systems 1 Typical Embedded System Hardware units 2 Basic Circuit Elements at the System 3 (i) Power Source 1. System own supply with separate supply
Chapter 1 Lesson 3 Hardware Elements in the Embedded Systems 1 Typical Embedded System Hardware units 2 Basic Circuit Elements at the System 3 (i) Power Source 1. System own supply with separate supply
Atmel Norway 2005. XMEGA Introduction
 Atmel Norway 005 XMEGA Introduction XMEGA XMEGA targets Leadership on Peripheral Performance Leadership in Low Power Consumption Extending AVR market reach XMEGA AVR family 44-100 pin packages 16K 51K
Atmel Norway 005 XMEGA Introduction XMEGA XMEGA targets Leadership on Peripheral Performance Leadership in Low Power Consumption Extending AVR market reach XMEGA AVR family 44-100 pin packages 16K 51K
MACHINE ARCHITECTURE & LANGUAGE
 in the name of God the compassionate, the merciful notes on MACHINE ARCHITECTURE & LANGUAGE compiled by Jumong Chap. 9 Microprocessor Fundamentals A system designer should consider a microprocessor-based
in the name of God the compassionate, the merciful notes on MACHINE ARCHITECTURE & LANGUAGE compiled by Jumong Chap. 9 Microprocessor Fundamentals A system designer should consider a microprocessor-based
RAM & ROM Based Digital Design. ECE 152A Winter 2012
 RAM & ROM Based Digital Design ECE 152A Winter 212 Reading Assignment Brown and Vranesic 1 Digital System Design 1.1 Building Block Circuits 1.1.3 Static Random Access Memory (SRAM) 1.1.4 SRAM Blocks in
RAM & ROM Based Digital Design ECE 152A Winter 212 Reading Assignment Brown and Vranesic 1 Digital System Design 1.1 Building Block Circuits 1.1.3 Static Random Access Memory (SRAM) 1.1.4 SRAM Blocks in
Chapter 13. PIC Family Microcontroller
 Chapter 13 PIC Family Microcontroller Lesson 01 PIC Characteristics and Examples PIC microcontroller characteristics Power-on reset Brown out reset Simplified instruction set High speed execution Up to
Chapter 13 PIC Family Microcontroller Lesson 01 PIC Characteristics and Examples PIC microcontroller characteristics Power-on reset Brown out reset Simplified instruction set High speed execution Up to
Chapter 2 Logic Gates and Introduction to Computer Architecture
 Chapter 2 Logic Gates and Introduction to Computer Architecture 2.1 Introduction The basic components of an Integrated Circuit (IC) is logic gates which made of transistors, in digital system there are
Chapter 2 Logic Gates and Introduction to Computer Architecture 2.1 Introduction The basic components of an Integrated Circuit (IC) is logic gates which made of transistors, in digital system there are
Advanced Computer Architecture-CS501. Computer Systems Design and Architecture 2.1, 2.2, 3.2
 Lecture Handout Computer Architecture Lecture No. 2 Reading Material Vincent P. Heuring&Harry F. Jordan Chapter 2,Chapter3 Computer Systems Design and Architecture 2.1, 2.2, 3.2 Summary 1) A taxonomy of
Lecture Handout Computer Architecture Lecture No. 2 Reading Material Vincent P. Heuring&Harry F. Jordan Chapter 2,Chapter3 Computer Systems Design and Architecture 2.1, 2.2, 3.2 Summary 1) A taxonomy of
Microprocessor or Microcontroller?
 Microprocessor or Microcontroller? A little History What is a computer? [Merriam-Webster Dictionary] one that computes; specifically : programmable electronic device that can store, retrieve, and process
Microprocessor or Microcontroller? A little History What is a computer? [Merriam-Webster Dictionary] one that computes; specifically : programmable electronic device that can store, retrieve, and process
MICROPROCESSOR BCA IV Sem MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 MICROPROCESSOR BCA IV Sem MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1) Which is the microprocessor comprises: a. Register section b. One or more ALU c. Control unit 2) What is the store by register? a. data b. operands
MICROPROCESSOR BCA IV Sem MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1) Which is the microprocessor comprises: a. Register section b. One or more ALU c. Control unit 2) What is the store by register? a. data b. operands
Data Acquisition Module with I2C interface «I2C-FLEXEL» User s Guide
 Data Acquisition Module with I2C interface «I2C-FLEXEL» User s Guide Sensors LCD Real Time Clock/ Calendar DC Motors Buzzer LED dimming Relay control I2C-FLEXEL PS2 Keyboards Servo Motors IR Remote Control
