a. guèye ndiaye, hounkponou edwige, Fatou Bintou guèye and cheikh saad Bouh Boye
|
|
|
- Abigail Wiggins
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Microbiology Insights OrIgInal research Open Access Full open access to this and thousands of other papers at Trend in Antibiotic Resistance of Streptococcus Pneumoniae and Haemophilus Influenzae strains Isolated from community Acquired Respiratory Tract Infections in Dakar, senegal Between 2005 and 2008 a. guèye ndiaye, hounkponou edwige, Fatou Bintou guèye and cheikh saad Bouh Boye Bacteriology and Virology laboratory, Dantec teaching hospital, Dakar, senegal. Abstract: Development of antibiotic resistance among common respiratory pathogens is a major cause of concern worldwide. Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae are among the most common respiratory pathogens. In this study, representative samples obtained from 3 different medical centers in Dakar, Senegal were subjected to antibiotic susceptibility testing. The samples were collected from 2005 to 2008 and the data obtained was compared to establish resistance patterns between the two years (i.e to ). S. pneumoniae exhibited a significant increase in the resistance to azithromycin and the intermediate susceptibility to penicillin G and cotrimoxazole. H. influenzae also exhibited a significant increase in resistance to azithromycin and intermediate susceptibility to chloramphenicol. None of H. influenzae samples were resistant to amoxicillin/clavulanic acid, cephalosporin and fluroquinolones and most of the S. pneumoniae isolates demonstrated high susceptibility to the antibiotics tested. Results from this study will provide greater insights to antibiotic therapy during respiratory tract infections in Dakar, Senegal. This study also establishes the importance of continuous monitoring of antibiotic susceptibility patterns that are often region-specific. Keywords: antibiotic resistance, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae Microbiology Insights 2010: This article is available from the author(s), publisher and licensee libertas academica ltd. This is an open access article. Unrestricted non-commercial use is permitted provided the original work is properly cited. Microbiology Insights 2010:3 45
2 Ndiaye et al Introduction Respiratory tract infections (RTI) caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae along with Haemophilus influenzae are a leading cause of death despite antibiotic therapy. S. pneumoniae is a causative organism for severe RTIs including acute otitis media, acute bacterial exacerbations of chronic bronchitis and sinusitis, bacteremia, and community-acquired pneumonia. 1 4 Including the above mentioned diseases, H. influenzae is also responsible for diseases such as childhood pneumonia and meningitis. There is increasing evidence of continuous evolution and geographical variation amongst these strains that is responsible for treatment complications. 2,5 7 A major concern is the development of anti-bacterial resistance, as result it is imperative to choose a treatment regimen that is region-specific based on the local susceptibility patterns of the bacteria. It has been previously established that the incidence of penicillin-resistant pneumococci has increased significantly, worldwide. 8 The macrolide resistance in S. pneumoniae is mediated by two mechanisms; methylation of ribosomal macrolide target sites encoded by erm(b) gene and drug efflux encoded by the mef(a) gene. 9 The development of resistance can often lead to complications in the otherwise empirical treatment of S. pneumoniae infections. On the other hand, H. influenzae strains exhibit disparate mechanisms of resistance. The most common mechanism of resistance to ampicillin and amoxicillin is β-lactamase production. 10 The data obtained from different countries reveal significant geographical heterogeneity in the antibiotic resistance pattern Hence, it is mandatory to determine resistance patterns that are region-specific rather than generalized. To date, none of the resistance studies focus on West Africa. In this retrospective study, we intend to report the antibacterial resistance pattern of S. pneumoniae, and H. influenzae, in Dakar, the capital city of Senegal. Clinical specimens were collected between 2005 and The changes in resistance pattern of these two organisms data obtained from was compared to results obtained from With this information, we aim to present valuable insights to the antibiotic treatment strategies that could aid in the physicians decisionmaking process. Material and Methods Sample collection Clinical isolates of S. pneumoniae and H. influenzae were collected from patients with upper (acute otitis media and sinusitis) or lower RTI (communityacquired pneumonia, acute bronchitis). The clinical specimens included sputum, bronchoalveolar lavage, acute otitis medium effusions, blood, pus swab, sinus fluids, and throat swab. Patients were recruited at the Departments of Paediatrics and ORL, University Hospital of Aristide Le Dantec; Pneumology Department of University Hospital of Fann, and a private medical setting in Dakar, Senegal. The samples were analyzed at the Bacteriology and Virology Laboratory of the University Hospital Aristide Le Dantec. They were immediately cultured, and the strains isolated were identified according to the standard methods of microbiology. Antimicrobial susceptibility data from were compared to data from Identification of bacterial isolates S. pneumoniae was identified by presence of tiny, round, flat, and transparent colonies, with central depression (checker piece and nail head colonies), hemolysis of α-viridans, negative catalase and oxidase test, absence of bile-esculin hydrolysis, lysis by bile-salts, susceptibility to optochin and others biochemical characters (using API Strep BioMérieux, La Balme-les-Grottes, France). H. influenzae was identified by presence of tiny, moist, and smooth gray colonies, absence of hemolysis, positive catalase and oxidase test, presence of growth factors X and V, satellite growth around streaks of Staphylococcus aureus, and others biochemical characters (using API NH galleria, BioMérieux, La Balme-les-Grottes, France). Antibiotic susceptibility testing Antibiotic susceptibility of all isolates of the test pathogens was analysed using the standard agar disk diffusion method and the E-test. The bacterial suspensions were suitably diluted to attain a final concentration of 10 5 CFU/ml (an optical density of 0.5 on the McFarland scale). H. influenzae suspension was inoculated on Haemophilus test medium, and S. pneumoniae was inoculated on Mueller- Hinton supplemented with 5% 46 Microbiology Insights 2010:3
3 Antibiotic resistance of Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae sheep blood. Disks (diffusion method) or strips (E-test) containing selected antibiotics were then placed on the inoculated plates. These plates were then incubated at 37 C in a CO 2 atmosphere for hours. The test panel for S. pneumoniae includes penicillin G, amoxicillin-clavulanic acid, cefuroxime, ceftriaxone, azithromycin, levofloxacin, cotrimoxazole, chloramphenicol, clindamycin, erythromycin, and tetracycline. The test panel for H. influenzae included ampicillin, amoxicillin-clavulanic acid, ceftriaxone, ofloxaxin, azithromycin, chloramphenicol, and tetracycline. ATCC strain of H. influenzae and ATCC strains of S. pneumoniae were used as quality control strains. Minimal inhibitory concentrations (MICs) were calculated as MIC 50 (MIC causing inhibition of 50% of isolates) and MIC 90 (MIC causing inhibition of 90% of isolates). Percentage susceptibilities were calculated based on Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) break points. 17 β-lactamase tests and typing of Hamophilus influenzae isolates The H. influenzae isolates were examined for production of β-lactamase using a nitrocefin-based test (Cefinase, Becton Dickinson Microbiology Systems, Cockeysville, MD). A latex particle agglutination test (Slidex, Biomerieux) was used to type all Haemophilus influenzae isolates. Erythromycin and clindamycin double-disc diffusion test The test was performed to identify the erythromycin resistant phenotype. On a blood agar plate, an erythromycin disk (15 µg) was placed 20 mm from the centre of a disc containing 10 µg of clindamycin. Blunting of the clindamycin inhibition zone proximal to the erythromycin disc indicated an inducible resistant phenotype, while susceptibility only to clindamycin with no blunting indicated the M-phenotype. Resistance to both erythromycin and clindamycin indicated constitutive resistance. Statistical analysis The WHONET software was used to analyze the antibacterial susceptibility test results. 18 Comparisons of resistance development were made using the chi square test for frequencies (k proportions test). Significance was realised at P # 0.05 (95% confidence interval). Results Patient demographics For both microorganisms, the most frequent sources of bacterial isolates were bronchoalveolar lavage and sputum for both the time periods. Between November 2005 and August 2006, 100 isolates of S. pneumoniae and 71 of H. influenzae were collected, and 105 isolates of S. pneumoniae and 75 H. influenzae were collected between July 2007 and May For H. influenzae, 43 strains have been isolated in and 39 in from bronchoalveolar lavage. For S. pneumoniae, 36 strains have been isolated in and 48 strains in from bronchoalveolar lavage. Strains from sputum were obtained from 33 isolates in and 30 in (19 isolates for H. influenzae in and 25 isolates for S. pneumoniae ). Most of the isolates included in this study were obtained from patients.15 years of age. Antibiotic susceptibility testing All antibiotics demonstrated acceptable MICs values toward the controls strains. S. pneumoniae The resistance pattern of S. pneumoniae for each test antibacterial is given in Figure 1. For both the time periods, S. pneumoniae exhibited high susceptibility towards most of the antibacterials. The rate of resistance increased for penicillin G, cotrimoxazole, chloramphenicol, and tetracycline from to However, this increase was not statistically significant. The rate of resistance to azithromycin significantly decreased from 2005 to The intermediate susceptibility increased for all antibacterial except for amoxicillin/clavulanic acid, ceftriaxone and chloramphenicol. The rate of isolates that exhibited intermediate susceptibility to penicillin G increased significantly from 7.0% in to 33.3% in There was also a significant increase in the intermediate susceptibility to cotrimoxazole from to Few isolates (6%, 43 Microbiology Insights 2010:3 47
