Digestive System Tour Lab
|
|
|
- Hector Osborne
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
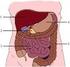
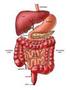
1 Digestive System Tour Lab Name Hour The information to answer these questions begins on Digestive System Diagram Label all parts A Mouth B Salivary glands C Esophagus D Stomach F Liver G Gallbladder H Pancreas I Small Intestine J K Appendix L Rectum M Anus page 9. Digestive System (cartoon) Label as directed A Mouth B Salivary glands C Esophagus D Stomach F Liver G Gallbladder H Pancreas I Small Intestine J K Appendix L Rectum M Anus N Saliva O Hydrochloric Acid P Pepsi Q Enzymes from liver and pancreas U Transverse colon V Descending colon W Nutrients X Water and vitamins Y Kidneys Z Circulatory System
2 Digestive System Tour Lab Page 2 A.D.A.M. video clip: Digestion Fill in the blanks Food is digested by the churning of the stomach walls and by secretion of and. (chemicals) speed up the breakdown of food. Trypsin breads down found in. Lipase breaks down the found in and butter. breaks down the sugar in milk. Food is moved through the small intestine where are absorbed and enter the. Blood is taken to the liver where are processed and are removed. The absorbs water and compacts the remainder of the feces. Feces are eliminated through the and. A.D.A.M. video clip: Peristalsis A.D.A.M. video clip: Heartburn Fill in the blanks Heartburn does not involve the heart, but is felt in the near the heart s location. The has a protective lining against the acid, but the does not. relieve heartburn by making the stomach juices less acidic. A.D.A.M. video clip: Swallowing Fill in the blanks Stage 1 pushes food into the throat. Stage 2 folds over voice box at entrance of windpipe. Stage 3 in the esophagus contract. Fill in the blanks Peristalsis is a series of contractions that moves food through the digestive tract. mixes and shifts the chime on the intestinal wall. A.D.A.M. video clip: Ulcers Fill in the blanks The stomach produces that breaks down food into simpler substances. The lining keeps the stomach from digesting itself. If the lining becomes too thin, an may form. Ulcers may be caused by bacteria, not stress. To control the bacteria, are prescribed. The Esophagus Connects the. About. Flat when. Made of several layers of. is the wavelike muscle contractions that force food through the digestive tract.
3 Digestive System Tour Lab Page 3 The Digestive System is a Giant Food Processor Match These: breaking down of food by the action of enzymes stored for future use The Mouth Food is. Teeth chop. Saliva moistens. broken down into glucose building blocks of cells broken down into amino acids used by cells for energy bile and enzymes from liver enter here water goes back into the bloodstream proteins, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals go into blood (A) small intestine (B) duodenum (C) carbohydrates (D) chemical digestion (E) fats (F) amino acids (G) proteins (H) glucose (I) large intestine The tongue moves. The Throat: The epiglottis. Muscles. The Salivary Glands: Produce. Saliva is an enzyme that. Food becomes moist and mushy. It is now called a. The Stomach (match these): Nutrients the stomach s own acid begins to eat through the stomach Nutrients are absorbed through the. control the ends of the stomach food enters the stomach through the digests protein and kills bacteria helps the hydrochloric acid digest proteins. 3 strong layers of muscle (A) Mucus (B) Hydrochloric Acid (C) The stomach (D) Sphincter muscles (E) Esophagus (F) Ulcer (G) Pepsin Describe the inside lining of the small intestine. Draw a diagram of the villi and label its parts. villi
4 Digestive System Tour Lab Page 4 Your Teeth are Specialized An adult has teeth. Incisors are for and. Canines are for and. Premolars and molars are for. Another name for the 3 rd molars is the teeth. Label the teeth in the diagram: A F Tooth Anatomy Hardest part of the tooth is the lies just beneath the enamel. is a soft tissue that contains living nerve cells. B C D G H H G F E D C B A E Small Intestine The longest. Divided into 3 parts: first segment second segment third segment Digestive enzymes. Nutrients. To stomach Label the Small Intestine: duodenum jejunum illium
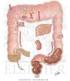
5 Digestive System Tour Lab Page 5 In the large intestine, and are absorbed back into the blood to be reused. What does the appendix do?. Label the : ascending colon transverse colon descending colon appendix rectum anus Tommy Torso (match Tommy s parts with their number) Check Out this X-ray Part name Tongue Part number Return all of my parts before leaving The digestive system organ colored yellow is probably the. Salivary Gland this station!!!!! Esophagus The digestive system organ colored pink is probably the. Stomach Liver What is the doctor about to tell Kermit?. Gallbladder Pancreas Duodenum Small Intestine Which Digestive System organ is shown in this x-ray? Appendix What name does Tommy prefer? Rectum Answer
6 Digestive System Tour Lab Page 6 The Liver, Gallbladder, and Pancreas Match these: use answers more than once stores vitamins produces ½ to 1 liter of enzymes daily produces bile (an enzyme which breaks down fats) stores bile breaks down old red blood cells A) Liver B) Gallbladder C) Pancreas produces enzymes which break down carbohydrates, fats, and proteins Try to SwallowThis Match these: how much food your stomach can hold how long it takes for food to completely digest the weight of your liver how much food you will process in a lifetime the length of your alimentary canal A) hours B) 27 feet C) 3-4 pounds D) 60, ,000 pounds E) 2 ½ pints removes poisons from the body Fetal Pig Model (match the pig part with the part number) Your Saliva Saliva contains the enzyme. What does amylase do?. What should happen to the cracker if partially chewed and left in your mouth? Did it work for you? pancreas small intestine gallbladder duodenum large intestine (caecum) large intestine (spiral colon) large intestine (descending colon) liver Part numbers stomach esophagus What seems to be the main difference between the pig s digestive system and that of humans?