Data Acquisition Module with I2C interface «I2C-FLEXEL» User s Guide Sensors LCD Real Time Clock/ Calendar DC Motors Buzzer LED dimming Relay control I2C-FLEXEL PS2 Keyboards Servo Motors IR Remote Control
Lab Experiment 1: The LPC 2148 Education Board
 Lab Experiment 1: The LPC 2148 Education Board 1 Introduction The aim of this course ECE 425L is to help you understand and utilize the functionalities of ARM7TDMI LPC2148 microcontroller. To do that,
Lab Experiment 1: The LPC 2148 Education Board 1 Introduction The aim of this course ECE 425L is to help you understand and utilize the functionalities of ARM7TDMI LPC2148 microcontroller. To do that,
Microcontroller Based Low Cost Portable PC Mouse and Keyboard Tester
 Leonardo Journal of Sciences ISSN 1583-0233 Issue 20, January-June 2012 p. 31-36 Microcontroller Based Low Cost Portable PC Mouse and Keyboard Tester Ganesh Sunil NHIVEKAR *, and Ravidra Ramchandra MUDHOLKAR
Leonardo Journal of Sciences ISSN 1583-0233 Issue 20, January-June 2012 p. 31-36 Microcontroller Based Low Cost Portable PC Mouse and Keyboard Tester Ganesh Sunil NHIVEKAR *, and Ravidra Ramchandra MUDHOLKAR
Microcomputer Components SAB 80515/SAB 80C515 8-Bit Single-Chip Microcontroller Family
 Microcomputer Components SAB 80515/SAB 80C515 8-Bit Single-Chip Microcontroller Family User's Manual 08.95 SAB 80515 / SAB 80C515 Family Revision History: 8.95 Previous Releases: 12.90/10.92 Page Subjects
Microcomputer Components SAB 80515/SAB 80C515 8-Bit Single-Chip Microcontroller Family User's Manual 08.95 SAB 80515 / SAB 80C515 Family Revision History: 8.95 Previous Releases: 12.90/10.92 Page Subjects
STEPPER MOTOR SPEED AND POSITION CONTROL
 STEPPER MOTOR SPEED AND POSITION CONTROL Group 8: Subash Anigandla Hemanth Rachakonda Bala Subramanyam Yannam Sri Divya Krovvidi Instructor: Dr. Jens - Peter Kaps ECE 511 Microprocessors Fall Semester
STEPPER MOTOR SPEED AND POSITION CONTROL Group 8: Subash Anigandla Hemanth Rachakonda Bala Subramanyam Yannam Sri Divya Krovvidi Instructor: Dr. Jens - Peter Kaps ECE 511 Microprocessors Fall Semester
456 26 Microcontrollers Figure 26-1 Objectives Key Words and Terms 26.1 OVERVIEW OF THE MICROCONTROLLER microcontroller
 This sample chapter is for review purposes only. Copyright The Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. All rights reserved. 456 Electronic Communication and Data Systems Objectives After studying this chapter, you
This sample chapter is for review purposes only. Copyright The Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. All rights reserved. 456 Electronic Communication and Data Systems Objectives After studying this chapter, you
Microprocessor and Microcontroller Architecture
 Microprocessor and Microcontroller Architecture 1 Von Neumann Architecture Stored-Program Digital Computer Digital computation in ALU Programmable via set of standard instructions input memory output Internal
Microprocessor and Microcontroller Architecture 1 Von Neumann Architecture Stored-Program Digital Computer Digital computation in ALU Programmable via set of standard instructions input memory output Internal
EMBEDDED SYSTEM BASICS AND APPLICATION
 EMBEDDED SYSTEM BASICS AND APPLICATION TOPICS TO BE DISCUSSED System Embedded System Components Classifications Processors Other Hardware Software Applications 2 INTRODUCTION What is a system? A system
EMBEDDED SYSTEM BASICS AND APPLICATION TOPICS TO BE DISCUSSED System Embedded System Components Classifications Processors Other Hardware Software Applications 2 INTRODUCTION What is a system? A system
Digitale Signalverarbeitung mit FPGA (DSF) Soft Core Prozessor NIOS II Stand Mai 2007. Jens Onno Krah
 (DSF) Soft Core Prozessor NIOS II Stand Mai 2007 Jens Onno Krah Cologne University of Applied Sciences www.fh-koeln.de jens_onno.krah@fh-koeln.de NIOS II 1 1 What is Nios II? Altera s Second Generation
(DSF) Soft Core Prozessor NIOS II Stand Mai 2007 Jens Onno Krah Cologne University of Applied Sciences www.fh-koeln.de jens_onno.krah@fh-koeln.de NIOS II 1 1 What is Nios II? Altera s Second Generation
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. Product Brief Integrated Portable System Processor DragonBall ΤΜ
