3 SOFTWARE AND PROGRAMMING LANGUAGES
|
|
|
- Peter Gardner
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 3 SOFTWARE AND PROGRAMMING LANGUAGES 3.1 INTRODUCTION In the previous lesson we discussed about the different parts and configurations of computer. It has been mentioned that programs or instructions have to be fed into the computer to perform specific task. It is therefore necessary to provide instructions to the computer in a systematic order to complete our task. We can divide the computer components into two major areas, namely, hardware and software. Hardware is the machine itself and its various individual equipment. It includes all mechanical, electronic and magnetic devices such as monitor, printer, electronic circuit, floppy and hard disk. In this lesson we will discuss about the other part, namely, software that makes use of hardware for performing various functions. 3.2 OBJECTIVES After going through this lesson you would be able to: explain the concept of software distinguish between different types of software differentiate application software from system software differentiate between different types of language distinguish between compiler and interpreter
2 Software and Programming Language :: WHAT IS SOFTWARE? As you know computer cannot do anything on its own and has to be guided by the user. In order to do any specific job you have to give a sequence of instructions to the computer. This set of instructions is called a computer program. Software refers to the set of computer programs, procedures that describe the programs and how they are to be used. We can say that it is the collection of programs, which increases the capabilities of the hardware. Software guides the computer at every step where to start and stop during a particular job. The process of software development is called programming. You should keep in mind that software and hardware are complementary to each other. Both have to work together to produce meaningful result. Another important point you should know that developing software is difficult, time consuming and expensive. 3.4 SOFTWARE TYPES Computer software is normally classified into two broad categories. Application Software System Software Application Software: Application software is a set of programs, which are written to perform specific tasks of the users of computers such as Accounts, Stores, Payroll, etc. These software are developed in high level language to help the user to get the computer perform the tasks. For example, you can develop a package to print mark sheet of every student of your class or generate accounts of a company, etc. Application software can be classified into two types: (a) Customized Packages (b) Generalized Packages. Customized Packages: These are developed especially for the user by a program using high-level computer languages. For example, when you develop a package to prepare a status report of your school i.e., name of the students, their addresses, Parent s name, Fee paid, marks obtained, etc., you are developing a customized package because the package developed for your school may not be of any use for other school. Generalized Package: These packages are written for the people who have to perform common task on a computer system. DBase, Lotus 1-2-3, FoxPro, MS Office, etc. are the names of the Generalized Packages. Any person can use these packages because they
3 62 :: Basic Computing Skills can be used for different application and purposes. These are meant for mass consumption. Another example of application software is programming language. Among the programming languages COBOL (Common Business Oriented Language) is more suitable for business application whereas FORTRAN (Formula Translation) is useful for scientific application. We will discuss about these languages in next section System Software: You know that an instruction is a set of programs that has to be fed to the computer for operation of computer system as a whole. When you switch on the computer the programs stored or written in ROM is executed which activates different units of your computer and makes it ready for you to work on it. This set of program can be called System Software. Therefore system software may be defined as a set of one or more programs designed to control the operations of computer system. System Software are general purpose programs designed for performing tasks such as controlling all operations required to move data into and out of the computer. It communicates with keyboard, printer, card reader, disk, tapes etc. It also monitors the use of various hardware like memory, CPU etc. System software acts as an interface between hardware and application software. System software allows application packages to be run on the computer with less time and effort. Remember that it is not possible to run application software without system software. Fig. 3.1: Hardware, Software and user
4 Software and Programming Language :: 63 Development of system software is a complex task and it requires extensive knowledge of computer technology. Due to its complexity, the users cannot develop it. Computer manufactures build and supply this system software with the computer. DOS, UNIX, WINDOWS, Language Compilers and Interpreters are some of the widely used system software. Out of these UNIX is a multi-user operating system whereas DOS and WINDOWS are PC-based. We will discuss in detail about DOS and WINDOWS in the next module. So without system software it is impossible to operate your computer. The fig.3.1 shows relation between hardware, software and you as a user of computer system. INTEXT QUESTIONS 1. What are program, programming and software? 2. Differentiate between System Software and Application Software. 3. Write True or False. (a) The set of instructions given to the computer is called programming. (b) Application Software is a set of programs to carry out operations for a specific application. (c) UNIX is a multi-user operating system. 3.5 PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE You are aware with the term language. It is a system of communication between two persons. Some of the basic natural languages that we are familiar with are English, Hindi, Oriya, etc. These are the languages used to communicate among various categories of persons. But how will you communicate with your computer. Your computer will not understand any of these natural languages for transfer of data and instruction. So there are computer-programming languages specially developed so that you could pass your data and instructions to the computer to do specific job. You must have heard names like FORTRAN, BASIC, COBOL, etc. These are programming languages. So instructions for performing a task are written in a particular computer programming language based on the type of job. As an example, for scientific application FORTRAN and C languages are used. On the other hand, COBOL is used mainly for business application.
5 64 :: Basic Computing Skills Types of Programming Languages There are two major types of programming languages. These are Low Level Languages and High Level Languages. Low Level languages are further divided into Machine language and Assembly language Low level languages The term low level means closeness to the way in which the machine has been built. Low Level languages are machine oriented and require extensive knowledge of computer hardware and its configuration. The low level languages are: Machine Language:Machine Language is the language of the computer and is the only language that is directly understood by the computer. We also call it machine code and it is written as strings of 1 s and 0 s. It is on this basis that the computer is designed. When this sequence of codes is fed to the computer, it recognizes the codes and converts it in to electrical signals needed to run it. For example, a program instruction may look like this: It is not an easy language for you to learn because of its complexity as it consists of 1's and 0's. It is most efficient for the computer as the instructions are directly executed. It is considered to the first generation language. It is also difficult to debug the program written in this language. Advantage The only advantage is that program of machine language run very fast because no translation program is required for the CPU. Disadvantages 1. It is very difficult to program in machine language. The programmer has to know details of hardware to write program. 2. Machine language is hardware dependent. 3. The programmer has to remember a lot of codes to write a program, which results in program errors. 4. It is difficult to debug the program. Assembly Language: It is the first step to improve the programming
6 Software and Programming Language :: 65 structure. In this language, the machine codes comprising of 1's and 0's are substituted by symbolic codes (called mnemonic codes) to improve their understanding. The set of symbols and letters forms the assembly language and a translator program (called Assembler) is required to translate the programs written in assembly language into machine language for execution by the computer. It is considered to be a second-generation language. Advantages: 1. The symbolic programming of Assembly Language is easier to understand and saves a lot of time and effort of the programmer. 2. It is relatively easier to correct errors and modify program instructions. 3. Assembly Language has almost the same efficiency of execution as the machine level language because this is one-to-one translator between assembly language program and its corresponding machine language program. Disadvantages: One of the major disadvantage is that assembly language is machine dependent. A program written for one computer might not run on other computers with different hardware configuration. INTEXT QUESTIONS 4. What is the difference between FORTRAN and COBOL? 5. Differentiate between Machine Language and Assembly Language. 6. Write True or False. (a) (b) (c) Low Level language and High-level language are two major types of programming languages. Machine language is the only language that is indirectly understood by the computer. Assembly language is second-generation language High Level Languages You know that assembly language and machine language require
7 66 :: Basic Computing Skills extensive knowledge of computer hardware. To overcome this limitation, a user writes the instructions in English like sentences to perform the logic of the problem irrespective of the type of computer you are using. The language used for this is referred to as high-level language. High-level languages are simple language that use English and mathematical symbols like +, -, %, /, etc. for its program construction. You should know that any higher-level language has to be converted to machine language for the computer to understand. Higher-level languages are problem-oriented languages because the instructions are suitable for solving a particular problem. For example COBOL (Common Business Oriented Language) is mostly suitable for business oriented language where there is very little processing and huge output. There are mathematical oriented languages like FORTRAN (Formula Translation) and BASIC (Beginners All-purpose Symbolic Instructions Code) where very large processing is required. Thus a problem-oriented language is designed in such a way that its instruction may be written more like the language of the problem. For example, businessmen use business term and scientists use scientific terms in their respective languages. Advantages of High Level Languages Higher-level languages have a major advantage over machine and assembly languages that higher-level languages are easy to learn and use. It is because that they are similar to the languages used by us in our day-to-day life. The programs can easily be debugged and are machine independent. 3.6 COMPILER It is a program that translates the instructions of higher-level languages to machine language. It is called compiler because it compiles every program instruction given in higher-level languages into machine language. Thus compiler is a program translator like assembler but more sophisticated. It scans the entire program first and then translates it into machine code. The program written by the programmer in higher-level language is called source program. After this program is converted to machine language by the compiler it is called object program.
