HLA Class I-Restricted Cytotoxic T-Cell Epitopes of the Respiratory Syncytial Virus Fusion Protein
|
|
|
- Joan Norman
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Nov. 2000, p Vol. 74, No X/00/$ Copyright 2000, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. HLA Class I-Restricted Cytotoxic T-Cell Epitopes of the Respiratory Syncytial Virus Fusion Protein A. H. BRANDENBURG, 1 L.DE WAAL, 1 H. H. TIMMERMAN, 1 P. HOOGERHOUT, 2 R. L. DE SWART, 1 AND A. D. M. E. OSTERHAUS 1 * Institute of Virology, Erasmus University Hospital, 3000 DR Rotterdam, 1 and Laboratory for Bacterial Vaccine Research, National Institute of Public Health and the Environment, 3720 BA Bilthoven, 2 The Netherlands Received 30 May 2000/Accepted 1 August 2000 Virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) play a major role in the clearance of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infection. We have generated cytotoxic T-cell clones (TCC) from two infants who had just recovered from severe RSV infection. These TCC were functionally characterized and used to identify HLA class I (B57 and C12)-restricted CTL epitopes of RSV. * Corresponding author. Mailing address: Institute of Virology, Erasmus University Rotterdam, P.O. Box 1738, 3000 DR Rotterdam, The Netherlands. Phone: Fax: osterhaus@viro.fgg.eur.nl. Present address: LVF, 8917 EN Leeuwarden, The Netherlands. Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is a common cause of upper respiratory tract infections but may especially in young infants, the elderly, or immunocompromised individuals cause severe lower respiratory tract infections (12). In rodent models, CD4, as well as CD8, RSV-specific T lymphocytes proved to be involved in both recovery from and immune pathogenesis of the infection (1, 2, 8, 19). Therefore, a fine balance must exist in these models between protective and disease-enhancing effects of virus-specific T lymphocytes. RSV-specific CD8 cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) against virtually all RSV proteins have been demonstrated to circulate in humans after RSV infection (4, 7, 9). CTL may be expected to play a crucial role in the clearance of RSV infections, but their role in protection and immune pathology remains unclear. Therefore, the identification of CTL epitopes of human RSV may contribute to future studies concerning the role of CTL in pathogenesis and protection from RSV infection. Here we describe the functional characterization of CD8 cytotoxic T-cell clones (TCC) generated from two infants who had just recovered from severe RSV infection. These TCC were also used to identify, for the first time, HLA class I-restricted CTL epitopes of RSV. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) were collected from two infants 4 weeks after a severe, laboratory-confirmed RSV infection. At the time of infection, they were 1 and 2 months old and had both been admitted to the intensive care unit. B-lymphoblastic cell lines (B-LCL) were generated by Epstein-Barr virus transformation (22), infected with RSV A2 (ATCC VR1322), and UV irradiated (24) to serve as autologous antigen-presenting cells (APC). PBMC ( /well in 96-well round-bottom plates) were stimulated with APC (10 4 / well) and expanded in RPMI 1640 medium supplemented with antibiotics, 10% pooled and heat-inactivated human serum, and recombinant human interleukin-2 (IL-2; 50 IU/ml). After 2 weeks, T cells were harvested and cloned by limiting dilution using phytohemagglutinin stimulation as previously described (25). TCC thus generated were expanded and tested for RSV specificity by [ 3 H]thymidine incorporation assays as previously described (22). All of the RSV-specific TCC proved to be of the CD8 phenotype in fluorescence-activated cell sorter analysis. TCC whose specificity for RSV was confirmed by a second proliferation assay were tested for protein specificity by a gamma interferon (IFN- ) ELIspot assay (Mabtech AB, Stockholm, Sweden). In this test, paraformaldehyde-fixed autologous B-LCL that had been infected with recombinant vaccinia viruses (rvv) expressing different RSV proteins (F, G, N, P, M2, SH, M, 1B, or 1C) were used as APC. Briefly, TCC ( /well) were incubated with APC (10 4 /well) for 4 h, transferred to anti-human IFN- -coated plates, and incubated for another 18 h. The ELIspot assay was further performed in accordance with the kit manufacturer s instructions. The results are shown as numbers of IFN- -producing cells (spots) per well. Thirty-four RSV-specific TCC were generated from the PBMC of patient 1, as detected in a [ 3 H]thymidine incorporation assay. Of these, 27 proved to be RSV F specific and 7 were RSV 1B specific in an IFN- ELIspot assay (Fig. 1A). Twentyfour RSV-specific TCC were generated from the PBMC of patient 2 as detected by a [ 3 H]thymidine incorporation assay. Of these, 10 were RSV F specific and 14 proved to be RSV 1C specific in an IFN- ELIspot assay (Fig. 1B). None of the clones detected by the [ 3 H]thymidine incorporation assay was found to be negative by the IFN- ELIspot assay. Since the F protein is considered to be a major CTL target (4, 7, 9), further efforts were focused on the identification of CTL epitopes in the F protein. To this end, 18-mer peptide amides overlapping by 12 amino acids, together spanning the entire F protein of RSV A2 (11, 18) (n 94), were generated in an automated multiple-peptide synthesizer as previously described (26). The purity of the peptides varied between 50 and 90%, as determined by analytical reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (C 8 column; gradient of 0.1% trifluoroacetic acid in water to 0.1% trifluoroacetic acid in acetonitrile). Autologous B-LCL of patients 1 and 2 were pulsed overnight with 1 and 3 M peptide, respectively. RSV F-specific TCC of patient 1 reacted with peptides 17 and 18 (Fig. 2A). All of the RSV F TCC of patient 2 reacted with peptide 91 and marginally with peptide 90 (Fig. 2B). Subsequently, two additional sets of partially overlapping 8- to 12-mer peptides (80 to 95% purity) were generated to determine the respective minimal epitopes. Autologous B-LCL of patients 1 and 2 were pulsed for 1 h with the different peptides at 1 and 3 M, respectively. All of the RSV F-specific TCC of patient 1 reacted with one nine-mer peptide (RARRELPRF) spanning residues 118 to 126 of the F protein (Fig. 2C). The RSV F TCC of patient 2 all reacted with one nine-mer peptide (IAVGLLLYC) spanning residues 551 to 559 of the F protein (Fig. 2D)
2 VOL. 74, 2000 NOTES FIG. 1. Responses of RSV-specific TCC from patients 1 (A) and 2 (B) measured by an IFN- ELIspot assay using autologous B-LCL infected with RSV A2 or rvv expressing the RSV F, 1B, or 1C protein. Results are indicated as numbers of spots per well. No responses against the B-LCL infected with the other rvv were found (data not shown).
3 10242 NOTES J. VIROL. FIG. 2. Fine mapping of T-cell epitopes on the RSV F protein. Responsiveness of TCC from patients 1 (A) and 2 (B) to partially overlapping 18-mer peptide amides (n 94) spanning the F protein was measured by an IFN- ELIspot assay. Minimal peptide activation of TCC from patients 1 (C) and 2 (D) was measured in an IFN- ELIspot assay using APC pulsed with two additional sets of overlapping 8- to 12-mer peptides. med, medium. The HLA restriction of the recognition by the RSV F TCC was also determined by the IFN- ELIspot assay using a set of allogeneic B-LCL with partially matched HLA types loaded with the respective minimal peptides, as shown in Fig. 3. Recognition of the RSV F epitope of patient 1 proved to be HLA B57 restricted. Recognition of the epitope of patient 2 proved to be C12 restricted. Well-growing TCC of both specificities from each of the FIG. 3. Determination of HLA restriction of RSV F protein recognition by specific TCC using a set of autologous and partially HLA class I-matched B-LCL for patients 1 (A) and 2 (B) by an IFN- ELIspot assay.
