Einstein s theory of relativity
|
|
|
- Alexandrina Elaine Bell
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Department of Mathematics, Institute of Origins, December 5, 2008
2 Overview UCL Institute of Origins Origins UCL has established the Institute of Origins to promote world leading research in topics related to the Origins and Evolution of the Universe. Our research themes are: Galaxy Evolution Mathematical Foundations Neutrino physics Planetary Science
3 Overview UCL Institute of Origins Origins UCL has established the Institute of Origins to promote world leading research in topics related to the Origins and Evolution of the Universe. Our research themes are: Galaxy Evolution Mathematical Foundations Neutrino physics Planetary Science
4 Overview UCL Institute of Origins Origins UCL has established the Institute of Origins to promote world leading research in topics related to the Origins and Evolution of the Universe. Our research themes are: Galaxy Evolution Mathematical Foundations Neutrino physics Planetary Science
5 Overview UCL Institute of Origins Origins UCL has established the Institute of Origins to promote world leading research in topics related to the Origins and Evolution of the Universe. Our research themes are: Galaxy Evolution Mathematical Foundations Neutrino physics Planetary Science
6 Overview UCL Institute of Origins Origins UCL has established the Institute of Origins to promote world leading research in topics related to the Origins and Evolution of the Universe. Our research themes are: Galaxy Evolution Mathematical Foundations Neutrino physics Planetary Science
7 Overview Overview Albert Einstein 1905 Einstein s Wonderful Year 1915 General relativity Special relativity the twin problem mass-energy equivalence General relativity matter and curvature black holes and wormholes Cosmology from the big bang to today dark matter, dark energy and all that
8 Overview Overview Albert Einstein 1905 Einstein s Wonderful Year 1915 General relativity Special relativity the twin problem mass-energy equivalence General relativity matter and curvature black holes and wormholes Cosmology from the big bang to today dark matter, dark energy and all that
9 Overview Overview Albert Einstein 1905 Einstein s Wonderful Year 1915 General relativity Special relativity the twin problem mass-energy equivalence General relativity matter and curvature black holes and wormholes Cosmology from the big bang to today dark matter, dark energy and all that
10 Overview Overview Albert Einstein 1905 Einstein s Wonderful Year 1915 General relativity Special relativity the twin problem mass-energy equivalence General relativity matter and curvature black holes and wormholes Cosmology from the big bang to today dark matter, dark energy and all that
11 Overview Overview Albert Einstein 1905 Einstein s Wonderful Year 1915 General relativity Special relativity the twin problem mass-energy equivalence General relativity matter and curvature black holes and wormholes Cosmology from the big bang to today dark matter, dark energy and all that
12 Overview Overview Albert Einstein 1905 Einstein s Wonderful Year 1915 General relativity Special relativity the twin problem mass-energy equivalence General relativity matter and curvature black holes and wormholes Cosmology from the big bang to today dark matter, dark energy and all that
13 Overview Overview Albert Einstein 1905 Einstein s Wonderful Year 1915 General relativity Special relativity the twin problem mass-energy equivalence General relativity matter and curvature black holes and wormholes Cosmology from the big bang to today dark matter, dark energy and all that
14 Overview Overview Albert Einstein 1905 Einstein s Wonderful Year 1915 General relativity Special relativity the twin problem mass-energy equivalence General relativity matter and curvature black holes and wormholes Cosmology from the big bang to today dark matter, dark energy and all that
15 Overview Overview Albert Einstein 1905 Einstein s Wonderful Year 1915 General relativity Special relativity the twin problem mass-energy equivalence General relativity matter and curvature black holes and wormholes Cosmology from the big bang to today dark matter, dark energy and all that
16 Overview Overview Albert Einstein 1905 Einstein s Wonderful Year 1915 General relativity Special relativity the twin problem mass-energy equivalence General relativity matter and curvature black holes and wormholes Cosmology from the big bang to today dark matter, dark energy and all that
17 Overview Overview Albert Einstein 1905 Einstein s Wonderful Year 1915 General relativity Special relativity the twin problem mass-energy equivalence General relativity matter and curvature black holes and wormholes Cosmology from the big bang to today dark matter, dark energy and all that
18 Overview Overview Albert Einstein 1905 Einstein s Wonderful Year 1915 General relativity Special relativity the twin problem mass-energy equivalence General relativity matter and curvature black holes and wormholes Cosmology from the big bang to today dark matter, dark energy and all that
19 Albert Einstein Albert Einstein ( )
20 Albert Einstein 1905 Annus Mirabilis particulate nature of light photoelectric effect Brownian motion confirming atomic theory electrodynamics of moving bodies special relativity mass-energy equivalence E = mc 2
21 Albert Einstein 1905 Annus Mirabilis particulate nature of light photoelectric effect Brownian motion confirming atomic theory electrodynamics of moving bodies special relativity mass-energy equivalence E = mc 2
22 Albert Einstein 1905 Annus Mirabilis particulate nature of light photoelectric effect Brownian motion confirming atomic theory electrodynamics of moving bodies special relativity mass-energy equivalence E = mc 2
23 Albert Einstein 1905 Annus Mirabilis particulate nature of light photoelectric effect Brownian motion confirming atomic theory electrodynamics of moving bodies special relativity mass-energy equivalence E = mc 2
24 Albert Einstein 1915 General relativity for about 10 years Einstein worked on a generalisation of Newtonian gravity Marcel Grossmann and Tullio Levi-Civita influenced Einstein by discussing and introducing him to Riemannian geometry Einstein, Albert (1915), Die Feldgleichungen der Gravitation (The Field Equations of Gravitation), Koniglich Preussische Akademie der Wissenschaften R ab 1 2 Rg ab = 8πT ab
25 Albert Einstein 1915 General relativity for about 10 years Einstein worked on a generalisation of Newtonian gravity Marcel Grossmann and Tullio Levi-Civita influenced Einstein by discussing and introducing him to Riemannian geometry Einstein, Albert (1915), Die Feldgleichungen der Gravitation (The Field Equations of Gravitation), Koniglich Preussische Akademie der Wissenschaften R ab 1 2 Rg ab = 8πT ab
26 Albert Einstein 1915 General relativity for about 10 years Einstein worked on a generalisation of Newtonian gravity Marcel Grossmann and Tullio Levi-Civita influenced Einstein by discussing and introducing him to Riemannian geometry Einstein, Albert (1915), Die Feldgleichungen der Gravitation (The Field Equations of Gravitation), Koniglich Preussische Akademie der Wissenschaften R ab 1 2 Rg ab = 8πT ab
27 Albert Einstein 1915 General relativity for about 10 years Einstein worked on a generalisation of Newtonian gravity Marcel Grossmann and Tullio Levi-Civita influenced Einstein by discussing and introducing him to Riemannian geometry Einstein, Albert (1915), Die Feldgleichungen der Gravitation (The Field Equations of Gravitation), Koniglich Preussische Akademie der Wissenschaften R ab 1 2 Rg ab = 8πT ab
28 Albert Einstein Albert Einstein 1947 Latter years Einstein refuses Quantum Theory subsequently refuses Quantum Field Theory God does not play dice
29 Albert Einstein Albert Einstein 1947 Latter years Einstein refuses Quantum Theory subsequently refuses Quantum Field Theory God does not play dice
30 Albert Einstein Albert Einstein 1947 Latter years Einstein refuses Quantum Theory subsequently refuses Quantum Field Theory God does not play dice
31 Albert Einstein Albert Einstein 1947 Latter years Einstein refuses Quantum Theory subsequently refuses Quantum Field Theory God does not play dice
32 Special relativity Speed of light in vacuum same in all inertial systems
33 Special relativity The twin problem: an apparent paradox
34 Special relativity Time dilation in special relativity Time dilation t t = 1 1 v 2 /c 2 t : time interval as measured by a moving observer v: the observer s velocity; c: denotes the speed of light t: time interval as measured by an observer at rest 1/ -term is often called Lorentz factor
35 Special relativity Time dilation how does it effect us? Time dilation The speed of light is about c meters per second. Let s compare this with the following velocities: speeding car at 100 mph (160 kmh or 44 meter per second) super sonic jet 1000 mph (1600 kmh or 444 meters per second) space shuttle mph (28800 kms or 8000 meter per second)
36 Special relativity Time dilation how does it effect us? Time dilation The speed of light is about c meters per second. Let s compare this with the following velocities: speeding car at 100 mph (160 kmh or 44 meter per second) super sonic jet 1000 mph (1600 kmh or 444 meters per second) space shuttle mph (28800 kms or 8000 meter per second)
37 Special relativity Time dilation how does it effect us? Time dilation The speed of light is about c meters per second. Let s compare this with the following velocities: speeding car at 100 mph (160 kmh or 44 meter per second) super sonic jet 1000 mph (1600 kmh or 444 meters per second) space shuttle mph (28800 kms or 8000 meter per second)
38 Special relativity Time dilation how does it effect us? Time dilation The speed of light is about c meters per second. Let s compare this with the following velocities: speeding car at 100 mph (160 kmh or 44 meter per second) super sonic jet 1000 mph (1600 kmh or 444 meters per second) space shuttle mph (28800 kms or 8000 meter per second)
39 Special relativity Time dilation how does it effect us? Let s have a look at the numbers ( ) t t ( ) t t ( ) t t car jet shuttle = = = Conclusion Special relativity does not effect our everyday life!