8 Software and Programming Language :: 67 Fig. 3.2: Computer Program A compiler can translate only those source programs, which have been written, in that language for which the compiler is meant for. For example, FORTRAN compiler will not compile source code written in COBOL language. Object program generated by compiler is machine dependent. It means programs compiled for one type of machine will not run in another type. Therefore every type of machine must have its personal compiler for a particular language. Machine independence is achieved by using standard higher-level language on different machines and converting them for use on specific machines through a compiler. 3.7 INTERPRETER An interpreter is another type of program translator used for translating higher-level language instructions into machine language instructions. It takes one statement of higher-level language at a time, translates it into machine language and executes it immediately. Translation and execution are carried out for each statement. It differs from compiler, which translate the entire source program into machine code and then involve in its execution. The advantage of interpreter compared to compiler is its fast response to changes in source program. It eliminates the need for a separate compilation after changes to each program. Interpreters are easy to write and do not require large memory in computer. The
9 68 :: Basic Computing Skills disadvantage of interpreter is that it is time-consuming method because each time a statement in a program is executed, it is first translated. Thus compiled machine language program runs much faster than an interpreted program. INTEXT QUESTIONS 7. What is the difference between interpreter and compiler? 8. Give some examples of high-level language. 9. Write True and False for the following statements (a) High level languages are problem-oriented language. (b) Object program generated by compiler is machine independent. (c) The disadvantage of interpreter is that it is time consuming. 3.8 WHAT YOU HAVE LEARNT In this lesson we discussed about two types of software, namely, system software and application software. System software controls the hardware part of the computer. It is designed for performing tasks such as controlling all operations required to move data into and out of the computer. It communicates with printer, card reader, disk, tapes, etc. and monitors the use of various components like memory, CPU, etc. Application software is a set of programs written for specific purpose. Examples of application software are MS WORD, Lotus 1-2-3, Tally Accounting software, etc. We also discussed about levels of computer language. 3.9 TERMINAL QUESTIONS 1. Describe the concept of software and hardware. 2. Define computer Language. 3. State the three different categories of computer languages. 4. What is machine language? Why is it required? 5. Describe the advantages and disadvantages of machine languages. 6. What is assembly language? Explain its advantages over machine languages.
10 Software and Programming Language :: Differentiate between (a) Source program and object program (b) Higher level language and machine language (c) Compiler and Interpreter 3.10 KEY TO INTEXT QUESTIONS 1. Program is a set of instructions given to the computer by the user. Software is a set of computer programs and procedure that describe the programs. Programming is the process of software development. 2. Application Software is a set of programs to carry out operations for a specific application. System software is a set of programs written for performing tasks such as controlling all operations required to move data into and out of the computer. 3. (a) False (b) True (c) True 4. FORTRAN is used for scientific applications whereas COBOL is used for business applications. 5. Machine language is the only language that is directly understood by the computer. It is written in binary form that is 0 and 1. The set of symbols and letters forms the Assembly Language. 6. (a) True (b) False (c) True 7. Both compiler and interpreter are program translators used for translating higher-level language into machine language. While compiler scans the entire program first and then translates it into machine code, an Interpreter translates and executes the program line by line. 8. FORTRAN (Formula Translation) and BASIC (Beginners All-Purpose Symbolic Instruction Code) are some of the high level languages. 9. (a) True (b) False (c) True
Basics of Computer 1.1 INTRODUCTION 1.2 OBJECTIVES
 Basics of Computer :: 1 1 Basics of Computer 1.1 INTRODUCTION In this lesson we present an overview of the basic design of a computer system: how the different parts of a computer system are organized
Basics of Computer :: 1 1 Basics of Computer 1.1 INTRODUCTION In this lesson we present an overview of the basic design of a computer system: how the different parts of a computer system are organized
High level code and machine code
 High level code and machine code Teacher s Notes Lesson Plan x Length 60 mins Specification Link 2.1.7/cde Programming languages Learning objective Students should be able to (a) explain the difference
High level code and machine code Teacher s Notes Lesson Plan x Length 60 mins Specification Link 2.1.7/cde Programming languages Learning objective Students should be able to (a) explain the difference
COMPUTER AND COMPUTERISED ACCOUNTING SYSTEM
 MODULE - 2 Computer and Computerised Accounting System 12 COMPUTER AND COMPUTERISED ACCOUNTING SYSTEM With the expansion of business the number of transactions increased. The manual method of keeping and
MODULE - 2 Computer and Computerised Accounting System 12 COMPUTER AND COMPUTERISED ACCOUNTING SYSTEM With the expansion of business the number of transactions increased. The manual method of keeping and
CS 3530 Operating Systems. L02 OS Intro Part 1 Dr. Ken Hoganson
 CS 3530 Operating Systems L02 OS Intro Part 1 Dr. Ken Hoganson Chapter 1 Basic Concepts of Operating Systems Computer Systems A computer system consists of two basic types of components: Hardware components,
CS 3530 Operating Systems L02 OS Intro Part 1 Dr. Ken Hoganson Chapter 1 Basic Concepts of Operating Systems Computer Systems A computer system consists of two basic types of components: Hardware components,
EKT150 Introduction to Computer Programming. Wk1-Introduction to Computer and Computer Program
 EKT150 Introduction to Computer Programming Wk1-Introduction to Computer and Computer Program A Brief Look At Computer Computer is a device that receives input, stores and processes data, and provides
EKT150 Introduction to Computer Programming Wk1-Introduction to Computer and Computer Program A Brief Look At Computer Computer is a device that receives input, stores and processes data, and provides
The Application of Visual Basic Computer Programming Language to Simulate Numerical Iterations
 Leonardo Journal of Sciences ISSN 1583-0233 Issue 9, July-December 2006 p. 125-136 The Application of Visual Basic Computer Programming Language to Simulate Numerical Iterations Department of Mechanical