7 Digestive System Tour Lab Page 7 Go to the Human Biology/Links page of our science website ( Go to the Human Biology/Links page of our science website ( Click on Digestive System Tour Lab Click on Digestive System Tour Lab Malnutrition fill in the chart A Balanced Diet Fill in the seven food groups on the pie chart. Matching: red blood cell production store energy, heat insulation provide energy the main part of cytoplasm helps move food along the digestive system strong bones, teeth, and muscles growth and tissue repair A) Protein B) Carbohydrate C) Water D) Vitamins E) Fibre (fiber) F) Fats and oils (lipids) G) Minerals Paper Model of Digestive System tape it here Cause Symptom Name of Disease Too little protein Poor growth and development Kwashiorkor Too little iron Too little fiber Poor wound healing/loss of teeth Bowed and weak legs Osteoporosis Summary of Digestion write the steps of digestion in their proper order (use the cartoon picture of digestion from page 1) Food is chopped and ground in the mouth
8 Paper Model of Digestive System Paper Model of Digestive System Pancreas Pancreas Esophagus Small Intestine Esophagus Small Intestine Stomach Stomach Liver Liver Gallbladder Gallbladder Appendix Anus Rectum Appendix Anus Rectum
9 Digestive System Diagram Salivary Glands Tongue Esophagus (food pipe) Gallbladder Liver Stomach Small Intestine (duodenum) (ascending colon) Pancreas (transverse colon) (descending colon) Small Intestine (jejunum) Small Intestine (illium) Appendix Anus Rectum
10 The Digestive System On your Digestive System Cartoon Label these parts: Mouth Esophagus Small Intestine Mechanical Digestion Mouth Saliva Hydrochloric Acid Pepsin Chemical Circulatory System Kidneys Digestion Trypsin Bile Lipase Enzymes from Liver and Pancreas Stomach Esophagus Nutrients Small Intestine Circulatory System (Transverse Colon) Kidneys #1 Descending Colon Water and Vitamins #2
11 The Digestive System On your Digestive System Cartoon Label these enzymes (chemicals): Saliva Hydrochloric Acid Pepsin Trypsin Lipase Mechanical Digestion Mouth Saliva Hydrochloric Acid Pepsin Chemical Digestion Trypsin Bile Lipase Enzymes from Liver and Pancreas Stomach Esophagus Nutrients Small Intestine Circulatory System (Transverse Colon) Kidneys #1 Descending Colon Water and Vitamins #2
12 The Digestive System On your Digestive System Cartoon Label these: Nutrients Water and Vitamins Mechanical Digestion Chemical Digestion Mechanical Digestion Mouth Saliva Hydrochloric Acid Pepsin Chemical Digestion Trypsin Bile Lipase Enzymes from Liver and Pancreas Stomach Esophagus Nutrients Small Intestine Circulatory System (Transverse Colon) Kidneys #1 Descending Colon Water and Vitamins #2
13 The Digestive System On your Digestive System Cartoon Label these: #1 (Urine/pee pee) #2 (Solid Waste/poop) Mechanical Digestion Mouth Saliva Hydrochloric Acid Pepsin Chemical Digestion Trypsin Bile Lipase Enzymes from Liver and Pancreas Stomach Esophagus Nutrients Small Intestine Circulatory System (Transverse Colon) Kidneys #1 Descending Colon Water and Vitamins #2
14 The Digestive System On your Digestive System Cartoon Color all parts Complete the SUMMARY of DIGESTION (both of these can be done at home if needed) Mechanical Digestion Mouth Saliva Hydrochloric Acid Pepsin Chemical Digestion Trypsin Bile Lipase Enzymes from Liver and Pancreas Stomach Esophagus Nutrients Small Intestine Circulatory System (Transverse Colon) Kidneys #1 Descending Colon Water and Vitamins #2
15 View the Video clip from A.D.A.M. found on the Human Biology/Links page of our website ( Digestion Answer all questions on the answer sheet Click here
16 View the Video clip from A.D.A.M. found on the Human Biology/Links page of our website ( Heartburn Answer all questions on the answer sheet Click here
17 View the Video clip from A.D.A.M. found on the Human Biology/Links page of our website ( Peristalsis Answer all questions on the answer sheet Click here
18 View the Video clip from A.D.A.M. found on the Human Biology/Links page of our website ( Swallowing Answer all questions on the answer sheet Click here
19 View the Video clip from A.D.A.M. found on the Human Biology/Links page of our website ( Ulcers Answer all questions on the answer sheet Click here
20 The Digestive System is a Giant Food Processor Mechanical Digestion Food is chopped and ground into small pieces in the mouth. Chemical Digestion Food is broken down into simple nutrients by the chemical action of enzymes. Nutrients Carbohydrates are broken down into simple sugars (glucose) which is used by the cells for energy. Proteins are broken down into amino acids (the building blocks of cells) which are used to repair old cells and build new cells (skin, blood, muscle, bone and nerve). Fats are stored for future use. They contain vitamins.
21 The Mouth Food is cooled or warmed to body temperature. Teeth chop and grind food and the tongue mashes the food. Saliva moistens the food and begins breaking down carbohydrates. The tongue moves the food to the back of the mouth to be swallowed. The Throat The Epiglottis closes off the wind pipe (trachea). Muscles push food into the esophagus. The Salivary Glands Produce saliva. Saliva is an enzyme (chemical) that begins the breakdown of starches. Food becomes moist and mushy so that it can be easily swallowed. The food is now called a Bolis.
22 3rd Molar (wisdom tooth) 2 nd Molar 1 st Molar Incisors Premolars Canine (Wisdom teeth) Your Teeth are specialized An adult has 32 teeth including 4 wisdom teeth. The Incisors are shaped like knives for cutting and slicing. The Canines have points for piercing and tearing. The Premolars and Molars have broad, bumpy surfaces for grinding. Tooth Anatomy Enamel is the hardest part of tooth. Made mostly of mineral. Dentin is softer than enamel. Contains some living cells. Pulp is also called the nerve of the cell. It is a soft tissue that contains living nerve cells.
23 The Esophagus Connects the pharynx (throat) to the stomach. About 10 inches long. Flat when empty but changes shape to allow food to travel to the stomach. Made of several layers of muscle that push food through to the stomach (peristalsis). Peristalsis is the name given for the wavelike muscle contractions found in the esophagus, small intestines and large intestines. It is sort of like squeezing toothpaste through a tube. Bottom s up I mean down I mean. Peristalsis Esophagus Yes, it is even possible to drink while upside down!!
24 The Stomach Food enters the stomach from the esophagus. Hydrochloric Acid is produced in the stomach to digest proteins and kill off bacteria. Pepsin (a digestive enzyme) is produced to help digest proteins. Mucus is produced by glands of the stomach to protect the stomach from its own acid. Sphincter muscles control both ends of the stomach to allow food to enter and exit. The stomach is made of 3 strong layers of muscle which mixes and mashes the food with digestive enzymes. An ulcer forms when the stomach s protection breaks down its own acid begin to eat through the stomach. Stomach Stomach
25 Small Intestine Small Intestine The longest part of the alimentary canal (digestive tract). Divided into 3 parts: Duodenum first segment Jejunum middle segment Illeum last segment Digestive enzymes from the liver and pancreas help to break down food further. Nutrients are absorbed into the body through the villi. Duodenum Jejunum Illeum
26 The Liver, Gallbladder, and Pancreas The Liver produces the enzyme (chemical) bile Bile breaks down fats. Bile is stored in the gallbladder and enters the duodenum (1 st part of small intestine) when needed. The Pancreas produces ½ to 1 liter of enzymes (chemicals) daily. These enzymes are used to break down carbohydrates as well as fats and proteins. Liver Pancreas The Liver: Stores vitamins Stores glycogen for energy Breaks down old red blood cells Removes poisons from the body Enzymes from the liver and pancreas enter the small intestine at the duodenum Liver Pancreas Gallbladder
27 Nutrients are absorbed through the small intestine where the blood carries them to all the cells of the body. The Basic Nutrients are: Amino Acids Simple Sugars Fatty Acids Small Intestine The inside lining of the small intestine contains Villi. These Villi tiny are fingerlike projections through which the nutrients are absorbed into the bloodstream. The Villi capture nutrients as they move through the small intestine. Villi Blood vessels Photograph of Villi magnified (very high power) Note; your microscope will not show nearly the detail as in this picture. Glands secreting digestive enzymes
28 In the : Indigestible parts of food move from the small intestine to the large intestine. Water and vitamins are absorbed back in the blood to be reused. The remaining waste passes to the RECTUM where peristalsis forces it through the ANUS and out of the body. Large intestine Rectum The is made of 3 parts: Ascending colon Transverse colon Descending colon Note: The Appendix serves no useful purpose. Perhaps it had a role in digesting rough foods many, many years ago. (transverse colon) (ascending colon) (descending colon) Appendix Anus Rectum
29 Try to swallow this some interesting facts about your digestive system. The average digestive tract (alimentary canal) is 27 feet long! During a lifetime, a person will process between 60,000 to 100,000 pounds of food! Just the sight and smell of food begins the digestive process (saliva in your mouth, esophagus begins to ripple, stomach produces digestive enzymes) Your stomach can expand to hold 2 ½ pints of food. The liver is the body s second largest organ weighing 3-4 pounds. (the skin is the largest organ) A meal takes between 15 to 48 hours to completely digest and move through the alimentary canal.
