ECG: MCQ. 1- In the fundamental rules of the ECG all the following are right EXCEP: a- It is a biphasic record of myocardial action
|
|
|
- Grant Ball
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ECG: MCQ 1- In the fundamental rules of the ECG all the following are right EXCEP: a- It is a biphasic record of myocardial action potential fluctuations. b- Deflection record occurs only during complete depolarization or repolarization. c- +ve wave occurs when depolarizing current approaches the +ve terminal electrode of the meter. d- -ve wave happens when repolarizing current approaches the +ve terminal electrode. 1
2 2- Regarding the causes of the ECG waves all the following are correct EXCEPT: a- P wave by atrial depolarization. ation b- QRS complex by ventricular depolarization. c- T wave by ventricular repolarization. d- U wave by papillary muscle depolarization. 3- The causes of the ECG intervals : a- PR by AV nodal conduction. b- ST by atrial repolarization. c- QT by ventricular depolarization and ventricular repolarization. d- All of the above. 2
3 4- In the ECG: a- ST segment is part of depolarization & coincides with plateau. b- T wave has the same voltage of QRS. c- QRS & T wave are in the same direction. d- QRS & T wave are in opposite directions. 5- The voltage of the ECG: a- Is normal summation of QRS complexes in standard limb leads. b- Is normally >1.5 mv. c- Is low in individual having body mass index (BMI) 35. d- All of the above. 3
4 5- Regarding the flow of electrical currents around the heart all the followings are correct EXCEPT: a- From left to right in the mid portion of the ventricular septum. b- From the base to the apex during almost depolarization. c- From the epicardium to the subendocardium di during repolarization. d- From the epicardium to the subendocardium during depolarization. 6- Axis of the heart is: a- Mean instantaneous vector of QRS complexes in vertical plane. b- Normally from-30 to +60. c- Deviated to left side in full term pregnant woman. d- Deviated to right side in long slender person (e.g., +80). 4
5 7- The P-wave of normal ECG: a- Has voltage and duration nearly equal 2.5X 2.5 mm. b- Is upright in avr. c- Represents right atrial depolarization in its second half. d- Coincides with atrial systole. 8- The configuration of QRS complex in normal ECG: a- Depends only on the direction of depolarizing current. b- Is mainly positive in right ventricular surface pattern. c- Exhibits growing R in chest leads. d- Is positive in avr. 5
6 9- As regards Q wave all the followings are correct EXCEPT: a- Represents septal depolarization from left to right in V 5. b- Its depth is not more than 1/4 its corresponding R. c- Its duration is not more than 0.04 sec. d- Deep and wide Q is seen in recent myocardial infarction. 10- In normal ECG: a- The average duration of QT interval is 0.50 sec. b- The ST segment is an isoelectric line. c- The T wave is rounded and symmetrical. d- The height of the T wave is > 10 mm in chest leads. 6
7 11- Regarding the Voltage of ECG: a- Algebraic summations of QRS complexes in LI, II, & III b- Normally from 1.5 mv to 3.5 mv c- Low in obesity, hypothyroidism, and hypernatremia d- High in ventricular hypertrophy and short stunted adult individuals 12- Regarding the PR interval of the ECG all the followings are correct EXCEPT: a- Represents atrial depolarization and conduction through AV node. b- Normal duration from 0.16 to 0.20 second c- Prolonged in right bundle branch block d- Prolonged in 1 st degree heart block. 7
8 13- Regarding the ECG findings in atrial (A) arrhythmias all the followings are correct EXCEPT: a- (A) fibrillation: caused by multiple atrial ectopic foci that discharged very rapidly and irregularly. b- (A) tachycardia: paroxymal rapid and irregular rate ( b/min). c- (A) flutter: saw tooth waves associated with partial AV block. d- (A) fibrillation: absence of P waves, very irregular rate and normal QRS. 14- Ventricular premature beat VPB is: a- Caused by an ectopic ventricular focus that discharges regularly. b- Preceded by P wave and has bizarre prolonged QRS. c- Followed by a compensatory pause. d- Occurs in series without normal beats in between.. 8
9 15- All the followings cause low voltage ECG EXCEPT: a- Hyponatremia. b- Body mass index (BMI) > 35. c- Hypothyroidim. d- Hypokalemia. 16- Left axis deviation of the ECG is described when: a- The axis of the heart is from -30 to +90. b- The QRS complex is prominent positive in lead avf. c- The QRS is prominent positive in lead I and prominent negative in lead III. d- Right ventricle is enlarged. 9
10 17- Regarding the ECG findings in heart block (HB) all the followings are correct EXCEPT: a- Complete (HB): complete dissociation between P waves and QRS complexes. b- 1 st degree(hb): PR interval is abnormally long. c- 2 nd degree (HB): a ventricular beat may follow every 2 nd or 3 rd atrial beat. d- 1 st degree(hb): PR interval lengthens progressively until a ventricular beat is dropped. 18- The ECG findings of bundle branch block (BBB): a- Associated with absence of P waves. b- HR rate is slowed <60 b/min. c- Double hump QRS complex occurs in V5 & V6 in right BBB. d- QRS complexes are prolonged & deformed. 10
11 19- Regarding the ECG of ventricular hypertrophy (VH): a- Axis of the heart is from - 30 to +90 in right VH. b- S wave in V 1 or V 2 plus R wave in V 5 or V 6 account > 35 mm in left VH in adults. c- S wave is deep in V 1 and V 2 and R wave is tall in V 5 and V 6 in right VH. d- Right VH may occur in systemic hypertension. 20- Regarding the ECG findings of myocardial infarction (MI) all the following are correct EXCEPT: a- Elevation of the ST segment in recent (acute) MI. b- Deep and wide Q in old MI. c- Low voltage in massive MI. d- Prominent U wave. 11
12 21- The ECG findings in electrolyte imbalance: a- Tall and peaked T wave in hypokalemia. b- T wave inversion & prominent U wave in hyperkalemia. c- Prolonged QT interval in hypocalcemia. d- High voltage in hyponatremia. V6(+ve) V1(+ve) 12
13 U wave: inconstant finding due to slow repolarization of the papillary muscles. + Terminal Electrode LI Last Depolarization ve to +ve current 1st 13
14 + Terminal Electrode LI 1st Repolarization +ve to ve current Last 14
15 V3(+ve) V4(+ve) 15
16 Atrial flutter with 2:1 and 4:1 heart block Atrial fibrillation Ventricular extrasystole (PVBs) 16
17 Ventricular fibrillation An electrode over a window in the left ventricle (necrotic area) records a Q wave 17
12-Lead EKG Interpretation. Judith M. Haluka BS, RCIS, EMT-P
 12-Lead EKG Interpretation Judith M. Haluka BS, RCIS, EMT-P ECG Grid Left to Right = Time/duration Vertical measure of voltage (amplitude) Expressed in mm P-Wave Depolarization of atrial muscle Low voltage
12-Lead EKG Interpretation Judith M. Haluka BS, RCIS, EMT-P ECG Grid Left to Right = Time/duration Vertical measure of voltage (amplitude) Expressed in mm P-Wave Depolarization of atrial muscle Low voltage
