Imaging Pediatric Leukodystrophies
|
|
|
- Juliana Hancock
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Imaging Pediatric Leukodystrophies Jonathan A Phelan MS IV 1 & Lisa H Lowe MD 2 1 Kansas City University of Medicine and Biosciences 2 Department of Radiology, Children s s Mercy Hospital and Clinics and 2 The University of Missouri-Kansas City
2 Learning objectives 1. Distinguish between normal and abnormal white matter in children 2. Formulate an approach to white matter disorders in children 3. Recognize the findings of common white matter problems in children
3 Introduction White matter (WM) disorders in children are extensive, complex and challenging to learn
4 Important Cell Organelles Lysosome (garbage disposal unit) Peroxisome (oxidation & catalation) Mitochondria (power house)
5 Lysosomal disorders Metachromatic leukodystrophy Krabbe s disease Mucopolysaccharidoses Gangliosidoses Peroxisomal disorders Zellweger syndrome Neonatal ALD XR adrenoleukodystrophy Mitochondrial dysfunction Leigh disease MELAS Kearns-Sayre syndrome Unknown metabolic defect Pelizaeus-Merzbacher Alexander s s disease Canavan disease
6 Pathophysiology of WM disorders: general concepts Faulty gene Structurally abnormal protein Enzyme defect Metabolic block
7 Pathophysiology of WM disorders: general concepts Accumulation of abnormal products Interfere with normal neuronal function Insufficient normal biochemical product Essential to metabolism of neurons/myelin Injure other organs (lung, heart, liver, kidney) Secondary effect on CNS Toxic to neurons/myelin
8 Treatment options WM disorders Supportive, symptomatic Substrate deprivation Bone marrow transplant Enzyme replacement Gene therapy Neural stem cell transplantation
9 What are the obstacles to learning pediatric WM disorders? Many classifications systems and most are not useful for imaging Organelle based Biochemical based Clinical syndrome Histochemical staining pattern
10 Other obstacles to learning pediatric WM disorders Various forms Single vs. multiple enzyme defects Various presentations Infant vs. juvenile vs. adult Present - nonspecific Overlap - imaging Advanced cases look alike 60% never get a Dx
11 How can we overcome these obstacles? Have an approach to imaging of WM leukodystrophies Be familiar with common autoimmune & infectious disorders that may affect WM in children Know the key history & imaging patterns useful to formulate a limited differential diagnosis
12 Outline Normal development Leukodystrophies Subcortical WM Deep WM Disorders with lack of WM myelination Nonspecific WM disorders
13 Normal developmental anatomy and pitfalls that simulate disease WM signal changes with age Adult appearance at 18 mo - 2 years Myelination progresses back to front Assess myelination with MRI Terminal myelination zones Periatrial and subcortical WM Lack of myelination can mimic WM disease
14 Normal milestones myelination Brain region Middle cerebellar peduncle, post limb internal capsule Anterior limb internal capsule, centrum semiovale Splenium corpus callosum Genu corpus callosum T1 Birth 2-33 mo 3-44 mo 4-66 mo T2 Birth 2mo 7-11 mo 4-66 mo 5-88 mo Occipital white matter, peripheral Frontal white matter, peripheral 4-77 mo 7-11mo T1 used < 6 mo, T2 used > 6 months mo 14-18m 18m
15 Newborn 5 months Normal progression of myelination 8 months
16 T2 nb 5mo 8mo T2 12mo 18mo 24mo
17 Normal terminal myelination zones 18-mo mo-male male with normal brain Normal variant that can persist into adulthood
18 How do we approach pediatric WM disorders: Ask some questions! 1. Are there any useful symptoms? Head size: Macrocephaly WM symptoms: Spasticity, hyperreflexia, ataxia Other organs: liver, msk, renal, eye, ear 2. Is the disorder primarily WM, gray matter or both? 3. Is it primarily SUBCORTICAL or DEEP white matter?
19 Subcortical vs. Deep? Note the region of sparing in the subcortical WM region Note the abnormal signal in the WM extends to the subcortical U fiber region
20 Approach to pediatric WM disorders Other questions: 1. Distribution - anterior, posterior, both? 2. Subcortical or deep WM cysts? 3. Thalamic involvement? 4. Brainstem involvement? 5. Delayed or lack of myelination? 6. Leading edge of enhancement? 7. Cortical dysplasia? 8. Elevated NAA, lactate or other peaks on MRS?
21 Imaging technique WM disorders US & CT - limited role US screen macrocephaly in developmentally normal children CT abnormal areas usually hypodense MRI Imaging modality of choice Routine brain + Gadolinium MRS Just do it! It may help you. TE 30msec & 270msec Multivoxel nice to compare sample volumes in normal & abnormal regions
22 Begin with Subcortical White Matter leukodystrophies Caveat: : nearly all have some gray matter involvement Approach according to Barkovich JE. Pediatric Neuroimaging 4th ed.
