INCCA Indian Network for Climate Change Assessment India: Greenhouse Gas Emissions 2007
|
|
|
- Beverley Barnett
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 INCCA Indian Network for Climate Change Assessment India: Greenhouse Gas Emissions 2007 Executive Summary Ministry of Environment and Forests Government of India May 2010
2
3 INCCA Indian Network for Climate Change Assessment India: Greenhouse Gas Emissions 2007 Executive Summary Ministry of Environment and Forests Government of India May 2010
4 Foreword I am pleased to introduce the publication India s Greenhouse Gas Emissions This Report, being brought out by the Indian Network of Climate Change Assessment (INCCA), provides updated information on India s Greenhouse Gas Emissions for the year Until today, the only official emissions estimates available were for the year This was very inadequate. I had been keen that to enable informed decision-making and to ensure transparency, we should publish updated emissions estimates. I am glad that our team of scientists took up this challenge and have prepared this report with estimates for 2007 in record time. More than 80 scientists from 17 institutions across India have contributed to this Assessment. I am particularly pleased that with this publication, India has become the first non-annex I (i.e. developing) country to publish such updated numbers. I am also happy to announce that we will publish our emissions inventory in a two-year cycle going forward. We will be the first developing country to do so.
5 According to the results, India ranks 5 th in aggregate GHG emissions in the world, behind USA, China, EU and Russia in Interestingly, the emissions of USA and China are almost 4 times that of India in It is also noteworthy that the emissions intensity of India s GDP declined by more than 30% during the period , due to the efforts and policies that we are proactively putting in place. This is a trend we intend to continue. As you are aware, we have already announced our intent to further reduce the emissions intensity of our GDP by 20-25% between 2005 and 2020 even as we pursue the path of inclusive growth. INCCA, launched on 14 th October 2009, is a network comprising 127 research institutions, tasked with undertaking research on the science of climate change and its impacts on the different sectors of the economy across the various regions of India. As I mentioned at the launch, we must make the 3 M s Measurement, Modelling and Monitoring the essence of our policy making and we must build indigenous capacity for this. This report is a step in this direction. I look forward to INCCA s next major publication a 4X4 assessment of the impacts of climate change on four sectors water resources, agriculture, forests and human health in four critical regions of India the Himalayan region, North east, Western Ghats and Coastal India, which will be released in November Once again, I congratulate our team of scientists who have put this assessment together. I look forward to the results of the other upcoming studies of INCCA. Jairam Ramesh Minister of State for Environment & Forests (Independent Charge)
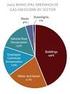
6 Executive Summary This assessment provides information on India s emissions of Greenhouse gases (Carbon Dioxide [CO 2 ], Methane [CH 4 ] and Nitrous Oxide [N 2 O]) emitted from anthropogenic activities at national level from: Energy; Industry; Agriculture; Waste; and Land Use Land Use Change & Forestry (LULUCF). The distribution of GHG emissions by sector are shown in Figure ES1. Detailed emissions estimates are provided in Annexure. Note: Other Energy: includes GHG emissions from petroleum refining, manufacturing of solid fuel, commercial & institutional sector, agriculture & fisheries and fugitive emissions from mining, transport and storage of coal, oil and natural gas. Other Industry: includes GHG emissions from production of glass and ceramics, soda ash, ammonia, nitric acid, carbides, titanium dioxide, methanol, ethylene oxide, acrylonitrile, carbon black, caprolactam, ferro alloys, aluminium, lead, zinc, copper, pulp and paper, food processing, textile, leather, mining and quarrying, non specific industries and use of lubricants and paraffin wax. Agriculture: includes GHG emissions from livestock, rice cultivation, agricultural soils and burning of crop residue. Waste: includes GHG emissions from municipal solid waste (MSW), industrial and domestic waste water. LULUCF: includes GHG emissions and removals from changes in forest land, crop land, grass land, wet land, settlements and combustion of fuel wood in forests. Figure ES1: GHG emissions by sector in 2007 (million tons of CO 2 eq). Figures on top indicate the emissions by sectors and in brackets indicate % of emission of the category with respect to the net CO 2 equivalent emissions. See glossary for defination of CO 2 equivalent. Indian Network for Climate Change Assessment Page 64
7 A. KEY RESULTS The net Greenhouse Gas (GHG) emissions from India in 2007, that is emissions with LULUCF, were million tons of CO 2 equivalent (eq) of which - CO 2 emissions were million tons; - CH 4 emissions were million tons; and - N 2 O emissions were 0.24 million tons GHG emissions from Energy, Industry, Agriculture, and Waste sectors constituted 58%, 22%, 17% and 3% of the net CO 2 eq emissions respectively. Energy sector emitted million tons of CO 2 eq, of which million tons of CO 2 eq were emitted from electricity generation and million tons of CO 2 eq from the transport sector. Industry sector emitted million tons of CO 2 eq. LULUCF sector was a net sink. It sequestered million tons of CO 2. India s per capita CO 2 eq emissions including LULUCF were 1.5 tons/capita in B AND 2007 GHG EMISSIONS - A COMPARISON The 1994 assessment is available in India s Initial National Communication to the UNFCCC. Both the 1994 and 2007 assessments have been prepared using the IPCC guidelines for preparation of national greenhouse gas emissions by sources and removal by sinks. The distinctive key features of the two assessments and the improvements in the 2007 assessments are indicated in Box ES1. The total GHG emissions without LULUCF have grown from million tons in 1994 to million tons in 2007 at a compounded annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.3% and with LULUCF the CAGR is 2.9%. Between 1994 and 2007, some of the sectors indicate significant growth in GHG emissions such as cement production (6.0%), electricity generation (5.6%) and transport (4.5%). A comparative analysis of GHG emissions by sector is shown in Table ES1. Box ES1: 2007 and Key Methodological Features and Improvements 1994 Assessment 2007 Assessment Estimates made using only revised 1996 IPCC guidelines. LULUCF included emissions from changes in forest land. Emission factors were a mix of default factors taken from IPCC and country specific (CS) emission factors. 26% of the source categories used CS factors. The 1994 assessment splits the emissions from industry in to two parts - fossil fuel and process. The fossil fuel emissions are reported in Energy and process emissions in Industry. In 1994, 7% of the total CO 2 eq emissions were made using Tier III approach. Estimates made using revised IPCC 1996 guidelines (1997), IPCC Good Practice Guidance (2000), the LULUCF Good Practice Guidance (2003). Carbon pools in addition to forests have been considered in the LULUCF sector (crop land, grass land, settlements). Emission factors were also a mix of default and CS but leading to improved accuracy as more number of CSs have been used in this assessment (35% of the source categories used CS factors). The 2007 assessment reports both fossil fuel related and process based emissions from Industry as a part of the Industry sector. In 2007, 12% of the emissions are made using Tier III approach, implying greater accuracy. Page 75 India: Greenhouse Gas Emissions 2007
8 Table ES1: A comparison of GHG emissions by sector between 1994 and 2007 in million tons of CO 2 eq CAGR (%) Electricity (28.4%) (37.8%) 5.6 Transport (6.4%) (7.5%) 4.5 Residential (6.3%) (7.2%) 4.4 Other Energy (6.3%) (5.3%) 1.9 Cement (4.9%) (6.8%) 6.0 Iron & Steel (7.2%) (6.2%) 2.0 Other Industry (10.0%) (8.7%) 2.2 Agriculture (27.6%) (17.6%) -0.2 Waste (1.9%) (3.0%) 7.3 Total without LULUCF LULUCF Total with LULUCF Note: Figure in brackets indicate percentage emissions from each sector with respect to total GHG emissions without LULUCF in 1994 and 2007 respectively C. IMPLEMENTATION ARRANGEMENT This assessment has been prepared under the aegis of the Indian Network for Climate Change Assessment (INCCA). An initiative being coordinated by the Ministry of Environment and Forests, Government of India. (Box ES2 & Figure ES2). D. SECTORAL DESCRIPTION OF THE EMISSIONS Energy: The energy sector emitted million tons of CO 2 eq due to fossil fuel combustion in electricity generation, transport, commercial/institutional establishments, agriculture/fisheries, and energy intensive industries such as petroleum refining and manufacturing of solid fuels, including biomass use in residential sector. Fugitive emissions from mining and extraction of coal, oil Box ES2: Indian Network for Climate Change Assessment (INCCA) Launched on October 14, 2009, the network comprises of 127 institutions and 228 scientists across India Role - Assess the drivers and implications of climate change through scientific research - Prepare climate change assessments once every two years (GHG estimations and impacts of climate change, associated vulnerabilities and adaptation) - Develop decision support systems - Build capacity towards management of climate change related risks and opportunities Indian Network for Climate Change Assessment Page 86