4 VOL. 74, 2000 NOTES FIG. 4. Cytotoxic responses (A) and cytokine production (B) of selected TCC with different protein specificities from patients 1 and 2. TCC were stimulated with autologous RSV-infected or control B-LCL and in the case of the F-specific TCC of patient 2, minimal-peptide- or control (measles virus) peptide-loaded B-LCL. Cytotoxic responses were measured in a chromium release assay using an effector-to-target cell ratio of 10. Cytokines in cell-free culture supernatant (IFN-, IL-4, IL-5, and IL-10) were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Levels of cytokines in the supernatant of TCC stimulated with control B-LCL were all below the detection limit and are not shown. patients were arbitrarily selected and tested for cytotoxic activity by a chromium release assay as previously described (23). Briefly, autologous 51 Cr-labeled, RSV-infected B-LCL and control B-LCL or, in the case of the F-specific TCC of patient 2, minimal-peptide-loaded B-LCL and control B-LCL were incubated with TCC for 4hat37 C at an effector-to-target cell ratio of 10:1, which was found to be the most discriminative ratio in preliminary experiments. Spontaneous 51 Cr release (target cells plus medium) and maximum 51 Cr release (target cells plus Triton X-100) were determined in 12 identical wells. Supernatants were harvested and analyzed in a gamma counter. Assay results were accepted only when the spontaneous-to-maximum release ratio was 25%. All of the TCC tested showed RSV-specific lysis (Fig. 4A). Virus-specific production of cytokines in cell-free culture supernatant was measured as previously described (6). TCC were stimulated with RSV-infected B-LCL or control B-LCL or, in the case of the F-specific TCC of patient 2, with minimal-peptide-loaded B- LCL or control B-LCL for 48 h. The concentrations of the following cytokines were measured using commercially available sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay systems in accordance with the manufacturers instructions: IL-4 (CLB, Amsterdam, The Netherlands; detection limit, 7 pg/ml), IFN- (Medgenix Diagnostics, Fleurs, Belgium; detection limit, 25 pg/ml), IL-10 (Pharmingen, San Diego, Calif.; detection limit, 20 pg/ml). All of the TCC produced predominantly IFN-, indicating a type 1 phenotype in vitro (Fig. 4B). In the present study, we identified two nine-mer CTL epitopes on the RSV fusion protein. To our knowledge, these are the first HLA class I-restricted CTL epitopes described for RSV in humans. We found CTL epitopes with an HLA restriction with a low prevalence in the population. But using the techniques described here on samples of more children with a recent RSV infection, CTL epitopes with more prevalent HLA restrictions may be identified. The TCC found in the children studied were all CD8 CTL with a type 1-like cytokine profile. No RSV-specific CD4 T cells were detected in the samples of these infants, while the use of similar stimulation protocols did result in the identification of such cells in other systems (14, 17, 20, 22). Virusspecific CTL responses play a major role in the clearance of RSV infections but may also be involved in pathogenesis (1, 3, 5, 8, 15). In mice, enhanced lung pathology induced by priming with formalin-inactivated RSV has been associated with the absence of a CTL response (13, 21). In young children, a CTL response against RSV has been described but poor responses were found in younger and more severely ill patients (10, 16). The poor CTL response in young children has been suggested to be one of the possible causes of more severe disease. In these two patients, it was possible to detect RSV-specific cytotoxic TCC, showing that also in very young children with clinically severe infections, priming of a CTL response does occur, although we cannot say anything about the quantitative responses. In conclusion, use of the IFN- ELIspot assay to determine epitope specificity proved to be sensitive and convenient, since only small numbers of T cells and APC were needed. This and similar studies may be important for future studies concerning
5 10244 NOTES J. VIROL. the role of CTL in the pathogenesis of RSV infection in children. This study was financially supported by the Sophia Foundation for Medical Research, Rotterdam, The Netherlands (grant 214). We thank Humphrey Brugghe and Bea van t Land for technical assistance and Conny Kruyssen for assistance in preparing the manuscript. REFERENCES 1. Alwan, W. H., W. J. Kozlowska, and P. J. M. Openshaw Distinct types of lung disease caused by functional subsets of antiviral T cells. J. Exp. Med. 179: Alwan, W. H., F. M. Record, and P. J. M. Openshaw CD4 T cells clear virus but augment disease in mice infected with respiratory syncytial virus. Comparison with the effects of CD8 T cells. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 88: Bangham, C. R., and A. J. McMichael Specific human cytotoxic T cells recognize B-cell lines persistently infected with respiratory syncytial virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83: Bangham, C. R. M., P. J. M. Openshaw, L. A. Ball, A. M. Q. King, G. W. Wertz, and B. A. Askonas Human and murine cytotoxic T cells specific to respiratory syncytial virus recognize the viral nucleoprotein (N), but not the major glycoproteins (G), expressed by vaccinia virus recombinants. J. Immunol. 137: Bangham, C. R. M., M. J. Cannon, D. T. Karzon, and B. A. Askonas Cytotoxic T-cell response to respiratory syncytial virus in mice. J. Virol. 56: Brandenburg, A. H., A. Kleinjan, B. van t Land, H. A. Moll, H. H. Timmerman, R. L. de Swart, H. J. Neijens, W. Fokkens, and A. D. M. E. Osterhaus. A type 1 like immune response is found in children with RSV infection regardless of clinical severity. J. Med. Virol., in press. 7. Cannon, M. J., and C. R. M. Bangham Recognition of respiratory syncytial virus fusion protein by mouse cytotoxic T cell clones and a human cytotoxic T cell line. J. Gen. Virol. 70: Cannon, M. J., P. J. M. Openshaw, and B. A. Askonas Cytotoxic T cells clear virus but augment lung pathology in mice infected with respiratory syncytial virus. J. Exp. Med. 168: Cherrie, A. H., K. Anderson, G. W. Wertz, and P. J. M. Openshaw Human cytotoxic T cells stimulated by antigen on dendritic cells recognize the N, SH, F, M, 22K, and 1b proteins of respiratory syncytial virus. J. Virol. 66: Chiba, Y., Y. Higashidate, K. Suga, K. Honjo, H. Tsatsumi, and P. L. Ogra Development of cell-mediated cytotoxic immunity to respiratory syncytial virus in human infants following naturally acquired infection. J. Med. Virol. 28: Collins, P. L., Y. T. Huang, and G. W. Wertz Nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding the fusion (F) glycoprotein of human respiratory syncytial virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 81: Collins, P. L., K. Mcintosh, and R. M. Chanock Respiratory syncytial virus, p In B. N. Fields, D. M. Knipe, and P. M. Howley (ed.), Fields virology, 3rd ed. Lippincott-Raven Publishers, Philadelphia, Pa. 13. Connors, M., A. B. Kulkarni, C.-Y. Firestone, K. L. Holmes, H. C. Morse III, A. V. Sotnikov, and B. R. Murphy Pulmonary histopathology induced by respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) challenge of formalin-inactivated RSVimmunized BALB/c mice is abrogated by depletion of CD4 T cells. J. Virol. 66: Evans, T. G., T. Fitzgerald, D. C. Gibbons, M. C. Keefer, and H. Soucier Th1/Th2 cytokine responses following HIV-1 immunization in seronegative volunteers. The AIDS Vaccine Evaluation Group. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 111: Fishaut, M., D. Tubergen, and K. Mcintosh Cellular response to respiratory viruses with particular reference to children with disorders of cell-mediated immunity. J. Pediatr. 96: Isaacs, D., C. R. M. Bangham, and A. J. McMichael Cell-mediated cytotoxic response to respiratory syncytial virus in infants with bronchiolitis. Lancet ii: Kallas, E. G., D. C. Gibbons, H. Soucier, T. Fitzgerald, J. J. Treanor, and T. G. Evans Detection of intracellular antigen-specific cytokines in human T cell populations. J. Infect. Dis. 179: Olmsted, R. A., N. Elango, G. A. Prince, B. R. Murphy, P. R. Johnson, B. Moss, R. M. Chanock, and P. L. Collins Expression of the F glycoprotein of respiratory syncytial virus by a recombinant vaccinia virus: comparison of the individual contributions of the F and G glycoproteins to host immunity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83: Openshaw, P. J Immunity and immunopathology to respiratory syncytial virus. The mouse model. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 152:S59 S Secrist, H., C. J. Chelen, Y. Wen, J. D. Marshall, and D. T. Umetsu Allergen immunotherapy decreases interleukin 4 production in CD4 T cells from allergic individuals. J. Exp. Med. 178: Srikiatkhachorn, A., and T. J. Braciale Virus-specific CD8 T lymphocytes downregulate T helper cell type 2 cytokine secretion and pulmonary eosinophilia during experimental murine respiratory syncytial virus infection. J. Exp. Med. 186: Van Binnendijk, R. S., M. C. Poelen, P. de Vries, H. O. Voorma, A. D. Osterhaus, and F. G. UytdeHaag Measles virus-specific human T cell clones. Characterization of specificity and function of CD4 helper/cytotoxic and CD8 cytotoxic T cell clones. J. Immunol. 142: Van Binnendijk, R. S., M. C. Poelen, K. C. Kuijpers, A. D. Osterhaus, and F. G. UytdeHaag The predominance of CD8 T cells after infection with measles virus suggests a role for CD8 class I MHC-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) in recovery from measles. Clonal analyses of human CD8 class I MHC-restricted CTL. J. Immunol. 144: Van Binnendijk, R. S., J. P. M. Versteeg-van Oosten, M. C. M. Poelen, H. F. Brugghe, P. Hoogerhout, A. D. M. E. Osterhaus, and F. G. C. M. UytdeHaag Human HLA class I- and HLA class II-restricted cloned cytotoxic T lymphocytes identify a cluster of epitopes on the measles virus fusion protein. J. Virol. 67: Verjans, G. M., L. Remeijer, R. S. van Binnendijk, J. G. Cornelissen, H. J. Volker-Dieben, S. G. Baarsma, and A. D. Osterhaus Identification and characterization of herpes simplex virus-specific CD4 T cells in corneas of herpetic stromal keratitis patients. J. Infect. Dis. 177: Wiertz, E. J., J. A. van Gaans-van den Brink, H. Gausepohl, A. Prochnicka- Chalufour, P. Hoogerhout, and J. T. Poolman Identification of T cell epitopes occurring in a meningococcal class 1 outer membrane protein using overlapping peptides assembled with simultaneous multiple peptide synthesis. J. Exp. Med. 176:79 88.