40 Special relativity Time dilation how does it effect us? Let s have a look at the numbers ( ) t t ( ) t t ( ) t t car jet shuttle = = = Conclusion Special relativity does not effect our everyday life!
41 Special relativity Time travel what can be done? Into the future The theory of special relativity, in principle, allows travelling into the future. Into the past Travelling into the past does not seem to work, unless time bends into, say, a circle.
42 Special relativity Time travel what can be done? Into the future The theory of special relativity, in principle, allows travelling into the future. Into the past Travelling into the past does not seem to work, unless time bends into, say, a circle.
43 Special relativity Time travel what can be done? Into the future The theory of special relativity, in principle, allows travelling into the future. Into the past Travelling into the past does not seem to work, unless time bends into, say, a circle.
44 Special relativity Mass-energy equivalence when a flashlight emits light, it loses mass when a flower absorbs sunlight, its mass increases when a uranium nucleus splits, the mass of the remnants is less than the original mass. The difference appears as light, heat, and kinetic energy
45 Special relativity Mass-energy equivalence when a flashlight emits light, it loses mass when a flower absorbs sunlight, its mass increases when a uranium nucleus splits, the mass of the remnants is less than the original mass. The difference appears as light, heat, and kinetic energy
46 Special relativity Mass-energy equivalence when a flashlight emits light, it loses mass when a flower absorbs sunlight, its mass increases when a uranium nucleus splits, the mass of the remnants is less than the original mass. The difference appears as light, heat, and kinetic energy
47 Special relativity Nuclear explosion
48 Curved spacetime Matter and the curvature of spacetime General relativity field equations R ab 1 2 Rg ab = 8πT ab properties of spacetime = properties of matter matter tells spacetime how to curve and spacetime tells matter how to move
49 Curved spacetime Matter and the curvature of spacetime General relativity field equations R ab 1 2 Rg ab = 8πT ab properties of spacetime = properties of matter matter tells spacetime how to curve and spacetime tells matter how to move
50 Curved spacetime Matter and the curvature of spacetime General relativity field equations R ab 1 2 Rg ab = 8πT ab properties of spacetime = properties of matter matter tells spacetime how to curve and spacetime tells matter how to move
51 Curved spacetime Matter and the curvature of spacetime General relativity field equations R ab 1 2 Rg ab = 8πT ab properties of spacetime = properties of matter matter tells spacetime how to curve and spacetime tells matter how to move
52 Curved spacetime Matter and the curvature of spacetime General relativity field equations R ab 1 2 Rg ab = 8πT ab properties of spacetime = properties of matter matter tells spacetime how to curve and spacetime tells matter how to move
53 Curved spacetime The motion of a particle in spacetime
54 Curved spacetime Black holes Are black holes black? black holes are such dense object that not even light can escape their gravitation attraction since they also attract other kind of matter, it is typically very hot near a black hole while the black hole indeed absorbs light, its vicinity is bright
55 Curved spacetime Black holes Are black holes black? black holes are such dense object that not even light can escape their gravitation attraction since they also attract other kind of matter, it is typically very hot near a black hole while the black hole indeed absorbs light, its vicinity is bright
56 Curved spacetime Black holes Are black holes black? black holes are such dense object that not even light can escape their gravitation attraction since they also attract other kind of matter, it is typically very hot near a black hole while the black hole indeed absorbs light, its vicinity is bright
57 Curved spacetime Black holes Are black holes black? black holes are such dense object that not even light can escape their gravitation attraction since they also attract other kind of matter, it is typically very hot near a black hole while the black hole indeed absorbs light, its vicinity is bright
58 Curved spacetime Black holes a realistic image Galactic centres A black hole may be observed by tracking the movement of a group of stars that orbit its centre.
59 Curved spacetime Wormholes in general relativity
60 Cosmology Cosmology What does cosmology mean? cosmology (κoσµoλoγια) cosmos and logic κoσµoζ a cosmos is an orderly or harmonious system so cosmology is study of the universe in its totality
61 Cosmology Cosmology What does cosmology mean? cosmology (κoσµoλoγια) cosmos and logic κoσµoζ a cosmos is an orderly or harmonious system so cosmology is study of the universe in its totality
62 Cosmology Cosmology What does cosmology mean? cosmology (κoσµoλoγια) cosmos and logic κoσµoζ a cosmos is an orderly or harmonious system so cosmology is study of the universe in its totality
63 Cosmology Cosmology What does cosmology mean? cosmology (κoσµoλoγια) cosmos and logic κoσµoζ a cosmos is an orderly or harmonious system so cosmology is study of the universe in its totality
64 Cosmology Beyond the big bang
65 Cosmology Afterglow light pattern the cosmic microwave background radiation
66 Cosmology The energy content of our Universe
67 Cosmology Dark matter
68 Cosmology What dark energy is not!
69 Cosmology What dark energy could be the cosmological constant The cosmological field equations of general relativity R ab 1 2 Rg ab + Λg ab = 8πT ab properties of spacetime + a cosmological constant = matter The field equations with cosmological matter R ab 1 2 Rg ab = 8πT ab Λg ab properties of spacetime = matter + cosmological matter
70 Cosmology What dark energy could be the cosmological constant The cosmological field equations of general relativity R ab 1 2 Rg ab + Λg ab = 8πT ab properties of spacetime + a cosmological constant = matter The field equations with cosmological matter R ab 1 2 Rg ab = 8πT ab Λg ab properties of spacetime = matter + cosmological matter
71 Cosmology What dark energy could be the cosmological constant The cosmological field equations of general relativity R ab 1 2 Rg ab + Λg ab = 8πT ab properties of spacetime + a cosmological constant = matter The field equations with cosmological matter R ab 1 2 Rg ab = 8πT ab Λg ab properties of spacetime = matter + cosmological matter
72 Cosmology Possible future of the Universe
73 Summary Summary Special relativity and general relativity are fascinating subject areas. Special relativity is full of paradoxes that can be solved. General relativity is more or less understood. Cosmology is about 96% non-understood.
