MAX PULSE TRAINING FOR CLINICIAN USE MAX PULSE DEVICE READINGS
|
|
|
- Kelly Skinner
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MAX PULSE TRAINING FOR CLINICIAN USE MAX PULSE DEVICE READINGS WAVE TYPE MEAN HEART RATE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM ECCENTRIC CONSTRICTION (EC) Represents the contraction power from the left ventricle. ARTERIAL ELASTICITY (AE) Analyzes blood circulation, vascular elasticity and the resistance of the vessels. REMAINING BLOOD VOLUME (RBV) Represents the remaining blood in the vessels after the systolic contraction of the heart.
2 DEFINITION OF PLETHYSMOGRAPHY Plethysmography is a waveform signal that indicates pulsation of chest wall and great arteries followed by the heartbeat, that is, the blood pressure and vascular diameter change through the cardiac cycle. These arterial pulsatile alterations propagating to peripheral vascular system mean "plethysmography. The goal of plethysmography is to observe the mechanical movement of the heart and kinetics of blood flow. Plethysmography manifests the pulsation of chest wall and great arteries followed by the heart beat as a waveform. Intensity of cardiac output Compliance of peripheral vessels Residual (or remained) blood volume
3 PATIENT SET UP PROCEDURE No caffeine two hours prior to the test. No acrylic on the left index finger (nail polish or gel are okay). Patient should be sitting with the left palm flat on a surface between the heart and waist. For a more accurate scan, remove any environmental irritations such as excessive noises, vibrations, etc. The temperature of a room should be kept at a comfortable level. If room temperature is too hot, peripheral vascular dilatation may occur, and if the room temperature is too cold, muscle spasm may occur. Therefore, these alterations may cause a distortion of organic results. A patient may need a few minutes to rest before starting the test. Anxiousness, tension, and stress will affect the screen negatively. Everyone should be measured in resting state as the pulse-wave is affected by blood pressure, blood flow etc. Note: It is important to educate the patient before the assessment begins, not to intentionally control breathing. For a more accurate analysis, natural breathing without any conscious respiratory manipulation is greatly desired. Avoid conditions that may put excessive pressure on the left arm or finger-tip. Those screened should be advised not to close their eyes, fall asleep, move or talk during the screening. The patient should be advised not to intentionally control breathing breath normally.
4 THE MAX PULSE DEVICE - MEASUREMENT SCREEN 1. The Heart Rate or Beats per Minute is displayed using a graph and numerical value that will change during the course of the three minute test. 2. Plethysmograph (PTG): The basic wave form signal that indicates pulsation of chest wall and great arteries followed by the heart beat. This shows the device picking up the pulse wave from the patients heartbeat through the fingertip in real time. 3. Accelerated Plethysmograph (APG): The final analysis wave form. The APG measures the blood circulation state and aging level of blood vessels in regards to vascular elasticity and hardening, through the signal at the finger tip. APG uses the second derivative of the waveform of the digital photoplethysmograph to stabilize the baseline and to separate components of the waveform more clearly and distinctly. 4. HRV (Heart Rate Variability) Tachogram: A green linear record displaying the HRV information collected during a three minute period of time (indicated by the pink bar) HR (Heart Rate) Variability: A graphical representation of time (yellow dots). The more the dots are dispersed and spread out in a group, the more adaptable the cardiovascular system. If the yellow dots are erratic, then the device has detected an artifact or irregular heart beat.
5 THE MAX PULSE DEVICE - REPORT 1 SCREEN 1. PTG (Plethysmograph) and APG (Accelerated Plethysmograph): This screen displays the three minute test average for the basic and finalized wave forms. Mathematical calculations are then derived from the multiple data points collected (i.e. points a, b, c, d & e) and are represented graphically The current date and time of the test. The drop down menu may be used to review and compare past test results. 3. Aging Vascular Health displays the average wave type, by percentage (the percentages may be spread out or 100% in a given wave type) collected by the Max Pulse during the three minute test. There are seven different wave types, with Wave Type 1 considered the ideal wave type, regardless of the patients age. The patient s Wave Type will be displayed in dark blue. The ideal wave (Wave Type 1) will be displayed in light gray in the background. If a patient s Wave Type is 1, then their Wave Type (dark blue) will be on top of the gray line, so it will not be seen. 3 3 TYPE-1 : 0.0% TYPE-2 : 99.1% TYPE-3 : 0.0% TYPE-4 : 0.9% TYPE-5 : 0.0% TYPE-6 : 0.0% TYPE-7 : 0.0%
6 THE MAX PULSE DEVICE - REPORT 1 SCREEN 4. Displays the Wave Type that was most prevalent during the three minute test. 5. This section statistically compares the patient to their peers (age and gender) and plots their data as sub-optimal, normal, or optimal. The information is graphically shown using bars and numerical values which can be compared to past or future results (see #4). 4 5 The definitions of the abbreviations, DPI, EC, AE, RBV, can also be found in the Max Pulse Patient Education Brochure and the Result Interpretation document Summary of patient results. DPI - Differential Pulse Wave Index: Represents the overall health of the cardiovascular system. DPI is the main indicator that represents aging vascular health. EC - Eccentric Constriction: Represents the contraction power of vessels from the left ventricle. AE - Arterial Elasticity: Analyzes the blood circulation, vascular elasticity and resistance of the vessels. It detects early cardiovascular disease like atherosclerosis and peripheral circulation dysfunction. RBV - Remaining Blood Volume: The remaining blood volume in the vessels after systolic contraction on the heart. If the blood vessels are healthy, there is little remaining blood volume. If the vascular state improves, the remaining blood volume will decrease, but will show an increase on the point scale. Please note this inverse relationship.
7 THE MAX PULSE DEVICE - REPORT 2 SCREEN 1. Displays the Average Heart Beat (Heart Rate (HR) or Beats Per Minute (BPM) during the three minute test. The Heart Beat measurement is an average of all the Heart Beats collected over three minutes These displays show the Highest Heart Beat and the Lowest Heart Beat collected during the three minute test. 3. The Artifact Beat displays any abnormal or erratic readings. If six beats or less are detected, than the test results are acceptable. If seven or more Artifact Beats are detected, see HRV Erratic Readings or High Artifact Beat. 4. An overall Stress Score is given in reference to the Physical and Mental Stresses and how they relate to the patient s ability to handle or deal with the internal and external stresses placed upon it. A score of 50 or less is ideal. One s Stress Score is directly related to their ANS and the relationship or disparity between the Physical/Mental Stresses and one s Stress Resistance. 5. This button will print a one page report of the information found on Report 1 and Report 2. The results are printed by the default printer as indicated within the laptop print set up. 6. HRV (Heart Rate Variability) Tachogram: A linear record displaying the HRV information collected during a three minute period of time. The wider the space between the upper and lower red line, the greater the adaptability of the cardiovascular system.