Leonardo Journal of Sciences ISSN 1583-0233 Issue 9, July-December 2006 p. 125-136 The Application of Visual Basic Computer Programming Language to Simulate Numerical Iterations Department of Mechanical
Ch. 10 Software Development. (Computer Programming)
 Ch. 10 Software Development (Computer Programming) 1 Definitions Software or Program Instructions that tell the computer what to do Programmer Someone who writes computer programs 2 Instruction Set A vocabulary
Ch. 10 Software Development (Computer Programming) 1 Definitions Software or Program Instructions that tell the computer what to do Programmer Someone who writes computer programs 2 Instruction Set A vocabulary
Chapter 12 Programming Concepts and Languages
 Chapter 12 Programming Concepts and Languages Chapter 12 Programming Concepts and Languages Paradigm Publishing, Inc. 12-1 Presentation Overview Programming Concepts Problem-Solving Techniques The Evolution
Chapter 12 Programming Concepts and Languages Chapter 12 Programming Concepts and Languages Paradigm Publishing, Inc. 12-1 Presentation Overview Programming Concepts Problem-Solving Techniques The Evolution
Topics. Introduction. Java History CS 146. Introduction to Programming and Algorithms Module 1. Module Objectives
 Introduction to Programming and Algorithms Module 1 CS 146 Sam Houston State University Dr. Tim McGuire Module Objectives To understand: the necessity of programming, differences between hardware and software,
Introduction to Programming and Algorithms Module 1 CS 146 Sam Houston State University Dr. Tim McGuire Module Objectives To understand: the necessity of programming, differences between hardware and software,
THREE YEAR DEGREE (HONS.) COURSE BACHELOR OF COMPUTER APPLICATION (BCA) First Year Paper I Computer Fundamentals
 THREE YEAR DEGREE (HONS.) COURSE BACHELOR OF COMPUTER APPLICATION (BCA) First Year Paper I Computer Fundamentals Full Marks 100 (Theory 75, Practical 25) Introduction to Computers :- What is Computer?
THREE YEAR DEGREE (HONS.) COURSE BACHELOR OF COMPUTER APPLICATION (BCA) First Year Paper I Computer Fundamentals Full Marks 100 (Theory 75, Practical 25) Introduction to Computers :- What is Computer?
1.1 Electronic Computers Then and Now
 1.1 Electronic Computers Then and Now The first electronic computer was built in the late 1930s by Dr.John Atanasoff and Clifford Berry at Iowa State University in USA. They designed their computer to
1.1 Electronic Computers Then and Now The first electronic computer was built in the late 1930s by Dr.John Atanasoff and Clifford Berry at Iowa State University in USA. They designed their computer to
Lesson 06: Basics of Software Development (W02D2
 Lesson 06: Basics of Software Development (W02D2) Balboa High School Michael Ferraro Lesson 06: Basics of Software Development (W02D2 Do Now 1. What is the main reason why flash
Lesson 06: Basics of Software Development (W02D2) Balboa High School Michael Ferraro Lesson 06: Basics of Software Development (W02D2 Do Now 1. What is the main reason why flash
Python Programming: An Introduction to Computer Science
 Python Programming: An Introduction to Computer Science Chapter 1 Computers and Programs 1 The Universal Machine n A computer -- a machine that stores and manipulates information under the control of a
Python Programming: An Introduction to Computer Science Chapter 1 Computers and Programs 1 The Universal Machine n A computer -- a machine that stores and manipulates information under the control of a
Objectives. Python Programming: An Introduction to Computer Science. Lab 01. What we ll learn in this class
 Python Programming: An Introduction to Computer Science Chapter 1 Computers and Programs Objectives Introduction to the class Why we program and what that means Introduction to the Python programming language
Python Programming: An Introduction to Computer Science Chapter 1 Computers and Programs Objectives Introduction to the class Why we program and what that means Introduction to the Python programming language
Embedded Software development Process and Tools: Lesson-3 Host and Target Machines
 Embedded Software development Process and Tools: Lesson-3 Host and Target Machines 1 1. Host-Target Based Development Approach 2 Host-Target System Development Approach During development process, a host
Embedded Software development Process and Tools: Lesson-3 Host and Target Machines 1 1. Host-Target Based Development Approach 2 Host-Target System Development Approach During development process, a host
Module 1. Introduction to Software Engineering. Version 2 CSE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 1 Introduction to Software Engineering Lesson 2 Structured Programming Specific Instructional Objectives At the end of this lesson the student will be able to: Identify the important features of
Module 1 Introduction to Software Engineering Lesson 2 Structured Programming Specific Instructional Objectives At the end of this lesson the student will be able to: Identify the important features of
Python Programming: An Introduction to Computer Science
 Python Programming: An Introduction to Computer Science Chapter 1 Computers and Programs 1 Objectives To understand the respective roles of hardware and software in a computing system. To learn what computer
Python Programming: An Introduction to Computer Science Chapter 1 Computers and Programs 1 Objectives To understand the respective roles of hardware and software in a computing system. To learn what computer
CHAPTER 1 ENGINEERING PROBLEM SOLVING. Copyright 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
 CHAPTER 1 ENGINEERING PROBLEM SOLVING Computing Systems: Hardware and Software The processor : controls all the parts such as memory devices and inputs/outputs. The Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) : performs
CHAPTER 1 ENGINEERING PROBLEM SOLVING Computing Systems: Hardware and Software The processor : controls all the parts such as memory devices and inputs/outputs. The Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) : performs
Introducción. Diseño de sistemas digitales.1
 Introducción Adapted from: Mary Jane Irwin ( www.cse.psu.edu/~mji ) www.cse.psu.edu/~cg431 [Original from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005, UCB] Diseño de sistemas digitales.1
Introducción Adapted from: Mary Jane Irwin ( www.cse.psu.edu/~mji ) www.cse.psu.edu/~cg431 [Original from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005, UCB] Diseño de sistemas digitales.1
AQA GCSE in Computer Science Computer Science Microsoft IT Academy Mapping
 AQA GCSE in Computer Science Computer Science Microsoft IT Academy Mapping 3.1.1 Constants, variables and data types Understand what is mean by terms data and information Be able to describe the difference
AQA GCSE in Computer Science Computer Science Microsoft IT Academy Mapping 3.1.1 Constants, variables and data types Understand what is mean by terms data and information Be able to describe the difference
Management Challenge. Managing Hardware Assets. Central Processing Unit. What is a Computer System?
