In the management of primary brain gliomas, accurate
|
|
|
- Madison French
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Correlation of F-FLT Uptake with Tumor Grade and Ki-67 Immunohistochemistry in Patients with Newly Diagnosed and Recurrent Gliomas Yuka Yamamoto 1, Yuko Ono 1, Fumitoshi Aga 1, Nobuyuki Kawai 2, Nobuyuki Kudomi 3, and Yoshihiro Nishiyama 1 1 Department of Radiology, Faculty of Medicine, Kagawa University, Kagawa, Japan; 2 Department of Neurosurgery, Faculty of Medicine, Kagawa University, Kagawa, Japan; and 3 Department of Medical Physics, Faculty of Medicine, Kagawa University, Kagawa, Japan We evaluated 39-deoxy-39- F-fluorothymidine ( F-FLT) uptake in patients with newly diagnosed and recurrent gliomas and correlated the results with tumor grade and proliferative activity. Methods: F-FLT PET was investigated retrospectively in 56 patients, including 36 with newly diagnosed gliomas and 20 with recurrent gliomas. The standardized uptake values for tumor and normal contralateral hemisphere were calculated, and the tumor-to-normal (T/N) ratio was determined. Tumor grading and proliferative activity were estimated in tissue specimens. Results: There was a significant difference in T/N ratio among different grades of newly diagnosed gliomas and between low- and highgrade newly diagnosed and recurrent gliomas. F-FLT uptake correlated more strongly with the proliferative activity in newly diagnosed gliomas than in recurrent gliomas. Conclusion: F-FLT PET seems to be useful in the noninvasive assessment of grade and proliferation in gliomas, especially newly diagnosed gliomas. Key Words: F-FLT; PET; glioma; proliferation J Nucl Med 2012; 53: DOI: /jnumed In the management of primary brain gliomas, accurate pathologic grading of the primary lesion is essential, since histologic features are a major independent prognostic factor next to patient age and performance status (1). Because tissue sampling is often obtained by stereotactic biopsy and, therefore, represents only a small part of the primary tumor, there is a probability that the true tumor grade will be underestimated (2). Thus, noninvasive imaging-based technology for the detection of malignant progression is required to select the best possible treatment regimen. PET with the glucose analog F-FDG gives metabolic information on the whole tumor in vivo and can guide stereotactic biopsies toward the most metabolically active part of the tumor (3). On F-FDG PET scans, high-grade brain tumors show F-FDG accumulation similar to that of normal gray matter, whereas low-grade brain tumors exhibit F-FDG activity similar to that of white matter. Therefore, high-grade tumors may be obscured by adjacent cortical activity, and low-grade tumors may not be distinguishable from adjacent normal white matter (4). 11 C-methionine, an amino acid, is another PET tracer that can be used for brain tumor imaging (3,5,6). 39-deoxy- 39- F-fluorothymidine ( F-FLT) has been investigated as a promising PET tracer for evaluating tumor proliferating activity in brain tumors (5 13). F-FLT is trapped within the cytosol after being monophosphorylated by thymidine kinase-1, a principle enzyme in the salvage pathway of DNA synthesis (14). Therefore, the accumulation of F- FLT is dependent on the presence of thymidine kinase-1, which is closely associated with cellular proliferation. Although Jacobs et al. (6) evaluated F-FLT PET, including kinetic modeling, in newly diagnosed and recurrent gliomas, they analyzed the data of both groups together. In several clinical studies, F-FLT has been validated for evaluation of tumor grade and cellular proliferation in newly diagnosed gliomas (5,10). To our knowledge, this is the first clinical study to compare these characteristics between newly diagnosed and recurrent gliomas using F- FLT PET. The purpose of this study was to retrospectively evaluate F-FLT uptake in patients with newly diagnosed and recurrent gliomas and to correlate the results with tumor grade and proliferative activity as indicated by the Ki-67 index. MATERIALS AND METHODS Received Feb., 2012; revision accepted Jul. 5, For correspondence and reprints contact: Yuka Yamamoto, Department of Radiology, Faculty of Medicine, Kagawa University, Ikenobe, Miki-cho, Kita-gun, Kagawa , Japan. yuka@kms.ac.jp Published online Oct., COPYRIGHT ª 2012 by the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging, Inc. Patients This study was approved by our institutional review board, and written informed consent was obtained from all patients. A total of 56 patients (22 men, 34 women; mean age, 52.9 y; age range, y) with brain gliomas who underwent F-FLT PET between June 2006 and August 2011 were retrospectively F-FLT PET IN GLIOMA Yamamoto et al. 1911
2 TABLE 1 Clinical Characteristics of 56 Patients with Brain Gliomas Characteristic Newly diagnosed (n 5 36) Recurrent (n 5 20) Sex Male 14 8 Female Age (y) Mean Range Tumor World Health Organization grade II 10 4 III 7 4 IV Initial therapy Surgery 4 Surgery/chemotherapy/ 12 radiotherapy Surgery/radiotherapy 4 selected. The clinical characteristics of the patients investigated are shown in Table 1. Of the patients, 36 had newly diagnosed gliomas and 20 had recurrent gliomas that had been treated previously. Among the latter 20 patients, 4 had been treated with surgery; 12 with surgery, chemotherapy, and radiotherapy; and 4 with surgery and radiotherapy. The median interval between the initial diagnosis and the recurrence was 105 wk (range, wk). Pathologic diagnosis had been obtained by stereotactic biopsy or open surgery. The median interval between the F-FLT PET scan and the pathologic diagnosis was 9 d (range, 1 42 d) for newly diagnosed gliomas and 14 d (range, 6 30 d) for recurrent gliomas. The tumor was graded according to the World Health Organization classification for neuroepithelial tumors (15). The distribution of tumor grades and types according to the World Health Organization classification was as follows: 12 grade II astrocytomas, 1 grade II oligoastrocytoma, 1 grade II ependymoma, 7 grade III anaplastic astrocytomas, 4 grade III anaplastic oligoastrocytomas, and 31 grade IV glioblastomas. F-FLT Synthesis and PET F-FLT was synthesized using the method described by Machulla et al. (16). The radiochemical purity of the produced F-FLT was greater than 98%. All acquisitions were performed using an ECAT EXACT HR1 scanner (Siemens Medical Solutions, USA, Inc.). PET scans were acquired in the 3-dimensional mode. Sixty minutes after an intravenous injection of F-FLT (3.7 MBq/kg), a 5-min transmission scan was obtained using an external source of 68 Ge for the purpose of attenuation correction. This acquisition was immediately followed by an emission scan for 15 min. PET images were reconstructed with ordered-subset expectation maximization using 6 iterations and 16 subsets. Data Analysis The images were visually analyzed by 2 experienced nuclear physicians independently, with side-by-side reference to MR or CT images for exact localization of the tumor. Any difference of opinion was resolved by consensus. Tumor lesions were identified as areas of focally increased uptake, exceeding that of normal brain background. Semiquantitative analysis was performed using the standardized uptake value (SUV). The region of interest was placed over the entire tumor using the transverse PET image. For the reference tissue, a circular region of interest of mm was manually placed on the uninvolved contralateral hemisphere in the plane that showed maximum F-FLT tumor uptake. Radioactivity concentrations measured in the region of interest were normalized to injected dose per patient s body weight by calculation of SUV. The maximal SUV for tumor and the mean SUV for reference tissue were calculated. The tumor to contralateral normal brain tissue (T/N) ratio was determined by dividing the tumor SUV by the SUV of the contralateral hemisphere. Ki-67 Immunohistochemistry Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections of resected specimens from brain tumors were made for immunohistochemical staining. The Ki-67 index was estimated as the percentage of Ki- 67 positive cell nuclei per 500 1,000 cells in the region of the tumor with the greatest staining density. Statistical Analysis All semiquantitative data were expressed as mean 6 SD. Differences in T/N ratio among glioma grades were compared using ANOVA. The significance of individual differences was evaluated using the Tukey honestly significant difference test. Differences in T/N ratio between low- and high-grade gliomas were analyzed using the Mann Whitney U test. The Ki-67 index and the T/N ratio were compared using linear regression analysis. Differences were considered statistically significant at a P value of less than RESULTS F-FLT Uptake and Glioma Grade In newly diagnosed gliomas, F-FLT PET detected 2 of 10 grade II gliomas, 5 of 7 grade III gliomas, and all 19 grade IV gliomas. The mean (6SD) T/N ratios were in grade II gliomas, in grade III gliomas, and in grade IV gliomas. There was a significant difference between gliomas of grades II and IV (P, 0.001) and gliomas of grades III and IV (P, 0.004) (Fig. 1A). No significant difference in T/N ratio was noted between gliomas of grades II and III (P ). When grades III and IV were grouped together as high-grade gliomas, the mean (6SD) value of T/N ratio in high-grade gliomas ( ) was significantly higher than that in low-grade gliomas ( ) (P, 0.001). Figure 2 shows a typical case of newly diagnosed grade IV glioma. In recurrent gliomas, F-FLT PET detected 1 of 4 grade II gliomas, 3 of 4 grade III gliomas, and all 12 grade IV gliomas. The mean (6SD) T/N ratios were in grade II gliomas, in grade III gliomas, and in grade IV gliomas. No significant differences in T/N ratio were noted among glioma grades (II vs. III, P ; II vs THE JOURNAL OF NUCLEAR MEDICINE Vol. 53 No. 12 December 2012
