Tancer mmunologyand mmunotherapy Springer-Verlag I982
|
|
|
- Jane Parrish
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cancer Immunol Immunother (1982) 13: Tancer mmunologyand mmunotherapy Springer-Verlag I982 Heterogeneity of Human Melanoma-Associated Antigens Defined by Monoclonal Antibodies and Conventional Xenoantisera Barry S. Wilson*, Neil E. Kay**, Kohzoh!mai***, and Soldano Ferrone Department of Pathology and Surgery, College of Physicians und Surgeons, Columbia University, 630 W. 168th Street, New York, NY 10032, USA Summary. Immunochemical analysis of cultured human melanoma cell detergent extracts and spent culture medium with conventional xenoantisera and monoclonal antibodies identified four types of 94,000 (94K) dalton molecules and two types of high-molecular-weight melanoma-associated antigens by the following characteristics: (1) association with other components, (2) mobility in SDS-PAGE under reducing and nonreducing conditions, (3) antigenicity, and (4) presence in spent culture medium. Conventional xenoantisera were found to contain antibody populations to antigenically distinct structures, some of which have similar apparent molecular weights. Immunodepletion studies showed that the antigenic determinant detected by the monoclonai antibody S to a high-molecular-weight melanoma-associated antigen was expressed on a subpopulation of the antigens defined by the conventional xenoantiserum #8995. These data prove that antibodies reactive with antigens of similar molecular weight cannot be assumed to identify the same structures, and indicate.that tumor-associated antigens may be heterogeneous in the expression of antigenic determinants defined by monoclonal antibodies. Introduction A number of tumor-associated antigens have been identified in human melanoma cells with both conventional xenoantisera [for review, see 8] and monoclonal antibodies [4, 5, 10, 12, 13, 20, 22-24]. In many cases antigens of similar molecular weight and subunit structure have been described. Thus, Dippold et al. [5], Woodbury et al. [23], and Wilson et al. [22], using monoclonal antibodies, and Galloway et al. [9], using conventional xenoantisera, have described a single chain melanoma-associated antigen (MAA) having a molecular weight in the range 94,000-97,000 (94K-97K) daltons. Furthermore, Mitchell et al. [15], using a monoclonal antibody Reprint requests should be addressed to S. Ferrone * Present address: Department of Pathology, University of Michigan Medical School, Ann Arbor, Michigan ** Visiting investigator from the Veterans Administration Hospital, Minneapolis, Minnesota *** Visiting investigator from Sapporo Medical College (Japan). Abbreviations used: MAA, melanoma-associated antigen; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; NP40, nonidet P40; MoAb, monoclonal antibody; SDS-PAGE, sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis; 2-ME, 2-mercaptoethanol have described a 95K dalton MAA, which is associated with three additional components having molecular weights of 116K, 29K, and 26K daltons, while Wilson et al. [20, 22], also using a monoclonal antibody, have identified a 94K dalton glycopolypeptide which is associated with 75K, 70K, and 25K dalton structures. Also, Galloway et al. [9], using conventional xenoantisera, described a 240K dalton spent medium MAA and, more recently, we characterized monoclonal antibodies immunoprecipitating a similar molecular weight glycopolypeptide from cultured melanoma cells [16, 20]. Whether these various antibodies are recognizing the same or different antigenic structures and whether a determinant defined by a monoclonal antibody is expressed on all the molecules comprising a given type of MAA are areas of investigation critical to future progress in the field of tumor-associated antigens. The need for this information is felt among investigators in the melanoma field, as indicated by the organization of workshops to exchange monoclonal antibodies and compare their specificity and by a recent paper by Brown et al. [3] who, through immunodepletion experiments, have shown that the 97K dalton glycoprotein recognized by their antibody is identical to the 95K dalton glycoprotein identified by the monoclonal antibody of Dippold et al. [5]. In this paper we have addressed ourselves to these problems by using xenoantisera and monoclonal antibodies to determine the antigenic relationship among structures with a similar apparent molecular weight and we have assessed whether the determinants identified by the monoclonal antibodies are expressed by all the molecules of a given type of MAA. We have focused on 94K dalton and high-molecular-weight antigens synthesized by cultured melanoma cells, since the former has been described in several reports and the latter appears to be restricted to melanoma [16, 20, 22]. Materials and Methods Cultured Human Cell Lines. Human cells in long-term culture were maintained in RPMI 1640 medium containing 10% calf serum. The growth characteristics and the histocompatibility antigenic profiles of the various cells used are reported elsewhere [20]. A confluent monolayer of melanoma cells (BwV) in a T-25 flask (Falcon Plastics, Cockeysville, MD) was intrinsically radiolabelled with 2 mci 3H-glucosamine D-[6-3H(N)], 30 mci/mmole (New England Nuclear, Boston, MA) according to the method described by Duksin and Bornstein [6]. The medium was removed and the monolayer was extensively washed with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) I'}qM)-71](FII~91OOl II(I(IKOI~ (11 9fl
2 70 before addition of 2 ml 0.5% Nonidet P-40 (NP-40) detergent in PBS containing 10 ~M of the proteolytic inhibitor, phenylmethylsulfonylfiuoride. The resulting extract was cleared by centrifugation at 7,000 g and stored at -20 C. Conventional Antisera. Antiserum #8986 was from a rabbit immunized with somatic cell hybrids derived from the fusion of human melanoma cells with murine fibroblasts [11]; following absorption with cultured lymphoid cells this xenoantiserum reacted with both melanoma and carcinoma cells in binding assays. The xenoantiserum #8995 to a high molecular weight MAA was produced by weekly injections of a 3 M KC1 extract from cultured human melanoma cells (M21) which had been bound to lentil lectin Sepharose [9]; following absorption with cultured lymphoid cells this xenoantiserum reacts with melanoma cells but does not react with carcinoma cells. The xenoantiserum #8823 was from a rabbit immunized with human Ia-like antigens bound to an immunoadsorbent formed by reacting an NP40 extract of cultured B lymphoid cells Raji with Staphylococcus aureus Cowan I strain bacteria loaded with antibodies from a rabbit anti-daudi cell xenoantiserum; the antiserum had been absorbed with cultured human T cells (Molt-4) prior to reaction with the bacteria [19]. This xenoantiserum (#8823) specifically reacted with Ia-like antigen-beating cells in serological assays. A xenoantiserum to human plasma fibronectin was prepared according to the method of Engvall and Ruoslahti [7]. MonoclonaI Antibodies (MoAb). The MoAbs S, S, and S, all IgG2a, were secreted by hybridomas constructed with the murine myeloma cells Sp 2/0-Ag 14 and splenocytes from BALB/c mice immunized with cultured human melanoma cells. Each hybridoma has been subcloned at least twice and has been propagated in vitro and in vivo. The MoAb S specifically reacts with nevi, melanoma, and some skin cell carcinomas, while the MoAb S reacts with both melanomas and various carcinomas [20, 22]. The MoAb S identifies an antigen present in the cytoplasm of a large variety of normal and malignant cells [20, 22]. The method of preparation and the serological and immunochemical characterization of the specificity of each monoclonal antibody have been described elsewhere [12, 16, 20, 22]. Indirect Immunoprecipitation and Sodium DodecyI Sulfate Polyacrylamide Gel EIectrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). Indirect immunoprecipitation was performed as described previously [1], except that protein A-Sepharose-4B was used in place of formalin-fixed bacteria, and pre-clearing of the NP-40 detergent cell extract was not necessary. For immunodepletion experiments, a 3H-glucosamine-labelled antigen preparation (300 ~tl) was reacted three successive times for 2 h at 4 C with 30 ~tl protein A-Sepharose 4B coupled with either normal IgG (negative control depletion) or xenoantibodies. The remaining unreactive antigens were then separated into equal aliquots and tested for reactivity with the same antibody as was used for depletion (to insure its completeness) and with other antibodies of interest. SDS-PAGE was performed in 80 x 1.5 mrn slab gels containing 7.5% polyacrylamide and the SDS buffer system of Laemmli [14]. The gels containing 3H-glucosamine-labelled antigens were processed for fluorography as described by Bonner and Laskey [2]. Human plasma fibronectin (220K), rabbit phosporylase a (94,000), bovine serum albumin (68,000), ovalbumin (44,000), carbonic anhydrase (29,000), and whale myoglobin (17,000) were used as molecular weight standards. Results Identification of a Family of AntigenicaUy Distinct 94K Dalton Molecules Synthesized and Shed by Melanoma Cells The MoAb S, S and the polyclonal xenoantisera #8823 and #8986 all immunoprecipitated structures which when electrophoresed under reducing conditions gave apparent