Oatlands College Theory Book. Physical Education Theory Book
|
|
|
- Vernon Wright
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Physical Education Theory Book 1
2 The Human Body Introduction Oatlands College Theory Book This section will deal with the human body, concentrating on the skeleton, muscles and main organs. It will look at how these work together to help our bodies to move. The skeleton, bones and joints Skeletons are far from scary, they re actually pretty amazing. Packed with over 200 bones, skeletons protect, shape, support and move our bodies, as well as producing red blood cells in the bone marrow. Your vertebral column or spine is divided into five sections and influences movement during sport. Joints are also important, giving you the freedom to flex or rotate parts of your body. However this gets harder with age, as your bones lose their strength and density. Functions of the skeleton The skeleton has over 200 bones. For the exam you need to be able to identify the main bones in the body. You also need to understand the five functions of the skeleton. These are: 1. Protection - the cranium and ribs protect the brain and vital organs in the chest. 2. Shape - gives shape to the body and makes you tall or short. 3. Support - holds your vital organs in place when playing sport. The vertebral column holds the body upright. 4. Movement - muscle are attached to bones, which are jointed. When the muscles contract the bones move. 5. Blood production - red blood cells (to carry oxygen) and white blood cells (to protect against infection) are produced in the bone marrow of some bones. 2
3 Fig. 1.1 Labelled Skeleton The vertebral column can be divided into five sections. Each has a role in sport: Cervical Fig 1.2 Vertebral column smallest vertebrae support the head and neck top vertebra (atlas) allows head to nod second vertebra (axis) allows head to rotate 3
4 Thoracic ribs are attached to the thoracic vertebrae, making a protective cage allow some movement, bending forward, backward and side to side Lumbar largest vertebrae large range of movement allows much flexibility; bending forward, backward and side to side prone to injury Sacrum bones of sacral vertebrae are fused together make a strong base and transmit force from legs to upper body Coccyx fused vertebrae, no special use Discs cartilage discs between vertebrae act as shock absorbers Joints and their function A joint is where two or more bones meet. The hip is a typical synovial joint. All synovial joints have the same components: Fig 1.3 Joints 4
5 Synovial joints Cartilage reduces friction. Acts as a shock absorber. Synovial fluid lubricates the joint. Synovial membrane produces synovial fluid. Tendon joins muscle to bone enabling movement. Ligament joins bone to bone, stabilising the joint. In sport you move your limbs in different directions using joint actions. Use the following terms to describe the movements: Movement Description Abduction Movement away from the mid-line of the body Adduction Movement towards the mid-line of the body Extension Straightening limbs at a joint Flexion Bending the limbs at a joint. Rotation A circular movement around a fixed point The three most important types of synovial joint in sport are: Type of joint Example(s) in the body Types of movement possible Hinge Elbow, knee Flexion, extension Ball and Flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, Shoulder, hip Socket rotation Pivot Between the atlas and axis in the Rotation neck Fig 1.4 Types of Joints 5
6 Bone growth The bones of embryos are made largely of cartilage. They are soft. The process of ossification uses calcium to create bone as the child grows and matures. Bones gradually become hard and strong. With age bones lose their density and strength. When severe this is called osteoporosis. Eating foods containing calcium and exercising regularly helps bones to develop and stay stronger for longer. There are 4 types of bone: Fig1.5 Bone growth Type of bone Example Function in sport Long Femur, humerus Movement - to generate strength and speed Short Carpals, tarsal Shock absorption - spreading load Flat (Plate) Ribs, cranium Protection of vital organs, attachment of muscles to help movement Irregular Vertebrae, face Provide shape, protection Fig1.6 The composition of a long bone 6
7 Hyaline cartilage - covers the ends of the bones, stops them rubbing together and absorbs shock. Epiphysis - the head of the bone. Cancellous bone - spongy bone that stores the red bone marrow; where blood cells are made. Epiphyseal plate the area where bones grow in length. Diaphysis - the shaft. Compact bone hard, dense bone. It gives strength to the hollow part of the bone. Periosteum a protective layer where there is no hyaline cartilage. Ligaments and tendons attach to the periosteum. Medullary cavity/marrow cavity - contains the yellow bone marrow; where white blood cells are made. Muscles and movement The heart is made of a unique muscle type known as cardiac and it never tires. But the body also has many other paired muscles, some voluntary that are attached to the skeleton and help the body move, some involuntary that work the internal organs and cannot be controlled. Muscles and posture also go hand in hand, where regular exercise tones muscle and improves your posture to reduce strain on other parts of the body. Muscle types Fig 1.7 Sprinters have more fast twitch fibres Cardiac muscle is unique to the heart. It never tires. The body's involuntary muscles work our internal organs. They are outside our control. 7
8 Voluntary muscles make the body move. They are attached to the skeleton and can be controlled. Voluntary muscles have fast twitch and slow twitch fibres. Fast twitch fibres contract quickly, but do not use oxygen well and tire quickly. Slow twitch fibres contract slowly, but use oxygen well and keep going for a long time. Top sprinters have more 'fast twitch' fibres. Endurance athletes tend to have more 'slow twitch' fibres. Voluntary muscles Name of muscle Function Example in sport Triceps Extend the arm at the elbow Press-up, throwing a javelin Biceps Flex the arm at the elbow Pull-up, drawing a bow in archery Deltoids Move the arm in all directions at the shoulder Bowling a cricket ball Pectorals Adduct the arm at the shoulder Forehand drive in tennis Trapezius Hold the shoulders in place, move head back and sideways Holding head up in rugby scrum Gluteals Adduct and extend leg at the hips Pulling back leg before kicking a ball Quadriceps Extend the leg at the knee Kicking a ball jumping upwards Hamstrings Flex the leg at the knee Bending knee before kicking a ball Gastrocnemius Pointing the toes, help to flex the knee Running Latissimus Adduct and extend the arm at the shoulder Butterfly stroke in swimming dorsi Abdominals Flex the trunk across the stomach Pulling the body down when hurdling 8
9 The key voluntary muscles used in sport are shown in the illustration. Fig 1.8 Drawing a bow uses the biceps. Origin and insertion of muscles The origin is the end of a muscle which is attached to a fixed bone. The insertion is the end of the muscle that is attached to the bone which moves. These diagrams show the major muscles you need to know. It is important to know where they are situated on your body and the muscles names. Fig 1.9 Voluntary Muscles 9
10 Muscles and movement Fig 1.10 In a tug of war muscles contract isometrically Muscles contract when they work. If a muscle contracts to create movement, it is called an isotonic contraction. An isotonic contraction can be concentric, which is where the muscle shortens as the fibres contract or eccentric, where the fibres contract as the muscle lengthens. When a muscle contracts with no resulting movement, it is an isometric contraction. Muscle pairs Antagonistic pairs of muscles create movement when one (the prime mover) contracts and the other (the antagonist) relaxes. Examples of antagonistic pairs working are: the quadriceps and hamstrings in the leg the biceps and triceps in the arm Fig1.11 Antagonistic Pair 10
11 Fig1.12 Antagonistic Pair Muscle tone and posture Muscle tone can be seen when muscles are in a state of slight tension and they are ready for action. Regular training tones muscles and helps to create good posture. In addition, muscles will hypertrophy (increase in size) and develop better endurance. Muscle tone developed by regular exercise makes daily tasks such as shopping and gardening easier. It also helps to prevent injury as good posture reduces the strain on muscles, tendons and ligaments. Fig 1.13 Good posture is important to tennis players. Good posture helps with sporting performance as special positions are often crucial to success, eg the position throughout the golf swing. People with good posture also feel better about themselves. An upright body position is often a sign of self confidence. People who are less confident will sometimes show this in their body language, for example by adopting a slouched posture. 11
12 Organs Fig 1.13 Organs of the Body 12
13 Cardiovascular System The Human Heart Fig 1.14 Cardiovascular System Fig1.15 Structure of a Human Heart 13
14 Respiratory System Fig 1.16 The Human Respiratory System Digestive System Fig 1.17 The Human Digestive System 14
15 Health and fitness Oatlands College Theory Book There are plenty of reasons why getting off the couch and into your games kit is a good thing. Our bodies are like cars; they need to move to function well! Physically, sport helps you lose weight, enjoy a more toned body and show stamina on the sports field. Regular exercise also boosts self-confidence and mental concentration. Even if you re no Tommy Walsh, being fit is a big plus; enhancing co-ordination, agility and cardiovascular fitness. You ll probably even pick up some new mates whilst you re at it. Benefits of Activity Regular exercise improves health and fitness. Health is defined as a state of complete mental, physical and social well-being; not merely the absence of illness or infirmity. Fitness is the ability to meet the demands of the environment. Mental benefits include: improved confidence relief of stress/tension and stress related illness Physical benefits include: losing weight improved posture improved body shape Social benefits include: meeting people making friends Fig 1.18 Competing improves self esteem Fig 1.19 Sport is a good way of relieving stress 15