Understanding the Electrocardiogram. David C. Kasarda M.D. FAAEM St. Luke s Hospital, Bethlehem
 Understanding the Electrocardiogram David C. Kasarda M.D. FAAEM St. Luke s Hospital, Bethlehem Overview 1. History 2. Review of the conduction system 3. EKG: Electrodes and Leads 4. EKG: Waves and Intervals
Understanding the Electrocardiogram David C. Kasarda M.D. FAAEM St. Luke s Hospital, Bethlehem Overview 1. History 2. Review of the conduction system 3. EKG: Electrodes and Leads 4. EKG: Waves and Intervals
Electrophysiology Introduction, Basics. The Myocardial Cell. Chapter 1- Thaler
 Electrophysiology Introduction, Basics Chapter 1- Thaler The Myocardial Cell Syncytium Resting state Polarized negative Membrane pump Depolarization fundamental electrical event of the heart Repolarization
Electrophysiology Introduction, Basics Chapter 1- Thaler The Myocardial Cell Syncytium Resting state Polarized negative Membrane pump Depolarization fundamental electrical event of the heart Repolarization
NEONATAL & PEDIATRIC ECG BASICS RHYTHM INTERPRETATION
 NEONATAL & PEDIATRIC ECG BASICS & RHYTHM INTERPRETATION VIKAS KOHLI MD FAAP FACC SENIOR CONSULATANT PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY APOLLO HOSPITAL MOB: 9891362233 ECG FAX LINE: 011-26941746 THE BASICS: GRAPH PAPER
NEONATAL & PEDIATRIC ECG BASICS & RHYTHM INTERPRETATION VIKAS KOHLI MD FAAP FACC SENIOR CONSULATANT PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY APOLLO HOSPITAL MOB: 9891362233 ECG FAX LINE: 011-26941746 THE BASICS: GRAPH PAPER
the basics Perfect Heart Institue, Piyavate Hospital
 ECG INTERPRETATION: the basics Damrong Sukitpunyaroj MD Damrong Sukitpunyaroj, MD Perfect Heart Institue, Piyavate Hospital Overview Conduction Pathways Systematic Interpretation Common abnormalities in
ECG INTERPRETATION: the basics Damrong Sukitpunyaroj MD Damrong Sukitpunyaroj, MD Perfect Heart Institue, Piyavate Hospital Overview Conduction Pathways Systematic Interpretation Common abnormalities in
BIPOLAR LIMB LEADS UNIPOLAR LIMB LEADS PRECORDIAL (UNIPOLAR) LEADS VIEW OF EACH LEAD INDICATIVE ECG CHANGES
 BIPOLAR LIMB LEADS Have both a distinctive positive and negative pole. Lead I LA (positive) RA (negative) Lead II LL (positive) RA (negative) Lead III LL (positive) LA (negative) UNIPOLAR LIMB LEADS Have
BIPOLAR LIMB LEADS Have both a distinctive positive and negative pole. Lead I LA (positive) RA (negative) Lead II LL (positive) RA (negative) Lead III LL (positive) LA (negative) UNIPOLAR LIMB LEADS Have
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What term is used to refer to the process of electrical discharge and the flow of electrical
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What term is used to refer to the process of electrical discharge and the flow of electrical
INTRODUCTORY GUIDE TO IDENTIFYING ECG IRREGULARITIES
 INTRODUCTORY GUIDE TO IDENTIFYING ECG IRREGULARITIES NOTICE: This is an introductory guide for a user to understand basic ECG tracings and parameters. The guide will allow user to identify some of the
INTRODUCTORY GUIDE TO IDENTIFYING ECG IRREGULARITIES NOTICE: This is an introductory guide for a user to understand basic ECG tracings and parameters. The guide will allow user to identify some of the
RAPID INTERPRETATION OF. EKG s
 Personal Quick Reference Sheets 333 (pages 333 to 346) There is no need to remove these reference pages from your book. To download and print them in full color, go to: www.themdsite.com Reference Sheets
Personal Quick Reference Sheets 333 (pages 333 to 346) There is no need to remove these reference pages from your book. To download and print them in full color, go to: www.themdsite.com Reference Sheets
The P Wave: Indicator of Atrial Enlargement
 Marquette University e-publications@marquette Physician Assistant Studies Faculty Research and Publications Health Sciences, College of 8-12-2010 The P Wave: Indicator of Atrial Enlargement Patrick Loftis
Marquette University e-publications@marquette Physician Assistant Studies Faculty Research and Publications Health Sciences, College of 8-12-2010 The P Wave: Indicator of Atrial Enlargement Patrick Loftis
QRS Complexes. Fast & Easy ECGs A Self-Paced Learning Program
 6 QRS Complexes Fast & Easy ECGs A Self-Paced Learning Program Q I A ECG Waveforms Normally the heart beats in a regular, rhythmic fashion producing a P wave, QRS complex and T wave I Step 4 of ECG Analysis
6 QRS Complexes Fast & Easy ECGs A Self-Paced Learning Program Q I A ECG Waveforms Normally the heart beats in a regular, rhythmic fashion producing a P wave, QRS complex and T wave I Step 4 of ECG Analysis
Biology 347 General Physiology Lab Advanced Cardiac Functions ECG Leads and Einthoven s Triangle
 Biology 347 General Physiology Lab Advanced Cardiac Functions ECG Leads and Einthoven s Triangle Objectives Students will record a six-lead ECG from a resting subject and determine the QRS axis of the
Biology 347 General Physiology Lab Advanced Cardiac Functions ECG Leads and Einthoven s Triangle Objectives Students will record a six-lead ECG from a resting subject and determine the QRS axis of the
By the end of this continuing education module the clinician will be able to:
 EKG Interpretation WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed March, 2015, Expires April, 2017 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2015 RN.ORG, S.A., RN.ORG, LLC Developed
EKG Interpretation WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed March, 2015, Expires April, 2017 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2015 RN.ORG, S.A., RN.ORG, LLC Developed
Introduction to Electrocardiography. The Genesis and Conduction of Cardiac Rhythm
 Introduction to Electrocardiography Munther K. Homoud, M.D. Tufts-New England Medical Center Spring 2008 The Genesis and Conduction of Cardiac Rhythm Automaticity is the cardiac cell s ability to spontaneously
Introduction to Electrocardiography Munther K. Homoud, M.D. Tufts-New England Medical Center Spring 2008 The Genesis and Conduction of Cardiac Rhythm Automaticity is the cardiac cell s ability to spontaneously
ACLS Chapter 3 Rhythm Review Instructor Lesson Plan to Accompany ACLS Study Guide 3e
 ACLS Chapter 3 Rhythm Review Lesson Plan Required reading before this lesson: ACLS Study Guide 3e Textbook Chapter 3 Materials needed: Multimedia projector, computer, ACLS Chapter 3 Recommended minimum
ACLS Chapter 3 Rhythm Review Lesson Plan Required reading before this lesson: ACLS Study Guide 3e Textbook Chapter 3 Materials needed: Multimedia projector, computer, ACLS Chapter 3 Recommended minimum
Systematic Approach to 12 Lead EKG Interpretation
 Systematic Approach to 12 Lead EKG Interpretation Maureen Knechtel MPAS, PA-C Wellmont CVA Heart Institute Disclosure Statement of Financial Interest I, Maureen Knechtel, do not have a financial interest/arrangement
Systematic Approach to 12 Lead EKG Interpretation Maureen Knechtel MPAS, PA-C Wellmont CVA Heart Institute Disclosure Statement of Financial Interest I, Maureen Knechtel, do not have a financial interest/arrangement