 Management Challenge Managing Hardware Assets What computer processing and storage capability does our organization need to handle its information and business transactions? What arrangement of computers
Management Challenge Managing Hardware Assets What computer processing and storage capability does our organization need to handle its information and business transactions? What arrangement of computers
Chapter 13: Program Development and Programming Languages
 Understanding Computers Today and Tomorrow 12 th Edition Chapter 13: Program Development and Programming Languages Learning Objectives Understand the differences between structured programming, object-oriented
Understanding Computers Today and Tomorrow 12 th Edition Chapter 13: Program Development and Programming Languages Learning Objectives Understand the differences between structured programming, object-oriented
Software: Systems and Application Software
 Software: Systems and Application Software Computer Software Operating System Popular Operating Systems Language Translators Utility Programs Applications Programs Types of Application Software Personal
Software: Systems and Application Software Computer Software Operating System Popular Operating Systems Language Translators Utility Programs Applications Programs Types of Application Software Personal
CONTROL DATA" 3200 Computer system / ~eal Time Applications
 CONTROL DATA" 3200 Computer system / ~eal Time Applications At this precise moment, events in science and industry are occurring which demand solutions and control. Among these events- in-real-time are
CONTROL DATA" 3200 Computer system / ~eal Time Applications At this precise moment, events in science and industry are occurring which demand solutions and control. Among these events- in-real-time are
Instructor Özgür ZEYDAN BEU Dept. of Enve. Eng. http://cevre.beun.edu.tr/zeydan/ CIV 112 Computer Programming Lecture Notes (1)
 Instructor Özgür ZEYDAN BEU Dept. of Enve. Eng. http://cevre.beun.edu.tr/zeydan/ CIV 112 Computer Programming Lecture Notes (1) Computer Programming A computer is a programmable machine. This means it
Instructor Özgür ZEYDAN BEU Dept. of Enve. Eng. http://cevre.beun.edu.tr/zeydan/ CIV 112 Computer Programming Lecture Notes (1) Computer Programming A computer is a programmable machine. This means it
Chapter 3: Operating-System Structures. Common System Components
 Chapter 3: Operating-System Structures System Components Operating System Services System Calls System Programs System Structure Virtual Machines System Design and Implementation System Generation 3.1
Chapter 3: Operating-System Structures System Components Operating System Services System Calls System Programs System Structure Virtual Machines System Design and Implementation System Generation 3.1
Levels of Programming Languages. Gerald Penn CSC 324
 Levels of Programming Languages Gerald Penn CSC 324 Levels of Programming Language Microcode Machine code Assembly Language Low-level Programming Language High-level Programming Language Levels of Programming
Levels of Programming Languages Gerald Penn CSC 324 Levels of Programming Language Microcode Machine code Assembly Language Low-level Programming Language High-level Programming Language Levels of Programming
dbdos PRO 2 FAQ dbase, LLC 2012 All rights reserved.
 dbdos PRO 2 FAQ What is dbdos PRO 2? dbdos PRO 2 is a virtual machine (VM) that is based on MS-DOS (DOS), which will allow users to run dbase for DOS programs. dbdos PRO 2 is focused on running existing
dbdos PRO 2 FAQ What is dbdos PRO 2? dbdos PRO 2 is a virtual machine (VM) that is based on MS-DOS (DOS), which will allow users to run dbase for DOS programs. dbdos PRO 2 is focused on running existing
An Introduction to Computer Science and Computer Organization Comp 150 Fall 2008
 An Introduction to Computer Science and Computer Organization Comp 150 Fall 2008 Computer Science the study of algorithms, including Their formal and mathematical properties Their hardware realizations
An Introduction to Computer Science and Computer Organization Comp 150 Fall 2008 Computer Science the study of algorithms, including Their formal and mathematical properties Their hardware realizations
Chapter 1. The largest computers, used mainly for research, are called a. microcomputers. b. maxicomputers. c. supercomputers. d. mainframe computers.
 Chapter 1 CD-ROM stands for: a. Compact Disk Random Only Memory b. Compact Disk Read Only Memory c. Computer Device Read Only Memory d. Computer Disk Random Online Memory Control Unit (CU) is the a. Main
Chapter 1 CD-ROM stands for: a. Compact Disk Random Only Memory b. Compact Disk Read Only Memory c. Computer Device Read Only Memory d. Computer Disk Random Online Memory Control Unit (CU) is the a. Main
================================================================
 ==== ==== ================================================================ DR 6502 AER 201S Engineering Design 6502 Execution Simulator ================================================================
==== ==== ================================================================ DR 6502 AER 201S Engineering Design 6502 Execution Simulator ================================================================
Chapter 12. Development Tools for Microcontroller Applications
 Chapter 12 Development Tools for Microcontroller Applications Lesson 01 Software Development Process and Development Tools Step 1: Development Phases Analysis Design Implementation Phase 1 Phase 2 Phase
Chapter 12 Development Tools for Microcontroller Applications Lesson 01 Software Development Process and Development Tools Step 1: Development Phases Analysis Design Implementation Phase 1 Phase 2 Phase
Chapter 14. Programming and Languages. McGraw-Hill/Irwin. Copyright 2008 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 14 Programming and Languages McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2008 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Competencies (Page 1 of 2) Describe the six steps of programming Discuss design
Chapter 14 Programming and Languages McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2008 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Competencies (Page 1 of 2) Describe the six steps of programming Discuss design
McGraw-Hill The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 20 1. 01 0
 1.1 McGraw-Hill The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2000 Objectives: To describe the evolution of programming languages from machine language to high-level languages. To understand how a program in a high-level
1.1 McGraw-Hill The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2000 Objectives: To describe the evolution of programming languages from machine language to high-level languages. To understand how a program in a high-level
Chapter 13: Program Development and Programming Languages
 15 th Edition Understanding Computers Today and Tomorrow Comprehensive Chapter 13: Program Development and Programming Languages Deborah Morley Charles S. Parker Copyright 2015 Cengage Learning Learning
15 th Edition Understanding Computers Today and Tomorrow Comprehensive Chapter 13: Program Development and Programming Languages Deborah Morley Charles S. Parker Copyright 2015 Cengage Learning Learning
High-Level Programming Languages. Nell Dale & John Lewis (adaptation by Michael Goldwasser)
 High-Level Programming Languages Nell Dale & John Lewis (adaptation by Michael Goldwasser) Low-Level Languages What are disadvantages of low-level languages? (e.g., machine code or assembly code) Programming
High-Level Programming Languages Nell Dale & John Lewis (adaptation by Michael Goldwasser) Low-Level Languages What are disadvantages of low-level languages? (e.g., machine code or assembly code) Programming
Building Applications Using Micro Focus COBOL
 Building Applications Using Micro Focus COBOL Abstract If you look through the Micro Focus COBOL documentation, you will see many different executable file types referenced: int, gnt, exe, dll and others.
Building Applications Using Micro Focus COBOL Abstract If you look through the Micro Focus COBOL documentation, you will see many different executable file types referenced: int, gnt, exe, dll and others.