16 Being a member of a sports club and regularly participating in sport will develop personal qualities from: Co-operation working with others. Competition testing yourself against others. Physical challenge testing yourself against the environment or your best performances. Aesthetic appreciation recognizing quality of movement in a performance. Health related fitness factors Everyone needs to have a level of fitness for everyday activities. Health related exercise improves the health related fitness factors which are also useful to sportspeople. These are: Cardiovascular fitness is the ability to exercise the whole body for long periods of time and is sometimes called stamina. Muscular strength is the amount of force a muscle can exert against a resistance. It helps sportspeople to hit, tackle and throw. Muscular endurance is the ability to use voluntary muscles many times without becoming tired. It helps sportspeople to sprint or repeat quick actions for longer. Flexibility is the range of movement possible at a joint. It helps performers to stretch and reach further. Body composition is the percentage of body weight which is fat, muscle or bone. It helps sportspeople depending on the type of sport they play, eg heavy rugby players are more effective in the scrum than lightweight players, but light long distance runners will always beat heavyweights. NB If you are studying AQA, you should also list speed as a health related fitness factor. Speed is the differential rate at which an individual is able to perform a movement or cover a distance in a period of time or how quickly an individual can move. This helps all games players to move into position or get away from opponents quickly. Fig 1.20 Flexibility helps footballers stretch for the ball. Fig 1.21 Jogging improves cardiovascular fitness 16
17 Skill related fitness factors Sportspeople exercise to improve fitness and performance. Skill related fitness factors are essential for success in sport. These are: Agility - the ability to change the position of the body quickly and with control. This helps team players dodge their opponents. Balance - the ability to retain the centre of mass above the base of support when stationary (static balance) or moving (dynamic balance). This helps gymnasts maintain their position and prevents games players from falling over at speed. Co-ordination - the ability to use two or more body parts together. This helps all athletes to move smoothly and quickly especially when also having to control a ball. Power - the ability to use strength at speed. This helps athletes to jump high, throw far or sprint quickly. Power = Strength x Speed. Reaction time - the time between the presentation of a stimulus and the onset of a movement. This helps swimmers to make a fast start. NB If you are studying Edexcel, you should list speed as a skill related fitness factor. Speed is the differential rate at which an individual is able to perform a movement or cover a distance in a period of time or how quickly an individual can move. This helps all games players to move into position or get away from opponents quickly. Fig 1.22 Dancers need good static and stationary balance Fig 1.23 Rugby players use agility to dodge opponents 17
18 Principles of training Getting the best out of your training requires a little planning. The best training programmes are built on principles of specificity, overload, progression and reversibility. You can also use the FITT acronym to help remember the key things to consider when tailoring programmes for individual sporting goals. It stands for; Frequency, Intensity, Time and Type. Calculating the target zone also helps assess how much aerobic or anaerobic training you need to do to improve fitness. Just don t forget to warm down! Fig 1.24 Training should be matched to an individual's needs By using the principles of training as a framework we can plan a personal training programme that uses scientific principles to improve performance, skill, game ability and physical fitness. A successful training programme will meet individual needs which are personal fitness needs based on age, gender, fitness level and the sport for which we are training. A successful training programme will also include exercise in the correct heart-rate target zone. The key principles when planning a programme are: Specificity training must be matched to the needs of the sporting activity to improve fitness in the body parts the sport uses. Overload - fitness can only be improved by training more than you normally do. You must work hard. Progression start slowly and gradually increase the amount of exercise and keep overloading. Reversibility any adaptation that takes place as a result of training will be reversed when you stop training. If you take a break or don t train often enough you will lose fitness. In planning a programme, use the FITT principles to add the detail: Frequency - decide how often to train. Intensity - choose how hard to train. Time - decide for how long to train. Type - decide which methods of training to use. 18
19 You should also consider the principle of moderation. It is important to have rest periods which allow the body to adapt. Too much training (overtraining) can lead to injury. Methods of training Training can be aerobic or anaerobic. Fig 1.25 Aerobic training improves cardiovascular fitness. In aerobic exercise, which is steady and not too fast, the heart is able to supply enough oxygen to the muscles. Aerobic training improves cardiovascular fitness. Anaerobic exercise is performed in short, fast bursts where the heart cannot supply enough oxygen to the muscles. Anaerobic training improves the ability of the muscles to work without enough oxygen when lactic acid is produced. Specific training methods can be used to improve each fitness factor. Fig 1.26 Weight training improves muscular strength, endurance and power Circuit training involves performing a series of exercises in a special order called a circuit. Each activity takes place at a 'station'. It can be designed to improve speed, agility, coordination, balance and muscular endurance. Continuous training involves working for a sustained period of time without rest. It improves cardio-vascular fitness. 19
20 Cross training involves using another sport or activity to improve your fitness. It happens when an athlete trains in a different environment. For example a volleyball player uses the power training for that sport to help with fitness for long jump. Fartlek training or 'speed play' training involves varying your speed and the type of terrain over which you run, walk, cycle or ski. It improves aerobic and anaerobic fitness. Interval training involves alternating between periods of hard exercise and rest. It improves speed and muscular endurance. Weight training uses weights to provide resistance to the muscles. It improves muscular strength (high weight, low reps), muscular endurance (low weight, high reps, many sets) and power (medium weight and reps performed quickly). Altitude training is aerobic training high above sea level, where oxygen levels are lower. It is used to increase aerobic fitness quickly. General methods of training can be applied to specific sports. For example, continuous training might involve swimming, cycling, rowing, aerobics or running. Calculating target zones and thresholds of training To train effectively you must know: Your current level of fitness The amount of aerobic training you need for your sport The amount of anaerobic training you need for your sport For example, sprinters use mainly anaerobic training and marathon runners use mainly aerobic training. You can use your maximum heart rate (MHR) to calculate how hard you should work your heart to develop either aerobic or anaerobic fitness. To calculate MHR: age = MHR 20
21 Fig 1.27 Improve aerobic fitness by working at 60-80% of MHR Aerobic fitness is another way of describing cardiovascular fitness, or stamina. You can improve aerobic fitness by working in your aerobic target zone. This is found between 60-80% of your MHR. You cross your aerobic threshold, the heart rate above which you gain aerobic fitness, at 60% of our MHR. You can improve your anaerobic fitness, which includes strength, power and muscular endurance, by working in your anaerobic target zone. This is found between % of your MHR. Anaerobic threshold is the heart rate above which you gain anaerobic fitness. You cross your anaerobic threshold at 80% of your MHR. Below 60% MHR you do not improve your aerobic or anaerobic fitness at all. When working anaerobically you create an oxygen debt and can only keep going for a short time. Oxygen debt is the amount of oxygen consumed during recovery above that which would normally be consumed during rest. This results from a shortfall of available oxygen during exercise. You can monitor your fitness levels by recording your recovery rate after exercise. The recovery rate is the time it takes for the pulse rate to return to normal after exercise. Remember that percentages of MHR are approximate and personal levels of activity and fitness will cause differences in the thresholds. 21
22 Stages of a training session Fig 1.28 Modified or conditioned games are used to improve technique. Fig 1.29 Competing against team mates can be the session's main activity. 1. Warm-up Whole body exercise to raise heart rate and body temperature. Stretching to prepare muscles, ligaments and joints. Practising skills and techniques to be used in the session. 2. Main activity - this could be: Fitness training - which may be linked to repeated technique work. Skill development - drills or team practices. Modified or Conditioned Games. 3. Warm down (sometimes called cool down) Light exercise to help remove carbon dioxide, lactic acid and other waste products. Gentle stretching to prevent muscle soreness and stiffness later. 22
23 Effects of training and exercise After exercise, you ll find your body experiences immediate and more gradual effects. The minute you start training, you ll notice more frequent muscle contraction, raised body temperature and pulse, and deeper breathing known as tidal volume. Longer-term effects occur as the body adapts to regular exercise, including your heart getting larger, bones becoming denser and the vital capacity of your breath deepening. Fig 1.30 Fig