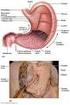
30 Which Digestive System organ is shown in the x-ray? Hint: It stores Bile that was produced in the liver. (If this doesn t help, do some other stations first)
31 Check out this x-ray: The digestive organ colored yellow is probably the Small intestine Large intestine Heart Pancreas The digestive organ colored pink is probable the Small intestine Large intestine Heart Pancreas (answer on your lab answer sheet) Hint: if you are not sure, do some other stations first. Have a seat, Kermit. What I m about to tell you might come as a big shock.
32 This is Tommy the Torso (but he prefers Elvis). Tommy is an expensive, hand painted model of the human torso. His organs are removable but must be handled with care. Hello there! Do This: 1. Carefully remove the Liver, Stomach, and Intestines. 2. Locate and identify the following parts and match them with the numbers on the model: Tongue Salivary Gland Esophagus Stomach Liver Gallbladder Pancreas Duodenum Small Intestine Appendix Rectum Choose from these numbers: 111/ /124 Return all parts before leaving this station. Ask if you need help /138/139 Place all answers on you lab answer sheet
33 Your Saliva contains the enzyme amylase which breaks down huge starch molecules into smaller simple sugars. A cracker is mostly carbohydrate (starch) but if you leave it in your mouth long enough, it will become sugar and you will notice a sweet taste!! Try it!!! Do this: 1. Take one unsalted cracker and chew but don t swallow. 2. Keep the bolus (chewed mush cracker) in your mouth for a minute. 3. After you notice the sweet taste you may swallow. Yum!! Only one quacker per customer!! Crackers are located on the front lab table.
34 How many Digestive System pig parts can you find in this Fetal Pig Model? Locate and identify the following parts and match them with the numbers on the model: Pancreas Small Intestine Gallbladder Duodenum (1 st part of small intestine) (caecum) (spiral colon) (Descending colon) Liver Stomach Esophagus Choose from these numbers:
35 Fetal Pig Internal Organs Front view Lungs Heart Diaphragm Liver Gallbladder Duodenum (first part of small intestine) Stomach (Spiral Colon) (Caecum) Pancreas Small Intestine
36 Fetal Pig Internal Organs Back view Lungs Stomach Esophagus Diaphragm Liver Small Intestine (Descending colon)
37 Paper Model of Digestive System Pancreas Liver Gallbladder Stomach Small Intestine Esophagus Pancreas Liver Gallbladder Stomach Small Intestine Esophagus
38 Build a paper model of the digestive system that looks like the picture below!! 1. Color each part so that it looks very similar to the picture. 2. Cut out each part carefully and tape it to the outline. Parts must be taped down in the proper order beginning with the pancreas. 3. Cut out the outline with all of the parts. Find the place on your lab answer sheet labeled Tape Paper Digestive System Here and tape your completed paper digestive system in that place. Liver Stomach Gallbladder Small Intestine (duodenum) (Transverse Colon) Pancreas Small Intestine (Illium) (Ascending Colon) Appendix Rectum Anus (descending Colon) Small Intestine (Jejunum)
39 On the computer Go to the Human Biology/Links page of our science website ( Click on Digestive System Tour Lab Find this page in the lab and click on the links. Answer all questions on your lab answer sheet: 1. A Balanced Diet Also found at Human Biology/Links page 2. Malnutrition Also found at Human Biology/Links page
40 Write these steps of digestion in their proper order. They are all messed up here. Summary of Digestion Hydrochloric acid and pepsin digest proteins in the stomach. The stomach squeezes to mix food. Nutrients are absorbed into the blood by villi in the small intestine. Water is absorbed from the food waste back into the body. The tongue pushes food to the back of the mouth where it is swallowed. Food is chopped and ground in the mouth. Bile (produced by the liver and stored in the gallbladder) enters the small intestine to break down fats. Solid waste material is forced out of the body by action of both voluntary and involuntary muscles (if ya know what I mean). Food moves to the small intestine (through the duodenum). Waste (food) leaves the small intestine and enters the large intestine. The food moves along the esophagus to the stomach.
41
42
43
10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411
 10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411 The human digestive system is made up of a group of organs working together. The digestive tract is made up of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and
10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411 The human digestive system is made up of a group of organs working together. The digestive tract is made up of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and
Digestive System Why is digestion important? How is food digested? Physical Digestion and Movement
 Digestive System The digestive system is made up of the digestive tract a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus and other organs that help the body break down
Digestive System The digestive system is made up of the digestive tract a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus and other organs that help the body break down
2) Digestion the breakdown of. There are two types of digestion: Mechanical and Chemical. 3) Absorption when the nutrients enter into the blood.
 The Digestive System Video on the digestive system (5 min) The digestive system is responsible for the breakdown of the we eat so that it can be absorbed into the. There are four main stages of the digestive
The Digestive System Video on the digestive system (5 min) The digestive system is responsible for the breakdown of the we eat so that it can be absorbed into the. There are four main stages of the digestive
The Human Digestive System
 The Human Digestive System Name: Section: Date: Page 1 of 10 Page 2 of 10 Page 3 of 10 Page 4 of 10 Page 5 of 10 Page 6 of 10 Putting it All Together Digestive Enzymes Page 7 of 10 Page 8 of 10 Page 9
The Human Digestive System Name: Section: Date: Page 1 of 10 Page 2 of 10 Page 3 of 10 Page 4 of 10 Page 5 of 10 Page 6 of 10 Putting it All Together Digestive Enzymes Page 7 of 10 Page 8 of 10 Page 9
Digestive System. Gross Anatomy and Physiology
 Digestive System Gross Anatomy and Physiology I. Introduction A. Base Function: Working with the circulatory system the digestive system provides the body with fuel. B. Main players: 1. Digestive tract:
Digestive System Gross Anatomy and Physiology I. Introduction A. Base Function: Working with the circulatory system the digestive system provides the body with fuel. B. Main players: 1. Digestive tract:
Digestive system Review
 Digestive system Review 1. Distinguish between chemical digestion and mechanical digestion. The physical breakdown of food begins in the mouth with two types of processes. The mouth is a complex structure
Digestive system Review 1. Distinguish between chemical digestion and mechanical digestion. The physical breakdown of food begins in the mouth with two types of processes. The mouth is a complex structure
Digestive System Notes
 Digestive System Notes Structure Function Relation Mouth cavity Mechanical digestion by teeth; chemical digestion of starch by saliva. Salivary glands Three pairs of glands which secrete saliva containing
Digestive System Notes Structure Function Relation Mouth cavity Mechanical digestion by teeth; chemical digestion of starch by saliva. Salivary glands Three pairs of glands which secrete saliva containing
Topic 3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems
 Topic 3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems Organ Systems Organ systems must have the ability to to changes within and outside of your body to maintain life
Topic 3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems Organ Systems Organ systems must have the ability to to changes within and outside of your body to maintain life
The Excretory and Digestive Systems
 The Excretory and Digestive Systems 38.2 The Process of Digestion Organs of the Digestive System The digestive system includes the: Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small and large intestine. Other structures
The Excretory and Digestive Systems 38.2 The Process of Digestion Organs of the Digestive System The digestive system includes the: Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small and large intestine. Other structures
I. The basic function of the digestive system is
 Chapter 15, Digestive System - ANATOMY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM I. The basic function of the digestive system is. This process is called. II. List 2 other names for the digestive tract: A. B. III. The digestive
Chapter 15, Digestive System - ANATOMY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM I. The basic function of the digestive system is. This process is called. II. List 2 other names for the digestive tract: A. B. III. The digestive
The Digestive System. You are what you eat!