23 First discuss SUBCORTICAL white matter disorders With macrocephaly: 1. If yes, consider: Alexander & Canavan disease 2. + subcortical cysts,, think of: van der Knapp disease 3. + ataxia & decreased myelination think of: Vanishing white matter disease Approach according to Barkovich JE. Pediatric Neuroimaging 4th ed. e
24 Canavan disease Spongiform leukodystrophy Autosomal recessive, Ashkenazi Jews Aspartoacylase deficiency; Chromosome 17 Presentation: hypotonia with head lag in first few weeks of life,, followed by macrocephaly & seizures, then spacticity Rapid progression Death 2 nd year of life
25 Canavan disease Hx: : 2-month2 month-old old hypotonic female Imaging: CT Hypodense Subcortical WM Globus pallidi Thalami Extreme capsule Claustra Image from Barkovich JE. Pediatric neuroimaging 2005
26 Canavan disease Imaging: MRI hypointense T1 & hyperintense T2 Diffuse subcortical WM Globus pallidi with normal putamina Internal & external capsules in rapid cases P GP
27 Canavan disease Restricted diffusion in WM acute disease ADC DWI
28 Canavan disease MRS Marked elevation NAA peak Specific for Canavan disease NAA Cr
29 T1 Canavan disease T2 T2 Spongiform leukodystrophy
30 Alexander disease Fibrinoid leukodystrophy Rosenthal fibers on histology Mutated GFAP (glial fibrillary acidic protein) Presentation macrocephaly 1 st year of life, developmental delay, failure to thrive 3 subgroups: Infantile most common; ; death in year of life Juvenile 7-14 years ataxia & spasticity Adult present like juvenile Dx: analysis of GFAP gene Prognosis: Death first year of life
31 Alexander disease Hx: : 2 year old male, macrocephaly & ataxia Imaging: : CT Hypodense subcortical WM Frontal Contrast enhancement Adjacent to frontal horns Caudate heads Image from Barkovich JE. Pediatric neuroimaging 2005
32 Alexander disease MR imaging criteria according to van der Knapp: Subcortical WM, frontal lobe predominance Contrast enhancment of gray and WM structures (esp adjacent to frontal horn tips and ventricular trigones) Brain stem abnormalities Abnormal basal ganglia, thalami DWI - increased water motion (bright on ADC map, dark on DWI) MRS low NAA +/- elevated myo-inositol van der Knapp MS, et al. Alexander disease: Diagnosis with MR imaging. AJNR 2001;22:
33 Alexander disease Bright, anterior subcortical to periventricular WM, basal ganglia & thalami Image courtesy of Mauricio Castillo, MD
34 Alexander disease
35 van der Knapp dz or Megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with cysts Imaging: Absent myelin in subcortical WM Spared deep WM and basal ganglia Subcortical cysts in posterior frontal and temporal lobes DWI increased diffusion (dark on DWI, bright on ADC map) MRS non-specific; low NAA levels
36 van der Knapp dz or Megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with cysts
37 Vanishing white matter disease Familial childhood ataxia with diffuse CNS hypomyelination Chromosome 3 Presentation: Relapsing-remitting periods of progressive ataxia & spastic diplegia Dx criteria: initial motor and mental (a) development is nl, (b) chronic episodic neuro deterioration, (c) cerebellar ataxia & spasticity (d) MRI shows symmetric WM signal of CSF Lab screening: elevated glycine in the CSF, serum and urine Prognosis: death 2 nd decade
38 Vanishing white matter disease WM gradually looks the same as CSF T2 FLAIR Image from van der Knapp. Magnetic Resonance of myelination and myelin disorders
39 Approach to SUBCORTICAL white matter disorders Without macrocephaly?: Galactosemia also involves liver Kearns Sayre especially if globus pallidus is involved
40 Galactosemia Autosomal recessive Defective conversion of glucose to galactose Galactose-1-phosphate phosphate-uridyl transferase Presentation: newborns or young children with signs of increased intracranial pressure and vomiting Untreated: severe liver disease & mental retardation, seizures, choreoathetosis Rx: dietary restriction of galactose Prognosis: varies
41 Galactosemia Imaging: CT nonspecific low density WM MRI delayed subcortical WM myelination on T2 (nl on T1); Occasional WM focal lesions and late atrophy MRS - normal FLAIR Image from Barkovich JE. Pediatric neuroimaging
42 Kearns Sayre Mitochondrial disorder Dx requires external opthalmoplegia, retinitis pigmentosa and onset of neurologic dysfunction < 20 years +/- protein in CSF, heart block & cerebellar ataxia Imaging: abnormal WM early, atrophy, later basal deep gray matter CT - WM hypodense with calcifications MRI -subcortical WM, globus pallidus DWI - restricted diffusion MRS non-specific increased lactate & low NAA