24 The bones, joints and muscles Fig 1.32 Fig 1.33 Flexibility at joints increases with regular training Immediate effects when first exercising: Muscles contract more often Blood flow to muscles increases Muscle temperature rises Little effect on bones and joints Effects of regular training: Muscles increase in size (hypertrophy) 24
25 Muscular endurance improves Muscles, tendons and ligaments around joints get stronger Joints become more stable and flexibility at joints increases Bone width and density increases The cardiovascular system Immediate effects when first exercising: Heart contracts more often increased heart rate. Heart contracts more powerfully increased stroke volume, which is the volume of blood pumped from heart with each beat. Blood diverted to muscles, eg it is diverted from the digestive system to the muscles. Blood temperature rises. Blood vessels near skin open to allow heat to be lost. Effects of regular training: Heart muscle increases in size and strength. Cardiac output increases. Cardiac means relating to the heart so this is the amount of blood that the heart pumps out to the body. Lower resting heart rate, quicker recovery from exercise. Reduced risk of heart disease. Increased number of capillaries in muscles. Increased volume of blood and red blood cells. The respiratory system Immediate effects when first exercising: Increased rate of breathing Increased depth of breathing rise in tidal volume Effects of regular training: Increased strength of diaphragm and intercostal muscles. Greater number of alveoli. Increased ability of the lungs to extract oxygen from the air. Increased vital capacity. Increased amount of oxygen delivered to, and carbon dioxide removed from, the body. 25
26 Age, psychological factors and technology It takes more than your body alone to perform. Age dictates how much strength you have, with optimum fitness experienced into your late twenties then declining by about 2% each year after. Being motivated is also important - you know, the difference between feeling really lazy versus wanting to go out there and kick some butt! Then again, it could be down to your personality type, which may draw you to competitive team sports or closed skills. In recent years, technology is another factor contributing to your PE prowess. Age Regular exercise and skill development are vital parts of growing up. However, heavy weight training and extreme distances should not be attempted by children as both affect joints and growth. Performance increases with age until your late twenties. After that age strength and endurance decline by 1-2% per year. Effects of ageing include: Fig 1.34 Performance potential increases with age until your late twenties. MHR (Maximum Heart Rate) decreases each year which means you can't work as hard. Arteries harden - blood flow to muscles is reduced. Stroke volume, cardiac output and vital capacity decrease. This reduces VO2 Max which is the maximum amount of oxygen that can be transported and used by the body in 1 minute. Muscles reduce in size and muscle strength decreases. Muscle fibres change from fast twitch to slow twitch. Body fat builds up as you are less able to use it for energy. Training can improve performance and reduce the effects, but cannot prevent the decline. 26
27 Psychological factors Psychological factors are the mental factors that help or prevent sportspeople from being in the right 'frame of mind' to perform well. In sport you have to want to perform and to improve your performance. Your determination to do this is called motivation. The intensity of it is called arousal. If training leads to boredom you will lose motivation. If you are 'wound up' you are suffering from anxiety: you will feel tension in your body and this can prevent you from performing well. Feedback is information about the outcome of a performance and it can greatly affect future performances. Your personality can affect your choice of sports and performance: Extroverts are socially outgoing. They need high arousal levels to perform. Coaches and team mates need to keep them 'excited' about performing. They prefer team games with open skills and lots of unpredictability. Open skills are used in sports where you cannot predict what will happen next, eg in an invasion game such as hockey. Introverts are usually shy. They perform better at lower arousal levels. Coaches and team mates need to allow them to stay calm and focused. Too much stimulation will cause them to be over-aroused and they will not perform well. They prefer sports with fine movements, closed skills and regular routines. Closed skills are used in sports where you can control the environment, eg putting in golf. Fig 1.35Extroverts are well suited to team games Fig 1.36 Introverts may be drawn to sports with closed skills such as golf 27
28 Some people like sports in which they can show direct aggression like boxing and rugby, where players make contact with each other. Others prefer sports which involve indirect aggression like tennis and volleyball, where players hit a ball to 'beat' their opponents. Technology Physiological and psychological factors have an impact on performance, but the use of technology is becoming increasingly significant. Technological advances are continuing to improve performance. Examples include: Equipment Fig 1.37 Specialist footwear can improve performance New materials and design used in tennis rackets, skis, footballs, javelins, bicycles etc improve control, speed and distance. Specialist clothing and footwear, including heat-reducing and lightweight materials and hydrodynamic full-body swimming suits, improve speed and endurance. Facilities All-weather surfaces, better drainage and roofed stadiums produce better playing conditions. Safety improvements in gymnastics training, including landing areas and harnesses, encourage greater skill development. ICT in training and coaching Use of video and statistical analysis helps identify areas for improvement and focuses coaching to improve performance more effectively. Fitness monitoring equipment analyses key physiological factors and helps with the planning of effective training. 28
29 Nutrition Fig 1.38 Food Pyramid Nutrition At the risk of sounding like your mum, a balanced diet really is essential for good health. There are seven building blocks for a healthy diet, including carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals and fibre. Add water to the mix and you re shaping up nicely! We take energy from food in the form of kilojoules. How much energy you need depends on your body type and the amount of physical activity you do. How you use or store energy influences your weight, shape and sporting performance. 29
30 Diet We all need to eat a balanced diet to maintain good health. It is vital that athletes have all the nutrients they need to help them perform at their best. 30
31 31
32 Energy requirements The energy the body takes from food is measured kilojoules or kilocalories.you need enough energy to meet the demands of your BMR and PAL. BMR stands for Basic Metabolic Rate; the number of kilojoules you use to stay alive each day. PAL stands for Physical Activity Level; the number of kilojoules you use to fuel all of your physical activity. BMR + PAL = your daily energy requirement. Big people need more energy for BMR. Athletes in endurance events and hard training need more energy for PAL. A heptathlete and a boxer will have different energy requirements If you consume more energy than you use you will put on weight. If you consume less energy than you use you will lose weight. People who under-eat will not have enough energy to perform effectively. Being overweight may not be a problem. It may be due to a person having a lot of muscle, rugby players for example, so it's not always harmful. However, people who are overfat or obese will not be effective sportspeople. 32
33 Body types There are 3 basic somatotypes (body types). Everyone tends towards one although few people are totally one or another. Your body type, shape and composition will determine how effective you are at sport. Endmorphs are well suited to weighlifting Ectomorphs - narrow-shaped body, are thin faced, with little fat or muscle. This is the ideal body type for long-distance runners. Mesomorphs - wedge-shaped body, wide shoulders, narrow hips, muscular. Ideal body type for sprinters. Endomorphs - pear-shaped body, wide hips, wide shoulders, can have a lot fat on body, arms and thighs. When fit, ideal body type for weightlifting, wrestling. A person's ideal body weight depends on their body type, age, gender, height, the size of their bones, and their muscle size. These factors also affect their participation and performance in sport. 33
MUSCLES G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION. Unit 1. Factors Affecting Participation and Performance. G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:.
 G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1 Factors Affecting Participation and Performance MUSCLES Name: G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:. By the end of this booklet you should: Be able to describe and explain how muscles
G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1 Factors Affecting Participation and Performance MUSCLES Name: G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:. By the end of this booklet you should: Be able to describe and explain how muscles
SKELETON AND JOINTS G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION. Unit 1. Factors Affecting Participation and Performance. G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:.
 G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1 Factors Affecting Participation and Performance SKELETON AND JOINTS Name: G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:. By the end of this booklet you should be able to: Understand what the
G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1 Factors Affecting Participation and Performance SKELETON AND JOINTS Name: G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:. By the end of this booklet you should be able to: Understand what the
Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology
 Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology These questions have been compiled based on the information available for the above qualification and unit. This mock should be
Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology These questions have been compiled based on the information available for the above qualification and unit. This mock should be
What is Physical Fitness?