ECG made extra easy. medics.cc
 ElectroCardioGraphyraphy ECG made extra easy Overview Objectives for this tutorial What is an ECG? Overview of performing electrocardiography on a patient Simple physiology Interpreting the ECG Objectives
ElectroCardioGraphyraphy ECG made extra easy Overview Objectives for this tutorial What is an ECG? Overview of performing electrocardiography on a patient Simple physiology Interpreting the ECG Objectives
Interpreting a rhythm strip
 3 Interpreting a rhythm strip Just the facts In this chapter, you ll learn: the components of an ECG complex and their significance and variations techniques for calculating the rate and rhythm of an ECG
3 Interpreting a rhythm strip Just the facts In this chapter, you ll learn: the components of an ECG complex and their significance and variations techniques for calculating the rate and rhythm of an ECG
HTEC 91. Topic for Today: Atrial Rhythms. NSR with PAC. Nonconducted PAC. Nonconducted PAC. Premature Atrial Contractions (PACs)
 HTEC 91 Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 4 Topic for Today: Atrial Rhythms PACs: Premature Atrial Contractions PAT: Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia AF: Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Flutter Premature Atrial
HTEC 91 Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 4 Topic for Today: Atrial Rhythms PACs: Premature Atrial Contractions PAT: Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia AF: Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Flutter Premature Atrial
Electrocardiography Review and the Normal EKG Response to Exercise
 Electrocardiography Review and the Normal EKG Response to Exercise Cardiac Anatomy Electrical Pathways in the Heart Which valves are the a-v valves? Closure of the a-v valves is associated with which heart
Electrocardiography Review and the Normal EKG Response to Exercise Cardiac Anatomy Electrical Pathways in the Heart Which valves are the a-v valves? Closure of the a-v valves is associated with which heart
How to read the ECG in athletes: distinguishing normal form abnormal
 How to read the ECG in athletes: distinguishing normal form abnormal Antonio Pelliccia, MD Institute of Sport Medicine and Science www.antoniopelliccia.it Cardiac adaptations to Rowing Vagotonia Sinus
How to read the ECG in athletes: distinguishing normal form abnormal Antonio Pelliccia, MD Institute of Sport Medicine and Science www.antoniopelliccia.it Cardiac adaptations to Rowing Vagotonia Sinus
Electrocardiography I Laboratory
 Introduction The body relies on the heart to circulate blood throughout the body. The heart is responsible for pumping oxygenated blood from the lungs out to the body through the arteries and also circulating
Introduction The body relies on the heart to circulate blood throughout the body. The heart is responsible for pumping oxygenated blood from the lungs out to the body through the arteries and also circulating
Equine Cardiovascular Disease
 Equine Cardiovascular Disease 3 rd most common cause of poor performance in athletic horses (after musculoskeletal and respiratory) Cardiac abnormalities are rare Clinical Signs: Poor performance/exercise
Equine Cardiovascular Disease 3 rd most common cause of poor performance in athletic horses (after musculoskeletal and respiratory) Cardiac abnormalities are rare Clinical Signs: Poor performance/exercise
An ECG Primer. Quick Look. I saw it, but I did not realize it. Elizabeth Peabody
 4 An ECG Primer Quick Look Cardiac Monitoring System - p. 64 ECG Paper - p. 73 Lead Polarity and Vectors - p. 77 Basic ECG Components - p. 79 Heart Rate and Pulse Rate - p. 91 Summary - p. 94 Chapter Quiz
4 An ECG Primer Quick Look Cardiac Monitoring System - p. 64 ECG Paper - p. 73 Lead Polarity and Vectors - p. 77 Basic ECG Components - p. 79 Heart Rate and Pulse Rate - p. 91 Summary - p. 94 Chapter Quiz
ST Segment Elevation Nothing is ever as hard (or easy) as it looks
 ST Segment Elevation Nothing is ever as hard (or easy) as it looks Cameron Guild, MD Division of Cardiology University of Mississippi Medical Center February 17, 2012 Objectives 1. Describe the electrical
ST Segment Elevation Nothing is ever as hard (or easy) as it looks Cameron Guild, MD Division of Cardiology University of Mississippi Medical Center February 17, 2012 Objectives 1. Describe the electrical
Table of Contents Error! Bookmark not defined.
 Table of Contents EKG TRACING...1 Figure 1 - EKG Tracing... Error! Bookmark not defined. STEP 1...1 Rate... 1 Figure 2 - Determining the Rate... 1 Step 2...2 Rhythm... 2 Figure 3 - Determining the Rhythm
Table of Contents EKG TRACING...1 Figure 1 - EKG Tracing... Error! Bookmark not defined. STEP 1...1 Rate... 1 Figure 2 - Determining the Rate... 1 Step 2...2 Rhythm... 2 Figure 3 - Determining the Rhythm
Electrodes placed on the body s surface can detect electrical activity, APPLIED ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY. Circulatory system
 4 READING AND INTERPRETING THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAM Electrodes placed on the body s surface can detect electrical activity, which occurs in the heart. The recording of these electrical events comprises an
4 READING AND INTERPRETING THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAM Electrodes placed on the body s surface can detect electrical activity, which occurs in the heart. The recording of these electrical events comprises an
EKG Abnormalities. I. Early repolarization abnormality:
 I. Early repolarization abnormality: EKG Abnormalities A. A normal variant. Early repolarization is most often seen in healthy young adults. Look for ST elevation, tall QRS voltage, "fishhook" deformity
I. Early repolarization abnormality: EKG Abnormalities A. A normal variant. Early repolarization is most often seen in healthy young adults. Look for ST elevation, tall QRS voltage, "fishhook" deformity
Electrolyte Physiology. Something in the way she moves
 Electrolyte Physiology Something in the way she moves me Electrolyte Movement CONCENTRATION GRADIENT ELECTRICAL GRADIENT DRIVING FORCE NERNST NUMBER (E-ion) CONDUCTANCE (G-ion) PERMEABILITY CHANNELS: small
Electrolyte Physiology Something in the way she moves me Electrolyte Movement CONCENTRATION GRADIENT ELECTRICAL GRADIENT DRIVING FORCE NERNST NUMBER (E-ion) CONDUCTANCE (G-ion) PERMEABILITY CHANNELS: small
ECG Measurments and Interpretation Programs
 ECG Measurments and Interpretation Programs Physician s Guide Distributed by Welch Allyn 4341 State Street Road, PO Box 220 Skaneateles Falls, NY 13153-0220 www.welchallyn.com Sales and Service information:
ECG Measurments and Interpretation Programs Physician s Guide Distributed by Welch Allyn 4341 State Street Road, PO Box 220 Skaneateles Falls, NY 13153-0220 www.welchallyn.com Sales and Service information:
Normal Sinus Rhythm. Sinus Bradycardia. Sinus Tachycardia. Rhythm ECG Characteristics Example (NSR) & consistent. & consistent.
 Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) Rate: 60-100 per minute Rhythm: R- R = P waves: Upright, similar P-R: 0.12-0.20 second & consistent P:qRs: 1P:1qRs Sinus Tachycardia Exercise Hypovolemia Medications Fever Hypoxia
Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) Rate: 60-100 per minute Rhythm: R- R = P waves: Upright, similar P-R: 0.12-0.20 second & consistent P:qRs: 1P:1qRs Sinus Tachycardia Exercise Hypovolemia Medications Fever Hypoxia
2 ECG basics. Leads and planes. Leads. Planes. from different perspectives, which are called leads and planes.
 558302.qxp 3/14/12 10:47 PM Page 12 2 ECG basics One of the most valuable diagnostic tools available, an electrocardiogram (ECG) records the heart s electrical activity as waveforms. By interpreting these
558302.qxp 3/14/12 10:47 PM Page 12 2 ECG basics One of the most valuable diagnostic tools available, an electrocardiogram (ECG) records the heart s electrical activity as waveforms. By interpreting these
The abbreviation EKG, for electrocardiogram,
 CLIN PEDIATR OnlineFirst, published on January 28, 2010 as doi:10.1177/0009922809336206 Simplified Pediatric Electrocardiogram Interpretation Clinical Pediatrics Volume XX Number X Month XXXX xx-xx 2009
CLIN PEDIATR OnlineFirst, published on January 28, 2010 as doi:10.1177/0009922809336206 Simplified Pediatric Electrocardiogram Interpretation Clinical Pediatrics Volume XX Number X Month XXXX xx-xx 2009
BASIC CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS Revised 10/2001
 BASIC CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS Revised 10/2001 A Basic Arrhythmia course is a recommended prerequisite for ACLS. A test will be given that will require you to recognize cardiac arrest rhythms and the most common
BASIC CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIAS Revised 10/2001 A Basic Arrhythmia course is a recommended prerequisite for ACLS. A test will be given that will require you to recognize cardiac arrest rhythms and the most common
Copyright 2006 Blaufuss Multimedia. All rights reserved. Page 1
 Copyright 2006 Blaufuss Multimedia. All rights reserved. Page 1 002 Sinus Rhythm, atrial rate 90 Mobitz II AVB, Ventricular rate 50 Left Atrial Enlargement Left Ventricular Hypertrophy RBBB a) Long R-R
Copyright 2006 Blaufuss Multimedia. All rights reserved. Page 1 002 Sinus Rhythm, atrial rate 90 Mobitz II AVB, Ventricular rate 50 Left Atrial Enlargement Left Ventricular Hypertrophy RBBB a) Long R-R
VCA Veterinary Specialty Center of Seattle
 An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graph of the heart`s electrical current, which allows evaluation of heart rate, rhythm and conduction. Identification of conduction problems within the heart begins with
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graph of the heart`s electrical current, which allows evaluation of heart rate, rhythm and conduction. Identification of conduction problems within the heart begins with
Evaluation copy. Analyzing the Heart with EKG. Computer
 Analyzing the Heart with EKG Computer An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring within the heart. In a healthy heart there is a natural pacemaker in
Analyzing the Heart with EKG Computer An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring within the heart. In a healthy heart there is a natural pacemaker in
ECG Signal Analysis Using Wavelet Transforms
 Bulg. J. Phys. 35 (2008) 68 77 ECG Signal Analysis Using Wavelet Transforms C. Saritha, V. Sukanya, Y. Narasimha Murthy Department of Physics and Electronics, S.S.B.N. COLLEGE (Autonomous) Anantapur 515
Bulg. J. Phys. 35 (2008) 68 77 ECG Signal Analysis Using Wavelet Transforms C. Saritha, V. Sukanya, Y. Narasimha Murthy Department of Physics and Electronics, S.S.B.N. COLLEGE (Autonomous) Anantapur 515
The Electrocardiogram (ECG)
 The Electrocardiogram (ECG) Preparation for RWM Lab Experiment The first ECG was measured by Augustus Désiré Waller in 1887 using Lippmann's capillary electrometer. Recorded ECG: http://www.youtube.com/watch_popup?v=q0jmfivadue&vq=large
The Electrocardiogram (ECG) Preparation for RWM Lab Experiment The first ECG was measured by Augustus Désiré Waller in 1887 using Lippmann's capillary electrometer. Recorded ECG: http://www.youtube.com/watch_popup?v=q0jmfivadue&vq=large
Objectives. The ECG in Pulmonary and Congenital Heart Disease. Lead II P-Wave Amplitude during COPD Exacerbation and after Treatment (50 pts.
 The ECG in Pulmonary and Congenital Heart Disease Gabriel Gregoratos, MD Objectives Review the pathophysiology and ECG signs of pulmonary dysfunction Review the ECG findings in patients with: COPD (chronic
The ECG in Pulmonary and Congenital Heart Disease Gabriel Gregoratos, MD Objectives Review the pathophysiology and ECG signs of pulmonary dysfunction Review the ECG findings in patients with: COPD (chronic
ECG Measurement and Interpretation
 ECG Measurement and Interpretation Statement of accuracy for analysing ECG units *2.530036* Physicians Guide Sales and Service Information The SCHILLER sales and service centre network is world-wide. For
ECG Measurement and Interpretation Statement of accuracy for analysing ECG units *2.530036* Physicians Guide Sales and Service Information The SCHILLER sales and service centre network is world-wide. For
Interpreting AV (Heart) Blocks: Breaking Down the Mystery
 Interpreting AV (Heart) Blocks: Breaking Down the Mystery 2 Contact Hours Copyright 2012 by RN.com. All Rights Reserved. Reproduction and distribution of these materials is prohibited without the express
Interpreting AV (Heart) Blocks: Breaking Down the Mystery 2 Contact Hours Copyright 2012 by RN.com. All Rights Reserved. Reproduction and distribution of these materials is prohibited without the express
School of Health Sciences
 School of Health Sciences Cardiology Teaching Package A Beginners Guide to Normal Heart Function, Sinus Rhythm & Common Cardiac Arrhythmias Welcome This document extends subjects covered in the Cardiology
School of Health Sciences Cardiology Teaching Package A Beginners Guide to Normal Heart Function, Sinus Rhythm & Common Cardiac Arrhythmias Welcome This document extends subjects covered in the Cardiology
For more information about the use of the Propaq monitor, refer to the Propaq Directions For Use.