molecular weights of 94K (Fig. 1). That these 94K dalton structures may be different is suggested by the fact that the MoAb S immunoprecipitates a 75K, a 70K, and a 25K dalton structure in addition to the 94K dalton molecule, and the 94K dalton molecule detected by MoAb S exhibits a much broader molecular weight heterogeneity than does the 94K dalton molecules identified by the other antibody reagents. Furthermore, SDS-PAGE under nonreducing conditions showed that the 94K dalton molecules detected by the xenoantiserum #8823 exhibited a decrease in apparent molecular weight to 82K daltons (Fig. 1), while the structures identified by MoAbs S, S and xenoantiserum #8986 showed a decrease in apparent molecular weight to 86K daltons. Interestingly, the 94K dalton structure identified by xenoantiserum #8986 resolves into two molecules under nonreducing conditions, one being similar to the type detected by the xenoantiserum #8823 and the other to the type detected by the MoAb S. This latter conclusion is consistent with the small amounts of the 75K and 70K dalton components immunoprecipitated by the xenoantiserum #8986. Additional evidence that melanoma cells synthesize three different 94K dalton molecules was obtained from sequential immunodepletion studies. A 3H-glucosamine-labelled NP40 melanoma Fig. 1. SDS-PAGE analysis of human melanoma cell-derived 94K dalton molecules defined by monoclonal antibodies and conventional xenoantisera. A 3H-glucosamine-labelled BwV melanoma cell NP40 extract was immunoprecipitated with antibodies bound to Sepharose 4B, after which the eluted antigens were boiled in the presence or absence of 2-mercaptoethanol and then subjected to SDS-PAGE
3 71 cell extract exhaustively depleted of all the 94K dalton molecules reactive with the MoAb S still contained the 94K dalton molecules detected with Mc,Ab S and with xenoantisera #8823 and #8986 (Fig. 2); conversely, depletion of a similar radiolabelled melanoma cell extract with the MoAb S did not effect the 94K dalton structures detectable by MoAb S and by the xenoantiserum #8823 and #8986 (data not shown). The xenoantisera were not used for immunodepleting the labelled cell extracts, since these reagents are only operationally specific and may contain small amounts of antibodies to all the various 94K dalton molecules, resulting in a false interpretation of antigenic similarity. Immunoprecipitation of the 3H-glucosamine-labelled spent culture medium from melanoma cells with the various antibodies to the 94K dalton structures was performed to determine whether these structures are shed by melanoma cells (Fig. 3). The MoAb S occasionally detected a small amount of 94K component in the spent medium of cultured melanoma cells, the xenoantiserum #8823 reacted with fibronectin while the MoAb and the xenoantiserum #8986 immunoprecipitated a major 94K and a minor 72K dalton structure. Immunodepletion experiments showed that the MoAb and the xenoantiserum #8986 each reacts with the same population of 94K dalton molecules present in the spent medium of 3H-glucosamine-labelled melanoma cells (Fig. 4). It should be noted that the minor 72K dalton structure detected by MoAb S and xenoantiserum #8986 is not easily identified in some melanoma cell lines, such as Colo 38 and M21. Furthermore, examination of unfractioned 3H-glu- cosamine spent media under reducing and nonreducing conditions revealed a fourth 94K dalton structure previously undetected (Fig. 3), which exhibits an increased apparent molecular weight under nonreducing conditions, suggesting that in its native state it is disulfde-linked to a small-molecular-weight polypeptide. Identification of Antigenically Distinct High-Molecular-Weight Melanoma-Associated Antigens Synthesized and Shed by Melanoma Cells The monoclonal antibodies S and the xenoantiserum #8995 both immunoprecipitate two components from 3H-glucosamine-labelled melanoma cells BwV (Fig. 5). One component at 280K daltons exhibits a slightly higher apparent molecular weight than melanoma BwV fibronectin, while the other structure is very large and can barely penetrate the top of the gel. The molecular weight of the latter component will be referred to as > 440K daltons (nonreduced human plasma fibronectin) until appropriate molecular weight determinations can be done. The MoAb S is unable to bind all the 280K and > 440K dalton molecules reacting with the xenoantisera #8995, since the latter can still immunoprecipitate the high-molecular-weight structures from a cell extract completely depleted of such molecules reactive with the monoclonal antibody (Fig. 6). These data indicate that the antigenic determinant detected by the MoAb S is not present on all the molecules comprising the 280K and > 440K dalton high-molecular-weight MAA system. Fig. 2. Sequential immunodepletion analysis of 94K dalton molecules synthesized by melanoma cells. A 3H-glucosamine-labelled BwV melanoma cell NP40 extract was exhaustively immunodepleted with normal human IgG Sepharose 4B or Sepharose 4B loaded with MoAb S. The supernatant was immunoprecipil~ated with xenoantibodies and then subjected to SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions (2% 2-mercaptoethanol) Fig. 3. SDS-PAGE analysis of 94K dalton molecules shed by cultured human melanoma ceils. Spent culture medium from 3H-glucosamine-labelled BwV melanoma cells was immunoprecipitated with xenoantibodies, after which the eluted antigens were boiled in the presence or absence of 2-mercaptoethanol and then analyzed by SDS-PAGE. Unfractionated 3H-glucosamine spent culture medium was from BwV melanoma ceils.
4 72 When spent medium of 3H-glucosamine-labelled cultured melanoma cells is used as an antigen source, the MoAb S reacts with a very large structure seen at the top of the gel (> 440K), while the xenoantiserum #8995 reacts with a component of approximately 300K daltons (Fig. 5). Even though the xenoantiserum detects the same high-molecular-weight cellular antigen identified by the monoclonal antibody, a > 440K dalton molecule was not immunoprecipirated from the spent culture medium by xenoantiserum #8995, because the amount of labelled antigens used and the exposure time in fluorography were not sufficient to detect this component. Althouth we have been unable to repeat this experiment with the appropriate conditions because the xenoantiserum #8995 is now unavailable, we have seen that other xenoantisera which immunoprecipitate the 280K and > 440K dalton cellular structures will also identify the > 440K dalton media molecule under the appropriate conditions. Fig. 4. Distribution of the antigenic determinant detected by MoAb S on 94K dalton molecules detected with the xenoantiserum #8986. A 3H-glucosamine-labelled preparation of BwV melanoma spent culture medium was exhaustively immunodepleted by sequential reactions with normal human IgG Sepharose 4B or xenoantibodies bound to Sepharose 4B. The remaining labelled antigens were immunoprecipitated by xenoantibodies bound to Sepharose 4B, and then subjected to SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions Fig. 6. Distribution of the antigenic determinant detected by MoAb S on the high-molecular-weight antigens detected by xenoantiserum #8995. A 3H-glucosamine-labelled BwV melanoma cell NP40 extract was exhaustively immunodepleted by sequential reaction with normal human IgG Sepharose 4B or xenoantibodies bound to Sepharose 4B. The remaining labelled antigens were irnmunoprecipirated by xenoantibodies bound to Sepharose 4B and then subjected to SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions -~ Fig. 5. SDS-PAGE analysis with the monoclonal antibody S and with the conventional xenoantiserum #8985 of high-molecular-weight MAA synthesized and shed by melanoma cells. An NP40 extract (first and second lane from the left) or the spent culture medium (third, fourth and fifth lane) of 3H-glucosamine-labelled BwV melanoma ceils was immunoprecipitated with the insolubilized xenoantibodies, after which the eluted antigens were boiled in the presence of 2-mercaptoethanol and analyzed by SDS-PAGE
