Shoulder dystocia is one of the
|
|
|
- Franklin Wilcox
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ALSO SERIES Shoulder Dystocia ELIZABETH G. BAXLEY, M.D., University of South Carolina School of Medicine, Columbia, South Carolina ROBERT W. GOBBO, M.D., University of California at Davis Family Practice Network, Merced, California Shoulder dystocia can be one of the most frightening emergencies in the delivery room. Although many factors have been associated with shoulder dystocia, most cases occur with no warning. Calm and effective management of this emergency is possible with recognition of the impaction and institution of specified maneuvers, such as the McRoberts maneuver, suprapubic pressure, internal rotation, or removal of the posterior arm, to relieve the impacted shoulder and allow for spontaneous delivery of the infant. The HELPERR mnemonic from the Advanced Life Support in Obstetrics course can be a useful tool for addressing this emergency. Although no ideal manipulation or treatment exists, all maneuvers in the HELPERR mnemonic aid physicians in completing one of three actions: enlarging the maternal pelvis through cephalad rotation of the symphysis and flattening of the sacrum; collapsing the fetal shoulder width; or altering the orientation of the longitudinal axis of the fetus to the plane of the obstruction. In rare cases in which these interventions are unsuccessful, additional management options, such as intentional clavicle fracture, symphysiotomy, and the Zavanelli maneuver, are described. (Am Fam Physician 2004;69: Copyright 2004 American Academy of Family Physicians.) This article is one in a series on "Advanced Life Support in Obstetrics (ALSO )," initially established by Mark Deutchman, M.D., professor in the Department of Family Medicine and director of the Family Medicine Perinatal Service and Advanced Training Track, University of Colorado Health Sciences Center, Denver, and now coordinated by Chip Taylor, M.D., M.P.H., ALSO Managing Editor, Newport, R.I. See page 1591 for definitions of strength-ofrecommendation labels. Shoulder dystocia is one of the most anxiety-provoking emergencies encountered by physicians practicing maternity care. Typically defined as a delivery in which additional maneuvers are required to deliver the fetus after normal gentle downward traction has failed, shoulder dystocia occurs when the fetal anterior shoulder impacts against the maternal symphysis following delivery of the vertex. Less commonly, shoulder dystocia results from impaction of the posterior shoulder on the sacral promontory. 1 The overall incidence of shoulder dystocia varies based on fetal weight, occurring in 0.6 to 1.4 percent of all infants with a birth weight of 2,500 g (5 lb, 8 oz) to 4,000 g (8 lb, 13 oz), increasing to a rate of 5 to 9 percent among fetuses weighing 4,000 to 4,500 g (9 lb, 14 oz) born to mothers without diabetes. 2-4 Shoulder dystocia occurs with equal frequency in primigravid and multigravid women, although it is more common in infants born to women with diabetes. 2,5 Several additional prenatal and intrapartum factors have been associated with an increased See editorial on page TABLE 1 Risk Factors for Shoulder Dystocia Maternal Abnormal pelvic anatomy Gestational diabetes Post-dates pregnancy Previous shoulder dystocia Short stature Fetal Suspected macrosomia Labor related Assisted vaginal delivery (forceps or vacuum) Protracted active phase of first-stage labor Protracted second-stage labor incidence of shoulder dystocia (Table 1). The single most common risk factor for shoulder dystocia is the use of a vacuum extractor or forceps during delivery. 2 However, most cases occur in fetuses of normal birth weight and are unanticipated, limiting the clinical usefulness of risk-factor identification. 6 Complications resulting from shoulder dystocia during delivery can affect the mother and infant (Table 2). Postpartum hemorrhage (11 percent) and fourth-degree lac- Downloaded from the American Family Physician Web site at Copyright 2004 American Academy of Family Physicians. For the private, noncommercial use of one individual user of the Web site. All other rights reserved. Contact copyrights@aafp.org for copyright questions and/or permission requests.
2 In women without diabetes, labor induction for suspected fetal macrosomia does not lower the rates of shoulder dystocia or cesarean delivery. erations (3.8 percent) are the most common maternal complications, and their incidence remains unchanged by rotation maneuvers or other manipulation. 7 Among the most common fetal complications are brachial plexus palsies, occurring in 4 to 15 percent of infants. 4,7,8 These rates remain constant, independent of operator experience. 4,5 Nearly all palsies resolve within six to 12 months, with fewer than 10 percent resulting in permanent injury. 7,9,10 Although shoulder dystocia and disimpaction maneuvers historically have been blamed for the etiology of these palsies, in utero positioning of the fetus, a precipitous second stage of labor, and maternal forces may contribute to their etiology. 4,6,10 Additional research demonstrates that a significant percentage of palsy-type injuries occur without association to shoulder dystocia and sometimes during cesarean delivery. 11,12 The TABLE 2 Complications of Shoulder Dystocia Maternal Postpartum hemorrhage Rectovaginal fistula Symphyseal separation or diathesis, with or without transient femoral neuropathy Third- or fourth-degree episiotomy or tear Uterine rupture Fetal Brachial plexus palsy Clavicle fracture Fetal death Fetal hypoxia, with or without permanent neurologic damage Fracture of the humerus rate of persistence is significantly higher at one year in cases of Erb s palsy without identified shoulder dystocia. Other common morbidities from shoulder dystocia include fractures of the clavicle and humerus, which typically heal without deformity. In severe cases, hypoxic injury or death may occur. 2,13 Prevention Evidence is lacking to support labor induction or elective cesarean delivery in women without diabetes who are at term when a fetus is suspected of having macrosomia. 14 In two studies of 313 women without diabetes, induction for suspected fetal macrosomia did not lower the rates of shoulder dystocia or cesarean delivery, nor did it improve the rates of maternal or neonatal morbidity. 15 [strength of recommendation (SOR) evidence level A, meta-analysis] While labor induction in women with gestational diabetes who require insulin may reduce the risk of macrosomia and shoulder dystocia, the risk of maternal or neonatal injury is not modified. Not enough evidence is available to routinely support elective delivery in this population. 16,17 [SOR evidence level B, systematic review including a single randomized trial] Similarly, prophylactic cesarean delivery is not recommended as a means of preventing morbidity in pregnancies in which fetal macrosomia is suspected. 9 [SOR evidence level C, expert opinion based on cost-effectiveness analysis] Analytic decision models have estimated that 2,345 cesarean deliveries, at a cost of nearly $5 million annually, would be needed to prevent one permanent brachial plexus injury in a patient without diabetes who had a fetus suspected of weighing more than 4,000 g. In the subgroup of women with diabetes, the frequency of shoulder dystocia, brachial plexus palsy, and cesarean delivery was higher, leading the authors to conclude that a policy of elective cesarean delivery in this group potentially may have greater merit. 9 [SOR evidence level C, expert opinion based on cost-effectiveness analysis] 1708-AMERICAN FAMILY PHYSICIAN VOLUME 69, NUMBER 7 / APRIL 1, 2004
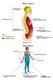
3 TABLE 3 The HELPERR Mnemonic Preliminary Management and Concerns When a shoulder dystocia occurs, umbilical cord compression between the fetal body and the maternal pelvis is a potential danger. While the safe amount of time in which significant fetal acidosis related to shoulder dystocia can be avoided is unknown, the fetal ph will drop by an estimated 0.14 per minute during delivery of the fetal trunk No significant linear relationship has been identified between the head-to-body delivery interval and fetal acid-base balance. 21 If shoulder dystocia is anticipated on the basis of risk factors, preparatory tasks can be accomplished before delivery. Key personnel can be alerted, and the patient and her family can be educated about the steps that will be taken in the event of a difficult delivery. The patient s bladder should be emptied, and the delivery room cleared of unnecessary clutter to make room for additional personnel and equipment. One method of preliminary intervention for shoulder dystocia in a patient with risk factors involves implementing the head and shoulder maneuver to deliver through until the anterior shoulder is visible. 