9 2007 Assessment BCKV Bidhan Chandra Krishi Viswavidyalaya CII Confederation of Indian Industry CIMFR Central Institute of Mining & Fuel Research CLRI Central Leather Research Institute CMA Cement Manufacturing Association CRRI Central Road Research Institute FSI Forest Survey of India IARI Indian Agricultural Research Institute IGFRI Indian Grass & Fodder Research Institute IISc Indian Institute of Science IVRI Indian Veterinary Research Institute NDRI National Dairy Research Institute NEERI National Environment Engineering Research Institute NPL National Physical Laboratory NRSC National Remote Sensing Centre PPAC Petroleum Planning and Analysis Cell TERI The Energy and Resources Institute Figure ES2: INCCA and Network for preparing the Greenhouse Gas Emissions For the complete list of institutions participating in INCCA, see Annexure 4 of the main document. Page 97 India: Greenhouse Gas Emissions 2007
10 Figure ES3: GHG emissions from Energy Sector (million tons of CO 2 eq). and natural gas are also accounted for in the energy sector. The distribution of the emissions across the source categories in energy sector is shown in Figure ES3. Electricity Generation: The total greenhouse gas emissions from electricity generation in 2007 was million tons CO 2 eq. This includes both grid and captive power. The CO 2 eq emissions from electricity generation were 65.4% of the total CO 2 eq emitted from the energy sector. Coal constituted about 90% of the total fuel mix used. Petroleum Refining and Solid Fuel Manufacturing: These energy intensive industries emitted million tons of CO 2 eq in The solid fuels include manufacturing of coke & briquettes. Transport: The transport sector emissions are reported from road transport, aviation, railways and navigation. In 2007, the transport sector emitted million tons of CO 2 eq. Road transport, being the dominant mode of transport in the country, emitted 87% of the total CO 2 equivalent emissions from the transport sector. The aviation sector in comparison only emitted 7% of the total CO 2 eq emissions. The rest were emitted by railways (5%) and navigation (1%) sectors. The bunker emissions from aviation and navigation have also been estimated but are not counted in the national totals. (Figure ES4). Residential & Commercial: The residential sector in India is one of the largest consumers of fuel outside the energy industries. Biomass constitutes the largest portion of the total fuel mix use in this sector. Commercial and institutional sector uses oil & natural gas over and above the conventional electricity for its power needs. The total CO 2 eq emission from residential & commercial/institution sector was million tons of CO 2 eq in Agriculture & Fisheries: The agriculture/ fisheries activities together emitted million tons of CO 2 eq due to energy use in the sector other than grid electricity. Indian Network for Climate Change Assessment Page 108
11 Figure ES4: GHG emissions from Transport Sector by mode of transport in 2007 (million tons of CO 2 eq). Fugitive Emissions: CH 4 escapes into the atmosphere due to mining of coal, and due to venting, flaring, transport and storage of oil and natural gas. The total CO 2 eq emissions from this source category in 2007 was million tons CO 2 eq. Industry: Industrial activities together emitted million tons of CO 2 eq of GHG in Industry sector emissions have been estimated from manufacturing of minerals, metals, chemicals, other specific industries, and from nonenergy product use. The emissions covered in the industry sector include fossil fuel combustion related emissions as well as the process based emissions. (Figure ES5). Cement and Other Minerals: The cement industry emitted million tons of CO 2, which is 32% of the total CO 2 eq emissions from the Industry sector. The emissions cover the entire technology mix for manufacturing of cement in the country covering large, medium and white cement Note: Other Metals: includes GHG emissions from production of ferroalloys, aluminium, lead, zinc and copper. Chemicals: includes GHG emissions from production of ammonia, nitric acid, adipic acid, caprolactam, carbide, titanium dioxide, petrochemicals and black carbon, methanol, ethylene, ethylene oxide, acrylonitrile, ethylene dichloride and vinyl chloride monomer and other chemicals (see glossary for details). Other Industries: includes GHG emissions from pulp and paper, food processing, textile and leather, mining and quarrying and non specific industries. It also includes emissions from non-energy product use. Figure ES5: GHG emissions from Industry Sector (million tons of CO 2 eq). plants. The other minerals like glass and ceramic production and soda ash use together emit 1.01 million tons of CO 2 eq. Iron and Steel and Other Metals: The iron and steel industry emitted million tons of CO 2 eq. The estimate covers integrated and mini steel plants. The production of other metals, namely, aluminum, ferroalloys, lead, zinc and copper production lead to an emission of 5.42 million tons of CO 2 eq. Page 11 9 India: Greenhouse Gas Emissions 2007
12 Chemicals: The chemical industries together emitted 8.1% of the total GHG emissions from the industry sector (33.50 million tons). See Fig. ES5 & Glossary for details of subcategories included. Other Industries: Other industries comprising of pulp/ paper, leather, textiles, food processing, mining and quarrying, and non specific industries comprising of rubber, plastic, watches, clocks, transport equipment, furniture etc., together emitted million tons. The rest of the emissions in the Industry sector came from the non-energy product uses and this sector emitted 0.85 million tons of CO 2 eq, and was mainly from use of oil products and coal-derived oils primarily intended for purposes other than combustion. Agriculture: The agriculture sector emitted million tons of CO 2 eq in Estimates of GHG emissions from the agriculture sector arise from enteric fermentation in livestock, manure management, rice paddy cultivation, agricultural soils and on field burning of crop residue. (Figure ES6) Livestock: Enteric fermentation in livestock released million tons of CO 2 eq (10.1 million tons of CH 4 ). This constituted 63.4% of the total GHG emissions (CO 2 eq) from agriculture sector in India. The estimates cover all livestock, namely, cattle, buffalo, sheep, goats, poultry, donkeys, camels, horses and others. Manure management emitted 2.44 million tons of CO 2 eq. Rice Cultivation: Rice cultivation emitted million tons of CO 2 eq or 3.27 million tons of CH 4. The emissions cover all forms of water management practiced in the country for rice cultivation, namely, irrigated, rainfed, deep water and upland rice. The upland rice are zero emitters and irrigated continuously flooded fields and deep water rice emit maximum methane per unit area. Figure ES6: GHG emissions from Agriculture Sector (million tons of CO 2 eq). Agricultural Soils and Field Burning of Crop Residue: Agricultural soils are a source of N 2 O, mainly due to application of nitrogenous fertilizers in the soils. Burning of crop residue leads to the emission of a number of gases and pollutants. Amongst them, CO 2 is considered to be C neutral, and therefore not included in the estimations. Only CH 4 and N 2 O are considered for this report. The total CO 2 eq emitted from these two sources were million tons. Land Use Land Use Change and Forestry: The estimates from LULUCF sector include emission by sources and or removal by sinks from changes in forest land, crop land, grassland, and settlements. Wet lands have not been considered due to paucity of data. The LULUCF sector in 2007 was a net sink. It sequestered million tons of CO 2 in (Figure ES7) Forest Land: This includes estimates of emissions and removal from above and below ground biomass in very Indian Network for Climate Change Assessment Page 12 10
13 Figure ES7: GHG emissions and removals from LULUCF sector (million tons of CO 2 eq). Figure ES8: GHG emissions from waste (million tons of CO 2 eq). dense, moderately dense, open forests, and scrub lands. Estimates indicate that forest land sequestered 67.8 million tons of CO 2 in However, fuel wood extracted nonsustainably from forests lead to an emission of million tons of CO 2 in Crop Lands: The emission estimates have been made from net sown area as well as fallow land. The crop land sequestered million tons of CO 2 in Grassland: Changes in Grassland resulted in the emission of million tons of CO 2 due to decrease in grass land area by 3.4 million ha between the two periods. Settlements: Land converted to settlements though increased by 0.01 million ha during the period, however, the conversions did not lead to an emission but a net removal of 0.04 million tons. Waste: The waste sector emissions were 57.3 million tons of CO 2 eq from municipal solid waste management, domestic waste water and industrial waste water management. (Figure ES8) Municipal Solid Waste (MSW): Systematic disposal of solid waste is carried out only in the cities in India resulting in CH 4 emissions due to aerobic conditions generated due to accumulation of waste over the years. It is estimated that the MSW generation and disposal resulted in the emissions of million tons of CO 2 eq in Waste Water: The waste water generation emissions are the sum total of emissions from domestic waste water and waste water disposal in industries. Waste water management in both these categories together emitted million tons of CO 2 Page India: Greenhouse Gas Emissions 2007
14 E. FUTURE DIRECTIONS The robustness of the GHG inventory making process is dependent on the Tier of methodology used. Higher the Tier, more representative is the emission estimated of the actual emissions. Of the total million tons of CO 2 equivalent emissions from India in 2007, 21% of the emissions have been estimated using Tier I methodology, 67% by Tier II and 12% by Tier III. Riding the Tier Ladder: For improving the inventory estimations of key categories using Tier II and Tier I methodologies, there is a need to move up the Tier ladder. Strategies needed include improvement in assimilation of activity data representing national circumstances, bridging data gaps, and eliminating uncertainties by developing country specific GHG emission factors. Capacity Building and National Greenhouse Gas Inventory Management System: Capacity building is essential at institutional and individual levels. Capacity at the institutional level addresses the needs of inventory preparation at national, sectoral and point source level that requires systematic collection and archiving of data on a continuous basis. Establishment of a National Inventory Management System is therefore necessary. It is also important to involve additional institutions with varied research experience, to widen the pool of researchers and enable the integration of latest practices. Indian Network for Climate Change Assessment Page 14 12
