DEVELOPMENT AND CURRENT STATE OF WASTE SECTOR
|
|
|
- Everett Jennings
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 WASTE MANAGEMENT DEVELOPMENT AND CURRENT STATE OF WASTE SECTOR Municipal Waste In accordance with Law on Environment, Solid Waste Management Regulation, Metropolitan Municipalities Law and Municipal Law; Metropolitan municipalities and municipalities out of adjacent zones and the highest civilian authority out of these zones are responsible for ensuring the disposal of domestic and domestic-type industrial solid waste while avoiding environmental damage, ensuring the maximal use of the landfills and ensuring the classification and seperation of recyclable solid waste to contribute to the economy and taking relevant measures to ensure these. Municipalities, while fulfilling their duties in collecting and transporting the solid waste to a great extent, can not show the required level of activity and attention in disposal within solid waste management. The great majority of the solid waste in the country are still not being disposed in accordance with the legislation. There exist many administrative, financial and technical reasons contributing to this existing situtation. Especially unsanitary disposal, errors in selection of the disposal sites and the drawbacks in administration are causing ever increasing problems. In solid waste production, primarily the amount of waste produced should be reduced. Moreover, the need for awareness raising in households for seperation of waste at the source, to make it ready for collection, is ongoing. Existence of many local administrative units in the same region makes it compulsory to have cooperation and coordination in solid waste services like in other infrastructural services. Local administrative union model applications, as promoted by the new legislation, come up as a facilitating bodies for realization of local-level environmental services. Within this framework, it is observed that the number of solid waste projects implemented by local administrative unions are increasing. Solid waste in Turkey is generally discharged to unsanitary landfill sites in an uncontrolled manner. Medical institutions are paying due attention on seperation of medical waste from other solid waste at its source, transportation and temporary storage. Equally, municipalities as well have made progress in proper disposal of the medical waste. Yet bearing these in mind, many municipalities could not establish disposal sites adequate in number and technical aspects to date. Studies on establishment of a nation-wide effective solid waste management system have been initiated. In this regard, Solid Waste Master Plan for the domestic-type waste is completed and further studies are ongoing for development of the National and Regional Waste Management Plan for other waste types. Solid Waste Master Plan Project, implemented under coordination of Ministry of Environment and Forestry (MOEF) and Undersecretariat of State Planning
2 Organization in 2006, has aimed at establishment of unions between municipalities for solid waste disposal across Turkey, development of economically sustainable Regional Solid Waste Facilities and ensuring the implementation of the projects within a plan. As foreseen by the relevant legislation, plans are developed for the establishment of sanitary landfill sites, reduction of amount of produced solid waste, ensuring recycling, reduction of solid waste transport costs and use of transport sites equipped with appropriate technologies where deemed necessary; 16 type of projects are developed in this regard so as to provide guidance to municipalities. MOEF s estimation of domestic solid waste production in 2008, calculated through per capita waste estimates, is 26,8 million tons. 13,3 million tons of these wastes are disposed in sanitary landfills while 0,3 million tons are processed in compost facilities. The number of sanitary landfill sites in operation have risen to 41 by MOEF have carried out various regional fieldwork in 2006 in order to determine the domestic waste composition of households in Turkey in addition to solid waste surveys sent to cities that are representative of Turkey, including 16 metropolitan municipalities. In the light of the fieldwork and declared information on composition, solid waste projections are calculated for the use of all municipalities. The outcome of these studies as 2008 municipal waste composition is shown in Figure 1. Figure 1: Composition of domestic waste (2008)
3 Packaging Waste Necessary legal and technical arrangements are established in order to reduce the environmental pollution caused by the packaging waste as an important component in the solid waste in the country and to recover these as economical assets. In accordance with the Control of Packaging Waste Regulation, packaging material producers are obliged to submit Packaging Material Producer Application Form and the market providers are obliged to submit Market Provider Application Form to the Ministry annually. Within the system defined under the regulation, since municipalities are responsible for waste collection as defined in Law on Metropolitan Municipalities and Law on Municipalities, responsibility of seperation of the packaging waste at the source and its transportation are also given to province and district municipalities. Seperate collection of packaging waste at the source can be done through service procurement as well as being able to be carried out by the province and district municipalities themselves. In accordance with the regulation; collection, transportation and recycling of the packaging waste is prohibited for those except the licensed enterprises. Municipalities are responsible for developing packaging waste management plans which define how, when and in which way packaging waste will be collected and are obliged to carry out their work in this scope. Approval of the plans, prepared within the scope of packaging waste management plans format and submitted to MOEF, has started for the first time in Medical Wastes Wastes produced in medical institutions are classified as medical wastes, hazardous wastes, domestic-type and packaging wastes; these are seperated without mixing at the source and collected with special bags and boxes. In compliance with the regulation; medical wastes must be collected at the source in red-colored special bags with signs of International Biohazard and Caution! Medical Waste seperately. Cutting and perforating wastes, as a sub-group of medical wastes, must be collected seperately from other medical wastes in special boxes with the same caution signs made out of special plastic or laminated cardboard. Wastes collected in medical institutions must be stored in temporary waste storage or containers until they are collected by the municipality. Transportation of medical wastes from temporary storage sites and containers as well as small sources to disposal sites are being carried out by entities and enterprises as authorized by the municipalities. According to 2006 data of Ministry of Health, the total number of hospitals in Turkey is with a total number of available beds in these hospitals being Calculations made taking into consideration of the occupancy rates according to cities reveal a daily estimate of 250 tons and an annual estimate of tons of medical waste produced in ambulatory treatment and inpatient treatment institutions. Medical Waste Control Regulation paved the path for implementation of alternative disposal technologies for the disposal of medical waste in Turkey. In this
4 framework, MOEF has instructed the municipalities to handle domestic solid waste and medical waste disposal in an integrated manner, to consider the medical waste disposal as a component and to prioritize sterilization as the best means of intermediate processing method as per country s circumstances tons of medical waste, corresponding to 14% of the total medical waste is sterilized and made innocuous by September Medical waste sterilization facilities taken into operation in 2008 is presented. Project design and licensing works are ongoing in many cities except these forementioned facilities. Waste oils An approximate amount of 1,5 million tons of vegetable oil is consumed in Turkey annually. It is estimated that thousand tons of fried waste vegetable oil is produced especially after frying processes. Used waste vegetable oils are causing 25% of the domestic wastewater pollution. Municipalities are given the responsibility for the collection of used frying oil from the residences as of 2008 in compliance with the regulations and in order to prevent contraction and clogging in wastewater collection systems (sewerage, collectors, etc.) caused by waste oils. Currently, works on establishment of a system for collecting and processing waste oils are already ongoing. These works carried out under the provisions of Waste Oil Control Regulation are performing registration of waste oil producers, determination of waste oil types and quantities produced in various sectors in Turkey, transportation of waste oils, licensing of recycling and disposal facilities as well as control of the activities of these facilities and determination of illegal practices. There are 21 enterprises licensed by MOEF to recycle waste oils. These enterprises monthly activity reports and collected waste oil quantities as well as the quantity of sales of the products reclaimed through recycling, efficiency of recycling and wastes incurring as a result of recycling processes are evaluated and registered by MOEF. Production of biodiesels from waste vegetable oils are predicated on with the regulation and licensing was made in this direction. As the quantity of collected waste oils increase, illegal waste oil markets and uncontrolled use of these waste oils will be forestalled. An environmentally-aware use of waste oils for energy recovery as an additional fuel in cement factories is encouraged. However refinement and regeneration of waste oils are more prioritized. Thus the aim is set at increasing the number of recycling and regeneration facilities and improvement of the conditions of 21 currently operating facilities. Waste Oils Management Project is aimed at collecting and waste engine oil used in motor vehicles by licensed and authorized crews in proper manners in car service stations, oil stations and public vehicle maintenance stations; and ensuring processing of these with avoiding harm to nature or humans and establishment of appropriate collection system, determination of oil producing sources and awareness raising. The amount of collected waste engine oil and collection points have increased gradually since the initiation of the work in May 2004 and expanded to whole country.
