Anatomy of the Hippocampus
|
|
|
- Phoebe Ross
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Anatomy of the Hippocampus Lecture 3.2 David S. Touretzky September, 2013
2 Human Hippocampus 2
3 Human Hippocampus 3
4 Hippocampus Means Seahorse Dissected human hippocampus next to a specimen of hippocampus leria, one of several dozen species. 4
5 Rat Hippocampal Formation septal temporal From (Amaral & Witter, 1989) 5
6 Ammon: Egyptian god with ram's horns 6
7 Rat Hippocampal Formation septal temporal 7
8 Components of Hippocampal Formation The hippocampus contains CA1 - CA3. CA = Cornu Amonis (Ammon's horn) Ammon's Horn The hippocampal formation includes CA, dentate gyrus ( tooth-like bump ), entorhinal cortex, subiculum, pre- and parasubiculum. Hilus: reciprocally connected to DG. 8
9 Early Anatomy: Cajal's Drawings 9
10 Rat Hippocampus 10
11 Monkey Hippocampus 11
12 Human Hippocampus The volume of the human hippocampus is about 100 times that of the rat, and 10 times that of the monkey. 12
13 Basic Circuit Layer III perforant path EC Layer II perf. path DG Mossy fibers The mossy fiber synapse is one of the largest and most powerful synapses in the brain. CA3 Schaffer collaterals CA1 Recurrent collaterals 13
14 Connectivity Is Mostly Uni-Directional 14
15 More of the Picture EC: entorhinal cortex Layer II projects to DG/CA3 Layer III projects to CA1/Sub mossy fibers project to CA Hilus mf CA3 Sch Schaffer collaterals to CA1 Sub Sub: subiculum DG CA1 CA3 pp DG: dentate gyrus CA1 & Sub project back to EC layer V Other cortical & subcortical areas EC 15
16 Even More PR: perirhinal cortex; POR: postrhinal cortex; EC: entorhinal cortex; PrS: presubiculum; PaS: parasubiculum; DG: dentate gyrus; CA: Cornu amonis; S: subiculum; RSP: retrosplenial cortex; Par/Oc: parietal/occipital cortex 16
17 Three Major Fiber Systems Angular bundle from EC: perforant path (and more) Fimbria/fornix to subcortical areas fimbria: red fornix: yellow Dorsal and ventral commissures link hippocampi dorsal: purple ventral: green 17
18 Alveus/Fimbria/Fornix Second input/output pathway for hippocampus (first is via angular bundle from EC) Communicates with subcortical structures: septal nuclei and mammillary bodies 18
19 (commissural pathway) (perforant path) 19
20 Dendritic Arborization of Principal Cells suprapyramidal blade infrapyramidal blade 20
21 Stucture of the Dentate Gyrus Granule cell layer holds principal cell bodies their axons form the mossy fiber pathway Molecular layer: gc dendritic tree; afferent connections Polymorphic cell layer (hilus): interneurons, mf collaterals 21
22 Mossy Fiber Synapse Onto CA3 Cells The dentate gyrus projection to CA3 terminates in large mossy fiber synapses. CA3 dendrites have thorny excresences with complex spine shapes. A mossy fiber can make synapses within one excresence. Each granule cells contacts only about 15 CA3 pyramidal cells. Each pyramidal cell receives input from only about 72 granule cells. 22
23 Structure of CA3 stratum radiatum: entorhinal afferents; mossy fibers enter from DG, make synapses in s. lucidum thorny excresences stratum lucidum stratum pyramidale stratum oriens: recurrent collaterals 23
24 Structure of CA1 stratum lacunosummoleculare: entorhinal afferents stratum radiatum: Schaeffer collaterals, commissural fibers stratum pyramidale stratum oriens 24
25 Interneurons in CA3/CA1 25
26 Structured Projections: EC Layer II vs. III EC layer II EC layer III 26
27 Layer II Projections MPP/LPP = medial/lateral perforant path 27
28 Layer III Projections 28
29 Temporal-Lobe.com 29
30 30
31 Some Numbers for the Rat Dentate Gyrus 1.2 million granule cells 4K basket cells 32K hilar interneurons (20K mossy cells) CA3/CA1 330K /420K pyramidal cells various interneurons Entorhinal cortex layer II Around 200K cells (20% interneurons?) Subiculum Around 180K cells 31
32 Rat Connectivity Perforant path projection to DG Around 4500 spines per granule cell (75% from EC) One EC cells makes about 18,000 synapses with granule cells CA3: three distinct inputs mossy fibers from DG 3,500 perforant path synapses from EC II 12,000 recurrent collaterals from other CA3 cells 8,000 to basilar dendrites (stratum oriens) 4,000 to apical dendrites (stratum radiatum) CA1: inputs from CA3 and EC From CA3 Schaffer collaterals: 4,500 basilar, 6500 apical synapses From EC layer III: 2,500 synapses 32
33 Why Does the Circuitry Look Like This? Why so many kinds of interneurons? Why have recurrent connections in some regions and not others? What do these regions compute? CA3 33
34 The Hippocampus Is Very Well Connected to Other Brain Areas Connected via EC and fimbria-fornix pathway to: Prefrontal / orbitorfrontal cortices Cingulate cortex Piriform cortex Perirhinal and Postrhinal cortices (sensory) Striatum Amygdala Septum Mammillary bodies Thalamus Hypothalamus 34
35 LEA/MEA = lateral/medial entorhinal area PER ` 35
36 Neuromodulatory Projections to HC NA: Attention 5HT: Mood DA: Reward ACh: Novelty locus coeruleus raphe nuclei substantia nigra acetylcholine medial septum 36
37 Hippocampal EEG Awake Active exploration: Resting: theta (8-12 Hz) plus gamma (40 Hz) LIA (Large-amplitude Irregular Activity) w/transient sharp waves Asleep REM sleep: theta Slow wave sleep: LIA S-SIA: small-amplitude irregular activity (Jarosiewicz & Skaggs) 37
38 Hippocampal EEG Awake (theta) ` REM sleep Sharp waves Slow wave sleep (LIA) LIA S SIA REM SIA LIA REM 38
39 What Does the Hippocampus Do? Formation of new episodic memories? Cognitive map? Anterograde amnesia (H.M. and others) Place cells in rats; spatial attention cells in monkeys Configural association theory? Lesioned rats are impaired on tasks requiring them to recognize cue configurations 39
Theta, Gamma, and Working Memory
 Theta, Gamma, and Working Memory Lecture 3.8 David S. Touretzky November, 2015 Outline Theta rhythm and gamma rhythms Phase precession in hippocampus Theta and gamma in entorhinal cortex Lisman working
Theta, Gamma, and Working Memory Lecture 3.8 David S. Touretzky November, 2015 Outline Theta rhythm and gamma rhythms Phase precession in hippocampus Theta and gamma in entorhinal cortex Lisman working
MEDIAL TEMPORAL LOBE (THE LIMBIC SYSTEM)
 MEDIAL TEMPORAL LOBE (THE LIMBIC SYSTEM) On the medial surface of the temporal lobe are three structures critical for normal human functioning. From rostral to caudal, they are the olfactory cortex, the
MEDIAL TEMPORAL LOBE (THE LIMBIC SYSTEM) On the medial surface of the temporal lobe are three structures critical for normal human functioning. From rostral to caudal, they are the olfactory cortex, the
Brain Structures That are Involved with Memory
 Early Theories of Brain Structures That are Involved with Psychology 372 Sensation Sensory Attention Rehearsal STM Storage Retrieval Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio
Early Theories of Brain Structures That are Involved with Psychology 372 Sensation Sensory Attention Rehearsal STM Storage Retrieval Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio
NEUROANATOMY 6 Limbic System
 NEUROANATOMY 6 Limbic System The Limbic System The part of the brain involved with learning, memory and emotion. It is affected in many neuropsychiatric diseases including schizophrenia, Alzheimer s disease
NEUROANATOMY 6 Limbic System The Limbic System The part of the brain involved with learning, memory and emotion. It is affected in many neuropsychiatric diseases including schizophrenia, Alzheimer s disease
Figure 2 Figure 3 Figure 1
 The brain is organized into three tiers; a lower tier made up by the brainstem and cerebellum, a middle tier containing the thalamus, basal ganglia and many components of the limbic system and an upper
The brain is organized into three tiers; a lower tier made up by the brainstem and cerebellum, a middle tier containing the thalamus, basal ganglia and many components of the limbic system and an upper
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. Sensory Pathway (PNS) OVERVIEW OF SPINAL CORD ANATOMY OF THE SPINAL CORD FUNCTIONS OF THE SPINAL CORD
 CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Central nervous system (CNS) brain and spinal cord enclosed in bony coverings Functions of the spinal cord spinal cord reflexes integration ti (summation of inhibitory and excitatory)
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Central nervous system (CNS) brain and spinal cord enclosed in bony coverings Functions of the spinal cord spinal cord reflexes integration ti (summation of inhibitory and excitatory)
OLFACTORY PATHWAYS AND LIMBIC SYSTEM
 903 Olfactory and Limbic OLFACTORY PATHWAYS AND LIMBIC SYSTEM I. OLFACTORY PATHWAYS The sense of smell is much less essential than vision, audition or the somatic senses, and will therefore receive less
903 Olfactory and Limbic OLFACTORY PATHWAYS AND LIMBIC SYSTEM I. OLFACTORY PATHWAYS The sense of smell is much less essential than vision, audition or the somatic senses, and will therefore receive less
Neuronal Computations Underlying the Firing of Place Cells and Their Role in Navigation
 Neuronal Computations Underlying the Firing of Place Cells and Their Role in Navigation Neil Burgess and John O Keefe Department of Anatomy, University College London, London, England HIPPOCAMPUS 7:749
Neuronal Computations Underlying the Firing of Place Cells and Their Role in Navigation Neil Burgess and John O Keefe Department of Anatomy, University College London, London, England HIPPOCAMPUS 7:749
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
 Chapter 7: The Nervous System Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways involved in a withdraw reflex Define
Chapter 7: The Nervous System Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways involved in a withdraw reflex Define
Unit 2 - Subcortical systems, neurochemistry and brain function
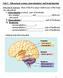 Unit 2 - Subcortical systems, neurochemistry and brain function Subcortical anatomy: Most of the five major subdivisions of the brain are subcortical. I. Telencephalon (cortical - part of forebrain) -
Unit 2 - Subcortical systems, neurochemistry and brain function Subcortical anatomy: Most of the five major subdivisions of the brain are subcortical. I. Telencephalon (cortical - part of forebrain) -
Structure and Function of Neurons
 CHPTER 1 Structure and Function of Neurons Varieties of neurons General structure Structure of unique neurons Internal operations and the functioning of a neuron Subcellular organelles Protein synthesis
CHPTER 1 Structure and Function of Neurons Varieties of neurons General structure Structure of unique neurons Internal operations and the functioning of a neuron Subcellular organelles Protein synthesis
Neuromodulation: acetylcholine and memory consolidation
 Clark Embodiment in cognitive science 40 Clark, A. and Toribio, J. (1995) Doing without representing? Synthese 101, 401 431 41 Smith, B.C. (1996) On the Origin of Objects, MIT Press 42 Brentano, F. (1874)
Clark Embodiment in cognitive science 40 Clark, A. and Toribio, J. (1995) Doing without representing? Synthese 101, 401 431 41 Smith, B.C. (1996) On the Origin of Objects, MIT Press 42 Brentano, F. (1874)
Spatial view cells in the hippocampus, and their idiothetic update based on place and head direction
 Neural Networks 8 (25) 229 24 25 Special issue Spatial view cells in the hippocampus, and their idiothetic update based on place and head direction Edmund T. Rolls *, Simon M. Stringer www.elsevier.com/locate/neunet
Neural Networks 8 (25) 229 24 25 Special issue Spatial view cells in the hippocampus, and their idiothetic update based on place and head direction Edmund T. Rolls *, Simon M. Stringer www.elsevier.com/locate/neunet
The Brain. What is it? Neurons Glial Cells Connective Tissue Connective Fiber White Matter Grey Matter Cerebro-spinal Fluid
 The Brain What is it? Neurons Glial Cells Connective Tissue Connective Fiber White Matter Grey Matter Cerebro-spinal Fluid A More Realistic View When we look at the brain we see mostly the Cerebral Cortex
The Brain What is it? Neurons Glial Cells Connective Tissue Connective Fiber White Matter Grey Matter Cerebro-spinal Fluid A More Realistic View When we look at the brain we see mostly the Cerebral Cortex
Mini-atlas of the Marmoset Brain
 Mini-atlas of the Marmoset Brain http://marmoset-brain.org Aya Senoo Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology Hironobu Tokuno Tokyo Metropolitan Institute of Medical Science Charles Watson Curtin
Mini-atlas of the Marmoset Brain http://marmoset-brain.org Aya Senoo Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology Hironobu Tokuno Tokyo Metropolitan Institute of Medical Science Charles Watson Curtin
Chapter 3 The Anatomy of the Nervous System
 Chapter 3 The Anatomy of the Nervous System Systems, Structures, and Cells That Make Up Your Nervous System 1 General Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain (in the skull) Spinal
Chapter 3 The Anatomy of the Nervous System Systems, Structures, and Cells That Make Up Your Nervous System 1 General Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain (in the skull) Spinal
Brain Matters: Brain Anatomy
 1 : Brain Anatomy Lesson Overview Students share what they already know about brain structure and function, and then, guided by descriptions of brain regions explore the G2C Online 3-D Brain to learn more
1 : Brain Anatomy Lesson Overview Students share what they already know about brain structure and function, and then, guided by descriptions of brain regions explore the G2C Online 3-D Brain to learn more
Nervous System Organization. PNS and CNS. Nerves. Peripheral Nervous System. Peripheral Nervous System. Motor Component.