 Clinical Support 8500 S.W. Creekside Pl. Beaverton, OR 97008-7107 U.S.A. Telephone: 503-526-4200 Toll Free: 800-289-2500 clinicalsupport@protocol.com ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY Introduction This article provides
Clinical Support 8500 S.W. Creekside Pl. Beaverton, OR 97008-7107 U.S.A. Telephone: 503-526-4200 Toll Free: 800-289-2500 clinicalsupport@protocol.com ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY Introduction This article provides
The new generation in ECG interpretation
 The new generation in ECG interpretation Philips DXL ECG Algorithm, Release PH100B The Philips DXL ECG Algorithm, developed by the Advanced Algorithm Research Center, uses sophisticated analytical methods
The new generation in ECG interpretation Philips DXL ECG Algorithm, Release PH100B The Philips DXL ECG Algorithm, developed by the Advanced Algorithm Research Center, uses sophisticated analytical methods
Diagnosis Code Crosswalk : ICD-9-CM to ICD-10-CM Cardiac Rhythm and Heart Failure Diagnoses
 Diagnosis Code Crosswalk : to 402.01 Hypertensive heart disease, malignant, with heart failure 402.11 Hypertensive heart disease, benign, with heart failure 402.91 Hypertensive heart disease, unspecified,
Diagnosis Code Crosswalk : to 402.01 Hypertensive heart disease, malignant, with heart failure 402.11 Hypertensive heart disease, benign, with heart failure 402.91 Hypertensive heart disease, unspecified,
Section Four: Pulmonary Artery Waveform Interpretation
 Section Four: Pulmonary Artery Waveform Interpretation All hemodynamic pressures and waveforms are generated by pressure changes in the heart caused by myocardial contraction (systole) and relaxation/filling
Section Four: Pulmonary Artery Waveform Interpretation All hemodynamic pressures and waveforms are generated by pressure changes in the heart caused by myocardial contraction (systole) and relaxation/filling
Scott Hubbell, MHSc, RRT-NPS, C-NPT, CCT Clinical Education Coordinator/Flight RRT EagleMed
 Scott Hubbell, MHSc, RRT-NPS, C-NPT, CCT Clinical Education Coordinator/Flight RRT EagleMed Identify the 12-Lead Views Explain the vessels of occlusion Describe the three I s Basic Interpretation of 12-Lead
Scott Hubbell, MHSc, RRT-NPS, C-NPT, CCT Clinical Education Coordinator/Flight RRT EagleMed Identify the 12-Lead Views Explain the vessels of occlusion Describe the three I s Basic Interpretation of 12-Lead
Introduction to Electrophysiology. Wm. W. Barrington, MD, FACC University of Pittsburgh Medical Center
 Introduction to Electrophysiology Wm. W. Barrington, MD, FACC University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Objectives Indications for EP Study How do we do the study Normal recordings Abnormal Recordings Limitations
Introduction to Electrophysiology Wm. W. Barrington, MD, FACC University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Objectives Indications for EP Study How do we do the study Normal recordings Abnormal Recordings Limitations
Electrocardiogram and Heart Sounds
 Electrocardiogram and Heart Sounds An introduction to the recording and analysis of electrocardiograms, and the sounds of the heart. Written by Staff of ADInstruments Introduction The beating of the heart
Electrocardiogram and Heart Sounds An introduction to the recording and analysis of electrocardiograms, and the sounds of the heart. Written by Staff of ADInstruments Introduction The beating of the heart
Electrocardiogram (ECG) as a diagnostic tool for the assessment of Cardiovascular status in alcoholics
 Biomedical Research 2011; 22 (3): 333-337 Electrocardiogram (ECG) as a diagnostic tool for the assessment of Cardiovascular status in alcoholics Venkatesh G Department of Physiology, Sri Siddhartha Medical
Biomedical Research 2011; 22 (3): 333-337 Electrocardiogram (ECG) as a diagnostic tool for the assessment of Cardiovascular status in alcoholics Venkatesh G Department of Physiology, Sri Siddhartha Medical
Tachyarrhythmias (fast heart rhythms)
 Patient information factsheet Tachyarrhythmias (fast heart rhythms) The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
Patient information factsheet Tachyarrhythmias (fast heart rhythms) The normal electrical system of the heart The heart has its own electrical conduction system. The conduction system sends signals throughout
ECG INTERPRETATION MANUAL
 Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network ECG INTERPRETATION MANUAL THE ABNORMAL ECG Lancashire And South Cumbria Cardiac Physiologist Training Manual AV NODAL BLOCKS (HEART BLOCKS) Disturbances of intra
Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network ECG INTERPRETATION MANUAL THE ABNORMAL ECG Lancashire And South Cumbria Cardiac Physiologist Training Manual AV NODAL BLOCKS (HEART BLOCKS) Disturbances of intra
Basics of EKG Interpretation: A Programmed Study - Barbara Ritter Ed.D, FNP
 Basics of EKG Interpretation: A Programmed Study - Barbara Ritter Ed.D, FNP Acknowledgement is given to Leslie K. Muma, MS, RN, NP for assistance in preparation of this learning module. Description The
Basics of EKG Interpretation: A Programmed Study - Barbara Ritter Ed.D, FNP Acknowledgement is given to Leslie K. Muma, MS, RN, NP for assistance in preparation of this learning module. Description The
ECG Findings. IV Access. 12 Lead Interpretation: STEMI and NSTEMI. ACLS Acute Coronary Syndrome Chest Pain Suggestive of Ischemia.
