Lymphatics are found in all tissues except the : CNS, cartilage, bone bone marrow, thymus, teeth, placenta.
|
|
|
- Hollie Eaton
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 LYMPHATIC SYSTEM
2 Lymphatics are found in all tissues except the : CNS, cartilage, bone bone marrow, thymus, teeth, placenta.
3 Lymphatics are sometimes difficult to demonstrate satisfactorily in normal tissues because these large, thin-walled vessels frequently collapse to the point of invisibility during tissue processing. Lymphatics are often most easily visualized and studied during pathological processes (e.g., inflammation). Lymphatics start as blind-ended lymphatic capillaries which coalesce to form lymphatic vessels and finally empty into the circulation via the lymphatic ducts (thoracic and right lymphatic).
4 Elephantiasis. Elephantiasis is a condition of extreme edema that occurs when lymph vessels become blocked by filarial worms. Here the left leg is swollen with the fluids accumulated in the tissues as a result of the blockage.
5
6
7
8
9 Angioedema /dermatol/protocolosweb/paginesgrans/angioedemag1.html
10 Angioedema refers to increased vascular permeability below the dermis leading to edema. This process is similar to urticaria and is the result of vasoactive mediators such as histamine, serotonin, and bradykinin. Angioedema has many causes, including: food, drugs/medication, hymenoptra exposure, complementmediated, hereditary, malignancy, and idiopathic.
11 Crucial in helping the body ward off disease and heal from injury Advanced infection from poor circulation
12 Importance of the Lymphatic System Two most important functions Maintenance of fluid balance in the internal environment. Immunity Importance of the lymphatic system in maintaining fluid balance. Plasma filters into the interstitial spaces from blood flowing through the capillaries. Much of this interstitial fluid is absorbed by tissue cells or reabsorbed by the blood before it flows out of the tissue. A small amount of interstitial fluid is left behind. If this would continue over even a brief period of time, the increased interstitial fluid would cause massive edema. This edema would causes tissue destruction or death This problem is avoided by the presence of lymphatic vessels that act as "drains" to collect the excess fluid and return it to the venous blood just before it reaches the heart. The lymphatic system is a specialized component of the circulatory system. Consists of a moving fluid (lymph) derived from the blood and tissue fluid and a group of vessels (lymphatics) that returns lymph to the blood. Lymphatic vessels parallel veins.
13 Functions of Lymphatic System Drain fluid from around cells Absorb fat from intestines Circulate lymph Filter lymph Immunity
14 The lymphatic system serves several important functions in the body. *It drains fluid from around cells to prevent fluid build up. *Lymphatic capillaries are also able to absorb fat from the intestines. *The fluid that is circulated by the lymphatic system is called lymph. Lymph is filtered by the lymphatic system to remove such things as microorganisms and wandering cancer cells. *The lymphatic system also gives us our immunity.
15 Lymph derived from tissue fluid contains more white blood cells than plasma enters node through afferent lymphatic vessels flows through node in one direction (lympha = clear fluid) flows through sinuses in lymph node cortex and then into the medulla exits the lymph node through efferent lymphatic vessels must be returned to blood stream to maintain blood volume and pressure
16 Lymphatic System: Overview Consists of two semi-independent parts: A network of lymphatic vessels Lymphoid tissues and organs scattered throughout the body Returns interstitial fluid and leaked plasma proteins back to the blood Lymph interstitial fluid once it has entered lymphatic vessels
17
18 Lymphatic System Consists of: - lymph - network of vessels - lymph nodes and nodules - tonsils - spleen - thymus gland - bone marrow
19 Lymphatic System: Overview Figure 20.1a
20 Lymphatic Vessels One-way system, lymph flows toward the heart Lymph vessels include: Microscopic, permeable, blindended capillaries Lymphatic collecting vessels Trunks and ducts
21 Lymphatic vessels resemble veins in structure with these exceptions: Lymphatics have thinner walls. Lymphatics contain more valves. Lymphatics contain lymph nodes located at certain intervals along their course.
22 Lymph Vessels no pump for lymph Lymph is kept moving by: - constriction of vessels - skeletal muscle pump - respiratory pump at intervals along vessels lymph flows into lymph nodes lymphatic vessels unite to form lymph trunks
23 Lymphatic Trunks formed by lymphatic vessels uniting large tubes empty their lymph into lymphatic ducts Lymphatic trunks are formed by the union of the largest collecting ducts Major trunks include: Paired lumbar, bronchomediastinal, subclavian, and jugular trunks A single intestinal trunk
24 Lymphatic Trunks Lymph is delivered into one of two large trunks Right lymphatic duct drains the right upper arm and the right side of the head and thorax Thoracic duct arises from the cisterna chyli and drains the rest of the body
25 Right lymphatic duct
26 Drainage The right duct drains lymph fluid from: the upper right section of the trunk, (right thoracic cavity, via the right bronchomediastinal trunk), the right arm (via the right subclavian trunk), and right side of the head and neck (via the right jugular trunk), also the lower lobe of the left lung. All other sections of the human body are drained by the thoracic duct.
27 From lymphatic capillaries, lymph flows through progressively larger lymphatic vessels to eventually reenter blood at the junction of the internal jugular and subclavian veins.
28 Components of the Lymphatic System A. Lymph fluid collected in lymph vessels Clear straw colored fluid same basic component as plasma
29 The Lymphatic Pump Although there is no muscular pumping organ connected with the lymphatic vessels to force lymph onward as the heart forces blood, still lymph moves slowly and steadily along its vessels. Lymph flows through the thoracic duct and reenters the general circulation at the rate of 125 ml/hour. Occurs despite the fact that most of the flow is against gravity or "uphill". It moves through the system in the right direction because of the large number of valves that permit fluid flow only in one direction. The movement is due to breathing movements and skeletal muscle contractions. Activities that result in central movement or flow are called lymphokinetic actions.
30 The mechanism of inspiration, resulting from the descent of the diaphragm, causes intraabdominal pressure to increase as intrathoracic pressure decreases. This simultaneously causes pressure to increase in the abdominal portion of the thoracic duct and to decrease in the thoracic portion. Research has shown that thoracic duct lymph is literally "pumped" into the venous system during inspiration. The rate of flow of lymph into venous circulation is proportional to the depth of inspiration. The total volume of lymph that enters the central veins during a given time period depends on both the depth of inspiration and the overall breathing rate. Contracting skeletal muscles also exert pressure on the lymphatics to push the lymph forward. a. During exercise, lymph flow may increase as much as 10-15x. Other pressure generating factors: Arterial pulsations Postural changes Passive compression (massage) of the body soft tissues.
31 The lymphatic veins flow into one of two lymph ducts. The right lymph duct drains the right arm, shoulder area, and the right side of the head and neck. The left lymph duct, or thoracic duct, drains everything else, including the legs, GI tract and other abdominal organs, thoracic organs, and the left side of the head and neck and left arm and shoulder. These ducts then drain into the subclavian veins on each side where they join the internal jugular veins to form the brachiocephalic veins. Lymph nodes lie along the lymph veins successively filtering lymph. Afferent lymph veins enter each node, efferent veins lead to the next node becoming afferent veins upon reaching it
32 Right Lymphatic Duct about 0.5 inches (1.5 cm) in length receives lymph from upper right quadrant empties into the right subclavian vein
33 In adults, the thoracic duct is typically 38-45cm in length and an average diameter of about 5mm. It usually starts from the level of the second lumbar vertebra and extends to the root of the neck. It originates in the abdomen from the confluence of the right and left lumbar trunk and the intestinal trunk, forming a significant pathway upward called the cisterna chyli. It extends vertically in the chest and curves posteriorly to the left carotid artery and left internal jugular vein at the C7 vertebral level to empty into the junction of the left subclavian vein and left jugular vein, below the clavicle, near the shoulders. It traverses the diaphragm at the aortic aperture and ascends the posterior mediastinum between the descending thoracic aorta (to its left) and the azygos vein (to its right).