43 Kearns Sayre Subcortical WM + spared deep WM + Globus pallidus Image from Barkovich JE. Pediatric neuroimaging
44 Next Deep White Matter Leukodystrophies Caveat: nearly all have some gray matter involvement
45 Approach to DEEP WM disorders THALAMIC involvement?: Krabbe disease GM 1 GM 2 Tay-Sach disease Sandhoff disease
46 Krabbe disease Globoid cell leukodystrophy Lysosomal enzyme deficiency galacto-sylceramide beta-galactosidase Multiple mutations (chromosome 14) Presentation: 3-66 mos, hypertonia, irritable, fever, developmental delay, poor feeding, optic atrophy, opsomyoclonus & hyperacusis Dx: enzyme assay WBC/skin fibroblasts Death in first few years
47 Krabbe disease CT is characteristic: Hyperdense thalami, hypodense deep WM Images from Barkovich JE. Pediatric neuroimaging and van der Knapp MR of Myelination and Myelin disorder
48 Krabbe disease MR imaging: Nonspecific abnormal deep WM,, post limbs internal capsule, cerebellar WM & nuclei Thalami involved later Cranial nerve & cauda equina enhancement DWI early reduced diffusion, later increased MRS Most abnormal in infants. Elevated myo- inositol, creatine (CR), reduced NAA, +/- lactate; Juvenile - less severe MRS Adult - mild decrease in NAA & mild elevations of Cr & myo-inositol
49 Krabbe disease MRI: T2 bright deep WM cerebrum & cerebellum, thalamus Image from van der Knapp. MRI of myelin disorders
50 Krabbe disease Deep cerebral + cerebellar WM bright + spared subcortical WM Image courtesy of Mauricio Castillo, MD; UNC-Chapel Hill, NC
51 Krabbe disease
52 GM 1 gangliosidosis Rare lysosomal disorder Deficient activity of beta-galactosidase Chromosome 3 Three forms: Infantile, childhood, adult Infantile - most common Dysmorphic facial features, osseous dysplasias, hepatosplenomegaly, hypotonia, mental retardation early childhood (between years), seizures, spasticity Death in a few years Childhood & adult forms more slowly progressive dysarthria, ataxia, myoclonus, normal facies, no hepatosplenomegaly
53 GM 2 gangliosidoses (Tay-Sachs & Sandhoff disease) Autosomal recessive sphingolipidosis Deficient hexosaminidase (2 parts) Isoenzyme A Tay Sachs disease Isoenzyme A & B Sandhoff disease Accumulation of GM2 ganglioside causes damage Clinical & imaging findings are similar for TSD & SD Presentation: Infant with hypotonia, psychomotor retardation Late first year - spasticity, weakness, dystonia, ataxia, then macrocephaly, abnormal movements, seizures After years severe dementia & bed ridden
54 GM1 &GM 2 (Tay-Sachs & Sandhoff disease) gangliosidoses Imaging nearly identical for GM1 & GM2 CT early hyperdense thalami & hypodense WM,, late atrophy MRI T2 bright periventricular WM Tay-Sacchs: Posteromedial thalami T2 bright with reduced diffusion Sandoff: Basal ganglia isointense with WM Late stage atrophy cerebral and cerebellar hemispheres
55 GM 1 gangliosidosis Imaging appearance: Nonspecific WM & same as GM2 CT- Hypodense WM, late atrophy MRI T2 bright WM Image courtesy of Mauricio Castillo, MD; UNC-Chapel Hill, NC
56 GM 2 (Tay-Sachs & Sandhoff disease) gangliosidoses Diffuse atrophy Hypoattenuated WM Hyperdense atrophic thalami Image courtesy of M Castillo, MD; UNC-Chapel Hill, NC
57 Approach to DEEP white matter disorders No THALAMIC involvement: Is there brainstem (corticospinal tract) involvement?: X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy if pons and medulla Maple syrup urine disease if internal capsule, cerebral peduncle and dorsal pons
58 Adrenoleukodystrophy Rare peroxisomal disorder Chromosome 28 mutation (300+ mutations) Acyl-CoA synthetase, peroxisomal membrane transport protein (prevents long chain fatty acid breakdown) CNS, adrenal, testes 2 main forms: Classic X-linked X type is most common Adrenomyeloneuropathy presents in adults with predominant brainstem & spinal cord disease Rare neonatal form: AR, multiple enzyme deficiencies
59 Classic X-linked X ALD Boys 5 12 years old Learning difficulties (ADHD), imparied vision, gait or hearing, abnormal pigmentation skin (adrenal insufficiency), 10% seizures, adrenal crisis, coma Progression is rapid DDx: None with appropriate history Acyl CoA oxidase deficiency similar imaging, but history differs; 2 year old girls & boys delayed cognitive & motor development
60 X-linked ALD Imaging: Several characteristic patterns All have confluent symmetric deep WM with leading edge enhancement (inflammatory reaction) Posterior - 80% Anterior - 15% Unilateral hemispheric rarely Restricted to internal capsules Pons & medulla CT low density, MRI T1 and T2 prolongation relaxation times, increased diffusion MRS (may be abnormal prior to visible changes on MRI) decreased NAA, increased choline, glutamine/glutamate, decreased myo-inositol, +/- lactate