15 Greenhouse gas emissions by sources and removal by sinks from India in 2007 (thousand tons) ANNEXURE CO 2 emissions CO 2 removals CH 4 N 2 O CO 2 equivalent GRAND TOTAL ENERGY Electricity generation Other energy industries Transport Road transport Railways Aviation Navigation Residential Commercial / Institutional Agriculture/ Fisheries Fugitive emissions INDUSTRY Minerals Cement production Glass & ceramic production Other uses of soda ash Chemicals Ammonia production Nitric acid production Carbide production Titanium dioxide production Methanol production Ethylene production EDC & VCM production Ethylene Oxide production Acrylonitrile production Carbon Black production caprolactam Other chemical Metals Iron & Steel production Ferroalloys production (contd ) Page India: Greenhouse Gas Emissions 2007
16 CO 2 emissions CO 2 removals CH 4 N 2 O CO 2 equivalent Aluminium production Lead production Zinc production Copper Other Industries Pulp and paper Food processing Textile and leather Mining and quarrying Nonspecific industries Non energy product use Lubricant Paraffin wax AGRICULTURE Enteric fermentation Livestock Manure management Rice cultivation Soils Burning of crop residue LULUCF Forestland Cropland Grassland Settlement Wetland NE NE Other land NO NO Fuel wood use in forests Waste Municipal Solid waste Domestic waste water Industrial waste water Bunkers* Aviation Bunkers Marine bunkers Note: LULUCF: Land Use Land Use Change & Forestry *Not included in the national totals. NE: Not estimated; NO: Not occurring Indian Network for Climate Change Assessment Page 16 14
17 GLOSSARY OF KEY TERMS Agriculture: This includes emissions from enteric fermentation, manure management, rice cultivation, managed soils and burning of crop residue. CAGR: The compound annual growth rate is calculated by taking the n th root of the total percentage growth rate, where n is the number of years in the period being considered. Chemicals: In this document chemicals include production of ammonia, nitric acid, adipic acid, caprolactam, carbide, titanium dioxide, petrochemicals and black carbon, methanol, ethylene, ethylene oxide, acrylonitrile, ethylene dichloride and vinyl chloride, monomer and other chemicals (dyes and pigments, inorganic acids except nitric acid, acyclic hydrocarbons, basic organic chemicals, inorganic compounds, alkalies and other inorganic bases except ammonia, synthetic aromatic products, luminophores, etc). CO 2 Equivalent: It is the sum total of all Greenhouse Gases in terms of their global warming potential. In this document the CO 2 equivalent includes the sum of Carbon dioxide, Methane multiplied by its GWP (21) and Nitrous oxide multiplied by its GWP (310). Country Specific Data: Data for either activities or emissions that are based on research carried out on-site either in a country or in a representative country. Emission Factor: A coefficient that quantifies the emissions or removals of a gas per unit activity. Emission factor are often based on a sample of measurement data, averaged to develop a representative rate of emission for a given activity level under a given set of operating conditions. Emissions: The release of greenhouse gases and / or their precursors into the atmosphere over a specified area and a period of time. Energy: This category included all GHG emissions arising from combustion of fossil fuel and fugitive release of GHG s. Emissions from the non-energy use are not included here and are reported under the industry sector. This category includes emissions due to fuel combustion from energy industries (electricity generation, petroleum refining, manufacturing of solid fuel), transport, commercial / institutional, residential, agriculture / forestry / fisheries, and fugitive emissions from coal mining and handling and from oil and natural gas. Enteric Fermentation: A process of digestion in herbivores (plant eating animals) which produces methane as a by-product. Estimation: The process of calculating emissions and / or removal Flaring: Deliberate of burning of natural gas and waste gas / vapour streams, without energy recovery. Fossil Fuel Combustion: Is the intentional oxidation of fossil fuel that provides heat or mechanical work to process. Fugitive Emission: Emission that are not emitted through an intentional release through stack or vent. This can include leaks from plants, pipelines and during mining. Global Warming Potential (GWP): GWPs are calculated as a ratio of radiative forcing of 1 kilogram greenhouse gas emitted to the atmosphere to that from 1 kilogram CO 2 over a period of time (e.g years). Good Practice: Is a set of procedures intended to ensure that GHG inventories are accurate, that neither over nor underestimated and that uncertainties are reduced as far as possible. It covers choice estimation methods, quality assurance and quality control, quantification of uncertainties and processes for data archiving and reporting. INCCA: Indian Network for Climate Change Assessment - an initiative being coordinated by the Ministry of Environment and Forests, Government of India. Industry: This includes emissions from industrial processes and Page India: Greenhouse Gas Emissions 2007
18 emissions due to fossil fuel combustion in manufacturing industries. The emissions are estimated from mineral industry (cement, lime, glass, ceramics, soda ash use), chemical industries (ammonia, nitric acid, adipic acid, caprolactam, carbide, titanium dioxide, petrochemicals and black carbon, methanol, ethylene, etc.), metal industry (iron and steel, ferroalloys, aluminium, magnesium, lead, sink, etc.), other industry and non-energy products from fuels and solvent use (paraffin wax and lubricants). Land Cover: The type of vegetation, rock, water, etc. covering the earth surface. Land Use: The type of activity being carried out by unit of land Land Use Land Use Change and Forestry (LULUCF): Includes emissions and removal from changes in areas of forest land, crop land, grass land, wet land, settlements and other lands. Million Tons: equal to 10 6 tons. Non Energy Products: Primary or secondary fossil fuels which act as diluent. Examples, lubricants, paraffin wax, bitumen, etc. Non Energy Use: Use of fossil fuels as feedstock, reductant or non-energy products. Non-specific industries: Includes rubber, plastic, medical precetion equipments, watches, clocks, other transport, furniture, re-cycling etc. Other Energy: Includes GHG emissions from petroleum refining, manufacturing of solid fuel, commercial & institutional sector, agriculture & fisheries and fugitive emissions from mining, transport and storage of coal, oil and natural gas. Other Minerals: In this document other minerals refer to glass and ceramics production and soda ash use. Per Capita Emissions: GHG emissions in CO 2 eq per person. Removals: Removal of greenhouse gases and or their precursors from the atmosphere by a sink Sequestration: The process of storing carbon in a carbon pool. Sink: Any process, activity or mechanism which removes greenhouse gases from the atmosphere. Source: Any process or activity which releases a greenhouse gas. Tier I: Its approach employs activity data that are relatively coarse, such as nationally or globally available estimates of deforestation rates; agriculture production statistics and global land cover maps. Tier II: It uses the same methodological approach as Tier 1 but it applies emission factors and activity data which are defined by the country Tier III: Applies higher order methods are used including models and inventory measurement systems tailored to address national circumstances, repeated over time, and driven by disaggregated levels. Uncertainty: Lack of knowledge of the true value of a variable. Waste: Includes methane emissions from anaerobic microbial decomposition of organic matter in solid waste disposal sites and methane produced from anaerobic decomposition of organic matter by bacteria in sewage facilities in industries and in domestic waste water. Other Industry: Includes GHG emissions from production of food processing, textile, leather, mining and quarrying, non specific industries and use of lubricants and paraffin wax. Indian Network for Climate Change Assessment (INCCA) Page 16
19
20 Contact Dr. Subodh K Sharma Adviser Ministry of Environment and Forests Room No. 112, Paryavaran Bhawan CGO Complex, Lodi Road New Delhi Tel/Fax : subodh.kumar@nic.in
Launch of IPCC Inventory Software
 Task Force on National Greenhouse Gas Inventories Launch of IPCC Inventory Software 2006 IPCC guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories Side-Event, SB 36 Sessions, Bonn 16 May 2012, Aim to introduce
Task Force on National Greenhouse Gas Inventories Launch of IPCC Inventory Software 2006 IPCC guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories Side-Event, SB 36 Sessions, Bonn 16 May 2012, Aim to introduce
11 th Workshop on GHG Inventories in Asia (WGIA11)
 11 th Workshop on GHG Inventories in Asia (WGIA11) 1994 Malaysia Ratified UNFCCC 2000 Initial National Communication 2009 National Green Technology & Climate Change Council 2012 to date Preparation of
11 th Workshop on GHG Inventories in Asia (WGIA11) 1994 Malaysia Ratified UNFCCC 2000 Initial National Communication 2009 National Green Technology & Climate Change Council 2012 to date Preparation of
Scope 1 describes direct greenhouse gas emissions from sources that are owned by or under the direct control of the reporting entity;
 9 Greenhouse Gas Assessment 9.1 Introduction This chapter presents an assessment of the potential greenhouse gas emissions associated with the Simandou Railway and evaluates the significance of these in