8 THE MAX PULSE DEVICE - REPORT 2 SCREEN 7. Power Spectral Density displays a linear graph of the Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) frequencies collected: Very Low Frequency (VLF), Low Frequency (LF), and High Frequency (HF). 8. A graphical representation of the ANS frequencies and how they compare to the ideal frequency levels, which is the range between the top and bottom of the I bar. Total Power (TP) is the combination of the VLF, LF, and HF A graphical representation of the ANS. The Sympathetic Nervous System (SNS) and the Parasympathetic Nervous System (PNS). The SNS is commonly referred to as fight or flight and the PNS is commonly referred to as rest and repair. The ANS is the regulatory branch of the central nervous system, that will help a patient adapt to changes in their environment. It adjusts or modifies some functions in response to stress. The ANS helps regulate blood vessel size, blood pressure and the heart s electrical activity and ability to contract. 10. A graphical representation of how the patient s stress levels and resistance are on a statistical scale of ranges. The ideal position for the Physical and Mental Stress bars are as far to the left or low stress levels. The Stress Resistance considered ideal is as far to the right as possible or High-Very High. At a minimum, the Resistance is best at or more than the Physical or Mental Stresses. The Stress Resistance represents the patient s ability to handle the internal and external stresses placed upon it.
9 WAVEFORM PATTERNS PATIENT EDUCATION PIECE
10 FREQUENCY DOMAIN PATIENT EDUCATION PIECE HEALTHY TP VLF LF HF UNHEALTHY TP VLF LF HF REDUCTION OF TP REDUCTION OF VLF REDUCTION OF LF REDUCTION OF HF - Decreased ANS function - Lowered regulation competence - Decreased ability to cope with the requirement of continuously changing environment - Lessen the ability of body temperature regulation - Hormone disorder - Loss of energy - Fatigue - Insufficient sleep - Lethargy - Chronic stress - Aging - Reduced electrical stability of heart - Functional indigestion
11 SAMPLE REPORT AND RESULTS INTERPRETATION PATIENT EDUCATION PIECE (NEXT PAGE)
12 HEART RATE VARIABILITY (HRV): Measures the degree of fluctuation in the length of intervals between heart beats. For healthy people, HRV a fluctuation in heart rates, while unhealthy people have a simple and consistent heart rate. Name MAX PULSE SAMPLE REPORT AUTONOMIC BALANCE & ACCELERATED PHOTOPLETHYSMOGRAPH HRV TACHOGRAM 140 Jane Doe ID Gender/Age F / 32 Reg. Date :44 Heart Beat 74 ARTERIOSCLEROSIS Arteriosclerosis occurs when the blood vessels that carry oxygen and nutrients from your heart to the rest of your body (arteries) become thick and stiff sometimes restricting blood flow to your organs and tissues. Healthy arteries are flexible and elastic, but over time, the walls of your arteries can harden. WAVEFORM PATTERNS & WHAT THEY MEAN FOR YOU: LEVEL 1 Blood circulation and artery state is great! HRV measures the adaptability of the cardiovascular system and autonomic nervous system, which is composed of the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) and parasympathetic nervous system (PNS). Your SNS plays the role of the accelerator, also known as flight or fight. Your PNS functions as the brake, also known as rest and repair. A healthy person has a balanced autonomic nervous system. BPM Highest Heart Beat Lowest Heart Beat Artifact 40 1 MIN 2 MIN 3 MIN TP VLF LF HF SSN PNS AGING VASCULAR HEALTH LEVEL 2 Blood circulation and artery state is good but a slight build up is beginning to occur. POWER SPECTRAL DENSITY VLF LF HF TYPE 1 : 90.9% TYPE 2: 8.0% TYPE 3: 0.0% TYPE 4: 1.1% TYPE 5: 0.0% TYPE 6: 0.0% TYPE 7: 0.0% FREQUENCY DOMAIN ANALYSIS: TP: Total Power, combination of the 3 frequencies VLF: Very Low Frequency LF: Low Frequency HF: High Frequency PHYSICAL STRESS MENTAL STRESS LOW NORMAL HIGH VERY HIGH ITEM DPI EC AE VALUE SUB-OPTIMAL (BELOW 30) NORMAL (30~70) OPTIMAL (ABOVE 70) LEVEL 3 & 4 Blood circulation and artery state is becoming poor and build up is starting. HEALTHY TP VLF LF HF UNHEALTHY TP VLF LF HF STRESS RESISTANCE RBV YOUR STRESS SCORE 46 / 100 WAVE TYPE TYPE 1 Summary of patient results as well as doctor and clinician recommendations for improving a patients cardiovascular health. LEVEL 5 Blood circulation and artery state is bad and build up is increasing. Reduction of TP: Decreased ANS function, decrease in regulatory competence and a decrease in the ability to cope with environmental change. Reduction of VLF: Decrease in the bodies ability to regulate body temperature and hormone levels. Reduction of LF: Loss of energy, fatigue, insufficient sleep and lethargy. Reduction of HF: Chronic stress, aging, reduced electrical stability of the heart. DPI - Differential Pulse Wave Index: Represents the overall health of the cardiovascular system. DPI is the main indicator that represents the aging of arteries. EC - Eccentric Constriction: Represents the contraction power of vessels from the left ventricle. AE - Arterial Elasticity: Analyzes the blood circulation, the vascular elasticity and resistance of the vessels. It detects early cardiovascular disease like atherosclerosis and peripheral circulation dysfunction. RBV - Remaining Blood Volume: The remaining blood volume in the vessels after systolic contraction on the heart. If the blood vessels are healthy, there is little remaining blood volume. If the vascular state improves, the remaining blood volume will decrease. LEVEL 6 & 7 Blood circulation and artery state is very bad and build up is becoming serious.
13 VASCULAR AGING PROCESS KEY DATA POINTS AND TERMS Differential Pulsewave Index (DPI): Represents the overall health of the cardiovascular system. DPI is the main indicator that represents the vascular aging process. A lower value represents an increase in vascular aging and vise versa. Eccentric Constriction (EC): Represents the contraction power of vessels from the left ventricle. If cardiac output is higher, the vascular state is good and the resultant value should be greater in value. Arterial Elasticity (AE): Represents the blood circulation, vascular elasticity and resistance of the vessels. It detects early cardiovascular disease like atherosclerosis and peripheral circulation dysfunction. Remaining Blood Volume (RBV): It is the remaining blood volume in the vessels after systolic contraction on the heart. If the blood vessels are healthy, there is little remaining blood volume. If the vascular state is better, the remaining blood volume will be lower. But, if the aging degree is in progress, EC will be weakened and RBV will remain high. It is an important indication of classifying the wave type.