5 Within the scope of these studies, tons of waste engine oil is collected from waste oil producers in a total of 79 provinces by paying visits in 5 year timespan including October 2009 and these are recycled in licensed facilities either as product or energy. The number of enterprises contributing to organization is 85 and the quantity of engine oil served to market by these enterprises in 2008 is tons. 63% of the waste oil collected in 5 years was collected from car service stations while 15% from industrial car parks, 11% from public institutions, 4% from municipalities, 5% from oil production facilities and 1% from the oil stations. Waste Batteries and Accumulators The responsibility of collection, transportation, recycling and disposal of waste batteries and accumulators lies with the producers. In order to ensure seperate collection of waste batteries from the domestic solid waste, a waste battery collection obligation is introduced for battery producers and exporters as per their quotas. An obligation is introduced for accumulator producer and exporters to collect waste accumulators as per defined deposit rates. The responsibility for seperate disposal of waste batteries from domestic wastes lies with the municipalities. Allocation of land for waste battery storage sites with impervious conditions, of which the establishment and operational costs will be born by battery producers, is also among the role and responsibility of the municipalities. Annual amount of batteries supplied to market in Turkey is approximately tons while annual amount of accumulators is tons. Within the scope of inventory studies realized under the framework of regulation, total amount of registered waste batteries equals 200 tons, total amount of waste accumulators equals to tons in Total amount of waste accumulator collected in accordance with the regulation corresponds to 67% of the accumulators supplied to the market in 2007, total amount of collected waste batteries corresponds to 2% of the batteries supplied to the market in Hazardous Waste Due to the priority given in the current state to production, product quality and costs given in production industry in Turkey, waste reduction and recycling maintained a secondary role. However developing environmental protection awareness over time, legal sanctions, difficulties faced in waste disposal and most importantly increasing significance of environmental protection measures in production in international trade have placed use of clean technologies and waste reduction in an important position. Efforts for reuse and recycling of hazardous wastes often focus on wastes that require simple technologies for collection and disposal. The most striking example of this could be recycling of barrels and silver. Waste markets are established under the chambers of commerce, by Union of Chambers of Commerce and Commodity Exchanges of Turkey (TOBB) with the support of MOEF, in order to reduce the amount of industrial waste and allow their reuse. As of 2008, there are 3 disposal facilities in Turkey for hazardous waste through incineration. Capacities of these facilities are inadequate in meeting the needs of industry.
6 Except these, a pilot scale facility which received license for recycling hazardous wastes through gassification with a capacity of tons/year is put into operation in Đstanbul Kemerburgaz. Moreover some cement factories are accepting hazardous wastes as alternative fuels for purposes of energy recovery. Due to technological inadequacy of stack gas treatment systems in cement factories in eliminating stack gases that are produced as a result of hazardous waste incineration, these factories are only able to accept certain types of wastes. Among these are used tyres, I. and II. category waste oils, paint sludge, solvents, plastic wastes etc. Energy recovery license is being distributed to allow the use of hazardous waste in cement kilns as an alternative fuel with 24 facilities already in possession of this license. Some of the hazardous wastes are also exported to be disposed in incineration facilities abroad. Production industry in Turkey is annually producing more than 20 million tons of waste. Approximately 1.12 million tons of this amount is made up of hazardous wastes. 8% of this amount is being recovered, 47% is being disposed and 45% is being reused. Approximately 80% of the established capacity of 6 facility licensed by MOEF for the disposal of industrial waste is currently in use tons of ash and slag coming from incineration facilities are disposed in sanitary landfills. Provision of services by hazardous waste facilities in regions of high population density and high industrialization rates in Turkey is advantageous both in terms of costs, utility and to keep the environmental loads at minimum. INSTITUTIONAL FRAMEWORK According to the constitution of Republic of Turkey; improving environment, preventing environmental pollution and protecting environment is a duty of all public institutions and citizens. Institutions responsible for waste management as per their fields of work are as follows. 1. Ministry of Environment and Forestry (MOEF): The main duty of MOEF is to define policies and principles in most general terms aiming at protecting the environment, preventing and reducing pollution, organizing the relevant legislation and ensuring its implementation. Responsibilities of MOEF in terms of waste management: These can be summarized in terms of preparation of by-laws and national regulations, producing policy and strategy for waste management, organization of nation-wide actions on waste management, research, coordination of waste management plan preparation, taking precautionary measures, defining technical standards, licensing, monitoring, regulation, keeping track of given licenses, data collection, exportation of wastes, release of permits regulating hazardous waste import and transportation of these wastes over Turkey and ensuring the continuation of trainings. 2. State Planning Organization (SPO): Undersecretariat of SPO under Prime Ministry is responsible for preparing Development Plans, medium-term and annual programmes and annual investment plans. In this regard, SPO is developing macro policies for waste management and taking relevant measures to ensure coherence of
7 legal and institutional arrangements with these policies. Moreover, the projects of central administrative institutions and the projects of municipalities that need foreign loan are appraised by SPO and the feasible one are included into public investment portfolio. 3. Undersecretariat of Treasury: It has a role in following up and finalizing credit negotiations where external financing is provided for the waste related projects. 4. Ministry of Health: It has a role in monitoring and ensuring coherence with respect to its mandate on public health. 5. Ministry of Interior: It is responsible in the process with respect to its mandate in developing, monitoring and controlling policies regarding local authorities. 6. Ministry of Finance: Ministry of Finance is responsible for tax arrangements, tax collection and follow-up. As regards this, it is responsible for preparing the legal arrangements for financing the waste management. 7. Ministry of Industry and Trade: It is responsible for supporting and controlling establishment of large and small scale industries, preparing standards for industrial products or publishing prepared standards, controlling the quality of industrial assets or to get this control done. 8. Directorate-General of Bank of Provinces: It is providing technical support to municipalities for the solid waste projects run by municipalities. It provides financing for solid waste management projects on municipality s request and be a credit guarantor. 9. Ministry of Transport: It is responsible for establishment and development of transport and communication systems and services as per country s needs. Authorization documents for waste transportation is given by Ministry of Transport and Communication. 10. Turkish Standards Institution: Among other responsibilities, it is responsible for preparing standards for waste management services. 11. Local Authorities: The most important task on protection of environmental quality is given to local authorities. Local authorities, also entrusted with the task of waste management within the framework of laws and regulations, are obliged to ensure the implementation of legal arrangements and take appropriate measures for ensuring a healthy environment for citizens to live within their territories of responsibility. 12. Sectoral Unions: Union of Chamber of Commerce and Commodity Exchanges of Turkey, Union of Chambers of Turkish Engineers and Architects, Chambers of Commerce, Chambers of Trade and sectorally established bodies like Turkish Cement Manufacturers Association, Union of Lime Producers are responsible for delivering information and carrying out studies on enforcement and control on issues like sectoral approaches to implementation of the legislation. LEGAL FRAMEWORK The most important aspects of provisions of laws related to waste is summarized below:
8 Law on Environment no. 2872: Article 8 - It is prohibited to discharge all sorts of waste and residue directly or indirectly into receiving environment, storing them or being engaged in a similar activity. Law on Amendments in Law on Environment no. 5491: Amendment in Article 11 - Metropolitan municipalities and municipalities are responsible for establishing domestic solid waste disposal facilities, ensuring their establishment, operating them or ensuring their operation. Those who benefit or will benefit from this service are liable for sharing the costs of investment, operation, maintenance and improvement to be carried out by responsible authorities. Municipality collects solid waste collection, transportation and disposal fees from those who benefit from this service in accordance with the tariffs to be decided upon by the municipal council. The fees collected in relation to this clause can not be used for services other than those related to solid waste Law on Metropolitan Municipalities no. 5216: Article planning solid waste management, ensuring its planning; providing services for revalorizing, storage and disposal of the solid wastes and excavation residues other than seperation of solid waste at the source and its transportation until transfer station and to establish facilities for their fulfillment... Municipal Law no. 5393: Articles 14 and carrying out or ensuring accomplishment of collection of solid wastes, their transportation, seperation, recycling, disposal and storage... Law on Municipal Revenues no (ÇTV): Article 97 - Waste producers participation to waste management services is ensured with polluter-pays principle. Turkish Penal Code no : With articles 181 and 182, penalties are established regarding polluting the environment with intent or negligence, penal sanctions up to jail sentences are foreseen for the responsibles. SIGNIFICANT SECTORAL POLICIES Waste problem is accepted as a priority for Turkey and policies are being developed to overcome this problem. Development plans are the main tools for coordination of public policy in Turkey. In this regard, plans are one among the main policy documents on solid waste. Significant policies regarding solid waste management, as they are reflected in 9th Development Plan, are given below: In domestic type solid waste management, seperation, collection, transportation, recycling and disposal phases will be considered as a whole in technical and financial terms; sanitary landfill method with low investment and operational costs as the most suitable solid waste disposal technology will be preferred.
