Performance Evaluation of a New CZT Detector for Nuclear Medicine: SOLSTICE
|
|
|
- Morgan Briggs
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Performance Evaluation of a New CZT Detector for Nuclear Medicine: SOLSTICE Jerome J Griesmer, Member, IEEE, Barry Kline, Member, IEEE, Joe Grosholz, Kevin Parnham, Daniel Gagnon, Member, IEEE Abstract - Solstice is a new concept of gamma camera designed to use the better energy resolution typically available in solid-state detectors. To that purpose, an array of 88 Cadmium Zinc Telluride (CdZnTe or CZT) crystals was characterized for gamma ray detection performance. The bias voltage was applied to the single electrode cathode side of the crystal (radiation side). The anode side of the individual crystals was further subdivided into 32 anodes connected to a charge sensitive preamplifier/shaper circuit for each pixel that provided a virtual ground potential for the anodes. Overall, the vast majority of pixels (85%) of pixels had an energy resolution (FWHM) better than 5% at 140 kev and an outstanding 3.6% FWHM at 140 kev was measured for the overall composite energy resolution over this large population of pixels. Results from the crystal characterization along with overall system performance are discussed. The imaging performance of the detector is covered in a separated paper at this conference [1]. I. INTRODUCTION The need for better energy resolution in gamma camera has been expressed since soon after its invention by Anger in While constant progress has been made in this respect, the future does not hold much hope of a significant improvement if the basic detection scheme is not changed. Solid-state detection devices, in particular the ones using CdZnTe (CZT), have been investigated for years without realizing any practical impact for imaging but seem now to offer a real possibility for practical and commercially affordable implementation. This paper describes the performance of a new CZT detector designed for nuclear medicine. It addresses strictly the electrical and physical performances; the imaging component being independently covered in a paper presented at this conference [1]. Several aspects of the development of a CZT detector will be covered. While a substantial amount of papers and information is available in the literature on the basic physics and signal processing of CZT, this paper clearly aims to address the significant engineering challenges that harnessing the power of semi-conductor detection represents. First, the major system components will be described. Second, a more detailed characterization of the CZT crystals/pixels within the system will be made and attempts to estimate global performance of the array in imaging conditions will be made. II. SYSTEM COMPONENTS The Solstice system (for SOLid STate Imager with Compact Electronics) can be decomposed in three major components. First, the CZT configuration itself in terms of dimension and pixelization, second, the analog processing and pre-amplification of the signal, and thirdly, the overall data flow and various additional corrections and compensation of the acquisition system. A. CZT Geometry The current study on CZT performance was made during the construction of the Solstice prototype. A total of 88 CZT crystals have been included in these tests and are believed to be representative of what the technology can deliver. The bias voltage was applied to the single electrode cathode side of the crystal. The anode side of the individual crystals was further subdivided into 32 anodes (pixels, see Figure 1) connected to an ASIC charge sensitive preamplifier-shaper circuit for each pixel that provided a virtual ground potential for the anodes. The improvement in energy resolution of CZT arrays by using sub-pixelation has been previously reported by others [3]. 1.5 mm 1.8 mm ~ 14.4 mm - J.J. Griesmer, B. Kline and, D.Gagnon are with Philips Medical Systems, Nuclear Medicine, 595 Miner Road, Cleveland, OH, J.Grosholz and K. Parnham are with ev-products, 373 Saxonburg Blvd, Saxonburg, PA, For correspondence, daniel.gagnon@ieee.org Figure 1. Pixel configuration and typical dimensions of the individual CZT crystals.
2 B. Pre-Amp Noise and System Noise The analog noise of the ASIC preamplifier circuit [2] is a critical design parameter. The specification for the device used was /pF electrons RMS. With a 2.8 pf pixel added, the resulting total would be 122 electrons RMS. For a gain of 0.2V/fC, and using 2.4 = FWHM*Vpk/VRMS and 2.06 fc/60 kev, we can predict a FWHM of 1.2% for a 116 kv equivalent pulse (equivalent value in kev of the test pulses that can be injected in the system for test and QC purposes). Actual measurements produced 1.7% FWHM for the ASIC, PCB and connector without crystal and 2.3% FWHM (235 electrons RMS) for the same test pulse with crystal. These are slightly higher than expected, but still under half of the 5% target system performance and introduces only an added 0.5% to the FWHM value (analog and quantum noise being added in quadrature). We also determined that one HV bias level would be used for all crystals in the array. Thus the crystal material and processing must be capable of producing pixels that behave within a limited range of properties. Another parameter that was evaluated was the threshold voltage used. We determined that the preamplifier ASICs offset voltage and noise were within a narrow enough range to allow a single comparator voltage to be used for all pixels. The required performance was to not trigger on the noise from the high gain, high offset pixels, while ensuring that the lowest gamma design energy would exceed the threshold for the lowest gain and lowest offset pixels. C. Basic Data Flow and Digital Path The Solstice camera is functionally segmented into subgroups of 64 pixels each. Each subgroup is treated as an independent section of the overall imaging detector. Within the subgroup, asynchronous analog pulses from the preamp/shaper ASICs compete for access to a single analog output port via a winner-takes-all arbitration circuit. Each successful pulse is multiplexed to a free-running analog-todigital converter (ADC). The data stream from the ADC is analyzed by digital peak-detection circuitry, and the energy measurement, along with the address of the winning pixel, are stored in a local FIFO memory for subsequent readout to a global acquisition memory. The peak-detection circuit, having determined the event s energy content and location, then releases the arbitration logic to accept another event. The data packets containing event energy and location from the 64-pixel subgroups are transferred via a global readout bus using a token-passing arbitration scheme. The architecture of the detector design packs four peak-detectors and one FIFO into a FPGA. The stored event data from each FIFO is placed on the readout bus as the token signal is received. A final FPGA packs the event data along with time stamps and other protocol for transmission to an image data acquisition computer. The projected rate capabilities of the Solstice detector are determined by the dead times associated with the independent 64-pixel subgroups. The primary contributors to that dead time are the time-to-peak for the shaped analog pulse, ADC pipeline delay, and the time required for the peak-detection and FIFO storage circuitry to operate. In the present design, this combined dead time is 1.7 usec per event. As the system incorporates no pileup rejection at the 64-pixel level, each subgroup follows a non-paralyzable throughput rate limitation of 118 kcps at the 20% loss point. Because each of the subgroups operates independently, the throughput rate will scale linearly with the number of subgroups. The current design is scalable; the projected throughput rate for the pixel prototype detector, comprising 48 such subgroups, should approach 5.6Mcps at the 20% loss point. In practice, the achievable rate is limited by the digital acquisition and framing hardware and software. The current prototype can run at 650 Kcps and will be increased to more than a 1 Mcps in the next revision. Figure 2 summarizes the basic functions and data flow. The extent of the processing of the digital signal before actually performing imaging (framing) is to apply an offset and gain to the energy signal and the application of a conventional uniformity correction to compensate for all remaining nonidealities of the detection system. Pixellated CZT Preamp Array 64 Winner- Takes-All Arbiter Next 64 Pixels Next 64 Pixels 64 Figure 2. Basic functions and data flow/data reduction in the Solstice camera. With the current architecture and dead time characteristics, several millions counts per second can be achieved with the detector without any loss in performance. III. CZT CHARACTERIZATION The performance evaluation of an imaging system is a complex task. We will review in this section some of the more explicit in the following comments. A. Temperature ADC Address Trigger Release ADC Address Trigger Release Peak Detect Latch Next Peak Detector Next Peak Detector Peak Detect Latch Early analysis of the heat dissipation from the ASIC and support parts showed significant problems. With close to 24mW per channel for the ASIC (46 mw per channel including the support chips) and the anticipation of several A r b i t e r / M u x Read FIFO Tri Drivers Token In Token Out Global Readout Bus
3 thousand channel required in a useful gamma camera (close to 3000 tested in this prototype), proper cooling of the array is essential. As is typical for semi-conductors, the leakage current has a high order positive relationship to temperature and excessive leakage current introduces additional analog noise that increases the energy resolution FWHM. An innovative daughter/mother board structure was devised to allow adequate cooling using only ambient air flow. The configuration allowed sufficient air flow across the ASIC limiting the temperature rise above inlet ambient to only 16 ºC on the ASIC package and only 6 to 8 ºC rise on the CZT crystals. This kept the leakage currents on the CZT crystals to a acceptable performance level. B. Bias Voltage After exposure to a uniform (line) source, spectrums of each individual pixel can be extracted and analyzed and additionally sub grouped as crystal averages and a global average can be calculated. The global average FWHM can also be measured directly by standard NEMA methods. The FWHM performance of the array to a variation of the cathode bias voltage was then studied. 1. Crystal Averages Graphs of the Figure 3 summarizes the findings for the crystal averages. Each curve show the measured average energy resolution per crystal, ranked from best to worst at the reference voltage. The order of the crystals is then maintained for all the subsequent curves. It is first interesting to note that while a general trend exists and seems to favor higher voltages, sensitivity to a variation in the high-voltage is high dependent on the crystal under consideration: Some crystals being essentially insensitive to the bias voltage, while others may double their energy resolution. A bias voltage of 420 V was finally implemented. 2. Individual Pixel Characteristics Global performance of the individual pixel (as measured by the energy resolution) showed interesting behavior. A detailed analysis of individual energy spectra showed some unexpected results. Families of pixels were created according the shape of the energy spectrum and to the response of the pixel to a variation of voltage. First, the vast majority of pixels was well behaved and had a classical energy spectrum. Energy resolutions as low as 2.7% were measured by the system. Figure 4 shows a typical pixel with an energy resolution of 3.6% FWHM for 57 Co (same as the composite average for the whole array). Crystal avg. FWHM vs. Cathode HV Figure 4. Energy spectrum for pixel 72x measured at 3.65% FWHM for 57 Co Rank 420V Figure 3. Energy resolution of individual crystal as a function of the applied voltage on the cathode. Ranking of crystals has been obtained at 420 V and maintained for all the other curves, Vertical axis in FWHM of energy resolution x 10. At 420 V the average of ALL crystals is below 6% In the following series of pairs of spectrum, we are illustrating the different pixel behavior. The lower voltage, 275 V, is on the left, the higher voltage, 420 V, is on the right. Comments are below each pair. Since the unusual response pixels are adjacent to "typical" response pixels, this may be attributed to the effects of local crystal structure variations. Similar effects have been reported by others [4, 5]. The challenge for the CZT supplier is to provide crystals with fewer defect areas within each crystal. Substantial improvements have been achieved since the first devices tested. It is also a characteristic of the Solstice imaging device that defective pixels do not produce any effect on the resultant image quality. The result of a dead pixel is only a small reduction in sensitivity. This has significant impact on the cost implications for crystal production.
