Q1. The table shows how much carbon dioxide is produced when you transfer the same amount of energy by burning coal, gas and oil.
|
|
|
- Henry Peters
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Q. The table shows how much carbon dioxide is produced when you transfer the same amount of energy by burning coal, gas and oil. (a) Use the information from the table to complete the bar-chart. The second bar-chart shows how much sulphur dioxide is produced by burning the same three fuels. () (c) Compare the amount of sulphur produced by burning gas with the amount produced by burning coal. Burning fuels also produces nitrogen oxides, even though the fuels contain no nitrogen. Explain why this happens. () () Page of 37
2 (d) When you release the same amount of energy from coal, gas and oil, different amounts of carbon dioxide are produced. Use the information below to explain why. (3) (e) What other element do coal and oil usually contain? () (Total 9 marks) Q. The table shows how much carbon dioxide is produced when you transfer the same amount of energy by burning coal, gas and oil. (a) Use the information from the table to complete the bar-chart. (3) Page of 37
3 The second bar-chart shows how much sulphur dioxide is produced by burning the same three fuels. Compare the amount of sulphur produced by burning gas with the amount produced by burning coal. () (c) (i) Coal and oil produce carbon dioxide and sulphur dioxide when they burn. What elements must they contain? () Burning fuels also produce nitrogen oxides, even though the fuels contain no nitrogen. Explain why this happens () (Total 9 marks) ## The table gives some information about a family of molecules in crude oil. NUMBER OF CARBON ATOMS IN MOLECULE MASS OF MOLECULE (atomic units) Page 3 of 37
4 (a) Show information from the table in the most appropriate way on the grid. (3) What is the mass of a molecule with three carbon atoms? () (c) The other atoms in each molecule are all hydrogen atoms. What family of substances do all the molecules belong to? () (d) The mass of a carbon atom is atomic units. The mass of a hydrogen atom is atomic unit. So the molecule with one carbon atom has four hydrogen atoms. Its formula is CH 4. Write down the formula: (i) of the molecule with two carbon atoms... of a molecule from the same family with five carbon atoms... () (Total 7 marks) Q4. Choose words from this list to complete the sentences, ammonia carbon dioxide hydrogen nitrogen electrical heat solar sound Page 4 of 37
5 (a) In air, the two most common gases are oxygen and.... When natural gas burns, energy is released mainly as.... (c) When natural gas burns, a gas is produced which turns limewater milky. The gas is.... (Total 3 marks) Q5. The gases produced when coal burns are cooled by ice and then bubbled through limewater. (a) Complete these sentences. (i) The coal is reacting with... when it burns. During burning, elements in the coal are converted to compounds called... () Choose words from this list to complete the sentences. carbon carbon dioxide sulphur sulphur dioxide sodium water (i) Liquid X is a compound made from hydrogen and oxygen. It is called... Sulphur dioxide is an acidic gas. It is given off when coal burns, because coal contains the element... (iii) Most fuels are compounds of hydrogen and... (3) Page 5 of 37
6 (c) Burning coal is an exothermic reaction. Explain what exothermic means () (d) (i) Which gas turns limewater cloudy?... Which element in the coal is oxidised to form this gas?... () (Total 8 marks) Q6. A student is using a spirit burner to heat some water. (a) Complete these sentences. Substances like methylated spirit which we burn to give out energy, are called.... The energy is given out as... energy. () Choose a word from this list to complete the sentence below. gases liquids solids The methylated spirit seems to disappear as it burns. The new substances produced during burning are mainly... () (Total 3 marks) Page 6 of 37
7 Q7. Natural gas is a fuel. (a) Complete these sentences. When the fuel burns completely, we cannot see the new substances produced because they are mainly colourless.... The energy of the fuel is released as.... (3) Choose words from this list to complete the sentence below. carbon carbon dioxide hydrogen nitrogen oxygen sulphur dioxide water vapour Three gases which can be produced when fuels burn are: (3) (Total 6 marks) Q8. The structural formulae of two saturated hydrocarbons are shown below. Page 7 of 37
8 Describe two ways in which they will differ in their physical properties (Total marks) Q9. Here is the word equation for a chemical reaction. methane + oxygen water + carbon dioxide Write down everything that the word equation tells you about the reaction (Total 4 marks) Q0. This experiment shows a candle burning then going out. (a) Choose words from this list to complete the sentences in parts (i) and below. air carbon dioxide hydrogen nitrogen oxygen (i) When the candle wax is burning it is reacting with... from the.... One product of the reaction is... () () Page 8 of 37
9 Complete the following sentence. In another experiment a 00 cm 3 beaker is used. The candle will then burn for about... seconds. () (Total 4 marks) Q. In a car engine petrol burns in oxygen from the air. Two of the gases in the exhaust fumes are carbon dioxide and water vapour. This indicates that petrol contains the elements... and... (Total marks) Q. Petrol burns in oxygen from the air in a car engine. Two of the gases in the exhaust fumes are carbon dioxide and water vapour. This indicates that petrol contains the elements... and.... (Total marks) Q3. Wax is a fuel. A young child watched a candle burning and wondered where the wax had gone. (a) Complete the sentence below. When wax burns, energy is released as... () Why does the wax disappear as it burns? () (Total marks) Page 9 of 37
10 Q4. Choose words from this list to complete the sentences below. a chemical an electrical a physical hydrogen nitrogen oxygen (a) Burning is... change. () When substances burn, they are reacting with... from the air. () (Total marks) Q5. The table shows some of the products which are obtained from the fractional distillation of crude oil. Fraction A B C Nature of products a mixture of gases a mixture of low boiling point liquids a mixture of high boiling point, yellow liquids (a) For each of the fractions A C give the name of an organic substance which could be part of the fraction and state a use for it. A... Use... () B... Use... () C... Use... () When burned in excess air, all the substances in fractions A C form the same two compounds. Give the formulae of these two compounds.... and... () (Total 7 marks) Page 0 of 37
11 Q6. Crude oil and natural gas are mixtures of hydrocarbons. They are obtained from wells drilled into rocks where they are trapped. (a) (i) What is the name of the process used to separate the different hydrocarbons in crude oil?... () Methane is one of the gases obtained when crude oil is separated. Give the name of another hydrocarbon gas obtained from this process.... () A fuel used in gas cookers is natural gas. It is mainly methane, CH 4. (i) Complete the word equation for the complete combustion of methane. methane + oxygen () What different gas is produced by the incomplete combustion of methane?... () (Total 5 marks) Q7. Crude oil is a mixture of long-chain hydrocarbons. It is cracked to produce a mixture of smaller alkanes and alkenes. Among the gases formed are ethane and ethene. (a) Write the structural formula for: (i) ethane () Page of 37
12 ethene () (iii) Give an example of one chemical reaction which both ethane and ethene undergo.... () (iv) Describe how to distinguish between ethane and ethene. Include a description of the practical method you would use and what you would expect to observe (3) Ethene may be polymerised to form a polymer. Give the name of the polymer and a use for it. Name... Use... () (Total 7 marks) Page of 37
13 Q8. The table shows the composition of some crude oil. Fraction Percentage in crude oil Gases 3 Petrol 7 Naphtha 0 Kerosine 5 Gas oil 0 Fuel oil 45 (a) Complete the pie chart for the composition of this crude oil. Remember to label the chart. (3) Page 3 of 37
14 The diagram shows the process of separating a different sample of crude oil into fractions. (i) What is the name given to this process?... () Which fraction has the lowest boiling point?... () (iii) Which fraction is the least volatile?... () (Total 6 marks) Q9. The amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is increased by reactions that occur in internal combustion engines (X) and is decreased by reactions in sea water (Y). Page 4 of 37
15 Describe, in as much detail as you can, the reactions which take place at X and Y. (a) X... () Y... (3) (Total 5 marks) Q0. Crude oil is a mixture of hydrocarbons. These hydrocarbons can be separated and some of them can be used to make other useful products. (a) Complete the sentence. Hydrocarbons are made up of... atoms and... atoms. () How are the small and large hydrocarbon molecules in crude oil separated? () Page 5 of 37
