SHEAR RESISTANCE OF RC INTERIOR ECCENTRIC BEAM-COLUMN JOINTS
|
|
|
- Elvin Lee
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 13 th World Conferene on Earthquake Engineering Vanouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 649 SHEAR RESISTANCE OF RC INTERIOR ECCENTRIC BEAM-COLUMN JOINTS Yasuaki GOTO 1, Osamu JOH 2 SUMMARY Experimental study was arried out to larify the influene of eentriity on the shear strength and failure mehanism of reinfored onrete interior beam-olumn joints. Four half-sale, ross-shaped speimens were tested to investigate the relationship of eentriity and strength redution. Test results show that the larger the eentri distane, the smaller the joint shear strength. Continuous analytial study by three-dimensional inelasti finite element analysis was arried out to examine preisely the shear failure mehanism of these joints. The analytial results show that the onentration of the shear stress of joint onrete is on the eentri side and in the region of onrete failure. INTRODUCTION The beam-olumn joints in many reinfored onrete (RC) buildings suffered damage during the disastrous Hyogoken-Nanbu earthquake in In 1999, design requirements for beam-olumn joints were enated in the AIJ (Arhitetural Institute of Japan) standard for RC strutures [1], whih is a well-known design guide in Japan. Researhers have investigated the ause of failure of these damaged buildings. They found that almost all damaged frames showed eentriity between the beam and olumn, and the joint shear strengths alulated aording to the AIJ RC standard were enough larger than the flexural strength of adjaent beams to ause flexural failure at the beam ends [2]. Therefore, they onluded the redution of joint shear strength might our in the atual buildings due to the eentriity between the beam and olumn. Beause there has not been muh researh on eentri beam-olumn joints, the influene of eentriity on joint shear strength and frame deformability has not been larified [3]. In some design odes that inlude the AIJ RC standard, the influene of eentriity on joint shear strength uses the effetive joint width [4][5]. For example, the effetive joint width aording to the AIJ RC standard is alulated as the beam width plus the minimum value of half the distane between the olumn fae and beam fae, or a quarter of the joint depth on both sides. The joint shear strength is alulated as the produt of the effetive joint area (defined by the effetive width and olumn depth) and the standard strength that depends on the joint onrete strength, onfiguration and onfinement ondition. In addition, joint reinforement does not effet joint shear strength, but it is does effet the onfinement of the joint ore onrete, whih results in dutile behavior of the frame. The failure mode of the beam-olumn sub-assemblage is defined as follows: when the joint shear 1 Assoiate Professor, Hokkaido University, Sapporo, Japan. gottsu@eng.hokudai.a.jp 2 Professor, Hokkaido University, Sapporo, Japan. joh@eng.hokudai.a.jp
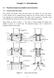
2 strength is large enough, adjaent beams will yield and beam flexural failure will our (B-type). But in the ase that the joint shear strength is not large enough against the beam flexural strength, joint shear failure ours with a large displaement after beam yielding (BJ-type). If large amounts of beam bars are provided, the beam flexural strength beomes so large that joint shear failure will our before beam yielding (J-type). Besides these failure types, flexural and shear failure of both beam and olumn members is expeted, and also bond failure will be observed in suh ases as poor bond onditions, whih ours when using large-diameter bars as longitudinal reinforements [6]. The RC frame is designed aording to the weak-beam, strong-olumn onept, so that large energy dissipation is expeted, whih leads to the preferable behavior of strutures. It is neessary to establish the evaluation of not only joint shear strength but also the deformability of several types of frame onfigurations in strutural design. This study presents test results on the performane of eentri beam-olumn sub-assemblages subjeted to vertial gravity and lateral earthquake loading, and the analytial results of the shear failure mehanism of joints. EXPERIMENTAL PROGRAM Experimental work Speimens All speimens were ross-shaped in order to fous on the interior beam-olumn sub-assemblages. Speimens had neither transverse beams nor floor slabs (plane frames). The size of eah beam and olumn was the same for all speimens (beam setion 200 x 350 mm, length 3,000 mm; olumn setion 450 x 300 mm, height 1,750 mm). The differenes in eentri distane between the beam enter and olumn enter of the speimens was set as 0, 60 or 125 mm, whih gives eentriity ratios of 0, 0.12 and 0.25, respetively. In addition, the joint reinforement ratios were set as 0.25% (use letter "M") and 0.53% (use letter "U") volumetri ratios. For the speimen names, the seond letter and first number after the hyphen represent the joint reinforement ratio and eentri distane, respetively. Table 1 shows the properties of all speimens. The joint shear strength of all speimens was alulated aording to the AIJ Standard. All speimens were designed not to show shear failure of the beam or olumn prior to expeted failure. In order to larify the influene of eentriity on the joint shear strength, all speimens were designed to fail beause of joint shear failure. Therefore, a large number of beam bars were provided in order to generate large input to eah joint. Figure 1 illustrates in detail the reinforement of the speimens. In the speimens, a steel over plate was attahed to the beam onrete at the beam ends in order to prevent the onrete from being rushed due to ompressive fore. The first letter of the speimen names indiates the joint shear input at beam yielding, whih is defined by the produt of the beam bar area and its tensile strength. Speimen eentri distane Table 1. Speimen list Beam l=3000 a t σ y Column h=1750 Joint hoop Beam Bars (kn) Column Bars reinforement 0 60 pw=0.25% 3-D22 SD685 pt=1.66% D16 SD pg=1.98% 6φ SR295 UU pw=0.53%
3 ,,,UU-125,UU e=0 150 joint setion steel over plate ( ) Stirrup UU D22 (SD685) beam setion ( ) lateral loading 1350 support 300 e=60 e=125 joint setion ( ) Hoop PL Fig. 1 Speimen detail 35 pw=0.25% pw=0.53% side view of joint axial loading UU-125 unit: mm Materials The design ompressive strength of the onrete was 24 MPa. The onrete onsisted of rushed stone having a maximum size of 13 mm. Table 2 summarizes the atual ompressive strengths of the onrete on test day. Table 3 shows the mehanial properties of the flexural reinforing bars and joint reinforement. The stress-strain relationship of eah bar was obtained by attahing a strain gage during the material testing, and the measured strain in this relationship was used to alulate the stress generated in the reinforement. Table 2. Conrete properties Speimen σ B ε max σ t E 1/3 (MPa) (µ) (MPa) (GPa) UU Table 3. Reinforement properties Classifiation σ y ε y σ max E s Elongation (MPa) (µ) (MPa) (GPa) (%) 6φ SR D6 SD D16 SD D22 SD Loading Figure 2 shows the loading setup. Speimens were tested in the upright position. The olumn was linked to a reation wall by hannel steel at the bottom and a hydrauli atuator at the top. The end of eah beam (refletion point) was linked to the reation floor by a pinned-end vertial support. Axial fore was generated by a hydrauli jak at the olumn bottom and an atuator at the olumn top. Speimens were also supported perpendiular to the loading plane (i.e., perpendiular to the paper). The torsion generated due to eentriity was restrained by H-shaped steel mounted at the olumn top and bottom. First, a onstant olumn axial fore was applied up to 1/6 of the onrete ompressive strength in stress, and then a lateral displaement was applied to the olumn top statially. Reversal displaements of 1/500, 1/200, 1/100 (2), 1/70 (2), 1/50 (2), 1/35 and 1/20 in the story drift angle were applied ylially. The numbers in parentheses indiate the number of repetitions of the same displaement.
4 500kN atuator for axial fore ross-shape steel for axial loading 1000kN load-ell pin restraint against torsion universal joint lateral loading atuator reation wall restraint against torsion pin speimen reation for beam universal joint olumn reation ounter weight 500kN hydrauli jak for axial fore 200kN load ell reation floor Fig. 2 Loading setup Disussion of test results Crak pattern Figure 3 shows the typial joint raking pattern that was observed after testing. Severe joint shear raking was observed on the flush side, but only a small rak appeared on the offset side. Beam bar yielding was not observed during testing. Speimen, in whih the eentri distane was equal to 0, (front) (bak) (flush side) (offset side) Fig. 3 Speimen appearane after test (blak piees in beam-end are steel overs)
5 had severe joint shear raking on both sides. The joint over onrete spalled out when the story drift angle beame larger than 0.03 and severe raking was observed. Torsional raking was also observed at the olumn faes of the eentri speimens where the beams were onneted. Story shear vs. story drift angle Figure 4 shows the envelope urves of story shear vs. story drift angle for all speimens. The initial stiffness of eah speimen was similar, but the degradation beame obvious after onrete ompressive frature was observed in the joint. This figure also indiates that the maximum strength primarily depends on the eentri distane. V(kN) R(10 rad) Maximum strength Joint onrete frature UU Fig. 4 Story shear vs. story drift angle Ultimate strength Table 4 shows the test results for the olumn shear of all speimens and ompares the beam flexural strength and joint shear strength alulated by the proposed equations. The failure mode of all speimens was defined as joint shear failure (J-type), beause no yielding of the beam bar was observed, but severe joint onrete frature was observed. Figure 5 shows the relationship between maximum strength and eentriity ratio. This figure indiates that the tendeny for the shear strength beomes smaller as the eentriity ratio inreases. Therefore, the influene of eentriity on strength redution should be examined. The alulated beam flexural strength (al1 in Table 4) is larger than the experimental results for all speimens, beause beam yielding did not our. The two proposed equations shown in the footnote of Table 4 are used to alulate the joint shear strength. These two equations differ in their onsideration of eentriity. In Table 4, al2 is alulated by equation 2, using the effetive joint width defined in Figure 6, and al3 is alulated by equation 3, with diret onsideration of the torsional moment. The value of the joint shear strength alulated using either the al2 or al3 equation underestimates the test results, while the ratio of the alulated to observed strength dereases as the eentri distane inreases. This means that the estimation of the fator of safety for joint shear failure hanges aording to the eentri distane. The definition of effetive joint width was also examined in order to improve the estimation. For the ase in whih the beam is onneted at the enter of the olumn, the effetive joint width is smaller than the width of the joint ore onrete. If large eentriity exists between the beam and the olumn, the proposed effetive width inludes the joint over onrete, whih was no longer effetive at the ultimate stage of the test due to having been spalled out. Therefore, the effetive joint width should be modified to exlude the thikness of the over onrete. The alulated values using the modified width (al4) also underestimate the test results, but the ratio is almost onstant despite the hange in eentri distane.