 12 Lead Interpretation: STEMI and NSTEMI Presented by Annmarie Keck, RN, BSN, CEN Northwest MedStar Clinical Outreach Educator ACLS Acute Coronary Syndrome Chest Pain Suggestive of Ischemia Immediate Assessment
12 Lead Interpretation: STEMI and NSTEMI Presented by Annmarie Keck, RN, BSN, CEN Northwest MedStar Clinical Outreach Educator ACLS Acute Coronary Syndrome Chest Pain Suggestive of Ischemia Immediate Assessment
Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias
 Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias Atrial Premature Atrial Complex Wandering Atrial Pacemaker Atrial Tachycardia (ectopic) Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia Atrial Flutter Atrial
Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias Atrial & Junctional Dysrhythmias Atrial Premature Atrial Complex Wandering Atrial Pacemaker Atrial Tachycardia (ectopic) Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia Atrial Flutter Atrial
HEART HEALTH WEEK 3 SUPPLEMENT. A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease HEART FAILURE. Relatively mild, symptoms with intense exercise
 WEEK 3 SUPPLEMENT HEART HEALTH A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease HEART FAILURE Heart failure can be defined as the failing (insufficiency) of the heart as a mechanical pump due to either acute
WEEK 3 SUPPLEMENT HEART HEALTH A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease HEART FAILURE Heart failure can be defined as the failing (insufficiency) of the heart as a mechanical pump due to either acute
The Basics of 12 Lead EKG s
 EMS Solutions Presents The Basics of 12 Lead EKG s NOTICE: You DO NOT Have the Right to Reprint or Resell this Publication. However, you MAY give this report away, provided you do not change or alter the
EMS Solutions Presents The Basics of 12 Lead EKG s NOTICE: You DO NOT Have the Right to Reprint or Resell this Publication. However, you MAY give this report away, provided you do not change or alter the
An Introduction to Tachyarrhythmias R. A. Seyon MN, NP, CCN(C) & Dr. R. G. Williams
 Arrhythmias 1 An Introduction to Tachyarrhythmias R. A. Seyon MN, NP, CCN(C) & Dr. R. G. Williams Things to keep in mind when analyzing arrhythmias: Electrical activity recorded in 12 and 15 leads Examine
Arrhythmias 1 An Introduction to Tachyarrhythmias R. A. Seyon MN, NP, CCN(C) & Dr. R. G. Williams Things to keep in mind when analyzing arrhythmias: Electrical activity recorded in 12 and 15 leads Examine
Clinical Observations with the Lead System
 Clinical Observations with the Lead System Frank Precordial By J. A. ABILDSKOv, M.D., W. W. STREET, M.D., N. SOLOMON, B.A., AND A. H. TOOMAJIAN, B.A. Several new lead systems for electrocardiography and
Clinical Observations with the Lead System Frank Precordial By J. A. ABILDSKOv, M.D., W. W. STREET, M.D., N. SOLOMON, B.A., AND A. H. TOOMAJIAN, B.A. Several new lead systems for electrocardiography and
Activity 4.2.3: EKG. Introduction. Equipment. Procedure
 Activity 4.2.3: EKG The following is used with permission of Vernier Software and Technology. This activity is based on the experiment Analyzing the Heart with EKG from the book Human Physiology with Vernier,
Activity 4.2.3: EKG The following is used with permission of Vernier Software and Technology. This activity is based on the experiment Analyzing the Heart with EKG from the book Human Physiology with Vernier,
Sleep Heart Health Study (SHHS) ECG Protocol
 Sleep Heart Health Study (SHHS) ECG Protocol SHHS 1 Electrocardiography (ECG) Baseline ECG is performed in all parent study clinic visits preceding the PSG. All sites perform a standard resting 12-lead
Sleep Heart Health Study (SHHS) ECG Protocol SHHS 1 Electrocardiography (ECG) Baseline ECG is performed in all parent study clinic visits preceding the PSG. All sites perform a standard resting 12-lead
QT analysis: A guide for statistical programmers. Prabhakar Munkampalli Statistical Analyst II Hyderabad, 7 th September 2012
 QT analysis: A guide for statistical programmers Prabhakar Munkampalli Statistical Analyst II Hyderabad, 7 th September 2012 Agenda ECG ICH E14 Thorough QT/QTc study Role of Statistical Programmer References
QT analysis: A guide for statistical programmers Prabhakar Munkampalli Statistical Analyst II Hyderabad, 7 th September 2012 Agenda ECG ICH E14 Thorough QT/QTc study Role of Statistical Programmer References
22 Arrhythmias. C. Scharf and F. Duru. Siegenthaler, Differential Diagnosis in Internal Medicine (ISBN9783131421418), 2007 Georg Thieme Verlag
 22 22 Arrhythmias C. Scharf and F. Duru 22 712 Arrhythmias 22.1 Differential Diagnosis of Arrhythmias 714 Medical History 714 Clinical Examination 714 Electrocardiogram (ECG) 715 Additional Tools for the
22 22 Arrhythmias C. Scharf and F. Duru 22 712 Arrhythmias 22.1 Differential Diagnosis of Arrhythmias 714 Medical History 714 Clinical Examination 714 Electrocardiogram (ECG) 715 Additional Tools for the
Lead avr: The Neglected Lead
 Chapter 22 Lead avr: The Neglected Lead M Chenniappan INTRODUCTION Lead avr, one of the 12 electrocardiographic leads, is frequently ignored in clinical medicine. In fact, many clinicians refer to the
Chapter 22 Lead avr: The Neglected Lead M Chenniappan INTRODUCTION Lead avr, one of the 12 electrocardiographic leads, is frequently ignored in clinical medicine. In fact, many clinicians refer to the
PRO-CPR. 2015 Guidelines: PALS Algorithm Overview. (Non-AHA supplementary precourse material)
 PRO-CPR 2015 Guidelines: PALS Algorithm Overview (Non-AHA supplementary precourse material) Please reference Circulation (from our website), the ECC Handbook, or the 2015 ACLS Course Manual for correct
PRO-CPR 2015 Guidelines: PALS Algorithm Overview (Non-AHA supplementary precourse material) Please reference Circulation (from our website), the ECC Handbook, or the 2015 ACLS Course Manual for correct
ECG Filtering. Willem Einthoven s EKG machine, 1903
 ECG Filtering Willem Einthoven s EKG machine, 1903 ECG Filtering Three common noise sources q Baseline wander q Power line interference q Muscle noise When filtering any biomedical signal care should be
ECG Filtering Willem Einthoven s EKG machine, 1903 ECG Filtering Three common noise sources q Baseline wander q Power line interference q Muscle noise When filtering any biomedical signal care should be
Banner Staff Service ECG Study Guide
 Banner Staff Service ECG Study Guide Edited by Larry H. Lybbert, MS, RN Table of Contents ECG STUDY GUIDE... 3 ECG INTERPRETATION BASICS... 4 EKG GRAPH PAPER...4 RATE MEASUREMENT...9 The Six Second Method...9
Banner Staff Service ECG Study Guide Edited by Larry H. Lybbert, MS, RN Table of Contents ECG STUDY GUIDE... 3 ECG INTERPRETATION BASICS... 4 EKG GRAPH PAPER...4 RATE MEASUREMENT...9 The Six Second Method...9
Signal-averaged electrocardiography late potentials
 SIGNAL AVERAGED ECG INTRODUCTION Signal-averaged electrocardiography (SAECG) is a special electrocardiographic technique, in which multiple electric signals from the heart are averaged to remove interference
SIGNAL AVERAGED ECG INTRODUCTION Signal-averaged electrocardiography (SAECG) is a special electrocardiographic technique, in which multiple electric signals from the heart are averaged to remove interference
Spatial Vector Electrocardiography
 Spatial Vector Electrocardiography A Method for Calculating the Spatial Electrical Vectors of the Heart from Conventional Leads By ROBERT P. GRANT, M.D. A new method for the interpretation of conventional