Software. Programming Language. Software. Instructor Özgür ZEYDAN. Bülent Ecevit University Department of Environmental Engineering
 Computer Bülent Ecevit University Department of Environmental Engineering Case & Inside units Hardware Peripherals Operating Systems Application : Instructions for the computer. A series of instructions
Computer Bülent Ecevit University Department of Environmental Engineering Case & Inside units Hardware Peripherals Operating Systems Application : Instructions for the computer. A series of instructions
Chapter 6: Programming Languages
 Chapter 6: Programming Languages Computer Science: An Overview Eleventh Edition by J. Glenn Brookshear Copyright 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 6: Programming Languages 6.1 Historical Perspective
Chapter 6: Programming Languages Computer Science: An Overview Eleventh Edition by J. Glenn Brookshear Copyright 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 6: Programming Languages 6.1 Historical Perspective
Chapter 3: Operating-System Structures. System Components Operating System Services System Calls System Programs System Structure Virtual Machines
 Chapter 3: Operating-System Structures System Components Operating System Services System Calls System Programs System Structure Virtual Machines Operating System Concepts 3.1 Common System Components
Chapter 3: Operating-System Structures System Components Operating System Services System Calls System Programs System Structure Virtual Machines Operating System Concepts 3.1 Common System Components
2. Advance Certificate Course in Information Technology
 Introduction: 2. Advance Certificate Course in Information Technology In the modern world, information is power. Acquiring information, storing, updating, processing, sharing, distributing etc. are essentials
Introduction: 2. Advance Certificate Course in Information Technology In the modern world, information is power. Acquiring information, storing, updating, processing, sharing, distributing etc. are essentials
Embedded Software development Process and Tools: Lesson-4 Linking and Locating Software
 Embedded Software development Process and Tools: Lesson-4 Linking and Locating Software 1 1. Linker 2 Linker Links the compiled codes of application software, object codes from library and OS kernel functions.
Embedded Software development Process and Tools: Lesson-4 Linking and Locating Software 1 1. Linker 2 Linker Links the compiled codes of application software, object codes from library and OS kernel functions.
Algorithm & Flowchart & Pseudo code. Staff Incharge: S.Sasirekha
 Algorithm & Flowchart & Pseudo code Staff Incharge: S.Sasirekha Computer Programming and Languages Computers work on a set of instructions called computer program, which clearly specify the ways to carry
Algorithm & Flowchart & Pseudo code Staff Incharge: S.Sasirekha Computer Programming and Languages Computers work on a set of instructions called computer program, which clearly specify the ways to carry
Types Of Operating Systems
 Types Of Operating Systems Date 10/01/2004 1/24/2004 Operating Systems 1 Brief history of OS design In the beginning OSes were runtime libraries The OS was just code you linked with your program and loaded
Types Of Operating Systems Date 10/01/2004 1/24/2004 Operating Systems 1 Brief history of OS design In the beginning OSes were runtime libraries The OS was just code you linked with your program and loaded
Fundamentals of Programming and Software Development Lesson Objectives
 Lesson Unit 1: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTERS Computer History Create a timeline illustrating the most significant contributions to computing technology Describe the history and evolution of the computer Identify
Lesson Unit 1: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTERS Computer History Create a timeline illustrating the most significant contributions to computing technology Describe the history and evolution of the computer Identify
Flowchart Techniques
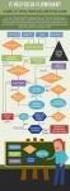 C H A P T E R 1 Flowchart Techniques 1.1 Programming Aids Programmers use different kinds of tools or aids which help them in developing programs faster and better. Such aids are studied in the following
C H A P T E R 1 Flowchart Techniques 1.1 Programming Aids Programmers use different kinds of tools or aids which help them in developing programs faster and better. Such aids are studied in the following
Introduction to programming
 Unit 1 Introduction to programming Summary Architecture of a computer Programming languages Program = objects + operations First Java program Writing, compiling, and executing a program Program errors
Unit 1 Introduction to programming Summary Architecture of a computer Programming languages Program = objects + operations First Java program Writing, compiling, and executing a program Program errors
In the two following sections we separately consider hardware and software requirements. Sometimes, they will be offered for sale as a package.
 Appendix A COMPUTER HARDWARE AND SOFTWARE In this appendix we discuss some of the issues in choosing hardware and software for image analysis. The purpose is to draw attention to the issues involved rather
Appendix A COMPUTER HARDWARE AND SOFTWARE In this appendix we discuss some of the issues in choosing hardware and software for image analysis. The purpose is to draw attention to the issues involved rather
1 PERSONAL COMPUTERS
 PERSONAL COMPUTERS 1 2 Personal computer a desktop computer a laptop a tablet PC or a handheld PC Software applications for personal computers include word processing spreadsheets databases web browsers
PERSONAL COMPUTERS 1 2 Personal computer a desktop computer a laptop a tablet PC or a handheld PC Software applications for personal computers include word processing spreadsheets databases web browsers
TYPES OF COMPUTERS AND THEIR PARTS MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. What is a computer? a. A programmable electronic device that processes data via instructions to output information for future use. b. Raw facts and figures that has no meaning
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. What is a computer? a. A programmable electronic device that processes data via instructions to output information for future use. b. Raw facts and figures that has no meaning
Module 1 Introduction to Information and Communication Technologies
 Module 1 Introduction to Information and Communication Technologies Lesson 3 What are the Hardware Components of a Computer? UNESCO EIPICT Module 1. Lesson 3 1 Rationale The hardware components are the
Module 1 Introduction to Information and Communication Technologies Lesson 3 What are the Hardware Components of a Computer? UNESCO EIPICT Module 1. Lesson 3 1 Rationale The hardware components are the
How To Understand Programming Languages And Programming Languages
 Objectives Differentiate between machine and and assembly languages Describe Describe various various ways ways to to develop develop Web Web pages pages including including HTML, HTML, scripting scripting
Objectives Differentiate between machine and and assembly languages Describe Describe various various ways ways to to develop develop Web Web pages pages including including HTML, HTML, scripting scripting
Module 12. Software Project Monitoring and Control. Version 2 CSE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 12 Software Project Monitoring and Control Lesson 31 Risk Management and Software Configuration Management Specific Instructional Objectives At the end of this lesson the student would be able to:
Module 12 Software Project Monitoring and Control Lesson 31 Risk Management and Software Configuration Management Specific Instructional Objectives At the end of this lesson the student would be able to:
Chapter 13 Computer Programs and Programming Languages. Discovering Computers 2012. Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World
 Chapter 13 Computer Programs and Programming Languages Discovering Computers 2012 Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World Objectives Overview Differentiate between machine and assembly languages Identify
