Lab Configuring Basic Router Settings with IOS CLI (Instructor Version)
|
|
|
- Peter Long
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
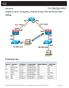
1 (Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/ N/A G0/ N/A PC-A NIC PC-B NIC Part 1: Set Up the Topology and Initialize Devices Cable equipment to match the network topology. Initialize and restart the router and switch. Part 2: Configure Devices and Verify Connectivity Assign static IPv4 information to the PC interfaces. Configure basic router settings. Verify network connectivity. Configure the router for SSH. Part 3: Display Router Information Retrieve hardware and software information from the router. Interpret the output from the startup configuration. Interpret the output from the routing table. Verify the status of the interfaces. Part 4: Configure IPv6 and Verify Connectivity Background / Scenario This is a comprehensive lab to review previously covered IOS router commands. In Parts 1 and 2, you will cable the equipment and complete basic configurations and IPv4 interface settings on the router Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 17
2 In Part 3, you will use SSH to connect to the router remotely and utilize IOS commands to retrieve information from the device to answer questions about the router. In Part 4, you will configure IPv6 on the router so that PC-B can acquire an IP address and then verify connectivity. For review purposes, this lab provides the commands necessary for specific router configurations. Note: The routers used with CCNA hands-on labs are Cisco 1941 Integrated Services Routers (ISRs) with Cisco IOS Release 15.2(4)M3 (universalk9 image). The switches used are Cisco Catalyst 2960 with Cisco IOS Release 15.0(2) (lanbasek9 image). Other routers, switches, and Cisco IOS versions can be used. Depending on the model and Cisco IOS version, the commands available and output produced might vary from what is shown in the labs. Refer to the Router Interface Summary Table at the end of this lab for the correct interface identifiers. Note: Make sure that the router and switch have been erased and have no startup configurations. Refer to Appendix A for the procedures to initialize and reload devices. Required Resources 1 Router (Cisco 1941 with Cisco IOS Release 15.2(4)M3 universal image or comparable) 1 Switch (Cisco 2960 with Cisco IOS Release 15.0(2) lanbasek9 image or comparable) 2 PCs (Windows 7, Vista, or XP with terminal emulation program, such as Tera Term) Console cables to configure the Cisco IOS devices via the console ports Ethernet cables as shown in the topology Note: The Gigabit Ethernet interfaces on Cisco 1941 ISRs are autosensing and an Ethernet straight-through cable can be used between the router and PC-B. If using another model Cisco router, it may be necessary to use an Ethernet crossover cable. Part 1: Set Up the Topology and Initialize Devices Step 1: Cable the network as shown in the topology. a. Attach the devices as shown in the topology diagram, and cable as necessary. b. Power on all the devices in the topology. Step 2: Initialize and reload the router and switch. Note: Appendix A details the steps to initialize and reload the devices. Part 2: Configure Devices and Verify Connectivity Step 1: Configure the PC interfaces. a. Configure the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway settings on PC-A. b. Configure the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway settings on PC-B. Step 2: Configure the router. a. Console into the router and enable privileged EXEC mode. Router> enable Router# b. Enter into global configuration mode Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 2 of 17
3 Router# config terminal Router(config)# c. Assign a device name to the router. Router(config)# hostname R1 d. Disable DNS lookup to prevent the router from attempting to translate incorrectly entered commands as though they were hostnames. R1(config)# no ip domain-lookup e. Require that a minimum of 10 characters be used for all passwords. R1(config)# security passwords min-length 10 Besides setting a minimum length, list other ways to strengthen passwords. Use capital letters, numbers, and special characters in passwords. f. Assign cisco12345 as the privileged EXEC encrypted password. R1(config)# enable secret cisco12345 g. Assign ciscoconpass as the console password, establish a timeout, enable login, and add the logging synchronous command. The logging synchronous command synchronizes debug and Cisco IOS software output and prevents these messages from interrupting your keyboard input. R1(config)# line con 0 R1(config-line)# password ciscoconpass R1(config-line)# exec-timeout 5 0 R1(config-line)# login R1(config-line)# logging synchronous R1(config-line)# exit R1(config)# For the exec-timeout command, what do the 5 and 0 represent? The session will timeout in 5 minutes and 0 seconds. h. Assign ciscovtypass as the vty password, establish a timeout, enable login, and add the logging synchronous command. R1(config)# line vty 0 4 R1(config-line)# password ciscovtypass R1(config-line)# exec-timeout 5 0 R1(config-line)# login R1(config-line)# logging synchronous R1(config-line)# exit R1(config)# i. Encrypt the clear text passwords. R1(config)# service password-encryption j. Create a banner that warns anyone accessing the device that unauthorized access is prohibited. R1(config)# banner motd #Unauthorized access prohibited# k. Configure an IP address and interface description. Activate both interfaces on the router Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 3 of 17
4 R1(config)# int g0/0 R1(config-if)# description Connection to PC-B R1(config-if)# ip address R1(config-if)# no shutdown R1(config-if)# int g0/1 R1(config-if)# description Connection to S1 R1(config-if)# ip address R1(config-if)# no shutdown R1(config-if)# exit R1(config)# exit R1# l. Set the clock on the router; for example: R1# clock set 17:00:00 18 Feb 2013 m. Save the running configuration to the startup configuration file. R1# copy running-config startup-config Destination filename [startup-config]? Building configuration... [OK] R1# What would be the result of reloading the router prior to completing the copy running-config startupconfig command? The contents of the running configuration would be erased. In this lab, the router would have no startup configuration. Upon a reboot, a user would be asked if they would like to enter initial configuration dialog. Step 3: Verify network connectivity. a. Ping PC-B from a command prompt on PC-A. Note: It may be necessary to disable the PCs firewall. Were the pings successful? Yes After completing this series of commands, what type of remote access could be used to access R1? Telnet b. Remotely access R1 from PC-A using the Tera Term Telnet client. Open Tera Term and enter the G0/1 interface IP address of R1 in the Host: field of the Tera Term: New Connection window. Ensure that the Telnet radio button is selected and then click OK to connect to the router Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 4 of 17
5 Was remote access successful? Yes Why is the Telnet protocol considered to be a security risk? A Telnet session can be seen in clear text. It is not encrypted. Passwords can easily be seen using a packet sniffer. Step 4: Configure the router for SSH access. a. Enable SSH connections and create a user in the local database of the router. R1# configure terminal R1(config)# ip domain-name CCNA-lab.com R1(config)# username admin privilege 15 secret adminpass1 R1(config)# line vty 0 4 R1(config-line)# transport input ssh R1(config-line)# login local R1(config-line)# exit R1(config)# crypto key generate rsa modulus 1024 R1(config)# exit b. Remotely access R1 from PC-A using the Tera Term SSH client. Open Tera Term and enter the G0/1 interface IP address of R1 in the Host: field of the Tera Term: New Connection window. Ensure that the SSH radio button is selected and then click OK to connect to the router Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 5 of 17