22 [SOR evidence level C, expert opinion] This step is accomplished by continuing the momentum of the fetal head delivery until the shoulder is visible. After controlled delivery of the head, the physician proceeds with immediate delivery of the anterior shoulder without stopping to suction the oropharynx. Reduction Maneuvers and the HELPERR Mnemonic Shoulder dystocia becomes obvious when the fetal head emerges and then retracts against the perineum, commonly referred to as the turtle sign. Excessive force must not be applied to the fetal head or neck, and fundal pressure must be avoided, because these activities are unlikely to free the impaction and may cause injury to the infant and H E L P E R R Call for help. This refers to activating the pre-arranged protocol or requesting the appropriate personnel to respond with necessary equipment to the labor and delivery unit. Evaluate for episiotomy. Episiotomy should be considered throughout the management of shoulder dystocia but is necessary only to make more room if rotation maneuvers are required. Shoulder dystocia is a bony impaction, so episiotomy alone will not release the shoulder. Because most cases of shoulder dystocia can be relieved with the McRoberts maneuver and suprapubic pressure, many women can be spared a surgical incision. Legs (the McRoberts maneuver) This procedure involves flexing and abducting the maternal hips, positioning the maternal thighs up onto the maternal abdomen. This position flattens the sacral promontory and results in cephalad rotation of the pubic symphysis. Nurses and family members present at the delivery can provide assistance for this maneuver. Suprapubic pressure The hand of an assistant should be placed suprapubically over the fetal anterior shoulder, applying pressure in a cardiopulmonary resuscitation style with a downward and lateral motion on the posterior aspect of the fetal shoulder. This maneuver should be attempted while continuing downward traction. Enter maneuvers (internal rotation) These maneuvers attempt to manipulate the fetus to rotate the anterior shoulder into an oblique plane and under the maternal symphysis (see Figure 2). These maneuvers can be difficult to perform when the anterior shoulder is wedged beneath the symphysis. At times, it is necessary to push the fetus up into the pelvis slightly to accomplish the maneuvers. Remove the posterior arm. Removing the posterior arm from the birth canal also shortens the bisacromial diameter, allowing the fetus to drop into the sacral hollow, freeing the impaction. The elbow then should be flexed and the forearm delivered in a sweeping motion over the fetal anterior chest wall. Grasping and pulling directly on the fetal arm may fracture the humerus. Roll the patient. The patient rolls from her existing position to the all-fours position. Often, the shoulder will dislodge during the act of turning, so that this movement alone may be sufficient to dislodge the impaction. In addition, once the position change is completed, gravitational forces may aid in the disimpaction of the fetal shoulders. Information from reference 25. mother. 23,24 [SOR evidence level B, consistent observational studies] The HELPERR mnemonic is a clinical tool that offers a structured framework for coping with shoulder dystocia (Table 3). 25 These maneuvers are designed to do one of three things: increase the functional size of the bony pelvis through flattening of the lumbar lordosis and cephalad rotation of the symphysis (i.e., the McRoberts maneuver) 25 ; decrease the bisacromial diameter (i.e., the breadth of the APRIL 1, 2004 / VOLUME 69, NUMBER 7 AMERICAN FAMILY PHYSICIAN-1709
4 The Authors shoulders) of the fetus through application of suprapubic pressure (i.e., internal pressure on the posterior aspect of the impacted shoulder); or change the relationship of the bisacromial diameter within the bony pelvis through internal rotation maneuvers. Although there is no indication that any one of these techniques is superior to another, together they effectively relieve the impacted shoulder. The order of the steps is not as important as the fact that they each be employed efficiently and appropriately. Persistence in any one ineffective maneuver should be avoided. Clinical judgment always should guide the progression of procedures used. CALL FOR HELP If standard levels of traction do not relieve the shoulder dystocia, the physician must move quickly to other maneuvers while asking for help and notifying the family. A critical step in addressing the emergency management of shoulder dystocia is ensuring that all involved hospital personnel are familiar with their roles and responsibilities. This delivery team may include a family physician or obstetrician, a pediatrician or neonatologist, one ELIZABETH G. BAXLEY, M.D., is professor and chair in the Department of Family and Preventive Medicine at the University of South Carolina School of Medicine, Columbia, where she received her medical degree. She completed a family practice residency at Anderson Memorial Hospital in Anderson, S.C., and a faculty development fellowship at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Dr. Baxley was managing editor of the 2000 Advanced Life Support in Obstetrics (ALSO) Provider syllabus revisions and served as board chair of the ALSO program from 1998 to ROBERT W. GOBBO, M.D., is associate director of the Mercy Medical Center Merced Family Practice Residency Program in Merced, Calif., which is part of the University of California at Davis Family Practice Network. He received his medical degree from the University of California, Los Angeles, School of Medicine and completed a family practice residency and obstetrics fellowship at the UCLA Family Medicine Residency in Santa Monica, Calif. Dr. Gobbo is coauthor of the ALSO course syllabus chapter on shoulder dystocia and served as an advisory faculty for ALSO. Address correspondence to Elizabeth G. Baxley, M.D., Department of Family and Preventive Medicine, University of South Carolina School of Medicine, 3209 Colonial Dr., Columbia, SC ( libby.baxley@palmettohealth.org). Reprints are not available from the authors. FIGURE 1. The McRoberts maneuver and suprapubic pressure. Reprinted with permission from Gobbo R, Baxley EG. Shoulder dystocia. In: ALSO: advanced life support in obstetrics provider course syllabus. Leawood, Kan.: American Academy of Family Physicians, or two labor nurses to assist with maneuvers, a neonatal or nursery nurse, and a clinician capable of providing anesthesia. The primary physician should direct the team s activities, and one person should record the timing and events, so that if one maneuver is not successful after a reasonable amount of time, another maneuver may be attempted. An institutional protocol should be designed to delineate individual roles, and hospital drills may be helpful to rehearse this protocol. EPISIOTOMY Episiotomy should be considered when a shoulder dystocia is encountered, although because the primary problem is a bony impaction, episiotomy by itself will not release the impaction. Episiotomy does provide additional room for the physician s hand when internal rotation maneuvers are required. Given the success of the McRoberts maneuver and suprapubic pressure in relieving a large percentage of cases of shoulder dystocia, ILLUSTRATION BY LARRY HOWELL 1710-AMERICAN FAMILY PHYSICIAN VOLUME 69, NUMBER 7 / APRIL 1, 2004
5 Shoulder Dystocia performing an episiotomy can wait until later in the sequence. LEGS (MCROBERTS MANEUVER) The simplicity of the McRoberts maneuver (Figure 1 25 ) and its proven effectiveness make it an ideal first step in the management of shoulder dystocia. This procedure results in a cephalad rotation of the symphysis pubis and a flattening of the sacral promontory. 26 These motions push the posterior shoulder over the sacral promontory, allowing it to fall into the hollow of the sacrum, and rotate the symphysis over the impacted shoulder. When this maneuver is successful, the fetus should be delivered with normal traction. The McRoberts maneuver alone is believed to relieve more than 40 percent of all shoulder dystocias and, when combined with suprapubic pressure, resolves more than 50 percent of shoulder dystocias. 6 [SOR evidence level B, retrospective cohort study] PRESSURE (SUPRAPUBIC) When applying suprapubic pressure, an assistant s hand should be placed on top of the mother s abdomen over the fetal anterior shoulder, applying pressure in a compression/ relaxation cycle analogous to cardiopulmonary resuscitation, so that the shoulder will adduct and pass under the symphysis. Pressure should be applied from the side of the mother, with the heel of the assistant s hand moving in a downward and lateral motion on the posterior aspect of the fetal impacted shoulder. Initially, the pressure can be continuous, but if delivery is not accomplished, a rocking motion is recommended to dislodge the shoulder from behind the pubic symphysis. Fundal pressure is never appropriate and only serves to worsen the impaction, potentially injuring the fetus or mother. 24 [SOR evidence level B, retrospective cohort study] ENTER (INTERNAL ROTATION MANEUVERS) Rotation maneuvers (Figure 2 27 ) may require The combination of the McRoberts maneuver with suprapubic pressure may relieve more than 50 percent of cases of shoulder dystocia. episiotomy to gain posterior vaginal space for the physician s hand. The Rubin II maneuver consists of inserting the fingers of one hand vaginally behind the posterior aspect of the anterior shoulder of the fetus and rotating the shoulder toward the fetal chest. This motion will adduct the fetal shoulder girdle, reducing its diameter. The McRoberts maneuver also Enter Maneuvers for Shoulder Dystocia Rubin II At vaginal examination apply pressure as indicated. If shoulders move into the oblique diameter, attempt delivery. Rubin II + Woods corkscrew maneuver If unsuccessful, add the Woods corkscrew maneuver and continue rotation in the same direction. Use both hands and apply pressure as indicated. If shoulders now move into the oblique, attempt delivery. If this is unsuccessful, continue rotation 180 degrees and deliver. Reverse Woods corkscrew maneuver If the last maneuver is unsuccessful, change to reverse Woods corkscrew maneuver. Slide fingers down to back of posterior shoulder and attempt 180-degree rotation in the opposite direction. NOTE: Rubin I = suprapubic pressure. FIGURE 2. The Enter maneuvers for shoulder dystocia, using the left occiput transverse position as an example. Reprinted with permission from Mr. Kim Hinshaw, consultant obstetrician and gynecologist, Newcastle, England. In: ALSO : advanced life support in obstetrics instructor course syllabus. Leawood, Kan.: American Academy of Family Physicians, 2002:67. ILLUSTRATION BY MR. KIM HINSHAW APRIL 1, 2004 / VOLUME 69, NUMBER 7 AMERICAN FAMILY PHYSICIAN-1711