5 73 Discussion Immunochemical analysis of human melanoma cells with conventional xenoantisera and monoclonal xenoantibodies has identified several antigenically distinct structures that have similar apparent molecular weights. Four types of 94K dalton molecules and two types of high-molecular-weight antigens were identified by the following characteristics: (1) association with other components, (2) mobility in SDS-PAGE under reducing and nonreducing conditions, (3) antigenicity, and (4) presence in spent culture media. The lvloab S reacts with a single 94K dalton molecule present on the plasma membrane and inconsistently found in spent media, while the MoAb and the xenoantiserum #8986 immunoprecipitate cellular 75K, 70K, and 25K dalton components in addition to a major 94K dalton and a minor 72K dalton structure which are readily shed into spent culture medium. Immunodepletion studies showed that the spent media 94K dalton molecule detected by MoAb S is the same structure as was identified with conventional xenoantisera and already described in a previous study [9]. The spent media 72K dalton molecule was not identified in the previous study since it is readily detectable in media from only some melanoma cell lines, which were not included in the earlier study. The xenoantiserum #8823 reacts with a cellular 94K dalton molecule distinct from the ones detected by our monoclonal antibodies, while a fourth 94K dalton molecule was detected in spent culture medium and was probably disulfide-bridged in its native state with a small-molecular-weight protein. We presently have no antibodies reactive with this 94K dalton media molecule. In regard to high-molecular-weight antigens, the MoAb S and the xenoantiserum #8995 recognize two glycosylated structures from detergent extracts of cultured melanoma cells, one at 280K daltons and the other > 440K daltons, while only the > 440K dalton structure was detectable in the spent culture medium. In addition, the xenoantiserum #8995 detects a 300K dalton molecule present in spent culture medium but not in labelled cell extracts. The latter structure is either not solubilized by treatment with nonionic detergent (NP40) or is rapidly transported outside the cells and into the medium following synthesis. The media molecule detected by xenoantiserum #8995 was previously estimated to be 240K [9] rather than 300K daltons, since melanoma-derived fibronectin used as a molecular weight standard was assumed to have the same apparent molecular weight as plasma fibronectin. We have recently found that melanoma-derived fibronectin has a 40K dalton greater apparent molecular weight than plasma fibronectin [21], hence increasing the molecular weight estimation of the spent medium MAA from 240K daltons to approximately 300K daltons. The comparison of conventional xenoantisera with monoclonal antibodies clearly illustrates the limitations inherent in the former reagent. The conventional xenoantisera, being only operationally monospecific, may contain antibodies to more than a single antigenic system and this can be very misleading since there are several types of distinct antigenic structures having very similar apparent molecular weights. Thus, in the case of the xenoantiserum #8995, its reactivity with a 280K dalton cellular antigen and a 300K dalton media molecule suggested that these structures were antigenically related rather than coincidently identified by two different types of antibodies in this antiserum; however, the results with monoclonal antibodies clearly show that the xenoantiserum contains two different types of antibodies. Another problem is that the specificity of xenoantisera may vary from bleeding to bleeding, resulting in limited supplies of a particular reagent. In fact, we have exhausted our supply of several xenoantisera, including #8995, and have tried unsuccessfully to produce other reagents with similar specificities. When we assessed the distribution of antigenic determinants detectable by monoclonal antibodies in the population of antigens defined with a conventional xenoantiserum, we found that the determinant detected by MoAb S was present on all the 94K dalton molecules, while the determinant defined by MoAb S is detectable on only a subpopulation of the high-molecular-weight antigens. Therefore, the family of > 440K/280K dalton molecules is heterogeneous in the expression of determinants defined by monoclonal antibodies. These results parallel our previous experiences with monoclonal antibodies to HLA-A,B,C and human h-like antigens [17, 18], suggesting that the high-molecular-weight MAA may be polymorphic. It will be interesting to determine whether the molecules carrying antigenic determinants detected by the monoclonal antibodies to the high-molecular-weight MAA are expressed on all the cells of a melanoma population and whether expression of a particular antigenic determinant is associated with a certain clinical course of this disease. Acknowledgements. This work was supported by grants AI 19189, CA 32609, CA 32619, CA 32634, and CA from the National Institutes of Health. The skillful secretarial assistance of Ms Ellen Schmeding is recognized. BSW was supported by a 'Special Felloship' from the Leukemia Society of America, and KI was the recipient of a public health service Fogarty International Research Fellowship award (5 FO5 TWO ). References 1. Allison JP, Belvedere M, Reisfeld RA, PeUegrino MA, Ferrone S (1978) Serologic and immunochemical characterization of HLA-A9 xenoantisera. J Immunol 121 : Bonnet WM, Laskey RA (1974) A film detection method for Tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem 46:83 3. Brown JP, Nishiyama K, Hellstrom I, Hellstrom KE (1981) Structural characterization of human melanoma-associated antigen p97 with monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol 127: Carrel S, Accolla RS, Carmagnola AL, Mach JP (1980) Common human melanoma-associated antigen(s) detected by monoclonal antibodies. Cancer Res 40: Dippold WG, Lloyd KO, Li LTC, Ikeda H, Oettgen HF, Old LJ (1980) Cell surface antigens of human malignant melanoma: Definition of six antigenic systems with mouse monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77: Duksin D, Bornstein P (1976) Impaired conversion of procollagen to collagen by fibroblasts and bone treated with tunicamycin, an inhibitor of protein glycosylation. J Biol Chem 252: Engvall E, Ruoslahti E (1977) Binding of soluble form of fibroblast surface protein, fibronectin, to collagen. Int J Cancer 20:1 8. Ferrone S, Pellegrino MA (1979) Serological detection of human melanoma-associated antigens. In: Immunodiagnosis of cancer. Deckker, New York, p Galloway DR, McCabe RP, Pellegrino MA, Ferrone S, Reisfeld RA (1981) Tumor-associated antigens in the spent media of human melanoma cells: Immunochemical characterization with xenoantisera. J Immunol 126: Imai K, Molinaro GA, Ferrone S (1980) Monoclonal antibodies to human melanoma-associated antigens. Transplant Proc 12:380
6 Imai K, Galloway DR, Ferrone S (1981a) Serological and immunochemical analysis of the specificity of the xenoantiserum 8986 elicited with hybrids between human melanoma cells and murine fibroblasts. Cancer Res 41: Imai K, Ng AK, Ferrone S (1981b) Characterization of monoclonal antibodies to human melanoma-associated antigens. J Natl Cancer Inst 66: Koprowski H, Steplewski A, Herlyn D, Herlyn M (1978) Study of antibodies against human melanoma produced by somatic cell hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 75: Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227: Mitchell KF, Fuhrer JP, Steplewski Z, Koprowski H (1980) Biochemical characterization of human melanoma cell surfaces: Dissection with monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77: Natali PG, Imai K, Wilson BS, Bigotti A, Cavaliere R, Pellegrino MA, Ferrone S (1981) Structural properties and tissue distribution of the antigen recognized by the monoclonal antibody S to human melanoma cells. J Natl Cancer Inst 67: Quaranta V, Pellegrino MA, Ferrone S (1981) Serological and immunochemical characterization of the specificity of four monoclonal antibodies to distinct antigenic determinants expressed on subpopulations of human Ia-like antigens. J Immunol 126: Russo C, Pellegrino MA, Ng AK, Wilson BS, Ferrone S (1982) Antigenic constitution of HLA-A,B,C molecules: Immunochemical analysis with monoclonal antibodies. In: Ferrone S, Solheim BG (eds) HLA typing: Methodology and clinical relevance. CRC Press, Boca Raton (in press) 19. Wilson BS, Indiveri F, Pellegrino MA, Ferrone S (1979) Production and characterization of DR xenoantisera: Use for detection of serum DR antigens. J Immunol 122: Wilson BS, Imai K, Natali PG, Ferrone S (1981) Distribution and molecular characterization of a cell-surface and a cytoplasmic antigen detectable in human melanoma cells with monoclonal antibodies. Int J Cancer 28: Wilson BS, Ruberto G, Ferrone S (1981) Sulfation and molecular weight of Iibronectin shed by human melanoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 101: Wilson BS, Imai K, Natali PG, Cavalieri R, Pellegrino MA, Ferrone S (1982) Antigenic profile of human melanoma cells: Analysis with monoclonal antibodies. In: Ferrone S, Reisfeld RA (eds) Melanoma antigens and antibodies. Plenum Press, New York London 23. Woodbury RG, Brown JP, Yeh MY, Hellstrom I, Hellstrom KE (1980) Identification of a cell-surface protein, p 97, in human melanomas and certain other neoplasms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77: Yeh MY, HeUstrom I, Brown JP, Warner GA, Hansen JP, HeUstrom KE (1979) Cell surface antigens of human melanoma defined by monoclonal antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76: 2927 Received September 22, 1981/Accepted February 10, 1982
Classic Immunoprecipitation
 292PR 01 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name Classic Immunoprecipitation Utilizes Protein A/G Agarose for Antibody Binding (Cat.
292PR 01 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name Classic Immunoprecipitation Utilizes Protein A/G Agarose for Antibody Binding (Cat.
CUSTOM ANTIBODIES. Fully customised services: rat and murine monoclonals, rat and rabbit polyclonals, antibody characterisation, antigen preparation
 CUSTOM ANTIBODIES Highly competitive pricing without compromising quality. Rat monoclonal antibodies for the study of gene expression and proteomics in mice and in mouse models of human diseases available.
CUSTOM ANTIBODIES Highly competitive pricing without compromising quality. Rat monoclonal antibodies for the study of gene expression and proteomics in mice and in mouse models of human diseases available.