9 Production of non-domestic wastes will be reduced, collection relevant to waste type and country s circumstances, transportation, recycling and disposal systems will be established. In order to identify the urban infrastructure needs regarding environmental protection across the country, urban infrastructure master plan and financing strategy will be prepared to define the municipalities needs for infrastructure like drinking water system, sewerage, wastewater treatment plant and solid waste disposal. Capacities of the municipalities will be developed in terms of planning, project design, implementation and operation of environmental infrastructure services. Technologies and systems that are most suitable to country s circumstances will be preferred in establishment, maintenance and operation of water, wastewater and solid waste infrastructure aiming at environmental protection. Financial and technical consultancy services that will be provided to municipalities for urban infrastructure investments will be activated. Through using environmentally friendly techniques in the industry, more efficient production will be achieved by increased efficacy of raw material use and thus wastes will be reduced. RELATION OF THE SECTOR WITH SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT Increase in production followed by increase in consumption brought an increase in life standards of the society along with an increased amount and changed composition of solid waste. Elimination of generated solid waste with least damage to environment especially became a major problem for the big cities. Solid waste management which covers control of urban solid waste and works regarding introducing healthy and economical solutions to this issue have taken its place among development priorities as regards providing services with international standards to urban citizens and protection of environmental quality. Policies aiming at preventing and reducing hazardous waste Considering the waste management hierarchy, it is evident that waste reduction and prevention will enhance the lifetime of sanitary landfills. Thus there are ongoing works to reduce the amount of materials that give waste a hazardous waste character. For example; works on reducing the carbon amount existent in electronic wastes are proceeding. On the other hand, some restrictions are introduced with regulations on use of heavy metals in batteries. Additionally, in a booklet published on domestic hazardous waste, hazardous materials used in households are defined and their non-hazardous substitutes are presented to the general public. Environmental protection awareness which actively developed after 1993, legal sanctions, difficulties in waste disposal and most importantly increased importance of the production related environmental protections measures in international trade have placed use of clean technologies and waste reduction in an important position.
10 Efforts in reuse and recycling of hazardous waste are concentrating on wastes that require simpler technologies for their collection and use. Waste markets established in the country, which are enabling recycling, need to be improved. Especially in chemicals sector in Turkey, there are trainings open to everyone as organized by trade associations and chambers of commerce. These trainings specifically focus on transmitting knowledge and applications of waste management systems, development of waste management plans and waste reduction for small and mediumsized enterprises. Recycling and Recovery Facilities Licensing of enterprises for seperation and recycling of packaging material waste was first initiated in In the four year period between 2003 to 2007, the number of licenses given to seperation facilities by MOEF reached 81 and that of recycling facilities reached 56. Among the licensed recycling facilities, 18 are paper, 6 are glass, 55 are plastic, 3 are metal and 2 are composite wastes recycling facilities. According to 2007 data, there are 52 facilities which recover hazardous wastes especially through recovery of energy and solvents. Total capacity of hazardous waste recovery facilities are approximately tons/year and their existing used capacities are approximately tons/year. There is a total of 13 facilities that carry out recovery of lead from waste accumulators dispersed in 10 cities. Ankara, Đstanbul and Bursa are the cities that have ongoing works regarding the use of landfill gas from sanitary landfills in Turkey. Gaziantep Metropolitan Municipality has also started studies in this regard. Radioactive Wastes and Environmentally Conscious Management The only low-level radioactive waste processing facility in Turkey was established in Primarily, equipment containing radioactive components are supposed to be sent to country of origin for disposal however in the case of unavailability of this transfer, equipments are required to be handed in to the forementioned facility. In such a case, transportation process should be realized through companies with radioactive waste transfer license or under the liability of the responsible staff for protection from radiation, working for companies which hold license to use and maintain radioactive equipment in full compliance with the relevant regulation. Transfer responsible of the companies with radioactive waste transfer license or the responsible staff for protection from radiation of the companies with radioactive equipment use and maintanance license are liable for transport safety and security of the transferred material during each radioactive waste transport, packaging, loading, unloading and during the transfer of radioactive waste.
11
In the Name of God. Waste Management Law
 In the Name of God Waste Management Law Article 1- To fulfil the fiftieth Principle of the Islamic Republic of Iran Constitutional Law and in order to protect the environment form harmful effects of waste
In the Name of God Waste Management Law Article 1- To fulfil the fiftieth Principle of the Islamic Republic of Iran Constitutional Law and in order to protect the environment form harmful effects of waste
Policy measures for the prevention and minimization of hazardous wastes
 WASTE AND WASTE MANAGEMENT PROGRESS AND ACHEIVEMENTS Policy measures for the prevention and minimization of hazardous wastes 1. At the international level, Mongolia joined The Basel Convention on the Control
WASTE AND WASTE MANAGEMENT PROGRESS AND ACHEIVEMENTS Policy measures for the prevention and minimization of hazardous wastes 1. At the international level, Mongolia joined The Basel Convention on the Control
WASTE QUESTIONNAIRE. Legal basis Council Directive 75/442/EEC of 15 July 1975 on waste (OJ L 194 25.07.1975 p. 39) EUR-Lex hyperlink html
 WASTE QUESTIONNAIRE Waste Framework Directive Legal basis Council Directive 75/442/EEC of 15 July 1975 on waste (OJ L 194 25.07.1975 p. 39) EUR-Lex hyperlink html A. Which parts of the provisions of the
WASTE QUESTIONNAIRE Waste Framework Directive Legal basis Council Directive 75/442/EEC of 15 July 1975 on waste (OJ L 194 25.07.1975 p. 39) EUR-Lex hyperlink html A. Which parts of the provisions of the
A. WASTE MANAGEMENT A.1. INTRODUCTION AND GENERAL ISSUES ON HAZARDOUS WASTES AND SOLID WASTES
 A. WASTE MANAGEMENT A.1. INTRODUCTION AND GENERAL ISSUES ON HAZARDOUS WASTES AND SOLID WASTES The objective of the German government s policy on waste is to achieve a recyclingbased economy that conserves
A. WASTE MANAGEMENT A.1. INTRODUCTION AND GENERAL ISSUES ON HAZARDOUS WASTES AND SOLID WASTES The objective of the German government s policy on waste is to achieve a recyclingbased economy that conserves
Waste Management. Background
 Waste Management Background Overview of current waste management In 1970, the main method of waste disposal in Iceland was open-pit burning. Over 50 burning pits were in operation, close to one pit per
Waste Management Background Overview of current waste management In 1970, the main method of waste disposal in Iceland was open-pit burning. Over 50 burning pits were in operation, close to one pit per
PHARMACEUTICAL AND CHEMICAL WASTE MANAGEMENT
 Medicines and Medical Devices Agency of Serbia PHARMACEUTICAL AND CHEMICAL WASTE MANAGEMENT Ivana Bozic, MSc Health, Safety and Environment ISWA Beacon Conference, Novi Sad, 08 10 December 2010 458, Vojvode
Medicines and Medical Devices Agency of Serbia PHARMACEUTICAL AND CHEMICAL WASTE MANAGEMENT Ivana Bozic, MSc Health, Safety and Environment ISWA Beacon Conference, Novi Sad, 08 10 December 2010 458, Vojvode