 nc. Order this document by MC68328/D Microprocessor and Memory Technologies Group MC68328 MC68328V Product Brief Integrated Portable System Processor DragonBall ΤΜ As the portable consumer market grows
nc. Order this document by MC68328/D Microprocessor and Memory Technologies Group MC68328 MC68328V Product Brief Integrated Portable System Processor DragonBall ΤΜ As the portable consumer market grows
The I2C Bus. NXP Semiconductors: UM10204 I2C-bus specification and user manual. 14.10.2010 HAW - Arduino 1
 The I2C Bus Introduction The I2C-bus is a de facto world standard that is now implemented in over 1000 different ICs manufactured by more than 50 companies. Additionally, the versatile I2C-bus is used
The I2C Bus Introduction The I2C-bus is a de facto world standard that is now implemented in over 1000 different ICs manufactured by more than 50 companies. Additionally, the versatile I2C-bus is used
CHAPTER 4 MARIE: An Introduction to a Simple Computer
 CHAPTER 4 MARIE: An Introduction to a Simple Computer 4.1 Introduction 195 4.2 CPU Basics and Organization 195 4.2.1 The Registers 196 4.2.2 The ALU 197 4.2.3 The Control Unit 197 4.3 The Bus 197 4.4 Clocks
CHAPTER 4 MARIE: An Introduction to a Simple Computer 4.1 Introduction 195 4.2 CPU Basics and Organization 195 4.2.1 The Registers 196 4.2.2 The ALU 197 4.2.3 The Control Unit 197 4.3 The Bus 197 4.4 Clocks
COMPUTER HARDWARE. Input- Output and Communication Memory Systems
 COMPUTER HARDWARE Input- Output and Communication Memory Systems Computer I/O I/O devices commonly found in Computer systems Keyboards Displays Printers Magnetic Drives Compact disk read only memory (CD-ROM)
COMPUTER HARDWARE Input- Output and Communication Memory Systems Computer I/O I/O devices commonly found in Computer systems Keyboards Displays Printers Magnetic Drives Compact disk read only memory (CD-ROM)
Develop a Dallas 1-Wire Master Using the Z8F1680 Series of MCUs
 Develop a Dallas 1-Wire Master Using the Z8F1680 Series of MCUs AN033101-0412 Abstract This describes how to interface the Dallas 1-Wire bus with Zilog s Z8F1680 Series of MCUs as master devices. The Z8F0880,
Develop a Dallas 1-Wire Master Using the Z8F1680 Series of MCUs AN033101-0412 Abstract This describes how to interface the Dallas 1-Wire bus with Zilog s Z8F1680 Series of MCUs as master devices. The Z8F0880,
Microcontrollers A Brief History of Microprocessors
 Microcontrollers A Brief History of Microprocessors The first microprocessor was developed by what was then a small company called Intel (short for Integrated Electronics) in the early 1970s. The client,
Microcontrollers A Brief History of Microprocessors The first microprocessor was developed by what was then a small company called Intel (short for Integrated Electronics) in the early 1970s. The client,
A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, 7e. Chapter 1 Introducing Hardware
 A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, 7e Chapter 1 Introducing Hardware Objectives Learn that a computer requires both hardware and software to work Learn about the many different hardware components
A+ Guide to Managing and Maintaining Your PC, 7e Chapter 1 Introducing Hardware Objectives Learn that a computer requires both hardware and software to work Learn about the many different hardware components
Timer A (0 and 1) and PWM EE3376
 Timer A (0 and 1) and PWM EE3376 General Peripheral Programming Model Each peripheral has a range of addresses in the memory map peripheral has base address (i.e. 0x00A0) each register used in the peripheral
Timer A (0 and 1) and PWM EE3376 General Peripheral Programming Model Each peripheral has a range of addresses in the memory map peripheral has base address (i.e. 0x00A0) each register used in the peripheral
Implementing SPI Master and Slave Functionality Using the Z8 Encore! F083A
 Application Note Implementing SPI Master and Slave Functionality Using the Z8 Encore! F083A AN026701-0308 Abstract This application note demonstrates a method of implementing the Serial Peripheral Interface
Application Note Implementing SPI Master and Slave Functionality Using the Z8 Encore! F083A AN026701-0308 Abstract This application note demonstrates a method of implementing the Serial Peripheral Interface
SKP16C62P Tutorial 1 Software Development Process using HEW. Renesas Technology America Inc.