 The Digestive System You are what you eat! Try to label the diagram (PENCIL!!) What is Digestion? Digestion: the breakdown of large macromolecules (proteins, fats, carbohydrates) into smaller molecules
The Digestive System You are what you eat! Try to label the diagram (PENCIL!!) What is Digestion? Digestion: the breakdown of large macromolecules (proteins, fats, carbohydrates) into smaller molecules
Topic 4: Digestion and Nutrition
 Topic 4: Digestion and Nutrition THE CONTENTS OF FOOD Food contains nutrients: Nutrients include: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Nutrients must be small enough to enter our cells. If they are too large they must be digested
Topic 4: Digestion and Nutrition THE CONTENTS OF FOOD Food contains nutrients: Nutrients include: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Nutrients must be small enough to enter our cells. If they are too large they must be digested
Magic School Bus Digestive System Brainpop Digestive System
 The Digestive System Magic School Bus Digestive System Brainpop Digestive System 1 Functions of the Digestive System: 1. Break up food into smaller pieces 2. Absorbing nutrients into the blood 3. Excreting
The Digestive System Magic School Bus Digestive System Brainpop Digestive System 1 Functions of the Digestive System: 1. Break up food into smaller pieces 2. Absorbing nutrients into the blood 3. Excreting
The Digestive System. Chapter 15
 The Digestive System Chapter 15 Introduction Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of food so the nutrients can be absorbed by cells Carried out by the digestive system Consists of
The Digestive System Chapter 15 Introduction Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of food so the nutrients can be absorbed by cells Carried out by the digestive system Consists of
Digestive System Grou p & lndividual Activity checklist
 Digestive System Grou p & lndividual Activity checklist oup Activitv: Each person in your group must research the following organs involved in the digestive process. They are listed below in sections (1-5).
Digestive System Grou p & lndividual Activity checklist oup Activitv: Each person in your group must research the following organs involved in the digestive process. They are listed below in sections (1-5).
Digestion. What we ll cover. Main stages of digestion. Digestion: A Closer Look. A Tour of the Human Digestive System. Mechanical digestion
 Digestion What we ll cover What are the digestive system structures and their functions? Where does carbohydrate, protein and fat digestion and absorption occur? What are the 3 accessory organs of digestion?
Digestion What we ll cover What are the digestive system structures and their functions? Where does carbohydrate, protein and fat digestion and absorption occur? What are the 3 accessory organs of digestion?
Chapter 49 - Nutrients and the Digestive System I. Nutrients (chemical substances necessary for organisms to grow and function properly)
 Chapter 49 - Nutrients and the Digestive System I. Nutrients (chemical substances necessary for organisms to grow and function properly) 6 basic nutrients - 4 food groups (milk, meat, fruit and vegetable,
Chapter 49 - Nutrients and the Digestive System I. Nutrients (chemical substances necessary for organisms to grow and function properly) 6 basic nutrients - 4 food groups (milk, meat, fruit and vegetable,
The Digestive System
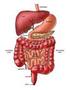 The Digestive System What do you know?? quiz-digestive-health Digestion Videos The Digestive System Inside-Dr-Ozs-Digestive-System-Video Now it is your turn to recreate the digestive system. How is food
The Digestive System What do you know?? quiz-digestive-health Digestion Videos The Digestive System Inside-Dr-Ozs-Digestive-System-Video Now it is your turn to recreate the digestive system. How is food
Medical Physiology Z.H.Al-Zubaydi
 Lec.13 Medical Physiology Z.H.Al-Zubaydi Functions of the Digestive System The major functions of the digestive tract include the following six processes, summarized in Figure 1: 1. Ingestion Food must
Lec.13 Medical Physiology Z.H.Al-Zubaydi Functions of the Digestive System The major functions of the digestive tract include the following six processes, summarized in Figure 1: 1. Ingestion Food must
Chapter 48. Nutrients in Food. Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids. Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids, continued
 Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids The three nutrients needed by the body in the greatest amounts are carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Nutrients in Food All of these nutrients are called organic compounds,
Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids The three nutrients needed by the body in the greatest amounts are carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Nutrients in Food All of these nutrients are called organic compounds,
1. Which substances in the small intestine of humans serve to increase the surface area for absorption?
 Digestion Review 1. Which substances in the small intestine of humans serve to increase the surface area for absorption? (a.) intestinal glands (b.) villi (c.) pseudopodia (d.) cilia (e.) flagella 2. The
Digestion Review 1. Which substances in the small intestine of humans serve to increase the surface area for absorption? (a.) intestinal glands (b.) villi (c.) pseudopodia (d.) cilia (e.) flagella 2. The
Digestive System Functions
 Digestive System Functions A. Gastrointestinal Processes 1. Ingestion: placing food in mouth (voluntary) 2. Propulsion: moving food through GI tract a. Peristalsis: alternating waves of contraction and
Digestive System Functions A. Gastrointestinal Processes 1. Ingestion: placing food in mouth (voluntary) 2. Propulsion: moving food through GI tract a. Peristalsis: alternating waves of contraction and
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM What is digestion? Digestion is the process of breaking down food so that it's small enough to be absorbed and used by the body for energy or in other bodily functions. Digestion involves
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM What is digestion? Digestion is the process of breaking down food so that it's small enough to be absorbed and used by the body for energy or in other bodily functions. Digestion involves
The 6 th International Junior Science Olympiad Training Programme
 The 6 th International Junior Science Olympiad Training Programme KEEPING HEALTHY SECTION 2: DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Notes to Teachers Learning Objectives: Processes of nutrition in human (0.25 hr) General plan
The 6 th International Junior Science Olympiad Training Programme KEEPING HEALTHY SECTION 2: DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Notes to Teachers Learning Objectives: Processes of nutrition in human (0.25 hr) General plan
The Digestive System. Chapter 16. Introduction. Histological Organization. Overview of Digestive System. Movement and Mixing of Digestive Materials
 The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
Horse Science: The Digestive System of the Horse Page 3
 Horse Science: The Digestive System of the Horse Page 3 The digestive system of the horse is different from that Mastication (chewing) is the mechanical reduction of of the other farm animals. Although
Horse Science: The Digestive System of the Horse Page 3 The digestive system of the horse is different from that Mastication (chewing) is the mechanical reduction of of the other farm animals. Although
The Gastrointestinal System It consists of: The digestive tract Mouth Pharynx Oesophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
 The Gastrointestinal System It consists of: The digestive tract Mouth Pharynx Oesophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine The digestive organs Teeth Tongue Salivary glands Liver Gall bladder Pancreas
The Gastrointestinal System It consists of: The digestive tract Mouth Pharynx Oesophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine The digestive organs Teeth Tongue Salivary glands Liver Gall bladder Pancreas
5. Secretion: release of water, acids. Enzymes, buffers by digestive tract.
 Digestive System CH-16 Lecture topics Functions of the digestive system: p. 488. 1. Ingestion: Taking food in 2. Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal p.490. voluntary: swalloing : skeletal
Digestive System CH-16 Lecture topics Functions of the digestive system: p. 488. 1. Ingestion: Taking food in 2. Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal p.490. voluntary: swalloing : skeletal
[DIGESTIVE SYSTEM] [Grade 3-5]
![[DIGESTIVE SYSTEM] [Grade 3-5] [DIGESTIVE SYSTEM] [Grade 3-5]](/thumbs/40/20967878.jpg) [DIGESTIVE SYSTEM] [Grade 3-5] BACKGROUND Tissue is the building block of body organs. Organs perform specialized functions in the body. Organs that work together to perform a particular function in the
[DIGESTIVE SYSTEM] [Grade 3-5] BACKGROUND Tissue is the building block of body organs. Organs perform specialized functions in the body. Organs that work together to perform a particular function in the
The Digestive System. The large intestine, or colon, holds waste products until elimination can occur. Its main function is to absorb.
