Going back to the original form of the internal energy equation, du = dq + dw expansion + dw other
|
|
|
- Polly Whitehead
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CALORIMETRY Internal energy is measured in terms of work and heat, du = dq + dw exp + dw other This equation is often applied to the first law of thermodynamics. This law states that the energy of the universe remains constant, or energy can be neither created nor destroyed, only changed from one form of energy to another. The sign of dq, and dw, indicates the direction of the flow of energy (+ means in, - means out). We define dw exp as the work done by a system expanding against an external pressure, dw exp = -p ext dv = -p dv and dw other is non expansion work (such as electrical work). It becomes clear that the change in internal energy of a system is not equal to the amount of heat supplied at constant pressure if the system is free to change its volume. This quantity is equal to the change in the enthalpy of the system, dh = du + p dv + V dp for a system that can only do expansion work, du = dq + dw exp and since we know that dw exp = -P dv, we obtain for the enthalpy change: dh = du + p dv +(-p dv) + V dp = dq + V dp if the reaction occurs at constant pressure, as it does if the reaction vessel is open to the atmosphere, then dp = 0 dh = dq v or H = q p for measurable changes. This means that when a system is subjected to constant pressure and only expansion work is possible, the change in enthalpy is equal to the thermal energy input/output. An enthalpy change can be measured using an isobaric calorimeter. H and U differ by an amount p V. So if we know the enthalpy change, the volume change, and the external pressure of the system, we can compute the internal energy change. For example: Certain compound converts to an alternate allotropic form Ξ 27 --> Ξ 31 where the subscripts indicate the molar volume of each allotropic form in g/cm 3. The internal energy change of this process is kj/mol at 1.0 atm of pressure. Compute the percent difference between the enthalpy change and the internal energy change for the process. 1.0 atm = Pa p V = Pa X (27-31) X 10-6 m 3 = X 10-3 kj % difference = [ X 10-3 kj / kj/mol] = 0.16% Thus it is reasonable to ignore the p V contribution for condensed phases. This is not so for reactions that consume or produce gasses. From the ideal gas law we obtain pv = nrt or p V = n gas RT, and the enthalpy equation becomes: H = U + n gas RT Going back to the original form of the internal energy equation, du = dq + dw expansion + dw other 1
2 It is clear that if dw expansion = 0, and dw other = 0 The internal energy change can also be measured as the change in a single property of the system, du = dq v or U = q v for large changes. Thus measuring the amount of heat that goes in or out of a constant-volume system is equivalent to measuring U. Such measurements are carried out using a bomb calorimeter. BOMB CALORIMETRY In this experiment the energy released by the reaction of a limiting reagent. For the change in internal energy of such a system: du = dq v Because the reaction takes place in a steel bomb the system cannot change its volume so no work is done. The reaction of choice is the combustion of an organic compound such as naphthalene. In a combustion reaction, the compound (limiting reagent) combines with oxygen (excess reagent) to form CO 2 and H 2 O. The reaction vessel (the bomb) and its contents are submerged in a pail with a known amount of water, which is placed in a thermally insulated calorimeter. This insulation ensures that the processes in the system are nearly adiabatic. Thus the energy released in the chemical reaction must be transferred entirely as heat (q v ) into the system. Suppose a sample is allowed to come to equilibrium at temperature T 0. Upon ignition, the heat released raises the temperature of the system to T 1, U = C (T 1 - T 0 ) = C T where C is the heat capacity of the bomb calorimeter as determined from the calibration step, C = U known / (T 1 - T 0 ) For a perfectly adiabatic process we would get the following plot: 2
3 And the above equation would be correct. However, no thermal insulation is perfect, some heat will leak in or out of the system during the change of state and the equilibration time. The plot is likely to deviate from the expected adiabatic pattern, Then, we would estimate T from the tangent to the T-t curves at t i and t f, T = (T f - T i ) - {(dt / dt)(t f - t i )} Note that the tangent lines are parallel, thus T could be obtained from anywhere in the plot. What if the tangent lines are not parallel? According to the National Bureau of Standards, t d is very close to the time at which the temperature has increased by 60% of the difference between t i and t f 3
4 Here, T is given by, T = (T f - T i ) - {(dt / dt) i (t d - t i )} - {(dt / dt) f (t f - t d )} In words: if the two tangent lines are parallel then we just have to measure the temperature difference between them; if the two tangent lines are not parallel then we need to take the difference at a certain point t d such that the shaded regions are of equal area. The heat capacity C, has been defined as a single entity. This quantity applies to the bomb calorimeter as long as the amount of water in the pail remains constant. If the amount of water is changed, then we need to redefine the heat capacity as C sys C = C sys = C water + C cal where C water is the heat capacity of the water and C cal is the heat capacity of the empty calorimeter. For a given amount of water, the heat capacity is: C water = [mass of H 2 O (g)] X [4.184 J/ 0 C X g] Thus the heat capacity of the empty calorimeter is, C cal = C sys - C water REQUIRED MATERIALS AND APPARATUS -Oxygen cylinder and high-pressure fittings and hose connector to the bomb -Pelletizing press -Analytical balance -Benzoic acid tablets for standardization (if tablets are not available, make your own in the pelletizing press) -Naphthalene and an unknown sample -Volumetric flasks: ml, ml, ml -Adiabatic or plain Bomb calorimeter; this generally consists of the following parts: *The high-pressure "bomb" made of steel *The pail, with a known amount of water *The sample pan *Ignition wire *A secondary water jacket to ensure adiabatic conditions for the reaction *An ignition unit *A thermometer or automated temperature recording device *Motor and stirrer 4
5 The bomb calorimeter EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE The first step of the experiment is to determine the value of C, the heat capacity of the calorimeter. We do this by measuring T for a known U. We will use high purity benzoic acid, C 6 H 5 COOH. The following reaction will occur upon ignition of the sample: C 6 H 5 COOH (s) + (15/2) O 2 (g) --> 7 CO 2 (g) + 3 H 2 O (l) We will determine the heat capacity of the calorimeter from the adiabatic T obtained from the combustion of a known amount of benzoic acid and a known mass of iron wire. The energies of combustion are: Benzoic Acid = kj/g Iron = kj/g When using powdered samples in a bomb calorimeter, the sample must be compressed into tightly-packed pellets so that the entire sample will combust. The weigh of each sample should not exceed the recomended amount, (~0.6 g for naphthalene and ~0.8 g for benzoic acid) because the bombs are rated to withstand a limited temperature rise. Never put the calorimeter lid or bomb parts down on the bench top. Use holders supplied to prevent unnecessary damage and have a classmate hold the calorimeter lid while the 5