4 Pixel #546, Typical. ~89% of all pixels. Overall shift and broadening of the peak at low bias Pixel #670. Unusable. 0.1% of all pixels. Overall shift and broadening of the peak at low bias Overall, pixels with split spectrum, double peaks or otherwise non-standard shape represented less than 1% of all the pixels. Additional tests performed by swapping crystal positions in the array confirm that the dominant response is the CZT crystal itself and the analog and digital noise contributions are minimal. Pixel #424, Improvement at low bias. ~5% of all pixels. Overall shift and narrowing of the peak at low bias Pixel #3f6. Split Peak at low bias. ~5% of all pixels. Overall shift and broadening of the peak at low bias Pixel #8f3. Split Peak at low and high bias. 0.5% of all pixels. Overall shift and broadening of the peak at low bias IV. DISCUSSION We have demonstrated in part II of this paper that the overall system surrounding the CZT, more specifically the ASIC preamp, the data flow and data arbitration, the conversion to digital and the application of the various corrections, is well under control and that we indeed measuring the performance of the CZT itself. This point is critically important as, contrary to other gamma ray detection schemes, detection material AND processing electronics are very intimately related. All the steps leading to forming a spectrum such as the one presented in Figure 4 for several thousand pixels, at close to half a million counts per second, AND maintaining 3.6% overall energy resolution is a strong indicator of the quality of the system. It also means that our observations on the different behavior of crystals and/or pixel are valid and do constitute a good basis for a more thorough analysis. Questions like: is a global threshold for the triggering system possible and adequate, what is the performance penalty in setting a global voltage for all the crystals, what is influencing the baseline for each individual channel, effect of temperature on the performance of the CZT and on the ASIC? All these questions will have a direct influence on the complexity (and cost) of any larger scale utilization of CZT in a gamma camera. In addition, having produced some of the results very early in the development of the prototype, refinements in the process of building and testing the crystals have been identified and will be part of the next iteration of device. In particular the process improvement identified in the construction of the crystal modules, that need to be easily removable for servicing, should bring better quality. Similarly, we have experienced reliability issues with the construction of the ASICs that have since then been identified, corrected and fully tested. Pixel #573. Double peak. 0.04% of all pixels. Overall shift and broadening of the peak at low bias
5 V. CONCLUSION It is believed that the results presented in this paper are among the best ever published for a large number of CZT crystals/pixels at room temperature. This is obviously a very important element in making the decision to build gamma camera based on CZT, but more is required. We have explored several aspects of the required surrounding technology and the results obtained so far indicate that the current combination of CZT-ASIC-Data Reduction is very flexible, scalable and would lend itself efficiently to a commercial implementation. VI. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS The authors would like to thank the members of the engineering team, Austin Bowen, Bob Davis, Eric Dillen, Harry Smith and Steve Vydrin from ev-products, and Pat Bender, Kevin Mantey, Kevin McMahon, Jason Radachy and Bob Zahn at Philips Medical Systems. VI. REFERENCES [1] GL.Zeng, D. Gagnon, CG. Matthews, JA. Kolthammer, JD. Radachy Image Reconstruction Algorithm for Rotating Slat Collimator IEEE MIC 2001, San Diego, Nov [2] DeGeronimo G, O Connor, Grosholz J. A Generation of CMOS Readout ASICx for CZT Detectors, Proc of IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium, Seatle, WA, Nov [3] Eskin JD. Et al. The Effect of Pixel Geometry on Spatial and Spectral Resolution of CdZnTe Imaging Array, Proc. of IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium, pp , San Francisco, CA, Oct [4] Amman M, et al. CdZnTe Material Uniformity and Coplanar-Grid Gamma-Ray Detector Performance, IEEE Trans Nucl. Sci.,vol 47, no 3, June [5] Brunnett BA, The Performance Effect of Crystal Boundaries in Cadmium Zinc Telluride Radiation Spectrometers. IEEE Trans Nucl. Sci.,vol 47, no 4, Aug. 2000
Nuclear Weapons and Material Security (WMS) Team Program Review WMS2013
 Office of Research & Development Nuclear Weapons and Material Security (WMS) Team Program Review WMS2013 Array of Virtual Frisch-Grid CZT Detectors with Common Cathode Readout for Correcting Charge Trapping
Office of Research & Development Nuclear Weapons and Material Security (WMS) Team Program Review WMS2013 Array of Virtual Frisch-Grid CZT Detectors with Common Cathode Readout for Correcting Charge Trapping
How To Make Hard Xray Pixel Detectors For Hard X-Ray Astrophysics
 Development of Focal Plane Detectors for the Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) Mission Vikram R. Rana a, Walter R. Cook III a, Fiona A. Harrison a, Peter H. Mao a, Hiromasa Miyasaka a a Space
Development of Focal Plane Detectors for the Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) Mission Vikram R. Rana a, Walter R. Cook III a, Fiona A. Harrison a, Peter H. Mao a, Hiromasa Miyasaka a a Space
SPADIC: CBM TRD Readout ASIC
 SPADIC: CBM TRD Readout ASIC Tim Armbruster tim.armbruster@ziti.uni-heidelberg.de HIC for FAIR, Darmstadt Schaltungstechnik Schaltungstechnik und und February 2011 Visit http://spadic.uni-hd.de 1. Introduction
SPADIC: CBM TRD Readout ASIC Tim Armbruster tim.armbruster@ziti.uni-heidelberg.de HIC for FAIR, Darmstadt Schaltungstechnik Schaltungstechnik und und February 2011 Visit http://spadic.uni-hd.de 1. Introduction
S2000 Spectrometer Data Sheet
 Description The Ocean Optics OEM S2000 Spectrometer includes the linear CCD-array optical bench, plus the circuits necessary for spectrometer operation. The result is a compact, flexible system with no
Description The Ocean Optics OEM S2000 Spectrometer includes the linear CCD-array optical bench, plus the circuits necessary for spectrometer operation. The result is a compact, flexible system with no
Electronics GRETINA Project
 Electronics GRETINA Project Requirement Document Sergio Zimmermann July 24, 2004 ANL Electronics Workshop, Schedule 1 Outline Doc Data Base Justification Document types Functional requirements List of
Electronics GRETINA Project Requirement Document Sergio Zimmermann July 24, 2004 ANL Electronics Workshop, Schedule 1 Outline Doc Data Base Justification Document types Functional requirements List of
RF Measurements Using a Modular Digitizer
 RF Measurements Using a Modular Digitizer Modern modular digitizers, like the Spectrum M4i series PCIe digitizers, offer greater bandwidth and higher resolution at any given bandwidth than ever before.