 The Digestive System By: Joyce Green About the Digestive System The digestive system is responsible for the processing and uptake of nutrition. Every cell in an organism needs energy and an array of nutrients
The Digestive System By: Joyce Green About the Digestive System The digestive system is responsible for the processing and uptake of nutrition. Every cell in an organism needs energy and an array of nutrients
General Structure and Function of the Digestive System
 General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Do Now Why does food have to be digested before cells can use it? What are the typical four layers of the digestive tract wall? What is the name of
General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Do Now Why does food have to be digested before cells can use it? What are the typical four layers of the digestive tract wall? What is the name of
Outline Digestive System
 Outline Digestive System The Digestive System Digestive System Lecture Packet 19 Chapter 15 I. Function II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine,
Outline Digestive System The Digestive System Digestive System Lecture Packet 19 Chapter 15 I. Function II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine,
By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford
 By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford Body systems Digestive System Circulatory System Respiratory System Excretory System Immune System Reproductive System Nervous System Muscular System Skeletal System Endocrine
By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford Body systems Digestive System Circulatory System Respiratory System Excretory System Immune System Reproductive System Nervous System Muscular System Skeletal System Endocrine
Chapter 2 Digestion and Absorption Chapter Outline
 Chapter 2 Digestion and Absorption Chapter Outline I. Anatomy of the Digestive Tract A. The Digestive Organs 1. Mouth to the Esophagus 2. Esophagus to the Stomach 3. The Small Intestine 4. The Large Intestine
Chapter 2 Digestion and Absorption Chapter Outline I. Anatomy of the Digestive Tract A. The Digestive Organs 1. Mouth to the Esophagus 2. Esophagus to the Stomach 3. The Small Intestine 4. The Large Intestine
Getting Energy from Food Your Digestive System
 9 Getting Energy from Food Your Digestive System The Digestive System You know how your body gets the oxygen it needs. But how do your body s cells get the nutrients they need? Nutrients come from the
9 Getting Energy from Food Your Digestive System The Digestive System You know how your body gets the oxygen it needs. But how do your body s cells get the nutrients they need? Nutrients come from the
Alimentary canal (gastrointestinal or GI tract) continuous coiled hollow tube
 The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Gross Anatomy Function The Digestive System Functions Ingestion taking in food Digestion breaking food down both physically and chemically Absorption movement of
The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Gross Anatomy Function The Digestive System Functions Ingestion taking in food Digestion breaking food down both physically and chemically Absorption movement of
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM from The Human Body Systems Series
 from The Human Body Systems Series Teacher's Guide 1 The Digestive System from The Human Body Systems Series catalog # 3206 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560 Sherman Avenue Suite 100
from The Human Body Systems Series Teacher's Guide 1 The Digestive System from The Human Body Systems Series catalog # 3206 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560 Sherman Avenue Suite 100
8. Be able to label a diagram of an earthworm. Know the function of each of the major parts of the earthworm.
 Review for Unit Test: The Digestive System 1. Know the meaning of these terms: heterotrophs digestion peristalsis microvilli autotrophs chemical digestion chyme lacteal intracellular digestion mechanical
Review for Unit Test: The Digestive System 1. Know the meaning of these terms: heterotrophs digestion peristalsis microvilli autotrophs chemical digestion chyme lacteal intracellular digestion mechanical
Digestive System AKA. GI System. Overview. GI Process Process Includes. G-I Tract Alimentary Canal
 Digestive System AKA G-I Tract Alimentary Canal Overview GI System Consists of Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, anus About 30 in length Accessory Organs Teeth, tongue,
Digestive System AKA G-I Tract Alimentary Canal Overview GI System Consists of Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, anus About 30 in length Accessory Organs Teeth, tongue,
Welcome back. Today, we embark on Lesson 6 where we ll study the human digestive system.
 Basic Human Anatomy Lesson 6: The Human Digestive System Welcome back. Today, we embark on Lesson 6 where we ll study the human digestive system. After completing this lesson, you should be able to define
Basic Human Anatomy Lesson 6: The Human Digestive System Welcome back. Today, we embark on Lesson 6 where we ll study the human digestive system. After completing this lesson, you should be able to define
Special organ structures and functions conduct these tasks through the successive parts of the overall system.
 Chapter 5 Digestion, Absorption, and Metabolism Chapter 5 Lesson 5.1 Key Concepts Through a balanced system of mechanical and chemical digestion, food is broken down into smaller substances and the nutrients
Chapter 5 Digestion, Absorption, and Metabolism Chapter 5 Lesson 5.1 Key Concepts Through a balanced system of mechanical and chemical digestion, food is broken down into smaller substances and the nutrients
Absorption and Transport of Nutrients
 Page1 Digestion Food travels from mouth esophagus stomach small intestine colon rectum anus. Food mixes with digestive juices, moving it through the digestive tract Large molecules of food are broken into
Page1 Digestion Food travels from mouth esophagus stomach small intestine colon rectum anus. Food mixes with digestive juices, moving it through the digestive tract Large molecules of food are broken into
Digestive System Lecture 5 Winter 2014
 Digestive System Lecture 5 Winter 2014 This lecture tells the story of the Flow of Matter from Food to Cells. The pictures are only there to help you visualize structures don t worry about names of structures
Digestive System Lecture 5 Winter 2014 This lecture tells the story of the Flow of Matter from Food to Cells. The pictures are only there to help you visualize structures don t worry about names of structures
Digestion, Absorption. How & where?
 Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
The Digestive System. Chapter 14. The Digestive System and Body Metabolism. Metabolism. Organs of the Digestive System. Digestion.