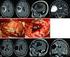
3 FIGURE 1. Relationship between World Health Organization grade and F-FLT T/N ratio in newly diagnosed gliomas (A) and recurrent gliomas (B). Box plots show median, 25th percentile, and 75th percentile of data, with minimum and maximum represented by whiskers. *P, as compared with grade IV group. **P, as compared with grade IV group. IV, P ; III vs. IV, P ) (Fig. 1B). There was a significant difference between the mean (6SD) T/N ratios in high-grade gliomas ( ) and low-grade gliomas ( ) (P, 0.01) although P value was weaker than that for newly diagnosed gliomas. F-FLT Uptake and Ki-67 Immunohistochemistry In newly diagnosed gliomas, linear regression analysis indicated a significant correlation between T/N ratio and the Ki-67 index (r , P, 0.001; Fig. 3A). In recurrent gliomas, although there was a correlation between T/N ratio and the Ki-67 index (r , P, 0.03; Fig. 3B), the correlation was weaker. DISCUSSION In the present study, we evaluated F-FLT uptake in patients with newly diagnosed and recurrent gliomas. F-FLT PET was found to be useful in the assessment of grade and proliferation in gliomas, especially newly diagnosed gliomas. With respect to the mechanism of F-FLT uptake by brain tumors, breakdown of the blood brain barrier (BBB) has been reported to contribute considerably to tracer uptake (9). F-FLT permeates the cell membrane by facilitated diffusion (17) and is phosphorylated by thymidine kinase-1, which leads to intracellular trapping (17,). During DNA synthesis, the concentration of thymidine kinase-1 increases about 10-fold and is, therefore, an accurate reflection of cellular proliferation (). Choi et al. (8) suggested that both thymidine kinase-1 activity and BBB permeability are major factors in F-FLT uptake by brain lesions. However, Jacobs et al. (6) reported that F-FLT could detect tumor regions that did not present with gross destruction of the BBB as shown by gadopentetate dimeglumine enhancement on MRI. The regional distribution of F-FLT uptake with and without gadopentetate dimeglumine enhancement on MRI suggests the presence of various tissue compartments in which F-FLT uptake may be due to breakdown of the BBB, increased transport, increased proliferation, or a variable combination of these mechanisms. Unfortunately, we did not take the opportunity to compare F-FLT PET images with gadopentetate dimeglumine enhancement or any other MRI parameter. Further studies are needed to evaluate the relationship between F-FLT uptake and gadopentetate dimeglumine enhancement in newly diagnosed and recurrent gliomas. In the present study, the T/N ratio of high-grade gliomas was significantly higher than that of either newly diagnosed or recurrent low-grade gliomas. Although this finding is FIGURE 2. Radiologic images of 27-y-old woman with newly diagnosed World Health Organization grade IV glioblastoma. Transverse T1-weighted MR image with contrast enhancement (A) shows enhanced mass in right frontal lobe. Transverse F- FLT PET image (B) shows increased uptake (T/N ratio ) in tumor. F-FLT PET IN GLIOMA Yamamoto et al. 1913
4 FIGURE 3. Linear regression analysis demonstrates significant correlation between F-FLT T/N ratio and proliferative activity (Ki-67 index) in newly diagnosed gliomas (A) (r , P, 0.001) and recurrent gliomas (B) (r , P, 0.03). similar to those from previous studies by Chen et al. (7) and Choi et al. (8), T/N ratios were very different. This difference might be explained by the inhomogeneity of the examination protocols such as differences in the start time for imaging, the calculation method for SUV, or the patient populations. Their studies (7,8) analyzed the data of newly diagnosed and recurrent tumors together. On the other hand, in the present study, data for newly diagnosed and recurrent gliomas were analyzed separately. Furthermore, in the present study, there was a significant difference in T/N ratio among the grades of newly diagnosed gliomas but not of recurrent gliomas. Of the 20 patients with recurrent gliomas, 16 (80%) had received chemoradiotherapy or radiotherapy before the PET study. Radiation and chemoradiotherapy, used as an adjuvant therapy for gliomas, can cause loosening of endothelial tight junctions, vascular leakage, or endothelial cell death and thus can increase vascular permeability (19). Radiation could also act to increase vascular permeability not only in the BBB but also in the blood tumor barrier (19). We suspect that in addition to increased proliferation, breakdown of the BBB and blood tumor barrier in recurrent gliomas contributes to the degree of F-FLT uptake. Furthermore, there is a biologic difference between newly diagnosed and recurrent gliomas. In recurrent gliomas, recurrent tumor and treatment-induced necrosis frequently coexist. Barwick et al. (20), in a review article, mentioned that F- FLT uptake reflected tumor proliferation when compared with histopathologic Ki-67 expression in non small cell lung cancer, colorectal cancer, lymphoma, and gliomas. Choi et al. (8) evaluated F-FLT uptake and proliferative activity in 9 patients with gliomas, including 1 recurrent glioma. They showed a significant correlation (r ) between F-FLT uptake and Ki-67 index. Chen et al. (7) evaluated F-FLT uptake and proliferative activity in 14 patients with gliomas, including 6 previously treated with radiation. They also showed a significant correlation (r ) between F-FLT uptake and Ki-67 index. In the present study, although F-FLT uptake correlated significantly with Ki-67 index in both newly diagnosed and recurrent gliomas, the correlation in recurrent gliomas was not as significant as that in newly diagnosed gliomas. In addition to increased proliferation, breakdown of the BBB and blood tumor barrier may contribute to the degree of F-FLT uptake in previously treated gliomas. Kinetic analysis of F-FLT PET might clarify whether the transport effect or metabolic trapping largely contributes to the increased uptake of F- FLT in the tumor (6). Jacobs et al. (6) compared F-FLT with 11 C-methionine in gliomas and showed that 11 C-methionine was more sensitive for tumor detection. An amino acid PET tracer such as 11 C- methionine and MRI may be the best mode for the initial diagnosis of gliomas. In contrast to amino acid tracers, F- FLT allows for noninvasive assessment of tumor proliferation. Schiepers et al. (13) evaluated the kinetics of F-FLT during treatment monitoring of recurrent high-grade glioma. Further studies including kinetic analysis are needed to evaluate the clinical usefulness of F-FLT PET in gliomas for assessing therapeutic response and survival in larger study groups. CONCLUSION F-FLT PET seems to be useful in the noninvasive assessment of grade and proliferation in gliomas, especially newly diagnosed gliomas. F-FLT PET might not provide information at the initial diagnosis of gliomas additional to that provided by amino acid PET tracers and MRI. Further studies might identify the role of F-FLT in assessing the response to antiproliferative treatment in patients with recurrent gliomas. DISCLOSURE STATEMENT The costs of publication of this article were defrayed in part by the payment of page charges. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked advertisement in accordance with USC section ACKNOWLEDGMENT No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported THE JOURNAL OF NUCLEAR MEDICINE Vol. 53 No. 12 December 2012