34
35 Main Channels of Lymphatics
36
37 Lymphatic Trunks Figure 20.2b
38 Thoracic Duct (left lymphatic duct) about inches (38-45 cm) in length begins as a dilation called the cisterna chyli main collecting duct of lymphatic system receives lymph from lower body and upper left quadrant empties into the left subclavian vein
39 Lymphatic Ducts Lymph empties into two conducting ducts: - the thoracic duct (left lymphatic duct) - the right lymphatic duct Lymph from these ducts enters the blood stream via the left subclavian vein and the right subclavian vein
40 Cisterna Chyli large lymph vessel formed by the union of lymph vessels from lower body located anterior to the second lumbar vertebra continues superiorly as thoracic duct
41 Lymphatic Vessels
42
43 Lymphatic Capillaries Figure 20.1b
44
45
46
47
48 Lymphatic Capillaries During inflammation, lymph capillaries can absorb: Cell debris Pathogens Cancer cells Cells in the lymph nodes cleanse and examine this debris Lacteals specialized lymph capillaries present in intestinal mucosa Absorb digested fat and deliver chyle to the blood
49
50 Lymphatic Capillaries Similar to blood capillaries, with modifications: Very permeable Loosely joined endothelial minivalves Withstand interstitial pressure and remain open The minivalves function as one-way gates that: Allow interstitial fluid to enter lymph capillaries Do not allow lymph to escape from the capillaries
51 Lymphatic Collecting Vessels Have the same three tunics as veins Have thinner walls, with more internal valves Anastomose more frequently Collecting vessels in the skin travel with superficial veins Deep vessels travel with arteries Nutrients are supplied from branching vasa vasorum
52 Lymph Transport The lymphatic system lacks a pumping organ Vessels are low-pressure conduits Uses the same methods as veins to propel lymph: Pulsations of nearby arteries Contractions of smooth muscle in the walls of the lymphatics
53 Lymphoid Cells Lymphocytes are the main cells involved in the immune response Two main varieties: T cells B cells
54 Other Lymphoid Cells Macrophages phagocytize foreign substances and help activate T cells Dendritic cells spiny-looking cells with functions similar to macrophages Reticular cells fibroblast like cells that produce a stroma, or network, that supports other cell types in lymphoid organs
55 Lymph Nodes Principal lymphoid organs of the body Embedded in connective tissue and clustered along lymphatic vessels Aggregations of these nodes occur near the body surface in inguinal, axillary, and cervical regions of the body Figure 20.4a
56
57 Lymph Nodes Two basic functions: Filtration macrophages destroy microorganisms and debris Immune system activation monitor for antigens and mount an attack against them
58 Lymph Nodes oval or bean-shaped masses of lymphatic tissue aid in defense and white blood cell formation located along length of lymphatic vessels scattered throughout the body usually in clusters
59 Lymph Nodes covered by a capsule contain capsular extensions called trabeculae (form partitions within node) internal to capsule are reticular fibers and fibroblasts - form framework of a lymph node Two main regions of a lymph node: - cortex - medulla
60 Structure of a Lymph Node Nodes are bean shaped and surrounded by a fibrous capsule Trabeculae extended inward from the capsule and divide the node into compartments Nodes have two histologically distinct regions: a cortex and a medulla Figure 20.4a
61 Structure of a Lymph Node Cortex contains follicles with germinal centers, heavy with dividing B cells Dendritic cells nearly encapsulate the follicles Deep cortex houses T cells in transit T cells circulate continuously among the blood, lymph nodes, and lymphatic stream
62 Structure of a Lymph Node Medullary cords extend from the cortex and contain B cells, T cells, and plasma cells Throughout the node are lymph sinuses crisscrossed by reticular fibers Macrophages reside on these fibers and phagocytize foreign matter
63 Structure of a Lymph Node Figure 20.4a, b
64 Circulation in the Lymph Nodes Lymph enters via afferent lymphatic vessels It then enters a large subcapsular sinus and travels into smaller sinuses It meanders through these sinuses and exits the node at the hilus via efferent vessels Because there are fewer efferent vessels, lymph stagnates somewhat in the node This allows lymphocytes and macrophages time to carry out protective functions
65 Lymphatic nodules The germinal center is the site of proliferation and differentiation of B-lymphocytes. Cell types of the germinal center include : activated B-lymphocytes (B-immunoblasts) mitotic cells plasma cells dendritic reticular cells macrophages
66
67
68
69 arteriole vein lymphatic vessel valve germinal center trabeculae cortex medulla
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77 Lymphoid Organs Figure 20.5
78
79
80 Lymphoid Tissue Diffuse lymphatic tissue scattered reticular tissue elements in every body organ Larger collections appear in the lamina propria of mucous membranes and lymphoid organs Lymphatic follicles (nodules) solid, spherical bodies consisting of tightly packed reticular elements and cells Germinal center composed of dendritic and B cells Found in isolation and as part of larger lymphoid organs
81 TYPES OF LYMPHATIC TISSUE There are three basic types of lymphatic (lymphoid) tissue: Loose lymphatic tissue. This is dominated by reticular cells and fibers and forms a loose, spongy network through which lymph flow is slow and cells are temporarily trapped. Dense lymphatic tissue. This tissue is dominated by large populations of closely aggregated lymphocytes. Nodular lymphatic tissue (lymphatic nodules). Lymphatic nodules are found in all the lymphatic organs apart from the thymus.
82 Lymphatic Organs Red bone marrow Thymus gland Lymph nodes Lymph nodules Spleen Primary organs Secondary organs
83 Lymphoid organs Primary lymphoid organs Bone marrow and thymus Secondary lymphoid organs Tonsils, spleen
84 Other Lymphoid Organs The spleen, thymus gland, and tonsils Peyer s patches and bits of lymphatic tissue scattered in connective tissue All are composed of reticular connective tissue All help protect the body Only lymph nodes filter lymph
85 Spleen
86 Spleen Largest lymphoid organ, located on the left side of the abdominal cavity beneath the diaphragm It is served by the splenic artery and vein, which enter and exit at the hilus Functions: Site of lymphocyte proliferation Immune surveillance and response Cleanses the blood
87 Functions of the Spleen Defense As blood passes through the sinusoids, reticuloendothelial cell (macrophages) lining these venous spaces remove microorganisms from the blood and destroy them by phagocytosis. Hematopoiesis Monocytes and lymphocytes complete their development to become activated in the spleen. Before birth, red blood cells are also formed in the spleen. Red blood cell and platelet destruction. Macrophages lining the spleen's sinusoids remove worn-out red blood cells and imperfect platelets from the blood and destroy them by phagocytosis. Also break apart the hemoglobin molecules from the destroyed red blood cells and salvage their iron and globin content by returning them to the blood stream for storage in bone marrow and liver. Blood reservoir Blood reservoir Pulp of the spleen and its venous sinuses store considerable blood which can be released during hemorrhage.