Spatial Vector Electrocardiography A Method for Calculating the Spatial Electrical Vectors of the Heart from Conventional Leads By ROBERT P. GRANT, M.D. A new method for the interpretation of conventional
ST Segment Monitoring. IntelliVue Patient Monitor and Information Center, Application Note
 ST Segment Monitoring ST/AR Algorithm IntelliVue Patient Monitor and Information Center, Application Note This application note describes principles and uses for continuous ST segment monitoring. It also
ST Segment Monitoring ST/AR Algorithm IntelliVue Patient Monitor and Information Center, Application Note This application note describes principles and uses for continuous ST segment monitoring. It also
Chapter 20: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart
 Chapter 20: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart Chapter Objectives ANATOMY OF THE HEART 1. Describe the location and orientation of the heart within the thorax and mediastinal cavity. 2. Describe the
Chapter 20: The Cardiovascular System: The Heart Chapter Objectives ANATOMY OF THE HEART 1. Describe the location and orientation of the heart within the thorax and mediastinal cavity. 2. Describe the
Basic Cardiac Rhythms Identification and Response
 Basic Cardiac Rhythms Identification and Response Module 1 ANATOMY, PHYSIOLOGY, & ELECTRICAL CONDUCTION Objectives Describe the normal cardiac anatomy and physiology and normal electrical conduction through
Basic Cardiac Rhythms Identification and Response Module 1 ANATOMY, PHYSIOLOGY, & ELECTRICAL CONDUCTION Objectives Describe the normal cardiac anatomy and physiology and normal electrical conduction through
Arrhythmia Monitoring Algorithm
 Arrhythmia Monitoring Algorithm Application Note Introduction The ST/AR (ST and Arrhythmia) algorithm is an ECG algorithm that the HeartStart MRx and XL+ monitor/defibrillators utilize for basic and cardiotach
Arrhythmia Monitoring Algorithm Application Note Introduction The ST/AR (ST and Arrhythmia) algorithm is an ECG algorithm that the HeartStart MRx and XL+ monitor/defibrillators utilize for basic and cardiotach
PSIO 603/BME 511 1 Dr. Janis Burt February 19, 2007 MRB 422; 626-6833 jburt@u.arizona.edu. MUSCLE EXCITABILITY - Ventricle
 SIO 63/BME 511 1 Dr. Janis Burt February 19, 27 MRB 422; 626-6833 MUSCLE EXCITABILITY - Ventricle READING: Boron & Boulpaep pages: 483-57 OBJECTIVES: 1. Draw a picture of the heart in vertical (frontal
SIO 63/BME 511 1 Dr. Janis Burt February 19, 27 MRB 422; 626-6833 MUSCLE EXCITABILITY - Ventricle READING: Boron & Boulpaep pages: 483-57 OBJECTIVES: 1. Draw a picture of the heart in vertical (frontal
Cardiovascular System & Its Diseases. Lecture #4 Heart Failure & Cardiac Arrhythmias
 Cardiovascular System & Its Diseases Lecture #4 Heart Failure & Cardiac Arrhythmias Dr. Derek Bowie, Department of Pharmacology & Therapeutics, Room 1317, McIntyre Bldg, McGill University derek.bowie@mcgill.ca
Cardiovascular System & Its Diseases Lecture #4 Heart Failure & Cardiac Arrhythmias Dr. Derek Bowie, Department of Pharmacology & Therapeutics, Room 1317, McIntyre Bldg, McGill University derek.bowie@mcgill.ca
How To Understand What You Know
 Heart Disorders Glossary ABG (Arterial Blood Gas) Test: A test that measures how much oxygen and carbon dioxide are in the blood. Anemia: A condition in which there are low levels of red blood cells in
Heart Disorders Glossary ABG (Arterial Blood Gas) Test: A test that measures how much oxygen and carbon dioxide are in the blood. Anemia: A condition in which there are low levels of red blood cells in
Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions
 Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions Student: 1. The pulmonary veins are unusual as veins because they are transporting. A. oxygenated blood B. de-oxygenated blood C. high fat blood D. nutrient-rich
Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions Student: 1. The pulmonary veins are unusual as veins because they are transporting. A. oxygenated blood B. de-oxygenated blood C. high fat blood D. nutrient-rich
Electrophysiology Daymar College. Lisa H. Young, RN, BSN, MAE 2011
 Electrophysiology Daymar College Lisa H. Young, RN, BSN, MAE 2011 Electrical Conduction Pathway Chemical Basis for Impulse Formation Cardiac Action Potential Phases http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oqpffilde0e
Electrophysiology Daymar College Lisa H. Young, RN, BSN, MAE 2011 Electrical Conduction Pathway Chemical Basis for Impulse Formation Cardiac Action Potential Phases http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oqpffilde0e
Lecture Outline. Cardiovascular Physiology. Cardiovascular System Function. Functional Anatomy of the Heart
 Lecture Outline Cardiovascular Physiology Cardiac Output Controls & Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System Function Functional components of the cardiovascular system: Heart Blood Vessels Blood General functions
Lecture Outline Cardiovascular Physiology Cardiac Output Controls & Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System Function Functional components of the cardiovascular system: Heart Blood Vessels Blood General functions
ACLS RHYTHM TEST. 2. A 74-year-old woman with chest pain. Blood pressure 192/90 and rates her pain 9/10.
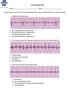 ACLS RHYTHM TEST Name Date Choose the best answer for each of the following questions. Each of the following strips is 6 seconds in length. 1. Identify the following rhythm a. Sinus bradycardia with 2
ACLS RHYTHM TEST Name Date Choose the best answer for each of the following questions. Each of the following strips is 6 seconds in length. 1. Identify the following rhythm a. Sinus bradycardia with 2
«Δυσλειτουργία βηματοδότη. Πως μπορούμε να την εκτιμήσουμε στο ιατρείο.» Koσσυβάκης Χάρης Καρδιολογικό Τμήμα Γ.Ν.Α. «Γ. ΓΕΝΝΗΜΑΤΑΣ
 «Δυσλειτουργία βηματοδότη. Πως μπορούμε να την εκτιμήσουμε στο ιατρείο.» Koσσυβάκης Χάρης Καρδιολογικό Τμήμα Γ.Ν.Α. «Γ. ΓΕΝΝΗΜΑΤΑΣ Diagnostic tools History: symptoms, physical examination 12 leads ECG,
«Δυσλειτουργία βηματοδότη. Πως μπορούμε να την εκτιμήσουμε στο ιατρείο.» Koσσυβάκης Χάρης Καρδιολογικό Τμήμα Γ.Ν.Α. «Γ. ΓΕΝΝΗΜΑΤΑΣ Diagnostic tools History: symptoms, physical examination 12 leads ECG,
DEFIBRILLATION AND THE AUTOMATIC EXTERNAL DEFIBRILLATOR A GUIDE
 DEFIBRILLATION AND THE AUTOMATIC EXTERNAL DEFIBRILLATOR A GUIDE Defibrillation and the AED, A guide Revised February 2012 Page 1 of 22 Original document complied by Pat Standen, Grampians Trauma, Emergency
DEFIBRILLATION AND THE AUTOMATIC EXTERNAL DEFIBRILLATOR A GUIDE Defibrillation and the AED, A guide Revised February 2012 Page 1 of 22 Original document complied by Pat Standen, Grampians Trauma, Emergency
Andrew T. Reisner, Gari D. Clifford, and Roger G. Mark
 CHAPTER 1 The Physiological Basis of the Electrocardiogram Andrew T. Reisner, Gari D. Clifford, and Roger G. Mark Before attempting any signal processing of the electrocardiogram it is important to first
CHAPTER 1 The Physiological Basis of the Electrocardiogram Andrew T. Reisner, Gari D. Clifford, and Roger G. Mark Before attempting any signal processing of the electrocardiogram it is important to first
The heart walls and coronary circulation
 CHAPTER 1 The heart walls and coronary circulation The heart is located in the central-left part of the thorax (lying on the diaphragm) and is oriented anteriorly, with the apex directed forward, downward,