5 REFERENCES 1. DeAngelis LM. Brain tumors. N Engl J Med. 2001;344: Ceyssens S, Van Laere K, de Groot T, Goffin J, Bormans G, Mortelmans L. [ 11 C] methionine PET, histopathology, and survival in primary brain tumors and recurrence. Am J Neuroradiol. 2006;27: Pirotte B, Goldman S, Massager N, et al. Comparison of F-FDG and 11 C- methionine for PET guided stereotactic brain biopsy of gliomas. J Nucl Med. 2004;45: Wong TZ, van der Westhuizen GJ, Coleman RE. Positron emission tomography imaging of brain tumors. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 2002;12: Hatakeyama T, Kawai N, Nishiyama Y, et al. 11 C-methionine (MET) and F- fluorothymidine (FLT) PET in patients with newly diagnosed glioma. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2008;35: Jacobs AH, Thomas A, Kracht LW, et al. F-fluoro-L-thymidine and 11 C-methylmethionine as markers of increased transport and proliferation in brain tumors. J Nucl Med. 2005;46: Chen W, Cloughesy T, Kamdar N, et al. Imaging proliferation in brain tumors with F-FLT PET: comparison with F-FDG. J Nucl Med. 2005;46: Choi SJ, Kim JS, Kim JH, et al. [ F]39-deoxy-39-fluorothymidine PET for the diagnosis and grading of brain tumors. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2005;32: Yamamoto Y, Wong TZ, Turkington TG, et al. 39-deoxy-39-[F-]fluorothymidine positron emission tomography in patients with recurrent glioblastoma multiforme: comparison with Gd-DTPA enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Mol Imaging Biol. 2006;8: Ullrich R, Backes H, Li H, et al. Glioma proliferation as assessed by 39-fluoro- 39-deoxy-l-thymidine positron emission tomography in patients with newly diagnosed high-grade glioma. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14: Spence AM, Muzi M, Link JM, et al. NCI-sponsored trial for evaluation of safety and preliminary efficacy of 39-deoxy-39-[F-]fluorothymidine (FLT) as a marker of proliferation in patients with recurrent gliomas: preliminary efficacy studies. Mol Imaging Biol. 2009;11: Chen W, Dalaloye S, Silverman DHS, et al. Predicting treatment response of malignant gliomas to bevacizumab and irinotecan by imaging proliferation with [ F]fluorothymidine positron emission tomography: a pilot study. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25: Schiepers C, Dahlbom M, Chen W, et al. Kinetics of 39-deoxy-39- F-fluorothymidine during treatment monitoring of recurrent high-grade glioma. J Nucl Med. 2010;51: Rasey JS, Grierson JR, Wiens LW, et al. Validation of FLT uptake as a measure of thymidine kinase-1 activity in A549 carcinoma cells. JNuclMed.2002;43: Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, et al. The 2007 WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta Neuropathol. 2007;114: Machulla HJ, Blocher A, Kuntzsch M, et al. Simplified labeling approach for synthesizing 39-deoxy-39-[ F]fluorothymidine ([ F]FLT). J Radioanal Nucl Chem. 2000;24: Mier W, Haberkorn U, Eisenhut M. [ F]FLT: portrait of a proliferation marker. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2002;29: Grierson JR, Shields AF. Radiosynthesis of 39-deoxy-39-[ F]fluorothymidine: [ F] FLT for imaging of cellular proliferation in vivo. Nucl Med Biol. 2000;27: Cao Y, Tsien CI, Shen Z, et al. Use of magnetic resonance imaging to assess blood-brain/blood-gliomas barrier opening during conformal radiotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23: Barwick T, Bencherif B, Mountz JM, Avril N. Molecular PET and PET/CT imaging tumour cell proliferation using F- fluoro-l-thymidine: a comprehensive evaluation. Nucl Med Commun. 2009;30: F-FLT PET IN GLIOMA Yamamoto et al. 1915
The imaging of cell proliferation has emerged as an
 Kinetics of 39-Deoxy-39- F-Fluorothymidine During Treatment Monitoring of Recurrent High-Grade Glioma Christiaan Schiepers 1, Magnus Dahlbom 1, Wei Chen 1, Timothy Cloughesy 2, Johannes Czernin 1, Michael
Kinetics of 39-Deoxy-39- F-Fluorothymidine During Treatment Monitoring of Recurrent High-Grade Glioma Christiaan Schiepers 1, Magnus Dahlbom 1, Wei Chen 1, Timothy Cloughesy 2, Johannes Czernin 1, Michael
Detection and staging of recurrent prostate cancer is still one of the important clinical problems in prostate cancer. A rise in PSA or biochemical
 Summary. 111 Detection and staging of recurrent prostate cancer is still one of the important clinical problems in prostate cancer. A rise in PSA or biochemical recurrence (BCR) is the first sign of recurrent
Summary. 111 Detection and staging of recurrent prostate cancer is still one of the important clinical problems in prostate cancer. A rise in PSA or biochemical recurrence (BCR) is the first sign of recurrent
False positive PET in lymphoma
 False positive PET in lymphoma Thomas Krause Introduction and conclusion 2 3 Introduction 4 FDG-PET in staging of lymphoma 34 studies with 2227 Patients CT FDG-PET Sensitivity 63 % 89 % (58%-100%) (63%-100%)
False positive PET in lymphoma Thomas Krause Introduction and conclusion 2 3 Introduction 4 FDG-PET in staging of lymphoma 34 studies with 2227 Patients CT FDG-PET Sensitivity 63 % 89 % (58%-100%) (63%-100%)
Uncontrolled cellular proliferation is a hallmark of neoplasia.
 Imaging Proliferation in Brain Tumors with F-FLT PET: Comparison with F-FDG Wei Chen, MD, PhD 1 ; Timothy Cloughesy, MD 2 ; Nirav Kamdar, BS 1 ; Nagichettiar Satyamurthy, PhD 1 ; Marvin Bergsneider, MD
Imaging Proliferation in Brain Tumors with F-FLT PET: Comparison with F-FDG Wei Chen, MD, PhD 1 ; Timothy Cloughesy, MD 2 ; Nirav Kamdar, BS 1 ; Nagichettiar Satyamurthy, PhD 1 ; Marvin Bergsneider, MD
BEYOND 18 F-FDG: INTRODUCTION TO NEW RADIOPHARMACEUTICALS
 BEYOND F-FDG: INTRODUCTION TO NEW RADIOPHARMACEUTICALS Asti Mattia Nuclear Medicine Department Santa Maria Nuova Hospital, Reggio Emilia, Italy SUMMARY: F-Labelled Choline analogues. Comparison between
BEYOND F-FDG: INTRODUCTION TO NEW RADIOPHARMACEUTICALS Asti Mattia Nuclear Medicine Department Santa Maria Nuova Hospital, Reggio Emilia, Italy SUMMARY: F-Labelled Choline analogues. Comparison between
Malignancy of intracerebral lesions evaluated with
 Journal of Clinical Neuroscience (2005) 12(7), 775 780 0967-5868/$ - see front matter doi:10.1016/j.jocn.2005.07.001 Clinical study Malignancy of intracerebral lesions evaluated with 11 C-methionine-PET
Journal of Clinical Neuroscience (2005) 12(7), 775 780 0967-5868/$ - see front matter doi:10.1016/j.jocn.2005.07.001 Clinical study Malignancy of intracerebral lesions evaluated with 11 C-methionine-PET
PRIMARY GLIOMA (oligodendroglioma, astrocytoma, oligodendroglioma, oligoastrocytoma, including anaplastic, gliosarcoma and glioblastoma multiforme)
 Protocol for Planning and Treatment The process to be followed when a course of chemotherapy is required to treat: PRIMARY GLIOMA (oligodendroglioma, astrocytoma, oligodendroglioma, oligoastrocytoma, including
Protocol for Planning and Treatment The process to be followed when a course of chemotherapy is required to treat: PRIMARY GLIOMA (oligodendroglioma, astrocytoma, oligodendroglioma, oligoastrocytoma, including
PET/CT in Lung Cancer
 PET/CT in Lung Cancer Rodolfo Núñez Miller, M.D. Nuclear Medicine and Diagnostic Imaging Section Division of Human Health International Atomic Energy Agency Vienna, Austria GLOBOCAN 2012 #1 #3 FDG-PET/CT
PET/CT in Lung Cancer Rodolfo Núñez Miller, M.D. Nuclear Medicine and Diagnostic Imaging Section Division of Human Health International Atomic Energy Agency Vienna, Austria GLOBOCAN 2012 #1 #3 FDG-PET/CT
Technological Innovation: High Field Open Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
 Technological Innovation: High Field Open Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Student Investigator: Thomas R. Pace UVM COM Class of 2012 Faculty Mentor: Christopher Filippi Department of Radiology Fletcher
Technological Innovation: High Field Open Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Student Investigator: Thomas R. Pace UVM COM Class of 2012 Faculty Mentor: Christopher Filippi Department of Radiology Fletcher
Apparent Diffusion Coefficients in the Evaluation of High-grade Cerebral Gliomas
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:60 64, January 2001 Apparent Diffusion Coefficients in the Evaluation of High-grade Cerebral Gliomas Mauricio Castillo, J. Keith Smith, Lester Kwock, and Kathy Wilber BACKGROUND
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:60 64, January 2001 Apparent Diffusion Coefficients in the Evaluation of High-grade Cerebral Gliomas Mauricio Castillo, J. Keith Smith, Lester Kwock, and Kathy Wilber BACKGROUND
PET/CT: Basic Principles, Applications in Oncology
 PET/CT: Basic Principles, Applications in Oncology Mabel Djang, HMS III Overview PET Basics and Limitations PET/CT - Advantages and Limitations Applications of PET/CT in oncology Summary 2 Principles of
PET/CT: Basic Principles, Applications in Oncology Mabel Djang, HMS III Overview PET Basics and Limitations PET/CT - Advantages and Limitations Applications of PET/CT in oncology Summary 2 Principles of
SPECT and PET imaging in porcine inflammation and infection models. UCPH pig model network seminar
 SPECT and PET imaging in porcine inflammation and infection models UCPH pig model network seminar Friday November 21. 2014, 8.30 12.00, auditorium A2 70.02, Thorvaldsensvej 40, 1871 Frederiksberg C. See
SPECT and PET imaging in porcine inflammation and infection models UCPH pig model network seminar Friday November 21. 2014, 8.30 12.00, auditorium A2 70.02, Thorvaldsensvej 40, 1871 Frederiksberg C. See
Comparison of Threshold-Based Segmentation Methods on Pre- and Post- Therapy PET Scans
 M. Phillips, S.F. Barrington, D.L.G. Hill, P.K. Marsden 1 Comparison of Threshold-Based Segmentation Methods on Pre- and Post- Therapy PET Scans Michael Phillips 1 Michael.Phillips.1@city.ac.uk Sally F.