6 Table 4. Test results Joint shear Beam flexural Speimen exp V Equation 2 Equation 3 Eq. 2 (modified width) (kn) al1v exp/al al2v exp/al al3v exp/al al4v exp/al J J J UU J al1: M u = 0.9 at σ y d (1) al2: b V ju = κ 2 φ Fj b ju D (2) al3: V ju =β jt al 2V ju (3) β jt = { 1+ ( e al 2V ju Tju ) }, T ju = ( 0.8 σ B pw σ wy ) b D where, unit: N, mm, MPa M u : beam flexural strength V ju : joint shear strength T ju : torsional strength a t : bar area σ : yield strength d y b : beam effetive depth κ : 1.0 (onfiguration fator) b 2 ju : effetive joint width 0. 7 φ : 0.85 (onfinement by transverse beams) F j : 0.8xσ (standard strength) D : olumn depth b : olumn width σ : onrete ompressive strength p B w : joint reinforement ratio σ : yield strength of joint reinforement wy exp V (kn) UU-125 e 1 =e/b Fig.5 Relation of observed strength and eentri distane B D/4 ANALYTICAL PROGRAM Failure mode Analytial method Referene speimens Three speimens of, and were seleted as referene speimens for the finite element method (FEM) analytial program to examine the influene of eentriity on the shear failure mehanism of an eentri beam-olumn joint. Analytial model A three-dimensional analysis program was needed for the onentri joint when the widths of the olumn and beam were not the same, and more needed for the eentri joint. This analysis was arried out using the DIANA (ver. 7.2) finite element program developed by TNO. The analytial model for eah speimen is shown in Figure 7. In the analysis, inremental displaements were given to both beam ends under onstant olumn axial fore, whereas the olumn displaement was given in the experimental work, beause no P-delta moment was generated with the axial loading system. Boundary onditions in the analysis were applied aording to the experiment. The torsion-restraining steel at the olumn end was also modeled using beam elements, beause pre-analysis showed that the presene of the fixed support greatly influened the result in the eentri joint. However, the fixed support was also applied in of the onentri joint. B b D/4 b 2 /2 b 1 /2 b 1 /2 1/2 D offset side flush side b ju Fig. 6 Joint effetive width (AIJ RC standard)
7 restraining steel against torsion Z Y X UM - 0 UM - 60 UM Fig. 7 Analytial model Material models (a) Conrete Eight-node solid brik elements with four Gaussian points were assumed for the onrete. In the onstitutive model of the onrete, an asending ompressive stress-strain relationship was represented by the CEB Model Code (1990)[7], and the failure was evaluated by the failure riterion of Druker-Prager [8]. The post-peak behavior of the onrete at the beam end was modeled to not show stress relaxing beause of the existene of the restraint steel over, whereas the other onrete was modeled as the softening model shown in Figure 8, as defined by equation (4) based on the ompressive frature energy by Nakamura et al. [9]. The equivalent element length was defined as the diameter of the sphere with a volume equal to that of the onrete element. The smeared rak model was represented in the onrete element, where tension softening was onsidered aording to the equation proposed by Hordijk [10]. where, G = 8.8 f (4) f G f : onrete ompressive frature energy (N/mm) f : onrete ompressive strength (MPa) σ σb λ σ B (MPa) L:Element size λ:redution fator of ompressive strength E0 0 σt E0 ε0 ε Gf/ L ε εu Fig. 8 Equivalent uni-axial stress-strain urve of onrete
8 (b) Reinforement All reinforement was assumed to be from two-node truss elements. The stress-strain relationship of these reinforements was assumed to be bi-linear or tri-linear in aordane with the material test results. () Bond The bond between the beam longitudinal reinforement and onrete was expressed by line interfae elements. Bond properties, inluding the stiffness and strength of bond stress vs. the slip relationship, depend on the ondition around the reinforement. The stress ondition around the joint is onsidered to be that shown in Figure 9. The beam bars in the ompressive region were subjeted to lamping stress orthogonally by the ompressive stress of the olumn bending, whih auses larger stiffness and larger bond strength. The model for the bond stress vs. slip relationship, reommended by the CEB Model Code and shown in Figure 10, was adopted in this analysis; two types of onditions were applied for the onsideration mentioned above, i.e. good ondition or other ondition in the bond. The bond properties are shown in Table 5. The bond for the other reinforement of the olumn bar and shear reinforement was assumed to be perfet (no slip). τ max τ(mpa) Good τ f = 0.4 τ max τ' max All Other τ f τ' f 0 Kh(Kh) ' Slip(mm) Fig. 9 Stress ondition in joint Fig. 10 Bond stress-slip relationship Table 5. Bond speifiation Speimen Bond ondition Good Other Good Other Good Other K h (MPa/mm) τ max (MPa) Definition of the ompressive failure of onrete element The failure riterion of Druker-Prager was adopted as the failure judgment in this analysis. To detet a failed onrete element, the three prinipal stresses alulated at eah Gaussian point in the element were substituted into equation (5), then the element was identified as failed when the values of this equation for all Gaussian points within it were zero. where, ( ) f I, J = α I + J k = 0 (5) sinφ 6 sinφ α =, k = 3 3 sin 3 3 sin 1 ( φ ) ( φ ) I : first invariant of stresses
9 J 2 : seond invariant of stresses φ : angle of internal angle : ohesion stress Redution fator of joint onrete Past experimental study has demonstrated that the onrete strut that is formed between shear raks an help the resistane mehanism of RC members subjeted to shear, but redution of the onrete ompressive strength ours aording to the inrement of the raking. Collins et al. [11] and Noguhi et al. [12] proposed an equation using the prinipal tensile strain of onrete to represent this harateristi. The researh work in this paper ould not onsider this influene, so the following proedure was adopted. First, an analysis was arried out using the normal strength obtained by material testing, and the maximum tensile strain of the onrete elements at ultimate strength was obtained in eah slie of blok shown in Figure 11. Then, the redution fator of eah slie of blok was alulated using Noguhi's equation (6), in whih the maximum tensile strain of the blok was substituted. Finally, the same analysis was arried out again using the redution fator for joint onrete, whih influened the stiffness of the joint onrete. The redution fator of eah speimen is shown in Table 6. where, 1 λ = ε 1u ε (6) λ : redution fator for onrete ompressive strength ε : prinipal tensile strain of onrete 1u ε 0 : strain at maximum ompressive strength 8 ~ 1 8(offset side) ~ 1(flush side) Table 6. Redution fator of onrete ompressive strength Y Z X Fig. 11 Loation of joint onrete elements Speimen Analytial results and disussion Story shear vs. story drift angle The analytial results of all speimens were ompared with the experimental results, as shown in Figure 12. The deterioration of stiffness in the analysis beame smaller than the experimental result, whih resulted in the larger ultimate strength. However, the strength redution aording to the inrement of eentri distane was obtained in the analytial results, and observed in the experimental results. showed greater post-peak redution of strength than did the eentri joints. This is beause the extension of the failure zone in the joint onrete was limited in the eentri joint of, whih will be detailed later. The failure mode of all speimens in the analysis was defined as joint shear (J-type), whih oinides with the experimental results.
10 V (kn) 200 (ana) : Analysis (exp) : Experiment (exp) (exp) (exp) (ana) (ana) (ana) R(10-3 rad) Fig. 12 Story shear vs. story drift angle Joint shear vs. joint shear distortion angle The analytial results on eah flush side and offset side are shown in Figure 13. Joint shear is alulated from equation (7) in the experimental results on the assumption that the beam moment arm is 7/8 of the effetive depth. On the other hand, the analytial value is obtained as the sum of the element shear loated in the layer at the middle height of the joint, whih is the integral of the shear stress obtained at the Gaussian points. The shear deformation of the analytial result is alulated from the displaement in the joint diagonal diretion, whih is the same proedure used in the experiment. The shear deformation angle on the flush side beame larger with the inrease of the eentri distane. On the ontrary, reverse joint deformation ourred on the offset side of, whih was similar to the experimental result, and was aused by the torsional fore that ated as a anel shear on this side. However, the joint deformation reversed at the large displaement due to the inrement of shear stress in the onrete element loated on the offset side. where, V j = C + C + T V = 2 T V (7) s s V j : joint shear C : ompressive fore ating at onrete C s : ompressive fore ating at beam bars T s : tensile fore at beam bars V : olumn shear V j (kn) solid: analysis broken: experiment flush side UM -0 UM -60 UM -125 γ s (10-3 rad) V j (kn) solid: analysis broken: experiment offset side UM -0 UM -60 UM -125 γ n (10-3 rad) Fig. 13 Joint shear vs. joint shear distortion angle
11 Torsional moment vs. torsional deformation angle The analytial results of the eentri joints are shown in Figure 14. The torsional moment was alulated as the produt of the joint shear and eentri distane, and the torsional displaement angle was alulated from the horizontal displaement of points that were loated on the top and bottom of the joint on both the flush side and offset side. The analysis shows good agreement with the experiment. M t (kn m) solid: analysis broken: experiment UM -60 UM -125 φ(10-3 rad) Fig. 14 Joint torsional moment vs. torsional deformation angle Compressive stress distribution of joint onrete Figure 15 shows the distribution of ompressive stress at the story drift angle of 1/100 radian and the maximum strength of two speimens, and, in order to examine the influene of eentriity on the stress distribution. Eah row in Figure 15 represents slies of the blok of elements. The region where the ompressive stress beame large is reognized approximately at the joint diagonal line, and so it is onsidered that a onrete ompressive strut was formed. The onrete strut was distributed eentrially to the beam-onneted portions. After the ultimate stage, the ompressive stress in the eentri joint () dereased due to failure on the flush side joint enter and the extended strut towers to the opposite side, while the strut extended uniformly on both sides in the onentri joint (). Shear stress distribution of joint onrete Figure 16 shows the shear stress distribution at the middle height of the joint in two speimens, and. Symmetri distribution was observed in the onentri joint and the stress dereased in all areas after the ultimate stage. Eentri distribution similar to the distribution of ompressive stress was also observed in the eentri joint, but the region where the shear stress inreased shifted to the offset side after the ultimate stage while the stress dereased on the flush side simultaneously. Failure of joint onrete In Figure 17, the hathed one indiates the failure of the joint onrete elements at the ultimate stage. Failure ourred in the elements olored in red, judging by the Druker-Prager riterion. In the onentri joint, the failure zone distributed symmetrially to the joint fae. However, failure was not observed on the offset side of the eentri joint.