 What is Physical Fitness? Physical fitness is made up of two components: Skill-related fitness and Health related fitness. Skill related fitness items are factors, which relate to the possibility of you
What is Physical Fitness? Physical fitness is made up of two components: Skill-related fitness and Health related fitness. Skill related fitness items are factors, which relate to the possibility of you
GCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION PE2 UNIT GUIDE. Content Title: Methods of training. Practical Application/Explanation. Fartlek training. Continuous training
 Content Title: Methods of training Key points GCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION Different methods of training How to design specific training sessions How to design a training programme PE2 UNIT GUIDE Practical Application/Explanation
Content Title: Methods of training Key points GCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION Different methods of training How to design specific training sessions How to design a training programme PE2 UNIT GUIDE Practical Application/Explanation
GCSE PE REVISION QUESTIONS 2011
 GCSE PE REVISION QUESTIONS 2011 Tick off list of revision topics Section 1 Reasons for taking part physical, social, mental Influences people, image, cultural, resources, health and well-being, socio-economic
GCSE PE REVISION QUESTIONS 2011 Tick off list of revision topics Section 1 Reasons for taking part physical, social, mental Influences people, image, cultural, resources, health and well-being, socio-economic
5TH GRADE FITNESS STUDY GUIDE
 PHYSICAL EDUCATION 5 TH GRADE FITNESS STUDY GUIDE PART I. Revised 5-13 DIRECTIONS: Review the following terms and concepts. Do not try to memorize the definitions, rather think about and understand: 1)
PHYSICAL EDUCATION 5 TH GRADE FITNESS STUDY GUIDE PART I. Revised 5-13 DIRECTIONS: Review the following terms and concepts. Do not try to memorize the definitions, rather think about and understand: 1)
Biomechanics, Psychology and Physical Training Instructions and answers for teachers These instructions should accompany the OCR resource
 Biomechanics, Psychology and Physical Training Instructions and answers for teachers These instructions should accompany the OCR resource Biomechanics, Psychology and Physical Training activity which supports
Biomechanics, Psychology and Physical Training Instructions and answers for teachers These instructions should accompany the OCR resource Biomechanics, Psychology and Physical Training activity which supports
SAMPLE ASSESSMENT TASKS PHYSICAL EDUCATION STUDIES GENERAL YEAR 11
 SAMPLE ASSESSMENT TASKS PHYSICAL EDUCATION STUDIES GENERAL YEAR 11 Copyright School Curriculum and Standards Authority, 2014 This document apart from any third party copyright material contained in it
SAMPLE ASSESSMENT TASKS PHYSICAL EDUCATION STUDIES GENERAL YEAR 11 Copyright School Curriculum and Standards Authority, 2014 This document apart from any third party copyright material contained in it
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeleton is the body s bony framework which consists of 206 bones. The bones are made up of water(45%), calcium and phosphorous(35%) and other organic materials(20%). The calcium
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeleton is the body s bony framework which consists of 206 bones. The bones are made up of water(45%), calcium and phosphorous(35%) and other organic materials(20%). The calcium
Final. Mark Scheme. Physical Education. (Specification 4891) Unit 1: Knowledge and Understanding for the Active Participant (Short Course)
 Version 2 General Certificate of Secondary Education (Short Course) June 203 Physical Education 4890 (Specification 489) Unit : Knowledge and Understanding for the Active Participant (Short Course) Final
Version 2 General Certificate of Secondary Education (Short Course) June 203 Physical Education 4890 (Specification 489) Unit : Knowledge and Understanding for the Active Participant (Short Course) Final
A1 Reasons for taking part in activity. A2 Health, fitness, exercise and performance
 Centre No. Paper Reference (complete below) Candidate No. / Surname Signature Initials Paper Reference 1827/01 Edexcel GCSE Physical Education End Of Unit Test SECTION 1: FITNESS A1 Reasons for taking
Centre No. Paper Reference (complete below) Candidate No. / Surname Signature Initials Paper Reference 1827/01 Edexcel GCSE Physical Education End Of Unit Test SECTION 1: FITNESS A1 Reasons for taking
General Certificate of Secondary Education (Short Course) June 2011. Unit 1: Knowledge and Understanding for the Active Participant (Short Course)
 Version 1 General Certificate of Secondary Education (Short Course) June 2011 Physical Education 48901 (Specification 4891) Unit 1: Knowledge and Understanding for the Active Participant (Short Course)
Version 1 General Certificate of Secondary Education (Short Course) June 2011 Physical Education 48901 (Specification 4891) Unit 1: Knowledge and Understanding for the Active Participant (Short Course)
UNIT 5: FITNESS BASIC ANATOMY & PROPER STRETCHING TECHNIQUE BASIC ANATOMY MAJOR MUSCLE GROUPS & BONES PROPER STRETCHING TECHNIQUE
 UNIT 5: FITNESS BASIC ANATOMY & PROPER STRETCHING TECHNIQUE TOPIC 1: TOPIC 2: BASIC ANATOMY MAJOR MUSCLE GROUPS & BONES PROPER STRETCHING TECHNIQUE GRADES 6-7 UNIT 5 FITNESS BASIC ANATOMY & GRADES PROPER
UNIT 5: FITNESS BASIC ANATOMY & PROPER STRETCHING TECHNIQUE TOPIC 1: TOPIC 2: BASIC ANATOMY MAJOR MUSCLE GROUPS & BONES PROPER STRETCHING TECHNIQUE GRADES 6-7 UNIT 5 FITNESS BASIC ANATOMY & GRADES PROPER
GCSE PHYSICAL EDUCATION
 GCSE PHYSICAL EDUCATION 48901: Knowledge and Understanding for the Active Participant (Short Course) Mark scheme June 2014 Version: 1.0 Final Mark schemes are prepared by the Lead Assessment Writer and
GCSE PHYSICAL EDUCATION 48901: Knowledge and Understanding for the Active Participant (Short Course) Mark scheme June 2014 Version: 1.0 Final Mark schemes are prepared by the Lead Assessment Writer and
Animal Systems: The Musculoskeletal System
 Animal Systems: The Musculoskeletal System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Animal Systems: The Musculoskeletal System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Standard Grade. Swimming. Name. Teacher. Class. P.E. Department Crieff High School. Miss Steele Jan 10 1
 Standard Grade Swimming Name Teacher Class P.E. Department Crieff High School Miss Steele Jan 10 1 Contents Tens Workbook Reference Swimming Section p87-92 and p127-128. Background Information Page 3 Stroke
Standard Grade Swimming Name Teacher Class P.E. Department Crieff High School Miss Steele Jan 10 1 Contents Tens Workbook Reference Swimming Section p87-92 and p127-128. Background Information Page 3 Stroke
Chapter 11. What are the functions of the skeletal system? More detail on bone
 Skeletal System Chapter 11 11.1 Overview of the skeletal system What are the functions of the skeletal system? 1. Supports the body 2. Protects the soft body parts 3. Produces blood cells 4. Stores minerals
Skeletal System Chapter 11 11.1 Overview of the skeletal system What are the functions of the skeletal system? 1. Supports the body 2. Protects the soft body parts 3. Produces blood cells 4. Stores minerals
THE BADMINTON ASSOCIATION OF ENGLAND MISSION STATEMENT
 THE BADMINTON ASSOCIATION OF ENGLAND MISSION STATEMENT Badminton is an Olympic Sport It is played by groups, families and individuals of all ages and it provides a healthy, lifelong sport activity that
THE BADMINTON ASSOCIATION OF ENGLAND MISSION STATEMENT Badminton is an Olympic Sport It is played by groups, families and individuals of all ages and it provides a healthy, lifelong sport activity that
USCGA Health and Physical Education Fitness Preparation Guidelines
 USCGA Health and Physical Education Fitness Preparation Guidelines MUSCULAR STRENGTH Muscular strength and endurance can be improved by systematically increasing the load (resistance) that you are using.
USCGA Health and Physical Education Fitness Preparation Guidelines MUSCULAR STRENGTH Muscular strength and endurance can be improved by systematically increasing the load (resistance) that you are using.