Custom Antibody Services
 prosci-inc.com Custom Antibody Services High Performance Antibodies and More Broad Antibody Catalog Extensive Antibody Services CUSTOM ANTIBODY SERVICES Established in 1998, ProSci Incorporated is a leading
prosci-inc.com Custom Antibody Services High Performance Antibodies and More Broad Antibody Catalog Extensive Antibody Services CUSTOM ANTIBODY SERVICES Established in 1998, ProSci Incorporated is a leading
KMS-Specialist & Customized Biosimilar Service
 KMS-Specialist & Customized Biosimilar Service 1. Polyclonal Antibody Development Service KMS offering a variety of Polyclonal Antibody Services to fit your research and production needs. we develop polyclonal
KMS-Specialist & Customized Biosimilar Service 1. Polyclonal Antibody Development Service KMS offering a variety of Polyclonal Antibody Services to fit your research and production needs. we develop polyclonal
Protein immunoblotting
 Protein immunoblotting (Western blotting) Dr. Serageldeen A. A. Sultan Lecturer of virology Dept. of Microbiology SVU, Qena, Egypt seaas@lycos.com Western blotting -It is an analytical technique used to
Protein immunoblotting (Western blotting) Dr. Serageldeen A. A. Sultan Lecturer of virology Dept. of Microbiology SVU, Qena, Egypt seaas@lycos.com Western blotting -It is an analytical technique used to
Chapter 2 Antibodies. Contents. Introduction
 Chapter 2 Antibodies Keywords Immunohistochemistry Antibody labeling Fluorescence microscopy Fluorescent immunocytochemistry Fluorescent immunohistochemistry Indirect immunocytochemistry Immunostaining
Chapter 2 Antibodies Keywords Immunohistochemistry Antibody labeling Fluorescence microscopy Fluorescent immunocytochemistry Fluorescent immunohistochemistry Indirect immunocytochemistry Immunostaining
Common Human Melanoma-associated Antigen(s) Detected by Monoclonal Antibodies
 [CANCER RESEARCH 40, 2523-2528, July 980] 0008-5472/80/0040-OOOOS02.00 Common Human Melanoma-associated Antigen(s) Detected by Monoclonal Antibodies Stefan Carrel, Roberto S. Accolla, Anna L. Carmagnola,
[CANCER RESEARCH 40, 2523-2528, July 980] 0008-5472/80/0040-OOOOS02.00 Common Human Melanoma-associated Antigen(s) Detected by Monoclonal Antibodies Stefan Carrel, Roberto S. Accolla, Anna L. Carmagnola,
Aviva Systems Biology
 Aviva Custom Antibody Service and Price Mouse Monoclonal Antibody Service Package Number Description Package Contents Time Price Customer provides antigen protein $6,174 Monoclonal package1 (From protein
Aviva Custom Antibody Service and Price Mouse Monoclonal Antibody Service Package Number Description Package Contents Time Price Customer provides antigen protein $6,174 Monoclonal package1 (From protein
Optimal Conditions for F(ab ) 2 Antibody Fragment Production from Mouse IgG2a
 Optimal Conditions for F(ab ) 2 Antibody Fragment Production from Mouse IgG2a Ryan S. Stowers, 1 Jacqueline A. Callihan, 2 James D. Bryers 2 1 Department of Bioengineering, Clemson University, Clemson,
Optimal Conditions for F(ab ) 2 Antibody Fragment Production from Mouse IgG2a Ryan S. Stowers, 1 Jacqueline A. Callihan, 2 James D. Bryers 2 1 Department of Bioengineering, Clemson University, Clemson,
Release of Monoclonal Antibody-defined Antigens by Human Colorectal Carcinoma and Melanoma Cells1
 [CANCER RESEARCH 41, 2723-2727, July 1981] 0008-5472/81/0041-OOOOS02.00 Release of Monoclonal Antibody-defined Antigens by Human Colorectal Carcinoma and Melanoma Cells1 Zenon Steplewski,2 Tong H. Chang,
[CANCER RESEARCH 41, 2723-2727, July 1981] 0008-5472/81/0041-OOOOS02.00 Release of Monoclonal Antibody-defined Antigens by Human Colorectal Carcinoma and Melanoma Cells1 Zenon Steplewski,2 Tong H. Chang,
Methionine Sulfoxide Immunoblotting Kit
 Methionine Sulfoxide Immunoblotting Kit Item No. 600160 Customer Service 800.364.9897 * Technical Support 888.526.5351 www.caymanchem.com TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 3 Materials Supplied 4 Precautions
Methionine Sulfoxide Immunoblotting Kit Item No. 600160 Customer Service 800.364.9897 * Technical Support 888.526.5351 www.caymanchem.com TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 3 Materials Supplied 4 Precautions
Custom Antibodies Services. GeneCust Europe. GeneCust Europe
 GeneCust Europe Laboratoire de Biotechnologie du Luxembourg S.A. 6 rue Dominique Lang L-3505 Dudelange Luxembourg Tél. : +352 27620411 Fax : +352 27620412 Email : info@genecust.com Web : www.genecust.com
GeneCust Europe Laboratoire de Biotechnologie du Luxembourg S.A. 6 rue Dominique Lang L-3505 Dudelange Luxembourg Tél. : +352 27620411 Fax : +352 27620412 Email : info@genecust.com Web : www.genecust.com
Chapter 18: Applications of Immunology
 Chapter 18: Applications of Immunology 1. Vaccinations 2. Monoclonal vs Polyclonal Ab 3. Diagnostic Immunology 1. Vaccinations What is Vaccination? A method of inducing artificial immunity by exposing
Chapter 18: Applications of Immunology 1. Vaccinations 2. Monoclonal vs Polyclonal Ab 3. Diagnostic Immunology 1. Vaccinations What is Vaccination? A method of inducing artificial immunity by exposing
Page finder. 1. Legal 3. 2. Handling 4 2.1. Safety warnings and precautions 4 2.2. Storage 4 2.3. Expiry 4
 GE Healthcare Amersham Low Molecular Weight Calibration Kit for SDS Electrophoresis A lyophilized mixture of six highly purified well-characterized proteins for use in molecular weight determination in
GE Healthcare Amersham Low Molecular Weight Calibration Kit for SDS Electrophoresis A lyophilized mixture of six highly purified well-characterized proteins for use in molecular weight determination in
Anti-ATF6 α antibody, mouse monoclonal (1-7)
 Anti-ATF6 α antibody, mouse monoclonal (1-7) 73-500 50 ug ATF6 (activating transcription factor 6) is an endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane-bound transcription factor activated in response to ER stress.
Anti-ATF6 α antibody, mouse monoclonal (1-7) 73-500 50 ug ATF6 (activating transcription factor 6) is an endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane-bound transcription factor activated in response to ER stress.
Antibody Production Price List
 Antibody Production Price List Presenting Insight Biotechnology s price list for custom polyclonal and monoclonal antibody production services. We are happy to tailor individual packages towards the specific
Antibody Production Price List Presenting Insight Biotechnology s price list for custom polyclonal and monoclonal antibody production services. We are happy to tailor individual packages towards the specific
Interim Progress Report R&D Project 348. Development of a Field Test Kit for Detection of Blue-Green Algal Toxins
 Interim Progress Report R&D Project 348 Development of a Field Test Kit for Detection of Blue-Green Algal Toxins Biocode Limited November 1992 R&D 348/04/A ENVIRONMENT AGENCY 135357 CONTENTS SUMMARY KEYWORDS
Interim Progress Report R&D Project 348 Development of a Field Test Kit for Detection of Blue-Green Algal Toxins Biocode Limited November 1992 R&D 348/04/A ENVIRONMENT AGENCY 135357 CONTENTS SUMMARY KEYWORDS
Geniron. Custom Antibody Services. Serum services Antibody Monoclonal. Purification Antibody Mono Y Genetic Immunization Genbody Polyclonal Antibody
 Geniron Custom Antibody Services Serum services Antibody Monoclonal Purification Antibody Mono Y Genetic Immunization Genbody Polyclonal Antibody Geniron Poly Y WE PROVIDE OUR SERVICES TO With Expertise
Geniron Custom Antibody Services Serum services Antibody Monoclonal Purification Antibody Mono Y Genetic Immunization Genbody Polyclonal Antibody Geniron Poly Y WE PROVIDE OUR SERVICES TO With Expertise
Rubisco; easy Purification and Immunochemical Determination
 Rubisco; easy Purification and Immunochemical Determination Ulrich Groß Justus-Liebig-Universität Gießen, Institute of Plant Nutrition, Department of Tissue Culture, Südanlage 6, D-35390 Giessen e-mail:
Rubisco; easy Purification and Immunochemical Determination Ulrich Groß Justus-Liebig-Universität Gießen, Institute of Plant Nutrition, Department of Tissue Culture, Südanlage 6, D-35390 Giessen e-mail:
Chapter 6: Antigen-Antibody Interactions
 Chapter 6: Antigen-Antibody Interactions I. Strength of Ag-Ab interactions A. Antibody Affinity - strength of total noncovalent interactions between single Ag-binding site on an Ab and a single epitope
Chapter 6: Antigen-Antibody Interactions I. Strength of Ag-Ab interactions A. Antibody Affinity - strength of total noncovalent interactions between single Ag-binding site on an Ab and a single epitope
Quantitative expression of epitopes defined by murine monoclonal antibodies on DR molecules from different HLA haplotypes
 Bioscience Reports 5, 923-93i (1985) 923 Printed in Great Britain Quantitative expression of epitopes defined by murine monoclonal antibodies on DR molecules from different HLA haplotypes Michelle LETARTE
Bioscience Reports 5, 923-93i (1985) 923 Printed in Great Britain Quantitative expression of epitopes defined by murine monoclonal antibodies on DR molecules from different HLA haplotypes Michelle LETARTE
ELISA BIO 110 Lab 1. Immunity and Disease
 ELISA BIO 110 Lab 1 Immunity and Disease Introduction The principal role of the mammalian immune response is to contain infectious disease agents. This response is mediated by several cellular and molecular
ELISA BIO 110 Lab 1 Immunity and Disease Introduction The principal role of the mammalian immune response is to contain infectious disease agents. This response is mediated by several cellular and molecular
WESTERN BLOTTING TIPS AND TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE
 WESTERN BLOTTING TIPS AND TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE TIPS FOR SUCCESSFUL WESTERB BLOTS TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE 1. Suboptimal protein transfer. This is the most common complaint with western blotting and could
WESTERN BLOTTING TIPS AND TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE TIPS FOR SUCCESSFUL WESTERB BLOTS TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE 1. Suboptimal protein transfer. This is the most common complaint with western blotting and could
Brief Definitive Reports
 Brief Definitive Reports GENERAL METHOD FOR ISOLATION AND RECOVERY OF B CELLS BEARING SPECIFIC RECEPTORS* BY TAT K. CHOI,$ DOUGLAS R. SLEIGHT, AND ALFRED NISONOFF (From the Department of Biological Chemistry,
Brief Definitive Reports GENERAL METHOD FOR ISOLATION AND RECOVERY OF B CELLS BEARING SPECIFIC RECEPTORS* BY TAT K. CHOI,$ DOUGLAS R. SLEIGHT, AND ALFRED NISONOFF (From the Department of Biological Chemistry,
Basics of Immunology
 Basics of Immunology 2 Basics of Immunology What is the immune system? Biological mechanism for identifying and destroying pathogens within a larger organism. Pathogens: agents that cause disease Bacteria,
Basics of Immunology 2 Basics of Immunology What is the immune system? Biological mechanism for identifying and destroying pathogens within a larger organism. Pathogens: agents that cause disease Bacteria,
The use of monoclonal antibodies in the setting of HSCT
 The use of monoclonal antibodies in the setting of HSCT S Montoto, Barts Cancer Institute, London, UK Geneva 3/April/2012 www.ebmt.org Some definitions of interest: Ab and Ag Antibody (Ab)=Immunoglobulin
The use of monoclonal antibodies in the setting of HSCT S Montoto, Barts Cancer Institute, London, UK Geneva 3/April/2012 www.ebmt.org Some definitions of interest: Ab and Ag Antibody (Ab)=Immunoglobulin
OBTAINING MONOCLONAL ANTIBODIES TO EPITOPES OF IVERMECTIN
 С.Сейфуллин атындағы Қазақ агротехникалық университетінің Ғылым жаршысы / Вестник науки Казахского агротехнического университета им. С. Сейфуллина. 2013. - 4 (79). C.8-14 OBTAINING MONOCLONAL ANTIBODIES
С.Сейфуллин атындағы Қазақ агротехникалық университетінің Ғылым жаршысы / Вестник науки Казахского агротехнического университета им. С. Сейфуллина. 2013. - 4 (79). C.8-14 OBTAINING MONOCLONAL ANTIBODIES
SCANTIBODIES Laboratory, Inc. Contract Monoclonal Antibody Production
 A Technical Publication of SCANTIBODIES Laboratory, Inc. Volume 1 Number 4 9336 Abraham Way Santee, CA 92071 USA (619) 258-9300 fax (619) 258-9366 www.scantibodies.com SCANTIBODIES Laboratory, Inc. Contract
A Technical Publication of SCANTIBODIES Laboratory, Inc. Volume 1 Number 4 9336 Abraham Way Santee, CA 92071 USA (619) 258-9300 fax (619) 258-9366 www.scantibodies.com SCANTIBODIES Laboratory, Inc. Contract
竞 争 性 分 析 Epitope Mapping 实 验 方 法
 竞 争 性 分 析 Epitope Mapping 实 验 方 法 ABSTRACT The simplest way to determine whether two monoclonal antibodies bind to distinct sites on a protein antigen is to carry out a competition assay. The assay can
竞 争 性 分 析 Epitope Mapping 实 验 方 法 ABSTRACT The simplest way to determine whether two monoclonal antibodies bind to distinct sites on a protein antigen is to carry out a competition assay. The assay can
Protein extraction from Tissues and Cultured Cells using Bioruptor Standard & Plus
 Protein extraction from Tissues and Cultured Cells using Bioruptor Standard & Plus Introduction Protein extraction from tissues and cultured cells is the first step for many biochemical and analytical
Protein extraction from Tissues and Cultured Cells using Bioruptor Standard & Plus Introduction Protein extraction from tissues and cultured cells is the first step for many biochemical and analytical
Antibody Services. Best Guarantees in the Industry! Monoclonal Antibody Services. Polyclonal Antibody Services. Express Antibody TM Services
 Antibody Services Best Guarantees in the Industry! Monoclonal Antibody Services Polyclonal Antibody Services Express Antibody TM Services Guaranteed Antibody Services Antibody Purification Services Your
Antibody Services Best Guarantees in the Industry! Monoclonal Antibody Services Polyclonal Antibody Services Express Antibody TM Services Guaranteed Antibody Services Antibody Purification Services Your
Antibody Purification and Labeling
 5 Antibody Purification and Labeling 5.1 Antibody Purification 65 Magne Protein A Beads and Magne Protein G Beads 67 5.2 Antibody Labeling 69 phab Amine and Thiol Reactive Dyes 71 63 Discover Reliable
5 Antibody Purification and Labeling 5.1 Antibody Purification 65 Magne Protein A Beads and Magne Protein G Beads 67 5.2 Antibody Labeling 69 phab Amine and Thiol Reactive Dyes 71 63 Discover Reliable
MAB Solut. MABSolys Génopole Campus 1 5 rue Henri Desbruères 91030 Evry Cedex. www.mabsolut.com. is involved at each stage of your project
 Mabsolus-2015-UK:Mise en page 1 03/07/15 14:13 Page1 Services provider Department of MABSolys from conception to validation MAB Solut is involved at each stage of your project Creation of antibodies Production
Mabsolus-2015-UK:Mise en page 1 03/07/15 14:13 Page1 Services provider Department of MABSolys from conception to validation MAB Solut is involved at each stage of your project Creation of antibodies Production
Custom Antibody Services
 Custom Antibody Services Custom service offerings DNA sequence Plasmid Peptide Structure Protein Peptide Small molecule Cells Spleen Lymphocytes Antigen Preparation Immunization Fusion & Subcloning Expansion
Custom Antibody Services Custom service offerings DNA sequence Plasmid Peptide Structure Protein Peptide Small molecule Cells Spleen Lymphocytes Antigen Preparation Immunization Fusion & Subcloning Expansion
Publikationsliste Claudia Götz
 Publikationsliste Claudia Götz 1. Reinhard,B., Götz, C., and Faillard, H.: Synthesis of N-Acetyl-9-Oacetylneuraminic acid α-p-aminophenylthioketoside and its application as ligand in the affinity chromatography
Publikationsliste Claudia Götz 1. Reinhard,B., Götz, C., and Faillard, H.: Synthesis of N-Acetyl-9-Oacetylneuraminic acid α-p-aminophenylthioketoside and its application as ligand in the affinity chromatography
TABLE OF CONTENT. Page ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS. iii ENGLISH ABSTRACT THAI ABSTRACT. vii LIST OF TABLES LIST OF FIGURES. xvi ABBREVIATIONS.
 x TABLE OF CONTENT ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ENGLISH ABSTRACT THAI ABSTRACT LIST OF TABLES LIST OF FIGURES ABBREVIATIONS iii iv vii xv xvi xviii CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION 1.1 Statement of problems 1 1.2 Literature
x TABLE OF CONTENT ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ENGLISH ABSTRACT THAI ABSTRACT LIST OF TABLES LIST OF FIGURES ABBREVIATIONS iii iv vii xv xvi xviii CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION 1.1 Statement of problems 1 1.2 Literature
Methods for Protein Analysis
 Methods for Protein Analysis 1. Protein Separation Methods The following is a quick review of some common methods used for protein separation: SDS-PAGE (SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis) separates
Methods for Protein Analysis 1. Protein Separation Methods The following is a quick review of some common methods used for protein separation: SDS-PAGE (SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis) separates
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP)
 Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) Day 1 A) DNA shearing 1. Samples Dissect tissue (One Mouse OBs) of interest and transfer to an eppendorf containing 0.5 ml of dissecting media (on ice) or PBS but without
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) Day 1 A) DNA shearing 1. Samples Dissect tissue (One Mouse OBs) of interest and transfer to an eppendorf containing 0.5 ml of dissecting media (on ice) or PBS but without
RhD typing. Practice for IV year medical students. Zita Csernus MD. National Blood Transfusion Service Blood Transfusion Centre Pécs
 immunisation Bed side test Antibody tests RhD typing Practice for IV year medical students Zita Csernus MD National Blood Transfusion Service Blood Transfusion Centre Pécs Rh Blood Group System Discovery:
immunisation Bed side test Antibody tests RhD typing Practice for IV year medical students Zita Csernus MD National Blood Transfusion Service Blood Transfusion Centre Pécs Rh Blood Group System Discovery:
The Use of Antibodies in Immunoassays
 TECHNICAL NOTE The Use of Antibodies in Immunoassays Introduction Structure of an IgG Antibody Immunological reagents are the backbone of every immunoassay system. Immunoassays can be utilized to quantitatively
TECHNICAL NOTE The Use of Antibodies in Immunoassays Introduction Structure of an IgG Antibody Immunological reagents are the backbone of every immunoassay system. Immunoassays can be utilized to quantitatively
Aviva Systems Biology
 Aviva Custom Antibody Services and Prices Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody Service Package Number Description Package Contents Time Price Polyclonal package 1 (From protein to antiserum) Polyclonal package 2
Aviva Custom Antibody Services and Prices Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody Service Package Number Description Package Contents Time Price Polyclonal package 1 (From protein to antiserum) Polyclonal package 2
6 Characterization of Casein and Bovine Serum Albumin
 6 Characterization of Casein and Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) Objectives: A) To separate a mixture of casein and bovine serum albumin B) to characterize these proteins based on their solubilities as a function
6 Characterization of Casein and Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) Objectives: A) To separate a mixture of casein and bovine serum albumin B) to characterize these proteins based on their solubilities as a function