Identification of T-cell epitopes of SARS-coronavirus for development of peptide-based vaccines and cellular immunity assessment methods
 RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES PKS Chan 陳 基 湘 S Ma 文 子 光 SM Ngai 倪 世 明 Key Messages 1. Subjects recovered from SARS-CoV infection retain memory of cellular immune response to epitopes
RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES PKS Chan 陳 基 湘 S Ma 文 子 光 SM Ngai 倪 世 明 Key Messages 1. Subjects recovered from SARS-CoV infection retain memory of cellular immune response to epitopes
Assays to evaluate cell-mediated immunity. Guus Rimmelzwaan Department of Virology Erasmus Medical Center Rotterdam The Netherlands
 Assays to evaluate cell-mediated immunity Guus Rimmelzwaan Department of Virology Erasmus Medical Center Rotterdam The Netherlands CBER/NIAID/WHO, Bethesda MD, December 11 2007 A working model of an antiviral
Assays to evaluate cell-mediated immunity Guus Rimmelzwaan Department of Virology Erasmus Medical Center Rotterdam The Netherlands CBER/NIAID/WHO, Bethesda MD, December 11 2007 A working model of an antiviral
The role of IBV proteins in protection: cellular immune responses. COST meeting WG2 + WG3 Budapest, Hungary, 2015
 The role of IBV proteins in protection: cellular immune responses COST meeting WG2 + WG3 Budapest, Hungary, 2015 1 Presentation include: Laboratory results Literature summary Role of T cells in response
The role of IBV proteins in protection: cellular immune responses COST meeting WG2 + WG3 Budapest, Hungary, 2015 1 Presentation include: Laboratory results Literature summary Role of T cells in response
Modelling and analysis of T-cell epitope screening data.
 Modelling and analysis of T-cell epitope screening data. Tim Beißbarth 2, Jason A. Tye-Din 1, Gordon K. Smyth 1, Robert P. Anderson 1 and Terence P. Speed 1 1 WEHI, 1G Royal Parade, Parkville, VIC 3050,
Modelling and analysis of T-cell epitope screening data. Tim Beißbarth 2, Jason A. Tye-Din 1, Gordon K. Smyth 1, Robert P. Anderson 1 and Terence P. Speed 1 1 WEHI, 1G Royal Parade, Parkville, VIC 3050,
Analysis of the adaptive immune response to West Nile virus
 Analysis of the adaptive immune response to West Nile virus Jonathan Bramson (PI) Robin Parsons Alina Lelic Galina Denisova Lesley Latham Carole Evelegh Dmitri Denisov Strategy for characterizing T cell
Analysis of the adaptive immune response to West Nile virus Jonathan Bramson (PI) Robin Parsons Alina Lelic Galina Denisova Lesley Latham Carole Evelegh Dmitri Denisov Strategy for characterizing T cell
specific B cells Humoral immunity lymphocytes antibodies B cells bone marrow Cell-mediated immunity: T cells antibodies proteins
 Adaptive Immunity Chapter 17: Adaptive (specific) Immunity Bio 139 Dr. Amy Rogers Host defenses that are specific to a particular infectious agent Can be innate or genetic for humans as a group: most microbes
Adaptive Immunity Chapter 17: Adaptive (specific) Immunity Bio 139 Dr. Amy Rogers Host defenses that are specific to a particular infectious agent Can be innate or genetic for humans as a group: most microbes
Identification of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus CD4+ and CD8+ T-Cell Epitopes in Vaccinated or Naturally Infected Humans
 Identification of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus CD4+ and CD8+ T-Cell Epitopes in Vaccinated or Naturally Infected Humans Schwaiger Julia Clinical Institute of Virology 29.06.2009 1 Thank you! Franz X.
Identification of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus CD4+ and CD8+ T-Cell Epitopes in Vaccinated or Naturally Infected Humans Schwaiger Julia Clinical Institute of Virology 29.06.2009 1 Thank you! Franz X.
Title: Mapping T cell epitopes in PCV2 capsid protein - NPB #08-159. Date Submitted: 12-11-09
 Title: Mapping T cell epitopes in PCV2 capsid protein - NPB #08-159 Investigator: Institution: Carol Wyatt Kansas State University Date Submitted: 12-11-09 Industry summary: Effective circovirus vaccines
Title: Mapping T cell epitopes in PCV2 capsid protein - NPB #08-159 Investigator: Institution: Carol Wyatt Kansas State University Date Submitted: 12-11-09 Industry summary: Effective circovirus vaccines
Mouse IFN-gamma ELISpot Kit
 Page 1 of 8 Mouse IFN-gamma ELISpot Kit Without Plates With Plates With Sterile Plates Quantity Catalog Nos. 862.031.001 862.031.001P 862.031.001S 1 x 96 tests 862.031.005 862.031.005P 862.031.005S 5 x
Page 1 of 8 Mouse IFN-gamma ELISpot Kit Without Plates With Plates With Sterile Plates Quantity Catalog Nos. 862.031.001 862.031.001P 862.031.001S 1 x 96 tests 862.031.005 862.031.005P 862.031.005S 5 x
Activation and effector functions of HMI
 Activation and effector functions of HMI Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 25 August 2015 ว ตถ ประสงค หล งจากช วโมงบรรยายน แล วน กศ กษาสามารถ
Activation and effector functions of HMI Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 25 August 2015 ว ตถ ประสงค หล งจากช วโมงบรรยายน แล วน กศ กษาสามารถ
02/08/2010. 1. Background. Outline
 Identification of immunodominant T-cell eptitopes in matrix protein of highly pathogenic porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus Ya-Xin Wang, PhD Student Outline 1. Background 2. Research Contents
Identification of immunodominant T-cell eptitopes in matrix protein of highly pathogenic porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus Ya-Xin Wang, PhD Student Outline 1. Background 2. Research Contents
New developments in antigen-specific immunotherapies Novel therapeutic vaccines offer hope in the fight against chronic infectious disease and cancer
 New developments in antigen-specific immunotherapies Novel therapeutic vaccines offer hope in the fight against chronic infectious disease and cancer Vaccination has been used effectively for more than
New developments in antigen-specific immunotherapies Novel therapeutic vaccines offer hope in the fight against chronic infectious disease and cancer Vaccination has been used effectively for more than
Custom Antibody Services
 prosci-inc.com Custom Antibody Services High Performance Antibodies and More Broad Antibody Catalog Extensive Antibody Services CUSTOM ANTIBODY SERVICES Established in 1998, ProSci Incorporated is a leading
prosci-inc.com Custom Antibody Services High Performance Antibodies and More Broad Antibody Catalog Extensive Antibody Services CUSTOM ANTIBODY SERVICES Established in 1998, ProSci Incorporated is a leading
Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION
 TORTORA FUNKE CASE Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION Differentiate between innate and acquired immunity. Chapter 17 Specific Defenses of the Host: The Immune Response B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein
TORTORA FUNKE CASE Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION Differentiate between innate and acquired immunity. Chapter 17 Specific Defenses of the Host: The Immune Response B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein
Natalia Taborda Vanegas. Doc. Sci. Student Immunovirology Group Universidad de Antioquia
 Pathogenesis of Dengue Natalia Taborda Vanegas Doc. Sci. Student Immunovirology Group Universidad de Antioquia Infection process Epidermis keratinocytes Dermis Archives of Medical Research 36 (2005) 425
Pathogenesis of Dengue Natalia Taborda Vanegas Doc. Sci. Student Immunovirology Group Universidad de Antioquia Infection process Epidermis keratinocytes Dermis Archives of Medical Research 36 (2005) 425
Prospects for Vaccines against Hepatitis C Viruses. T. Jake Liang. M.D. Liver Diseases Branch NIDDK, NIH, HHS
 Prospects for Vaccines against Hepatitis C Viruses T. Jake Liang. M.D. Liver Diseases Branch NIDDK, NIH, HHS HCV Vaccine Prevention strategies Protective immunity Barriers and solutions Vaccine candidates
Prospects for Vaccines against Hepatitis C Viruses T. Jake Liang. M.D. Liver Diseases Branch NIDDK, NIH, HHS HCV Vaccine Prevention strategies Protective immunity Barriers and solutions Vaccine candidates
Downloaded from: http://researchonline.lshtm.ac.uk/19718/
 Dockrell, H M; Brahmbhatt, S; Robertson, B D; Britton, S; Fruth, U; Gebre, N; Hunegnaw, M; Hussain, R; Manadhar, R; Murrillo, L; Pessolani, M C; Roche, P; Salgado, J L; Sampaio, E; Shahid, F; Thole, J