4 Ndiaye et al % of complete resistance * PG AMC CXM CRO AZT LEV/OF CO CMP CLI ERY TET Antibacterials Figure 1 Rate of complete resistance of S. Pneumoniae. Note: *P # Abbreviations: PG, Penicillin G; AMC, AmoxClavulanic acid; CXM, Cefuroxime; CRO, Ceftriaxone; AZT, Azithromycin; LEV, Levofloxacin; ERY, Erythromycin; CLI, Clindamycin; CO, Cotrimoxazole; CMP, Chloramphenicol; TET, Tetracycline. isolates in ; 4%, 28 isolates in ) were completely resistant to erythromycin and all were of the M phenotype ( erythromycin-resistant, clindamycin susceptible). In order to further characterize the resistance pattern, data was individually analyzed according to isolates collected from sterile vs. nonsterile sites (Table 1). A difference was observed only in the resistance to penicillin G (8%, 5 isolates bronchitis/pneumonia samples; 0%, Otitis/Sinusitis samples in 2006). Table 1. Antibiotic resistance to S. pneumoniae according to sterile/non-sterile isolates. Antibiotic % Resistance (2006) % Resistance (2008) Otites/Sinusites (AOM, Pus swap, Sinus efflusions) n = 7 n = 22 Penicillin G 0 23 AmoxClavulanic acid 0 0 Cefuroxime 0 0 Ceftriaxone 0 0 Azithromycin 0 0 Levofloxacin/Ofloxacin 0 0 Erythromycin 0 5 Cotrimoxazole Chloramphenicol 0 5 Tetracycline Bronchites/Pneumonia (Sputum, BAL) n = 64 n = 83 Penicillin G 8 35 AmoxClavulanic acid 0 0 Cefuroxime 0 0 Ceftriaxone 0 0 Azithromycin 6 0 Levofloxacin /Ofloxacin 0 0 Erythromycin 6 4 Cotrimoxazole Chloramphenicol 2 6 Tetracycline Microbiology Insights 2010:3
5 Antibiotic resistance of Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae Rate of complete resistance of H.influenzae % of complete resistance * AMP AMC CXM CRO OF AZT CMP TET Antibacterials Figure 2 Rate at intermediate susceptibility of S. pneumoniae. Note: *P # Abbreviations: AMP, Ampicillin; AMC, AmoxClavulanic acid; CRO, Ceftriaxone; AZT, Azithromycin; OF, Ofloxacin; CMP, Chloramphenicol; TET, Tetracycline. H. influenzae The resistance pattern of H. influenzae for each test antimicrobial is given in Figure 2. None of the isolates was resistant to amoxicillin/clavulanic acid, cephalosporin, and fluorquinolones For ampicillin, azithromycin, and chloramphenicol, the rate of resistance decreased from to However, this difference was significant only for azithromycin. Except for chloramphenicol and tetracycline, the rate of intermediate susceptibility remained fairly constant from to A significant increase in intermediate susceptibility was observed only for chloramphenicol. The rate of β-lactamase producing isolates decreased from 37% (37 isolates) in to 27% (20 isolates) in (p = 0.049). Subsequently, data was also analyzed according to the site of sample collection (Table 2). A difference was observed in the ampicillin resistance (29%, 7 isolates in otitis/sinusitis vs. 39%, 30 isolates in bronchitis/pneumonia sample in 2006). However, a decrease in resistance was observed in 2008 in otitis vs. bronchitis samples. Table 2. Antibiotic resistance to H. influenzae according to sterile/non-sterile isolates. Antibiotic % Resistance 2006 % Resistance 2008 Otites/Sinusites (AOM, Pus swap, Sinus efflusions) n = 24 n = 6 Ampicillin AmoxClavulanic acid 0 0 Cefuroxime 0 0 Ceftriaxone 0 0 Azithromycin 8 0 Levofloxacin/Ofloxacin 0 0 Chloramphenicol 8 16 Bronchites/Pneumonia (Sputum, BAL) n = 76 n = 69 Ampicillin AmoxClavulanic acid 0 0 Cefuroxime 0 0 Ceftriaxone 0 0 Azithromycin 13 0 Levofloxacin/Ofloxacin 0 0 Chloramphenicol 13 4 Microbiology Insights 2010:3 49
6 Ndiaye et al Discussion The main aim of this study was to determine the trend of resistance of two common bacterial pathogens (S. pneumoniae and H. influenzae) responsible for development of RTIs in Dakar, Senegal from 2005 to Samples for this study were recovered from patients recruited at 3 different medical centres in Dakar. The majority of isolates were recovered from patients more than 15 years of age. Camara et al (Camara et al, 2003), have shown that 35% of bacteria isolated from meningitis were H. influenzae type-b. In this study, we have type the strains and found only 5 Hib among from children aged of 6 9 and one from children aged of 11 years. A total of 92% of isolated were non HIb. In Senegal Hib vaccine is included in the Expended Program for Immunization. This could explain the small number of Hib Isolates. Individual data collected and analyzed for each of the three locations in presented in Table 3. Although information on previous antibiotic therapy could provide valuable information, since this is a retrospective study we were unable to obtain this information. The most significant changes were observed in the resistance of S. pneumoniae to penicillin G. Rates of intermediate susceptible isolates increased from 7% in 2005 to 33.3% in These rates were lower than those previously reported by Benbachir et al; 8.6% of pneumococcal isolates were fully resistant and 53.1% had intermediate susceptibility to penicillin G. 19 The rate of complete resistance to penicillin G was 1% in which is similar to a previous study reporting data from paediatric patients. 20 Benbachir et al observed that resistance to other antibiotics (erythromycin, chloramphenicol and trimethoprim/ sulfamethoxazole) is more frequent among pneumococcal isolates with reduced susceptibility to penicillin G as compared to the more susceptible isolates. 19 In this study, although sharp differences were observed between penicillin G susceptible and non- susceptible isolates they were not statistically significant. In particular, the rates of resistance to trimethoprim/ sulfamethoxazole and tetracycline were relatively high among penicillin G resistant isolates. On the other hand the rates of resistance to amoxicillin/ clavulanic acid, cefuroxime, cefaclor, azithromycin, and ofloxacin were almost negligible. Resistance of H. influenzae to ampicillin deceased from 35.4% in to 26.7% in These rates of resistance are in accordance with findings from a study conducted in the paediatric department of Fann hospital in Dakar on meningitis, 20 as well as other studies conducted in other countries in Africa In our study, we observed that β-lactamase production was the primary mechanism of ampicillin resistance for H. influenzae; all isolates that were resistant to ampicillin produced β-lactamase. The same results were observed in a previous study conducted in other parts of the world. 10 Among other antibiotics tested the resistance to azithromycin decreased significantly between the two years whereas the decrease in resistance to chloramphenicol and tetracycline was insignificant. In conclusion, the results from this study indicate that a significant increase of resistance of S. pneumoniae isolates to penicillin G. Resistance of H. influenzae remain relatively high; β-lactamase production was the primary reason for these high rates of resistance of H. influenzae associated with ampicillin. All bacteria remain susceptible to cephalosporins, fluoroquinolones, and macrolides. The results from this study re-emphasize the need for continuous epidemiological monitoring of antibiotic resistance. Selecting an appropriate treatment regimen can often be a challenging task owing to rapid changes in resistance patterns. Thus the appropriate use of antibiotics should be guided by current trends in antibiotic resistance. The data reported thus far is intended to achieve this objective in Dakar. However, these trends should not be extrapolated to other regions of Senegal as it has been previously reported that resistance patterns exhibit significant geographic heterogeneity. Also, additional surveillance data is necessary from paediatric samples to report differences in the resistance pattern between adults and children, if any. Disclosures This manuscript has been read and approved by all authors. This paper is unique and is not under consideration by any other publication and has not been published elsewhere. The authors and peer reviewers of this paper report no conflicts of interest. The authors 50 Microbiology Insights 2010:3