 Nervous System Organization PNS and CNS Chapters 8 and 9 Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) connects CNS to sensory receptors, muscles and glands Central Nervous System (CNS) control/integrating center brain
Nervous System Organization PNS and CNS Chapters 8 and 9 Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) connects CNS to sensory receptors, muscles and glands Central Nervous System (CNS) control/integrating center brain
John E. Lisman* and Nonna A. Otmakhova. Volen Center for Complex Systems, Department of Biology, Brandeis University, Waltham, Massachusetts
 Storage, Recall, and Novelty Detection of Sequences by the Hippocampus: Elaborating on the SOCRATIC Model to Account for Normal and Aberrant Effects of Dopamine John E. Lisman* and Nonna A. Otmakhova Volen
Storage, Recall, and Novelty Detection of Sequences by the Hippocampus: Elaborating on the SOCRATIC Model to Account for Normal and Aberrant Effects of Dopamine John E. Lisman* and Nonna A. Otmakhova Volen
The Hypothalamus. Functions of the Hypothalamus. The Hypothalamus. Medical Neuroscience Dr. Wiegand
 The Medical Neuroscience Dr. Wiegand Neural Influences Neural Influences Hormonal Influences Hormonal Influences The Autonomic Nervous System Limbic System Endocrine System system Endocrine 1 The Diencephalon
The Medical Neuroscience Dr. Wiegand Neural Influences Neural Influences Hormonal Influences Hormonal Influences The Autonomic Nervous System Limbic System Endocrine System system Endocrine 1 The Diencephalon
2 Neurons. 4 The Brain: Cortex
 1 Neuroscience 2 Neurons output integration axon cell body, membrane potential Frontal planning control auditory episodes soma motor Temporal Parietal action language objects space vision Occipital inputs
1 Neuroscience 2 Neurons output integration axon cell body, membrane potential Frontal planning control auditory episodes soma motor Temporal Parietal action language objects space vision Occipital inputs
Human Neuroanatomy. Grades 9-12. Driving Question: How did the evolution of the human brain impact the structure and function it has today?
 Human Neuroanatomy Grades 9-12 Driving Question: How did the evolution of the human brain impact the structure and function it has today? Objectives: Students will be able to Describe the basic parts and
Human Neuroanatomy Grades 9-12 Driving Question: How did the evolution of the human brain impact the structure and function it has today? Objectives: Students will be able to Describe the basic parts and
What is the basic component of the brain and spinal cord communication system?
 EXPLORING PSYCHOLOGY David Myers The Biology of Mind Chapter 2 Neural Communication Neurons How Neurons Communicate How Neurotransmitters Influence Us The Nervous System The Peripheral Nervous System The
EXPLORING PSYCHOLOGY David Myers The Biology of Mind Chapter 2 Neural Communication Neurons How Neurons Communicate How Neurotransmitters Influence Us The Nervous System The Peripheral Nervous System The
Spatial Memory and Hippocampal Function: Where are we now?
 Psicológica (2002), 23, 109-138. Spatial Memory and Hippocampal Function: Where are we now? Mark Good * Cardiff University The main aim of this paper is to provide an overview of current debates concerning
Psicológica (2002), 23, 109-138. Spatial Memory and Hippocampal Function: Where are we now? Mark Good * Cardiff University The main aim of this paper is to provide an overview of current debates concerning
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
 Chapter 7: The Nervous System I. Organization of the Nervous System Objectives: List the general functions of the nervous system Explain the structural and functional classifications of the nervous system
Chapter 7: The Nervous System I. Organization of the Nervous System Objectives: List the general functions of the nervous system Explain the structural and functional classifications of the nervous system
FUNCTIONAL EEG ANALYZE IN AUTISM. Dr. Plamen Dimitrov
 FUNCTIONAL EEG ANALYZE IN AUTISM Dr. Plamen Dimitrov Preamble Autism or Autistic Spectrum Disorders (ASD) is a mental developmental disorder, manifested in the early childhood and is characterized by qualitative
FUNCTIONAL EEG ANALYZE IN AUTISM Dr. Plamen Dimitrov Preamble Autism or Autistic Spectrum Disorders (ASD) is a mental developmental disorder, manifested in the early childhood and is characterized by qualitative
Pierre Gloor (1923 2003): An Appreciation
 Epilepsia, 45(7):882 886, 2004 Blackwell Publishing, Inc. C 2004 International League Against Epilepsy In Memoriam Pierre Gloor (1923 2003): An Appreciation Massimo Avoli On October 24, 2003, the world
Epilepsia, 45(7):882 886, 2004 Blackwell Publishing, Inc. C 2004 International League Against Epilepsy In Memoriam Pierre Gloor (1923 2003): An Appreciation Massimo Avoli On October 24, 2003, the world
Neurobiology of Depression in Relation to ECT. PJ Cowen Department of Psychiatry, University of Oxford
 Neurobiology of Depression in Relation to ECT PJ Cowen Department of Psychiatry, University of Oxford Causes of Depression Genetic Childhood experience Life Events (particularly losses) Life Difficulties
Neurobiology of Depression in Relation to ECT PJ Cowen Department of Psychiatry, University of Oxford Causes of Depression Genetic Childhood experience Life Events (particularly losses) Life Difficulties
Basal Ganglia. Motor systems
 409 systems Basal Ganglia You have just read about the different motorrelated cortical areas. Premotor areas are involved in planning, while MI is involved in execution. What you don t know is that the
409 systems Basal Ganglia You have just read about the different motorrelated cortical areas. Premotor areas are involved in planning, while MI is involved in execution. What you don t know is that the
Investigating Neural Representations: The Tale of Place Cells
 Investigating Neural Representations: The Tale of Place Cells William Bechtel Department of Philosophy, Center for Chronobiology, and Interdisciplinary Program in Cognitive Science University of California,
Investigating Neural Representations: The Tale of Place Cells William Bechtel Department of Philosophy, Center for Chronobiology, and Interdisciplinary Program in Cognitive Science University of California,
Nervous System: PNS and CNS
 Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
ROLE OF HIPPOCAMPAL NEUROGENESIS IN THE PATHOPHYSIOLOGY AND TREATMENT OF DEPRESSION
 Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.net 210 Neurobiology of Mood Disorders, 2013, 210-233 ROLE OF HIPPOCAMPAL NEUROGENESIS IN THE PATHOPHYSIOLOGY AND TREATMENT OF DEPRESSION BENJAMIN ADAM
Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.net 210 Neurobiology of Mood Disorders, 2013, 210-233 ROLE OF HIPPOCAMPAL NEUROGENESIS IN THE PATHOPHYSIOLOGY AND TREATMENT OF DEPRESSION BENJAMIN ADAM
ECT VERKNINGSMEKANISMER
 ECT VERKNINGSMEKANISMER LEVEL OF ORGANISATION - LEVEL OF STUDY transcendence/ existence interactions complex behaviour patterns of reaction and behaviour cognition, affect and emotion brain functional
ECT VERKNINGSMEKANISMER LEVEL OF ORGANISATION - LEVEL OF STUDY transcendence/ existence interactions complex behaviour patterns of reaction and behaviour cognition, affect and emotion brain functional
Dynamics of Cerebral Cortical Networks 9.1 Introduction
 Dynamics of Cerebral Cortical Networks ALEXANDER PROTOPAPAS and JAMES M. BOWER 9.1 Introduction Previous chapters in this volume have considered detailed models of single cells and small networks of cells.
Dynamics of Cerebral Cortical Networks ALEXANDER PROTOPAPAS and JAMES M. BOWER 9.1 Introduction Previous chapters in this volume have considered detailed models of single cells and small networks of cells.
Vision: Receptors. Modes of Perception. Vision: Summary 9/28/2012. How do we perceive our environment? Sensation and Perception Terminology
 How do we perceive our environment? Complex stimuli are broken into individual features, relayed to the CNS, then reassembled as our perception Sensation and Perception Terminology Stimulus: physical agent
How do we perceive our environment? Complex stimuli are broken into individual features, relayed to the CNS, then reassembled as our perception Sensation and Perception Terminology Stimulus: physical agent
Pyramidal neurons: dendritic structure and synaptic integration
 Pyramidal neurons: dendritic structure and synaptic integration Nelson Spruston Abstract Pyramidal neurons are characterized by their distinct apical and basal dendritic trees and the pyramidal shape of
Pyramidal neurons: dendritic structure and synaptic integration Nelson Spruston Abstract Pyramidal neurons are characterized by their distinct apical and basal dendritic trees and the pyramidal shape of
DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN
 DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the threedimensional structure of the brain and teach you one of the great methods of studying
DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the threedimensional structure of the brain and teach you one of the great methods of studying
Sheep Brain Dissection
 Sheep Brain Dissection http://www.carolina.com/product/preserved+organisms/preserved+animals+%28mammal s%29/sheep+organs/preserved+sheep+dissection.do Michigan State University Neuroscience Program Brain
Sheep Brain Dissection http://www.carolina.com/product/preserved+organisms/preserved+animals+%28mammal s%29/sheep+organs/preserved+sheep+dissection.do Michigan State University Neuroscience Program Brain
Charles A. Nelson III Children s Hospital Boston/Harvard Medical School Harvard Center on the Developing Child
 Charles A. Nelson III Children s Hospital Boston/Harvard Medical School Harvard Center on the Developing Child Presented at NICHD Cognition Workshop, 14-15 March 2011, Bethesda, MD Outline I. Declaration
Charles A. Nelson III Children s Hospital Boston/Harvard Medical School Harvard Center on the Developing Child Presented at NICHD Cognition Workshop, 14-15 March 2011, Bethesda, MD Outline I. Declaration
How To Understand The Hypothalamus
 883 Hypothalamus HYPOTHALAMUS Introduction The hypothalamus is a very small, but extremely important part of the diencephalon that is involved in the mediation of endocrine, autonomic and behavioral functions.
883 Hypothalamus HYPOTHALAMUS Introduction The hypothalamus is a very small, but extremely important part of the diencephalon that is involved in the mediation of endocrine, autonomic and behavioral functions.
Slide 4: Forebrain Structures. Slide 5: 4 Lobes of the Cerebral Cortex. Slide 6: The Cerebral Hemispheres (L & R)
 Slide 1: [Film Clip: The Brain #2- Phineas Gage] Integrated Bodily Communications Within Brain (Hemispheres and structures) The remaining Nervous System Endocrine System (Hormonal communication) Our bodies-
Slide 1: [Film Clip: The Brain #2- Phineas Gage] Integrated Bodily Communications Within Brain (Hemispheres and structures) The remaining Nervous System Endocrine System (Hormonal communication) Our bodies-
http://abcnews.go.com/politics/video/obama-says-brain-initiative-will-be-transformative-18861944
 http://abcnews.go.com/politics/video/obama-says-brain-initiative-will-be-transformative-18861944 What are the nervous system s functions? The nervous system organizes and controls an individual s appropriate
http://abcnews.go.com/politics/video/obama-says-brain-initiative-will-be-transformative-18861944 What are the nervous system s functions? The nervous system organizes and controls an individual s appropriate
UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON EDUCATION & PSYCHOLOGY PSYCHOLOGY SEMESTER 1 EXAMINATIONS 2014/2015 COGNITIVE & BIOLOGICAL PERSPECTIVES MODULE NO: PSC4003
 [EDP 005] UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON EDUCATION & PSYCHOLOGY PSYCHOLOGY SEMESTER 1 EXAMINATIONS 2014/2015 COGNITIVE & BIOLOGICAL PERSPECTIVES MODULE NO: PSC4003 Date: Wednesday 21 st January, 2015 Time: 2.00pm
[EDP 005] UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON EDUCATION & PSYCHOLOGY PSYCHOLOGY SEMESTER 1 EXAMINATIONS 2014/2015 COGNITIVE & BIOLOGICAL PERSPECTIVES MODULE NO: PSC4003 Date: Wednesday 21 st January, 2015 Time: 2.00pm
LIST OF FIGURES. Figure 1: Diagrammatic representation of electromagnetic wave. Figure 2: A representation of the electromagnetic spectrum.
 LIST OF FIGURES Figure 1: Diagrammatic representation of electromagnetic wave. Figure 2: A representation of the electromagnetic spectrum. Figure 3: Picture depicting the internal circuit of mobile phone
LIST OF FIGURES Figure 1: Diagrammatic representation of electromagnetic wave. Figure 2: A representation of the electromagnetic spectrum. Figure 3: Picture depicting the internal circuit of mobile phone
Cerebellum and Basal Ganglia
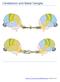 Cerebellum and Basal Ganglia 1 Contents Cerebellum and Basal Ganglia... 1 Introduction... 3 A brief review of cerebellar anatomy... 4 Basic Circuit... 4 Parallel and climbing fiber input has a very different
Cerebellum and Basal Ganglia 1 Contents Cerebellum and Basal Ganglia... 1 Introduction... 3 A brief review of cerebellar anatomy... 4 Basic Circuit... 4 Parallel and climbing fiber input has a very different
Local Generation of Fast Ripples in Epileptic Brain
 The Journal of Neuroscience, March 1, 2002, 22(5):2012 2021 Local Generation of Fast Ripples in Epileptic Brain Anatol Bragin, 1,3 Istvan Mody, 1,3 Charles L. Wilson, 1,3 and Jerome Engel Jr 1,2,3 Departments
The Journal of Neuroscience, March 1, 2002, 22(5):2012 2021 Local Generation of Fast Ripples in Epileptic Brain Anatol Bragin, 1,3 Istvan Mody, 1,3 Charles L. Wilson, 1,3 and Jerome Engel Jr 1,2,3 Departments
Different Contributions of the Hippocampus and Perirhinal Cortex to Recognition Memory
 The Journal of Neuroscience, February 1, 1999, 19(3):1142 1148 Different Contributions of the Hippocampus and Perirhinal Cortex to Recognition Memory Huimin Wan, 1 John P. Aggleton, 2 and Malcolm W. Brown
The Journal of Neuroscience, February 1, 1999, 19(3):1142 1148 Different Contributions of the Hippocampus and Perirhinal Cortex to Recognition Memory Huimin Wan, 1 John P. Aggleton, 2 and Malcolm W. Brown
The Amygdala Is Enlarged in Children But Not Adolescents with Autism; the Hippocampus Is Enlarged at All Ages
 6392 The Journal of Neuroscience, July 14, 2004 24(28):6392 6401 Neurobiology of Disease The Amygdala Is Enlarged in Children But Not Adolescents with Autism; the Hippocampus Is Enlarged at All Ages Cynthia
6392 The Journal of Neuroscience, July 14, 2004 24(28):6392 6401 Neurobiology of Disease The Amygdala Is Enlarged in Children But Not Adolescents with Autism; the Hippocampus Is Enlarged at All Ages Cynthia
Laminating the hippocampus
 Nature Reviews Neuroscience AOP, published online 8 March 2006; doi:10.1038/nrn1882 REVIEWS Laminating the hippocampus Eckart Förster, Shanting Zhao and Michael Frotscher Abstract Lamination of neurons
Nature Reviews Neuroscience AOP, published online 8 March 2006; doi:10.1038/nrn1882 REVIEWS Laminating the hippocampus Eckart Förster, Shanting Zhao and Michael Frotscher Abstract Lamination of neurons
CONTE Summer Lab Experience Application
 CONTE Summer Lab Experience Application When preparing your application for funding from the CONTE Summer Lab Experience through the Undergraduate Program in Neuroscience, please read these instructions
CONTE Summer Lab Experience Application When preparing your application for funding from the CONTE Summer Lab Experience through the Undergraduate Program in Neuroscience, please read these instructions
Nervous System: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves (Chapter 13) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College
 Nervous System: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves (Chapter 13) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Primary Sources for figures and content: Eastern Campus Marieb,
Nervous System: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves (Chapter 13) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Primary Sources for figures and content: Eastern Campus Marieb,
Acta H ' pathologica 9 Springer-Verlag 1991
 Acta Neuropathol (1991) 82:239-259 Acta H ' pathologica 9 Springer-Verlag 1991 Review Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes H. Braak and E. Braak* Zentrum der Morphologie, Theodor-Stern-Kai
Acta Neuropathol (1991) 82:239-259 Acta H ' pathologica 9 Springer-Verlag 1991 Review Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes H. Braak and E. Braak* Zentrum der Morphologie, Theodor-Stern-Kai
Brains, Ontologies & Virtual Machines
 How Minds Work Brains, Ontologies & Virtual Machines Stan Franklin Computer Science Division & Institute for Intelligent Systems The University of Memphis 1 Question: How do minds work? What would an answer
How Minds Work Brains, Ontologies & Virtual Machines Stan Franklin Computer Science Division & Institute for Intelligent Systems The University of Memphis 1 Question: How do minds work? What would an answer
Lab Exercise 9. Nervous Tissue. Brain. Cranial Nerves. Spinal Cord. Spinal Nerves
 Lab Exercise 9 Nervous Tissue Brain Cranial Nerves Spinal Cord Spinal Nerves Textbook Reference: See Chapter 11 for histology of nerve tissue and spinal cord See Chapter 12 for brain and spinal cord anatomy
Lab Exercise 9 Nervous Tissue Brain Cranial Nerves Spinal Cord Spinal Nerves Textbook Reference: See Chapter 11 for histology of nerve tissue and spinal cord See Chapter 12 for brain and spinal cord anatomy
A TEST OF THE REVERBERATORY ACTIVITY HYPOTHESIS FOR HIPPOCAMPAL PLACE CELLS
 Neuroscience 130 (2005) 519 526 A TEST OF THE REVERBERATORY ACTIVITY HYPOTHESIS FOR HIPPOCAMPAL PLACE CELLS E. I. MOSER, a M.-B. MOSER, a P. LIPA, b M. NEWTON, b F. P. HOUSTON, b C. A. BARNES b AND B.
Neuroscience 130 (2005) 519 526 A TEST OF THE REVERBERATORY ACTIVITY HYPOTHESIS FOR HIPPOCAMPAL PLACE CELLS E. I. MOSER, a M.-B. MOSER, a P. LIPA, b M. NEWTON, b F. P. HOUSTON, b C. A. BARNES b AND B.