61 X-linked ALD Hx: 6-year6 year-old boy with SNHL Pons, medulla, posterior deep WM, leading edge enhancement T2 T1 T1+Gd
62 X-linked ALD Posterior (85%) distribution is most common Note 3 zones: Burned out Inflammatory Demyelinating
63 X-linked ALD Hx: 12 year old male with ataxia & ADHD Atypical frontal distribution (15%) MRS elevated glutamine/glutamate & lactate
64 Maple syrup urine disease (MSUD) Rare, heterogenous group of disorders with abnormal oxidative decarboxylation of branched chain fatty acids 5 clinical phenotypes correlate with degree of enzyme activity Classic MSUD present week of life 1 with vomiting, dystonia, seizures,, and die in a few weeks without treatment Other forms MSUD are less severe, present in later childhood with metabolic crisis
65 Maple syrup urine disease (MSUD) Imaging classic MSUD: Sonography echogenic periventricular WM, basal ganglia & thalami CT & MRI very characteristic profound cerebral edema Deep cerebellar WM, dorsal pons, cerebral peduncles, internal capsule, deep cerebral WM Restricted diffusion, drop in ADC by 20-30% MRS Mild elevation lactate, abnormal methyl proton peak at.9ppm on long echo (TE-270 ms) Imaging milder forms of MSUD: Lack of myelination superimposed on damage to areas listed in classical MSUD
66 Maple syrup urine disease Hx: 1 week old male vomiting & lethargy MRI: Restricted diffusion in the cerebellar WM, cerebral peduncles & dorsal pons T2 DWI ADC map
67 Maple syrup urine disease MRS: Lactate peak and branched chain amino acid peak Cho NAA NAA Cr Lactate Branched chain amino acids Image from Barkovich JE. Pediatric neuroimaging, 4 th ed.
68 Approach to DEEP white matter disorders Is there is brainstem (corticospinal tract) involvement?: 1. If NO,, consider: Metachromatic leukodystrophy Phenylketonuria Mucopolysaccharidoses Lowe disease Merosin deficient muscular dystrophy Radiation or chemotherapy damage
69 Metachromatic leukodystrophy Autosomal recessive Lysosomal disorder Arylsulfatase (AS) deficiency Sulfatides accumulate in brain, kidneys, liver, GB, peripheral nerves Dx: low AS in urine & peripheral blood 3 types: infant, juvenile, adult Infantile form is most common
70 Metachromatic leukodystrophy Infantile form: months Early motor signs of peripheral neuropathy Later decrease intelligence, speech, coordination Death 6 month - 4 years after DX
71 Metachromatic leukodystrophy Imaging: Deep WM, symmetric, confluent Bright on T2; no enhancement Spares subcortical WM early Tigroid or leopard skin appearance due to perivascular space distension Other sites of involvement: Corpus callosum, internal capsule, corticospinal tracts, cerebellar WM
72 Metachromatic leukodystrophy Hx: 2-year2 year-old male with vomiting CT: Nonspecific low density of deep WM
73 Metachromatic leukodystrophy MRI: Deep WM, sparing subcortical WM & no leading edge of enhancement T2 FLAIR T1+Gd
74 Metachromatic leukodystrophy Advanced disease with tigroid appearance
75 Mucopolysaccharidosis Group of rare lysosomal enzyme deficiency disorders All involve metabolism of glycosaminoglycans Imaging: Delayed myelination, atrophy, hydrocephalus, cysts in periventricular WM, corpus callosum, basal ganglia Presentation, prognosis depend on specific disorder Hurler disease is most common
76 Mucopolysaccharidosis Hx: : 15-month month-old old male with Hurler syndrome MRI: T2 deep WM bright signal, distended perivascular spaces give
77 Mucopolysaccharidosis Cysts - perivascular spaces & corpus callosum
78 Mucopolysaccharidoses Inferior beak of spine Cysts - perivascular spaces & corpus callosum
79 Oculocerebrorenal syndrome (Lowe disease) X linked, autosomal recessive Phosphatidylinositol-4,5 4,5-biphosphate-5 phosphatase enzyme anomaly Involves brain, lens, kidneys Clinical findings: Congenital cataracts Glaucoma Mental retardation Renal tubular dysfunction (Fanconi syndrome) Metabolic bone disease
80 Oculocerebrorenal syndrome (Lowe disease) Imaging findings can be distinct: Bilateral, symmetrical deep WM low density on CT, with T1 and T2 shortening on MRI Cystic areas within abnormal WM Sparing subcortical U fibers MRS: Some cases elevation of myo- inositol peak due to gliosis or enzyme accumulation
81 Lowe disease CT: Nonspecific hypodense deep WM MRI: Deep WM bright on T2 early Image courtesy of Mauricio Castillo, MD; UNC-Chapel Hill, NC
82 Lowe disease Congenital cataracts WM cysts on T1 Orbit images courtesy of Mauricio Castillo, MD; UNC-Chapel Hill, NC Image from Barkovich JE. Pediatric Neuroimaging, 4 th ed.