12 beam onneted (R= rad) R= rad R= rad R= rad R= rad (maximum strength) beam onneted R= rad R= rad R= rad R= rad Y Z X (MPa) Fig. 16 Distribution of shear stress in joint onrete beam onneted (R= rad) beam onneted 8 Z 7 (maximum strength) Y X (MPa) Fig. 15 Distribution of ompressive stress in joint onrete beam onneted Y Fig. 17 Distribution of failure elements (at maximum strength) Z X 1 CONCLUSIONS The seismi performane of eentri interior beam-olumn onnetions was investigated experimentally and analytially. The experimental work was arried out using four speimens that were given onstant vertial fore and yli horizontal loading. Then, an analytial study on the speimens was arried out using three-dimensional FEM. Experimental and analytial results revealed the following: 1) Comparison of the observed strength between speimens that failed in joint shear indiates that, as the eentri distane inreases, the joint shear strength dereases. This tendeny was observed in the experiment as well as the analysis. 2) The alulation of joint shear strength using the joint effetive width presribed in the AIJ standard underestimates the experimental results. The degree of underestimation depends on the eentri distane. 3) The joint shear strength alulated by the AIJ equation using the modified effetive joint width, whih is defined by taking the effetiveness of the joint onrete into onsideration, showed the good agreement with the experimental results.
13 4) The finite element analysis showed that the eentri distribution of the ompressive and shear stresses in the eentri joint onrete elements aused the loal failure of the onrete, whereas there was uniform distribution in the onentri joint. However, the strength dereased more gradually in the eentri joint than in the onentri joint, beause the onrete elements loated on the offset side beame effetive resistane after the ultimate stage. ACKNOWLEDGMENT This work was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Sientifi Researh (C), No , from Japan Soiety for the Promotion of Siene (JSPS). REFERENCES 1. Arhitetural Institute of Japan "AIJ Standard for Strutural Calulation of Reinfored Conrete Strutures - Based on Allowable Stress Conept", (Japanese), Arhitetural Institute of Japan "Reommendation to RC Strutural Design after Hanshin-Awaji Earthquake Disaster - Cause of partiularly damaged and orresponding RC strutural design details", (Japanese), Joh O., Goto Y. and Shibata T. "Behavior of Reinfored Conrete Beam-Column Joints with Eentriity", Design of Beam-Column Joints for Seismi Resistane, SP-123, Amerian Conrete Institute, pp , ACI-ASCE Committee 352 "Reommendations for Design Beam-Column Connetions in Monolithi Reinfored Conrete Strutures (ACI 352R-02) ", Amerian Conrete Institute, Farmington Hills, Arhitetural Institute of Japan "Design Guidelines for Earthquake Resistant Reinfored Conrete Buildings Based on Inelasti Displaement Conept", (Japanese), Meinheit D. F. and Jirsa J. O. "Shear Strength of R/C Beam-Column Connetions", ASCE, Journal of the Strutural Division, Vol. 107, No.ST11, pp , CEB "CEB-FIP Model Code1990 Design Code", Thomas Telford Servie Ltd, W. F. Chen "Plastiity of Reinfored Conrete" MaGraw-Hill International Company, Nakamura H. and Higai T. "Compressive frature energy and frature zone length of onrete", Seminar on post-peak behavior of RC strutures subjeted to seismi loads,jci-c51e,vol.2, pp , TNO Building and Constrution Researh "DIANA User's Manual Non-linear Analysis, Release 7" 11. Vehio F. J. and Collins M. P. "The Modified Compression-Field Theory for Reinfored Conrete Elements Subjeted to Shear", ACI Strutural Journal, Vol.83, No.2, pp , Morita S. et al. "Basi Experiments and Development of Analytial Models to Improve Auray of FEM Analysis of RC Strutures", (Japanese) Grant-in-Aid for Sientifi Researh (A), Japan Ministry of Eduation, 1989
Earthquake Loss for Reinforced Concrete Building Structures Before and After Fire damage
 Earthquake Loss for Reinfored Conrete Building Strutures Before and After Fire damage Pai-Mei LIU, Yi-Hsuan Tu and Maw-Shyong SHEU 3 ABSTRACT The purpose of this paper is to propose a rational analytial
Earthquake Loss for Reinfored Conrete Building Strutures Before and After Fire damage Pai-Mei LIU, Yi-Hsuan Tu and Maw-Shyong SHEU 3 ABSTRACT The purpose of this paper is to propose a rational analytial
In order to be able to design beams, we need both moments and shears. 1. Moment a) From direct design method or equivalent frame method
 BEAM DESIGN In order to be able to design beams, we need both moments and shears. 1. Moment a) From diret design method or equivalent frame method b) From loads applied diretly to beams inluding beam weight
BEAM DESIGN In order to be able to design beams, we need both moments and shears. 1. Moment a) From diret design method or equivalent frame method b) From loads applied diretly to beams inluding beam weight
Fig. 1.1 Rectangular foundation plan.
 Footings Example 1 Design of a square spread footing of a seven-story uilding Design and detail a typial square spread footing of a six ay y five ay seven-story uilding, founded on stiff soil, supporting
Footings Example 1 Design of a square spread footing of a seven-story uilding Design and detail a typial square spread footing of a six ay y five ay seven-story uilding, founded on stiff soil, supporting
Chapter 1: Introduction
 Chapter 1: Introdution 1.1 Pratial olumn base details in steel strutures 1.1.1 Pratial olumn base details Every struture must transfer vertial and lateral loads to the supports. In some ases, beams or
Chapter 1: Introdution 1.1 Pratial olumn base details in steel strutures 1.1.1 Pratial olumn base details Every struture must transfer vertial and lateral loads to the supports. In some ases, beams or
CHAPTER J DESIGN OF CONNECTIONS
 J-1 CHAPTER J DESIGN OF CONNECTIONS INTRODUCTION Chapter J of the addresses the design and heking of onnetions. The hapter s primary fous is the design of welded and bolted onnetions. Design requirements
J-1 CHAPTER J DESIGN OF CONNECTIONS INTRODUCTION Chapter J of the addresses the design and heking of onnetions. The hapter s primary fous is the design of welded and bolted onnetions. Design requirements
Explanatory Examples on Indian Seismic Code IS 1893 (Part I)
 Doument No. :: IITK-GSDMA-EQ1-V.0 inal Report :: A - Earthquake Codes IITK-GSDMA Projet on Building Codes Explanatory Examples on Indian Seismi Code IS 1893 (Part I) by Dr. Sudhir K Jain Department of
Doument No. :: IITK-GSDMA-EQ1-V.0 inal Report :: A - Earthquake Codes IITK-GSDMA Projet on Building Codes Explanatory Examples on Indian Seismi Code IS 1893 (Part I) by Dr. Sudhir K Jain Department of
SHAFTS: TORSION LOADING AND DEFORMATION
 ECURE hird Edition SHAFS: ORSION OADING AND DEFORMAION A. J. Clark Shool of Engineering Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering 6 Chapter 3.1-3.5 by Dr. Ibrahim A. Assakkaf SPRING 2003 ENES 220
ECURE hird Edition SHAFS: ORSION OADING AND DEFORMAION A. J. Clark Shool of Engineering Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering 6 Chapter 3.1-3.5 by Dr. Ibrahim A. Assakkaf SPRING 2003 ENES 220
SUBSTRUCTURE EXAMPLE. Full Height Abutment on Spread Footing
 SUBSTRUCTURE EXAMPLE Full Height Abutment on Spread Footing This example illustrates the design of a full height abutment on spread footings for a single span ast-in-plae post-tensioned onrete box girder
SUBSTRUCTURE EXAMPLE Full Height Abutment on Spread Footing This example illustrates the design of a full height abutment on spread footings for a single span ast-in-plae post-tensioned onrete box girder
Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Review 6 (5) (2013) 143-148. Research Article
 Jestr Journal o Engineering Siene and Tehnology Review 6 (5) (13) 143-148 Researh Artile JOURNAL OF Engineering Siene and Tehnology Review www.jestr.org Numerial Analyses on Seismi Behaviour o Conrete-illed
Jestr Journal o Engineering Siene and Tehnology Review 6 (5) (13) 143-148 Researh Artile JOURNAL OF Engineering Siene and Tehnology Review www.jestr.org Numerial Analyses on Seismi Behaviour o Conrete-illed
) ( )( ) ( ) ( )( ) ( ) ( ) (1)
 OPEN CHANNEL FLOW Open hannel flow is haraterized by a surfae in ontat with a gas phase, allowing the fluid to take on shapes and undergo behavior that is impossible in a pipe or other filled onduit. Examples
OPEN CHANNEL FLOW Open hannel flow is haraterized by a surfae in ontat with a gas phase, allowing the fluid to take on shapes and undergo behavior that is impossible in a pipe or other filled onduit. Examples
protection p1ann1ng report
 f1re~~ protetion p1ann1ng report BUILDING CONSTRUCTION INFORMATION FROM THE CONCRETE AND MASONRY INDUSTRIES Signifiane of Fire Ratings for Building Constrution NO. 3 OF A SERIES The use of fire-resistive
f1re~~ protetion p1ann1ng report BUILDING CONSTRUCTION INFORMATION FROM THE CONCRETE AND MASONRY INDUSTRIES Signifiane of Fire Ratings for Building Constrution NO. 3 OF A SERIES The use of fire-resistive
BEARING CAPACITY OF SOIL
 BEARING CAPACITY OF SOIL Dr. S. K. Prasad Professor of Civil Engineering S. J. College of Engineering, Mysore 7.0 Syllabus. Definition of ultimate, net and safe bearing apaities, Allowable bearing pressure
BEARING CAPACITY OF SOIL Dr. S. K. Prasad Professor of Civil Engineering S. J. College of Engineering, Mysore 7.0 Syllabus. Definition of ultimate, net and safe bearing apaities, Allowable bearing pressure
Impact Simulation of Extreme Wind Generated Missiles on Radioactive Waste Storage Facilities
 Impat Simulation of Extreme Wind Generated issiles on Radioative Waste Storage Failities G. Barbella Sogin S.p.A. Via Torino 6 00184 Rome (Italy), barbella@sogin.it Abstrat: The strutural design of temporary
Impat Simulation of Extreme Wind Generated issiles on Radioative Waste Storage Failities G. Barbella Sogin S.p.A. Via Torino 6 00184 Rome (Italy), barbella@sogin.it Abstrat: The strutural design of temporary
The following excerpt are pages from the North American Product Technical Guide, Volume 2: Anchor Fastening, Edition 16.