Chapter 13 Computer Programs and Programming Languages Discovering Computers 2012 Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World Objectives Overview Differentiate between machine and assembly languages Identify
Programming Logic controllers
 Programming Logic controllers Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) is a microprocessor based system that uses programmable memory to store instructions and implement functions such as logic, sequencing,
Programming Logic controllers Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) is a microprocessor based system that uses programmable memory to store instructions and implement functions such as logic, sequencing,
Computer Layers. Hardware BOOT. Operating System. Applications
 Computers Software Computer Layers Hardware BOOT Operating System Applications Software Classifications System Software (operating system) Application Software Utility Software Malware Viruses and worms
Computers Software Computer Layers Hardware BOOT Operating System Applications Software Classifications System Software (operating system) Application Software Utility Software Malware Viruses and worms
CS3600 SYSTEMS AND NETWORKS
 CS3600 SYSTEMS AND NETWORKS NORTHEASTERN UNIVERSITY Lecture 2: Operating System Structures Prof. Alan Mislove (amislove@ccs.neu.edu) Operating System Services Operating systems provide an environment for
CS3600 SYSTEMS AND NETWORKS NORTHEASTERN UNIVERSITY Lecture 2: Operating System Structures Prof. Alan Mislove (amislove@ccs.neu.edu) Operating System Services Operating systems provide an environment for
lesson 1 An Overview of the Computer System
 essential concepts lesson 1 An Overview of the Computer System This lesson includes the following sections: The Computer System Defined Hardware: The Nuts and Bolts of the Machine Software: Bringing the
essential concepts lesson 1 An Overview of the Computer System This lesson includes the following sections: The Computer System Defined Hardware: The Nuts and Bolts of the Machine Software: Bringing the
Microsoft Access is an outstanding environment for both database users and professional. Introduction to Microsoft Access and Programming SESSION
 539752 ch01.qxd 9/9/03 11:38 PM Page 5 SESSION 1 Introduction to Microsoft Access and Programming Session Checklist Understanding what programming is Using the Visual Basic language Programming for the
539752 ch01.qxd 9/9/03 11:38 PM Page 5 SESSION 1 Introduction to Microsoft Access and Programming Session Checklist Understanding what programming is Using the Visual Basic language Programming for the
ASSEMBLY LANGUAGE PROGRAMMING (6800) (R. Horvath, Introduction to Microprocessors, Chapter 6)
 ASSEMBLY LANGUAGE PROGRAMMING (6800) (R. Horvath, Introduction to Microprocessors, Chapter 6) 1 COMPUTER LANGUAGES In order for a computer to be able to execute a program, the program must first be present
ASSEMBLY LANGUAGE PROGRAMMING (6800) (R. Horvath, Introduction to Microprocessors, Chapter 6) 1 COMPUTER LANGUAGES In order for a computer to be able to execute a program, the program must first be present
After going through this lesson you would be able to:
 18 :: Data Entry Operations 2 Operating System 2.1 INTRODUCTION The operating system in these days uses a graphical user interface (GUI). Here you do not have to remember all the commands by heart. The
18 :: Data Entry Operations 2 Operating System 2.1 INTRODUCTION The operating system in these days uses a graphical user interface (GUI). Here you do not have to remember all the commands by heart. The
Machine Architecture and Number Systems. Major Computer Components. Schematic Diagram of a Computer. The CPU. The Bus. Main Memory.
 1 Topics Machine Architecture and Number Systems Major Computer Components Bits, Bytes, and Words The Decimal Number System The Binary Number System Converting from Decimal to Binary Major Computer Components
1 Topics Machine Architecture and Number Systems Major Computer Components Bits, Bytes, and Words The Decimal Number System The Binary Number System Converting from Decimal to Binary Major Computer Components
Computer Systems Structure Main Memory Organization
 Computer Systems Structure Main Memory Organization Peripherals Computer Central Processing Unit Main Memory Computer Systems Interconnection Communication lines Input Output Ward 1 Ward 2 Storage/Memory
Computer Systems Structure Main Memory Organization Peripherals Computer Central Processing Unit Main Memory Computer Systems Interconnection Communication lines Input Output Ward 1 Ward 2 Storage/Memory
Computer Engineering
 Computer Engineering Unit Value 3.0 (typically 180 hours for a full-time course) This standard unit is primarily for use by the Technical Institutes when operating the following Courses : Diploma in Computer
Computer Engineering Unit Value 3.0 (typically 180 hours for a full-time course) This standard unit is primarily for use by the Technical Institutes when operating the following Courses : Diploma in Computer
Bachelors of Computer Application Programming Principle & Algorithm (BCA-S102T)
 Unit- I Introduction to c Language: C is a general-purpose computer programming language developed between 1969 and 1973 by Dennis Ritchie at the Bell Telephone Laboratories for use with the Unix operating
Unit- I Introduction to c Language: C is a general-purpose computer programming language developed between 1969 and 1973 by Dennis Ritchie at the Bell Telephone Laboratories for use with the Unix operating
MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCOMPUTER BASICS
 Introduction MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCOMPUTER BASICS At present there are many types and sizes of computers available. These computers are designed and constructed based on digital and Integrated Circuit
Introduction MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCOMPUTER BASICS At present there are many types and sizes of computers available. These computers are designed and constructed based on digital and Integrated Circuit
Introduction to C++ Programming I. Ian Aitchison and Peter King
 Introduction to C++ Programming I Ian Aitchison and Peter King August 1997 Contents 1 The Computer 11 1.1 Central Processing Unit... 13 1.2 Memory.... 13 1.2.1 Main memory..... 14 1.2.2 External Memory...
Introduction to C++ Programming I Ian Aitchison and Peter King August 1997 Contents 1 The Computer 11 1.1 Central Processing Unit... 13 1.2 Memory.... 13 1.2.1 Main memory..... 14 1.2.2 External Memory...
Tech Application Chapter 3 STUDY GUIDE
 Name: Class: Date: Tech Application Chapter 3 STUDY GUIDE Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. This type of device retains data
Name: Class: Date: Tech Application Chapter 3 STUDY GUIDE Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. This type of device retains data
Example of Standard API
 16 Example of Standard API System Call Implementation Typically, a number associated with each system call System call interface maintains a table indexed according to these numbers The system call interface
16 Example of Standard API System Call Implementation Typically, a number associated with each system call System call interface maintains a table indexed according to these numbers The system call interface
Chapter 3. Operating Systems
 Christian Jacob Chapter 3 Operating Systems 3.1 Evolution of Operating Systems 3.2 Booting an Operating System 3.3 Operating System Architecture 3.4 References Chapter Overview Page 2 Chapter 3: Operating
Christian Jacob Chapter 3 Operating Systems 3.1 Evolution of Operating Systems 3.2 Booting an Operating System 3.3 Operating System Architecture 3.4 References Chapter Overview Page 2 Chapter 3: Operating
How To Understand The History Of An Operating System
 7 Operating Systems 7.1 Source: Foundations of Computer Science Cengage Learning Objectives After studying this chapter, the student should be able to: 7.2 Understand the role of the operating system.
7 Operating Systems 7.1 Source: Foundations of Computer Science Cengage Learning Objectives After studying this chapter, the student should be able to: 7.2 Understand the role of the operating system.