6 Was remote access successful? Yes Part 3: Display Router Information In Part 3, you will use show commands from an SSH session to retrieve information from the router. Step 1: Establish an SSH session to R1. Using Tera Term on PC-B, open an SSH session to R1 at IP address and log in as admin with the password adminpass1. Step 2: Retrieve important hardware and software information. a. Use the show version command to answer questions about the router. R1# show version Cisco IOS Software, C1900 Software (C1900-UNIVERSALK9-M), Version 15.2(4)M3, RELEASE SOFTWARE (fc1) Technical Support: Copyright (c) by Cisco Systems, Inc. Compiled Thu 26-Jul-12 19:34 by prod_rel_team ROM: System Bootstrap, Version 15.0(1r)M15, RELEASE SOFTWARE (fc1) R1 uptime is 10 minutes System returned to ROM by power-on System image file is "flash0:c1900-universalk9-mz.spa m3.bin" Last reload type: Normal Reload Last reload reason: power-on This product contains cryptographic features and is subject to United States and local country laws governing import, export, transfer and use. Delivery of Cisco cryptographic products does not imply third-party authority to import, export, distribute or use encryption Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 6 of 17
7 Importers, exporters, distributors and users are responsible for compliance with U.S. and local country laws. By using this product you agree to comply with applicable laws and regulations. If you are unable to comply with U.S. and local laws, return this product immediately. A summary of U.S. laws governing Cisco cryptographic products may be found at: If you require further assistance please contact us by sending to export@cisco.com. Cisco CISCO1941/K9 (revision 1.0) with K/77824K bytes of memory. Processor board ID FTX Z 2 Gigabit Ethernet interfaces 2 Serial(sync/async) interfaces 1 terminal line DRAM configuration is 64 bits wide with parity disabled. 255K bytes of non-volatile configuration memory K bytes of ATA System CompactFlash 0 (Read/Write) License Info: License UDI: Device# PID SN *0 CISCO1941/K9 FTX Z Technology Package License Information for Module:'c1900' Technology Technology-package Technology-package Current Type Next reboot ipbase ipbasek9 Permanent ipbasek9 security None None None data None None None Configuration register is 0x2142 (will be 0x2102 at next reload) What is the name of the IOS image that the router is running? Image version may vary, but answers should be something like c1900-universalk9-mz.spa m3.bin. How much non-volatile random-access memory (NVRAM) does the router have? 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 7 of 17
8 Answers may vary, but the output from the show version on 1941 router is: 255K bytes of non-volatile configuration memory. How much Flash memory does the router have? Answers may vary, but the default output from the show version command on the 1941 router is K bytes of ATA System CompactFlash 0 (Read/Write). b. The show commands often provide multiple screens of outputs. Filtering the output allows a user to display certain sections of the output. To enable the filtering command, enter a pipe ( ) character after a show command, followed by a filtering parameter and a filtering expression. You can match the output to the filtering statement by using the include keyword to display all lines from the output that contain the filtering expression. Filter the show version command, using show version include register to answer the following question. R1# show version include register Configuration register is 0x2142 What is the boot process for the router on the next reload? Answers may vary. In most cases (0x2102), the router will undergo a normal boot, load the IOS from the Flash memory, and load the startup configuration from the NVRAM if present. If the config register is 0x2142, the router will bypass the startup config and begin at the user-mode command prompt. If the initial boot fails, the router goes into ROMMON mode. Step 3: Display the startup configuration. Use the show startup-config command on the router to answer the following questions. R1# show start Using 1674 out of bytes version 15.2 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec service password-encryption hostname R1 boot-start-marker boot-end-marker security passwords min-length 10 enable secret 4 3mxoP2KRPf3sFHYl6Vm6.ssJJi9tOJqqb6DMG/YH5No no aaa new-model no ipv6 cef ip source-route 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 8 of 17
9 no ip domain lookup ip domain name CCNA-lab.com ip cef multilink bundle-name authenticated license udi pid CISCO2911/K9 sn FTX Z username admin privilege 15 secret f020214B interface Embedded-Service-Engine0/0 no ip address shutdown interface GigabitEthernet0/0 description Connection to PC-B ip address duplex auto speed auto interface GigabitEthernet0/1 description Connection to S1 ip address duplex auto speed auto interface Serial0/0/0 no ip address shutdown clock rate interface Serial0/0/1 no ip address shutdown ip forward-protocol nd no ip http server no ip http secure-server control-plane banner motd ^CUnauthorized access prohibited^c line con Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 9 of 17
10 exec-timeout 5 0 password F410A160B F logging synchronous login line aux 0 line 2 no activation-character no exec transport preferred none transport input all transport output pad telnet rlogin lapb-ta mop udptn v120 ssh stopbits 1 line vty 0 4 exec-timeout 5 0 password F411F0D1C F logging synchronous login local transport input ssh scheduler allocate end How are passwords presented in the output? Passwords are encrypted due to the service password-encryption command. The line con password of ciscoconpass is encrypted as F410A160B F. The line vty password of ciscovtypass is encrypted as F411F0D1C F. Use the show startup-config begin vty command. line vty 0 4 exec-timeout 5 0 password F411F0D1C F login local transport input ssh scheduler allocate end What is the result of using this command? A user receives the startup configuration output beginning with the line that includes the first instance of the filtering expression. Step 4: Display the routing table on the router. Use the show ip route command on the router to answer the following questions Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 10 of 17
11 R1# show ip route Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2 i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2 ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, H - NHRP, l - LISP + - replicated route, % - next hop override Gateway of last resort is not set C L C L /24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks /24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/ /32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/ /24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks /24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/ /32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1 What code is used in the routing table to indicate a directly connected network? The C designates a directly connected subnet. An L designates a local interface. Both answers are correct. How many route entries are coded with a C code in the routing table? 2 Step 5: Display a summary list of the interfaces on the router. Use the show ip interface brief command on the router to answer the following question. R1# show ip interface brief Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol Embedded-Service-Engine0/0 unassigned YES unset administratively down down GigabitEthernet0/ YES manual up up GigabitEthernet0/ YES manual up up Serial0/0/0 unassigned YES unset administratively down down Serial0/0/1 unassigned YES unset administratively down down R1# What command changed the status of the Gigabit Ethernet ports from administratively down to up? no shutdown Part 4: Configure IPv6 and Verify Connectivity Step 1: Assign IPv6 addresses to R1 G0/0 and enable IPv6 routing. Note: Assigning an IPv6 address in addition to an IPv4 address on an interface is known as dual stacking, because both the IPv4 and IPv6 protocol stacks are active. By enabling IPv6 unicast routing on R1, PC-B receives the R1 G0/0 IPv6 network prefix and can autoconfigure its IPv6 address and its default gateway Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 11 of 17
