Lab Configuring Syslog and NTP (Instructor Version)
|
|
|
- Franklin Hodges
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 (Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 S0/0/0 (DCE) N/A R2 S0/0/ N/A G0/ N/A PC-B NIC Part 1: Configure Basic Device Settings Part 2: Configure NTP Part 3: Configure Syslog Background / Scenario Syslog messages that are generated by the network devices can be collected and archived on a syslog server. The information can be used for monitoring, debugging, and troubleshooting purposes. The administrator can control where the messages are stored and displayed. Syslog messages can be timestamped for analysis of the sequence of network events; therefore, it is important to synchronize the clock across the network devices with a Network Time Protocol (NTP) server. In this lab, you will configure R1 as the NTP server and R2 as a Syslog and NTP client. The syslog server application, such as Tftp32d or other similar program, will be running on PC-B. Furthermore, you will control the severity level of log messages that are collected and archived on the syslog server. Note: The routers used with CCNA hands-on labs are Cisco 1941 Integrated Services Routers (ISRs) with Cisco IOS Release 15.2(4)M3 (universalk9 image). Other routers and Cisco IOS versions can be used. Depending on the model and Cisco IOS version, the commands available and output produced might vary from what is shown in the labs. Refer to the Router Interface Summary Table at the end of this lab for the correct interface identifiers. Note: Make sure that the routers have been erased and have no startup configurations. If you are unsure, contact your instructor. Instructor Note: Refer to the Instructor Lab Manual for the procedures to initialize and reload devices Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 14
2 Required Resources 2 Routers (Cisco 1941 with Cisco IOS Release 15.2(4)M3 universal image or comparable) 1 PC (Windows 7, Vista, or XP with terminal emulation program, such as Tera Term, and Syslog software, such as tftpd32) Console cables to configure the Cisco IOS devices via the console ports Ethernet and serial cables as shown in the topology Part 1: Configure Basic Device Settings In Part 1, you will set up the network topology and configure basic settings, such as the interface IP addresses, routing, device access, and passwords. Step 1: Cable the network as shown in the topology. Step 2: Initialize and reload the routers as necessary. Step 3: Configure basic settings for each router. a. Disable DNS lookup. b. Configure the device name. c. Encrypt plain text passwords. d. Create a message of the day (MOTD) banner warning users that unauthorized access is prohibited. e. Assign class as the encrypted privileged EXEC mode password. f. Assign cisco as the console and vty password and enable login. g. Set console logging to synchronous mode. h. Apply the IP addresses to Serial and Gigabit Ethernet interfaces according to the Addressing Table and activate the physical interfaces. i. Set the clock rate to for the DCE serial interface. Step 4: Configure routing. Enable single-area OSPF on the routers with process ID 1. Add all the networks into the OSPF process for area 0. Step 5: Configure PC-B. Configure the IP address and default gateway for PC-B according to the Addressing Table. Step 6: Verify end-to-end connectivity. Verify that each device is able to ping every other device in the network successfully. If not, troubleshoot until there is end-to-end connectivity. Step 7: Save the running configuration to the startup configuration Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 2 of 14
3 Part 2: Configure NTP In Part 2, you will configure R1 as the NTP server and R2 as the NTP client of R1. Synchronized time is important for syslog and debug functions. If the time is not synchronized, it is difficult to determine what network event caused the message. Step 1: Display the current time. Issue the show clock command to display the current time on R1. R1# show clock *12:30: UTC Tue May Record the information regarding the current time displayed in the following table. Date Answer will vary. In this example: May 14, 2013 Time Answer will vary. In this example: 12:30: Time Zone Answer will vary. In this example: UTC Step 2: Set the time. Use the clock set command to set the time on R1. The following is an example of setting the date and time. R1# clock set 9:39:00 05 july 2013 R1# *Jul 5 09:39:00.000: %SYS-6-CLOCKUPDATE: System clock has been updated from 12:30:54 UTC Tue May to 09:39:00 UTC Fri Jul , configured from console by console. Note: The time can also be set using the clock timezone command in the global configuration mode. For more information regarding this command, research the clock timezone command at to determine the zone for your region. Step 3: Configure the NTP master. Configure R1 as the NTP master by using the ntp master stratum-number command in global configuration mode. The stratum number indicates the number of NTP hops away from an authoritative time source. In this lab, the number 5 is the stratum level of this NTP server. R1(config)# ntp master 5 Step 4: Configure the NTP client. a. Issue show clock command on R2. Record the current time displayed on R2 in the following table. Date Time Time Zone Answer will vary. Answer will vary. Answer will vary. b. Configure R2 as the NTP client. Use the ntp server command to point to the IP address or hostname of the NTP server. The ntp update-calendar command periodically updates the calendar with NTP time. R2(config)# ntp server R2(config)# ntp update-calendar 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 3 of 14
4 Step 5: Verify NTP configuration. a. Use the show ntp associations command to verify that R2 has an NTP association with R1. R2# show ntp associations address ref clock st when poll reach delay offset disp *~ * sys.peer, # selected, + candidate, - outlyer, x falseticker, ~ configured b. Issue show clock on R1 and R2 to compare the timestamp. Note: It could take a few minutes before the timestamp on R2 is synchronized with R1. R1# show clock 09:43: UTC Fri Jul R2# show clock 09:43: UTC Fri Jul Part 3: Configure Syslog Syslog messages from network devices can be collected and archived on a syslog server. In this lab, Tftpd32 will be used as the syslog server software. The network administrator can control the types of messages that can be sent to the syslog server. Step 1: (Optional) Install syslog server. If a syslog server is not already installed on the PC, download and install the latest version of a syslog server, such as Tftpd32, on the PC. The latest version of Tftpd32 can be found at the following link: Step 2: Start the syslog server on PC-B. After starting the Tftpd32 application, click the syslog server tab Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 4 of 14
5 Step 3: Verify that the timestamp service is enabled on R2. Use the show run command to verify that the timestamp service is enabled for logging on R2. R2# show run include timestamp service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec If the timestamp service is not enabled, use the following command to enable it. R2(config)# service timestamps log datetime msec Step 4: Configure R2 to log messages to the syslog server. Configure R2 to send Syslog messages to the syslog server, PC-B. The IP address of the PC-B syslog server is R2(config)# logging host Step 5: Display the default logging settings. Use the show logging command to display the default logging settings. R2# show logging Syslog logging: enabled (0 messages dropped, 2 messages rate-limited, 0 flushes, 0 overruns, xml disabled, filtering disabled) No Active Message Discriminator. No Inactive Message Discriminator. Console logging: level debugging, 47 messages logged, xml disabled, filtering disabled Monitor logging: level debugging, 0 messages logged, xml disabled, filtering disabled Buffer logging: level debugging, 47 messages logged, xml disabled, filtering disabled Exception Logging: size (4096 bytes) Count and timestamp logging messages: disabled Persistent logging: disabled No active filter modules. Trap logging: level informational, 49 message lines logged Logging to (udp port 514, audit disabled, link up), 6 message lines logged, 0 message lines rate-limited, 0 message lines dropped-by-md, xml disabled, sequence number disabled filtering disabled Logging Source-Interface: VRF Name: 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 5 of 14
6 What is the IP address of the syslog server? What protocol and port is syslog using? UDP port 514 At what level is trap logging enabled? informational Step 6: Configure and observe the effect of logging severity levels on R2. a. Use the logging trap? command to determine the various trap levels availability. When configuring a level, the messages sent to the syslog server are the trap level configured and any lower levels. R2(config)# logging trap? <0-7> Logging severity level alerts Immediate action needed (severity=1) critical Critical conditions (severity=2) debugging Debugging messages (severity=7) emergencies System is unusable (severity=0) errors Error conditions (severity=3) informational Informational messages (severity=6) notifications Normal but significant conditions (severity=5) warnings Warning conditions (severity=4) <cr> If the logging trap warnings command was issued, which severity levels of messages are logged? warnings (level 4) errors (level 3), critical (level 2), alerts (level 1), and emergency (level 0) b. Change the logging severity level to 4. R2(config)# logging trap warnings or R2(config)# logging trap 4 c. Create interface Loopback0 on R2 and observe the log messages on both the terminal window and the syslog server window on PC-B. R2(config)# interface lo 0 R2(config-if)# Jul 5 09:57:47.162: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface Loopback0, changed state to up Jul 5 09:57:48.162: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Loopback0, changed state to up 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 6 of 14
7 d. Remove the Loopback 0 interface on R2 and observe the log messages. R2(config-if)# no interface lo 0 R2(config)# Jul 5 10:02:58.910: %LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface Loopback0, changed state to administratively down Jul 5 10:02:59.910: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Loopback0, changed state to down At severity level 4, are there any log messages on the syslog server? If any log messages appeared, explain what appeared and why. There was a summary warning log message indicating a change in the interface state. The addition of the interface was not enough to trigger and send more detailed informational messages to the syslog server at level 4. e. Change the logging severity level to 6. R2(config)# logging trap informational or R2(config)# logging trap 6 f. Clear the syslog entries on PC-B. Click Clear in the Tftpd32 dialog box. g. Create the Loopback 1 interface on R2. R2(config)# interface lo 1 Jul 5 10:05:46.650: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface Loopback1, changed state to up Jul 5 10:05:47.650: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Loopback1, changed state to up h. Remove the Loopback 1 interface from R2. R2(config-if)# no interface lo Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 7 of 14
8 R2(config-if)# Jul 5 10:08:29.742: %LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface Loopback1, changed state to administratively down Jul 5 10:08:30.742: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Loopback1, changed state to down i. Observe the syslog server output. Compare this result with the results at trapping level 4. What is your observation? Reflection More log messages were trapped when the severity was set to 6 (informational) than when it was set at 4 (warnings). What is the problem with setting the level of severity too high (lowest level number) or too low (highest level number) for syslog? When the severity level is set too high (lowest level number), the generated log could be missing important, but not critical messages. However, setting it too low (highest level number), it can generate too many entries and fill the logs with unnecessary information Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 8 of 14
9 Router Interface Summary Table Router Interface Summary Router Model Ethernet Interface #1 Ethernet Interface #2 Serial Interface #1 Serial Interface # Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) 1900 Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 (G0/0) 2801 Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) 2811 Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) 2900 Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 (G0/0) Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) Gigabit Ethernet 0/1 (G0/1) Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) Gigabit Ethernet 0/1 (G0/1) Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) Serial 0/1/0 (S0/1/0) Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) Serial 0/1/1 (S0/1/1) Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) Note: To find out how the router is configured, look at the interfaces to identify the type of router and how many interfaces the router has. There is no way to effectively list all the combinations of configurations for each router class. This table includes identifiers for the possible combinations of Ethernet and Serial interfaces in the device. The table does not include any other type of interface, even though a specific router may contain one. An example of this might be an ISDN BRI interface. The string in parenthesis is the legal abbreviation that can be used in Cisco IOS commands to represent the interface. Device Configs Router R1 R1#show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 1572 bytes version 15.2 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec service password-encryption hostname R1 boot-start-marker boot-end-marker enable secret 4 06YFDUHH61wAE/kLkDq9BGho1QM5EnRtoyr8cHAUg.2 no aaa new-model memory-size iomem 15 ip cef 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 9 of 14
10 no ip domain lookup no ipv6 cef multilink bundle-name authenticated redundancy interface Embedded-Service-Engine0/0 no ip address shutdown interface GigabitEthernet0/0 no ip address shutdown duplex auto speed auto interface GigabitEthernet0/1 no ip address shutdown duplex auto speed auto interface Serial0/0/0 ip address Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 10 of 14
11 clock rate interface Serial0/0/1 no ip address shutdown router ospf 1 network area 0 ip forward-protocol nd no ip http server no ip http secure-server control-plane banner motd ^CUnauthorized access is prohibited.^c line con 0 password 7 110A D logging synchronous login line aux 0 line 2 no activation-character no exec transport preferred none transport input all transport output pad telnet rlogin lapb-ta mop udptn v120 ssh stopbits 1 line vty 0 4 password F login transport input all scheduler allocate ntp master 5 end Router R2 Building configuration... Current configuration : 1742 bytes 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 11 of 14
12 version 15.2 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec service password-encryption hostname R2 boot-start-marker boot-end-marker enable secret 4 06YFDUHH61wAE/kLkDq9BGho1QM5EnRtoyr8cHAUg.2 no aaa new-model memory-size iomem 15 ip cef no ip domain lookup no ipv6 cef multilink bundle-name authenticated redundancy interface Embedded-Service-Engine0/0 no ip address shutdown 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 12 of 14
13 interface GigabitEthernet0/0 ip address duplex auto speed auto interface GigabitEthernet0/1 no ip address shutdown duplex auto speed auto interface Serial0/0/0 ip address interface Serial0/0/1 no ip address shutdown clock rate router ospf 1 network area 0 network area 0 ip forward-protocol nd no ip http server no ip http secure-server logging host control-plane banner motd ^CUnauthorized access is prohibited.^c line con 0 password 7 121A0C logging synchronous login line aux 0 line 2 no activation-character no exec transport preferred none transport input all 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 13 of 14
14 transport output pad telnet rlogin lapb-ta mop udptn v120 ssh stopbits 1 line vty 0 4 password F login transport input all scheduler allocate ntp update-calendar ntp server end 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 14 of 14
Skills Assessment Student Training Exam
 Skills Assessment Student Training Exam Topology Assessment Objectives Part 1: Initialize Devices (8 points, 5 minutes) Part 2: Configure Device Basic Settings (28 points, 30 minutes) Part 3: Configure
Skills Assessment Student Training Exam Topology Assessment Objectives Part 1: Initialize Devices (8 points, 5 minutes) Part 2: Configure Device Basic Settings (28 points, 30 minutes) Part 3: Configure
Skills Assessment Student Training (Answer Key)
 CCNA: Connecting Networks Skills Assessment Student Training (Answer Key) Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Assessment
CCNA: Connecting Networks Skills Assessment Student Training (Answer Key) Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Assessment
Lab 5.3.9b Managing Router Configuration Files Using TFTP
 Lab 5.3.9b Managing Router Configuration Files Using TFTP Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Download and install TFTP server software.
Lab 5.3.9b Managing Router Configuration Files Using TFTP Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Download and install TFTP server software.
PT Activity: Configure Cisco Routers for Syslog, NTP, and SSH Operations
 PT Activity: Configure Cisco Routers for Syslog, NTP, and SSH Operations Instructor Version Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 FA0/1
PT Activity: Configure Cisco Routers for Syslog, NTP, and SSH Operations Instructor Version Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 FA0/1
Chapter 8 Lab B: Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client
 Chapter 8 Lab B: Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client Topology Note: ISR G2 devices have Gigabit Ethernet interfaces instead of FastEthernet Interfaces. All contents are Copyright 1992 2012
Chapter 8 Lab B: Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client Topology Note: ISR G2 devices have Gigabit Ethernet interfaces instead of FastEthernet Interfaces. All contents are Copyright 1992 2012
Objectives. Background. Required Resources. CCNA Security
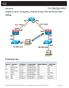 Chapter 8 Lab B, Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client Topology IP Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 FA0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Chapter 8 Lab B, Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client Topology IP Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 FA0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Simple MPLS network topology for Dynamips/Olive
 Simple MPLS network topology for Dynamips/Olive R1 version 12.4 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec no service password-encryption hostname R1 boot-start-marker
Simple MPLS network topology for Dynamips/Olive R1 version 12.4 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec no service password-encryption hostname R1 boot-start-marker
Lab 5.5 Configuring Logging
 Lab 5.5 Configuring Logging Learning Objectives Configure a router to log to a Syslog server Use Kiwi Syslog Daemon as a Syslog server Configure local buffering on a router Topology Diagram Scenario In
Lab 5.5 Configuring Logging Learning Objectives Configure a router to log to a Syslog server Use Kiwi Syslog Daemon as a Syslog server Configure local buffering on a router Topology Diagram Scenario In
Brest. Backup : copy flash:ppe_brest1 running-config
 Brest Backup : copy flash:ppe_brest1 running-config Cisco SF300-08 Mise en place des services : - Serveurs : 10.3.50.0/24 VLAN 2 (port 1) - DSI : 10.3.51.0/24 VLAN 3 (port 2) - Direction : 10.3.52.0/24
Brest Backup : copy flash:ppe_brest1 running-config Cisco SF300-08 Mise en place des services : - Serveurs : 10.3.50.0/24 VLAN 2 (port 1) - DSI : 10.3.51.0/24 VLAN 3 (port 2) - Direction : 10.3.52.0/24
Lab 11.5.6.1 Configure Syslog on AP
 Lab 11.5.6.1 Configure Syslog on AP Estimated Time: 25 minutes Number of Team Members: Students will work in teams of two. Objective In this lab, students will configure and use syslog logging to monitor
Lab 11.5.6.1 Configure Syslog on AP Estimated Time: 25 minutes Number of Team Members: Students will work in teams of two. Objective In this lab, students will configure and use syslog logging to monitor
Lab - Using IOS CLI with Switch MAC Address Tables
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12
Lab: Basic Router Configuration
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Def. Gateway R1 Fa0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R2 Fa0/0 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Def. Gateway R1 Fa0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R2 Fa0/0 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
CS3695/M6-109 Lab 8-NPS02 VOIP Sniffing Ver. 8 Rev. 0
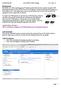 Background For this lab, we will be analyzing some Wireshark capture files that were captured using the ARP Poisoning technique on Cisco VIOP (Voice Over IP) phones As this lab took special equipment (i.e.
Background For this lab, we will be analyzing some Wireshark capture files that were captured using the ARP Poisoning technique on Cisco VIOP (Voice Over IP) phones As this lab took special equipment (i.e.
Note: This case study utilizes Packet Tracer. Please see the Chapter 5 Packet Tracer file located in Supplemental Materials.
 Note: This case study utilizes Packet Tracer. Please see the Chapter 5 Packet Tracer file located in Supplemental Materials. CHAPTER 5 OBJECTIVES Configure a router with an initial configuration. Use the
Note: This case study utilizes Packet Tracer. Please see the Chapter 5 Packet Tracer file located in Supplemental Materials. CHAPTER 5 OBJECTIVES Configure a router with an initial configuration. Use the
How To Configure A Cisco Router With A Cio Router
 CHAPTER 1 This chapter provides procedures for configuring the basic parameters of your Cisco router, including global parameter settings, routing protocols, interfaces, and command-line access. It also
CHAPTER 1 This chapter provides procedures for configuring the basic parameters of your Cisco router, including global parameter settings, routing protocols, interfaces, and command-line access. It also
Configurazione Rete VoIP
 Configurazione Rete VoIP 1x CISCO 7940G 1x CISCO 3725 with cme-full-7.0.0.1.tar 1x CISCO IP Communicator Startup Config router CISCO 3725 Procedura Operativa: Topologia di rete Operazioni preliminary sul
Configurazione Rete VoIP 1x CISCO 7940G 1x CISCO 3725 with cme-full-7.0.0.1.tar 1x CISCO IP Communicator Startup Config router CISCO 3725 Procedura Operativa: Topologia di rete Operazioni preliminary sul
Lab 8.3.1.2 Configure Basic AP Security through IOS CLI
 Lab 8.3.1.2 Configure Basic AP Security through IOS CLI Estimated Time: 30 minutes Number of Team Members: Students will work in teams of two. Objective In this lab, the student will learn the following
Lab 8.3.1.2 Configure Basic AP Security through IOS CLI Estimated Time: 30 minutes Number of Team Members: Students will work in teams of two. Objective In this lab, the student will learn the following
Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths Instructor Version 2500 Objective onfigure Load balance across multiple paths. Observe the load balancing process. Background/Preparation able a network similar
Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths Instructor Version 2500 Objective onfigure Load balance across multiple paths. Observe the load balancing process. Background/Preparation able a network similar
Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths
 Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths Objective Configure Load balance across multiple paths. Observe the load balancing process. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in the
Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths Objective Configure Load balance across multiple paths. Observe the load balancing process. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in the
Table of Contents. Cisco Using the Cisco IOS Firewall to Allow Java Applets From Known Sites while Denying Others
 Cisco IOS Firewall to Allow Java Applets From Known Sites w Table of Contents Using the Cisco IOS Firewall to Allow Java Applets From Known Sites while Denying Others...1 Introduction...1 To Deny Java
Cisco IOS Firewall to Allow Java Applets From Known Sites w Table of Contents Using the Cisco IOS Firewall to Allow Java Applets From Known Sites while Denying Others...1 Introduction...1 To Deny Java
Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI
 Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Serial 0/0/0 (DCE) 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 FastEthernet 0/0 172.16.0.1 255.255.0.0
Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Serial 0/0/0 (DCE) 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 FastEthernet 0/0 172.16.0.1 255.255.0.0
Lab 6.1.3 Configure Local AAA on Cisco Router
 Lab 6.1.3 Configure Local AAA on Cisco Router Objective Scenario Topology In this lab, the students will complete the following tasks: Securing and testing access to the privileged EXEC, VTY, and console
Lab 6.1.3 Configure Local AAA on Cisco Router Objective Scenario Topology In this lab, the students will complete the following tasks: Securing and testing access to the privileged EXEC, VTY, and console
Lab 8.4.3a Managing Cisco IOS Images with TFTP
 Lab 8.4.3a Managing Cisco IOS Images with TFTP Host Device Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Analyze the Cisco IOS image and router flash memory.
Lab 8.4.3a Managing Cisco IOS Images with TFTP Host Device Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Analyze the Cisco IOS image and router flash memory.
Lab 7: Firewalls Stateful Firewalls and Edge Router Filtering
 Lab 7: Firewalls Stateful Firewalls and Edge Router Filtering 7.1 Details Aim: Rich Macfarlane The aim of this lab is to introduce the concepts of stateful firewalls, using Cisco Contextbased Access Control
Lab 7: Firewalls Stateful Firewalls and Edge Router Filtering 7.1 Details Aim: Rich Macfarlane The aim of this lab is to introduce the concepts of stateful firewalls, using Cisco Contextbased Access Control
Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI
 Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP address Subnet mask R1 R1 Serial 0/0/0 (DCE) 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 FastEthernet 0/0 172.16.0.1 255.255.0.0
Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP address Subnet mask R1 R1 Serial 0/0/0 (DCE) 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 FastEthernet 0/0 172.16.0.1 255.255.0.0
Lab 4.1.4 Creating a Network Map using CDP Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 4.1.4 Creating a Network Map using CDP Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) commands to get information about neighboring network devices. Background/Preparation CDP
Lab 4.1.4 Creating a Network Map using CDP Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) commands to get information about neighboring network devices. Background/Preparation CDP
Configurazione Rete VoIP
 Configurazione Rete VoIP 1x CISCO 7940G 1x CISCO 3725 with cme-full-7.0.0.1.tar 1x CISCO IP Communicator Startup Config router CISCO 3725 Procedura Operativa: Topologia di rete Operazioni preliminary sul
Configurazione Rete VoIP 1x CISCO 7940G 1x CISCO 3725 with cme-full-7.0.0.1.tar 1x CISCO IP Communicator Startup Config router CISCO 3725 Procedura Operativa: Topologia di rete Operazioni preliminary sul
Lab 1.2.3 Review of Basic Router Configuration with RIP. Objective. Background / Preparation. General Configuration Tips
 Lab 1.2.3 Review of Basic Router Configuration with RIP Objective Cable and configure workstations and routers Setup IP addressing scheme using Class B networks Configure Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
Lab 1.2.3 Review of Basic Router Configuration with RIP Objective Cable and configure workstations and routers Setup IP addressing scheme using Class B networks Configure Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
Enabling Management Protocols: NTP, SNMP, and Syslog
 SECTION 7 Enabling Management Protocols: NTP, SNMP, and Syslog In this Section This section describes how to enable basic management protocols on a Cisco AS5800 and Cisco AS5300 as part of a dial access
SECTION 7 Enabling Management Protocols: NTP, SNMP, and Syslog In this Section This section describes how to enable basic management protocols on a Cisco AS5800 and Cisco AS5300 as part of a dial access
Lab 4.2.4 Advanced Telnet Operations
 Lab 4.2.4 Advanced Telnet Operations Objective Use the telnet command to remotely access other routers. Verify that the application layer between the source and the destination is working properly. Suspend
Lab 4.2.4 Advanced Telnet Operations Objective Use the telnet command to remotely access other routers. Verify that the application layer between the source and the destination is working properly. Suspend
Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway
 Felix Rohrer Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1 S2 VLAN 99 192.168.99.12 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1
Felix Rohrer Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1 S2 VLAN 99 192.168.99.12 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1
Connect the Host to attach to Fast Ethernet switch port Fa0/2. Configure the host as shown in the topology diagram above.
 Lab 1.2.2 Capturing and Analyzing Network Traffic Host Name IP Address Fa0/0 Subnet Mask IP Address S0/0/0 Subnet Mask Default Gateway RouterA 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 192.168.1.1 (DCE) 255.255.255.0 N/A
Lab 1.2.2 Capturing and Analyzing Network Traffic Host Name IP Address Fa0/0 Subnet Mask IP Address S0/0/0 Subnet Mask Default Gateway RouterA 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 192.168.1.1 (DCE) 255.255.255.0 N/A
Lab 8.4.3b Managing Cisco IOS images with ROMMON and TFTP
 Lab 8.4.3b Managing Cisco IOS images with ROMMON and TFTP Host Device Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Analyze the Cisco IOS image and router
Lab 8.4.3b Managing Cisco IOS images with ROMMON and TFTP Host Device Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Analyze the Cisco IOS image and router
Objectives. Router as a Computer. Router components and their functions. Router components and their functions
 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public Objectives Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1 Identify a router as a computer with an OS and
2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public Objectives Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1 Identify a router as a computer with an OS and
Configuring the Cisco Secure PIX Firewall with a Single Intern
 Configuring the Cisco Secure PIX Firewall with a Single Intern Table of Contents Configuring the Cisco Secure PIX Firewall with a Single Internal Network...1 Interactive: This document offers customized
Configuring the Cisco Secure PIX Firewall with a Single Intern Table of Contents Configuring the Cisco Secure PIX Firewall with a Single Internal Network...1 Interactive: This document offers customized
One-Step Lockdown with Cisco SDM
 One-Step Lockdown with Cisco SDM Router Hardening Automagically The process of turning off unnecessary services is called hardening a router to prevent attacks or exploits. The basic steps of router hardening
One-Step Lockdown with Cisco SDM Router Hardening Automagically The process of turning off unnecessary services is called hardening a router to prevent attacks or exploits. The basic steps of router hardening
TotalCloud Phone System
 TotalCloud Phone System Cisco SF 302-08P PoE VLAN Configuration Guide Note: The below information and configuration is for deployment of the Cbeyond managed switch solution using the Cisco 302 8 port Power
TotalCloud Phone System Cisco SF 302-08P PoE VLAN Configuration Guide Note: The below information and configuration is for deployment of the Cbeyond managed switch solution using the Cisco 302 8 port Power
APNIC Members Training Course Security workshop. 2-4 July, 2008. Port Vila Vanuatu. In conjunction with PACNOG 4
 APNIC Members Training Course Security workshop 2-4 July, 2008 Port Vila Vanuatu In conjunction with PACNOG 4 Router device security lab 1. APNIC s remote lab In these exercises you will be remotely accessing
APNIC Members Training Course Security workshop 2-4 July, 2008 Port Vila Vanuatu In conjunction with PACNOG 4 Router device security lab 1. APNIC s remote lab In these exercises you will be remotely accessing
BRI to PRI Connection Using Data Over Voice
 BRI to PRI Connection Using Data Over Voice Document ID: 14962 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Conventions Background Information Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot
BRI to PRI Connection Using Data Over Voice Document ID: 14962 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Conventions Background Information Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot
Ejemplo de configuración de punta a punta SBC en un Cisco 7600 Series Router
 Ejemplo de configuración de punta a punta SBC en un Cisco 7600 Series Router Descargue este capítulo Ejemplo de configuración de punta a punta SBC en un Cisco 7600 Series Router Descargue el libro completo
Ejemplo de configuración de punta a punta SBC en un Cisco 7600 Series Router Descargue este capítulo Ejemplo de configuración de punta a punta SBC en un Cisco 7600 Series Router Descargue el libro completo
Lab 1.5.1 Introductory Lab 1 Getting Started and Building Start.txt
 Lab 1.5.1 Introductory Lab 1 Getting Started and Building Start.txt Objective This lab will introduce to the student the CCNP lab equipment and certain IOS features that might be new. This introductory
Lab 1.5.1 Introductory Lab 1 Getting Started and Building Start.txt Objective This lab will introduce to the student the CCNP lab equipment and certain IOS features that might be new. This introductory
Configuring Basic Settings
 CHAPTER 10 This chapter describes how to configure basic settings on your ASA that are typically required for a functioning configuration. This chapter includes the following sections: Configuring the
CHAPTER 10 This chapter describes how to configure basic settings on your ASA that are typically required for a functioning configuration. This chapter includes the following sections: Configuring the
Lab 3.5.1: Basic VLAN Configuration (Instructor Version)
 (Instructor Version) Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0
(Instructor Version) Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0
Configuring a Leased Line
 CHAPTER 4 Configuring a Leased Line The configuration in this chapter describes how to configure a Cisco 1700 router for IP and IPX over a synchronous serial line. Before You Begin The configuration in
CHAPTER 4 Configuring a Leased Line The configuration in this chapter describes how to configure a Cisco 1700 router for IP and IPX over a synchronous serial line. Before You Begin The configuration in
Felix Rohrer. PT Activity 7.5.3: Troubleshooting Wireless WRT300N. Topology Diagram
 Felix Rohrer PT Activity 7.5.3: Troubleshooting Wireless WRT300N Topology Diagram All contents are Copyright 1992 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Felix Rohrer PT Activity 7.5.3: Troubleshooting Wireless WRT300N Topology Diagram All contents are Copyright 1992 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Configuring Basic Settings
 CHAPTER 12 This chapter describes how to configure basic settings on your ASASM that are typically required for a functioning configuration. This chapter includes the following sections: Configuring the
CHAPTER 12 This chapter describes how to configure basic settings on your ASASM that are typically required for a functioning configuration. This chapter includes the following sections: Configuring the
Lab 4.5.4 Diagramming External Traffic Flows
 Lab 4.5.4 Diagramming External Traffic Flows Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Business Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 R2 R3 FC-CPE-1 FC-CPE-2 ISP Fa0/1 172.17.0.1
Lab 4.5.4 Diagramming External Traffic Flows Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Business Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 R2 R3 FC-CPE-1 FC-CPE-2 ISP Fa0/1 172.17.0.1
CCNA Exploration 4.0.5.0 Routing Protocols and Concepts Student Lab Manual
 4.0.5.0 Routing Protocols and Concepts Student Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution
4.0.5.0 Routing Protocols and Concepts Student Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution
Case Study 1: Registering IP Phones with a remote Call
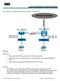 Case Study 1: Registering IP Phones with a remote Call Manager Objectives Place calls from IP Phones under R1 to IP Phones under R2 Place calls from any IP Phone (under R1 and under R2) to the regular
Case Study 1: Registering IP Phones with a remote Call Manager Objectives Place calls from IP Phones under R1 to IP Phones under R2 Place calls from any IP Phone (under R1 and under R2) to the regular
How To Learn Cisco Cisco Ios And Cisco Vlan
 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices: Accelerated Course CCNAX v2.0; 5 Days, Instructor-led Course Description Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices: Accelerated (CCNAX) v2.0 is a 60-hour instructor-led
Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices: Accelerated Course CCNAX v2.0; 5 Days, Instructor-led Course Description Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices: Accelerated (CCNAX) v2.0 is a 60-hour instructor-led
Lab 1.4.1 Introductory Lab 1 - Getting Started and Building Start.txt
 Lab 1.4.1 Introductory Lab 1 - Getting Started and Building Start.txt Objective This lab may introduce new CCNP lab equipment and certain IOS features. This introductory activity also describes how to
Lab 1.4.1 Introductory Lab 1 - Getting Started and Building Start.txt Objective This lab may introduce new CCNP lab equipment and certain IOS features. This introductory activity also describes how to
Virtual Fragmentation Reassembly
 Virtual Fragmentation Reassembly Currently, the Cisco IOS Firewall specifically context-based access control (CBAC) and the intrusion detection system (IDS) cannot identify the contents of the IP fragments
Virtual Fragmentation Reassembly Currently, the Cisco IOS Firewall specifically context-based access control (CBAC) and the intrusion detection system (IDS) cannot identify the contents of the IP fragments
CCNA Security. Chapter Two Securing Network Devices. 2009 Cisco Learning Institute.
 CCNA Security Chapter Two Securing Network Devices 1 The Edge Router What is the edge router? - The last router between the internal network and an untrusted network such as the Internet - Functions as
CCNA Security Chapter Two Securing Network Devices 1 The Edge Router What is the edge router? - The last router between the internal network and an untrusted network such as the Internet - Functions as
Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices 1 Course, Class Outline
 www.etidaho.com (208) 327-0768 Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices 1 Course, Class Outline 5 Days Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices, Part 1 (ICND1) v2.0 is a five-day, instructorled training course
www.etidaho.com (208) 327-0768 Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices 1 Course, Class Outline 5 Days Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices, Part 1 (ICND1) v2.0 is a five-day, instructorled training course
ICND1 Lab Guide. 100-101 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 Version 2.0. Labs powered by
 ICND1 Lab Guide 100-101 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 Version 2.0 ii Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 100-101 Lab Guide LM20130929/BV2.01 iii 25 Century Blvd. Ste. 500
ICND1 Lab Guide 100-101 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 Version 2.0 ii Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 100-101 Lab Guide LM20130929/BV2.01 iii 25 Century Blvd. Ste. 500
Lab 5.3.7 Configuring DHCP with SDM and the Cisco IOS CLI
 Lab 5.3.7 Configuring DHCP with SDM and the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 Customer Serial 0/0/1 (DTE) 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 Fast Ethernet 0/0 192.168.1.1
Lab 5.3.7 Configuring DHCP with SDM and the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 Customer Serial 0/0/1 (DTE) 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 Fast Ethernet 0/0 192.168.1.1
ENetwork Basic Configuration PT Practice SBA
 ENetwork Basic Configuration PT Practice SBA A few things to keep in mind while completing this activity: 1. Do not use the browser Back button or close or reload any exam windows during the exam. 2. Do
ENetwork Basic Configuration PT Practice SBA A few things to keep in mind while completing this activity: 1. Do not use the browser Back button or close or reload any exam windows during the exam. 2. Do
The Cisco IOS Firewall feature set is supported on the following platforms: Cisco 2600 series Cisco 3600 series
 Cisco IOS Firewall Feature Set Feature Summary The Cisco IOS Firewall feature set is available in Cisco IOS Release 12.0. This document includes information that is new in Cisco IOS Release 12.0(1)T, including
Cisco IOS Firewall Feature Set Feature Summary The Cisco IOS Firewall feature set is available in Cisco IOS Release 12.0. This document includes information that is new in Cisco IOS Release 12.0(1)T, including
P and FTP Proxy caching Using a Cisco Cache Engine 550 an
 P and FTP Proxy caching Using a Cisco Cache Engine 550 an Table of Contents HTTP and FTP Proxy caching Using a Cisco Cache Engine 550 and a PIX Firewall...1 Introduction...1 Before You Begin...1 Conventions...1
P and FTP Proxy caching Using a Cisco Cache Engine 550 an Table of Contents HTTP and FTP Proxy caching Using a Cisco Cache Engine 550 and a PIX Firewall...1 Introduction...1 Before You Begin...1 Conventions...1
Telnet, Console and AUX Port Passwords on Cisco Routers Configuration Example
 Telnet, Console and AUX Port Passwords on Cisco Routers Configuration Example Document ID: 45843 Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Configure Passwords
Telnet, Console and AUX Port Passwords on Cisco Routers Configuration Example Document ID: 45843 Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Configure Passwords
Chapter 4: Lab A: Configuring CBAC and Zone-Based Firewalls
 Chapter 4: Lab A: Configuring CBAC and Zone-Based Firewalls Topology IP Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 FA0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 FA0/5
Chapter 4: Lab A: Configuring CBAC and Zone-Based Firewalls Topology IP Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 FA0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 FA0/5
LAN-Cell to Cisco Tunneling
 LAN-Cell to Cisco Tunneling Page 1 of 13 LAN-Cell to Cisco Tunneling This Tech Note guides you through setting up a VPN connection between a LAN-Cell and a Cisco router. As the figure below shows, the
LAN-Cell to Cisco Tunneling Page 1 of 13 LAN-Cell to Cisco Tunneling This Tech Note guides you through setting up a VPN connection between a LAN-Cell and a Cisco router. As the figure below shows, the
Configuring a Cisco 2509-RJ Terminal Router
 created by: Rainer Bemsel Version 1.0 Dated: Dec/08/2012 For my Cisco LAB, I ve purchased a used Cisco 2509-RJ with RJ45-RJ45 roll-over cables. This TechTip shows my configuration setup, so you can easily
created by: Rainer Bemsel Version 1.0 Dated: Dec/08/2012 For my Cisco LAB, I ve purchased a used Cisco 2509-RJ with RJ45-RJ45 roll-over cables. This TechTip shows my configuration setup, so you can easily
Table of Contents. Cisco Configuring IPSec Cisco Secure VPN Client to Central Router Controlling Access
 Table of Contents Configuring IPSec Cisco Secure VPN Client to Central Router Controlling Access...1 Introduction...1 Prerequisites...1 Requirements...1 Components Used...1 Conventions...1 Configure...2
Table of Contents Configuring IPSec Cisco Secure VPN Client to Central Router Controlling Access...1 Introduction...1 Prerequisites...1 Requirements...1 Components Used...1 Conventions...1 Configure...2
Configuring Fax Pass-Through
 Configuring Fax Pass-Through This chapter describes the configuration of fax pass-through. With fax pass-through, modulated fax information from the PSTN is passed in-band over a voice speech path in an
Configuring Fax Pass-Through This chapter describes the configuration of fax pass-through. With fax pass-through, modulated fax information from the PSTN is passed in-band over a voice speech path in an
CCNA Exploration 4.0: ESwitching Basic Switching / Wireless PT Practice SBA. Switch S1 S1#sh ru Building configuration...
 CCNA Exploration 4.0: ESwitching Basic Switching / Wireless PT Practice SBA Switch S1 S1#sh ru Building configuration... Current configuration : 1639 bytes version 12.2 no service timestamps log datetime
CCNA Exploration 4.0: ESwitching Basic Switching / Wireless PT Practice SBA Switch S1 S1#sh ru Building configuration... Current configuration : 1639 bytes version 12.2 no service timestamps log datetime
Configuring a Router
 CHAPTER 3 Configuring a Router This chapter provides information and commands concerning the following topics: Configuring a router, specifically: Names Passwords Interfaces MOTD banners IP host tables
CHAPTER 3 Configuring a Router This chapter provides information and commands concerning the following topics: Configuring a router, specifically: Names Passwords Interfaces MOTD banners IP host tables
CCNA Security 1.1 Student Lab Manual
 1.1 Student Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors
1.1 Student Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors
Applicazioni Telematiche
 Angelo Coiro Laboratorio Applicazioni Telematiche L emulatore Packet Tracer Packet Tracer Cisco Packet Tracer is an academic software that allows to emulate Cisco devices Packet Tracer can be used for
Angelo Coiro Laboratorio Applicazioni Telematiche L emulatore Packet Tracer Packet Tracer Cisco Packet Tracer is an academic software that allows to emulate Cisco devices Packet Tracer can be used for
Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1 (Instructor Version)
 (Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or to provide
(Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or to provide
Welcome to Todd Lammle s CCNA Bootcamp
 Welcome to Todd Lammle s CCNA Bootcamp Todd Lammle Cisco Authorized CCNA Bootcamps are now available, delivered by CCSI instructor, and popular Sybex author Todd Lammle. Todd Lammle CCNA Training Boot
Welcome to Todd Lammle s CCNA Bootcamp Todd Lammle Cisco Authorized CCNA Bootcamps are now available, delivered by CCSI instructor, and popular Sybex author Todd Lammle. Todd Lammle CCNA Training Boot
Configuring Voice and Data Support on VWIC3s
 First Published: July 21, 2010, OL-22847-01 This module describes how to configure voice and data support on the next generation of voice/wan Interface Cards (VWICs) also known as VWIC3s. The following
First Published: July 21, 2010, OL-22847-01 This module describes how to configure voice and data support on the next generation of voice/wan Interface Cards (VWICs) also known as VWIC3s. The following
Chapter 1: Planning Maintenance for Complex Networks. TSHOOT v6 Chapter 1 2007 2010, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
 : Planning Maintenance for Complex Networks CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP Networks TSHOOT v6 1 Objectives Evaluate commonly-practiced models and methodologies for network maintenance
: Planning Maintenance for Complex Networks CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP Networks TSHOOT v6 1 Objectives Evaluate commonly-practiced models and methodologies for network maintenance
3.1 Connecting to a Router and Basic Configuration
 3.1 Connecting to a Router and Basic Configuration Objective This lab will focus on the ability to connect a PC to a router in order to establish a console session and observe the user interface. A console
3.1 Connecting to a Router and Basic Configuration Objective This lab will focus on the ability to connect a PC to a router in order to establish a console session and observe the user interface. A console
Lab 3.1.2 Creating a Logical Network Diagram
 Lab 3.1.2 Creating a Logical Network Diagram Objectives Use router and switch commands to obtain information about an existing network. Use Cisco Network Assistant to obtain information about an existing
Lab 3.1.2 Creating a Logical Network Diagram Objectives Use router and switch commands to obtain information about an existing network. Use Cisco Network Assistant to obtain information about an existing
INTERCONNECTING CISCO NETWORK DEVICES PART 1 V2.0 (ICND 1)
 INTERCONNECTING CISCO NETWORK DEVICES PART 1 V2.0 (ICND 1) COURSE OVERVIEW: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices, Part 1 (ICND1) v2.0 is a five-day, instructor-led training course that teaches learners
INTERCONNECTING CISCO NETWORK DEVICES PART 1 V2.0 (ICND 1) COURSE OVERVIEW: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices, Part 1 (ICND1) v2.0 is a five-day, instructor-led training course that teaches learners
CCNA Discovery 4.1.3 Working at a Small to Medium Business or ISP Student Packet Tracer Lab Manual
 4.1.3 Working at a Small to Medium Business or ISP Student Packet Tracer Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, In Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial
4.1.3 Working at a Small to Medium Business or ISP Student Packet Tracer Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, In Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial
and 2, implemented With Cisco Unified Border Control Element (CUBE)
 www.xo.com XO SIP Service Customer Configuration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager (CUCM) 8.0.3 XO SIP Packages 1 and 2, implemented With Cisco Unified Border Control Element (CUBE) 1 PRODUCT
www.xo.com XO SIP Service Customer Configuration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager (CUCM) 8.0.3 XO SIP Packages 1 and 2, implemented With Cisco Unified Border Control Element (CUBE) 1 PRODUCT
LAB Configuring NAT. Objective. Background/Preparation
 LAB Configuring NAT Objective Configure a router to use network address translation (NAT) to convert internal IP addresses, typically private addresses, into outside public addresses. Configure static
LAB Configuring NAT Objective Configure a router to use network address translation (NAT) to convert internal IP addresses, typically private addresses, into outside public addresses. Configure static
Cisco Routers and Switches
 Cisco Routers and Switches Phoenix Cisco User Group (PCUG) Tools, tips, and tricks you never knew Hello! Jeremy D. Cioara - CCIE, MCSE, CNE AdTEC Networks - Chief Information Officer Cisco IP Telephony
Cisco Routers and Switches Phoenix Cisco User Group (PCUG) Tools, tips, and tricks you never knew Hello! Jeremy D. Cioara - CCIE, MCSE, CNE AdTEC Networks - Chief Information Officer Cisco IP Telephony
Configuration Professional: Site to Site IPsec VPN Between Two IOS Routers Configuration Example
 Configuration Professional: Site to Site IPsec VPN Between Two IOS Routers Configuration Example Document ID: 113337 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configuration
Configuration Professional: Site to Site IPsec VPN Between Two IOS Routers Configuration Example Document ID: 113337 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configuration
- The PIX OS Command-Line Interface -
 1 PIX OS Versions - The PIX OS Command-Line Interface - The operating system for Cisco PIX/ASA firewalls is known as the PIX OS. Because the PIX product line was acquired and not originally developed by
1 PIX OS Versions - The PIX OS Command-Line Interface - The operating system for Cisco PIX/ASA firewalls is known as the PIX OS. Because the PIX product line was acquired and not originally developed by
Configuring the Switch with the CLI Setup Program
 APPENDIXC Configuring the Switch with the CLI Setup Program This appendix provides a command-line interface (CLI) setup procedure for a standalone switch. To set up the switch by using Express Setup, see
APPENDIXC Configuring the Switch with the CLI Setup Program This appendix provides a command-line interface (CLI) setup procedure for a standalone switch. To set up the switch by using Express Setup, see
Motorola TEAM WSM - Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express (CME) Integration
 Motorola TEAM WSM - Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express (CME) Integration Summary This setup covers the of the TEAM VoWLAN solution with a Cisco Communications Manager Express 4.1 +. This integration
Motorola TEAM WSM - Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express (CME) Integration Summary This setup covers the of the TEAM VoWLAN solution with a Cisco Communications Manager Express 4.1 +. This integration
642 523 Securing Networks with PIX and ASA
 642 523 Securing Networks with PIX and ASA Course Number: 642 523 Length: 1 Day(s) Course Overview This course is part of the training for the Cisco Certified Security Professional and the Cisco Firewall
642 523 Securing Networks with PIX and ASA Course Number: 642 523 Length: 1 Day(s) Course Overview This course is part of the training for the Cisco Certified Security Professional and the Cisco Firewall
Cisco Certified Network Associate Exam. Operation of IP Data Networks. LAN Switching Technologies. IP addressing (IPv4 / IPv6)
 Cisco Certified Network Associate Exam Exam Number 200-120 CCNA Associated Certifications CCNA Routing and Switching Operation of IP Data Networks Operation of IP Data Networks Recognize the purpose and
Cisco Certified Network Associate Exam Exam Number 200-120 CCNA Associated Certifications CCNA Routing and Switching Operation of IP Data Networks Operation of IP Data Networks Recognize the purpose and
Juniper Networks WX Series Large. Integration on Cisco
 APPLICATION NOTE Juniper Networks WX Series Large Deployment with WCCP Off-Path Integration on Cisco Integrating Multiple Juniper Networks WX Series Application Acceleration Platforms into a Cisco Infrastructure
APPLICATION NOTE Juniper Networks WX Series Large Deployment with WCCP Off-Path Integration on Cisco Integrating Multiple Juniper Networks WX Series Application Acceleration Platforms into a Cisco Infrastructure
Lab 2.3.2 Configuring OSPF with Loopback Addresses
 Lab 2.3.2 Configuring OSPF with Loopback Addresses Objective Configure routers with a Class C IP addressing scheme. Observe the election process for designated routers (DR) and backup designated routers
Lab 2.3.2 Configuring OSPF with Loopback Addresses Objective Configure routers with a Class C IP addressing scheme. Observe the election process for designated routers (DR) and backup designated routers
100-101: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 v2.0 (ICND1)
 100-101: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 v2.0 (ICND1) Course Overview This course provides students with the knowledge and skills to implement and support a small switched and routed network.
100-101: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 v2.0 (ICND1) Course Overview This course provides students with the knowledge and skills to implement and support a small switched and routed network.
Procedure: You can find the problem sheet on Drive D: of the lab PCs. Part 1: Router & Switch
 University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Computer Engineering Department Computer Networks Laboratory 907528 Lab. 2 Network Devices & Packet Tracer Objectives 1. To become familiar with
University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Computer Engineering Department Computer Networks Laboratory 907528 Lab. 2 Network Devices & Packet Tracer Objectives 1. To become familiar with
Logging in Cisco IOS. The minimum you should know
 The minimum you should know Severity-levels Router(config)#logging trap? Logging severity level alerts Immediate action needed (severity=1) critical Critical conditions (severity=2) debugging Debugging
The minimum you should know Severity-levels Router(config)#logging trap? Logging severity level alerts Immediate action needed (severity=1) critical Critical conditions (severity=2) debugging Debugging
During this lab time you will configure the routing protocol OSPF with IPv4 addresses.
 Lab 2: OSPF During this lab time you will configure the routing protocol OSPF with IPv4 addresses. It is your responsibility to create an appropriate IPv4 subnet plan and address plan. To ensure a timely
Lab 2: OSPF During this lab time you will configure the routing protocol OSPF with IPv4 addresses. It is your responsibility to create an appropriate IPv4 subnet plan and address plan. To ensure a timely
"Charting the Course...
 Description "Charting the Course... Course Summary Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices: Accelerated (CCNAX), is a course consisting of ICND1 and ICND2 content in its entirety, but with the content
Description "Charting the Course... Course Summary Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices: Accelerated (CCNAX), is a course consisting of ICND1 and ICND2 content in its entirety, but with the content
Chapter 1 Introduction to Network Maintenance Objectives
 Introduction to Network Maintenance Objectives Describe network maintenance tasks Explain the difference between proactive and reactive network maintenance. Describe well-known network maintenance models.
Introduction to Network Maintenance Objectives Describe network maintenance tasks Explain the difference between proactive and reactive network maintenance. Describe well-known network maintenance models.
Planning Maintenance for Complex Networks
 Planning Maintenance for Complex Networks CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP Networks Olga Torstensson TSHOOT v6 1 Maintenance Models and Methodologies A network engineer s job description
Planning Maintenance for Complex Networks CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP Networks Olga Torstensson TSHOOT v6 1 Maintenance Models and Methodologies A network engineer s job description
Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing
 Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing Topology Objectives Background Review a basic EIGRP configuration. Explore the EIGRP topology table. Identify successors, feasible successors, and feasible distances.
Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing Topology Objectives Background Review a basic EIGRP configuration. Explore the EIGRP topology table. Identify successors, feasible successors, and feasible distances.
Lab 5.3.8 Configuring PAT with SDM and Static NAT using Cisco IOS Commands
 Lab 5.3.8 Configuring PAT with SDM and Static NAT using Cisco IOS Commands Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 CustomerRouter Serial 0/0/0 (DTE) 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 Fast Ethernet
Lab 5.3.8 Configuring PAT with SDM and Static NAT using Cisco IOS Commands Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 CustomerRouter Serial 0/0/0 (DTE) 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 Fast Ethernet
Deployment Guidelines for QoS Configuration in DSL Environment
 White Paper Deployment Guidelines for QoS Configuration in DSL Environment Overview In the late 1980s, DSL technology was developed to provide higher-speed digital data transmission over local telephone
White Paper Deployment Guidelines for QoS Configuration in DSL Environment Overview In the late 1980s, DSL technology was developed to provide higher-speed digital data transmission over local telephone
CCT vs. CCENT Skill Set Comparison
 Operation of IP Data Networks Recognize the purpose and functions of various network devices such as Routers, Switches, Bridges and Hubs Select the components required to meet a given network specification
Operation of IP Data Networks Recognize the purpose and functions of various network devices such as Routers, Switches, Bridges and Hubs Select the components required to meet a given network specification
HOW TO CONFIGURE CISCO FIREWALL PART I
 HOW TO CONFIGURE CISCO FIREWALL PART I Cisco Abstract: Please find below a step by step process to configure the PIX Firewall from scratch. A simple scenario is given here where you have a corporate network
HOW TO CONFIGURE CISCO FIREWALL PART I Cisco Abstract: Please find below a step by step process to configure the PIX Firewall from scratch. A simple scenario is given here where you have a corporate network