 Chapter 14 The Digestive System The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Digestion of ingested food of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of Constructive and degradative cellular activities
Chapter 14 The Digestive System The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Digestion of ingested food of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of Constructive and degradative cellular activities
1. Essay: The Digestive and Absorption Processes of Macronutrients
 Jenny Kim Professor Rosario Nutrition: Macronutrients Project June 26, 2014 1. Essay: The Digestive and Absorption Processes of Macronutrients Whenever we eat, the foods we ingest in our bodies undergo
Jenny Kim Professor Rosario Nutrition: Macronutrients Project June 26, 2014 1. Essay: The Digestive and Absorption Processes of Macronutrients Whenever we eat, the foods we ingest in our bodies undergo
GI TRACT ORGANS ACCESSORY ORGANS
 Digestive System GI TRACT ORGANS Oral cavity Oropharynx Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large Intestine Anus ACCESSORY ORGANS Salivary glands Pancreas Liver Gall bladder GI TRACT LAYERS Mucosa Submucosa
Digestive System GI TRACT ORGANS Oral cavity Oropharynx Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large Intestine Anus ACCESSORY ORGANS Salivary glands Pancreas Liver Gall bladder GI TRACT LAYERS Mucosa Submucosa
Learning Objectives. Introduction to Medical Careers. Vocabulary: Chapter 16 FACTS. Functions. Organs. Digestive System Chapter 16
 Learning Objectives Introduction to Medical Careers Digestive System Chapter 16 Define at least 10 terms relating to the digestive Describe the four functions of the digestive Identify different structures
Learning Objectives Introduction to Medical Careers Digestive System Chapter 16 Define at least 10 terms relating to the digestive Describe the four functions of the digestive Identify different structures
The Vertebrate (mostly human) Digestive System
 The Vertebrate (mostly human) Digestive System Mouth - mastication, lubrication, digestion Pharynx and Esophagus - swallowing Stomach - some digestion Small intestine - most digestion and absorption Large
The Vertebrate (mostly human) Digestive System Mouth - mastication, lubrication, digestion Pharynx and Esophagus - swallowing Stomach - some digestion Small intestine - most digestion and absorption Large
30.3 The Digestive System
 30.3 The Digestive System Lesson Objectives Describe the organs of the digestive system and explain their functions. Explain what happens during digestion. Describe how nutrients are absorbed into the
30.3 The Digestive System Lesson Objectives Describe the organs of the digestive system and explain their functions. Explain what happens during digestion. Describe how nutrients are absorbed into the
Note Taking Guide. Topic # 3024 Comparative Digestive Systems
 Note Taking Guide Topic # 3024 Comparative Digestive Systems Digestive Systems Overview 1. Digestion Digestion: Food enters the mouth and goes through mechanical and chemical changes as it passes through
Note Taking Guide Topic # 3024 Comparative Digestive Systems Digestive Systems Overview 1. Digestion Digestion: Food enters the mouth and goes through mechanical and chemical changes as it passes through
A comparison of the different livestock systems. By: Kristy Baird
 A comparison of the different livestock systems By: Kristy Baird Describe the basic function of the primary components of the digestive system. Compare the function and location of the digestive organs
A comparison of the different livestock systems By: Kristy Baird Describe the basic function of the primary components of the digestive system. Compare the function and location of the digestive organs
Chapter 17 Digestive System. Alimentary Canal. Movements of the Tube
 Chapter 17 Digestive System Functions of Digestive System ingestion mechanical digestion chemical digestion propulsion absorption defecation Consists of the alimentary canal and accessory organs 1 Alimentary
Chapter 17 Digestive System Functions of Digestive System ingestion mechanical digestion chemical digestion propulsion absorption defecation Consists of the alimentary canal and accessory organs 1 Alimentary
Digestion, Absorption. How & where?
 Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
Chapter 15 Digestive System.
 Chapter 15 Digestive System. I. The Gastrointestinal Tract. a. The digestive system mechanically and chemically breaks down food into molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream or lymph. Residues
Chapter 15 Digestive System. I. The Gastrointestinal Tract. a. The digestive system mechanically and chemically breaks down food into molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream or lymph. Residues
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems. Lesson 1 Understanding Animal Digestion
 Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 1 Understanding Animal Digestion 1 Terms Absorption Amino acids Anus Avian Bile Cecum Chyme Crop Cud Digestion Digestive system Enzymes Eructated Feces Gizzard
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 1 Understanding Animal Digestion 1 Terms Absorption Amino acids Anus Avian Bile Cecum Chyme Crop Cud Digestion Digestive system Enzymes Eructated Feces Gizzard
Divisions of Digestive System. Organs of the Alimentary Canal. Anatomy of the Digestive System: Organs of the Alimentary Canal. CHAPTER 14 p.
 Divisions of Digestive System Anatomy of the Digestive System: Organs of the Alimentary Canal CHAPTER 14 p. 412-423 1. Alimentary Canal or Gastrointestinal Tract (GI)-digests and absorbs food coiled hollow
Divisions of Digestive System Anatomy of the Digestive System: Organs of the Alimentary Canal CHAPTER 14 p. 412-423 1. Alimentary Canal or Gastrointestinal Tract (GI)-digests and absorbs food coiled hollow
DIGESTION is the physical and
 Digestion DIGESTION is the physical and chemical breakdown of feeds as they pass through the gastrointestinal tract. The structures of the gastrointestinal tract include the mouth, the esophagus, the stomach,
Digestion DIGESTION is the physical and chemical breakdown of feeds as they pass through the gastrointestinal tract. The structures of the gastrointestinal tract include the mouth, the esophagus, the stomach,
Digestive System. About the Digestive System. How Digestion Works
 Digestive System The first step in the digestive process happens before we even taste food. Just by smelling that homemade apple pie or thinking about how delicious that ripe tomato is going to be, you
Digestive System The first step in the digestive process happens before we even taste food. Just by smelling that homemade apple pie or thinking about how delicious that ripe tomato is going to be, you
Chapter 15 Digestion and Nutrition
 Chapter 15 Digestion and Nutrition Digestive System: Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of foods so that nutrients can be absorbed by cells. Consists of the canal which is all of
Chapter 15 Digestion and Nutrition Digestive System: Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of foods so that nutrients can be absorbed by cells. Consists of the canal which is all of
The Goat s Digestive System. Roy Beckford UF/IFAS Lee County
 The Goat s Digestive System Roy Beckford UF/IFAS Lee County Ruminants The goat is a member of a class of animals called ruminants. These animals ruminate (chew their cud). Unlike us, they have special
The Goat s Digestive System Roy Beckford UF/IFAS Lee County Ruminants The goat is a member of a class of animals called ruminants. These animals ruminate (chew their cud). Unlike us, they have special
Human Digestive System Anatomy
 Human Digestive System Anatomy Biology 104 Objectives: 1. Learn the anatomy of the digestive system. You should be able to find all terms in bold on the human torso models. 2. Relate structure of the system
Human Digestive System Anatomy Biology 104 Objectives: 1. Learn the anatomy of the digestive system. You should be able to find all terms in bold on the human torso models. 2. Relate structure of the system
stomach this The Digestive System in American Sign Language and English with Paul Buttenhoff and Cara Barnett Click here to see ASL version of title
 t stomach this The Digestive System in American Sign Language and English with Paul Buttenhoff and Cara Barnett Click here to see ASL version of title Click here to go to Table of Contents This project
t stomach this The Digestive System in American Sign Language and English with Paul Buttenhoff and Cara Barnett Click here to see ASL version of title Click here to go to Table of Contents This project
AP Biology. What do animals need to live? Animal Nutrition. Nutritional requirements. How do animals get their food? Different diets; different lives
 Animal Nutrition What do animals need to live? Animals make energy using: food food oxygen Animals build bodies using: food for raw materials amino acids, sugars, fats, nucleotides O 2 ATP energy for synthesis
Animal Nutrition What do animals need to live? Animals make energy using: food food oxygen Animals build bodies using: food for raw materials amino acids, sugars, fats, nucleotides O 2 ATP energy for synthesis
Supported by. A seven part series exploring the fantastic world of science.