CARDIAC REHABILITATION HOME EXERCISE ADVICE
 CARDIAC REHABILITATION HOME EXERCISE ADVICE Introduction Exercise is a very important as part of your rehabilitation and your future health. You will need to exercise at least three times per week, minimum,
CARDIAC REHABILITATION HOME EXERCISE ADVICE Introduction Exercise is a very important as part of your rehabilitation and your future health. You will need to exercise at least three times per week, minimum,
Fitness Training A Sensible Guide to Preparing for Selection in the Gurkhas
 Fitness Training A Sensible Guide to Preparing for Selection in the Gurkhas Background Physical fitness has a number of components: aerobic endurance (stamina), strength, speed, flexibility, muscle endurance,
Fitness Training A Sensible Guide to Preparing for Selection in the Gurkhas Background Physical fitness has a number of components: aerobic endurance (stamina), strength, speed, flexibility, muscle endurance,
CURRICULUM OVERVIEW. Please contact your child s subject teacher or Head of Department for answers to subject related questions
 CURRICULUM OVERVIEW Please contact your child s subject teacher or Head of Department for answers to subject related questions SUBJECT SHORT COURSE GCSE PE YEAR GROUP Y9 &10 This course is for students
CURRICULUM OVERVIEW Please contact your child s subject teacher or Head of Department for answers to subject related questions SUBJECT SHORT COURSE GCSE PE YEAR GROUP Y9 &10 This course is for students
A proper warm-up is important before any athletic performance with the goal of preparing the athlete both mentally and physically for exercise and
 A proper warm-up is important before any athletic performance with the goal of preparing the athlete both mentally and physically for exercise and competition. A warm-up is designed to prepare an athlete
A proper warm-up is important before any athletic performance with the goal of preparing the athlete both mentally and physically for exercise and competition. A warm-up is designed to prepare an athlete
Muscle Fibres. Anatomy and Physiology Advanced Diploma Course Sample Pages Page 1
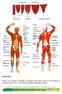 Muscle Fibres Muscles are composed of thousands of individual muscle fibres, which are held together by connective tissue. However, muscle fibres may differ in physiological makeup. Anatomy and Physiology
Muscle Fibres Muscles are composed of thousands of individual muscle fibres, which are held together by connective tissue. However, muscle fibres may differ in physiological makeup. Anatomy and Physiology
Year 2 Science: The Human Body Resource Pack
 Year 2 Science: The Human Body Resource Pack Body Systems II Body Systems Digestion our bodies break down food and use Skeletal system the skeleton is made up of bones that support our the nutrients to
Year 2 Science: The Human Body Resource Pack Body Systems II Body Systems Digestion our bodies break down food and use Skeletal system the skeleton is made up of bones that support our the nutrients to
Personal Fitness Plan
 Personal Fitness Plan 7 th Grade 1 week plan/1 week food log Name Period 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Date When you complete this project, you will accomplish the following: Set specific short-term and long-term personal
Personal Fitness Plan 7 th Grade 1 week plan/1 week food log Name Period 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Date When you complete this project, you will accomplish the following: Set specific short-term and long-term personal
Aerobics: Knowledge and Practice
 Aerobics: Knowledge and Practice Brought to you by the Wellness Center and Vanderbilt Recreation Group Fitness Program Overview The goal of this self-study course is to provide aspiring aerobics instructors
Aerobics: Knowledge and Practice Brought to you by the Wellness Center and Vanderbilt Recreation Group Fitness Program Overview The goal of this self-study course is to provide aspiring aerobics instructors
Final. Mark Scheme. Physical Education. (Specification 4890)
 Version 2 General Certificate of Secondary Education June 2013 Physical Education 48903 (Specification 4890) Unit 3: Knowledge and Understanding for the Active Participant (Full Course and Double Award)
Version 2 General Certificate of Secondary Education June 2013 Physical Education 48903 (Specification 4890) Unit 3: Knowledge and Understanding for the Active Participant (Full Course and Double Award)
9 TH GRADE KINETIC WELLNESS
 Teacher: Mr. Hartung 9 TH GRADE KINETIC WELLNESS Introduction to 9 th Grade Physical Education Introduction/Overview Chapter 1 10 reasons to get and stay in shape - Key terms you should be able to define
Teacher: Mr. Hartung 9 TH GRADE KINETIC WELLNESS Introduction to 9 th Grade Physical Education Introduction/Overview Chapter 1 10 reasons to get and stay in shape - Key terms you should be able to define
Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review
 Name: Period: Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review 1. List four functions of the skeletal system: a. b. c. d. 2. Define ossification and identify the roles of the osteoblasts, osteocytes, and
Name: Period: Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review 1. List four functions of the skeletal system: a. b. c. d. 2. Define ossification and identify the roles of the osteoblasts, osteocytes, and
This very important area is often the least understood or completely ignored by some coaches when designing a fitness program for their athletes.
 This very important area is often the least understood or completely ignored by some coaches when designing a fitness program for their athletes. An understanding of the various energy systems of our body
This very important area is often the least understood or completely ignored by some coaches when designing a fitness program for their athletes. An understanding of the various energy systems of our body
Always warm up before commencing any exercise. Wear the correct clothing and footwear; do not train if you are unwell or injured.
 SUGGESTED FITNESS PROGRAMME General Exercise Guidance Good exercise training advice is highly specific to the individual. It should be understood, therefore, that the advice provided here can only be general.
SUGGESTED FITNESS PROGRAMME General Exercise Guidance Good exercise training advice is highly specific to the individual. It should be understood, therefore, that the advice provided here can only be general.
MUSCULAR SYSTEM REVIEW. 1. Identify the general functions of the muscular system
 MUSCULAR SYSTEM REVIEW 1. Identify the general functions of the muscular system 2. Define the four characteristics of muscular tissue a. irritability (excitability) - b. extensibility- c. contractibility
MUSCULAR SYSTEM REVIEW 1. Identify the general functions of the muscular system 2. Define the four characteristics of muscular tissue a. irritability (excitability) - b. extensibility- c. contractibility
Strength Training for the Runner
 Strength Training for the Runner Strength Training for the Runner What? The goal of resistance training for runners is not necessarily adding muscle mass but 1. improving muscular strength, 2. improving
Strength Training for the Runner Strength Training for the Runner What? The goal of resistance training for runners is not necessarily adding muscle mass but 1. improving muscular strength, 2. improving
Strength and Conditioning Program
 Strength and Conditioning Program Guidelines All speed work must be performed when the body is fully rested. Proper sprinting techniques must be taught and mastered by the player. Adequate rest must follow
Strength and Conditioning Program Guidelines All speed work must be performed when the body is fully rested. Proper sprinting techniques must be taught and mastered by the player. Adequate rest must follow
Muscular System. Principles of Health Science Dr. Wood
 Muscular System Principles of Health Science Dr. Wood Characteristics of muscles Excitability: : irritability or ability to respond to stimulus Contractibility: : ability to contract (become short and
Muscular System Principles of Health Science Dr. Wood Characteristics of muscles Excitability: : irritability or ability to respond to stimulus Contractibility: : ability to contract (become short and
Final. Mark Scheme. Physical Education. (Specification 4890)
 Version 1 General Certificate of Secondary Education June 2012 Physical Education 48903 (Specification 4890) Unit 3: Knowledge and Understanding for the Active Participant (Full Course and Double Award)
Version 1 General Certificate of Secondary Education June 2012 Physical Education 48903 (Specification 4890) Unit 3: Knowledge and Understanding for the Active Participant (Full Course and Double Award)
Muscular System Grades 3-5 BACKGROUND
 Muscular System Grades 3-5 BACKGROUND The Muscular System Muscle makes up most of everything underneath the skin. This is the tissue that makes up the heart, body organs, and skeletal muscles. Muscle accounts
Muscular System Grades 3-5 BACKGROUND The Muscular System Muscle makes up most of everything underneath the skin. This is the tissue that makes up the heart, body organs, and skeletal muscles. Muscle accounts
The Process of Strength and Conditioning for Golfers
 The Process of Strength and Conditioning for Golfers The use of different sporting activities and resistance work to develop a strength and conditioning program specific to golf. Many club golfers are
The Process of Strength and Conditioning for Golfers The use of different sporting activities and resistance work to develop a strength and conditioning program specific to golf. Many club golfers are
GCSE P.E. REVISION BOOKLET
 GCSE P.E. Short Course REVISION BOOKLET Name: How many mice, like the one above, can you find in this revision booklet?! 2 GCSE PE Revision! Dear Student, Here are a few ideas to help you to revise in
GCSE P.E. Short Course REVISION BOOKLET Name: How many mice, like the one above, can you find in this revision booklet?! 2 GCSE PE Revision! Dear Student, Here are a few ideas to help you to revise in
What is Pilates? Pilates for Horses?