RF Measurements Using a Modular Digitizer Modern modular digitizers, like the Spectrum M4i series PCIe digitizers, offer greater bandwidth and higher resolution at any given bandwidth than ever before.
Characteristics of an Integrated Germanium Detector Based Gamma-Ray Spectrometer for Monitoring Systems
 Characteristics of an Integrated Germanium Detector Based Gamma-Ray Spectrometer for Monitoring Systems Ronald M. Keyser, Timothy R. Twomey, Sam Hitch ORTEC 801 South Illinois Avenue Oak Ridge, TN, 37831
Characteristics of an Integrated Germanium Detector Based Gamma-Ray Spectrometer for Monitoring Systems Ronald M. Keyser, Timothy R. Twomey, Sam Hitch ORTEC 801 South Illinois Avenue Oak Ridge, TN, 37831
Activitity (of a radioisotope): The number of nuclei in a sample undergoing radioactive decay in each second. It is commonly expressed in curies
 Activitity (of a radioisotope): The number of nuclei in a sample undergoing radioactive decay in each second. It is commonly expressed in curies (Ci), where 1 Ci = 3.7x10 10 disintegrations per second.
Activitity (of a radioisotope): The number of nuclei in a sample undergoing radioactive decay in each second. It is commonly expressed in curies (Ci), where 1 Ci = 3.7x10 10 disintegrations per second.
Status of CBM-XYTER Development
 Status of CBM-XYTER Development Latest Results of the CSA/ADC Test-Chip Tim Armbruster tim.armbruster@ziti.uni-heidelberg.de Heidelberg University Schaltungstechnik Schaltungstechnik und und 14th CBM CM
Status of CBM-XYTER Development Latest Results of the CSA/ADC Test-Chip Tim Armbruster tim.armbruster@ziti.uni-heidelberg.de Heidelberg University Schaltungstechnik Schaltungstechnik und und 14th CBM CM
X- and Gamma Ray Imaging Systems based on CdTe-CMOS Detector Technology
 X- and Gamma Ray Imaging Systems based on dte-mos Detector Technology Konstantinos Spartiotis, Ray Durrant, nssi Leppänen, Henrik Lohman, Olli Männistö, Tuomas Pantsar, Jouni Pyyhtiä, Tom Schulman, Oy
X- and Gamma Ray Imaging Systems based on dte-mos Detector Technology Konstantinos Spartiotis, Ray Durrant, nssi Leppänen, Henrik Lohman, Olli Männistö, Tuomas Pantsar, Jouni Pyyhtiä, Tom Schulman, Oy
PLAS: Analog memory ASIC Conceptual design & development status
 PLAS: Analog memory ASIC Conceptual design & development status Ramón J. Aliaga Instituto de Física Corpuscular (IFIC) Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas (CSIC) Universidad de Valencia Vicente
PLAS: Analog memory ASIC Conceptual design & development status Ramón J. Aliaga Instituto de Física Corpuscular (IFIC) Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas (CSIC) Universidad de Valencia Vicente
Discontinued. LUXEON V Portable. power light source. Introduction
 Preliminary Technical Datasheet DS40 power light source LUXEON V Portable Introduction LUXEON is a revolutionary, energy efficient and ultra compact new light source, combining the lifetime and reliability
Preliminary Technical Datasheet DS40 power light source LUXEON V Portable Introduction LUXEON is a revolutionary, energy efficient and ultra compact new light source, combining the lifetime and reliability
IEC 1000-4-2 ESD Immunity and Transient Current Capability for the SP72X Series Protection Arrays
 IEC 00-4-2 ESD Immunity and Transient Current Capability for the SP72X Series Protection Arrays Application Note July 1999 AN9612.2 Author: Wayne Austin The SP720, SP721, SP723, and SP724 are protection
IEC 00-4-2 ESD Immunity and Transient Current Capability for the SP72X Series Protection Arrays Application Note July 1999 AN9612.2 Author: Wayne Austin The SP720, SP721, SP723, and SP724 are protection
NTE2053 Integrated Circuit 8 Bit MPU Compatible A/D Converter
 NTE2053 Integrated Circuit 8 Bit MPU Compatible A/D Converter Description: The NTE2053 is a CMOS 8 bit successive approximation Analog to Digital converter in a 20 Lead DIP type package which uses a differential
NTE2053 Integrated Circuit 8 Bit MPU Compatible A/D Converter Description: The NTE2053 is a CMOS 8 bit successive approximation Analog to Digital converter in a 20 Lead DIP type package which uses a differential
Microcontroller-based experiments for a control systems course in electrical engineering technology
 Microcontroller-based experiments for a control systems course in electrical engineering technology Albert Lozano-Nieto Penn State University, Wilkes-Barre Campus, Lehman, PA, USA E-mail: AXL17@psu.edu
Microcontroller-based experiments for a control systems course in electrical engineering technology Albert Lozano-Nieto Penn State University, Wilkes-Barre Campus, Lehman, PA, USA E-mail: AXL17@psu.edu
LTC1390 8-Channel Analog Multiplexer with Serial Interface U DESCRIPTIO
 FEATRES -Wire Serial Digital Interface Data Retransmission Allows Series Connection with Serial A/D Converters Single V to ±V Supply Operation Analog Inputs May Extend to Supply Rails Low Charge Injection
FEATRES -Wire Serial Digital Interface Data Retransmission Allows Series Connection with Serial A/D Converters Single V to ±V Supply Operation Analog Inputs May Extend to Supply Rails Low Charge Injection
Basler. Line Scan Cameras
 Basler Line Scan Cameras High-quality line scan technology meets a cost-effective GigE interface Real color support in a compact housing size Shading correction compensates for difficult lighting conditions
Basler Line Scan Cameras High-quality line scan technology meets a cost-effective GigE interface Real color support in a compact housing size Shading correction compensates for difficult lighting conditions
Truly digital PET imaging
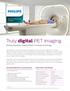 Advanced Molecular Imaging Vereos PET/CT Truly digital PET imaging Philips proprietary Digital Photon Counting technology Vereos PET/CT is the first commercially available scanner to offer truly digital
Advanced Molecular Imaging Vereos PET/CT Truly digital PET imaging Philips proprietary Digital Photon Counting technology Vereos PET/CT is the first commercially available scanner to offer truly digital
Establishing Great Software Development Process(es) for Your Organization. By Dale Mayes DMayes@HomePortEngineering.com
 Establishing Great Software Development Process(es) for Your Organization By Dale Mayes DMayes@HomePortEngineering.com Class: ETP-410 Embedded Systems Conference San Francisco 2005 Abstract: There are
Establishing Great Software Development Process(es) for Your Organization By Dale Mayes DMayes@HomePortEngineering.com Class: ETP-410 Embedded Systems Conference San Francisco 2005 Abstract: There are
Spike-Based Sensing and Processing: What are spikes good for? John G. Harris Electrical and Computer Engineering Dept
 Spike-Based Sensing and Processing: What are spikes good for? John G. Harris Electrical and Computer Engineering Dept ONR NEURO-SILICON WORKSHOP, AUG 1-2, 2006 Take Home Messages Introduce integrate-and-fire
Spike-Based Sensing and Processing: What are spikes good for? John G. Harris Electrical and Computer Engineering Dept ONR NEURO-SILICON WORKSHOP, AUG 1-2, 2006 Take Home Messages Introduce integrate-and-fire
Truly digital PET imaging
 Truly digital PET imaging Philips proprietary Digital Photon Counting technology Vereos PET/CT is the first commercially available scanner to offer truly digital PET, resulting in significantly improved
Truly digital PET imaging Philips proprietary Digital Photon Counting technology Vereos PET/CT is the first commercially available scanner to offer truly digital PET, resulting in significantly improved
A Laser Scanner Chip Set for Accurate Perception Systems