74 Summary Summary Special relativity and general relativity are fascinating subject areas. Special relativity is full of paradoxes that can be solved. General relativity is more or less understood. Cosmology is about 96% non-understood.
75 Summary Summary Special relativity and general relativity are fascinating subject areas. Special relativity is full of paradoxes that can be solved. General relativity is more or less understood. Cosmology is about 96% non-understood.
76 Summary Summary Special relativity and general relativity are fascinating subject areas. Special relativity is full of paradoxes that can be solved. General relativity is more or less understood. Cosmology is about 96% non-understood.
77 Summary Summary Special relativity and general relativity are fascinating subject areas. Special relativity is full of paradoxes that can be solved. General relativity is more or less understood. Cosmology is about 96% non-understood.
How To Understand General Relativity
 Chapter S3 Spacetime and Gravity What are the major ideas of special relativity? Spacetime Special relativity showed that space and time are not absolute Instead they are inextricably linked in a four-dimensional
Chapter S3 Spacetime and Gravity What are the major ideas of special relativity? Spacetime Special relativity showed that space and time are not absolute Instead they are inextricably linked in a four-dimensional
Evolution of the Universe from 13 to 4 Billion Years Ago
 Evolution of the Universe from 13 to 4 Billion Years Ago Prof. Dr. Harold Geller [email protected] http://physics.gmu.edu/~hgeller/ Department of Physics and Astronomy George Mason University Unity in the
Evolution of the Universe from 13 to 4 Billion Years Ago Prof. Dr. Harold Geller [email protected] http://physics.gmu.edu/~hgeller/ Department of Physics and Astronomy George Mason University Unity in the
World of Particles Big Bang Thomas Gajdosik. Big Bang (model)
 Big Bang (model) What can be seen / measured? basically only light (and a few particles: e ±, p, p, ν x ) in different wave lengths: microwave to γ-rays in different intensities (measured in magnitudes)
Big Bang (model) What can be seen / measured? basically only light (and a few particles: e ±, p, p, ν x ) in different wave lengths: microwave to γ-rays in different intensities (measured in magnitudes)
Big Bang Cosmology. Big Bang vs. Steady State
 Big Bang vs. Steady State Big Bang Cosmology Perfect cosmological principle: universe is unchanging in space and time => Steady-State universe - Bondi, Hoyle, Gold. True? No! Hubble s Law => expansion
Big Bang vs. Steady State Big Bang Cosmology Perfect cosmological principle: universe is unchanging in space and time => Steady-State universe - Bondi, Hoyle, Gold. True? No! Hubble s Law => expansion
Your years of toil Said Ryle to Hoyle Are wasted years, believe me. The Steady State Is out of date Unless my eyes deceive me.
 Your years of toil Said Ryle to Hoyle Are wasted years, believe me. The Steady State Is out of date Unless my eyes deceive me. My telescope Has dashed your hope; Your tenets are refuted. Let me be terse:
Your years of toil Said Ryle to Hoyle Are wasted years, believe me. The Steady State Is out of date Unless my eyes deceive me. My telescope Has dashed your hope; Your tenets are refuted. Let me be terse:
PHY1020 BASIC CONCEPTS IN PHYSICS I
 PHY1020 BASIC CONCEPTS IN PHYSICS I Jackson Levi Said 14 lectures/tutorials/past paper session Project on one of the interesting fields in physics (30%) Exam in January/February (70%) 1 The Course RECOMMENDED
PHY1020 BASIC CONCEPTS IN PHYSICS I Jackson Levi Said 14 lectures/tutorials/past paper session Project on one of the interesting fields in physics (30%) Exam in January/February (70%) 1 The Course RECOMMENDED
Curriculum for Excellence. Higher Physics. Success Guide
 Curriculum for Excellence Higher Physics Success Guide Electricity Our Dynamic Universe Particles and Waves Electricity Key Area Monitoring and Measuring A.C. Monitoring alternating current signals with
Curriculum for Excellence Higher Physics Success Guide Electricity Our Dynamic Universe Particles and Waves Electricity Key Area Monitoring and Measuring A.C. Monitoring alternating current signals with
Origins of the Cosmos Summer 2016. Pre-course assessment
 Origins of the Cosmos Summer 2016 Pre-course assessment In order to grant two graduate credits for the workshop, we do require you to spend some hours before arriving at Penn State. We encourage all of
Origins of the Cosmos Summer 2016 Pre-course assessment In order to grant two graduate credits for the workshop, we do require you to spend some hours before arriving at Penn State. We encourage all of
Pretest Ch 20: Origins of the Universe
 Name: _Answer key Pretest: _2_/ 58 Posttest: _58_/ 58 Pretest Ch 20: Origins of the Universe Vocab/Matching: Match the definition on the left with the term on the right by placing the letter of the term
Name: _Answer key Pretest: _2_/ 58 Posttest: _58_/ 58 Pretest Ch 20: Origins of the Universe Vocab/Matching: Match the definition on the left with the term on the right by placing the letter of the term
165 points. Name Date Period. Column B a. Cepheid variables b. luminosity c. RR Lyrae variables d. Sagittarius e. variable stars
 Name Date Period 30 GALAXIES AND THE UNIVERSE SECTION 30.1 The Milky Way Galaxy In your textbook, read about discovering the Milky Way. (20 points) For each item in Column A, write the letter of the matching
Name Date Period 30 GALAXIES AND THE UNIVERSE SECTION 30.1 The Milky Way Galaxy In your textbook, read about discovering the Milky Way. (20 points) For each item in Column A, write the letter of the matching
Astro 102 Test 5 Review Spring 2016. See Old Test 4 #16-23, Test 5 #1-3, Old Final #1-14
 Astro 102 Test 5 Review Spring 2016 See Old Test 4 #16-23, Test 5 #1-3, Old Final #1-14 Sec 14.5 Expanding Universe Know: Doppler shift, redshift, Hubble s Law, cosmic distance ladder, standard candles,
Astro 102 Test 5 Review Spring 2016 See Old Test 4 #16-23, Test 5 #1-3, Old Final #1-14 Sec 14.5 Expanding Universe Know: Doppler shift, redshift, Hubble s Law, cosmic distance ladder, standard candles,
The Einstein field equations
 The Einstein field equations Part I: the right-hand side Atle Hahn GFM, Universidade de Lisboa Lisbon, 21st January 2010 Contents: 1 Einstein field equations: overview 2 Special relativity: review 3 Classical
The Einstein field equations Part I: the right-hand side Atle Hahn GFM, Universidade de Lisboa Lisbon, 21st January 2010 Contents: 1 Einstein field equations: overview 2 Special relativity: review 3 Classical
A Universe of Galaxies
 A Universe of Galaxies Today s Lecture: Other Galaxies (Chapter 16, pages 366-397) Types of Galaxies Habitats of Galaxies Dark Matter Other Galaxies Originally called spiral nebulae because of their shape.
A Universe of Galaxies Today s Lecture: Other Galaxies (Chapter 16, pages 366-397) Types of Galaxies Habitats of Galaxies Dark Matter Other Galaxies Originally called spiral nebulae because of their shape.