Pure-IP Western Blot Detection Kit
 Product Manual Pure-IP Western Blot Detection Kit Catalog Number PRB-5002 20 blots FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction The technique of immunoprecipitation (IP) is used
Product Manual Pure-IP Western Blot Detection Kit Catalog Number PRB-5002 20 blots FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction The technique of immunoprecipitation (IP) is used
Approaches that can be used to study expression of specific proteins
 Approaches that can be used to study expression of specific proteins Receptors and transporters Homogenate binding studies Receptor autoradiography Radiochemical Western blotting Immunohistochemistry/cytochemistry
Approaches that can be used to study expression of specific proteins Receptors and transporters Homogenate binding studies Receptor autoradiography Radiochemical Western blotting Immunohistochemistry/cytochemistry
Antibody Function & Structure
 Antibody Function & Structure Specifically bind to antigens in both the recognition phase (cellular receptors) and during the effector phase (synthesis and secretion) of humoral immunity Serology: the
Antibody Function & Structure Specifically bind to antigens in both the recognition phase (cellular receptors) and during the effector phase (synthesis and secretion) of humoral immunity Serology: the
Elabscience Biotechnology Co.,Ltd
 Biotechnology Co.,Ltd Your one-stop custom antibody service Antibody is a kind of protein that is the most widely used in the fields of biology and medicine. Antibodies, as the preparations for disease
Biotechnology Co.,Ltd Your one-stop custom antibody service Antibody is a kind of protein that is the most widely used in the fields of biology and medicine. Antibodies, as the preparations for disease
CHAPTER 2 ANTIGEN/ANTIBODY INTERACTIONS
 CHAPTER 2 ANTIGEN/ANTIBODY INTERACTIONS See APPENDIX (1) THE PRECIPITIN CURVE; (2) LABELING OF ANTIBODIES The defining characteristic of HUMORAL immune responses (which distinguishes them from CELL-MEDIATED
CHAPTER 2 ANTIGEN/ANTIBODY INTERACTIONS See APPENDIX (1) THE PRECIPITIN CURVE; (2) LABELING OF ANTIBODIES The defining characteristic of HUMORAL immune responses (which distinguishes them from CELL-MEDIATED
VETERINARY SERVICES MEMORANDUM NO. 800.90
 August 5, 1998 VETERINARY SERVICES MEMORANDUM NO. 800.90 Subject: To: Guidelines for Veterinary Biological Relative Potency Assays and Reference Preparations Based on ELISA Antigen Quantification Veterinary
August 5, 1998 VETERINARY SERVICES MEMORANDUM NO. 800.90 Subject: To: Guidelines for Veterinary Biological Relative Potency Assays and Reference Preparations Based on ELISA Antigen Quantification Veterinary
Custom Polyclonal Anti-Peptide Antibody, Brochure
 Custom Polyclonal Anti-Peptide Antibody, Brochure Interest in any of the products, request or order them at Bio-Connect. Bio-Connect B.V. T NL +31 (0)26 326 44 50 T BE +32 (0)2 503 03 48 Begonialaan 3a
Custom Polyclonal Anti-Peptide Antibody, Brochure Interest in any of the products, request or order them at Bio-Connect. Bio-Connect B.V. T NL +31 (0)26 326 44 50 T BE +32 (0)2 503 03 48 Begonialaan 3a
CHAPTER 6 ANTIBODY GENETICS: ISOTYPES, ALLOTYPES, IDIOTYPES
 CHAPTER 6 ANTIBODY GENETICS: ISOTYPES, ALLOTYPES, IDIOTYPES See APPENDIX: (3) OUCHTERLONY; (4) AFFINITY CHROMATOGRAPHY Human immunoglobulins are made up of LIGHT and HEAVY chains encoded by a total of
CHAPTER 6 ANTIBODY GENETICS: ISOTYPES, ALLOTYPES, IDIOTYPES See APPENDIX: (3) OUCHTERLONY; (4) AFFINITY CHROMATOGRAPHY Human immunoglobulins are made up of LIGHT and HEAVY chains encoded by a total of
New HLA class I epitopes defined by murine monoclonal antibodies
 Human Immunology 71 (2010) 456 461 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect New HLA class I epitopes defined by murine monoclonal antibodies Nadim El-Awar a, *, Paul I. Terasaki b, Anh Nguyen a, Mamie
Human Immunology 71 (2010) 456 461 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect New HLA class I epitopes defined by murine monoclonal antibodies Nadim El-Awar a, *, Paul I. Terasaki b, Anh Nguyen a, Mamie
Direct Antiglobulin Test (DAT)
 Exercise 8 Exercise 9 Direct Antiglobulin Test (DAT) Elution Study Task Aim Introduction To perform the DAT and elution procedure with correct interpretation of results. To perform with 100% accuracy the
Exercise 8 Exercise 9 Direct Antiglobulin Test (DAT) Elution Study Task Aim Introduction To perform the DAT and elution procedure with correct interpretation of results. To perform with 100% accuracy the
VI. ABO and H Blood Groups
 MLAB 243 4 A. History of ABO System. Discovered in 900 by Karl Landsteiner and remains the most important of the blood group systems as far as the transfusion of blood is concerned. 2. Landsteiner tested
MLAB 243 4 A. History of ABO System. Discovered in 900 by Karl Landsteiner and remains the most important of the blood group systems as far as the transfusion of blood is concerned. 2. Landsteiner tested
LAB 14 ENZYME LINKED IMMUNOSORBENT ASSAY (ELISA)
 STUDENT GUIDE LAB 14 ENZYME LINKED IMMUNOSORBENT ASSAY (ELISA) GOAL The goal of this laboratory lesson is to explain the concepts and technique of enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). OBJECTIVES
STUDENT GUIDE LAB 14 ENZYME LINKED IMMUNOSORBENT ASSAY (ELISA) GOAL The goal of this laboratory lesson is to explain the concepts and technique of enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). OBJECTIVES
The Body s Defenses CHAPTER 24
 CHAPTER 24 The Body s Defenses PowerPoint Lectures for Essential Biology, Third Edition Neil Campbell, Jane Reece, and Eric Simon Essential Biology with Physiology, Second Edition Neil Campbell, Jane Reece,
CHAPTER 24 The Body s Defenses PowerPoint Lectures for Essential Biology, Third Edition Neil Campbell, Jane Reece, and Eric Simon Essential Biology with Physiology, Second Edition Neil Campbell, Jane Reece,
Advanced BioDesign Outlines Solutions. Antibody Overview. by Advanced BioDesign. Project Start. Immunogenicity. Selecting Your Antigen
 Advanced BioDesign Outlines Solutions by Advanced BioDesign Antibody Overview Launching an immunisation programme is an important experimental step that needs care. With Advanced BioDesign, you may develop
Advanced BioDesign Outlines Solutions by Advanced BioDesign Antibody Overview Launching an immunisation programme is an important experimental step that needs care. With Advanced BioDesign, you may develop
Chapter 6. Antigen-Antibody Properties 10/3/2012. Antigen-Antibody Interactions: Principles and Applications. Precipitin reactions
 Chapter 6 Antigen-Antibody Interactions: Principles and Applications Antigen-Antibody Properties You must remember antibody affinity (single) VS avidity (multiple) High affinity: bound tightly and longer!
Chapter 6 Antigen-Antibody Interactions: Principles and Applications Antigen-Antibody Properties You must remember antibody affinity (single) VS avidity (multiple) High affinity: bound tightly and longer!
Chapter 3.2» Custom Monoclonal
 198 3 3.2 Custom Monoclonal 199 Mouse monoclonal antibody development Chapter 3.2» Custom Monoclonal 200 In vitro monoclonals expression service 201 Mouse monoclonal antibody additional services 202 Magnetic
198 3 3.2 Custom Monoclonal 199 Mouse monoclonal antibody development Chapter 3.2» Custom Monoclonal 200 In vitro monoclonals expression service 201 Mouse monoclonal antibody additional services 202 Magnetic
Supplemental Material. Paradoxical association of enhanced cholesterol efflux with increased incident cardiovascular risks
 Supplemental Material Paradoxical association of enhanced cholesterol efflux with increased incident cardiovascular risks Xin-Min Li, PhD 1, W. H. Wilson Tang, MD 1,2, Marian K. Mosior, PhD 3, Ying Huang,
Supplemental Material Paradoxical association of enhanced cholesterol efflux with increased incident cardiovascular risks Xin-Min Li, PhD 1, W. H. Wilson Tang, MD 1,2, Marian K. Mosior, PhD 3, Ying Huang,
3 months 1.5 months 1.5 months. 1 month
 Rabbit monoclonal antibody (Mab) is secreted by the plasma B-cell of the rabbit. Traditional generation of rabbit Mab relies on a rabbit myeloma for B- cell fusion (
Rabbit monoclonal antibody (Mab) is secreted by the plasma B-cell of the rabbit. Traditional generation of rabbit Mab relies on a rabbit myeloma for B- cell fusion (
Amersham High Molecular Weight Calibration Kit for native electrophoresis
 Amersham High Molecular Weight Calibration Kit for native electrophoresis A lyophilized mixture of five highly purified well-characterized proteins for use in molecular weight estimation under non-denaturing
Amersham High Molecular Weight Calibration Kit for native electrophoresis A lyophilized mixture of five highly purified well-characterized proteins for use in molecular weight estimation under non-denaturing
specific B cells Humoral immunity lymphocytes antibodies B cells bone marrow Cell-mediated immunity: T cells antibodies proteins
 Adaptive Immunity Chapter 17: Adaptive (specific) Immunity Bio 139 Dr. Amy Rogers Host defenses that are specific to a particular infectious agent Can be innate or genetic for humans as a group: most microbes
Adaptive Immunity Chapter 17: Adaptive (specific) Immunity Bio 139 Dr. Amy Rogers Host defenses that are specific to a particular infectious agent Can be innate or genetic for humans as a group: most microbes
Western Blotting: Mini-gels
 Western Blotting: Mini-gels Materials a Protein Extraction Buffer (for callus or kernel), Solution Stock Final Volume Tris-HCl ph 80 1 M 200 mm 20 ml NaCl 4 M 100 mm 25 ml Sucrose 2 M 400 mm 20 ml EDTA
