Lab Configuring OSPF with Loopback Addresses
|
|
|
- Verity Chapman
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
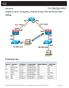
1 Lab Configuring OSPF with Loopback Addresses Objective Configure routers with a Class C IP addressing scheme. Observe the election process for designated routers (DR) and backup designated routers (BDR) on the multiaccess network. Configure loopback addresses for Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) stability. Assign each OSPF interface a priority to force the election of a specific router as DR. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one shown in the diagram. Any router that meets the interface requirements displayed on the above diagram may be used. For example, router series 800, 1600, 1700, 2500, and 2600 or any such combination can be used. Please refer to the chart at the end of the lab to correctly identify the interface identifiers to be used based on the equipment in the lab. The configuration output used in this lab is produced from 1721 series routers. Any other router used may produce slightly different output. Perform the following steps on each router unless specifically instructed otherwise. Start a HyperTerminal session. Note: Go to the erase and reload instructions at the end of this lab. Perform those steps on all routers in this lab assignment before continuing. 1-8 CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v Lab Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
2 Step 1 Configure the routers On the routers, enter the global configuration mode and configure the hostname as shown in the chart. Then configure the console, virtual terminal and enable passwords. Next configure the interfaces according and the IP hostnames. If there are any problems configuring the router basics, refer to the lab Review of Basic Router Configuring with RIP. Do not configure loopback interfaces and routing protocol yet. Step 2 Save the configuration information for all the routers Why save the running configuration to the startup configuration? Step 3 Configure the hosts with the proper IP address, subnet mask and default gateway Each workstation should be able to ping all of the attached routers. That is because they are all part of the same subnetwork. Troubleshoot as necessary. Remember to assign a specific IP address and default gateway to the workstation. If running Windows 98, check by using Start > Run > winipcfg. If running Windows 2000, check by using the ipconfig command in a DOS window. Step 4 View the routers configuration and interface information a. At the privileged EXEC mode prompt type: show running-config b. Using the show ip interface brief command, check the status of each interface. c. What is the state of the interfaces on each router? London: FastEthernet 0: Serial 0: Serial 1: Loopback0: Ottawa: FastEthernet 0: Serial 0: Serial 1: Loopback0: Brasilia: FastEthernet 0: Serial 0: Serial 1: Loopback0: 2-8 CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v Lab Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
3 Step 5 Verify connectivity of the routers a. Ping all of the connected FastEthernet interfaces from each other. b. Were the pings successful? c. If the pings were not successful, troubleshoot the router configuration, until the ping is successful. Step 6 Configure OSPF routing on router London a. Configure an OSPF routing process on the router London. Use OSPF process number 1 and ensure all networks are in area 0. London(config)#router ospf 1 London(config-router)#network area 0 London(config-router)#end b. Examine the London router running configuration file. c. Did the IOS version automatically add any lines under router OSPF 1? d. If there were no changes to the running configuration, type the following commands. London(config)#router ospf 1 London(config-router)#log-adjacency-changes London(config-router)#end e. Show the routing table for router: London#show ip route f. Are there any entries in the routing table? g. Why? Step 7 Configure OSPF routing on router Ottawa a. Configure an OSPF routing process on the router Ottawa. Use OSPF process number 1 and ensure all networks are in area 0. Ottawa(config)#router ospf 1 Ottawa(config-router)#network area 0 Ottawa(config-router)#end b. Examine the Ottawa running configuration file. c. Did the IOS version automatically add any lines under router OSPF 1? d. If there were no changes to the running configuration, type the following commands. Ottawa(config)#router ospf 1 Ottawa(config-router)#log-adjacency-changes Ottawa(config-router)#end 3-8 CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v Lab Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
4 Step 8 Configure OSPF routing on router Brasilia a. Configure an OSPF routing process on the router Brasilia. Use OSPF process number 1 and ensure all networks are in area 0. Brasilia(config)#router ospf 1 Brasilia(config-router)#network area 0 Brasilia(config-router)#end b. Examine the Brasilia router running configuration file. Did the IOS version automatically add any lines under router OSPF 1? c. What did it add? d. If there were no changes to the running configuration, type the following commands: Brasilia(config)#router ospf 1 Brasilia(config-router)#log-adjacency-changes Brasilia(config-router)#end Step 9 Test network connectivity a. Ping the Brasilia router from the London router. Was it successful? b. If not troubleshoot as necessary. Step 10 Show OSPF adjacencies a. Type the command show ip ospf neighbor on all routers to verify that the OSPF routing has formed adjacencies. b. Is there a designated router identified? c. Is there a backup designated router? d. Type the command show ip ospf neighbor detail for more information. e. What is the neighbor priority of from router Brasilia? f. What interface is Identified as being part of Area 0? Step 11 Configure the loopback interfaces Configure the loopback interface on each router to allow for an interface that will not go down due to network change or failure. This task is performed by typing interface loopback # at the global configuration mode prompt, where the # represents the number of the loopback interface from 0-2,147,483,647. London(config)#interface loopback 0 London(config-if)#ip address London(config-router)#end Ottawa(config)#interface loopback 0 Ottawa(config-if)#ip address Ottawa(config-router)#end Brasilia(config)#interface loopback 0 Brasilia(config-if)#ip address CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v Lab Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