9 Greenhouse Gas Assessment 9.1 Introduction This chapter presents an assessment of the potential greenhouse gas emissions associated with the Simandou Railway and evaluates the significance of these in
The Contribution of Global Agriculture to Greenhouse Gas Emissions
 The Contribution of Global Agriculture to Greenhouse Gas Emissions Dr. Tommy Boland, School of Agriculture and Food Science, University College Dublin, Belfield, Dublin 4 tommy.boland@ucd.ie Acknowledge
The Contribution of Global Agriculture to Greenhouse Gas Emissions Dr. Tommy Boland, School of Agriculture and Food Science, University College Dublin, Belfield, Dublin 4 tommy.boland@ucd.ie Acknowledge
Australia s emissions in a global context
 Australia s emissions in a global context 7 Key points Australia s per capita emissions are the highest in the OECD and among the highest in the world. Emissions from the energy sector would be the main
Australia s emissions in a global context 7 Key points Australia s per capita emissions are the highest in the OECD and among the highest in the world. Emissions from the energy sector would be the main
NEW ZEALAND S GREENHOUSE GAS INVENTORY & NET POSITION REPORT 1990 2012
 SNAPSHOT APRIL 2014 NEW ZEALAND S GREENHOUSE GAS INVENTORY & NET POSITION REPORT 1990 2012 Key points: In 2012, New Zealand s total greenhouse gas emissions were 76.0 million tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent
SNAPSHOT APRIL 2014 NEW ZEALAND S GREENHOUSE GAS INVENTORY & NET POSITION REPORT 1990 2012 Key points: In 2012, New Zealand s total greenhouse gas emissions were 76.0 million tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent
Biomass Renewable Energy from Plants and Animals
 Renewable Biomass Biomass Basics Biomass Renewable Energy from Plants and Animals Biomass is organic material made from plants and animals. Biomass contains stored energy from the sun. Plants absorb the
Renewable Biomass Biomass Basics Biomass Renewable Energy from Plants and Animals Biomass is organic material made from plants and animals. Biomass contains stored energy from the sun. Plants absorb the
Annual European Union greenhouse gas inventory 1990 2013 and inventory report 2015
 EEA Technical report No 19/2015 Annual European Union greenhouse gas inventory 1990 2013 and inventory report 2015 Submission to the UNFCCC Secretariat ISSN 1725-2237 EEA Technical report No 19/2015 Annual
EEA Technical report No 19/2015 Annual European Union greenhouse gas inventory 1990 2013 and inventory report 2015 Submission to the UNFCCC Secretariat ISSN 1725-2237 EEA Technical report No 19/2015 Annual
CANADA S EMISSIONS TRENDS
 CANADA S EMISSIONS TRENDS Environment Canada July 2011 Canada s Emissions Trends 1 Cat. No. En84-83/2011E ISBN 978-1-100-17743-4 Information contained in this publication or product may be reproduced,
CANADA S EMISSIONS TRENDS Environment Canada July 2011 Canada s Emissions Trends 1 Cat. No. En84-83/2011E ISBN 978-1-100-17743-4 Information contained in this publication or product may be reproduced,
Communicating Your Commitment: Your Guide to Clean Energy Messaging
 Communicating Your Commitment: Your Guide to Clean Energy Messaging Congratulations on your recent purchase of clean energy from Renewable Choice! Whether you ve purchased green power in the form of renewable
Communicating Your Commitment: Your Guide to Clean Energy Messaging Congratulations on your recent purchase of clean energy from Renewable Choice! Whether you ve purchased green power in the form of renewable
Report of the Conference of the Parties on its nineteenth session, held in Warsaw from 11 to 23 November 2013
 United Nations FCCC/CP/2013/10/Add.3 Distr.: General 31 January 2014 Original: English Conference of the Parties Contents Report of the Conference of the Parties on its nineteenth session, held in Warsaw
United Nations FCCC/CP/2013/10/Add.3 Distr.: General 31 January 2014 Original: English Conference of the Parties Contents Report of the Conference of the Parties on its nineteenth session, held in Warsaw
FIRST NATIONAL COMMUNICATIONS OF KENYA PROBLEMS AND CONSTRAINTS
 FIRST NATIONAL COMMUNICATIONS OF KENYA PROBLEMS AND CONSTRAINTS CONTENT OF THE 1 ST NATIONAL COMMUNICATION 9 Chapters Executive Summary National Circumstances Sustainable Development GHG Inventory Vulnerability
FIRST NATIONAL COMMUNICATIONS OF KENYA PROBLEMS AND CONSTRAINTS CONTENT OF THE 1 ST NATIONAL COMMUNICATION 9 Chapters Executive Summary National Circumstances Sustainable Development GHG Inventory Vulnerability
Towards climate-smart agriculture
 Towards climate-smart agriculture Background notes for the informal meeting of the Ministers of Agriculture Luxembourg, 15 September 2015 Table of contents Agricultural impact on climate change Climate
Towards climate-smart agriculture Background notes for the informal meeting of the Ministers of Agriculture Luxembourg, 15 September 2015 Table of contents Agricultural impact on climate change Climate
This chapter provides projections of U.S. greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions through
 5 Projected Greenhouse Gas Emissions This chapter provides projections of U.S. greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions through 2030, including the effects of policies and measures in effect as of September 2012,
5 Projected Greenhouse Gas Emissions This chapter provides projections of U.S. greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions through 2030, including the effects of policies and measures in effect as of September 2012,
Harvesting energy with fertilizers
 Harvesting energy with fertilizers Sustainable agriculture in Europe 1 Harvesting energy with fertilizers The reason for agriculture s existence is to supply energy to mankind. Agriculture converts solar
Harvesting energy with fertilizers Sustainable agriculture in Europe 1 Harvesting energy with fertilizers The reason for agriculture s existence is to supply energy to mankind. Agriculture converts solar
This fact sheet provides an overview of options for managing solid
 What Is Integrated Solid Waste Management? This fact sheet provides an overview of options for managing solid waste, identifies the important issues you should consider when planning for solid waste management,
What Is Integrated Solid Waste Management? This fact sheet provides an overview of options for managing solid waste, identifies the important issues you should consider when planning for solid waste management,
Republic of Rwanda: Greenhouse gas emissions baseline projection
 Republic of Rwanda: Greenhouse gas emissions baseline projection Seton Stiebert March 2013 www.iisd.org Published by the International Institute for Sustainable Development. International Institute for
Republic of Rwanda: Greenhouse gas emissions baseline projection Seton Stiebert March 2013 www.iisd.org Published by the International Institute for Sustainable Development. International Institute for
FIRST BIENNIAL REPORT OF THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION
 Informal translation FEDERAL SERVICE FOR HYDROMETEOROLOGY AND ENVIRONMENTAL MONITORING FIRST BIENNIAL REPORT OF THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION Submitted in accordance with Decision 1/СР.16 of the Conference of
Informal translation FEDERAL SERVICE FOR HYDROMETEOROLOGY AND ENVIRONMENTAL MONITORING FIRST BIENNIAL REPORT OF THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION Submitted in accordance with Decision 1/СР.16 of the Conference of
GHG INVENTORY FOR SOUTH AFRICA
 GHG INVENTORY FOR SOUTH AFRICA 2000-2010 environmental affairs Environmental Affairs Department: REPUBLIC OF SOUTH AFRICA 2 GHG INVENTORY FOR SOUTH AFRICA 2000-2010 GHG NATIONAL INVENTORY REPORT SOUTH
GHG INVENTORY FOR SOUTH AFRICA 2000-2010 environmental affairs Environmental Affairs Department: REPUBLIC OF SOUTH AFRICA 2 GHG INVENTORY FOR SOUTH AFRICA 2000-2010 GHG NATIONAL INVENTORY REPORT SOUTH
FACTS ABOUT CLIMATE CHANGE
 FACTS ABOUT CLIMATE CHANGE 1. What is climate change? Climate change is a long-term shift in the climate of a specific location, region or planet. The shift is measured by changes in features associated
FACTS ABOUT CLIMATE CHANGE 1. What is climate change? Climate change is a long-term shift in the climate of a specific location, region or planet. The shift is measured by changes in features associated
Need for up-to-date data to support inventory compilers in implementing IPCC methodologies to estimate emissions and removals for AFOLU Sector
 Task Force on National Greenhouse Gas Inventories Need for up-to-date data to support inventory compilers in implementing IPCC methodologies to estimate emissions and removals for AFOLU Sector Joint FAO-IPCC-IFAD
Task Force on National Greenhouse Gas Inventories Need for up-to-date data to support inventory compilers in implementing IPCC methodologies to estimate emissions and removals for AFOLU Sector Joint FAO-IPCC-IFAD
In 2013, the Spanish economy emits 316.9 million tonnes of greenhouse effect gases, 7.8% less than in 2012
 20 November 2015 Environmental accounts. Atmospheric Emission Accounts. Base 2010. Accounting series 2010-2013 In 2013, the Spanish economy emits 316.9 million tonnes of greenhouse effect gases, 7.8% less
20 November 2015 Environmental accounts. Atmospheric Emission Accounts. Base 2010. Accounting series 2010-2013 In 2013, the Spanish economy emits 316.9 million tonnes of greenhouse effect gases, 7.8% less
USA - California Cap-and-Trade Program
 1 5 International Carbon Action Partnership USA - California Cap-and-Trade Program General Information Summary Status: ETS in force Jurisdictions: California Initiated in 2012, the Californian cap-and-trade
1 5 International Carbon Action Partnership USA - California Cap-and-Trade Program General Information Summary Status: ETS in force Jurisdictions: California Initiated in 2012, the Californian cap-and-trade
CAIT COUNTRY GREENHOUSE GAS EMISSIONS: SOURCES & METHODS
 CAIT COUNTRY GREENHOUSE GAS EMISSIONS: SOURCES & METHODS June 2015 World Resources Institute This document accompanies the CAIT Climate Data Explorer Historical Emissions Country GHG Emissions dataset.