Modification of the Responses of Hippocampal Neurons in the Monkey During the Learning of a Conditional Spatial Response Task
 HIPPOCAMPUS, VOL. 3, NO. 1, PAGES 29-42, JANUARY 1993 Modification of the Responses of Hippocampal Neurons in the Monkey During the Learning of a Conditional Spatial Response Task Peter M. B. Cahusac,*
HIPPOCAMPUS, VOL. 3, NO. 1, PAGES 29-42, JANUARY 1993 Modification of the Responses of Hippocampal Neurons in the Monkey During the Learning of a Conditional Spatial Response Task Peter M. B. Cahusac,*
The Brain of a Normal Human
 The Brain of a Normal Human Your Brain Evolved Over Time Human Brain Logic and reasoning Mammalian Brain More complex feelings and reactions Lizard Brain Basic functions The Brain Stem or Hindbrain (The
The Brain of a Normal Human Your Brain Evolved Over Time Human Brain Logic and reasoning Mammalian Brain More complex feelings and reactions Lizard Brain Basic functions The Brain Stem or Hindbrain (The
The neuroscience of depression: why does it matter? Dr Susan Mizen Exeter
 The neuroscience of depression: why does it matter? Dr Susan Mizen Exeter Mark Solms and the Freudian Brain Neuroscience and the clinical features of depression Clinical features Anhedonia and decreased
The neuroscience of depression: why does it matter? Dr Susan Mizen Exeter Mark Solms and the Freudian Brain Neuroscience and the clinical features of depression Clinical features Anhedonia and decreased
Feedback Inhibition Enables Theta-Nested Gamma Oscillations andgridfiringfields
 Article Feedback Inhibition Enables Theta-Nested Gamma Oscillations andgridfiringfields Hugh Pastoll, 1,2,3 Lukas Solanka, 2,3 Mark C.W. van Rossum, 2 and Matthew F. Nolan 1, * 1 Centre for Integrative
Article Feedback Inhibition Enables Theta-Nested Gamma Oscillations andgridfiringfields Hugh Pastoll, 1,2,3 Lukas Solanka, 2,3 Mark C.W. van Rossum, 2 and Matthew F. Nolan 1, * 1 Centre for Integrative
Tinnitus and the Brain
 Tinnitus and the Brain Dirk De Ridder & Berthold Langguth Moving animals have developed a brain in order to reduce the inherent uncertainty present in an ever changing environment. The auditory system
Tinnitus and the Brain Dirk De Ridder & Berthold Langguth Moving animals have developed a brain in order to reduce the inherent uncertainty present in an ever changing environment. The auditory system
Learning with Your Brain. Teaching With the Brain in Mind
 Learning with Your Brain Should what (and how) we teach be associated with what we know about the brain and the nervous system? Jonathan Karp, Ph.D. Dept of Biology 5/20/2004 Teaching With the Brain in
Learning with Your Brain Should what (and how) we teach be associated with what we know about the brain and the nervous system? Jonathan Karp, Ph.D. Dept of Biology 5/20/2004 Teaching With the Brain in
BIO130 Chapter 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Lecture Outline
 BIO130 Chapter 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Lecture Outline Brain structure 1. Cerebrum Hemispheres: left & right Cerebral cortex Gyri Sulci Fissures Longitudinal fissure Corpus callosum Lobes Central
BIO130 Chapter 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Lecture Outline Brain structure 1. Cerebrum Hemispheres: left & right Cerebral cortex Gyri Sulci Fissures Longitudinal fissure Corpus callosum Lobes Central
Auditory neuroanatomy: the Spanish heritage. Santiago Ramón y Cajal, 1852 1934
 Auditory neuroanatomy: the Spanish heritage Santiago Ramón y Cajal, 1852 1934 Rafael Lorente de Nó, 1902 1990 3 The nervous system is made up of cells. Estimates of the number of cells vary from
Auditory neuroanatomy: the Spanish heritage Santiago Ramón y Cajal, 1852 1934 Rafael Lorente de Nó, 1902 1990 3 The nervous system is made up of cells. Estimates of the number of cells vary from
Name Date Hour. Nerve Histology Microscope Lab
 Name Date Hour Nerve Histology Microscope Lab PRE-LAB: Answer the following questions using your reading and class notes before starting the microscope lab. 1. What is the difference between the functions
Name Date Hour Nerve Histology Microscope Lab PRE-LAB: Answer the following questions using your reading and class notes before starting the microscope lab. 1. What is the difference between the functions
Parkinson s Disease: A Review of Motor and Nonmotor Symptoms
 Diana Hong Parkinson s Disease: A Review of Motor and Nonmotor Symptoms Abstract: Although Parkinson s disease (PD) is considered a motor system disorder caused by the degeneration of dopaminergic neurons
Diana Hong Parkinson s Disease: A Review of Motor and Nonmotor Symptoms Abstract: Although Parkinson s disease (PD) is considered a motor system disorder caused by the degeneration of dopaminergic neurons
31.1 The Neuron. BUILD Vocabulary. Lesson Objectives
 Name Class Date 31.1 The Neuron Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the nervous system. Describe the function of neurons. Describe how a nerve impulse is transmitted. BUILD Vocabulary A. The chart
Name Class Date 31.1 The Neuron Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the nervous system. Describe the function of neurons. Describe how a nerve impulse is transmitted. BUILD Vocabulary A. The chart
NEURON AND NEURAL TRAMSMISSION: ANATOMY OF A NEURON. created by Dr. Joanne Hsu
 NEURON AND NEURAL TRAMSMISSION: ANATOMY OF A NEURON NEURON AND NEURAL TRAMSMISSION: MICROSCOPIC VIEW OF NEURONS A photograph taken through a light microscope (500x) of neurons in the spinal cord. NEURON
NEURON AND NEURAL TRAMSMISSION: ANATOMY OF A NEURON NEURON AND NEURAL TRAMSMISSION: MICROSCOPIC VIEW OF NEURONS A photograph taken through a light microscope (500x) of neurons in the spinal cord. NEURON
David M. Smith Department of Psychology Cornell University Room 252 Uris Hall Ithaca, NY 14850 (607)227-0045 dms248@cornell.edu
 David M. Smith Department of Psychology Cornell University Room 252 Uris Hall Ithaca, NY 14850 (607)227-0045 dms248@cornell.edu Education Indiana University-Purdue University, Indianapolis, IN Major: Cognitive
David M. Smith Department of Psychology Cornell University Room 252 Uris Hall Ithaca, NY 14850 (607)227-0045 dms248@cornell.edu Education Indiana University-Purdue University, Indianapolis, IN Major: Cognitive
MITOCW MIT9_14S09_lec33-mp3
 MITOCW MIT9_14S09_lec33-mp3 The following content is provided under a Creative Commons License. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free.
MITOCW MIT9_14S09_lec33-mp3 The following content is provided under a Creative Commons License. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free.