Where is Fundamental Physics Heading? Nathan Seiberg IAS Apr. 30, 2014
 Where is Fundamental Physics Heading? Nathan Seiberg IAS Apr. 30, 2014 Disclaimer We do not know what will be discovered. This is the reason we perform experiments. This is the reason scientific research
Where is Fundamental Physics Heading? Nathan Seiberg IAS Apr. 30, 2014 Disclaimer We do not know what will be discovered. This is the reason we perform experiments. This is the reason scientific research
Chapter 23 The Beginning of Time
 Chapter 23 The Beginning of Time 23.1 The Big Bang Our goals for learning What were conditions like in the early universe? What is the history of the universe according to the Big Bang theory? What were
Chapter 23 The Beginning of Time 23.1 The Big Bang Our goals for learning What were conditions like in the early universe? What is the history of the universe according to the Big Bang theory? What were
The Cosmic Microwave Background and the Big Bang Theory of the Universe
 The Cosmic Microwave Background and the Big Bang Theory of the Universe 1. Concepts from General Relativity 1.1 Curvature of space As we discussed earlier, Einstein s equivalence principle states that
The Cosmic Microwave Background and the Big Bang Theory of the Universe 1. Concepts from General Relativity 1.1 Curvature of space As we discussed earlier, Einstein s equivalence principle states that
Carol and Charles see their pencils fall exactly straight down.
 Section 24-1 1. Carol is in a railroad car on a train moving west along a straight stretch of track at a constant speed of 120 km/h, and Charles is in a railroad car on a train at rest on a siding along
Section 24-1 1. Carol is in a railroad car on a train moving west along a straight stretch of track at a constant speed of 120 km/h, and Charles is in a railroad car on a train at rest on a siding along
The first minutes of the Universe released energy which changed to matter, forming stars and galaxies. Introduction
 THE COSMIC ENGINE CHAPTER 18 The Universe begins The first minutes of the Universe released energy which changed to matter, forming stars and galaxies Introduction Cosmology, the study of the Universe
THE COSMIC ENGINE CHAPTER 18 The Universe begins The first minutes of the Universe released energy which changed to matter, forming stars and galaxies Introduction Cosmology, the study of the Universe
Malcolm S. Longair. Galaxy Formation. With 141 Figures and 12 Tables. Springer
 Malcolm S. Longair Galaxy Formation With 141 Figures and 12 Tables Springer Contents Part I Preliminaries 1. Introduction, History and Outline 3 1.1 Prehistory 3 1.2 The Theory of the Expanding Universe
Malcolm S. Longair Galaxy Formation With 141 Figures and 12 Tables Springer Contents Part I Preliminaries 1. Introduction, History and Outline 3 1.1 Prehistory 3 1.2 The Theory of the Expanding Universe
Data Provided: A formula sheet and table of physical constants is attached to this paper. DARK MATTER AND THE UNIVERSE
 Data Provided: A formula sheet and table of physical constants is attached to this paper. DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS AND ASTRONOMY Autumn Semester (2014-2015) DARK MATTER AND THE UNIVERSE 2 HOURS Answer question
Data Provided: A formula sheet and table of physical constants is attached to this paper. DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS AND ASTRONOMY Autumn Semester (2014-2015) DARK MATTER AND THE UNIVERSE 2 HOURS Answer question
Class 2 Solar System Characteristics Formation Exosolar Planets
 Class 1 Introduction, Background History of Modern Astronomy The Night Sky, Eclipses and the Seasons Kepler's Laws Newtonian Gravity General Relativity Matter and Light Telescopes Class 2 Solar System
Class 1 Introduction, Background History of Modern Astronomy The Night Sky, Eclipses and the Seasons Kepler's Laws Newtonian Gravity General Relativity Matter and Light Telescopes Class 2 Solar System
Gravitation and Newton s Synthesis
 Gravitation and Newton s Synthesis Vocabulary law of unviversal Kepler s laws of planetary perturbations casual laws gravitation motion casuality field graviational field inertial mass gravitational mass
Gravitation and Newton s Synthesis Vocabulary law of unviversal Kepler s laws of planetary perturbations casual laws gravitation motion casuality field graviational field inertial mass gravitational mass
Special Relativity. Photo by Philippe Halsman. Used with permission from Mrs. P. Halsman.
 Albert Einstein and the Miracle Year Special Relativity The year 1905 is often referred to as the Annus Mirabilis (or year of miracles). In this year, Albert Einstein, a 23-year old with an undergraduate
Albert Einstein and the Miracle Year Special Relativity The year 1905 is often referred to as the Annus Mirabilis (or year of miracles). In this year, Albert Einstein, a 23-year old with an undergraduate
Name Date Class ELECTRONS IN ATOMS. Standard Curriculum Core content Extension topics
 13 ELECTRONS IN ATOMS Conceptual Curriculum Concrete concepts More abstract concepts or math/problem-solving Standard Curriculum Core content Extension topics Honors Curriculum Core honors content Options
13 ELECTRONS IN ATOMS Conceptual Curriculum Concrete concepts More abstract concepts or math/problem-solving Standard Curriculum Core content Extension topics Honors Curriculum Core honors content Options
The Sun and Solar Energy
 I The Sun and Solar Energy One of the most important forces behind global change on Earth is over 90 million miles distant from the planet. The Sun is the ultimate, original source of the energy that drives
I The Sun and Solar Energy One of the most important forces behind global change on Earth is over 90 million miles distant from the planet. The Sun is the ultimate, original source of the energy that drives
REALIZING EINSTEIN S DREAM Exploring Our Mysterious Universe
 REALIZING EINSTEIN S DREAM Exploring Our Mysterious Universe The End of Physics Albert A. Michelson, at the dedication of Ryerson Physics Lab, U. of Chicago, 1894 The Miracle Year - 1905 Relativity Quantum
REALIZING EINSTEIN S DREAM Exploring Our Mysterious Universe The End of Physics Albert A. Michelson, at the dedication of Ryerson Physics Lab, U. of Chicago, 1894 The Miracle Year - 1905 Relativity Quantum
Transcript 22 - Universe
 Transcript 22 - Universe A few introductory words of explanation about this transcript: This transcript includes the words sent to the narrator for inclusion in the latest version of the associated video.
Transcript 22 - Universe A few introductory words of explanation about this transcript: This transcript includes the words sent to the narrator for inclusion in the latest version of the associated video.
The Messier Objects As A Tool in Teaching Astronomy
 The Messier Objects As A Tool in Teaching Astronomy Dr. Jesus Rodrigo F. Torres President, Rizal Technological University Individual Member, International Astronomical Union Chairman, Department of Astronomy,
The Messier Objects As A Tool in Teaching Astronomy Dr. Jesus Rodrigo F. Torres President, Rizal Technological University Individual Member, International Astronomical Union Chairman, Department of Astronomy,
Topic 3. Evidence for the Big Bang
 Topic 3 Primordial nucleosynthesis Evidence for the Big Bang! Back in the 1920s it was generally thought that the Universe was infinite! However a number of experimental observations started to question
Topic 3 Primordial nucleosynthesis Evidence for the Big Bang! Back in the 1920s it was generally thought that the Universe was infinite! However a number of experimental observations started to question
DIRECT ORBITAL DYNAMICS: USING INDEPENDENT ORBITAL TERMS TO TREAT BODIES AS ORBITING EACH OTHER DIRECTLY WHILE IN MOTION
 1 DIRECT ORBITAL DYNAMICS: USING INDEPENDENT ORBITAL TERMS TO TREAT BODIES AS ORBITING EACH OTHER DIRECTLY WHILE IN MOTION Daniel S. Orton email: [email protected] Abstract: There are many longstanding
1 DIRECT ORBITAL DYNAMICS: USING INDEPENDENT ORBITAL TERMS TO TREAT BODIES AS ORBITING EACH OTHER DIRECTLY WHILE IN MOTION Daniel S. Orton email: [email protected] Abstract: There are many longstanding
FXA 2008. UNIT G485 Module 5 5.5.1 Structure of the Universe. Δλ = v λ c CONTENTS OF THE UNIVERSE. Candidates should be able to :
 1 Candidates should be able to : CONTENTS OF THE UNIVERSE Describe the principal contents of the universe, including stars, galaxies and radiation. Describe the solar system in terms of the Sun, planets,
1 Candidates should be able to : CONTENTS OF THE UNIVERSE Describe the principal contents of the universe, including stars, galaxies and radiation. Describe the solar system in terms of the Sun, planets,
Notes: Most of the material in this chapter is taken from Young and Freedman, Chap. 13.