CAIT COUNTRY GREENHOUSE GAS EMISSIONS: SOURCES & METHODS June 2015 World Resources Institute This document accompanies the CAIT Climate Data Explorer Historical Emissions Country GHG Emissions dataset.
Scope 1 describes direct greenhouse gas emissions from sources that are owned by or under the direct control of the reporting entity;
 10 Greenhouse Gas Assessment 10.1 Introduction This chapter presents an assessment of the potential greenhouse gas emissions associated with the Simandou Mine and evaluates the significance of these in
10 Greenhouse Gas Assessment 10.1 Introduction This chapter presents an assessment of the potential greenhouse gas emissions associated with the Simandou Mine and evaluates the significance of these in
EMISSIONS OF AIR POLLUTANTS IN THE UK, 1970 TO 2014
 STATISTICAL RELEASE: 17 DECEMBER 2015 EMISSIONS OF AIR POLLUTANTS IN THE UK, 1970 TO 2014 There has been a long term decrease in the emissions of all of the air pollutants covered by this statistical release
STATISTICAL RELEASE: 17 DECEMBER 2015 EMISSIONS OF AIR POLLUTANTS IN THE UK, 1970 TO 2014 There has been a long term decrease in the emissions of all of the air pollutants covered by this statistical release
Frank Mitloehner, PhD Air Quality CE Specialist Animal Science, UC Davis
 Mitigation Solutions for Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Animal Waste International Symposium on Near-Term Solutions for Climate Change Mitigation in California March 5-7, 2007 Frank Mitloehner, PhD Air Quality
Mitigation Solutions for Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Animal Waste International Symposium on Near-Term Solutions for Climate Change Mitigation in California March 5-7, 2007 Frank Mitloehner, PhD Air Quality
TURKEY Greenhouse Gas Inventory,1990 to 2005
 TURKEY Greenhouse Gas Inventory,1990 to 2005 Annual Report for submission under the Framework Convention on Climate Change National Inventory Report Ankara, 2007 Data sheet Title: Turkish National Inventory
TURKEY Greenhouse Gas Inventory,1990 to 2005 Annual Report for submission under the Framework Convention on Climate Change National Inventory Report Ankara, 2007 Data sheet Title: Turkish National Inventory
Revealing the costs of air pollution from industrial facilities in Europe a summary for policymakers
 Revealing the costs of air pollution from industrial facilities in Europe a summary for policymakers A new European Environment Agency (EEA report, Revealing the costs of air pollution from industrial
Revealing the costs of air pollution from industrial facilities in Europe a summary for policymakers A new European Environment Agency (EEA report, Revealing the costs of air pollution from industrial
FCCC/SBI/ICA/2015/TASR.1/KOR
 United Nations FCCC/SBI/ICA/2015/TASR.1/KOR Distr.: General 10 February 2016 English only Summary report on the technical analysis of the first biennial update report of the Republic of Korea submitted
United Nations FCCC/SBI/ICA/2015/TASR.1/KOR Distr.: General 10 February 2016 English only Summary report on the technical analysis of the first biennial update report of the Republic of Korea submitted
UNFCCC RESOURCE GUIDE
 United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change UNFCCC FOR PREPARING THE NATIONAL COMMUNICATIONS OF NON-ANNEX I PARTIES MODULE 3 NATIONAL GREENHOUSE GAS INVENTORIES United Nations Framework Convention
United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change UNFCCC FOR PREPARING THE NATIONAL COMMUNICATIONS OF NON-ANNEX I PARTIES MODULE 3 NATIONAL GREENHOUSE GAS INVENTORIES United Nations Framework Convention
Papapostolou 1, E. Kondili 1, J.K. Kaldellis 2
 Technological and Environmental Impacts Evaluation of Biomass and Biofuels Supply Chain Papapostolou 1, E. Kondili 1, J.K. Kaldellis 2 1 Optimisation of Production Systems Lab 2 Soft Energy Applications
Technological and Environmental Impacts Evaluation of Biomass and Biofuels Supply Chain Papapostolou 1, E. Kondili 1, J.K. Kaldellis 2 1 Optimisation of Production Systems Lab 2 Soft Energy Applications
A pound of coal supplies enough electricity to power ten 100-watt light bulbs for about an hour.
 Did You Know? A pound of coal supplies enough electricity to power ten 100-watt light bulbs for about an hour. Nonrenewable Coal Coal Basics Coal Takes Millions of Years To Create Coal is a combustible
Did You Know? A pound of coal supplies enough electricity to power ten 100-watt light bulbs for about an hour. Nonrenewable Coal Coal Basics Coal Takes Millions of Years To Create Coal is a combustible
Comprehensive emissions per capita for industrialised countries
 THE AUSTRALIA INSTITUTE Comprehensive emissions per capita for industrialised countries Hal Turton and Clive Hamilton The Australia Institute September 2001 the Parties included in Annex I shall implement
THE AUSTRALIA INSTITUTE Comprehensive emissions per capita for industrialised countries Hal Turton and Clive Hamilton The Australia Institute September 2001 the Parties included in Annex I shall implement
Chapter 2: Stationary Combustion CHAPTER 2 STATIONARY COMBUSTION. 2006 IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories 2.1
 CHAPTER 2 STATIONARY COMBUSTION 2006 IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories 2.1 Volume 2: Energy Authors Darío R. Gómez (Argentina) and John D. Watterson (UK) Branca B. Americano (Brazil),
CHAPTER 2 STATIONARY COMBUSTION 2006 IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories 2.1 Volume 2: Energy Authors Darío R. Gómez (Argentina) and John D. Watterson (UK) Branca B. Americano (Brazil),
BIOMASS: BIOGAS GENERATOR. Curriculum: Biomass Power (organic chemistry, chemical/carbon cycles, plants, energy resources/transformations)
 BIOMASS: BIOGAS GENERATOR Curriculum: Biomass Power (organic chemistry, chemical/carbon cycles, plants, energy resources/transformations) Grade Level: Middle School (6-8) Small groups (3 to 4) Time: 90
BIOMASS: BIOGAS GENERATOR Curriculum: Biomass Power (organic chemistry, chemical/carbon cycles, plants, energy resources/transformations) Grade Level: Middle School (6-8) Small groups (3 to 4) Time: 90
5.5 QUALITY ASSURANCE AND QUALITY CONTROL
 0 0 0. QUALITY ASSURANCE AND QUALITY CONTROL.. Introduction The IPCC Good Practice Guidance and Uncertainty Management (GPG000, IPCC, 000), Chapter, Quality Assurance and Quality Control, defines quality
0 0 0. QUALITY ASSURANCE AND QUALITY CONTROL.. Introduction The IPCC Good Practice Guidance and Uncertainty Management (GPG000, IPCC, 000), Chapter, Quality Assurance and Quality Control, defines quality
US Natural Gas Statistics
 Downstream Gas Statistics data sources and methodologies 1. Introduction The UK s gas markets can be separated into two sections: upstream (gas supply) and downstream (gas demand). The Department of Energy
Downstream Gas Statistics data sources and methodologies 1. Introduction The UK s gas markets can be separated into two sections: upstream (gas supply) and downstream (gas demand). The Department of Energy
Balancing chemical reaction equations (stoichiometry)
 Balancing chemical reaction equations (stoichiometry) This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit
Balancing chemical reaction equations (stoichiometry) This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit
Nitrogen Management Project Protocol (NMPP) Special Topics Webinar & Project Developer Training
 Nitrogen Management Project Protocol (NMPP) Special Topics Webinar & Project Developer Training January 17 th 2013 Scott Hernandez Business Development Manager Teresa Lang Policy Manager & NMPP Lead Agenda
Nitrogen Management Project Protocol (NMPP) Special Topics Webinar & Project Developer Training January 17 th 2013 Scott Hernandez Business Development Manager Teresa Lang Policy Manager & NMPP Lead Agenda
International Standard for Determining Greenhouse Gas Emissions for Cities
 International Standard for Determining Greenhouse Gas Emissions for Cities The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) advices that, to avoid the worst impacts from climate change, global CO 2
International Standard for Determining Greenhouse Gas Emissions for Cities The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) advices that, to avoid the worst impacts from climate change, global CO 2
Carbon Sequestration Tool Background and User Guide
 Carbon Sequestration Tool Background and User Guide Table of Contents Quick Start Methodology Content of Worksheets Frequently Asked Questions Quick Start 1. Determine which of the two carbon tools you
Carbon Sequestration Tool Background and User Guide Table of Contents Quick Start Methodology Content of Worksheets Frequently Asked Questions Quick Start 1. Determine which of the two carbon tools you
The Nitrogen Cycle. What is Nitrogen? Human Alteration of the Global Nitrogen Cycle. How does the nitrogen cycle work?