 A Laser Scanner Chip Set for Accurate Perception Systems 313 A Laser Scanner Chip Set for Accurate Perception Systems S. Kurtti, J.-P. Jansson, J. Kostamovaara, University of Oulu Abstract This paper presents
A Laser Scanner Chip Set for Accurate Perception Systems 313 A Laser Scanner Chip Set for Accurate Perception Systems S. Kurtti, J.-P. Jansson, J. Kostamovaara, University of Oulu Abstract This paper presents
An Innovative, portable MCA based on Digital Signal Processing. R.D. Bingham, R.M. Keyser, T.R. Twomey
 An Innovative, portable MCA based on Digital Signal Processing R.D. Bingham, R.M. Keyser, T.R. Twomey ORTEC, PerkinElmer Instruments, Inc Oak Ridge TN 37831-0895 USA Abstract Digital Signal Processing
An Innovative, portable MCA based on Digital Signal Processing R.D. Bingham, R.M. Keyser, T.R. Twomey ORTEC, PerkinElmer Instruments, Inc Oak Ridge TN 37831-0895 USA Abstract Digital Signal Processing
Algorithms for digital γ-ray spectroscopy
 NUKLEONIKA 2013;58(2):333 338 ORIGINAL PAPER Algorithms for digital γ-ray spectroscopy Zbigniew Guik, Tomas Krakowski Abstract. The data processing in modern nuclear spectroscopy is dominated by digital
NUKLEONIKA 2013;58(2):333 338 ORIGINAL PAPER Algorithms for digital γ-ray spectroscopy Zbigniew Guik, Tomas Krakowski Abstract. The data processing in modern nuclear spectroscopy is dominated by digital
A 10,000 Frames/s 0.18 µm CMOS Digital Pixel Sensor with Pixel-Level Memory
 Presented at the 2001 International Solid State Circuits Conference February 5, 2001 A 10,000 Frames/s 0.1 µm CMOS Digital Pixel Sensor with Pixel-Level Memory Stuart Kleinfelder, SukHwan Lim, Xinqiao
Presented at the 2001 International Solid State Circuits Conference February 5, 2001 A 10,000 Frames/s 0.1 µm CMOS Digital Pixel Sensor with Pixel-Level Memory Stuart Kleinfelder, SukHwan Lim, Xinqiao
PoS(PhotoDet 2012)068
 Characterization of the Hamamatsu R11265 multi-anode photomultiplier tube with single photon signals Luca CADAMURO, Marta CALVI, Andrea GIACHERO,, Matteo MAINO, Clara MATTEUZZI, Gianluigi PESSINA Dipartimento
Characterization of the Hamamatsu R11265 multi-anode photomultiplier tube with single photon signals Luca CADAMURO, Marta CALVI, Andrea GIACHERO,, Matteo MAINO, Clara MATTEUZZI, Gianluigi PESSINA Dipartimento
GRETA. I-Yang Lee. For the GRETA Steering Committee. Workshop on the Experimental Equipment for RIA March 18-22, 2003, Oak Ridge, Tennessee
 GRETA I-Yang Lee For the GRETA Steering Committee Workshop on the Experimental Equipment for RIA March 18-22, 2003, Oak Ridge, Tennessee Gamma-ray Tracking Concepts Compton Suppressed Ge Veto Ν det = 100
GRETA I-Yang Lee For the GRETA Steering Committee Workshop on the Experimental Equipment for RIA March 18-22, 2003, Oak Ridge, Tennessee Gamma-ray Tracking Concepts Compton Suppressed Ge Veto Ν det = 100
Applications: X-ray Microtomography, Streak Tube and CRT Readout, Industrial & Medical Imaging X-RAY GROUP
 Now Powered by LightField FEATURES BENEFITS Back Illuminated CCD (248B) For highest sensitivity Front illuminated CCD (248F) Affordable technology for moderate light level applications Ultra low noise
Now Powered by LightField FEATURES BENEFITS Back Illuminated CCD (248B) For highest sensitivity Front illuminated CCD (248F) Affordable technology for moderate light level applications Ultra low noise
ATLAS Tile Calorimeter Readout Electronics Upgrade Program for the High Luminosity LHC
 ATLAS Tile Calorimeter Readout Electronics Upgrade Program for the High Luminosity LHC Augusto Santiago Cerqueira On behalf of the ATLAS Tile Calorimeter Group Federal University of Juiz de Fora, Brazil
ATLAS Tile Calorimeter Readout Electronics Upgrade Program for the High Luminosity LHC Augusto Santiago Cerqueira On behalf of the ATLAS Tile Calorimeter Group Federal University of Juiz de Fora, Brazil
Architectural Level Power Consumption of Network on Chip. Presenter: YUAN Zheng
 Architectural Level Power Consumption of Network Presenter: YUAN Zheng Why Architectural Low Power Design? High-speed and large volume communication among different parts on a chip Problem: Power consumption
Architectural Level Power Consumption of Network Presenter: YUAN Zheng Why Architectural Low Power Design? High-speed and large volume communication among different parts on a chip Problem: Power consumption
PRECISION CAPACITOR CHARGING SWITCHING POWER SUPPLIES
 GENERAL ATOMICS ENERGY PRODUCTS Engineering Bulletin PRECISION CAPACITOR CHARGING SWITCHING POWER SUPPLIES Joe Jichetti, Andrew Bushnell, Robert McDowell Presented at: IEEE Pulsed Power Conference June
GENERAL ATOMICS ENERGY PRODUCTS Engineering Bulletin PRECISION CAPACITOR CHARGING SWITCHING POWER SUPPLIES Joe Jichetti, Andrew Bushnell, Robert McDowell Presented at: IEEE Pulsed Power Conference June
Reconfigurable System-on-Chip Design
 Reconfigurable System-on-Chip Design MITCHELL MYJAK Senior Research Engineer Pacific Northwest National Laboratory PNNL-SA-93202 31 January 2013 1 About Me Biography BSEE, University of Portland, 2002
Reconfigurable System-on-Chip Design MITCHELL MYJAK Senior Research Engineer Pacific Northwest National Laboratory PNNL-SA-93202 31 January 2013 1 About Me Biography BSEE, University of Portland, 2002
Design of Prototype Scientific CMOS Image Sensors
 PRE-PRINT: SPIE Astronomical Telescopes and Instrumentation, 23-28 June 2008, Marseille, France Paper #7021-2 to be published in Proceedings of SPIE Vol. 7021 Design of Prototype Scientific CMOS Image
PRE-PRINT: SPIE Astronomical Telescopes and Instrumentation, 23-28 June 2008, Marseille, France Paper #7021-2 to be published in Proceedings of SPIE Vol. 7021 Design of Prototype Scientific CMOS Image
Overview of the GRETINA Auxiliary Detector Interface
 28 Jan 2006 Aux.Det.Wkshp 1 Overview of the GRETINA Auxiliary Detector Interface David Radford ORNL Auxiliary Detectors Workshop Washington Universtity 28 Jan 2006 28 Jan 2006 Aux.Det.Wkshp 2 Outline The
28 Jan 2006 Aux.Det.Wkshp 1 Overview of the GRETINA Auxiliary Detector Interface David Radford ORNL Auxiliary Detectors Workshop Washington Universtity 28 Jan 2006 28 Jan 2006 Aux.Det.Wkshp 2 Outline The
Conversion Between Analog and Digital Signals
 ELET 3156 DL - Laboratory #6 Conversion Between Analog and Digital Signals There is no pre-lab work required for this experiment. However, be sure to read through the assignment completely prior to starting
ELET 3156 DL - Laboratory #6 Conversion Between Analog and Digital Signals There is no pre-lab work required for this experiment. However, be sure to read through the assignment completely prior to starting
A Survey of Video Processing with Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FGPA)
 A Survey of Video Processing with Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FGPA) Heather Garnell Abstract This paper is a high-level, survey of recent developments in the area of video processing using reconfigurable
A Survey of Video Processing with Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FGPA) Heather Garnell Abstract This paper is a high-level, survey of recent developments in the area of video processing using reconfigurable
High-Speed, 5 V, 0.1 F CMOS RS-232 Driver/Receivers ADM202/ADM203
 a FEATURES kb Transmission Rate ADM: Small (. F) Charge Pump Capacitors ADM3: No External Capacitors Required Single V Power Supply Meets EIA-3-E and V. Specifications Two Drivers and Two Receivers On-Board
a FEATURES kb Transmission Rate ADM: Small (. F) Charge Pump Capacitors ADM3: No External Capacitors Required Single V Power Supply Meets EIA-3-E and V. Specifications Two Drivers and Two Receivers On-Board