14 HRV AND AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM (ANS) KEY DATA POINTS AND TERMS Heart Rate Variability (HRV): HRV is the degree of fluctuation in the length of intervals between heart beats. They are named R - R intervals and are measured in millisecond (ms). R-R intervals are obtained from an ECG or plethysmogram. HRV measures the overall health status and autonomic nervous system tone and balance. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS): The autonomic nervous system is responsible for non-voluntary control of our internal organs and systems like the heart, lungs, intestines, glands, etc. ANS has its central and peripheral components accessing all internal organs. There are two branches: - Sympathetic: The sympathetic branch activates the glands and organs that defend the body against attack. It is commonly called the fight-or-flight system. Its nerves direct more blood to the muscles and the brain. When activated, heart rate and blood pressure increase and blood flow to the digestive and eliminative organs decreases. For many organs increased stimulation of the sympathetic nervous system causes increase in their function, e.g. rising HR, increased heart stroke volume, adrenal secretion, etc. These specific effects serve our body as a very effective mechanism of survival by engaging in stress ( fight or flight ). - Parasympathetic (Vagal): It is anabolic, or concerned with rebuilding the body. Its nerves stimulate digestion, as well as the immune system and eliminative organs. The feeling often associated with the parasympathetic state can be one of lethargy or fatigue. This indicates a state of repair and rebuilding in progress. Increased stimulation of the parasympathetic nervous system lowers HR, decreases stroke volume, adrenal secretions, etc. These specific effects serve our body as a very effective mechanism of survival by engaging in relaxation ( rest and repair ) response.
15 FREQUENCY DOMAIN ANALYSIS The frequency-domain graph shows how much of the signal lies within each given frequency band over a range of frequencies. The Max Pulse analyzes specific domain ranges associated with HRV and ANS function: High Frequency (HF) at 0.15 to 0.4 Hz Low Frequency (LF) at 0.04 to 0.15 Hz Very Low Frequency at and 0.04 Hz Very Low Frequency (VLF): Very Low Frequency is a band of power spectrum range between and 0.04 Hz. Generally this frequency range indicates overall activity of various slow mechanisms of sympathetic function. Very Low Frequency band is calculated in milliseconds squared (ms2). With longer time recordings it is considered to represent sympathetic tone as well as slower hormonal and thermoregulatory effects. There are some findings indicating that in shorter recordings VLF has fair representation of various mental stress factors (negative emotions, worries, rumination etc.) Low Frequency (LF): Low Frequency is a band of power spectrum range between 0.04 and 0.15 Hz. This measure reflects both sympathetic and parasympathetic activity. Generally it is a strong indicator of sympathetic activity. Parasympathetic influence is represented by LF when respiration rate is lower than 7 breaths per minute or when taking a deep breath. Thus, when subject is in the state of relaxation with a slow and even breathing, the LF values can be very high indicating increased parasympathetic activity rather than an increase in sympathetic regulation. Low Frequency band is calculated in milliseconds squared (ms2). LF shows the activity of sympathetic nerve and parasympathetic nerve at the same time, but it mostly indicates the sympathetic nerve system.
16 FREQUENCY DOMAIN ANALYSIS High Frequency (HF): High Frequency is a band of power spectrum range between 0.15 and 0.4 Hz. This band reflects parasympathetic (vagal) activity. HF is also known as a respiratory band because it corresponds to the beat-to-beat variations caused by respiration. This phenomenon is known as Respiratory Sinus Arrhythmia (RSA). Heart rate increases during inhalation and decreases during exhalation. This band reflects parasympathetic or vagal activity of the ANS, which was confirmed after a large number of studies indicated that total vagal blockade essentially eliminates the HF oscillations and reduces power in the LF range. Total Power (TP): Total Power is a short-term estimate of the total power, of the power spectral density, in the range of frequencies between 0 and.4 Hz. This measure reflects overall autonomic activity where sympathetic activity is the primary contributor, and is calculated in milliseconds squared (ms2). Total Power is a general reading obtained by each of the three specific frequencies above. If it is located within the I-bar or above, it means that the autonomic nervous system is functioning well. If it falls below the I-bar, it means the autonomic nervous system is functioning poorly and that stress resistance is also weak. The clinical meaning of TP in frequency domain is similar to that of HRV. Sympathetic (SNS) and Parasympathetic (PNS) Measurement: This measure indicates overall balance between sympathetic and parasympathetic systems. It is the ratio between the power of Low Frequency and High Frequency bands. A higher ratio reflects domination of the SNS, while a lower ratio indicates domination of the PNS. This ratio is used to quantify the overall balance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems. The balance is indicated on a bar graph with 2 bars, one each for SNS and PNS. Frequency domain measurement confirms that the LF and HF oscillatory components are relative indices of cardiac sympathetic and vagal (parasympathetic) activity respectively.
17 SAMPLE REPORT 1
18 SAMPLE REPORT 2
19 SAMPLE REPORT 3
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM AND HEART RATE VARIABILITY
 AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM AND HEART RATE VARIABILITY Introduction The autonomic nervous system regulates, among other things, the functions of the vascular system. The regulation is fast and involuntary.
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM AND HEART RATE VARIABILITY Introduction The autonomic nervous system regulates, among other things, the functions of the vascular system. The regulation is fast and involuntary.
Summary. Master-/Bachelor Thesis
 Summary Master-/Bachelor Thesis "The regulating effect of breathing- therapeutic interventions relating to the autonomic nervous system" Gabriele Pieper Background Like many of the complementary methods
Summary Master-/Bachelor Thesis "The regulating effect of breathing- therapeutic interventions relating to the autonomic nervous system" Gabriele Pieper Background Like many of the complementary methods
Vtial sign #1: PULSE. Vital Signs: Assessment and Interpretation. Factors that influence pulse rate: Importance of Vital Signs
 Vital Signs: Assessment and Interpretation Elma I. LeDoux, MD, FACP, FACC Associate Professor of Medicine Vtial sign #1: PULSE Reflects heart rate (resting 60-90/min) Should be strong and regular Use 2
Vital Signs: Assessment and Interpretation Elma I. LeDoux, MD, FACP, FACC Associate Professor of Medicine Vtial sign #1: PULSE Reflects heart rate (resting 60-90/min) Should be strong and regular Use 2
The EasySense unit can detect that the Smart Q Heart Rate Sensor is connected and the range it is set to.