83 Congenital muscular dystrophies Heterogeneous inherited group of disorder resulting from mutation of lamina-alpha alpha-2 2 gene on chromosome 6 Presentation: Hypotonia & weakness from birth, possibly arthrogyroposis, diminished deep tendon reflexes, normal intelligence Moderate elevation of serum creatine kinase
84 Congenital muscular dystrophies Major types (according to van der Knapp): Fukuyama congenital muscular dystrophy Associated cortical dysplasia Walker-Warburg Warburg syndrome Associated cortical dysplasia Muscle eye brain syndrome Merosin deficient congenital muscular dystrophy (classic form) MDC1C brain mostly normal MDC1D brain not normal
85 Fukuyama congenital muscular dystrophy Japanese Autosomal recessive Onset: infantile marked hypotonia, many ocular anomalies Imaging (findings are not specific): Diffuse cortical dysplasia Cerebellar cortical dysplasia & subcortical cysts WM abnormal signal Pons hypoplasia
86 Fukuyama congenital muscular dystrophy 5-month-old old Japanese female Cortical dysplasia, WM abnormal T1 T2 T2
87 Merosin deficient muscular dystrophy 3 types of congenital muscular dystrophy (according to Barkovich): 1. Children with normal brains 2. Children with CNS symptoms, abnormal myelin & normal cortex 3. Children with CNS symptoms, abnormal myelin & cortical involvement Imaging: Delayed or hypomyelinated deep cerebral WM, with mild pontine & cerebellar hypoplasia Dx: : muscle biopsy, MRI & clinical evaluation
88 Merosin deficient (classical) congenital muscular dystrophy Nonspecific deep WM bright on T2 T2 T2
89 Congenital muscular dystrophy without merosin deficiency CT: Nonspecific deep WM & generalized atrophy MRI: : Lack of myelination without WM destruction MRS: : Controversial T2 FLAIR FLAIR Image courtesy of Mauricio Castillo, MD; UNC-Chapel Hill, NC
90 Conclusion White matter disorders in children are complex, but an organized approach can allow formulation of a narrow differential diagnosis
Neonatal Hypotonia. Clinical Approach to Floppy Baby
 Neonatal Hypotonia Clinical Approach to Floppy Baby Hypotonia in the newborn is a common presenting feature of systemic illness or neurologic dysfunction at any level of the central or peripheral nervous
Neonatal Hypotonia Clinical Approach to Floppy Baby Hypotonia in the newborn is a common presenting feature of systemic illness or neurologic dysfunction at any level of the central or peripheral nervous
Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders Galactosemia Biotinidase Deficiency
 Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders Galactosemia Biotinidase Deficiency Dr. Kathy Grange, MD Division of Genetics and Genomic Medicine Department of Pediatrics Washington University School of Medicine What
Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders Galactosemia Biotinidase Deficiency Dr. Kathy Grange, MD Division of Genetics and Genomic Medicine Department of Pediatrics Washington University School of Medicine What
DIAGNOSING CHILDHOOD MUSCULAR DYSTROPHIES
 DIAGNOSING CHILDHOOD MUSCULAR DYSTROPHIES Extracts from a review article by KN North and KJ Jones: Recent advances in diagnosis of the childhood muscular dystrophies Journal of Paediatrics and Child Health
DIAGNOSING CHILDHOOD MUSCULAR DYSTROPHIES Extracts from a review article by KN North and KJ Jones: Recent advances in diagnosis of the childhood muscular dystrophies Journal of Paediatrics and Child Health
Developmental delay and Cerebral palsy. Present the differential diagnosis of developmental delay.