7 Antibiotic resistance of Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae Table 3. Antibiotic resistance according to geographical location. Haemophilus influenzae Streptococcus pneumoniae Antibiotic % of Resistance Antibiotic % of Resistance 2006 (n = 9) 2008 (n = 3) 2006 (n = 3) 2008 (n = 5) ORL private Ampicillin Penicillin G 0 20 AmoxClavulanic acid 0 0 AmoxClavulanic acid 0 0 Cefuroxime 0 0 Cefuroxime 0 0 Ceftriaxone 0 0 Ceftriaxone 0 0 Azithromycin 11 0 Azithromycin 0 0 Levofloxacin/Ofloxacin 0 0 Levofloxacin/Ofloxacin 0 0 Chloramphenicol 11 0 Erythromycin 0 0 Cotrimoxazole Chloramphenicol 0 0 Tetracycline ORL HALD/Pediatric HALD 2006 (n = 52) 2008 (n = 31) 2006 (n = 40) 2008 (n = 57) Ampicillin Penicillin G 8 20 AmoxClavulanic acid 0 0 AmoxClavulanic acid 0 0 Cefuroxime 0 0 Cefuroxime 0 0 Ceftriaxone 0 0 Ceftriaxone 0 0 Azithromycin 12 0 Azithromycin 8 0 Levofloxacin/Ofloxacin 0 0 Levofloxacin/Ofloxacin 0 0 Chloramphenicol 12 2 Erythromycin 0 0 Cotrimoxazole Chloramphenicol 0 0 Tetracycline Pneumology fann 2006 (n = 39) 2008 (n = 41) 2006 (n = 30) 2008 (n = 43) Ampicillin Penicillin G 7 32 AmoxClavulanic acid 0 0 AmoxClavulanic acid 0 0 Cefuroxime 0 0 Cefuroxime 0 0 Ceftriaxone 0 0 Ceftriaxone 0 0 Azithromycin 10 0 Azithromycin 7 0 Levofloxacin/Ofloxacin 0 0 Levofloxacin/Ofloxacin 0 0 Chloramphenicol 10 5 Erythromycin 7 5 Cotrimoxazole Chloramphenicol 0 7 Tetracycline confirm that they have permission to reproduce any copyrighted material. References 1. Hoberman A, Marchant CD, Kaplan SL, Feldman S. Treatment of acute otitis media consensus recommendations. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2002;41(6): Ball P. Epidemiology and treatment of chronic bronchitis and its exacerbations. Chest. 1995;108(2 Suppl):43S 52S. 3. Anon JB, Jacobs MR, Poole MD, et al. Antimicrobial treatment guidelines for acute bacterial rhinosinusitis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2004;130(1 Suppl): Niederman MS, Mandell LA, Anzueto A, et al. Guidelines for the management of adults with community-acquired pneumonia. Diagnosis, assessment of severity, antimicrobial therapy, and prevention. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;163(7): Microbiology Insights 2010:3 51
8 Ndiaye et al 5. Mandell LA. Community-acquired pneumonia: etiology, epidemiology and treatment. Chest. 1995;108: Goldstein F, Bryskier A, Appelbaum PC, et al. The etiology of respiratory tract infections and the antibacterial activity of fluoro quinolones and other oral bacterial agents against respiratory pathogens. Clinical Microbiology and Infection. 1998;4(2): Jacobs MR, Felmingham D, Appelbaum PC, Grüneberg RN, the Alexander Project Group. The Alexander Project : susceptibility of pathogens isolated from community-acquired respiratory tract infection to commonly used antimicrobial agents. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2003;52: Felmingham D, Gruneberg RN. The Alexander project : Latest susceptibility data from this international study of bacterial pathogens from community-acquired lower respiratory tract infections. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2000;45: Klugman KP, Lonks JR. Hidden epidemic of macrolide-resistant pneumococci. Emerg Infect Dis. 2005;11(6): Tristram S, Jacobs MR, Appelbaum PC. Antimicrobial resistance in Haemophilus influenzae. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2007;20(2): Zhang R, Eggleston K, Rotimi V, Zeckhauser RJ. Antibiotic resistance as a global threat: Evidence from China, Kuwait and the United States. Globalization and Health. 2006;2: Chohan L, Hollier LM, Bishop K, Kilpatrick CC. Patterns of Antibiotic Resistance Among Group B Streptococcus Isolates: Infect Dis Obstet Gynecol. 2006;2006: Matsubara K, Nishiyama Y, Katayama K, et al. Change of antimicrobial susceptibility of group B streptococci over 15 years in Japan. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2001;48(4): Bae S, Lee J, Lee J, et al. Antimicrobial Resistance in Haemophilus influenzae Respiratory Tract Isolates in Korea: Results of a Nationwide Acute Respiratory Infections Surveillance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010;54(1): Sakata H. Changes over 10 years of ampicillin-resistant Haemophilus influenzae isolated from children. Jpn J Antibiot. 2009;62(4): Borgmann S, Jakobiak T, Gruber H, Schröder H, Sagel U. Prescriptions of broad-spectrum antibiotics to outpatients do not match increased prevalence and antibiotic resistance of respiratory pathogens in Bavaria. Pol J Microbiol. 2009;58(2): Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. M2-A Performance standards for antimicrobial disk susceptibility tests. Ninth edition. Approved Standard. Wayne. PA: CLSI. 18. WHO (2004). WhoNet Software [online]; Accessed 22/01/2009. URL: Benbachir M, Benredjed S, Boye CS, et al. Two-Year Surveillance of Antibiotic Resistance in Streptococcus pneumoniae in four African Cities. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2001;45(2): Camara B Cisse MF, Faye PM Ba, et al. Purulent meningitis in a paediatric hospital (Dakar, Senegal. Med Mal Infect. 2003;33(8): Sife Mefo H, Sife H, Mbonda E, et al. Les méningites purulentes de l enfant au Nord Cameroun: Aspects cliniques, Bactériologiques et thérapeutiques. Med Afr Noire. 1999;46(1): Akoua Koffi C, Anghui H, Faye-Kette H, et al. Aspects bactériologiques des méningites purulentes au CHU de Yopoughon, Med Mal Infect. 2000;31: DagnraA Y, Tigossou S, Prince-David M. Prévalence et sensibilité aux antibiotiques des bactéries isolées des méningites. Med Mal Infect. 2000;30(5): Biendo M, Yala F, Kounkou R, et al. Les méningites bactériennes du nouveau-né et de l enfant à Brazzaville: aspects bactériologiques et épidémiologiques (à propos de 348 cas). Afr Med. 1990;29(284): Emele FE. Etiologic spectrum and pattern of antimicrobial drug susceptibility in bacterial meningitis in Sokoto, Nigeria. Acta Pediatr. 2000;89: Thabet L, Bousseta K, Kaabachi O, et al. Bacteriological profile of bacterial meningitis in the Tunis childern hospital. Med Mal Infect. 2002;32(1): Camara B, Faye PM, Diouf S, et al. Pediatric haemophilus influenzae b meningitis in Dakar. Med Mal Infect. 2007;37(11): Publish with Libertas Academica and every scientist working in your field can read your article I would like to say that this is the most author-friendly editing process I have experienced in over 150 publications. Thank you most sincerely. The communication between your staff and me has been terrific. Whenever progress is made with the manuscript, I receive notice. Quite honestly, I ve never had such complete communication with a journal. LA is different, and hopefully represents a kind of scientific publication machinery that removes the hurdles from free flow of scientific thought. Your paper will be: Available to your entire community free of charge Fairly and quickly peer reviewed Yours! You retain copyright 52 Microbiology Insights 2010:3
Appropriate Treatment for Children with Upper Respiratory Infection
 BCBS ACO Measure Appropriate Treatment for Children with Upper Respiratory Infection HEDIS Measure CPT II coding required: YES Click here to go to Table of Contents BCBS Measure: Page 50 of 234 Dated:
BCBS ACO Measure Appropriate Treatment for Children with Upper Respiratory Infection HEDIS Measure CPT II coding required: YES Click here to go to Table of Contents BCBS Measure: Page 50 of 234 Dated:
2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY
 Measure #65 (NQF 0069): Appropriate Treatment for Children with Upper Respiratory Infection (URI) National Quality Strategy Domain: Efficiency and Cost Reduction 2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES:
Measure #65 (NQF 0069): Appropriate Treatment for Children with Upper Respiratory Infection (URI) National Quality Strategy Domain: Efficiency and Cost Reduction 2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES:
Disc Diffusion Susceptibility Methods
 Disc Diffusion Susceptibility Methods Introduction When a filter paper disc impregnated with a chemical is placed on agar the chemical will diffuse from the disc into the agar. This diffusion will place
Disc Diffusion Susceptibility Methods Introduction When a filter paper disc impregnated with a chemical is placed on agar the chemical will diffuse from the disc into the agar. This diffusion will place
Biological Sciences Initiative
 Biological Sciences Initiative HHMI Student Activities Measuring Antibiotic Resistance Introduction: You might be aware that antibiotics were once thought of as a magic bullet; a nearly perfect drug for
Biological Sciences Initiative HHMI Student Activities Measuring Antibiotic Resistance Introduction: You might be aware that antibiotics were once thought of as a magic bullet; a nearly perfect drug for
WARNING LETTER. According to its approved product labeling (PI) (in pertinent part, emphasis original):
 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES Public Health Service Food and Drug Administration Silver Spring, MD 20993-0002 TRANSMITTED BY FACSIMILE Sapan A. Shah, Ph.D. President and Chief Executive Officer
DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES Public Health Service Food and Drug Administration Silver Spring, MD 20993-0002 TRANSMITTED BY FACSIMILE Sapan A. Shah, Ph.D. President and Chief Executive Officer
Treatment costs associated with community-acquired pneumonia by community level of antimicrobial resistance
 Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (2008) 61, 1162 1168 doi:10.1093/jac/dkn073 Advance Access publication 29 February 2008 Treatment costs associated with community-acquired pneumonia by community level
Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (2008) 61, 1162 1168 doi:10.1093/jac/dkn073 Advance Access publication 29 February 2008 Treatment costs associated with community-acquired pneumonia by community level
Welcome to Implementing Inquirybased Microbial Project. Veronica Ardi, PhD
 Welcome to Implementing Inquirybased Microbial Project Veronica Ardi, PhD Microbiology Laboratory Courses CourseSmart: ebook resources http://instructors.coursesmart.com/ Microbiology Laboratory Courses
Welcome to Implementing Inquirybased Microbial Project Veronica Ardi, PhD Microbiology Laboratory Courses CourseSmart: ebook resources http://instructors.coursesmart.com/ Microbiology Laboratory Courses