88
89
90
91
92
93 Additional Spleen Functions Stores breakdown products of RBCs for later reuse Spleen macrophages salvage and store iron for later use by bone marrow Site of fetal erythrocyte production (normally ceases after birth) Stores blood platelets
94 Structure of the Spleen Surrounded by a fibrous capsule, it has trabeculae that extend inward and contains lymphocytes, macrophages, and huge numbers of erythrocytes Two distinct areas: White pulp containing mostly lymphocytes suspended on reticular fibers and involved in immune functions Red pulp remaining splenic tissue concerned with disposing of worn-out RBCs and bloodborne pathogens
95
96 Structure of the Spleen Figure 20.6a, b
97
98
99
100
101 splenomegaly
102 Thymus A bilobed organ that secretes hormones (thymosin and thymopoietin) that cause T lymphocytes to become immunocompetent Size of the thymus varies with age: In infants, it is found in the inferior neck and extends into the mediastinum where it partially overlies the heart It increases in size and is most active during childhood It stops growing during adolescence and then gradually atrophies
103
104 Thymus Gland Location behind the sternum in the mediastinum The capsule divides it into 2 lobes Development Infant conspicuous Puberty maximum size Maturity decreases in size Function Differentiation and maturation of T cells
105 Thymus Gland
106
107 Internal Anatomy of the Thymus Thymic lobes contain an outer cortex and inner medulla Cortex contains densely packed lymphocytes and scattered macrophages Medulla contains fewer lymphocytes and thymic (Hassall s) corpuscles
108 Thymus The thymus differs from other lymphoid organs in important ways It functions strictly in T lymphocyte maturation It does not directly fight antigens The stroma of the thymus consists of star-shaped epithelial cells (not reticular fibers) These thymocytes secrete the hormones that stimulate lymphocytes to become immunocompetent
109 Geography of the thymus: Thymic epithelial cells control the maturation of thymocytes
110 Hassal's Corpuscle
111
112
113 Hassal's Corpuscle Hassall's corpuscles (or thymic corpuscles) are structures found in the medulla of the human thymus, formed from type VI epithelial reticular cells. The function of Hassall's corpuscles is currently unclear, and the absence of this structure in the murine thymus has restricted mechanistic dissection. It is known that Hassall's corpuscles are a potent source of the cytokine TSLP. In vitro, TSLP directs the maturation of dendritic cells, and increases the ability of dendritic cells to convert naive thymocytes to a Foxp3+ regulatory T cell lineage. It is unknown if this is the physiological function of Hassall's corpuscles in vivo.
114
115
116
117 Tonsils Simplest lymphoid organs; form a ring of lymphatic tissue around the pharynx Location: Palatine tonsils either side of the posterior end of the oral cavity Lingual tonsils lie at the base of the tongue Pharyngeal tonsil posterior wall of the nasopharynx Tubal tonsils surround the openings of the auditory tubes into the pharynx
118 Depending on their localisation we distinguish between palatine tonsils (THE tonsils), which are located in the lateral wall of the oropharynx and covered by a stratified squamous epithelium, lingual tonsils which are situated in the lamina propria at the root of the tongue and also covered by a stratified squamous epithelium, and pharyngeal tonsils (also called nasopharyngeal tonsils or adenoids) which are located in the upper posterior part of the throat (nasopharynx) and covered by a pseudostratified ciliated epithelium with goblet cells. The tonsils do not have afferent lymph vessels. Efferent lymph vessels are present.
119 Tonsils Lymphoid tissue of tonsils contains follicles with germinal centers Tonsil masses are not fully encapsulated Epithelial tissue overlying tonsil masses invaginates, forming blindended crypts Crypts trap and destroy bacteria and particulate matter
120 Tonsils
121
122 Palatine tonsils Pharyngeal tonsils
123 Aggregates of Lymphoid Follicles Peyer s patches isolated clusters of lymphoid tissue, similar to tonsils Found in the wall of the distal portion of the small intestine Similar structures are found in the appendix Peyer s patches and the appendix: Destroy bacteria, preventing them from breaching the intestinal wall Generate memory lymphocytes for long-term immunity
124
125 Ileum- Peyers Patch
126 MALT MALT mucosa-associated lymphatic tissue: Peyer s patches, tonsils, and the appendix (digestive tract) Lymphoid nodules in the walls of the bronchi (respiratory tract) MALT protects the digestive and respiratory systems from foreign matter
127 Gut-Associated Lymphoid Tissue - GALT Small accumulations of lymphocytes or solitary lymph follicles are found scattered in beneath the epithelium throughout the gastrointestinal tract. The most prominent accumulations occur in the ileum and appendix in the form of Peyer's patches. In the ileum, they form dome-shaped protrusions into the lumen. Beneath the epithelial lining of the domes, Peyer's patches extend from the lamina propria to the submucosa. Within Peyer's patches, lymph follicles with germinal centers are typically located deep in the submucosa. The epithelium in contact with the lymphoid tissue is specialised to facilitate the contact of antigens with cells of the immune system. The epithelium appears columnar and contains cells with deeply invaginated basal surfaces - microfold cells or M-cells. Immune system cells can enter these invaginations (intraepithelial pockets) where they are exposed to materials which have been endocytosed by the epithelial cells and then released into the invaginations. Goblet cells are rare or absent in the epithelium which covers the domes.