Western Blotting: Mini-gels Materials a Protein Extraction Buffer (for callus or kernel), Solution Stock Final Volume Tris-HCl ph 80 1 M 200 mm 20 ml NaCl 4 M 100 mm 25 ml Sucrose 2 M 400 mm 20 ml EDTA
Electrophoresis and Electroblotting of Proteins
 Electrophoresis and Electroblotting of Proteins The purpose of the next lab exercises will be to study the relative amounts of β-actin in cells of the B-16 melanoma, liver and muscle of mice. Electrophoresis
Electrophoresis and Electroblotting of Proteins The purpose of the next lab exercises will be to study the relative amounts of β-actin in cells of the B-16 melanoma, liver and muscle of mice. Electrophoresis
MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY PRODUCTION
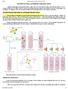 MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY PRODUCTION Antibodies having single specificity produced from a single clone of B cell are referred as Mono clonal antibodies (MAbs). In 1975, Georges Köhler and Cesar Milstein devised
MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY PRODUCTION Antibodies having single specificity produced from a single clone of B cell are referred as Mono clonal antibodies (MAbs). In 1975, Georges Köhler and Cesar Milstein devised
Mouse IFN-gamma ELISpot Kit
 Page 1 of 8 Mouse IFN-gamma ELISpot Kit Without Plates With Plates With Sterile Plates Quantity Catalog Nos. 862.031.001 862.031.001P 862.031.001S 1 x 96 tests 862.031.005 862.031.005P 862.031.005S 5 x
Page 1 of 8 Mouse IFN-gamma ELISpot Kit Without Plates With Plates With Sterile Plates Quantity Catalog Nos. 862.031.001 862.031.001P 862.031.001S 1 x 96 tests 862.031.005 862.031.005P 862.031.005S 5 x
Dot Blot Analysis. Teacher s Guidebook. (Cat. # BE 502) think proteins! think G-Biosciences www.gbiosciences.com
 PR110 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name Dot Blot Analysis Teacher s Guidebook (Cat. # BE 502) think proteins! think G-Biosciences
PR110 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name Dot Blot Analysis Teacher s Guidebook (Cat. # BE 502) think proteins! think G-Biosciences
Non Specific Binding (NSB) in Antigen-Antibody Assays
 Non Specific Binding (NSB) in Antigen-Antibody Assays Chem 395 Spring 2007 Instructor : Dr. James Rusling Presenter : Bhaskara V. Chikkaveeraiah OUTLINE Immunoassays Introduction Factors contributing to
Non Specific Binding (NSB) in Antigen-Antibody Assays Chem 395 Spring 2007 Instructor : Dr. James Rusling Presenter : Bhaskara V. Chikkaveeraiah OUTLINE Immunoassays Introduction Factors contributing to
Blood-Based Cancer Diagnostics
 The Biotechnology Education Company Blood-Based Cancer Diagnostics EDVO-Kit 141 Store entire experiment at room temperature. EXPERIMENT OBJECTIVE: The objective of this experiment is to learn and understand
The Biotechnology Education Company Blood-Based Cancer Diagnostics EDVO-Kit 141 Store entire experiment at room temperature. EXPERIMENT OBJECTIVE: The objective of this experiment is to learn and understand
Antigens & Antibodies II. Polyclonal antibodies vs Monoclonal antibodies
 A Brief Review of Antibody Structure A Brief Review of Antibody Structure The basic antibody is a dimer of dimer (2 heavy chain-light chain pairs) composed of repeats of a single structural unit known
A Brief Review of Antibody Structure A Brief Review of Antibody Structure The basic antibody is a dimer of dimer (2 heavy chain-light chain pairs) composed of repeats of a single structural unit known
In Vitro And In Vivo Production Of Antibodies
 In Vitro And In Vivo Production Of Antibodies OCTOBER 27, 2015 BY ADMIN Overview An antibody is a protein normally produced by the B cells of the immune system. Their original purpose is to identify and
In Vitro And In Vivo Production Of Antibodies OCTOBER 27, 2015 BY ADMIN Overview An antibody is a protein normally produced by the B cells of the immune system. Their original purpose is to identify and
Monoclonal Antibodies against the Lymphokine Osteoclast Activating Factor
 Production of Hybridomas Secreting Monoclonal Antibodies against the Lymphokine Osteoclast Activating Factor RICHARD A. LUBEN, MARJORIE A. MOHLER, and GLENN E. NEDWIN, Division of Biomedical Sciences and
Production of Hybridomas Secreting Monoclonal Antibodies against the Lymphokine Osteoclast Activating Factor RICHARD A. LUBEN, MARJORIE A. MOHLER, and GLENN E. NEDWIN, Division of Biomedical Sciences and
Title: Mapping T cell epitopes in PCV2 capsid protein - NPB #08-159. Date Submitted: 12-11-09
 Title: Mapping T cell epitopes in PCV2 capsid protein - NPB #08-159 Investigator: Institution: Carol Wyatt Kansas State University Date Submitted: 12-11-09 Industry summary: Effective circovirus vaccines
Title: Mapping T cell epitopes in PCV2 capsid protein - NPB #08-159 Investigator: Institution: Carol Wyatt Kansas State University Date Submitted: 12-11-09 Industry summary: Effective circovirus vaccines
1.Gene Synthesis. 2.Peptide & Phospho-P. Assembly PCR. Design & Synthesis. Advantages. Specifications. Advantages
 1.Gene Synthesis Assembly PCR Looking for a cdna for your research but could not fish out the gene through traditional cloning methods or a supplier? Abnova provides a gene synthesis service via assembly
1.Gene Synthesis Assembly PCR Looking for a cdna for your research but could not fish out the gene through traditional cloning methods or a supplier? Abnova provides a gene synthesis service via assembly
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE
 STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE Title: Antibody Production at Strategic Diagnostics Inc. SOP#: M-119 Version #: 1 Date Approved: August 6, 2009 Author: Strategic Diagnostic Inc. Date Modified: 1. PURPOSE
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE Title: Antibody Production at Strategic Diagnostics Inc. SOP#: M-119 Version #: 1 Date Approved: August 6, 2009 Author: Strategic Diagnostic Inc. Date Modified: 1. PURPOSE
Copyright is owned by the Author of the thesis. Permission is given for a copy to be downloaded by an individual for the purpose of research and
 Copyright is owned by the Author of the thesis. Permission is given for a copy to be downloaded by an individual for the purpose of research and private study only. The thesis may not be reproduced elsewhere
Copyright is owned by the Author of the thesis. Permission is given for a copy to be downloaded by an individual for the purpose of research and private study only. The thesis may not be reproduced elsewhere
DELFIA assays bring convenience in monoclonal antibody development
 DELFIA DELFIA assays bring convenience in monoclonal development INTRODUCTION The DELFIA system provides a method of discovering specific, high-affinity monoclonal antibodies (Mabs) even in low concentrations
DELFIA DELFIA assays bring convenience in monoclonal development INTRODUCTION The DELFIA system provides a method of discovering specific, high-affinity monoclonal antibodies (Mabs) even in low concentrations
(6.8 mci/mmol) were purchased from New England Nuclear. were washed twice with an equal volume of 0.15 M NaCl
 Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 72, No. 10, pp. 4142-4146, October 1975 Medical Sciences Hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase deficiency: Association of reduced catalytic activity with reduced levels
Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 72, No. 10, pp. 4142-4146, October 1975 Medical Sciences Hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase deficiency: Association of reduced catalytic activity with reduced levels
Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION
 TORTORA FUNKE CASE Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION Differentiate between innate and acquired immunity. Chapter 17 Specific Defenses of the Host: The Immune Response B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein
TORTORA FUNKE CASE Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION Differentiate between innate and acquired immunity. Chapter 17 Specific Defenses of the Host: The Immune Response B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein
Pharmaceutical Biotechnology. Recombinant DNA technology Western blotting and SDS-PAGE
 Pharmaceutical Biotechnology Recombinant DNA technology Western blotting and SDS-PAGE Recombinant DNA Technology Protein Synthesis Western Blot Western blots allow investigators to determine the molecular
Pharmaceutical Biotechnology Recombinant DNA technology Western blotting and SDS-PAGE Recombinant DNA Technology Protein Synthesis Western Blot Western blots allow investigators to determine the molecular
Final Review. Aptamers. Making Aptamers: SELEX 6/3/2011. sirna and mirna. Central Dogma. RNAi: A translation regulation mechanism.
 Central Dogma Final Review Section Week 10 DNA RNA Protein DNA DNA replication DNA RNA transcription RNA Protein translation **RNA DNA reverse transcription http://bass.bio.uci.edu/~hudel/bs99a/lecture20/lecture1_1.html
Central Dogma Final Review Section Week 10 DNA RNA Protein DNA DNA replication DNA RNA transcription RNA Protein translation **RNA DNA reverse transcription http://bass.bio.uci.edu/~hudel/bs99a/lecture20/lecture1_1.html
Detection of a Species-specific Antigen of Gardnerella vaginalis by Western Blot Analysis
 Journal of General Microbiology (1986), 132, 1969-1973. Printed in Great Britain 1969 Detection of a Species-specific Antigen of Gardnerella vaginalis by Western Blot Analysis By Y. L. BOUSTOULLER,* A.
Journal of General Microbiology (1986), 132, 1969-1973. Printed in Great Britain 1969 Detection of a Species-specific Antigen of Gardnerella vaginalis by Western Blot Analysis By Y. L. BOUSTOULLER,* A.