12 a. Assign an IPv6 global unicast address to interface G0/0, assign the link-local address in addition to the unicast address on the interface, and enable IPv6 routing. R1# configure terminal R1(config)# interface g0/0 R1(config-if)# ipv6 address 2001:db8:acad:a::1/64 R1(config-if)# ipv6 address fe80::1 link-local R1(config-if)# no shutdown R1(config-if)# exit R1(config)# ipv6 unicast-routing R1(config)# exit b. Use the show ipv6 int brief command to verify IPv6 settings on R1. R1#show ipv6 int brief Em0/0 unassigned GigabitEthernet0/0 FE80::1 2001:DB8:ACAD:A::1 GigabitEthernet0/1 unassigned Serial0/0/0 unassigned Serial0/0/1 Unassigned [administratively down/down] [up/up] [up/up] [administratively down/down] [administratively down/down] If no IPv6 address is assigned to G0/1, why is it listed as [up/up]? The [up/up] status reflects the Layer 1 and Layer 2 status of the interface and does not rely on Layer 3 for status. c. Issue the ipconfig command on PC-B to examine the IPv6 configuration. Reflection What is the IPv6 address assigned to PC-B? Answers will vary. IPv6 address of 2001:db8:acad:a:d428:7de2:997c:b05a What is the default gateway assigned to PC-B? fe80::1 Issue a ping from PC-B to the R1 default gateway link local address. Was it successful? Yes Issue a ping from PC-B to the R1 IPv6 unicast address 2001:db8:acad:a::1. Was it successful? Yes 1. In researching a network connectivity issue, a technician suspects that an interface was not enabled. What show command could the technician use to troubleshoot this issue? Answers may vary. However, show ip interface brief or show startup-config would provide the information Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 12 of 17
13 2. In researching a network connectivity issue, a technician suspects that an interface was assigned an incorrect subnet mask. What show command could the technician use to troubleshoot this issue? show startup-config or show running-config 3. After configuring IPv6 on the R1 G0/0 PC-B LAN, if you were to ping from PC-A to the PC-B IPv6 address, would the ping succeed? Why or why not? The ping would fail because R1 interface G0/1 was not configured with IPv6 and PC-A only has an IPv4 address. Router Interface Summary Table Router Interface Summary Router Model Ethernet Interface #1 Ethernet Interface #2 Serial Interface #1 Serial Interface # Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) 1900 Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 (G0/0) Gigabit Ethernet 0/1 (G0/1) Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) 2801 Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) Serial 0/1/0 (S0/1/0) Serial 0/1/1 (S0/1/1) 2811 Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) 2900 Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 (G0/0) Gigabit Ethernet 0/1 (G0/1) Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) Note: To find out how the router is configured, look at the interfaces to identify the type of router and how many interfaces the router has. There is no way to effectively list all the combinations of configurations for each router class. This table includes identifiers for the possible combinations of Ethernet and Serial interfaces in the device. The table does not include any other type of interface, even though a specific router may contain one. An example of this might be an ISDN BRI interface. The string in parenthesis is the legal abbreviation that can be used in Cisco IOS commands to represent the interface. Appendix A: Initializing and Reloading a Router and Switch Step 1: Initialize and reload the router. a. Console into the router and enable privileged EXEC mode. Router> enable Router# b. Type the erase startup-config command to remove the startup configuration from NVRAM. Router# erase startup-config Erasing the nvram filesystem will remove all configuration files Continue? [confirm] [OK] Erase of nvram: complete Router# 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 13 of 17
14 c. Issue the reload command to remove an old configuration from memory. When prompted to Proceed with reload, press Enter to confirm the reload. (Pressing any other key aborts the reload.) Router# reload Proceed with reload? [confirm] *Nov 29 18:28:09.923: %SYS-5-RELOAD: Reload requested by console. Reload Reason: Reload Command. Note: You may be prompted to save the running configuration prior to reloading the router. Type no and press Enter. System configuration has been modified. Save? [yes/no]: no d. After the router reloads, you are prompted to enter the initial configuration dialog. Enter no and press Enter. Would you like to enter the initial configuration dialog? [yes/no]: no e. You are prompted to terminate autoinstall. Type yes and then press Enter. Would you like to terminate autoinstall? [yes]: yes Step 2: Initialize and reload the switch. a. Console into the switch and enter privileged EXEC mode. Switch> enable Switch# b. Use the show flash command to determine if any VLANs have been created on the switch. Switch# show flash Directory of flash:/ 2 -rwx 1919 Mar :06:33 +00:00 private-config.text 3 -rwx 1632 Mar :06:33 +00:00 config.text 4 -rwx Mar :06:33 +00:00 multiple-fs 5 -rwx Mar :37:06 +00:00 c2960-lanbasek9-mz se.bin 6 -rwx 616 Mar :07:13 +00:00 vlan.dat bytes total ( bytes free) Switch# c. If the vlan.dat file was found in flash, then delete this file. Switch# delete vlan.dat Delete filename [vlan.dat]? d. You are prompted to verify the filename. At this point, you can change the filename or just press Enter if you have entered the name correctly. e. You are prompted to confirm deleting this file. Press Enter to confirm deletion. (Pressing any other key aborts the deletion.) Delete flash:/vlan.dat? [confirm] Switch# f. Use the erase startup-config command to erase the startup configuration file from NVRAM. You are prompted to confirm removing the configuration file. Press Enter to confirm to erase this file. (Pressing any other key aborts the operation.) Switch# erase startup-config 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 14 of 17
15 Erasing the nvram filesystem will remove all configuration files Continue? [confirm] [OK] Erase of nvram: complete Switch# g. Reload the switch to remove any old configuration information from memory. You are prompted to confirm reloading the switch. Press Enter to proceed with the reload. (Pressing any other key aborts the reload.) Switch# reload Proceed with reload? [confirm] Note: You may be prompted to save the running configuration prior to reloading the switch. Type no and press Enter. System configuration has been modified. Save? [yes/no]: no h. After the switch reloads, you should be prompted to enter the initial configuration dialog. Type no and press Enter. Would you like to enter the initial configuration dialog? [yes/no]: no Switch> Device Configs Router R1 R1#show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 1742 bytes version 15.2 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec service password-encryption hostname R1 boot-start-marker boot-end-marker security passwords min-length 10 enable secret 4 3mxoP2KRPf3sFHYl6Vm6.ssJJi9tOJqqb6DMG/YH5No no aaa new-model no ip domain lookup 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 15 of 17
16 ip domain name CCNA-lab.com ip cef ipv6 unicast-routing ipv6 cef multilink bundle-name authenticated license udi pid CISCO1941/K9 sn FTX Z license accept end user agreement username admin privilege 15 password F B interface Embedded-Service-Engine0/0 no ip address shutdown interface GigabitEthernet0/0 description Connection to PC-B ip address duplex auto speed auto ipv6 address FE80::1 link-local ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:A::1/64 interface GigabitEthernet0/1 description Connection to S1 ip address duplex auto speed auto interface Serial0/0/0 no ip address shutdown clock rate interface Serial0/0/1 no ip address shutdown ip forward-protocol nd no ip http server 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 16 of 17
17 no ip http secure-server control-plane banner motd ^CUnauthorized access prohibited^c line con 0 exec-timeout 5 0 password logging synchronous login line aux 0 line 2 no activation-character no exec transport preferred none transport input all transport output pad telnet rlogin lapb-ta mop udptn v120 ssh stopbits 1 line vty 0 4 exec-timeout 5 0 password B180F0B3C3F3D logging synchronous login local transport input ssh scheduler allocate end 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 17 of 17
Lab Configuring Syslog and NTP (Instructor Version)
 (Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
(Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
Lab 5.3.9b Managing Router Configuration Files Using TFTP
 Lab 5.3.9b Managing Router Configuration Files Using TFTP Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Download and install TFTP server software.
Lab 5.3.9b Managing Router Configuration Files Using TFTP Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Download and install TFTP server software.