CHAPTER 1 The heart walls and coronary circulation The heart is located in the central-left part of the thorax (lying on the diaphragm) and is oriented anteriorly, with the apex directed forward, downward,
Anatomi & Fysiologi 060301. The cardiovascular system (chapter 20) The circulation system transports; What the heart can do;
 The cardiovascular system consists of; The cardiovascular system (chapter 20) Principles of Anatomy & Physiology 2009 Blood 2 separate pumps (heart) Many blood vessels with varying diameter and elasticity
The cardiovascular system consists of; The cardiovascular system (chapter 20) Principles of Anatomy & Physiology 2009 Blood 2 separate pumps (heart) Many blood vessels with varying diameter and elasticity
Tips and Tricks to Demystify 12 Lead ECG Interpretation
 Tips and Tricks to Demystify 12 Lead ECG Interpretation Mission: Lifeline North Dakota Regional EMS and Hospital Conference Samantha Kapphahn, DO Essentia Health- Interventional Cardiology June 5th, 2014
Tips and Tricks to Demystify 12 Lead ECG Interpretation Mission: Lifeline North Dakota Regional EMS and Hospital Conference Samantha Kapphahn, DO Essentia Health- Interventional Cardiology June 5th, 2014
Biopac Student Lab Lesson 6 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY (ECG) II Introduction. Rev. 06132012
 42 Aero Camino, Goleta, CA 93117 www.biopac.com Biopac Student Lab Lesson 6 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY (ECG) II Introduction Rev. 06132012 Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D. Associate Professor Emeritus Indiana University
42 Aero Camino, Goleta, CA 93117 www.biopac.com Biopac Student Lab Lesson 6 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY (ECG) II Introduction Rev. 06132012 Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D. Associate Professor Emeritus Indiana University
EKG Refresh and Practice Normal Sinus Rhythm. P-Waves: PRInterval:
 EKG Refresh and Practice Normal Sinus. : 60-100 beats per minute r Rhythrn: Atrial - - o Pwaves: Uniform in appearance Upright w/ normal shape One Preceding each QRS Nor more than.10 second o PR interval:
EKG Refresh and Practice Normal Sinus. : 60-100 beats per minute r Rhythrn: Atrial - - o Pwaves: Uniform in appearance Upright w/ normal shape One Preceding each QRS Nor more than.10 second o PR interval:
Bradycardia CHAPTER 12 CODE SCENARIO
 Senecal-12.qxd 14/04/2005 09:44 AM Page 69 CHAPTER 12 Bradycardia CODE SCENARIO A code is called for a 78-year-old man who was admitted to the hospital for syncope of unknown etiology. He was resting comfortably
Senecal-12.qxd 14/04/2005 09:44 AM Page 69 CHAPTER 12 Bradycardia CODE SCENARIO A code is called for a 78-year-old man who was admitted to the hospital for syncope of unknown etiology. He was resting comfortably
Feature Vector Selection for Automatic Classification of ECG Arrhythmias
 Feature Vector Selection for Automatic Classification of ECG Arrhythmias Ch.Venkanna 1, B. Raja Ganapathi 2 Assistant Professor, Dept. of ECE, G.V.P. College of Engineering (A), Madhurawada, A.P., India
Feature Vector Selection for Automatic Classification of ECG Arrhythmias Ch.Venkanna 1, B. Raja Ganapathi 2 Assistant Professor, Dept. of ECE, G.V.P. College of Engineering (A), Madhurawada, A.P., India
ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY (I) THE GENESIS OF THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAM
 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY (I) THE GENESIS OF THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAM Scridon Alina, Șerban Răzvan Constantin 1. Definition The electrocardiogram (abbreviated ECG or EKG) represents the graphic recording of electrical
ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY (I) THE GENESIS OF THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAM Scridon Alina, Șerban Răzvan Constantin 1. Definition The electrocardiogram (abbreviated ECG or EKG) represents the graphic recording of electrical
Electrophysiologic Studies on Mobitz Type II Second-Degree Heart Block
 Electrophysiologic Studies on Mobitz Type II Second-Degree Heart Block By JOSEPH F. SPEAR, PH.D., AND E. NEIL MOORE, D.V.M., PH.D. SUMMARY Experimental studies were carried out in animals with intracellular
Electrophysiologic Studies on Mobitz Type II Second-Degree Heart Block By JOSEPH F. SPEAR, PH.D., AND E. NEIL MOORE, D.V.M., PH.D. SUMMARY Experimental studies were carried out in animals with intracellular
Lethal Arrhythmias: Presented by: RN.com 12400 High Bluff Dr San Diego, CA 92130
 Lethal Arrhythmias: Advanced Rhythm Interpretation Presented by: RN.com 12400 High Bluff Dr San Diego, CA 92130 This course has been approved for five (5.0) contact hours. This course expires January 24,
Lethal Arrhythmias: Advanced Rhythm Interpretation Presented by: RN.com 12400 High Bluff Dr San Diego, CA 92130 This course has been approved for five (5.0) contact hours. This course expires January 24,
PATIENT MONITORING SYSTEM USING ANDROID TECHNOLOGY
 Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology IJCSMC, Vol. 2, Issue. 5, May 2013, pg.191
Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology IJCSMC, Vol. 2, Issue. 5, May 2013, pg.191
DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services
 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services NEW product from the Medicare Learning Network (MLN) Provider Compliance Tips for Computed Tomography (CT) Scans Podcast,
DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services NEW product from the Medicare Learning Network (MLN) Provider Compliance Tips for Computed Tomography (CT) Scans Podcast,
#AS148 - Automated ECG Analysis
 BIOPAC Systems, Inc. 42 Aero Camino Goleta, Ca 93117 Ph (805)685-0066 Fax (805)685-0067 www.biopac.com info@biopac.com #AS148 - Automated ECG Analysis An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graphical recording
BIOPAC Systems, Inc. 42 Aero Camino Goleta, Ca 93117 Ph (805)685-0066 Fax (805)685-0067 www.biopac.com info@biopac.com #AS148 - Automated ECG Analysis An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graphical recording
The heart then repolarises (or refills) in time for the next stimulus and contraction.
 Atrial Fibrillation BRIEFLY, HOW DOES THE HEART PUMP? The heart has four chambers. The upper chambers are called atria. One chamber is called an atrium, and the lower chambers are called ventricles. In
Atrial Fibrillation BRIEFLY, HOW DOES THE HEART PUMP? The heart has four chambers. The upper chambers are called atria. One chamber is called an atrium, and the lower chambers are called ventricles. In
Welcome to Vibrationdata
 Welcome to Vibrationdata Acoustics Shock Vibration Signal Processing December 2004 Newsletter Ni hao Feature Articles One of my goals is to measure a wide variety of oscillating signals. In some sense,
Welcome to Vibrationdata Acoustics Shock Vibration Signal Processing December 2004 Newsletter Ni hao Feature Articles One of my goals is to measure a wide variety of oscillating signals. In some sense,
Wide-Complex Tachycardias in the ED: Myths and Pitfalls
 Wide-Complex Tachycardias in the ED: Myths and Pitfalls, FACEP, FAAEM Professor and Vice Chair Director, Emergency Cardiology Fellowship Department of Emergency Medicine University of Maryland School of
Wide-Complex Tachycardias in the ED: Myths and Pitfalls, FACEP, FAAEM Professor and Vice Chair Director, Emergency Cardiology Fellowship Department of Emergency Medicine University of Maryland School of