128 Developmental Aspects lymph nodes are apparent by the fifth week of embryonic development Lymphatic organs (except the thymus) arise from mesoderm The thymus (endodermal origin) forms as an outgrowth of the pharynx Except for the spleen and tonsils, lymphoid organs are poorly developed at birth
129 Two forms of immunity: Humoral or antibody mediated immunity B cells (mature in bone) make antibodies: specific proteins that bind to specific antigens OR Cell-mediated immunity T cytoxic lymphocytes attack virus infected or tumor cells directly
130
The Lymphatic System. Dr. Naim Kittana, PhD
 The Lymphatic System Dr. Naim Kittana, PhD 1 Disclosure The material and the illustrations are adopted from the textbook Human Anatomy and Physiology / Ninth edition/ Eliane N. Marieb 2013 Dr. Naim Kittana,
The Lymphatic System Dr. Naim Kittana, PhD 1 Disclosure The material and the illustrations are adopted from the textbook Human Anatomy and Physiology / Ninth edition/ Eliane N. Marieb 2013 Dr. Naim Kittana,
Unit 9: The Lymphatic and Immune Systems NURSING PHYSIOLOGY (NRSG237)
 Unit 9: The Lymphatic and Immune Systems Dr. Moattar Raza Rizvi NURSING PHYSIOLOGY (NRSG237) Functions: Transports Excess Interstitial Fluid Back to Bloodstream Lymphatic vessels collect lymph from loose
Unit 9: The Lymphatic and Immune Systems Dr. Moattar Raza Rizvi NURSING PHYSIOLOGY (NRSG237) Functions: Transports Excess Interstitial Fluid Back to Bloodstream Lymphatic vessels collect lymph from loose
The Lymphatic System
 The Lymphatic System network of tissues, organs and vessels that help to maintain the body s fluid balance & protect it from pathogens lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, tonsils, etc without
The Lymphatic System network of tissues, organs and vessels that help to maintain the body s fluid balance & protect it from pathogens lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, tonsils, etc without
The Structure and Function of the Lymphatic System
 The Structure and Function of the Lymphatic System The lymphatic system runs though the body and is made up of organs and lymphatic tissue, this includes organs like the spleen and thymus and also lymphatic
The Structure and Function of the Lymphatic System The lymphatic system runs though the body and is made up of organs and lymphatic tissue, this includes organs like the spleen and thymus and also lymphatic
Lymph capillaries, Lymphatic collecting vessels, Valves, Lymph Duct, Lymph node, Vein
 WLHS/A&P/Oppelt Name Lymphatic System Practice 1. Figure 12-1 provides an overview of the lymphatic vessels. First color code the following structures. Color code in Figure 12-1 Heart Veins Lymphatic vessels/lymph
WLHS/A&P/Oppelt Name Lymphatic System Practice 1. Figure 12-1 provides an overview of the lymphatic vessels. First color code the following structures. Color code in Figure 12-1 Heart Veins Lymphatic vessels/lymph
Diagram showing Systemic and Portal Circulation
 Diagram showing Systemic and Portal Circulation The Lymphatic System The Lymphatic System comprises of lymphatic capillaries, lymphatic vessels, nodes and ducts. Lymph fluid is not blood plasma, it contains
Diagram showing Systemic and Portal Circulation The Lymphatic System The Lymphatic System comprises of lymphatic capillaries, lymphatic vessels, nodes and ducts. Lymph fluid is not blood plasma, it contains
Chapter 14: The Lymphatic System and Immunity
 Chapter 14: The Lymphatic System and Immunity Major function of the Lymphatic System o Network of vessels that collect and carry excess fluid from interstitial spaces back to blood circulation o Organs
Chapter 14: The Lymphatic System and Immunity Major function of the Lymphatic System o Network of vessels that collect and carry excess fluid from interstitial spaces back to blood circulation o Organs
Chapter 19 Ci C r i cula l t a i t o i n
 Chapter 19 Circulation A closed system Circulatory System Consisting of Heart, Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, Blood & the Lymphatic system Blood Make up The blood is made up of Plasma and three main types
Chapter 19 Circulation A closed system Circulatory System Consisting of Heart, Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, Blood & the Lymphatic system Blood Make up The blood is made up of Plasma and three main types
37 2 Blood and the Lymphatic System Slide 1 of 34
 1 of 34 Blood is a connective tissue that contains both dissolved substances and specialized cells. 2 of 34 The functions of blood include: collecting oxygen from the lungs, nutrients from the digestive
1 of 34 Blood is a connective tissue that contains both dissolved substances and specialized cells. 2 of 34 The functions of blood include: collecting oxygen from the lungs, nutrients from the digestive
The Circulatory System. Chapter 17 Lesson 1
 The Circulatory System Chapter 17 Lesson 1 Functions of the Circulatory System Your circulatory system maintains an internal environment in which all the cells in your body are nourished. As your heart
The Circulatory System Chapter 17 Lesson 1 Functions of the Circulatory System Your circulatory system maintains an internal environment in which all the cells in your body are nourished. As your heart
THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY
 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Biology 2402 CHAPTER 22 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY Pathogens are disease-producing organisms. Survival and good health depends on
Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Biology 2402 CHAPTER 22 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY Pathogens are disease-producing organisms. Survival and good health depends on
Section B: Epithelial Tissue 1. Where are epithelial tissues found within the body? 2. What are the functions of the epithelial tissues?
 Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
A. function: supplies body with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide. a. O2 diffuses from air into pulmonary capillary blood
 A. function: supplies body with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide 1. ventilation = movement of air into and out of lungs 2. diffusion: B. organization a. O2 diffuses from air into pulmonary capillary blood
A. function: supplies body with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide 1. ventilation = movement of air into and out of lungs 2. diffusion: B. organization a. O2 diffuses from air into pulmonary capillary blood
2161-1 - Page 1. Name: 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. Questions 10 and 11 refer to the following:
 Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
Respiratory System. Chapter 21
 Respiratory System Chapter 21 Structural Anatomy Upper respiratory system Lower respiratory system throat windpipe voice box Function of Respiratory System Gas exchange Contains receptors for sense of
Respiratory System Chapter 21 Structural Anatomy Upper respiratory system Lower respiratory system throat windpipe voice box Function of Respiratory System Gas exchange Contains receptors for sense of
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 14 The Lymphoid System and Immunity. Multiple-Choice Questions
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 14 The Lymphoid System and Immunity Multiple-Choice Questions 1) The lymphoid system is composed of A) lymphatic vessels. B) lymph nodes.
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 14 The Lymphoid System and Immunity Multiple-Choice Questions 1) The lymphoid system is composed of A) lymphatic vessels. B) lymph nodes.
Vertebrate Body Organization
 Vertebrate Body Organization Digestive tube suspended in coelom from mouth to anus Body supported by internal skeleton of jointed bones Vertebrae and Cranium protects nervous system Diaphragm divides coelom
Vertebrate Body Organization Digestive tube suspended in coelom from mouth to anus Body supported by internal skeleton of jointed bones Vertebrae and Cranium protects nervous system Diaphragm divides coelom
Functions of Blood System. Blood Cells
 Functions of Blood System Transport: to and from tissue cells Nutrients to cells: amino acids, glucose, vitamins, minerals, lipids (as lipoproteins). Oxygen: by red blood corpuscles (oxyhaemoglobin - 4
Functions of Blood System Transport: to and from tissue cells Nutrients to cells: amino acids, glucose, vitamins, minerals, lipids (as lipoproteins). Oxygen: by red blood corpuscles (oxyhaemoglobin - 4
Unit Four. Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Human Anatomy & Physiology 16 Lymphatic System URLs http://www.howstuffworks.com/immune-system.htm http://www.thebody.com/step/immune.html http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/biobk/ BioBookIMMUN.html
Human Anatomy & Physiology 16 Lymphatic System URLs http://www.howstuffworks.com/immune-system.htm http://www.thebody.com/step/immune.html http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/biobk/ BioBookIMMUN.html
The Immune System. 2 Types of Defense Mechanisms. Lines of Defense. Line of Defense. Lines of Defense
 The Immune System 2 Types of Defense Mechanisms Immune System the system that fights infection by producing cells to inactivate foreign substances to avoid infection and disease. Immunity the body s ability
The Immune System 2 Types of Defense Mechanisms Immune System the system that fights infection by producing cells to inactivate foreign substances to avoid infection and disease. Immunity the body s ability
Human Anatomy and Physiology The Respiratory System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology The Respiratory System Basic functions of the respiratory system: as a Gas exchange supply oxygen to aerobic tissues in the body and remove carbon dioxide waste product. in-
Human Anatomy and Physiology The Respiratory System Basic functions of the respiratory system: as a Gas exchange supply oxygen to aerobic tissues in the body and remove carbon dioxide waste product. in-
= Lymphatic systems =
 = Lymphatic systems = Why do we need it? Lymph node Lymphatic vessel Lymphatic vessel Vein Capillary Artery tissues blood Capillaries Speaker: 許 書 豪 解 剖 學 科 助 理 教 授 1 Lymphatic tissue and organ Lymphatic
= Lymphatic systems = Why do we need it? Lymph node Lymphatic vessel Lymphatic vessel Vein Capillary Artery tissues blood Capillaries Speaker: 許 書 豪 解 剖 學 科 助 理 教 授 1 Lymphatic tissue and organ Lymphatic
Immune and Lymphatic Systems
 1. All of the following organs actively FIGHT pathogens EXCEPT: a. Cervical lymph nodes b. Tonsils c. Spleen d. Thymus e. Axillary lymph nodes 2. T lymphocytes gain immunocompetence within the: a. Bone
1. All of the following organs actively FIGHT pathogens EXCEPT: a. Cervical lymph nodes b. Tonsils c. Spleen d. Thymus e. Axillary lymph nodes 2. T lymphocytes gain immunocompetence within the: a. Bone
The Tissue Level of Organization
 The Tissue Level of Organization Tissues A groups of similar cells, usually having similar embryonic origin and specialized function Histology: the study of tissues Four general types Epithelial Muscle
The Tissue Level of Organization Tissues A groups of similar cells, usually having similar embryonic origin and specialized function Histology: the study of tissues Four general types Epithelial Muscle
The Immune System: A Tutorial
 The Immune System: A Tutorial Modeling and Simulation of Biological Systems 21-366B Shlomo Ta asan Images taken from http://rex.nci.nih.gov/behindthenews/uis/uisframe.htm http://copewithcytokines.de/ The
The Immune System: A Tutorial Modeling and Simulation of Biological Systems 21-366B Shlomo Ta asan Images taken from http://rex.nci.nih.gov/behindthenews/uis/uisframe.htm http://copewithcytokines.de/ The
Animal Tissues. I. Epithelial Tissue
 Animal Tissues There are four types of tissues found in animals: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. In this lab you will learn the major characteristics of each tissue
Animal Tissues There are four types of tissues found in animals: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. In this lab you will learn the major characteristics of each tissue
The lymphatic system and the immune system
 Freephone helpline 0808 808 5555 information@lymphomas.org.uk www.lymphomas.org.uk The lymphatic system and the immune system Lymphoma is a cancer that usually grows in the body s lymphatic system. The
Freephone helpline 0808 808 5555 information@lymphomas.org.uk www.lymphomas.org.uk The lymphatic system and the immune system Lymphoma is a cancer that usually grows in the body s lymphatic system. The
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley. Practice Exam 1
 Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam 1 1. Which definition is the best definition of the term gross anatomy? a. The study of cells. b. The study of tissues. c. The study of structures
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam 1 1. Which definition is the best definition of the term gross anatomy? a. The study of cells. b. The study of tissues. c. The study of structures
Immunity. Humans have three types of immunity innate, adaptive, and passive: Innate Immunity
 Immunity Humans have three types of immunity innate, adaptive, and passive: Innate Immunity Everyone is born with innate (or natural) immunity, a type of general protection. Many of the germs that affect
Immunity Humans have three types of immunity innate, adaptive, and passive: Innate Immunity Everyone is born with innate (or natural) immunity, a type of general protection. Many of the germs that affect
2) Macrophages function to engulf and present antigen to other immune cells.
 Immunology The immune system has specificity and memory. It specifically recognizes different antigens and has memory for these same antigens the next time they are encountered. The Cellular Components
Immunology The immune system has specificity and memory. It specifically recognizes different antigens and has memory for these same antigens the next time they are encountered. The Cellular Components
Chapter 16: Circulation
 Section 1 (The Body s Transport System) Chapter 16: Circulation 7 th Grade Cardiovascular system (the circulatory system) includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood carries needed substances to the cells
Section 1 (The Body s Transport System) Chapter 16: Circulation 7 th Grade Cardiovascular system (the circulatory system) includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood carries needed substances to the cells
Ground substance is the component of connective tissue between the cells and the fibers
 Connective Tissues Directions: Insert and install your Interactions: Foundations CD. a. Click the "Contents" button. b. Open the Tissue Level of Organization file. c. Click on Anatomy Overviews. d. Work
Connective Tissues Directions: Insert and install your Interactions: Foundations CD. a. Click the "Contents" button. b. Open the Tissue Level of Organization file. c. Click on Anatomy Overviews. d. Work
Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back
 Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back to the left atria from the left ventricle, blood is pumped
Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back to the left atria from the left ventricle, blood is pumped
Page 1. Introduction The blood vessels of the body form a closed delivery system that begins and ends at the heart.
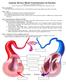 Anatomy Review: Blood Vessel Structure & Function Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction The blood vessels
Anatomy Review: Blood Vessel Structure & Function Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction The blood vessels
Biology 2402 A&P II - Lymphatic System and Immunity Ch. 14
 Biology 2402 A&P II - Lymphatic System and Immunity Ch. 14 Functions: Fluid balance by returning excess tissue fluid to the blood; returning solutes (especially plasma proteins) to the blood; filter body
Biology 2402 A&P II - Lymphatic System and Immunity Ch. 14 Functions: Fluid balance by returning excess tissue fluid to the blood; returning solutes (especially plasma proteins) to the blood; filter body
Functions of Blood. Collects O 2 from lungs, nutrients from digestive tract, and waste products from tissues Helps maintain homeostasis
 Blood Objectives Describe the functions of blood Describe blood plasma Explain the functions of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets Summarize the process of blood clotting What is Blood?
Blood Objectives Describe the functions of blood Describe blood plasma Explain the functions of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets Summarize the process of blood clotting What is Blood?
Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture
 I. Histology the study of tissues A. 4 basic tissue types epithelial connective muscle nervous Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture B. Usually found in combinations to form organs. C. As you
I. Histology the study of tissues A. 4 basic tissue types epithelial connective muscle nervous Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture B. Usually found in combinations to form organs. C. As you
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE PULMONARY SYSTEM Section 1 Part B Reading Assignment: Des Jardins - Chapter 1, pp. THE LOWER AIRWAY I.
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE PULMONARY SYSTEM Section 1 Part B Reading Assignment: Des Jardins - Chapter 1, pp. THE LOWER AIRWAY I. Cartilaginous Airways A. Trachea 1. extends from the cricoid cartilage
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE PULMONARY SYSTEM Section 1 Part B Reading Assignment: Des Jardins - Chapter 1, pp. THE LOWER AIRWAY I. Cartilaginous Airways A. Trachea 1. extends from the cricoid cartilage
Divisions of Digestive System. Organs of the Alimentary Canal. Anatomy of the Digestive System: Organs of the Alimentary Canal. CHAPTER 14 p.
 Divisions of Digestive System Anatomy of the Digestive System: Organs of the Alimentary Canal CHAPTER 14 p. 412-423 1. Alimentary Canal or Gastrointestinal Tract (GI)-digests and absorbs food coiled hollow
Divisions of Digestive System Anatomy of the Digestive System: Organs of the Alimentary Canal CHAPTER 14 p. 412-423 1. Alimentary Canal or Gastrointestinal Tract (GI)-digests and absorbs food coiled hollow
10. T and B cells are types of a. endocrine cells. c. lymphocytes. b. platelets. d. complement cells.
 Virus and Immune System Review Directions: Write your answers on a separate piece of paper. 1. Why does a cut in the skin threaten the body s nonspecific defenses against disease? a. If a cut bleeds, disease-fighting
Virus and Immune System Review Directions: Write your answers on a separate piece of paper. 1. Why does a cut in the skin threaten the body s nonspecific defenses against disease? a. If a cut bleeds, disease-fighting
THE GI TRACT IS A CONTINUOUS MULTILAYERED TUBE EXTENDING FROM THE MOUTH TO THE ANUS THAT IS SUPPORTED AND PARTIALLY COVERED BY THE PERITONEUM.