Objectives. Router as a Computer. Router components and their functions. Router components and their functions
 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public Objectives Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1 Identify a router as a computer with an OS and
2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public Objectives Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1 Identify a router as a computer with an OS and
Chapter 8 Lab B: Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client
 Chapter 8 Lab B: Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client Topology Note: ISR G2 devices have Gigabit Ethernet interfaces instead of FastEthernet Interfaces. All contents are Copyright 1992 2012
Chapter 8 Lab B: Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client Topology Note: ISR G2 devices have Gigabit Ethernet interfaces instead of FastEthernet Interfaces. All contents are Copyright 1992 2012
Lab - Using IOS CLI with Switch MAC Address Tables
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12
Lab: Basic Router Configuration
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Def. Gateway R1 Fa0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R2 Fa0/0 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Def. Gateway R1 Fa0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R2 Fa0/0 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths Instructor Version 2500 Objective onfigure Load balance across multiple paths. Observe the load balancing process. Background/Preparation able a network similar
Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths Instructor Version 2500 Objective onfigure Load balance across multiple paths. Observe the load balancing process. Background/Preparation able a network similar
Skills Assessment Student Training (Answer Key)
 CCNA: Connecting Networks Skills Assessment Student Training (Answer Key) Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Assessment
CCNA: Connecting Networks Skills Assessment Student Training (Answer Key) Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Assessment
Skills Assessment Student Training Exam
 Skills Assessment Student Training Exam Topology Assessment Objectives Part 1: Initialize Devices (8 points, 5 minutes) Part 2: Configure Device Basic Settings (28 points, 30 minutes) Part 3: Configure
Skills Assessment Student Training Exam Topology Assessment Objectives Part 1: Initialize Devices (8 points, 5 minutes) Part 2: Configure Device Basic Settings (28 points, 30 minutes) Part 3: Configure
Objectives. Background. Required Resources. CCNA Security
 Chapter 8 Lab B, Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client Topology IP Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 FA0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Chapter 8 Lab B, Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client Topology IP Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 FA0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 2900 Series Integrated Services Router
 Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 2900 Series Integrated Services Router Document ID: 112033 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions Step by
Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 2900 Series Integrated Services Router Document ID: 112033 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions Step by
PT Activity: Configure Cisco Routers for Syslog, NTP, and SSH Operations
 PT Activity: Configure Cisco Routers for Syslog, NTP, and SSH Operations Instructor Version Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 FA0/1
PT Activity: Configure Cisco Routers for Syslog, NTP, and SSH Operations Instructor Version Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 FA0/1
Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI
 Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Serial 0/0/0 (DCE) 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 FastEthernet 0/0 172.16.0.1 255.255.0.0
Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Serial 0/0/0 (DCE) 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 FastEthernet 0/0 172.16.0.1 255.255.0.0
Lab 8.4.3a Managing Cisco IOS Images with TFTP
 Lab 8.4.3a Managing Cisco IOS Images with TFTP Host Device Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Analyze the Cisco IOS image and router flash memory.
Lab 8.4.3a Managing Cisco IOS Images with TFTP Host Device Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Analyze the Cisco IOS image and router flash memory.
How To Configure A Cisco Router With A Cio Router
 CHAPTER 1 This chapter provides procedures for configuring the basic parameters of your Cisco router, including global parameter settings, routing protocols, interfaces, and command-line access. It also
CHAPTER 1 This chapter provides procedures for configuring the basic parameters of your Cisco router, including global parameter settings, routing protocols, interfaces, and command-line access. It also
3.1 Connecting to a Router and Basic Configuration
 3.1 Connecting to a Router and Basic Configuration Objective This lab will focus on the ability to connect a PC to a router in order to establish a console session and observe the user interface. A console
3.1 Connecting to a Router and Basic Configuration Objective This lab will focus on the ability to connect a PC to a router in order to establish a console session and observe the user interface. A console
Lab 4.1.4 Creating a Network Map using CDP Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 4.1.4 Creating a Network Map using CDP Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) commands to get information about neighboring network devices. Background/Preparation CDP
Lab 4.1.4 Creating a Network Map using CDP Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) commands to get information about neighboring network devices. Background/Preparation CDP
Brest. Backup : copy flash:ppe_brest1 running-config
 Brest Backup : copy flash:ppe_brest1 running-config Cisco SF300-08 Mise en place des services : - Serveurs : 10.3.50.0/24 VLAN 2 (port 1) - DSI : 10.3.51.0/24 VLAN 3 (port 2) - Direction : 10.3.52.0/24
Brest Backup : copy flash:ppe_brest1 running-config Cisco SF300-08 Mise en place des services : - Serveurs : 10.3.50.0/24 VLAN 2 (port 1) - DSI : 10.3.51.0/24 VLAN 3 (port 2) - Direction : 10.3.52.0/24
Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI
 Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP address Subnet mask R1 R1 Serial 0/0/0 (DCE) 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 FastEthernet 0/0 172.16.0.1 255.255.0.0
Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP address Subnet mask R1 R1 Serial 0/0/0 (DCE) 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 FastEthernet 0/0 172.16.0.1 255.255.0.0
Connect the Host to attach to Fast Ethernet switch port Fa0/2. Configure the host as shown in the topology diagram above.
 Lab 1.2.2 Capturing and Analyzing Network Traffic Host Name IP Address Fa0/0 Subnet Mask IP Address S0/0/0 Subnet Mask Default Gateway RouterA 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 192.168.1.1 (DCE) 255.255.255.0 N/A
Lab 1.2.2 Capturing and Analyzing Network Traffic Host Name IP Address Fa0/0 Subnet Mask IP Address S0/0/0 Subnet Mask Default Gateway RouterA 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 192.168.1.1 (DCE) 255.255.255.0 N/A
Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths
 Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths Objective Configure Load balance across multiple paths. Observe the load balancing process. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in the
Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths Objective Configure Load balance across multiple paths. Observe the load balancing process. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in the
Lab 5.3.7 Configuring DHCP with SDM and the Cisco IOS CLI
 Lab 5.3.7 Configuring DHCP with SDM and the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 Customer Serial 0/0/1 (DTE) 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 Fast Ethernet 0/0 192.168.1.1
Lab 5.3.7 Configuring DHCP with SDM and the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 Customer Serial 0/0/1 (DTE) 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 Fast Ethernet 0/0 192.168.1.1
Lab 1.2.3 Review of Basic Router Configuration with RIP. Objective. Background / Preparation. General Configuration Tips
 Lab 1.2.3 Review of Basic Router Configuration with RIP Objective Cable and configure workstations and routers Setup IP addressing scheme using Class B networks Configure Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
Lab 1.2.3 Review of Basic Router Configuration with RIP Objective Cable and configure workstations and routers Setup IP addressing scheme using Class B networks Configure Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
Lab 4.2.4 Advanced Telnet Operations
 Lab 4.2.4 Advanced Telnet Operations Objective Use the telnet command to remotely access other routers. Verify that the application layer between the source and the destination is working properly. Suspend
Lab 4.2.4 Advanced Telnet Operations Objective Use the telnet command to remotely access other routers. Verify that the application layer between the source and the destination is working properly. Suspend
CCNA Exploration 4.0.5.0 Routing Protocols and Concepts Student Lab Manual
 4.0.5.0 Routing Protocols and Concepts Student Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution
4.0.5.0 Routing Protocols and Concepts Student Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution
Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 806, 826, 827, 828, 831, 836, 837 and 881 Series Routers
 Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 806, 826, 827, 828, 831, 836, 837 and 881 Series Routers Document ID: 12065 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions
Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 806, 826, 827, 828, 831, 836, 837 and 881 Series Routers Document ID: 12065 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions
Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 3600 and 3800 Series Routers
 Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 3600 and 3800 Series Routers Document ID: 22189 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions Step by Step Procedure
Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 3600 and 3800 Series Routers Document ID: 22189 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions Step by Step Procedure
Lab 8.4.3b Managing Cisco IOS images with ROMMON and TFTP
 Lab 8.4.3b Managing Cisco IOS images with ROMMON and TFTP Host Device Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Analyze the Cisco IOS image and router
Lab 8.4.3b Managing Cisco IOS images with ROMMON and TFTP Host Device Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Analyze the Cisco IOS image and router
Basic Software Configuration Using the Cisco IOS Command-Line Interface
 Basic Software Configuration Using the Cisco IOS Command-Line Interface This document describes how to use the Cisco IOS command-line interface (CLI) to perform a basic software configuration for your
Basic Software Configuration Using the Cisco IOS Command-Line Interface This document describes how to use the Cisco IOS command-line interface (CLI) to perform a basic software configuration for your
CCNA Security 1.1 Student Lab Manual
 1.1 Student Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors
1.1 Student Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors
Lab 8.3.1.2 Configure Basic AP Security through IOS CLI
 Lab 8.3.1.2 Configure Basic AP Security through IOS CLI Estimated Time: 30 minutes Number of Team Members: Students will work in teams of two. Objective In this lab, the student will learn the following
Lab 8.3.1.2 Configure Basic AP Security through IOS CLI Estimated Time: 30 minutes Number of Team Members: Students will work in teams of two. Objective In this lab, the student will learn the following
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and
 This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNP: Implementing
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNP: Implementing
Lab 8.3.3b Configuring a Remote Router Using SSH
 Lab 8.3.3b Configuring a Remote Router Using SSH Objectives Use SDM to configure a router to accept SSH connections. Configure SSH client software on a PC. Establish a connection to a Cisco ISR using SSH
Lab 8.3.3b Configuring a Remote Router Using SSH Objectives Use SDM to configure a router to accept SSH connections. Configure SSH client software on a PC. Establish a connection to a Cisco ISR using SSH
Lab 5.3.8 Configuring PAT with SDM and Static NAT using Cisco IOS Commands
 Lab 5.3.8 Configuring PAT with SDM and Static NAT using Cisco IOS Commands Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 CustomerRouter Serial 0/0/0 (DTE) 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 Fast Ethernet
Lab 5.3.8 Configuring PAT with SDM and Static NAT using Cisco IOS Commands Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 CustomerRouter Serial 0/0/0 (DTE) 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 Fast Ethernet
Procedure: You can find the problem sheet on Drive D: of the lab PCs. Part 1: Router & Switch
 University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Computer Engineering Department Computer Networks Laboratory 907528 Lab. 2 Network Devices & Packet Tracer Objectives 1. To become familiar with
University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Computer Engineering Department Computer Networks Laboratory 907528 Lab. 2 Network Devices & Packet Tracer Objectives 1. To become familiar with
CS3695/M6-109 Lab 8-NPS02 VOIP Sniffing Ver. 8 Rev. 0
 Background For this lab, we will be analyzing some Wireshark capture files that were captured using the ARP Poisoning technique on Cisco VIOP (Voice Over IP) phones As this lab took special equipment (i.e.
Background For this lab, we will be analyzing some Wireshark capture files that were captured using the ARP Poisoning technique on Cisco VIOP (Voice Over IP) phones As this lab took special equipment (i.e.
Note: This case study utilizes Packet Tracer. Please see the Chapter 5 Packet Tracer file located in Supplemental Materials.
 Note: This case study utilizes Packet Tracer. Please see the Chapter 5 Packet Tracer file located in Supplemental Materials. CHAPTER 5 OBJECTIVES Configure a router with an initial configuration. Use the
Note: This case study utilizes Packet Tracer. Please see the Chapter 5 Packet Tracer file located in Supplemental Materials. CHAPTER 5 OBJECTIVES Configure a router with an initial configuration. Use the
Objectives Understand Cisco IOS system architecture components. Work with the Cisco IOS Command Line Interface (CLI) and common commands.
 Objectives Understand Cisco IOS system architecture components. Work with the Cisco IOS Command Line Interface (CLI) and common commands. Learn about Cisco IOS troubleshooting techniques. Understand upgrading
Objectives Understand Cisco IOS system architecture components. Work with the Cisco IOS Command Line Interface (CLI) and common commands. Learn about Cisco IOS troubleshooting techniques. Understand upgrading
Chapter 8 Lab A: Configuring a Site-to-Site VPN Using Cisco IOS and SDM
 Chapter 8 Lab A: Configuring a Site-to-Site VPN Using Cisco IOS and SDM Topology IP Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 Fa0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
Chapter 8 Lab A: Configuring a Site-to-Site VPN Using Cisco IOS and SDM Topology IP Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 Fa0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
Digitally Signed Cisco Software
 Digitally Signed Cisco Software Last Updated: January 16, 2013 The Digitally Signed Cisco Software feature describes how to identify digitally signed Cisco software, gather software authentication information
Digitally Signed Cisco Software Last Updated: January 16, 2013 The Digitally Signed Cisco Software feature describes how to identify digitally signed Cisco software, gather software authentication information
Lab 3.1.2 Creating a Logical Network Diagram
 Lab 3.1.2 Creating a Logical Network Diagram Objectives Use router and switch commands to obtain information about an existing network. Use Cisco Network Assistant to obtain information about an existing
Lab 3.1.2 Creating a Logical Network Diagram Objectives Use router and switch commands to obtain information about an existing network. Use Cisco Network Assistant to obtain information about an existing
Cisco Configuration Professional Quick Start Guide
 Cisco Configuration Professional Quick Start Guide April 29, 2011 This document explains how to start using Cisco Configuration Professional Express (Cisco CP Express) and Cisco Configuration Professional
Cisco Configuration Professional Quick Start Guide April 29, 2011 This document explains how to start using Cisco Configuration Professional Express (Cisco CP Express) and Cisco Configuration Professional
Lab 1.4.1 Introductory Lab 1 - Getting Started and Building Start.txt
 Lab 1.4.1 Introductory Lab 1 - Getting Started and Building Start.txt Objective This lab may introduce new CCNP lab equipment and certain IOS features. This introductory activity also describes how to
Lab 1.4.1 Introductory Lab 1 - Getting Started and Building Start.txt Objective This lab may introduce new CCNP lab equipment and certain IOS features. This introductory activity also describes how to
How To Configure InterVLAN Routing on Layer 3 Switches
 How To Configure InterVLAN Routing on Layer 3 Switches Document ID: 41860 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure InterVLAN Routing Task Step by Step Instructions
How To Configure InterVLAN Routing on Layer 3 Switches Document ID: 41860 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure InterVLAN Routing Task Step by Step Instructions
Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco Catalyst 2948G L3, 4840G, and 4908G L3 Switch Routers
 Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco Catalyst 2948G L3, 4840G, and 4908G L3 Switch Routers Document ID: 12738 Contents Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Step by Step Procedure
Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco Catalyst 2948G L3, 4840G, and 4908G L3 Switch Routers Document ID: 12738 Contents Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Step by Step Procedure
Lab 2.3.2 Configuring OSPF with Loopback Addresses
 Lab 2.3.2 Configuring OSPF with Loopback Addresses Objective Configure routers with a Class C IP addressing scheme. Observe the election process for designated routers (DR) and backup designated routers
Lab 2.3.2 Configuring OSPF with Loopback Addresses Objective Configure routers with a Class C IP addressing scheme. Observe the election process for designated routers (DR) and backup designated routers
Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing
 Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing Topology Objectives Background Review a basic EIGRP configuration. Explore the EIGRP topology table. Identify successors, feasible successors, and feasible distances.
Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing Topology Objectives Background Review a basic EIGRP configuration. Explore the EIGRP topology table. Identify successors, feasible successors, and feasible distances.