M. Phillips, S.F. Barrington, D.L.G. Hill, P.K. Marsden 1 Comparison of Threshold-Based Segmentation Methods on Pre- and Post- Therapy PET Scans Michael Phillips 1 Michael.Phillips.1@city.ac.uk Sally F.
Management of low grade glioma s: update on recent trials
 Management of low grade glioma s: update on recent trials M.J. van den Bent The Brain Tumor Center at Erasmus MC Cancer Center Rotterdam, the Netherlands Low grades Female, born 1976 1 st seizure 2005,
Management of low grade glioma s: update on recent trials M.J. van den Bent The Brain Tumor Center at Erasmus MC Cancer Center Rotterdam, the Netherlands Low grades Female, born 1976 1 st seizure 2005,
L Lang-Lazdunski, A Bille, S Marshall, R Lal, D Landau, J Spicer
 Pleurectomy/decortication, hyperthermic pleural lavage with povidone-iodine and systemic chemotherapy in malignant pleural mesothelioma. A 10-year experience. L Lang-Lazdunski, A Bille, S Marshall, R Lal,
Pleurectomy/decortication, hyperthermic pleural lavage with povidone-iodine and systemic chemotherapy in malignant pleural mesothelioma. A 10-year experience. L Lang-Lazdunski, A Bille, S Marshall, R Lal,
Brain Tumor Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Brain Tumor Treatment Brain Tumors Overview A brain tumor is a group of abnormal cells that grows in or around the brain. Tumors can directly destroy healthy brain cells. They can
Scan for mobile link. Brain Tumor Treatment Brain Tumors Overview A brain tumor is a group of abnormal cells that grows in or around the brain. Tumors can directly destroy healthy brain cells. They can
Continuing Medical Education Article Imaging of Multiple Myeloma and Related Plasma Cell Dyscrasias JNM, July 2012, Volume 53, Number 7
 Continuing Medical Education Article Imaging of Multiple Myeloma and Related Plasma Cell Dyscrasias JNM, July 2012, Volume 53, Number 7 Authors Ronald C. Walker 1,2, Tracy L. Brown 3, Laurie B. Jones-Jackson
Continuing Medical Education Article Imaging of Multiple Myeloma and Related Plasma Cell Dyscrasias JNM, July 2012, Volume 53, Number 7 Authors Ronald C. Walker 1,2, Tracy L. Brown 3, Laurie B. Jones-Jackson
NEW HYBRID IMAGING TECHNOLOGY MAY HAVE BIG POTENTIAL FOR IMPROVING DIAGNOSIS OF PROSTATE CANCER
 Media Release April 7, 2009 For Immediate Release NEW HYBRID IMAGING TECHNOLOGY MAY HAVE BIG POTENTIAL FOR IMPROVING DIAGNOSIS OF PROSTATE CANCER London, Ontario Improved hybrid imaging techniques developed
Media Release April 7, 2009 For Immediate Release NEW HYBRID IMAGING TECHNOLOGY MAY HAVE BIG POTENTIAL FOR IMPROVING DIAGNOSIS OF PROSTATE CANCER London, Ontario Improved hybrid imaging techniques developed
Mississippi Medicaid. Provider Reference Guide. For Part 220. Radiology Services
 Mississippi Medicaid Provider Reference Guide For Part 220 Radiology Services This is a companion document to the Mississippi Administrative Code Title 23 and must be utilized as a reference only. Table
Mississippi Medicaid Provider Reference Guide For Part 220 Radiology Services This is a companion document to the Mississippi Administrative Code Title 23 and must be utilized as a reference only. Table
PET. Can we afford PET-CT. Positron annihilation. PET-CT scanner. PET detection
 PET-CT Can we afford PET-CT John Buscombe New technology Combines functional information-pet anatomical information-ct Machine able to perform both studies in single imaging episode PET imaging depends
PET-CT Can we afford PET-CT John Buscombe New technology Combines functional information-pet anatomical information-ct Machine able to perform both studies in single imaging episode PET imaging depends
PET/CT in Lymphoma. Ur Metser, M.D. Division Head, Molecular Imaging Joint Department of Medical Imaging, UHN- MSH- WCH University of Toronto
 PET/CT in Lymphoma Ur Metser, M.D. Division Head, Molecular Imaging Joint Department of Medical Imaging, UHN- MSH- WCH University of Toronto Outline 1. Introduction: PET/CT, how does it work? 2.Current
PET/CT in Lymphoma Ur Metser, M.D. Division Head, Molecular Imaging Joint Department of Medical Imaging, UHN- MSH- WCH University of Toronto Outline 1. Introduction: PET/CT, how does it work? 2.Current
Treating Thyroid Cancer using I-131 Maximum Tolerable Dose Method
 Treating Thyroid Cancer using I-131 Maximum Tolerable Dose Method Christopher Martel, M.Sc., CHP Lisa Thornhill,, NRRPT, RT(NM) Boston University Medical Center Thyroid Carcinoma New cases and deaths in
Treating Thyroid Cancer using I-131 Maximum Tolerable Dose Method Christopher Martel, M.Sc., CHP Lisa Thornhill,, NRRPT, RT(NM) Boston University Medical Center Thyroid Carcinoma New cases and deaths in
Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT)
 Scan for mobile link. Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) Intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) uses linear accelerators to safely and painlessly deliver precise radiation doses to a tumor while
Scan for mobile link. Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) Intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) uses linear accelerators to safely and painlessly deliver precise radiation doses to a tumor while
Integrating Chemotherapy and Liver Surgery for the Management of Colorectal Metastases
 I Congresso de Oncologia D Or July 5-6, 2013 Integrating Chemotherapy and Liver Surgery for the Management of Colorectal Metastases Michael A. Choti, MD, MBA, FACS Department of Surgery Johns Hopkins University
I Congresso de Oncologia D Or July 5-6, 2013 Integrating Chemotherapy and Liver Surgery for the Management of Colorectal Metastases Michael A. Choti, MD, MBA, FACS Department of Surgery Johns Hopkins University
RESEARCH EDUCATE ADVOCATE. Just Diagnosed with Melanoma Now What?
 RESEARCH EDUCATE ADVOCATE Just Diagnosed with Melanoma Now What? INTRODUCTION If you are reading this, you have undergone a biopsy (either of a skin lesion or a lymph node) or have had other tests in which
RESEARCH EDUCATE ADVOCATE Just Diagnosed with Melanoma Now What? INTRODUCTION If you are reading this, you have undergone a biopsy (either of a skin lesion or a lymph node) or have had other tests in which
The Need for Accurate Lung Cancer Staging
 The Need for Accurate Lung Cancer Staging Peter Baik, DO Thoracic Surgery Cancer Treatment Centers of America Oklahoma Osteopathic Association 115th Annual Convention Financial Disclosures: None 2 Objectives
The Need for Accurate Lung Cancer Staging Peter Baik, DO Thoracic Surgery Cancer Treatment Centers of America Oklahoma Osteopathic Association 115th Annual Convention Financial Disclosures: None 2 Objectives
Avastin in breast cancer: Summary of clinical data
 Avastin in breast cancer: Summary of clinical data Worldwide, over one million people are diagnosed with breast cancer every year 1. It is the most frequently diagnosed cancer in women 1,2, and the leading
Avastin in breast cancer: Summary of clinical data Worldwide, over one million people are diagnosed with breast cancer every year 1. It is the most frequently diagnosed cancer in women 1,2, and the leading
Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Staging and Prognosis of Three Separate Cases.
 Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Staging and Prognosis of Three Separate Cases. Abstract This paper describes the staging, imaging, treatment, and prognosis of renal cell carcinoma. Three case studies
Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Staging and Prognosis of Three Separate Cases. Abstract This paper describes the staging, imaging, treatment, and prognosis of renal cell carcinoma. Three case studies
Glioblastoma (cancer affecting the brain) A guide for journalists on glioblastoma and its treatment
 Glioblastoma (cancer affecting the brain) A guide for journalists on glioblastoma and its treatment Section 1 Glioblastoma Section 2 Epidemiology and prognosis Section 3 Treatment Contents Contents 2 3
Glioblastoma (cancer affecting the brain) A guide for journalists on glioblastoma and its treatment Section 1 Glioblastoma Section 2 Epidemiology and prognosis Section 3 Treatment Contents Contents 2 3
HER2 Status: What is the Difference Between Breast and Gastric Cancer?
 Ask the Experts HER2 Status: What is the Difference Between Breast and Gastric Cancer? Bharat Jasani MBChB, PhD, FRCPath Marco Novelli MBChB, PhD, FRCPath Josef Rüschoff, MD Robert Y. Osamura, MD, FIAC
Ask the Experts HER2 Status: What is the Difference Between Breast and Gastric Cancer? Bharat Jasani MBChB, PhD, FRCPath Marco Novelli MBChB, PhD, FRCPath Josef Rüschoff, MD Robert Y. Osamura, MD, FIAC
Adjuvant Therapy Non Small Cell Lung Cancer. Sunil Nagpal MD Director, Thoracic Oncology Jan 30, 2015
 Adjuvant Therapy Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Sunil Nagpal MD Director, Thoracic Oncology Jan 30, 2015 No Disclosures Number of studies Studies Per Month 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 1 2 3
Adjuvant Therapy Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Sunil Nagpal MD Director, Thoracic Oncology Jan 30, 2015 No Disclosures Number of studies Studies Per Month 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 1 2 3
What is Glioblastoma? How is GBM classified according to the WHO Grading System? What risk factors pertain to GBM?
 GBM (English) What is Glioblastoma? Glioblastoma or glioblastoma multiforme is one of the most common brain tumors accounting for approximately 12 to 15 percent of all brain tumors. The name of the tumor
GBM (English) What is Glioblastoma? Glioblastoma or glioblastoma multiforme is one of the most common brain tumors accounting for approximately 12 to 15 percent of all brain tumors. The name of the tumor
Technology appraisal guidance Published: 27 June 2007 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta121
 Carmustine implants and temozolomide for the treatment of newly diagnosed high-grade glioma Technology appraisal guidance Published: 27 June 2007 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta121 NICE 2007. All rights reserved.
Carmustine implants and temozolomide for the treatment of newly diagnosed high-grade glioma Technology appraisal guidance Published: 27 June 2007 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta121 NICE 2007. All rights reserved.
Malignant Pleural Diseases Advances Clinicians Should Know F Gleeson
 Malignant Pleural Diseases Advances Clinicians Should Know F Gleeson The following relevant disclosures, conflicts of interest and/ or financial relationships exist related to this presentation: Consultant
Malignant Pleural Diseases Advances Clinicians Should Know F Gleeson The following relevant disclosures, conflicts of interest and/ or financial relationships exist related to this presentation: Consultant
Targeting Specific Cell Signaling Pathways for the Treatment of Malignant Peritoneal Mesothelioma
 The Use of Kinase Inhibitors: Translational Lab Results Targeting Specific Cell Signaling Pathways for the Treatment of Malignant Peritoneal Mesothelioma Sheelu Varghese, Ph.D. H. Richard Alexander, M.D.
The Use of Kinase Inhibitors: Translational Lab Results Targeting Specific Cell Signaling Pathways for the Treatment of Malignant Peritoneal Mesothelioma Sheelu Varghese, Ph.D. H. Richard Alexander, M.D.
Inclusion of Biological Information in Treatment Planning Optimization Dag Rune Olsen
 Inclusion of Biological Information in Treatment Planning Optimization Dag Rune Olsen Institute for Cancer Research, Norwegian Radium Hospital, University of Oslo Theragnostics biological conformality
Inclusion of Biological Information in Treatment Planning Optimization Dag Rune Olsen Institute for Cancer Research, Norwegian Radium Hospital, University of Oslo Theragnostics biological conformality
Variations in PET/CT Methodology for Oncologic Imaging at U.S. Academic Medical Centers: An Imaging Response Assessment Team Survey
 Variations in PET/CT Methodology for Oncologic Imaging at U.S. Academic Medical Centers: An Imaging Response Assessment Team Survey Michael M. Graham 1, Ramsey D. Badawi 2, and Richard L. Wahl 3 1 University
Variations in PET/CT Methodology for Oncologic Imaging at U.S. Academic Medical Centers: An Imaging Response Assessment Team Survey Michael M. Graham 1, Ramsey D. Badawi 2, and Richard L. Wahl 3 1 University
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF LUNG CANCER
 GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF LUNG CANCER BY Ali Shamseddine, MD (Coordinator); as04@aub.edu.lb Fady Geara, MD Bassem Shabb, MD Ghassan Jamaleddine, MD CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR THE TREATMENT
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF LUNG CANCER BY Ali Shamseddine, MD (Coordinator); as04@aub.edu.lb Fady Geara, MD Bassem Shabb, MD Ghassan Jamaleddine, MD CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR THE TREATMENT
ARTICLE IN PRESS. European Journal of Radiology xxx (2008) xxx xxx. Initial experience
 European Journal of Radiology xxx (2008) xxx xxx 18 F-FDOPA PET/MRI fusion in patients with primary/recurrent gliomas: Initial experience Carlos J. Ledezma a, Wei Chen b, Victor Sai c, Bonnie Freitas a,
European Journal of Radiology xxx (2008) xxx xxx 18 F-FDOPA PET/MRI fusion in patients with primary/recurrent gliomas: Initial experience Carlos J. Ledezma a, Wei Chen b, Victor Sai c, Bonnie Freitas a,
Anatomic locations in high grade glioma
 256 Oslobanu, Florian Anatomic locations in high grade glioma Anatomic locations in high grade glioma A. Oslobanu 1, St.I. Florian 2 University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Iuliu Hatieganu Cluj-Napoca 1 Assistant
256 Oslobanu, Florian Anatomic locations in high grade glioma Anatomic locations in high grade glioma A. Oslobanu 1, St.I. Florian 2 University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Iuliu Hatieganu Cluj-Napoca 1 Assistant
Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW
 Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW Kidney cancer is the third most common genitourinary cancer in adults. There are approximately 54,000 new cancer cases each year in the United States, and the incidence of kidney
Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW Kidney cancer is the third most common genitourinary cancer in adults. There are approximately 54,000 new cancer cases each year in the United States, and the incidence of kidney
Multimodality imaging of brain tumours: High Grade Brain Tumours
 20th Advance Course Multimodality imaging of brain tumours: High Grade Brain Tumours Àlex Rovira Unitat de Ressonància Magnètica Servei de Radiologia Hospital Vall d Hebron. Barcelona. alex.rovira@idi
20th Advance Course Multimodality imaging of brain tumours: High Grade Brain Tumours Àlex Rovira Unitat de Ressonància Magnètica Servei de Radiologia Hospital Vall d Hebron. Barcelona. alex.rovira@idi
CancerStemCell Markers in Lung Cancers: Proofsof. Reservations. Lourdes Cortes-Dericks, PhD University of Hamburg Hamburg, Germany
 CancerStemCell Markers in Lung Cancers: Proofsof ConceptsandSome Reservations Lourdes Cortes-Dericks, PhD University of Hamburg Hamburg, Germany Lung cancer: highest death rate and poorest patient survival
CancerStemCell Markers in Lung Cancers: Proofsof ConceptsandSome Reservations Lourdes Cortes-Dericks, PhD University of Hamburg Hamburg, Germany Lung cancer: highest death rate and poorest patient survival
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy for Tumors of the Central File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: intensity_modulated_radiation_therapy_for_tumors
Corporate Medical Policy Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy for Tumors of the Central File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: intensity_modulated_radiation_therapy_for_tumors
There are 2 types of clinical trials that are of interest to the. The Clinical Trials Network of the Society of Nuclear Medicine
 The Clinical Trials Network of the Society of Nuclear Medicine Michael M. Graham, PhD, MD The Clinical Trials Network of the Society of Nuclear Medicine was formed to provide quality assurance of both
The Clinical Trials Network of the Society of Nuclear Medicine Michael M. Graham, PhD, MD The Clinical Trials Network of the Society of Nuclear Medicine was formed to provide quality assurance of both
Radiation therapy involves using many terms you may have never heard before. Below is a list of words you could hear during your treatment.