5 Brasilia(config-router)#end Step 12 Save the configuration information for all the routers After saving the configurations on all of the routers, power them down and back up again. Step 13 Show OSPF adjacencies a. Type the command show ip ospf neighbor on all routers to verify that the OSPF routing has formed adjacencies. b. Is there a designated router identified? c. Write down the router ID and link address of the DR. d. Is there a backup designated router? e. Write down the router ID and link address of the BDR. f. What is the third router referred to as? g. Write down that Routers ID and link address h. Type the command show ip ospf neighbor detail for more information. i. What is the neighbor priority of from router Brasilia? j. What interface is Identified as being part of Area 0? Step 14. Verify OSPF interface configuration a. Type show ip ospf interface fastethernet 0 on the London router. b. What is the OSPF state of the interface? c. What is the default priority of the interface? d. What is the network type of the interface? Step 15 Configure London to always be the DR To ensure that London router always becomes the DR for this multi-access segment, the OSPF priority must be set. London is the most powerful router in the network and so best suited to become DR. To assign the London loopback a higher IP address is not advised, as the numbering system has advantages for troubleshooting. Also London is not to act as DR for all segments to which it may belong. Set the priority of the interface to 50 on the London router only. Step 16 Watch election process a. To watch the OSPF election process restart all of the routers and as soon as the router prompt is available type: Ottawa>enable Ottawa#debug ip ospf events b. Which router was elected DR? c. Which router was elected BDR? d. Why? e. To turn off all debugging type undebug all. 5-8 CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v Lab Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
6 Step 17 Show OSPF Adjacencies a. Type the command show ip ospf neighbor on the Ottawa router to verify that the OSPF routing has formed adjacencies. b. What is the priority of the DR? Once the previous steps are completed log off by typing exit, and turn the router off. Then remove and store the cables and adapter. 6-8 CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v Lab Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
7 Erasing and reloading the router Enter into the privileged EXEC mode by typing enable. If prompted for a password, enter class. If that does not work, ask the instructor for assistance. Router>enable At the privileged EXEC mode, enter the command erase startup-config. Router#erase startup-config The responding line prompt will be: Erasing the nvram filesystem will remove all files! Continue? [confirm] Press Enter to confirm. The response should be: Erase of nvram: complete Now at the privileged EXEC mode, enter the command reload. Router(config)#reload The responding line prompt will be: System configuration has been modified. Save? [yes/no]: Type n and then press Enter. The responding line prompt will be: Proceed with reload? [confirm] Press Enter to confirm. In the first line of the response will be: Reload requested by console. After the router has reloaded the line prompt will be: Would you like to enter the initial configuration dialog? [yes/no]: Type n and then press Enter. The responding line prompt will be: Press RETURN to get started! Press Enter. Now the router is ready for the assigned lab to be performed. 7-8 CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v Lab Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
8 Router Interface Summary Router Model Ethernet Ethernet Serial Serial Interface #1 Interface #2 Interface #1 Interface #2 800 (806) Ethernet 0 (E0) Ethernet 1 (E1) 1600 Ethernet 0 (E0) Ethernet 1 (E1) Serial 0 (S0) Serial 1 (S1) 1700 FastEthernet 0 (FA0) FastEthernet 1 (FA1) Serial 0 (S0) Serial 1 (S1) 2500 Ethernet 0 (E0) Ethernet 1 (E1) Serial 0 (S0) Serial 1 (S1) 2600 FastEthernet 0/0 (FA0/0) FastEthernet 0/1 (FA0/1) Serial 0/0 (S0/0) Serial 0/1 (S0/1) In order to find out exactly how the router is configured, look at the interfaces. This will identify what type and how many interfaces the router has. There is no way to effectively list all of the combinations of configurations for each router class. What is provided are the identifiers for the possible combinations of interfaces in the device. This interface chart does not include any other type of interface even though a specific router may contain one. An example of this might be an ISDN BRI interface. The string in parenthesis is the legal abbreviation that can be used in IOS command to represent the interface. 8-8 CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v Lab Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths
 Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths Objective Configure Load balance across multiple paths. Observe the load balancing process. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in the
Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths Objective Configure Load balance across multiple paths. Observe the load balancing process. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in the
Lab 4.2.4 Advanced Telnet Operations
 Lab 4.2.4 Advanced Telnet Operations Objective Use the telnet command to remotely access other routers. Verify that the application layer between the source and the destination is working properly. Suspend
Lab 4.2.4 Advanced Telnet Operations Objective Use the telnet command to remotely access other routers. Verify that the application layer between the source and the destination is working properly. Suspend
Lab 4.1.4 Creating a Network Map using CDP Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 4.1.4 Creating a Network Map using CDP Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) commands to get information about neighboring network devices. Background/Preparation CDP
Lab 4.1.4 Creating a Network Map using CDP Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) commands to get information about neighboring network devices. Background/Preparation CDP
Lab 1.2.3 Review of Basic Router Configuration with RIP. Objective. Background / Preparation. General Configuration Tips
 Lab 1.2.3 Review of Basic Router Configuration with RIP Objective Cable and configure workstations and routers Setup IP addressing scheme using Class B networks Configure Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
Lab 1.2.3 Review of Basic Router Configuration with RIP Objective Cable and configure workstations and routers Setup IP addressing scheme using Class B networks Configure Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths Instructor Version 2500 Objective onfigure Load balance across multiple paths. Observe the load balancing process. Background/Preparation able a network similar
Lab 7.2.9 Load Balancing Across Multiple Paths Instructor Version 2500 Objective onfigure Load balance across multiple paths. Observe the load balancing process. Background/Preparation able a network similar
Lab 3.1.2 Creating a Logical Network Diagram
 Lab 3.1.2 Creating a Logical Network Diagram Objectives Use router and switch commands to obtain information about an existing network. Use Cisco Network Assistant to obtain information about an existing
Lab 3.1.2 Creating a Logical Network Diagram Objectives Use router and switch commands to obtain information about an existing network. Use Cisco Network Assistant to obtain information about an existing
Lab 6.2.3 Managing the MAC Address Table
 Lab 6.2.3 Managing the MAC Address Table Objective Create a basic switch configuration. Manage the switch MAC table. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in the diagram. The configuration
Lab 6.2.3 Managing the MAC Address Table Objective Create a basic switch configuration. Manage the switch MAC table. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in the diagram. The configuration
Lab 5.3.9b Managing Router Configuration Files Using TFTP
 Lab 5.3.9b Managing Router Configuration Files Using TFTP Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Download and install TFTP server software.