Dockrell, H M; Brahmbhatt, S; Robertson, B D; Britton, S; Fruth, U; Gebre, N; Hunegnaw, M; Hussain, R; Manadhar, R; Murrillo, L; Pessolani, M C; Roche, P; Salgado, J L; Sampaio, E; Shahid, F; Thole, J
Name (print) Name (signature) Period. (Total 30 points)
 AP Biology Worksheet Chapter 43 The Immune System Lambdin April 4, 2011 Due Date: Thurs. April 7, 2011 You may use the following: Text Notes Power point Internet One other person in class "On my honor,
AP Biology Worksheet Chapter 43 The Immune System Lambdin April 4, 2011 Due Date: Thurs. April 7, 2011 You may use the following: Text Notes Power point Internet One other person in class "On my honor,
About Our Products. Blood Products. Purified Infectious/Inactivated Agents. Native & Recombinant Viral Proteins. DNA Controls and Primers for PCR
 About Our Products Purified Infectious/Inactivated Agents ABI produces a variety of specialized reagents, allowing researchers to choose the best preparations for their studies. Available reagents include
About Our Products Purified Infectious/Inactivated Agents ABI produces a variety of specialized reagents, allowing researchers to choose the best preparations for their studies. Available reagents include
CONTENT. Chapter 1 Review of Literature. List of figures. List of tables
 Abstract Abbreviations List of figures CONTENT I-VI VII-VIII IX-XII List of tables XIII Chapter 1 Review of Literature 1. Vaccination against intracellular pathogens 1-34 1.1 Role of different immune responses
Abstract Abbreviations List of figures CONTENT I-VI VII-VIII IX-XII List of tables XIII Chapter 1 Review of Literature 1. Vaccination against intracellular pathogens 1-34 1.1 Role of different immune responses
Comparison of whole blood and PBMC assays for T-cell functional analysis
 Deenadayalan et al. BMC Research Notes 213, 6:12 SHORT REPORT Open Access Comparison of whole blood and assays for T-cell functional analysis Anbarasu Deenadayalan, Prabhavathi Maddineni and Alamelu Raja
Deenadayalan et al. BMC Research Notes 213, 6:12 SHORT REPORT Open Access Comparison of whole blood and assays for T-cell functional analysis Anbarasu Deenadayalan, Prabhavathi Maddineni and Alamelu Raja
Chapter 43: The Immune System
 Name Period Our students consider this chapter to be a particularly challenging and important one. Expect to work your way slowly through the first three concepts. Take particular care with Concepts 43.2
Name Period Our students consider this chapter to be a particularly challenging and important one. Expect to work your way slowly through the first three concepts. Take particular care with Concepts 43.2
III III a IIOI OlD III OlD IIO 1101 010 III DID III 100 III0 II uii IIi
 III III a IIOI OlD III OlD IIO 1101 010 III DID III 100 III0 II uii IIi US oi ^^_._.,o.i ^,) United States (12) Patent Application Publication Buyse et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 28, (54) HPV POLYEPITOPE
III III a IIOI OlD III OlD IIO 1101 010 III DID III 100 III0 II uii IIi US oi ^^_._.,o.i ^,) United States (12) Patent Application Publication Buyse et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 28, (54) HPV POLYEPITOPE
Why use passive immunity?
 Vaccines Active vs Passive Immunization Active is longer acting and makes memory and effector cells Passive is shorter acting, no memory and no effector cells Both can be obtained through natural processes:
Vaccines Active vs Passive Immunization Active is longer acting and makes memory and effector cells Passive is shorter acting, no memory and no effector cells Both can be obtained through natural processes:
Carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester-based proliferative assays for assessment of T cell function in the diagnostic laboratory
 Immunology and Cell Biology (1999) 77, 559 564 Special Feature Carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester-based proliferative assays for assessment of T cell function in the diagnostic laboratory DA FULCHER
Immunology and Cell Biology (1999) 77, 559 564 Special Feature Carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester-based proliferative assays for assessment of T cell function in the diagnostic laboratory DA FULCHER
The Costimulatory Molecule CD27 Maintains Clonally
 Immunity, Volume 35 Supplemental Information The Costimulatory Molecule CD7 Maintains Clonally Diverse CD8 + T Cell Responses of Low Antigen Affinity to Protect against Viral Variants Klaas P.J.M. van
Immunity, Volume 35 Supplemental Information The Costimulatory Molecule CD7 Maintains Clonally Diverse CD8 + T Cell Responses of Low Antigen Affinity to Protect against Viral Variants Klaas P.J.M. van
1 2 3 4 5 6 Figure 4.1: Gel picture showing Generation of HIV-1subtype C codon optimized env expressing recombinant plasmid pvax-1:
 Full-fledged work is in progress towards construction and cloning of codon optimized envelope with subsequent aims towards immunization of mice to study immune responses. 1 2 4 5 6 Figure 4.1: Gel picture
Full-fledged work is in progress towards construction and cloning of codon optimized envelope with subsequent aims towards immunization of mice to study immune responses. 1 2 4 5 6 Figure 4.1: Gel picture
TABLE OF CONTENT. Page ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS. iii ENGLISH ABSTRACT THAI ABSTRACT. vii LIST OF TABLES LIST OF FIGURES. xvi ABBREVIATIONS.
 x TABLE OF CONTENT ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ENGLISH ABSTRACT THAI ABSTRACT LIST OF TABLES LIST OF FIGURES ABBREVIATIONS iii iv vii xv xvi xviii CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION 1.1 Statement of problems 1 1.2 Literature
x TABLE OF CONTENT ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ENGLISH ABSTRACT THAI ABSTRACT LIST OF TABLES LIST OF FIGURES ABBREVIATIONS iii iv vii xv xvi xviii CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION 1.1 Statement of problems 1 1.2 Literature
Detection of T-cell T and their application to vaccine design
 QuickTime and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture Detection of T-cell T epitopes and their application to vaccine design EpiVax Inc. 16 Bassett Street Providence Rhode Island
QuickTime and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture Detection of T-cell T epitopes and their application to vaccine design EpiVax Inc. 16 Bassett Street Providence Rhode Island
ELISA BIO 110 Lab 1. Immunity and Disease
 ELISA BIO 110 Lab 1 Immunity and Disease Introduction The principal role of the mammalian immune response is to contain infectious disease agents. This response is mediated by several cellular and molecular
ELISA BIO 110 Lab 1 Immunity and Disease Introduction The principal role of the mammalian immune response is to contain infectious disease agents. This response is mediated by several cellular and molecular
T Cell Maturation,Activation and Differentiation
 T Cell Maturation,Activation and Differentiation Positive Selection- In thymus, permits survival of only those T cells whose TCRs recognize self- MHC molecules (self-mhc restriction) Negative Selection-
T Cell Maturation,Activation and Differentiation Positive Selection- In thymus, permits survival of only those T cells whose TCRs recognize self- MHC molecules (self-mhc restriction) Negative Selection-
Identification of CD4+ T cell epitopes specific for the breast cancer associated antigen NY-BR-1
 9/8/2015 Identification of CD4+ T cell epitopes specific for the breast cancer associated antigen NY-BR-1 Stefan Eichmüller, PhD GMP & T Cell Therapy Unit, German Cancer Research Center, Heidelberg, Germany
9/8/2015 Identification of CD4+ T cell epitopes specific for the breast cancer associated antigen NY-BR-1 Stefan Eichmüller, PhD GMP & T Cell Therapy Unit, German Cancer Research Center, Heidelberg, Germany
The Body s Defenses CHAPTER 24
 CHAPTER 24 The Body s Defenses PowerPoint Lectures for Essential Biology, Third Edition Neil Campbell, Jane Reece, and Eric Simon Essential Biology with Physiology, Second Edition Neil Campbell, Jane Reece,
CHAPTER 24 The Body s Defenses PowerPoint Lectures for Essential Biology, Third Edition Neil Campbell, Jane Reece, and Eric Simon Essential Biology with Physiology, Second Edition Neil Campbell, Jane Reece,
Final Review. Aptamers. Making Aptamers: SELEX 6/3/2011. sirna and mirna. Central Dogma. RNAi: A translation regulation mechanism.