6 can be applied during this maneuver and may facilitate its success. If the Rubin II maneuver is unsuccessful, the Woods corkscrew maneuver may be attempted. The physician places at least two fingers on the anterior aspect of the fetal posterior shoulder, applying gentle upward pressure around the circumference of the arc in the same direction as with the Rubin II maneuver. This motion creates a more effective rotation. The Rubin II and Woods corkscrew maneuvers may be combined to increase torque forces by using two fingers behind the fetal anterior shoulder and two fingers in front of the fetal posterior shoulder. Procedurally, this step often is difficult because of limited space for the physician s hand. Downward traction should be continued during these rotational maneuvers, simulating the rotation of a screw being removed. If the Rubin II or Woods corkscrew maneuvers fail, the reverse Woods corkscrew maneuver may be tried. In this maneuver, the physician s fingers are placed on the back of the posterior shoulder of the fetus, and the fetus is rotated in the opposite direction as in the Woods corkscrew or Rubin II maneuvers. This maneuver adducts the fetal posterior shoulder in an attempt to rotate the shoulders out of the impacted position and into an oblique plane for delivery. REMOVAL OF THE POSTERIOR ARM Removal of the posterior arm involves placing the physician s hand in the vagina and locating the fetal arm, which sometimes is displaced behind the fetus and must be nudged anteriorly. The physician s hand, wrist, and forearm may need to enter the vagina, necessitating an episiotomy or exten- TABLE 4 Maneuvers of Last Resort for Shoulder Dystocia Deliberate clavicle fracture Direct upward pressure on the mid-portion of the fetal clavicle; reduces the shoulder-to-shoulder distance. Zavanelli maneuver Cephalic replacement followed by cesarean delivery; involves rotating the fetal head into a direct occiput anterior position, then flexing and pushing the vertex back into the birth canal, while holding continuous upward pressure until cesarean delivery is accomplished. Tocolysis may be a helpful adjunct to this procedure, although it has not been proved to enhance success over cases in which it was not used. 28 An operating team, anesthesiologist, and physicians capable of performing a cesarean delivery must be present, and this maneuver should never be attempted if a nuchal cord previously has been clamped and cut. General anesthesia Musculoskeletal or uterine relaxation with halothane (Fluothane) or another general anesthetic may bring about enough uterine relaxation to affect delivery. Oral or intravenous nitroglycerin may be used as an alternative to general anesthesia. Abdominal surgery with hysterotomy General anesthesia is induced and cesarean incision performed, after which the surgeon rotates the infant transabdominally through the hysterotomy incision, allowing the shoulders to rotate, much like a Woods corkscrew maneuver. Vaginal extraction is then accomplished by another physician. 29 Symphysiotomy Intentional division of the fibrous cartilage of the symphysis pubis under local anesthesia has been used more widely in developing countries than in North America. It should be used only when all other maneuvers have failed and capability of cesarean delivery is unavailable. 30,31 Information from references 25, and 28 through AMERICAN FAMILY PHYSICIAN VOLUME 69, NUMBER 7 / APRIL 1, 2004
7 Shoulder Dystocia sion. The fetal elbow is then flexed, and the forearm is delivered in a sweeping motion over the anterior chest wall of the fetus. The upper arm should never be grasped and pulled directly, because this step may result in a fracture of the humerus. The posterior hand, followed by the arm and shoulder, will be reduced, facilitating delivery of the infant. Often, the fetus spontaneously rotates in a corkscrew manner as the arm is removed. The anterior shoulder will then fall under the symphysis and deliver. ROLL THE PATIENT Rolling the patient onto her hands and knees, known as the all-fours or Gaskin maneuver, is a safe, rapid, and effective technique for the reduction of shoulder dystocia. 32 [SOR evidence level B, cohort study] Radiographic studies indicate that pelvic diameters increase when laboring women change from the dorsal recumbent position. 33 The true obstetric conjugate increases by as much as 10 mm, and the sagittal measurement of the pelvic outlet increases by up to 20 mm. Once the patient is repositioned, the physician provides gentle downward traction to deliver the posterior shoulder with the aid of gravity. The all-fours position is compatible with all intravaginal manipulations for shoulder dystocia, which can then be reattempted in this new position. All-fours positioning may be disorienting to physicians who are unfamiliar with attending a delivery in this position. Performing a few normal deliveries in this position before encountering a case of shoulder dystocia may prepare physicians for more emergent situations. MANEUVERS OF LAST RESORT If the maneuvers described in HELPERR are unsuccessful, several techniques have been described as last-resort maneuvers (Table 4). 25,28-31 Once the infant is delivered, quick assessment and employment of resuscitation efforts, if necessary, are vital. The internal rotation maneuvers are designed to manipulate the fetus to rotate the anterior shoulder into an oblique plane and under the maternal symphysis. DOCUMENTATION Documentation of the management of shoulder dystocia should concentrate on the maneuvers performed and the duration of the event. Terms such as mild, moderate, or severe shoulder dystocia offer little information about the situation or care encountered. Other team members assisting the delivery should be listed, as well as cord ph, if obtained. Specific notation regarding which arm was impacted against the pubis should be made in the event that subsequent nerve palsy develops. The delivery should be reviewed with the parents, and the management and prognosis for any infant palsy should be explained. The authors indicate that they do not have any conflicts of interest. Sources of funding: none reported. ALSO is a registered trademark of the American Academy of Family Physicians. REFERENCES 1. Hankins GD, Clark SL. Brachial plexus palsy involving the posterior shoulder at spontaneous vaginal delivery. Am J Perinatol 1995;12: Sokol RJ, Blackwell SC, for the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Committee on Practice Bulletins Gynecology. ACOG practice bulletin no. 40: shoulder dystocia. November 2002 (replaces practice pattern no. 7, October 1997). Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2003;80: Nesbitt TS, Gilbert WM, Herrchen B. Shoulder dystocia and associated risk factors with macrosomic infants born in California. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998;179: Acker DB, Sachs BP, Friedman EA. Risk factors for shoulder dystocia. Obstet Gynecol 1985;66: Mocanu EV, Greene RA, Byrne BM, Turner MJ. Obstetric and neonatal outcomes of babies weighing more than 4.5 kg: an analysis by parity. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2000;92: Geary M, McParland P, Johnson H, Stronge J. Shoulder dystocia is it predictable? Eur J Obstet APRIL 1, 2004 / VOLUME 69, NUMBER 7 AMERICAN FAMILY PHYSICIAN-1713
8 Shoulder Dystocia Gynecol Reprod Biol 1995;62: Gherman RB, Goodwin TM, Souter I, Neumann K, Ouzounian JG, Paul RH. The McRoberts maneuver for the alleviation of shoulder dystocia: how successful is it? Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;176: Gherman RB, Ouzounian JG, Goodwin TM. Obstetric maneuvers for shoulder dystocia and associated fetal morbidity. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998;178: Rouse DJ, Owen J, Goldenberg RL, Cliver SP. The effectiveness and costs of elective cesarean delivery for fetal macrosomia diagnosed by ultrasound. JAMA 1996;276: Gherman RB, Ouzounian JG, Miller DA, Kwok L, Goodwin TM. Spontaneous vaginal delivery: a risk factor for Erb s palsy? Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998; 178: Sandmire HF, DeMott RK. Erb s palsy: concepts of causation. Obstet Gynecol 2000;95(6 pt 1): Gherman RB, Goodwin TM, Ouzounian JG, Miller DA, Paul RH. Brachial plexus palsy associated with cesarean section: an in utero injury? Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;177: Lam MH, Wong GY, Lao TT. Reappraisal of neonatal clavicular fracture: relationship between infant size and neonatal morbidity. Obstet Gynecol 2002; 100: Benacerraf BR, Gelman R, Frigoletto FD Jr. Sonographically estimated fetal weights: accuracy and limitation. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998;159: Irion O, Boulvain M. Induction of labour for suspected fetal macrosomia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2003;(2):CD Kjos SL, Henry OA, Montoro M, Buchanan TA, Mestman JH. Insulin-requiring diabetes in pregnancy: a randomized trial of active induction of labor and expectant management. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1993;169: Boulvain M, Stan C, Irion O. Elective delivery in diabetic pregnant women. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2003;(2):CD Wood C, Ng KH, Hounslow D, Benning H. The influence of differences of birth times upon fetal condition in normal deliveries. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Commonw 1973;80: Wood C, Ng KH, Hounslow D, Benning H. Time an important variable in normal delivery. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Commonw 1973;80: Beer E, Folghera MG. Time for resolving shoulder dystocia. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998;179: Stallings SP, Edwards RK, Johnson JW. Correlation of head-to-body delivery intervals in shoulder dystocia and umbilical artery acidosis. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001;185: Welch RA. Head and shoulder maneuver. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;176: Baskett TF, Allen AC. Perinatal implications of shoulder dystocia. Obstet Gynecol 1995;86: Gross SJ, Shime J, Farine D. Shoulder dystocia: predictors and outcome. A five-year review. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1987;156: Gobbo R, Baxley EG. Shoulder dystocia. In: ALSO: advanced life support in obstetrics provider course syllabus. Leawood, Kan.: American Academy of Family Physicians, Gherman RB, Tramont J, Muffley P, Goodwin TM. Analysis of McRoberts maneuver by x-ray pelvimetry. Obstet Gynecol 2000;95: Nesbitte T, Lonsdorf DB. How to teach using mannequins (this example uses the shoulder dystocia scenario). In: ALSO: advanced life support in obstetrics instructor course syllabus. Leawood, Kan.: American Academy of Family Physicians, 2002: Sandberg EC. The Zavanelli maneuver: 12 years of recorded experience. Obstet Gynecol 1999;93: O Shaughnessy MJ. Hysterotomy facilitation of the vaginal delivery of the posterior arm in a case of severe shoulder dystocia. Obstet Gynecol 1998;92 (4 pt 2): Gherman RB, Ouzounian JG, Incerpi MH, Goodwin TM. Symphyseal separation and transient femoral neuropathy associated with the McRoberts maneuver. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1998;178: AMERICAN FAMILY PHYSICIAN VOLUME 69, NUMBER 7 / APRIL 1, 2004