Lab 5.3.9b Managing Router Configuration Files Using TFTP Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Download and install TFTP server software.
Lab 8.4.3a Managing Cisco IOS Images with TFTP
 Lab 8.4.3a Managing Cisco IOS Images with TFTP Host Device Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Analyze the Cisco IOS image and router flash memory.
Lab 8.4.3a Managing Cisco IOS Images with TFTP Host Device Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Analyze the Cisco IOS image and router flash memory.
Lab 1.4.1 Introductory Lab 1 - Getting Started and Building Start.txt
 Lab 1.4.1 Introductory Lab 1 - Getting Started and Building Start.txt Objective This lab may introduce new CCNP lab equipment and certain IOS features. This introductory activity also describes how to
Lab 1.4.1 Introductory Lab 1 - Getting Started and Building Start.txt Objective This lab may introduce new CCNP lab equipment and certain IOS features. This introductory activity also describes how to
Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI
 Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Serial 0/0/0 (DCE) 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 FastEthernet 0/0 172.16.0.1 255.255.0.0
Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Serial 0/0/0 (DCE) 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 FastEthernet 0/0 172.16.0.1 255.255.0.0
Lab 5.3.7 Configuring DHCP with SDM and the Cisco IOS CLI
 Lab 5.3.7 Configuring DHCP with SDM and the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 Customer Serial 0/0/1 (DTE) 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 Fast Ethernet 0/0 192.168.1.1
Lab 5.3.7 Configuring DHCP with SDM and the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 Customer Serial 0/0/1 (DTE) 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 Fast Ethernet 0/0 192.168.1.1
LAB Configuring NAT. Objective. Background/Preparation
 LAB Configuring NAT Objective Configure a router to use network address translation (NAT) to convert internal IP addresses, typically private addresses, into outside public addresses. Configure static
LAB Configuring NAT Objective Configure a router to use network address translation (NAT) to convert internal IP addresses, typically private addresses, into outside public addresses. Configure static
Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI
 Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP address Subnet mask R1 R1 Serial 0/0/0 (DCE) 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 FastEthernet 0/0 172.16.0.1 255.255.0.0
Lab 5.3.5 Configuring Basic Router Settings with the Cisco IOS CLI Device Host Name Interface IP address Subnet mask R1 R1 Serial 0/0/0 (DCE) 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 FastEthernet 0/0 172.16.0.1 255.255.0.0
Lab - Using IOS CLI with Switch MAC Address Tables
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12
Lab: Basic Router Configuration
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Def. Gateway R1 Fa0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R2 Fa0/0 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Def. Gateway R1 Fa0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R2 Fa0/0 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
3.1 Connecting to a Router and Basic Configuration
 3.1 Connecting to a Router and Basic Configuration Objective This lab will focus on the ability to connect a PC to a router in order to establish a console session and observe the user interface. A console
3.1 Connecting to a Router and Basic Configuration Objective This lab will focus on the ability to connect a PC to a router in order to establish a console session and observe the user interface. A console
Lab 1.5.1 Introductory Lab 1 Getting Started and Building Start.txt
 Lab 1.5.1 Introductory Lab 1 Getting Started and Building Start.txt Objective This lab will introduce to the student the CCNP lab equipment and certain IOS features that might be new. This introductory
Lab 1.5.1 Introductory Lab 1 Getting Started and Building Start.txt Objective This lab will introduce to the student the CCNP lab equipment and certain IOS features that might be new. This introductory
Lab 5.3.8 Configuring PAT with SDM and Static NAT using Cisco IOS Commands
 Lab 5.3.8 Configuring PAT with SDM and Static NAT using Cisco IOS Commands Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 CustomerRouter Serial 0/0/0 (DTE) 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 Fast Ethernet
Lab 5.3.8 Configuring PAT with SDM and Static NAT using Cisco IOS Commands Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 CustomerRouter Serial 0/0/0 (DTE) 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 Fast Ethernet
Lab 3 Routing Information Protocol (RIPv1) on a Cisco Router Network
 Lab 3 Routing Information Protocol (RIPv1) on a Cisco Router Network CMPE 150 Fall 2005 Introduction Today you are going to be thrown into using Cisco s Internetwork Operating System (IOS) to configure
Lab 3 Routing Information Protocol (RIPv1) on a Cisco Router Network CMPE 150 Fall 2005 Introduction Today you are going to be thrown into using Cisco s Internetwork Operating System (IOS) to configure
Connect the Host to attach to Fast Ethernet switch port Fa0/2. Configure the host as shown in the topology diagram above.
 Lab 1.2.2 Capturing and Analyzing Network Traffic Host Name IP Address Fa0/0 Subnet Mask IP Address S0/0/0 Subnet Mask Default Gateway RouterA 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 192.168.1.1 (DCE) 255.255.255.0 N/A
Lab 1.2.2 Capturing and Analyzing Network Traffic Host Name IP Address Fa0/0 Subnet Mask IP Address S0/0/0 Subnet Mask Default Gateway RouterA 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 192.168.1.1 (DCE) 255.255.255.0 N/A
Lab 4.5.4 Diagramming External Traffic Flows
 Lab 4.5.4 Diagramming External Traffic Flows Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Business Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 R2 R3 FC-CPE-1 FC-CPE-2 ISP Fa0/1 172.17.0.1
Lab 4.5.4 Diagramming External Traffic Flows Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Business Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 R2 R3 FC-CPE-1 FC-CPE-2 ISP Fa0/1 172.17.0.1
Objectives. Router as a Computer. Router components and their functions. Router components and their functions
 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public Objectives Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1 Identify a router as a computer with an OS and
2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public Objectives Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1 Identify a router as a computer with an OS and
Skills Assessment Student Training Exam
 Skills Assessment Student Training Exam Topology Assessment Objectives Part 1: Initialize Devices (8 points, 5 minutes) Part 2: Configure Device Basic Settings (28 points, 30 minutes) Part 3: Configure
Skills Assessment Student Training Exam Topology Assessment Objectives Part 1: Initialize Devices (8 points, 5 minutes) Part 2: Configure Device Basic Settings (28 points, 30 minutes) Part 3: Configure
Lab 4.5.2 Diagramming Intranet Traffic Flows
 Lab 4.5.2 Diagramming Intranet Traffic Flows Objective Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Business Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 FC-CPE-1 Fa0/1 172.17.0.1 Fa0/0 10.0.0.1
Lab 4.5.2 Diagramming Intranet Traffic Flows Objective Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Business Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 FC-CPE-1 Fa0/1 172.17.0.1 Fa0/0 10.0.0.1
Note: This case study utilizes Packet Tracer. Please see the Chapter 5 Packet Tracer file located in Supplemental Materials.