 SKP16C62P Tutorial 1 Software Development Process using HEW Renesas Technology America Inc. 1 Overview The following tutorial is a brief introduction on how to develop and debug programs using HEW (Highperformance
SKP16C62P Tutorial 1 Software Development Process using HEW Renesas Technology America Inc. 1 Overview The following tutorial is a brief introduction on how to develop and debug programs using HEW (Highperformance
AVR151: Setup and Use of the SPI. Introduction. Features. Atmel AVR 8-bit Microcontroller APPLICATION NOTE
 Atmel AVR 8-bit Microcontroller AVR151: Setup and Use of the SPI APPLICATION NOTE Introduction This application note describes how to set up and use the on-chip Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) of the
Atmel AVR 8-bit Microcontroller AVR151: Setup and Use of the SPI APPLICATION NOTE Introduction This application note describes how to set up and use the on-chip Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) of the
DS1104 R&D Controller Board
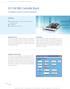 DS1104 R&D Controller Board Cost-effective system for controller development Highlights Single-board system with real-time hardware and comprehensive I/O Cost-effective PCI hardware for use in PCs Application
DS1104 R&D Controller Board Cost-effective system for controller development Highlights Single-board system with real-time hardware and comprehensive I/O Cost-effective PCI hardware for use in PCs Application
Display Message on Notice Board using GSM
 Advance in Electronic and Electric Engineering. ISSN 2231-1297, Volume 3, Number 7 (2013), pp. 827-832 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/aeee.htm Display Message on Notice Board
Advance in Electronic and Electric Engineering. ISSN 2231-1297, Volume 3, Number 7 (2013), pp. 827-832 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/aeee.htm Display Message on Notice Board
ET-BASE AVR ATmega64/128
 ET-BASE AVR ATmega64/128 ET-BASE AVR ATmega64/128 which is a Board Microcontroller AVR family from ATMEL uses MCU No.ATmega64 and ATmega128 64PIN. Board ET-BASE AVR ATmega64/128 uses MCU s resources on
ET-BASE AVR ATmega64/128 ET-BASE AVR ATmega64/128 which is a Board Microcontroller AVR family from ATMEL uses MCU No.ATmega64 and ATmega128 64PIN. Board ET-BASE AVR ATmega64/128 uses MCU s resources on
Remote PLC system using GSM network with application to home security system
 PLC using GS with application to home security A. Alheraish, W. Alomar, and. Abu-Al-Ela Department of Electrical Engineering, King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia PLC using GS Keywords Programmable
PLC using GS with application to home security A. Alheraish, W. Alomar, and. Abu-Al-Ela Department of Electrical Engineering, King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia PLC using GS Keywords Programmable
C Programming. for Embedded Microcontrollers. Warwick A. Smith. Postbus 11. Elektor International Media BV. 6114ZG Susteren The Netherlands
 C Programming for Embedded Microcontrollers Warwick A. Smith Elektor International Media BV Postbus 11 6114ZG Susteren The Netherlands 3 the Table of Contents Introduction 11 Target Audience 11 What is
C Programming for Embedded Microcontrollers Warwick A. Smith Elektor International Media BV Postbus 11 6114ZG Susteren The Netherlands 3 the Table of Contents Introduction 11 Target Audience 11 What is
THREE YEAR DEGREE (HONS.) COURSE BACHELOR OF COMPUTER APPLICATION (BCA) First Year Paper I Computer Fundamentals
 THREE YEAR DEGREE (HONS.) COURSE BACHELOR OF COMPUTER APPLICATION (BCA) First Year Paper I Computer Fundamentals Full Marks 100 (Theory 75, Practical 25) Introduction to Computers :- What is Computer?
THREE YEAR DEGREE (HONS.) COURSE BACHELOR OF COMPUTER APPLICATION (BCA) First Year Paper I Computer Fundamentals Full Marks 100 (Theory 75, Practical 25) Introduction to Computers :- What is Computer?
DS1621 Digital Thermometer and Thermostat
 Digital Thermometer and Thermostat www.dalsemi.com FEATURES Temperature measurements require no external components Measures temperatures from 55 C to +125 C in 0.5 C increments. Fahrenheit equivalent
Digital Thermometer and Thermostat www.dalsemi.com FEATURES Temperature measurements require no external components Measures temperatures from 55 C to +125 C in 0.5 C increments. Fahrenheit equivalent
İSTANBUL AYDIN UNIVERSITY
 İSTANBUL AYDIN UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGİNEERİNG SOFTWARE ENGINEERING THE PROJECT OF THE INSTRUCTION SET COMPUTER ORGANIZATION GÖZDE ARAS B1205.090015 Instructor: Prof. Dr. HASAN HÜSEYİN BALIK DECEMBER
İSTANBUL AYDIN UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGİNEERİNG SOFTWARE ENGINEERING THE PROJECT OF THE INSTRUCTION SET COMPUTER ORGANIZATION GÖZDE ARAS B1205.090015 Instructor: Prof. Dr. HASAN HÜSEYİN BALIK DECEMBER
ADVANCED PROCESSOR ARCHITECTURES AND MEMORY ORGANISATION Lesson-17: Memory organisation, and types of memory
 ADVANCED PROCESSOR ARCHITECTURES AND MEMORY ORGANISATION Lesson-17: Memory organisation, and types of memory 1 1. Memory Organisation 2 Random access model A memory-, a data byte, or a word, or a double
ADVANCED PROCESSOR ARCHITECTURES AND MEMORY ORGANISATION Lesson-17: Memory organisation, and types of memory 1 1. Memory Organisation 2 Random access model A memory-, a data byte, or a word, or a double
Digital Systems Based on Principles and Applications of Electrical Engineering/Rizzoni (McGraw Hill
 Digital Systems Based on Principles and Applications of Electrical Engineering/Rizzoni (McGraw Hill Objectives: Analyze the operation of sequential logic circuits. Understand the operation of digital counters.
Digital Systems Based on Principles and Applications of Electrical Engineering/Rizzoni (McGraw Hill Objectives: Analyze the operation of sequential logic circuits. Understand the operation of digital counters.