 The following exerpt are pages from the North Amerian Produt Tehnial Guide, Volume 2: Anhor Fastening, Edition 16. Please refer to the publiation in its entirety for omplete details on this produt inluding
The following exerpt are pages from the North Amerian Produt Tehnial Guide, Volume 2: Anhor Fastening, Edition 16. Please refer to the publiation in its entirety for omplete details on this produt inluding
A novel active mass damper for vibration control of bridges
 IABMAS 08, International Conferene on Bridge Maintenane, Safety and Management, 3-7 July 008, Seoul, Korea A novel ative mass damper for vibration ontrol of bridges U. Starossek & J. Sheller Strutural
IABMAS 08, International Conferene on Bridge Maintenane, Safety and Management, 3-7 July 008, Seoul, Korea A novel ative mass damper for vibration ontrol of bridges U. Starossek & J. Sheller Strutural
THE PERFORMANCE OF TRANSIT TIME FLOWMETERS IN HEATED GAS MIXTURES
 Proeedings of FEDSM 98 998 ASME Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting June 2-25, 998 Washington DC FEDSM98-529 THE PERFORMANCE OF TRANSIT TIME FLOWMETERS IN HEATED GAS MIXTURES John D. Wright Proess
Proeedings of FEDSM 98 998 ASME Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting June 2-25, 998 Washington DC FEDSM98-529 THE PERFORMANCE OF TRANSIT TIME FLOWMETERS IN HEATED GAS MIXTURES John D. Wright Proess
Measurement of Powder Flow Properties that relate to Gravity Flow Behaviour through Industrial Processing Lines
 Measurement of Powder Flow Properties that relate to Gravity Flow ehaviour through Industrial Proessing Lines A typial industrial powder proessing line will inlude several storage vessels (e.g. bins, bunkers,
Measurement of Powder Flow Properties that relate to Gravity Flow ehaviour through Industrial Proessing Lines A typial industrial powder proessing line will inlude several storage vessels (e.g. bins, bunkers,
bi directional loading). Prototype ten story
 NEESR SG: Behavior, Analysis and Design of Complex Wall Systems The laboratory testing presented here was conducted as part of a larger effort that employed laboratory testing and numerical simulation
NEESR SG: Behavior, Analysis and Design of Complex Wall Systems The laboratory testing presented here was conducted as part of a larger effort that employed laboratory testing and numerical simulation
Channel Assignment Strategies for Cellular Phone Systems
 Channel Assignment Strategies for Cellular Phone Systems Wei Liu Yiping Han Hang Yu Zhejiang University Hangzhou, P. R. China Contat: wliu5@ie.uhk.edu.hk 000 Mathematial Contest in Modeling (MCM) Meritorious
Channel Assignment Strategies for Cellular Phone Systems Wei Liu Yiping Han Hang Yu Zhejiang University Hangzhou, P. R. China Contat: wliu5@ie.uhk.edu.hk 000 Mathematial Contest in Modeling (MCM) Meritorious
6. Fasteners and Fastening methods. Introduction. Fastener types. Fastener application. Screw thread terminology. Screw thread terminology (Fig. 6.
 6. Fasteners and Fastening methods Ojetives Desrie many types of fastening systems and their uses. Understand priniples of stress area, pith diameters, and thread types and forms. Understand different
6. Fasteners and Fastening methods Ojetives Desrie many types of fastening systems and their uses. Understand priniples of stress area, pith diameters, and thread types and forms. Understand different
SEISMIC DESIGN. Various building codes consider the following categories for the analysis and design for earthquake loading:
 SEISMIC DESIGN Various building codes consider the following categories for the analysis and design for earthquake loading: 1. Seismic Performance Category (SPC), varies from A to E, depending on how the
SEISMIC DESIGN Various building codes consider the following categories for the analysis and design for earthquake loading: 1. Seismic Performance Category (SPC), varies from A to E, depending on how the
Static Fairness Criteria in Telecommunications
 Teknillinen Korkeakoulu ERIKOISTYÖ Teknillisen fysiikan koulutusohjelma 92002 Mat-208 Sovelletun matematiikan erikoistyöt Stati Fairness Criteria in Teleommuniations Vesa Timonen, e-mail: vesatimonen@hutfi
Teknillinen Korkeakoulu ERIKOISTYÖ Teknillisen fysiikan koulutusohjelma 92002 Mat-208 Sovelletun matematiikan erikoistyöt Stati Fairness Criteria in Teleommuniations Vesa Timonen, e-mail: vesatimonen@hutfi
Computational Analysis of Two Arrangements of a Central Ground-Source Heat Pump System for Residential Buildings
 Computational Analysis of Two Arrangements of a Central Ground-Soure Heat Pump System for Residential Buildings Abstrat Ehab Foda, Ala Hasan, Kai Sirén Helsinki University of Tehnology, HVAC Tehnology,
Computational Analysis of Two Arrangements of a Central Ground-Soure Heat Pump System for Residential Buildings Abstrat Ehab Foda, Ala Hasan, Kai Sirén Helsinki University of Tehnology, HVAC Tehnology,
IMPROVING THE STRUT AND TIE METHOD BY INCLUDING THE CONCRETE SOFTENING EFFECT
 International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 7, Issue 2, March-April 2016, pp. 117 127, Article ID: IJCIET_07_02_009 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=7&itype=2
International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 7, Issue 2, March-April 2016, pp. 117 127, Article ID: IJCIET_07_02_009 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=7&itype=2
New approaches in Eurocode 3 efficient global structural design
 New approaches in Eurocode 3 efficient global structural design Part 1: 3D model based analysis using general beam-column FEM Ferenc Papp* and József Szalai ** * Associate Professor, Department of Structural
New approaches in Eurocode 3 efficient global structural design Part 1: 3D model based analysis using general beam-column FEM Ferenc Papp* and József Szalai ** * Associate Professor, Department of Structural
arxiv:astro-ph/0304006v2 10 Jun 2003 Theory Group, MS 50A-5101 Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory One Cyclotron Road Berkeley, CA 94720 USA
 LBNL-52402 Marh 2003 On the Speed of Gravity and the v/ Corretions to the Shapiro Time Delay Stuart Samuel 1 arxiv:astro-ph/0304006v2 10 Jun 2003 Theory Group, MS 50A-5101 Lawrene Berkeley National Laboratory
LBNL-52402 Marh 2003 On the Speed of Gravity and the v/ Corretions to the Shapiro Time Delay Stuart Samuel 1 arxiv:astro-ph/0304006v2 10 Jun 2003 Theory Group, MS 50A-5101 Lawrene Berkeley National Laboratory
WATER CLOSET SUPPORTS TECHNICAL DATA
 WATER CLOSET SUPPORTS TECHNICAL DATA Smith engineers have developed an unusually omplete line of fixture supports for mounting all types of "off the floor" fixtures. Supports have been designed for water
WATER CLOSET SUPPORTS TECHNICAL DATA Smith engineers have developed an unusually omplete line of fixture supports for mounting all types of "off the floor" fixtures. Supports have been designed for water
10.1 The Lorentz force law
 Sott Hughes 10 Marh 2005 Massahusetts Institute of Tehnology Department of Physis 8.022 Spring 2004 Leture 10: Magneti fore; Magneti fields; Ampere s law 10.1 The Lorentz fore law Until now, we have been
Sott Hughes 10 Marh 2005 Massahusetts Institute of Tehnology Department of Physis 8.022 Spring 2004 Leture 10: Magneti fore; Magneti fields; Ampere s law 10.1 The Lorentz fore law Until now, we have been
Classical Electromagnetic Doppler Effect Redefined. Copyright 2014 Joseph A. Rybczyk
 Classial Eletromagneti Doppler Effet Redefined Copyright 04 Joseph A. Rybzyk Abstrat The lassial Doppler Effet formula for eletromagneti waves is redefined to agree with the fundamental sientifi priniples
Classial Eletromagneti Doppler Effet Redefined Copyright 04 Joseph A. Rybzyk Abstrat The lassial Doppler Effet formula for eletromagneti waves is redefined to agree with the fundamental sientifi priniples
HEAT CONDUCTION. q A q T
 HEAT CONDUCTION When a temperature gradient eist in a material, heat flows from the high temperature region to the low temperature region. The heat transfer mehanism is referred to as ondution and the
HEAT CONDUCTION When a temperature gradient eist in a material, heat flows from the high temperature region to the low temperature region. The heat transfer mehanism is referred to as ondution and the
Residual strength evaluation by DBEM for a cracked lap joint
 Residual strength evaluation b DBEM for a raked lap joint R. Citarella Department of Industrial Engineering, via Giovanni Paolo II, 132, Fisiano (SA), Universit of Salerno, Ital ritarella@unisa.it ABSTRACT.