 Note: This case study utilizes Packet Tracer. Please see the Chapter 5 Packet Tracer file located in Supplemental Materials. CHAPTER 5 OBJECTIVES Configure a router with an initial configuration. Use the
Note: This case study utilizes Packet Tracer. Please see the Chapter 5 Packet Tracer file located in Supplemental Materials. CHAPTER 5 OBJECTIVES Configure a router with an initial configuration. Use the
Router Lab Reference Guide
 Router Lab Reference Guide 1 PURPOSE AND GOALS The routing lab allows testing different IP-related protocols and solutions in a close to live environment. You can learn how to configure Cisco routers and
Router Lab Reference Guide 1 PURPOSE AND GOALS The routing lab allows testing different IP-related protocols and solutions in a close to live environment. You can learn how to configure Cisco routers and
During this lab time you will configure the routing protocol OSPF with IPv4 addresses.
 Lab 2: OSPF During this lab time you will configure the routing protocol OSPF with IPv4 addresses. It is your responsibility to create an appropriate IPv4 subnet plan and address plan. To ensure a timely
Lab 2: OSPF During this lab time you will configure the routing protocol OSPF with IPv4 addresses. It is your responsibility to create an appropriate IPv4 subnet plan and address plan. To ensure a timely
Lab 5.5.3 Developing ACLs to Implement Firewall Rule Sets
 Lab 5.5.3 Developing ACLs to Implement Firewall Rule Sets All contents are Copyright 1992 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 1 of 8 Device Interface
Lab 5.5.3 Developing ACLs to Implement Firewall Rule Sets All contents are Copyright 1992 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 1 of 8 Device Interface
Chapter 8 Lab B: Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client
 Chapter 8 Lab B: Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client Topology Note: ISR G2 devices have Gigabit Ethernet interfaces instead of FastEthernet Interfaces. All contents are Copyright 1992 2012
Chapter 8 Lab B: Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client Topology Note: ISR G2 devices have Gigabit Ethernet interfaces instead of FastEthernet Interfaces. All contents are Copyright 1992 2012
Cisco Router Configuration Tutorial
 Cisco Router Configuration Tutorial Cisco Inter-network Operating System: Cisco IOS Modes of Operation The Cisco IOS software provides access to several different command modes. Each command mode provides
Cisco Router Configuration Tutorial Cisco Inter-network Operating System: Cisco IOS Modes of Operation The Cisco IOS software provides access to several different command modes. Each command mode provides
Lab 5.5.4 Configuring the Cisco 2960 Switch
 Lab 5.5.4 Configuring the Cisco 2960 Switch Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port S1 CustomerSwitch VLAN 1 192.168.1.5 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 N/A R1 CustomerRouter
Lab 5.5.4 Configuring the Cisco 2960 Switch Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port S1 CustomerSwitch VLAN 1 192.168.1.5 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 N/A R1 CustomerRouter
Network Simulator Lab Study Plan
 The CCNA 640-802 Network Simulator has 300 lab exercises, organized both by type (Skill Builder, Configuration Scenario, Troubleshooting Scenario, and Subnetting Exercise) and by major topic within each
The CCNA 640-802 Network Simulator has 300 lab exercises, organized both by type (Skill Builder, Configuration Scenario, Troubleshooting Scenario, and Subnetting Exercise) and by major topic within each
Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding. Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1
 Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1 1 1 Objectives Identify a router as a computer with an OS and hardware designed for the routing process. Demonstrate
Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1 1 1 Objectives Identify a router as a computer with an OS and hardware designed for the routing process. Demonstrate
Lab 2 - Basic Router Configuration
 CS326 Fall 2001 Room: PAI 5.48 Name: Lab 2 - Basic Router Configuration In this lab you will learn: the various configuration modes of Cisco 2621 routers how to set up IP addresses for such routers how
CS326 Fall 2001 Room: PAI 5.48 Name: Lab 2 - Basic Router Configuration In this lab you will learn: the various configuration modes of Cisco 2621 routers how to set up IP addresses for such routers how
PT Activity 8.1.2: Network Discovery and Documentation Topology Diagram
 Topology Diagram All contents are Copyright 1992 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 1 of 6 Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet
Topology Diagram All contents are Copyright 1992 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 1 of 6 Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet
Lab Configuring Syslog and NTP (Instructor Version)
 (Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
(Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
Configuring a Leased Line
 CHAPTER 4 Configuring a Leased Line The configuration in this chapter describes how to configure a Cisco 1700 router for IP and IPX over a synchronous serial line. Before You Begin The configuration in
CHAPTER 4 Configuring a Leased Line The configuration in this chapter describes how to configure a Cisco 1700 router for IP and IPX over a synchronous serial line. Before You Begin The configuration in
Configuring a Gateway of Last Resort Using IP Commands
 Configuring a Gateway of Last Resort Using IP Commands Document ID: 16448 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions ip default gateway ip default network Flag a Default
Configuring a Gateway of Last Resort Using IP Commands Document ID: 16448 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions ip default gateway ip default network Flag a Default
How to Configure Cisco 2600 Routers
 Helsinki University of Technology Department of Communications and Networking How to Configure Cisco 2600 Routers Juha Järvinen 10.6.2004 [email protected] Modified by Zhong Yunqiu 7.8.2008 Table
Helsinki University of Technology Department of Communications and Networking How to Configure Cisco 2600 Routers Juha Järvinen 10.6.2004 [email protected] Modified by Zhong Yunqiu 7.8.2008 Table
Lab 4.5.3 Diagramming Traffic Flows to and from Remote Sites
 Lab 4.5.3 Diagramming Traffic Flows to and from Remote Sites Objective Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Business Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 R2 R3 FC-CPE-1 FC-CPE-2
Lab 4.5.3 Diagramming Traffic Flows to and from Remote Sites Objective Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Business Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 R2 R3 FC-CPE-1 FC-CPE-2