ORDINANCE NO. 3 OF 2009
 PENN TOWNSHIP CUMBERLAND COUNTY BOARD OF SUPERVISORS 1301 Centerville Road Tel: 717-486-3104 Newville, PA 17241 Fax: 717-486-3522 Email: [email protected] Website: www.penntwpcc.org ORDINANCE NO. 3 OF
PENN TOWNSHIP CUMBERLAND COUNTY BOARD OF SUPERVISORS 1301 Centerville Road Tel: 717-486-3104 Newville, PA 17241 Fax: 717-486-3522 Email: [email protected] Website: www.penntwpcc.org ORDINANCE NO. 3 OF
Policy and Regulations Faridabad (India)
 Policy and Regulations Faridabad (2009) Policy and Regulations Faridabad (India) 1.1 Policies No specific regulations have been framed for addressing the management of plastic waste, and it is thus governed
Policy and Regulations Faridabad (2009) Policy and Regulations Faridabad (India) 1.1 Policies No specific regulations have been framed for addressing the management of plastic waste, and it is thus governed
Integrated waste management system for the reuse of used frying oils to produce biodiesel for municipality fleet of Oeiras
 LIFE ENVIRONMENT Programme Integrated waste management system for the reuse of used frying oils to produce biodiesel for municipality fleet of Oeiras Project co-funded by the LIFE Environment programme
LIFE ENVIRONMENT Programme Integrated waste management system for the reuse of used frying oils to produce biodiesel for municipality fleet of Oeiras Project co-funded by the LIFE Environment programme
Waste management of hazardous waste in Poland
 Waste management of hazardous waste in Poland Administrative structure of Poland. There are three levels of administrative structure in Poland: regions (called województwo) sub-regions (called powiat)
Waste management of hazardous waste in Poland Administrative structure of Poland. There are three levels of administrative structure in Poland: regions (called województwo) sub-regions (called powiat)
SANITATION COUNTRY PROFILE NORWAY
 SANITATION COUNTRY PROFILE NORWAY Decision-Making Programmes and Projects Status Capacity-Building, Education, Training and Awareness-Raising Information Research and Technologies Financing Cooperation
SANITATION COUNTRY PROFILE NORWAY Decision-Making Programmes and Projects Status Capacity-Building, Education, Training and Awareness-Raising Information Research and Technologies Financing Cooperation
Monitoring & Recording Hazardous & Non-Hazardous Waste
 GIIRS Emerging Market Assessment Resource Guide: What s in this Guide? I. Definition: What is II. Methods for Disposal: Non-Hazardous Waste III. Methods for Storage and Disposal: Hazardous Waste IV. Additional
GIIRS Emerging Market Assessment Resource Guide: What s in this Guide? I. Definition: What is II. Methods for Disposal: Non-Hazardous Waste III. Methods for Storage and Disposal: Hazardous Waste IV. Additional
Florida Department of Environmental Protection
 Florida Department of Environmental Protection Background Mobile vehicle and equipment washing involves washing at a location where vehicles are based (such as a trucking company, warehouse, bus station,
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Background Mobile vehicle and equipment washing involves washing at a location where vehicles are based (such as a trucking company, warehouse, bus station,
Packaging Management Law 5771 2011
 1 This is an unofficial translation. The binding version is the official Hebrew text. Readers are consequently advised to consult qualified professional counsel before making any decision in connection
1 This is an unofficial translation. The binding version is the official Hebrew text. Readers are consequently advised to consult qualified professional counsel before making any decision in connection
Urban Environmental Management in Singapore. Jothieswaran P Chief Engineer Pollution Control Department National Environment Agency
 Urban Environmental Management in Singapore Jothieswaran P Chief Engineer Pollution Control Department National Environment Agency Introduction City state comprising a main island and some islets Land
Urban Environmental Management in Singapore Jothieswaran P Chief Engineer Pollution Control Department National Environment Agency Introduction City state comprising a main island and some islets Land
Waste Management Policy
 University of Sussex Waste Management Policy May 2007 1 University of Sussex Waste Management Policy Contents 1. Introduction 2. Policy Statement 3. Policy Objectives 4. Application 5. Organisation and
University of Sussex Waste Management Policy May 2007 1 University of Sussex Waste Management Policy Contents 1. Introduction 2. Policy Statement 3. Policy Objectives 4. Application 5. Organisation and
Costs related to health-care waste management
 11 Costs related to health-care waste management 11.1 Principles According to the polluter pays principle, each health-care establishment should be financially liable for the safe management of any waste
11 Costs related to health-care waste management 11.1 Principles According to the polluter pays principle, each health-care establishment should be financially liable for the safe management of any waste
Slide 1. Enviros Consulting Ltd
 Slide 1 Regulation of Waste Management Activities Past, Present and Future! Steve Bell Technical Manager Waste Management Thursday, 26 July 2007 Presentation Aims An insight of where we have come from
Slide 1 Regulation of Waste Management Activities Past, Present and Future! Steve Bell Technical Manager Waste Management Thursday, 26 July 2007 Presentation Aims An insight of where we have come from
Integrated Solid Waste Management Oran, Algeria. Program Overview by R20 Regions of Climate Action
 Integrated Solid Waste Management Oran, Algeria Program Overview by R20 Regions of Climate Action A PROGRAM BY Under the leadership of the Algerian Ministry of Environment and Land Planning, R20 Regions
Integrated Solid Waste Management Oran, Algeria Program Overview by R20 Regions of Climate Action A PROGRAM BY Under the leadership of the Algerian Ministry of Environment and Land Planning, R20 Regions
Use of Substitute Fuels in Large Combustion Plants (LCPs)
 Use of Substitute Fuels in Large Combustion Plants (LCPs) By Pat Swords Content of the Presentation What are substitute fuels What is the experience to date with these fuels What are the regulatory implications
Use of Substitute Fuels in Large Combustion Plants (LCPs) By Pat Swords Content of the Presentation What are substitute fuels What is the experience to date with these fuels What are the regulatory implications
European waste policy:
 Waste: the problem European waste policy: prevention a dream? EU Waste policy: general principles and summary of legislation Waste Framework Directive - 2008 Waste Electr(on)ical Equipment 2002 and review
Waste: the problem European waste policy: prevention a dream? EU Waste policy: general principles and summary of legislation Waste Framework Directive - 2008 Waste Electr(on)ical Equipment 2002 and review
MAPPING NEEDS AND ACTIVITIES ON WASTE MANAGEMENT
 Asia Pacific Workshop on Global Partnership on Waste Management: MAPPING NEEDS AND ACTIVITIES ON WASTE MANAGEMENT COUNTRY REPORT BY DALSON CHUNG DIRECTOR (INDUSTRY DEVELOPMENT AND PROMOTION OFFICE) NATIONAL
Asia Pacific Workshop on Global Partnership on Waste Management: MAPPING NEEDS AND ACTIVITIES ON WASTE MANAGEMENT COUNTRY REPORT BY DALSON CHUNG DIRECTOR (INDUSTRY DEVELOPMENT AND PROMOTION OFFICE) NATIONAL
Country specific notes on municipal waste data
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION EUROSTAT Directorate E: Sectoral and regional statistics Unit E-2: Environmental Statistics and Accounts; Sustainable Development Country specific notes on municipal waste data Last
EUROPEAN COMMISSION EUROSTAT Directorate E: Sectoral and regional statistics Unit E-2: Environmental Statistics and Accounts; Sustainable Development Country specific notes on municipal waste data Last
Oman Environmental Services Holding Company
 Oman Environmental Services Holding Company Population 654,000 3 Schools with a total of 909 students 1970 Less waste generated 10 km of paved roads and 1,700km of unpaved roads 1 small Hospital with unreliable
Oman Environmental Services Holding Company Population 654,000 3 Schools with a total of 909 students 1970 Less waste generated 10 km of paved roads and 1,700km of unpaved roads 1 small Hospital with unreliable
Latifa MOUHIR Department Process Engineering and Environment Faculty of Science and Technology Hassan II University. Mohammedia. Morocco.