 Supported by A seven part series exploring the fantastic world of science. Find out about the different types of teeth in your mouth. Milk Teeth As a child you have 20 milk teeth. Your first tooth appears
Supported by A seven part series exploring the fantastic world of science. Find out about the different types of teeth in your mouth. Milk Teeth As a child you have 20 milk teeth. Your first tooth appears
Functions of the GI Tract. Chapter 18. Functions of the GI Tract (continued)
 Functions of the GI Tract Chapter 18 The Digestive System Motility: Movement of of food through the GI tract. Ingestion: Taking food into the mouth. Mastication: Chewing the food and mixing it with saliva.
Functions of the GI Tract Chapter 18 The Digestive System Motility: Movement of of food through the GI tract. Ingestion: Taking food into the mouth. Mastication: Chewing the food and mixing it with saliva.
From ead to oe. Developed and Published by. 2010 AIMS Education Foundation
 TM From H T ead to oe Developed and Published by AIMS Education Foundation This book contains materials developed by the AIMS Education Foundation. AIMS (Activities Integrating Mathematics and Science)
TM From H T ead to oe Developed and Published by AIMS Education Foundation This book contains materials developed by the AIMS Education Foundation. AIMS (Activities Integrating Mathematics and Science)
Integumentary System Digestive System. Outline. Integumentary System 11/4/2008. Week 11 BA & BP November 4, 2008 Nadia Arora, ND
 Integumentary System Digestive System Week 11 BA & BP November 4, 2008 Nadia Arora, ND Outline Integumentary system and body membranes Types of body membranes and their function General structure and main
Integumentary System Digestive System Week 11 BA & BP November 4, 2008 Nadia Arora, ND Outline Integumentary system and body membranes Types of body membranes and their function General structure and main
The digestive system, also called the gastrointestinal
 exercise 8 Chemical and Physical Processes of Digestion Objectives 1. To define digestive tract, accessory glands, digestion, hydrolases, salivary amylase, carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, bile salts,
exercise 8 Chemical and Physical Processes of Digestion Objectives 1. To define digestive tract, accessory glands, digestion, hydrolases, salivary amylase, carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, bile salts,
Lesson 2: Digestion of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates
 Lesson 2: Digestion of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates Inquiry Focus: How does the body get energy from food? Student Learning Objectives: By the end of the lesson, students will be able to do the following:
Lesson 2: Digestion of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates Inquiry Focus: How does the body get energy from food? Student Learning Objectives: By the end of the lesson, students will be able to do the following:
1. gustatory cells: Surface cells in the throat and on the taste buds in the mouth that transmit
 Chapter 3 Digestion and Absorption Key Terms 1. gustatory cells: Surface cells in the throat and on the taste buds in the mouth that transmit taste information. 2. absorption: The movement of substances
Chapter 3 Digestion and Absorption Key Terms 1. gustatory cells: Surface cells in the throat and on the taste buds in the mouth that transmit taste information. 2. absorption: The movement of substances
Material AICLE. 5º de Primaria.: Food and nutrition (Solucionario)
 Material AICLE. 5º de Primaria.: Food and nutrition (Solucionario) 3 SOLUTIONS Activity 3. Listen to the following audio and complete this chart. Then, check your answers using the information in activity
Material AICLE. 5º de Primaria.: Food and nutrition (Solucionario) 3 SOLUTIONS Activity 3. Listen to the following audio and complete this chart. Then, check your answers using the information in activity
Digestive System. Student Learning Objectives: Structures to be studied: Introduction
 Digestive System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary structures of the digestive system. Describe the use of various important nutrient materials in the body. Structures to be studied: Oral
Digestive System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary structures of the digestive system. Describe the use of various important nutrient materials in the body. Structures to be studied: Oral
The Respiratory System
 Human Anatomy III: Respiratory, Urinary & Digestive Systems The Respiratory System Major functions include: Obtaining oxygen Removing carbon dioxide Maintenance of ph balance Respiration may be accomplished
Human Anatomy III: Respiratory, Urinary & Digestive Systems The Respiratory System Major functions include: Obtaining oxygen Removing carbon dioxide Maintenance of ph balance Respiration may be accomplished
Digestive System Simulation
 Digestive System Simulation Lesson Concept Link The digestive system consists of the mouth/teeth, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestine, colon, rectum/anus. (Teacher Note: The pancreas, liver,
Digestive System Simulation Lesson Concept Link The digestive system consists of the mouth/teeth, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestine, colon, rectum/anus. (Teacher Note: The pancreas, liver,
The Digestive System: Where does food go? Teacher Version
 The Digestive System: Where does food go? Teacher Version In this lab you will learn about your digestive system. We will use everyday objects like yarn and a ziplock bag to understand how long our digestive
The Digestive System: Where does food go? Teacher Version In this lab you will learn about your digestive system. We will use everyday objects like yarn and a ziplock bag to understand how long our digestive
BTEP Certificate in Beauty Therapy. Distance Learning Materials. The Human Body. Module 2
 BTEP Certificate in Beauty Therapy Distance Learning Materials The Human Body Module 2 The Human Body About the Course Team Laura Sibanda has worked in hairdressing & beauty therapy for 13 years. She holds
BTEP Certificate in Beauty Therapy Distance Learning Materials The Human Body Module 2 The Human Body About the Course Team Laura Sibanda has worked in hairdressing & beauty therapy for 13 years. She holds
Each gland has at least one duct that takes saliva to the oral cavity.
 kufa university Physiology College of Nursing first year student Ass. Lect :- Hisham Qassem M. Lecture No :-3 The Digestive System Digestive system consists of: 1. Gastrointestinal Tract (GIT). 2. Accessory
kufa university Physiology College of Nursing first year student Ass. Lect :- Hisham Qassem M. Lecture No :-3 The Digestive System Digestive system consists of: 1. Gastrointestinal Tract (GIT). 2. Accessory
Eating, pooping, and peeing THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Ingested food is not technically in the body until it is absorbed so it needs to be: Mechanically and chemically reduced Transported by the blood to the cells Large portions are not
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Ingested food is not technically in the body until it is absorbed so it needs to be: Mechanically and chemically reduced Transported by the blood to the cells Large portions are not
Lab 18 The Digestive System
 Lab 18 The Digestive System Laboratory Objectives Identify on a diagram, model or cadaver the parts of the digestive system and accessory organs. Describe the general histology of the digestive system.
Lab 18 The Digestive System Laboratory Objectives Identify on a diagram, model or cadaver the parts of the digestive system and accessory organs. Describe the general histology of the digestive system.