Introduction to Computers and Programming
 M01_GADD7119_01_SE_C01.QXD 1/30/08 12:55 AM Page 1 CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Computers and Programming TOPICS 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Hardware and Software 1.3 How Computers Store Data 1.4 How a Program Works
M01_GADD7119_01_SE_C01.QXD 1/30/08 12:55 AM Page 1 CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Computers and Programming TOPICS 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Hardware and Software 1.3 How Computers Store Data 1.4 How a Program Works
Embedded Software development Process and Tools: Lesson-1
 Embedded Software development Process and Tools: Lesson-1 Introduction to Embedded Software Development Process and Tools 1 1. Development Process and Hardware Software 2 Development Process Consists of
Embedded Software development Process and Tools: Lesson-1 Introduction to Embedded Software Development Process and Tools 1 1. Development Process and Hardware Software 2 Development Process Consists of
Objectives. Chapter 2: Operating-System Structures. Operating System Services (Cont.) Operating System Services. Operating System Services (Cont.
 Objectives To describe the services an operating system provides to users, processes, and other systems To discuss the various ways of structuring an operating system Chapter 2: Operating-System Structures
Objectives To describe the services an operating system provides to users, processes, and other systems To discuss the various ways of structuring an operating system Chapter 2: Operating-System Structures
3 SYSTEM DEVELOPMENT METHODOLOGIES
 3 SYSTEM DEVELOPMENT METHODOLOGIES 3.1 INTRODUCTION Different types of system development methodologies are used in designing information system. Depending upon the actual requirement of the system, different
3 SYSTEM DEVELOPMENT METHODOLOGIES 3.1 INTRODUCTION Different types of system development methodologies are used in designing information system. Depending upon the actual requirement of the system, different
This lesson can be adapted to the grade level by the presenter. Decide the level of content and activities as appropriate.
 Binary Coding Preparation Grade Level: K-5 Group Size: 20-30 Time: 50 Minutes Presenters: 1-3 This lesson can be adapted to the grade level by the presenter. Decide the level of content and activities
Binary Coding Preparation Grade Level: K-5 Group Size: 20-30 Time: 50 Minutes Presenters: 1-3 This lesson can be adapted to the grade level by the presenter. Decide the level of content and activities
Parts of a Computer. Preparation. Objectives. Standards. Materials. 1 1999 Micron Technology Foundation, Inc. All Rights Reserved
 Parts of a Computer Preparation Grade Level: 4-9 Group Size: 20-30 Time: 75-90 Minutes Presenters: 1-3 Objectives This lesson will enable students to: Identify parts of a computer Categorize parts of a
Parts of a Computer Preparation Grade Level: 4-9 Group Size: 20-30 Time: 75-90 Minutes Presenters: 1-3 Objectives This lesson will enable students to: Identify parts of a computer Categorize parts of a
Fall 2009. Lecture 1. Operating Systems: Configuration & Use CIS345. Introduction to Operating Systems. Mostafa Z. Ali. mzali@just.edu.
 Fall 2009 Lecture 1 Operating Systems: Configuration & Use CIS345 Introduction to Operating Systems Mostafa Z. Ali mzali@just.edu.jo 1-1 Chapter 1 Introduction to Operating Systems An Overview of Microcomputers
Fall 2009 Lecture 1 Operating Systems: Configuration & Use CIS345 Introduction to Operating Systems Mostafa Z. Ali mzali@just.edu.jo 1-1 Chapter 1 Introduction to Operating Systems An Overview of Microcomputers
River Dell Regional School District. Computer Programming with Python Curriculum
 River Dell Regional School District Computer Programming with Python Curriculum 2015 Mr. Patrick Fletcher Superintendent River Dell Regional Schools Ms. Lorraine Brooks Principal River Dell High School
River Dell Regional School District Computer Programming with Python Curriculum 2015 Mr. Patrick Fletcher Superintendent River Dell Regional Schools Ms. Lorraine Brooks Principal River Dell High School
1 INTRODUCTION TO SYSTEM ANALYSIS AND DESIGN
 1 INTRODUCTION TO SYSTEM ANALYSIS AND DESIGN 1.1 INTRODUCTION Systems are created to solve problems. One can think of the systems approach as an organized way of dealing with a problem. In this dynamic
1 INTRODUCTION TO SYSTEM ANALYSIS AND DESIGN 1.1 INTRODUCTION Systems are created to solve problems. One can think of the systems approach as an organized way of dealing with a problem. In this dynamic
COMPUTER BASICS. Seema Sirpal Delhi University Computer Centre
 COMPUTER BASICS Seema Sirpal Delhi University Computer Centre What is a Computer? An electronic device that stores, retrieves, and processes data, and can be programmed with instructions. A computer is
COMPUTER BASICS Seema Sirpal Delhi University Computer Centre What is a Computer? An electronic device that stores, retrieves, and processes data, and can be programmed with instructions. A computer is
6 USING WINDOWS XP 6.1 INTRODUCTION
 6 USING WINDOWS XP 6.1 INTRODUCTION The windows operating system started with the introduction of Windows OS and Windows for work group for networking. Since then it has come a long way and Windows 95,
6 USING WINDOWS XP 6.1 INTRODUCTION The windows operating system started with the introduction of Windows OS and Windows for work group for networking. Since then it has come a long way and Windows 95,
Chapter 1. Dr. Chris Irwin Davis Email: cid021000@utdallas.edu Phone: (972) 883-3574 Office: ECSS 4.705. CS-4337 Organization of Programming Languages
 Chapter 1 CS-4337 Organization of Programming Languages Dr. Chris Irwin Davis Email: cid021000@utdallas.edu Phone: (972) 883-3574 Office: ECSS 4.705 Chapter 1 Topics Reasons for Studying Concepts of Programming
Chapter 1 CS-4337 Organization of Programming Languages Dr. Chris Irwin Davis Email: cid021000@utdallas.edu Phone: (972) 883-3574 Office: ECSS 4.705 Chapter 1 Topics Reasons for Studying Concepts of Programming
WJEC GCSE in Computer Science Computer Science Microsoft IT Academy Mapping
 WJEC GCSE in Computer Science Computer Science Microsoft IT Academy Mapping 1. Computer Systems 1.1 Identify and describe computer systems Windows Server Administration Fundamentals: Lesson 1 Server Overview
WJEC GCSE in Computer Science Computer Science Microsoft IT Academy Mapping 1. Computer Systems 1.1 Identify and describe computer systems Windows Server Administration Fundamentals: Lesson 1 Server Overview
Welcome to Introduction to Computers and Programming Course using Python
 Welcome to Introduction to Computers and Programming Course using Python V22.0002, Section 3, Spring 2010 Course Introduction Professor: Sana Odeh odeh@courant.nyu.edu Office hours: Mondays 2:00 pm - 4
Welcome to Introduction to Computers and Programming Course using Python V22.0002, Section 3, Spring 2010 Course Introduction Professor: Sana Odeh odeh@courant.nyu.edu Office hours: Mondays 2:00 pm - 4
ZIMBABWE SCHOOL EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL. COMPUTER STUDIES 7014/01 PAPER 1 Multiple Choice SPECIMEN PAPER
 ZIMBABWE SCHOOL EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level COMPUTER STUDIES 7014/01 PAPER 1 Multiple Choice SPECIMEN PAPER Candidates answer on the question paper Additional materials:
ZIMBABWE SCHOOL EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level COMPUTER STUDIES 7014/01 PAPER 1 Multiple Choice SPECIMEN PAPER Candidates answer on the question paper Additional materials:
ATSBA: Advanced Technologies Supporting Business Areas. Programming with Java. 1 Overview and Introduction
 ATSBA: Advanced Technologies Supporting Business Areas Programming with Java 1 Overview and Introduction 1 1 Overview and Introduction 1 Overview and Introduction 1.1 Programming and Programming Languages
ATSBA: Advanced Technologies Supporting Business Areas Programming with Java 1 Overview and Introduction 1 1 Overview and Introduction 1 Overview and Introduction 1.1 Programming and Programming Languages
Systems Engineering and Integration for the NSG (SEIN) SharePoint Developer
 Systems Engineering and Integration for the NSG (SEIN) SharePoint Developer Location: Multiple Locations US and worldwide Start Date: September 2012 Travel: NGA sites US and worldwide Clearance: TS/SCI
Systems Engineering and Integration for the NSG (SEIN) SharePoint Developer Location: Multiple Locations US and worldwide Start Date: September 2012 Travel: NGA sites US and worldwide Clearance: TS/SCI
Software: Systems and. Application Software. Software and Hardware. Types of Software. Software can represent 75% or more of the total cost of an IS.