 What is Pilates? Pilates is a conditioning system that increases core stability, strength and body awareness; redresses imbalances, and re aligns the body from the inside out. It can improve posture, achieve
What is Pilates? Pilates is a conditioning system that increases core stability, strength and body awareness; redresses imbalances, and re aligns the body from the inside out. It can improve posture, achieve
The Power Plate is the innovative, time saving and results driven way to improve your fitness and well being.
 Welcome to the world of Power Plate Exercise The Power Plate is the innovative, time saving and results driven way to improve your fitness and well being. It works by accelerating the body s natural response
Welcome to the world of Power Plate Exercise The Power Plate is the innovative, time saving and results driven way to improve your fitness and well being. It works by accelerating the body s natural response
Men s Basketball STRENGTH & CONDITIONING PROGRAM. Developed by: Chad Kish, PhD
 Men s Basketball STRENGTH & CONDITIONING PROGRAM Developed by: Chad Kish, PhD PURPOSE The purpose of the Cardinals strength and conditioning manual is to provide the athlete with a general overview of
Men s Basketball STRENGTH & CONDITIONING PROGRAM Developed by: Chad Kish, PhD PURPOSE The purpose of the Cardinals strength and conditioning manual is to provide the athlete with a general overview of
UNIVERSAL FITNESS NETWORK, Inc. 2315 West Monica Dunlap, IL 61525 (309)-360-5615 bahenso@comcast.net FACTS ABOUT THE PHYSICAL FITNESS ASSESSMENT TESTS
 UNIVERSAL FITNESS NETWORK, Inc. 2315 West Monica Dunlap, IL 61525 (309)-360-5615 bahenso@comcast.net FACTS ABOUT THE PHYSICAL FITNESS ASSESSMENT TESTS Universal Fitness Network, Inc. specializes in physical
UNIVERSAL FITNESS NETWORK, Inc. 2315 West Monica Dunlap, IL 61525 (309)-360-5615 bahenso@comcast.net FACTS ABOUT THE PHYSICAL FITNESS ASSESSMENT TESTS Universal Fitness Network, Inc. specializes in physical
7. Skeletal System: Bone Structure and Function
 7. Skeletal System: Bone Structure and Function For the next two chapters (7 and 9) we will study the skeletal system. Although the major feature of this system is the bones, the skeletal system also consists
7. Skeletal System: Bone Structure and Function For the next two chapters (7 and 9) we will study the skeletal system. Although the major feature of this system is the bones, the skeletal system also consists
Patient Information. and Physical Activity Diary. Wythenshawe Hospital Cardiac Rehabilitation. Name:... The ticker club Registered Charity No.
 Wythenshawe Hospital Cardiac Rehabilitation Patient Information Remember : Lifelong regular physical activity - 0 minutes, five times per week is important for your general health. I feel so much better
Wythenshawe Hospital Cardiac Rehabilitation Patient Information Remember : Lifelong regular physical activity - 0 minutes, five times per week is important for your general health. I feel so much better
SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY
 2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3 SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY Unit 1 Body systems and the effects of physical activity K/507/4452 Guided learning hours: 90 Version 2 - Revised content - March 2016
2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3 SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY Unit 1 Body systems and the effects of physical activity K/507/4452 Guided learning hours: 90 Version 2 - Revised content - March 2016
Standard 1 Students demonstrate the motor skills and movement patterns needed to perform a variety of physical activities.
 Grade Three Third grade is a pivotal time in the development of students movement skills. Third graders who demonstrate and understand the proper form for locomotor and nonlocomotor skills now shift their
Grade Three Third grade is a pivotal time in the development of students movement skills. Third graders who demonstrate and understand the proper form for locomotor and nonlocomotor skills now shift their
Info. from the nurses of the Medical Service. LOWER BACK PAIN Exercise guide
 Info. from the nurses of the Medical Service LOWER BACK PAIN Exercise guide GS/ME 03/2009 EXERCISE GUIDE One of the core messages for people suffering with lower back pain is to REMAIN ACTIVE. This leaflet
Info. from the nurses of the Medical Service LOWER BACK PAIN Exercise guide GS/ME 03/2009 EXERCISE GUIDE One of the core messages for people suffering with lower back pain is to REMAIN ACTIVE. This leaflet
Weight Room Rules. 7. A towel is recommended for use in the Weight Room to use as a barrier when working on the benches and mats.
 Weight Room Rules 1. The Weight Room and Recreation Facilities are for the use of Barnard students, Barnard faculty & staff, Barnard alumnae (with Sport Pass) and Columbia undergraduate students (CC, SEAS).
Weight Room Rules 1. The Weight Room and Recreation Facilities are for the use of Barnard students, Barnard faculty & staff, Barnard alumnae (with Sport Pass) and Columbia undergraduate students (CC, SEAS).
MODULE THREE WELLNESS PLAN
 MODULE THREE WELLNESS PLAN Fill in all logs and answer the reflection questions completely with supporting details.. SECTION 1: GOALS Include your goals for each area of wellness before completing the
MODULE THREE WELLNESS PLAN Fill in all logs and answer the reflection questions completely with supporting details.. SECTION 1: GOALS Include your goals for each area of wellness before completing the
LEVEL II DEVELOPING FITNESS PHYSIOLOGY. January 2008 Page 1
 DEVELOPING FITNESS January 2008 Page 1 DEVELOPING FITNESS There are many reasons why young hockey players should develop high levels of fitness; they will be less prone to injury; they will recover faster
DEVELOPING FITNESS January 2008 Page 1 DEVELOPING FITNESS There are many reasons why young hockey players should develop high levels of fitness; they will be less prone to injury; they will recover faster
MODERE WEIGHT MANAGEMENT EXERCISE PROGRAM
 Congratulations on taking your health, fitness and body composition to the next level! Long term weight loss is impossible without a sustainable exercise routine. The Modere Weight Management Exercise
Congratulations on taking your health, fitness and body composition to the next level! Long term weight loss is impossible without a sustainable exercise routine. The Modere Weight Management Exercise
Flyball Dogs and Injury Prevention Conditioning, warm-up and cool-down
 Flyball Dogs and Injury Prevention Conditioning, warm-up and cool-down Carol J. Helfer, D.V.M. Canine Peak Performance www.caninepeakperformance.com Most injuries seen in flyball and agility dogs are repetitive
Flyball Dogs and Injury Prevention Conditioning, warm-up and cool-down Carol J. Helfer, D.V.M. Canine Peak Performance www.caninepeakperformance.com Most injuries seen in flyball and agility dogs are repetitive
Contact us for more info: 020 7736 8191 /
 Winter Sports Advanced Ski Exercises - Introduction The following exercises are for individuals who already have a significant level of fitness. If you are unsure as to whether they are appropriate for
Winter Sports Advanced Ski Exercises - Introduction The following exercises are for individuals who already have a significant level of fitness. If you are unsure as to whether they are appropriate for
Strength Training. Designed Specifically for Novice/Junior/Senior Skaters and Coaches
 Strength Training Designed Specifically for Novice/Junior/Senior Skaters and Coaches Strength Training Instructor Guidelines Instructor Qualifications A. Degree in exercise, physical education or sports
Strength Training Designed Specifically for Novice/Junior/Senior Skaters and Coaches Strength Training Instructor Guidelines Instructor Qualifications A. Degree in exercise, physical education or sports
PHYSIOLOGICAL ASPECTS OF PHYSICAL EDUCATION
 3 SOLVED PAPER Chapter PHYSIOLOGICAL ASPECTS OF PHYSICAL EDUCATION WARMING UP Warming up is a short time activity carried out prior to any severe or skilled activity. It is important to warm up before
3 SOLVED PAPER Chapter PHYSIOLOGICAL ASPECTS OF PHYSICAL EDUCATION WARMING UP Warming up is a short time activity carried out prior to any severe or skilled activity. It is important to warm up before
Archery: Coaching Young Athletes. Developing Fundamental Movement Skills
 Archery: Coaching Young Athletes Developing Fundamental Movement Skills Make a long term commitment Long Term Athlete Development Long Term Athlete Development (LTAD) is a strategy for helping youngsters