Antibiotic resistance does it matter in paediatric clinical practice? Jette Bangsborg Department of Clinical Microbiology Herlev Hospital
 Antibiotic resistance does it matter in paediatric clinical practice? Jette Bangsborg Department of Clinical Microbiology Herlev Hospital Background The Department of Clinical Microbiology at Herlev Hospital
Antibiotic resistance does it matter in paediatric clinical practice? Jette Bangsborg Department of Clinical Microbiology Herlev Hospital Background The Department of Clinical Microbiology at Herlev Hospital
ANNUAL REPORT ON STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS BACTERAEMIA CASES IN DENMARK 2008 (part I)
 ANNUAL REPORT ON STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS BACTERAEMIA CASES IN DENMARK 2008 (part I) STAPHYLOCOCCUS LABORATORY, STATENS SERUM INSTITUT 1 Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia annual report, part I The format
ANNUAL REPORT ON STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS BACTERAEMIA CASES IN DENMARK 2008 (part I) STAPHYLOCOCCUS LABORATORY, STATENS SERUM INSTITUT 1 Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia annual report, part I The format
Activity of oral antibiotics against respiratory tract pathogens in Spain
 Rev Esp Quimioterap, Diciembre 2003; Vol.16 (Nº 4): 436-443 2003 Prous Science, S.A.- Sociedad Española de Quimioterapia Original Activity of oral antibiotics against respiratory tract pathogens in Spain
Rev Esp Quimioterap, Diciembre 2003; Vol.16 (Nº 4): 436-443 2003 Prous Science, S.A.- Sociedad Española de Quimioterapia Original Activity of oral antibiotics against respiratory tract pathogens in Spain
Laboratory Exercise # 11: Differentiation of the Species Staphylococcus and Streptococcus
 Laboratory Exercise # 11: Differentiation of the Species Staphylococcus and Streptococcus Purpose: The purpose of this laboratory exercise is to explore the differences between Staphylococcal species and
Laboratory Exercise # 11: Differentiation of the Species Staphylococcus and Streptococcus Purpose: The purpose of this laboratory exercise is to explore the differences between Staphylococcal species and
Levofloxacin for the Treatment of Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Bronchitis: Position in Recent Guidelines
 Levofloxacin for the Treatment of Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Bronchitis: Position in Recent Guidelines Review Article From left to right Hartmut M Lode, MD, PhD M Schmidt-Ioanas, MD, PhD Department
Levofloxacin for the Treatment of Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Bronchitis: Position in Recent Guidelines Review Article From left to right Hartmut M Lode, MD, PhD M Schmidt-Ioanas, MD, PhD Department
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections Overview A urine culture must ALWAYS be interpreted in the context of the urinalysis and patient symptoms. If a patient has no signs of infection on urinalysis, no symptoms of
Urinary Tract Infections Overview A urine culture must ALWAYS be interpreted in the context of the urinalysis and patient symptoms. If a patient has no signs of infection on urinalysis, no symptoms of
ANNUAL REPORT ON STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS BACTERAEMIA CASES IN DENMARK 2009 (part I)
 ANNUAL REPORT ON STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS BACTERAEMIA CASES IN DENMARK 2009 (part I) STAPHYLOCOCCUS LABORATORY, STATENS SERUM INSTITUT 1 Staphylococcus aureus Bacteraemia Annual Report, Part I The annual
ANNUAL REPORT ON STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS BACTERAEMIA CASES IN DENMARK 2009 (part I) STAPHYLOCOCCUS LABORATORY, STATENS SERUM INSTITUT 1 Staphylococcus aureus Bacteraemia Annual Report, Part I The annual
PLAN OF ACTION FOR. Physician Name Signature License Date
 PLAN OF ACTION FOR Patient s copy (patient s name) I Feel Well Lignes I feel short directrices of breath: I cough up sputum daily. No Yes, colour: I cough regularly. No Yes I Feel Worse I have changes
PLAN OF ACTION FOR Patient s copy (patient s name) I Feel Well Lignes I feel short directrices of breath: I cough up sputum daily. No Yes, colour: I cough regularly. No Yes I Feel Worse I have changes
Labquality External Quality Assessment Programmes General Bacteriology 1 4/2010
 Labquality External Quality Assessment Programmes General Bacteriology 1 4/2010 Photos and text: Markku Koskela, M.D., Ph.D. Clinical microbiology specialist Oulu, Finland Sample 13/2010 Cerebrospinal
Labquality External Quality Assessment Programmes General Bacteriology 1 4/2010 Photos and text: Markku Koskela, M.D., Ph.D. Clinical microbiology specialist Oulu, Finland Sample 13/2010 Cerebrospinal
Do general practitioners prescribe more antimicrobials when the weekend comes?
 DOI 10.1186/s40064-015-1505-6 RESEARCH Open Access Do general practitioners prescribe more antimicrobials when the weekend comes? Meera Tandan 1*, Sinead Duane 1 and Akke Vellinga 1,2 Abstract Inappropriate
DOI 10.1186/s40064-015-1505-6 RESEARCH Open Access Do general practitioners prescribe more antimicrobials when the weekend comes? Meera Tandan 1*, Sinead Duane 1 and Akke Vellinga 1,2 Abstract Inappropriate
Diagnosis, Treatment and Prevention of Typhoid Fever in the Children of Bangladesh: A Microbiologist s View.
 Diagnosis, Treatment and Prevention of Typhoid Fever in the Children of Bangladesh: A Microbiologist s View. Samir K Saha, Ph.D. Department of Microbiology Dhaka Shishu Hospital Bangladesh Typhoid Fever:Salmonella
Diagnosis, Treatment and Prevention of Typhoid Fever in the Children of Bangladesh: A Microbiologist s View. Samir K Saha, Ph.D. Department of Microbiology Dhaka Shishu Hospital Bangladesh Typhoid Fever:Salmonella
school for boys Persistent streptococcal throat infection in a preparatory BY J. H. D. BRISCOE
 J. Hyg., Camb. (1985), 95, 671-676 671 Printed in Great Britain Persistent streptococcal throat infection in a preparatory school for boys BY J. H. D. BRISCOE Eton Court House, Eton, Windsor, Berkshire
J. Hyg., Camb. (1985), 95, 671-676 671 Printed in Great Britain Persistent streptococcal throat infection in a preparatory school for boys BY J. H. D. BRISCOE Eton Court House, Eton, Windsor, Berkshire
Liofilchem - Antibiotic Disk Interpretative Criteria and Quality Control - F14013 - Rev.7 / 20.02.2013
 Liofilchem Antibiotic Disk Interpretative Criteria and Quality Control F0 Rev.7 /.02. Amikacin AK Amoxicillin + Clavulanic acid AUG (+) ATCC 352 Coagulasenegative staphylococci Amoxicillin + Clavulanic
Liofilchem Antibiotic Disk Interpretative Criteria and Quality Control F0 Rev.7 /.02. Amikacin AK Amoxicillin + Clavulanic acid AUG (+) ATCC 352 Coagulasenegative staphylococci Amoxicillin + Clavulanic
PRIORITY RESEARCH TOPICS
 PRIORITY RESEARCH TOPICS Understanding all the issues associated with antimicrobial resistance is probably impossible, but it is clear that there are a number of key issues about which we need more information.
PRIORITY RESEARCH TOPICS Understanding all the issues associated with antimicrobial resistance is probably impossible, but it is clear that there are a number of key issues about which we need more information.
Use of Antibiotics for Adult Upper Respiratory Infections in Outpatient Settings: A National Ambulatory Network Study
 Vol. 38, No. 5 349 Health Services Research Use of Antibiotics for Adult Upper Respiratory Infections in Outpatient Settings: A National Ambulatory Network Study James M. Gill, MD, MPH; Peter Fleischut;
Vol. 38, No. 5 349 Health Services Research Use of Antibiotics for Adult Upper Respiratory Infections in Outpatient Settings: A National Ambulatory Network Study James M. Gill, MD, MPH; Peter Fleischut;
GLOBAL OVERVIEW OF ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE STD AGENTS
 GLOBAL OVERVIEW OF ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE STD AGENTS IN Dr.P.Bhalla Director Professor and Head Dept. of Microbiology Maulana Azad Medical College New Delhi, INDIA STDs & RTIs l HIV l Gonococcal infections/
GLOBAL OVERVIEW OF ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE STD AGENTS IN Dr.P.Bhalla Director Professor and Head Dept. of Microbiology Maulana Azad Medical College New Delhi, INDIA STDs & RTIs l HIV l Gonococcal infections/
Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea, Clostridium difficile- Associated Diarrhea and Colitis
 Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea, Clostridium difficile- Associated Diarrhea and Colitis ANTIBIOTIC-ASSOCIATED DIARRHEA Disturbance of the normal colonic microflora Leading to alterations in bacterial degradation
Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea, Clostridium difficile- Associated Diarrhea and Colitis ANTIBIOTIC-ASSOCIATED DIARRHEA Disturbance of the normal colonic microflora Leading to alterations in bacterial degradation
A baseline survey of antimicrobial resistance in bacteria from selected New Zealand foods, 2009 2010
 A baseline survey of antimicrobial resistance in bacteria from New Zealand foods, 2009 2010 MAF Technical Paper No: 2011/53 Helen Heffernan 1, Teck Lok Wong 2, Jennifer Lindsay 2, Barbara Bowen1 and Rosemary
A baseline survey of antimicrobial resistance in bacteria from New Zealand foods, 2009 2010 MAF Technical Paper No: 2011/53 Helen Heffernan 1, Teck Lok Wong 2, Jennifer Lindsay 2, Barbara Bowen1 and Rosemary
Annual Report on Staphylococcus aureus Bacteraemia Cases 2006
 Annual Report on Staphylococcus aureus Bacteraemia Cases 2006 STAPHYLOCOCCUS LABORATORY, STATENS SERUM INSTITUT, 2006 Members of the Danish Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia group Thomas Benfield, Dr. med.