Data Cables. Schmitt TTL LABORATORY ELECTRONICS II
 Data Cables Data cables link one instrument to another. Signals can attenuate or disperse on long wires. A direct wire works best for short cables of less than 10 ft. A TTL cable connection can use a Schmitt
Data Cables Data cables link one instrument to another. Signals can attenuate or disperse on long wires. A direct wire works best for short cables of less than 10 ft. A TTL cable connection can use a Schmitt
A 5 Degree Feedback Control Robotic Arm (Haptic Arm)
 A 5 Degree Feedback Control Robotic Arm (Haptic Arm) 1 Prof. Sheetal Nirve, 2 Mr.Abhilash Patil, 3 Mr.Shailesh Patil, 4 Mr.Vishal Raut Abstract: Haptics is the science of applying touch sensation and control
A 5 Degree Feedback Control Robotic Arm (Haptic Arm) 1 Prof. Sheetal Nirve, 2 Mr.Abhilash Patil, 3 Mr.Shailesh Patil, 4 Mr.Vishal Raut Abstract: Haptics is the science of applying touch sensation and control
Monitoring of Intravenous Drip Rate
 Monitoring of Intravenous Drip Rate Vidyadhar V. Kamble, Prem C. Pandey, Chandrashekar P. Gadgil, and Dinesh S. Choudhary Abstract A drip rate meter, for monitoring intravenous infusion, is developed using
Monitoring of Intravenous Drip Rate Vidyadhar V. Kamble, Prem C. Pandey, Chandrashekar P. Gadgil, and Dinesh S. Choudhary Abstract A drip rate meter, for monitoring intravenous infusion, is developed using
ASSEMBLY PROGRAMMING ON A VIRTUAL COMPUTER
 ASSEMBLY PROGRAMMING ON A VIRTUAL COMPUTER Pierre A. von Kaenel Mathematics and Computer Science Department Skidmore College Saratoga Springs, NY 12866 (518) 580-5292 pvonk@skidmore.edu ABSTRACT This paper
ASSEMBLY PROGRAMMING ON A VIRTUAL COMPUTER Pierre A. von Kaenel Mathematics and Computer Science Department Skidmore College Saratoga Springs, NY 12866 (518) 580-5292 pvonk@skidmore.edu ABSTRACT This paper
LSN 2 Computer Processors
 LSN 2 Computer Processors Department of Engineering Technology LSN 2 Computer Processors Microprocessors Design Instruction set Processor organization Processor performance Bandwidth Clock speed LSN 2
LSN 2 Computer Processors Department of Engineering Technology LSN 2 Computer Processors Microprocessors Design Instruction set Processor organization Processor performance Bandwidth Clock speed LSN 2
Palaparthi.Jagadeesh Chand. Associate Professor in ECE Department, Nimra Institute of Science & Technology, Vijayawada, A.P.
 Patient Monitoring Using Embedded Palaparthi.Jagadeesh Chand Associate Professor in ECE Department, Nimra Institute of Science & Technology, Vijayawada, A.P Abstract The aim of this project is to inform
Patient Monitoring Using Embedded Palaparthi.Jagadeesh Chand Associate Professor in ECE Department, Nimra Institute of Science & Technology, Vijayawada, A.P Abstract The aim of this project is to inform
DS1307ZN. 64 x 8 Serial Real-Time Clock
 DS137 64 x 8 Serial Real-Time Clock www.maxim-ic.com FEATURES Real-time clock (RTC) counts seconds, minutes, hours, date of the month, month, day of the week, and year with leap-year compensation valid
DS137 64 x 8 Serial Real-Time Clock www.maxim-ic.com FEATURES Real-time clock (RTC) counts seconds, minutes, hours, date of the month, month, day of the week, and year with leap-year compensation valid
ETEC 421 - Digital Controls PIC Lab 10 Pulse Width Modulation
 ETEC 421 - Digital Controls PIC Lab 10 Pulse Width Modulation Program Definition: Write a program to control the speed of a dc motor using pulse width modulation. Discussion: The speed of a dc motor is
ETEC 421 - Digital Controls PIC Lab 10 Pulse Width Modulation Program Definition: Write a program to control the speed of a dc motor using pulse width modulation. Discussion: The speed of a dc motor is
Programming Logic controllers
 Programming Logic controllers Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) is a microprocessor based system that uses programmable memory to store instructions and implement functions such as logic, sequencing,
Programming Logic controllers Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) is a microprocessor based system that uses programmable memory to store instructions and implement functions such as logic, sequencing,
Home Security System Using Gsm Modem
 RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Home Security System Using Gsm Modem Mehek Potnis 1, Ayesha Chimnani 1, Vishal Chawla 1 Mr. Amit Hatekar 2 1. Undergraduate Students, Department of EXTC, Thadomal Shahani Engineering
RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Home Security System Using Gsm Modem Mehek Potnis 1, Ayesha Chimnani 1, Vishal Chawla 1 Mr. Amit Hatekar 2 1. Undergraduate Students, Department of EXTC, Thadomal Shahani Engineering
Computer Systems Design and Architecture by V. Heuring and H. Jordan
 1-1 Chapter 1 - The General Purpose Machine Computer Systems Design and Architecture Vincent P. Heuring and Harry F. Jordan Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Colorado - Boulder
1-1 Chapter 1 - The General Purpose Machine Computer Systems Design and Architecture Vincent P. Heuring and Harry F. Jordan Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Colorado - Boulder
The Programming Interface
 : In-System Programming Features Program any AVR MCU In-System Reprogram both data Flash and parameter EEPROM memories Eliminate sockets Simple -wire SPI programming interface Introduction In-System programming
: In-System Programming Features Program any AVR MCU In-System Reprogram both data Flash and parameter EEPROM memories Eliminate sockets Simple -wire SPI programming interface Introduction In-System programming
PACKAGE OUTLINE DALLAS DS2434 DS2434 GND. PR 35 PACKAGE See Mech. Drawings Section
 PRELIMINARY DS2434 Battery Identification Chip FEATURES Provides unique ID number to battery packs PACKAGE OUTLINE Eliminates thermistors by sensing battery temperature on chip DALLAS DS2434 1 2 3 256
PRELIMINARY DS2434 Battery Identification Chip FEATURES Provides unique ID number to battery packs PACKAGE OUTLINE Eliminates thermistors by sensing battery temperature on chip DALLAS DS2434 1 2 3 256
Computer Systems Structure Main Memory Organization
 Computer Systems Structure Main Memory Organization Peripherals Computer Central Processing Unit Main Memory Computer Systems Interconnection Communication lines Input Output Ward 1 Ward 2 Storage/Memory
Computer Systems Structure Main Memory Organization Peripherals Computer Central Processing Unit Main Memory Computer Systems Interconnection Communication lines Input Output Ward 1 Ward 2 Storage/Memory
Introduction to Microcontrollers
 Introduction to Microcontrollers Motorola M68HC11 Specs Assembly Programming Language BUFFALO Topics of Discussion Microcontrollers M68HC11 Package & Pinouts Accumulators Index Registers Special Registers
Introduction to Microcontrollers Motorola M68HC11 Specs Assembly Programming Language BUFFALO Topics of Discussion Microcontrollers M68HC11 Package & Pinouts Accumulators Index Registers Special Registers
Objectives. Basics of Serial Communication. Simplex vs Duplex. CMPE328 Microprocessors (Spring 2007-08) Serial Interfacing. By Dr.
 CMPE328 Microprocessors (Spring 27-8) Serial Interfacing By Dr. Mehmet Bodur Objectives Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to: List the advantages of serial communication over parallel communication
CMPE328 Microprocessors (Spring 27-8) Serial Interfacing By Dr. Mehmet Bodur Objectives Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to: List the advantages of serial communication over parallel communication
Part Number Description Packages available
 Features 3 digital I/O Serial Data output Connects directly to RF Modules Easy Enc / Dec Pairing Function Minimal External Components Required Performs all encoding/decoding of data for Reliable Operation.
Features 3 digital I/O Serial Data output Connects directly to RF Modules Easy Enc / Dec Pairing Function Minimal External Components Required Performs all encoding/decoding of data for Reliable Operation.
SPI. Overview and Use of the PICmicro Serial Peripheral Interface. Getting Started: SPI
 SPI Overview and Use of the PICmicro Serial Peripheral Interface In this presentation, we will look at what the Serial Peripheral Interface, otherwise known as the SPI, is, and how it is used to communicate
SPI Overview and Use of the PICmicro Serial Peripheral Interface In this presentation, we will look at what the Serial Peripheral Interface, otherwise known as the SPI, is, and how it is used to communicate
Introduction the Serial Communications Huang Sections 9.2, 10.2 SCI Block User Guide SPI Block User Guide
 Introduction the Serial Communications Huang Sections 9.2, 10.2 SCI Block User Guide SPI Block User Guide Parallel Data Transfer Suppose you need to transfer data from one HCS12 to another. How can you
Introduction the Serial Communications Huang Sections 9.2, 10.2 SCI Block User Guide SPI Block User Guide Parallel Data Transfer Suppose you need to transfer data from one HCS12 to another. How can you
Advanced Microcontrollers Grzegorz Budzyń Lecture. 3: Electrical parameters of microcontrollers 8051 family
 Advanced Microcontrollers Grzegorz Budzyń Lecture 3: Electrical parameters of microcontrollers 8051 family Plan Electrical parameters of microcontrollers 8051 core(8-bit) Main features 8051 based microcontrollers
Advanced Microcontrollers Grzegorz Budzyń Lecture 3: Electrical parameters of microcontrollers 8051 family Plan Electrical parameters of microcontrollers 8051 core(8-bit) Main features 8051 based microcontrollers
AN1229. Class B Safety Software Library for PIC MCUs and dspic DSCs OVERVIEW OF THE IEC 60730 STANDARD INTRODUCTION
 Class B Safety Software Library for PIC MCUs and dspic DSCs AN1229 Authors: Veena Kudva & Adrian Aur Microchip Technology Inc. OVERVIEW OF THE IEC 60730 STANDARD INTRODUCTION This application note describes
Class B Safety Software Library for PIC MCUs and dspic DSCs AN1229 Authors: Veena Kudva & Adrian Aur Microchip Technology Inc. OVERVIEW OF THE IEC 60730 STANDARD INTRODUCTION This application note describes
Serial Communications
 April 2014 7 Serial Communications Objectives - To be familiar with the USART (RS-232) protocol. - To be able to transfer data from PIC-PC, PC-PIC and PIC-PIC. - To test serial communications with virtual
April 2014 7 Serial Communications Objectives - To be familiar with the USART (RS-232) protocol. - To be able to transfer data from PIC-PC, PC-PIC and PIC-PIC. - To test serial communications with virtual
DS1621 Digital Thermometer and Thermostat
 www.maxim-ic.com FEATURES Temperature measurements require no external components Measures temperatures from -55 C to +125 C in 0.5 C increments. Fahrenheit equivalent is -67 F to 257 F in 0.9 F increments
www.maxim-ic.com FEATURES Temperature measurements require no external components Measures temperatures from -55 C to +125 C in 0.5 C increments. Fahrenheit equivalent is -67 F to 257 F in 0.9 F increments
Module 2. Embedded Processors and Memory. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1
 Module 2 Embedded Processors and Memory Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 5 Memory-I Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Instructional Objectives After going through this lesson the student would Pre-Requisite
Module 2 Embedded Processors and Memory Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 5 Memory-I Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Instructional Objectives After going through this lesson the student would Pre-Requisite
User s Manual of Board Microcontroller ET-MEGA2560-ADK ET-MEGA2560-ADK
 User s Manual of Board Microcontroller ET-MEGA2560-ADK ET-MEGA2560-ADK Because Arduino that is the development project on AVR MCU as Open Source has been published, it is popular and widespread shortly.
User s Manual of Board Microcontroller ET-MEGA2560-ADK ET-MEGA2560-ADK Because Arduino that is the development project on AVR MCU as Open Source has been published, it is popular and widespread shortly.
(Refer Slide Time: 00:01:16 min)
 Digital Computer Organization Prof. P. K. Biswas Department of Electronic & Electrical Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No. # 04 CPU Design: Tirning & Control
Digital Computer Organization Prof. P. K. Biswas Department of Electronic & Electrical Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No. # 04 CPU Design: Tirning & Control
PROJECT PRESENTATION ON CELLPHONE OPERATED ROBOTIC ASSISTANT
 PROJECT PRESENTATION ON CELLPHONE OPERATED ROBOTIC ASSISTANT ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT SVNIT, SURAT-395007, INDIA Prepared by: Anurag Gupta (U05EC401) Dhrumeel Bakshi (U05EC326) Dileep Dhakal
PROJECT PRESENTATION ON CELLPHONE OPERATED ROBOTIC ASSISTANT ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT SVNIT, SURAT-395007, INDIA Prepared by: Anurag Gupta (U05EC401) Dhrumeel Bakshi (U05EC326) Dileep Dhakal
The Central Processing Unit:
 The Central Processing Unit: What Goes on Inside the Computer Chapter 4 Objectives Identify the components of the central processing unit and how they work together and interact with memory Describe how
The Central Processing Unit: What Goes on Inside the Computer Chapter 4 Objectives Identify the components of the central processing unit and how they work together and interact with memory Describe how
AND8336. Design Examples of On Board Dual Supply Voltage Logic Translators. Prepared by: Jim Lepkowski ON Semiconductor. http://onsemi.
 Design Examples of On Board Dual Supply Voltage Logic Translators Prepared by: Jim Lepkowski ON Semiconductor Introduction Logic translators can be used to connect ICs together that are located on the
Design Examples of On Board Dual Supply Voltage Logic Translators Prepared by: Jim Lepkowski ON Semiconductor Introduction Logic translators can be used to connect ICs together that are located on the
CHAPTER 6: Computer System Organisation 1. The Computer System's Primary Functions
 CHAPTER 6: Computer System Organisation 1. The Computer System's Primary Functions All computers, from the first room-sized mainframes, to today's powerful desktop, laptop and even hand-held PCs, perform
CHAPTER 6: Computer System Organisation 1. The Computer System's Primary Functions All computers, from the first room-sized mainframes, to today's powerful desktop, laptop and even hand-held PCs, perform
Memory Basics. SRAM/DRAM Basics
 Memory Basics RAM: Random Access Memory historically defined as memory array with individual bit access refers to memory with both Read and Write capabilities ROM: Read Only Memory no capabilities for
Memory Basics RAM: Random Access Memory historically defined as memory array with individual bit access refers to memory with both Read and Write capabilities ROM: Read Only Memory no capabilities for
Computers. Hardware. The Central Processing Unit (CPU) CMPT 125: Lecture 1: Understanding the Computer
 Computers CMPT 125: Lecture 1: Understanding the Computer Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University January 3, 2009 A computer performs 2 basic functions: 1.