 Human Alteration of the Global Nitrogen Cycle Heather McGraw, Mandy Williams, Suzanne Heinzel, and Cristen Whorl, Give SIUE Permission to Put Our Presentation on E-reserve at Lovejoy Library. What is Nitrogen?
Human Alteration of the Global Nitrogen Cycle Heather McGraw, Mandy Williams, Suzanne Heinzel, and Cristen Whorl, Give SIUE Permission to Put Our Presentation on E-reserve at Lovejoy Library. What is Nitrogen?
Submission by Norway to the ADP
 Submission by Norway to the ADP Norway s Intended Nationally Determined Contribution 1. Introduction Norway is fully committed to the UNFCCC negotiation process towards adopting at COP21 a protocol, another
Submission by Norway to the ADP Norway s Intended Nationally Determined Contribution 1. Introduction Norway is fully committed to the UNFCCC negotiation process towards adopting at COP21 a protocol, another
Climate Change and Renewable Energy A Perspective from a Measurements Viewpoint
 Climate Change and Renewable Energy A Perspective from a Measurements Viewpoint Regional Workshop on Metrology and Technology Challenges of Climate Change and Renewable Energy Guatemala City, Guatemala
Climate Change and Renewable Energy A Perspective from a Measurements Viewpoint Regional Workshop on Metrology and Technology Challenges of Climate Change and Renewable Energy Guatemala City, Guatemala
Nonrenewable Natural Gas. Natural Gas Basics. How Was Natural Gas Formed?
 Did You Know? Because natural gas is colorless, odorless, and tasteless, mercaptan (a chemical that smells like sulfur) is added before distribution, to give it a distinct unpleasant odor (it smells like
Did You Know? Because natural gas is colorless, odorless, and tasteless, mercaptan (a chemical that smells like sulfur) is added before distribution, to give it a distinct unpleasant odor (it smells like
Determination of the Impact of Waste Management Activities on Greenhouse Gas Emissions: 2005 Update Final Report Contract No.
 Determination of the Impact of Waste Management Activities on Greenhouse Gas : 2005 Update Final Report Contract No. K2216-04-0006 Submitted to: Environment Canada and Natural Resources Canada Submitted
Determination of the Impact of Waste Management Activities on Greenhouse Gas : 2005 Update Final Report Contract No. K2216-04-0006 Submitted to: Environment Canada and Natural Resources Canada Submitted
CLIMATE CHANGE & FORESTS; STATUS OF SCIENCE, POLICY & RESEARCH. Prof. Ravindranath Indian Institute of Science Bangalore
 CLIMATE CHANGE & FORESTS; STATUS OF SCIENCE, POLICY & RESEARCH Prof. Ravindranath Indian Institute of Science Bangalore Forests and climate change 1. Deforestation and land use change contribute to CO
CLIMATE CHANGE & FORESTS; STATUS OF SCIENCE, POLICY & RESEARCH Prof. Ravindranath Indian Institute of Science Bangalore Forests and climate change 1. Deforestation and land use change contribute to CO
GREENHOUSE GAS EMISSIONS INVENTORY FOR THE STATE OF BAJA CALIFORNIA 2005
 GREENHOUSE GAS EMISSIONS INVENTORY FOR THE STATE OF BAJA CALIFORNIA Prepared for: ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION SECRETARY IN THE STATE OF BAJA CALIFORNIA Agreement Num. OMG/SPA/066/07 Prepared by: MARIO MOLINA
GREENHOUSE GAS EMISSIONS INVENTORY FOR THE STATE OF BAJA CALIFORNIA Prepared for: ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION SECRETARY IN THE STATE OF BAJA CALIFORNIA Agreement Num. OMG/SPA/066/07 Prepared by: MARIO MOLINA
Assignment 8: Comparison of gasification, pyrolysis and combustion
 AALTO UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY KE-40.4120 Introduction to biorefineries and biofuels Assignment 8: Comparison of gasification, pyrolysis and combustion Aino Siirala 309141 Assignment submitted
AALTO UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY KE-40.4120 Introduction to biorefineries and biofuels Assignment 8: Comparison of gasification, pyrolysis and combustion Aino Siirala 309141 Assignment submitted
National Inventory System
 Regional workshop for the Capacity Development for sustainable national Greenhouse Gas Inventories AFOLU sector (CD-REDD II) Programme National Inventory System Daniela Romano Institute for Environmental
Regional workshop for the Capacity Development for sustainable national Greenhouse Gas Inventories AFOLU sector (CD-REDD II) Programme National Inventory System Daniela Romano Institute for Environmental
Calculating Greenhouse Gas Emissions
 GIIRS Emerging Market Assessment Resource Guide: What s in this Guide? I. Definition: What Are Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Emissions? II. Why Calculate GHGs? III. How to Calculate Company-wide GHGs IV. Outsourcing
GIIRS Emerging Market Assessment Resource Guide: What s in this Guide? I. Definition: What Are Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Emissions? II. Why Calculate GHGs? III. How to Calculate Company-wide GHGs IV. Outsourcing
REPUBLIC OF TURKEY INTENDED NATIONALLY DETERMINED CONTRIBUTION
 REPUBLIC OF TURKEY INTENDED NATIONALLY DETERMINED CONTRIBUTION In accordance with decisions 1/CP.19 and 1/CP.20, the Republic of Turkey hereby presents its Intended Nationally Determined Contribution (INDC)
REPUBLIC OF TURKEY INTENDED NATIONALLY DETERMINED CONTRIBUTION In accordance with decisions 1/CP.19 and 1/CP.20, the Republic of Turkey hereby presents its Intended Nationally Determined Contribution (INDC)
The importance of energy balances to estimate greenhouse gas emissions
 The importance of energy balances to estimate greenhouse gas emissions Roberta Quadrelli Head - Energy Balances, Prices, Emissions, Efficiency IEA Energy Data Centre Capacity Development for Mainstreaming
The importance of energy balances to estimate greenhouse gas emissions Roberta Quadrelli Head - Energy Balances, Prices, Emissions, Efficiency IEA Energy Data Centre Capacity Development for Mainstreaming
THE INTRODUCTION CANADA AND AGRICULTURE THE GREENHOUSE EFFECT AND GLOBAL WARMING
 THE INTRODUCTION The earth is surrounded by atmosphere composed of many gases. These gases allow the sun s rays to penetrate to the earth s surface while at the same time prevent much of the heat from
THE INTRODUCTION The earth is surrounded by atmosphere composed of many gases. These gases allow the sun s rays to penetrate to the earth s surface while at the same time prevent much of the heat from
National Greenhouse Gas Inventory System in Finland
 January 00 1 National Greenhouse Gas Inventory System in Finland Helsinki 00 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 Foreword Statistics Finland has prepared this description of Finland s Greenhouse Gas Inventory System as part
January 00 1 National Greenhouse Gas Inventory System in Finland Helsinki 00 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 Foreword Statistics Finland has prepared this description of Finland s Greenhouse Gas Inventory System as part
Where does the wine sector sit in terms of Australian climate policy and the global carbon market
 Where does the wine sector sit in terms of Australian climate policy and the global carbon market The Carbon Farming Initiative and Emission Reduction Fund Geoff Cowey viticulture@awri.com.au The_AWRI
Where does the wine sector sit in terms of Australian climate policy and the global carbon market The Carbon Farming Initiative and Emission Reduction Fund Geoff Cowey viticulture@awri.com.au The_AWRI
Finland s First Biennial Report. under the UNFCCC
 Finland s First Biennial Report under the UNFCCC 30 December 2013 Contents 1 INTRODUCTION... 3 2 INFORMATION ON GREENHOUSE GAS EMISSIONS AND TRENDS... 4 2.1 Total greenhouse gas emissions and trends...
Finland s First Biennial Report under the UNFCCC 30 December 2013 Contents 1 INTRODUCTION... 3 2 INFORMATION ON GREENHOUSE GAS EMISSIONS AND TRENDS... 4 2.1 Total greenhouse gas emissions and trends...
Waste a source of energy. Regional Solid Waste Management Plan Review: Engaging solutions for tomorrow. Incineration. Incineration
 Waste a source of energy Regional Solid Waste Management Plan Review: Engaging solutions for tomorrow Garbage School 301: Waste to Energy All organic materials contains energy Plant or animal based Plastics
Waste a source of energy Regional Solid Waste Management Plan Review: Engaging solutions for tomorrow Garbage School 301: Waste to Energy All organic materials contains energy Plant or animal based Plastics
Annex 5A Trends in international carbon dioxide emissions
 Annex 5A Trends in international carbon dioxide emissions 5A.1 A global effort will be needed to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and to arrest climate change. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
Annex 5A Trends in international carbon dioxide emissions 5A.1 A global effort will be needed to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and to arrest climate change. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
Chapter 1.9 Global Environmental Concerns
 Chapter 1.9 Global Environmental Concerns Part I Objective Type Questions 1. The spread of the Stratosphere above the Earth s surface is a) Below 15 km b) 10 to 50 km c) above 50 km d) above 100 km 2.
Chapter 1.9 Global Environmental Concerns Part I Objective Type Questions 1. The spread of the Stratosphere above the Earth s surface is a) Below 15 km b) 10 to 50 km c) above 50 km d) above 100 km 2.