Research. Shoulder dystocia is an uncommon
 Research www.ajog.org OBSTETRICS Effects of shoulder dystocia training on the incidence of brachial plexus injury Steven R. Inglis, MD; Nikolaus Feier, MD; Jyothi B. Chetiyaar, MD; Margaret H. Naylor,
Research www.ajog.org OBSTETRICS Effects of shoulder dystocia training on the incidence of brachial plexus injury Steven R. Inglis, MD; Nikolaus Feier, MD; Jyothi B. Chetiyaar, MD; Margaret H. Naylor,
Associated Factors in 1611 Cases of Brachial Plexus Injury
 Associated Factors in 1611 Cases of Brachial Plexus Injury WILLIAM M. GILBERT, MD, THOMAS S. NESBITT, MD, MPH, AND BEATE DANIELSEN, PhD Objective: To identify risk factors associated with brachial plexus
Associated Factors in 1611 Cases of Brachial Plexus Injury WILLIAM M. GILBERT, MD, THOMAS S. NESBITT, MD, MPH, AND BEATE DANIELSEN, PhD Objective: To identify risk factors associated with brachial plexus
Normal and Abnormal Labor and Delivery. Valerie Swiatkowski, MD
 Normal and Abnormal Labor and Delivery Valerie Swiatkowski, MD Objectives At the end of this lecture, you will be able to: Diagnose labor and define the stages Assess a laboring patient Diagnose abnormal
Normal and Abnormal Labor and Delivery Valerie Swiatkowski, MD Objectives At the end of this lecture, you will be able to: Diagnose labor and define the stages Assess a laboring patient Diagnose abnormal
Current Claims Issues in Labor, Delivery, and Discharge
 Current Claims Issues in Labor, Delivery, and Discharge Mize Conner, JD, MD, Bellegrove, OB-GYN Current Claims Issues in Labor and Delivery and Discharge OB Emergencies Response Time VBAC Shoulder Dystocia
Current Claims Issues in Labor, Delivery, and Discharge Mize Conner, JD, MD, Bellegrove, OB-GYN Current Claims Issues in Labor and Delivery and Discharge OB Emergencies Response Time VBAC Shoulder Dystocia
How To Know If A Delivery Is Complicated By Shoulder Dystocia
 Deconstructing A permanent brachial plexus injury is devastating to a child. It affects not only what the child can and can t do, but also his or her self-image. This injury rarely occurs in the absence
Deconstructing A permanent brachial plexus injury is devastating to a child. It affects not only what the child can and can t do, but also his or her self-image. This injury rarely occurs in the absence
Guide to Pregnancy and Birth Injury Claims
 Being pregnant, especially for the first time can be a very daunting experience where you often have to put all of your faith in your midwife or doctor. The majority of pregnancies and births occur without
Being pregnant, especially for the first time can be a very daunting experience where you often have to put all of your faith in your midwife or doctor. The majority of pregnancies and births occur without
Evaluation and Follow-up of Fetal Hydronephrosis
 Evaluation and Follow-up of Fetal Hydronephrosis Deborah M. Feldman, MD, Marvalyn DeCambre, MD, Erin Kong, Adam Borgida, MD, Mujgan Jamil, MBBS, Patrick McKenna, MD, James F. X. Egan, MD Objective. To
Evaluation and Follow-up of Fetal Hydronephrosis Deborah M. Feldman, MD, Marvalyn DeCambre, MD, Erin Kong, Adam Borgida, MD, Mujgan Jamil, MBBS, Patrick McKenna, MD, James F. X. Egan, MD Objective. To
C. P. Noel McCarthy, MD 1936 1936--2009 2009 Risk Reduction Strategies in Risk Obstetrics & Gynecology
 C. P. Noel McCarthy, MD 1936-2009 Risk Reduction Strategies in Obstetrics & Gynecology John F. Rodis, MD Professor of Clinical Obstetrics & Gynecology Columbia University College of Physicians & Surgeons
C. P. Noel McCarthy, MD 1936-2009 Risk Reduction Strategies in Obstetrics & Gynecology John F. Rodis, MD Professor of Clinical Obstetrics & Gynecology Columbia University College of Physicians & Surgeons
Registered Midwife Clinical Privileges REAPPOINTMENT 2015-2016 Effective from July 1, 2015 to June 30, 2016
 Name: Initial privileges (initial appointment) Renewal of privileges (reappointment) All new applicants must meet the following requirements as approved by the governing body, effective: 04/Jun/2013. Applicant:
Name: Initial privileges (initial appointment) Renewal of privileges (reappointment) All new applicants must meet the following requirements as approved by the governing body, effective: 04/Jun/2013. Applicant:
ROTATIONAL POSITIONING
 ROTATIONAL POSITIONING A method for rotating posterior babies during labour Problems associated with persistent posterior positioning Prolonged labour 12% for posterior vs. 1.7% Assisted delivery 24.6%
ROTATIONAL POSITIONING A method for rotating posterior babies during labour Problems associated with persistent posterior positioning Prolonged labour 12% for posterior vs. 1.7% Assisted delivery 24.6%
Assessment of Fetal Growth
 Assessment of Fetal Growth Unit / Trust: 1. INTRODUCTION The aim of this guideline template is to outline the methods used to assess fetal growth and the referral pathways utilising customised antenatal
Assessment of Fetal Growth Unit / Trust: 1. INTRODUCTION The aim of this guideline template is to outline the methods used to assess fetal growth and the referral pathways utilising customised antenatal
KENTUCKY BOARD OF NURSING 312 Whittington Parkway, Suite 300 Louisville, Kentucky 40222-5172 http://kbn.ky.gov ADVISORY OPINION STATEMENT
 (Revised 4/2016) KENTUCKY BOARD OF NURSING 312 Whittington Parkway, Suite 300 Louisville, Kentucky 40222-5172 http://kbn.ky.gov ADVISORY OPINION STATEMENT ROLES OF NURSES IN THE CARE OF PRENATAL AND INTRAPARTUM
(Revised 4/2016) KENTUCKY BOARD OF NURSING 312 Whittington Parkway, Suite 300 Louisville, Kentucky 40222-5172 http://kbn.ky.gov ADVISORY OPINION STATEMENT ROLES OF NURSES IN THE CARE OF PRENATAL AND INTRAPARTUM
Registered Nurse Initiated Activities Decision Support Tool No. 8A: Obstetrical Emergencies Cord Prolapse
 Registered Nurse Initiated Activities Decision Support Tool No. 8A: Obstetrical Emergencies Cord Prolapse Decision support tools are evidenced-based documents used to guide the assessment, diagnosis and
Registered Nurse Initiated Activities Decision Support Tool No. 8A: Obstetrical Emergencies Cord Prolapse Decision support tools are evidenced-based documents used to guide the assessment, diagnosis and
CORD BLOOD COLLECTION / ANALYSIS- AT BIRTH
 WOMEN AND NEWBORN HEALTH SERVICE King Edward Memorial Hospital CLINICAL GUIDELINES OBSTETRICS AND MIDWIFERY King Edward Memorial Hospital WOMEN AND NEWBORN HEALTH SERVICE INTRAPARTUM CARE SPECIMEN COLLECTION
WOMEN AND NEWBORN HEALTH SERVICE King Edward Memorial Hospital CLINICAL GUIDELINES OBSTETRICS AND MIDWIFERY King Edward Memorial Hospital WOMEN AND NEWBORN HEALTH SERVICE INTRAPARTUM CARE SPECIMEN COLLECTION
Effects of Pregnancy & Delivery on Pelvic Floor
 Effects of Pregnancy & Delivery on Pelvic Floor 吳 銘 斌 M.D., Ph.D. 財 團 法 人 奇 美 醫 院 婦 產 部 婦 女 泌 尿 暨 骨 盆 醫 學 科 ; 台 北 醫 學 大 學 醫 學 院 婦 產 學 科 ; 古 都 府 城 台 南 Introduction Pelvic floor disorders (PFDs) include
Effects of Pregnancy & Delivery on Pelvic Floor 吳 銘 斌 M.D., Ph.D. 財 團 法 人 奇 美 醫 院 婦 產 部 婦 女 泌 尿 暨 骨 盆 醫 學 科 ; 台 北 醫 學 大 學 醫 學 院 婦 產 學 科 ; 古 都 府 城 台 南 Introduction Pelvic floor disorders (PFDs) include
8/13/2014. Blood, Sweat (and Tears): Delayed Cord Clamping and Delivery Room Temperature. Delayed Cord Clamping
 8/13/2014 Blood, Sweat (and Tears): Delayed Cord Clamping and Delivery Room Temperature James F. Smith, Jr., MD Professor and Chair Obstetrics and Gynecology Creighton University School of Medicine The
8/13/2014 Blood, Sweat (and Tears): Delayed Cord Clamping and Delivery Room Temperature James F. Smith, Jr., MD Professor and Chair Obstetrics and Gynecology Creighton University School of Medicine The
A8b. Resuscitation of a Term Infant with Meconium Staining. Session Summary. Session Objectives. References
 A8b Resuscitation of a Term Infant with Meconium Staining Karen Wright, PhD, NNP-BC Assistant Professor and Coordinator, Neonatal Nurse Practitioner Program Dept. of Women, Children, and Family Nursing,
A8b Resuscitation of a Term Infant with Meconium Staining Karen Wright, PhD, NNP-BC Assistant Professor and Coordinator, Neonatal Nurse Practitioner Program Dept. of Women, Children, and Family Nursing,
Rural Health Advisory Committee s Rural Obstetric Services Work Group
 Rural Health Advisory Committee s Rural Obstetric Services Work Group March 15 th webinar topic: Rural Obstetric Patient and Community Issues Audio: 888-742-5095, conference code 6054760826 Rural Obstetric
Rural Health Advisory Committee s Rural Obstetric Services Work Group March 15 th webinar topic: Rural Obstetric Patient and Community Issues Audio: 888-742-5095, conference code 6054760826 Rural Obstetric
Medical Negligence. Standard of Care 2/25/2014. Medico Legal Risk Reduction in Obstetrics
 Medico Legal Risk Reduction in Obstetrics James E. Looper, Jr. Hall Booth Smith, PC JLooper@hallboothsmith.com 615 313 9911 Medical Negligence To prevail on a medical-malpractice claim, a plaintiff must
Medico Legal Risk Reduction in Obstetrics James E. Looper, Jr. Hall Booth Smith, PC JLooper@hallboothsmith.com 615 313 9911 Medical Negligence To prevail on a medical-malpractice claim, a plaintiff must
What is ACLS Maternal Focus?
 Carla Rider, MBA, BSN, RNC-LRN, Administrative Director Women s Services Meredith Green, MSN Candidate, BSN, RN, Clinical Educator Women s Services What is? ACLS Component 1 American Heart Association
Carla Rider, MBA, BSN, RNC-LRN, Administrative Director Women s Services Meredith Green, MSN Candidate, BSN, RN, Clinical Educator Women s Services What is? ACLS Component 1 American Heart Association
Exercise 1: Knee to Chest. Exercise 2: Pelvic Tilt. Exercise 3: Hip Rolling. Starting Position: Lie on your back on a table or firm surface.