Archery: Coaching Young Athletes Developing Fundamental Movement Skills Make a long term commitment Long Term Athlete Development Long Term Athlete Development (LTAD) is a strategy for helping youngsters
Lower Back Pain An Educational Guide
 Lower Back Pain An Educational Guide A publication from the Center of Pain Medicine and Physiatric Rehabilitation 2002 Medical Parkway Ste 150 1630 Main St Ste 215 Annapolis, MD 21401 Chester, MD 21619
Lower Back Pain An Educational Guide A publication from the Center of Pain Medicine and Physiatric Rehabilitation 2002 Medical Parkway Ste 150 1630 Main St Ste 215 Annapolis, MD 21401 Chester, MD 21619
IMGPT: Exercise After a Heart Attack 610 944 8140 805 N. RICHMOND ST (Located next to Fleetwood HS) Why is exercise important following a heart
 Why is exercise important following a heart attack? Slow progression back into daily activity is important to strengthen the heart muscle and return blood flow to normal. By adding aerobic exercises, your
Why is exercise important following a heart attack? Slow progression back into daily activity is important to strengthen the heart muscle and return blood flow to normal. By adding aerobic exercises, your
Strength Training For Runners
 Strength Training For Runners Be the strongest, fastest athlete you can be Agenda Why to strength train and the benefits Myths about runners and strength training What to do How often Example program About
Strength Training For Runners Be the strongest, fastest athlete you can be Agenda Why to strength train and the benefits Myths about runners and strength training What to do How often Example program About
9/3/2013 JOINTS. Joints. Axial Skeleton STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION:
 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS Joints A connection between 2 or more bones A pivot point for bony motion The features of the joint help determine The ROM freedom Functional potential of the joint Axial
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS Joints A connection between 2 or more bones A pivot point for bony motion The features of the joint help determine The ROM freedom Functional potential of the joint Axial
Chapter 6: The Muscular System
 Chapter 6: The Muscular System I. Overview of Muscle Tissues Objectives: Describe the similarities and differences in the structure and function of the three types of muscle tissue, and indicate where
Chapter 6: The Muscular System I. Overview of Muscle Tissues Objectives: Describe the similarities and differences in the structure and function of the three types of muscle tissue, and indicate where
BEACH VOLLEYBALL TRAINING PROGRAM
 2008 ELITE PERFORMANCE ATHLETE CONDITIONING BEACH VOLLEYBALL TRAINING PROGRAM Team BC 2008 Steve Van Schubert, CAT(C), CSCS Training Schedule General Outline Phase 1 2 Weeks Phase 2 3 Weeks Phase 3 3 Weeks
2008 ELITE PERFORMANCE ATHLETE CONDITIONING BEACH VOLLEYBALL TRAINING PROGRAM Team BC 2008 Steve Van Schubert, CAT(C), CSCS Training Schedule General Outline Phase 1 2 Weeks Phase 2 3 Weeks Phase 3 3 Weeks
Knee Conditioning Program. Purpose of Program
 Prepared for: Prepared by: OrthoInfo Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle.
Prepared for: Prepared by: OrthoInfo Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle.
Fit for Flight. Developing a Personal Fitness Program
 Fit for Flight Developing a Personal Fitness Program The purpose of this brochure is to provide you with basic guidelines for developing a balanced physical fitness program and customizing a workout to
Fit for Flight Developing a Personal Fitness Program The purpose of this brochure is to provide you with basic guidelines for developing a balanced physical fitness program and customizing a workout to
Marathon Training Program for Your First Marathon. By Ben Wisbey Coach Endurance Sports Training
 Marathon Training Program for Your First Marathon By Ben Wisbey Coach Endurance Sports Training Endurance Sports Training offers individually written training programs for runners of all abilities. For
Marathon Training Program for Your First Marathon By Ben Wisbey Coach Endurance Sports Training Endurance Sports Training offers individually written training programs for runners of all abilities. For
Avoid The Dreaded Back Injury by Proper Lifting Techniques
 Avoid The Dreaded Back Injury by Proper Lifting Techniques If you ve ever strained your back while lifting something, you ll know the importance of lifting safely. Agenda Introduction About the Back The
Avoid The Dreaded Back Injury by Proper Lifting Techniques If you ve ever strained your back while lifting something, you ll know the importance of lifting safely. Agenda Introduction About the Back The
Muscular System. Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body
 Muscular System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body Structures to be identified: Muscle actions: Extension Flexion Abduction
Muscular System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body Structures to be identified: Muscle actions: Extension Flexion Abduction
Final. Mark Scheme. Physical Education. (Specification 4890) Unit 5: Knowledge and Understanding for the Involved Participant (Double Award)
 Version 3 General Certificate of Secondary Education June 13 Physical Education 4895 (Specification 489) Unit 5: Knowledge and Understanding for the Involved Participant (Double Award) Final Mark Scheme
Version 3 General Certificate of Secondary Education June 13 Physical Education 4895 (Specification 489) Unit 5: Knowledge and Understanding for the Involved Participant (Double Award) Final Mark Scheme
Contact your Doctor or Nurse for more information.
 A spinal cord injury is damage to your spinal cord that affects your movement, feeling, or the way your organs work. The injury can happen by cutting, stretching, or swelling of the spinal cord. Injury
A spinal cord injury is damage to your spinal cord that affects your movement, feeling, or the way your organs work. The injury can happen by cutting, stretching, or swelling of the spinal cord. Injury
Divisions of the Skeletal System
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46344 1 Divisions of the Skeletal System OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this
OpenStax-CNX module: m46344 1 Divisions of the Skeletal System OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this
THE BIG SIX. Six Best Volleyball Strength Training Exercises. By Dennis Jackson, CSCS www.strength-and
 THE BIG SIX Six Best Volleyball Strength Training Exercises By Dennis Jackson, CSCS www.strength-and and-power power-for for-volleyball.com THE SQUAT What it is The two most common squatting exercises
THE BIG SIX Six Best Volleyball Strength Training Exercises By Dennis Jackson, CSCS www.strength-and and-power power-for for-volleyball.com THE SQUAT What it is The two most common squatting exercises
9-12 Physical Education and Leisure Curriculum Framework. Revised 2011
 9-12 Physical Education and Leisure Curriculum Framework Revised 2011 Course Title: Physical Education and Leisure Course/Unit Credit: 1 Course Number: 485000 Teacher Licensure: Please refer to the Course
9-12 Physical Education and Leisure Curriculum Framework Revised 2011 Course Title: Physical Education and Leisure Course/Unit Credit: 1 Course Number: 485000 Teacher Licensure: Please refer to the Course
The type of cancer Your specific treatment Your pre training levels before diagnose (your current strength and fitness levels)
 Exercise and Breast Cancer: Things you can do! Cancer within the fire service is one of the most dangerous threats to our firefighter s health & wellness. According to the latest studies firefighters are
Exercise and Breast Cancer: Things you can do! Cancer within the fire service is one of the most dangerous threats to our firefighter s health & wellness. According to the latest studies firefighters are
Exercise Principles and Guidelines for Persons with Cerebral Palsy and Neuromuscular Disorders
 Exercise Principles and Guidelines for Persons with Cerebral Palsy and Neuromuscular Disorders INTRODUCTION: Health and well being are the result of many factors: Physical activity is one of these factors.
Exercise Principles and Guidelines for Persons with Cerebral Palsy and Neuromuscular Disorders INTRODUCTION: Health and well being are the result of many factors: Physical activity is one of these factors.
Body systems and energy for physical activity
 Body systems and energy for physical activity Chapter 1 Chapter 1 Body systems and energy for physical activity Introduction The body consists of complex structures that are made up of many parts, and
Body systems and energy for physical activity Chapter 1 Chapter 1 Body systems and energy for physical activity Introduction The body consists of complex structures that are made up of many parts, and
12-week Half Marathon Training Program By Ben Wisbey
 12-week Half Marathon Training Program By Ben Wisbey Introduction The half marathon is often the intermediate goal for those runners looking at doing their first marathon. It is also the longest distance
12-week Half Marathon Training Program By Ben Wisbey Introduction The half marathon is often the intermediate goal for those runners looking at doing their first marathon. It is also the longest distance
Sports Injury Treatment
 Sports Injury Treatment Participating in a variety of sports is fun and healthy for children and adults. However, it's critical that before you participate in any sport, you are aware of the precautions
Sports Injury Treatment Participating in a variety of sports is fun and healthy for children and adults. However, it's critical that before you participate in any sport, you are aware of the precautions
Stair Workouts Get in Shape: Step up
 Stair Workouts Get in Shape: Step up Warning: If you feel any knee pain, refrain from continuing that particular exercise. Avoid the no pain, no gain motto and modify with regular walking or any activity
Stair Workouts Get in Shape: Step up Warning: If you feel any knee pain, refrain from continuing that particular exercise. Avoid the no pain, no gain motto and modify with regular walking or any activity
JUNIPERO SERRA VOLLEYBALL OFF SEASON TRAINING SCHEDULE
 JUNIPERO SERRA VOLLEYBALL OFF SEASON TRAINING SCHEDULE 2007 OFF SEASON WORKOUT Our off season workout is centered around Speed, Agility & Quickness which are athletic attributes that are very trainable
JUNIPERO SERRA VOLLEYBALL OFF SEASON TRAINING SCHEDULE 2007 OFF SEASON WORKOUT Our off season workout is centered around Speed, Agility & Quickness which are athletic attributes that are very trainable
Fact sheet Exercises for older adults undergoing rehabilitation
 Fact sheet Exercises for older adults undergoing rehabilitation Flexibility refers to the amount of movement possible around a joint and is necessary for normal activities of daily living such as stretching,
Fact sheet Exercises for older adults undergoing rehabilitation Flexibility refers to the amount of movement possible around a joint and is necessary for normal activities of daily living such as stretching,
Chapter 4 Exercise Metabolism and Bioenergetics:
 CPT Study Guide, Version 4 On the actual exam, you will be tested in the following subject areas (exam breakdown): Basic and Applied Sciences Assessment Exercise Technique and Training Instruction Program
CPT Study Guide, Version 4 On the actual exam, you will be tested in the following subject areas (exam breakdown): Basic and Applied Sciences Assessment Exercise Technique and Training Instruction Program
Human Body Vocabulary Words Week 1
 Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
Passive Range of Motion Exercises
 Exercise and ALS The physical or occupational therapist will make recommendations for exercise based upon each patient s specific needs and abilities. Strengthening exercises are not generally recommended
Exercise and ALS The physical or occupational therapist will make recommendations for exercise based upon each patient s specific needs and abilities. Strengthening exercises are not generally recommended
The Santa Monica Orthopaedic and Sports Medicine Research Foundation. The PEP Program: Prevent injury and Enhance Performance
 The Santa Monica Orthopaedic and Sports Medicine Research Foundation The PEP Program: Prevent injury and Enhance Performance This prevention program consists of a warm-up, stretching, strengthening, plyometrics,
The Santa Monica Orthopaedic and Sports Medicine Research Foundation The PEP Program: Prevent injury and Enhance Performance This prevention program consists of a warm-up, stretching, strengthening, plyometrics,
The advanced back rehabilitation programme
 Physiotherapy Department The advanced back rehabilitation programme This booklet explains what happens during the advanced back rehabilitation programme and how the exercises may help your condition. We
Physiotherapy Department The advanced back rehabilitation programme This booklet explains what happens during the advanced back rehabilitation programme and how the exercises may help your condition. We
8/25/2014 JOINTS. The Skeletal System. Axial Skeleton STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION:
 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS The Skeletal System Made up of the numerous bones of the human body Gives support and framework to the body Protects vital organs Manufactures blood cells Storage of calcium
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS The Skeletal System Made up of the numerous bones of the human body Gives support and framework to the body Protects vital organs Manufactures blood cells Storage of calcium
Functional Firefighter Fitness
 Functional Firefighter Fitness The information provided is for informational purposes only and is not intended as a substitute for the advice of, or treatment that may be prescribed by your physician.
Functional Firefighter Fitness The information provided is for informational purposes only and is not intended as a substitute for the advice of, or treatment that may be prescribed by your physician.
Name. Most of the bones of the limbs (arms & legs) act as levers. These levers are powered by muscles.
 Bones as Levers 1 Name Bones as Levers You may not think of your limbs as being machines, but they are. The action of a muscle pulling on a bone often works like a type of simple machine called a lever.
Bones as Levers 1 Name Bones as Levers You may not think of your limbs as being machines, but they are. The action of a muscle pulling on a bone often works like a type of simple machine called a lever.
Pilates for Kyphosis A BASI Pilates program designed to help correct thoracic kyphosis
 Pilates for Kyphosis A BASI Pilates program designed to help correct thoracic kyphosis 1 Lucy Penrose 19/01/2014 Wimbledon UK, April 2013 Abstract Kyphosis refers to an exaggerated curve in the thoracic
Pilates for Kyphosis A BASI Pilates program designed to help correct thoracic kyphosis 1 Lucy Penrose 19/01/2014 Wimbledon UK, April 2013 Abstract Kyphosis refers to an exaggerated curve in the thoracic
THE SPEED PROGRAM THE following is A list Of POinTS THAT PRODucE RESulTS in SPEED improvement: CHANGE THE GAME
 THE SPEED PROGRAM Remember, perfect technique is the #1 emphasis with the BFS Speed Program. Faster times will follow perfect technique. The Speed Program is as follows: 1. Start with a Sprint Learning
THE SPEED PROGRAM Remember, perfect technique is the #1 emphasis with the BFS Speed Program. Faster times will follow perfect technique. The Speed Program is as follows: 1. Start with a Sprint Learning
Range of Motion Exercises
 Range of Motion Exercises Range of motion (ROM) exercises are done to preserve flexibility and mobility of the joints on which they are performed. These exercises reduce stiffness and will prevent or at
Range of Motion Exercises Range of motion (ROM) exercises are done to preserve flexibility and mobility of the joints on which they are performed. These exercises reduce stiffness and will prevent or at
Living Room Bodyweight Workout Week 1 March or jog in place for 1 min to increase heart rate and lubricate joints.
 Warm Up- Living Room Bodyweight Workout Week 1 March or jog in place for 1 min to increase heart rate and lubricate joints. Protocol- All exercises will be done for 2 sets of 10 repetitions. After the
Warm Up- Living Room Bodyweight Workout Week 1 March or jog in place for 1 min to increase heart rate and lubricate joints. Protocol- All exercises will be done for 2 sets of 10 repetitions. After the
Knee sprains. What is a knee strain? How do knee strains occur? what you ll find in this brochure
 what you ll find in this brochure What is a knee strain? How do knee strains occur? What you should do if a knee strain occurs. What rehabilitation you should do. Example of a return to play strategy.
what you ll find in this brochure What is a knee strain? How do knee strains occur? What you should do if a knee strain occurs. What rehabilitation you should do. Example of a return to play strategy.
ACL Reconstruction Rehabilitation Program
 ACL Reconstruction Rehabilitation Program 1. Introduction to Rehabilitation 2. The Keys to Successful Rehabilitation 3. Stage 1 (to the end of week 1) 4. Stage 2 (to the end of week 2) 5. Stage 3 (to the
ACL Reconstruction Rehabilitation Program 1. Introduction to Rehabilitation 2. The Keys to Successful Rehabilitation 3. Stage 1 (to the end of week 1) 4. Stage 2 (to the end of week 2) 5. Stage 3 (to the
Clinical Care Program
 Clinical Care Program Therapy for the Cardiac Patient What s CHF? Not a kind of heart disease o Heart disease is called cardiomyopathy o Heart failure occurs when the heart can t pump enough blood to meet
Clinical Care Program Therapy for the Cardiac Patient What s CHF? Not a kind of heart disease o Heart disease is called cardiomyopathy o Heart failure occurs when the heart can t pump enough blood to meet
SISSRGU203A Participate in conditioning for Rugby Union
 SISSRGU203A Participate in conditioning for Rugby Union Release: 2 SISSRGU203A Participate in conditioning for Rugby Union Modification History Not Applicable Unit Descriptor This unit describes the performance
SISSRGU203A Participate in conditioning for Rugby Union Release: 2 SISSRGU203A Participate in conditioning for Rugby Union Modification History Not Applicable Unit Descriptor This unit describes the performance
EASY EXERCISES A CHAIR BASED PROGRAMME FOR OLDER ADULTS
 EASY EXERCISES A CHAIR BASED PROGRAMME FOR OLDER ADULTS Table of Contents Foreword Why be active? How will chair exercises help? Safety Advice Before you start Sit Tall How to do the Programme The Programme
EASY EXERCISES A CHAIR BASED PROGRAMME FOR OLDER ADULTS Table of Contents Foreword Why be active? How will chair exercises help? Safety Advice Before you start Sit Tall How to do the Programme The Programme