 C H A P T E R 4 Software: Systems and Application Software Software and Hardware Software can represent 75% or more of the total cost of an IS. Less costly hdwr. More complex sftwr. Expensive developers
C H A P T E R 4 Software: Systems and Application Software Software and Hardware Software can represent 75% or more of the total cost of an IS. Less costly hdwr. More complex sftwr. Expensive developers
Chapter 8 Memory Units
 Chapter 8 Memory Units Contents: I. Introduction Basic units of Measurement II. RAM,ROM,PROM,EPROM Storage versus Memory III. Auxiliary Storage Devices-Magnetic Tape, Hard Disk, Floppy Disk IV.Optical
Chapter 8 Memory Units Contents: I. Introduction Basic units of Measurement II. RAM,ROM,PROM,EPROM Storage versus Memory III. Auxiliary Storage Devices-Magnetic Tape, Hard Disk, Floppy Disk IV.Optical
A Computer Glossary. For the New York Farm Viability Institute Computer Training Courses
 A Computer Glossary For the New York Farm Viability Institute Computer Training Courses 2006 GLOSSARY This Glossary is primarily applicable to DOS- and Windows-based machines and applications. Address:
A Computer Glossary For the New York Farm Viability Institute Computer Training Courses 2006 GLOSSARY This Glossary is primarily applicable to DOS- and Windows-based machines and applications. Address:
dbdos PRO 3 FAQ db_config.exe Creates Shortcut Run DOS program dbase, LLC 2012 All rights reserved.
 dbdos PRO 3 FAQ What is dbdos PRO 3? dbdos PRO 3 is a virtual machine (VM) that is based on MS-DOS (DOS), which will allow users to run dbase for DOS programs. dbdos PRO 3 is focused on running existing
dbdos PRO 3 FAQ What is dbdos PRO 3? dbdos PRO 3 is a virtual machine (VM) that is based on MS-DOS (DOS), which will allow users to run dbase for DOS programs. dbdos PRO 3 is focused on running existing
Name: Class: Date: 9. The compiler ignores all comments they are there strictly for the convenience of anyone reading the program.
 Name: Class: Date: Exam #1 - Prep True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Programming is the process of writing a computer program in a language that the computer can respond to
Name: Class: Date: Exam #1 - Prep True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Programming is the process of writing a computer program in a language that the computer can respond to
Operating System Structures
 Operating System Structures Meelis ROOS mroos@ut.ee Institute of Computer Science Tartu University fall 2009 Literature A. S. Tanenbaum. Modern Operating Systems. 2nd ed. Prentice Hall. 2001. G. Nutt.
Operating System Structures Meelis ROOS mroos@ut.ee Institute of Computer Science Tartu University fall 2009 Literature A. S. Tanenbaum. Modern Operating Systems. 2nd ed. Prentice Hall. 2001. G. Nutt.
SECTION C [short essay] [Not to exceed 120 words, Answer any SIX questions. Each question carries FOUR marks] 6 x 4=24 marks
![SECTION C [short essay] [Not to exceed 120 words, Answer any SIX questions. Each question carries FOUR marks] 6 x 4=24 marks SECTION C [short essay] [Not to exceed 120 words, Answer any SIX questions. Each question carries FOUR marks] 6 x 4=24 marks](/thumbs/35/17285180.jpg) UNIVERSITY OF KERALA First Degree Programme in Computer Applications Model Question Paper Semester I Course Code- CP 1121 Introduction to Computer Science TIME : 3 hrs Maximum Mark: 80 SECTION A [Very
UNIVERSITY OF KERALA First Degree Programme in Computer Applications Model Question Paper Semester I Course Code- CP 1121 Introduction to Computer Science TIME : 3 hrs Maximum Mark: 80 SECTION A [Very
Embedded Software development Process and Tools:
 Embedded Software development Process and Tools: Lesson-2 Integrated Development Environment (IDE) 1 1. IDE 2 Consists of Simulators editors, compilers, assemblers, etc., IDE 3 emulators logic analyzers
Embedded Software development Process and Tools: Lesson-2 Integrated Development Environment (IDE) 1 1. IDE 2 Consists of Simulators editors, compilers, assemblers, etc., IDE 3 emulators logic analyzers
Overview and History of Operating Systems
 Overview and History of Operating Systems These are the notes for lecture 1. Please review the Syllabus notes before these. Overview / Historical Developments An Operating System... Sits between hardware
Overview and History of Operating Systems These are the notes for lecture 1. Please review the Syllabus notes before these. Overview / Historical Developments An Operating System... Sits between hardware
Learning Outcome 1 The learner will: Understand the meaning of Information System and related terms. Indicative Content
 Unit Title: Introduction to Management Information Systems Unit Reference Number: F/505/4045 Guided Learning Hours: 100 Level: Level 4 Number of Credits: 12 Unit purpose and aim(s): This unit aims to give
Unit Title: Introduction to Management Information Systems Unit Reference Number: F/505/4045 Guided Learning Hours: 100 Level: Level 4 Number of Credits: 12 Unit purpose and aim(s): This unit aims to give
The Reincarnation of Virtual Machines
 The Reincarnation of Virtual Machines By Mendel Rosenblum Co-Founder of VMware Associate Professor, Computer Science Stanford University Abstract:VMware, Inc. has grown to be the industry leader in x86-based
The Reincarnation of Virtual Machines By Mendel Rosenblum Co-Founder of VMware Associate Professor, Computer Science Stanford University Abstract:VMware, Inc. has grown to be the industry leader in x86-based