Six greenhouse gases covered by the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) and its Kyoto Protocol are:
 Fact sheet: The need for mitigation United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change Along with adaptation, mitigation is one of the two central approaches in the international climate change process.
Fact sheet: The need for mitigation United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change Along with adaptation, mitigation is one of the two central approaches in the international climate change process.
Facts on CO 2 Capture and Storage
 Facts on CO 2 Capture and Storage A Summary of a Special Report by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change A summary by: CARBON DIOXIDE CAPTURE AND STORAGE (CCS) is a technique by which CO2 could
Facts on CO 2 Capture and Storage A Summary of a Special Report by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change A summary by: CARBON DIOXIDE CAPTURE AND STORAGE (CCS) is a technique by which CO2 could
PRESENTATION 2 MAJOR ENVIRONMENTAL PROBLEMS
 UNEP GLOBAL JUDGES PROGRAMME APPLICATION OF ENVIRONMENTAL LAW BY NATIONAL COURTS AND TRIBUNALS PRESENTATION 2 MAJOR ENVIRONMENTAL PROBLEMS OUTLINE OF PRESENTATION A) Major environmental issues B) Responses
UNEP GLOBAL JUDGES PROGRAMME APPLICATION OF ENVIRONMENTAL LAW BY NATIONAL COURTS AND TRIBUNALS PRESENTATION 2 MAJOR ENVIRONMENTAL PROBLEMS OUTLINE OF PRESENTATION A) Major environmental issues B) Responses
Improvement of Lithuania s National System for GHG inventory preparation
 Improvement of Lithuania s National System for GHG inventory preparation Compliance Committee Enforcement Branch sixteenth meeting 15-17 November 2011 Bonn, Germany Ministry of Environment of the Republic
Improvement of Lithuania s National System for GHG inventory preparation Compliance Committee Enforcement Branch sixteenth meeting 15-17 November 2011 Bonn, Germany Ministry of Environment of the Republic
Groupwork CCS. Bio-Energy with CCS (BECCS) Platzhalter Logo/Schriftzug (Anpassung im Folienmaster: Menü «Ansicht» «Folienmaster»)
 Groupwork CCS Bio-Energy with CCS (BECCS) group 5 02.05.2015 1 Content What is BECCS? Stakeholder Analysis Resources on Global scale SWOT analysis Climate BECCS Technology Conclusions Outlook group 5 02.05.2015
Groupwork CCS Bio-Energy with CCS (BECCS) group 5 02.05.2015 1 Content What is BECCS? Stakeholder Analysis Resources on Global scale SWOT analysis Climate BECCS Technology Conclusions Outlook group 5 02.05.2015
To approve Intended Nationally Determined Contributions of the Republic of Armenia under the UNFCCC according to the following Annex.
 Protocol Decision No 41, 10 September, 2015 Government of the Republic of Armenia On approving the Intended Nationally Determined Contributions of the Republic of Armenia under the UN Framework Convention
Protocol Decision No 41, 10 September, 2015 Government of the Republic of Armenia On approving the Intended Nationally Determined Contributions of the Republic of Armenia under the UN Framework Convention
Agriculture and Land use (ALU) Software: A tool for GHG Inventory and LEDS
 Agriculture and Land use (ALU) Software: A tool for GHG Inventory and LEDS Asia Low Emission Development Strategies (LEDS) Forum: Catalyzing an Era of Green Growth (18-21 September 2012, Bangkok, Thailand
Agriculture and Land use (ALU) Software: A tool for GHG Inventory and LEDS Asia Low Emission Development Strategies (LEDS) Forum: Catalyzing an Era of Green Growth (18-21 September 2012, Bangkok, Thailand
2012 Guidelines to Defra / DECC's GHG Conversion Factors for Company Reporting
 2012 Guidelines to Defra / DECC's Conversion Factors for Company Reporting Produced by AEA for the Department of Energy and Climate Change (DECC) and the Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs
2012 Guidelines to Defra / DECC's Conversion Factors for Company Reporting Produced by AEA for the Department of Energy and Climate Change (DECC) and the Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs
Implications of Abundant Natural Gas
 Implications of Abundant Natural Gas JAE EDMONDS AND HAEWON MCJEON APRIL 2013 May 29, 2013 1 Background May 29, 2013 2 The natural gas revolution The application of technologies for accessing unconventional
Implications of Abundant Natural Gas JAE EDMONDS AND HAEWON MCJEON APRIL 2013 May 29, 2013 1 Background May 29, 2013 2 The natural gas revolution The application of technologies for accessing unconventional
Data collection and analysis
 Regional workshop for the Capacity Development for sustainable national Greenhouse Gas Inventories AFOLU sector (CD-REDD II) Programme Data collection and analysis Daniela Romano Institute for Environmental
Regional workshop for the Capacity Development for sustainable national Greenhouse Gas Inventories AFOLU sector (CD-REDD II) Programme Data collection and analysis Daniela Romano Institute for Environmental
Emission inventory system in Latvia
 Emission inventory system in Latvia Agita Gancone Latvian Environment, Geology and Meteorology Centre 28-29 September, Ankara Content Some information about Latvia, Legal background; Roles; Resources;
Emission inventory system in Latvia Agita Gancone Latvian Environment, Geology and Meteorology Centre 28-29 September, Ankara Content Some information about Latvia, Legal background; Roles; Resources;
BIOENERGY (FROM NORWEGIAN FORESTS) GOOD OR BAD FOR THE CLIMATE?
 Presentation at NordGen Skog conference Odense, September 13-14, 2011 BIOENERGY (FROM NORWEGIAN FORESTS) GOOD OR BAD FOR THE CLIMATE? Per Kristian Rørstad Dept. of Ecology and Natural Resource Management
Presentation at NordGen Skog conference Odense, September 13-14, 2011 BIOENERGY (FROM NORWEGIAN FORESTS) GOOD OR BAD FOR THE CLIMATE? Per Kristian Rørstad Dept. of Ecology and Natural Resource Management
Improving Sustainability of Municipal Solid Waste Management in China by Source Separated Collection and Biological Treatment of the Organic Fraction
 Improving Sustainability of Municipal Solid Waste Management in China by Source Separated Collection and Biological Treatment of the Organic Fraction Adrie Veeken 1,2, Pim Hamminga 1,3 and Zhang Mingshu
Improving Sustainability of Municipal Solid Waste Management in China by Source Separated Collection and Biological Treatment of the Organic Fraction Adrie Veeken 1,2, Pim Hamminga 1,3 and Zhang Mingshu
Policy & Management Applications of Blue Carbon. fact SHEET
 Policy & Management Applications of Blue Carbon fact SHEET Policy & Management Applications of Blue Carbon Coastal Blue Carbon - An Important Wetland Ecosystem Service Coastal Blue Carbon refers to the
Policy & Management Applications of Blue Carbon fact SHEET Policy & Management Applications of Blue Carbon Coastal Blue Carbon - An Important Wetland Ecosystem Service Coastal Blue Carbon refers to the
NEW ZEALAND S RESPONSE TO CLIMATE CHANGE
 NEW ZEALAND S RESPONSE TO CLIMATE CHANGE 1 NEW ZEALAND S RESPONSE TO CLIMATE CHANGE In simplifying this information, some detail has been omitted. For more complete information about climate change science
NEW ZEALAND S RESPONSE TO CLIMATE CHANGE 1 NEW ZEALAND S RESPONSE TO CLIMATE CHANGE In simplifying this information, some detail has been omitted. For more complete information about climate change science
Institutional Arrangements For Inventory System in Korea
 5 th Workshop on GHG Inventories in Asia Region Institutional Arrangements For Inventory System in Korea Sept. 2007 By Park, Soon Chul Korea Energy Management Corporation Chapter.1 Overview Legal Institution
5 th Workshop on GHG Inventories in Asia Region Institutional Arrangements For Inventory System in Korea Sept. 2007 By Park, Soon Chul Korea Energy Management Corporation Chapter.1 Overview Legal Institution
Coal-To-Gas & Coal-To-Liquids
 Located in the Energy Center at Discovery Park, Purdue University Coal-To-Gas & Coal-To-Liquids CCTR Basic Facts File #3 Brian H. Bowen, Marty W. Irwin The Energy Center at Discovery Park Purdue University
Located in the Energy Center at Discovery Park, Purdue University Coal-To-Gas & Coal-To-Liquids CCTR Basic Facts File #3 Brian H. Bowen, Marty W. Irwin The Energy Center at Discovery Park Purdue University
Residential & Commercial Sectors Overview CLIMATE
 CLIMATE TECHBOOK Residential and Commercial Emissions in the United States Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions data can be reported either by economic sector, which includes electric power generation as a separate
CLIMATE TECHBOOK Residential and Commercial Emissions in the United States Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions data can be reported either by economic sector, which includes electric power generation as a separate
PRIZE WINNING ENTRY (FIRST PRIZE) IN ICAR NATIONAL ESSAY COMPETITION FOR SCHOOL CHILDREN 2007. Global Climatic Changes & Its Effect on Agriculture
 PRIZE WINNING ENTRY (FIRST PRIZE) IN ICAR NATIONAL ESSAY COMPETITION FOR SCHOOL CHILDREN 2007 Global Climatic Changes & Its Effect on Agriculture by ZARIN A S, CLASS XII D Model Technical Higher Sec. School,
PRIZE WINNING ENTRY (FIRST PRIZE) IN ICAR NATIONAL ESSAY COMPETITION FOR SCHOOL CHILDREN 2007 Global Climatic Changes & Its Effect on Agriculture by ZARIN A S, CLASS XII D Model Technical Higher Sec. School,
Living & Working Managing Natural Resources and Waste