The Digestive System Grade 5
 TEACHING LEARNING COLLABORATIVE (TLC) LIFE SCIENCE The Digestive System Grade 5 Created by: Shelly Bell (Kelseyville Elementary School), Bart Pontoni (Riviera Elementary School), Shane Lee (Pomo Elementary
TEACHING LEARNING COLLABORATIVE (TLC) LIFE SCIENCE The Digestive System Grade 5 Created by: Shelly Bell (Kelseyville Elementary School), Bart Pontoni (Riviera Elementary School), Shane Lee (Pomo Elementary
Name Digestive System and Body Metabolism Notes Ch 14
 Name Digestive System and Body Metabolism Notes Ch 14 Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy ( ) Constructive and degradative
Name Digestive System and Body Metabolism Notes Ch 14 Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy ( ) Constructive and degradative
SMALL AND LARGE INTESTINE SECRETIONS
 SMALL AND LARGE INTESTINE SECRETIONS Objectives At the end of lecture student should be able to know, Digestive system Digestive system secretions Small intestine Component of small intestine Intestinal
SMALL AND LARGE INTESTINE SECRETIONS Objectives At the end of lecture student should be able to know, Digestive system Digestive system secretions Small intestine Component of small intestine Intestinal
The Digestive System
 School of Social Work The Digestive System Undergraduate researcher: Nancy D. Bergerson (2010). 1 The Digestive System breaks down and absorbs food. When food is eaten, it is not in a form the body can
School of Social Work The Digestive System Undergraduate researcher: Nancy D. Bergerson (2010). 1 The Digestive System breaks down and absorbs food. When food is eaten, it is not in a form the body can
Digestion in the small and Large Intestines
 9.5 Digestion in the small and Large Intestines Do some foods keep you feeling full for a long time? Do you ever feel that after eating certain foods, you are hungry again in a short time? Some foods stay
9.5 Digestion in the small and Large Intestines Do some foods keep you feeling full for a long time? Do you ever feel that after eating certain foods, you are hungry again in a short time? Some foods stay
Digestive System Module 7: Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look
 OpenStax-CNX module: m49457 1 Digestive System Module 7: Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look Donna Browne Based on Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look by OpenStax This work is
OpenStax-CNX module: m49457 1 Digestive System Module 7: Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look Donna Browne Based on Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look by OpenStax This work is
Functions of the digestive system
 Digestive system Functions of the digestive system Digestion-mechanical and chemical breakdown of material Motility-movement of material from the oral cavity to the anus-swallowing / peristalsis Secretion-exocrine
Digestive system Functions of the digestive system Digestion-mechanical and chemical breakdown of material Motility-movement of material from the oral cavity to the anus-swallowing / peristalsis Secretion-exocrine
Introduction. Digestive System. Physiology. Anatomy. Physiology. Alimentary Canal. Chapter 21
 Chapter 21 Digestive System Susan G. Salvo Introduction Digestive process is a disassembly line Digestive system provides processes in which proteins, carbohydrates, and fats are broken down and used a
Chapter 21 Digestive System Susan G. Salvo Introduction Digestive process is a disassembly line Digestive system provides processes in which proteins, carbohydrates, and fats are broken down and used a
Care and Problems of the Digestive System. Chapter 18 Lesson 2
 Care and Problems of the Digestive System Chapter 18 Lesson 2 Care of the Digestive System Good eating habits are the best way to avoid or minimize digestive system problems. Eat a variety of foods Avoid
Care and Problems of the Digestive System Chapter 18 Lesson 2 Care of the Digestive System Good eating habits are the best way to avoid or minimize digestive system problems. Eat a variety of foods Avoid
Gateways to Science SAMPLE. STAAR Edition. Teacher Edition
 Gateways to Science STAAR Edition Grade 7 Teacher Edition What Are My Traits? Gateways to Science, STAAR Edition, Grade 7 Page 1 of 2 INTRODUCTION to Gateways Gateways to Science Features Safety Alert
Gateways to Science STAAR Edition Grade 7 Teacher Edition What Are My Traits? Gateways to Science, STAAR Edition, Grade 7 Page 1 of 2 INTRODUCTION to Gateways Gateways to Science Features Safety Alert
THE GI TRACT IS A CONTINUOUS MULTILAYERED TUBE EXTENDING FROM THE MOUTH TO THE ANUS THAT IS SUPPORTED AND PARTIALLY COVERED BY THE PERITONEUM.
 THE GI TRACT IS A CONTINUOUS MULTILAYERED TUBE EXTENDING FROM THE MOUTH TO THE ANUS THAT IS SUPPORTED AND PARTIALLY COVERED BY THE PERITONEUM. OVERVIEW OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Two groups of organs compose
THE GI TRACT IS A CONTINUOUS MULTILAYERED TUBE EXTENDING FROM THE MOUTH TO THE ANUS THAT IS SUPPORTED AND PARTIALLY COVERED BY THE PERITONEUM. OVERVIEW OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Two groups of organs compose
The Take-Apart Human Body
 The Take-Apart Human Body As any teacher knows, children are naturally curious about their bodies. Their questions are endless, and present a tremendous educational opportunity: How do my ears work? Where
The Take-Apart Human Body As any teacher knows, children are naturally curious about their bodies. Their questions are endless, and present a tremendous educational opportunity: How do my ears work? Where
Overview... 1 What is the Outreach Program?... 1 Concepts... 2 Objectives... 3 Arizona Science Standards... 3 College and Career Ready ELA
 Overview... 1 What is the Outreach Program?... 1 Concepts... 2 Objectives... 3 Arizona Science Standards... 3 College and Career Ready ELA Standards... 4 Next Generation Science Standards... 4 Learning
Overview... 1 What is the Outreach Program?... 1 Concepts... 2 Objectives... 3 Arizona Science Standards... 3 College and Career Ready ELA Standards... 4 Next Generation Science Standards... 4 Learning
LAB 3: DIGESTION OF ORGANIC MACROMOLECULES
 LAB 3: DIGESTION OF ORGANIC MACROMOLECULES INTRODUCTION Enzymes are a special class of proteins that lower the activation energy of biological reactions. These biological catalysts change the rate of chemical
LAB 3: DIGESTION OF ORGANIC MACROMOLECULES INTRODUCTION Enzymes are a special class of proteins that lower the activation energy of biological reactions. These biological catalysts change the rate of chemical
NAME: DATE: Home Economics: The parts of the digestive system and their functions. Home Economics
 Home Economics The parts of the digestive system and their functions It is not necessary to carry out all the activities contained in this unit. Please see Teachers Notes for explanations, additional activities,
Home Economics The parts of the digestive system and their functions It is not necessary to carry out all the activities contained in this unit. Please see Teachers Notes for explanations, additional activities,
Mechanical digestion: physical breaking of food chewing by teeth churning by stomach segmentation by intestines (= mixing food) p.611/ Fig. 22.
 The Digestive System 1. Describe the general functions of the digestive system Ingestion: Taking food in Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal voluntary: swalloing involuntary: peristalsis
The Digestive System 1. Describe the general functions of the digestive system Ingestion: Taking food in Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal voluntary: swalloing involuntary: peristalsis
LESSONS: 1. Students will listen to It Takes Guts and complete a lyric note- sheet.
 It Takes Guts: A Multimedia Digestive System Journey Teacher Lesson Plan and Student activity package Learning Objectives: 1. Students will listen to It Takes Guts and complete a lyric note- sheet. 2.
It Takes Guts: A Multimedia Digestive System Journey Teacher Lesson Plan and Student activity package Learning Objectives: 1. Students will listen to It Takes Guts and complete a lyric note- sheet. 2.
Level 3. Applying the Principles of Nutrition to a Physical Activity Programme Level 3
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number APNU3.0 Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title MOCK PAPER Time allocation 50 minutes Level 3 Applying
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number APNU3.0 Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title MOCK PAPER Time allocation 50 minutes Level 3 Applying
Biology 13A Lab #13: Nutrition and Digestion
 Biology 13A Lab #13: Nutrition and Digestion Lab #13 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 102 Introduction...... 103 Food Chemistry & Nutrition.... 104 Activity 1: Testing for the Presence
Biology 13A Lab #13: Nutrition and Digestion Lab #13 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 102 Introduction...... 103 Food Chemistry & Nutrition.... 104 Activity 1: Testing for the Presence