Annual Report on Staphylococcus aureus Bacteraemia Cases 2006 STAPHYLOCOCCUS LABORATORY, STATENS SERUM INSTITUT, 2006 Members of the Danish Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia group Thomas Benfield, Dr. med.
Date: November 30, 2010
 Department of Health and Human Services Public Health Service Food and Drug Administration Center for Drug Evaluation and Research Date: November 30, 2010 To: Through: From: Subject: Drug Name(s): Application
Department of Health and Human Services Public Health Service Food and Drug Administration Center for Drug Evaluation and Research Date: November 30, 2010 To: Through: From: Subject: Drug Name(s): Application
Vancomycin. Beta-lactams. Beta-lactams. Vancomycin (Glycopeptide) Rifamycins (rifampin) MID 4
 Antibiotic Classes Introduction to Antimicrobials Rachel J. Gordon, MD, MPH Assistant Professor of Clinical Medicine and Epidemiology Beta-lactams Inhibit cell wall synthesis Penicillins Cephalosporins
Antibiotic Classes Introduction to Antimicrobials Rachel J. Gordon, MD, MPH Assistant Professor of Clinical Medicine and Epidemiology Beta-lactams Inhibit cell wall synthesis Penicillins Cephalosporins
Effects of Antibiotics on Bacterial Growth and Protein Synthesis: Student Laboratory Manual
 Effects of Antibiotics on Bacterial Growth and Protein Synthesis: Student Laboratory Manual I. Purpose...1 II. Introduction...1 III. Inhibition of Bacterial Growth Protocol...2 IV. Inhibition of in vitro
Effects of Antibiotics on Bacterial Growth and Protein Synthesis: Student Laboratory Manual I. Purpose...1 II. Introduction...1 III. Inhibition of Bacterial Growth Protocol...2 IV. Inhibition of in vitro
Drug Use Review. Edward Cox, M.D. Director Office of Antimicrobial Products
 Department of Health and Human Services Public Health Service Food and Drug Administration Center for Drug Evaluation and Research Drug Use Review Date: April 5, 2012 To: Through: Edward Cox, M.D. Director
Department of Health and Human Services Public Health Service Food and Drug Administration Center for Drug Evaluation and Research Drug Use Review Date: April 5, 2012 To: Through: Edward Cox, M.D. Director
PERTUSSIS SURVEILLANCE AND RESPONSE PROTOCOL
 PERTUSSIS SURVEILLANCE AND RESPONSE PROTOCOL Public Health Action 1. Educate the public, particularly parents of infants, about the dangers of whooping cough and the advantages of initiating immunization
PERTUSSIS SURVEILLANCE AND RESPONSE PROTOCOL Public Health Action 1. Educate the public, particularly parents of infants, about the dangers of whooping cough and the advantages of initiating immunization
Ceftriaxone Therapy Vs. Ciprofloxacin In Treatment Of Typhoid Fever In Adult Patients.
 Dec QMJ VOL.5 No.8 Ceftriaxone Therapy Vs. Ciprofloxacin In Treatment Of Typhoid Fever In Adult Patients. Radhi F.Alshaibani* الخلاصھ لا زالت حمى التایفوید سببا مھما من اسباب الامراض وفقدان ساعات العمل
Dec QMJ VOL.5 No.8 Ceftriaxone Therapy Vs. Ciprofloxacin In Treatment Of Typhoid Fever In Adult Patients. Radhi F.Alshaibani* الخلاصھ لا زالت حمى التایفوید سببا مھما من اسباب الامراض وفقدان ساعات العمل
8/5/2014. We have no commercial or financial conflict of interest
 Erica Runningdeer, MSN, MPH, RN Illinois Department of Public Health Gail Itokazu, PharmD John H Storger Jr. Hospital of Cook County Sarah Becca Peglow, MD Rush University Medical Center John H Stroger,
Erica Runningdeer, MSN, MPH, RN Illinois Department of Public Health Gail Itokazu, PharmD John H Storger Jr. Hospital of Cook County Sarah Becca Peglow, MD Rush University Medical Center John H Stroger,
COPD is a common disease, associated with high. Acute Exacerbation of COPD* Factors Associated With Poor Treatment Outcome
 Acute Exacerbation of COPD* Factors Associated With Poor Treatment Outcome Naresh A. Dewan, MBBS, FCCP; Salem Rafique, MD; Badar Kanwar, MD; Hemant Satpathy, MD; Kay Ryschon, MS; Glenn S. Tillotson, MS;
Acute Exacerbation of COPD* Factors Associated With Poor Treatment Outcome Naresh A. Dewan, MBBS, FCCP; Salem Rafique, MD; Badar Kanwar, MD; Hemant Satpathy, MD; Kay Ryschon, MS; Glenn S. Tillotson, MS;
Transportation of Specimens for Neisseria gonorrhoeae Culture
 TRANSPORTATION OF SPECIMENS FOR NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE MARCH 2014 ation of Specimens for Neisseria gonorrhoeae Culture There is a critical need to ensure accurate antimicrobial resistance testing for Neisseria
TRANSPORTATION OF SPECIMENS FOR NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE MARCH 2014 ation of Specimens for Neisseria gonorrhoeae Culture There is a critical need to ensure accurate antimicrobial resistance testing for Neisseria
The Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing Device Manufacturer: Development Process, Timelines, and Challenges
 The Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing Device Manufacturer: Development Process, Timelines, and Challenges Sheila Farnham, MT(ASCP) President Susceptibility Testing Manufacturers Association January
The Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing Device Manufacturer: Development Process, Timelines, and Challenges Sheila Farnham, MT(ASCP) President Susceptibility Testing Manufacturers Association January
SELECTIVE AND DIFFERENTIAL MEDIA
 SELECTIVE AND DIFFERENTIAL MEDIA Selective and differential media are used to isolate or identify particular organisms. Selective media allow certain types of organisms to grow, and inhibit the growth
SELECTIVE AND DIFFERENTIAL MEDIA Selective and differential media are used to isolate or identify particular organisms. Selective media allow certain types of organisms to grow, and inhibit the growth
Urinary tract infections caused by extended spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL) producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae
 African Journal of Biotechnology Vol. 10(73), pp. 16661-16666, 21 November, 2011 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/ajb DOI: 10.5897/AJB11.2449 ISSN 1684 5315 2011 Academic Journals Full
African Journal of Biotechnology Vol. 10(73), pp. 16661-16666, 21 November, 2011 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/ajb DOI: 10.5897/AJB11.2449 ISSN 1684 5315 2011 Academic Journals Full
Materials and methods. Results. Phenotypes of macrolide lincosamide streptogramin (MLS) resistance. Bacterial isolates
 Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (1998) 41, 621 627 JAC Antimicrobial susceptibility of viridans group streptococci in Taiwan with an emphasis on the high rates of resistance to penicillin and macrolides
Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (1998) 41, 621 627 JAC Antimicrobial susceptibility of viridans group streptococci in Taiwan with an emphasis on the high rates of resistance to penicillin and macrolides
The 14th EURL-AR Proficiency Test - enterococci, staphylococci and E. coli 2013. Lina Cavaco Susanne Karlsmose Rene S. Hendriksen Frank M.