 Living & Working Managing Natural Resources and Waste 5.13 Managing Natural Resources and Waste Background 5.13.1 This chapter focuses on how we manage resources within the AONB. It includes renewable
Living & Working Managing Natural Resources and Waste 5.13 Managing Natural Resources and Waste Background 5.13.1 This chapter focuses on how we manage resources within the AONB. It includes renewable
NEW ZEALAND. Submission to the ADP. New Zealand s Intended Nationally Determined Contribution. 7 July 2015
 NEW ZEALAND Submission to the ADP New Zealand s Intended Nationally Determined Contribution 7 July 2015 New Zealand hereby communicates its intended nationally determined contribution and the accompanying
NEW ZEALAND Submission to the ADP New Zealand s Intended Nationally Determined Contribution 7 July 2015 New Zealand hereby communicates its intended nationally determined contribution and the accompanying
Generating Current Electricity: Complete the following summary table for each way that electrical energy is generated. Pros:
 P a g e 1 Generating Current Electricity: Complete the following summary table for each way that electrical energy is generated. Generating Electrical Energy Using Moving Water: Hydro-Electric Generation
P a g e 1 Generating Current Electricity: Complete the following summary table for each way that electrical energy is generated. Generating Electrical Energy Using Moving Water: Hydro-Electric Generation
Costs of air pollution from European industrial facilities 2008 2012 an updated assessment
 Costs of air pollution from European industrial facilities 2008 2012 an updated assessment Summary In 2012, air pollution from European industrial facilities cost at least EUR 59 billion (and up to EUR
Costs of air pollution from European industrial facilities 2008 2012 an updated assessment Summary In 2012, air pollution from European industrial facilities cost at least EUR 59 billion (and up to EUR
The Intended Nationally Determined Contribution of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia under the UNFCCC
 The Intended Nationally Determined Contribution of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia under the UNFCCC Riyadh, November 2015 The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia is pleased to submit its Intended Nationally Determined
The Intended Nationally Determined Contribution of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia under the UNFCCC Riyadh, November 2015 The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia is pleased to submit its Intended Nationally Determined
Natural Gas Information Contents
 Natural Gas Information Contents What is natural gas Natural Gas Components Physical Properties of Natural Gas Different Forms of Natural Gas The Use of Natural Gas Co-generation System Natural Gas and
Natural Gas Information Contents What is natural gas Natural Gas Components Physical Properties of Natural Gas Different Forms of Natural Gas The Use of Natural Gas Co-generation System Natural Gas and
Intended Nationally Determined Contribution (INDC) Under the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change
 PAPUA NEW GUINEA Intended Nationally Determined Contribution (INDC) Under the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change Summary Papua New Guinea (PNG) has both very low absolute emissions and
PAPUA NEW GUINEA Intended Nationally Determined Contribution (INDC) Under the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change Summary Papua New Guinea (PNG) has both very low absolute emissions and
What are the causes of air Pollution
 What are the causes of air Pollution Pollutant Particulate Matter (PM-PM 10 and PM 2.5 ) Description and main UK sources Particulate Matter is generally categorised on the basis of the size of the particles
What are the causes of air Pollution Pollutant Particulate Matter (PM-PM 10 and PM 2.5 ) Description and main UK sources Particulate Matter is generally categorised on the basis of the size of the particles
Status of the World s Soil Resources
 5 December 2015 Status of the World s Soil Resources The Intergovernmental Technical Panel on Soils (ITPS), the main scientific advisory body to the Global Soil Partnership (GSP) hosted by the Food and
5 December 2015 Status of the World s Soil Resources The Intergovernmental Technical Panel on Soils (ITPS), the main scientific advisory body to the Global Soil Partnership (GSP) hosted by the Food and
Physical flow accounts: principles and general concepts
 Physical flow accounts: principles and general concepts Julian Chow United Nations Statistics Division 1 st Sub-Regional Course on SEEA 23-27 September 2013 Malaysia SEEA Conceptual Framework Outside territory
Physical flow accounts: principles and general concepts Julian Chow United Nations Statistics Division 1 st Sub-Regional Course on SEEA 23-27 September 2013 Malaysia SEEA Conceptual Framework Outside territory
Unit 6: Homework Questions
 1. The most sustainable type of development is: A) dispersed development B) compact development C) satellite development D) corridor development E) strip development 2. Urban sprawl is synonymous with
1. The most sustainable type of development is: A) dispersed development B) compact development C) satellite development D) corridor development E) strip development 2. Urban sprawl is synonymous with
THE INDC OF THE EUROPEAN UNION AND ITS 28 MEMBER STATES
 THE INDC OF THE EUROPEAN UNION AND ITS 28 MEMBER STATES 1 Our objectives for the INDC process From nationally determined to collectively ambitious and individually fair well in advance of Paris Clarity
THE INDC OF THE EUROPEAN UNION AND ITS 28 MEMBER STATES 1 Our objectives for the INDC process From nationally determined to collectively ambitious and individually fair well in advance of Paris Clarity
growing sources of employment in the country. In
 SRI LANKA 8,000 7,000 6,000 5,000 Fig. 1: Employment by Major Economic Activity ('000s), 2002-2008 Agriculture, Hunting, Forestry, Mining and Wholesale and Retail Trade Hotels and Restaurants Agriculture,
SRI LANKA 8,000 7,000 6,000 5,000 Fig. 1: Employment by Major Economic Activity ('000s), 2002-2008 Agriculture, Hunting, Forestry, Mining and Wholesale and Retail Trade Hotels and Restaurants Agriculture,
Physical Environment. There are economic reasons for countries to cut down their rainforests.
 Tropical Rainforests Reasons for their Destruction Tropical Rainforests are found in the Amazon Basin of South America, (e.g. Brazil) Central Africa (e.g. Congo) and South East Asia (e.g. Indonesia). There
Tropical Rainforests Reasons for their Destruction Tropical Rainforests are found in the Amazon Basin of South America, (e.g. Brazil) Central Africa (e.g. Congo) and South East Asia (e.g. Indonesia). There
[]n. Craving energy. Oil and gas formation. Oil and gas formation. Resources: Fossil Fuels. Supplying our energy needs: Source of energy in the US
![[]n. Craving energy. Oil and gas formation. Oil and gas formation. Resources: Fossil Fuels. Supplying our energy needs: Source of energy in the US []n. Craving energy. Oil and gas formation. Oil and gas formation. Resources: Fossil Fuels. Supplying our energy needs: Source of energy in the US](/thumbs/40/20541015.jpg) Craving energy Supplying our energy needs: Source of energy in the US Resources: Fossil Fuels Energy consumption in the US Reading: Ch 13 Oil and gas formation Oil and gas formation 1. Need accumulation
Craving energy Supplying our energy needs: Source of energy in the US Resources: Fossil Fuels Energy consumption in the US Reading: Ch 13 Oil and gas formation Oil and gas formation 1. Need accumulation
The European Chlor-Alkali industry: an electricity intensive sector exposed to carbon leakage
 Brussels, December 2010 The European Chlor-Alkali industry: an electricity intensive sector exposed to carbon leakage The revised EU ETS (Emission Trading Scheme) Directive 2009/29/EC will have financial
Brussels, December 2010 The European Chlor-Alkali industry: an electricity intensive sector exposed to carbon leakage The revised EU ETS (Emission Trading Scheme) Directive 2009/29/EC will have financial
Liquid Biofuels for Transport
 page 1/11 Scientific Facts on Liquid Biofuels for Transport Prospects, risks and opportunities Source document: FAO (2008) Summary & Details: GreenFacts Context - Serious questions are being raised about
page 1/11 Scientific Facts on Liquid Biofuels for Transport Prospects, risks and opportunities Source document: FAO (2008) Summary & Details: GreenFacts Context - Serious questions are being raised about
Phosphorus and Sulfur
 Global Change Instruction Program Phosphorus and Sulfur The Important Nutrient Phosphorus Phosphorus is a key nutrient, fueling organic productivity on land and in water. A portion of its cycle is shown
Global Change Instruction Program Phosphorus and Sulfur The Important Nutrient Phosphorus Phosphorus is a key nutrient, fueling organic productivity on land and in water. A portion of its cycle is shown
Extracting Energy from Biomass
 Key Terms cellular respiration fermentation greenhouse gases 1.3 Extracting Energy from Biomass greenhouse effect acid precipitation cellular respiration a process that releases energy from organic molecules,
Key Terms cellular respiration fermentation greenhouse gases 1.3 Extracting Energy from Biomass greenhouse effect acid precipitation cellular respiration a process that releases energy from organic molecules,