 Latifa MOUHIR Department Process Engineering and Environment Faculty of Science and Technology Hassan II University. Mohammedia. Morocco. E mail: [email protected]. INTRODUCTION MEDICAL AND PHARMACEUTICAL
Latifa MOUHIR Department Process Engineering and Environment Faculty of Science and Technology Hassan II University. Mohammedia. Morocco. E mail: [email protected]. INTRODUCTION MEDICAL AND PHARMACEUTICAL
2006 Standard Application Processing Time. 10 months. 14 months
 Air and Radiation Management Administration General Permit to Construct - without expanded public review Air Quality Permit to Construct - with expanded public review but limited public interest 11 months
Air and Radiation Management Administration General Permit to Construct - without expanded public review Air Quality Permit to Construct - with expanded public review but limited public interest 11 months
R4R GUIDELINES FOR LOCAL AND REGIONAL AUTHORITIES
 R4R GUIDELINES FOR LOCAL AND REGIONAL AUTHORITIES Helping cities and regions to improve their selective collection and recycling strategies November 2014 1. THE R4R PROJECT IN A NUTSHELL 1.1 The birth
R4R GUIDELINES FOR LOCAL AND REGIONAL AUTHORITIES Helping cities and regions to improve their selective collection and recycling strategies November 2014 1. THE R4R PROJECT IN A NUTSHELL 1.1 The birth
Waste management in the Netherlands. Herman Huisman RWS Environment
 Waste management in the Netherlands Herman Huisman RWS Environment Whistler, May 29th 2014 Content Waste policy EU Netherlands performance in waste management Instruments we used Integrate waste management
Waste management in the Netherlands Herman Huisman RWS Environment Whistler, May 29th 2014 Content Waste policy EU Netherlands performance in waste management Instruments we used Integrate waste management
LEGAL FRAMEWORK, POTENTIAL AND OUTLOOK FOR BIOENERGY SECTOR IN VIETNAM
 Conference on Bioenergy in Viet Nam October 6 th, 2014, HCM City LEGAL FRAMEWORK, POTENTIAL AND OUTLOOK FOR BIOENERGY SECTOR IN VIETNAM By Nguyen Duc Cuong Director of Center for Renewable Energy & CDM,
Conference on Bioenergy in Viet Nam October 6 th, 2014, HCM City LEGAL FRAMEWORK, POTENTIAL AND OUTLOOK FOR BIOENERGY SECTOR IN VIETNAM By Nguyen Duc Cuong Director of Center for Renewable Energy & CDM,
Energy Production from Municipal Waste: Business Potential and Project Opportunities
 Energy Production from Municipal Waste: Business Potential and Project Opportunities MARTIAL BECK, Vice President & General Manager, European Chamber of Commerce of the Philippines www.renewables-made-in-germany.com
Energy Production from Municipal Waste: Business Potential and Project Opportunities MARTIAL BECK, Vice President & General Manager, European Chamber of Commerce of the Philippines www.renewables-made-in-germany.com
ALBEMARLE COUNTY CODE CHAPTER 13 SOLID WASTE DISPOSAL AND RECYCLING. ARTICLE I. IN GENERAL
 CHAPTER 13 SOLID WASTE DISPOSAL AND RECYCLING. Sections: ARTICLE I. IN GENERAL 13-100 Definitions. 13-101 Permit required. 13-102 Waste collection and recycling permit application. 13-103 Waste collection
CHAPTER 13 SOLID WASTE DISPOSAL AND RECYCLING. Sections: ARTICLE I. IN GENERAL 13-100 Definitions. 13-101 Permit required. 13-102 Waste collection and recycling permit application. 13-103 Waste collection
Practices in China. Outline
 Waste Management Policies and Practices in China Ministry of Environmental Protection Regional Workshop of the Greater Mekong Sub-region to share the lessons learnt from the Vietnam experience on the National
Waste Management Policies and Practices in China Ministry of Environmental Protection Regional Workshop of the Greater Mekong Sub-region to share the lessons learnt from the Vietnam experience on the National
WASTE MANAGEMENT. Prevention and minimization and environmentally sound management of hazardous wastes
 ISRAEL - NATIONAL REPORT CSD-18 WASTE MANAGEMENT Introduction Integrated waste management is an important component of Israel's environmental policy. To address the challenges of both solid and hazardous
ISRAEL - NATIONAL REPORT CSD-18 WASTE MANAGEMENT Introduction Integrated waste management is an important component of Israel's environmental policy. To address the challenges of both solid and hazardous
Medical Waste Management Issues in Asia
 Medical Waste Management Issues in Asia C. Visvanathan Environmental Engineering & Management Program Asian Institute of Technology Thailand 1 [email protected] Web: http://www.faculty.ait.ac.th/visu/ Asia
Medical Waste Management Issues in Asia C. Visvanathan Environmental Engineering & Management Program Asian Institute of Technology Thailand 1 [email protected] Web: http://www.faculty.ait.ac.th/visu/ Asia
Can I Recycle Some of My Industrial or Hazardous Wastes?
 TCEQ REGULATORY GUIDANCE Waste Permits Division RG-240 August 2006 Can I Recycle Some of My Industrial or Hazardous Wastes? Purpose. The purpose of this document is to assist those who recycle industrial
TCEQ REGULATORY GUIDANCE Waste Permits Division RG-240 August 2006 Can I Recycle Some of My Industrial or Hazardous Wastes? Purpose. The purpose of this document is to assist those who recycle industrial
SOLID WASTE MANAGEMENT IN TURKEY Current Status and Developments
 SOLID WASTE MANAGEMENT IN TURKEY Current Status and Developments Res. Asst. Başak TARHAN, M.Sc. Prof. Dr. Kahraman ÜNLÜ Middle East Technical University Department of Environmental Engineering INTRODUCTION
SOLID WASTE MANAGEMENT IN TURKEY Current Status and Developments Res. Asst. Başak TARHAN, M.Sc. Prof. Dr. Kahraman ÜNLÜ Middle East Technical University Department of Environmental Engineering INTRODUCTION
Solid Waste Management in LAC: Actual and Future CH4 Emissions and Reductions
 Solid Waste Management in LAC: Actual and Future CH4 Emissions and Reductions The World Bank, August 2008 This presentation will focus on: 1. Current Situation of MSWM service provision in LAC and identification
Solid Waste Management in LAC: Actual and Future CH4 Emissions and Reductions The World Bank, August 2008 This presentation will focus on: 1. Current Situation of MSWM service provision in LAC and identification
Greening Our Future By Educating Tomorrow s Workforce. Module 2: Lean Manufacturing and the Environment
 Greening Our Future By Educating Tomorrow s Workforce Module 2: Lean Manufacturing and the Environment 11/16/2011 Module 2: Lean Manufacturing and the Environment What You Will Learn From This Module:
Greening Our Future By Educating Tomorrow s Workforce Module 2: Lean Manufacturing and the Environment 11/16/2011 Module 2: Lean Manufacturing and the Environment What You Will Learn From This Module:
LCA EXPERIENCE IN THE FIELD OF RECYCLING OF PLASTICS FROM ELECTRONIC WASTE
 LCA EXPERIENCE IN THE FIELD OF RECYCLING OF PLASTICS FROM ELECTRONIC WASTE B. DeBenedetti, L. Maffia, G.L. Baldo 2 Dipartimento di Scienza dei Materiali ed Ingegneria Chimica, Politecnico di Torino, Italy
LCA EXPERIENCE IN THE FIELD OF RECYCLING OF PLASTICS FROM ELECTRONIC WASTE B. DeBenedetti, L. Maffia, G.L. Baldo 2 Dipartimento di Scienza dei Materiali ed Ingegneria Chimica, Politecnico di Torino, Italy
PUBLISHED IN OFFICIAL GAZETTE OF THE REPUBLIC OF MACEDONIA NO. 6/2004 LAW ON WASTE MANAGEMENT
 PUBLISHED IN OFFICIAL GAZETTE OF THE REPUBLIC OF MACEDONIA NO. 6/2004 LAW ON WASTE MANAGEMENT Skopje, October 2004 CONTENTS OF THE LAW ON WASTE MANAGEMENT I. GENERAL PROVISIONS Article 1 Subject of regulation
PUBLISHED IN OFFICIAL GAZETTE OF THE REPUBLIC OF MACEDONIA NO. 6/2004 LAW ON WASTE MANAGEMENT Skopje, October 2004 CONTENTS OF THE LAW ON WASTE MANAGEMENT I. GENERAL PROVISIONS Article 1 Subject of regulation
UNCSD Thematic Seminar on Waste Management. January 12, 2010
 UNCSD Thematic Seminar on Waste Management January 12, 2010 WASTE MANAGEMENT IN THE CARIBBEAN This presentation will look at the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats related to waste management
UNCSD Thematic Seminar on Waste Management January 12, 2010 WASTE MANAGEMENT IN THE CARIBBEAN This presentation will look at the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats related to waste management
Municipal waste management in Austria
 Municipal waste management in Austria Prepared by Márton Herczeg ETC/SCP February 2013 EEA project manager Almut Reichel Author affiliation Márton Herczeg, Copenhagen Resource Institute, http://www.cri.dk/