 Dictionary Radiation therapy involves using many terms you may have never heard before. Below is a list of words you could hear during your treatment. Applicator A device used to hold a radioactive source
Dictionary Radiation therapy involves using many terms you may have never heard before. Below is a list of words you could hear during your treatment. Applicator A device used to hold a radioactive source
High Grade Gliomas: Update in Treatment and Care Ryan T. Merrell, M.D. Clinical Assistant Professor of Neurology NorthShore University HealthSystem
 High Grade Gliomas: Update in Treatment and Care Ryan T. Merrell, M.D. Clinical Assistant Professor of Neurology NorthShore University HealthSystem rmerrell@northshore.org Objectives Provide updates on
High Grade Gliomas: Update in Treatment and Care Ryan T. Merrell, M.D. Clinical Assistant Professor of Neurology NorthShore University HealthSystem rmerrell@northshore.org Objectives Provide updates on
Low-dose CT Imaging. Edgar Fearnow, M.D. Section Chief, Computed Tomography, Lancaster General Hospital
 Lung Cancer Screening with Low-dose CT Imaging Edgar Fearnow, M.D. Section Chief, Computed Tomography, Lancaster General Hospital Despite recent declines in the incidence of lung cancer related to the
Lung Cancer Screening with Low-dose CT Imaging Edgar Fearnow, M.D. Section Chief, Computed Tomography, Lancaster General Hospital Despite recent declines in the incidence of lung cancer related to the
Small Cell Lung Cancer
 Small Cell Lung Cancer Types of Lung Cancer Non-small cell carcinoma (NSCC) (87%) Adenocarcinoma (38%) Squamous cell (20%) Large cell (5%) Small cell carcinoma (13%) Small cell lung cancer is virtually
Small Cell Lung Cancer Types of Lung Cancer Non-small cell carcinoma (NSCC) (87%) Adenocarcinoma (38%) Squamous cell (20%) Large cell (5%) Small cell carcinoma (13%) Small cell lung cancer is virtually
Brain Cancer. This reference summary will help you understand how brain tumors are diagnosed and what options are available to treat them.
 Brain Cancer Introduction Brain tumors are not rare. Thousands of people are diagnosed every year with tumors of the brain and the rest of the nervous system. The diagnosis and treatment of brain tumors
Brain Cancer Introduction Brain tumors are not rare. Thousands of people are diagnosed every year with tumors of the brain and the rest of the nervous system. The diagnosis and treatment of brain tumors
QUANTITATIVE IMAGING IN MULTICENTER CLINICAL TRIALS: PET
 Centers for Quantitative Imaging Excellence (CQIE) LEARNING MODULE QUANTITATIVE IMAGING IN MULTICENTER CLINICAL TRIALS: PET American College of Radiology Clinical Research Center v.1 Centers for Quantitative
Centers for Quantitative Imaging Excellence (CQIE) LEARNING MODULE QUANTITATIVE IMAGING IN MULTICENTER CLINICAL TRIALS: PET American College of Radiology Clinical Research Center v.1 Centers for Quantitative
Disease/Illness GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER. What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? www.simpsonmillar.co.uk Telephone 0844 858 3200
 GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
GUIDE TO ASBESTOS LUNG CANCER What Is Asbestos Lung Cancer? Like tobacco smoking, exposure to asbestos can result in the development of lung cancer. Similarly, the risk of developing asbestos induced lung
In Practice Whole Body MR for Visualizing Metastatic Prostate Cancer
 In Practice Whole Body MR for Visualizing Metastatic Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer in men worldwide, accounting for 15% of all new cancer cases. 1 Great strides have
In Practice Whole Body MR for Visualizing Metastatic Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer in men worldwide, accounting for 15% of all new cancer cases. 1 Great strides have
KIDNEY FUNCTION RELATION TO SIZE OF THE TUMOR IN RENAL CELL CANCINOMA
 KIDNEY FUNCTION RELATION TO SIZE OF THE TUMOR IN RENAL CELL CANCINOMA O.E. Stakhvoskyi, E.O. Stakhovsky, Y.V. Vitruk, O.A. Voylenko, P.S. Vukalovich, V.A. Kotov, O.M. Gavriluk National Canсer Institute,
KIDNEY FUNCTION RELATION TO SIZE OF THE TUMOR IN RENAL CELL CANCINOMA O.E. Stakhvoskyi, E.O. Stakhovsky, Y.V. Vitruk, O.A. Voylenko, P.S. Vukalovich, V.A. Kotov, O.M. Gavriluk National Canсer Institute,
High-grade glioma in a patient with breast cancer
 Asian Journal of Surgery (2014) 37, 162e166 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.e-asianjournalsurgery.com CASE REPORT High-grade glioma in a patient with breast cancer Che-Chao
Asian Journal of Surgery (2014) 37, 162e166 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.e-asianjournalsurgery.com CASE REPORT High-grade glioma in a patient with breast cancer Che-Chao
Interview with David Djang, MD On PET Scan in Oncology: Principles and Practice
 Interview with David Djang, MD On PET Scan in Oncology: Principles and Practice By Howard (Jack) West, MD May, 2009 Hello and welcome to the GRACE audio podcast on PET scanning. This one is with Dr. David
Interview with David Djang, MD On PET Scan in Oncology: Principles and Practice By Howard (Jack) West, MD May, 2009 Hello and welcome to the GRACE audio podcast on PET scanning. This one is with Dr. David
Colorectal Cancer Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Colorectal Cancer Treatment Colorectal cancer overview Colorectal cancer, also called large bowel cancer, is the term used to describe malignant tumors found in the colon and rectum.
Scan for mobile link. Colorectal Cancer Treatment Colorectal cancer overview Colorectal cancer, also called large bowel cancer, is the term used to describe malignant tumors found in the colon and rectum.
Patient Prep Information
 Stereotactic Breast Biopsy Patient Prep Information Imaging Services Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center Table Weight Limits for each facility Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center
Stereotactic Breast Biopsy Patient Prep Information Imaging Services Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center Table Weight Limits for each facility Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center
Prostate Cancer. Treatments as unique as you are
 Prostate Cancer Treatments as unique as you are UCLA Prostate Cancer Program Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer among men. The UCLA Prostate Cancer Program brings together the elements essential
Prostate Cancer Treatments as unique as you are UCLA Prostate Cancer Program Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer among men. The UCLA Prostate Cancer Program brings together the elements essential
Rotation Specific Goals & Objectives: University Health Network-Princess Margaret Hospital/ Sunnybrook Breast/Melanoma
 Rotation Specific Goals & Objectives: University Health Network-Princess Margaret Hospital/ Sunnybrook Breast/Melanoma Medical Expert: Breast Rotation Specific Competencies/Objectives 1.0 Medical History
Rotation Specific Goals & Objectives: University Health Network-Princess Margaret Hospital/ Sunnybrook Breast/Melanoma Medical Expert: Breast Rotation Specific Competencies/Objectives 1.0 Medical History
Management of Postmenopausal Women with T1 ER+ Tumors: Options and Tradeoffs. Case Study. Surgery. Lumpectomy and Radiation
 Management of Postmenopausal Women with T1 ER+ Tumors: Options and Tradeoffs Michael Alvarado, MD Associate Professor of Surgery University of California San Francisco Case Study 59 yo woman with new palpable
Management of Postmenopausal Women with T1 ER+ Tumors: Options and Tradeoffs Michael Alvarado, MD Associate Professor of Surgery University of California San Francisco Case Study 59 yo woman with new palpable
Historical Basis for Concern
 Androgens After : Are We Ready? Mohit Khera, MD, MBA Assistant Professor of Urology Division of Male Reproductive Medicine and Surgery Scott Department of Urology Baylor College of Medicine Historical
Androgens After : Are We Ready? Mohit Khera, MD, MBA Assistant Professor of Urology Division of Male Reproductive Medicine and Surgery Scott Department of Urology Baylor College of Medicine Historical
OBJECTIVES By the end of this segment, the community participant will be able to:
 Cancer 101: Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Linda U. Krebs, RN, PhD, AOCN, FAAN OCEAN Native Navigators and the Cancer Continuum (NNACC) (NCMHD R24MD002811) Cancer 101: Diagnosis & Staging (Watanabe-Galloway
Cancer 101: Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Linda U. Krebs, RN, PhD, AOCN, FAAN OCEAN Native Navigators and the Cancer Continuum (NNACC) (NCMHD R24MD002811) Cancer 101: Diagnosis & Staging (Watanabe-Galloway
Quantitative Imaging In Clinical Trials Using PET/CT: Update
 Quantitative Imaging In Clinical Trials Using PET/CT: Update Paul Kinahan, Robert Doot Imaging Research Laboratory Department of Radiology University of Washington, Seattle, WA Supported by RSNA Quantitative
Quantitative Imaging In Clinical Trials Using PET/CT: Update Paul Kinahan, Robert Doot Imaging Research Laboratory Department of Radiology University of Washington, Seattle, WA Supported by RSNA Quantitative
Metastatic Breast Cancer 201. Carolyn B. Hendricks, MD October 29, 2011
 Metastatic Breast Cancer 201 Carolyn B. Hendricks, MD October 29, 2011 Overview Is rebiopsy necessary at the time of recurrence or progression of disease? How dose a very aggressive treatment upfront compare
Metastatic Breast Cancer 201 Carolyn B. Hendricks, MD October 29, 2011 Overview Is rebiopsy necessary at the time of recurrence or progression of disease? How dose a very aggressive treatment upfront compare
Salute to Dr. Saul Hertz Diagnostic and Therapeutic Uses of Radioiodine
 Salute to Dr. Saul Hertz Diagnostic and Therapeutic Uses of Radioiodine Salute to Dr. Saul Hertz Diagnostic and Therapeutic Uses of Radioiodine Douglas Van Nostrand, MD, FACP, FACNM Director, Nuclear Medicine
Salute to Dr. Saul Hertz Diagnostic and Therapeutic Uses of Radioiodine Salute to Dr. Saul Hertz Diagnostic and Therapeutic Uses of Radioiodine Douglas Van Nostrand, MD, FACP, FACNM Director, Nuclear Medicine
PET POSITIVE PLEURAL PLAQUES DECADES AFTER PLEURODESIS: MESOLTHELIOMA? Ellen A. Middleton 1. Jonathan C. Daniel 2. Kenneth S.