16 (c) The diagram shows that one useful product of cracking is fuels. Name one of the other useful products. () (Total 5 marks) Q. Crude oil is separated into fractions by fractional distillation. The table gives information about some of the fractions. Fraction Boiling point range in C Number of carbon atoms per molecule Gas Below 0 4 Petrol Paraffin Diesel Lubricant Bitumen Above 500 Above 35 (a) What is the relationship between the boiling point of a fraction and the number of carbon atoms in its molecules? () Give one further difference, other than boiling point, between diesel and paraffin that also depends on the number of carbon atoms in their molecules. () (c) All the fractions contain hydrocarbons. Name the two elements in a hydrocarbon.... and... () (Total 3 marks) Page 6 of 37
17 Q. Propane has a small, hydrocarbon molecule, so it is used as a fuel. (a) Complete the sentences by choosing the correct words from the box. carbohydrate high hydrogen hydroxide low volatile Propane is a hydrocarbon with a... boiling point. Propane is a hydrocarbon because it is made of... and carbon only. () Describe, in as much detail as you can, what happens when propane burns (3) (Total 5 marks) Q3. Crude oil contains many different hydrocarbons. (i) Which formula in the list represents a hydrocarbon? Draw a ring around the correct formula. CO C 6 H O 6 C 8 H 8 H O () Page 7 of 37
18 Which word from the list below best describes crude oil? Draw a ring around the correct word. alloy compound element mixture () (iii) Choose, from the list below, words to complete the passage about the separation of the hydrocarbons in crude oil by fractional distillation. atoms burned condensed evaporated filtered fractions ions molecules neutralised During fractional distillation the many hydrocarbons in crude oil are separated into... each of which contains... with a similar number of carbon.... To do this the oil is first... and then... at a number of different temperatures. (5) (Total 7 marks) Q4. (a) Burning fuels changes the Earth s atmosphere. The new substances produced are mainly gases. The following is a list of types of reaction. combustion cracking electrolysis fermentation neutralisation reduction Choose, from the list, the word which has the same meaning as burning. () Page 8 of 37
19 The table shows the gases formed when four fuels, A to D, are completely burned in air. FUEL GAS FORMED ON BURNING CARBON DIOXIDE CO WATER VAPOUR H O SULPHUR DIOXIDE SO A B C D Which fuel, A to D, is hydrogen, H?... () (Total marks) Q5. Crude oil is obtained by drilling into the Earth s crust. The diagram shows a section through the Earth s crust to show how this is done. (a) Crude oil contains many hydrocarbons. Which elements do hydrocarbons contain?... () Page 9 of 37
20 The crude oil is separated by fractional distillation. The diagram shows a column used for this. (i) Explain, as fully as you can, how fractional distillation works (3) Naphtha burns more easily than diesel oil. Explain why () (iii) Naphtha contains a saturated hydrocarbon with the formula C 7 H 6. Draw the structural formula of this compound. () (Total 7 marks) Page 0 of 37
21 Q6. (a) Crude oil is a mixture of many compounds. Most of the compounds consist of molecules made only of carbon and hydrogen. Choose one word from the list below to complete the sentence. carbohydrates carbonates hydrocarbons hydrogencarbonates Compounds made only of carbon and hydrogen are called... () The fractions contain molecules with similar numbers of carbon atoms. The main fractions are shown in the table below. NAME OF FRACTION petroleum gases gasoline naphtha kerosene diesel oil lubricating oil residue NUMBER OF CARBON ATOMS IN MOLECULES to 4 4 to 7 to 4 to 5 4 to 9 8 to 30 more than 30 Naphtha burns more easily than diesel oil. Explain why. () (Total marks) Q7. Crude oil is a complex mixture of hydrocarbons, mainly alkanes. The number of carbon atoms in the molecules ranges from to over 00. (a) How does the boiling point change as the number of carbon atoms in the molecules increases? () Name the method used to separate petroleum into fractions. () Page of 37
22 (c) The simplest hydrocarbon is methane, CH 4. Its structure can be represented: Draw the structure of ethane, C H 6. () (Total 3 marks) Q8. The diagram below shows a camping stove used by some students. A student wrote the report below to explain how the stove works. The report has had some words removed. Complete the report using words from the list. air chemical change liquids physical change argon gases nitrogen solid carbon dioxide heat energy oxygen water vapour To use the stove a fuel called methylated spirits is poured into the burner and lit with a match. The holes in the base let... into the stove. This contains the gas called... which is needed for the fuel to burn. When the fuel burns, new substances are formed. This shows that a... takes place. When all of the methylated spirits has burned nothing is left in the burner. This shows that the new substances must all be.... Methylated spirits contains carbon and hydrogen. When the fuel burns the carbon is changed into.... Page of 37
23 The hydrogen is changed into.... When the fuel burns it gives out... which cooks the food in the pan. (Total 7 marks) Q9. Crude oil is a mixture of many saturated hydrocarbons. They can be separated into fractions by the process of fractional distillation. State what is meant by: (i) hydrocarbon () saturated () (iii) fraction () (Total 4 marks) Q30. Crude oil is a mixture of many saturated hydrocarbons. They can be separated into fractions by the process of fractional distillation. State what is meant by: (i) hydrocarbon () saturated () (iii) fraction () (Total 4 marks) Page 3 of 37
24 M. (a) both bars correct height (to better than half a square) mark for both both bars correctly labelled (w.r.t. relative heights if these incorrect) for mark a lot less / much less / 8 times less (converse must specify coal) gains mark (c) ideas that at high temperatures (produced when fuels burn) nitrogen and oxygen from air / atmosphere combine / react or nitrogen from air / atmosphere oxidises for mark each (d) ideas that coal produces most carbon dioxide / more CO than gas / oil because coal is (mostly) carbon gas produces less carbon dioxide than coal / oil oil and gas also contain hydrogen / contain more hydrogen atoms than carbon atoms / also produce water any three for mark each 3 (e) sulphur for mark [9] M. (a) each bar correct height ( bars) to less than ½ square mark for each both bars correctly labelled (in relation to size of bars) for mark 3 less gains mark but a lot less / much less / 8 times less or more if referring to coal gains marks Page 4 of 37
25 (c) (i) carbon sulphur for mark each ideas that at high temperatures, (produced when fuels burn) nitrogen and oxygen from atmosphere combine / react for mark each [9] M3. (a) vertical axis appropriately scaled [i.e. using more than half the grid] all three points correctly plotted* (to < ½ a square) reasonably straight line drawn through points (to < half a square)* [*credit both these marks for bars correctly drawn since discontinuous variable] each for mark x [If points incorrectly plotted credit mark for the best fit straight line or curve but not point-to-point] 3 44 (atomic units) for mark (e.c.f. i.e. credit consistent with candidate s graph) (c) hydrocarbons / alkanes for mark (d) C H 6 C 5 H each for mark [NB figures must be subscripted] [7] Page 5 of 37
26 M4. (a) nitrogen / N [Do not allow N or N ] for mark heat for mark (c) carbon dioxide / CO for mark [3] M5. (a) (i) oxygen (not air) oxides/monoxides/dioxides for mark each Do not allow specific examples (i) water (iii) sulphur carbon for mark each 3 (c) gives out/releases heat/energy for mark (d) (i) carbon dioxide carbon for mark each (allow correct symbols/formulae) [8] M6. (a) fuels heat allow light for mark each gases for mark [3] Page 6 of 37
27 M7. (a) substances/chemicals/compounds gains mark but gases (accept vapours) gains marks heat (accept light) for mark 3 carbon dioxide/co water (vapour)/h O sulphur dioxide/so (accept correct formulae) in any order for mark each 3 [6] M8. B will have higher melting point higher boiling point be less volatile be more viscous (allow less flammable) any two for mark each [] M9. idea of react/reactant/burn/combine idea of produce/product/formed/make (NOT a chemical symbol equation) methane + oxygen identified as reactants carbon dioxide + water identified as products each for mark [4] Page 7 of 37
28 M0. (a) (i) oxygen air each for mark carbon dioxide for mark 30 seconds 5 inclusive for mark [4] ## carbon; hydrogen (any order) each for mark [] ## hydrogen carbon in any order each for mark [] M3. (a) heat/light any reference to the products being (colourless) gases/smoke [] M4. (a) a chemical oxygen [] Page 8 of 37
29 M5. (a) Substance Use A any pair from award one mark for a correct use for an incorrect fuel methane or fuel natural gas or refinery gas ethane propane fuel or making ethene for polymerisation bottled or camping gas or fuel accept relevant trade names e.g. Calor Gas butane bottled or camping gas or fuel or lighter fuel B any pair from petrol or gasoline accept car engines do not credit just cars fuel for cars naptha paraffin or kerosene accept jet or aircraft fuel petrol or chemicals or feedstock or solvent heating fuel or aviation fuel C any pair from naptha petrol or chemicals or feedstock or solvent Page 9 of 37
30 paraffin or kerosene diesel or diesel oil or (light) gas oil heating fuel or aviation fuel vehicle fuel or heating fuel (lubricating) oil lubricating or oiling qualified, eg. oiling a gate fuel oil industrial or heating fuel heavy gas oil fuel for stationary or slow speed diesel engines CO and H O both required [7] M6. (a) (i) fractional distillation both words required accept fractionation any one from ethane propane butane (i) carbon dioxide water (vapour) accept steam do not credit symbols carbon monoxide accept CO do not credit soot or carbon oxide [5] Page 30 of 37
31 M7. (a) (i) do not credit CH 3 CH 3 do not credit C H 4 (iii) burn or react with oxygen or combustion or oxidation accept react with chlorine (iv) bubble each gas through (test tube containing) bromine water accept add bromine (water to gas collected) or burn ethene decolourises it or turns the brown colourless accept ethene burns with smoky flame do not accept makes it go clear ethane does not affect it or leaves it brown accept ethane burns with clear flame note carefully the spelling of ethene and ethane both the correct name and use are required for the mark poly (ethene) or polythene; any soft or pliable plastic article or any suitable harder plastic item accept polyethene or polyethylene [7] M8. (a) all plots correct 3 or plots correct gains mark all sectors correctly labelled Page 3 of 37
32 (i) (fractional) distillation gases (iii) bitumen [6] M9. (a) any two mark each burning / combustion fossil fuels or (locked up) carbon accept fuel / named fuel oxygen used any three from produces (calcium) carbonate which is insoluble produces (calcium) hydrogencarbonate which is soluble photosynthesis releases oxygen 3 [5] M0. (a) carbon hydrogen any order fractional distillation accept description heat or evaporate / boil (mark) separated when they condense or by boiling points ( mark) Page 3 of 37
33 (c) alkenes accept names or unsaturated hydrocarbons [5] M. (a) the higher the boiling point, the greater the number of carbon atoms volatility / viscosity / runnyness / flammability / smokiness / amount of oxygen needed for burning / melting point do not credit how heavy it is / how it burns (c) hydrogen and carbon (both) allow H and C (upper case) [3] M. (a) low hydrogen any three from flame accept it is a blue / yellow colour reacts with oxygen accept burns in oxygen / bonds broken carbon dioxide carbon monoxide forms accept CO arco / bonds forming in CO /CO and H O bonds forming mark max accept an oxide of hydrogen or H O water (vapour) forms accept heat or light released / temperature increase / exothermic energy released 3 [5] M3. (i) C 8 H 8 for one mark Page 33 of 37
34 mixture for one mark (iii) fractions molecules atoms evaporated condensed in this order for mark each 5 [7] M4. (a) combustion for one mark B for one mark [] M5. (a) hydrogen and carbon for mark (i) the oil is evaporated / boiled / liquid converted to gas / vaporised oil is condensed/changed back to liquid/cooled below boiling point (not just cooled) liquids of different boiling points condense at different levels / fractions with lower boiling points form near the top / boiling point linked to chain length or Mr each for mark 3 Assume they mean naphtha unless they say otherwise. smaller molecules /contains less atoms /lower boiling point /more volatile /less bonds to break /lower activation energy If the answer is given the opposite way around then diesel must be specified. any one for mark Page 34 of 37
35 (iii) correct number of atoms = correct number of bonds (attached to correct atoms) = Accept diagrams which show electrons correctly. CH 3 CH CH CH CH CH CH 3 = for marks [7] M6. (a) hydrocarbons for mark less carbon atoms / smaller molecule for mark [] M7. (a) the more C atoms the higher the b.pt./temperature Allow just higher. Not answer based on melting point for mark (fractional) distillation/fractionation for mark (c) must include H atoms and lines not CH 3 CH 3 for mark [3] Page 35 of 37
36 M8. air/gases oxygen O chemical change/reaction gases carbon dioxide/co water [vapour] H O (heat or heat energy or energy) for mark each [7] M9. (i) carbon and hydrogen only or compound of for mark each single bonds only or no double bonds etc or contains maximum number of hydrogen atoms for mark (iii) molecules of similar chain length similar boiling points limited range of boiling points etc any for mark [4] M30. (i) carbon and hydrogen only or compound of for mark each single bonds only or no double bonds etc or contains maximum number of hydrogen atoms for mark (iii) molecules of similar chain length similar boiling points limited range of boiling points etc any for mark [4] Page 36 of 37
37 Page 37 of 37
Specimen Paper. Chemistry 1F. Time allowed! 60 minutes
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number Specimen Paper For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier Question 1 Mark Science
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number Specimen Paper For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier Question 1 Mark Science
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *0123456789* CHEMISTRY 0620/03 Paper 3 Theory (Core) For Examination from 2016 SPECIMEN PAPER 1 hour
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *0123456789* CHEMISTRY 0620/03 Paper 3 Theory (Core) For Examination from 2016 SPECIMEN PAPER 1 hour
Specimen Paper. Time allowed! 60 minutes
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number Specimen Paper For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier Question 1 Mark Chemistry
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number Specimen Paper For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier Question 1 Mark Chemistry
Q1. A student studied the reaction between dilute hydrochloric acid and an excess of calcium carbonate.
 Q. A student studied the reaction between dilute hydrochloric acid and an excess of calcium carbonate. calcium carbonate + hydrochloric acid calcium chloride + water + carbon dioxide The student measured
Q. A student studied the reaction between dilute hydrochloric acid and an excess of calcium carbonate. calcium carbonate + hydrochloric acid calcium chloride + water + carbon dioxide The student measured
20.2 Chemical Equations
 All of the chemical changes you observed in the last Investigation were the result of chemical reactions. A chemical reaction involves a rearrangement of atoms in one or more reactants to form one or more
All of the chemical changes you observed in the last Investigation were the result of chemical reactions. A chemical reaction involves a rearrangement of atoms in one or more reactants to form one or more
Alkanes. Chapter 1.1
 Alkanes Chapter 1.1 Organic Chemistry The study of carbon-containing compounds and their properties What s so special about carbon? Carbon has 4 bonding electrons. Thus, it can form 4 strong covalent bonds
Alkanes Chapter 1.1 Organic Chemistry The study of carbon-containing compounds and their properties What s so special about carbon? Carbon has 4 bonding electrons. Thus, it can form 4 strong covalent bonds
COMBUSTION. In order to operate a heat engine we need a hot source together with a cold sink
 COMBUSTION In order to operate a heat engine we need a hot source together with a cold sink Occasionally these occur together in nature eg:- geothermal sites or solar powered engines, but usually the heat
COMBUSTION In order to operate a heat engine we need a hot source together with a cold sink Occasionally these occur together in nature eg:- geothermal sites or solar powered engines, but usually the heat
The energy level diagram for this reaction is shown below.
 Q. Methanol can be made when methane reacts with oxygen. (a) The energy level diagram for this reaction is shown below. (i) What is the energy change represented by A? () (ii) Use the energy level diagram
Q. Methanol can be made when methane reacts with oxygen. (a) The energy level diagram for this reaction is shown below. (i) What is the energy change represented by A? () (ii) Use the energy level diagram
GCSE Chemistry Quiz Chemical Reactions
 GCSE Chemistry Quiz Chemical Reactions A chemical reaction is a process where the molecular structure changes. Chemical reactions are all around us. We can see many reactions such as fireworks and explosions.
GCSE Chemistry Quiz Chemical Reactions A chemical reaction is a process where the molecular structure changes. Chemical reactions are all around us. We can see many reactions such as fireworks and explosions.
Chapter 16: Tests for ions and gases
 The position of hydrogen in the reactivity series Hydrogen, although not a metal, is included in the reactivity series because it, like metals, can be displaced from aqueous solution, only this time the
The position of hydrogen in the reactivity series Hydrogen, although not a metal, is included in the reactivity series because it, like metals, can be displaced from aqueous solution, only this time the
IB Chemistry. DP Chemistry Review
 DP Chemistry Review Topic 1: Quantitative chemistry 1.1 The mole concept and Avogadro s constant Assessment statement Apply the mole concept to substances. Determine the number of particles and the amount
DP Chemistry Review Topic 1: Quantitative chemistry 1.1 The mole concept and Avogadro s constant Assessment statement Apply the mole concept to substances. Determine the number of particles and the amount
Chemical Reactions Practice Test
 Chemical Reactions Practice Test Chapter 2 Name Date Hour _ Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The only sure evidence for a chemical reaction
Chemical Reactions Practice Test Chapter 2 Name Date Hour _ Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The only sure evidence for a chemical reaction
MEMORANDUM GRADE 11. PHYSICAL SCIENCES: CHEMISTRY Paper 2
 MEMORANDUM GRADE 11 PHYSICAL SCIENCES: CHEMISTRY Paper 2 MARKS: 150 TIME: 3 hours Learning Outcomes and Assessment Standards LO1 LO2 LO3 AS 11.1.1: Plan and conduct a scientific investigation to collect
MEMORANDUM GRADE 11 PHYSICAL SCIENCES: CHEMISTRY Paper 2 MARKS: 150 TIME: 3 hours Learning Outcomes and Assessment Standards LO1 LO2 LO3 AS 11.1.1: Plan and conduct a scientific investigation to collect
Page 1. 6. Which hydrocarbon is a member of the alkane series? (1) 1. Which is the structural formula of methane? (1) (2) (2) (3) (3) (4) (4)
 1. Which is the structural formula of methane? 6. Which hydrocarbon is a member of the alkane series? 7. How many carbon atoms are contained in an ethyl group? 1 3 2 4 2. In the alkane series, each molecule
1. Which is the structural formula of methane? 6. Which hydrocarbon is a member of the alkane series? 7. How many carbon atoms are contained in an ethyl group? 1 3 2 4 2. In the alkane series, each molecule
ASimple Guide to Oil Refining
 ASimple Guide to Oil Refining We all know that motor oil and gasoline come from crude oil. What many people do not realize is that crude oil is also the starting point for many diverse products such as
ASimple Guide to Oil Refining We all know that motor oil and gasoline come from crude oil. What many people do not realize is that crude oil is also the starting point for many diverse products such as
Final. Mark Scheme CH1HP. Science A / Chemistry. (Specification 4405 / 4402) Unit 1: Chemistry 1
 02.3 General Certificate of Secondary Education January 203 Science A / Chemistry CHHP (Specification 4405 / 4402) Unit : Chemistry Final Mark Scheme Mark schemes are prepared by the Principal Examiner
02.3 General Certificate of Secondary Education January 203 Science A / Chemistry CHHP (Specification 4405 / 4402) Unit : Chemistry Final Mark Scheme Mark schemes are prepared by the Principal Examiner
Chemistry Assessment Unit AS 1
 Centre Number 71 Candidate Number ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY (AS) General Certificate of Education January 2011 Chemistry Assessment Unit AS 1 assessing Basic Concepts in Physical and Inorganic Chemistry [AC111]
Centre Number 71 Candidate Number ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY (AS) General Certificate of Education January 2011 Chemistry Assessment Unit AS 1 assessing Basic Concepts in Physical and Inorganic Chemistry [AC111]
Final. Mark Scheme. Science A / Chemistry CH1HP. (Specification 4405 / 4402) Unit 1: Chemistry 1. General Certificate of Secondary Education June 2013
 Version.0 General Certificate of Secondary Education June 203 Science A / Chemistry CHHP (Specification 4405 / 4402) Unit : Chemistry Final Mark Scheme Mark schemes are prepared by the Principal Examiner
Version.0 General Certificate of Secondary Education June 203 Science A / Chemistry CHHP (Specification 4405 / 4402) Unit : Chemistry Final Mark Scheme Mark schemes are prepared by the Principal Examiner
States of Matter and the Kinetic Molecular Theory - Gr10 [CAPS]
![States of Matter and the Kinetic Molecular Theory - Gr10 [CAPS] States of Matter and the Kinetic Molecular Theory - Gr10 [CAPS]](/thumbs/40/21739317.jpg) OpenStax-CNX module: m38210 1 States of Matter and the Kinetic Molecular Theory - Gr10 [CAPS] Free High School Science Texts Project This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative
OpenStax-CNX module: m38210 1 States of Matter and the Kinetic Molecular Theory - Gr10 [CAPS] Free High School Science Texts Project This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative
SUPPLEMENTARY TOPIC 3 ENERGY AND CHEMICAL REACTIONS
 SUPPLEMENTARY TOPIC 3 ENERGY AND CHEMICAL REACTIONS Rearranging atoms. In a chemical reaction, bonds between atoms in one or more molecules (reactants) break and new bonds are formed with other atoms to
SUPPLEMENTARY TOPIC 3 ENERGY AND CHEMICAL REACTIONS Rearranging atoms. In a chemical reaction, bonds between atoms in one or more molecules (reactants) break and new bonds are formed with other atoms to
Question Bank Organic Chemistry-I
 Question Bank Organic Chemistry-I 1. (a) What do you understand by the following terms : (i) Organic chemistry (ii) Organic compounds (iii) Catenation? [3] (b) Why are there very large number of organic
Question Bank Organic Chemistry-I 1. (a) What do you understand by the following terms : (i) Organic chemistry (ii) Organic compounds (iii) Catenation? [3] (b) Why are there very large number of organic
KS3 Science: Chemistry Contents
 summary KS3 Science MyWorks Guide Chemistry KS3 Science: Chemistry Mini zes: 40 Super zes: 5 Extension zes: 4 Skills zes: 6 TOTAL 54 What are MyWorks zes? MyWorks zes are short individual learning tasks
summary KS3 Science MyWorks Guide Chemistry KS3 Science: Chemistry Mini zes: 40 Super zes: 5 Extension zes: 4 Skills zes: 6 TOTAL 54 What are MyWorks zes? MyWorks zes are short individual learning tasks
Coal-To-Gas & Coal-To-Liquids
 Located in the Energy Center at Discovery Park, Purdue University Coal-To-Gas & Coal-To-Liquids CCTR Basic Facts File #3 Brian H. Bowen, Marty W. Irwin The Energy Center at Discovery Park Purdue University
Located in the Energy Center at Discovery Park, Purdue University Coal-To-Gas & Coal-To-Liquids CCTR Basic Facts File #3 Brian H. Bowen, Marty W. Irwin The Energy Center at Discovery Park Purdue University
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 ambridge International Examinations ambridge International General ertificate of Secondary Education *012345678* EMISTRY 0620/01 Paper 1 Multiple hoice (ore) For Examination from 2016 SPEIMEN PPER dditional
ambridge International Examinations ambridge International General ertificate of Secondary Education *012345678* EMISTRY 0620/01 Paper 1 Multiple hoice (ore) For Examination from 2016 SPEIMEN PPER dditional
Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission
 2015. M33 Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2015 CHEMISTRY ORDINARY LEVEL TUESDAY, 16 JUNE AFTERNOON 2.00 TO 5.00 400 MARKS Answer eight questions
2015. M33 Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2015 CHEMISTRY ORDINARY LEVEL TUESDAY, 16 JUNE AFTERNOON 2.00 TO 5.00 400 MARKS Answer eight questions
Mark Scheme (Results) January 2012. International GCSE Chemistry (4CH0) Paper 2C
 Mark Scheme (Results) January 202 International GCSE Chemistry (4CH0) Paper 2C Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications come from Pearson, the world s leading learning company. We
Mark Scheme (Results) January 202 International GCSE Chemistry (4CH0) Paper 2C Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications come from Pearson, the world s leading learning company. We
83 to 87% carbon 11-15% hydrogen 0.1-7% sulphur 0.06-1.5% oxygen 0.1-0.5% nitrogen
 Petroleum chemistry rude is the name for a liquid mixture of different hydrocarbon connections found in the earth. Petroleum, strictly speaking is crude oil, but it is used to describe all kinds of hydrocarbons.
Petroleum chemistry rude is the name for a liquid mixture of different hydrocarbon connections found in the earth. Petroleum, strictly speaking is crude oil, but it is used to describe all kinds of hydrocarbons.
Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations
 Chapter 3 Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations Concept Check 3.1 You have 1.5 moles of tricycles. a. How many moles of seats do you have? b. How many moles of tires do you have? c. How could
Chapter 3 Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations Concept Check 3.1 You have 1.5 moles of tricycles. a. How many moles of seats do you have? b. How many moles of tires do you have? c. How could
EDEXCEL IGCSE chemistry (separate award)
 EDEXCEL IGCSE chemistry (separate award) Section 1: Principles of chemistry a) States of matter 1.1 understand the arrangement, movement and energy of the particles in each of the three states of matter:
EDEXCEL IGCSE chemistry (separate award) Section 1: Principles of chemistry a) States of matter 1.1 understand the arrangement, movement and energy of the particles in each of the three states of matter:
5. Which temperature is equal to +20 K? 1) 253ºC 2) 293ºC 3) 253 C 4) 293 C
 1. The average kinetic energy of water molecules increases when 1) H 2 O(s) changes to H 2 O( ) at 0ºC 3) H 2 O( ) at 10ºC changes to H 2 O( ) at 20ºC 2) H 2 O( ) changes to H 2 O(s) at 0ºC 4) H 2 O( )
1. The average kinetic energy of water molecules increases when 1) H 2 O(s) changes to H 2 O( ) at 0ºC 3) H 2 O( ) at 10ºC changes to H 2 O( ) at 20ºC 2) H 2 O( ) changes to H 2 O(s) at 0ºC 4) H 2 O( )
CHM220 Addition lab. Experiment: Reactions of alkanes, alkenes, and cycloalkenes*
 CM220 Addition lab Experiment: Reactions of alkanes, alkenes, and cycloalkenes* Purpose: To investigate the physical properties, solubility, and density of some hydrocarbon. To compare the chemical reactivity
CM220 Addition lab Experiment: Reactions of alkanes, alkenes, and cycloalkenes* Purpose: To investigate the physical properties, solubility, and density of some hydrocarbon. To compare the chemical reactivity
Instructions Answer all questions in the spaces provided. Do all rough work in this book. Cross through any work you do not want to be marked.
 GCSE CHEMISTRY Higher Tier Chemistry 1H H Specimen 2018 Time allowed: 1 hour 45 minutes Materials For this paper you must have: a ruler a calculator the periodic table (enclosed). Instructions Answer all
GCSE CHEMISTRY Higher Tier Chemistry 1H H Specimen 2018 Time allowed: 1 hour 45 minutes Materials For this paper you must have: a ruler a calculator the periodic table (enclosed). Instructions Answer all
EXAMPLE EXERCISE 4.1 Change of Physical State
 EXAMPLE EXERCISE 4.1 Change of Physical State State the term that applies to each of the following changes of physical state: (a) Snow changes from a solid to a liquid. (b) Gasoline changes from a liquid
EXAMPLE EXERCISE 4.1 Change of Physical State State the term that applies to each of the following changes of physical state: (a) Snow changes from a solid to a liquid. (b) Gasoline changes from a liquid
CHAPTER 3: MATTER. Active Learning Questions: 1-6, 9, 13-14; End-of-Chapter Questions: 1-18, 20, 24-32, 38-42, 44, 49-52, 55-56, 61-64
 CHAPTER 3: MATTER Active Learning Questions: 1-6, 9, 13-14; End-of-Chapter Questions: 1-18, 20, 24-32, 38-42, 44, 49-52, 55-56, 61-64 3.1 MATTER Matter: Anything that has mass and occupies volume We study
CHAPTER 3: MATTER Active Learning Questions: 1-6, 9, 13-14; End-of-Chapter Questions: 1-18, 20, 24-32, 38-42, 44, 49-52, 55-56, 61-64 3.1 MATTER Matter: Anything that has mass and occupies volume We study
Chapter 1: Moles and equations. Learning outcomes. you should be able to:
 Chapter 1: Moles and equations 1 Learning outcomes you should be able to: define and use the terms: relative atomic mass, isotopic mass and formula mass based on the 12 C scale perform calculations, including
Chapter 1: Moles and equations 1 Learning outcomes you should be able to: define and use the terms: relative atomic mass, isotopic mass and formula mass based on the 12 C scale perform calculations, including
Chapter 7: Chemical Energy
 Chapter 7: Chemical Energy Goals of Period 7 Section 7.1: To describe atoms, chemical elements and compounds Section 7.2: To discuss the electromagnetic force and physical changes Section 7.3: To illustrate
Chapter 7: Chemical Energy Goals of Period 7 Section 7.1: To describe atoms, chemical elements and compounds Section 7.2: To discuss the electromagnetic force and physical changes Section 7.3: To illustrate
GCSE COMBINED SCIENCE: TRILOGY
 GCSE COMBINED SCIENCE: TRILOGY Higher Tier Paper 4: Chemistry 2H H Specimen 2018 Time allowed: 1 hour 15 minutes Materials For this paper you must have: a ruler a calculator the periodic table (enclosed)
GCSE COMBINED SCIENCE: TRILOGY Higher Tier Paper 4: Chemistry 2H H Specimen 2018 Time allowed: 1 hour 15 minutes Materials For this paper you must have: a ruler a calculator the periodic table (enclosed)
Final. Mark Scheme CH1FP. Science A / Chemistry. (Specification 4405 / 4402) Unit 1: Chemistry 1
 02.3 General Certificate of Secondary Education January 203 Science A / Chemistry CHFP (Specification 4405 / 4402) Unit : Chemistry Final Mark Scheme Mark schemes are prepared by the Principal Examiner
02.3 General Certificate of Secondary Education January 203 Science A / Chemistry CHFP (Specification 4405 / 4402) Unit : Chemistry Final Mark Scheme Mark schemes are prepared by the Principal Examiner
Desalination of Sea Water E7-1
 Experiment 7 Desalination of Sea Water E7-1 E7-2 The Task The goal of this experiment is to investigate the nature and some properties of sea water. Skills At the end of the laboratory session you should
Experiment 7 Desalination of Sea Water E7-1 E7-2 The Task The goal of this experiment is to investigate the nature and some properties of sea water. Skills At the end of the laboratory session you should
Physical and Chemical Properties and Changes
 Physical and Chemical Properties and Changes An understanding of material things requires an understanding of the physical and chemical characteristics of matter. A few planned experiments can help you
Physical and Chemical Properties and Changes An understanding of material things requires an understanding of the physical and chemical characteristics of matter. A few planned experiments can help you
Module 5: Combustion Technology. Lecture 33: Combustion air calculation
 1 P age Module 5: Combustion Technology Lecture 33: Combustion air calculation 2 P age Keywords: Heat of combustion, stoichiometric air, excess air, natural gas combustion Combustion air calculation The
1 P age Module 5: Combustion Technology Lecture 33: Combustion air calculation 2 P age Keywords: Heat of combustion, stoichiometric air, excess air, natural gas combustion Combustion air calculation The
Module 1: History of Fuels. Lecture 6: Fundamental definitions, properties and various measurements
 1 P age Module 1: History of Fuels Lecture 6: Fundamental definitions, properties and various measurements 2 P age Keywords: Characterisation, analytical methods, standards 1.3 Fundamental definitions,
1 P age Module 1: History of Fuels Lecture 6: Fundamental definitions, properties and various measurements 2 P age Keywords: Characterisation, analytical methods, standards 1.3 Fundamental definitions,
F322: Chains, Energy and Resources 2.2.4 Alcohols
 F322: hains, Energy and Resources 2.2.4 Alcohols 167 marks 1. This question is about the six alcohols below. butan-2-ol 2-methylpentan-3-ol propan-1-ol ethane-1,2-diol 2-methylpropan-2-ol propan-2-ol Which
F322: hains, Energy and Resources 2.2.4 Alcohols 167 marks 1. This question is about the six alcohols below. butan-2-ol 2-methylpentan-3-ol propan-1-ol ethane-1,2-diol 2-methylpropan-2-ol propan-2-ol Which
F321 MOLES. Example If 1 atom has a mass of 1.241 x 10-23 g 1 mole of atoms will have a mass of 1.241 x 10-23 g x 6.02 x 10 23 = 7.
 Moles 1 MOLES The mole the standard unit of amount of a substance (mol) the number of particles in a mole is known as Avogadro s constant (N A ) Avogadro s constant has a value of 6.02 x 10 23 mol -1.
Moles 1 MOLES The mole the standard unit of amount of a substance (mol) the number of particles in a mole is known as Avogadro s constant (N A ) Avogadro s constant has a value of 6.02 x 10 23 mol -1.
Remember the best arguments are based on the strongest evidence and can explain why opposing arguments are incorrect.
 Magnesium and carbon dioxide Student sheet Burning magnesium in carbon dioxide what will happen? Either the magnesium will go out or it will continue to burn. Which will it be? You will use the evidence
Magnesium and carbon dioxide Student sheet Burning magnesium in carbon dioxide what will happen? Either the magnesium will go out or it will continue to burn. Which will it be? You will use the evidence
Laboratory 22: Properties of Alcohols
 Introduction Alcohols represent and important class of organic molecules. In this experiment you will study the physical and chemical properties of alcohols. Solubility in water, and organic solvents,
Introduction Alcohols represent and important class of organic molecules. In this experiment you will study the physical and chemical properties of alcohols. Solubility in water, and organic solvents,
hij GCSE Additional Science Chemistry 2 Higher Tier Chemistry 2H SPECIMEN MARK SCHEME Version 1.0
 hij GCSE Additional Science Chemistry 2 Higher Tier Chemistry 2H SPECIMEN MARK SCHEME Version.0 Copyright 20 AQA and its licensors. All rights reserved. The Assessment and Qualifications Alliance (AQA)
hij GCSE Additional Science Chemistry 2 Higher Tier Chemistry 2H SPECIMEN MARK SCHEME Version.0 Copyright 20 AQA and its licensors. All rights reserved. The Assessment and Qualifications Alliance (AQA)
Gas Detection for Refining. HA University
 Gas Detection for Refining HA University Refinery Process and Detection Needs Refining i Crude Oil Final Products Coke Asphalt Waxes, Lubricating Oils and Greases Kerosene, Jet Fuel, Diesel Fuel, Home
Gas Detection for Refining HA University Refinery Process and Detection Needs Refining i Crude Oil Final Products Coke Asphalt Waxes, Lubricating Oils and Greases Kerosene, Jet Fuel, Diesel Fuel, Home
Unit Vocabulary: o Organic Acid o Alcohol. o Ester o Ether. o Amine o Aldehyde
 Unit Vocabulary: Addition rxn Esterification Polymer Alcohol Ether Polymerization Aldehyde Fermentation Primary Alkane Functional group Saponification Alkene Halide (halocarbon) Saturated hydrocarbon Alkyne
Unit Vocabulary: Addition rxn Esterification Polymer Alcohol Ether Polymerization Aldehyde Fermentation Primary Alkane Functional group Saponification Alkene Halide (halocarbon) Saturated hydrocarbon Alkyne
7-5.5. Translate chemical symbols and the chemical formulas of common substances to show the component parts of the substances including:
 7-5.5 Translate chemical symbols and the chemical formulas of common substances to show the component parts of the substances including: NaCl [salt], H 2 O [water], C 6 H 12 O 6 [simple sugar], O 2 [oxygen
7-5.5 Translate chemical symbols and the chemical formulas of common substances to show the component parts of the substances including: NaCl [salt], H 2 O [water], C 6 H 12 O 6 [simple sugar], O 2 [oxygen
Heterogeneous Homogenous. Mixtures; Solutions. Phases of matter: Solid. Phases of Matter: Liquid. Phases of Matter: Gas. Solid, Liquid, Gas
 Phases of matter: Solid Heterogeneous Homogenous Mixtures Solutions Phases of Matter: Liquid Atoms and molecules are more spaced out and now can move. The material can be slightly compressed into a smaller
Phases of matter: Solid Heterogeneous Homogenous Mixtures Solutions Phases of Matter: Liquid Atoms and molecules are more spaced out and now can move. The material can be slightly compressed into a smaller
GRADE 12 PHYSICAL SCIENCE 3 HOURS TRIALS PAPER 2 (CHEMISTRY) 150 MARKS
 Name: GRADE 12 PHYSICAL SCIENCE 3 HOURS TRIALS PAPER 2 (CHEMISTRY) 150 MARKS PLEASE READ THE FOLLOWING INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY 1. This paper consists of: a question paper of 7 pages a data and formula booklet
Name: GRADE 12 PHYSICAL SCIENCE 3 HOURS TRIALS PAPER 2 (CHEMISTRY) 150 MARKS PLEASE READ THE FOLLOWING INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY 1. This paper consists of: a question paper of 7 pages a data and formula booklet
Making Biodiesel from Virgin Vegetable Oil: Teacher Manual
 Making Biodiesel from Virgin Vegetable Oil: Teacher Manual Learning Goals: Students will understand how to produce biodiesel from virgin vegetable oil. Students will understand the effect of an exothermic
Making Biodiesel from Virgin Vegetable Oil: Teacher Manual Learning Goals: Students will understand how to produce biodiesel from virgin vegetable oil. Students will understand the effect of an exothermic
Chapter 5 Student Reading
 Chapter 5 Student Reading THE POLARITY OF THE WATER MOLECULE Wonderful water Water is an amazing substance. We drink it, cook and wash with it, swim and play in it, and use it for lots of other purposes.
Chapter 5 Student Reading THE POLARITY OF THE WATER MOLECULE Wonderful water Water is an amazing substance. We drink it, cook and wash with it, swim and play in it, and use it for lots of other purposes.
Click on the icons to go to the other modules. oil. refining
 Click on the icons to go to the other modules. oil refining module 4 BP energy education programme 2008 Learning Area, Outcomes and Phase Learning Area Outcomes Phase Program Society and Environment Science
Click on the icons to go to the other modules. oil refining module 4 BP energy education programme 2008 Learning Area, Outcomes and Phase Learning Area Outcomes Phase Program Society and Environment Science
Summer Holidays Questions
 Summer Holidays Questions Chapter 1 1) Barium hydroxide reacts with hydrochloric acid. The initial concentration of the 1 st solution its 0.1M and the volume is 100ml. The initial concentration of the
Summer Holidays Questions Chapter 1 1) Barium hydroxide reacts with hydrochloric acid. The initial concentration of the 1 st solution its 0.1M and the volume is 100ml. The initial concentration of the
Properties and Classifications of Matter
 PS-3.1 Distinguish chemical properties of matter (including reactivity) from physical properties of matter (including boiling point, freezing/melting point, density [with density calculations], solubility,
PS-3.1 Distinguish chemical properties of matter (including reactivity) from physical properties of matter (including boiling point, freezing/melting point, density [with density calculations], solubility,
Review - After School Matter Name: Review - After School Matter Tuesday, April 29, 2008
 Name: Review - After School Matter Tuesday, April 29, 2008 1. Figure 1 The graph represents the relationship between temperature and time as heat was added uniformly to a substance starting at a solid
Name: Review - After School Matter Tuesday, April 29, 2008 1. Figure 1 The graph represents the relationship between temperature and time as heat was added uniformly to a substance starting at a solid
CHEMICAL FORMULAS AND EQUATIONS
 reflect Imagine that you and three other classmates had enough supplies and the recipe to make one pepperoni pizza. The recipe might include a ball of dough, a cup of pizza sauce, a cup of cheese, and
reflect Imagine that you and three other classmates had enough supplies and the recipe to make one pepperoni pizza. The recipe might include a ball of dough, a cup of pizza sauce, a cup of cheese, and
STOICHIOMETRY OF COMBUSTION
 STOICHIOMETRY OF COMBUSTION FUNDAMENTALS: moles and kilomoles Atomic unit mass: 1/12 126 C ~ 1.66 10-27 kg Atoms and molecules mass is defined in atomic unit mass: which is defined in relation to the 1/12
STOICHIOMETRY OF COMBUSTION FUNDAMENTALS: moles and kilomoles Atomic unit mass: 1/12 126 C ~ 1.66 10-27 kg Atoms and molecules mass is defined in atomic unit mass: which is defined in relation to the 1/12
Chemical Changes. Measuring a Chemical Reaction. Name(s)
 Chemical Changes Name(s) In the particle model of matter, individual atoms can be bound tightly to other atoms to form molecules. For example, water molecules are made up of two hydrogen atoms bound to
Chemical Changes Name(s) In the particle model of matter, individual atoms can be bound tightly to other atoms to form molecules. For example, water molecules are made up of two hydrogen atoms bound to
Balancing chemical reaction equations (stoichiometry)
 Balancing chemical reaction equations (stoichiometry) This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit
Balancing chemical reaction equations (stoichiometry) This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *0123456789* CHEMISTRY 0620/04 Paper 4 Theory (Extended) For Examination from 2016 SPECIMEN PAPER
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *0123456789* CHEMISTRY 0620/04 Paper 4 Theory (Extended) For Examination from 2016 SPECIMEN PAPER
*0500/402* 0500/402. CHEMISTRY STANDARD GRADE Credit Level. Fill in these boxes and read what is printed below. Full name of centre
 FOR OFFIIL USE 0500/402 NTIONL QULIFITIONS 2009 MONDY, MY 0.50 M 2.20 PM Total HEMISTRY STNDRD GRDE redit Level Fill in these boxes and read what is printed below. Full name of centre Town Forename(s)
FOR OFFIIL USE 0500/402 NTIONL QULIFITIONS 2009 MONDY, MY 0.50 M 2.20 PM Total HEMISTRY STNDRD GRDE redit Level Fill in these boxes and read what is printed below. Full name of centre Town Forename(s)
Molar Mass of Butane
 Cautions Butane is toxic and flammable. No OPEN Flames should be used in this experiment. Purpose The purpose of this experiment is to determine the molar mass of butane using Dalton s Law of Partial Pressures
Cautions Butane is toxic and flammable. No OPEN Flames should be used in this experiment. Purpose The purpose of this experiment is to determine the molar mass of butane using Dalton s Law of Partial Pressures
GCSE. Chemistry B. Mark Scheme for January 2013. General Certificate of Secondary Education. Unit B741/01: Modules C1, C2, C3 (Foundation Tier)
 GCSE Chemistry B General Certificate of Secondary Education Unit B741/01: Modules C1, C2, C3 (Foundation Tier) Mark Scheme for January 2013 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and
GCSE Chemistry B General Certificate of Secondary Education Unit B741/01: Modules C1, C2, C3 (Foundation Tier) Mark Scheme for January 2013 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and
DIN 2403 Identification of pipelines according to the fluid conveyed. Marking of pipes according to fluid transported
 DIN 2403 Identification of pipelines according to the fluid conveyed. Marking of pipes according to fluid transported 1 Field of application This standard specifies the colours for the identification of
DIN 2403 Identification of pipelines according to the fluid conveyed. Marking of pipes according to fluid transported 1 Field of application This standard specifies the colours for the identification of
In this experiment, we will use three properties to identify a liquid substance: solubility, density and boiling point..
 Identification of a Substance by Physical Properties 2009 by David A. Katz. All rights reserved. Permission for academic use provided the original copyright is included Every substance has a unique set
Identification of a Substance by Physical Properties 2009 by David A. Katz. All rights reserved. Permission for academic use provided the original copyright is included Every substance has a unique set
Learner Guide. Cambridge O Level Chemistry
 Learner Guide Cambridge O Level Chemistry 5070 Cambridge International Examinations retains the copyright on all its publications. Registered Centres are permitted to copy material from this booklet for
Learner Guide Cambridge O Level Chemistry 5070 Cambridge International Examinations retains the copyright on all its publications. Registered Centres are permitted to copy material from this booklet for
Chapter 2 Chemical and Physical Properties of Sulphur Dioxide and Sulphur Trioxide
 Chapter 2 Chemical and Physical Properties of Sulphur Dioxide and Sulphur Trioxide 2.1 Introduction In order to appreciate the impact of the properties of liquid sulphur dioxide and liquid sulphur trioxide
Chapter 2 Chemical and Physical Properties of Sulphur Dioxide and Sulphur Trioxide 2.1 Introduction In order to appreciate the impact of the properties of liquid sulphur dioxide and liquid sulphur trioxide
Name Date Class STOICHIOMETRY. SECTION 12.1 THE ARITHMETIC OF EQUATIONS (pages 353 358)
 Name Date Class 1 STOICHIOMETRY SECTION 1.1 THE ARITHMETIC OF EQUATIONS (pages 353 358) This section explains how to calculate the amount of reactants required or product formed in a nonchemical process.
Name Date Class 1 STOICHIOMETRY SECTION 1.1 THE ARITHMETIC OF EQUATIONS (pages 353 358) This section explains how to calculate the amount of reactants required or product formed in a nonchemical process.
Technical Note: Conversion of fuel data to MWh
 Technical Note: Conversion of fuel data to MWh Questions 12.2 and 12.3 of the information request ask for energy and fuel inputs to be reported according to standardized units commonly used for measuring
Technical Note: Conversion of fuel data to MWh Questions 12.2 and 12.3 of the information request ask for energy and fuel inputs to be reported according to standardized units commonly used for measuring
Bomb Calorimetry. Electrical leads. Stirrer
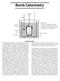 Bomb Calorimetry Stirrer Electrical leads Oxygen inlet valve Bomb Fuse Calorimeter Outer jacket Not shown: heating and cooling system for outer jacket, and controls that keep the outer jacket at the same
Bomb Calorimetry Stirrer Electrical leads Oxygen inlet valve Bomb Fuse Calorimeter Outer jacket Not shown: heating and cooling system for outer jacket, and controls that keep the outer jacket at the same
Compounds vs mixtures. Physics and Chemistry IES Jaume Salvador i Pedrol February 2009
 Compounds vs mixtures Physics and Chemistry IES Jaume Salvador i Pedrol February 2009 Compounds Remember that a compound is a substance made up from two or more elements, chemically joined together. This
Compounds vs mixtures Physics and Chemistry IES Jaume Salvador i Pedrol February 2009 Compounds Remember that a compound is a substance made up from two or more elements, chemically joined together. This
Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission
 Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2007 CHEMISTRY - ORDINARY LEVEL TUESDAY, 19 JUNE AFTERNOON 2.00 TO 5.00 400 MARKS Answer eight questions in
Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2007 CHEMISTRY - ORDINARY LEVEL TUESDAY, 19 JUNE AFTERNOON 2.00 TO 5.00 400 MARKS Answer eight questions in
PREPARATION FOR CHEMISTRY LAB: COMBUSTION
 1 Name: Lab Instructor: PREPARATION FOR CHEMISTRY LAB: COMBUSTION 1. What is a hydrocarbon? 2. What products form in the complete combustion of a hydrocarbon? 3. Combustion is an exothermic reaction. What
1 Name: Lab Instructor: PREPARATION FOR CHEMISTRY LAB: COMBUSTION 1. What is a hydrocarbon? 2. What products form in the complete combustion of a hydrocarbon? 3. Combustion is an exothermic reaction. What
AS1 MOLES. oxygen molecules have the formula O 2 the relative mass will be 2 x 16 = 32 so the molar mass will be 32g mol -1
 Moles 1 MOLES The mole the standard unit of amount of a substance the number of particles in a mole is known as Avogadro s constant (L) Avogadro s constant has a value of 6.023 x 10 23 mol -1. Example
Moles 1 MOLES The mole the standard unit of amount of a substance the number of particles in a mole is known as Avogadro s constant (L) Avogadro s constant has a value of 6.023 x 10 23 mol -1. Example
Edexcel GCSE in Chemistry - 2CH01 Accredited specification booklet
 Edexcel GCSE in Chemistry - 2CH01 Accredited specification booklet This booklet provides: an introduction to the sample assessments an introduction to the specification annotated specification pages the
Edexcel GCSE in Chemistry - 2CH01 Accredited specification booklet This booklet provides: an introduction to the sample assessments an introduction to the specification annotated specification pages the
Correlation of Nelson Chemistry Alberta 20 30 to the Alberta Chemistry 20 30 Curriculum
 Correlation of Nelson Chemistry Alberta 20 30 to the Alberta Chemistry 20 30 Curriculum Unit 5 Organic Chemistry General Outcomes Students will: 1. explore organic compounds as a common form of matter
Correlation of Nelson Chemistry Alberta 20 30 to the Alberta Chemistry 20 30 Curriculum Unit 5 Organic Chemistry General Outcomes Students will: 1. explore organic compounds as a common form of matter
Austin Peay State University Department of Chemistry CHEM 1021 TESTING FOR ORGANIC FUNCTIONAL GROUPS
 TESTING FOR ORGANIC FUNCTIONAL GROUPS Caution: Chromic acid is hazardous as are many of the organic substances in today s experiment. Treat all unknowns with extreme care. Many organic substances are flammable.
TESTING FOR ORGANIC FUNCTIONAL GROUPS Caution: Chromic acid is hazardous as are many of the organic substances in today s experiment. Treat all unknowns with extreme care. Many organic substances are flammable.
INTI COLLEGE MALAYSIA A? LEVEL PROGRAMME CHM 111: CHEMISTRY MOCK EXAMINATION: DECEMBER 2000 SESSION. 37 74 20 40 60 80 m/e
 CHM111(M)/Page 1 of 5 INTI COLLEGE MALAYSIA A? LEVEL PROGRAMME CHM 111: CHEMISTRY MOCK EXAMINATION: DECEMBER 2000 SESSION SECTION A Answer ALL EIGHT questions. (52 marks) 1. The following is the mass spectrum
CHM111(M)/Page 1 of 5 INTI COLLEGE MALAYSIA A? LEVEL PROGRAMME CHM 111: CHEMISTRY MOCK EXAMINATION: DECEMBER 2000 SESSION SECTION A Answer ALL EIGHT questions. (52 marks) 1. The following is the mass spectrum
Chemical Equations & Stoichiometry
 Chemical Equations & Stoichiometry Chapter Goals Balance equations for simple chemical reactions. Perform stoichiometry calculations using balanced chemical equations. Understand the meaning of the term
Chemical Equations & Stoichiometry Chapter Goals Balance equations for simple chemical reactions. Perform stoichiometry calculations using balanced chemical equations. Understand the meaning of the term
Coal Gasification & Fischer-Tropsch
 Coal Gasification & Fischer-Tropsch CCTR Basic Facts File #1 Brian H. Bowen, Marty W. Irwin The Energy Center at Discovery Park Purdue University Potter Engineering Center, 500 Central Drive West Lafayette,
Coal Gasification & Fischer-Tropsch CCTR Basic Facts File #1 Brian H. Bowen, Marty W. Irwin The Energy Center at Discovery Park Purdue University Potter Engineering Center, 500 Central Drive West Lafayette,
Fuel and Heats of Reactions.
 Fuels & Thermochemistry Topic Notes Fuel and Heats of Reactions. Crude Oil is a fossil fuel and formed from the bodies of tiny sea creatures that died millions of years ago, as the layers of mud and slit
Fuels & Thermochemistry Topic Notes Fuel and Heats of Reactions. Crude Oil is a fossil fuel and formed from the bodies of tiny sea creatures that died millions of years ago, as the layers of mud and slit
EXPERIMENT 12: Empirical Formula of a Compound
 EXPERIMENT 12: Empirical Formula of a Compound INTRODUCTION Chemical formulas indicate the composition of compounds. A formula that gives only the simplest ratio of the relative number of atoms in a compound
EXPERIMENT 12: Empirical Formula of a Compound INTRODUCTION Chemical formulas indicate the composition of compounds. A formula that gives only the simplest ratio of the relative number of atoms in a compound
Recovery of Elemental Copper from Copper (II) Nitrate
 Recovery of Elemental Copper from Copper (II) Nitrate Objectives: Challenge: Students should be able to - recognize evidence(s) of a chemical change - convert word equations into formula equations - perform
Recovery of Elemental Copper from Copper (II) Nitrate Objectives: Challenge: Students should be able to - recognize evidence(s) of a chemical change - convert word equations into formula equations - perform
Molecular Models Experiment #1
 Molecular Models Experiment #1 Objective: To become familiar with the 3-dimensional structure of organic molecules, especially the tetrahedral structure of alkyl carbon atoms and the planar structure of
Molecular Models Experiment #1 Objective: To become familiar with the 3-dimensional structure of organic molecules, especially the tetrahedral structure of alkyl carbon atoms and the planar structure of
Chapter Test A. States of Matter MULTIPLE CHOICE. a fixed amount of STAs2 a. a solid. b. a liquid. c. a gas. d. any type of matter.
 Assessment Chapter Test A States of Matter MULTIPLE CHOICE Write the letter of the correct answer in the space provided. 1. Boyle s law explains the relationship between volume and pressure for a fixed
Assessment Chapter Test A States of Matter MULTIPLE CHOICE Write the letter of the correct answer in the space provided. 1. Boyle s law explains the relationship between volume and pressure for a fixed
Apparatus error for each piece of equipment = 100 x margin of error quantity measured
 1) Error Analysis Apparatus Errors (uncertainty) Every time you make a measurement with a piece of apparatus, there is a small margin of error (i.e. uncertainty) in that measurement due to the apparatus
1) Error Analysis Apparatus Errors (uncertainty) Every time you make a measurement with a piece of apparatus, there is a small margin of error (i.e. uncertainty) in that measurement due to the apparatus
The Empirical Formula of a Compound
 The Empirical Formula of a Compound Lab #5 Introduction A look at the mass relationships in chemistry reveals little order or sense. The ratio of the masses of the elements in a compound, while constant,
The Empirical Formula of a Compound Lab #5 Introduction A look at the mass relationships in chemistry reveals little order or sense. The ratio of the masses of the elements in a compound, while constant,
MOLES, MOLECULES, FORMULAS. Part I: What Is a Mole And Why Are Chemists Interested in It?
 NAME PARTNERS SECTION DATE_ MOLES, MOLECULES, FORMULAS This activity is designed to introduce a convenient unit used by chemists and to illustrate uses of the unit. Part I: What Is a Mole And Why Are Chemists
NAME PARTNERS SECTION DATE_ MOLES, MOLECULES, FORMULAS This activity is designed to introduce a convenient unit used by chemists and to illustrate uses of the unit. Part I: What Is a Mole And Why Are Chemists
Chapter 2. The Chemistry of Life Worksheets
 Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Life Worksheets (Opening image courtesy of David Iberri, http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/file:camkii.png, and under the Creative Commons license CC-BY-SA 3.0.) Lesson 2.1: Matter
Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Life Worksheets (Opening image courtesy of David Iberri, http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/file:camkii.png, and under the Creative Commons license CC-BY-SA 3.0.) Lesson 2.1: Matter
hij GCSE Science / Chemistry Higher Tier Unit 1 Chemistry SPECIMEN MARK SCHEME Version 1.0
 hij GCSE Science / Chemistry Higher Tier Unit Chemistry SPECIMEN MARK SCHEME Version.0 Copyright 20 AQA and its licensors. All rights reserved. The Assessment and Qualifications Alliance (AQA) is a company
hij GCSE Science / Chemistry Higher Tier Unit Chemistry SPECIMEN MARK SCHEME Version.0 Copyright 20 AQA and its licensors. All rights reserved. The Assessment and Qualifications Alliance (AQA) is a company
H 3 C CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 3. Copyright 2012 Nelson Education Ltd. Chapter 1: Organic Compounds 1.1-1
 Section 1.1: Alkanes Mini Investigation: Arranging Carbon Atoms, page 10 A. Three different molecules of C 5 H 12 are possible. B. Five arrangements are possible for C 6 H 14, as predicted: H 3 C CH 2
Section 1.1: Alkanes Mini Investigation: Arranging Carbon Atoms, page 10 A. Three different molecules of C 5 H 12 are possible. B. Five arrangements are possible for C 6 H 14, as predicted: H 3 C CH 2
The most common active ingredient used in deodorants is aluminium chlorohydrate. But not all deodorants contain aluminium chlorohydrate:
 Engineeringfragrance make a deodorant practical activity 2 student instructions page 1 of 5 chemical compounds The most common active ingredient used in deodorants is aluminium chlorohydrate. But not all
Engineeringfragrance make a deodorant practical activity 2 student instructions page 1 of 5 chemical compounds The most common active ingredient used in deodorants is aluminium chlorohydrate. But not all
Assessment Schedule 2013 Chemistry: Demonstrate understanding of the properties of organic compounds (91391)
 NCEA Level 3 Chemistry (91391) 2013 page 1 of 8 Assessment Schedule 2013 Chemistry: Demonstrate understanding of the properties of organic compounds (91391) Evidence Statement Q Evidence Achievement Achievement
NCEA Level 3 Chemistry (91391) 2013 page 1 of 8 Assessment Schedule 2013 Chemistry: Demonstrate understanding of the properties of organic compounds (91391) Evidence Statement Q Evidence Achievement Achievement
YIELD YIELD REACTANTS PRODUCTS
 Balancing Chemical Equations A Chemical Equation: is a representation of a chemical reaction in terms of chemical formulas Example: 1. Word Description of a Chemical Reaction When methane gas (CH 4 ) burns
Balancing Chemical Equations A Chemical Equation: is a representation of a chemical reaction in terms of chemical formulas Example: 1. Word Description of a Chemical Reaction When methane gas (CH 4 ) burns
SCIENCE 20 UNIT A: CHEMICAL CHANGE DISTANCE LEARNING STUDENT GUIDE
 SCIENCE 20 UNIT A: CHEMICAL CHANGE DISTANCE LEARNING STUDENT GUIDE Science 20 Distance Learning Student Guide This document is intended for You may find the following Internet sites useful: Students Teachers
SCIENCE 20 UNIT A: CHEMICAL CHANGE DISTANCE LEARNING STUDENT GUIDE Science 20 Distance Learning Student Guide This document is intended for You may find the following Internet sites useful: Students Teachers
Experiment 8: Chemical Moles: Converting Baking Soda to Table Salt
 Experiment 8: Chemical Moles: Converting Baking Soda to Table Salt What is the purpose of this lab? We want to develop a model that shows in a simple way the relationship between the amounts of reactants
Experiment 8: Chemical Moles: Converting Baking Soda to Table Salt What is the purpose of this lab? We want to develop a model that shows in a simple way the relationship between the amounts of reactants
 Questions Q1. Lithium, sodium and potassium are metals in group 1 of the periodic table. They are good conductors of heat and electricity. The freshly-cut metals are shiny. (a) (i) Give another physical
Questions Q1. Lithium, sodium and potassium are metals in group 1 of the periodic table. They are good conductors of heat and electricity. The freshly-cut metals are shiny. (a) (i) Give another physical