 Exercise 1: Knee to Chest Starting Position: Lie on your back on a table or firm surface. Action: Clasp your hands behind the thigh and pull it towards your chest. Keep the opposite leg flat on the surface
Exercise 1: Knee to Chest Starting Position: Lie on your back on a table or firm surface. Action: Clasp your hands behind the thigh and pull it towards your chest. Keep the opposite leg flat on the surface
Chapter 5. The Shoulder Joint. The Shoulder Joint. Bones. Bones. Bones
 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Reprinted by permission. Chapter 5 The Shoulder Joint Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, Ed.D, ATC, CSCS Structural Kinesiology The Shoulder Joint 5-1 The Shoulder
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Reprinted by permission. Chapter 5 The Shoulder Joint Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, Ed.D, ATC, CSCS Structural Kinesiology The Shoulder Joint 5-1 The Shoulder
Clinical Policy Title: Home uterine activity monitoring
 Clinical Policy Title: Home uterine activity monitoring Clinical Policy Number: 12.01.01 Effective Date: August 19, 2015 Initial Review Date: July 17, 2013 Most Recent Review Date: July 15, 2015 Next Review
Clinical Policy Title: Home uterine activity monitoring Clinical Policy Number: 12.01.01 Effective Date: August 19, 2015 Initial Review Date: July 17, 2013 Most Recent Review Date: July 15, 2015 Next Review
M A T E R N I T Y C A R E. Managing Pain. During Labor & Delivery
 M A T E R N I T Y C A R E Managing Pain During Labor & Delivery Managing Your Pain One of the most common concerns about labor and delivery is pain. How much will it hurt? How will I cope? At MidMichigan
M A T E R N I T Y C A R E Managing Pain During Labor & Delivery Managing Your Pain One of the most common concerns about labor and delivery is pain. How much will it hurt? How will I cope? At MidMichigan
Umbilical Arterial Blood Gas and Perinatal Outcome in the Second Twin according to the Planned Mode of Delivery
 643 Ivyspring International Publisher Research Paper International Journal of Medical Sciences 2011; 8(8):643-648 Umbilical Arterial Blood Gas and Perinatal Outcome in the Second Twin according to the
643 Ivyspring International Publisher Research Paper International Journal of Medical Sciences 2011; 8(8):643-648 Umbilical Arterial Blood Gas and Perinatal Outcome in the Second Twin according to the
Spinal Exercise Program/Core Stabilization Program Adapted from The Spine in Sports: Robert G. Watkins
 Spinal Exercise Program/Core Stabilization Program Adapted from The Spine in Sports: Robert G. Watkins Below is a description of a Core Stability Program, designed to improve the strength and coordination
Spinal Exercise Program/Core Stabilization Program Adapted from The Spine in Sports: Robert G. Watkins Below is a description of a Core Stability Program, designed to improve the strength and coordination
My Birth Experience at Mercy
 My Birth Experience at Mercy This booklet provides information about labor and birth practices at Mercy and includes an optional birth plan that you can complete prior to your baby s birth. Discuss your
My Birth Experience at Mercy This booklet provides information about labor and birth practices at Mercy and includes an optional birth plan that you can complete prior to your baby s birth. Discuss your
Maternity Care Primary C-Section Rate Specifications 2014 (07/01/2013 to 06/30/2014 Dates of Service)
 Summary of Changes Denominator Changes: Two additions were made to the denominator criteria. The denominator was changed to include patients who had: a vertex position delivery AND a term pregnancy of
Summary of Changes Denominator Changes: Two additions were made to the denominator criteria. The denominator was changed to include patients who had: a vertex position delivery AND a term pregnancy of
Get the Facts, Be Informed, Make YOUR Best Decision. Pelvic Organ Prolapse
 Pelvic Organ Prolapse ETHICON Women s Health & Urology, a division of ETHICON, INC., a Johnson & Johnson company, is dedicated to providing innovative solutions for common women s health problems and to
Pelvic Organ Prolapse ETHICON Women s Health & Urology, a division of ETHICON, INC., a Johnson & Johnson company, is dedicated to providing innovative solutions for common women s health problems and to
Birth injury. Amy J. Gagnon, M.D. Maternal-Fetal Medicine. Colorado Perinatal Care Council November 18, 2011
 Birth injury Amy J. Gagnon, M.D. Maternal-Fetal Medicine Colorado Perinatal Care Council November 18, 2011 Birth injury: overview Cephalohematoma Subgaleal hemorrhage Retinal hemorrhage Facial nerve palsy
Birth injury Amy J. Gagnon, M.D. Maternal-Fetal Medicine Colorado Perinatal Care Council November 18, 2011 Birth injury: overview Cephalohematoma Subgaleal hemorrhage Retinal hemorrhage Facial nerve palsy
Maj Alison Baum. R3, Nellis FMR
 Maj Alison Baum R3, Nellis FMR What are some of your thoughts about birth plans? http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hh62v0c xf04 Labor: Pain management wishes Doulas Episiotomy Intermittent fetal monitoring
Maj Alison Baum R3, Nellis FMR What are some of your thoughts about birth plans? http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hh62v0c xf04 Labor: Pain management wishes Doulas Episiotomy Intermittent fetal monitoring
This Protocol is adapted from the University of Colorado Protocol dated August 26, 2009.
 Protocol for Post-Placental IUD insertion July 14, 2010 This Protocol is adapted from the University of Colorado Protocol dated August 26, 2009. Background Post-placental intrauterine device (IUD) insertion
Protocol for Post-Placental IUD insertion July 14, 2010 This Protocol is adapted from the University of Colorado Protocol dated August 26, 2009. Background Post-placental intrauterine device (IUD) insertion
CONFIDENT CODING FOR OB/GYN CONFIDENT CODING FOR OB/GYN
 Arlene J. Smith, CPC AAPC National Advisory Board 2007-2009 1 So when exactly does the global period start? Unraveling the confusion in antepartum care coding Correct coding for multiple gestations! Vaginal
Arlene J. Smith, CPC AAPC National Advisory Board 2007-2009 1 So when exactly does the global period start? Unraveling the confusion in antepartum care coding Correct coding for multiple gestations! Vaginal
Range of Motion. A guide for you after spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord Injury Rehabilitation Program
 Range of Motion A guide for you after spinal cord injury Spinal Cord Injury Rehabilitation Program This booklet has been written by the health care providers who provide care to people who have a spinal
Range of Motion A guide for you after spinal cord injury Spinal Cord Injury Rehabilitation Program This booklet has been written by the health care providers who provide care to people who have a spinal
Who Is Involved in Your Care?
 Patient Education Page 3 Pregnancy and Giving Birth Who Is Involved in Your Care? Our goal is to surround you and your family with a safe environment for the birth of your baby. We look forward to providing
Patient Education Page 3 Pregnancy and Giving Birth Who Is Involved in Your Care? Our goal is to surround you and your family with a safe environment for the birth of your baby. We look forward to providing
Effect of Increased Body Mass Index on the Accuracy of Estimated Fetal Weight by Sonography in Twins
 Article Effect of Increased Body Mass Index on the Accuracy of Estimated Fetal Weight by Sonography in Twins Manisha Gandhi, MD, Lauren Ferrara, MD, Victoria Belogolovkin, MD, Erin Moshier, MS, Andrei
Article Effect of Increased Body Mass Index on the Accuracy of Estimated Fetal Weight by Sonography in Twins Manisha Gandhi, MD, Lauren Ferrara, MD, Victoria Belogolovkin, MD, Erin Moshier, MS, Andrei
HELPFUL HINTS FOR A HEALTHY BACK
 HELPFUL HINTS FOR A HEALTHY BACK 1. Standing and Walking For correct posture, balance your head above your shoulders, eyes straight ahead, everything else falls into place. Try to point toes straight ahead
HELPFUL HINTS FOR A HEALTHY BACK 1. Standing and Walking For correct posture, balance your head above your shoulders, eyes straight ahead, everything else falls into place. Try to point toes straight ahead
Summa Health System. A Woman s Guide to Hysterectomy
 Summa Health System A Woman s Guide to Hysterectomy Hysterectomy A hysterectomy is a surgical procedure to remove a woman s uterus (womb). The uterus is the organ which shelters and nourishes a baby during
Summa Health System A Woman s Guide to Hysterectomy Hysterectomy A hysterectomy is a surgical procedure to remove a woman s uterus (womb). The uterus is the organ which shelters and nourishes a baby during
Managing the Risk of Uterine Rupture During a Trial of Labor After Cesarean Section
 Managing the Risk of Uterine Rupture During a Trial of Labor After Cesarean Section By NORCAL Mutual Insurance Company Introduction While a successful vaginal birth after cesarean section (VBAC) is associated
Managing the Risk of Uterine Rupture During a Trial of Labor After Cesarean Section By NORCAL Mutual Insurance Company Introduction While a successful vaginal birth after cesarean section (VBAC) is associated
Obtaining Valid Consent to Participate in Perinatal Research Where Consent is Time Critical
 Obtaining Valid Consent to Participate in Perinatal Research Where Consent is Time Critical February 2016 Obtaining Valid Consent to Participate in Perinatal Research Where Consent is Time Critical This
Obtaining Valid Consent to Participate in Perinatal Research Where Consent is Time Critical February 2016 Obtaining Valid Consent to Participate in Perinatal Research Where Consent is Time Critical This
Regions Hospital Delineation of Privileges Nurse Practitioner
 Regions Hospital Delineation of Privileges Nurse Practitioner Applicant s Last First M. Instructions: Place a check-mark where indicated for each core group you are requesting. Review education and basic
Regions Hospital Delineation of Privileges Nurse Practitioner Applicant s Last First M. Instructions: Place a check-mark where indicated for each core group you are requesting. Review education and basic
Advanced ICD-10-CM/PCS Coding for OB/Pregnancy
 Advanced ICD-10-CM/PCS Coding for OB/Pregnancy October 14, 2014 Karen Feltner, RHIA, CCS Plan for Today What are we discussing today? What is different in ICD-10-CM for pregnancy? What about ICD-10-PCS
Advanced ICD-10-CM/PCS Coding for OB/Pregnancy October 14, 2014 Karen Feltner, RHIA, CCS Plan for Today What are we discussing today? What is different in ICD-10-CM for pregnancy? What about ICD-10-PCS
Caesarean section and quality of obstetric care
 Caesarean section and quality of obstetric care Gjennombruddsprosjekt for keisersnitt September 2014 Michael Robson The National Maternity Hospital Dublin, Ireland Mrobson@nmh.ie Gjennombruddsprosjekt
Caesarean section and quality of obstetric care Gjennombruddsprosjekt for keisersnitt September 2014 Michael Robson The National Maternity Hospital Dublin, Ireland Mrobson@nmh.ie Gjennombruddsprosjekt
Knee Conditioning Program. Purpose of Program
 Prepared for: Prepared by: OrthoInfo Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle.