 PET POSITIVE PLEURAL PLAQUES DECADES AFTER PLEURODESIS: MESOLTHELIOMA? Ellen A. Middleton 1 Jonathan C. Daniel 2 Kenneth S. Knox 1 Kathleen Williams 1 Departments of Medicine 1 and Surgery 2, University
PET POSITIVE PLEURAL PLAQUES DECADES AFTER PLEURODESIS: MESOLTHELIOMA? Ellen A. Middleton 1 Jonathan C. Daniel 2 Kenneth S. Knox 1 Kathleen Williams 1 Departments of Medicine 1 and Surgery 2, University
AMERICAN BRAIN TUMOR ASSOCIATION. Proton Therapy
 AMERICAN BRAIN TUMOR ASSOCIATION Proton Therapy Acknowledgements About the American Brain Tumor Association Founded in 1973, the American Brain Tumor Association (ABTA) was the first national nonprofit
AMERICAN BRAIN TUMOR ASSOCIATION Proton Therapy Acknowledgements About the American Brain Tumor Association Founded in 1973, the American Brain Tumor Association (ABTA) was the first national nonprofit
Functional neuroimaging. Imaging brain function in real time (not just the structure of the brain).
 Functional neuroimaging Imaging brain function in real time (not just the structure of the brain). The brain is bloody & electric Blood increase in neuronal activity increase in metabolic demand for glucose
Functional neuroimaging Imaging brain function in real time (not just the structure of the brain). The brain is bloody & electric Blood increase in neuronal activity increase in metabolic demand for glucose
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment Comparison to NCCN Guidelines
 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment Comparison to NCCN Guidelines April 2008 (presented at 6/12/08 cancer committee meeting) By Shelly Smits, RHIT, CCS, CTR Conclusions by Dr. Ian Thompson, MD Dr. James
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment Comparison to NCCN Guidelines April 2008 (presented at 6/12/08 cancer committee meeting) By Shelly Smits, RHIT, CCS, CTR Conclusions by Dr. Ian Thompson, MD Dr. James
Temporal Trends in Demographics and Overall Survival of Non Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients at Moffitt Cancer Center From 1986 to 2008
 Special Report Temporal Trends in Demographics and Overall Survival of Non Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients at Moffitt Cancer Center From 1986 to 2008 Matthew B. Schabath, PhD, Zachary J. Thompson, PhD,
Special Report Temporal Trends in Demographics and Overall Survival of Non Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients at Moffitt Cancer Center From 1986 to 2008 Matthew B. Schabath, PhD, Zachary J. Thompson, PhD,
Case Report: Whole-body Oncologic Imaging with syngo TimCT
 Case Report: Whole-body Oncologic Imaging with syngo TimCT Eric Hatfield, M.D. 1 ; Agus Priatna, Ph.D. 2 ; John Kotyk, Ph.D. 1 ; Benjamin Tan, M.D. 1 ; Alto Stemmer 3 ; Stephan Kannengiesser, Ph.D. 3 ;
Case Report: Whole-body Oncologic Imaging with syngo TimCT Eric Hatfield, M.D. 1 ; Agus Priatna, Ph.D. 2 ; John Kotyk, Ph.D. 1 ; Benjamin Tan, M.D. 1 ; Alto Stemmer 3 ; Stephan Kannengiesser, Ph.D. 3 ;
The Center for Prostate Cancer. Personalized Treatment. Clinical Excellence.
 The Center for Prostate Cancer Personalized Treatment. Clinical Excellence. The Center for Prostate Cancer Leaders in Prostate Cancer Treatment and Research The Center for Prostate Cancer at the North
The Center for Prostate Cancer Personalized Treatment. Clinical Excellence. The Center for Prostate Cancer Leaders in Prostate Cancer Treatment and Research The Center for Prostate Cancer at the North
Protein kinase C alpha expression and resistance to neo-adjuvant gemcitabine-containing chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer
 Protein kinase C alpha expression and resistance to neo-adjuvant gemcitabine-containing chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer Dan Vogl Lay Abstract Early stage non-small cell lung cancer can be cured
Protein kinase C alpha expression and resistance to neo-adjuvant gemcitabine-containing chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer Dan Vogl Lay Abstract Early stage non-small cell lung cancer can be cured
PET/CT in Breast Cancer
 PET/CT in Breast Cancer Rodolfo Núñez Miller, M.D. Nuclear Medicine and Diagnostic Imaging Section Division of Human Health International Atomic Energy Agency Vienna, Austria Overview Introduction Locorregional
PET/CT in Breast Cancer Rodolfo Núñez Miller, M.D. Nuclear Medicine and Diagnostic Imaging Section Division of Human Health International Atomic Energy Agency Vienna, Austria Overview Introduction Locorregional
Seton Medical Center Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patterns of Care Study Rate of Treatment with Chemoembolization 2007 2012 N = 50
 General Data Seton Medical Center Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patterns of Care Study Rate of Treatment with Chemoembolization 2007 2012 N = 50 The vast majority of the patients in this study were diagnosed
General Data Seton Medical Center Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patterns of Care Study Rate of Treatment with Chemoembolization 2007 2012 N = 50 The vast majority of the patients in this study were diagnosed
Avastin in breast cancer: Summary of clinical data
 Avastin in breast cancer: Summary of clinical data Worldwide, over one million people are diagnosed with breast cancer every year 1. It is the most frequently diagnosed cancer in women 1,2, and the leading
Avastin in breast cancer: Summary of clinical data Worldwide, over one million people are diagnosed with breast cancer every year 1. It is the most frequently diagnosed cancer in women 1,2, and the leading
RADIOLOGY SERVICES. By Dr Lim Eng Kok 1
 INTRODUCTION RADIOLOGY SERVICES By Dr Lim Eng Kok 1 Radiology is the branch of medicine that deals with the use of ionising (e.g. x- rays and radio-isotopes) and non-ionising radiation (e.g. ultrasound
INTRODUCTION RADIOLOGY SERVICES By Dr Lim Eng Kok 1 Radiology is the branch of medicine that deals with the use of ionising (e.g. x- rays and radio-isotopes) and non-ionising radiation (e.g. ultrasound
Multi-slice Helical CT Scanning of the Chest
 Multi-slice Helical CT Scanning of the Chest Comparison of different low-dose acquisitions Lung cancer is the main cause of deaths due to cancer in human males and the incidence is constantly increasing.
Multi-slice Helical CT Scanning of the Chest Comparison of different low-dose acquisitions Lung cancer is the main cause of deaths due to cancer in human males and the incidence is constantly increasing.
How are Parts of the Brain Related to Brain Function?
 How are Parts of the Brain Related to Brain Function? Scientists have found That the basic anatomical components of brain function are related to brain size and shape. The brain is composed of two hemispheres.
How are Parts of the Brain Related to Brain Function? Scientists have found That the basic anatomical components of brain function are related to brain size and shape. The brain is composed of two hemispheres.
TITLE: Comparison of the dosimetric planning of partial breast irradiation with and without the aid of 3D virtual reality simulation (VRS) software.