 Chapter 5. Gravitation Notes: Most of the material in this chapter is taken from Young and Freedman, Chap. 13. 5.1 Newton s Law of Gravitation We have already studied the effects of gravity through the
Chapter 5. Gravitation Notes: Most of the material in this chapter is taken from Young and Freedman, Chap. 13. 5.1 Newton s Law of Gravitation We have already studied the effects of gravity through the
Remodelling the Big Bang
 Remodelling the Big Bang Dewey B. Larson Unquestionably, the most significant development that has taken place in cosmology in recent years is the replacement of the original Big Bang theory by a totally
Remodelling the Big Bang Dewey B. Larson Unquestionably, the most significant development that has taken place in cosmology in recent years is the replacement of the original Big Bang theory by a totally
Testing dark matter halos using rotation curves and lensing
 Testing dark matter halos using rotation curves and lensing Darío Núñez Instituto de Ciencias Nucleares, UNAM Instituto Avanzado de Cosmología A. González, J. Cervantes, T. Matos Observational evidences
Testing dark matter halos using rotation curves and lensing Darío Núñez Instituto de Ciencias Nucleares, UNAM Instituto Avanzado de Cosmología A. González, J. Cervantes, T. Matos Observational evidences
Modeling the Expanding Universe
 H9 Modeling the Expanding Universe Activity H9 Grade Level: 8 12 Source: This activity is produced by the Universe Forum at NASA s Office of Space Science, along with their Structure and Evolution of the
H9 Modeling the Expanding Universe Activity H9 Grade Level: 8 12 Source: This activity is produced by the Universe Forum at NASA s Office of Space Science, along with their Structure and Evolution of the
Objectives. PAM1014 Introduction to Radiation Physics. Constituents of Atoms. Atoms. Atoms. Atoms. Basic Atomic Theory
 PAM1014 Introduction to Radiation Physics Basic Atomic Theory Objectives Introduce and Molecules The periodic Table Electronic Energy Levels Atomic excitation & de-excitation Ionisation Molecules Constituents
PAM1014 Introduction to Radiation Physics Basic Atomic Theory Objectives Introduce and Molecules The periodic Table Electronic Energy Levels Atomic excitation & de-excitation Ionisation Molecules Constituents
Advanced Topics in Physics: Special Relativity Course Syllabus
 Advanced Topics in Physics: Special Relativity Course Syllabus Day Period What How 1. Introduction 2. Course Information 3. Math Pre-Assessment Day 1. Morning 1. Physics Pre-Assessment 2. Coordinate Systems
Advanced Topics in Physics: Special Relativity Course Syllabus Day Period What How 1. Introduction 2. Course Information 3. Math Pre-Assessment Day 1. Morning 1. Physics Pre-Assessment 2. Coordinate Systems
THE MEANING OF THE FINE STRUCTURE CONSTANT
 THE MEANING OF THE FINE STRUCTURE CONSTANT Robert L. Oldershaw Amherst College Amherst, MA 01002 USA [email protected] Abstract: A possible explanation is offered for the longstanding mystery surrounding
THE MEANING OF THE FINE STRUCTURE CONSTANT Robert L. Oldershaw Amherst College Amherst, MA 01002 USA [email protected] Abstract: A possible explanation is offered for the longstanding mystery surrounding
The Theory of Relativity
 The Theory of Relativity 1. THE SPECIAL THEORY In 1905, his annum mirabilis, Einstein revolutionized physics with, among other things, his special theory of relativity. With it he completely overturned
The Theory of Relativity 1. THE SPECIAL THEORY In 1905, his annum mirabilis, Einstein revolutionized physics with, among other things, his special theory of relativity. With it he completely overturned
Chapter 15 Cosmology: Will the universe end?
 Cosmology: Will the universe end? 1. Who first showed that the Milky Way is not the only galaxy in the universe? a. Kepler b. Copernicus c. Newton d. Hubble e. Galileo Ans: d 2. The big bang theory and
Cosmology: Will the universe end? 1. Who first showed that the Milky Way is not the only galaxy in the universe? a. Kepler b. Copernicus c. Newton d. Hubble e. Galileo Ans: d 2. The big bang theory and
MASS DEFECT AND BINDING ENERGY
 MASS DEFECT AND BINDING ENERGY The separate laws of Conservation of Mass and Conservation of Energy are not applied strictly on the nuclear level. It is possible to convert between mass and energy. Instead
MASS DEFECT AND BINDING ENERGY The separate laws of Conservation of Mass and Conservation of Energy are not applied strictly on the nuclear level. It is possible to convert between mass and energy. Instead
Astronomy & Physics Resources for Middle & High School Teachers
 Astronomy & Physics Resources for Middle & High School Teachers Gillian Wilson http://www.faculty.ucr.edu/~gillianw/k12 A cosmologist is.... an astronomer who studies the formation and evolution of the
Astronomy & Physics Resources for Middle & High School Teachers Gillian Wilson http://www.faculty.ucr.edu/~gillianw/k12 A cosmologist is.... an astronomer who studies the formation and evolution of the
Chapter 1 Mach s Principle and the Concept of Mass
 Chapter 1 Mach s Principle and the Concept of Mass Inertia originates in a kind of interaction between bodies. Albert Einstein [1] In theoretical physics, especially in inertial and gravitational theories,
Chapter 1 Mach s Principle and the Concept of Mass Inertia originates in a kind of interaction between bodies. Albert Einstein [1] In theoretical physics, especially in inertial and gravitational theories,
Objectives 404 CHAPTER 9 RADIATION
 Objectives Explain the difference between isotopes of the same element. Describe the force that holds nucleons together. Explain the relationship between mass and energy according to Einstein s theory
Objectives Explain the difference between isotopes of the same element. Describe the force that holds nucleons together. Explain the relationship between mass and energy according to Einstein s theory
Background Biology and Biochemistry Notes A
 Background Biology and Biochemistry Notes A Vocabulary dependent variable evidence experiment hypothesis independent variable model observation prediction science scientific investigation scientific law
Background Biology and Biochemistry Notes A Vocabulary dependent variable evidence experiment hypothesis independent variable model observation prediction science scientific investigation scientific law
Science Standard 4 Earth in Space Grade Level Expectations
 Science Standard 4 Earth in Space Grade Level Expectations Science Standard 4 Earth in Space Our Solar System is a collection of gravitationally interacting bodies that include Earth and the Moon. Universal
Science Standard 4 Earth in Space Grade Level Expectations Science Standard 4 Earth in Space Our Solar System is a collection of gravitationally interacting bodies that include Earth and the Moon. Universal
Basics of Nuclear Physics and Fission
 Basics of Nuclear Physics and Fission A basic background in nuclear physics for those who want to start at the beginning. Some of the terms used in this factsheet can be found in IEER s on-line glossary.