6 pail is being replaced/removed. If the thermometer has been calibrated for total immersion and you want to get fuzzy with the experimental data, correct the thermometer readings for the part that is not immersed in the bath. To do that, place a second thermometer near the exposed stem, the stem correction is given by, C stem = X n X [T bath - T stem ] where n is the exposed stem lenght (in degrees) outside the bath and is a constant of the thermometer's glass. FILLING THE BOMB -Cut the iron wire, to the correct lenght (~10 cm) and weight it in an analytical balance. Weigh the recomended amount of sample, record exact mass. Put the solid pellet in the ignition cup and wrap the wire around the ends of the electrode terminals. Bend the wire so that it is in good contact with the pellet but does not touch the ignition cup anywhere. The wire should touch only the terminals and the pellet. -Taking care to keep the wire connected to the electrodes and in contact with the sample, place the head of the bomb into its container and seal as tightly as possible by hand, ensure that the oxygen outlet valve is open during this time. -To get the air out of the bomb: First, close the outlet valve on the bomb's top. With the valves on the oxygen tank closed, attach the inlet tube from the tank to the bomb. Close the oxygen valve tightly and charge the bomb with oxygen to ~5-10 atm. How does the filling process work? If the bomb outlet is closed, the inlet is connected to the oxygen tank, and the release valve in the hose connector is closed, then both the bomb and the hose connector are filled at the pressure shown in the tank's pressure gauge. When the gauge marks the required pressure, close the tank's valve. Now the bomb and the hose connector are filled at the same pressure. If you open the release valve in the hose connector, then the pressure drops to atmospheric pressure. But the bomb's inlet valve only allows gas passage in and not out, then the valve is closed by the excess pressure. -Now you should bleed the gas out of the bomb by opening the outlet valve on the bomb head until you no longer hear a hissing sound. The bomb is now filled with oxygen at atmospheric pressure and free of air and contaminants. The fill-and empty cycle should be repeated just to make sure that no gasses other than oxygen remain in the bomb. Then fill the bomb to ~25-30 atm (not higher than 30 atm) and disconnect it from the tank. -Fill the calorimeter's pail with ml DI water, the water must be enough to cover the bomb. Place the pail into the insulating jacket and be sure that it sits flat. In order to ensure that the pail is placed correctly, the insulating jacket has a set of bumps which fit into a set of depressions in the bottom of the pail. -Lower the bomb into the pail, there is a circular depression where the bomb fits. Attach the fuse leads to the connecters on the top of the bomb. Check for gas leaks; if there are any bubbles of gas escaping from around the oxygen bomb DO NOT FIRE THE BOMB. -Cover the water bath with its lid, connect the stirrer to the motor using the rubber O-ring and insert the temperature probe in the hole. The standard temperature probe is usually a Beckmann thermometer. These thermometers are very fragile and very expensive. BE CAREFUL! -The Beckmann thermometer has a very narrow reading range (~5-8 degrees), the temperature of the water in the pail should be higher than the lower limit of the calibration 6
7 range but not too high as to let the heat of reaction take the readings above the upper calibration range. The water temperature might need to be adjusted before filling the pail. From this point on, do not stop the work until the run is over -Start the stirrer and start collecting data, reading the thermometer every 15 sec. It is recommended that you take and record temperature readings for about two minutes before to firing the charge. They will be required to correct T for non-adiabatic conditions. Once the readings are fairly stable, fire the bomb. -To fire the bomb, hold the ignition button down for 2 to 5 seconds. Do Not hold it down more than 5 seconds. The red light should turn on briefly as you push the button. -Record the temperature until the readings are fairly stable. Continue to take readings for two minutes after the temperature has reached an apparent state of equilibrium. -When the run is complete, turn off the stirring motor, lift and move the cover. Lift the pail out of the calorimeter. Remove the bomb and open the gas outlet valve to relieve the inside pressure. Once the pressure has decreased, remove the top of the bomb. When releasing oxygen outlet valve do so under a working fume hood. -Clean and wipe dry all bomb parts. -Determine the mass of unburned iron wire and subtract from the initial mass of iron wire. -If the inside of the bomb is coated with soot, then the oxygen pressure was not large enough. Discard this run and try a higher oxygen pressure but do not exceed 30 atm. -Repeat the procedure with a naphthalene pellet. Then with an unknown. DATA PROCESSING -Plot temperature as a function of time for each run and determine the adiabatic T and the heat capacity C of the calorimeter. -Determine the U of combustion per gram of weighted samples of naphthalene and the unknown using the adiabatic T and the calorimeter heat capacity. -Determine the molar U of combustion for naphthalene. -Since the standard enthalpy and energy of a real gas are defined as the standard enthalpy and energy of the gas in the zero-pressure limit, we can compute the molar enthalpy change H molar using H molar = U molar + RT n gas Compute H molar for naphthalene with and without the RT n gas term. How different are the results? -Submit all graphs with your report. 7
Experiment 1: Adiabatic Bomb Calorimeter (Dated: September 27, 2010)
 Experiment 1: Adiabatic Bomb Calorimeter (Dated: September 27, 2010) I. INTRODUCTION Heat released in a chemical reaction can be determined experimentally by using an adiabatic calorimeter. The reaction
Experiment 1: Adiabatic Bomb Calorimeter (Dated: September 27, 2010) I. INTRODUCTION Heat released in a chemical reaction can be determined experimentally by using an adiabatic calorimeter. The reaction
Introductory Laboratory EST - Experiment 9 Calorimetry - 1 - Introductory Laboratory Energy Science and Technology. Experiment 9. Physical Chemistry
 Introductory Laboratory EST - Experiment 9 Calorimetry - 1 - Introductory Laboratory Energy Science and Technology Experiment 9 Physical Chemistry Calorimetry Abstract The heat of combustion of Naphthalene
Introductory Laboratory EST - Experiment 9 Calorimetry - 1 - Introductory Laboratory Energy Science and Technology Experiment 9 Physical Chemistry Calorimetry Abstract The heat of combustion of Naphthalene
Determination of the enthalpy of combustion using a bomb calorimeter TEC
 Determination of the enthalpy of TEC Related concepts First law of thermodynamics, Hess s law of constant heat summation, enthalpy of combustion, enthalpy of formation, heat capacity. Principle The bomb
Determination of the enthalpy of TEC Related concepts First law of thermodynamics, Hess s law of constant heat summation, enthalpy of combustion, enthalpy of formation, heat capacity. Principle The bomb
Adiabatic Bomb Calorimetry
 CHEM 366 II-1 Adiabatic Bomb Calorimetry Introduction Obtaining energy in the form of heat from the combustion or oxidation of thermodynamically unstable (and often kinetically inert) hydrocarbons and
CHEM 366 II-1 Adiabatic Bomb Calorimetry Introduction Obtaining energy in the form of heat from the combustion or oxidation of thermodynamically unstable (and often kinetically inert) hydrocarbons and
Determination of the enthalpy of combustion using a bomb calorimeter TEC. Safety precautions
 Safety precautions Naphthalene is harmful if swallowed. May cause cancer. Is further very toxic to aquatic organisms and can have long-term harmful effects in bodies of water. Equipment 1 Bomb calorimeter
Safety precautions Naphthalene is harmful if swallowed. May cause cancer. Is further very toxic to aquatic organisms and can have long-term harmful effects in bodies of water. Equipment 1 Bomb calorimeter
Heat of Combustion PCh 6-99
 UMR ChemLabs Heat of Combustion PCh 6-99 Gary L. Bertrand, Professor of Chemistry A calorimeter (calor L = heat + metron Gr = measure) should be literally a device to measure heat. In reality, most calorimeters
UMR ChemLabs Heat of Combustion PCh 6-99 Gary L. Bertrand, Professor of Chemistry A calorimeter (calor L = heat + metron Gr = measure) should be literally a device to measure heat. In reality, most calorimeters
Combustion Calorimetry
 ombustion alorimetry 1 Please Note: Each lab group will be required to pick the compound they use in this experiment. The compound must contain only carbon and hydrogen or carbon, hydrogen and oxygen.
ombustion alorimetry 1 Please Note: Each lab group will be required to pick the compound they use in this experiment. The compound must contain only carbon and hydrogen or carbon, hydrogen and oxygen.