 Developmental delay and Cerebral palsy objectives 1. developmental delay Define developmental delay Etiologies of developmental delay Present the differential diagnosis of developmental delay. 2. cerebral
Developmental delay and Cerebral palsy objectives 1. developmental delay Define developmental delay Etiologies of developmental delay Present the differential diagnosis of developmental delay. 2. cerebral
Making the Connections District 75 NYCDOE
 Medical Syndromes and Their Effect on Learning Making the Connections District 75 NYCDOE Cerebral Palsy The most frequent medical condition in 12:1:4 classes Associated with other disabilities including
Medical Syndromes and Their Effect on Learning Making the Connections District 75 NYCDOE Cerebral Palsy The most frequent medical condition in 12:1:4 classes Associated with other disabilities including
NORD Guides for Physicians #1. Physician s Guide to. Tyrosinemia. Type 1
 NORD Guides for Physicians #1 The National Organization for Rare Disorders Physician s Guide to Tyrosinemia Type 1 The original version of this booklet was made possible by donations in honor of Danielle
NORD Guides for Physicians #1 The National Organization for Rare Disorders Physician s Guide to Tyrosinemia Type 1 The original version of this booklet was made possible by donations in honor of Danielle
Myelinization. THOMAS P. NAIDICH, MD FACR Mt. Sinai Medical Center New York, NY USA
 Myelinization THOMAS P. NAIDICH, MD FACR Mt. Sinai Medical Center New York, NY USA ALTERS BRAIN WATER LOCALLY MYELIN CONTAINS: GLYCOLIPIDS PHOSPHOLIPIDS & CHOLESTEROL Maturation of the White Matter Maturation
Myelinization THOMAS P. NAIDICH, MD FACR Mt. Sinai Medical Center New York, NY USA ALTERS BRAIN WATER LOCALLY MYELIN CONTAINS: GLYCOLIPIDS PHOSPHOLIPIDS & CHOLESTEROL Maturation of the White Matter Maturation
Louise Simmons Clinical Nurse Specialist Inherited Metabolic Disorders (IMD) Birmingham Children s Hospital
 Louise Simmons Clinical Nurse Specialist Inherited Metabolic Disorders (IMD) Birmingham Children s Hospital Individually rare Collectively not uncommon - 1:700 - Childhood cancer 1:500 Genetically inherited
Louise Simmons Clinical Nurse Specialist Inherited Metabolic Disorders (IMD) Birmingham Children s Hospital Individually rare Collectively not uncommon - 1:700 - Childhood cancer 1:500 Genetically inherited
Parts of the Brain. Chapter 1
 Chapter 1 Parts of the Brain Living creatures are made up of cells. Groups of cells, similar in appearance and with the same function, form tissue. The brain is a soft mass of supportive tissues and nerve
Chapter 1 Parts of the Brain Living creatures are made up of cells. Groups of cells, similar in appearance and with the same function, form tissue. The brain is a soft mass of supportive tissues and nerve
Neuromuscular diseases
 Neuromuscular diseases Spinal muscular atrophy - SMA characterized by degeneration of the anterior horn cells in the spinal cord and motor nuclei in the lower brainstem. SMA type 1, is also known as Werdnig-
Neuromuscular diseases Spinal muscular atrophy - SMA characterized by degeneration of the anterior horn cells in the spinal cord and motor nuclei in the lower brainstem. SMA type 1, is also known as Werdnig-
Management in the pre-hospital setting
 Management in the pre-hospital setting Inflammation of the joints Two main types: Osteoarthritis - cartilage loss from wear and tear Rheumatoid arthritis - autoimmune disorder Affects all age groups,
Management in the pre-hospital setting Inflammation of the joints Two main types: Osteoarthritis - cartilage loss from wear and tear Rheumatoid arthritis - autoimmune disorder Affects all age groups,
Cerebral palsy can be classified according to the type of abnormal muscle tone or movement, and the distribution of these motor impairments.
 The Face of Cerebral Palsy Segment I Discovering Patterns What is Cerebral Palsy? Cerebral palsy (CP) is an umbrella term for a group of non-progressive but often changing motor impairment syndromes, which
The Face of Cerebral Palsy Segment I Discovering Patterns What is Cerebral Palsy? Cerebral palsy (CP) is an umbrella term for a group of non-progressive but often changing motor impairment syndromes, which
NEUROIMAGING in Parkinsonian Syndromes
 NEUROIMAGING in Parkinsonian Syndromes (Focus on Structural Techniques: CT and MRI) Dr. Roberto Cilia Parkinson Institute, ICP, Milan, Italy OUTLINE Primary Parkinsonism Idiopathic Parkinson s Disease
NEUROIMAGING in Parkinsonian Syndromes (Focus on Structural Techniques: CT and MRI) Dr. Roberto Cilia Parkinson Institute, ICP, Milan, Italy OUTLINE Primary Parkinsonism Idiopathic Parkinson s Disease
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
 Chapter 7: The Nervous System I. Organization of the Nervous System Objectives: List the general functions of the nervous system Explain the structural and functional classifications of the nervous system
Chapter 7: The Nervous System I. Organization of the Nervous System Objectives: List the general functions of the nervous system Explain the structural and functional classifications of the nervous system
New Approaches to Neuroimaging of Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy. Alexandra Binnie, HMS III Gillian Lieberman, M.D.