Basics of Nuclear Physics and Fission A basic background in nuclear physics for those who want to start at the beginning. Some of the terms used in this factsheet can be found in IEER s on-line glossary.
The Hidden Lives of Galaxies. Jim Lochner, USRA & NASA/GSFC
 The Hidden Lives of Galaxies Jim Lochner, USRA & NASA/GSFC What is a Galaxy? Solar System Distance from Earth to Sun = 93,000,000 miles = 8 light-minutes Size of Solar System = 5.5 light-hours What is
The Hidden Lives of Galaxies Jim Lochner, USRA & NASA/GSFC What is a Galaxy? Solar System Distance from Earth to Sun = 93,000,000 miles = 8 light-minutes Size of Solar System = 5.5 light-hours What is
Cosmic Journey: Teacher Packet
 Cosmic Journey: Teacher Packet Compiled by: Morehead State University Star Theatre with help from Bethany DeMoss Table of Contents Table of Contents 1 Corresponding Standards 2 Vocabulary 4 Sizing up the
Cosmic Journey: Teacher Packet Compiled by: Morehead State University Star Theatre with help from Bethany DeMoss Table of Contents Table of Contents 1 Corresponding Standards 2 Vocabulary 4 Sizing up the
Natural Science I: Einstein's Universe Fall 2013 Meyer 121
 Natural Science I: Einstein's Universe MAP-UA-0204-010 Fall 2013 Meyer 121 Tuesday and Thursday 2:00 3:15 p.m. Dr. Burton Budick Office Meyer 705 Office Phone: (212)-998-7683 E-mail: [email protected] Office
Natural Science I: Einstein's Universe MAP-UA-0204-010 Fall 2013 Meyer 121 Tuesday and Thursday 2:00 3:15 p.m. Dr. Burton Budick Office Meyer 705 Office Phone: (212)-998-7683 E-mail: [email protected] Office
SIZE. Energy. Non-Mechanical Energy. Mechanical Energy. Part II. Examples of Non-Mechanical Energy. Examples of Mechanical Energy.
 Energy Part II Non-Mechanical Energy Wait a minute if all energy is either kinetic or potential and TME = KE + PE then how can there possibly be such thing as non-mechanical energy!?!? Mechanical Energy
Energy Part II Non-Mechanical Energy Wait a minute if all energy is either kinetic or potential and TME = KE + PE then how can there possibly be such thing as non-mechanical energy!?!? Mechanical Energy
NEW DEVELOPMENTS 2008
 NEW DEVELOPMENTS 2008 THE HIDDEN MEANING OF PLANCK S CONSTANT [ March 2008] The next great awakening of the human intellect may well produce a method of understanding the qualitative content of the equations.
NEW DEVELOPMENTS 2008 THE HIDDEN MEANING OF PLANCK S CONSTANT [ March 2008] The next great awakening of the human intellect may well produce a method of understanding the qualitative content of the equations.
A Theory for the Cosmological Constant and its Explanation of the Gravitational Constant
 A Theory for the Cosmological Constant and its Explanation of the Gravitational Constant H.M.Mok Radiation Health Unit, 3/F., Saiwanho Health Centre, Hong Kong SAR Govt, 8 Tai Hong St., Saiwanho, Hong
A Theory for the Cosmological Constant and its Explanation of the Gravitational Constant H.M.Mok Radiation Health Unit, 3/F., Saiwanho Health Centre, Hong Kong SAR Govt, 8 Tai Hong St., Saiwanho, Hong
The Universe. The Solar system, Stars and Galaxies
 The Universe The Universe is everything. All us, the room, the U.S. the earth, the solar system, all the other stars in the Milky way galaxy, all the other galaxies... everything. How big and how old is
The Universe The Universe is everything. All us, the room, the U.S. the earth, the solar system, all the other stars in the Milky way galaxy, all the other galaxies... everything. How big and how old is
Journal of Theoretics Journal Home Page
 Journal of Theoretics Journal Home Page MASS BOOM VERSUS BIG BANG: THE ROLE OF PLANCK S CONSTANT by Antonio Alfonso-Faus E.U.I.T. Aeronáutica Plaza Cardenal Cisneros s/n 8040 Madrid, SPAIN e-mail: [email protected]
Journal of Theoretics Journal Home Page MASS BOOM VERSUS BIG BANG: THE ROLE OF PLANCK S CONSTANT by Antonio Alfonso-Faus E.U.I.T. Aeronáutica Plaza Cardenal Cisneros s/n 8040 Madrid, SPAIN e-mail: [email protected]
On a Flat Expanding Universe
 Adv. Studies Theor. Phys., Vol. 7, 2013, no. 4, 191-197 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com On a Flat Expanding Universe Bo Lehnert Alfvén Laboratory Royal Institute of Technology, SE-10044 Stockholm, Sweden
Adv. Studies Theor. Phys., Vol. 7, 2013, no. 4, 191-197 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com On a Flat Expanding Universe Bo Lehnert Alfvén Laboratory Royal Institute of Technology, SE-10044 Stockholm, Sweden
Exploring the Universe Through the Hubble Space Telescope
 Exploring the Universe Through the Hubble Space Telescope WEEK FIVE: THE HUBBLE DEEP FIELD + LIMITATIONS OF HUBBLE, COLLABORATIONS, AND THE FUTURE OF ASTRONOMY Date: October 14, 2013 Instructor: Robert
Exploring the Universe Through the Hubble Space Telescope WEEK FIVE: THE HUBBLE DEEP FIELD + LIMITATIONS OF HUBBLE, COLLABORATIONS, AND THE FUTURE OF ASTRONOMY Date: October 14, 2013 Instructor: Robert
STRING THEORY: Past, Present, and Future
 STRING THEORY: Past, Present, and Future John H. Schwarz Simons Center March 25, 2014 1 OUTLINE I) Early History and Basic Concepts II) String Theory for Unification III) Superstring Revolutions IV) Remaining
STRING THEORY: Past, Present, and Future John H. Schwarz Simons Center March 25, 2014 1 OUTLINE I) Early History and Basic Concepts II) String Theory for Unification III) Superstring Revolutions IV) Remaining
Build Your Own Universe
 Build Your Own Universe You will need: At least 10,000,000,000,000,00 0,000,000,000,000,000,000,00 0,000,000,000,000,000,000,00 0,000,000,000,000,000,000,00 0,000 x Down quarks At least 10,000,000,000,000,000,
Build Your Own Universe You will need: At least 10,000,000,000,000,00 0,000,000,000,000,000,000,00 0,000,000,000,000,000,000,00 0,000,000,000,000,000,000,00 0,000 x Down quarks At least 10,000,000,000,000,000,
Atomic Structure Ron Robertson
 Atomic Structure Ron Robertson r2 n:\files\courses\1110-20\2010 possible slides for web\atomicstructuretrans.doc I. What is Light? Debate in 1600's: Since waves or particles can transfer energy, what is
Atomic Structure Ron Robertson r2 n:\files\courses\1110-20\2010 possible slides for web\atomicstructuretrans.doc I. What is Light? Debate in 1600's: Since waves or particles can transfer energy, what is
HUNTER COLLEGE READING/WRITING CENTER THE WRITING PROCESS Invention: Annotating a Text
 HUNTER COLLEGE READING/WRITING CENTER THE WRITING PROCESS Invention: Annotating a Text Annotating a text, or marking the pages with notes, is an excellent, if not essential, way to make the most out of
HUNTER COLLEGE READING/WRITING CENTER THE WRITING PROCESS Invention: Annotating a Text Annotating a text, or marking the pages with notes, is an excellent, if not essential, way to make the most out of
Unit 1.7: Earth and Space Science The Structure of the Cosmos
 Lesson Summary: This week students will search for evidence provided in passages that lend support about the structure and organization of the Cosmos. Then students will summarize a passage. Materials
Lesson Summary: This week students will search for evidence provided in passages that lend support about the structure and organization of the Cosmos. Then students will summarize a passage. Materials