Prepared for: Prepared by: OrthoInfo Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle.
Body cavities. Body Planes
 Body cavities Body Planes Directional terms http://homepage.smc.edu/wissmann_paul/anatomy1textbook/1anatomytextch1.html abdomen abdominal front of elbow antecubital arm brachial groin inguinal armpit axillary
Body cavities Body Planes Directional terms http://homepage.smc.edu/wissmann_paul/anatomy1textbook/1anatomytextch1.html abdomen abdominal front of elbow antecubital arm brachial groin inguinal armpit axillary
ST Segment Analysis (STAN) as an Adjunct to Electronic Fetal Monitoring, Part II: Clinical Studies and Future Directions
 ST Segment Analysis (STAN) as an Adjunct to Electronic Fetal Monitoring, Part II: Clinical Studies and Future Directions Michael A. Belfort, MBBCH, MD, PhD*, George R. Saade, MD KEYWORDS ST segment analysis
ST Segment Analysis (STAN) as an Adjunct to Electronic Fetal Monitoring, Part II: Clinical Studies and Future Directions Michael A. Belfort, MBBCH, MD, PhD*, George R. Saade, MD KEYWORDS ST segment analysis
Measurement of fetal scalp lactate to determine fetal well being in labour
 Measurement of fetal scalp lactate to determine fetal well being in labour Clinical question Among women at term in labour is the measurement of fetal scalp lactate superior to fetal scalp ph in predicting
Measurement of fetal scalp lactate to determine fetal well being in labour Clinical question Among women at term in labour is the measurement of fetal scalp lactate superior to fetal scalp ph in predicting
What Every Pregnant Woman Needs to Know About Cesarean Section. Be informed. Know your rights. Protect yourself. Protect your baby.
 Be informed. Know your rights. Protect yourself. Protect your baby. What Every Pregnant Woman Needs to Know About Cesarean Section 2012 Childbirth Connection If you re expecting a baby, there s a good
Be informed. Know your rights. Protect yourself. Protect your baby. What Every Pregnant Woman Needs to Know About Cesarean Section 2012 Childbirth Connection If you re expecting a baby, there s a good
BIRTH INJURY AND NEWBORN BRAIN DAMAGE
 BIRTH INJURY AND NEWBORN BRAIN DAMAGE ROBERT J. TALASKA 1415 North Loop West Suite 200 Houston, Texas 77008 713.869.1240 713.869.1465 fax State Bar of Texas 15 TH ANNUAL ADVANCED MEDICAL MALPRACTICE COURSE
BIRTH INJURY AND NEWBORN BRAIN DAMAGE ROBERT J. TALASKA 1415 North Loop West Suite 200 Houston, Texas 77008 713.869.1240 713.869.1465 fax State Bar of Texas 15 TH ANNUAL ADVANCED MEDICAL MALPRACTICE COURSE
Newborn Scenario. Consolidated Instructor Manual. Frances Wickham Lee, DBA Heidi H. Schmoll, RN, MSN-Ed. Content Author: Sheila Smith RN, PhD
 Newborn Scenario Consolidated Instructor Manual Frances Wickham Lee, DBA Heidi H. Schmoll, RN, MSN-Ed. Content Author: Sheila Smith RN, PhD 1/23/13 Table of Contents Curricular Information 3 Faculty Information
Newborn Scenario Consolidated Instructor Manual Frances Wickham Lee, DBA Heidi H. Schmoll, RN, MSN-Ed. Content Author: Sheila Smith RN, PhD 1/23/13 Table of Contents Curricular Information 3 Faculty Information
Newborn outcomes after cesarean section for fetal distress in BC
 Newborn outcomes after cesarean section for fetal distress in BC Patricia Janssen, PhD, UBC School of Population and Public Health Scientist, Child and Family Research Institute Kevin Jenniskens, MSc,
Newborn outcomes after cesarean section for fetal distress in BC Patricia Janssen, PhD, UBC School of Population and Public Health Scientist, Child and Family Research Institute Kevin Jenniskens, MSc,
THE SUPREME COURT OF APPEAL OF SOUTH AFRICA JUDGMENT. Mrs Nondumiso Sindiswe Sibisi NO
 THE SUPREME COURT OF APPEAL OF SOUTH AFRICA JUDGMENT Reportable Case No: 311/2013 In the matter between: Mrs Nondumiso Sindiswe Sibisi NO Appellant and Dr D P Maitin Respondent Neutral Citation: Sibisi
THE SUPREME COURT OF APPEAL OF SOUTH AFRICA JUDGMENT Reportable Case No: 311/2013 In the matter between: Mrs Nondumiso Sindiswe Sibisi NO Appellant and Dr D P Maitin Respondent Neutral Citation: Sibisi
Managing Risk in Perinatal Care
 Managing Risk in Perinatal Care Stan Davis MD, FACOG Laerdal SUN Conference Philadelphia 2014 Objectives 1) Discuss the medical/legal environment in the perinatal area 2) Identify issues specific to perinatal
Managing Risk in Perinatal Care Stan Davis MD, FACOG Laerdal SUN Conference Philadelphia 2014 Objectives 1) Discuss the medical/legal environment in the perinatal area 2) Identify issues specific to perinatal
Claiming Compensation for Birth Injuries.
 Clinical Negligence: Claiming Compensation for Birth Injuries. T H O M P S O N S F A C T S H E E T About birth injury Compensation Types of birth injury cases where compensation may be possible How to
Clinical Negligence: Claiming Compensation for Birth Injuries. T H O M P S O N S F A C T S H E E T About birth injury Compensation Types of birth injury cases where compensation may be possible How to
Structure and Function of the Hip
 Structure and Function of the Hip Objectives Identify the bones and bony landmarks of the hip and pelvis Identify and describe the supporting structures of the hip joint Describe the kinematics of the
Structure and Function of the Hip Objectives Identify the bones and bony landmarks of the hip and pelvis Identify and describe the supporting structures of the hip joint Describe the kinematics of the
Certified Professional Midwives Caring for Mothers and Babies in Virginia
 Certified Professional Midwives Caring for Mothers and Babies in Virginia Commonwealth Midwives Alliance Certified Professional Midwives in VA Licensed by the BOM since January 2006 5 member Midwifery
Certified Professional Midwives Caring for Mothers and Babies in Virginia Commonwealth Midwives Alliance Certified Professional Midwives in VA Licensed by the BOM since January 2006 5 member Midwifery
Birth Injury Odyssey: Observations from Both Sides
 Birth Injury Odyssey: Observations from Both Sides By: Daniel J. Huff, Esq. Huff, Powell & Bailey, LLC 999 Peachtree Street, Suite 950 Atlanta, Georgia 30309 Taylor Tribble, Esq. Huff, Powell & Bailey,
Birth Injury Odyssey: Observations from Both Sides By: Daniel J. Huff, Esq. Huff, Powell & Bailey, LLC 999 Peachtree Street, Suite 950 Atlanta, Georgia 30309 Taylor Tribble, Esq. Huff, Powell & Bailey,
UNMH Certified Nurse-Midwife (CNM) Clinical Privileges
 All new applicants must meet the following requirements as approved by the UNMH Board of Trustees effective: 03/27/2015 INSTRUCTIONS Applicant: Check off the "Requested" box for each privilege requested.
All new applicants must meet the following requirements as approved by the UNMH Board of Trustees effective: 03/27/2015 INSTRUCTIONS Applicant: Check off the "Requested" box for each privilege requested.