Remote RadEye Product Family
 Remote RadEye Product Family Overview The Remote RadEye x-ray camera provides the ultimate flexibility in design and product options for your complex imaging applications. Our unique camera design separates
Remote RadEye Product Family Overview The Remote RadEye x-ray camera provides the ultimate flexibility in design and product options for your complex imaging applications. Our unique camera design separates
Timing Errors and Jitter
 Timing Errors and Jitter Background Mike Story In a sampled (digital) system, samples have to be accurate in level and time. The digital system uses the two bits of information the signal was this big
Timing Errors and Jitter Background Mike Story In a sampled (digital) system, samples have to be accurate in level and time. The digital system uses the two bits of information the signal was this big
PowerAmp Design. PowerAmp Design PAD135 COMPACT HIGH VOLATGE OP AMP
 PowerAmp Design COMPACT HIGH VOLTAGE OP AMP Rev G KEY FEATURES LOW COST SMALL SIZE 40mm SQUARE HIGH VOLTAGE 200 VOLTS HIGH OUTPUT CURRENT 10A PEAK 40 WATT DISSIPATION CAPABILITY 200V/µS SLEW RATE APPLICATIONS
PowerAmp Design COMPACT HIGH VOLTAGE OP AMP Rev G KEY FEATURES LOW COST SMALL SIZE 40mm SQUARE HIGH VOLTAGE 200 VOLTS HIGH OUTPUT CURRENT 10A PEAK 40 WATT DISSIPATION CAPABILITY 200V/µS SLEW RATE APPLICATIONS
White paper. CCD and CMOS sensor technology Technical white paper
 White paper CCD and CMOS sensor technology Technical white paper Table of contents 1. Introduction to image sensors 3 2. CCD technology 4 3. CMOS technology 5 4. HDTV and megapixel sensors 6 5. Main differences
White paper CCD and CMOS sensor technology Technical white paper Table of contents 1. Introduction to image sensors 3 2. CCD technology 4 3. CMOS technology 5 4. HDTV and megapixel sensors 6 5. Main differences
Design of analog-to-digital converters for energy-sensitive hybrid pixel detectors
 Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 466 (2001) 218 225 Design of analog-to-digital converters for energy-sensitive hybrid pixel detectors David San Segundo Bello a,b, *, Bram Nauta b,
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 466 (2001) 218 225 Design of analog-to-digital converters for energy-sensitive hybrid pixel detectors David San Segundo Bello a,b, *, Bram Nauta b,
14.5GHZ 2.2KW CW GENERATOR. GKP 22KP 14.5GHz WR62 3x400V
 14.5GHZ 2.2KW CW GENERATOR GKP 22KP 14.5GHz WR62 3x400V UTILIZATION OF GKP 22KP GENERATOR With its characteristics of power stability whatever the load, very fast response time at a pulse, low ripple,
14.5GHZ 2.2KW CW GENERATOR GKP 22KP 14.5GHz WR62 3x400V UTILIZATION OF GKP 22KP GENERATOR With its characteristics of power stability whatever the load, very fast response time at a pulse, low ripple,
LASP Electrical Engineer Group Capabilities
 LASP Electrical Engineer Group Capabilities Neil White Phone: 303-492-7959 Email: neil.white@lasp.colorado.edu The 29 th annual National Space Symposium April 8-12 Planetary Science Space Physics Solar
LASP Electrical Engineer Group Capabilities Neil White Phone: 303-492-7959 Email: neil.white@lasp.colorado.edu The 29 th annual National Space Symposium April 8-12 Planetary Science Space Physics Solar
MONOCHROME RGB YCbCr VIDEO DIGITIZER
 Active Silicon SNAPPER-PMC-8/24 MONOCHROME RGB YCbCr VIDEO DIGITIZER High quality analogue video acquisition board with square pixel sampling for CCIR, EIA (RS-170) standards, and nonstandard video formats.
Active Silicon SNAPPER-PMC-8/24 MONOCHROME RGB YCbCr VIDEO DIGITIZER High quality analogue video acquisition board with square pixel sampling for CCIR, EIA (RS-170) standards, and nonstandard video formats.
Silicon Seminar. Optolinks and Off Detector Electronics in ATLAS Pixel Detector
 Silicon Seminar Optolinks and Off Detector Electronics in ATLAS Pixel Detector Overview Requirements The architecture of the optical links for the ATLAS pixel detector ROD BOC Optoboard Requirements of
Silicon Seminar Optolinks and Off Detector Electronics in ATLAS Pixel Detector Overview Requirements The architecture of the optical links for the ATLAS pixel detector ROD BOC Optoboard Requirements of
Performance Analysis of Storage Area Network Switches
 Performance Analysis of Storage Area Network Switches Andrea Bianco, Paolo Giaccone, Enrico Maria Giraudo, Fabio Neri, Enrico Schiattarella Dipartimento di Elettronica - Politecnico di Torino - Italy e-mail:
Performance Analysis of Storage Area Network Switches Andrea Bianco, Paolo Giaccone, Enrico Maria Giraudo, Fabio Neri, Enrico Schiattarella Dipartimento di Elettronica - Politecnico di Torino - Italy e-mail:
A Digital Spectrometer Approach to Obtaining Multiple Time-Resolved Gamma-Ray. Spectra for Pulsed Spectroscopy. W. K. Warburton a
 1 IRRMA6 #21 A Digital Spectrometer Approach to Obtaining Multiple Time-Resolved Gamma-Ray Spectra for Pulsed Spectroscopy H. Tan a,, S. Mitra b, A. Fallu-Labruyere a, W. Hennig a, Y. X. Chu a, L. Wielopolski
1 IRRMA6 #21 A Digital Spectrometer Approach to Obtaining Multiple Time-Resolved Gamma-Ray Spectra for Pulsed Spectroscopy H. Tan a,, S. Mitra b, A. Fallu-Labruyere a, W. Hennig a, Y. X. Chu a, L. Wielopolski
Achieving New Levels of Channel Density in Downstream Cable Transmitter Systems: RF DACs Deliver Smaller Size and Lower Power Consumption
 Achieving New Levels of Channel Density in Downstream Cable Transmitter Systems: RF DACs Deliver Smaller Size and Lower Power Consumption Introduction By: Analog Devices, Inc. (ADI) Daniel E. Fague, Applications
Achieving New Levels of Channel Density in Downstream Cable Transmitter Systems: RF DACs Deliver Smaller Size and Lower Power Consumption Introduction By: Analog Devices, Inc. (ADI) Daniel E. Fague, Applications
Performance Comparison of an Algorithmic Current- Mode ADC Implemented using Different Current Comparators
 Performance Comparison of an Algorithmic Current- Mode ADC Implemented using Different Current Comparators Veepsa Bhatia Indira Gandhi Delhi Technical University for Women Delhi, India Neeta Pandey Delhi
Performance Comparison of an Algorithmic Current- Mode ADC Implemented using Different Current Comparators Veepsa Bhatia Indira Gandhi Delhi Technical University for Women Delhi, India Neeta Pandey Delhi
Tube Liquid Sensor OPB350 / OCB350 Series
 Features: Can identify if liquid is present in clear tubes that have an outside diameter of 1/16 [1.6mm], 1/8" [3.2mm], 3/16" [4.8 mm] or 1/4" [6.3 mm] Opaque plastic housing enhances ambient light rejection
Features: Can identify if liquid is present in clear tubes that have an outside diameter of 1/16 [1.6mm], 1/8" [3.2mm], 3/16" [4.8 mm] or 1/4" [6.3 mm] Opaque plastic housing enhances ambient light rejection
LED DIMMING A HELPFUL GUIDE...
 LED DIMMING A HELPFUL GUIDE... Introduction There are five types of dimming control interfaces described in this document: 2-Wire Forward Phase, 2-Wire Reverse Phase, 3-Wire (Lutron), 4-Wire (0 10V), and
LED DIMMING A HELPFUL GUIDE... Introduction There are five types of dimming control interfaces described in this document: 2-Wire Forward Phase, 2-Wire Reverse Phase, 3-Wire (Lutron), 4-Wire (0 10V), and
Hexadecimal and Numeric Indicators. Technical Data 5082-7300 5082-7302 5082-7304 5082-7340
 H Hexadecimal and Numeric Indicators Technical Data 5082-7300 5082-7302 5082-7304 5082-7340 Features Numeric 5082-7300/-7302 0-9, Test State, Minus Sign, Blank States Decimal Point 7300 Right Hand D.P.
H Hexadecimal and Numeric Indicators Technical Data 5082-7300 5082-7302 5082-7304 5082-7340 Features Numeric 5082-7300/-7302 0-9, Test State, Minus Sign, Blank States Decimal Point 7300 Right Hand D.P.
A receiver TDC chip set for accurate pulsed time-of-flight laser ranging
 A receiver TDC chip set for accurate pulsed time-of-flight laser ranging Juha Kostamovaara, Sami Kurtti, Jussi-Pekka Jansson University of Oulu, Department of Electrical Engineering, Electronics Laboratory,
A receiver TDC chip set for accurate pulsed time-of-flight laser ranging Juha Kostamovaara, Sami Kurtti, Jussi-Pekka Jansson University of Oulu, Department of Electrical Engineering, Electronics Laboratory,
The accurate calibration of all detectors is crucial for the subsequent data
 Chapter 4 Calibration The accurate calibration of all detectors is crucial for the subsequent data analysis. The stability of the gain and offset for energy and time calibration of all detectors involved
Chapter 4 Calibration The accurate calibration of all detectors is crucial for the subsequent data analysis. The stability of the gain and offset for energy and time calibration of all detectors involved
A 1-GSPS CMOS Flash A/D Converter for System-on-Chip Applications
 A -GSPS CMOS Flash A/D Converter for System-on-Chip Applications Jincheol Yoo, Kyusun Choi, and Ali Tangel Department of Computer Science & Department of Computer & Engineering Communications Engineering
A -GSPS CMOS Flash A/D Converter for System-on-Chip Applications Jincheol Yoo, Kyusun Choi, and Ali Tangel Department of Computer Science & Department of Computer & Engineering Communications Engineering
DEVELOPMENT OF DEVICES AND METHODS FOR PHASE AND AC LINEARITY MEASUREMENTS IN DIGITIZERS
 DEVELOPMENT OF DEVICES AND METHODS FOR PHASE AND AC LINEARITY MEASUREMENTS IN DIGITIZERS U. Pogliano, B. Trinchera, G.C. Bosco and D. Serazio INRIM Istituto Nazionale di Ricerca Metrologica Torino (Italia)
DEVELOPMENT OF DEVICES AND METHODS FOR PHASE AND AC LINEARITY MEASUREMENTS IN DIGITIZERS U. Pogliano, B. Trinchera, G.C. Bosco and D. Serazio INRIM Istituto Nazionale di Ricerca Metrologica Torino (Italia)
1. Oscilloscope is basically a graph-displaying device-it draws a graph of an electrical signal.
 CHAPTER 3: OSCILLOSCOPE AND SIGNAL GENERATOR 3.1 Introduction to oscilloscope 1. Oscilloscope is basically a graph-displaying device-it draws a graph of an electrical signal. 2. The graph show signal change
CHAPTER 3: OSCILLOSCOPE AND SIGNAL GENERATOR 3.1 Introduction to oscilloscope 1. Oscilloscope is basically a graph-displaying device-it draws a graph of an electrical signal. 2. The graph show signal change
Switch Fabric Implementation Using Shared Memory
 Order this document by /D Switch Fabric Implementation Using Shared Memory Prepared by: Lakshmi Mandyam and B. Kinney INTRODUCTION Whether it be for the World Wide Web or for an intra office network, today
Order this document by /D Switch Fabric Implementation Using Shared Memory Prepared by: Lakshmi Mandyam and B. Kinney INTRODUCTION Whether it be for the World Wide Web or for an intra office network, today
Computer Network. Interconnected collection of autonomous computers that are able to exchange information
 Introduction Computer Network. Interconnected collection of autonomous computers that are able to exchange information No master/slave relationship between the computers in the network Data Communications.
Introduction Computer Network. Interconnected collection of autonomous computers that are able to exchange information No master/slave relationship between the computers in the network Data Communications.
High Resolution Spatial Electroluminescence Imaging of Photovoltaic Modules
 High Resolution Spatial Electroluminescence Imaging of Photovoltaic Modules Abstract J.L. Crozier, E.E. van Dyk, F.J. Vorster Nelson Mandela Metropolitan University Electroluminescence (EL) is a useful
High Resolution Spatial Electroluminescence Imaging of Photovoltaic Modules Abstract J.L. Crozier, E.E. van Dyk, F.J. Vorster Nelson Mandela Metropolitan University Electroluminescence (EL) is a useful
USB readout board for PEBS Performance test
 June 11, 2009 Version 1.0 USB readout board for PEBS Performance test Guido Haefeli 1 Li Liang 2 Abstract In the context of the PEBS [1] experiment a readout board was developed in order to facilitate
June 11, 2009 Version 1.0 USB readout board for PEBS Performance test Guido Haefeli 1 Li Liang 2 Abstract In the context of the PEBS [1] experiment a readout board was developed in order to facilitate
X 4 CONFIDENTIAL X 4 OTHER PROGRAMME: CUSTOMER: CONTRACT NO.: WPD NO.: DRD NO.: CONTRACTUAL DOC.:
 Date: Aug. 2002 Page: ii Contraves Space AG Schaffhauserstr. 580 CH-8052 Zurich Switzerland CLASS 1 UNRESTRICTED 1 2 INDUSTRY 2 3 RESTRICTED 3 CATEGORY CONFIGURED, FOR APPROVAL NOT CONFIGURED, FOR APPROVAL
Date: Aug. 2002 Page: ii Contraves Space AG Schaffhauserstr. 580 CH-8052 Zurich Switzerland CLASS 1 UNRESTRICTED 1 2 INDUSTRY 2 3 RESTRICTED 3 CATEGORY CONFIGURED, FOR APPROVAL NOT CONFIGURED, FOR APPROVAL
ISSCC 2003 / SESSION 4 / CLOCK RECOVERY AND BACKPLANE TRANSCEIVERS / PAPER 4.7
 ISSCC 2003 / SESSION 4 / CLOCK RECOVERY AND BACKPLANE TRANSCEIVERS / PAPER 4.7 4.7 A 2.7 Gb/s CDMA-Interconnect Transceiver Chip Set with Multi-Level Signal Data Recovery for Re-configurable VLSI Systems
ISSCC 2003 / SESSION 4 / CLOCK RECOVERY AND BACKPLANE TRANSCEIVERS / PAPER 4.7 4.7 A 2.7 Gb/s CDMA-Interconnect Transceiver Chip Set with Multi-Level Signal Data Recovery for Re-configurable VLSI Systems
Gamma and X-Ray Detection
 Gamma and X-Ray Detection DETECTOR OVERVIEW The kinds of detectors commonly used can be categorized as: a. Gas-filled Detectors b. Scintillation Detectors c. Semiconductor Detectors The choice of a particular
Gamma and X-Ray Detection DETECTOR OVERVIEW The kinds of detectors commonly used can be categorized as: a. Gas-filled Detectors b. Scintillation Detectors c. Semiconductor Detectors The choice of a particular
Developments in Point of Load Regulation
 Developments in Point of Load Regulation By Paul Greenland VP of Marketing, Power Management Group, Point of load regulation has been used in electronic systems for many years especially when the load
Developments in Point of Load Regulation By Paul Greenland VP of Marketing, Power Management Group, Point of load regulation has been used in electronic systems for many years especially when the load
1090 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON NUCLEAR SCIENCE, VOL. 50, NO. 4, AUGUST 2003. Intelligent Gamma-Ray Spectroscopy Using 3-D Position-Sensitive Detectors
 1090 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON NUCLEAR SCIENCE, VOL. 50, NO. 4, AUGUST 2003 Intelligent Gamma-Ray Spectroscopy Using 3-D Position-Sensitive Detectors Carolyn E. Lehner, Student Member, IEEE, Zhong He, Senior
1090 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON NUCLEAR SCIENCE, VOL. 50, NO. 4, AUGUST 2003 Intelligent Gamma-Ray Spectroscopy Using 3-D Position-Sensitive Detectors Carolyn E. Lehner, Student Member, IEEE, Zhong He, Senior
Spacecraft Computer Systems. Colonel John E. Keesee
 Spacecraft Computer Systems Colonel John E. Keesee Overview Spacecraft data processing requires microcomputers and interfaces that are functionally similar to desktop systems However, space systems require:
Spacecraft Computer Systems Colonel John E. Keesee Overview Spacecraft data processing requires microcomputers and interfaces that are functionally similar to desktop systems However, space systems require:
DESIGN CHALLENGES OF TECHNOLOGY SCALING
 DESIGN CHALLENGES OF TECHNOLOGY SCALING IS PROCESS TECHNOLOGY MEETING THE GOALS PREDICTED BY SCALING THEORY? AN ANALYSIS OF MICROPROCESSOR PERFORMANCE, TRANSISTOR DENSITY, AND POWER TRENDS THROUGH SUCCESSIVE
DESIGN CHALLENGES OF TECHNOLOGY SCALING IS PROCESS TECHNOLOGY MEETING THE GOALS PREDICTED BY SCALING THEORY? AN ANALYSIS OF MICROPROCESSOR PERFORMANCE, TRANSISTOR DENSITY, AND POWER TRENDS THROUGH SUCCESSIVE
Analysis and Improvement of Mach Zehnder Modulator Linearity Performance for Chirped and Tunable Optical Carriers
 886 JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 20, NO. 5, MAY 2002 Analysis and Improvement of Mach Zehnder Modulator Linearity Performance for Chirped and Tunable Optical Carriers S. Dubovitsky, Member, IEEE,
886 JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 20, NO. 5, MAY 2002 Analysis and Improvement of Mach Zehnder Modulator Linearity Performance for Chirped and Tunable Optical Carriers S. Dubovitsky, Member, IEEE,
HIGH RELIABILITY POWER SUPPLY TESTING
 HIGH RELIABILITY POWER SUPPLY TESTING Dale Cigoy Keithley Instruments, Inc. The reliability of a power supply must match or exceed the rest of the system in which it is installed. Generally, this requires
HIGH RELIABILITY POWER SUPPLY TESTING Dale Cigoy Keithley Instruments, Inc. The reliability of a power supply must match or exceed the rest of the system in which it is installed. Generally, this requires
Cold-Junction-Compensated K-Thermocoupleto-Digital Converter (0 C to +1024 C)
 19-2235; Rev 1; 3/02 Cold-Junction-Compensated K-Thermocoupleto-Digital General Description The performs cold-junction compensation and digitizes the signal from a type-k thermocouple. The data is output
19-2235; Rev 1; 3/02 Cold-Junction-Compensated K-Thermocoupleto-Digital General Description The performs cold-junction compensation and digitizes the signal from a type-k thermocouple. The data is output
Lab 2.0 Thermal Camera Interface
 Lab 2.0 Thermal Camera Interface Lab 1 - Camera directional-stand (recap) The goal of the lab 1 series was to use a PS2 joystick to control the movement of a pan-tilt module. To this end, you implemented
Lab 2.0 Thermal Camera Interface Lab 1 - Camera directional-stand (recap) The goal of the lab 1 series was to use a PS2 joystick to control the movement of a pan-tilt module. To this end, you implemented
CMS Tracker module / hybrid tests and DAQ development for the HL-LHC
 CMS Tracker module / hybrid tests and DAQ development for the HL-LHC S. Mersi, G. Auzinger georg.auzinger@cern.ch 1 Outline Reminder: the Ph2 CMS Tracker upgrade pt Modules: principle, elements, electronics
CMS Tracker module / hybrid tests and DAQ development for the HL-LHC S. Mersi, G. Auzinger georg.auzinger@cern.ch 1 Outline Reminder: the Ph2 CMS Tracker upgrade pt Modules: principle, elements, electronics
Features INVERTING. 0.6mA NONINVERTING INVERTING. 0.6mA NONINVERTING
 MIC442/442/4428 Dual 1.A-Peak Low-Side MOSFET Driver General Description The MIC442/442/4428 family are highly-reliable dual lowside MOSFET drivers fabricated on a BiCMOS/DMOS process for low power consumption
MIC442/442/4428 Dual 1.A-Peak Low-Side MOSFET Driver General Description The MIC442/442/4428 family are highly-reliable dual lowside MOSFET drivers fabricated on a BiCMOS/DMOS process for low power consumption
Application Note AN1
 TAKING INVENTIVE STEPS IN INFRARED. MINIATURE INFRARED GAS SENSORS GOLD SERIES UK Patent App. No. 799A USA Patent App. No. 9/78,7 World Patents Pending SENSOR OVERVIEW Application Note AN The Dynament
TAKING INVENTIVE STEPS IN INFRARED. MINIATURE INFRARED GAS SENSORS GOLD SERIES UK Patent App. No. 799A USA Patent App. No. 9/78,7 World Patents Pending SENSOR OVERVIEW Application Note AN The Dynament
Web Streamed SDR s in Service at GB2RHQ Hack Green Bunker
 Web Streamed SDR s in Service at GB2RHQ Hack Green Bunker Gateway to the Net. We are fortunate to have a very fast internet service into Hack Green via a 5Ghz microwave link. The service provides a bandwidth
Web Streamed SDR s in Service at GB2RHQ Hack Green Bunker Gateway to the Net. We are fortunate to have a very fast internet service into Hack Green via a 5Ghz microwave link. The service provides a bandwidth
 Tracking Moving Objects In Video Sequences Yiwei Wang, Robert E. Van Dyck, and John F. Doherty Department of Electrical Engineering The Pennsylvania State University University Park, PA16802 Abstract{Object
Tracking Moving Objects In Video Sequences Yiwei Wang, Robert E. Van Dyck, and John F. Doherty Department of Electrical Engineering The Pennsylvania State University University Park, PA16802 Abstract{Object
An Overview of Digital Imaging Systems for Radiography and Fluoroscopy
 An Overview of Digital Imaging Systems for Radiography and Fluoroscopy Michael Yester, Ph.D. University of Alabama at Birmingham Outline Introduction Imaging Considerations Receptor Properties General
An Overview of Digital Imaging Systems for Radiography and Fluoroscopy Michael Yester, Ph.D. University of Alabama at Birmingham Outline Introduction Imaging Considerations Receptor Properties General
Tutorial 4.6 Gamma Spectrum Analysis
 Tutorial 4.6 Gamma Spectrum Analysis Slide 1. Gamma Spectrum Analysis In this module, we will apply the concepts that were discussed in Tutorial 4.1, Interactions of Radiation with Matter. Slide 2. Learning
Tutorial 4.6 Gamma Spectrum Analysis Slide 1. Gamma Spectrum Analysis In this module, we will apply the concepts that were discussed in Tutorial 4.1, Interactions of Radiation with Matter. Slide 2. Learning
Basler racer. Line Scan Cameras. Next generation CMOS sensors with 2k to 12k resolution and up to 80 khz line rate
 Basler racer Line Scan Cameras Next generation CMOS sensors with 2k to 12k resolution and up to 80 khz line rate Flexible and easy integration, supported by a very compact design Low power consumption
Basler racer Line Scan Cameras Next generation CMOS sensors with 2k to 12k resolution and up to 80 khz line rate Flexible and easy integration, supported by a very compact design Low power consumption
Efficient Heart Rate Monitoring
 Efficient Heart Rate Monitoring By Sanjeev Kumar, Applications Engineer, Cypress Semiconductor Corp. Heart rate is one of the most frequently measured parameters of the human body and plays an important
Efficient Heart Rate Monitoring By Sanjeev Kumar, Applications Engineer, Cypress Semiconductor Corp. Heart rate is one of the most frequently measured parameters of the human body and plays an important
Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN (MAVEN) Mission
 Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN (MAVEN) Mission MAVEN Science Community Workshop December 2, 2012 Particles and Fields Package Solar Energetic Particle Instrument (SEP) Davin Larson and the SEP
Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN (MAVEN) Mission MAVEN Science Community Workshop December 2, 2012 Particles and Fields Package Solar Energetic Particle Instrument (SEP) Davin Larson and the SEP
IDM-200 -V. Interchangeable HPGe Detector Module (IDM) for Systems Integrators
 IDM-200 -V Interchangeable HPGe Detector Module (IDM) for Systems Integrators Free from liquid nitrogen, free from maintenance, free from integration complexities. Convenient-to-mount, all-in-one integrated
IDM-200 -V Interchangeable HPGe Detector Module (IDM) for Systems Integrators Free from liquid nitrogen, free from maintenance, free from integration complexities. Convenient-to-mount, all-in-one integrated
Application Note 83 Fundamentals of RS 232 Serial Communications
 Application Note 83 Fundamentals of Serial Communications Due to it s relative simplicity and low hardware overhead (as compared to parallel interfacing), serial communications is used extensively within
Application Note 83 Fundamentals of Serial Communications Due to it s relative simplicity and low hardware overhead (as compared to parallel interfacing), serial communications is used extensively within
(Amplifying) Photo Detectors: Avalanche Photodiodes Silicon Photomultiplier
 (Amplifying) Photo Detectors: Avalanche Photodiodes Silicon Photomultiplier (no PiN and pinned Diodes) Peter Fischer P. Fischer, ziti, Uni Heidelberg, Seite 1 Overview Reminder: Classical Photomultiplier
(Amplifying) Photo Detectors: Avalanche Photodiodes Silicon Photomultiplier (no PiN and pinned Diodes) Peter Fischer P. Fischer, ziti, Uni Heidelberg, Seite 1 Overview Reminder: Classical Photomultiplier
UPS PIco. to be used with. Raspberry Pi B+, A+, B, and A. HAT Compliant. Raspberry Pi is a trademark of the Raspberry Pi Foundation
 UPS PIco Uninterruptible Power Supply with Peripherals and I 2 C control Interface to be used with Raspberry Pi B+, A+, B, and A HAT Compliant Raspberry Pi is a trademark of the Raspberry Pi Foundation
UPS PIco Uninterruptible Power Supply with Peripherals and I 2 C control Interface to be used with Raspberry Pi B+, A+, B, and A HAT Compliant Raspberry Pi is a trademark of the Raspberry Pi Foundation
True Single Phase Clocking Flip-Flop Design using Multi Threshold CMOS Technique
 True Single Phase Clocking Flip-Flop Design using Multi Threshold CMOS Technique Priyanka Sharma ME (ECE) Student NITTTR Chandigarh Rajesh Mehra Associate Professor Department of ECE NITTTR Chandigarh
True Single Phase Clocking Flip-Flop Design using Multi Threshold CMOS Technique Priyanka Sharma ME (ECE) Student NITTTR Chandigarh Rajesh Mehra Associate Professor Department of ECE NITTTR Chandigarh
css Custom Silicon Solutions, Inc.