Residual strength evaluation b DBEM for a raked lap joint R. Citarella Department of Industrial Engineering, via Giovanni Paolo II, 132, Fisiano (SA), Universit of Salerno, Ital ritarella@unisa.it ABSTRACT.
protection p1ann1ng report
 ( f1re protetion p1ann1ng report I BUILDING CONSTRUCTION INFORMATION FROM THE CONCRETE AND MASONRY INDUSTRIES NO. 15 OF A SERIES A Comparison of Insurane and Constrution Costs for Low-Rise Multifamily
( f1re protetion p1ann1ng report I BUILDING CONSTRUCTION INFORMATION FROM THE CONCRETE AND MASONRY INDUSTRIES NO. 15 OF A SERIES A Comparison of Insurane and Constrution Costs for Low-Rise Multifamily
REINFORCED CONCRETE BEAMS: T-BEAMS AND DOUBLY REINFORCED BEAMS
 CHAPTER Reinored Conrete Design Fith Edition REINFORCED CONCRETE BEAMS: T-BEAMS AND DOUBLY REINFORCED BEAMS A. J. Clark Shool o Engineering Department o Civil and Environmental Engineering Part I Conrete
CHAPTER Reinored Conrete Design Fith Edition REINFORCED CONCRETE BEAMS: T-BEAMS AND DOUBLY REINFORCED BEAMS A. J. Clark Shool o Engineering Department o Civil and Environmental Engineering Part I Conrete
Impedance Method for Leak Detection in Zigzag Pipelines
 10.478/v10048-010-0036-0 MEASUREMENT SCIENCE REVIEW, Volume 10, No. 6, 010 Impedane Method for Leak Detetion in igzag Pipelines A. Lay-Ekuakille 1, P. Vergallo 1, A. Trotta 1 Dipartimento d Ingegneria
10.478/v10048-010-0036-0 MEASUREMENT SCIENCE REVIEW, Volume 10, No. 6, 010 Impedane Method for Leak Detetion in igzag Pipelines A. Lay-Ekuakille 1, P. Vergallo 1, A. Trotta 1 Dipartimento d Ingegneria
4.15 USING METEOSAT SECOND GENERATION HIGH RESOLUTION VISIBLE DATA FOR THE IMPOVEMENT OF THE RAPID DEVELOPPING THUNDERSTORM PRODUCT
 4.15 USNG METEOSAT SECOND GENEATON HGH ESOLUTON VSBLE DATA FO THE MPOVEMENT OF THE APD DEVELOPPNG THUNDESTOM PODUCT Oleksiy Kryvobok * Ukrainian HydroMeteorologial nstitute Kyiv, Ukraine Stephane Senesi
4.15 USNG METEOSAT SECOND GENEATON HGH ESOLUTON VSBLE DATA FO THE MPOVEMENT OF THE APD DEVELOPPNG THUNDESTOM PODUCT Oleksiy Kryvobok * Ukrainian HydroMeteorologial nstitute Kyiv, Ukraine Stephane Senesi
Optimum proportions for the design of suspension bridge
 Journal of Civil Engineering (IEB), 34 (1) (26) 1-14 Optimum proportions for the design of suspension bridge Tanvir Manzur and Alamgir Habib Department of Civil Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering
Journal of Civil Engineering (IEB), 34 (1) (26) 1-14 Optimum proportions for the design of suspension bridge Tanvir Manzur and Alamgir Habib Department of Civil Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering
Chapter 5 Single Phase Systems
 Chapter 5 Single Phase Systems Chemial engineering alulations rely heavily on the availability of physial properties of materials. There are three ommon methods used to find these properties. These inlude
Chapter 5 Single Phase Systems Chemial engineering alulations rely heavily on the availability of physial properties of materials. There are three ommon methods used to find these properties. These inlude
Chapter 1 Microeconomics of Consumer Theory
 Chapter 1 Miroeonomis of Consumer Theory The two broad ategories of deision-makers in an eonomy are onsumers and firms. Eah individual in eah of these groups makes its deisions in order to ahieve some
Chapter 1 Miroeonomis of Consumer Theory The two broad ategories of deision-makers in an eonomy are onsumers and firms. Eah individual in eah of these groups makes its deisions in order to ahieve some
Findings and Recommendations
 Contrating Methods and Administration Findings and Reommendations Finding 9-1 ESD did not utilize a formal written pre-qualifiations proess for seleting experiened design onsultants. ESD hose onsultants
Contrating Methods and Administration Findings and Reommendations Finding 9-1 ESD did not utilize a formal written pre-qualifiations proess for seleting experiened design onsultants. ESD hose onsultants
THERMAL TO MECHANICAL ENERGY CONVERSION: ENGINES AND REQUIREMENTS Vol. I - Thermodynamic Cycles of Reciprocating and Rotary Engines - R.S.
 THERMAL TO MECHANICAL ENERGY CONVERSION: ENGINES AND REQUIREMENTS Vol. I - Thermodynami Cyles of Reiproating and Rotary Engines - R.S.Kavtaradze THERMODYNAMIC CYCLES OF RECIPROCATING AND ROTARY ENGINES
THERMAL TO MECHANICAL ENERGY CONVERSION: ENGINES AND REQUIREMENTS Vol. I - Thermodynami Cyles of Reiproating and Rotary Engines - R.S.Kavtaradze THERMODYNAMIC CYCLES OF RECIPROCATING AND ROTARY ENGINES
Intelligent Measurement Processes in 3D Optical Metrology: Producing More Accurate Point Clouds
 Intelligent Measurement Proesses in 3D Optial Metrology: Produing More Aurate Point Clouds Charles Mony, Ph.D. 1 President Creaform in. mony@reaform3d.om Daniel Brown, Eng. 1 Produt Manager Creaform in.
Intelligent Measurement Proesses in 3D Optial Metrology: Produing More Aurate Point Clouds Charles Mony, Ph.D. 1 President Creaform in. mony@reaform3d.om Daniel Brown, Eng. 1 Produt Manager Creaform in.
Improved SOM-Based High-Dimensional Data Visualization Algorithm
 Computer and Information Siene; Vol. 5, No. 4; 2012 ISSN 1913-8989 E-ISSN 1913-8997 Published by Canadian Center of Siene and Eduation Improved SOM-Based High-Dimensional Data Visualization Algorithm Wang
Computer and Information Siene; Vol. 5, No. 4; 2012 ISSN 1913-8989 E-ISSN 1913-8997 Published by Canadian Center of Siene and Eduation Improved SOM-Based High-Dimensional Data Visualization Algorithm Wang
DESIGN OF SLABS. Department of Structures and Materials Engineering Faculty of Civil and Environmental Engineering University Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia
 DESIGN OF SLABS Department of Structures and Materials Engineering Faculty of Civil and Environmental Engineering University Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia Introduction Types of Slab Slabs are plate elements
DESIGN OF SLABS Department of Structures and Materials Engineering Faculty of Civil and Environmental Engineering University Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia Introduction Types of Slab Slabs are plate elements
DESIGN OF SLABS. 3) Based on support or boundary condition: Simply supported, Cantilever slab,
 DESIGN OF SLABS Dr. G. P. Chandradhara Professor of Civil Engineering S. J. College of Engineering Mysore 1. GENERAL A slab is a flat two dimensional planar structural element having thickness small compared
DESIGN OF SLABS Dr. G. P. Chandradhara Professor of Civil Engineering S. J. College of Engineering Mysore 1. GENERAL A slab is a flat two dimensional planar structural element having thickness small compared
A Keyword Filters Method for Spam via Maximum Independent Sets
 Vol. 7, No. 3, May, 213 A Keyword Filters Method for Spam via Maximum Independent Sets HaiLong Wang 1, FanJun Meng 1, HaiPeng Jia 2, JinHong Cheng 3 and Jiong Xie 3 1 Inner Mongolia Normal University 2
Vol. 7, No. 3, May, 213 A Keyword Filters Method for Spam via Maximum Independent Sets HaiLong Wang 1, FanJun Meng 1, HaiPeng Jia 2, JinHong Cheng 3 and Jiong Xie 3 1 Inner Mongolia Normal University 2
A Holistic Method for Selecting Web Services in Design of Composite Applications
 A Holisti Method for Seleting Web Servies in Design of Composite Appliations Mārtiņš Bonders, Jānis Grabis Institute of Information Tehnology, Riga Tehnial University, 1 Kalu Street, Riga, LV 1658, Latvia,
A Holisti Method for Seleting Web Servies in Design of Composite Appliations Mārtiņš Bonders, Jānis Grabis Institute of Information Tehnology, Riga Tehnial University, 1 Kalu Street, Riga, LV 1658, Latvia,
REDUCTION FACTOR OF FEEDING LINES THAT HAVE A CABLE AND AN OVERHEAD SECTION
 C I E 17 th International Conferene on Eletriity istriution Barelona, 1-15 May 003 EUCTION FACTO OF FEEING LINES THAT HAVE A CABLE AN AN OVEHEA SECTION Ljuivoje opovi J.. Elektrodistriuija - Belgrade -
C I E 17 th International Conferene on Eletriity istriution Barelona, 1-15 May 003 EUCTION FACTO OF FEEING LINES THAT HAVE A CABLE AN AN OVEHEA SECTION Ljuivoje opovi J.. Elektrodistriuija - Belgrade -
Mechanics of the tapered interference fit in dental implants
 ARTICLE IN PRESS Journal of Biomehanis 36 (2003) 1649 1658 Mehanis of the tapered interferene fit in dental implants Din@er Bozkaya, Sinan M.uft.u* Department of Mehanial Engineering, Northeastern University,
ARTICLE IN PRESS Journal of Biomehanis 36 (2003) 1649 1658 Mehanis of the tapered interferene fit in dental implants Din@er Bozkaya, Sinan M.uft.u* Department of Mehanial Engineering, Northeastern University,
Detailing of Reinforcment in Concrete Structures
 Chapter 8 Detailing of Reinforcment in Concrete Structures 8.1 Scope Provisions of Sec. 8.1 and 8.2 of Chapter 8 shall apply for detailing of reinforcement in reinforced concrete members, in general. For
Chapter 8 Detailing of Reinforcment in Concrete Structures 8.1 Scope Provisions of Sec. 8.1 and 8.2 of Chapter 8 shall apply for detailing of reinforcement in reinforced concrete members, in general. For
Technical Notes 3B - Brick Masonry Section Properties May 1993
 Technical Notes 3B - Brick Masonry Section Properties May 1993 Abstract: This Technical Notes is a design aid for the Building Code Requirements for Masonry Structures (ACI 530/ASCE 5/TMS 402-92) and Specifications
Technical Notes 3B - Brick Masonry Section Properties May 1993 Abstract: This Technical Notes is a design aid for the Building Code Requirements for Masonry Structures (ACI 530/ASCE 5/TMS 402-92) and Specifications
Heat Generation and Removal in Solid State Lasers
 Chapter 1 Heat Generation and Removal in Solid State Lasers V. Ashoori, M. Shayganmanesh and S. Radmard Additional information is available at the end of the hapter http://dx.doi.org/10.577/63 1. Introdution
Chapter 1 Heat Generation and Removal in Solid State Lasers V. Ashoori, M. Shayganmanesh and S. Radmard Additional information is available at the end of the hapter http://dx.doi.org/10.577/63 1. Introdution
MECHANICS OF SOLIDS - BEAMS TUTORIAL 1 STRESSES IN BEAMS DUE TO BENDING. On completion of this tutorial you should be able to do the following.
 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS - BEAMS TUTOIAL 1 STESSES IN BEAMS DUE TO BENDING This is the first tutorial on bending of beams designed for anyone wishing to study it at a fairly advanced level. You should judge
MECHANICS OF SOLIDS - BEAMS TUTOIAL 1 STESSES IN BEAMS DUE TO BENDING This is the first tutorial on bending of beams designed for anyone wishing to study it at a fairly advanced level. You should judge
THE EFFECT OF WATER VAPOR ON COUNTERFLOW DIFFUSION FLAMES
 THE EFFECT OF WATER VAPOR ON COUNTERFLOW DIFFUSION FLAMES by Jaeil Suh and Arvind Atreya Combustion and Heat Tkansfer Laboratory Department of Mehanial Engineering and Applied Mehanis The University of
THE EFFECT OF WATER VAPOR ON COUNTERFLOW DIFFUSION FLAMES by Jaeil Suh and Arvind Atreya Combustion and Heat Tkansfer Laboratory Department of Mehanial Engineering and Applied Mehanis The University of
IN SITU TESTS FOR SEISMIC ASSESSMENT OF R.C. STRUCTURES
 Otober -7, 8, Beijing, China IN SITU TESTS FOR SEISMIC ASSESSMENT OF R.C. STRUCTURES S. Biondi, E. Candigliota Assoiate Professor, Department of Design, Rehabilitation and Control of Arhitetural Strutures,
Otober -7, 8, Beijing, China IN SITU TESTS FOR SEISMIC ASSESSMENT OF R.C. STRUCTURES S. Biondi, E. Candigliota Assoiate Professor, Department of Design, Rehabilitation and Control of Arhitetural Strutures,
Granular Problem Solving and Software Engineering
 Granular Problem Solving and Software Engineering Haibin Zhu, Senior Member, IEEE Department of Computer Siene and Mathematis, Nipissing University, 100 College Drive, North Bay, Ontario, P1B 8L7, Canada
Granular Problem Solving and Software Engineering Haibin Zhu, Senior Member, IEEE Department of Computer Siene and Mathematis, Nipissing University, 100 College Drive, North Bay, Ontario, P1B 8L7, Canada
Draft Table of Contents. Building Code Requirements for Structural Concrete and Commentary ACI 318-14
 Draft Table of Contents Building Code Requirements for Structural Concrete and Commentary ACI 318-14 BUILDING CODE REQUIREMENTS FOR STRUCTURAL CONCRETE (ACI 318 14) Chapter 1 General 1.1 Scope of ACI 318
Draft Table of Contents Building Code Requirements for Structural Concrete and Commentary ACI 318-14 BUILDING CODE REQUIREMENTS FOR STRUCTURAL CONCRETE (ACI 318 14) Chapter 1 General 1.1 Scope of ACI 318
Capacity at Unsignalized Two-Stage Priority Intersections
 Capaity at Unsignalized Two-Stage Priority Intersetions by Werner Brilon and Ning Wu Abstrat The subjet of this paper is the apaity of minor-street traffi movements aross major divided four-lane roadways
Capaity at Unsignalized Two-Stage Priority Intersetions by Werner Brilon and Ning Wu Abstrat The subjet of this paper is the apaity of minor-street traffi movements aross major divided four-lane roadways
User s Guide VISFIT: a computer tool for the measurement of intrinsic viscosities
 File:UserVisfit_2.do User s Guide VISFIT: a omputer tool for the measurement of intrinsi visosities Version 2.a, September 2003 From: Multiple Linear Least-Squares Fits with a Common Interept: Determination
File:UserVisfit_2.do User s Guide VISFIT: a omputer tool for the measurement of intrinsi visosities Version 2.a, September 2003 From: Multiple Linear Least-Squares Fits with a Common Interept: Determination
Algorithm of Removing Thin Cloud-fog Cover from Single Remote Sensing Image
 Journal of Information & Computational Siene 11:3 (2014 817 824 February 10, 2014 Available at http://www.jois.om Algorithm of Removing Thin Cloud-fog Cover from Single Remote Sensing Image Yinqi Xiong,
Journal of Information & Computational Siene 11:3 (2014 817 824 February 10, 2014 Available at http://www.jois.om Algorithm of Removing Thin Cloud-fog Cover from Single Remote Sensing Image Yinqi Xiong,
A Comparison of Service Quality between Private and Public Hospitals in Thailand
 International Journal of Business and Soial Siene Vol. 4 No. 11; September 2013 A Comparison of Servie Quality between Private and Hospitals in Thailand Khanhitpol Yousapronpaiboon, D.B.A. Assistant Professor
International Journal of Business and Soial Siene Vol. 4 No. 11; September 2013 A Comparison of Servie Quality between Private and Hospitals in Thailand Khanhitpol Yousapronpaiboon, D.B.A. Assistant Professor
ECO-CORE AND ITS PERFORMANCE IN SANDWICH STRUCTURAL APPLICATION
 ECO-CORE AND ITS ERFORMANCE IN SANDWICH STRUCTURAL ALICATION K. N. Shivakumar and H. Chen Center or Composite Materials Researh Department o Mehanial and Chemial Engineering North Carolina A&T State University
ECO-CORE AND ITS ERFORMANCE IN SANDWICH STRUCTURAL ALICATION K. N. Shivakumar and H. Chen Center or Composite Materials Researh Department o Mehanial and Chemial Engineering North Carolina A&T State University
Miss S. S. Nibhorkar 1 1 M. E (Structure) Scholar,
 Volume, Special Issue, ICSTSD Behaviour of Steel Bracing as a Global Retrofitting Technique Miss S. S. Nibhorkar M. E (Structure) Scholar, Civil Engineering Department, G. H. Raisoni College of Engineering
Volume, Special Issue, ICSTSD Behaviour of Steel Bracing as a Global Retrofitting Technique Miss S. S. Nibhorkar M. E (Structure) Scholar, Civil Engineering Department, G. H. Raisoni College of Engineering
Seismic performance evaluation of an existing school building in Turkey
 CHALLENGE JOURNAL OF STRUCTURAL MECHANICS 1 (4) (2015) 161 167 Seismic performance evaluation of an existing school building in Turkey Hüseyin Bilgin * Department of Civil Engineering, Epoka University,
CHALLENGE JOURNAL OF STRUCTURAL MECHANICS 1 (4) (2015) 161 167 Seismic performance evaluation of an existing school building in Turkey Hüseyin Bilgin * Department of Civil Engineering, Epoka University,
Seismic design of beam-column joints in RC moment resisting frames Review of codes
 Structural Engineering and Mechanics, Vol. 23, No. 5 (2006) 579-597 579 Technical Report Seismic design of beam-column joints in RC moment resisting frames Review of codes S. R. Uma Department of Civil
Structural Engineering and Mechanics, Vol. 23, No. 5 (2006) 579-597 579 Technical Report Seismic design of beam-column joints in RC moment resisting frames Review of codes S. R. Uma Department of Civil
ANALYSIS FOR BEHAVIOR AND ULTIMATE STRENGTH OF CONCRETE CORBELS WITH HYBRID REINFORCEMENT
 International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 6, Issue 10, Oct 2015, pp. 25-35 Article ID: IJCIET_06_10_003 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=6&itype=10
International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 6, Issue 10, Oct 2015, pp. 25-35 Article ID: IJCIET_06_10_003 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=6&itype=10
MATERIALS AND MECHANICS OF BENDING
 HAPTER Reinforced oncrete Design Fifth Edition MATERIALS AND MEHANIS OF BENDING A. J. lark School of Engineering Department of ivil and Environmental Engineering Part I oncrete Design and Analysis b FALL
HAPTER Reinforced oncrete Design Fifth Edition MATERIALS AND MEHANIS OF BENDING A. J. lark School of Engineering Department of ivil and Environmental Engineering Part I oncrete Design and Analysis b FALL
Intraoperative Spinal Sonography in Thoracic and Lumbar Fractures: Evaluation of
 353 Intraoperative Spinal Sonography in Thorai and Lumbar Fratures: Evaluation of Harrington Rod Instrumentation Robert M. Quener' erta M. Montalvo' Frank J. Eismonf arth. Green 3 Thirty-seven patients
353 Intraoperative Spinal Sonography in Thorai and Lumbar Fratures: Evaluation of Harrington Rod Instrumentation Robert M. Quener' erta M. Montalvo' Frank J. Eismonf arth. Green 3 Thirty-seven patients
Recovering Articulated Motion with a Hierarchical Factorization Method
 Reovering Artiulated Motion with a Hierarhial Fatorization Method Hanning Zhou and Thomas S Huang University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 405 North Mathews Avenue, Urbana, IL 680, USA {hzhou, huang}@ifpuiuedu
Reovering Artiulated Motion with a Hierarhial Fatorization Method Hanning Zhou and Thomas S Huang University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 405 North Mathews Avenue, Urbana, IL 680, USA {hzhou, huang}@ifpuiuedu