Clarification of Terms
 Shoulder Girdle Clarification of Terms Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus What is the purpose (or function) of the shoulder and entire upper
Shoulder Girdle Clarification of Terms Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus What is the purpose (or function) of the shoulder and entire upper
Advanced Fetal Assessment and Monitoring: Online Program. Advanced Practice Strategies, LLC
 Advanced Fetal Assessment and Monitoring: Online Program Advanced Fetal Assessment and Monitoring: Online Program Comments from the Authors As a physician who does a great deal of medical legal expert
Advanced Fetal Assessment and Monitoring: Online Program Advanced Fetal Assessment and Monitoring: Online Program Comments from the Authors As a physician who does a great deal of medical legal expert
Obstetrical Emergencies
 Date: July 18, 2014 Page 1 of 5 Obstetrical Emergencies Purpose: To provide the process for the assessment and management of the patient with an obstetrical related emergency. Pre-Medical Control 1. Follow
Date: July 18, 2014 Page 1 of 5 Obstetrical Emergencies Purpose: To provide the process for the assessment and management of the patient with an obstetrical related emergency. Pre-Medical Control 1. Follow
OBSTETRICAL POLICY. Page
 OBSTETRICAL POLICY REIMBURSEMENT POLICY Policy Number: ADMINISTRATIVE 200.14 T0 Effective Date: April 1, 2016 Table of Contents APPLICABLE LINES OF BUSINESS/PRODUCTS... APPLICATION... OVERVIEW... REIMBURSEMENT
OBSTETRICAL POLICY REIMBURSEMENT POLICY Policy Number: ADMINISTRATIVE 200.14 T0 Effective Date: April 1, 2016 Table of Contents APPLICABLE LINES OF BUSINESS/PRODUCTS... APPLICATION... OVERVIEW... REIMBURSEMENT
Motor Vehicle Injuries
 Motor Vehicle Injuries Prenatal Counseling about Seat Belt Use during Pregnancy and Injuries from Car Crashes during Pregnancy Background The CDC has identified prevention of motor vehicle injuries as
Motor Vehicle Injuries Prenatal Counseling about Seat Belt Use during Pregnancy and Injuries from Car Crashes during Pregnancy Background The CDC has identified prevention of motor vehicle injuries as
Evaluation of cardiotocographic and cord blood changes in induced labor with dinoprostone and misoprostol
 International Journal of Reproduction, Contraception, Obstetrics and Gynecology Pandey K et al. Int J Reprod Contracept Obstet Gynecol. 2014 Mar;3(1):199-203 www.ijrcog.org pissn 2320-1770 eissn 2320-1789
International Journal of Reproduction, Contraception, Obstetrics and Gynecology Pandey K et al. Int J Reprod Contracept Obstet Gynecol. 2014 Mar;3(1):199-203 www.ijrcog.org pissn 2320-1770 eissn 2320-1789
FEMALE ANATOMY. the Functions of the Female Organs
 FEMALE ANATOMY the Functions of the Female Organs An educational video for every woman who is told she needs pelvic surgery, including exploratory surgery or removal of the uterus, fallopian tubes, or
FEMALE ANATOMY the Functions of the Female Organs An educational video for every woman who is told she needs pelvic surgery, including exploratory surgery or removal of the uterus, fallopian tubes, or
Nonoperative Management of Herniated Cervical Intervertebral Disc With Radiculopathy. Spine Volume 21(16) August 15, 1996, pp 1877-1883
 Nonoperative Management of Herniated Cervical Intervertebral Disc With Radiculopathy 1 Spine Volume 21(16) August 15, 1996, pp 1877-1883 Saal, Joel S. MD; Saal, Jeffrey A. MD; Yurth, Elizabeth F. MD FROM
Nonoperative Management of Herniated Cervical Intervertebral Disc With Radiculopathy 1 Spine Volume 21(16) August 15, 1996, pp 1877-1883 Saal, Joel S. MD; Saal, Jeffrey A. MD; Yurth, Elizabeth F. MD FROM
Hysterectomy. What is a hysterectomy? Why is hysterectomy done? Are there alternatives to hysterectomy?
 ROBERT LEVITT, MD JESSICA BERGER-WEISS, MD ADRIENNE POTTS, MD HARTAJ POWELL, MD, MPH COURTNEY LEVENSON, MD LAUREN BURNS, MSN, RN, WHNP OBGYNCWC.COM What is a hysterectomy? Hysterectomy Hysterectomy is
ROBERT LEVITT, MD JESSICA BERGER-WEISS, MD ADRIENNE POTTS, MD HARTAJ POWELL, MD, MPH COURTNEY LEVENSON, MD LAUREN BURNS, MSN, RN, WHNP OBGYNCWC.COM What is a hysterectomy? Hysterectomy Hysterectomy is
Fetal Prognosis in Varix of the Intrafetal Umbilical Vein
 Fetal Prognosis in Varix of the Intrafetal Umbilical Vein Waldo Sepulveda, MD, Antonio Mackenna, MD, Jorge Sanchez, MD, Edgardo Corral, MD, Eduardo Carstens, MD To assess the clinical significance of varix
Fetal Prognosis in Varix of the Intrafetal Umbilical Vein Waldo Sepulveda, MD, Antonio Mackenna, MD, Jorge Sanchez, MD, Edgardo Corral, MD, Eduardo Carstens, MD To assess the clinical significance of varix
Oregon Birth Outcomes, by Planned Birth Place and Attendant Pursuant to: HB 2380 (2011)
 Oregon Birth Outcomes, by Birth Place and Attendant Pursuant to: HB 2380 (2011) In 2011, the Oregon Legislature passed House Bill 2380, which required the Oregon Public Health Division to add two questions
Oregon Birth Outcomes, by Birth Place and Attendant Pursuant to: HB 2380 (2011) In 2011, the Oregon Legislature passed House Bill 2380, which required the Oregon Public Health Division to add two questions
MET: Posterior (backward) Rotation of the Innominate Bone.
 MET: Posterior (backward) Rotation of the Innominate Bone. Purpose: To reduce an anterior rotation of the innominate bone at the SI joint. To increase posterior (backward) rotation of the SI joint. Precautions:
MET: Posterior (backward) Rotation of the Innominate Bone. Purpose: To reduce an anterior rotation of the innominate bone at the SI joint. To increase posterior (backward) rotation of the SI joint. Precautions:
Stretching in the Office
 Stretching in the Office Legs: Quads, Hamstrings, IT band, Hip flexors, Gluts, Calves Quads: Standing @ desk maintaining upright posture, grab one leg @ a time by foot or ankle and bring it towards backside
Stretching in the Office Legs: Quads, Hamstrings, IT band, Hip flexors, Gluts, Calves Quads: Standing @ desk maintaining upright posture, grab one leg @ a time by foot or ankle and bring it towards backside
MANA Home Birth Data 2004-2009: Consumer Considerations
 MANA Home Birth Data 2004-2009: Consumer Considerations By: Lauren Korfine, PhD U.S. maternity care costs continue to rise without evidence of improving outcomes for women or babies. The cesarean section
MANA Home Birth Data 2004-2009: Consumer Considerations By: Lauren Korfine, PhD U.S. maternity care costs continue to rise without evidence of improving outcomes for women or babies. The cesarean section
Lumbar Spondylolisthesis or Anterolisthesis Patient Educational Information
 Lumbar Spondylolisthesis or Anterolisthesis Patient Educational Information What is a Spondylolisthesis or Anterolisthesis? Spondylolisthesis is a condition of the spine when one of the vertebra slips
Lumbar Spondylolisthesis or Anterolisthesis Patient Educational Information What is a Spondylolisthesis or Anterolisthesis? Spondylolisthesis is a condition of the spine when one of the vertebra slips
July 2009. Copyright 2009 design VeRoniQue. all Rights Reserved.
 The Role of SuppoRT GaRmenTS for The ChanGinG physiology of The pregnant and postpartum Body July 2009 ExECutivE Summary pregnancy and childbirth represent two of the greatest health transitions that women
The Role of SuppoRT GaRmenTS for The ChanGinG physiology of The pregnant and postpartum Body July 2009 ExECutivE Summary pregnancy and childbirth represent two of the greatest health transitions that women
CLINICAL AUDIT REPORT LABOUR WARD LOWER UMFOLOZI DISTRICT WAR MEMORIAL HOSPITAL
 CLINICAL AUDIT REPORT LABOUR WARD LOWER UMFOLOZI DISTRICT WAR MEMORIAL HOSPITAL Dr A K M Hoque - Medical Manager Dr W Edelstein - Senior Specialist Perinatal mortality rate is a sensitive indicator used
CLINICAL AUDIT REPORT LABOUR WARD LOWER UMFOLOZI DISTRICT WAR MEMORIAL HOSPITAL Dr A K M Hoque - Medical Manager Dr W Edelstein - Senior Specialist Perinatal mortality rate is a sensitive indicator used
P REPLACEMENT SURGERY
 P REPLACEMENT SURGERY DIRECT ANTERIOR APPROACH M I N I M I Z I N G R E C O V E R Y. M A X I M I Z I N G R E S U L T S. CENTER FOR MINIMAL INVASIVE JOINT SURGERY 2301 25TH STREET SOUTH FARGO ND 58103 701-241-9300
P REPLACEMENT SURGERY DIRECT ANTERIOR APPROACH M I N I M I Z I N G R E C O V E R Y. M A X I M I Z I N G R E S U L T S. CENTER FOR MINIMAL INVASIVE JOINT SURGERY 2301 25TH STREET SOUTH FARGO ND 58103 701-241-9300
How To Choose Between A Vaginal Birth Or A Cesarean Section
 Be informed. Know your rights. Protect yourself. Protect your baby. What Every Pregnant Woman Needs to Know About Cesarean Section 2012 Childbirth Connection If you re expecting a baby, there s a good
Be informed. Know your rights. Protect yourself. Protect your baby. What Every Pregnant Woman Needs to Know About Cesarean Section 2012 Childbirth Connection If you re expecting a baby, there s a good
General and Objectives Clinical Skills for. Nursing Students in Maternity and Gynecology. Nursing Department
 General and Objectives Clinical Skills for Nursing Students in Maternity and Gynecology Nursing Department Objectives and clinical skills of Antenatal unit Provide antenatal care to woman during normal
General and Objectives Clinical Skills for Nursing Students in Maternity and Gynecology Nursing Department Objectives and clinical skills of Antenatal unit Provide antenatal care to woman during normal
Facing a Hysterectomy? If you ve been diagnosed with early stage gynecologic cancer, learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery
 Facing a Hysterectomy? If you ve been diagnosed with early stage gynecologic cancer, learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Condition: Early Stage Gynecologic Cancer A variety of gynecologic
Facing a Hysterectomy? If you ve been diagnosed with early stage gynecologic cancer, learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery The Condition: Early Stage Gynecologic Cancer A variety of gynecologic
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Umbilical cord complications in two subsequent pregnancies
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Umbilical cord complications in two subsequent pregnancies June 2006 2 Hetzel PG, Godi E, Bührer C, Department of Neonatology (HPG, BC), University Children s Hospital, Basel,
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Umbilical cord complications in two subsequent pregnancies June 2006 2 Hetzel PG, Godi E, Bührer C, Department of Neonatology (HPG, BC), University Children s Hospital, Basel,
Diagnosis of Acromioclavicular Joint Injuries
 PO Box 15 Rocky Hill, CT 06067 (860) 463-9003 Chiroeducation@aol.com www.chirocredit.com ChiroCredit.com is proud to present a section from one of our continuing education programs: Physical Diagnosis
PO Box 15 Rocky Hill, CT 06067 (860) 463-9003 Chiroeducation@aol.com www.chirocredit.com ChiroCredit.com is proud to present a section from one of our continuing education programs: Physical Diagnosis
How To Test For Fetal Blood
 Fetal (FBS) / paired cord blood sampling guideline (GL839) Approval Approval Group Job Title, Chair of Committee Date Maternity & Children s Services Clinical Governance Committee Mr Mark Selinger, Consultant
Fetal (FBS) / paired cord blood sampling guideline (GL839) Approval Approval Group Job Title, Chair of Committee Date Maternity & Children s Services Clinical Governance Committee Mr Mark Selinger, Consultant
Spine Conditioning Program Purpose of Program
 Prepared for: Prepared by: OrthoInfo Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle.