 Central Dogma Final Review Section Week 10 DNA RNA Protein DNA DNA replication DNA RNA transcription RNA Protein translation **RNA DNA reverse transcription http://bass.bio.uci.edu/~hudel/bs99a/lecture20/lecture1_1.html
Central Dogma Final Review Section Week 10 DNA RNA Protein DNA DNA replication DNA RNA transcription RNA Protein translation **RNA DNA reverse transcription http://bass.bio.uci.edu/~hudel/bs99a/lecture20/lecture1_1.html
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: adoptive_immunotherapy 11/1993 3/2016 3/2017 3/2016 Description of Procedure or Service The spontaneous regression
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: adoptive_immunotherapy 11/1993 3/2016 3/2017 3/2016 Description of Procedure or Service The spontaneous regression
International Beryllium Conference, Montreal, Canada March 10, 2005
 Alternative Lymphocyte Proliferation Tests: BrdU and Flow Cytometry Based Tests International Beryllium Conference, Montreal, Canada March 10, 2005 Tim K. Takaro Department of Environmental and Occupational
Alternative Lymphocyte Proliferation Tests: BrdU and Flow Cytometry Based Tests International Beryllium Conference, Montreal, Canada March 10, 2005 Tim K. Takaro Department of Environmental and Occupational
Immunity and how vaccines work
 1 Introduction Immunity is the ability of the human body to protect itself from infectious disease. The defence mechanisms of the body are complex and include innate (non-specific, non-adaptive) mechanisms
1 Introduction Immunity is the ability of the human body to protect itself from infectious disease. The defence mechanisms of the body are complex and include innate (non-specific, non-adaptive) mechanisms
Chapter 18: Applications of Immunology
 Chapter 18: Applications of Immunology 1. Vaccinations 2. Monoclonal vs Polyclonal Ab 3. Diagnostic Immunology 1. Vaccinations What is Vaccination? A method of inducing artificial immunity by exposing
Chapter 18: Applications of Immunology 1. Vaccinations 2. Monoclonal vs Polyclonal Ab 3. Diagnostic Immunology 1. Vaccinations What is Vaccination? A method of inducing artificial immunity by exposing
Mapping the T-Cell Epitope of the Paraflagellar Rod Protein 3 of Parasitic Hemoflagellate, Trypanosoma Cruzi
 Author Mapping the T-Cell Epitope of the Paraflagellar Rod Protein 3 of Parasitic Hemoflagellate, Trypanosoma Cruzi Zhu Judy Wei Biological Sciences Though she hopes to attend medical school, Judy Wei
Author Mapping the T-Cell Epitope of the Paraflagellar Rod Protein 3 of Parasitic Hemoflagellate, Trypanosoma Cruzi Zhu Judy Wei Biological Sciences Though she hopes to attend medical school, Judy Wei
Specialty Lab and Immunological Testing Services
 Specialty Lab and Immunological Testing Services OVER 30 YEARS OF SPECIALTY LAB EXPERIENCE Precision for Medicine recognizes the critical role that sample testing and handling play in achieving high-quality,
Specialty Lab and Immunological Testing Services OVER 30 YEARS OF SPECIALTY LAB EXPERIENCE Precision for Medicine recognizes the critical role that sample testing and handling play in achieving high-quality,
Generation of EBV-immortalized B cell lines
 UCANU 0014 Version November 01, 2011 Page 1 van 6 Generation of EBVimmortalized B cell lines CMCI (Center for molecular and Cellular Intervention) University Medical Center Utrecht Written by Name Function
UCANU 0014 Version November 01, 2011 Page 1 van 6 Generation of EBVimmortalized B cell lines CMCI (Center for molecular and Cellular Intervention) University Medical Center Utrecht Written by Name Function
DEPARTMENT OF IMMUNOLOGY Chair of Histology and Immunology Medical University of Gdańsk
 DEPARTMENT OF IMMUNOLOGY Chair of Histology and Immunology Medical University of Gdańsk Research group Head: Jolanta Myśliwska, MD, PhD Professor of immunology Joanna Więckiewicz, M. Sc. Dominik Rachoń,
DEPARTMENT OF IMMUNOLOGY Chair of Histology and Immunology Medical University of Gdańsk Research group Head: Jolanta Myśliwska, MD, PhD Professor of immunology Joanna Więckiewicz, M. Sc. Dominik Rachoń,
Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell (PBMC) Manual
 Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell (PBMC) Manual INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZBM0063.04 SHIPPING CONDITIONS Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells, cryopreserved Cryopreserved human peripheral blood mononuclear
Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell (PBMC) Manual INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZBM0063.04 SHIPPING CONDITIONS Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells, cryopreserved Cryopreserved human peripheral blood mononuclear
Principles of Vaccination
 Immunology and Vaccine-Preventable Diseases Immunology is a complicated subject, and a detailed discussion of it is beyond the scope of this text. However, an understanding of the basic function of the
Immunology and Vaccine-Preventable Diseases Immunology is a complicated subject, and a detailed discussion of it is beyond the scope of this text. However, an understanding of the basic function of the
The immune system. Bone marrow. Thymus. Spleen. Bone marrow. NK cell. B-cell. T-cell. Basophil Neutrophil. Eosinophil. Myeloid progenitor
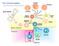 The immune system Basophil Neutrophil Bone marrow Eosinophil Myeloid progenitor Dendritic cell Pluripotent Stem cell Lymphoid progenitor Platelets Bone marrow Thymus NK cell T-cell B-cell Spleen Cancer
The immune system Basophil Neutrophil Bone marrow Eosinophil Myeloid progenitor Dendritic cell Pluripotent Stem cell Lymphoid progenitor Platelets Bone marrow Thymus NK cell T-cell B-cell Spleen Cancer
A white paper for consideration by the NIAID Microbial Sequencing Program
 Hepatitis C Virus Sequencing: Viral evolution, immune recognition and vaccine development. A white paper for consideration by the NIAID Microbial Sequencing Program Todd M. Allen, Ph.D. Assistant Professor
Hepatitis C Virus Sequencing: Viral evolution, immune recognition and vaccine development. A white paper for consideration by the NIAID Microbial Sequencing Program Todd M. Allen, Ph.D. Assistant Professor
SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS
 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS Summary and Conclusions This study has attempted to document the following effects of targeting protein antigens to the macrophage scavenger receptors by maleylation. 1. Modification
SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS Summary and Conclusions This study has attempted to document the following effects of targeting protein antigens to the macrophage scavenger receptors by maleylation. 1. Modification
Basics of Immunology
 Basics of Immunology 2 Basics of Immunology What is the immune system? Biological mechanism for identifying and destroying pathogens within a larger organism. Pathogens: agents that cause disease Bacteria,
Basics of Immunology 2 Basics of Immunology What is the immune system? Biological mechanism for identifying and destroying pathogens within a larger organism. Pathogens: agents that cause disease Bacteria,
1.Gene Synthesis. 2.Peptide & Phospho-P. Assembly PCR. Design & Synthesis. Advantages. Specifications. Advantages
 1.Gene Synthesis Assembly PCR Looking for a cdna for your research but could not fish out the gene through traditional cloning methods or a supplier? Abnova provides a gene synthesis service via assembly
1.Gene Synthesis Assembly PCR Looking for a cdna for your research but could not fish out the gene through traditional cloning methods or a supplier? Abnova provides a gene synthesis service via assembly
PRODUCT INFORMATION SHEET Monoclonal antibodies detecting human antigens
 www.iqproducts.nl PRODUCT INFORMATION SHEET Monoclonal antibodies detecting human antigens IFN- γ PURE [RUO] [REF] IQP-160P s 50 tests FITC [RUO] [REF] IQP-160F s 50 tests R-PE [RUO] [REF] IQP-160R s 50
www.iqproducts.nl PRODUCT INFORMATION SHEET Monoclonal antibodies detecting human antigens IFN- γ PURE [RUO] [REF] IQP-160P s 50 tests FITC [RUO] [REF] IQP-160F s 50 tests R-PE [RUO] [REF] IQP-160R s 50
Human CD4+T Cell Care Manual
 Human CD4+T Cell Care Manual INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZBM0067.02 SHIPPING CONDITIONS Human CD4+T Cells, cryopreserved Cryopreserved human CD4+T cells are shipped on dry ice and should be stored in liquid nitrogen
Human CD4+T Cell Care Manual INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZBM0067.02 SHIPPING CONDITIONS Human CD4+T Cells, cryopreserved Cryopreserved human CD4+T cells are shipped on dry ice and should be stored in liquid nitrogen
Hepatitis C Vaccines: Are we making progress?
 Hepatitis C Vaccines: Are we making progress? Second International Hepatitis Cure and Eradication Meeting. Vancouver November, 2015 Objectives: Review the need for a preventive vaccine in 2015. Identify
Hepatitis C Vaccines: Are we making progress? Second International Hepatitis Cure and Eradication Meeting. Vancouver November, 2015 Objectives: Review the need for a preventive vaccine in 2015. Identify
KMS-Specialist & Customized Biosimilar Service
 KMS-Specialist & Customized Biosimilar Service 1. Polyclonal Antibody Development Service KMS offering a variety of Polyclonal Antibody Services to fit your research and production needs. we develop polyclonal
KMS-Specialist & Customized Biosimilar Service 1. Polyclonal Antibody Development Service KMS offering a variety of Polyclonal Antibody Services to fit your research and production needs. we develop polyclonal
Chapter 6: Antigen-Antibody Interactions
 Chapter 6: Antigen-Antibody Interactions I. Strength of Ag-Ab interactions A. Antibody Affinity - strength of total noncovalent interactions between single Ag-binding site on an Ab and a single epitope
Chapter 6: Antigen-Antibody Interactions I. Strength of Ag-Ab interactions A. Antibody Affinity - strength of total noncovalent interactions between single Ag-binding site on an Ab and a single epitope
B cell activation and Humoral Immunity
 B cell activation and Humoral Immunity Humoral immunity is mediated by secreted antibodies and its physiological function is defense against extracellular microbes (including viruses) and microbial exotoxins.
B cell activation and Humoral Immunity Humoral immunity is mediated by secreted antibodies and its physiological function is defense against extracellular microbes (including viruses) and microbial exotoxins.
The importance of the CD4
 CD4 T Cells Are Required for the Development of Cytotoxic CD8 T Cells During Mycobacterium tuberculosis Infection 1 Natalya V. Serbina, 2 Vanja Lazarevic, and JoAnne L. Flynn 3 The control of acute and
CD4 T Cells Are Required for the Development of Cytotoxic CD8 T Cells During Mycobacterium tuberculosis Infection 1 Natalya V. Serbina, 2 Vanja Lazarevic, and JoAnne L. Flynn 3 The control of acute and
Your partner in immunology
 Your partner in immunology Expertise Expertise Reactivity Reactivity Quality Quality Advice Advice Who are we? Specialist of antibody engineering Covalab is a French biotechnology company, specialised
Your partner in immunology Expertise Expertise Reactivity Reactivity Quality Quality Advice Advice Who are we? Specialist of antibody engineering Covalab is a French biotechnology company, specialised
Autologous Cellular Therapies. Adrian Gee Center for Cell & Gene Therapy Baylor College of Medicine Production Assistance for Cellular Therapy (PACT)
 Autologous Cellular Therapies Adrian Gee Center for Cell & Gene Therapy Baylor College of Medicine Production Assistance for Cellular Therapy (PACT) Autologous Cellular Therapies Definition Advantages
Autologous Cellular Therapies Adrian Gee Center for Cell & Gene Therapy Baylor College of Medicine Production Assistance for Cellular Therapy (PACT) Autologous Cellular Therapies Definition Advantages
Aviva Systems Biology
 Aviva Custom Antibody Service and Price Mouse Monoclonal Antibody Service Package Number Description Package Contents Time Price Customer provides antigen protein $6,174 Monoclonal package1 (From protein
Aviva Custom Antibody Service and Price Mouse Monoclonal Antibody Service Package Number Description Package Contents Time Price Customer provides antigen protein $6,174 Monoclonal package1 (From protein
Recognition of T cell epitopes (Abbas Chapter 6)
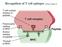 Recognition of T cell epitopes (Abbas Chapter 6) Functions of different APCs (Abbas Chapter 6)!!! Directon Routes of antigen entry (Abbas Chapter 6) Flow of Information Barrier APCs LNs Sequence of Events
Recognition of T cell epitopes (Abbas Chapter 6) Functions of different APCs (Abbas Chapter 6)!!! Directon Routes of antigen entry (Abbas Chapter 6) Flow of Information Barrier APCs LNs Sequence of Events
QuantiFERON TB Gold In Tube Method (QGIT Test) Manufacturer: Cellestis Inc. (USA) a QIAGEN Company
 QuantiFERON TB Gold In Tube Method (QGIT Test) Manufacturer: Cellestis Inc. (USA) a QIAGEN Company P1078 TB APPRISE TB Ante vs. Postpartum Prevention with INH in HIV Seropositive mothers and their Exposed
QuantiFERON TB Gold In Tube Method (QGIT Test) Manufacturer: Cellestis Inc. (USA) a QIAGEN Company P1078 TB APPRISE TB Ante vs. Postpartum Prevention with INH in HIV Seropositive mothers and their Exposed
The murine model of listeriosis has proven to be a powerful
 Role of CD4 T Cell Help and Costimulation in CD8 T Cell Responses During Listeria monocytogenes Infection 1 Devon J. Shedlock, 2 * Jason K. Whitmire, 2,3 Joyce Tan, 4 Andrew S. MacDonald, Rafi Ahmed, and
Role of CD4 T Cell Help and Costimulation in CD8 T Cell Responses During Listeria monocytogenes Infection 1 Devon J. Shedlock, 2 * Jason K. Whitmire, 2,3 Joyce Tan, 4 Andrew S. MacDonald, Rafi Ahmed, and
CDC TB Testing Guidelines and Recent Literature Update
 Pocket Guide QuantiFERON -TB Gold CDC TB Testing Guidelines and Recent Literature Update Using IGRAs for TB screening in your patients June 2010 A full copy of the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Pocket Guide QuantiFERON -TB Gold CDC TB Testing Guidelines and Recent Literature Update Using IGRAs for TB screening in your patients June 2010 A full copy of the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Chapter 3.2» Custom Monoclonal
 198 3 3.2 Custom Monoclonal 199 Mouse monoclonal antibody development Chapter 3.2» Custom Monoclonal 200 In vitro monoclonals expression service 201 Mouse monoclonal antibody additional services 202 Magnetic
198 3 3.2 Custom Monoclonal 199 Mouse monoclonal antibody development Chapter 3.2» Custom Monoclonal 200 In vitro monoclonals expression service 201 Mouse monoclonal antibody additional services 202 Magnetic
MAB Solut. MABSolys Génopole Campus 1 5 rue Henri Desbruères 91030 Evry Cedex. www.mabsolut.com. is involved at each stage of your project
 Mabsolus-2015-UK:Mise en page 1 03/07/15 14:13 Page1 Services provider Department of MABSolys from conception to validation MAB Solut is involved at each stage of your project Creation of antibodies Production
Mabsolus-2015-UK:Mise en page 1 03/07/15 14:13 Page1 Services provider Department of MABSolys from conception to validation MAB Solut is involved at each stage of your project Creation of antibodies Production
TRANSGENE SA, FRANCE 2. INSTITUT PASTEUR, FRANCE On behalf. AFEF 2013, Lille 02 nd October 2013
 A MULTIVALENT ADENOVIRUS-BASED IMMUNOTHERAPEUTIC FOR TREATMENT OF CHRONIC HEPATITIS B INDUCES BROAD, ROBUST AND POLYFUNCTIONAL T CELLS IN NAIVE MICE AND EXERT AN EARLY ANTIVIRAL EFFECT IN HBV TOLERANT
A MULTIVALENT ADENOVIRUS-BASED IMMUNOTHERAPEUTIC FOR TREATMENT OF CHRONIC HEPATITIS B INDUCES BROAD, ROBUST AND POLYFUNCTIONAL T CELLS IN NAIVE MICE AND EXERT AN EARLY ANTIVIRAL EFFECT IN HBV TOLERANT
CHAPTER 8 IMMUNOLOGICAL IMPLICATIONS OF PEPTIDE CARBOHYDRATE MIMICRY
 CHAPTER 8 IMMUNOLOGICAL IMPLICATIONS OF PEPTIDE CARBOHYDRATE MIMICRY Immunological Implications of Peptide-Carbohydrate Mimicry 8.1 Introduction The two chemically dissimilar molecules, a peptide (12mer)
CHAPTER 8 IMMUNOLOGICAL IMPLICATIONS OF PEPTIDE CARBOHYDRATE MIMICRY Immunological Implications of Peptide-Carbohydrate Mimicry 8.1 Introduction The two chemically dissimilar molecules, a peptide (12mer)
Custom Antibody Services
 Custom Antibody Services Custom service offerings DNA sequence Plasmid Peptide Structure Protein Peptide Small molecule Cells Spleen Lymphocytes Antigen Preparation Immunization Fusion & Subcloning Expansion
Custom Antibody Services Custom service offerings DNA sequence Plasmid Peptide Structure Protein Peptide Small molecule Cells Spleen Lymphocytes Antigen Preparation Immunization Fusion & Subcloning Expansion
TOWARDS AN HIV VACCINE
 why is it so hard to make an HIV vaccine and where are we now? Neal Nathanson, MD Emeritus Professor Department of Microbiology University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine 1 Estimated number of persons
why is it so hard to make an HIV vaccine and where are we now? Neal Nathanson, MD Emeritus Professor Department of Microbiology University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine 1 Estimated number of persons
PperCHIP. High-Content Peptide Microarrays. Epitope Mapping & Serum Profiling Services
 PepperChip High-Content Peptide Microarrays PepperMap Epitope Mapping & Serum Profiling Services PperCHIP access to custom and dard peptide microarrays up to 9,000 features per in a uniquely flexible and
PepperChip High-Content Peptide Microarrays PepperMap Epitope Mapping & Serum Profiling Services PperCHIP access to custom and dard peptide microarrays up to 9,000 features per in a uniquely flexible and
TG1050, A NOVEL IMMUNOTHERAPEUTIC TO TREAT CHRONIC HEPATITIS B, CAN CONTROL HBsAg AND PROVOKE HBsAg SEROCONVERSION IN HBV-PERSISTENT MOUSE MODELS
 TG1050, A NOVEL IMMUNOTHERAPEUTIC TO TREAT CHRONIC HEPATITIS B, CAN CONTROL HBsAg AND PROVOKE HBsAg SEROCONVERSION IN HBV-PERSISTENT MOUSE MODELS Karine Lélu 1, Alexei Evlachev 1, Roland Kratzer 1, Sarah
TG1050, A NOVEL IMMUNOTHERAPEUTIC TO TREAT CHRONIC HEPATITIS B, CAN CONTROL HBsAg AND PROVOKE HBsAg SEROCONVERSION IN HBV-PERSISTENT MOUSE MODELS Karine Lélu 1, Alexei Evlachev 1, Roland Kratzer 1, Sarah
The Immune System: A Tutorial
 The Immune System: A Tutorial Modeling and Simulation of Biological Systems 21-366B Shlomo Ta asan Images taken from http://rex.nci.nih.gov/behindthenews/uis/uisframe.htm http://copewithcytokines.de/ The
The Immune System: A Tutorial Modeling and Simulation of Biological Systems 21-366B Shlomo Ta asan Images taken from http://rex.nci.nih.gov/behindthenews/uis/uisframe.htm http://copewithcytokines.de/ The
Chapter 3. Immunity and how vaccines work
 Chapter 3 Immunity and how vaccines work 3.1 Objectives: To understand and describe the immune system and how vaccines produce immunity To understand the differences between Passive and Active immunity
Chapter 3 Immunity and how vaccines work 3.1 Objectives: To understand and describe the immune system and how vaccines produce immunity To understand the differences between Passive and Active immunity
ANIMALS FORM & FUNCTION BODY DEFENSES NONSPECIFIC DEFENSES PHYSICAL BARRIERS PHAGOCYTES. Animals Form & Function Activity #4 page 1
 AP BIOLOGY ANIMALS FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #4 NAME DATE HOUR BODY DEFENSES NONSPECIFIC DEFENSES PHYSICAL BARRIERS PHAGOCYTES Animals Form & Function Activity #4 page 1 INFLAMMATORY RESPONSE ANTIMICROBIAL
AP BIOLOGY ANIMALS FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #4 NAME DATE HOUR BODY DEFENSES NONSPECIFIC DEFENSES PHYSICAL BARRIERS PHAGOCYTES Animals Form & Function Activity #4 page 1 INFLAMMATORY RESPONSE ANTIMICROBIAL
Reconsideration Code 86386. Reconsideration Code Description Nuclear Matrix Protein 22 (NMP22), qualitative
 Calendar Year 2013 Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) New and Reconsidered Clinical Laboratory Fee Schedule (CLFS) Test Codes And Final Payment Determinations Reconsideration Code 86386 Reconsideration
Calendar Year 2013 Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) New and Reconsidered Clinical Laboratory Fee Schedule (CLFS) Test Codes And Final Payment Determinations Reconsideration Code 86386 Reconsideration
The public health risk of influenza in pigs recent insights, key knowledge gaps
 The public health risk of influenza in pigs recent insights, key knowledge gaps Prof. Kristien Van Reeth Laboratory of Virology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Ghent University, Belgium H1N1, H3N2 and
The public health risk of influenza in pigs recent insights, key knowledge gaps Prof. Kristien Van Reeth Laboratory of Virology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Ghent University, Belgium H1N1, H3N2 and
CFSE Cell Division Assay Kit
 CFSE Cell Division Assay Kit Item No. 10009853 Customer Service 800.364.9897 * Technical Support 888.526.5351 www.caymanchem.com TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 3 Materials Supplied 4 Precautions
CFSE Cell Division Assay Kit Item No. 10009853 Customer Service 800.364.9897 * Technical Support 888.526.5351 www.caymanchem.com TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 3 Materials Supplied 4 Precautions
HuCAL Custom Monoclonal Antibodies
 HuCAL Custom Monoclonal HuCAL Custom Monoclonal Antibodies Highly Specific, Recombinant Antibodies in 8 Weeks Highly Specific Monoclonal Antibodies in Just 8 Weeks HuCAL PLATINUM (Human Combinatorial Antibody
HuCAL Custom Monoclonal HuCAL Custom Monoclonal Antibodies Highly Specific, Recombinant Antibodies in 8 Weeks Highly Specific Monoclonal Antibodies in Just 8 Weeks HuCAL PLATINUM (Human Combinatorial Antibody
With a staggering one billion individuals worldwide
 Immunology and Microbiology A Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 Human Asymptomatic CD8 þ T-Cell Epitopes-Based Vaccine Protects Against Ocular Herpes in a Humanized HLA Transgenic Rabbit Model Ruchi Srivastava,
Immunology and Microbiology A Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 Human Asymptomatic CD8 þ T-Cell Epitopes-Based Vaccine Protects Against Ocular Herpes in a Humanized HLA Transgenic Rabbit Model Ruchi Srivastava,
Cellular Implants as mini-factories for the production of therapeutic antibodies against Altzheimer s disease. rapport research week Jonas Schiffmann
 Cellular Implants as mini-factories for the production of therapeutic antibodies against Altzheimer s disease rapport research week Jonas Schiffmann Supported by Aurélien Lathuilière, Bernard Schneider
Cellular Implants as mini-factories for the production of therapeutic antibodies against Altzheimer s disease rapport research week Jonas Schiffmann Supported by Aurélien Lathuilière, Bernard Schneider
Autoimmunity and immunemediated. FOCiS. Lecture outline
 1 Autoimmunity and immunemediated inflammatory diseases Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails Genetics of autoimmune diseases Therapeutic
1 Autoimmunity and immunemediated inflammatory diseases Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails Genetics of autoimmune diseases Therapeutic
CD3/TCR stimulation and surface detection Determination of specificity of intracellular detection of IL-7Rα by flow cytometry
 CD3/TCR stimulation and surface detection Stimulation of HPB-ALL cells with the anti-cd3 monoclonal antibody OKT3 was performed as described 3. In brief, antibody-coated plates were prepared by incubating
CD3/TCR stimulation and surface detection Stimulation of HPB-ALL cells with the anti-cd3 monoclonal antibody OKT3 was performed as described 3. In brief, antibody-coated plates were prepared by incubating
The Evaluation of Interferon-beta Levels in HPV-positive Cervical Cancer Cell Lines
 The Evaluation of Interferon-beta Levels in HPV-positive Cervical Cancer Cell Lines Olivia M. Ford and Jennifer T. Thomas, Ph.D. Human Papillomavirus (HPV) is the most common viral sexually transmitted
The Evaluation of Interferon-beta Levels in HPV-positive Cervical Cancer Cell Lines Olivia M. Ford and Jennifer T. Thomas, Ph.D. Human Papillomavirus (HPV) is the most common viral sexually transmitted
Introduction to Flow Cytometry
 Outline Introduction to Flow Cytometry Basic Concept of Flow Cytometry Introduction to Instrument Subsystems Daisy Kuo Assistant Product Manager E-mail: daisy_kuo@bd.com BDBiosciences Application Examples
Outline Introduction to Flow Cytometry Basic Concept of Flow Cytometry Introduction to Instrument Subsystems Daisy Kuo Assistant Product Manager E-mail: daisy_kuo@bd.com BDBiosciences Application Examples
Why study T cell epitopes in allergic disease?