Lab 4.1.2 Characterizing Network Applications
 Lab 4.1.2 Characterizing Network Applications Objective Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Business Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 FC-CPE-1 Fa0/1 172.17.0.1 Fa0/0 10.0.0.1
Lab 4.1.2 Characterizing Network Applications Objective Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Business Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 FC-CPE-1 Fa0/1 172.17.0.1 Fa0/0 10.0.0.1
Lab 8.4.3b Managing Cisco IOS images with ROMMON and TFTP
 Lab 8.4.3b Managing Cisco IOS images with ROMMON and TFTP Host Device Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Analyze the Cisco IOS image and router
Lab 8.4.3b Managing Cisco IOS images with ROMMON and TFTP Host Device Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 Objectives Analyze the Cisco IOS image and router
Objectives. Background. Required Resources. CCNA Security
 Chapter 8 Lab B, Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client Topology IP Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 FA0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Chapter 8 Lab B, Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client Topology IP Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 FA0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway
 Felix Rohrer Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1 S2 VLAN 99 192.168.99.12 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1
Felix Rohrer Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1 S2 VLAN 99 192.168.99.12 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1
CCNA Exploration 4.0.5.0 Routing Protocols and Concepts Student Lab Manual
 4.0.5.0 Routing Protocols and Concepts Student Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution
4.0.5.0 Routing Protocols and Concepts Student Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution
Configuring the Switch with the CLI-Based Setup Program
 APPENDIX D Configuring the Switch with the CLI-Based Setup Program This appendix provides a command-line interface (CLI)-based setup procedure for a standalone switch. For product overview information,
APPENDIX D Configuring the Switch with the CLI-Based Setup Program This appendix provides a command-line interface (CLI)-based setup procedure for a standalone switch. For product overview information,
Applicazioni Telematiche
 Angelo Coiro Laboratorio Applicazioni Telematiche L emulatore Packet Tracer Packet Tracer Cisco Packet Tracer is an academic software that allows to emulate Cisco devices Packet Tracer can be used for
Angelo Coiro Laboratorio Applicazioni Telematiche L emulatore Packet Tracer Packet Tracer Cisco Packet Tracer is an academic software that allows to emulate Cisco devices Packet Tracer can be used for
Configure ISDN Backup and VPN Connection
 Case Study 2 Configure ISDN Backup and VPN Connection Cisco Networking Academy Program CCNP 2: Remote Access v3.1 Objectives In this case study, the following concepts are covered: AAA authentication Multipoint
Case Study 2 Configure ISDN Backup and VPN Connection Cisco Networking Academy Program CCNP 2: Remote Access v3.1 Objectives In this case study, the following concepts are covered: AAA authentication Multipoint
Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing CCNA 3 Labs and Study Guide Allan Johnson
 Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing CCNA 3 Labs and Allan Johnson Introduction Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing CCNA 3 Labs and s is a supplement to your classroom and laboratory experience
Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing CCNA 3 Labs and Allan Johnson Introduction Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing CCNA 3 Labs and s is a supplement to your classroom and laboratory experience
Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source static
 Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source static Table of Contents Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source static Command...1 Introduction...1 Before You Begin...1 Conventions...1
Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source static Table of Contents Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source static Command...1 Introduction...1 Before You Begin...1 Conventions...1
CCNA2 Chapter 11 Practice
 CCNA2 Chapter 11 Practice Two neighbouring routers are configured for OSPF, but they have different hello and dead intervals. What will happen? They will become adjacent as long as they are configured
CCNA2 Chapter 11 Practice Two neighbouring routers are configured for OSPF, but they have different hello and dead intervals. What will happen? They will become adjacent as long as they are configured
BRI to PRI Connection Using Data Over Voice
 BRI to PRI Connection Using Data Over Voice Document ID: 14962 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Conventions Background Information Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot
BRI to PRI Connection Using Data Over Voice Document ID: 14962 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Conventions Background Information Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot
Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source list C
 Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source list C Table of Contents Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source list Command...1 Introduction...1 Before You Begin...1 Conventions...1
Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source list C Table of Contents Sample Configuration Using the ip nat outside source list Command...1 Introduction...1 Before You Begin...1 Conventions...1
Basic Router and Switch Instructions (Cisco Devices)
 Basic Router and Switch Instructions (Cisco Devices) Basic Device Connection 1. Connect to the device via the console cable (light blue cable) and the use of a terminal program (Windows Hyperterminal,
Basic Router and Switch Instructions (Cisco Devices) Basic Device Connection 1. Connect to the device via the console cable (light blue cable) and the use of a terminal program (Windows Hyperterminal,
Lab 3.5.1: Basic VLAN Configuration (Instructor Version)
 (Instructor Version) Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0
(Instructor Version) Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0
Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 3600 and 3800 Series Routers
 Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 3600 and 3800 Series Routers Document ID: 22189 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions Step by Step Procedure
Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 3600 and 3800 Series Routers Document ID: 22189 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions Step by Step Procedure
Welcome to Todd Lammle s CCNA Bootcamp