 The 14th EURL-AR Proficiency Test - enterococci, staphylococci and E. coli 2013 Lina Cavaco Susanne Karlsmose Rene S. Hendriksen Frank M. Aarestrup The 14TH EURL-AR Proficiency Test Enterococci, Staphylococci
The 14th EURL-AR Proficiency Test - enterococci, staphylococci and E. coli 2013 Lina Cavaco Susanne Karlsmose Rene S. Hendriksen Frank M. Aarestrup The 14TH EURL-AR Proficiency Test Enterococci, Staphylococci
SEA-HLM-415 Distribution: General. Establishment of national laboratory-based surveillance of antimicrobial resistance
 SEA-HLM-415 Distribution: General Establishment of national laboratory-based surveillance of antimicrobial resistance World Health Organization 2011 All rights reserved. Requests for publications, or for
SEA-HLM-415 Distribution: General Establishment of national laboratory-based surveillance of antimicrobial resistance World Health Organization 2011 All rights reserved. Requests for publications, or for
Antibiotic Guidelines: Ear Nose and Throat (ENT) Infections. Contents
 Antibiotic Guidelines: Ear Nose and Throat (ENT) Infections. Classification: Clinical Guideline Lead Author: Antibiotic Steering Committee Additional author(s): Authors Division: DCSS & Tertiary Medicine
Antibiotic Guidelines: Ear Nose and Throat (ENT) Infections. Classification: Clinical Guideline Lead Author: Antibiotic Steering Committee Additional author(s): Authors Division: DCSS & Tertiary Medicine
Haemophilus Influenzae (meningitis and invasive
 Haemophilus Influenzae (meningitis and invasive disease)! Report immediately 24/7 by phone upon initial suspicion or laboratory test order PROTOCOL CHECKLIST Enter available information into Merlin upon
Haemophilus Influenzae (meningitis and invasive disease)! Report immediately 24/7 by phone upon initial suspicion or laboratory test order PROTOCOL CHECKLIST Enter available information into Merlin upon
Optimizing Antimicrobial Susceptibility Test Reporting
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Sept. 2011, p. S15 S19 0095-1137/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jcm.00712-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. VOL. 49, NO. 9 SUPPL. Optimizing
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Sept. 2011, p. S15 S19 0095-1137/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jcm.00712-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. VOL. 49, NO. 9 SUPPL. Optimizing
Management of Extended Spectrum Beta- Lactamase (ESBL) Producing Enterobacteriaceae in health care settings
 Management of Extended Spectrum Beta- Lactamase (ESBL) Producing Enterobacteriaceae in health care settings Dr. Mary Vearncombe PIDAC-IPC February 2012 Objectives: To provide an overview of the RP/AP Annex
Management of Extended Spectrum Beta- Lactamase (ESBL) Producing Enterobacteriaceae in health care settings Dr. Mary Vearncombe PIDAC-IPC February 2012 Objectives: To provide an overview of the RP/AP Annex
JIANGSU CARTMAY INDUSTRIAL CO.,LTD www.labfurniture.asia mail: info@labfurniture.asia
 The basic layout, the main functions and instrumentation concept of micro Inspection Division laboratory, 1, Virology Laboratory 1. Functions: for the city to monitor the prevalence of HIV disease, dealing
The basic layout, the main functions and instrumentation concept of micro Inspection Division laboratory, 1, Virology Laboratory 1. Functions: for the city to monitor the prevalence of HIV disease, dealing
FACULTY OF MEDICAL SCIENCE
 Doctor of Philosophy Program in Microbiology FACULTY OF MEDICAL SCIENCE Naresuan University 171 Doctor of Philosophy Program in Microbiology The time is critical now for graduate education and research
Doctor of Philosophy Program in Microbiology FACULTY OF MEDICAL SCIENCE Naresuan University 171 Doctor of Philosophy Program in Microbiology The time is critical now for graduate education and research
Frequently Asked Questions
 Guidelines for Testing and Treatment of Gonorrhea in Ontario, 2013 Frequently Asked Questions Table of Contents Background... 1 Treatment Recommendations... 2 Treatment of Contacts... 4 Administration
Guidelines for Testing and Treatment of Gonorrhea in Ontario, 2013 Frequently Asked Questions Table of Contents Background... 1 Treatment Recommendations... 2 Treatment of Contacts... 4 Administration
LABORATORY PROCEDURE BBL Pneumoslide Test for Streptococcus pneumoniae
 I. INTENDED USE LABORATORY PROCEDURE BBL Pneumoslide Test for Streptococcus pneumoniae The BBL Pneumoslide Test is a serologic latex slide agglutination method for the qualitative detection of capsular
I. INTENDED USE LABORATORY PROCEDURE BBL Pneumoslide Test for Streptococcus pneumoniae The BBL Pneumoslide Test is a serologic latex slide agglutination method for the qualitative detection of capsular
Venkatadri Babu. et al. / International Journal of Biological & Pharmaceutical Research. 2014; 5(1): 66-70.
 66 e- ISSN 0976-3651 Print ISSN 2229-7480 International Journal of Biological & Pharmaceutical Research Journal homepage: www.ijbpr.com IJBPR MULTIDRUG RESISTANT ESCHERICHIA COLI AND KLEBSIELLA PNEUMONIAE
66 e- ISSN 0976-3651 Print ISSN 2229-7480 International Journal of Biological & Pharmaceutical Research Journal homepage: www.ijbpr.com IJBPR MULTIDRUG RESISTANT ESCHERICHIA COLI AND KLEBSIELLA PNEUMONIAE
Nursing college, Second stage Microbiology Dr.Nada Khazal K. Hendi L14: Hospital acquired infection, nosocomial infection
 L14: Hospital acquired infection, nosocomial infection Definition A hospital acquired infection, also called a nosocomial infection, is an infection that first appears between 48 hours and four days after
L14: Hospital acquired infection, nosocomial infection Definition A hospital acquired infection, also called a nosocomial infection, is an infection that first appears between 48 hours and four days after
The prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibility patterns of beta-hemolytic streptococci colonizing the throats of schoolchildren in Assam, India
 Brief Original Article The prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibility patterns of beta-hemolytic streptococci colonizing the throats of schoolchildren in Assam, India Utpala Devi, Prasanta Kumar Borah,
Brief Original Article The prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibility patterns of beta-hemolytic streptococci colonizing the throats of schoolchildren in Assam, India Utpala Devi, Prasanta Kumar Borah,
How To Treat Mrsa From A Dead Body
 HUSRES Annual Report 2012 Martti Vaara www.huslab.fi www.intra.hus.fi Martti Vaara 2013 1 The basis of this HUSRES 2012 report is the HUSLAB/Whonet database 2012, which contains susceptibility data on
HUSRES Annual Report 2012 Martti Vaara www.huslab.fi www.intra.hus.fi Martti Vaara 2013 1 The basis of this HUSRES 2012 report is the HUSLAB/Whonet database 2012, which contains susceptibility data on
Antimicrobial Stewardship for Hospital Acquired Infection Prevention: Focus on C. difficile infection
 Antimicrobial Stewardship for Hospital Acquired Infection Prevention: Focus on C. difficile infection Emi Minejima, PharmD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pharmacy USC School of Pharmacy minejima@usc.edu
Antimicrobial Stewardship for Hospital Acquired Infection Prevention: Focus on C. difficile infection Emi Minejima, PharmD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pharmacy USC School of Pharmacy minejima@usc.edu
British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy
 British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy BSAC to actively support the EUCAST Disc Diffusion Method for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing in preference to the current BSAC Disc Diffusion Method
British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy BSAC to actively support the EUCAST Disc Diffusion Method for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing in preference to the current BSAC Disc Diffusion Method
HUSRES Annual Report 2008 Martti Vaara. www.huslab.fi www.intra.hus.fi
 HUSRES Annual Report 2008 Martti Vaara www.huslab.fi www.intra.hus.fi The basis of this HUSRES 2008 report is the HUSLAB/Whonet database 2008, which contains susceptibility data on about 180.000 bacteria
HUSRES Annual Report 2008 Martti Vaara www.huslab.fi www.intra.hus.fi The basis of this HUSRES 2008 report is the HUSLAB/Whonet database 2008, which contains susceptibility data on about 180.000 bacteria
Introduction. Introduction. Why do we need microbiological diagnostics of udder infections? Microbiological diagnostics How is it done?
 Introduction Microbiological diagnostics of udder infections Karin Persson Waller National Veterinary Institute (SVA) Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences Uppsala, Sweden Mastitis = in most cases
Introduction Microbiological diagnostics of udder infections Karin Persson Waller National Veterinary Institute (SVA) Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences Uppsala, Sweden Mastitis = in most cases
Normal flora, which make up about 90% of the cells of a human body, are microbes that
 Indigenous Unknowns Lab Report Introduction: Normal flora, which make up about 90% of the cells of a human body, are microbes that live and grow on the body without causing disease under normal conditions.
Indigenous Unknowns Lab Report Introduction: Normal flora, which make up about 90% of the cells of a human body, are microbes that live and grow on the body without causing disease under normal conditions.
There may be up to 5 to 6 million cases of. Treatment Costs of Community- Acquired Pneumonia in an Employed Population*
 Treatment Costs of Community- Acquired Pneumonia in an Employed Population* Gene L. Colice, MD, FCCP; Melissa A. Morley, MA; Carl Asche, PhD; and Howard G. Birnbaum, PhD Background: Community-acquired
Treatment Costs of Community- Acquired Pneumonia in an Employed Population* Gene L. Colice, MD, FCCP; Melissa A. Morley, MA; Carl Asche, PhD; and Howard G. Birnbaum, PhD Background: Community-acquired
Drug Sensitivity Pattern ofe. coli Causing Urinary Tract Infection in Diabetic and Non-diabetic Patients
 The Journal of International Medical Research 1996; 24: 296-301 in Diabetic and Non-diabetic Patients F JINNAH\ M S ISLAM\ M A K RUMI\ M G MORSHED 2 AND F H UQ3 'Department of Microbiology and Immunology,
The Journal of International Medical Research 1996; 24: 296-301 in Diabetic and Non-diabetic Patients F JINNAH\ M S ISLAM\ M A K RUMI\ M G MORSHED 2 AND F H UQ3 'Department of Microbiology and Immunology,
Treatment of skin and soft tissue infections due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in adults
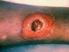 1 of 6 9/24/2010 11:16 AM Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2010 UpToDate Treatment of skin and soft tissue infections due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in adults Author
1 of 6 9/24/2010 11:16 AM Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2010 UpToDate Treatment of skin and soft tissue infections due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in adults Author
ANTIBIOTICS IN SEPSIS
 ANTIBIOTICS IN SEPSIS Jennifer Curello, PharmD, BCPS Clinical Pharmacist, Infectious Diseases Antimicrobial Stewardship Program Ronald Reagan UCLA Medical Center October 27, 2014 The power of antibiotics
ANTIBIOTICS IN SEPSIS Jennifer Curello, PharmD, BCPS Clinical Pharmacist, Infectious Diseases Antimicrobial Stewardship Program Ronald Reagan UCLA Medical Center October 27, 2014 The power of antibiotics
Use of Azithromycin in Children with Non-Cystic Fibrosis Bronchiectasis or Chronic Suppurative Lung Disease
 Use of Azithromycin in Children with Non-Cystic Fibrosis Bronchiectasis or Chronic Suppurative Lung Document ID CHQ-GDL-01061 Version no. 2.0 Approval date 28/08/2015 Executive sponsor Executive Director
Use of Azithromycin in Children with Non-Cystic Fibrosis Bronchiectasis or Chronic Suppurative Lung Document ID CHQ-GDL-01061 Version no. 2.0 Approval date 28/08/2015 Executive sponsor Executive Director
Flow Cytometry Analysis of the Activity of Disinfecting Agents Tested with Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli
 Polish Journal of Microbiology 2005, Vol. 54, No 1, 21 26 Flow Cytometry Analysis of the Activity of Disinfecting Agents Tested with Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli A. WO NIAK-KOSEK and J. KAWIAK*
Polish Journal of Microbiology 2005, Vol. 54, No 1, 21 26 Flow Cytometry Analysis of the Activity of Disinfecting Agents Tested with Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli A. WO NIAK-KOSEK and J. KAWIAK*
Short Report: Failure of Burkholderia pseudomallei to Grow in an Automated Blood Culture System
 Accepted for Publication, Published online October 13, 2014; doi:10.4269/ajtmh.14-0018. The latest version is at http://ajtmh.org/cgi/doi/10.4269/ajtmh.14-0018 In order to provide our readers with timely
Accepted for Publication, Published online October 13, 2014; doi:10.4269/ajtmh.14-0018. The latest version is at http://ajtmh.org/cgi/doi/10.4269/ajtmh.14-0018 In order to provide our readers with timely
Adjustment of antibiotic treatment according to the results of blood cultures leads to decreased antibiotic use and costs
 Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (2006) 57, 326 330 doi:10.1093/jac/dki463 Advance Access publication 29 December 2005 Adjustment of antibiotic treatment according to the results of blood cultures
Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (2006) 57, 326 330 doi:10.1093/jac/dki463 Advance Access publication 29 December 2005 Adjustment of antibiotic treatment according to the results of blood cultures
Etiology and treatment of chronic bacterial prostatitis the Croatian experience
 Etiology and treatment of chronic bacterial prostatitis the Croatian experience Višnja Škerk University Hospital for Infectious Diseases "Dr. Fran Mihaljevic" Zagreb Croatia Milano, Malpensa, 14 Nov 2008
Etiology and treatment of chronic bacterial prostatitis the Croatian experience Višnja Škerk University Hospital for Infectious Diseases "Dr. Fran Mihaljevic" Zagreb Croatia Milano, Malpensa, 14 Nov 2008
BBL Mueller Hinton II Agar L007393 Rev. 11 July 2006
 ! I II BBL Mueller Hinton II Agar L007393 Rev. 11 July 2006 QUALITY CONTROL PROCEDURES INTRODUCTION Mueller Hinton II Agar is used in the standardized disc diffusion procedure for determining the susceptibility
! I II BBL Mueller Hinton II Agar L007393 Rev. 11 July 2006 QUALITY CONTROL PROCEDURES INTRODUCTION Mueller Hinton II Agar is used in the standardized disc diffusion procedure for determining the susceptibility
BD Modified CNA Agar BD Modified CNA Agar with Crystal Violet
 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE READY-TO-USE PLATED MEDIA PA-255082.02 Rev.: June 2003 BD Modified CNA Agar BD Modified CNA Agar with Crystal Violet INTENDED USE BD Modified CNA Agar is a selective medium for the
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE READY-TO-USE PLATED MEDIA PA-255082.02 Rev.: June 2003 BD Modified CNA Agar BD Modified CNA Agar with Crystal Violet INTENDED USE BD Modified CNA Agar is a selective medium for the
Introduction to Infection Control
 CHAPTER 3 Introduction to Infection Control George Byrns and Mary Elkins Learning Objectives 1 Define terms used in infection control. 2. Review significant risk factors for infection. 3. Identify the
CHAPTER 3 Introduction to Infection Control George Byrns and Mary Elkins Learning Objectives 1 Define terms used in infection control. 2. Review significant risk factors for infection. 3. Identify the
Fotograf: Wilse, A. B. / Oslo byarkiv
 Fotograf: Wilse, A. B. / Oslo byarkiv Is it possible to reverse antibiotic resistance? Dag Berild Department of Infectious Diseases Oslo University Hospital «Take home messages» All use of antibiotics
Fotograf: Wilse, A. B. / Oslo byarkiv Is it possible to reverse antibiotic resistance? Dag Berild Department of Infectious Diseases Oslo University Hospital «Take home messages» All use of antibiotics
Prevention of Acute COPD exacerbations
 December 3, 2015 Prevention of Acute COPD exacerbations George Pyrgos MD 1 Disclosures No funding received for this presentation I have previously conducted clinical trials with Boehringer Ingelheim. Principal
December 3, 2015 Prevention of Acute COPD exacerbations George Pyrgos MD 1 Disclosures No funding received for this presentation I have previously conducted clinical trials with Boehringer Ingelheim. Principal
Antibiotic Prophylaxis for the Prevention of Infective Endocarditis and Prosthetic Joint Infections for Dentists
 PRACTICE ADVISORY SERVICE FAQ 6 Crescent Road, Toronto, ON Canada M4W 1T1 T: 416.961.6555 F: 416.961.5814 Toll Free: 1.800.565.4591 www.rcdso.org Antibiotic Prophylaxis for the Prevention of Infective
PRACTICE ADVISORY SERVICE FAQ 6 Crescent Road, Toronto, ON Canada M4W 1T1 T: 416.961.6555 F: 416.961.5814 Toll Free: 1.800.565.4591 www.rcdso.org Antibiotic Prophylaxis for the Prevention of Infective
MEDICAL MICROBIOLOGY 603 OR POPULATION HEALTH SCIENCES 603 CLINICAL AND PUBLIC HEALTH MICROBIOLOGY January 18-May 6, 2011
 MEDICAL MICROBIOLOGY 603 OR POPULATION HEALTH SCIENCES 603 CLINICAL AND PUBLIC HEALTH MICROBIOLOGY January 18-May 6, 2011 Lectures: M, W, F 1:20-2:30 P.M. ( All lectures will be ~ 70 Minutes ) Office Hours
MEDICAL MICROBIOLOGY 603 OR POPULATION HEALTH SCIENCES 603 CLINICAL AND PUBLIC HEALTH MICROBIOLOGY January 18-May 6, 2011 Lectures: M, W, F 1:20-2:30 P.M. ( All lectures will be ~ 70 Minutes ) Office Hours
HUSRES Annual Report 2010 Martti Vaara www.huslab.fi www.intra.hus.fi
 HUSRES Annual Report 2010 Martti Vaara www.huslab.fi www.intra.hus.fi Martti Vaara, 2/2011 1 The basis of this HUSRES 2010 report is the HUSLAB/Whonet database 2010, which contains susceptibility data
HUSRES Annual Report 2010 Martti Vaara www.huslab.fi www.intra.hus.fi Martti Vaara, 2/2011 1 The basis of this HUSRES 2010 report is the HUSLAB/Whonet database 2010, which contains susceptibility data
GUIDELINE Sinusitis. David M. Poetker MD, MA Associate Professor. Division of Rhinology and Sinus Surgery
 GUIDELINE Sinusitis David M. Poetker MD, MA Associate Professor Division of Rhinology and Sinus Surgery Guideline Fokkens et al. The European Position Paper on Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps 2012. Rhinology.
GUIDELINE Sinusitis David M. Poetker MD, MA Associate Professor Division of Rhinology and Sinus Surgery Guideline Fokkens et al. The European Position Paper on Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps 2012. Rhinology.
Pertussis Information for GPs and other Health Care Providers on Clinical and Public Health Management. March 2010
 Pertussis Information for GPs and other Health Care Providers on Clinical and Public Health Management March 2010 Infectious Agent Bordetella pertussis (a bacterium) Clinical Features Infants and Young
Pertussis Information for GPs and other Health Care Providers on Clinical and Public Health Management March 2010 Infectious Agent Bordetella pertussis (a bacterium) Clinical Features Infants and Young
Antimicrobial sensitivity pattern of Salmonella typhi isolated from blood culture in a referral hospital
 Bangladesh J Med Microbiol 2011; 05 (01): 16-20 Bangladesh Society of Medical Microbiologists Original Article Antimicrobial sensitivity pattern of Salmonella typhi isolated from blood culture in a referral
Bangladesh J Med Microbiol 2011; 05 (01): 16-20 Bangladesh Society of Medical Microbiologists Original Article Antimicrobial sensitivity pattern of Salmonella typhi isolated from blood culture in a referral
IQCP GUIDELINES and TEMPLATE FOR GETTING STARTED
 IQCP GUIDELINES and TEMPLATE FOR GETTING STARTED Linda C. Bruno, M.A., MT(ASCP) Director, Microbiology and Molecular Labs ACL Laboratories, Rosemont, IL June 1, 2015 Disclosures - No disclosures 2 IQCP
IQCP GUIDELINES and TEMPLATE FOR GETTING STARTED Linda C. Bruno, M.A., MT(ASCP) Director, Microbiology and Molecular Labs ACL Laboratories, Rosemont, IL June 1, 2015 Disclosures - No disclosures 2 IQCP
The National Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring System (NARMS)
 The National Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring System (NARMS) Strategic Plan 2012-2016 Table of Contents Background... 2 Mission... 3 Overview of Accomplishments, 1996-2011... 4 Strategic Goals and Objectives...
The National Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring System (NARMS) Strategic Plan 2012-2016 Table of Contents Background... 2 Mission... 3 Overview of Accomplishments, 1996-2011... 4 Strategic Goals and Objectives...
INOCULATION PROCEDURES FOR MEDIA QC
 INOCULATION PROCEDURES FOR MEDIA QC The following inoculation procedures are used by Hardy Diagnostics for performance testing. Refer to the Quality Control section of each Technical Data Sheet in the
INOCULATION PROCEDURES FOR MEDIA QC The following inoculation procedures are used by Hardy Diagnostics for performance testing. Refer to the Quality Control section of each Technical Data Sheet in the
Holy Family University, Student Health Services, Directions for Completion of Health Packet
 1 Holy Family University, Student Health Services, Directions for Completion of Health Packet All forms are to be returned to Health Services by Summer Orientation for the Fall Semester and the first day
1 Holy Family University, Student Health Services, Directions for Completion of Health Packet All forms are to be returned to Health Services by Summer Orientation for the Fall Semester and the first day
2013 Indiana Healthcare Provider and Hospital Administrator Multi-Drug Resistant Organism Survey
 2013 Indiana Healthcare Provider and Hospital Administrator Multi-Drug Resistant Organism Survey Antibiotic resistance is a global issue that has significant impact in the field of infectious diseases.
2013 Indiana Healthcare Provider and Hospital Administrator Multi-Drug Resistant Organism Survey Antibiotic resistance is a global issue that has significant impact in the field of infectious diseases.
CF ATLANTA Research & Development Program at Emory University and Georgia Tech (CF@LANTA) Clinical & Translational Research Core
 CF ATLANTA Research & Development Program at Emory University and Georgia Tech (CF@LANTA) Clinical & Translational Research Core Arlene Stecenko, MD Director, Emory + Children s Cystic Fibrosis Care Center
CF ATLANTA Research & Development Program at Emory University and Georgia Tech (CF@LANTA) Clinical & Translational Research Core Arlene Stecenko, MD Director, Emory + Children s Cystic Fibrosis Care Center
AECOPD. Guideline for. The Management of Acute Exacerbations of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (AECOPD) 2006 Update
 Guideline for Administered by the Alberta Medical Association 2006 Update The Management of Acute Exacerbations of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (AECOPD) AECOPD This clinical practice guideline
Guideline for Administered by the Alberta Medical Association 2006 Update The Management of Acute Exacerbations of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (AECOPD) AECOPD This clinical practice guideline
Medical Microbiology Microscopic slides and media
 Medical Microbiology Microscopic slides and media Head of Microbiology Department and Laboratory Medical Immunology : Janina Grzegorczyk MD, PhD, professor Implementators: Małgorzata Brauncajs MD Zbigniew
Medical Microbiology Microscopic slides and media Head of Microbiology Department and Laboratory Medical Immunology : Janina Grzegorczyk MD, PhD, professor Implementators: Małgorzata Brauncajs MD Zbigniew
Antibiotics for respiratory, ear and urinary tract disorders and consistency among GPs
 Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (2008) 62, 587 592 doi:10.1093/jac/dkn230 Advance Access publication 10 June 2008 Antibiotics for respiratory, ear and urinary tract disorders and consistency among
Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (2008) 62, 587 592 doi:10.1093/jac/dkn230 Advance Access publication 10 June 2008 Antibiotics for respiratory, ear and urinary tract disorders and consistency among
Pertussis Whooping Cough Update
 May 3, 1 Dear Kitsap County Providers, This is an update about our current status of pertussis cases here in Kitsap County. We currently have 35 cases as outlined below. See the epidemiology curve (Figure
May 3, 1 Dear Kitsap County Providers, This is an update about our current status of pertussis cases here in Kitsap County. We currently have 35 cases as outlined below. See the epidemiology curve (Figure
Antibiotic use in the management of uncomplicated URTIs and bronchitis
 Antibiotic use in the management of uncomplicated URTIs and bronchitis Aims of clinical audit To review your prescribing of antibiotics for uncomplicated upper respiratory tract infections (URTIs) and
Antibiotic use in the management of uncomplicated URTIs and bronchitis Aims of clinical audit To review your prescribing of antibiotics for uncomplicated upper respiratory tract infections (URTIs) and
Antimicrobial Resistance of Urinary Escherichia coli Isolates
 Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical Research April 2010; 9 (2): 205-209 Pharmacotherapy Group, Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Benin, Benin City, 300001 Nigeria. All rights reserved. Research Article
Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical Research April 2010; 9 (2): 205-209 Pharmacotherapy Group, Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Benin, Benin City, 300001 Nigeria. All rights reserved. Research Article
Test Method for the Continuous Reduction of Bacterial Contamination on Copper Alloy Surfaces
 Test Method for the Continuous Reduction of Bacterial Contamination on Copper Alloy Surfaces Test Organisms: Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 6538) Enterobacter aerogenes (ATCC 13048) Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Test Method for the Continuous Reduction of Bacterial Contamination on Copper Alloy Surfaces Test Organisms: Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 6538) Enterobacter aerogenes (ATCC 13048) Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Laboratory confirmation requires isolation of Bordetella pertussis or detection of B. pertussis nucleic acid, preferably from a nasopharyngeal swab.
 Pertussis Epidemiology in New Zealand New Zealand has continued to experience outbreaks of pertussis in recent decades. This is in part due to historically low immunisation rates and in part because immunity
Pertussis Epidemiology in New Zealand New Zealand has continued to experience outbreaks of pertussis in recent decades. This is in part due to historically low immunisation rates and in part because immunity
Excess mortality in Europe in the winter season 2014/15, in particular amongst the elderly.
 Excess mortality in Europe in the winter season 2014/15, in particular amongst the elderly. An analysis of all-cause mortality from 15 European countries participating in the EuroMOMO network (www.euromomo.eu)
Excess mortality in Europe in the winter season 2014/15, in particular amongst the elderly. An analysis of all-cause mortality from 15 European countries participating in the EuroMOMO network (www.euromomo.eu)
Blue Team Teaching Module: Periorbital/Orbital Infections
 Blue Team Teaching Module: Periorbital/Orbital Infections Format: 1. Case 2. Topic Summary 3. Questions 4. References Case: A 3-year-old boy presents with 2 days of increasing redness, swelling, and pain
Blue Team Teaching Module: Periorbital/Orbital Infections Format: 1. Case 2. Topic Summary 3. Questions 4. References Case: A 3-year-old boy presents with 2 days of increasing redness, swelling, and pain
National Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring System - Enteric Bacteria. A program to monitor antimicrobial resistance in humans and animals
 National Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring System - Enteric Bacteria A program to monitor antimicrobial resistance in humans and animals Antimicrobial resistance in foodborne pathogens is an important
National Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring System - Enteric Bacteria A program to monitor antimicrobial resistance in humans and animals Antimicrobial resistance in foodborne pathogens is an important
Version 11.1 May 2012
 BSAC Methods for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing Version 11.1 May 2012 All enquiries to: Jenny Andrews at: + 44 (0) 121 507 5693 Email: jenny.andrews1@nhs.net Contents Page Working Party members 5
BSAC Methods for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing Version 11.1 May 2012 All enquiries to: Jenny Andrews at: + 44 (0) 121 507 5693 Email: jenny.andrews1@nhs.net Contents Page Working Party members 5
Outpatient treatment for upper respiratory tract infections: an evaluation of. Running title: Outpatient respiratory tract infection treatment
 AAC Accepted Manuscript Posted Online 13 April 2015 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.00652-15 Copyright 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Title
AAC Accepted Manuscript Posted Online 13 April 2015 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.00652-15 Copyright 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Title