 THE GI TRACT IS A CONTINUOUS MULTILAYERED TUBE EXTENDING FROM THE MOUTH TO THE ANUS THAT IS SUPPORTED AND PARTIALLY COVERED BY THE PERITONEUM. OVERVIEW OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Two groups of organs compose
THE GI TRACT IS A CONTINUOUS MULTILAYERED TUBE EXTENDING FROM THE MOUTH TO THE ANUS THAT IS SUPPORTED AND PARTIALLY COVERED BY THE PERITONEUM. OVERVIEW OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Two groups of organs compose
THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS
 Name Period Date THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS System Function Diagram Major Organs Digestive 1. take in food (ingestion) 2. digest food into smaller molecules and absorb nutrients 3. remove undigestable food
Name Period Date THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS System Function Diagram Major Organs Digestive 1. take in food (ingestion) 2. digest food into smaller molecules and absorb nutrients 3. remove undigestable food
Urinary System Lab Guide
 Urinary System Lab Guide I. Prelab Questions Name 1. Describe the location of the kidneys. 2. Describe the following structures: a. renal cortex b. renal pyramid c. renal column d. minor calyx e. renal
Urinary System Lab Guide I. Prelab Questions Name 1. Describe the location of the kidneys. 2. Describe the following structures: a. renal cortex b. renal pyramid c. renal column d. minor calyx e. renal
The Digestive System. Chapter 16. Introduction. Histological Organization. Overview of Digestive System. Movement and Mixing of Digestive Materials
 The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
White Blood Cells (WBCs) or Leukocytes
 Lec.5 Z.H.Al-Zubaydi Medical Physiology White Blood Cells (WBCs) or Leukocytes Although leukocytes are far less numerous than red blood cells, they are important to body defense against disease. On average,
Lec.5 Z.H.Al-Zubaydi Medical Physiology White Blood Cells (WBCs) or Leukocytes Although leukocytes are far less numerous than red blood cells, they are important to body defense against disease. On average,
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY
 ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
Supplemental Material CBE Life Sciences Education. Su et al.
 Supplemental Material CBE Life Sciences Education Su et al. APPENDIX Human Body's Immune System Test This test consists of 31 questions, with only 1 answer to be selected for each question. Please select
Supplemental Material CBE Life Sciences Education Su et al. APPENDIX Human Body's Immune System Test This test consists of 31 questions, with only 1 answer to be selected for each question. Please select
Lab Exercise 4. Epithelial Tissues. Connective Tissue Proper. What you need to be able to do on the exam after completing this lab exercise:
 Lab Exercise 4 Epithelial Tissues Connective Tissue Proper Textbook Reference: See Chapter 4 What you need to be able to do on the exam after completing this lab exercise: Be able to identify each type
Lab Exercise 4 Epithelial Tissues Connective Tissue Proper Textbook Reference: See Chapter 4 What you need to be able to do on the exam after completing this lab exercise: Be able to identify each type
Chapter 2 - Anatomy & Physiology of the Respiratory System
 Chapter 2 - Anatomy & Physiology of the Respiratory System Written by - AH Kendrick & C Newall 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Gross Anatomy of the Lungs, 2.3 Anatomy of the Thorax, 2.4 Anatomy and Histology of the
Chapter 2 - Anatomy & Physiology of the Respiratory System Written by - AH Kendrick & C Newall 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Gross Anatomy of the Lungs, 2.3 Anatomy of the Thorax, 2.4 Anatomy and Histology of the
The digestive system eliminated waste from the digestive tract. But we also need a way to eliminate waste from the rest of the body.
 Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system 1
Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system 1
Provided by the American Venous Forum: veinforum.org
 CHAPTER 1 NORMAL VENOUS CIRCULATION Original author: Frank Padberg Abstracted by Teresa L.Carman Introduction The circulatory system is responsible for circulating (moving) blood throughout the body. The
CHAPTER 1 NORMAL VENOUS CIRCULATION Original author: Frank Padberg Abstracted by Teresa L.Carman Introduction The circulatory system is responsible for circulating (moving) blood throughout the body. The
CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Lung cancer affects a life-sustaining system of the body, the respiratory system. The respiratory system is responsible for one of the essential
CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Lung cancer affects a life-sustaining system of the body, the respiratory system. The respiratory system is responsible for one of the essential
Tissue Types. 1. Epithelial Tissue (or epithelium) is the lining, covering, and glandular tissue of the body
 Tissue Types A. Tissues 1. Tissues: groups of cells similar in structure and function 2. Four Types of Tissues: a. Epithelium: for covering b. Connective Tissue: for support c. Muscle: for movement d.
Tissue Types A. Tissues 1. Tissues: groups of cells similar in structure and function 2. Four Types of Tissues: a. Epithelium: for covering b. Connective Tissue: for support c. Muscle: for movement d.
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab
 BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
Human Anatomy and Physiology II Laboratory
 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Laboratory The Circulation (Two Weeks) 1 This lab involves two weeks work studying the vasculature of the human body. Both weeks involve the exercise in the lab manual entitled
Human Anatomy and Physiology II Laboratory The Circulation (Two Weeks) 1 This lab involves two weeks work studying the vasculature of the human body. Both weeks involve the exercise in the lab manual entitled
Circulatory System Review
 Circulatory System Review 1. Draw a table to describe the similarities and differences between arteries and veins? Anatomy Direction of blood flow: Oxygen concentration: Arteries Thick, elastic smooth
Circulatory System Review 1. Draw a table to describe the similarities and differences between arteries and veins? Anatomy Direction of blood flow: Oxygen concentration: Arteries Thick, elastic smooth
12.1: The Function of Circulation page 478
 12.1: The Function of Circulation page 478 Key Terms: Circulatory system, heart, blood vessel, blood, open circulatory system, closed circulatory system, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein, aorta, atrioventricular
12.1: The Function of Circulation page 478 Key Terms: Circulatory system, heart, blood vessel, blood, open circulatory system, closed circulatory system, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein, aorta, atrioventricular
Cardiovascular System. Blood Components
 Cardiovascular System Blood Components 1 Components of Blood Formed elements: erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets Plasma: water, proteins, other solutes The components of blood can be divided into two
Cardiovascular System Blood Components 1 Components of Blood Formed elements: erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets Plasma: water, proteins, other solutes The components of blood can be divided into two
Self- Lymphatic Massage for Arm, Breast or Trunk Lymphedema
 Self- Lymphatic Massage for Arm, Breast or Trunk Lymphedema Patient Education Improving health through education The lymphatic system is part of our circulatory system. It helps balance the fluids of our
Self- Lymphatic Massage for Arm, Breast or Trunk Lymphedema Patient Education Improving health through education The lymphatic system is part of our circulatory system. It helps balance the fluids of our
Digestive System AKA. GI System. Overview. GI Process Process Includes. G-I Tract Alimentary Canal
 Digestive System AKA G-I Tract Alimentary Canal Overview GI System Consists of Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, anus About 30 in length Accessory Organs Teeth, tongue,
Digestive System AKA G-I Tract Alimentary Canal Overview GI System Consists of Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, anus About 30 in length Accessory Organs Teeth, tongue,
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin
 Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
Thymus Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand what thymus cancer is and what treatment options are available.