Municipal waste management in Austria Prepared by Márton Herczeg ETC/SCP February 2013 EEA project manager Almut Reichel Author affiliation Márton Herczeg, Copenhagen Resource Institute, http://www.cri.dk/
WASTE MANAGEMENT APPROACH IN THE EMIRATES OF ABU DHABI (Focus Waste to Energy) Dr. Udayan Banerjee Center of Waste Management Abu Dhabi
 WASTE MANAGEMENT APPROACH IN THE EMIRATES OF ABU DHABI (Focus Waste to Energy) Dr. Udayan Banerjee Center of Waste Management Abu Dhabi National Regulatory Framework UAE Federal Law # 24 of 1999 - Protection
WASTE MANAGEMENT APPROACH IN THE EMIRATES OF ABU DHABI (Focus Waste to Energy) Dr. Udayan Banerjee Center of Waste Management Abu Dhabi National Regulatory Framework UAE Federal Law # 24 of 1999 - Protection
AGENCY SUMMARY NARRATIVE
 AGENCY SUMMARY Mission Statement and Statutory Authority DEQ s mission is to be a leader in restoring, maintaining and enhancing the quality of Oregon s air, water and land. The Department of Environmental
AGENCY SUMMARY Mission Statement and Statutory Authority DEQ s mission is to be a leader in restoring, maintaining and enhancing the quality of Oregon s air, water and land. The Department of Environmental
Waste Management in Berlin
 Waste Management in Berlin Part One Michael Resch Europe a continent with city-specific and very widely differenciated Waste Management Systems P, P, P+P or PPP? Dumper, Pyromaniac, Separator, Waste and
Waste Management in Berlin Part One Michael Resch Europe a continent with city-specific and very widely differenciated Waste Management Systems P, P, P+P or PPP? Dumper, Pyromaniac, Separator, Waste and
TITLE 6. Health and Sanitation CHAPTER 1. Health and Sanitation
 TITLE 6 Chapter 1 Chapter 2 Pollution Abatement CHAPTER 1 6-1-1 Health Officer; Duties and Powers 6-1-2 Rules and Regulations 6-1-3 Health Nuisances 6-1-4 Compulsory Connection to Sewer and Water 6-1-5
TITLE 6 Chapter 1 Chapter 2 Pollution Abatement CHAPTER 1 6-1-1 Health Officer; Duties and Powers 6-1-2 Rules and Regulations 6-1-3 Health Nuisances 6-1-4 Compulsory Connection to Sewer and Water 6-1-5
An Introduction to Product Takeback
 An Introduction to Product Takeback Overview Driving forces behind product takeback Product takeback legislation Product end-of-life options Reverse logistics Case study Motivation for Product Takeback
An Introduction to Product Takeback Overview Driving forces behind product takeback Product takeback legislation Product end-of-life options Reverse logistics Case study Motivation for Product Takeback
Using a decision support software in planning a waste management system in Hungary
 Using a decision support software in planning a waste management system in Hungary ANGELIKA CSERNY, ANETT UTASI, ENDRE DOMOKOS Institute of Environmental Engineering University of Pannonia Veszprém, Egyetem
Using a decision support software in planning a waste management system in Hungary ANGELIKA CSERNY, ANETT UTASI, ENDRE DOMOKOS Institute of Environmental Engineering University of Pannonia Veszprém, Egyetem
IWR Integrated Waste Recycling. Integrated System for treatment and recycling of Municipal Solid Waste
 IWR Integrated Waste Recycling Integrated System for treatment and recycling of Municipal Solid Waste 1 1. Introduction IWR is an integrated system, realised by different Italian companies, manufacturers
IWR Integrated Waste Recycling Integrated System for treatment and recycling of Municipal Solid Waste 1 1. Introduction IWR is an integrated system, realised by different Italian companies, manufacturers
Physical flow accounts: principles and general concepts
 Physical flow accounts: principles and general concepts Julian Chow United Nations Statistics Division 1 st Sub-Regional Course on SEEA 23-27 September 2013 Malaysia SEEA Conceptual Framework Outside territory
Physical flow accounts: principles and general concepts Julian Chow United Nations Statistics Division 1 st Sub-Regional Course on SEEA 23-27 September 2013 Malaysia SEEA Conceptual Framework Outside territory
GOALS, OBJECTIVES AND POLICIES
 GOALS, OBJECTIVES AND POLICIES The following goal, objective and policy statements have been developed for the use of local policy makers in guiding and directing the decision making process as it relates
GOALS, OBJECTIVES AND POLICIES The following goal, objective and policy statements have been developed for the use of local policy makers in guiding and directing the decision making process as it relates
Law of Mongolia on Concessions
 Economic Policy Reform and Competitiveness Project April 2005 Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia This publication was produced for review by the United States Agency for International Development The views expressed
Economic Policy Reform and Competitiveness Project April 2005 Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia This publication was produced for review by the United States Agency for International Development The views expressed
6 CONSIDERATION OF ALTERNATIVES
 6 CONSIDERATION OF ALTERNATIVES 6.1.1 Schedule 4 of the Town and Country Planning (Environmental Impact Assessment) (Scotland) Regulations 2011 sets out the information for inclusion in Environmental Statements
6 CONSIDERATION OF ALTERNATIVES 6.1.1 Schedule 4 of the Town and Country Planning (Environmental Impact Assessment) (Scotland) Regulations 2011 sets out the information for inclusion in Environmental Statements
2009 No. 890 ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION. The Waste Batteries and Accumulators Regulations 2009
 STATUTORY INSTRUMENTS 2009 No. 890 ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION The Waste Batteries and Accumulators Regulations 2009 Made - - - - *** 2009 Laid before Parliament *** 2009 Coming into force in accordance with
STATUTORY INSTRUMENTS 2009 No. 890 ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION The Waste Batteries and Accumulators Regulations 2009 Made - - - - *** 2009 Laid before Parliament *** 2009 Coming into force in accordance with
Source Reduction, on-site handling and processing of Solid waste. CE 431: Solid Waste Management
 Source Reduction, on-site handling and processing of Solid waste CE 431: Solid Waste Management Functional Elements of Waste Management System Source Reduction/Waste Minimization First element of any waste
Source Reduction, on-site handling and processing of Solid waste CE 431: Solid Waste Management Functional Elements of Waste Management System Source Reduction/Waste Minimization First element of any waste
State of the Nation Report
 State of the Nation Report Landfilling Practices and Regulation in Denmark Contents 1. Summary of Solid Waste Management Sector... 2 2. Overview of Landfill Practices... 5 3. Key Stakeholders in the solid
State of the Nation Report Landfilling Practices and Regulation in Denmark Contents 1. Summary of Solid Waste Management Sector... 2 2. Overview of Landfill Practices... 5 3. Key Stakeholders in the solid
Numbered 2010/11 Prime Ministry Circular about Istanbul International Finance Center Administrative Structure was published in the Official Gazette
 Numbered 2010/11 Prime Ministry Circular about Istanbul International Finance Center Administrative Structure was published in the Official Gazette dated May 1, 2010 and numbered 27568. UNOFFICIAL TRANSLATION
Numbered 2010/11 Prime Ministry Circular about Istanbul International Finance Center Administrative Structure was published in the Official Gazette dated May 1, 2010 and numbered 27568. UNOFFICIAL TRANSLATION
Introduction to Waste Treatment Technologies. Contents. Household waste
 Contents Introduction to waste treatment technologies 3 Section 1: The treatment of recyclable waste 4 Bulking facilities 5 Materials Reclamation Facility (MRF) 6 Reuse and recycling centres 8 Composting
Contents Introduction to waste treatment technologies 3 Section 1: The treatment of recyclable waste 4 Bulking facilities 5 Materials Reclamation Facility (MRF) 6 Reuse and recycling centres 8 Composting
Published in "Official Gazette of the Republic of Macedonia" No. 67/2004 LAW ON AMBIENT AIR QUALITY I. GENERAL PROVISIONS
 Published in "Official Gazette of the Republic of Macedonia" No. 67/2004 LAW ON AMBIENT AIR QUALITY I. GENERAL PROVISIONS Article 1 Subject of regulation (1) This Law shall regulate the measures for avoidance,