1 Introduction. 1 There may, of course, in principle, exist other universes, but they are not accessible to our
 1 1 Introduction Cosmology is the study of the universe as a whole, its structure, its origin, and its evolution. Cosmology is soundly based on observations, mostly astronomical, and laws of physics. These
1 1 Introduction Cosmology is the study of the universe as a whole, its structure, its origin, and its evolution. Cosmology is soundly based on observations, mostly astronomical, and laws of physics. These
The Birth of the Universe Newcomer Academy High School Visualization One
 The Birth of the Universe Newcomer Academy High School Visualization One Chapter Topic Key Points of Discussion Notes & Vocabulary 1 Birth of The Big Bang Theory Activity 4A the How and when did the universe
The Birth of the Universe Newcomer Academy High School Visualization One Chapter Topic Key Points of Discussion Notes & Vocabulary 1 Birth of The Big Bang Theory Activity 4A the How and when did the universe
PHYSICS FOUNDATIONS SOCIETY THE DYNAMIC UNIVERSE TOWARD A UNIFIED PICTURE OF PHYSICAL REALITY TUOMO SUNTOLA
 PHYSICS FOUNDATIONS SOCIETY THE DYNAMIC UNIVERSE TOWARD A UNIFIED PICTURE OF PHYSICAL REALITY TUOMO SUNTOLA Published by PHYSICS FOUNDATIONS SOCIETY Espoo, Finland www.physicsfoundations.org Printed by
PHYSICS FOUNDATIONS SOCIETY THE DYNAMIC UNIVERSE TOWARD A UNIFIED PICTURE OF PHYSICAL REALITY TUOMO SUNTOLA Published by PHYSICS FOUNDATIONS SOCIETY Espoo, Finland www.physicsfoundations.org Printed by
Section 15.1 Energy and Its Forms (pages 446 452)
 Section 15.1 and Its Forms (pages 446 452) This section describes how energy and work are related. It defines kinetic energy and potential energy, and gives examples for calculating these forms of energy.
Section 15.1 and Its Forms (pages 446 452) This section describes how energy and work are related. It defines kinetic energy and potential energy, and gives examples for calculating these forms of energy.
Energy and Energy Transformations Test Review
 Energy and Energy Transformations Test Review Completion: 1. Mass 13. Kinetic 2. Four 14. thermal 3. Kinetic 15. Thermal energy (heat) 4. Electromagnetic/Radiant 16. Thermal energy (heat) 5. Thermal 17.
Energy and Energy Transformations Test Review Completion: 1. Mass 13. Kinetic 2. Four 14. thermal 3. Kinetic 15. Thermal energy (heat) 4. Electromagnetic/Radiant 16. Thermal energy (heat) 5. Thermal 17.
What Einstein meant when he said God does not play dice...
 What Einstein meant when he said God does not play dice... Vasant Natarajan We analyze Einstein s views on God and religion, and his views on Quantum Mechanics. One of Albert Einstein s most famous statements
What Einstein meant when he said God does not play dice... Vasant Natarajan We analyze Einstein s views on God and religion, and his views on Quantum Mechanics. One of Albert Einstein s most famous statements
Neutron Stars. How were neutron stars discovered? The first neutron star was discovered by 24-year-old graduate student Jocelyn Bell in 1967.
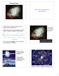 Neutron Stars How were neutron stars discovered? The first neutron star was discovered by 24-year-old graduate student Jocelyn Bell in 1967. Using a radio telescope she noticed regular pulses of radio
Neutron Stars How were neutron stars discovered? The first neutron star was discovered by 24-year-old graduate student Jocelyn Bell in 1967. Using a radio telescope she noticed regular pulses of radio
The unifying field Theory
 The unifying field Theory M T Keshe 2000-2009, all rights reserved Date of release 28.10.2009 Abstract In this paper the origin of electromagnetic fields or electromagnetism and how they are created within
The unifying field Theory M T Keshe 2000-2009, all rights reserved Date of release 28.10.2009 Abstract In this paper the origin of electromagnetic fields or electromagnetism and how they are created within
NASA LAUNCHPAD Educational Product Educators & Students Grades 9-12 www.nasa.gov NP-2009-12-232-LaRC
 National Aeronautics and Space Administration NASA eclips TM Educator Guide NASA LAUNCHPAD Making Waves Educational Product Educators & Students Grades 9-12 NP-2009-12-232-LaRC www.nasa.gov eclips Making
National Aeronautics and Space Administration NASA eclips TM Educator Guide NASA LAUNCHPAD Making Waves Educational Product Educators & Students Grades 9-12 NP-2009-12-232-LaRC www.nasa.gov eclips Making
23. The Beginning of Time. Agenda. Agenda. ESA s Venus Express. Conditions in the Early Universe. 23.1 Running the Expansion Backward
 23. The Beginning of Time Somewhere, something incredible is waiting to be known. Agenda Announce: Solar Altitude Lab (#2) due today Read Ch. 24 for Thursday Observation make-up next week Project Presentations
23. The Beginning of Time Somewhere, something incredible is waiting to be known. Agenda Announce: Solar Altitude Lab (#2) due today Read Ch. 24 for Thursday Observation make-up next week Project Presentations
Time and Causation in Gödel s Universe.
 Time and Causation in Gödel s Universe. John L. Bell In 1949 the great logician Kurt Gödel constructed the first mathematical models of the universe in which travel into the past is, in theory at least,
Time and Causation in Gödel s Universe. John L. Bell In 1949 the great logician Kurt Gödel constructed the first mathematical models of the universe in which travel into the past is, in theory at least,
7. In which part of the electromagnetic spectrum are molecules most easily detected? A. visible light B. radio waves C. X rays D.
 1. Most interstellar matter is too cold to be observed optically. Its radiation can be detected in which part of the electromagnetic spectrum? A. gamma ray B. ultraviolet C. infrared D. X ray 2. The space
1. Most interstellar matter is too cold to be observed optically. Its radiation can be detected in which part of the electromagnetic spectrum? A. gamma ray B. ultraviolet C. infrared D. X ray 2. The space
In studying the Milky Way, we have a classic problem of not being able to see the forest for the trees.
 In studying the Milky Way, we have a classic problem of not being able to see the forest for the trees. A panoramic painting of the Milky Way as seen from Earth, done by Knut Lundmark in the 1940 s. The
In studying the Milky Way, we have a classic problem of not being able to see the forest for the trees. A panoramic painting of the Milky Way as seen from Earth, done by Knut Lundmark in the 1940 s. The
MASTER OF SCIENCE IN PHYSICS MASTER OF SCIENCES IN PHYSICS (MS PHYS) (LIST OF COURSES BY SEMESTER, THESIS OPTION)
 MASTER OF SCIENCE IN PHYSICS Admission Requirements 1. Possession of a BS degree from a reputable institution or, for non-physics majors, a GPA of 2.5 or better in at least 15 units in the following advanced
MASTER OF SCIENCE IN PHYSICS Admission Requirements 1. Possession of a BS degree from a reputable institution or, for non-physics majors, a GPA of 2.5 or better in at least 15 units in the following advanced
The facts we know today will be the same tomorrow but today s theories may tomorrow be obsolete.