Prevention & Recovery Conference November 28, 29 & 30 Norman, Ok
 Prevention & Recovery Conference November 28, 29 & 30 Norman, Ok What is Addiction? The American Society of Addiction Medicine (ASAM) released on August 15, 2011 their latest definition of addiction:
Prevention & Recovery Conference November 28, 29 & 30 Norman, Ok What is Addiction? The American Society of Addiction Medicine (ASAM) released on August 15, 2011 their latest definition of addiction:
1 PYRAMIDS - CORTICOSPINAL FIBERS
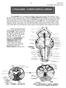 151 Brain stem Pyramids/Corticospinal Tract 1 PYRAMIDS - CORTICOSPINAL FIBERS The pyramids are two elongated swellings on the ventral aspect of the medulla. Each pyramid contains approximately 1,000,000
151 Brain stem Pyramids/Corticospinal Tract 1 PYRAMIDS - CORTICOSPINAL FIBERS The pyramids are two elongated swellings on the ventral aspect of the medulla. Each pyramid contains approximately 1,000,000
THE COGNITIVE NEUROSCIENCE OF MEMORY
 THE COGNITIVE NEUROSCIENCE OF MEMORY What is memory? It is often associated with the thinking of again or recalling to the mind of something learned at an earlier time. Descriptions of this sort imply
THE COGNITIVE NEUROSCIENCE OF MEMORY What is memory? It is often associated with the thinking of again or recalling to the mind of something learned at an earlier time. Descriptions of this sort imply
Memory Consolidation: Systems
 Memory Consolidation: Systems 741 Memory Consolidation: Systems K A Paller, Northwestern University, Evanston, IL, USA ã 29 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. The Consolidation of a Memory At the moment
Memory Consolidation: Systems 741 Memory Consolidation: Systems K A Paller, Northwestern University, Evanston, IL, USA ã 29 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. The Consolidation of a Memory At the moment
An Introduction to ERP Studies of Attention
 An Introduction to ERP Studies of Attention Logan Trujillo, Ph.D. Post-Doctoral Fellow University of Texas at Austin Cognitive Science Course, Fall 2008 What is Attention? Everyone knows what attention
An Introduction to ERP Studies of Attention Logan Trujillo, Ph.D. Post-Doctoral Fellow University of Texas at Austin Cognitive Science Course, Fall 2008 What is Attention? Everyone knows what attention
Excitotoxic Septal Lesions Result in Spatial Memory Deficits and Altered Flexibility of Hippocampal Single-Unit Representations
 The Journal of Neuroscience, August 1, 1999, 19(15):6661 6672 Excitotoxic Septal Lesions Result in Spatial Memory Deficits and Altered Flexibility of Hippocampal Single-Unit Representations Stefan Leutgeb
The Journal of Neuroscience, August 1, 1999, 19(15):6661 6672 Excitotoxic Septal Lesions Result in Spatial Memory Deficits and Altered Flexibility of Hippocampal Single-Unit Representations Stefan Leutgeb
Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology by Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.)
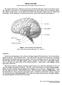 BRAIN ANATOMY Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology by Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.) The anatomy of the brain is often discussed in terms of either the embryonic scheme or the medical scheme. The embryonic
BRAIN ANATOMY Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology by Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.) The anatomy of the brain is often discussed in terms of either the embryonic scheme or the medical scheme. The embryonic
3D Slicer. John Muschelli and Vadim Zipunnikov. Department of Biostatistics. November 18, 2011
 3D Slicer John Muschelli and Vadim Zipunnikov Department of Biostatistics November 18, 2011 John Muschelli and Vadim Zipunnikov (JHU) 3D-Slicer November 18, 2011 1 / 39 What is Slicer http://www.slicer.org;
3D Slicer John Muschelli and Vadim Zipunnikov Department of Biostatistics November 18, 2011 John Muschelli and Vadim Zipunnikov (JHU) 3D-Slicer November 18, 2011 1 / 39 What is Slicer http://www.slicer.org;
Introduction to the Structure and Function of the Central Nervous System
 CHAPTER 3 Introduction to the Structure and Function of the Central Nervous System GENERAL TERMINOLOGY AN OVERVIEW OF THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems Major Divisions
CHAPTER 3 Introduction to the Structure and Function of the Central Nervous System GENERAL TERMINOLOGY AN OVERVIEW OF THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems Major Divisions
Brain Computer Interfaces (BCI) Communication Training of brain activity
 Brain Computer Interfaces (BCI) Communication Training of brain activity Brain Computer Interfaces (BCI) picture rights: Gerwin Schalk, Wadsworth Center, NY Components of a Brain Computer Interface Applications
Brain Computer Interfaces (BCI) Communication Training of brain activity Brain Computer Interfaces (BCI) picture rights: Gerwin Schalk, Wadsworth Center, NY Components of a Brain Computer Interface Applications
Everything you must know about sleep but are too tired to ask
 Everything you must know about sleep but are too tired to ask The Sleep Deprivation Crisis Most people are moderately to severely sleep deprived. 71% do not meet the recommended 8 hrs/nt. (7.1 or 6.1?)
Everything you must know about sleep but are too tired to ask The Sleep Deprivation Crisis Most people are moderately to severely sleep deprived. 71% do not meet the recommended 8 hrs/nt. (7.1 or 6.1?)
Lecture One: Brain Basics
 Lecture One: Brain Basics Brain Fractured Femur Bone Spinal Cord 1 How does pain get from here to here 2 How does the brain work? Every cell in your body is wired to send a signal to your brain The brain
Lecture One: Brain Basics Brain Fractured Femur Bone Spinal Cord 1 How does pain get from here to here 2 How does the brain work? Every cell in your body is wired to send a signal to your brain The brain
3. The neuron has many branch-like extensions called that receive input from other neurons. a. glia b. dendrites c. axons d.
 Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer: A difficulty: 1 factual
Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer: A difficulty: 1 factual
Chapter Fourteen. Emotion, Reward, Aggression, and Stress
 Chapter Fourteen Emotion, Reward, Aggression, and Stress EMOTIONS! Emotions generally include a Physical component, and a Subjective component or quality, and a Valence Emotions a product of Evolution?
Chapter Fourteen Emotion, Reward, Aggression, and Stress EMOTIONS! Emotions generally include a Physical component, and a Subjective component or quality, and a Valence Emotions a product of Evolution?
Meeting Report: XX WFN World Congress on Parkinson s Disease and Related Disorders
 Meeting Report: XX WFN World Congress on Parkinson s Disease and Related Disorders Karen Frei, Erik Ch. Wolters Abstract: The twentieth World Congress on Parkinson s Disease and Related Disorders was held
Meeting Report: XX WFN World Congress on Parkinson s Disease and Related Disorders Karen Frei, Erik Ch. Wolters Abstract: The twentieth World Congress on Parkinson s Disease and Related Disorders was held
Exercise. Rule #1 Exercise boosts brain power.