- Advanced IOS Functions -
 1 The Configuration Register - Advanced IOS Functions - The configuration register (config-register) is a hexadecimal value that controls various aspects of how a router boots, including: Baud Rate Boot
1 The Configuration Register - Advanced IOS Functions - The configuration register (config-register) is a hexadecimal value that controls various aspects of how a router boots, including: Baud Rate Boot
Lab 1.5.1 Introductory Lab 1 Getting Started and Building Start.txt
 Lab 1.5.1 Introductory Lab 1 Getting Started and Building Start.txt Objective This lab will introduce to the student the CCNP lab equipment and certain IOS features that might be new. This introductory
Lab 1.5.1 Introductory Lab 1 Getting Started and Building Start.txt Objective This lab will introduce to the student the CCNP lab equipment and certain IOS features that might be new. This introductory
Applicazioni Telematiche
 Angelo Coiro Laboratorio Applicazioni Telematiche L emulatore Packet Tracer Packet Tracer Cisco Packet Tracer is an academic software that allows to emulate Cisco devices Packet Tracer can be used for
Angelo Coiro Laboratorio Applicazioni Telematiche L emulatore Packet Tracer Packet Tracer Cisco Packet Tracer is an academic software that allows to emulate Cisco devices Packet Tracer can be used for
Lab 6.2.3 Managing the MAC Address Table
 Lab 6.2.3 Managing the MAC Address Table Objective Create a basic switch configuration. Manage the switch MAC table. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in the diagram. The configuration
Lab 6.2.3 Managing the MAC Address Table Objective Create a basic switch configuration. Manage the switch MAC table. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in the diagram. The configuration
Configuring the Switch with the CLI-Based Setup Program
 APPENDIX D Configuring the Switch with the CLI-Based Setup Program This appendix provides a command-line interface (CLI)-based setup procedure for a standalone switch. For product overview information,
APPENDIX D Configuring the Switch with the CLI-Based Setup Program This appendix provides a command-line interface (CLI)-based setup procedure for a standalone switch. For product overview information,
Configuring a Leased Line
 CHAPTER 4 Configuring a Leased Line The configuration in this chapter describes how to configure a Cisco 1700 router for IP and IPX over a synchronous serial line. Before You Begin The configuration in
CHAPTER 4 Configuring a Leased Line The configuration in this chapter describes how to configure a Cisco 1700 router for IP and IPX over a synchronous serial line. Before You Begin The configuration in
Do Not Duplicate: Post beta, not for release. Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices, Part 1 ICND1. Volume 1. Lab Guide. Version 2.
 ICND1 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices, Part 1 Volume 1 Version 2.0 Lab Guide Part Number: 97-3244-01 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. San Jose, CA Asia Pacific Headquarters Cisco Systems
ICND1 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices, Part 1 Volume 1 Version 2.0 Lab Guide Part Number: 97-3244-01 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. San Jose, CA Asia Pacific Headquarters Cisco Systems
TotalCloud Phone System
 TotalCloud Phone System Cisco SF 302-08P PoE VLAN Configuration Guide Note: The below information and configuration is for deployment of the Cbeyond managed switch solution using the Cisco 302 8 port Power
TotalCloud Phone System Cisco SF 302-08P PoE VLAN Configuration Guide Note: The below information and configuration is for deployment of the Cbeyond managed switch solution using the Cisco 302 8 port Power
Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding. Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1
 Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1 1 1 Objectives Identify a router as a computer with an OS and hardware designed for the routing process. Demonstrate
Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1 1 1 Objectives Identify a router as a computer with an OS and hardware designed for the routing process. Demonstrate
Lab 3 Routing Information Protocol (RIPv1) on a Cisco Router Network
 Lab 3 Routing Information Protocol (RIPv1) on a Cisco Router Network CMPE 150 Fall 2005 Introduction Today you are going to be thrown into using Cisco s Internetwork Operating System (IOS) to configure
Lab 3 Routing Information Protocol (RIPv1) on a Cisco Router Network CMPE 150 Fall 2005 Introduction Today you are going to be thrown into using Cisco s Internetwork Operating System (IOS) to configure
Lab 2 - Basic Router Configuration
 CS326 Fall 2001 Room: PAI 5.48 Name: Lab 2 - Basic Router Configuration In this lab you will learn: the various configuration modes of Cisco 2621 routers how to set up IP addresses for such routers how
CS326 Fall 2001 Room: PAI 5.48 Name: Lab 2 - Basic Router Configuration In this lab you will learn: the various configuration modes of Cisco 2621 routers how to set up IP addresses for such routers how
Chapter 7 Lab 7-1, Configuring Switches for IP Telephony Support
 Chapter 7 Lab 7-1, Configuring Switches for IP Telephony Support Topology Objectives Background Configure auto QoS to support IP phones. Configure CoS override for data frames. Configure the distribution
Chapter 7 Lab 7-1, Configuring Switches for IP Telephony Support Topology Objectives Background Configure auto QoS to support IP phones. Configure CoS override for data frames. Configure the distribution
Configuring a Router
 CHAPTER 3 Configuring a Router This chapter provides information and commands concerning the following topics: Configuring a router, specifically: Names Passwords Interfaces MOTD banners IP host tables
CHAPTER 3 Configuring a Router This chapter provides information and commands concerning the following topics: Configuring a router, specifically: Names Passwords Interfaces MOTD banners IP host tables
Router Lab Reference Guide
 Router Lab Reference Guide 1 PURPOSE AND GOALS The routing lab allows testing different IP-related protocols and solutions in a close to live environment. You can learn how to configure Cisco routers and
Router Lab Reference Guide 1 PURPOSE AND GOALS The routing lab allows testing different IP-related protocols and solutions in a close to live environment. You can learn how to configure Cisco routers and
Lab 3.5.1: Basic VLAN Configuration (Instructor Version)
 (Instructor Version) Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0
(Instructor Version) Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0
Basic Configuration of the Cisco 12000 Series Internet Router
 CHAPTER 2 Basic Configuration of the Cisco 12000 Series Internet Router This chapter describes how to boot and configure the Cisco 12000 Series Internet Router. It discusses the following subjects: Cisco
CHAPTER 2 Basic Configuration of the Cisco 12000 Series Internet Router This chapter describes how to boot and configure the Cisco 12000 Series Internet Router. It discusses the following subjects: Cisco
CCNA 2 v5.0 Routing Protocols Final Exam Answers
 CCNA 2 v5.0 Routing Protocols Final Exam Answers 1 Refer to the exhibit. What can be concluded about network 192.168.1.0 in the R2 routing table? This network was learned through summary LSAs from an ABR.*
CCNA 2 v5.0 Routing Protocols Final Exam Answers 1 Refer to the exhibit. What can be concluded about network 192.168.1.0 in the R2 routing table? This network was learned through summary LSAs from an ABR.*
ICND1-100-101 IOS CLI Study Guide (CCENT)
 ICND1-100-101 IOS CLI Study Guide (CCENT) Hostname: 2. hostname SW1 SWITCH CONFIGURATION Mgmt IP: 2. interface vlan 1 3. ip address 10.0.0.2 4. no shut Gateway: 2. ip default-gateway 10.0.0.1 Local User/Pwd:
ICND1-100-101 IOS CLI Study Guide (CCENT) Hostname: 2. hostname SW1 SWITCH CONFIGURATION Mgmt IP: 2. interface vlan 1 3. ip address 10.0.0.2 4. no shut Gateway: 2. ip default-gateway 10.0.0.1 Local User/Pwd:
Connecting to the Firewall Services Module and Managing the Configuration
 CHAPTER 3 Connecting to the Firewall Services Module and This chapter describes how to access the command-line interface and work with the configuration. This chapter includes the following sections: Connecting
CHAPTER 3 Connecting to the Firewall Services Module and This chapter describes how to access the command-line interface and work with the configuration. This chapter includes the following sections: Connecting
Simple MPLS network topology for Dynamips/Olive
 Simple MPLS network topology for Dynamips/Olive R1 version 12.4 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec no service password-encryption hostname R1 boot-start-marker
Simple MPLS network topology for Dynamips/Olive R1 version 12.4 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec no service password-encryption hostname R1 boot-start-marker
Lab 11.5.6.1 Configure Syslog on AP
 Lab 11.5.6.1 Configure Syslog on AP Estimated Time: 25 minutes Number of Team Members: Students will work in teams of two. Objective In this lab, students will configure and use syslog logging to monitor
Lab 11.5.6.1 Configure Syslog on AP Estimated Time: 25 minutes Number of Team Members: Students will work in teams of two. Objective In this lab, students will configure and use syslog logging to monitor
Case Study 1: Registering IP Phones with a remote Call
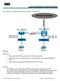 Case Study 1: Registering IP Phones with a remote Call Manager Objectives Place calls from IP Phones under R1 to IP Phones under R2 Place calls from any IP Phone (under R1 and under R2) to the regular
Case Study 1: Registering IP Phones with a remote Call Manager Objectives Place calls from IP Phones under R1 to IP Phones under R2 Place calls from any IP Phone (under R1 and under R2) to the regular
Telnet, Console and AUX Port Passwords on Cisco Routers Configuration Example
 Telnet, Console and AUX Port Passwords on Cisco Routers Configuration Example Document ID: 45843 Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Configure Passwords
Telnet, Console and AUX Port Passwords on Cisco Routers Configuration Example Document ID: 45843 Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Configure Passwords
LAB MANUAL for Computer Network
 LAB MANUAL for Computer Network CSE-310 F Computer Network Lab L T P - - 3 Class Work : 25 Marks Exam : 25 MARKS Total : 50 Marks This course provides students with hands on training regarding the design,
LAB MANUAL for Computer Network CSE-310 F Computer Network Lab L T P - - 3 Class Work : 25 Marks Exam : 25 MARKS Total : 50 Marks This course provides students with hands on training regarding the design,
Lab 6.1.3 Configure Local AAA on Cisco Router
 Lab 6.1.3 Configure Local AAA on Cisco Router Objective Scenario Topology In this lab, the students will complete the following tasks: Securing and testing access to the privileged EXEC, VTY, and console
Lab 6.1.3 Configure Local AAA on Cisco Router Objective Scenario Topology In this lab, the students will complete the following tasks: Securing and testing access to the privileged EXEC, VTY, and console
Lab 7: Firewalls Stateful Firewalls and Edge Router Filtering
 Lab 7: Firewalls Stateful Firewalls and Edge Router Filtering 7.1 Details Aim: Rich Macfarlane The aim of this lab is to introduce the concepts of stateful firewalls, using Cisco Contextbased Access Control
Lab 7: Firewalls Stateful Firewalls and Edge Router Filtering 7.1 Details Aim: Rich Macfarlane The aim of this lab is to introduce the concepts of stateful firewalls, using Cisco Contextbased Access Control
Chapter 4: Lab A: Configuring CBAC and Zone-Based Firewalls
 Chapter 4: Lab A: Configuring CBAC and Zone-Based Firewalls Topology IP Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 FA0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 FA0/5
Chapter 4: Lab A: Configuring CBAC and Zone-Based Firewalls Topology IP Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 FA0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 FA0/5
Lab 5.5.4 Configuring the Cisco 2960 Switch
 Lab 5.5.4 Configuring the Cisco 2960 Switch Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port S1 CustomerSwitch VLAN 1 192.168.1.5 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 N/A R1 CustomerRouter
Lab 5.5.4 Configuring the Cisco 2960 Switch Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port S1 CustomerSwitch VLAN 1 192.168.1.5 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 N/A R1 CustomerRouter
APNIC Members Training Course Security workshop. 2-4 July, 2008. Port Vila Vanuatu. In conjunction with PACNOG 4
 APNIC Members Training Course Security workshop 2-4 July, 2008 Port Vila Vanuatu In conjunction with PACNOG 4 Router device security lab 1. APNIC s remote lab In these exercises you will be remotely accessing
APNIC Members Training Course Security workshop 2-4 July, 2008 Port Vila Vanuatu In conjunction with PACNOG 4 Router device security lab 1. APNIC s remote lab In these exercises you will be remotely accessing
Angelos Stavrou. OF COURSE there is no Magic so lets see show things work in practice...
 Cisco Inter-network Operating System (IOS) A short guide for the NetAdmin Angelos Stavrou Let's start out at the very beginning with the question: "What is a Command?" The most important thing to understand
Cisco Inter-network Operating System (IOS) A short guide for the NetAdmin Angelos Stavrou Let's start out at the very beginning with the question: "What is a Command?" The most important thing to understand
BRI to PRI Connection Using Data Over Voice
 BRI to PRI Connection Using Data Over Voice Document ID: 14962 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Conventions Background Information Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot
BRI to PRI Connection Using Data Over Voice Document ID: 14962 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Conventions Background Information Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot
ICND1 Lab Guide. 100-101 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 Version 2.0. Labs powered by
 ICND1 Lab Guide 100-101 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 Version 2.0 ii Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 100-101 Lab Guide LM20130929/BV2.01 iii 25 Century Blvd. Ste. 500
ICND1 Lab Guide 100-101 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 Version 2.0 ii Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 100-101 Lab Guide LM20130929/BV2.01 iii 25 Century Blvd. Ste. 500
Configuring a Cisco 2509-RJ Terminal Router
 created by: Rainer Bemsel Version 1.0 Dated: Dec/08/2012 For my Cisco LAB, I ve purchased a used Cisco 2509-RJ with RJ45-RJ45 roll-over cables. This TechTip shows my configuration setup, so you can easily
created by: Rainer Bemsel Version 1.0 Dated: Dec/08/2012 For my Cisco LAB, I ve purchased a used Cisco 2509-RJ with RJ45-RJ45 roll-over cables. This TechTip shows my configuration setup, so you can easily
Cisco - Configure the 1721 Router for VLANs Using a Switch Module (WIC-4ESW)
 Page 1 of 20 Configure the 1721 Router for VLANs Using a Switch Module (WIC-4ESW) Document ID: 50036 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Network Diagram The Role of Switched
Page 1 of 20 Configure the 1721 Router for VLANs Using a Switch Module (WIC-4ESW) Document ID: 50036 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Network Diagram The Role of Switched
Basic Router and Switch Instructions (Cisco Devices)
 Basic Router and Switch Instructions (Cisco Devices) Basic Device Connection 1. Connect to the device via the console cable (light blue cable) and the use of a terminal program (Windows Hyperterminal,