 css Custom Silicon Solutions, Inc. CSS555(C) CSS555/ PART DESCRIPTION The CSS555 is a micro-power version of the popular 555 Timer IC. It is pin-for-pin compatible with the standard 555 timer and features
css Custom Silicon Solutions, Inc. CSS555(C) CSS555/ PART DESCRIPTION The CSS555 is a micro-power version of the popular 555 Timer IC. It is pin-for-pin compatible with the standard 555 timer and features
A New Programmable RF System for System-on-Chip Applications
 Vol. 6, o., April, 011 A ew Programmable RF System for System-on-Chip Applications Jee-Youl Ryu 1, Sung-Woo Kim 1, Jung-Hun Lee 1, Seung-Hun Park 1, and Deock-Ho Ha 1 1 Dept. of Information and Communications
Vol. 6, o., April, 011 A ew Programmable RF System for System-on-Chip Applications Jee-Youl Ryu 1, Sung-Woo Kim 1, Jung-Hun Lee 1, Seung-Hun Park 1, and Deock-Ho Ha 1 1 Dept. of Information and Communications
QUICK START GUIDE FOR DEMONSTRATION CIRCUIT 956 24-BIT DIFFERENTIAL ADC WITH I2C LTC2485 DESCRIPTION
 LTC2485 DESCRIPTION Demonstration circuit 956 features the LTC2485, a 24-Bit high performance Σ analog-to-digital converter (ADC). The LTC2485 features 2ppm linearity, 0.5µV offset, and 600nV RMS noise.
LTC2485 DESCRIPTION Demonstration circuit 956 features the LTC2485, a 24-Bit high performance Σ analog-to-digital converter (ADC). The LTC2485 features 2ppm linearity, 0.5µV offset, and 600nV RMS noise.
Temperature Sensors. Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs) Thermistors IC Temperature Sensors
 Temperature Sensors Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs) Thermistors IC Temperature Sensors Drew Gilliam GE/MfgE 330: Introduction to Mechatronics 03.19.2003 Introduction There are a wide variety of
Temperature Sensors Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs) Thermistors IC Temperature Sensors Drew Gilliam GE/MfgE 330: Introduction to Mechatronics 03.19.2003 Introduction There are a wide variety of
1 Form A Solid State Relay
 Form A Solid State Relay VOAT, VOAABTR FEATURES 9 S S DC S' 3 S' High speed SSR - t on /t off < 8 μs Maximum R ON. Isolation test voltage 3 V RMS Load voltage V Load current A DC configuration DIP- package
Form A Solid State Relay VOAT, VOAABTR FEATURES 9 S S DC S' 3 S' High speed SSR - t on /t off < 8 μs Maximum R ON. Isolation test voltage 3 V RMS Load voltage V Load current A DC configuration DIP- package
Calorimetry in particle physics experiments
 Calorimetry in particle physics experiments Unit n. 8 Calibration techniques Roberta Arcidiacono Lecture overview Introduction Hardware Calibration Test Beam Calibration In-situ Calibration (EM calorimeters)
Calorimetry in particle physics experiments Unit n. 8 Calibration techniques Roberta Arcidiacono Lecture overview Introduction Hardware Calibration Test Beam Calibration In-situ Calibration (EM calorimeters)
Automotive Applications of 3D Laser Scanning Introduction
 Automotive Applications of 3D Laser Scanning Kyle Johnston, Ph.D., Metron Systems, Inc. 34935 SE Douglas Street, Suite 110, Snoqualmie, WA 98065 425-396-5577, www.metronsys.com 2002 Metron Systems, Inc
Automotive Applications of 3D Laser Scanning Kyle Johnston, Ph.D., Metron Systems, Inc. 34935 SE Douglas Street, Suite 110, Snoqualmie, WA 98065 425-396-5577, www.metronsys.com 2002 Metron Systems, Inc
DMX-K-DRV. Integrated Step Motor Driver + (Basic Controller) Manual
 DMX-K-DRV Integrated Step Motor Driver + (Basic Controller) Manual DMX-K-DRV Manual page 1 rev 1.33 COPYRIGHT 2007 ARCUS, ALL RIGHTS RESERVED First edition, June 2007 ARCUS TECHNOLOGY copyrights this document.
DMX-K-DRV Integrated Step Motor Driver + (Basic Controller) Manual DMX-K-DRV Manual page 1 rev 1.33 COPYRIGHT 2007 ARCUS, ALL RIGHTS RESERVED First edition, June 2007 ARCUS TECHNOLOGY copyrights this document.
Implementation of Canny Edge Detector of color images on CELL/B.E. Architecture.
 Implementation of Canny Edge Detector of color images on CELL/B.E. Architecture. Chirag Gupta,Sumod Mohan K cgupta@clemson.edu, sumodm@clemson.edu Abstract In this project we propose a method to improve
Implementation of Canny Edge Detector of color images on CELL/B.E. Architecture. Chirag Gupta,Sumod Mohan K cgupta@clemson.edu, sumodm@clemson.edu Abstract In this project we propose a method to improve
AxioCam MR The All-round Camera for Biology, Medicine and Materials Analysis Digital Documentation in Microscopy
 Microscopy from Carl Zeiss AxioCam MR The All-round Camera for Biology, Medicine and Materials Analysis Digital Documentation in Microscopy New Dimensions in Performance AxioCam MR from Carl Zeiss Both
Microscopy from Carl Zeiss AxioCam MR The All-round Camera for Biology, Medicine and Materials Analysis Digital Documentation in Microscopy New Dimensions in Performance AxioCam MR from Carl Zeiss Both
CT RADIATION DOSE REPORT FROM DICOM. Frank Dong, PhD, DABR Diagnostic Physicist Imaging Institute Cleveland Clinic Foundation Cleveland, OH
 CT RADIATION DOSE REPORT FROM DICOM Frank Dong, PhD, DABR Diagnostic Physicist Imaging Institute Cleveland Clinic Foundation Cleveland, OH CT Patient comes out... Patient goes in... Big Black Box Radiology
CT RADIATION DOSE REPORT FROM DICOM Frank Dong, PhD, DABR Diagnostic Physicist Imaging Institute Cleveland Clinic Foundation Cleveland, OH CT Patient comes out... Patient goes in... Big Black Box Radiology
CHAPTER 7 SCINTILLATION COUNTING
 CHAPTER 7 SCINTILLATION COUNTING Radiation of various types is widely utilized for non-destructive inspection and testing such as in medical diagnosis, industrial inspection, material analysis and other
CHAPTER 7 SCINTILLATION COUNTING Radiation of various types is widely utilized for non-destructive inspection and testing such as in medical diagnosis, industrial inspection, material analysis and other