Enthalpy of Combustion via Calorimetry
 Enthalpy of Combustion via Calorimetry Introduction This experiment measures the enthalpy change when a system consisting of a known amount of a substance in the presence of excess oxygen is quantitatively
Enthalpy of Combustion via Calorimetry Introduction This experiment measures the enthalpy change when a system consisting of a known amount of a substance in the presence of excess oxygen is quantitatively
HEAT OF COMBUSTION BY OXYGEN BOMB CALORIMETER. References: See relevant chapters in undergraduate text.
 HEAT OF COMBUSTION BY OXYGEN BOMB CALORIMETER References: See relevant chapters in undergraduate text. Background: Study text sections on calorimetry and "thermochemistry" carefully. Know definitions of
HEAT OF COMBUSTION BY OXYGEN BOMB CALORIMETER References: See relevant chapters in undergraduate text. Background: Study text sections on calorimetry and "thermochemistry" carefully. Know definitions of
DETERMINING THE ENTHALPY OF FORMATION OF CaCO 3
 DETERMINING THE ENTHALPY OF FORMATION OF CaCO 3 Standard Enthalpy Change Standard Enthalpy Change for a reaction, symbolized as H 0 298, is defined as The enthalpy change when the molar quantities of reactants
DETERMINING THE ENTHALPY OF FORMATION OF CaCO 3 Standard Enthalpy Change Standard Enthalpy Change for a reaction, symbolized as H 0 298, is defined as The enthalpy change when the molar quantities of reactants
Bomb Calorimetry. Electrical leads. Stirrer
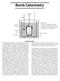 Bomb Calorimetry Stirrer Electrical leads Oxygen inlet valve Bomb Fuse Calorimeter Outer jacket Not shown: heating and cooling system for outer jacket, and controls that keep the outer jacket at the same
Bomb Calorimetry Stirrer Electrical leads Oxygen inlet valve Bomb Fuse Calorimeter Outer jacket Not shown: heating and cooling system for outer jacket, and controls that keep the outer jacket at the same
The Molar Mass of a Gas
 The Molar Mass of a Gas Goals The purpose of this experiment is to determine the number of grams per mole of a gas by measuring the pressure, volume, temperature, and mass of a sample. Terms to Know Molar
The Molar Mass of a Gas Goals The purpose of this experiment is to determine the number of grams per mole of a gas by measuring the pressure, volume, temperature, and mass of a sample. Terms to Know Molar
Module 5: Combustion Technology. Lecture 34: Calculation of calorific value of fuels
 1 P age Module 5: Combustion Technology Lecture 34: Calculation of calorific value of fuels 2 P age Keywords : Gross calorific value, Net calorific value, enthalpy change, bomb calorimeter 5.3 Calculation
1 P age Module 5: Combustion Technology Lecture 34: Calculation of calorific value of fuels 2 P age Keywords : Gross calorific value, Net calorific value, enthalpy change, bomb calorimeter 5.3 Calculation
Thermochemistry: Calorimetry and Hess s Law
 Thermochemistry: Calorimetry and Hess s Law Some chemical reactions are endothermic and proceed with absorption of heat while others are exothermic and proceed with an evolution of heat. The magnitude
Thermochemistry: Calorimetry and Hess s Law Some chemical reactions are endothermic and proceed with absorption of heat while others are exothermic and proceed with an evolution of heat. The magnitude
Bomb Calorimetry and Heat of Combustion
 UC Berkeley College of Chemistry Chemistry 125 Physical Chemistry Laboratory Bomb Calorimetry and Heat of Combustion Author: Jonathan Melville Collaborators: David Gygi and Effie Zhou Graduate Student
UC Berkeley College of Chemistry Chemistry 125 Physical Chemistry Laboratory Bomb Calorimetry and Heat of Combustion Author: Jonathan Melville Collaborators: David Gygi and Effie Zhou Graduate Student
Apparatus error for each piece of equipment = 100 x margin of error quantity measured
 1) Error Analysis Apparatus Errors (uncertainty) Every time you make a measurement with a piece of apparatus, there is a small margin of error (i.e. uncertainty) in that measurement due to the apparatus
1) Error Analysis Apparatus Errors (uncertainty) Every time you make a measurement with a piece of apparatus, there is a small margin of error (i.e. uncertainty) in that measurement due to the apparatus
DETERMINING THE MOLAR MASS OF CARBON DIOXIDE
 DETERMINING THE MOLAR MASS OF CARBON DIOXIDE PURPOSE: The goal of the experiment is to determine the molar mass of carbon dioxide and compare the experimentally determined value to the theoretical value.
DETERMINING THE MOLAR MASS OF CARBON DIOXIDE PURPOSE: The goal of the experiment is to determine the molar mass of carbon dioxide and compare the experimentally determined value to the theoretical value.
COMMON LABORATORY APPARATUS
 COMMON LABORATORY APPARATUS Beakers are useful as a reaction container or to hold liquid or solid samples. They are also used to catch liquids from titrations and filtrates from filtering operations. Bunsen
COMMON LABORATORY APPARATUS Beakers are useful as a reaction container or to hold liquid or solid samples. They are also used to catch liquids from titrations and filtrates from filtering operations. Bunsen
Answer, Key Homework 6 David McIntyre 1
 Answer, Key Homework 6 David McIntyre 1 This print-out should have 0 questions, check that it is complete. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page: find all choices before making
Answer, Key Homework 6 David McIntyre 1 This print-out should have 0 questions, check that it is complete. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page: find all choices before making
Experiment 6 Coffee-cup Calorimetry
 6-1 Experiment 6 Coffee-cup Calorimetry Introduction: Chemical reactions involve the release or consumption of energy, usually in the form of heat. Heat is measured in the energy units, Joules (J), defined
6-1 Experiment 6 Coffee-cup Calorimetry Introduction: Chemical reactions involve the release or consumption of energy, usually in the form of heat. Heat is measured in the energy units, Joules (J), defined
EXPERIMENT 15: Ideal Gas Law: Molecular Weight of a Vapor
 EXPERIMENT 15: Ideal Gas Law: Molecular Weight of a Vapor Purpose: In this experiment you will use the ideal gas law to calculate the molecular weight of a volatile liquid compound by measuring the mass,
EXPERIMENT 15: Ideal Gas Law: Molecular Weight of a Vapor Purpose: In this experiment you will use the ideal gas law to calculate the molecular weight of a volatile liquid compound by measuring the mass,
Practical 1: Measure the molar volume of a gas
 Practical Student sheet Practical : Wear eye protection. Ensure the delivery tube does not become blocked. Ethanoic acid will sting if it gets into cuts in the skin. Equipment boiling tube stand and clamp
Practical Student sheet Practical : Wear eye protection. Ensure the delivery tube does not become blocked. Ethanoic acid will sting if it gets into cuts in the skin. Equipment boiling tube stand and clamp
PREPARATION FOR CHEMISTRY LAB: COMBUSTION
 1 Name: Lab Instructor: PREPARATION FOR CHEMISTRY LAB: COMBUSTION 1. What is a hydrocarbon? 2. What products form in the complete combustion of a hydrocarbon? 3. Combustion is an exothermic reaction. What
1 Name: Lab Instructor: PREPARATION FOR CHEMISTRY LAB: COMBUSTION 1. What is a hydrocarbon? 2. What products form in the complete combustion of a hydrocarbon? 3. Combustion is an exothermic reaction. What
Reaction of Magnesium with Hydrochloric Acid (Gas Laws) Chemicals Needed:
 Reaction of Magnesium with Hydrochloric Acid (Gas Laws) Your Name: Date: Partner(s) Names: Objectives: React magnesium metal with hydrochloric acid, collecting the hydrogen over water. Calculate the grams
Reaction of Magnesium with Hydrochloric Acid (Gas Laws) Your Name: Date: Partner(s) Names: Objectives: React magnesium metal with hydrochloric acid, collecting the hydrogen over water. Calculate the grams
Determining Equivalent Weight by Copper Electrolysis
 Purpose The purpose of this experiment is to determine the equivalent mass of copper based on change in the mass of a copper electrode and the volume of hydrogen gas generated during an electrolysis reaction.