The immune response Antibodies Antigens Epitopes (antigenic determinants) the part of a protein antigen recognized by an antibody Haptens small
 The immune response Antibodies Antigens Epitopes (antigenic determinants) the part of a protein antigen recognized by an antibody Haptens small molecules that can elicit an immune response when linked
The immune response Antibodies Antigens Epitopes (antigenic determinants) the part of a protein antigen recognized by an antibody Haptens small molecules that can elicit an immune response when linked
Angelo Peschiaroli, N. Valerio Dorrello, Daniele Guardavaccaro, Monica Venere, Thanos Halazonetis, Nicholas E. Sherman, and Michele Pagano
 Molecular Cell, Volume 23 Supplemental Data SCF βtrcp -Mediated Degradation of Claspin Regulates Recovery from the DNA Replication Checkpoint Response Angelo Peschiaroli, N. Valerio Dorrello, Daniele Guardavaccaro,
Molecular Cell, Volume 23 Supplemental Data SCF βtrcp -Mediated Degradation of Claspin Regulates Recovery from the DNA Replication Checkpoint Response Angelo Peschiaroli, N. Valerio Dorrello, Daniele Guardavaccaro,
perfectprotein Antibodies ntelechon
 Antibodies ntelechon Milstein and Köhler: The hybridoma technology December 1974, Cambridge: Georges J.F. Köhler, a postdoctorial fellow of César Milstein, had given eternal life to normal antibody producing
Antibodies ntelechon Milstein and Köhler: The hybridoma technology December 1974, Cambridge: Georges J.F. Köhler, a postdoctorial fellow of César Milstein, had given eternal life to normal antibody producing
QED Bioscience Inc. Revision 05/04/11 ADVANCED ANTIBODY TECHNOLOGIES
 CUSTOM POLYCLONAL ANTIBODY DEVELOPMENT QED is committed to excellence across all facets of our operations, and to responding to the ever-changing needs of our customers. We have been developing monoclonal
CUSTOM POLYCLONAL ANTIBODY DEVELOPMENT QED is committed to excellence across all facets of our operations, and to responding to the ever-changing needs of our customers. We have been developing monoclonal
EZ-Run Protein Gel Solution. EZ-Run Protein Standards. EZ-Run Gel Staining Solution. Traditional SDS-Page Reagents. Protein Electrophoresis
 EZ-Run Protein Gel Solution EZ-Run Protein Standards EZ-Run Gel Staining Solution Traditional SDS-Page Reagents Protein Electrophoresis protein electrophoresis Introduction Sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide
EZ-Run Protein Gel Solution EZ-Run Protein Standards EZ-Run Gel Staining Solution Traditional SDS-Page Reagents Protein Electrophoresis protein electrophoresis Introduction Sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide
SCREENING, STABILIZATION AND EXPANSION OF SECRETORY HYBRIDOMAS IN CULTURE AS A STEADY SOURCE OF MONOCLONAL ANTIBODIES (Mabs).
 SCREENING, STABILIZATION AND EXPANSION OF SECRETORY HYBRIDOMAS IN CULTURE AS A STEADY SOURCE OF MONOCLONAL ANTIBODIES (Mabs). Maddaly Ravi a Sukanya Shyama Sundar a, Kaavya Krishna Kumar a, Deepa Parvathi.V
SCREENING, STABILIZATION AND EXPANSION OF SECRETORY HYBRIDOMAS IN CULTURE AS A STEADY SOURCE OF MONOCLONAL ANTIBODIES (Mabs). Maddaly Ravi a Sukanya Shyama Sundar a, Kaavya Krishna Kumar a, Deepa Parvathi.V
Chem 405 Biochemistry Lab I Experiment 2 Quantitation of an unknown protein solution.
 Chem 405 Biochemistry Lab I Experiment 2 Quantitation of an unknown protein solution. Introduction: The determination of protein concentration is frequently required in biochemical work. Several methods
Chem 405 Biochemistry Lab I Experiment 2 Quantitation of an unknown protein solution. Introduction: The determination of protein concentration is frequently required in biochemical work. Several methods
Monash Antibody Technologies Facility
 Monash Antibody Technologies Facility The Monash Antibody Technologies Facility: A high throughput monoclonal antibody production platform for phospho-kinomics Tecan Symposium Zürich September 2007 What
Monash Antibody Technologies Facility The Monash Antibody Technologies Facility: A high throughput monoclonal antibody production platform for phospho-kinomics Tecan Symposium Zürich September 2007 What
ArC Amine Reactive Compensation Bead Kit
 ArC Amine Reactive Compensation Bead Kit Catalog no. A1346 Table 1. Contents and storage information. Material Amount Composition Storage Stability ArC reactive beads (Component A) ArC negative beads (Component
ArC Amine Reactive Compensation Bead Kit Catalog no. A1346 Table 1. Contents and storage information. Material Amount Composition Storage Stability ArC reactive beads (Component A) ArC negative beads (Component
Posttranslational Modifications of Sindbis Virus Glycoproteins: Electrophoretic Analysis of Pulse-Chase- Labeled Infected Cells
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Apr. 1982, p. 64-70 0022-538X/82/040064-07$02.00/0 Vol. 42, No. 1 Posttranslational Modifications of Sindbis Virus Glycoproteins: Electrophoretic Analysis of Pulse-Chase- Labeled Infected
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Apr. 1982, p. 64-70 0022-538X/82/040064-07$02.00/0 Vol. 42, No. 1 Posttranslational Modifications of Sindbis Virus Glycoproteins: Electrophoretic Analysis of Pulse-Chase- Labeled Infected
+ On leave from the Department of Pathology and Internal Medicine
 THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGKAL CHEMISTRY Vol. 257, No. 6, Issue of March 25, pp. 2770-2774, 1982 Printed In U.S.A. Immunochemical Cross-reactivity between Cyanogen Bromide Fragments of Human Serum Albumin* Noelle
THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGKAL CHEMISTRY Vol. 257, No. 6, Issue of March 25, pp. 2770-2774, 1982 Printed In U.S.A. Immunochemical Cross-reactivity between Cyanogen Bromide Fragments of Human Serum Albumin* Noelle
Questions related to peptide antibodies
 www.lifetechindia.com Some Commonly Asked Questions about custom antibody production (Click over the Q# to see details) Questions related to protein antigens and general information Q1 How much antigen
www.lifetechindia.com Some Commonly Asked Questions about custom antibody production (Click over the Q# to see details) Questions related to protein antigens and general information Q1 How much antigen
Biology 309 Lab Notebook
 Name: Biology 309 Lab Notebook This is a guided lab notebook for you to keep well-organized notes about procedures and record experimental data for experiments as they are performed. It is guided because,
Name: Biology 309 Lab Notebook This is a guided lab notebook for you to keep well-organized notes about procedures and record experimental data for experiments as they are performed. It is guided because,
Protocol for Western Blotting
 Protocol for Western Blotting Materials Materials used on Day 3 Protease inhibitor stock: 1 μg/μl pepstatin A in DMSO 200 μm leupeptin in OG Buffer 200 mm PMSF: Freshly made. Ex) 34.8 mg PMSF in 1 ml isopropanol
Protocol for Western Blotting Materials Materials used on Day 3 Protease inhibitor stock: 1 μg/μl pepstatin A in DMSO 200 μm leupeptin in OG Buffer 200 mm PMSF: Freshly made. Ex) 34.8 mg PMSF in 1 ml isopropanol
Proteins. Protein Trivia. Optimizing electrophoresis
 Proteins ELECTROPHORESIS Separation of a charged particle in an electric field Michael A. Pesce, Ph.D Department of Pathology New York-Presbyterian Hospital Columbia University Medical Center Rate of migration
Proteins ELECTROPHORESIS Separation of a charged particle in an electric field Michael A. Pesce, Ph.D Department of Pathology New York-Presbyterian Hospital Columbia University Medical Center Rate of migration
PRODUCTION OF MONOCLONAL ANTIBODIES FOR USE IN IMMUNOASSAYS BASED ON THE MAGNETIZABLE SOLID PHASE SEPARATION TECHNIQUE
 PRODUCTION OF MONOCLONAL ANTIBODIES FOR USE IN IMMUNOASSAYS BASED ON THE MAGNETIZABLE SOLID PHASE SEPARATION TECHNIQUE W. CHAROENSIRIWATANA, N. JANEJAI, P.KRASAO XA9643133 Department of Medical Sciences,
PRODUCTION OF MONOCLONAL ANTIBODIES FOR USE IN IMMUNOASSAYS BASED ON THE MAGNETIZABLE SOLID PHASE SEPARATION TECHNIQUE W. CHAROENSIRIWATANA, N. JANEJAI, P.KRASAO XA9643133 Department of Medical Sciences,
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE FOR THE DIRECT ANTIGLOBULIN TEST
 STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE FOR THE DIRECT ANTIGLOBULIN TEST TITLE: Standard Operating Procedure for Performing the Direct Antiglobulin Test 1.0 Principle To detect in vivo sensitization of red blood
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE FOR THE DIRECT ANTIGLOBULIN TEST TITLE: Standard Operating Procedure for Performing the Direct Antiglobulin Test 1.0 Principle To detect in vivo sensitization of red blood
1.5 Function of analyte For albumin, see separate entry. The immunoglobulins are components of the humoral arm of the immune system.
 Total protein (serum, plasma) 1 Name and description of analyte 1.1 Name of analyte Total protein 1.2 Alternative names None 1.3 NMLC code 1.4 Description of analyte This is a quantitative measurement
Total protein (serum, plasma) 1 Name and description of analyte 1.1 Name of analyte Total protein 1.2 Alternative names None 1.3 NMLC code 1.4 Description of analyte This is a quantitative measurement