 Thymus Cancer Introduction Thymus cancer is a rare cancer. It starts in the small organ that lies in the upper chest under the breastbone. The thymus makes white blood cells that protect the body against
Thymus Cancer Introduction Thymus cancer is a rare cancer. It starts in the small organ that lies in the upper chest under the breastbone. The thymus makes white blood cells that protect the body against
Inflammation and Healing. Review of Normal Defenses. Review of Normal Capillary Exchange. BIO 375 Pathophysiology
 Inflammation and Healing BIO 375 Pathophysiology Review of Normal Defenses Review of Normal Capillary Exchange 1 Inflammation Inflammation is a biochemical and cellular process that occurs in vascularized
Inflammation and Healing BIO 375 Pathophysiology Review of Normal Defenses Review of Normal Capillary Exchange 1 Inflammation Inflammation is a biochemical and cellular process that occurs in vascularized
Digestive System Digestive Tract
 Digestive System Digestive Tract Dept. of Histology and Embryology 周 莉 教 授 Introduction of digestive system * a long tube extending from the mouth to the anus, and associated with glands. * its main function:
Digestive System Digestive Tract Dept. of Histology and Embryology 周 莉 教 授 Introduction of digestive system * a long tube extending from the mouth to the anus, and associated with glands. * its main function:
Name (print) Name (signature) Period. (Total 30 points)
 AP Biology Worksheet Chapter 43 The Immune System Lambdin April 4, 2011 Due Date: Thurs. April 7, 2011 You may use the following: Text Notes Power point Internet One other person in class "On my honor,
AP Biology Worksheet Chapter 43 The Immune System Lambdin April 4, 2011 Due Date: Thurs. April 7, 2011 You may use the following: Text Notes Power point Internet One other person in class "On my honor,
The Digestive System. Chapter 14. The Digestive System and Body Metabolism. Metabolism. Organs of the Digestive System. Digestion.
 Chapter 14 The Digestive System The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Digestion of ingested food of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of Constructive and degradative cellular activities
Chapter 14 The Digestive System The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Digestion of ingested food of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of Constructive and degradative cellular activities
Immune System Memory Game
 Immune System Memory Game Recommended Age: 12 years old Time: 45 minutes Everyday our bodies come in contact with millions of tiny organisms and particles that could potentially make us sick. Despite this,
Immune System Memory Game Recommended Age: 12 years old Time: 45 minutes Everyday our bodies come in contact with millions of tiny organisms and particles that could potentially make us sick. Despite this,
BLOOD-Chp. Chp.. 6 What are the functions of blood? What is the composition of blood? 3 major types of plasma proteins
 6.1 Blood: An overview BLOOD-Chp Chp.. 6 What are the functions of blood? Transportation: oxygen, nutrients, wastes, carbon dioxide and hormones Defense: against invasion by pathogens Regulatory functions:
6.1 Blood: An overview BLOOD-Chp Chp.. 6 What are the functions of blood? Transportation: oxygen, nutrients, wastes, carbon dioxide and hormones Defense: against invasion by pathogens Regulatory functions:
Maxillary Sinus. (Antrum of Higmore)
 Maxillary Sinus (Antrum of Higmore) The maxillary sinus is a pneumatic space. It is the largest bilateral air sinus located in the body of the maxilla and opens in the middle nasal meatus of the nasal
Maxillary Sinus (Antrum of Higmore) The maxillary sinus is a pneumatic space. It is the largest bilateral air sinus located in the body of the maxilla and opens in the middle nasal meatus of the nasal
The Digestive System. Chapter 15
 The Digestive System Chapter 15 Introduction Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of food so the nutrients can be absorbed by cells Carried out by the digestive system Consists of
The Digestive System Chapter 15 Introduction Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of food so the nutrients can be absorbed by cells Carried out by the digestive system Consists of
Human Digestive System Anatomy
 Human Digestive System Anatomy Biology 104 Objectives: 1. Learn the anatomy of the digestive system. You should be able to find all terms in bold on the human torso models. 2. Relate structure of the system
Human Digestive System Anatomy Biology 104 Objectives: 1. Learn the anatomy of the digestive system. You should be able to find all terms in bold on the human torso models. 2. Relate structure of the system
Digestive System. Gross Anatomy and Physiology
 Digestive System Gross Anatomy and Physiology I. Introduction A. Base Function: Working with the circulatory system the digestive system provides the body with fuel. B. Main players: 1. Digestive tract:
Digestive System Gross Anatomy and Physiology I. Introduction A. Base Function: Working with the circulatory system the digestive system provides the body with fuel. B. Main players: 1. Digestive tract:
Histology. Epithelial Tissue
 Histology Epithelial Tissue Epithelial Tissue Lines internal and external body surfaces Forms glands Epithelial Tissue Little extracellular matrix Attached on one side Avascular Basement membrane Apical
Histology Epithelial Tissue Epithelial Tissue Lines internal and external body surfaces Forms glands Epithelial Tissue Little extracellular matrix Attached on one side Avascular Basement membrane Apical
Just as a plumbing system carries water through a series of
 37 2 Blood and the Lymphatic System Just as a plumbing system carries water through a series of pipes to different parts of a house, the circulatory system carries blood through a series of blood vessels
37 2 Blood and the Lymphatic System Just as a plumbing system carries water through a series of pipes to different parts of a house, the circulatory system carries blood through a series of blood vessels
Exchange solutes and water with cells of the body
 Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
33.1 The Circulatory System
 33.1 The Circulatory System Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the human circulatory system. Describe the structure of the heart and explain how it pumps blood through the body. Name three types
33.1 The Circulatory System Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the human circulatory system. Describe the structure of the heart and explain how it pumps blood through the body. Name three types
Each day about 50% of total blood proteins leak out of the capillaries into tissue fluid and return to blood via lymphatics
 LYMPHATIC SYSTEM CHAPTER 20 The 2 most important functions of the lymphatic system: 1. Maintain fluid balance in the internal environment 2. Immunity 2 systems that need Lymphatic: Cardiovascular Immune
LYMPHATIC SYSTEM CHAPTER 20 The 2 most important functions of the lymphatic system: 1. Maintain fluid balance in the internal environment 2. Immunity 2 systems that need Lymphatic: Cardiovascular Immune
Biol 111 Comparative & Human Anatomy Lab 9: Circulatory System of the Cat Spring 2014
 Biol 111 Comparative & Human Anatomy Lab 9: Circulatory System of the Cat Spring 2014 Philip J. Bergmann Lab Objectives 1. To learn how blood flows through a dual circuit circulation with lungs. 2. To
Biol 111 Comparative & Human Anatomy Lab 9: Circulatory System of the Cat Spring 2014 Philip J. Bergmann Lab Objectives 1. To learn how blood flows through a dual circuit circulation with lungs. 2. To
The Gastrointestinal System It consists of: The digestive tract Mouth Pharynx Oesophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
 The Gastrointestinal System It consists of: The digestive tract Mouth Pharynx Oesophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine The digestive organs Teeth Tongue Salivary glands Liver Gall bladder Pancreas
The Gastrointestinal System It consists of: The digestive tract Mouth Pharynx Oesophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine The digestive organs Teeth Tongue Salivary glands Liver Gall bladder Pancreas