Purpose The purpose of this experiment is to determine the equivalent mass of copper based on change in the mass of a copper electrode and the volume of hydrogen gas generated during an electrolysis reaction.
Chapter 18 Temperature, Heat, and the First Law of Thermodynamics. Problems: 8, 11, 13, 17, 21, 27, 29, 37, 39, 41, 47, 51, 57
 Chapter 18 Temperature, Heat, and the First Law of Thermodynamics Problems: 8, 11, 13, 17, 21, 27, 29, 37, 39, 41, 47, 51, 57 Thermodynamics study and application of thermal energy temperature quantity
Chapter 18 Temperature, Heat, and the First Law of Thermodynamics Problems: 8, 11, 13, 17, 21, 27, 29, 37, 39, 41, 47, 51, 57 Thermodynamics study and application of thermal energy temperature quantity
Experiment 12E LIQUID-VAPOR EQUILIBRIUM OF WATER 1
 Experiment 12E LIQUID-VAPOR EQUILIBRIUM OF WATER 1 FV 6/26/13 MATERIALS: PURPOSE: 1000 ml tall-form beaker, 10 ml graduated cylinder, -10 to 110 o C thermometer, thermometer clamp, plastic pipet, long
Experiment 12E LIQUID-VAPOR EQUILIBRIUM OF WATER 1 FV 6/26/13 MATERIALS: PURPOSE: 1000 ml tall-form beaker, 10 ml graduated cylinder, -10 to 110 o C thermometer, thermometer clamp, plastic pipet, long
Experiment 2: Using Bomb Calorimetry to Determine the Resonance Energy of Benzene
 Experiment 2: Using Bomb Calorimetry to Determine the Resonance Energy of Benzene Reading: SGN: p.145-151 (152-157 may also be useful) Quanta: Benzene, Resonance Benzene was historically a very difficult
Experiment 2: Using Bomb Calorimetry to Determine the Resonance Energy of Benzene Reading: SGN: p.145-151 (152-157 may also be useful) Quanta: Benzene, Resonance Benzene was historically a very difficult
MOLECULAR WEIGHT BY BOILING POINT ELEVATION
 MOLECULAR WEIGHT BY BOILING POINT ELEVATION BACKGROUND This experiment demonstrates the use of colligative properties. The goal is to measure the molecular weight of a non-volatile solute by determining
MOLECULAR WEIGHT BY BOILING POINT ELEVATION BACKGROUND This experiment demonstrates the use of colligative properties. The goal is to measure the molecular weight of a non-volatile solute by determining
Bomb Calorimetry. Example 4. Energy and Enthalpy
 Bomb Calorimetry constant volume often used for combustion reactions heat released by reaction is absorbed by calorimeter contents need heat capacity of calorimeter q cal = q rxn = q bomb + q water Example
Bomb Calorimetry constant volume often used for combustion reactions heat released by reaction is absorbed by calorimeter contents need heat capacity of calorimeter q cal = q rxn = q bomb + q water Example
EXPERIMENT 4 THE DETERMINATION OF THE CALORIC CONTENT OF A CASHEW NUT
 EXPERIMENT 4 THE DETERMINATION OF THE CALORIC CONTENT OF A CASHEW NUT Textbook reference: pp103-105 Purpose: In this Activity, students determine how many calories are released per gram when cashews burn
EXPERIMENT 4 THE DETERMINATION OF THE CALORIC CONTENT OF A CASHEW NUT Textbook reference: pp103-105 Purpose: In this Activity, students determine how many calories are released per gram when cashews burn
Transfer of heat energy often occurs during chemical reactions. A reaction
 Chemistry 111 Lab: Thermochemistry Page I-3 THERMOCHEMISTRY Heats of Reaction The Enthalpy of Formation of Magnesium Oxide Transfer of heat energy often occurs during chemical reactions. A reaction may
Chemistry 111 Lab: Thermochemistry Page I-3 THERMOCHEMISTRY Heats of Reaction The Enthalpy of Formation of Magnesium Oxide Transfer of heat energy often occurs during chemical reactions. A reaction may
HEAT OF FORMATION OF AMMONIUM NITRATE
 303 HEAT OF FORMATION OF AMMONIUM NITRATE OBJECTIVES FOR THE EXPERIMENT The student will be able to do the following: 1. Calculate the change in enthalpy (heat of reaction) using the Law of Hess. 2. Find
303 HEAT OF FORMATION OF AMMONIUM NITRATE OBJECTIVES FOR THE EXPERIMENT The student will be able to do the following: 1. Calculate the change in enthalpy (heat of reaction) using the Law of Hess. 2. Find
Chemistry 112 Laboratory Experiment 6: The Reaction of Aluminum and Zinc with Hydrochloric Acid
 Chemistry 112 Laboratory Experiment 6: The Reaction of Aluminum and Zinc with Hydrochloric Acid Introduction Many metals react with acids to form hydrogen gas. In this experiment, you will use the reactions
Chemistry 112 Laboratory Experiment 6: The Reaction of Aluminum and Zinc with Hydrochloric Acid Introduction Many metals react with acids to form hydrogen gas. In this experiment, you will use the reactions
Exp 13 Volumetric Analysis: Acid-Base titration
 Exp 13 Volumetric Analysis: Acid-Base titration Exp. 13 video (time: 47:17 minutes) Titration - is the measurement of the volume of a standard solution required to completely react with a measured volume
Exp 13 Volumetric Analysis: Acid-Base titration Exp. 13 video (time: 47:17 minutes) Titration - is the measurement of the volume of a standard solution required to completely react with a measured volume
Physical Properties of a Pure Substance, Water
 Physical Properties of a Pure Substance, Water The chemical and physical properties of a substance characterize it as a unique substance, and the determination of these properties can often allow one to
Physical Properties of a Pure Substance, Water The chemical and physical properties of a substance characterize it as a unique substance, and the determination of these properties can often allow one to
LAB 15: HEAT ENGINES AND
 251 Name Date Partners LAB 15: HEAT ENGINES AND THE FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS... the quantity of heat produced by the friction of bodies, whether solid or liquid, is always proportional to the quantity
251 Name Date Partners LAB 15: HEAT ENGINES AND THE FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS... the quantity of heat produced by the friction of bodies, whether solid or liquid, is always proportional to the quantity
Problem Set 1 3.20 MIT Professor Gerbrand Ceder Fall 2003
 LEVEL 1 PROBLEMS Problem Set 1 3.0 MIT Professor Gerbrand Ceder Fall 003 Problem 1.1 The internal energy per kg for a certain gas is given by U = 0. 17 T + C where U is in kj/kg, T is in Kelvin, and C
LEVEL 1 PROBLEMS Problem Set 1 3.0 MIT Professor Gerbrand Ceder Fall 003 Problem 1.1 The internal energy per kg for a certain gas is given by U = 0. 17 T + C where U is in kj/kg, T is in Kelvin, and C
To measure the solubility of a salt in water over a range of temperatures and to construct a graph representing the salt solubility.
 THE SOLUBILITY OF A SALT IN WATER AT VARIOUS TEMPERATURES 2007, 1995, 1991 by David A. Katz. All rights reserved. Permission for academic use provided the original copyright is included. OBJECTIVE To measure
THE SOLUBILITY OF A SALT IN WATER AT VARIOUS TEMPERATURES 2007, 1995, 1991 by David A. Katz. All rights reserved. Permission for academic use provided the original copyright is included. OBJECTIVE To measure
Molar Mass of Butane
 Cautions Butane is toxic and flammable. No OPEN Flames should be used in this experiment. Purpose The purpose of this experiment is to determine the molar mass of butane using Dalton s Law of Partial Pressures
Cautions Butane is toxic and flammable. No OPEN Flames should be used in this experiment. Purpose The purpose of this experiment is to determine the molar mass of butane using Dalton s Law of Partial Pressures
In this experiment, we will use three properties to identify a liquid substance: solubility, density and boiling point..
 Identification of a Substance by Physical Properties 2009 by David A. Katz. All rights reserved. Permission for academic use provided the original copyright is included Every substance has a unique set
Identification of a Substance by Physical Properties 2009 by David A. Katz. All rights reserved. Permission for academic use provided the original copyright is included Every substance has a unique set
Module 1: History of Fuels. Lecture 6: Fundamental definitions, properties and various measurements
 1 P age Module 1: History of Fuels Lecture 6: Fundamental definitions, properties and various measurements 2 P age Keywords: Characterisation, analytical methods, standards 1.3 Fundamental definitions,
1 P age Module 1: History of Fuels Lecture 6: Fundamental definitions, properties and various measurements 2 P age Keywords: Characterisation, analytical methods, standards 1.3 Fundamental definitions,
Burn Baby Burn: The Power Within! Feedstock Calorimetry. (by Mary C. Criss & Shannon Ralph)
 Burn Baby Burn: The Power Within! Feedstock Calorimetry (by Mary C. Criss & Shannon Ralph) Objective The purpose of this experiment is to determine the amount of chemical energy stored in different biofuel
Burn Baby Burn: The Power Within! Feedstock Calorimetry (by Mary C. Criss & Shannon Ralph) Objective The purpose of this experiment is to determine the amount of chemical energy stored in different biofuel
Experiment 1: Colligative Properties
 Experiment 1: Colligative Properties Determination of the Molar Mass of a Compound by Freezing Point Depression. Objective: The objective of this experiment is to determine the molar mass of an unknown
Experiment 1: Colligative Properties Determination of the Molar Mass of a Compound by Freezing Point Depression. Objective: The objective of this experiment is to determine the molar mass of an unknown
Austin Peay State University Department of Chemistry CHEM 1111. Empirical Formula of a Compound
 Cautions Magnesium ribbon is flammable. Nitric acid (HNO 3 ) is toxic, corrosive and contact with eyes or skin may cause severe burns. Ammonia gas (NH 3 ) is toxic and harmful. Hot ceramic crucibles and
Cautions Magnesium ribbon is flammable. Nitric acid (HNO 3 ) is toxic, corrosive and contact with eyes or skin may cause severe burns. Ammonia gas (NH 3 ) is toxic and harmful. Hot ceramic crucibles and
Operating Instruction Manual. No. 204M. Oxygen Bomb Calorimeter
 Operating Instruction Manual No. 204M 1341 Oxygen Bomb Calorimeter SCOPE These instructions cover the steps to be taken in setting up and operating a Parr 1341 Plain Oxygen Bomb Calorimeter. The user should
Operating Instruction Manual No. 204M 1341 Oxygen Bomb Calorimeter SCOPE These instructions cover the steps to be taken in setting up and operating a Parr 1341 Plain Oxygen Bomb Calorimeter. The user should
Chapter 10 Temperature and Heat
 Chapter 10 Temperature and Heat What are temperature and heat? Are they the same? What causes heat? What Is Temperature? How do we measure temperature? What are we actually measuring? Temperature and Its
Chapter 10 Temperature and Heat What are temperature and heat? Are they the same? What causes heat? What Is Temperature? How do we measure temperature? What are we actually measuring? Temperature and Its
UNIT 1 THERMOCHEMISTRY
 UNIT 1 THERMOCHEMISTRY THERMOCHEMISTRY LEARNING OUTCOMES Students will be expected to: THERMOCHEMISTRY STSE analyse why scientific and technological activities take place in a variety individual and group
UNIT 1 THERMOCHEMISTRY THERMOCHEMISTRY LEARNING OUTCOMES Students will be expected to: THERMOCHEMISTRY STSE analyse why scientific and technological activities take place in a variety individual and group
a) Use the following equation from the lecture notes: = ( 8.314 J K 1 mol 1) ( ) 10 L
 hermodynamics: Examples for chapter 4. 1. One mole of nitrogen gas is allowed to expand from 0.5 to 10 L reversible and isothermal process at 300 K. Calculate the change in molar entropy using a the ideal
hermodynamics: Examples for chapter 4. 1. One mole of nitrogen gas is allowed to expand from 0.5 to 10 L reversible and isothermal process at 300 K. Calculate the change in molar entropy using a the ideal
Molar Mass and the Ideal Gas Law Prelab
 Molar Mass and the Ideal Gas Law Prelab Name Total /10 SHOW ALL WORK NO WORK = NO CREDIT 1. What is the purpose of this experiment? 2. Determine the mass (in grams) of magnesium metal required to produce
Molar Mass and the Ideal Gas Law Prelab Name Total /10 SHOW ALL WORK NO WORK = NO CREDIT 1. What is the purpose of this experiment? 2. Determine the mass (in grams) of magnesium metal required to produce
Introduction to Bomb Calorimetry
 No. 483M Introduction to Bomb Calorimetry The information presented here is intended to give Parr Calorimeter users an overview of the basic principals involved in measuring the heat of combustion (calorific
No. 483M Introduction to Bomb Calorimetry The information presented here is intended to give Parr Calorimeter users an overview of the basic principals involved in measuring the heat of combustion (calorific
globe reactions made easy Process perfection
 globe reactions made easy Process perfection Benefits More reactions in less time: The Globe oil drain unit and quick clamp allow single hand vessel changes in seconds Space saving: 50ml, 100ml, 250ml,
globe reactions made easy Process perfection Benefits More reactions in less time: The Globe oil drain unit and quick clamp allow single hand vessel changes in seconds Space saving: 50ml, 100ml, 250ml,
Lab Manual Introductory Chemistry: A Green Approach Version 4.1. 2010, escience Labs, Inc. All rights reserved esciencelabs.com 888.375.
 Lab Manual Introductory Chemistry: A Green Approach Version 4.1 2010, escience Labs, Inc. All rights reserved esciencelabs.com 888.375.5487 Table of Contents Lab 1: Introduc on and Safety Lab 2: The Scien
Lab Manual Introductory Chemistry: A Green Approach Version 4.1 2010, escience Labs, Inc. All rights reserved esciencelabs.com 888.375.5487 Table of Contents Lab 1: Introduc on and Safety Lab 2: The Scien
1. The Determination of Boiling Point
 1. The Determination of Boiling Point Objective In this experiment, you will first check your thermometer for errors by determining the temperature of two stable equilibrium systems. You will then use
1. The Determination of Boiling Point Objective In this experiment, you will first check your thermometer for errors by determining the temperature of two stable equilibrium systems. You will then use
Pre-Lab Notebook Content: Your notebook should include the title, date, purpose, procedure; data tables.