 New Approaches to Neuroimaging of Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy Alexandra Binnie, HMS III Gillian Lieberman, M.D. What is Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy (PML)? A demyelinating
New Approaches to Neuroimaging of Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy Alexandra Binnie, HMS III Gillian Lieberman, M.D. What is Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy (PML)? A demyelinating
Genetic Mutations. Indicator 4.8: Compare the consequences of mutations in body cells with those in gametes.
 Genetic Mutations Indicator 4.8: Compare the consequences of mutations in body cells with those in gametes. Agenda Warm UP: What is a mutation? Body cell? Gamete? Notes on Mutations Karyotype Web Activity
Genetic Mutations Indicator 4.8: Compare the consequences of mutations in body cells with those in gametes. Agenda Warm UP: What is a mutation? Body cell? Gamete? Notes on Mutations Karyotype Web Activity
Multiple Sclerosis: An imaging review and update on new treatments.
 Multiple Sclerosis: An imaging review and update on new treatments. Dr Marcus Likeman Consultant Neuroradiologist North Bristol NHS Trust Bristol Royal Hospital for Children MRI appearances - White Matter
Multiple Sclerosis: An imaging review and update on new treatments. Dr Marcus Likeman Consultant Neuroradiologist North Bristol NHS Trust Bristol Royal Hospital for Children MRI appearances - White Matter
MRI in Differential Diagnosis
 MRI in Differential Diagnosis Jill Conway, MD, MA, MSCE Director, Carolinas MS Center Clerkship Director, UNCSOM-Charlotte Campus Charlotte, NC DISCLOSURES Speaking, consulting, and/or advisory boards
MRI in Differential Diagnosis Jill Conway, MD, MA, MSCE Director, Carolinas MS Center Clerkship Director, UNCSOM-Charlotte Campus Charlotte, NC DISCLOSURES Speaking, consulting, and/or advisory boards
CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling. Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy
 CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect02: BOSS Discrete Event Simulator Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy Appendix of Purves et al., 4e Larry Wittie Computer Science, StonyBrook
CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect02: BOSS Discrete Event Simulator Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy Appendix of Purves et al., 4e Larry Wittie Computer Science, StonyBrook
Optional Tests Offered Before and During Pregnancy
 Plano Women s Healthcare Optional Tests Offered Before and During Pregnancy Alpha-Fetoprotein Test (AFP) and Quad Screen These are screening tests that can assess your baby s risk of having such birth
Plano Women s Healthcare Optional Tests Offered Before and During Pregnancy Alpha-Fetoprotein Test (AFP) and Quad Screen These are screening tests that can assess your baby s risk of having such birth
Guidance for evaluation of new neurological symptoms in patients receiving TYSABRI
 Guidance for evaluation of new neurological symptoms in patients receiving TYSABRI Background information Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) PML is a demyelinating disease that attacks the
Guidance for evaluation of new neurological symptoms in patients receiving TYSABRI Background information Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) PML is a demyelinating disease that attacks the
Unit 2 - Subcortical systems, neurochemistry and brain function
 Unit 2 - Subcortical systems, neurochemistry and brain function Subcortical anatomy: Most of the five major subdivisions of the brain are subcortical. I. Telencephalon (cortical - part of forebrain) -
Unit 2 - Subcortical systems, neurochemistry and brain function Subcortical anatomy: Most of the five major subdivisions of the brain are subcortical. I. Telencephalon (cortical - part of forebrain) -
Cerebral palsy, neonatal death and stillbirth rates Victoria, 1973-1999
 Cerebral Palsy: Aetiology, Associated Problems and Management Lecture for FRACP candidates July 2010 Definitions and prevalence Risk factors and aetiology Associated problems Management options Cerebral
Cerebral Palsy: Aetiology, Associated Problems and Management Lecture for FRACP candidates July 2010 Definitions and prevalence Risk factors and aetiology Associated problems Management options Cerebral
Mary Case, MD Professor of Pathology St. Louis University USA. 2015 MO Juvenile Justice Association Conference Lake Ozark, MO
 Mary Case, MD Professor of Pathology St. Louis University USA 2015 MO Juvenile Justice Association Conference Lake Ozark, MO I have nothing to disclose 75 80% of child abuse deaths are due to head trauma