Prepared for: Prepared by: OrthoInfo Purpose of Program After an injury or surgery, an exercise conditioning program will help you return to daily activities and enjoy a more active, healthy lifestyle.
Provider Notification Obstetrical Billing
 Provider Notification Obstetrical Billing Date of Notification September 1, 20 Revision Date September 17, 2015 Plans Affected Mercy Care Plan and Mercy Care Long Term Care Plan Referrals As outlined in
Provider Notification Obstetrical Billing Date of Notification September 1, 20 Revision Date September 17, 2015 Plans Affected Mercy Care Plan and Mercy Care Long Term Care Plan Referrals As outlined in
Fetal Acid Base Status and Umbilical Cord Sampling. David Acker, MD
 Fetal Acid Base Status and Umbilical Cord Sampling David Acker, MD Part I: Some Background Intra-uterine Event as Causative of CP Cord ph < 7.00 and base excess of > 12 Early onset neonatal encephalopathy
Fetal Acid Base Status and Umbilical Cord Sampling David Acker, MD Part I: Some Background Intra-uterine Event as Causative of CP Cord ph < 7.00 and base excess of > 12 Early onset neonatal encephalopathy
Chapter 14. Board of Certified Direct-Entry Midwives.
 Chapter 14. Board of Certified Direct-Entry Midwives. (Words in boldface and underlined indicate language being added; words [CAPITALIZED AND BRACKETED] indicate language being deleted. Complete new sections
Chapter 14. Board of Certified Direct-Entry Midwives. (Words in boldface and underlined indicate language being added; words [CAPITALIZED AND BRACKETED] indicate language being deleted. Complete new sections
Examination of the Pregnant Abdomen
 Medical students often find the examination of the pregnant abdomen daunting. This document provides a framework for you to develop a comprehensive understanding of the pregnant abdomen examination at
Medical students often find the examination of the pregnant abdomen daunting. This document provides a framework for you to develop a comprehensive understanding of the pregnant abdomen examination at
Adult Forearm Fractures
 Adult Forearm Fractures Your forearm is made up of two bones, the radius and ulna. In most cases of adult forearm fractures, both bones are broken. Fractures of the forearm can occur near the wrist at
Adult Forearm Fractures Your forearm is made up of two bones, the radius and ulna. In most cases of adult forearm fractures, both bones are broken. Fractures of the forearm can occur near the wrist at
To outline nursing management of patients receiving epidural anesthesia during labor (Includes walking epidurals and combined spinal-epidurals).
 HOSPITAL NAME INSTITUTIONAL POLICY AND PROCEDURE (IPP) Department: Manual: Section: TITLE/DESCRIPTION POLICY NUMBER LABOR: EPIDURAL EFFECTIVE DATE REVIEW DUE REPLACES NUMBER NO. OF PAGES APPROVED BY APPLIES
HOSPITAL NAME INSTITUTIONAL POLICY AND PROCEDURE (IPP) Department: Manual: Section: TITLE/DESCRIPTION POLICY NUMBER LABOR: EPIDURAL EFFECTIVE DATE REVIEW DUE REPLACES NUMBER NO. OF PAGES APPROVED BY APPLIES
Corporate Reimbursement Policy
 Corporate Reimbursement Policy Guidelines for Global Maternity Reimbursement File Name: Origination: Last Review: Next Review: guidelines_for_global_maternity_reimbursement 10/2003 7/2016 7/2017 Description
Corporate Reimbursement Policy Guidelines for Global Maternity Reimbursement File Name: Origination: Last Review: Next Review: guidelines_for_global_maternity_reimbursement 10/2003 7/2016 7/2017 Description
Stretching the Low Back THERAPIST ASSISTED AND CLIENT SELF-CARE STRETCHES FOR THE LUMBOSACRAL SPINE
 EXPERT CONTENT by Joseph E. Muscolino photos by Yanik Chauvin body mechanics THE ESSENCE OF MOST MANUAL THERAPIES, and certainly clinical orthopedic massage therapy, is to loosen taut soft tissues, thereby
EXPERT CONTENT by Joseph E. Muscolino photos by Yanik Chauvin body mechanics THE ESSENCE OF MOST MANUAL THERAPIES, and certainly clinical orthopedic massage therapy, is to loosen taut soft tissues, thereby
Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body
 Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
REHAB 544 FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY OF THE UPPER EXTREMITY & LOWER EXTREMITY
 REHAB 544 FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY OF THE UPPER EXTREMITY & LOWER EXTREMITY Mark Guthrie, PhD Rehabilitation Medicine University of Washington REHAB 544: Musculoskeletal Anatomy of the Upper & Lower Extremities,
REHAB 544 FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY OF THE UPPER EXTREMITY & LOWER EXTREMITY Mark Guthrie, PhD Rehabilitation Medicine University of Washington REHAB 544: Musculoskeletal Anatomy of the Upper & Lower Extremities,
.org. Clavicle Fracture (Broken Collarbone) Anatomy. Description. Cause. Symptoms
 Clavicle Fracture (Broken Collarbone) Page ( 1 ) A broken collarbone is also known as a clavicle fracture. This is a very common fracture that occurs in people of all ages. Anatomy The collarbone (clavicle)
Clavicle Fracture (Broken Collarbone) Page ( 1 ) A broken collarbone is also known as a clavicle fracture. This is a very common fracture that occurs in people of all ages. Anatomy The collarbone (clavicle)
Ultrasound Billing CPT Codes Summary and Notes
 Ultrasound Billing CPT Codes Summary and Notes CPT codes for ultrasound examinations are considered to be complete studies unless specified as limited studies in their code definitions. A limited study
Ultrasound Billing CPT Codes Summary and Notes CPT codes for ultrasound examinations are considered to be complete studies unless specified as limited studies in their code definitions. A limited study
SOUTHERN WEST MIDLANDS NEWBORN NETWORK
 SOUTHERN WEST MIDLANDS NEWBORN NETWORK Hereford, Worcester, Birmingham, Sandwell & Solihull Title Person Responsible for Review Delayed Umbilical Cord Clamping Dr Andrew Gallagher Date Guideline Agreed:
SOUTHERN WEST MIDLANDS NEWBORN NETWORK Hereford, Worcester, Birmingham, Sandwell & Solihull Title Person Responsible for Review Delayed Umbilical Cord Clamping Dr Andrew Gallagher Date Guideline Agreed:
Pain Relief Options for Labor. Providing You with Quality Care, Information and Support
 Pain Relief Options for Labor Providing You with Quality Care, Information and Support What can I expect during my labor and delivery? As a patient in the Labor and Delivery Suite at Lucile Packard Children
Pain Relief Options for Labor Providing You with Quality Care, Information and Support What can I expect during my labor and delivery? As a patient in the Labor and Delivery Suite at Lucile Packard Children
Professional Liability Insurance Changes in Practice as a Result of the Affordability or Availability of Professional Liability Insurance
 Overview of the 2015 ACOG Survey on Professional Liability By Andrea M. Carpentieri, MA, James J. Lumalcuri, MSW, Jennie Shaw, MPH, and Gerald F. Joseph, Jr., MD, FACOG The 2015 Survey on Professional
Overview of the 2015 ACOG Survey on Professional Liability By Andrea M. Carpentieri, MA, James J. Lumalcuri, MSW, Jennie Shaw, MPH, and Gerald F. Joseph, Jr., MD, FACOG The 2015 Survey on Professional
Water Birth Online Course. Women s Services
 Water Birth Online Course Women s Services 1 Water Birth Instructions for Online Class 1. Read through all the slides. 2. Print out the certificate at the end of the slides. 3. Sign and date the certificate.
Water Birth Online Course Women s Services 1 Water Birth Instructions for Online Class 1. Read through all the slides. 2. Print out the certificate at the end of the slides. 3. Sign and date the certificate.
Toe fractures are one of the most
 Evaluation and Management of Toe Fractures ROBERT L. HATCH, M.D., M.P.H., and SCOTT HACKING, M.D., University of Florida College of Medicine, Gainesville, Florida Fractures of the toe are one of the most
Evaluation and Management of Toe Fractures ROBERT L. HATCH, M.D., M.P.H., and SCOTT HACKING, M.D., University of Florida College of Medicine, Gainesville, Florida Fractures of the toe are one of the most