 Determination of Molar Mass by Freezing Point Depression M. Burkart & M. Kim Experimental Notes: Students work in pairs. Safety: Goggles and closed shoes must be worn. Dispose of all chemical in the plastic
Determination of Molar Mass by Freezing Point Depression M. Burkart & M. Kim Experimental Notes: Students work in pairs. Safety: Goggles and closed shoes must be worn. Dispose of all chemical in the plastic
Thermochemistry I: Endothermic & Exothermic Reactions
 THERMOCHEMISTRY I 77 Thermochemistry I: Endothermic & Exothermic Reactions OBJECTIVES: Learn elementary concepts of calorimetry and thermochemistry Practice techniques of careful temperature, mass, and
THERMOCHEMISTRY I 77 Thermochemistry I: Endothermic & Exothermic Reactions OBJECTIVES: Learn elementary concepts of calorimetry and thermochemistry Practice techniques of careful temperature, mass, and
Mixtures and Pure Substances
 Unit 2 Mixtures and Pure Substances Matter can be classified into two groups: mixtures and pure substances. Mixtures are the most common form of matter and consist of mixtures of pure substances. They
Unit 2 Mixtures and Pure Substances Matter can be classified into two groups: mixtures and pure substances. Mixtures are the most common form of matter and consist of mixtures of pure substances. They
ENGINE COOLING SYSTEM
 ENGINE COOLING SYSTEM 1988 Toyota Celica 1987-88 TOYOTA Engine Cooling Systems Celica DESCRIPTION The basic liquid cooling system consists of a radiator, water pump, thermostat, cooling fan, pressure cap,
ENGINE COOLING SYSTEM 1988 Toyota Celica 1987-88 TOYOTA Engine Cooling Systems Celica DESCRIPTION The basic liquid cooling system consists of a radiator, water pump, thermostat, cooling fan, pressure cap,
Where the exp subscripts refer to the experimental temperature and pressure acquired in the laboratory.
 Molar Volume of Carbon Dioxide Reading assignment: Julia Burdge, Chemistry 3rd edition, Chapter 10. Goals To determine the molar volume of carbon dioxide gas and the amount of sodium carbonate in a sample.
Molar Volume of Carbon Dioxide Reading assignment: Julia Burdge, Chemistry 3rd edition, Chapter 10. Goals To determine the molar volume of carbon dioxide gas and the amount of sodium carbonate in a sample.
IDEAL AND NON-IDEAL GASES
 2/2016 ideal gas 1/8 IDEAL AND NON-IDEAL GASES PURPOSE: To measure how the pressure of a low-density gas varies with temperature, to determine the absolute zero of temperature by making a linear fit to
2/2016 ideal gas 1/8 IDEAL AND NON-IDEAL GASES PURPOSE: To measure how the pressure of a low-density gas varies with temperature, to determine the absolute zero of temperature by making a linear fit to
MOISTURE (Karl Fischer, Buffered)
 MOIST.03-1 MOISTURE (Karl Fischer, Buffered) PRINCIPLE SCOPE The sample is dissolved in a mixture of methanol and formamide (50:50 v/v) and then titrated with standardized Karl Fischer reagent. The titration
MOIST.03-1 MOISTURE (Karl Fischer, Buffered) PRINCIPLE SCOPE The sample is dissolved in a mixture of methanol and formamide (50:50 v/v) and then titrated with standardized Karl Fischer reagent. The titration
Glassware Calibration Guidelines Laura B. Secor and Dwight R. Stoll, 02/01/2012 Adapted from National Bureau of Standards Document 74-461
 Glassware Calibration Guidelines Laura B. Secor and Dwight R. Stoll, 02/0/202 Adapted from National Bureau of Standards Document 74-46 The purpose of calibrating glassware is to determine the volume of
Glassware Calibration Guidelines Laura B. Secor and Dwight R. Stoll, 02/0/202 Adapted from National Bureau of Standards Document 74-46 The purpose of calibrating glassware is to determine the volume of
Problem Set 4 Solutions
 Chemistry 360 Dr Jean M Standard Problem Set 4 Solutions 1 Two moles of an ideal gas are compressed isothermally and reversibly at 98 K from 1 atm to 00 atm Calculate q, w, ΔU, and ΔH For an isothermal
Chemistry 360 Dr Jean M Standard Problem Set 4 Solutions 1 Two moles of an ideal gas are compressed isothermally and reversibly at 98 K from 1 atm to 00 atm Calculate q, w, ΔU, and ΔH For an isothermal
Problem Set 3 Solutions
 Chemistry 360 Dr Jean M Standard Problem Set 3 Solutions 1 (a) One mole of an ideal gas at 98 K is expanded reversibly and isothermally from 10 L to 10 L Determine the amount of work in Joules We start
Chemistry 360 Dr Jean M Standard Problem Set 3 Solutions 1 (a) One mole of an ideal gas at 98 K is expanded reversibly and isothermally from 10 L to 10 L Determine the amount of work in Joules We start
Chemistry 119: Experiment 7. Potentiometric Titration of Ascorbic Acid in Vitamin C Tablets
 Chemistry 119: Experiment 7 Potentiometric Titration of Ascorbic Acid in Vitamin C Tablets Vitamin C is another name for ascorbic acid (C 6 H 8 O 6, see below ), a weak acid that can be determined by titration
Chemistry 119: Experiment 7 Potentiometric Titration of Ascorbic Acid in Vitamin C Tablets Vitamin C is another name for ascorbic acid (C 6 H 8 O 6, see below ), a weak acid that can be determined by titration
1 Exercise 2.19a pg 86
 In this solution set, an underline is used to show the last significant digit of numbers. For instance in x = 2.51693 the 2,5,1, and 6 are all significant. Digits to the right of the underlined digit,
In this solution set, an underline is used to show the last significant digit of numbers. For instance in x = 2.51693 the 2,5,1, and 6 are all significant. Digits to the right of the underlined digit,
Phys222 W11 Quiz 1: Chapters 19-21 Keys. Name:
 Name:. In order for two objects to have the same temperature, they must a. be in thermal equilibrium.
Name:. In order for two objects to have the same temperature, they must a. be in thermal equilibrium.
Experiment 3 Limiting Reactants
 3-1 Experiment 3 Limiting Reactants Introduction: Most chemical reactions require two or more reactants. Typically, one of the reactants is used up before the other, at which time the reaction stops. The
3-1 Experiment 3 Limiting Reactants Introduction: Most chemical reactions require two or more reactants. Typically, one of the reactants is used up before the other, at which time the reaction stops. The
18 Conductometric Titration
 Lab Activity 18 CONDUCTOMETRIC TITRATION LAB ACTIVITY 18 Conductometric Titration Background Titration is the a method of determining the concentration of an unknown solution (the analyte) by reacting
Lab Activity 18 CONDUCTOMETRIC TITRATION LAB ACTIVITY 18 Conductometric Titration Background Titration is the a method of determining the concentration of an unknown solution (the analyte) by reacting
We will study the temperature-pressure diagram of nitrogen, in particular the triple point.