Published in "Official Gazette of the Republic of Macedonia" No. 67/2004 LAW ON AMBIENT AIR QUALITY I. GENERAL PROVISIONS Article 1 Subject of regulation (1) This Law shall regulate the measures for avoidance,
This fact sheet provides an overview of options for managing solid
 What Is Integrated Solid Waste Management? This fact sheet provides an overview of options for managing solid waste, identifies the important issues you should consider when planning for solid waste management,
What Is Integrated Solid Waste Management? This fact sheet provides an overview of options for managing solid waste, identifies the important issues you should consider when planning for solid waste management,
A case study from Thailand. Dr. Alice SHARP Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology Thammasat Univeristy
 Waste to Energy: A case study from Thailand Dr. Alice SHARP Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology Thammasat Univeristy Status of Waste and Waste Management Systems National Policy on Waste Management
Waste to Energy: A case study from Thailand Dr. Alice SHARP Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology Thammasat Univeristy Status of Waste and Waste Management Systems National Policy on Waste Management
How To Understand The Environment In Turkey
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ELECTRONICS, MECHANICAL and MECHATRONICS ENGINEERING Vol.2 Num.1 pp.(86-91) EFFECTS OF HIGH ECONOMIC IMPORTANCE OF INDUSTRIAL BRANCHES ON HUMAN LIFE QUALITY AND ENVIRONMENT Doguş
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ELECTRONICS, MECHANICAL and MECHATRONICS ENGINEERING Vol.2 Num.1 pp.(86-91) EFFECTS OF HIGH ECONOMIC IMPORTANCE OF INDUSTRIAL BRANCHES ON HUMAN LIFE QUALITY AND ENVIRONMENT Doguş
How To Understand And Understand Solid And Hazardous Waste
 Learning Objectives Solid and Hazardous Wastes Gene D. Schroder PhD To understand the sources of solid and hazardous wastes. To understand methods of solid waste disposal. To evaluate the health risks
Learning Objectives Solid and Hazardous Wastes Gene D. Schroder PhD To understand the sources of solid and hazardous wastes. To understand methods of solid waste disposal. To evaluate the health risks
POLLUTION PREVENTION FACT SHEET: AUTOMOBILE MAINTENANCE
 POLLUTION PREVENTION FACT SHEET: AUTOMOBILE MAINTENANCE Description This pollution prevention measure involves creating a program of targeted outreach and training for businesses involved in automobile
POLLUTION PREVENTION FACT SHEET: AUTOMOBILE MAINTENANCE Description This pollution prevention measure involves creating a program of targeted outreach and training for businesses involved in automobile
The Comprehensive Environmental Response,
 Purpose and Applicability of Regulations Chapter 7 The Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act (CERCLA) was enacted by Congress in 1980 to clean up the nation s hazardous
Purpose and Applicability of Regulations Chapter 7 The Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act (CERCLA) was enacted by Congress in 1980 to clean up the nation s hazardous
K A N S A S DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND ENVIRONMENT PERMIT APPLICATION FOR A RECLAMATION FACILITY. 1. Applicant's Name
 K A N S A S DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND ENVIRONMENT PERMIT APPLICATION FOR A RECLAMATION FACILITY 1. Applicant's Name Address (Street or Rural Route) (City & State) (Zip) Person to contact Title Phone Fax
K A N S A S DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND ENVIRONMENT PERMIT APPLICATION FOR A RECLAMATION FACILITY 1. Applicant's Name Address (Street or Rural Route) (City & State) (Zip) Person to contact Title Phone Fax
Municipal Authorities Best Practice in Engaging. Packaging and Food Waste. March 2014
 Municipal Authorities Best Practice in Engaging Communities on Packaging and Food Waste March 2014 European waste management hierarchy European Directive on Waste The Waste Directive 2008/98/EC marked
Municipal Authorities Best Practice in Engaging Communities on Packaging and Food Waste March 2014 European waste management hierarchy European Directive on Waste The Waste Directive 2008/98/EC marked
Managing Floor Drains and Flammable Traps
 Managing Floor Drains and Flammable Traps Contents: Problem... 1 Solution... 2 Maintenance... 2 Waste Management Options... 2 For More Information... 4 BMP Chart... 5 This fact sheet discusses recommended
Managing Floor Drains and Flammable Traps Contents: Problem... 1 Solution... 2 Maintenance... 2 Waste Management Options... 2 For More Information... 4 BMP Chart... 5 This fact sheet discusses recommended
BURNIE WASTE MANAGEMENT STRATEGY 2013-2017
 BURNIE WASTE MANAGEMENT STRATEGY 2013-2017 October 2013 COUNCIL STRATEGY Burnie Waste Management Strategy 2013-2017 Approved By: Council Document Code: CD-WS-W-001 Doc Controller: Director Works and Services
BURNIE WASTE MANAGEMENT STRATEGY 2013-2017 October 2013 COUNCIL STRATEGY Burnie Waste Management Strategy 2013-2017 Approved By: Council Document Code: CD-WS-W-001 Doc Controller: Director Works and Services
TURKISH NUCLEAR POWER PROGRAMME NUCLEAR ENERGY PROJECT IMPLEMENTATION DEPARTMENT
 TURKISH NUCLEAR POWER PROGRAMME NUCLEAR ENERGY PROJECT IMPLEMENTATION DEPARTMENT 0 75 75 150 km Kocaeli (İzmit) BOSBORUS 0 İzmir Konya ANKARA 150 mi İçel (Mersin) REPUPLIC OF CYPRUS Iskenderun Adana SYRIA
TURKISH NUCLEAR POWER PROGRAMME NUCLEAR ENERGY PROJECT IMPLEMENTATION DEPARTMENT 0 75 75 150 km Kocaeli (İzmit) BOSBORUS 0 İzmir Konya ANKARA 150 mi İçel (Mersin) REPUPLIC OF CYPRUS Iskenderun Adana SYRIA
Hazardous Waste Procedures. Faculty of Science University of Ottawa
 Hazardous Waste Procedures University of Ottawa Contents Hazardous Materials Waste Overview:... 3 Regulations:... 3 General requirements related to packaging waste:... 4 Table 1: List of Appropriate Waste
Hazardous Waste Procedures University of Ottawa Contents Hazardous Materials Waste Overview:... 3 Regulations:... 3 General requirements related to packaging waste:... 4 Table 1: List of Appropriate Waste
MARSHALL UNIVERSITY HAZARDOUS WASTE DISPOSAL SECTION
 MARSHALL UNIVERSITY HAZARDOUS WASTE DISPOSAL SECTION TABLE OF CONTENTS POLICY STATEMENT.2 REFERENCE PROCEDURE 3 l.0 Purpose.3 2.0 Scope 3 3.0 Definitions 4 4.0 Responsibilities 5 5.0 Procedure.7 11/16/2005
MARSHALL UNIVERSITY HAZARDOUS WASTE DISPOSAL SECTION TABLE OF CONTENTS POLICY STATEMENT.2 REFERENCE PROCEDURE 3 l.0 Purpose.3 2.0 Scope 3 3.0 Definitions 4 4.0 Responsibilities 5 5.0 Procedure.7 11/16/2005
REPUBLIC OF TURKEY INTENDED NATIONALLY DETERMINED CONTRIBUTION
 REPUBLIC OF TURKEY INTENDED NATIONALLY DETERMINED CONTRIBUTION In accordance with decisions 1/CP.19 and 1/CP.20, the Republic of Turkey hereby presents its Intended Nationally Determined Contribution (INDC)
REPUBLIC OF TURKEY INTENDED NATIONALLY DETERMINED CONTRIBUTION In accordance with decisions 1/CP.19 and 1/CP.20, the Republic of Turkey hereby presents its Intended Nationally Determined Contribution (INDC)
ON-SITE WASTEWATER TREATMENT SYSTEMS ACT
 ON-SITE WASTEWATER TREATMENT SYSTEMS ACT Revised and reproduced by the Colorado Department of Public Health and Environment June, 2012 (PLEASE NOTE: This is an unofficial copy of this statute. The official
ON-SITE WASTEWATER TREATMENT SYSTEMS ACT Revised and reproduced by the Colorado Department of Public Health and Environment June, 2012 (PLEASE NOTE: This is an unofficial copy of this statute. The official
Birmingham City University / Students Union Aspects and Impacts Register. Waste. Impacts description
 Birmingham City University / Students Union and Impacts Register Waste Production of non - hazardous waste Production of hazardous waste Storage of non - hazardous waste Potential for waste to be disposed
Birmingham City University / Students Union and Impacts Register Waste Production of non - hazardous waste Production of hazardous waste Storage of non - hazardous waste Potential for waste to be disposed
11. The key for waste management Waste segregation
 11. The key for waste management Waste segregation 11.1 Segregation at the place of origin The background idea Segregation means the separation of the entire waste generated in a hospital in defined, different