 SAMPLE CLINICAL RESEARCH APPLICATION ABSTRACT: TITLE: Comparison of the dosimetric planning of partial breast irradiation with and without the aid of 3D virtual reality simulation (VRS) software. Hypothesis:
SAMPLE CLINICAL RESEARCH APPLICATION ABSTRACT: TITLE: Comparison of the dosimetric planning of partial breast irradiation with and without the aid of 3D virtual reality simulation (VRS) software. Hypothesis:
MOH Policy for dispensing NEOPLASTIC DISEASES DRUGS
 MOH Policy for dispensing NEOPLASTIC DISEASES DRUGS All prescriptions for antineoplastic drugs must be accompanied by the MOH special form. All the attachments mentioned on this form shall be submitted
MOH Policy for dispensing NEOPLASTIC DISEASES DRUGS All prescriptions for antineoplastic drugs must be accompanied by the MOH special form. All the attachments mentioned on this form shall be submitted
A new score predicting the survival of patients with spinal cord compression from myeloma
 A new score predicting the survival of patients with spinal cord compression from myeloma (1) Sarah Douglas, Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Lubeck, Germany; sarah_douglas@gmx.de (2) Steven
A new score predicting the survival of patients with spinal cord compression from myeloma (1) Sarah Douglas, Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Lubeck, Germany; sarah_douglas@gmx.de (2) Steven
LYMPHOMA IN DOGS. Diagnosis/Initial evaluation. Treatment and Prognosis
 LYMPHOMA IN DOGS Lymphoma is a relatively common cancer in dogs. It is a cancer of lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) and lymphoid tissues. Lymphoid tissue is normally present in many places in the
LYMPHOMA IN DOGS Lymphoma is a relatively common cancer in dogs. It is a cancer of lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) and lymphoid tissues. Lymphoid tissue is normally present in many places in the
Effects of Herceptin on circulating tumor cells in HER2 positive early breast cancer
 Effects of Herceptin on circulating tumor cells in HER2 positive early breast cancer J.-L. Zhang, Q. Yao, J.-H. Chen,Y. Wang, H. Wang, Q. Fan, R. Ling, J. Yi and L. Wang Xijing Hospital Vascular Endocrine
Effects of Herceptin on circulating tumor cells in HER2 positive early breast cancer J.-L. Zhang, Q. Yao, J.-H. Chen,Y. Wang, H. Wang, Q. Fan, R. Ling, J. Yi and L. Wang Xijing Hospital Vascular Endocrine
PET/CT-MRI First clinical experience
 20 th April 2013, Barcelona, Sp PET/CT-MRI First clinical experience Philippe Appenzeller, MD Staff Radiologist and Nuclear Medicine Physician Department Medical Imaging, University Hospital Zurich PET/CT-MR
20 th April 2013, Barcelona, Sp PET/CT-MRI First clinical experience Philippe Appenzeller, MD Staff Radiologist and Nuclear Medicine Physician Department Medical Imaging, University Hospital Zurich PET/CT-MR
Lung Cancer. Public Outcomes Report. Submitted by Omar A. Majid, MD
 Public Outcomes Report Lung Cancer Submitted by Omar A. Majid, MD Lung cancer is the most common cancer-related cause of death among men and women. It has been estimated that there will be 226,1 new cases
Public Outcomes Report Lung Cancer Submitted by Omar A. Majid, MD Lung cancer is the most common cancer-related cause of death among men and women. It has been estimated that there will be 226,1 new cases
The Di Bella Method (DBM) improves Survival, Objective Response and Performance Status in Breast Cancer
 BIT's 4th World Cancer Congress 2011 People s Republic of China Dalian The Di Bella Method (DBM) improves Survival, Objective Response and Performance Status in treated with DBM therapy Retrospective observational
BIT's 4th World Cancer Congress 2011 People s Republic of China Dalian The Di Bella Method (DBM) improves Survival, Objective Response and Performance Status in treated with DBM therapy Retrospective observational
Helen Joseph Breast Care Clinic - Johannesburg, South Africa
 - Johannesburg, South Africa General Information New breast cancer cases treated per year 360 Breast multidisciplinarity team members 12 Radiologists, surgeons, pathologists, medical oncologists, radiotherapists
- Johannesburg, South Africa General Information New breast cancer cases treated per year 360 Breast multidisciplinarity team members 12 Radiologists, surgeons, pathologists, medical oncologists, radiotherapists
Changes in Breast Cancer Reports After Second Opinion. Dr. Vicente Marco Department of Pathology Hospital Quiron Barcelona. Spain
 Changes in Breast Cancer Reports After Second Opinion Dr. Vicente Marco Department of Pathology Hospital Quiron Barcelona. Spain Second Opinion in Breast Pathology Usually requested when a patient is referred
Changes in Breast Cancer Reports After Second Opinion Dr. Vicente Marco Department of Pathology Hospital Quiron Barcelona. Spain Second Opinion in Breast Pathology Usually requested when a patient is referred
New Options to Treat Brain Tumors
 New Options to Treat Brain Tumors Guest Expert: Joachim, MD Associate Professor of Neuro-Oncology Director, Yale Cancer Center Brain Tumor Program www.wnpr.org www.yalecancercenter.org Welcome to Yale
New Options to Treat Brain Tumors Guest Expert: Joachim, MD Associate Professor of Neuro-Oncology Director, Yale Cancer Center Brain Tumor Program www.wnpr.org www.yalecancercenter.org Welcome to Yale
Case Report. Central Neurocytoma. Fotis Souslian, MD; Dino Terzic, MD; Ramachandra Tummala, MD. Department of Neurosurgery, University of Minnesota
 1 Case Report Central Neurocytoma Fotis, MD; Dino Terzic, MD; Ramachandra Tummala, MD Department of Neurosurgery, University of Minnesota Case This is a previously healthy 20 year old female, with 3 months
1 Case Report Central Neurocytoma Fotis, MD; Dino Terzic, MD; Ramachandra Tummala, MD Department of Neurosurgery, University of Minnesota Case This is a previously healthy 20 year old female, with 3 months
Standardized MRI Protocol for Brain Tumor Clinical Trials. Benjamin M. Ellingson, Ph.D. Assistant Professor of Radiology at UCLA
 Standardized MRI Protocol for Brain Tumor Clinical Trials Benjamin M. Ellingson, Ph.D. Assistant Professor of Radiology at UCLA Standardized MRI Protocol for Therapeutic Studies FDA Meeting in January
Standardized MRI Protocol for Brain Tumor Clinical Trials Benjamin M. Ellingson, Ph.D. Assistant Professor of Radiology at UCLA Standardized MRI Protocol for Therapeutic Studies FDA Meeting in January
Ensemble Learning of Colorectal Cancer Survival Rates
 Ensemble Learning of Colorectal Cancer Survival Rates Chris Roadknight School of Computing Science University of Nottingham Malaysia Campus Malaysia Chris.roadknight@nottingham.edu.my Uwe Aickelin School
Ensemble Learning of Colorectal Cancer Survival Rates Chris Roadknight School of Computing Science University of Nottingham Malaysia Campus Malaysia Chris.roadknight@nottingham.edu.my Uwe Aickelin School
Local control in ductal carcinoma in situ treated by excision alone: incremental benefit of larger margins
 The American Journal of Surgery 190 (2005) 521 525 George Peter s Award Winner Local control in ductal carcinoma in situ treated by excision alone: incremental benefit of larger margins Heather R. MacDonald,
The American Journal of Surgery 190 (2005) 521 525 George Peter s Award Winner Local control in ductal carcinoma in situ treated by excision alone: incremental benefit of larger margins Heather R. MacDonald,
Avastin: Glossary of key terms
 Avastin: Glossary of key terms Adenocarcinoma Adenoma Adjuvant therapy Angiogenesis Anti-angiogenics Antibody Antigen Avastin (bevacizumab) Benign A form of carcinoma that originates in glandular tissue.
Avastin: Glossary of key terms Adenocarcinoma Adenoma Adjuvant therapy Angiogenesis Anti-angiogenics Antibody Antigen Avastin (bevacizumab) Benign A form of carcinoma that originates in glandular tissue.
Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too.
 Male Breast Cancer Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too. Many people do not know that men can get breast
Male Breast Cancer Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too. Many people do not know that men can get breast
There must be an appropriate administrative structure for each residency program.
 Specific Standards of Accreditation for Residency Programs in Radiation Oncology 2015 VERSION 3.0 INTRODUCTION The purpose of this document is to provide program directors and surveyors with an interpretation
Specific Standards of Accreditation for Residency Programs in Radiation Oncology 2015 VERSION 3.0 INTRODUCTION The purpose of this document is to provide program directors and surveyors with an interpretation
Aggressive lymphomas. Michael Crump Princess Margaret Hospital
 Aggressive lymphomas Michael Crump Princess Margaret Hospital What are the aggressive lymphomas? Diffuse large B cell Mediastinal large B cell Anaplastic large cell Burkitt lymphoma (transformed lymphoma:
Aggressive lymphomas Michael Crump Princess Margaret Hospital What are the aggressive lymphomas? Diffuse large B cell Mediastinal large B cell Anaplastic large cell Burkitt lymphoma (transformed lymphoma:
