Five-Layer Density Column
|
|
|
- Moris Scott
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Five-Layer ensity olumn density column consists of layers of liquids of different densities which do not mix with each other, and which are clearly distinguishable from each other. The highest density material is at the bottom of the column, and as you proceed up the column, the density of each successive layer decreases, with the lowest density layer on top. Three methods for construction of a five-layer density column are discussed in this write-up. ll methods use the same five liquids. Method 1 gives the names of the liquids and the order for adding them, and its goal is to directly construct the density column without any experimentation. Method 2 assumes names and densities of the five materials to be unknown, and involves open-ended experimenting, with few instructions, to construct the column. Method 3 also assumes names and densities of the materials to be unknown, and outlines a systematic way to approach the experimentation involved in constructing the column. MTHO 1 Obtain a clear plastic container whose size meets your needs, and carefully add appropriate amounts of the following materials in the order specified (the first material listed is the most dense, and should be added first: water -- color with an appropriate amount of food color before pouring canola oil -- don't add food color (it won't dissolve in oil) 60% isopropyl alcohol -- you can buy 70% isopropyl at drug stores and grocery stores -- it's used as rubbing alcohol and disinfectant -- you then have to dilute it to make it 60% -- add 2 ml of water to every 10 ml of alcohol, or 20 ml of water to every 100 ml of alcohol -- before pouring, color with an appropriate amount of food color different from the first one -- baby oil is, and can be used here, but ordinary is easily obtained at pharmacies and is cheaper -- don't add food color (it won't dissolve in oil) 91% isopropyl alcohol -- you can buy 91% isopropyl at most drug stores, and sometimes at grocery stores -- it's used as a disinfectant, particularly for pierced ears -- before pouring, color with an appropriate amount of food color different from the previous two Helpful Hints: Layers should probably be a minimum of about 1/2 inch thick, and pouring should be gentle, to avoid a layer falling through the layer it is being poured on and interacting with the layer below that one. If the container is small, consider using a pipette or eyedropper. This is easier than pouring, and allows you to add the liquids very slowly and gently to prevent unwanted mixing. Sometimes the material the container is made of plays a role in how well the layers form, possibly due to surface tension effects. Try tilting the container a little so that the liquid you are adding runs down the side more slowly. Or try laying the new liquid very gently on the previous layer by having the dropper tip just barely above the liquid surface, so that the new liquid doesn't fall and hit the surface hard. on t use too much food coloring depending on the amount of liquid you are using, even one drop of food color may be enough. If the color is too dark, you can't see through it, and it's not as effective. MTHO 2 Treat the five materials as unknowns. Play around with them (i.e., experiment!) to determine which ones will allow food color dissolve in them, and the relative order of their densities. Use your results to construct the density column. Five-Layer ensity olumn...9/29/05 1 on Rathjen...xploratorium Teacher Institute Lyon St., San Francisco, [email protected] 2005 xploratorium,
2 MTHO 3 Students receive liquids in containers labeled,,, and. Neither the identity or density of any of the materials is given. Students also receive a copy of the ata Table below (or have them draw their own if desired). This is what students will fill in as they experiment. (NOT FOR THRS: In addition to the blank ata Table below, you will also find later in this handout a Sample ompleted ata Table showing expected results, and a Teacher Reference ata Table showing actual substance names). Procedure use small test containers to find whether or not food coloring will mix with each of the five substances, and record in the data table for the liquids in which food color will dissolve, add food color to the supply FOR experimenting further with pairs of liquids -- also see Helpful Hints for Method 1 above use small test containers to carefully mix each of the required combinations to complete the table (e.g., with, with, etc.) -- note whether they mix or whether they form two layers -- if they mix, indicate MI on the table -- if layers are formed, record the letter of the substance which is on top in the upper part of the data box, and the letter of the layer which is on the bottom in the lower part of the data box ata Table SUSTN FOO OLOR ISSOLVS - Five-Layer ensity olumn...9/29/05 2 on Rathjen...xploratorium Teacher Institute Lyon St., San Francisco, [email protected] 2005 xploratorium,
3 nalysis ach time a substance is on the OTTOM of a two-substance combination, give it a score of -1. ach time a substance is on the TOP of a two-substance combination, give it a score of +1. ach time two substances MI, give each a score of 0. When all combinations have been scored, add up the total score for each substance. The one with the LOWST score is the MOST NS, and should be added first to the density column. The substance with the next lowest score should be added next, etc. (THR NOT: For more on this, see the Teacher Reference ata Table, and the detailed analysis following it.) Making the ensity olumn dd the liquids to the density column in the order determined above. Helpful Hints: For the liquids in which food color will dissolve, add food color to the liquid FOR adding the liquid to the density column. lso see Helpful Hints noted for Method 1 above. THR INFORMTION FOR NSITY OLUMNS Sample ompleted Student ata Table (having students include numbers is optional) SUSTN NO YS NO YS YS FOO OLOR ISSOLVS (+1) (-1) MI (+1) (-1) (+1) (-1) (+1) (-1) MI MI (+1) (-1) (+1) (-1) MI Five-Layer ensity olumn...9/29/05 3 on Rathjen...xploratorium Teacher Institute Lyon St., San Francisco, [email protected] 2005 xploratorium,
4 Teacher Reference ompleted ata Table SUSTN NOL OIL WTR MINRL OIL 91%LOHOL 60%LOHOL FOO OLOR ISSOLVS NO YS NO YS YS NOL OIL WTR MINRL OIL 91%LOHOL 60%LOHOL NOL OIL canola water MI 91% alcohol canola 60% alcohol canola WTR water MI MI MINRL OIL 91% alcohol 60% alcohol 91%LOHOL 60%LOHOL MI nalysis of results shows the following: Substance (canola oli) was on top once, and on the bottom twice; we will call this a net score of 1 Substance (water) was on the bottom twice, for a net score of 2 Substance () was on the top twice and the bottom once, for a net score of +1 Substance (91% alcohol) was on top twice for a net score of +2 Substance (60% alcohol) was on top once and on the bottom once, for a net score of 0 rranging the substances in order, from most dense to least dense (i.e., starting with 2, and proceeding to +2, we find the order of density to be: WTR, NOL OIL, 60% LOHOL, MINRL OIL, 91% LOHOL. When placed into a container in this order, with food colors added to the water and the two alcohols, a 5-layer density column will be formed. Five-Layer ensity olumn...9/29/05 4 on Rathjen...xploratorium Teacher Institute Lyon St., San Francisco, [email protected] 2005 xploratorium,
5 Other Miscellaneous Items Post-Lab Question: For each of the statements below, circle T if true, or F if false a. T F water mixes with alcohol b. T F water mixes with oil c. T F oil mixes with alcohol c. T F oils mix with each other d. T F alcohols mix with each other NOT ON HLPFUL HINTS: RING TH HLPFUL HINTS FOR MIING LIQUIS N MKING TH OLUMN MKS FOR MOR FFIINT PROSS WITH TTR HN FOR INITIL SUSS. UT IF TRYING THINGS FIRST IS INTRIGUING, IT IS HIGHLY NOURG. TH HINTS M FROM TUL TRIL N RROR PRINS, N IN FT WR GNRT S MUH Y FILUR, N TH N TO FIN TTR THNIQU, THN Y INITIL SUSS. YOU N OFTN LRN LOT FROM "FILUR," N IN YPSSING IT YOU SOMTIMS LOS SOM OF TH RIHNSS OF TH PRIN. ON GOO THING OUT MKING SMLL OLUMN IS THT YOU ON'T WST MUH MTRIL IF YOU LOW IT N HV TO STRT OVR! References Sarquis, Jerry L.. Mickey Sarquis, John P. Williams, Teaching hemistry with Toys, T ooks, See Frustration ottles, pp orgford, hristie L., Lee SR. Summerlin, hemical ctivities; Teacher dition, merican hemical Society, See Layers of Liquids, pp Five-Layer ensity olumn...9/29/05 5 on Rathjen...xploratorium Teacher Institute Lyon St., San Francisco, [email protected] 2005 xploratorium,
Polarity and Properties Lab PURPOSE: To investigate polar and non-polar molecules and the affect of polarity on molecular properties.
 Name!!!! date Polarity and Properties Lab PURPOSE: To investigate polar and non-polar molecules and the affect of polarity on molecular properties. STATION 1: Oil and water do not mix. We all know that.
Name!!!! date Polarity and Properties Lab PURPOSE: To investigate polar and non-polar molecules and the affect of polarity on molecular properties. STATION 1: Oil and water do not mix. We all know that.
IDENTIFICATION OF POLYMERS 1998 by David A. Katz. All rights reserved
 IDENTIFICATION OF POLYMERS 1998 by David A. Katz. All rights reserved David A. Katz Chemist, Educator, Science Communicator, and Consultant 133 N. Desert Stream Dr., Tucson, AZ 85745 Voice/Fax: 520-624-2207
IDENTIFICATION OF POLYMERS 1998 by David A. Katz. All rights reserved David A. Katz Chemist, Educator, Science Communicator, and Consultant 133 N. Desert Stream Dr., Tucson, AZ 85745 Voice/Fax: 520-624-2207
CALCULATING THE SIZE OF AN ATOM
 Ch 100: Fundamentals of Chemistry 1 CALCULATING THE SIZE OF AN ATOM Introduction: The atom is so very small that only highly sophisticated instruments are able to measure its dimensions. In this experiment
Ch 100: Fundamentals of Chemistry 1 CALCULATING THE SIZE OF AN ATOM Introduction: The atom is so very small that only highly sophisticated instruments are able to measure its dimensions. In this experiment
Ink Analysis 2005, 2004, 2002, 1993 by David A. Katz. All rights reserved.
 Ink Analysis 2005, 2004, 2002, 1993 by David A. Katz. All rights reserved. Ink from most ball-point pens and markers can be developed by paper chromatography using 70% isopropyl rubbing alcohol as the
Ink Analysis 2005, 2004, 2002, 1993 by David A. Katz. All rights reserved. Ink from most ball-point pens and markers can be developed by paper chromatography using 70% isopropyl rubbing alcohol as the
Buoyant Force and Archimedes' Principle
 Buoyant Force and Archimedes' Principle Introduction: Buoyant forces keep Supertankers from sinking and party balloons floating. An object that is more dense than a liquid will sink in that liquid. If
Buoyant Force and Archimedes' Principle Introduction: Buoyant forces keep Supertankers from sinking and party balloons floating. An object that is more dense than a liquid will sink in that liquid. If
Vitamin C Content of Fruit Juice
 1 Vitamin C Content of Fruit Juice Introduction Vitamin C Vitamins are organic compounds that have important biological functions. For instance, in humans they enable a variety of enzymes in the body to
1 Vitamin C Content of Fruit Juice Introduction Vitamin C Vitamins are organic compounds that have important biological functions. For instance, in humans they enable a variety of enzymes in the body to
SEPARATION OF A MIXTURE OF SUBSTANCES LAB
 SEPARATION OF A MIXTURE OF SUBSTANCES LAB Purpose: Every chemical has a set of defined physical properties, and when combined they present a unique fingerprint for that chemical. When chemicals are present
SEPARATION OF A MIXTURE OF SUBSTANCES LAB Purpose: Every chemical has a set of defined physical properties, and when combined they present a unique fingerprint for that chemical. When chemicals are present
Lab Activity on Air Pressure, Wind and Air Circulation Caused by Heating of the Atmosphere
 Lab Activity on Air Pressure, Wind and Air Circulation Caused by Heating of the Atmosphere 2002 Ann Bykerk-Kauffman, Dept. of Geological and Environmental Sciences, California State University, Chico *
Lab Activity on Air Pressure, Wind and Air Circulation Caused by Heating of the Atmosphere 2002 Ann Bykerk-Kauffman, Dept. of Geological and Environmental Sciences, California State University, Chico *
Test Bank - Chapter 3 Multiple Choice
 Test Bank - Chapter 3 The questions in the test bank cover the concepts from the lessons in Chapter 3. Select questions from any of the categories that match the content you covered with students. The
Test Bank - Chapter 3 The questions in the test bank cover the concepts from the lessons in Chapter 3. Select questions from any of the categories that match the content you covered with students. The
Laboratory #8: Structural Geology Thinking in 3D
 Name: Lab day: Tuesday Wednesday Thursday ENVG /SC 10110-20110L Planet Earth Laboratory Laboratory #8: Structural Geology Thinking in 3D http://www.nd.edu/~cneal/physicalgeo/lab-structural/index.html Readings:
Name: Lab day: Tuesday Wednesday Thursday ENVG /SC 10110-20110L Planet Earth Laboratory Laboratory #8: Structural Geology Thinking in 3D http://www.nd.edu/~cneal/physicalgeo/lab-structural/index.html Readings:
Gear PEPSI CAN STOVE INSTRUCTIONS
 Gear PEPSI CAN STOVE INSTRUCTIONS [NOTE: Updated Instructions are now available. The new stove is less likely to develop flame leaks and the fuel/air mixture is improved. Instructions for a simmer ring
Gear PEPSI CAN STOVE INSTRUCTIONS [NOTE: Updated Instructions are now available. The new stove is less likely to develop flame leaks and the fuel/air mixture is improved. Instructions for a simmer ring
Chemistry of Biodiesel Production. Teacher Notes. DAY 1: Biodiesel synthesis (50 minutes)
 Chemistry of Biodiesel Production Teacher Notes DAY 1: Biodiesel synthesis (50 minutes) NOTE: The lab preparation instructions / lab protocol assumes classes of 32 students, with 8 groups of 4 students
Chemistry of Biodiesel Production Teacher Notes DAY 1: Biodiesel synthesis (50 minutes) NOTE: The lab preparation instructions / lab protocol assumes classes of 32 students, with 8 groups of 4 students
Unit 1 - Pure Substances and Mixtures Chapter 2: Solutions
 2.1 Solutes & Solvents Vocabulary: Unit 1 - Pure Substances and Mixtures Chapter 2: Solutions solvent the larger part of a solution - the part of a solution into which the solutes dissolve solute the smaller
2.1 Solutes & Solvents Vocabulary: Unit 1 - Pure Substances and Mixtures Chapter 2: Solutions solvent the larger part of a solution - the part of a solution into which the solutes dissolve solute the smaller
Buoyant Force and Archimedes Principle
 Buoyant Force and Archimedes Principle Predict the behavior of fluids as a result of properties including viscosity and density Demonstrate why objects sink or float Apply Archimedes Principle by measuring
Buoyant Force and Archimedes Principle Predict the behavior of fluids as a result of properties including viscosity and density Demonstrate why objects sink or float Apply Archimedes Principle by measuring
CH204 Experiment 2. Experiment 1 Post-Game Show. Experiment 1 Post-Game Show continued... Dr. Brian Anderson Fall 2008
 CH204 Experiment 2 Dr. Brian Anderson Fall 2008 Experiment 1 Post-Game Show pipette and burette intensive and extensive properties interpolation determining random experimental error What about gross error
CH204 Experiment 2 Dr. Brian Anderson Fall 2008 Experiment 1 Post-Game Show pipette and burette intensive and extensive properties interpolation determining random experimental error What about gross error
8.9 - Flash Column Chromatography Guide
 8.9 - Flash Column Chromatography Guide Overview: Flash column chromatography is a quick and (usually) easy way to separate complex mixtures of compounds. We will be performing relatively large scale separations
8.9 - Flash Column Chromatography Guide Overview: Flash column chromatography is a quick and (usually) easy way to separate complex mixtures of compounds. We will be performing relatively large scale separations
PAPER CHROMATOGRAPHY
 PAPER CHROMATOGRAPHY INTRODUCTION Chromatography is a technique that is used to separate and to identify components of a mixture. This analytical technique has a wide range of applications in the real
PAPER CHROMATOGRAPHY INTRODUCTION Chromatography is a technique that is used to separate and to identify components of a mixture. This analytical technique has a wide range of applications in the real
LAB #11: RESONANCE IN AIR COLUMNS
 OBJECTIVES: LAB #11: RESONANCE IN AIR COLUMNS To determine the speed of sound in air by using the resonances of air columns. EQUIPMENT: Equipment Needed Qty Equipment Needed Qty Resonance Tube Apparatus
OBJECTIVES: LAB #11: RESONANCE IN AIR COLUMNS To determine the speed of sound in air by using the resonances of air columns. EQUIPMENT: Equipment Needed Qty Equipment Needed Qty Resonance Tube Apparatus
COMMON LABORATORY APPARATUS
 COMMON LABORATORY APPARATUS Beakers are useful as a reaction container or to hold liquid or solid samples. They are also used to catch liquids from titrations and filtrates from filtering operations. Bunsen
COMMON LABORATORY APPARATUS Beakers are useful as a reaction container or to hold liquid or solid samples. They are also used to catch liquids from titrations and filtrates from filtering operations. Bunsen
Fig. 1. Background. Name: Class: Date:
 Background Bubbles make a great stand in for cell membranes. They re fluid, flexible, and can self-repair. Bubbles and cell membranes are alike because their parts are so similar. If you could zoom down
Background Bubbles make a great stand in for cell membranes. They re fluid, flexible, and can self-repair. Bubbles and cell membranes are alike because their parts are so similar. If you could zoom down
Air Hockey Training Camp Care and repair of your Air Hockey Playfield
 The playfield is the single most expensive part of your Dynamo Air Hockey table. Proper care will keep your table attractive and functional for your players, and bring them back for more games. CLEAN YOUR
The playfield is the single most expensive part of your Dynamo Air Hockey table. Proper care will keep your table attractive and functional for your players, and bring them back for more games. CLEAN YOUR
Written By Kelly Lundstrom & Kennda Lynch January 31, 2012 Milk Dye ACTIVITY PLAN
 Milk Dye ACTIVITY PLAN Objective: Students will use the scientific method to test the difference between using whole milk and skim milk in this milk and food dye experiment. Students will explore ideas
Milk Dye ACTIVITY PLAN Objective: Students will use the scientific method to test the difference between using whole milk and skim milk in this milk and food dye experiment. Students will explore ideas
Activity Sheets Enzymes and Their Functions
 Name: Date: Activity Sheets Enzymes and Their Functions amylase What are Enzymes? starch glucose Enzymes are compounds that assist chemical reactions by increasing the rate at which they occur. For example,
Name: Date: Activity Sheets Enzymes and Their Functions amylase What are Enzymes? starch glucose Enzymes are compounds that assist chemical reactions by increasing the rate at which they occur. For example,
Experiment 5 Preparation of Cyclohexene
 Experiment 5 Preparation of yclohexene In this experiment we will prepare cyclohexene from cyclohexanol using an acid catalyzed dehydration reaction. We will use the cyclohexanol that we purified in our
Experiment 5 Preparation of yclohexene In this experiment we will prepare cyclohexene from cyclohexanol using an acid catalyzed dehydration reaction. We will use the cyclohexanol that we purified in our
Chapter 3 Student Reading
 Chapter 3 Student Reading If you hold a solid piece of lead or iron in your hand, it feels heavy for its size. If you hold the same size piece of balsa wood or plastic, it feels light for its size. The
Chapter 3 Student Reading If you hold a solid piece of lead or iron in your hand, it feels heavy for its size. If you hold the same size piece of balsa wood or plastic, it feels light for its size. The
Making Biodiesel from Virgin Vegetable Oil: Teacher Manual
 Making Biodiesel from Virgin Vegetable Oil: Teacher Manual Learning Goals: Students will understand how to produce biodiesel from virgin vegetable oil. Students will understand the effect of an exothermic
Making Biodiesel from Virgin Vegetable Oil: Teacher Manual Learning Goals: Students will understand how to produce biodiesel from virgin vegetable oil. Students will understand the effect of an exothermic
Phases of the Moon. Preliminaries:
 Phases of the Moon Sometimes when we look at the Moon in the sky we see a small crescent. At other times it appears as a full circle. Sometimes it appears in the daylight against a bright blue background.
Phases of the Moon Sometimes when we look at the Moon in the sky we see a small crescent. At other times it appears as a full circle. Sometimes it appears in the daylight against a bright blue background.
Teaching Time: One 25-minute period. Lesson Summary Students use iron filings to observe the 2 and 3- D field lines around a magnet.
 Lesson Summary Students use iron filings to observe the 2 and 3- D field lines around a magnet. Prior Knowledge & Skills Completed the lesson: The Earth as a Magnet: Exploring Interactions in Geospace
Lesson Summary Students use iron filings to observe the 2 and 3- D field lines around a magnet. Prior Knowledge & Skills Completed the lesson: The Earth as a Magnet: Exploring Interactions in Geospace
Chemistry 112 Laboratory Experiment 6: The Reaction of Aluminum and Zinc with Hydrochloric Acid
 Chemistry 112 Laboratory Experiment 6: The Reaction of Aluminum and Zinc with Hydrochloric Acid Introduction Many metals react with acids to form hydrogen gas. In this experiment, you will use the reactions
Chemistry 112 Laboratory Experiment 6: The Reaction of Aluminum and Zinc with Hydrochloric Acid Introduction Many metals react with acids to form hydrogen gas. In this experiment, you will use the reactions
Chapter 5, Lesson 3 Why Does Water Dissolve Salt?
 Chapter 5, Lesson 3 Why Does Water Dissolve Salt? Key Concepts The polarity of water molecules enables water to dissolve many ionically bonded substances. Salt (sodium chloride) is made from positive sodium
Chapter 5, Lesson 3 Why Does Water Dissolve Salt? Key Concepts The polarity of water molecules enables water to dissolve many ionically bonded substances. Salt (sodium chloride) is made from positive sodium
Quick Peek. H Students will learn about. H Students will design and. Students will learn about density, buoyancy, and how submarines dive.
 Quick Peek sink, float, Hover design a submarine! Students will learn about density, buoyancy, and how submarines dive. Suggested Grade Levels: 4 8 Illinois State Learning Goals science 11.A, 11.B, 12.D,
Quick Peek sink, float, Hover design a submarine! Students will learn about density, buoyancy, and how submarines dive. Suggested Grade Levels: 4 8 Illinois State Learning Goals science 11.A, 11.B, 12.D,
Cells, Diffusion, Osmosis, and Biological Membranes
 Cells, Diffusion, Osmosis, and Biological Membranes A. Objectives Upon completion of this lab activity, you should be able to: 1. Define and correctly use the following terms: solute, solvent, selectively
Cells, Diffusion, Osmosis, and Biological Membranes A. Objectives Upon completion of this lab activity, you should be able to: 1. Define and correctly use the following terms: solute, solvent, selectively
Instructions for Use PROCRIT (PRO KRIT) (epoetin alfa)
 Instructions for Use PROCRIT (PROKRIT) (epoetin alfa) Use these Instructions for Use if you or your caregiver has been trained to give PROCRIT injections at home. Do not give yourself the injection unless
Instructions for Use PROCRIT (PROKRIT) (epoetin alfa) Use these Instructions for Use if you or your caregiver has been trained to give PROCRIT injections at home. Do not give yourself the injection unless
oil liquid water water liquid Answer, Key Homework 2 David McIntyre 1
 Answer, Key Homework 2 David McIntyre 1 This print-out should have 14 questions, check that it is complete. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page: find all choices before making
Answer, Key Homework 2 David McIntyre 1 This print-out should have 14 questions, check that it is complete. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page: find all choices before making
SOLUBILITY OF A SALT IN WATER AT VARIOUS TEMPERATURES LAB
 SOLUBILITY OF A SALT IN WATER AT VARIOUS TEMPERATURES LAB Purpose: Most ionic compounds are considered by chemists to be salts and many of these are water soluble. In this lab, you will determine the solubility,
SOLUBILITY OF A SALT IN WATER AT VARIOUS TEMPERATURES LAB Purpose: Most ionic compounds are considered by chemists to be salts and many of these are water soluble. In this lab, you will determine the solubility,
Measurement and Calibration
 Adapted from: H. A. Neidig and J. N. Spencer Modular Laboratory Program in Chemistry Thompson Learning;, University of Pittsburgh Chemistry 0110 Laboratory Manual, 1998. Purpose To gain an understanding
Adapted from: H. A. Neidig and J. N. Spencer Modular Laboratory Program in Chemistry Thompson Learning;, University of Pittsburgh Chemistry 0110 Laboratory Manual, 1998. Purpose To gain an understanding
Acids & Bases Around the House Use a ph indicator to find acids and bases
 Use a ph indicator to find acids and bases Description: Visitors predict whether various household solutions are acids or bases, and test their hypotheses using a universal ph indicator. Then, visitors
Use a ph indicator to find acids and bases Description: Visitors predict whether various household solutions are acids or bases, and test their hypotheses using a universal ph indicator. Then, visitors
OA3-10 Patterns in Addition Tables
 OA3-10 Patterns in Addition Tables Pages 60 63 Standards: 3.OA.D.9 Goals: Students will identify and describe various patterns in addition tables. Prior Knowledge Required: Can add two numbers within 20
OA3-10 Patterns in Addition Tables Pages 60 63 Standards: 3.OA.D.9 Goals: Students will identify and describe various patterns in addition tables. Prior Knowledge Required: Can add two numbers within 20
ES 106 Laboratory # 3 INTRODUCTION TO OCEANOGRAPHY. Introduction The global ocean covers nearly 75% of Earth s surface and plays a vital role in
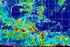 ES 106 Laboratory # 3 INTRODUCTION TO OCEANOGRAPHY 3-1 Introduction The global ocean covers nearly 75% of Earth s surface and plays a vital role in the physical environment of Earth. For these reasons,
ES 106 Laboratory # 3 INTRODUCTION TO OCEANOGRAPHY 3-1 Introduction The global ocean covers nearly 75% of Earth s surface and plays a vital role in the physical environment of Earth. For these reasons,
Lab: Properties of Polar and Nonpolar Substances
 Lab: Properties of Polar and Nonpolar Substances Purpose: To explain the interactions of matter in relation to polarity. Stations 1 and 2 - il and water do not mix As a metaphor, oil and water are often
Lab: Properties of Polar and Nonpolar Substances Purpose: To explain the interactions of matter in relation to polarity. Stations 1 and 2 - il and water do not mix As a metaphor, oil and water are often
Chromatography...Oh Yeah!
 Chromatography...Oh Yeah! What s In Kool-Aid? An Introduction to Extraction and Chromatography OVERVIEW: The purpose of the experiment is to separate and analyze the components of prepared Kool- Aid using
Chromatography...Oh Yeah! What s In Kool-Aid? An Introduction to Extraction and Chromatography OVERVIEW: The purpose of the experiment is to separate and analyze the components of prepared Kool- Aid using
Experiment 12- Classification of Matter Experiment
 Experiment 12- Classification of Matter Experiment Matter can be classified into two groups: mixtures and pure substances. Mixtures are the most common form of matter and consist of mixtures of pure substances.
Experiment 12- Classification of Matter Experiment Matter can be classified into two groups: mixtures and pure substances. Mixtures are the most common form of matter and consist of mixtures of pure substances.
Mathematics Test Book 1
 Mathematics Test ook 1 Grade 7 March 9 13, 2009 21317 eveloped and published under contract with the New York State Education epartment by T/McGraw-Hill LL, a subsidiary of The McGraw-Hill ompanies, Inc.,
Mathematics Test ook 1 Grade 7 March 9 13, 2009 21317 eveloped and published under contract with the New York State Education epartment by T/McGraw-Hill LL, a subsidiary of The McGraw-Hill ompanies, Inc.,
Lab Activity on Global Wind Patterns
 Lab Activity on Global Wind Patterns 2002 Ann Bykerk-Kauffman, Dept. of Geological and Environmental Sciences, California State University, Chico * Objectives When you have completed this lab you should
Lab Activity on Global Wind Patterns 2002 Ann Bykerk-Kauffman, Dept. of Geological and Environmental Sciences, California State University, Chico * Objectives When you have completed this lab you should
Distillation Experiment
 Distillation Experiment CHM226 Background The distillation process is a very important technique used to separate compounds based on their boiling points. A substance will boil only when the vapor pressure
Distillation Experiment CHM226 Background The distillation process is a very important technique used to separate compounds based on their boiling points. A substance will boil only when the vapor pressure
SORTING PLASTICS FOR RECYCLING INTRODUCTION
 SORTING PLASTICS FOR RECYCLING INTRODUCTION Description Students use the difference in densities of polymers and flame tests as a basis for the development of a scheme to separate plastics. Goals for This
SORTING PLASTICS FOR RECYCLING INTRODUCTION Description Students use the difference in densities of polymers and flame tests as a basis for the development of a scheme to separate plastics. Goals for This
Name. Lab 3: ENZYMES. In this lab, you ll investigate some of the properties of enzymes.
 Name Lab 3: ENZYMES In this lab, you ll investigate some of the properties of enzymes. So what are enzymes? Enzymes are large protein molecules (macromolecules) They catalyze or speed up chemical reactions
Name Lab 3: ENZYMES In this lab, you ll investigate some of the properties of enzymes. So what are enzymes? Enzymes are large protein molecules (macromolecules) They catalyze or speed up chemical reactions
DNA Electrophoresis Lesson Plan
 DNA Electrophoresis Lesson Plan Primary Learning Outcomes: Students will learn how to properly load a well in an agarose gel. Students will learn how to analyze the results of DNA electrophoresis. Students
DNA Electrophoresis Lesson Plan Primary Learning Outcomes: Students will learn how to properly load a well in an agarose gel. Students will learn how to analyze the results of DNA electrophoresis. Students
Recovery of Elemental Copper from Copper (II) Nitrate
 Recovery of Elemental Copper from Copper (II) Nitrate Objectives: Challenge: Students should be able to - recognize evidence(s) of a chemical change - convert word equations into formula equations - perform
Recovery of Elemental Copper from Copper (II) Nitrate Objectives: Challenge: Students should be able to - recognize evidence(s) of a chemical change - convert word equations into formula equations - perform
EXPERIMENT 10: TITRATION AND STANDARDIZATION
 EXPERIMENT 10: TITRATION AND STANDARDIZATION PURPOSE To determine the molarity of a NaOH solution by titrating it with a standard HCl solution. To determine the molarity of acetic acid in vinegar using
EXPERIMENT 10: TITRATION AND STANDARDIZATION PURPOSE To determine the molarity of a NaOH solution by titrating it with a standard HCl solution. To determine the molarity of acetic acid in vinegar using
POTATO FLOAT. Common Preconceptions:
 POTATO FLOAT Unit: Salinity Patterns & the Water Cycle l Grade Level: Middle l Time Required: 30 min. (in class) after solutions are prepared by the teacher l Content Standard: NSES Physical Science, properties
POTATO FLOAT Unit: Salinity Patterns & the Water Cycle l Grade Level: Middle l Time Required: 30 min. (in class) after solutions are prepared by the teacher l Content Standard: NSES Physical Science, properties
Air Hockey Training Camp Care and repair of your Air Hockey Playfield
 The playfield is the single most expensive part of your Dynamo Air Hockey table. Proper care will keep your table attractive and functional for your players, and bring them back for more games. CLEAN YOUR
The playfield is the single most expensive part of your Dynamo Air Hockey table. Proper care will keep your table attractive and functional for your players, and bring them back for more games. CLEAN YOUR
* Readily available from supermarkets and health food stores. 80-145 minutes (total over 3 to 7 days) SOSE: Investigate Australia s salinity crisis
 Lesson Plan 12 Salt and germination Brief description This fascinating, cheap and very reliable experiment clearly demonstrates the damaging effects of salinity (salt) on seed germination. Mung beans are
Lesson Plan 12 Salt and germination Brief description This fascinating, cheap and very reliable experiment clearly demonstrates the damaging effects of salinity (salt) on seed germination. Mung beans are
DIFFUSION (HYPERTONIC, HYPOTONIC, & ISOTONIC SOLUTIONS) THE GUMMY BEAR LAB PASS
 DIFFUSION (HYPERTONIC, HYPOTONIC, & ISOTONIC SOLUTIONS) THE GUMMY BEAR LAB PASS Have you ever wondered why your fingers have wrinkles after soaking in a bath tub? Your students have probably wondered the
DIFFUSION (HYPERTONIC, HYPOTONIC, & ISOTONIC SOLUTIONS) THE GUMMY BEAR LAB PASS Have you ever wondered why your fingers have wrinkles after soaking in a bath tub? Your students have probably wondered the
Partner: Jack 17 November 2011. Determination of the Molar Mass of Volatile Liquids
 Partner: Jack 17 November 2011 Determination of the Molar Mass of Volatile Liquids Purpose: The purpose of this experiment is to determine the molar mass of three volatile liquids. The liquid is vaporized
Partner: Jack 17 November 2011 Determination of the Molar Mass of Volatile Liquids Purpose: The purpose of this experiment is to determine the molar mass of three volatile liquids. The liquid is vaporized
Cell Cycle in Onion Root Tip Cells (IB)
 Cell Cycle in Onion Root Tip Cells (IB) A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules,
Cell Cycle in Onion Root Tip Cells (IB) A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules,
H H H O. Pre-Lab Exercises Lab 6: Organic Chemistry. Lab 6: Organic Chemistry Chemistry 100. 1. Define the following: a.
 Lab 6: Organic hemistry hemistry 100 1. Define the following: a. ydrocarbon Pre-Lab Exercises Lab 6: Organic hemistry Name Date Section b. Saturated hydrocarbon c. Unsaturated hydrocarbon 2. The formula
Lab 6: Organic hemistry hemistry 100 1. Define the following: a. ydrocarbon Pre-Lab Exercises Lab 6: Organic hemistry Name Date Section b. Saturated hydrocarbon c. Unsaturated hydrocarbon 2. The formula
Heat and Temperature: Teacher s Guide
 Heat and Temperature: Teacher s Guide Grade Level: 6-8 Curriculum Focus: Physical Science Lesson Duration: Two class periods Program Description Humans have always been feverish about temperature. But
Heat and Temperature: Teacher s Guide Grade Level: 6-8 Curriculum Focus: Physical Science Lesson Duration: Two class periods Program Description Humans have always been feverish about temperature. But
Hot Leaks. See how the temperature of liquids changes the way they flow.
 P h y s i c s Q u e s t A c t i v i t i e s Activity 2 1 Hot Leaks See how the temperature of liquids changes the way they flow. Safety: This experiment requires using the hot water tap and straight pins.
P h y s i c s Q u e s t A c t i v i t i e s Activity 2 1 Hot Leaks See how the temperature of liquids changes the way they flow. Safety: This experiment requires using the hot water tap and straight pins.
LAB 24 Transpiration
 Name: AP Biology Lab 24 LAB 24 Transpiration Objectives: To understand how water moves from roots to leaves in terms of the physical/chemical properties of water and the forces provided by differences
Name: AP Biology Lab 24 LAB 24 Transpiration Objectives: To understand how water moves from roots to leaves in terms of the physical/chemical properties of water and the forces provided by differences
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE HUMIRA 40 MG/0.8 ML SINGLE-USE PEN
 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE HUMIRA (Hu-MARE-ah) (adalimumab) 40 MG/0.8 ML SINGLE-USE PEN Do not try to inject HUMIRA yourself until you have been shown the right way to give the injections and have read and understand
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE HUMIRA (Hu-MARE-ah) (adalimumab) 40 MG/0.8 ML SINGLE-USE PEN Do not try to inject HUMIRA yourself until you have been shown the right way to give the injections and have read and understand
Separation by Solvent Extraction
 Experiment 3 Separation by Solvent Extraction Objectives To separate a mixture consisting of a carboxylic acid and a neutral compound by using solvent extraction techniques. Introduction Frequently, organic
Experiment 3 Separation by Solvent Extraction Objectives To separate a mixture consisting of a carboxylic acid and a neutral compound by using solvent extraction techniques. Introduction Frequently, organic
Name Lab #3: Solubility of Organic Compounds Objectives: Introduction: soluble insoluble partially soluble miscible immiscible
 Lab #3: Solubility of rganic Compounds bjectives: - Understanding the relative solubility of organic compounds in various solvents. - Exploration of the effect of polar groups on a nonpolar hydrocarbon
Lab #3: Solubility of rganic Compounds bjectives: - Understanding the relative solubility of organic compounds in various solvents. - Exploration of the effect of polar groups on a nonpolar hydrocarbon
Density Lab. If you get stuck or are uncertain, please ask questions and/or refer to the hints at the end of the lab. Name: Section: Due Date:
 Name: Section: Due Date: Lab 01B-1 If you get stuck or are uncertain, please ask questions and/or refer to the hints at the end of the lab. Density Lab Density is an important concept in oceanography,
Name: Section: Due Date: Lab 01B-1 If you get stuck or are uncertain, please ask questions and/or refer to the hints at the end of the lab. Density Lab Density is an important concept in oceanography,
Enzyme Pre-Lab. Using the Enzyme worksheet and Enzyme lab handout answer the Pre-Lab questions the pre-lab must be complete before beginning the lab.
 Enzyme Pre-Lab Using the Enzyme worksheet and Enzyme lab handout answer the Pre-Lab questions the pre-lab must be complete before beginning the lab. Background: In this investigation, you will study several
Enzyme Pre-Lab Using the Enzyme worksheet and Enzyme lab handout answer the Pre-Lab questions the pre-lab must be complete before beginning the lab. Background: In this investigation, you will study several
Explain the role of blood and bloodstain patterns in forensics science. Analyze and identify bloodstain patterns by performing bloodstain analysis
 Lab 4 Blood Learning Objectives Explain the role of blood and bloodstain patterns in forensics science Analyze and identify bloodstain patterns by performing bloodstain analysis Introduction Blood, a
Lab 4 Blood Learning Objectives Explain the role of blood and bloodstain patterns in forensics science Analyze and identify bloodstain patterns by performing bloodstain analysis Introduction Blood, a
The Ultimate XBOX 360 Guide to Fix 3 Red Lights (RROD)
 The Ultimate XBOX 360 Guide to Fix 3 Red Lights (RROD) We offer a wide range of repair kits to meet just about everyone's needs. We offer kits ranging from just hardware, to kits that include hardware,
The Ultimate XBOX 360 Guide to Fix 3 Red Lights (RROD) We offer a wide range of repair kits to meet just about everyone's needs. We offer kits ranging from just hardware, to kits that include hardware,
Keep Your Head Above Water
 Grade 8 Activity Keep Your Head Above Water Do things that float behave differently in salt and fresh water? What lets them float, and when do they sink? Concepts Water has physical properties of density
Grade 8 Activity Keep Your Head Above Water Do things that float behave differently in salt and fresh water? What lets them float, and when do they sink? Concepts Water has physical properties of density
Chem 100 Lab Experiment #9 - ACID/BASE INDICATORS
 Lab #9 Chem 100 Lab Experiment #9 - ACID/BASE INDICATORS Name: Purpose: In this laboratory we will investigate how indicators can be used to test for the presence of acids or bases in a number of common
Lab #9 Chem 100 Lab Experiment #9 - ACID/BASE INDICATORS Name: Purpose: In this laboratory we will investigate how indicators can be used to test for the presence of acids or bases in a number of common
BioResearch. RAFT 3D Cell Culture Kit Protocol
 BioResearch RAFT 3D Cell Culture Kit Protocol RAFT 3D Cell Culture Kit This protocol describes in detail how to produce RAFT 3D Cell Cultures in 96-well plates, 24-well plates and 24-well inserts. It is
BioResearch RAFT 3D Cell Culture Kit Protocol RAFT 3D Cell Culture Kit This protocol describes in detail how to produce RAFT 3D Cell Cultures in 96-well plates, 24-well plates and 24-well inserts. It is
FOURTH GRADE EARTHQUAKES 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 FOURTH GRADE EARTHQUAKES 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FOURTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing different structures of volcanoes. DURING: Modeling three types
FOURTH GRADE EARTHQUAKES 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FOURTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing different structures of volcanoes. DURING: Modeling three types
Solving Geometric Applications
 1.8 Solving Geometric Applications 1.8 OBJECTIVES 1. Find a perimeter 2. Solve applications that involve perimeter 3. Find the area of a rectangular figure 4. Apply area formulas 5. Apply volume formulas
1.8 Solving Geometric Applications 1.8 OBJECTIVES 1. Find a perimeter 2. Solve applications that involve perimeter 3. Find the area of a rectangular figure 4. Apply area formulas 5. Apply volume formulas
CHM220 Addition lab. Experiment: Reactions of alkanes, alkenes, and cycloalkenes*
 CM220 Addition lab Experiment: Reactions of alkanes, alkenes, and cycloalkenes* Purpose: To investigate the physical properties, solubility, and density of some hydrocarbon. To compare the chemical reactivity
CM220 Addition lab Experiment: Reactions of alkanes, alkenes, and cycloalkenes* Purpose: To investigate the physical properties, solubility, and density of some hydrocarbon. To compare the chemical reactivity
2 THE LAWS OF TABLE TENNIS
 2 THE LAWS OF TABLE TENNIS 2.1 THE TABLE 2.1.1 The upper surface of the table, known as the playing surface, shall be rectangular, 2.74m long and 1.525m wide, and shall lie in a horizontal plane 76cm above
2 THE LAWS OF TABLE TENNIS 2.1 THE TABLE 2.1.1 The upper surface of the table, known as the playing surface, shall be rectangular, 2.74m long and 1.525m wide, and shall lie in a horizontal plane 76cm above
RAINBOW ELECTROPHORESIS 1 An Introduction to Gel Electrophoresis
 RAINBOW ELECTROPHORESIS 1 An Introduction to Gel Electrophoresis INTRODUCTION This laboratory will demonstrate the basics of electrophoresis and the theory behind the separation of molecules on an agarose
RAINBOW ELECTROPHORESIS 1 An Introduction to Gel Electrophoresis INTRODUCTION This laboratory will demonstrate the basics of electrophoresis and the theory behind the separation of molecules on an agarose
Evaluation copy. Case File 9. A Killer Cup of Coffee? GlobalTech manager dies
 Case File 9 Killer Cup of Coffee: Using colorimetry to determine concentration of a poison Determine the concentration of cyanide in the solution. A Killer Cup of Coffee? SOUTH PAINTER, Tuesday: It was
Case File 9 Killer Cup of Coffee: Using colorimetry to determine concentration of a poison Determine the concentration of cyanide in the solution. A Killer Cup of Coffee? SOUTH PAINTER, Tuesday: It was
Ocean in Motion 2: What Causes Ocean Currents and How Do We Measure Them?
 Ocean in Motion 2: What Causes Ocean Currents and How Do We Measure Them? A. Overview 1. The Ocean in Motion -- Circulation In this program, students will learn about the driving forces responsible for
Ocean in Motion 2: What Causes Ocean Currents and How Do We Measure Them? A. Overview 1. The Ocean in Motion -- Circulation In this program, students will learn about the driving forces responsible for
Mixtures and Pure Substances
 Unit 2 Mixtures and Pure Substances Matter can be classified into two groups: mixtures and pure substances. Mixtures are the most common form of matter and consist of mixtures of pure substances. They
Unit 2 Mixtures and Pure Substances Matter can be classified into two groups: mixtures and pure substances. Mixtures are the most common form of matter and consist of mixtures of pure substances. They
SHELL INDUSTRIAL APTITUDE BATTERY PREPARATION GUIDE
 SHELL INDUSTRIAL APTITUDE BATTERY PREPARATION GUIDE 2011 Valtera Corporation. All rights reserved. TABLE OF CONTENTS OPERATIONS AND MAINTENANCE JOB REQUIREMENTS... 1 TEST PREPARATION... 2 USE OF INDUSTRIAL
SHELL INDUSTRIAL APTITUDE BATTERY PREPARATION GUIDE 2011 Valtera Corporation. All rights reserved. TABLE OF CONTENTS OPERATIONS AND MAINTENANCE JOB REQUIREMENTS... 1 TEST PREPARATION... 2 USE OF INDUSTRIAL
Sample Table. Columns. Column 1 Column 2 Column 3 Row 1 Cell 1 Cell 2 Cell 3 Row 2 Cell 4 Cell 5 Cell 6 Row 3 Cell 7 Cell 8 Cell 9.
 Working with Tables in Microsoft Word The purpose of this document is to lead you through the steps of creating, editing and deleting tables and parts of tables. This document follows a tutorial format
Working with Tables in Microsoft Word The purpose of this document is to lead you through the steps of creating, editing and deleting tables and parts of tables. This document follows a tutorial format
Assessment For The California Mathematics Standards Grade 6
 Introduction: Summary of Goals GRADE SIX By the end of grade six, students have mastered the four arithmetic operations with whole numbers, positive fractions, positive decimals, and positive and negative
Introduction: Summary of Goals GRADE SIX By the end of grade six, students have mastered the four arithmetic operations with whole numbers, positive fractions, positive decimals, and positive and negative
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE HUMIRA 40 MG/0.8 ML, 20 MG/0.4 ML AND 10 MG/0.2 ML SINGLE-USE PREFILLED SYRINGE
 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE HUMIRA (Hu-MARE-ah) (adalimumab) 40 MG/0.8 ML, 20 MG/0.4 ML AND 10 MG/0.2 ML SINGLE-USE PREFILLED SYRINGE Do not try to inject HUMIRA yourself until you have been shown the right way
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE HUMIRA (Hu-MARE-ah) (adalimumab) 40 MG/0.8 ML, 20 MG/0.4 ML AND 10 MG/0.2 ML SINGLE-USE PREFILLED SYRINGE Do not try to inject HUMIRA yourself until you have been shown the right way
CRITICAL REVIEW ESSAY SENIOR EXIT PROJECT COSMETOLOGY
 CRITICAL REVIEW ESSAY SENIOR EXIT PROJECT COSMETOLOGY Objective: To write a critical review essay and Reference List (using standard APA style) from multiple sources. Assignment: Read the three articles:
CRITICAL REVIEW ESSAY SENIOR EXIT PROJECT COSMETOLOGY Objective: To write a critical review essay and Reference List (using standard APA style) from multiple sources. Assignment: Read the three articles:
WHERE DOES THE WATER GO IN THE WATER CYCLE?
 WHERE DOES THE WATER GO IN THE WATER CYCLE? OBJECTIVES Identify the water cycle as a system that is a combination of systems Describe each process in the water cycle, including the changes in state (if
WHERE DOES THE WATER GO IN THE WATER CYCLE? OBJECTIVES Identify the water cycle as a system that is a combination of systems Describe each process in the water cycle, including the changes in state (if
Determining Equivalent Weight by Copper Electrolysis
 Purpose The purpose of this experiment is to determine the equivalent mass of copper based on change in the mass of a copper electrode and the volume of hydrogen gas generated during an electrolysis reaction.
Purpose The purpose of this experiment is to determine the equivalent mass of copper based on change in the mass of a copper electrode and the volume of hydrogen gas generated during an electrolysis reaction.
Density. mass m volume V
 Density Readin assinment: Chan, Chemistry 10 th edition, pp. 18-19. Goals The purpose of this experiment is to become familiar with the concept of density. We will determine the density of water and of
Density Readin assinment: Chan, Chemistry 10 th edition, pp. 18-19. Goals The purpose of this experiment is to become familiar with the concept of density. We will determine the density of water and of
TEACHER ACTIVITY GUIDE
 Page 1/5 EXPECTED OUTCOMES TEACHER ACTIVITY GUIDE ROOT BEER PRODUCTION Taken from IFT Experiments in Food Science Series This activity will allow student an opportunity to explore yeast fermentation by
Page 1/5 EXPECTED OUTCOMES TEACHER ACTIVITY GUIDE ROOT BEER PRODUCTION Taken from IFT Experiments in Food Science Series This activity will allow student an opportunity to explore yeast fermentation by
Performing Calculatons
 Performing Calculatons There are three basic units for measurement in the organic laboratory mass, volume, and number, measured in moles. Most of the other types of measurements are combinations of them,
Performing Calculatons There are three basic units for measurement in the organic laboratory mass, volume, and number, measured in moles. Most of the other types of measurements are combinations of them,
Physical Properties of a Pure Substance, Water
 Physical Properties of a Pure Substance, Water The chemical and physical properties of a substance characterize it as a unique substance, and the determination of these properties can often allow one to
Physical Properties of a Pure Substance, Water The chemical and physical properties of a substance characterize it as a unique substance, and the determination of these properties can often allow one to
sciencemuseumoutreach Kitchen Science 1 Demonstrations to do at home
 sciencemuseumoutreach Kitchen Science 1 Demonstrations to do at home The Creative Canal Project (CCP) is part of the Science Museum s Outreach Department, which works with teachers, students, families
sciencemuseumoutreach Kitchen Science 1 Demonstrations to do at home The Creative Canal Project (CCP) is part of the Science Museum s Outreach Department, which works with teachers, students, families
Surface Tension: Liquids Stick Together Teacher Version
 Surface Tension: Liquids Stick Together Teacher Version In this lab you will learn about properties of liquids, specifically cohesion, adhesion, and surface tension. These principles will be demonstrated
Surface Tension: Liquids Stick Together Teacher Version In this lab you will learn about properties of liquids, specifically cohesion, adhesion, and surface tension. These principles will be demonstrated
Experiment 2 Kinetics II Concentration-Time Relationships and Activation Energy
 2-1 Experiment 2 Kinetics II Concentration-Time Relationships and Activation Energy Introduction: The kinetics of a decomposition reaction involving hydroxide ion and crystal violet, an organic dye used
2-1 Experiment 2 Kinetics II Concentration-Time Relationships and Activation Energy Introduction: The kinetics of a decomposition reaction involving hydroxide ion and crystal violet, an organic dye used
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 4B Chapter 4: Cell Structure
 Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 4B Chapter 4: Cell Structure The Microscope: A Tool of the Scientist You may refer to pages 66-67, 72-73 in your textbook for a general discussion of microscopes.
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 4B Chapter 4: Cell Structure The Microscope: A Tool of the Scientist You may refer to pages 66-67, 72-73 in your textbook for a general discussion of microscopes.
The Determination of an Equilibrium Constant
 The Determination of an Equilibrium Constant Computer 10 Chemical reactions occur to reach a state of equilibrium. The equilibrium state can be characterized by quantitatively defining its equilibrium
The Determination of an Equilibrium Constant Computer 10 Chemical reactions occur to reach a state of equilibrium. The equilibrium state can be characterized by quantitatively defining its equilibrium
A Quick Start Guide to Using PowerPoint For Image-based Presentations
 A Quick Start Guide to Using PowerPoint For Image-based Presentations By Susan Jane Williams & William Staffeld, Knight Visual Resources Facility College of Architecture, Art and Planning Cornell University.
A Quick Start Guide to Using PowerPoint For Image-based Presentations By Susan Jane Williams & William Staffeld, Knight Visual Resources Facility College of Architecture, Art and Planning Cornell University.
OA4-13 Rounding on a Number Line Pages 80 81
 OA4-13 Rounding on a Number Line Pages 80 81 STANDARDS 3.NBT.A.1, 4.NBT.A.3 Goals Students will round to the closest ten, except when the number is exactly halfway between a multiple of ten. PRIOR KNOWLEDGE
OA4-13 Rounding on a Number Line Pages 80 81 STANDARDS 3.NBT.A.1, 4.NBT.A.3 Goals Students will round to the closest ten, except when the number is exactly halfway between a multiple of ten. PRIOR KNOWLEDGE
The Properties of Water (Instruction Sheet)
 The Properties of Water (Instruction Sheet) Property : High Polarity Activity #1 Surface Tension: PILE IT ON. Materials: 1 DRY penny, 1 eye dropper, water. 1. Make sure the penny is dry. 2. Begin by estimating
The Properties of Water (Instruction Sheet) Property : High Polarity Activity #1 Surface Tension: PILE IT ON. Materials: 1 DRY penny, 1 eye dropper, water. 1. Make sure the penny is dry. 2. Begin by estimating
Science Safety is Elementary Grade Three
 Ohio Standards Connection: Scientific Inquiry Benchmark C Develop, design and safely conduct scientific investigations and communicate the results. Indicator 4 Identify and apply science safety procedures.
Ohio Standards Connection: Scientific Inquiry Benchmark C Develop, design and safely conduct scientific investigations and communicate the results. Indicator 4 Identify and apply science safety procedures.
Experiment 5: Column Chromatography
 Experiment 5: Column Chromatography Separation of Ferrocene & Acetylferrocene by Column Chromatography Reading: Mohrig, Hammond & Schatz Ch. 18 pgs 235-253 watch the technique video on the course website!
Experiment 5: Column Chromatography Separation of Ferrocene & Acetylferrocene by Column Chromatography Reading: Mohrig, Hammond & Schatz Ch. 18 pgs 235-253 watch the technique video on the course website!