 Heart Rate Sensor Heart Rate Sensor (Product No PC-3147) Pulse rate Range: 0 to 200 bpm Resolution: 1 bpm Waveform Range: -2000 to 2000 mv Resolution: 1 mv Introduction The Smart Q Heart Rate Sensor monitors
Heart Rate Sensor Heart Rate Sensor (Product No PC-3147) Pulse rate Range: 0 to 200 bpm Resolution: 1 bpm Waveform Range: -2000 to 2000 mv Resolution: 1 mv Introduction The Smart Q Heart Rate Sensor monitors
Factors Affecting Blood Pressure. Vessel Elasticity Blood Volume Cardiac Output
 Factors that Affect Pressure Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction pressure is affected by several factors:
Factors that Affect Pressure Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction pressure is affected by several factors:
Heart Rate and Physical Fitness
 Heart Rate and Physical Fitness The circulatory system is responsible for the internal transport of many vital substances in humans, including oxygen, carbon dioxide, and nutrients. The components of the
Heart Rate and Physical Fitness The circulatory system is responsible for the internal transport of many vital substances in humans, including oxygen, carbon dioxide, and nutrients. The components of the
Doppler. Doppler. Doppler shift. Doppler Frequency. Doppler shift. Doppler shift. Chapter 19
 Doppler Doppler Chapter 19 A moving train with a trumpet player holding the same tone for a very long time travels from your left to your right. The tone changes relative the motion of you (receiver) and
Doppler Doppler Chapter 19 A moving train with a trumpet player holding the same tone for a very long time travels from your left to your right. The tone changes relative the motion of you (receiver) and
Effect of Coughing on Heart Rate. Evaluation copy
 Effect of Coughing on Heart Rate Computer 6 Involuntary coughing is the result of irritation of special sensory nerves in the respiratory tract. This helps to clear potentially damaging substances from
Effect of Coughing on Heart Rate Computer 6 Involuntary coughing is the result of irritation of special sensory nerves in the respiratory tract. This helps to clear potentially damaging substances from
Chapter 6: HRV Measurement and Interpretation
 Chapter 6: HRV Measurement and Interpretation Heart-rhythm analysis is more than a measurement of heart rate; it is a much deeper measurement of the complex interactions between the brain, the heart and
Chapter 6: HRV Measurement and Interpretation Heart-rhythm analysis is more than a measurement of heart rate; it is a much deeper measurement of the complex interactions between the brain, the heart and
Exchange solutes and water with cells of the body
 Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
Project 4.2.1: Heart Rate
 Project 4.2.1: Heart Rate Introduction Even before you were born, one of the first things your doctor did when you went for an office visit was listen to your heart. Your heart rate, the number of times
Project 4.2.1: Heart Rate Introduction Even before you were born, one of the first things your doctor did when you went for an office visit was listen to your heart. Your heart rate, the number of times
Time series analysis of data from stress ECG
 Communications to SIMAI Congress, ISSN 827-905, Vol. 3 (2009) DOI: 0.685/CSC09XXX Time series analysis of data from stress ECG Camillo Cammarota Dipartimento di Matematica La Sapienza Università di Roma,
Communications to SIMAI Congress, ISSN 827-905, Vol. 3 (2009) DOI: 0.685/CSC09XXX Time series analysis of data from stress ECG Camillo Cammarota Dipartimento di Matematica La Sapienza Università di Roma,
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
What to Know About. Atrial Fibrillation
 Atrial Fibrillation What to Know About Atrial Fibrillation Understanding Afib Atrial fibrillation, or Afib, is a condition in which the heart beats irregularly speeding up or slowing down, or beating too
Atrial Fibrillation What to Know About Atrial Fibrillation Understanding Afib Atrial fibrillation, or Afib, is a condition in which the heart beats irregularly speeding up or slowing down, or beating too
Our Human Body On-site student activities Years 5 6
 Our Human Body On-site student activities Years 5 6 Our Human Body On-site student activities: Years 5-6 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to
Our Human Body On-site student activities Years 5 6 Our Human Body On-site student activities: Years 5-6 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to
Activity 4.2.3: EKG. Introduction. Equipment. Procedure
 Activity 4.2.3: EKG The following is used with permission of Vernier Software and Technology. This activity is based on the experiment Analyzing the Heart with EKG from the book Human Physiology with Vernier,
Activity 4.2.3: EKG The following is used with permission of Vernier Software and Technology. This activity is based on the experiment Analyzing the Heart with EKG from the book Human Physiology with Vernier,
Physiotherapy in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Information for patients Gina Wall Senior Physiotherapist
 Physiotherapy in Rheumatoid Arthritis Information for patients Gina Wall Senior Physiotherapist What do Physiotherapists do? We conduct assessments by asking detailed questions about your symptoms, medical
Physiotherapy in Rheumatoid Arthritis Information for patients Gina Wall Senior Physiotherapist What do Physiotherapists do? We conduct assessments by asking detailed questions about your symptoms, medical
Functions of Blood System. Blood Cells
 Functions of Blood System Transport: to and from tissue cells Nutrients to cells: amino acids, glucose, vitamins, minerals, lipids (as lipoproteins). Oxygen: by red blood corpuscles (oxyhaemoglobin - 4
Functions of Blood System Transport: to and from tissue cells Nutrients to cells: amino acids, glucose, vitamins, minerals, lipids (as lipoproteins). Oxygen: by red blood corpuscles (oxyhaemoglobin - 4
Nervous System: PNS and CNS
 Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
Engage: Brainstorming Body Systems. Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below.
 Engage: Brainstorming Body s Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below. Body Nervous Circulatory Excretory Immune Digestive Respiratory Skeletal Muscular Endocrine Integumentary
Engage: Brainstorming Body s Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below. Body Nervous Circulatory Excretory Immune Digestive Respiratory Skeletal Muscular Endocrine Integumentary
Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back
 Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back to the left atria from the left ventricle, blood is pumped
Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back to the left atria from the left ventricle, blood is pumped
Stress Psychophysiology. Introduction. The Brain. Chapter 2
 Stress Psychophysiology Chapter 2 Introduction This chapter covers the process & structures activated during the physiological response to stress. Two stress pathways are available; one for short term
Stress Psychophysiology Chapter 2 Introduction This chapter covers the process & structures activated during the physiological response to stress. Two stress pathways are available; one for short term
Animal Systems: The Musculoskeletal System
 Animal Systems: The Musculoskeletal System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Animal Systems: The Musculoskeletal System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Page 1. Introduction The blood vessels of the body form a closed delivery system that begins and ends at the heart.
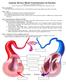 Anatomy Review: Blood Vessel Structure & Function Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction The blood vessels
Anatomy Review: Blood Vessel Structure & Function Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction The blood vessels
Efficient Heart Rate Monitoring
 Efficient Heart Rate Monitoring By Sanjeev Kumar, Applications Engineer, Cypress Semiconductor Corp. Heart rate is one of the most frequently measured parameters of the human body and plays an important
Efficient Heart Rate Monitoring By Sanjeev Kumar, Applications Engineer, Cypress Semiconductor Corp. Heart rate is one of the most frequently measured parameters of the human body and plays an important
Provided by the American Venous Forum: veinforum.org
 CHAPTER 1 NORMAL VENOUS CIRCULATION Original author: Frank Padberg Abstracted by Teresa L.Carman Introduction The circulatory system is responsible for circulating (moving) blood throughout the body. The
CHAPTER 1 NORMAL VENOUS CIRCULATION Original author: Frank Padberg Abstracted by Teresa L.Carman Introduction The circulatory system is responsible for circulating (moving) blood throughout the body. The
Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide
 Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Define the terms anatomy and physiology. List and discuss in order of increasing complexity, the body from the cell to the whole organism. Define the
Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Define the terms anatomy and physiology. List and discuss in order of increasing complexity, the body from the cell to the whole organism. Define the
About the health benefits of walking, march and Nording Walking.
 About the health benefits of walking, march and Nording Walking. Project and realization: Marta Szymańska, Kl. I F Walking is the most natural and the simplest form of physical activity. It doesn t require
About the health benefits of walking, march and Nording Walking. Project and realization: Marta Szymańska, Kl. I F Walking is the most natural and the simplest form of physical activity. It doesn t require
Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities: Years 7-8 Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities Years 7 8
 Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities Years 7 8 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to use as guides and focus material during
Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities Years 7 8 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to use as guides and focus material during
3 rd Russian-Bavarian Conference on Bio-Medical Engineering
 3 rd Russian-Bavarian Conference on Bio-Medical Engineering Blood Pressure Estimation based on Pulse Transit Time and Compensation of Vertical Position Dipl.-Inform. Med. Christian Douniama Dipl.-Ing.
3 rd Russian-Bavarian Conference on Bio-Medical Engineering Blood Pressure Estimation based on Pulse Transit Time and Compensation of Vertical Position Dipl.-Inform. Med. Christian Douniama Dipl.-Ing.
Bulletproof Stress Detective Quickstart Guide for Android
 Bulletproof Stress Detective Quickstart Guide for Android General Overview Welcome to the Stress Detective application for Android! Please follow the instructions below to start measuring your heart rate
Bulletproof Stress Detective Quickstart Guide for Android General Overview Welcome to the Stress Detective application for Android! Please follow the instructions below to start measuring your heart rate
The role of negative -ION in the improvement of our health
 What are IONS and where do they come from? IONS are particles with a positive or a negative electrical charge The percentage and number of +IONS and -IONS change depending on the time and place. IONS can
What are IONS and where do they come from? IONS are particles with a positive or a negative electrical charge The percentage and number of +IONS and -IONS change depending on the time and place. IONS can
The Body s Transport System
 Circulation Name Date Class The Body s Transport System This section describes how the heart, blood vessels, and blood work together to carry materials throughout the body. Use Target Reading Skills As
Circulation Name Date Class The Body s Transport System This section describes how the heart, blood vessels, and blood work together to carry materials throughout the body. Use Target Reading Skills As
HEART HEALTH WEEK 3 SUPPLEMENT. A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease HEART FAILURE. Relatively mild, symptoms with intense exercise
 WEEK 3 SUPPLEMENT HEART HEALTH A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease HEART FAILURE Heart failure can be defined as the failing (insufficiency) of the heart as a mechanical pump due to either acute
WEEK 3 SUPPLEMENT HEART HEALTH A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease HEART FAILURE Heart failure can be defined as the failing (insufficiency) of the heart as a mechanical pump due to either acute
Heart Rate Data Collection Software Application User Guide
 Y O R K B I O F E E D B A C K w w w. y o r k - b i o f e e d b a c k. c o. u k G l y n B l a c k e t t Heart Rate Data Collection Software Application User Guide Table of Contents 1 Introduction...1 2
Y O R K B I O F E E D B A C K w w w. y o r k - b i o f e e d b a c k. c o. u k G l y n B l a c k e t t Heart Rate Data Collection Software Application User Guide Table of Contents 1 Introduction...1 2
Circulatory System Review
 Circulatory System Review 1. Draw a table to describe the similarities and differences between arteries and veins? Anatomy Direction of blood flow: Oxygen concentration: Arteries Thick, elastic smooth
Circulatory System Review 1. Draw a table to describe the similarities and differences between arteries and veins? Anatomy Direction of blood flow: Oxygen concentration: Arteries Thick, elastic smooth
Electrocardiography I Laboratory
 Introduction The body relies on the heart to circulate blood throughout the body. The heart is responsible for pumping oxygenated blood from the lungs out to the body through the arteries and also circulating
Introduction The body relies on the heart to circulate blood throughout the body. The heart is responsible for pumping oxygenated blood from the lungs out to the body through the arteries and also circulating
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School
 Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Anatomy and Physiology Units and Anatomy and Physiology A Unit 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (6 days) Essential Question: How do the systems of the human
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Anatomy and Physiology Units and Anatomy and Physiology A Unit 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (6 days) Essential Question: How do the systems of the human
Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR
 Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR Overview This document gives you more information about the body s structure (anatomy) and function (physiology). This information will help
Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR Overview This document gives you more information about the body s structure (anatomy) and function (physiology). This information will help
Blood Pressure Regulation
 Blood Pressure Regulation Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction There are two basic mechanisms for regulating
Blood Pressure Regulation Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction There are two basic mechanisms for regulating
CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Lung cancer affects a life-sustaining system of the body, the respiratory system. The respiratory system is responsible for one of the essential
CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Lung cancer affects a life-sustaining system of the body, the respiratory system. The respiratory system is responsible for one of the essential
Measurement of Protection from Cell Phone Radiation by 8ight Protect Disc
 Measurement of Protection from Radiation by Protect Disc Research conducted by Lisa Tully, PhD, lisatully@earthlink.net Energy Medicine Research Institute, Boulder, CO May, Abstract A study was conducted
Measurement of Protection from Radiation by Protect Disc Research conducted by Lisa Tully, PhD, lisatully@earthlink.net Energy Medicine Research Institute, Boulder, CO May, Abstract A study was conducted
Heart Rhythm Scanner
 Heart Rhythm Scanner Heart Rate Variability Analysis System User s Manual Version 2.0 Copyright 1998-2005 Biocom Technologies All rights reserved. Biocom Technologies makes no claim that its products treat
Heart Rhythm Scanner Heart Rate Variability Analysis System User s Manual Version 2.0 Copyright 1998-2005 Biocom Technologies All rights reserved. Biocom Technologies makes no claim that its products treat
Evaluation copy. Analyzing the Heart with EKG. Computer
 Analyzing the Heart with EKG Computer An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring within the heart. In a healthy heart there is a natural pacemaker in
Analyzing the Heart with EKG Computer An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring within the heart. In a healthy heart there is a natural pacemaker in
Diagram 2(i): Structure of the Neuron
 Diagram 2(i): Structure of the Neuron Generally speaking, we can divide the nervous system into different parts, according to location and function. So far we have mentioned the central nervous system
Diagram 2(i): Structure of the Neuron Generally speaking, we can divide the nervous system into different parts, according to location and function. So far we have mentioned the central nervous system
Research on physiological signal processing
 Research on physiological signal processing Prof. Tapio Seppänen Biosignal processing team Department of computer science and engineering University of Oulu Finland Tekes 10-12.9.2013 Research topics Research
Research on physiological signal processing Prof. Tapio Seppänen Biosignal processing team Department of computer science and engineering University of Oulu Finland Tekes 10-12.9.2013 Research topics Research
Detection of Heart Diseases by Mathematical Artificial Intelligence Algorithm Using Phonocardiogram Signals
 International Journal of Innovation and Applied Studies ISSN 2028-9324 Vol. 3 No. 1 May 2013, pp. 145-150 2013 Innovative Space of Scientific Research Journals http://www.issr-journals.org/ijias/ Detection
International Journal of Innovation and Applied Studies ISSN 2028-9324 Vol. 3 No. 1 May 2013, pp. 145-150 2013 Innovative Space of Scientific Research Journals http://www.issr-journals.org/ijias/ Detection
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot
 Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
Edwards FloTrac Sensor & Edwards Vigileo Monitor. Measuring Continuous Cardiac Output with the FloTrac Sensor and Vigileo Monitor
 Edwards FloTrac Sensor & Edwards Vigileo Monitor Measuring Continuous Cardiac Output with the FloTrac Sensor and Vigileo Monitor 1 Topics System Configuration Physiological Principles Pulse pressure relationship
Edwards FloTrac Sensor & Edwards Vigileo Monitor Measuring Continuous Cardiac Output with the FloTrac Sensor and Vigileo Monitor 1 Topics System Configuration Physiological Principles Pulse pressure relationship
Anatomi & Fysiologi 060301. The cardiovascular system (chapter 20) The circulation system transports; What the heart can do;
 The cardiovascular system consists of; The cardiovascular system (chapter 20) Principles of Anatomy & Physiology 2009 Blood 2 separate pumps (heart) Many blood vessels with varying diameter and elasticity
The cardiovascular system consists of; The cardiovascular system (chapter 20) Principles of Anatomy & Physiology 2009 Blood 2 separate pumps (heart) Many blood vessels with varying diameter and elasticity
Low Blood Pressure. This reference summary explains low blood pressure and how it can be prevented and controlled.
 Low Blood Pressure Introduction Low blood pressure, or hypotension, is when your blood pressure reading is 90/60 or lower. Some people have low blood pressure all of the time. In other people, blood pressure
Low Blood Pressure Introduction Low blood pressure, or hypotension, is when your blood pressure reading is 90/60 or lower. Some people have low blood pressure all of the time. In other people, blood pressure
Milwaukee School of Engineering Gerrits@msoe.edu. Case Study: Factors that Affect Blood Pressure Instructor Version
 Case Study: Factors that Affect Blood Pressure Instructor Version Goal This activity (case study and its associated questions) is designed to be a student-centered learning activity relating to the factors
Case Study: Factors that Affect Blood Pressure Instructor Version Goal This activity (case study and its associated questions) is designed to be a student-centered learning activity relating to the factors
Breathing and Holding Your Breath copyright, 2005, Dr. Ingrid Waldron and Jennifer Doherty, Department of Biology, University of Pennsylvania 1
 Breathing and Holding Your Breath copyright, 2005, Dr. Ingrid Waldron and Jennifer Doherty, Department of Biology, University of Pennsylvania 1 Introduction Everybody breathes all day, every day. Why?
Breathing and Holding Your Breath copyright, 2005, Dr. Ingrid Waldron and Jennifer Doherty, Department of Biology, University of Pennsylvania 1 Introduction Everybody breathes all day, every day. Why?
The Take-Apart Human Body
 The Take-Apart Human Body As any teacher knows, children are naturally curious about their bodies. Their questions are endless, and present a tremendous educational opportunity: How do my ears work? Where
The Take-Apart Human Body As any teacher knows, children are naturally curious about their bodies. Their questions are endless, and present a tremendous educational opportunity: How do my ears work? Where
Sensory Sanctuary Staff Occupational Therapy Stress Management Program julie.greenberg@downstate.edu
 Abdominal Breathing Technique How it s done: With one hand on the chest and the other on the belly, take a deep breath in through the nose, ensuring the diaphragm (not the chest) inflates with enough air
Abdominal Breathing Technique How it s done: With one hand on the chest and the other on the belly, take a deep breath in through the nose, ensuring the diaphragm (not the chest) inflates with enough air
Monitoring EKG. Evaluation copy
 Monitoring EKG Computer 28 An electrocardiogram, or EKG, is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring within the heart. A typical EKG tracing consists of five identifiable deflections. Each
Monitoring EKG Computer 28 An electrocardiogram, or EKG, is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring within the heart. A typical EKG tracing consists of five identifiable deflections. Each
Cardiovascular Physiology
 Cardiovascular Physiology Heart Physiology for the heart to work properly contraction and relaxation of chambers must be coordinated cardiac muscle tissue differs from smooth and skeletal muscle tissues
Cardiovascular Physiology Heart Physiology for the heart to work properly contraction and relaxation of chambers must be coordinated cardiac muscle tissue differs from smooth and skeletal muscle tissues
Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions
 Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions Student: 1. The pulmonary veins are unusual as veins because they are transporting. A. oxygenated blood B. de-oxygenated blood C. high fat blood D. nutrient-rich
Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions Student: 1. The pulmonary veins are unusual as veins because they are transporting. A. oxygenated blood B. de-oxygenated blood C. high fat blood D. nutrient-rich
MEASURING AND RECORDING BLOOD PRESSURE
 MEASURING AND RECORDING BLOOD PRESSURE INTRODUCTION The blood pressure, along with the body temperature, pulse, and respirations, is one of the vital signs. These measurements are used to quickly, easily,
MEASURING AND RECORDING BLOOD PRESSURE INTRODUCTION The blood pressure, along with the body temperature, pulse, and respirations, is one of the vital signs. These measurements are used to quickly, easily,
Practical class 3 THE HEART
 Practical class 3 THE HEART OBJECTIVES By the time you have completed this assignment and any necessary further reading or study you should be able to:- 1. Describe the fibrous pericardium and serous pericardium,
Practical class 3 THE HEART OBJECTIVES By the time you have completed this assignment and any necessary further reading or study you should be able to:- 1. Describe the fibrous pericardium and serous pericardium,
Chapter 16: Circulation
 Section 1 (The Body s Transport System) Chapter 16: Circulation 7 th Grade Cardiovascular system (the circulatory system) includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood carries needed substances to the cells
Section 1 (The Body s Transport System) Chapter 16: Circulation 7 th Grade Cardiovascular system (the circulatory system) includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood carries needed substances to the cells
Exercise, the Electrocardiogram, and Peripheral Circulation
 iworx Physiology Lab Experiment Experiment HH-3 Exercise, the Electrocardiogram, and Peripheral Circulation Note: The lab presented here is intended for evaluation purposes only. iworx users should refer
iworx Physiology Lab Experiment Experiment HH-3 Exercise, the Electrocardiogram, and Peripheral Circulation Note: The lab presented here is intended for evaluation purposes only. iworx users should refer
Altitude. Thermoregulation & Extreme Environments. The Stress of Altitude. Reduced PO 2. O 2 Transport Cascade. Oxygen loading at altitude:
 Altitude Thermoregulation & Extreme Environments Reduced PO 2 The Stress of Altitude O 2 Transport Cascade Progressive change in environments oxygen pressure & various body areas Oxygen loading at altitude:
Altitude Thermoregulation & Extreme Environments Reduced PO 2 The Stress of Altitude O 2 Transport Cascade Progressive change in environments oxygen pressure & various body areas Oxygen loading at altitude:
31.1 The Neuron. BUILD Vocabulary. Lesson Objectives
 Name Class Date 31.1 The Neuron Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the nervous system. Describe the function of neurons. Describe how a nerve impulse is transmitted. BUILD Vocabulary A. The chart
Name Class Date 31.1 The Neuron Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the nervous system. Describe the function of neurons. Describe how a nerve impulse is transmitted. BUILD Vocabulary A. The chart
The Circulatory System. Chapter 17 Lesson 1
 The Circulatory System Chapter 17 Lesson 1 Functions of the Circulatory System Your circulatory system maintains an internal environment in which all the cells in your body are nourished. As your heart
The Circulatory System Chapter 17 Lesson 1 Functions of the Circulatory System Your circulatory system maintains an internal environment in which all the cells in your body are nourished. As your heart
What Can I Do about Atrial Fibrillation (AF)?
 Additional Device Information 9529 Reveal XT Insertable Cardiac Monitor The Reveal XT Insertable Cardiac Monitor is an implantable patientactivated and automatically activated monitoring system that records
Additional Device Information 9529 Reveal XT Insertable Cardiac Monitor The Reveal XT Insertable Cardiac Monitor is an implantable patientactivated and automatically activated monitoring system that records
North Bergen School District Benchmarks
 Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Laerdal Patient Monitor Help Page 1 June 14, 2012, Rev E
 Laerdal Patient Monitor Help Page 1 Using the Laerdal Patient Monitor The Laerdal Patient Monitor software is used to simulate a typical Patient Monitor found in hospitals and ambulances. It is made available
Laerdal Patient Monitor Help Page 1 Using the Laerdal Patient Monitor The Laerdal Patient Monitor software is used to simulate a typical Patient Monitor found in hospitals and ambulances. It is made available
Chapter 12. Temperature Regulation. Temperature Regulation. Heat Balance. An Overview of Heat Balance. Temperature Regulation. Temperature Regulation
 Chapter 12 Body core temperature regulation Critical for: Cellular structures Metabolic pathways Too high Protein structure of cells destroyed Too low Slowed metabolism Cardiac arrhythmias Homeothermic
Chapter 12 Body core temperature regulation Critical for: Cellular structures Metabolic pathways Too high Protein structure of cells destroyed Too low Slowed metabolism Cardiac arrhythmias Homeothermic
The heart then repolarises (or refills) in time for the next stimulus and contraction.
 Atrial Fibrillation BRIEFLY, HOW DOES THE HEART PUMP? The heart has four chambers. The upper chambers are called atria. One chamber is called an atrium, and the lower chambers are called ventricles. In
Atrial Fibrillation BRIEFLY, HOW DOES THE HEART PUMP? The heart has four chambers. The upper chambers are called atria. One chamber is called an atrium, and the lower chambers are called ventricles. In
Before you know about your future see your past before improving your future hair see what has been and is the state of your hair now Ravi Bhanot
 Chapter 1 All you need to know about hair almost Before you know about your future see your past before improving your future hair see what has been and is the state of your hair now Ravi Bhanot Typically
Chapter 1 All you need to know about hair almost Before you know about your future see your past before improving your future hair see what has been and is the state of your hair now Ravi Bhanot Typically
Endocrine System: Practice Questions #1
 Endocrine System: Practice Questions #1 1. Removing part of gland D would most likely result in A. a decrease in the secretions of other glands B. a decrease in the blood calcium level C. an increase in
Endocrine System: Practice Questions #1 1. Removing part of gland D would most likely result in A. a decrease in the secretions of other glands B. a decrease in the blood calcium level C. an increase in
Human Growth and Reproduction
 Human Growth and Reproduction Sperm reach ovum and cluster around it Only one sperm is allowed to penetrate egg When the sperm penetrates the egg, the egg immediately releases a chemical creating a hard
Human Growth and Reproduction Sperm reach ovum and cluster around it Only one sperm is allowed to penetrate egg When the sperm penetrates the egg, the egg immediately releases a chemical creating a hard
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What term is used to refer to the process of electrical discharge and the flow of electrical
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What term is used to refer to the process of electrical discharge and the flow of electrical
Pulmonary Ventilation
 Pulmonary Ventilation Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction Pulmonary ventilation, or breathing, is the
Pulmonary Ventilation Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction Pulmonary ventilation, or breathing, is the
Reduce Stress with This 15-Minute Restorative Yoga Sequence
 Reduce Stress with This 15-Minute Restorative Yoga Sequence Try this short, stress-busting restorative yoga sequence to ease tension around the holidays, at work, and more Stress it s something everyone
Reduce Stress with This 15-Minute Restorative Yoga Sequence Try this short, stress-busting restorative yoga sequence to ease tension around the holidays, at work, and more Stress it s something everyone
Therefore, the first step to successfully managing anxiety is to learn to understand and recognize it. Self-awareness is essential. The Facts!
 WHAT IS ANXIETY? Why is it important to learn about anxiety? Most people do not recognize their anxiety for what it is, and instead think there is something wrong with them. Some people are preoccupied
WHAT IS ANXIETY? Why is it important to learn about anxiety? Most people do not recognize their anxiety for what it is, and instead think there is something wrong with them. Some people are preoccupied
How to measure blood pressure using digital monitors
 How to measure blood pressure using digital monitors What is high blood pressure? Blood pressure is the pressure exerted by circulating blood upon the walls of blood vessels. Systolic pressure is the blood
How to measure blood pressure using digital monitors What is high blood pressure? Blood pressure is the pressure exerted by circulating blood upon the walls of blood vessels. Systolic pressure is the blood
MEDITATION TO ADJUST YOUR MAGNETIC FIELD AFTER AN EARTHQUAKE
 MEDITATION TO ADJUST YOUR MAGNETIC FIELD AFTER AN EARTHQUAKE What It Will Do for You: The magnetic relationship of the 2 hemispheres of the brain is readjusted with this meditation. How to Do It Sit straight.
MEDITATION TO ADJUST YOUR MAGNETIC FIELD AFTER AN EARTHQUAKE What It Will Do for You: The magnetic relationship of the 2 hemispheres of the brain is readjusted with this meditation. How to Do It Sit straight.
Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture
 1 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 2 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and certain
1 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 2 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and certain
FUNCTIONAL EEG ANALYZE IN AUTISM. Dr. Plamen Dimitrov
 FUNCTIONAL EEG ANALYZE IN AUTISM Dr. Plamen Dimitrov Preamble Autism or Autistic Spectrum Disorders (ASD) is a mental developmental disorder, manifested in the early childhood and is characterized by qualitative
FUNCTIONAL EEG ANALYZE IN AUTISM Dr. Plamen Dimitrov Preamble Autism or Autistic Spectrum Disorders (ASD) is a mental developmental disorder, manifested in the early childhood and is characterized by qualitative
CARDIAC REHABILITATION PROGRAM
 CARDIAC REHABILITATION PROGRAM Preparation for the Cardiac Rehabilitation Program After your heart problem is stable, your physician or cardiologist will refer you to the Cardiac Rehabilitation program.
CARDIAC REHABILITATION PROGRAM Preparation for the Cardiac Rehabilitation Program After your heart problem is stable, your physician or cardiologist will refer you to the Cardiac Rehabilitation program.
Congestive Heart Failure
 Healthy People 2010 Conference Health Education on the Internet Welcome Mr. System Administrator Congestive Heart Failure What is congestive heart failure? How does it occur? What are the symptoms? How
Healthy People 2010 Conference Health Education on the Internet Welcome Mr. System Administrator Congestive Heart Failure What is congestive heart failure? How does it occur? What are the symptoms? How
Heart Diseases and their Complications
 Heart Diseases and their Complications Health Promotion and Education Program Rev. 2014 2014, MMM Healthcare, Inc. - PMC Medicare Choice, Inc. Reproduction of this material is prohibited. MP-HEP-PPT-252-01-021914-E
Heart Diseases and their Complications Health Promotion and Education Program Rev. 2014 2014, MMM Healthcare, Inc. - PMC Medicare Choice, Inc. Reproduction of this material is prohibited. MP-HEP-PPT-252-01-021914-E
LUNG VOLUMES AND CAPACITIES
 LUNG VOLUMES AND CAPACITIES STANDARDS 3.1.10A, 3.1.12A Identify the function of subsystems within a larger system; analyze and describe the function, interaction and relationship Westminster College among
LUNG VOLUMES AND CAPACITIES STANDARDS 3.1.10A, 3.1.12A Identify the function of subsystems within a larger system; analyze and describe the function, interaction and relationship Westminster College among
The Power Plate is the innovative, time saving and results driven way to improve your fitness and well being.
 Welcome to the world of Power Plate Exercise The Power Plate is the innovative, time saving and results driven way to improve your fitness and well being. It works by accelerating the body s natural response
Welcome to the world of Power Plate Exercise The Power Plate is the innovative, time saving and results driven way to improve your fitness and well being. It works by accelerating the body s natural response
Ventilation Perfusion Relationships
 Ventilation Perfusion Relationships VENTILATION PERFUSION RATIO Ideally, each alveolus in the lungs would receive the same amount of ventilation and pulmonary capillary blood flow (perfusion). In reality,
Ventilation Perfusion Relationships VENTILATION PERFUSION RATIO Ideally, each alveolus in the lungs would receive the same amount of ventilation and pulmonary capillary blood flow (perfusion). In reality,
2161-1 - Page 1. Name: 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. Questions 10 and 11 refer to the following:
 Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
Chapter 15. The Autonomic Nervous. The Autonomic Nervous System. Autonomic Motor Pathways. ANS vs. SNS
 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter 15 The subconscious involuntary nervous system Regulates activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle & certain glands The Autonomic Nervous System 1 2 ANS vs. SNS Somatic
The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter 15 The subconscious involuntary nervous system Regulates activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle & certain glands The Autonomic Nervous System 1 2 ANS vs. SNS Somatic
Pattern Identification According to Qi and Blood
 CHAPTER EIGHT Pattern Identification According to Qi and Blood Pattern identification according to qi and blood is a commonly used method for pattern identification which analyzes manifestations obtained
CHAPTER EIGHT Pattern Identification According to Qi and Blood Pattern identification according to qi and blood is a commonly used method for pattern identification which analyzes manifestations obtained
Please Do Not Call 911
 The Last Hours of Life - What to Expect Names and Phone Numbers You May Need Name Phone Family Dr. Palliative Dr. After Hours Access Centre Visiting Nurse Hospice Clergy Funeral Contact Please Do Not Call
The Last Hours of Life - What to Expect Names and Phone Numbers You May Need Name Phone Family Dr. Palliative Dr. After Hours Access Centre Visiting Nurse Hospice Clergy Funeral Contact Please Do Not Call
Republic Polytechnic. Continuing Education & Training. Course Structure: Anatomy & Physiology
 Republic Polytechnic Continuing Education & Training Course Structure: Anatomy & Physiology Module Anatomy and Physiology Description This module introduces the basic human anatomical organization, tissue
Republic Polytechnic Continuing Education & Training Course Structure: Anatomy & Physiology Module Anatomy and Physiology Description This module introduces the basic human anatomical organization, tissue
A Patient s Guide to the Calypso System for Breast Cancer Treatment
 A Patient s Guide to the Calypso System for Breast Cancer Treatment Contents Introduction How Radiation Works To Treat Cancer Radiation Treatment for Breast Cancer Special Concerns for Treating the Left
A Patient s Guide to the Calypso System for Breast Cancer Treatment Contents Introduction How Radiation Works To Treat Cancer Radiation Treatment for Breast Cancer Special Concerns for Treating the Left
MEASURING VITAL SIGNS TRAINING CHECKLIST
 Measuring Vital Signs A guide to help Direct Support Professionals learn how to measure, and report vital sign measurements. Outcomes: Know how to take each individual s vital signs. Demonstrate the correct
Measuring Vital Signs A guide to help Direct Support Professionals learn how to measure, and report vital sign measurements. Outcomes: Know how to take each individual s vital signs. Demonstrate the correct
General Information about Sleep Studies and What to Expect
 General Information about Sleep Studies and What to Expect Why do I need a sleep study? Your doctor has ordered a sleep study because your doctor is concerned you may have a sleep disorder that is impacting
General Information about Sleep Studies and What to Expect Why do I need a sleep study? Your doctor has ordered a sleep study because your doctor is concerned you may have a sleep disorder that is impacting
Objective: Identify effects of stress on everyday issues and strategies to reduce or control stress.
 Lesson Plan: Dealing with Stress Objective: Identify effects of stress on everyday issues and strategies to reduce or control stress. Time: 45-60 minutes Structure: On-line homework before class (Stress
Lesson Plan: Dealing with Stress Objective: Identify effects of stress on everyday issues and strategies to reduce or control stress. Time: 45-60 minutes Structure: On-line homework before class (Stress
Chapter 15. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes. general properties Anatomy. Autonomic effects on target organs
 Chapter 15 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes general properties Anatomy Autonomic effects on target organs Central control of autonomic function 15-1 Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Chapter 15 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes general properties Anatomy Autonomic effects on target organs Central control of autonomic function 15-1 Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Laboratory Guide. Anatomy and Physiology
 Laboratory Guide Anatomy and Physiology TBME04, Fall 2010 Name: Passed: Last updated 2010-08-13 Department of Biomedical Engineering Linköpings Universitet Introduction This laboratory session is intended
Laboratory Guide Anatomy and Physiology TBME04, Fall 2010 Name: Passed: Last updated 2010-08-13 Department of Biomedical Engineering Linköpings Universitet Introduction This laboratory session is intended
GENERAL HEART DISEASE KNOW THE FACTS
 GENERAL HEART DISEASE KNOW THE FACTS WHAT IS Heart disease is a broad term meaning any disease affecting the heart. It is commonly used to refer to coronary heart disease (CHD), a more specific term to
GENERAL HEART DISEASE KNOW THE FACTS WHAT IS Heart disease is a broad term meaning any disease affecting the heart. It is commonly used to refer to coronary heart disease (CHD), a more specific term to
Raynaud s phenomenon, Scleroderma and associated disorders
 Patient information Raynaud s phenomenon, Scleroderma and associated disorders Vascular Surgery Surgical Division PIF 202/V5 What is Raynaud s phenomenon? Raynaud s phenomenon is a condition where the
Patient information Raynaud s phenomenon, Scleroderma and associated disorders Vascular Surgery Surgical Division PIF 202/V5 What is Raynaud s phenomenon? Raynaud s phenomenon is a condition where the