 Welcome to Todd Lammle s CCNA Bootcamp Todd Lammle Cisco Authorized CCNA Bootcamps are now available, delivered by CCSI instructor, and popular Sybex author Todd Lammle. Todd Lammle CCNA Training Boot
Welcome to Todd Lammle s CCNA Bootcamp Todd Lammle Cisco Authorized CCNA Bootcamps are now available, delivered by CCSI instructor, and popular Sybex author Todd Lammle. Todd Lammle CCNA Training Boot
Lab 9.1.1 Organizing CCENT Objectives by OSI Layer
 Lab 9.1.1 Organizing CCENT Objectives by OSI Layer Objectives Organize the CCENT objectives by which layer or layers they address. Background / Preparation In this lab, you associate the objectives of
Lab 9.1.1 Organizing CCENT Objectives by OSI Layer Objectives Organize the CCENT objectives by which layer or layers they address. Background / Preparation In this lab, you associate the objectives of
Packet Tracer 3 Lab VLSM 2 Solution
 Packet Tracer 3 Lab VLSM 2 Solution Objective Create a simulated network topology using Packet Tracer Design an IP addressing scheme using a Class B subnetwork address and VLSM Apply IP addresses to the
Packet Tracer 3 Lab VLSM 2 Solution Objective Create a simulated network topology using Packet Tracer Design an IP addressing scheme using a Class B subnetwork address and VLSM Apply IP addresses to the
Lab 4.2.3 Analyzing Network Traffic
 Lab 4.2.3 Analyzing Network Traffic Objective Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Network Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 FC-CPE-1 Fa0/1 172.17.0.1 Fa0/0 10.0.0.1 255.255.0.0
Lab 4.2.3 Analyzing Network Traffic Objective Device Designation Device Name Address Subnet Mask Discovery Server Network Services 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0 R1 FC-CPE-1 Fa0/1 172.17.0.1 Fa0/0 10.0.0.1 255.255.0.0
LAB THREE STATIC ROUTING
 LAB THREE STATIC ROUTING In this lab you will work with four different network topologies. The topology for Parts 1-4 is shown in Figure 3.1. These parts address router configuration on Linux PCs and a
LAB THREE STATIC ROUTING In this lab you will work with four different network topologies. The topology for Parts 1-4 is shown in Figure 3.1. These parts address router configuration on Linux PCs and a
Connecting to the Firewall Services Module and Managing the Configuration
 CHAPTER 3 Connecting to the Firewall Services Module and This chapter describes how to access the command-line interface and work with the configuration. This chapter includes the following sections: Connecting
CHAPTER 3 Connecting to the Firewall Services Module and This chapter describes how to access the command-line interface and work with the configuration. This chapter includes the following sections: Connecting
Configuring the Switch with the CLI Setup Program
 APPENDIXC Configuring the Switch with the CLI Setup Program This appendix provides a command-line interface (CLI) setup procedure for a standalone switch. To set up the switch by using Express Setup, see
APPENDIXC Configuring the Switch with the CLI Setup Program This appendix provides a command-line interface (CLI) setup procedure for a standalone switch. To set up the switch by using Express Setup, see
Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 806, 826, 827, 828, 831, 836, 837 and 881 Series Routers
 Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 806, 826, 827, 828, 831, 836, 837 and 881 Series Routers Document ID: 12065 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions
Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco 806, 826, 827, 828, 831, 836, 837 and 881 Series Routers Document ID: 12065 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions
Lab 7.1.9b Introduction to Fluke Protocol Inspector
 Lab 7.1.9b Introduction to Fluke Protocol Inspector DCE SanJose1 S0/0 S0/0 SanJose2 #1 #2 Objective This lab is a tutorial demonstrating how to use the Fluke Networks Protocol Inspector to analyze network
Lab 7.1.9b Introduction to Fluke Protocol Inspector DCE SanJose1 S0/0 S0/0 SanJose2 #1 #2 Objective This lab is a tutorial demonstrating how to use the Fluke Networks Protocol Inspector to analyze network
Lab 8.3.1.2 Configure Basic AP Security through IOS CLI
 Lab 8.3.1.2 Configure Basic AP Security through IOS CLI Estimated Time: 30 minutes Number of Team Members: Students will work in teams of two. Objective In this lab, the student will learn the following
Lab 8.3.1.2 Configure Basic AP Security through IOS CLI Estimated Time: 30 minutes Number of Team Members: Students will work in teams of two. Objective In this lab, the student will learn the following
INTERCONNECTING CISCO NETWORK DEVICES PART 1 V2.0 (ICND 1)
 INTERCONNECTING CISCO NETWORK DEVICES PART 1 V2.0 (ICND 1) COURSE OVERVIEW: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices, Part 1 (ICND1) v2.0 is a five-day, instructor-led training course that teaches learners
INTERCONNECTING CISCO NETWORK DEVICES PART 1 V2.0 (ICND 1) COURSE OVERVIEW: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices, Part 1 (ICND1) v2.0 is a five-day, instructor-led training course that teaches learners
CCNA Exploration 4.0: (II) Routing Protocols and Concepts. Chapter 1: Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding
 Http://elmaestrodelared.blogspot.com CCNA Exploration 4.0: (II) Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1: Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding 1. If a router cannot find a valid configuration
Http://elmaestrodelared.blogspot.com CCNA Exploration 4.0: (II) Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 1: Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding 1. If a router cannot find a valid configuration
Configuring a Cisco 2509-RJ Terminal Router
 created by: Rainer Bemsel Version 1.0 Dated: Dec/08/2012 For my Cisco LAB, I ve purchased a used Cisco 2509-RJ with RJ45-RJ45 roll-over cables. This TechTip shows my configuration setup, so you can easily
created by: Rainer Bemsel Version 1.0 Dated: Dec/08/2012 For my Cisco LAB, I ve purchased a used Cisco 2509-RJ with RJ45-RJ45 roll-over cables. This TechTip shows my configuration setup, so you can easily
RIPv2 with Variable Length Subnet Masks (VLSMs)
 RIPv2 with Variable Length Subnet Masks (VLSMs) This chapter will discuss the RIPv2 routing process. This is an important subject to understand as it pertains to all routers and configurations that use
RIPv2 with Variable Length Subnet Masks (VLSMs) This chapter will discuss the RIPv2 routing process. This is an important subject to understand as it pertains to all routers and configurations that use
100-101: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 v2.0 (ICND1)
 100-101: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 v2.0 (ICND1) Course Overview This course provides students with the knowledge and skills to implement and support a small switched and routed network.