Suggested Answers, Problem Set 5 Health Economics
 Suggested Answers, Problem Set 5 Health Eonomis Bill Evans Spring 2013 1. The graph is at the end of the handout. Fluoridated water strengthens teeth and redues inidene of avities. As a result, at all
Suggested Answers, Problem Set 5 Health Eonomis Bill Evans Spring 2013 1. The graph is at the end of the handout. Fluoridated water strengthens teeth and redues inidene of avities. As a result, at all
Lemon Signaling in Cross-Listings Michal Barzuza*
 Lemon Signaling in Cross-Listings Mihal Barzuza* This paper analyzes the deision to ross-list by managers and ontrolling shareholders assuming that they have private information with respet to the amount
Lemon Signaling in Cross-Listings Mihal Barzuza* This paper analyzes the deision to ross-list by managers and ontrolling shareholders assuming that they have private information with respet to the amount
Concrete Frame Design Manual
 Concrete Frame Design Manual Turkish TS 500-2000 with Turkish Seismic Code 2007 For SAP2000 ISO SAP093011M26 Rev. 0 Version 15 Berkeley, California, USA October 2011 COPYRIGHT Copyright Computers and Structures,
Concrete Frame Design Manual Turkish TS 500-2000 with Turkish Seismic Code 2007 For SAP2000 ISO SAP093011M26 Rev. 0 Version 15 Berkeley, California, USA October 2011 COPYRIGHT Copyright Computers and Structures,
Base Plate and Anchor Rod Design
 Steel Design Guide Base late and nhor Rod Design Seond Edition JMES M. FISHER, h.d.,.e. Comuterized Strutural Design, S.C. Milwaukee, Wisonsin and LWRENCE. KLOIBER,.E. LeJuene Steel Comany Minneaolis,
Steel Design Guide Base late and nhor Rod Design Seond Edition JMES M. FISHER, h.d.,.e. Comuterized Strutural Design, S.C. Milwaukee, Wisonsin and LWRENCE. KLOIBER,.E. LeJuene Steel Comany Minneaolis,
A Comparison of Default and Reduced Bandwidth MR Imaging of the Spine at 1.5 T
 9 A Comparison of efault and Redued Bandwidth MR Imaging of the Spine at 1.5 T L. Ketonen 1 S. Totterman 1 J. H. Simon 1 T. H. Foster 2. K. Kido 1 J. Szumowski 1 S. E. Joy1 The value of a redued bandwidth
9 A Comparison of efault and Redued Bandwidth MR Imaging of the Spine at 1.5 T L. Ketonen 1 S. Totterman 1 J. H. Simon 1 T. H. Foster 2. K. Kido 1 J. Szumowski 1 S. E. Joy1 The value of a redued bandwidth
SEISMIC CAPACITY OF EXISTING RC SCHOOL BUILDINGS IN OTA CITY, TOKYO, JAPAN
 SEISMIC CAPACITY OF EXISTING RC SCHOOL BUILDINGS IN OTA CITY, TOKYO, JAPAN Toshio OHBA, Shigeru TAKADA, Yoshiaki NAKANO, Hideo KIMURA 4, Yoshimasa OWADA 5 And Tsuneo OKADA 6 SUMMARY The 995 Hyogoken-nambu
SEISMIC CAPACITY OF EXISTING RC SCHOOL BUILDINGS IN OTA CITY, TOKYO, JAPAN Toshio OHBA, Shigeru TAKADA, Yoshiaki NAKANO, Hideo KIMURA 4, Yoshimasa OWADA 5 And Tsuneo OKADA 6 SUMMARY The 995 Hyogoken-nambu
Numerical modelling of shear connection between concrete slab and sheeting deck
 7th fib International PhD Symposium in Civil Engineering 2008 September 10-13, Universität Stuttgart, Germany Numerical modelling of shear connection between concrete slab and sheeting deck Noémi Seres
7th fib International PhD Symposium in Civil Engineering 2008 September 10-13, Universität Stuttgart, Germany Numerical modelling of shear connection between concrete slab and sheeting deck Noémi Seres
OpenScape 4000 CSTA V7 Connectivity Adapter - CSTA III, Part 2, Version 4.1. Developer s Guide A31003-G9310-I200-1-76D1
 OpenSape 4000 CSTA V7 Connetivity Adapter - CSTA III, Part 2, Version 4.1 Developer s Guide A31003-G9310-I200-1-76 Our Quality and Environmental Management Systems are implemented aording to the requirements
OpenSape 4000 CSTA V7 Connetivity Adapter - CSTA III, Part 2, Version 4.1 Developer s Guide A31003-G9310-I200-1-76 Our Quality and Environmental Management Systems are implemented aording to the requirements
Analysis and Repair of an Earthquake-Damaged High-rise Building in Santiago, Chile
 Analysis and Repair of an Earthquake-Damaged High-rise Building in Santiago, Chile J. Sherstobitoff Ausenco Sandwell, Vancouver, Canada P. Cajiao AMEC, Vancouver, Canada P. Adebar University of British
Analysis and Repair of an Earthquake-Damaged High-rise Building in Santiago, Chile J. Sherstobitoff Ausenco Sandwell, Vancouver, Canada P. Cajiao AMEC, Vancouver, Canada P. Adebar University of British
SLAB DESIGN. Introduction ACI318 Code provides two design procedures for slab systems:
 Reading Assignment SLAB DESIGN Chapter 9 of Text and, Chapter 13 of ACI318-02 Introduction ACI318 Code provides two design procedures for slab systems: 13.6.1 Direct Design Method (DDM) For slab systems
Reading Assignment SLAB DESIGN Chapter 9 of Text and, Chapter 13 of ACI318-02 Introduction ACI318 Code provides two design procedures for slab systems: 13.6.1 Direct Design Method (DDM) For slab systems
HEAT EXCHANGERS-2. Associate Professor. IIT Delhi E-mail: prabal@mech.iitd.ac.in. P.Talukdar/ Mech-IITD
 HEA EXHANGERS-2 Prabal alukdar Assoiate Professor Department of Mehanial Engineering II Delhi E-mail: prabal@meh.iitd.a.in Multipass and rossflow he subsripts 1 and 2 represent the inlet and outlet, respetively..
HEA EXHANGERS-2 Prabal alukdar Assoiate Professor Department of Mehanial Engineering II Delhi E-mail: prabal@meh.iitd.a.in Multipass and rossflow he subsripts 1 and 2 represent the inlet and outlet, respetively..
BEHAVIOR OF SHORT CONCRETE COLUMNS REINFORCED BY CFRP BARS AND SUBJECTED TO ECCENTRIC LOAD
 International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 6, Issue 10, Oct 2015, pp. 15-24 Article ID: IJCIET_06_10_002 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=6&itype=10
International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 6, Issue 10, Oct 2015, pp. 15-24 Article ID: IJCIET_06_10_002 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=6&itype=10
THE USE OF MULTIPLE COMBINED NON DESTRUCTIVE TESTING IN THE CONCRETE STRENGHT ASSESSENT: APPLICATIONS ON LABORATORY SPECIMENS
 THE USE OF MULTIPLE COMBINED NON DESTUCTIVE TESTING IN THE CONCETE STENGHT ASSESSENT: APPLICATIONS ON LABOATOY SPECIMENS affaele Puinotti Dipartimento di Meania e Materiali, Università Mediterranea di
THE USE OF MULTIPLE COMBINED NON DESTUCTIVE TESTING IN THE CONCETE STENGHT ASSESSENT: APPLICATIONS ON LABOATOY SPECIMENS affaele Puinotti Dipartimento di Meania e Materiali, Università Mediterranea di
Weighting Methods in Survey Sampling
 Setion on Survey Researh Methods JSM 01 Weighting Methods in Survey Sampling Chiao-hih Chang Ferry Butar Butar Abstrat It is said that a well-designed survey an best prevent nonresponse. However, no matter
Setion on Survey Researh Methods JSM 01 Weighting Methods in Survey Sampling Chiao-hih Chang Ferry Butar Butar Abstrat It is said that a well-designed survey an best prevent nonresponse. However, no matter
Effects of Inter-Coaching Spacing on Aerodynamic Noise Generation Inside High-speed Trains
 Effets of Inter-Coahing Spaing on Aerodynami Noise Generation Inside High-speed Trains 1 J. Ryu, 1 J. Park*, 2 C. Choi, 1 S. Song Hanyang University, Seoul, South Korea 1 ; Korea Railroad Researh Institute,
Effets of Inter-Coahing Spaing on Aerodynami Noise Generation Inside High-speed Trains 1 J. Ryu, 1 J. Park*, 2 C. Choi, 1 S. Song Hanyang University, Seoul, South Korea 1 ; Korea Railroad Researh Institute,
Electrician'sMathand BasicElectricalFormulas
 Eletriian'sMathand BasiEletrialFormulas MikeHoltEnterprises,In. 1.888.NEC.CODE www.mikeholt.om Introdution Introdution This PDF is a free resoure from Mike Holt Enterprises, In. It s Unit 1 from the Eletrial
Eletriian'sMathand BasiEletrialFormulas MikeHoltEnterprises,In. 1.888.NEC.CODE www.mikeholt.om Introdution Introdution This PDF is a free resoure from Mike Holt Enterprises, In. It s Unit 1 from the Eletrial
SEISMIC RETROFITTING TECHNIQUE USING CARBON FIBERS FOR REINFORCED CONCRETE BUILDINGS
 Fracture Mechanics of Concrete Structures Proceedings FRAMCOS-3 AEDIFICA TIO Publishers, D-79104 Freiburg, Germany SEISMIC RETROFITTING TECHNIQUE USING CARBON FIBERS FOR REINFORCED CONCRETE BUILDINGS H.