 Exercise Rule #1 Exercise boosts brain power. Our brains were built for walking 12 miles a day! To improve your thinking skills, move. Exercise gets blood to your brain, bringing it glucose for energy
Exercise Rule #1 Exercise boosts brain power. Our brains were built for walking 12 miles a day! To improve your thinking skills, move. Exercise gets blood to your brain, bringing it glucose for energy
Transverse Sections of the Spinal Cord
 Transverse Sections of the Spinal Cord The spinal cord is perhaps the most simply arranged part of the CNS. Its basic structure, indicated in a schematic drawing of the eighth cervical segment (Figure
Transverse Sections of the Spinal Cord The spinal cord is perhaps the most simply arranged part of the CNS. Its basic structure, indicated in a schematic drawing of the eighth cervical segment (Figure
The intermedius nucleus of the medulla: A potential site for the integration of cervical information and the generation of autonomic responses
 The intermedius nucleus of the medulla: A potential site for the integration of cervical information and the generation of autonomic responses 1 Journal of Chemical Neuroanatomy November 2009, 38, pp.
The intermedius nucleus of the medulla: A potential site for the integration of cervical information and the generation of autonomic responses 1 Journal of Chemical Neuroanatomy November 2009, 38, pp.
NMDA RECEPTORS, PLACE CELLS AND HIPPOCAMPAL SPATIAL MEMORY
 NMDA RECEPTORS, PLACE CELLS AND HIPPOCAMPAL SPATIAL MEMORY Kazu Nakazawa*, Thomas J. McHugh*,Matthew A. Wilson and Susumu Tonegawa* N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) in the rodent hippocampus have
NMDA RECEPTORS, PLACE CELLS AND HIPPOCAMPAL SPATIAL MEMORY Kazu Nakazawa*, Thomas J. McHugh*,Matthew A. Wilson and Susumu Tonegawa* N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) in the rodent hippocampus have
Stroke & Alzheimer s Disease: An Inflammatory Duo
 Stroke & Alzheimer s Disease: An Inflammatory Duo Stroke and Dementia One in 3 will experience a stroke, dementia or both 64% of persons with a stroke have some degree of cognitive impairment and up to
Stroke & Alzheimer s Disease: An Inflammatory Duo Stroke and Dementia One in 3 will experience a stroke, dementia or both 64% of persons with a stroke have some degree of cognitive impairment and up to
Exercise 5 Nervous Tissue
 Exercise 5 Nervous Tissue Objectives After completing the laboratory exercise for nervous tissue you should be able to: Introduction Identify a "typical" multipolar neuron in the light microscope. Identify
Exercise 5 Nervous Tissue Objectives After completing the laboratory exercise for nervous tissue you should be able to: Introduction Identify a "typical" multipolar neuron in the light microscope. Identify
LESSON 4: BRAIN STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
 LESSON 4: BRAIN STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION THE TRIUNE BRAIN Neo? axon brain stem cerebral hemispheres cortex dendrite limbic system neural plasticity neurons neurotransmitter sensory flooding sensory gating
LESSON 4: BRAIN STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION THE TRIUNE BRAIN Neo? axon brain stem cerebral hemispheres cortex dendrite limbic system neural plasticity neurons neurotransmitter sensory flooding sensory gating
What role does the nucleolus have in cell functioning? Glial cells
 Nervous System Lab The nervous system of vertebrates can be divided into the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which contains nerves,
Nervous System Lab The nervous system of vertebrates can be divided into the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which contains nerves,
Place cells, neocortex and spatial navigation: a short review
 Journal of Physiology - Paris 97 (2003) 537 546 www.elsevier.com/locate/jphysparis Place cells, neocortex and spatial navigation: a short review Bruno Poucet *, Pierre-Pascal Lenck-Santini, Vietminh Paz-Villagran,
Journal of Physiology - Paris 97 (2003) 537 546 www.elsevier.com/locate/jphysparis Place cells, neocortex and spatial navigation: a short review Bruno Poucet *, Pierre-Pascal Lenck-Santini, Vietminh Paz-Villagran,
Review Paper Cognitive Neuroscience and Education: Understanding the Teaching Learning Strategies, Learning Disabilities and Neuromyths
 Research Journal of Educational Sciences ISSN 2321-0508 Review Paper Cognitive Neuroscience and Education: Understanding the Teaching Learning Strategies, Learning Disabilities and Neuromyths Abstract
Research Journal of Educational Sciences ISSN 2321-0508 Review Paper Cognitive Neuroscience and Education: Understanding the Teaching Learning Strategies, Learning Disabilities and Neuromyths Abstract
CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling. Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy
 CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect02: BOSS Discrete Event Simulator Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy Appendix of Purves et al., 4e Larry Wittie Computer Science, StonyBrook
CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect02: BOSS Discrete Event Simulator Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy Appendix of Purves et al., 4e Larry Wittie Computer Science, StonyBrook
A Controlled Attractor Network Model of Path Integration in the Rat
 A Controlled Attractor Network Model of Path Integration in the Rat John Conklin Systems Design Engineering, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario, N2L 3G1, Canada, jmlconkl@uwaterloo.ca Chris Eliasmith
A Controlled Attractor Network Model of Path Integration in the Rat John Conklin Systems Design Engineering, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario, N2L 3G1, Canada, jmlconkl@uwaterloo.ca Chris Eliasmith
Fall 2014 Exam 1 Answer Key
 Fall 2014 Exam 1 Answer Key 1. Early psychologists like E. R. Hilgard spoke of studying mental processes by breaking up research into three sections. Often they called these sections the trilogy of the
Fall 2014 Exam 1 Answer Key 1. Early psychologists like E. R. Hilgard spoke of studying mental processes by breaking up research into three sections. Often they called these sections the trilogy of the
THE HUMAN BRAIN. observations and foundations
 THE HUMAN BRAIN observations and foundations brains versus computers a typical brain contains something like 100 billion miniscule cells called neurons estimates go from about 50 billion to as many as
THE HUMAN BRAIN observations and foundations brains versus computers a typical brain contains something like 100 billion miniscule cells called neurons estimates go from about 50 billion to as many as
Depression. The Brain Finally Gets Into the Act. Barry L. Jacobs. Princeton University
 CURRENT DIRECTIONS IN PSYCHOLOGICAL SCIENCE Depression The Brain Finally Gets Into the Act Barry L. Jacobs Princeton University ABSTRACT The theory of clinical depression presented here integrates etiological
CURRENT DIRECTIONS IN PSYCHOLOGICAL SCIENCE Depression The Brain Finally Gets Into the Act Barry L. Jacobs Princeton University ABSTRACT The theory of clinical depression presented here integrates etiological
Appendix 4 Simulation software for neuronal network models
 Appendix 4 Simulation software for neuronal network models D.1 Introduction This Appendix describes the Matlab software that has been made available with Cerebral Cortex: Principles of Operation (Rolls
Appendix 4 Simulation software for neuronal network models D.1 Introduction This Appendix describes the Matlab software that has been made available with Cerebral Cortex: Principles of Operation (Rolls