100-101: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 v2.0 (ICND1) Course Overview This course provides students with the knowledge and skills to implement and support a small switched and routed network.
Procedure: You can find the problem sheet on Drive D: of the lab PCs. Part 1: Router & Switch
 University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Computer Engineering Department Computer Networks Laboratory 907528 Lab. 2 Network Devices & Packet Tracer Objectives 1. To become familiar with
University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Computer Engineering Department Computer Networks Laboratory 907528 Lab. 2 Network Devices & Packet Tracer Objectives 1. To become familiar with
Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing
 Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing Topology Objectives Background Review a basic EIGRP configuration. Explore the EIGRP topology table. Identify successors, feasible successors, and feasible distances.
Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing Topology Objectives Background Review a basic EIGRP configuration. Explore the EIGRP topology table. Identify successors, feasible successors, and feasible distances.
Lab 8.3.3b Configuring a Remote Router Using SSH
 Lab 8.3.3b Configuring a Remote Router Using SSH Objectives Use SDM to configure a router to accept SSH connections. Configure SSH client software on a PC. Establish a connection to a Cisco ISR using SSH
Lab 8.3.3b Configuring a Remote Router Using SSH Objectives Use SDM to configure a router to accept SSH connections. Configure SSH client software on a PC. Establish a connection to a Cisco ISR using SSH
Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices 1 Course, Class Outline
 www.etidaho.com (208) 327-0768 Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices 1 Course, Class Outline 5 Days Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices, Part 1 (ICND1) v2.0 is a five-day, instructorled training course
www.etidaho.com (208) 327-0768 Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices 1 Course, Class Outline 5 Days Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices, Part 1 (ICND1) v2.0 is a five-day, instructorled training course
Working knowledge of TCP/IP protocol Suite IPX/SPX protocols Suite, MCSE or CNE or experienced in supporting a LAN environment.
 Cisco Certified Network Associate (640-802) Overview & Objectives This course will lead to a CISCO Certification (CCNA). This is the CISCO: Fundamental of Internetworking and WAN Configuration but with
Cisco Certified Network Associate (640-802) Overview & Objectives This course will lead to a CISCO Certification (CCNA). This is the CISCO: Fundamental of Internetworking and WAN Configuration but with
- Advanced IOS Functions -
 1 The Configuration Register - Advanced IOS Functions - The configuration register (config-register) is a hexadecimal value that controls various aspects of how a router boots, including: Baud Rate Boot
1 The Configuration Register - Advanced IOS Functions - The configuration register (config-register) is a hexadecimal value that controls various aspects of how a router boots, including: Baud Rate Boot
Cisco - Configure the 1721 Router for VLANs Using a Switch Module (WIC-4ESW)
 Page 1 of 20 Configure the 1721 Router for VLANs Using a Switch Module (WIC-4ESW) Document ID: 50036 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Network Diagram The Role of Switched
Page 1 of 20 Configure the 1721 Router for VLANs Using a Switch Module (WIC-4ESW) Document ID: 50036 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Network Diagram The Role of Switched
Configuring PROFINET
 CHAPTER 9 This chapter describes how to configure the PROFINET feature on the Cisco IE 3000 switch. Understanding PROFINET, page 9-1, page 9-4 Displaying the PROFINET Configuration, page 9-5 Troubleshooting
CHAPTER 9 This chapter describes how to configure the PROFINET feature on the Cisco IE 3000 switch. Understanding PROFINET, page 9-1, page 9-4 Displaying the PROFINET Configuration, page 9-5 Troubleshooting
Lab 3.10.2 Use Network Inspector to Observe STP Behavior
 Lab 3.10.2 Use Network Inspector to Observe STP Behavior Objective The purpose of this lab is to observe STP behavior with the Network Inspector switch trace feature. Scenario A new switched network has
Lab 3.10.2 Use Network Inspector to Observe STP Behavior Objective The purpose of this lab is to observe STP behavior with the Network Inspector switch trace feature. Scenario A new switched network has
CCNA Discovery 4.0.3.0 Networking for Homes and Small Businesses Student Packet Tracer Lab Manual
 4.0.3.0 Networking for Homes and Small Businesses Student Packet Tracer Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial
4.0.3.0 Networking for Homes and Small Businesses Student Packet Tracer Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial
Configuring a Router
 CHAPTER 3 Configuring a Router This chapter provides information and commands concerning the following topics: Configuring a router, specifically: Names Passwords Interfaces MOTD banners IP host tables
CHAPTER 3 Configuring a Router This chapter provides information and commands concerning the following topics: Configuring a router, specifically: Names Passwords Interfaces MOTD banners IP host tables
CCNA Access List Sim
 1 P a g e CCNA Access List Sim Question An administrator is trying to ping and telnet from Switch to Router with the results shown below: Switch> Switch> ping 10.4.4.3 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending
1 P a g e CCNA Access List Sim Question An administrator is trying to ping and telnet from Switch to Router with the results shown below: Switch> Switch> ping 10.4.4.3 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending
Router and Routing Basics
 Router and Routing Basics Malin Bornhager Halmstad University Session Number 2002, Svenska-CNAP Halmstad University 1 Routing Protocols and Concepts CCNA2 Routing and packet forwarding Static routing Dynamic
Router and Routing Basics Malin Bornhager Halmstad University Session Number 2002, Svenska-CNAP Halmstad University 1 Routing Protocols and Concepts CCNA2 Routing and packet forwarding Static routing Dynamic