 K4. Triple Point of Nitrogen I. OBJECTIVE OF THE EXPERIMENT We will study the temperature-pressure diagram of nitrogen, in particular the triple point. II. BAKGROUND THOERY States of matter Matter is made
K4. Triple Point of Nitrogen I. OBJECTIVE OF THE EXPERIMENT We will study the temperature-pressure diagram of nitrogen, in particular the triple point. II. BAKGROUND THOERY States of matter Matter is made
CHEM 105 HOUR EXAM III 28-OCT-99. = -163 kj/mole determine H f 0 for Ni(CO) 4 (g) = -260 kj/mole determine H f 0 for Cr(CO) 6 (g)
 CHEM 15 HOUR EXAM III 28-OCT-99 NAME (please print) 1. a. given: Ni (s) + 4 CO (g) = Ni(CO) 4 (g) H Rxn = -163 k/mole determine H f for Ni(CO) 4 (g) b. given: Cr (s) + 6 CO (g) = Cr(CO) 6 (g) H Rxn = -26
CHEM 15 HOUR EXAM III 28-OCT-99 NAME (please print) 1. a. given: Ni (s) + 4 CO (g) = Ni(CO) 4 (g) H Rxn = -163 k/mole determine H f for Ni(CO) 4 (g) b. given: Cr (s) + 6 CO (g) = Cr(CO) 6 (g) H Rxn = -26
EXPERIMENT 12: Empirical Formula of a Compound
 EXPERIMENT 12: Empirical Formula of a Compound INTRODUCTION Chemical formulas indicate the composition of compounds. A formula that gives only the simplest ratio of the relative number of atoms in a compound
EXPERIMENT 12: Empirical Formula of a Compound INTRODUCTION Chemical formulas indicate the composition of compounds. A formula that gives only the simplest ratio of the relative number of atoms in a compound
Melting Point, Boiling Point, and Index of Refraction
 Melting Point, Boiling Point, and Index of Refraction Melting points, boiling points, and index of refractions are easily measured physical properties of organic compounds useful in product characterization
Melting Point, Boiling Point, and Index of Refraction Melting points, boiling points, and index of refractions are easily measured physical properties of organic compounds useful in product characterization
EXPERIMENT 13: THE IDEAL GAS LAW AND THE MOLECULAR WEIGHT OF GASES
 Name Section EXPERIMENT 13: THE IDEAL GAS LAW AND THE MOLECULAR WEIGHT OF GASES PRE-LABORATORY QUESTIONS The following preparatory questions should be answered before coming to lab. They are intended to
Name Section EXPERIMENT 13: THE IDEAL GAS LAW AND THE MOLECULAR WEIGHT OF GASES PRE-LABORATORY QUESTIONS The following preparatory questions should be answered before coming to lab. They are intended to
Physical Chemistry Laboratory I CHEM 445 Experiment 6 Vapor Pressure of a Pure Liquid (Revised, 01/09/06)
 1 Physical Chemistry Laboratory I CHEM 445 Experiment 6 Vapor Pressure of a Pure Liquid (Revised, 01/09/06) The vapor pressure of a pure liquid is an intensive property of the compound. That is, the vapor
1 Physical Chemistry Laboratory I CHEM 445 Experiment 6 Vapor Pressure of a Pure Liquid (Revised, 01/09/06) The vapor pressure of a pure liquid is an intensive property of the compound. That is, the vapor
1. Thermite reaction 2. Enthalpy of reaction, H 3. Heating/cooling curves and changes in state 4. More thermite thermodynamics
 Chem 105 Fri 10-23-09 1. Thermite reaction 2. Enthalpy of reaction, H 3. Heating/cooling curves and changes in state 4. More thermite thermodynamics 10/23/2009 1 Please PICK UP your graded EXAM in front.
Chem 105 Fri 10-23-09 1. Thermite reaction 2. Enthalpy of reaction, H 3. Heating/cooling curves and changes in state 4. More thermite thermodynamics 10/23/2009 1 Please PICK UP your graded EXAM in front.
ANALYSIS OF FOOD AND NATURAL PRODUCTS LABORATORY EXERCISE
 ANALYSIS OF FOOD AND NATURAL PRODUCTS LABORATORY EXERCISE Determination of total nitrogen in food and crude protein calculation (Kjeldahl method) Responsible person: Assoc.Prof. Ing.Kateřina Riddellová,
ANALYSIS OF FOOD AND NATURAL PRODUCTS LABORATORY EXERCISE Determination of total nitrogen in food and crude protein calculation (Kjeldahl method) Responsible person: Assoc.Prof. Ing.Kateřina Riddellová,
Chapter 6 Thermodynamics: The First Law
 Key Concepts 6.1 Systems Chapter 6 Thermodynamics: The First Law Systems, States, and Energy (Sections 6.1 6.8) thermodynamics, statistical thermodynamics, system, surroundings, open system, closed system,
Key Concepts 6.1 Systems Chapter 6 Thermodynamics: The First Law Systems, States, and Energy (Sections 6.1 6.8) thermodynamics, statistical thermodynamics, system, surroundings, open system, closed system,
AP CHEMISTRY 2009 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B)
 AP CHEMISTRY 2009 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B) Question 3 (10 points) 2 H 2 O 2 (aq) 2 H 2 O(l) + O 2 (g) The mass of an aqueous solution of H 2 O 2 is 6.951 g. The H 2 O 2 in the solution decomposes completely
AP CHEMISTRY 2009 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B) Question 3 (10 points) 2 H 2 O 2 (aq) 2 H 2 O(l) + O 2 (g) The mass of an aqueous solution of H 2 O 2 is 6.951 g. The H 2 O 2 in the solution decomposes completely
Calibration of Volumetric Glassware
 CHEM 311L Quantitative Analysis Laboratory Revision 2.3 Calibration of Volumetric Glassware In this laboratory exercise, we will calibrate the three types of glassware typically used by an analytical chemist;
CHEM 311L Quantitative Analysis Laboratory Revision 2.3 Calibration of Volumetric Glassware In this laboratory exercise, we will calibrate the three types of glassware typically used by an analytical chemist;
VAPOR PRESSURE AS A FUNCTION OF TEMPERATURE. This laboratory covers material presented in section 11.8 of the 9 th Ed. of the Chang text.
 VAPOR PRESSURE AS A FUNCTION OF TEMPERATURE Objectives: (1) Observe and measure the change in the vapor pressure (dependent variable) as a function of temperature (independent variable). (2) Analyze the
VAPOR PRESSURE AS A FUNCTION OF TEMPERATURE Objectives: (1) Observe and measure the change in the vapor pressure (dependent variable) as a function of temperature (independent variable). (2) Analyze the
Thermodynamics AP Physics B. Multiple Choice Questions
 Thermodynamics AP Physics B Name Multiple Choice Questions 1. What is the name of the following statement: When two systems are in thermal equilibrium with a third system, then they are in thermal equilibrium
Thermodynamics AP Physics B Name Multiple Choice Questions 1. What is the name of the following statement: When two systems are in thermal equilibrium with a third system, then they are in thermal equilibrium
ACID-BASE TITRATIONS: DETERMINATION OF CARBONATE BY TITRATION WITH HYDROCHLORIC ACID BACKGROUND
 #3. Acid - Base Titrations 27 EXPERIMENT 3. ACID-BASE TITRATIONS: DETERMINATION OF CARBONATE BY TITRATION WITH HYDROCHLORIC ACID BACKGROUND Carbonate Equilibria In this experiment a solution of hydrochloric
#3. Acid - Base Titrations 27 EXPERIMENT 3. ACID-BASE TITRATIONS: DETERMINATION OF CARBONATE BY TITRATION WITH HYDROCHLORIC ACID BACKGROUND Carbonate Equilibria In this experiment a solution of hydrochloric
IB Chemistry. DP Chemistry Review
 DP Chemistry Review Topic 1: Quantitative chemistry 1.1 The mole concept and Avogadro s constant Assessment statement Apply the mole concept to substances. Determine the number of particles and the amount
DP Chemistry Review Topic 1: Quantitative chemistry 1.1 The mole concept and Avogadro s constant Assessment statement Apply the mole concept to substances. Determine the number of particles and the amount
vap H = RT 1T 2 = 30.850 kj mol 1 100 kpa = 341 K
 Thermodynamics: Examples for chapter 6. 1. The boiling point of hexane at 1 atm is 68.7 C. What is the boiling point at 1 bar? The vapor pressure of hexane at 49.6 C is 53.32 kpa. Assume that the vapor
Thermodynamics: Examples for chapter 6. 1. The boiling point of hexane at 1 atm is 68.7 C. What is the boiling point at 1 bar? The vapor pressure of hexane at 49.6 C is 53.32 kpa. Assume that the vapor
Recovery of Elemental Copper from Copper (II) Nitrate
 Recovery of Elemental Copper from Copper (II) Nitrate Objectives: Challenge: Students should be able to - recognize evidence(s) of a chemical change - convert word equations into formula equations - perform
Recovery of Elemental Copper from Copper (II) Nitrate Objectives: Challenge: Students should be able to - recognize evidence(s) of a chemical change - convert word equations into formula equations - perform
PHOTOSYNTHESIS AND RESPIRATION
 PHOTOSYNTHESIS AND RESPIRATION STANDARDS: 3.2.10.B.3, 3.2.10.C.4 3.3.10.B.4 Westminster College INTRODUCTION Plants make sugar, storing the energy of the sun as chemical energy, by the process of photosynthesis.