 Why study T cell epitopes in allergic disease? T cells contribute to pathology directly and indirectly through modulation of immune responses Involvement in SIT Epitopes as a tool to monitor disease and
Why study T cell epitopes in allergic disease? T cells contribute to pathology directly and indirectly through modulation of immune responses Involvement in SIT Epitopes as a tool to monitor disease and
Characterization of monoclonal antibody epitope specificity using Biacore s SPR technology
 A P P L I C A T I O N N O T E 1 Characterization of monoclonal antibody epitope specificity using Biacore s SPR technology Abstract Biacore s SPR technology based on surface plasmon resonance technology
A P P L I C A T I O N N O T E 1 Characterization of monoclonal antibody epitope specificity using Biacore s SPR technology Abstract Biacore s SPR technology based on surface plasmon resonance technology
HuCAL Custom Monoclonal Antibodies
 HuCAL Custom Monoclonal Antibodies Highly Specific Monoclonal Antibodies in just 8 Weeks PROVEN, HIGHLY SPECIFIC, HIGH AFFINITY ANTIBODIES IN 8 WEEKS WITHOUT HuCAL PLATINUM IMMUNIZATION (Human Combinatorial
HuCAL Custom Monoclonal Antibodies Highly Specific Monoclonal Antibodies in just 8 Weeks PROVEN, HIGHLY SPECIFIC, HIGH AFFINITY ANTIBODIES IN 8 WEEKS WITHOUT HuCAL PLATINUM IMMUNIZATION (Human Combinatorial
Hapten - a small molecule that is antigenic but not (by itself) immunogenic.
 Chapter 3. Antigens Terminology: Antigen: Substances that can be recognized by the surface antibody (B cells) or by the TCR (T cells) when associated with MHC molecules Immunogenicity VS Antigenicity:
Chapter 3. Antigens Terminology: Antigen: Substances that can be recognized by the surface antibody (B cells) or by the TCR (T cells) when associated with MHC molecules Immunogenicity VS Antigenicity:
Principles of Vaccination
 Immunology and Vaccine-Preventable Diseases Immunology is a complicated subject, and a detailed discussion of it is beyond the scope of this text. However, an understanding of the basic function of the
Immunology and Vaccine-Preventable Diseases Immunology is a complicated subject, and a detailed discussion of it is beyond the scope of this text. However, an understanding of the basic function of the
Core Topic 2. The immune system and how vaccines work
 Core Topic 2 The immune system and how vaccines work Learning outcome To be able to describe in outline the immune system and how vaccines work in individuals and populations Learning objectives Explain
Core Topic 2 The immune system and how vaccines work Learning outcome To be able to describe in outline the immune system and how vaccines work in individuals and populations Learning objectives Explain
Curriculum Vitae. Peter Graves Livingston M.D. EDUCATION: CERTIFICATIONS and HONORS:
 Curriculum Vitae Peter Graves Livingston M.D. Birthplace: Boston, Massachusetts Medical License: Florida ME 102736 Work Address: Macula and Diabetic Eye Center, LLC 4916 26 th Street West, Suite 200 Bradenton,
Curriculum Vitae Peter Graves Livingston M.D. Birthplace: Boston, Massachusetts Medical License: Florida ME 102736 Work Address: Macula and Diabetic Eye Center, LLC 4916 26 th Street West, Suite 200 Bradenton,
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE
 Title: Lymphocyte Proliferation Assay (LPA) Using 3 H- Thymidine Incorporation Assay Core Name: Lloyd Mayer, Mount Sinai Medical Center Effective Date: 02/16/2012 Trial Number: ITN047AI SOP # ITN2800 SOP
Title: Lymphocyte Proliferation Assay (LPA) Using 3 H- Thymidine Incorporation Assay Core Name: Lloyd Mayer, Mount Sinai Medical Center Effective Date: 02/16/2012 Trial Number: ITN047AI SOP # ITN2800 SOP
BVIG/SBMI Meeting 2007. Bart N. Lambrecht, MD, PhD. Department of Respiratory Diseases University Hospital Gent, Belgium
 Dendritic cells : from bench to bedside BVIG/SBMI Meeting 2007 Bart N. Lambrecht, MD, PhD Department of Respiratory Diseases University Hospital Gent, Belgium Outline Role of DCs in the immune system Role
Dendritic cells : from bench to bedside BVIG/SBMI Meeting 2007 Bart N. Lambrecht, MD, PhD Department of Respiratory Diseases University Hospital Gent, Belgium Outline Role of DCs in the immune system Role
New HLA class I epitopes defined by murine monoclonal antibodies
 Human Immunology 71 (2010) 456 461 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect New HLA class I epitopes defined by murine monoclonal antibodies Nadim El-Awar a, *, Paul I. Terasaki b, Anh Nguyen a, Mamie
Human Immunology 71 (2010) 456 461 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect New HLA class I epitopes defined by murine monoclonal antibodies Nadim El-Awar a, *, Paul I. Terasaki b, Anh Nguyen a, Mamie
SCANTIBODIES Laboratory, Inc. Contract Monoclonal Antibody Production
 A Technical Publication of SCANTIBODIES Laboratory, Inc. Volume 1 Number 4 9336 Abraham Way Santee, CA 92071 USA (619) 258-9300 fax (619) 258-9366 www.scantibodies.com SCANTIBODIES Laboratory, Inc. Contract
A Technical Publication of SCANTIBODIES Laboratory, Inc. Volume 1 Number 4 9336 Abraham Way Santee, CA 92071 USA (619) 258-9300 fax (619) 258-9366 www.scantibodies.com SCANTIBODIES Laboratory, Inc. Contract
B Cells and Antibodies
 B Cells and Antibodies Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School Lecture outline Functions of antibodies B cell activation; the role of helper T cells in antibody production
B Cells and Antibodies Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School Lecture outline Functions of antibodies B cell activation; the role of helper T cells in antibody production
Lisa Y. Armitige, MD, PhD has the following disclosures to make:
 Interferon Gamma Release Assays (IGRAs) Lisa Y. Armitige, MD, PhD May 13, 2015 TB for Pulmonologist Phoenix, AZ March 13, 2015 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Lisa Y. Armitige, MD, PhD has the following
Interferon Gamma Release Assays (IGRAs) Lisa Y. Armitige, MD, PhD May 13, 2015 TB for Pulmonologist Phoenix, AZ March 13, 2015 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Lisa Y. Armitige, MD, PhD has the following
Rheumatoid arthritis: an overview. Christine Pham MD
 Rheumatoid arthritis: an overview Christine Pham MD RA prevalence Chronic inflammatory disease affecting approximately 0.5 1% of the general population Prevalence is higher in North America (approaching
Rheumatoid arthritis: an overview Christine Pham MD RA prevalence Chronic inflammatory disease affecting approximately 0.5 1% of the general population Prevalence is higher in North America (approaching
Immunology and immunotherapy in allergic disease
 Immunology and immunotherapy in allergic disease Jing Shen, MD Faculty Advisor: Matthew Ryan, MD The University of Texas Medical Branch Department of Otolaryngology Grand Rounds Presentation February 2005
Immunology and immunotherapy in allergic disease Jing Shen, MD Faculty Advisor: Matthew Ryan, MD The University of Texas Medical Branch Department of Otolaryngology Grand Rounds Presentation February 2005
Human adenoviruses (HAdV)
 Adenovirus-Specific CD4 T Cell Clones Recognizing Endogenous Antigen Inhibit Viral Replication In Vitro through Cognate Interaction 1 Bianca Heemskerk, 2 * Tamara van Vreeswijk,* Louise A. Veltrop-Duits,*
Adenovirus-Specific CD4 T Cell Clones Recognizing Endogenous Antigen Inhibit Viral Replication In Vitro through Cognate Interaction 1 Bianca Heemskerk, 2 * Tamara van Vreeswijk,* Louise A. Veltrop-Duits,*