Lab 8.5.3 Configuring the PIX Firewall as a DHCP Server
 Lab 8.5.3 Configuring the PIX Firewall as a DHCP Server Objective Scenario Estimated Time: 15 minutes Number of Team Members: Two teams with four students per team. In this lab, students will learn the
Lab 8.5.3 Configuring the PIX Firewall as a DHCP Server Objective Scenario Estimated Time: 15 minutes Number of Team Members: Two teams with four students per team. In this lab, students will learn the
Basic Software Configuration Using the Cisco IOS Command-Line Interface
 Basic Software Configuration Using the Cisco IOS Command-Line Interface This document describes how to use the Cisco IOS command-line interface (CLI) to perform a basic software configuration for your
Basic Software Configuration Using the Cisco IOS Command-Line Interface This document describes how to use the Cisco IOS command-line interface (CLI) to perform a basic software configuration for your
CISCO CATALYST 3550 Series Switches
 CISCO CATALYST 3550 Series Switches The switches that belong to this series are stackable and are multilayer switches that provide QoS, high availability and security that are responsible for enhancing
CISCO CATALYST 3550 Series Switches The switches that belong to this series are stackable and are multilayer switches that provide QoS, high availability and security that are responsible for enhancing
Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco Catalyst 2948G L3, 4840G, and 4908G L3 Switch Routers
 Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco Catalyst 2948G L3, 4840G, and 4908G L3 Switch Routers Document ID: 12738 Contents Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Step by Step Procedure
Password Recovery Procedure for the Cisco Catalyst 2948G L3, 4840G, and 4908G L3 Switch Routers Document ID: 12738 Contents Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Step by Step Procedure
How To Learn Cisco Cisco Ios And Cisco Vlan
 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices: Accelerated Course CCNAX v2.0; 5 Days, Instructor-led Course Description Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices: Accelerated (CCNAX) v2.0 is a 60-hour instructor-led
Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices: Accelerated Course CCNAX v2.0; 5 Days, Instructor-led Course Description Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices: Accelerated (CCNAX) v2.0 is a 60-hour instructor-led
Router Security Audit Logs
 Router Security Audit Logs The Router Security Audit Logs feature allows users to configure audit trails, which track changes that have been made to a router that is running Cisco IOS software. History
Router Security Audit Logs The Router Security Audit Logs feature allows users to configure audit trails, which track changes that have been made to a router that is running Cisco IOS software. History
OSPF Configuring Multi-Area OSPF
 OSPF Configuring Multi-Area OSPF Objective In this lab configure a multiarea OSPF operation, interarea summarization, external route summarization, and default routing. Scenario International Travel Agency
OSPF Configuring Multi-Area OSPF Objective In this lab configure a multiarea OSPF operation, interarea summarization, external route summarization, and default routing. Scenario International Travel Agency
PT Activity: Configure Cisco Routers for Syslog, NTP, and SSH Operations
 PT Activity: Configure Cisco Routers for Syslog, NTP, and SSH Operations Instructor Version Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 FA0/1
PT Activity: Configure Cisco Routers for Syslog, NTP, and SSH Operations Instructor Version Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 FA0/1
ICND1 Lab Guide. 640-822 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 Version: Beta. Labs powered by
 ICND1 Lab Guide 640-822 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 Version: Beta Labs powered by Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 640-822 Lab Guide 25 Century Blvd. Ste. 500 Nashville,
ICND1 Lab Guide 640-822 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 Version: Beta Labs powered by Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 640-822 Lab Guide 25 Century Blvd. Ste. 500 Nashville,
Introduction about cisco company and its products (network devices) Tell about cisco offered courses and its salary benefits (ccna ccnp ccie )
 CCNA Introduction about cisco company and its products (network devices) Tell about cisco offered courses and its salary benefits (ccna ccnp ccie ) Inform about ccna its basic course of networking Emergence
CCNA Introduction about cisco company and its products (network devices) Tell about cisco offered courses and its salary benefits (ccna ccnp ccie ) Inform about ccna its basic course of networking Emergence
How To Configure InterVLAN Routing on Layer 3 Switches
 How To Configure InterVLAN Routing on Layer 3 Switches Document ID: 41860 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure InterVLAN Routing Task Step by Step Instructions
How To Configure InterVLAN Routing on Layer 3 Switches Document ID: 41860 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure InterVLAN Routing Task Step by Step Instructions
CCNP ROUTE 6.0 Student Lab Manual
 CCNP ROUTE 6.0 Student Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors
CCNP ROUTE 6.0 Student Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors
Cisco Configuration Professional Quick Start Guide
 Cisco Configuration Professional Quick Start Guide April 29, 2011 This document explains how to start using Cisco Configuration Professional Express (Cisco CP Express) and Cisco Configuration Professional
Cisco Configuration Professional Quick Start Guide April 29, 2011 This document explains how to start using Cisco Configuration Professional Express (Cisco CP Express) and Cisco Configuration Professional
Lab 4.4.8a Configure a Cisco GRE over IPSec Tunnel using SDM
 Lab 4.4.8a Configure a Cisco GRE over IPSec Tunnel using SDM Objective Scenario Topology In this lab, the students will complete the following tasks: Prepare to configure Virtual Private Network (VPN)
Lab 4.4.8a Configure a Cisco GRE over IPSec Tunnel using SDM Objective Scenario Topology In this lab, the students will complete the following tasks: Prepare to configure Virtual Private Network (VPN)