11. The key for waste management Waste segregation 11.1 Segregation at the place of origin The background idea Segregation means the separation of the entire waste generated in a hospital in defined, different
New York State Department of Environmental Conservation 625 Broadway, Albany, NY 12233 www.dec.ny.gov. Environmental Self Audit For Small Businesses
 New York State Department of Environmental Conservation 625 Broadway, Albany, NY 12233 www.dec.ny.gov Environmental Self Audit For Small Businesses Disclaimer The materials in this document are intended
New York State Department of Environmental Conservation 625 Broadway, Albany, NY 12233 www.dec.ny.gov Environmental Self Audit For Small Businesses Disclaimer The materials in this document are intended
About this document. UPS Attention: Sustainability Report Editor 55 Glenlake Parkway N.E. Atlanta, Georgia 30328
 UPS Corporate Sustainability Report: Supplemental Data Table of Contents Water 2 Effluents and Waste 3 Compliance 5 Key Performance 7 Indicators About this document In, UPS reported its annual Corporate
UPS Corporate Sustainability Report: Supplemental Data Table of Contents Water 2 Effluents and Waste 3 Compliance 5 Key Performance 7 Indicators About this document In, UPS reported its annual Corporate
AffaldVarme Aarhus. AffaldVarme Aarhus. Teknik og Miljø Aarhus Kommune
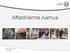 x The Municipality of Aarhus City Council 7 committees Municipal Authority Mayor s Dept. Dept. for Social Affairs and Employment Dept. for Technology and Environmental Issues Dept. for health and Care
x The Municipality of Aarhus City Council 7 committees Municipal Authority Mayor s Dept. Dept. for Social Affairs and Employment Dept. for Technology and Environmental Issues Dept. for health and Care
The economic basis of municipal waste management A comparison between Poland, Sweden and Lithuania
 The economic basis of municipal waste management A comparison between Poland, Sweden and Lithuania Team: Małgorzata Zakręcka (CUT), ([email protected]), Neringa Kedavičiūtė (KTU), ([email protected]),
The economic basis of municipal waste management A comparison between Poland, Sweden and Lithuania Team: Małgorzata Zakręcka (CUT), ([email protected]), Neringa Kedavičiūtė (KTU), ([email protected]),
SUSTAINABILITY CHARTER. May 2012. 1 R&CA Sustainability Charter V1
 SUSTAINABILITY CHARTER May 2012 1 R&CA Sustainability Charter V1 Introduction By their very nature, restaurant and catering businesses are significant users of energy, water and raw materials. Cooking
SUSTAINABILITY CHARTER May 2012 1 R&CA Sustainability Charter V1 Introduction By their very nature, restaurant and catering businesses are significant users of energy, water and raw materials. Cooking
MEMORANDUM 1. INTRODUCTION 2. METHODS FOR FINANCING AND WASTE FLOW MANAGEMENT. John Sedley. Russ Smith, Anke Bergner, Capital Regional District
 MEMORANDUM TO: Russ Smith, Anke Bergner, Capital Regional District cc. John Sedley FROM: Konrad Fichtner, P.Eng. FOR INFO OF: PLEASE RESPOND BY: PROJECT No.: 5130323 00 RE: Solid Waste System Financing
MEMORANDUM TO: Russ Smith, Anke Bergner, Capital Regional District cc. John Sedley FROM: Konrad Fichtner, P.Eng. FOR INFO OF: PLEASE RESPOND BY: PROJECT No.: 5130323 00 RE: Solid Waste System Financing
End-of-life vehicles. Information for authorised treatment facilities
 End-of-life vehicles Information for authorised treatment facilities 1. What is this guide about? This booklet is a simple guide to SEPA s requirements under the end-of-life vehicle (ELV) legislation.
End-of-life vehicles Information for authorised treatment facilities 1. What is this guide about? This booklet is a simple guide to SEPA s requirements under the end-of-life vehicle (ELV) legislation.
GUIDANCE NOTES FOR WASTE MANAGEMENT
 GUIDANCE NOTES FOR WASTE MANAGEMENT HEALTH & SAFETY UNIT SPRING 2006 CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION...2 2 DOES MY WASTE REQUIRE SPECIAL DISPOSAL OR TREATMENT?...2 3 WHAT IS HAZARDOUS WASTE?...3 4 RESPONSIBILITIES...3
GUIDANCE NOTES FOR WASTE MANAGEMENT HEALTH & SAFETY UNIT SPRING 2006 CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION...2 2 DOES MY WASTE REQUIRE SPECIAL DISPOSAL OR TREATMENT?...2 3 WHAT IS HAZARDOUS WASTE?...3 4 RESPONSIBILITIES...3
CHAPTER 65. 1. Section 2 of P.L.1989, c.34 (C.13:1E-48.2) is amended to read as follows:
 CHAPTER 65 AN ACT concerning medical waste disposal, amending and supplementing P.L.1989, c.34, supplementing P.L.1977, c.74 (C.58:10A-1 et seq.), and amending P.L.1988, c.61. BE IT ENACTED by the Senate
CHAPTER 65 AN ACT concerning medical waste disposal, amending and supplementing P.L.1989, c.34, supplementing P.L.1977, c.74 (C.58:10A-1 et seq.), and amending P.L.1988, c.61. BE IT ENACTED by the Senate
THE SUSTAINABLE WASTE MANAGEMENT IN THE CITY OF RIO DE JANEIRO
 THE SUSTAINABLE WASTE MANAGEMENT IN THE CITY OF RIO DE JANEIRO The search for environmental and economic sustainability with social responsibility José Henrique Penido Monteiro COMLURB Cia. Municipal de
THE SUSTAINABLE WASTE MANAGEMENT IN THE CITY OF RIO DE JANEIRO The search for environmental and economic sustainability with social responsibility José Henrique Penido Monteiro COMLURB Cia. Municipal de
A Green Idea. Reclaiming Urban Wood Waste And Urban Forest Debris. For Fuel/Combustion & Renewable Energy
 A Green Idea Reclaiming Urban Wood Waste And Urban Forest Debris For Fuel/Combustion & Renewable Energy Presentation Edward Kalebich Chief Operating Officer Robbins Community Power Facility located Chicago
A Green Idea Reclaiming Urban Wood Waste And Urban Forest Debris For Fuel/Combustion & Renewable Energy Presentation Edward Kalebich Chief Operating Officer Robbins Community Power Facility located Chicago
THE CORPORATION OF THE CITY OF COURTENAY BYLAW NO. 2182. A bylaw to amend Storm Sewer Bylaw No. 1402, 1986
 THE CORPORATION OF THE CITY OF COURTENAY BYLAW NO. 2182 A bylaw to amend Storm Sewer Bylaw No. 1402, 1986 The Council of the Corporation of the City of Courtenay in open meeting assembled enacts as follows:
THE CORPORATION OF THE CITY OF COURTENAY BYLAW NO. 2182 A bylaw to amend Storm Sewer Bylaw No. 1402, 1986 The Council of the Corporation of the City of Courtenay in open meeting assembled enacts as follows:
Asia 3R Conference. 30 Oct 1 Nov 06. Integrated Solid Waste Management in Singapore
 Asia 3R Conference 30 Oct 1 Nov 06 Integrated Solid Waste Management in Singapore National Environment Agency And Ministry of the Environment & Water Resources Singapore Ministry of Environment and Water
Asia 3R Conference 30 Oct 1 Nov 06 Integrated Solid Waste Management in Singapore National Environment Agency And Ministry of the Environment & Water Resources Singapore Ministry of Environment and Water
ISIC Rev.4 draft, Section E. Water supply; sewerage; waste management and remediation activities
 ISIC Rev.4 draft, Section E Water supply; sewerage; waste management and remediation activities United Nations Statistics Division Workshop on Classifications, Montevideo, Uruguay, 14-18 March 2005 Why
ISIC Rev.4 draft, Section E Water supply; sewerage; waste management and remediation activities United Nations Statistics Division Workshop on Classifications, Montevideo, Uruguay, 14-18 March 2005 Why
Ministry of National Infrastructures. Charging of Electric Vehicles. Policy Principles
 Ministry of National Infrastructures Charging of Electric Vehicles Policy Principles Contents Contents 1. Status and future prospects Overview 1.1 The electric vehicle (EV) market in Israel 1.2 Actions
Ministry of National Infrastructures Charging of Electric Vehicles Policy Principles Contents Contents 1. Status and future prospects Overview 1.1 The electric vehicle (EV) market in Israel 1.2 Actions
Principles of municipal waste management in Finland and their applications in Helsinki ja Tampere Regions
 Principles of municipal waste management in Finland and their applications in Helsinki ja Tampere Regions FORUM OF MUNICIPALITIES November 28, 2014, Tallinn, Estonia Simo Isoaho Senior Advisor JLY Finnish
Principles of municipal waste management in Finland and their applications in Helsinki ja Tampere Regions FORUM OF MUNICIPALITIES November 28, 2014, Tallinn, Estonia Simo Isoaho Senior Advisor JLY Finnish