Basic Router and Switch Instructions (Cisco Devices) Basic Device Connection 1. Connect to the device via the console cable (light blue cable) and the use of a terminal program (Windows Hyperterminal,
Brocade to Cisco Comparisons
 1 2 3 Console cables - The console cables are not interchangeable between Brocade and Cisco. Each vendor provides their console cable with each manageable unit it sells. Passwords - Neither Cisco or Brocade
1 2 3 Console cables - The console cables are not interchangeable between Brocade and Cisco. Each vendor provides their console cable with each manageable unit it sells. Passwords - Neither Cisco or Brocade
CCT vs. CCENT Skill Set Comparison
 Operation of IP Data Networks Recognize the purpose and functions of various network devices such as Routers, Switches, Bridges and Hubs Select the components required to meet a given network specification
Operation of IP Data Networks Recognize the purpose and functions of various network devices such as Routers, Switches, Bridges and Hubs Select the components required to meet a given network specification
Troubleshooting IP Routing
 C H A P T E R 7 Troubleshooting IP Routing This troubleshooting chapter has several goals. First, it explains several tools and functions not covered in Chapters 4 through 6 specifically, tools that can
C H A P T E R 7 Troubleshooting IP Routing This troubleshooting chapter has several goals. First, it explains several tools and functions not covered in Chapters 4 through 6 specifically, tools that can
CT5760 Controller and Catalyst 3850 Switch Configuration Example
 CT5760 Controller and Catalyst 3850 Switch Configuration Example Document ID: 116342 Contributed by Antoine KMEID and Serge Yasmine, Cisco TAC Engineers. Aug 13, 2013 Contents Introduction Prerequisites
CT5760 Controller and Catalyst 3850 Switch Configuration Example Document ID: 116342 Contributed by Antoine KMEID and Serge Yasmine, Cisco TAC Engineers. Aug 13, 2013 Contents Introduction Prerequisites
Document ID: 45741. Introduction
 Products & Services 6bone Connection Using 6to4 Tunnels for IPv6 Document ID: 45741 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions How 6to4 Tunnels Work Limitations of 6to4
Products & Services 6bone Connection Using 6to4 Tunnels for IPv6 Document ID: 45741 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions How 6to4 Tunnels Work Limitations of 6to4
ENetwork Basic Configuration PT Practice SBA
 ENetwork Basic Configuration PT Practice SBA A few things to keep in mind while completing this activity: 1. Do not use the browser Back button or close or reload any exam windows during the exam. 2. Do
ENetwork Basic Configuration PT Practice SBA A few things to keep in mind while completing this activity: 1. Do not use the browser Back button or close or reload any exam windows during the exam. 2. Do
Configuring the Switch with the CLI Setup Program
 APPENDIXC Configuring the Switch with the CLI Setup Program This appendix provides a command-line interface (CLI) setup procedure for a standalone switch. To set up the switch by using Express Setup, see
APPENDIXC Configuring the Switch with the CLI Setup Program This appendix provides a command-line interface (CLI) setup procedure for a standalone switch. To set up the switch by using Express Setup, see
Configurazione Rete VoIP
 Configurazione Rete VoIP 1x CISCO 7940G 1x CISCO 3725 with cme-full-7.0.0.1.tar 1x CISCO IP Communicator Startup Config router CISCO 3725 Procedura Operativa: Topologia di rete Operazioni preliminary sul
Configurazione Rete VoIP 1x CISCO 7940G 1x CISCO 3725 with cme-full-7.0.0.1.tar 1x CISCO IP Communicator Startup Config router CISCO 3725 Procedura Operativa: Topologia di rete Operazioni preliminary sul
- The PIX OS Command-Line Interface -
 1 PIX OS Versions - The PIX OS Command-Line Interface - The operating system for Cisco PIX/ASA firewalls is known as the PIX OS. Because the PIX product line was acquired and not originally developed by
1 PIX OS Versions - The PIX OS Command-Line Interface - The operating system for Cisco PIX/ASA firewalls is known as the PIX OS. Because the PIX product line was acquired and not originally developed by
Course "Netzwerke" LAB 2 Basic Router Configuration
 Course "Netzwerke" LAB 2 Basic Router Configuration Learning Objectives Review of previously learned skills. Basic IOS Command Line Interface operation. Basic Router configuration. Verification and testing
Course "Netzwerke" LAB 2 Basic Router Configuration Learning Objectives Review of previously learned skills. Basic IOS Command Line Interface operation. Basic Router configuration. Verification and testing
Cisco Router Configuration Basics. Scalable Infrastructure Workshop
 Cisco Router Configuration Basics Scalable Infrastructure Workshop Router Components p RAM n Holds operating system, data structures, packet buffers, ARP cache, and routing tables n Reset on reload n Router
Cisco Router Configuration Basics Scalable Infrastructure Workshop Router Components p RAM n Holds operating system, data structures, packet buffers, ARP cache, and routing tables n Reset on reload n Router
Basic Router Configuration
 CHAPTER 3 This chapter provides procedures for configuring the basic parameters of your Cisco router, including global parameter settings, routing protocols, interfaces, and command-line access. It also
CHAPTER 3 This chapter provides procedures for configuring the basic parameters of your Cisco router, including global parameter settings, routing protocols, interfaces, and command-line access. It also
Virtual Fragmentation Reassembly
 Virtual Fragmentation Reassembly Currently, the Cisco IOS Firewall specifically context-based access control (CBAC) and the intrusion detection system (IDS) cannot identify the contents of the IP fragments
Virtual Fragmentation Reassembly Currently, the Cisco IOS Firewall specifically context-based access control (CBAC) and the intrusion detection system (IDS) cannot identify the contents of the IP fragments
Lab 5.5 Configuring Logging
 Lab 5.5 Configuring Logging Learning Objectives Configure a router to log to a Syslog server Use Kiwi Syslog Daemon as a Syslog server Configure local buffering on a router Topology Diagram Scenario In
Lab 5.5 Configuring Logging Learning Objectives Configure a router to log to a Syslog server Use Kiwi Syslog Daemon as a Syslog server Configure local buffering on a router Topology Diagram Scenario In
Chapter 2 Reading Organizer
 Chapter 2 Reading Organizer After completion of this chapter, you should be able to: Explain the advantages and disadvantages of static routing Configure initial settings on a Cisco switch Configure switch
Chapter 2 Reading Organizer After completion of this chapter, you should be able to: Explain the advantages and disadvantages of static routing Configure initial settings on a Cisco switch Configure switch
Configuring Switch Ports and VLAN Interfaces for the Cisco ASA 5505 Adaptive Security Appliance
 CHAPTER 5 Configuring Switch Ports and VLAN Interfaces for the Cisco ASA 5505 Adaptive Security Appliance This chapter describes how to configure the switch ports and VLAN interfaces of the ASA 5505 adaptive
CHAPTER 5 Configuring Switch Ports and VLAN Interfaces for the Cisco ASA 5505 Adaptive Security Appliance This chapter describes how to configure the switch ports and VLAN interfaces of the ASA 5505 adaptive
Configurazione Rete VoIP
 Configurazione Rete VoIP 1x CISCO 7940G 1x CISCO 3725 with cme-full-7.0.0.1.tar 1x CISCO IP Communicator Startup Config router CISCO 3725 Procedura Operativa: Topologia di rete Operazioni preliminary sul
Configurazione Rete VoIP 1x CISCO 7940G 1x CISCO 3725 with cme-full-7.0.0.1.tar 1x CISCO IP Communicator Startup Config router CISCO 3725 Procedura Operativa: Topologia di rete Operazioni preliminary sul