Computers CMPT 125: Lecture 1: Understanding the Computer Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University January 3, 2009 A computer performs 2 basic functions: 1.
Modeling Sequential Elements with Verilog. Prof. Chien-Nan Liu TEL: 03-4227151 ext:34534 Email: jimmy@ee.ncu.edu.tw. Sequential Circuit
 Modeling Sequential Elements with Verilog Prof. Chien-Nan Liu TEL: 03-4227151 ext:34534 Email: jimmy@ee.ncu.edu.tw 4-1 Sequential Circuit Outputs are functions of inputs and present states of storage elements
Modeling Sequential Elements with Verilog Prof. Chien-Nan Liu TEL: 03-4227151 ext:34534 Email: jimmy@ee.ncu.edu.tw 4-1 Sequential Circuit Outputs are functions of inputs and present states of storage elements
SECTION C [short essay] [Not to exceed 120 words, Answer any SIX questions. Each question carries FOUR marks] 6 x 4=24 marks
![SECTION C [short essay] [Not to exceed 120 words, Answer any SIX questions. Each question carries FOUR marks] 6 x 4=24 marks SECTION C [short essay] [Not to exceed 120 words, Answer any SIX questions. Each question carries FOUR marks] 6 x 4=24 marks](/thumbs/35/17285180.jpg) UNIVERSITY OF KERALA First Degree Programme in Computer Applications Model Question Paper Semester I Course Code- CP 1121 Introduction to Computer Science TIME : 3 hrs Maximum Mark: 80 SECTION A [Very
UNIVERSITY OF KERALA First Degree Programme in Computer Applications Model Question Paper Semester I Course Code- CP 1121 Introduction to Computer Science TIME : 3 hrs Maximum Mark: 80 SECTION A [Very
C8051F020 Utilization in an Embedded Digital Design Project Course. Daren R. Wilcox Southern Polytechnic State University Marietta, Georgia
 C8051F020 Utilization in an Embedded Digital Design Project Course Daren R. Wilcox Southern Polytechnic State University Marietta, Georgia Abstract In this paper, the utilization of the C8051F020 in an
C8051F020 Utilization in an Embedded Digital Design Project Course Daren R. Wilcox Southern Polytechnic State University Marietta, Georgia Abstract In this paper, the utilization of the C8051F020 in an
Interfacing To Alphanumeric Displays
 Interfacing To Alphanumeric Displays To give directions or data values to users, many microprocessor-controlled instruments and machines need to display letters of the alphabet and numbers. In systems
Interfacing To Alphanumeric Displays To give directions or data values to users, many microprocessor-controlled instruments and machines need to display letters of the alphabet and numbers. In systems
ENGI E1112 Departmental Project Report: Computer Science/Computer Engineering
 ENGI E1112 Departmental Project Report: Computer Science/Computer Engineering Daniel Estrada Taylor, Dev Harrington, Sekou Harris December 2012 Abstract This document is the final report for ENGI E1112,
ENGI E1112 Departmental Project Report: Computer Science/Computer Engineering Daniel Estrada Taylor, Dev Harrington, Sekou Harris December 2012 Abstract This document is the final report for ENGI E1112,
Chapter 1 Computer System Overview
 Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles Chapter 1 Computer System Overview Eighth Edition By William Stallings Operating System Exploits the hardware resources of one or more processors Provides
Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles Chapter 1 Computer System Overview Eighth Edition By William Stallings Operating System Exploits the hardware resources of one or more processors Provides
Design of a High Speed Communications Link Using Field Programmable Gate Arrays
 Customer-Authored Application Note AC103 Design of a High Speed Communications Link Using Field Programmable Gate Arrays Amy Lovelace, Technical Staff Engineer Alcatel Network Systems Introduction A communication
Customer-Authored Application Note AC103 Design of a High Speed Communications Link Using Field Programmable Gate Arrays Amy Lovelace, Technical Staff Engineer Alcatel Network Systems Introduction A communication
Design and Implementation of Home Monitoring System Using RF Technology
 International Journal of Advances in Electrical and Electronics Engineering 59 Available online at www.ijaeee.com & www.sestindia.org/volume-ijaeee/ ISSN: 2319-1112 Design and Implementation of Home Monitoring
International Journal of Advances in Electrical and Electronics Engineering 59 Available online at www.ijaeee.com & www.sestindia.org/volume-ijaeee/ ISSN: 2319-1112 Design and Implementation of Home Monitoring
Von der Hardware zur Software in FPGAs mit Embedded Prozessoren. Alexander Hahn Senior Field Application Engineer Lattice Semiconductor
 Von der Hardware zur Software in FPGAs mit Embedded Prozessoren Alexander Hahn Senior Field Application Engineer Lattice Semiconductor AGENDA Overview Mico32 Embedded Processor Development Tool Chain HW/SW
Von der Hardware zur Software in FPGAs mit Embedded Prozessoren Alexander Hahn Senior Field Application Engineer Lattice Semiconductor AGENDA Overview Mico32 Embedded Processor Development Tool Chain HW/SW