PHOTOSYNTHESIS AND RESPIRATION STANDARDS: 3.2.10.B.3, 3.2.10.C.4 3.3.10.B.4 Westminster College INTRODUCTION Plants make sugar, storing the energy of the sun as chemical energy, by the process of photosynthesis.
thermometer as simple as a styrofoam cup and a thermometer. In a calorimeter the reactants are placed into the
 Thermochemistry Readin assinment: Chan, Chemistry 10 th edition, pp. 249-258. Goals We will become familiar with the principles of calorimetry in order to determine the heats of reaction for endothermic
Thermochemistry Readin assinment: Chan, Chemistry 10 th edition, pp. 249-258. Goals We will become familiar with the principles of calorimetry in order to determine the heats of reaction for endothermic
Physical and Chemical Properties and Changes
 Physical and Chemical Properties and Changes An understanding of material things requires an understanding of the physical and chemical characteristics of matter. A few planned experiments can help you
Physical and Chemical Properties and Changes An understanding of material things requires an understanding of the physical and chemical characteristics of matter. A few planned experiments can help you
The Determination of an Equilibrium Constant
 The Determination of an Equilibrium Constant Computer 10 Chemical reactions occur to reach a state of equilibrium. The equilibrium state can be characterized by quantitatively defining its equilibrium
The Determination of an Equilibrium Constant Computer 10 Chemical reactions occur to reach a state of equilibrium. The equilibrium state can be characterized by quantitatively defining its equilibrium
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Given: 4 NO2(g) + O2(g) 2 N2O5(g) ΔH = -110.2 kj find ΔH for N2O5(g) 2 NO2(g) + 1/2 O2(g).
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Given: 4 NO2(g) + O2(g) 2 N2O5(g) ΔH = -110.2 kj find ΔH for N2O5(g) 2 NO2(g) + 1/2 O2(g).
Stoichiometry: Baking Soda and Vinegar Reactions
 Stoichiometry: Baking Soda and Vinegar Reactions California Science Content Standards: Teacher Version 3. Conservation of Matter and Stoichiometry: The conservation of atoms in chemical reactions leads
Stoichiometry: Baking Soda and Vinegar Reactions California Science Content Standards: Teacher Version 3. Conservation of Matter and Stoichiometry: The conservation of atoms in chemical reactions leads
THE KINETIC THEORY OF GASES
 Chapter 19: THE KINETIC THEORY OF GASES 1. Evidence that a gas consists mostly of empty space is the fact that: A. the density of a gas becomes much greater when it is liquefied B. gases exert pressure
Chapter 19: THE KINETIC THEORY OF GASES 1. Evidence that a gas consists mostly of empty space is the fact that: A. the density of a gas becomes much greater when it is liquefied B. gases exert pressure
Determination of the Percentage Oxygen in Air
 CHEM 121L General Chemistry Laboratory Revision 1.1 Determination of the Percentage Oxygen in Air In this laboratory exercise we will determine the percentage by volume of Oxygen in Air. We will do this
CHEM 121L General Chemistry Laboratory Revision 1.1 Determination of the Percentage Oxygen in Air In this laboratory exercise we will determine the percentage by volume of Oxygen in Air. We will do this
Experiment 8 Synthesis of Aspirin
 Experiment 8 Synthesis of Aspirin Aspirin is an effective analgesic (pain reliever), antipyretic (fever reducer) and anti-inflammatory agent and is one of the most widely used non-prescription drugs. The
Experiment 8 Synthesis of Aspirin Aspirin is an effective analgesic (pain reliever), antipyretic (fever reducer) and anti-inflammatory agent and is one of the most widely used non-prescription drugs. The
Introduction to the Ideal Gas Law
 Course PHYSICS260 Assignment 5 Consider ten grams of nitrogen gas at an initial pressure of 6.0 atm and at room temperature. It undergoes an isobaric expansion resulting in a quadrupling of its volume.
Course PHYSICS260 Assignment 5 Consider ten grams of nitrogen gas at an initial pressure of 6.0 atm and at room temperature. It undergoes an isobaric expansion resulting in a quadrupling of its volume.
Heat. Investigating the function of the expansion valve of the heat pump. LD Physics Leaflets P2.6.3.2. Thermodynamic cycle Heat pump
 Heat Thermodynamic cycle Heat pump LD Physics Leaflets P2.6.3.2 Investigating the function of the expansion valve of the heat pump Objects of the experiment g To study the operational components of the
Heat Thermodynamic cycle Heat pump LD Physics Leaflets P2.6.3.2 Investigating the function of the expansion valve of the heat pump Objects of the experiment g To study the operational components of the
Determination of a Chemical Formula
 1 Determination of a Chemical Formula Introduction Molar Ratios Elements combine in fixed ratios to form compounds. For example, consider the compound TiCl 4 (titanium chloride). Each molecule of TiCl
1 Determination of a Chemical Formula Introduction Molar Ratios Elements combine in fixed ratios to form compounds. For example, consider the compound TiCl 4 (titanium chloride). Each molecule of TiCl
Determining the Quantity of Iron in a Vitamin Tablet. Evaluation copy
 Determining the Quantity of Iron in a Vitamin Tablet Computer 34 As biochemical research becomes more sophisticated, we are learning more about the role of metallic elements in the human body. For example,
Determining the Quantity of Iron in a Vitamin Tablet Computer 34 As biochemical research becomes more sophisticated, we are learning more about the role of metallic elements in the human body. For example,
Chemistry 212 VAPOR PRESSURE OF WATER LEARNING OBJECTIVES
 Chemistry 212 VAPOR PRESSURE OF WATER LEARNING OBJECTIVES The learning objectives of this experiment are to explore the relationship between the temperature and vapor pressure of water. determine the molar
Chemistry 212 VAPOR PRESSURE OF WATER LEARNING OBJECTIVES The learning objectives of this experiment are to explore the relationship between the temperature and vapor pressure of water. determine the molar