 The Scale of the Universe Some Introductory Material and Pretty Pictures The facts we know today will be the same tomorrow but today s theories may tomorrow be obsolete. A scientific theory is regarded
The Scale of the Universe Some Introductory Material and Pretty Pictures The facts we know today will be the same tomorrow but today s theories may tomorrow be obsolete. A scientific theory is regarded
1. Mass, Force and Gravity
 STE Physics Intro Name 1. Mass, Force and Gravity Before attempting to understand force, we need to look at mass and acceleration. a) What does mass measure? The quantity of matter(atoms) b) What is the
STE Physics Intro Name 1. Mass, Force and Gravity Before attempting to understand force, we need to look at mass and acceleration. a) What does mass measure? The quantity of matter(atoms) b) What is the
Energy. Mechanical Energy
 Principles of Imaging Science I (RAD119) Electromagnetic Radiation Energy Definition of energy Ability to do work Physicist s definition of work Work = force x distance Force acting upon object over distance
Principles of Imaging Science I (RAD119) Electromagnetic Radiation Energy Definition of energy Ability to do work Physicist s definition of work Work = force x distance Force acting upon object over distance
Specific Intensity. I ν =
 Specific Intensity Initial question: A number of active galactic nuclei display jets, that is, long, nearly linear, structures that can extend for hundreds of kiloparsecs. Many have two oppositely-directed
Specific Intensity Initial question: A number of active galactic nuclei display jets, that is, long, nearly linear, structures that can extend for hundreds of kiloparsecs. Many have two oppositely-directed
Main properties of atoms and nucleus
 Main properties of atoms and nucleus. Atom Structure.... Structure of Nuclei... 3. Definition of Isotopes... 4. Energy Characteristics of Nuclei... 5. Laws of Radioactive Nuclei Transformation... 3. Atom
Main properties of atoms and nucleus. Atom Structure.... Structure of Nuclei... 3. Definition of Isotopes... 4. Energy Characteristics of Nuclei... 5. Laws of Radioactive Nuclei Transformation... 3. Atom
WHERE DID ALL THE ELEMENTS COME FROM??
 WHERE DID ALL THE ELEMENTS COME FROM?? In the very beginning, both space and time were created in the Big Bang. It happened 13.7 billion years ago. Afterwards, the universe was a very hot, expanding soup
WHERE DID ALL THE ELEMENTS COME FROM?? In the very beginning, both space and time were created in the Big Bang. It happened 13.7 billion years ago. Afterwards, the universe was a very hot, expanding soup
Einstein Rings: Nature s Gravitational Lenses
 National Aeronautics and Space Administration Einstein Rings: Nature s Gravitational Lenses Leonidas Moustakas and Adam Bolton Taken from: Hubble 2006 Science Year in Review The full contents of this book
National Aeronautics and Space Administration Einstein Rings: Nature s Gravitational Lenses Leonidas Moustakas and Adam Bolton Taken from: Hubble 2006 Science Year in Review The full contents of this book
Modeling Galaxy Formation
 Galaxy Evolution is the study of how galaxies form and how they change over time. As was the case with we can not observe an individual galaxy evolve but we can observe different galaxies at various stages
Galaxy Evolution is the study of how galaxies form and how they change over time. As was the case with we can not observe an individual galaxy evolve but we can observe different galaxies at various stages
5. The Nature of Light. Does Light Travel Infinitely Fast? EMR Travels At Finite Speed. EMR: Electric & Magnetic Waves
 5. The Nature of Light Light travels in vacuum at 3.0. 10 8 m/s Light is one form of electromagnetic radiation Continuous radiation: Based on temperature Wien s Law & the Stefan-Boltzmann Law Light has
5. The Nature of Light Light travels in vacuum at 3.0. 10 8 m/s Light is one form of electromagnetic radiation Continuous radiation: Based on temperature Wien s Law & the Stefan-Boltzmann Law Light has
AZ State Standards. Concept 3: Conservation of Energy and Increase in Disorder Understand ways that energy is conserved, stored, and transferred.
 Forms of Energy AZ State Standards Concept 3: Conservation of Energy and Increase in Disorder Understand ways that energy is conserved, stored, and transferred. PO 1. Describe the following ways in which
Forms of Energy AZ State Standards Concept 3: Conservation of Energy and Increase in Disorder Understand ways that energy is conserved, stored, and transferred. PO 1. Describe the following ways in which
An Introduction to Astronomy and Cosmology. 1) Astronomy - an Observational Science
 An Introduction to Astronomy and Cosmology 1) Astronomy - an Observational Science Why study Astronomy 1 A fascinating subject in its own right. The origin and Evolution of the universe The Big Bang formation
An Introduction to Astronomy and Cosmology 1) Astronomy - an Observational Science Why study Astronomy 1 A fascinating subject in its own right. The origin and Evolution of the universe The Big Bang formation
Test 2 --- Natural Sciences 102, Professors Rieke --- VERSION B March 3, 2010
 Enter your answers on the form provided. Be sure to write your name and student ID number on the first blank at the bottom of the form. Please mark the version (B) in the Key ID space at the top of the
Enter your answers on the form provided. Be sure to write your name and student ID number on the first blank at the bottom of the form. Please mark the version (B) in the Key ID space at the top of the
Chapter 15.3 Galaxy Evolution
 Chapter 15.3 Galaxy Evolution Elliptical Galaxies Spiral Galaxies Irregular Galaxies Are there any connections between the three types of galaxies? How do galaxies form? How do galaxies evolve? P.S. You
Chapter 15.3 Galaxy Evolution Elliptical Galaxies Spiral Galaxies Irregular Galaxies Are there any connections between the three types of galaxies? How do galaxies form? How do galaxies evolve? P.S. You
What is Energy? What is the relationship between energy and work?
 What is Energy? What is the relationship between energy and work? Compare kinetic and potential energy What are the different types of energy? What is energy? Energy is the ability to do work. Great, but
What is Energy? What is the relationship between energy and work? Compare kinetic and potential energy What are the different types of energy? What is energy? Energy is the ability to do work. Great, but
TEACHER BACKGROUND INFORMATION THERMAL ENERGY
 TEACHER BACKGROUND INFORMATION THERMAL ENERGY In general, when an object performs work on another object, it does not transfer all of its energy to that object. Some of the energy is lost as heat due to
TEACHER BACKGROUND INFORMATION THERMAL ENERGY In general, when an object performs work on another object, it does not transfer all of its energy to that object. Some of the energy is lost as heat due to
9 th Grade Physical Science Springfield Local Schools Common Course Syllabi. Course Description
 9 th Grade Physical Science Springfield Local Schools Common Course Syllabi Course Description The purpose of the Physical Science course is to satisfy the Ohio Core science graduation requirement. The
9 th Grade Physical Science Springfield Local Schools Common Course Syllabi Course Description The purpose of the Physical Science course is to satisfy the Ohio Core science graduation requirement. The
Chapter 6. Work and Energy
 Chapter 6 Work and Energy The concept of forces acting on a mass (one object) is intimately related to the concept of ENERGY production or storage. A mass accelerated to a non-zero speed carries energy
Chapter 6 Work and Energy The concept of forces acting on a mass (one object) is intimately related to the concept of ENERGY production or storage. A mass accelerated to a non-zero speed carries energy
1 A Solar System Is Born
 CHAPTER 3 1 A Solar System Is Born SECTION Formation of the Solar System BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is a nebula? How did our solar system
CHAPTER 3 1 A Solar System Is Born SECTION Formation of the Solar System BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is a nebula? How did our solar system