5. Secretion: release of water, acids. Enzymes, buffers by digestive tract.
 Digestive System CH-16 Lecture topics Functions of the digestive system: p. 488. 1. Ingestion: Taking food in 2. Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal p.490. voluntary: swalloing : skeletal
Digestive System CH-16 Lecture topics Functions of the digestive system: p. 488. 1. Ingestion: Taking food in 2. Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal p.490. voluntary: swalloing : skeletal
Circulatory System and Blood
 Circulatory System and Blood 1. Identify the arteries in the diagram and give one function for each. Y: Common carotid artery: sends oxygenated blood to the brain, provide nutrients. X: Subclavian artery:
Circulatory System and Blood 1. Identify the arteries in the diagram and give one function for each. Y: Common carotid artery: sends oxygenated blood to the brain, provide nutrients. X: Subclavian artery:
Anatomy and Physiology
 Learning Activities It is important that you do not lecture all of the time. If you employ a variety of teaching styles, your students will stay focused better and they will find it easier to process the
Learning Activities It is important that you do not lecture all of the time. If you employ a variety of teaching styles, your students will stay focused better and they will find it easier to process the
Blood vessels. transport blood throughout the body
 Circulatory System Parts and Organs Blood vessels transport blood throughout the body Arteries blood vessels that carry blood AWAY from the heart Pulmonary arteries carry the deoxygenated blood from heart
Circulatory System Parts and Organs Blood vessels transport blood throughout the body Arteries blood vessels that carry blood AWAY from the heart Pulmonary arteries carry the deoxygenated blood from heart
By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford
 By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford Body systems Digestive System Circulatory System Respiratory System Excretory System Immune System Reproductive System Nervous System Muscular System Skeletal System Endocrine
By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford Body systems Digestive System Circulatory System Respiratory System Excretory System Immune System Reproductive System Nervous System Muscular System Skeletal System Endocrine
I. The basic function of the digestive system is
 Chapter 15, Digestive System - ANATOMY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM I. The basic function of the digestive system is. This process is called. II. List 2 other names for the digestive tract: A. B. III. The digestive
Chapter 15, Digestive System - ANATOMY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM I. The basic function of the digestive system is. This process is called. II. List 2 other names for the digestive tract: A. B. III. The digestive
Blood, Lymphatic and Immune Systems
 Component 3-Terminology in Healthcare and Public Health Settings Unit 4-Blood, Lymphatic and Immune Systems This material was developed by The University of Alabama at Birmingham, funded by the Department
Component 3-Terminology in Healthcare and Public Health Settings Unit 4-Blood, Lymphatic and Immune Systems This material was developed by The University of Alabama at Birmingham, funded by the Department
Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION
 TORTORA FUNKE CASE Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION Differentiate between innate and acquired immunity. Chapter 17 Specific Defenses of the Host: The Immune Response B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein
TORTORA FUNKE CASE Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION Differentiate between innate and acquired immunity. Chapter 17 Specific Defenses of the Host: The Immune Response B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein
Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology Course Outline, Objectives and Accreditation Information
 201 Webster Building 3411 Silverside Road Wilmington, DE 19810 Phone: 1-888-658-6641 Fax: 1-302-477-9744 learn@corexcel.com www.corexcel.com Course Outline, Objectives and Accreditation Information Chapter
201 Webster Building 3411 Silverside Road Wilmington, DE 19810 Phone: 1-888-658-6641 Fax: 1-302-477-9744 learn@corexcel.com www.corexcel.com Course Outline, Objectives and Accreditation Information Chapter
UNIT 3 : MAINTAINING DYNAMIC EQUILIBRIUM
 BIOLOGY - 2201 UNIT 3 : MAINTAINING DYNAMIC EQUILIBRIUM What happens to your body as you run? Breathing, heart rate, temperature, muscle pain, thirsty... Homeotasis Homeostasis is the process of maintaining
BIOLOGY - 2201 UNIT 3 : MAINTAINING DYNAMIC EQUILIBRIUM What happens to your body as you run? Breathing, heart rate, temperature, muscle pain, thirsty... Homeotasis Homeostasis is the process of maintaining
Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues
 Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues Lab #3 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 28 Introduction...... 28 Activity 1: Eukaryotic Cell Structure... 29 Activity 2: Perspectives on Tissue Preparations.
Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues Lab #3 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 28 Introduction...... 28 Activity 1: Eukaryotic Cell Structure... 29 Activity 2: Perspectives on Tissue Preparations.
Blood Vessels and Circulation
 13 Blood Vessels and Circulation FOCUS: Blood flows from the heart through the arterial blood vessels to capillaries, and from capillaries back to the heart through veins. The pulmonary circulation transports
13 Blood Vessels and Circulation FOCUS: Blood flows from the heart through the arterial blood vessels to capillaries, and from capillaries back to the heart through veins. The pulmonary circulation transports
Organ Systems Overview
 E x e r c i s e 2 Organ Systems Overview Time Allotment: 1½ hours (rat dissection: 1 hour; if performing reproductive system dissection, ½ hour each for male and female; dissectible human torso model:
E x e r c i s e 2 Organ Systems Overview Time Allotment: 1½ hours (rat dissection: 1 hour; if performing reproductive system dissection, ½ hour each for male and female; dissectible human torso model:
P a g e 52 A & P II SWARTZ NOTES Page 52
 P a g e 52 A & P II SWARTZ NOTES Page 52 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY The lymphatic system consists of a fluid called lymph, vessels that convey lymph called lymphatics, and a number of structures
P a g e 52 A & P II SWARTZ NOTES Page 52 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY The lymphatic system consists of a fluid called lymph, vessels that convey lymph called lymphatics, and a number of structures
ANIMALS FORM & FUNCTION BODY DEFENSES NONSPECIFIC DEFENSES PHYSICAL BARRIERS PHAGOCYTES. Animals Form & Function Activity #4 page 1
 AP BIOLOGY ANIMALS FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #4 NAME DATE HOUR BODY DEFENSES NONSPECIFIC DEFENSES PHYSICAL BARRIERS PHAGOCYTES Animals Form & Function Activity #4 page 1 INFLAMMATORY RESPONSE ANTIMICROBIAL
AP BIOLOGY ANIMALS FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #4 NAME DATE HOUR BODY DEFENSES NONSPECIFIC DEFENSES PHYSICAL BARRIERS PHAGOCYTES Animals Form & Function Activity #4 page 1 INFLAMMATORY RESPONSE ANTIMICROBIAL
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 2 ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 2 ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY Human beings are arguably the most complex organisms on this planet. Imagine billions of microscopic parts, each with its own identity,
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 2 ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY Human beings are arguably the most complex organisms on this planet. Imagine billions of microscopic parts, each with its own identity,
Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide
 Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Define the terms anatomy and physiology. List and discuss in order of increasing complexity, the body from the cell to the whole organism. Define the
Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Define the terms anatomy and physiology. List and discuss in order of increasing complexity, the body from the cell to the whole organism. Define the
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION
 CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot
 Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
Each gland has at least one duct that takes saliva to the oral cavity.
 kufa university Physiology College of Nursing first year student Ass. Lect :- Hisham Qassem M. Lecture No :-3 The Digestive System Digestive system consists of: 1. Gastrointestinal Tract (GIT). 2. Accessory
kufa university Physiology College of Nursing first year student Ass. Lect :- Hisham Qassem M. Lecture No :-3 The Digestive System Digestive system consists of: 1. Gastrointestinal Tract (GIT). 2. Accessory
CHAPTER 20: URINARY SYSTEM
 OBJECTIVES: 1. Name the major function of the urinary system, and name and locate (on a diagram) the organs that compose the system. 2. Explain what the term renal refers to. 3. Define the term retroperitoneal.
OBJECTIVES: 1. Name the major function of the urinary system, and name and locate (on a diagram) the organs that compose the system. 2. Explain what the term renal refers to. 3. Define the term retroperitoneal.