Fracture Mechanics of Concrete Structures Proceedings FRAMCOS-3 AEDIFICA TIO Publishers, D-79104 Freiburg, Germany SEISMIC RETROFITTING TECHNIQUE USING CARBON FIBERS FOR REINFORCED CONCRETE BUILDINGS H.
Revista Brasileira de Ensino de Fsica, vol. 21, no. 4, Dezembro, 1999 469. Surface Charges and Electric Field in a Two-Wire
 Revista Brasileira de Ensino de Fsia, vol., no. 4, Dezembro, 999 469 Surfae Charges and Eletri Field in a Two-Wire Resistive Transmission Line A. K. T.Assis and A. J. Mania Instituto de Fsia Gleb Wataghin'
Revista Brasileira de Ensino de Fsia, vol., no. 4, Dezembro, 999 469 Surfae Charges and Eletri Field in a Two-Wire Resistive Transmission Line A. K. T.Assis and A. J. Mania Instituto de Fsia Gleb Wataghin'
Open and Extensible Business Process Simulator
 UNIVERSITY OF TARTU FACULTY OF MATHEMATICS AND COMPUTER SCIENCE Institute of Computer Siene Karl Blum Open and Extensible Business Proess Simulator Master Thesis (30 EAP) Supervisors: Luiano Garía-Bañuelos,
UNIVERSITY OF TARTU FACULTY OF MATHEMATICS AND COMPUTER SCIENCE Institute of Computer Siene Karl Blum Open and Extensible Business Proess Simulator Master Thesis (30 EAP) Supervisors: Luiano Garía-Bañuelos,
Implementation of a constitutive model for masonry shells as a stand-alone subroutine
 Implementation of a onstitutive model for masonry shells as a stand-alone subroutine Paulo B. Lourenço, Késio Paláio, Franiso Prieto Report 02-DE/E-13 The present researh has been arried out under ontrat
Implementation of a onstitutive model for masonry shells as a stand-alone subroutine Paulo B. Lourenço, Késio Paláio, Franiso Prieto Report 02-DE/E-13 The present researh has been arried out under ontrat
An integrated optimization model of a Closed- Loop Supply Chain under uncertainty
 ISSN 1816-6075 (Print), 1818-0523 (Online) Journal of System and Management Sienes Vol. 2 (2012) No. 3, pp. 9-17 An integrated optimization model of a Closed- Loop Supply Chain under unertainty Xiaoxia
ISSN 1816-6075 (Print), 1818-0523 (Online) Journal of System and Management Sienes Vol. 2 (2012) No. 3, pp. 9-17 An integrated optimization model of a Closed- Loop Supply Chain under unertainty Xiaoxia
10 UNSTEADY FLOW IN OPEN CHANNELS
 0 UNTEY FLOW IN OEN CHNNEL 0. Introdution Unsteady flow in open hannels differs from that in losed onduits in that the eistene of a free surfae allows the flow ross-setion to freely hange, a fator whih
0 UNTEY FLOW IN OEN CHNNEL 0. Introdution Unsteady flow in open hannels differs from that in losed onduits in that the eistene of a free surfae allows the flow ross-setion to freely hange, a fator whih
MECHANICS OF SOLIDS - BEAMS TUTORIAL 2 SHEAR FORCE AND BENDING MOMENTS IN BEAMS
 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS - BEAMS TUTORIAL 2 SHEAR FORCE AND BENDING MOMENTS IN BEAMS This is the second tutorial on bending of beams. You should judge your progress by completing the self assessment exercises.
MECHANICS OF SOLIDS - BEAMS TUTORIAL 2 SHEAR FORCE AND BENDING MOMENTS IN BEAMS This is the second tutorial on bending of beams. You should judge your progress by completing the self assessment exercises.
ROSE SCHOOL A SIMPLIFIED MECHANICS BASED PROCEDURE FOR THE SEISMIC RISK ASSESSMENT OF UNREINFORCED MASONRY BUILDINGS
 I.U.S.S. Istituto Universitario di Studi Superiori di Pavia Università degli Studi di Pavia EUROPEAN SCHOOL OF ADVANCED STUDIES IN REDUCTION OF SEISMIC RISK ROSE SCHOOL A SIMPLIFIED MECHANICS BASED PROCEDURE
I.U.S.S. Istituto Universitario di Studi Superiori di Pavia Università degli Studi di Pavia EUROPEAN SCHOOL OF ADVANCED STUDIES IN REDUCTION OF SEISMIC RISK ROSE SCHOOL A SIMPLIFIED MECHANICS BASED PROCEDURE
A PERFORMANCE TEST STUDY ON CHINESE G4 LEAD RUBBER BEARINGS
 13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 24 Paper No. 676 A PERFORMANCE TEST STUDY ON CHINESE G4 LEAD RUBBER BEARINGS Demin FENG 1, Cliff CHEN 2, Wenguang LIU
13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 24 Paper No. 676 A PERFORMANCE TEST STUDY ON CHINESE G4 LEAD RUBBER BEARINGS Demin FENG 1, Cliff CHEN 2, Wenguang LIU
Requirements for the Use of PRESSS Moment-Resisting Frame Systems
 Requirements for the Use of PRESSS Moment-Resisting Frame Systems Neil M. Hawkins, Ph.D. Professor Emeritus Department of Civil Engineering University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Urbana, Illinois S.
Requirements for the Use of PRESSS Moment-Resisting Frame Systems Neil M. Hawkins, Ph.D. Professor Emeritus Department of Civil Engineering University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Urbana, Illinois S.
DEVELOPMENT AND APPLICATIONS OF TUNED/HYBRID MASS DAMPERS USING MULTI-STAGE RUBBER BEARINGS FOR VIBRATION CONTROL OF STRUCTURES
 13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 2243 DEVELOPMENT AND APPLICATIONS OF TUNED/HYBRID MASS DAMPERS USING MULTI-STAGE RUBBER BEARINGS FOR
13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 2243 DEVELOPMENT AND APPLICATIONS OF TUNED/HYBRID MASS DAMPERS USING MULTI-STAGE RUBBER BEARINGS FOR
FOUNDATION DESIGN. Instructional Materials Complementing FEMA 451, Design Examples
 FOUNDATION DESIGN Proportioning elements for: Transfer of seismic forces Strength and stiffness Shallow and deep foundations Elastic and plastic analysis Foundation Design 14-1 Load Path and Transfer to
FOUNDATION DESIGN Proportioning elements for: Transfer of seismic forces Strength and stiffness Shallow and deep foundations Elastic and plastic analysis Foundation Design 14-1 Load Path and Transfer to
Page 1 of 18 28.4.2008 Sven Alexander Last revised 1.3.2010. SB-Produksjon STATICAL CALCULATIONS FOR BCC 250
 Page 1 of 18 CONTENT PART 1 BASIC ASSUMPTIONS PAGE 1.1 General 1. Standards 1.3 Loads 1. Qualities PART ANCHORAGE OF THE UNITS.1 Beam unit equilibrium 3. Beam unit anchorage in front..1 Check of capacity..
Page 1 of 18 CONTENT PART 1 BASIC ASSUMPTIONS PAGE 1.1 General 1. Standards 1.3 Loads 1. Qualities PART ANCHORAGE OF THE UNITS.1 Beam unit equilibrium 3. Beam unit anchorage in front..1 Check of capacity..
SEISMIC DESIGN PROVISIONS FOR PRECAST CONCRETE STRUCTURES. S.K. Ghosh, Ph. D. President S.K. Ghosh Associates Inc. Northbrook, IL BACKGROUND
 SEISMIC DESIGN PROVISIONS FOR PRECAST CONCRETE STRUCTURES S.K. Ghosh, Ph. D. President S.K. Ghosh Associates Inc. Northbrook, IL BACKGROUND Until recently, precast concrete structures could be built in
SEISMIC DESIGN PROVISIONS FOR PRECAST CONCRETE STRUCTURES S.K. Ghosh, Ph. D. President S.K. Ghosh Associates Inc. Northbrook, IL BACKGROUND Until recently, precast concrete structures could be built in
Behavior Analysis-Based Learning Framework for Host Level Intrusion Detection
 Behavior Analysis-Based Learning Framework for Host Level Intrusion Detetion Haiyan Qiao, Jianfeng Peng, Chuan Feng, Jerzy W. Rozenblit Eletrial and Computer Engineering Department University of Arizona
Behavior Analysis-Based Learning Framework for Host Level Intrusion Detetion Haiyan Qiao, Jianfeng Peng, Chuan Feng, Jerzy W. Rozenblit Eletrial and Computer Engineering Department University of Arizona
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS NQF LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 1 - LOADING SYSTEMS TUTORIAL 3 LOADED COMPONENTS
 EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIICATE/DIPLOMA MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS NQ LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 1 - LOADING SYSTEMS TUTORIAL 3 LOADED COMPONENTS 1. Be able to determine the effects of loading in static engineering
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIICATE/DIPLOMA MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS NQ LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 1 - LOADING SYSTEMS TUTORIAL 3 LOADED COMPONENTS 1. Be able to determine the effects of loading in static engineering