Mary Case, MD Professor of Pathology St. Louis University USA 2015 MO Juvenile Justice Association Conference Lake Ozark, MO I have nothing to disclose 75 80% of child abuse deaths are due to head trauma
NEUROLOCALIZATION MADE EASY
 NEUROLOCALIZATION MADE EASY Jared B. Galle, DVM, Diplomate ACVIM (Neurology) Dogwood Veterinary Referral Center 4920 Ann Arbor-Saline Road Ann Arbor, MI 48103 Localizing a neurologic problem to an anatomical
NEUROLOCALIZATION MADE EASY Jared B. Galle, DVM, Diplomate ACVIM (Neurology) Dogwood Veterinary Referral Center 4920 Ann Arbor-Saline Road Ann Arbor, MI 48103 Localizing a neurologic problem to an anatomical
Muscular Dystrophy and Multiple Sclerosis. ultimately lead to the crippling of the muscular system, there are many differences between these
 Battles 1 Becky Battles Instructor s Name English 1013 21 November 2006 Muscular Dystrophy and Multiple Sclerosis Although muscular dystrophy and multiple sclerosis are both progressive diseases that ultimately
Battles 1 Becky Battles Instructor s Name English 1013 21 November 2006 Muscular Dystrophy and Multiple Sclerosis Although muscular dystrophy and multiple sclerosis are both progressive diseases that ultimately
CEREBRAL PALSY AND MENTAL RETARDATION DEFINITION
 CEREBRAL PALSY AND MENTAL RETARDATION DEFINITION It is a disorder of posture movement and tone due to a static encephalopathy acquired during brain growth in fetal life infancy or early childhood. Though
CEREBRAL PALSY AND MENTAL RETARDATION DEFINITION It is a disorder of posture movement and tone due to a static encephalopathy acquired during brain growth in fetal life infancy or early childhood. Though
Patient Information. Ordering Physician Information. Indication for Testing (REQUIRED)
 EPILEPSY EXOME CLINICAL CHECKLIST REQUIRED Please check all clinical features that apply, and use the additional space provided at the bottom of the form if needed Patient Information Name: Last First
EPILEPSY EXOME CLINICAL CHECKLIST REQUIRED Please check all clinical features that apply, and use the additional space provided at the bottom of the form if needed Patient Information Name: Last First
A Definition of Multiple Sclerosis
 English 182 READING PRACTICE by Alyx Meltzer, Spring 2009 Vocabulary Preview (see bolded, underlined words) gait: (n) a particular way of walking transient: (adj) temporary; synonym = transitory remission:
English 182 READING PRACTICE by Alyx Meltzer, Spring 2009 Vocabulary Preview (see bolded, underlined words) gait: (n) a particular way of walking transient: (adj) temporary; synonym = transitory remission:
Newborn Screening Test
 Important Information for Parents about the Newborn Screening Test Newborn Screening Branch Genetic Disease Screening Program http://cdph.ca.gov/nbs California Department of Public Health Publication Date:
Important Information for Parents about the Newborn Screening Test Newborn Screening Branch Genetic Disease Screening Program http://cdph.ca.gov/nbs California Department of Public Health Publication Date:
Motor dysfunction 2: Spinal cord injury and subcortical motor disorders ANATOMY REVIEW: Basal Ganglia
 Motor dysfunction 2: Spinal cord injury and subcortical motor disorders ANATOMY REVIEW: Basal Ganglia A group of subcortical nuclei caudate, putamen, globus pallidus Caudate & Putamen = Neostriatum caudate
Motor dysfunction 2: Spinal cord injury and subcortical motor disorders ANATOMY REVIEW: Basal Ganglia A group of subcortical nuclei caudate, putamen, globus pallidus Caudate & Putamen = Neostriatum caudate
Jennifer A. Defant, M.S., C.G.C. Certified Genetic Counselor Division of Genetics and Metabolism University of Florida
 Jennifer A. Defant, M.S., C.G.C. Certified Genetic Counselor Division of Genetics and Metabolism University of Florida 60% of childhood hearing loss is genetic Syndromic Nonsyndromic 40% of childhood hearing
Jennifer A. Defant, M.S., C.G.C. Certified Genetic Counselor Division of Genetics and Metabolism University of Florida 60% of childhood hearing loss is genetic Syndromic Nonsyndromic 40% of childhood hearing
Brain Cancer. This reference summary will help you understand how brain tumors are diagnosed and what options are available to treat them.
 Brain Cancer Introduction Brain tumors are not rare. Thousands of people are diagnosed every year with tumors of the brain and the rest of the nervous system. The diagnosis and treatment of brain tumors
Brain Cancer Introduction Brain tumors are not rare. Thousands of people are diagnosed every year with tumors of the brain and the rest of the nervous system. The diagnosis and treatment of brain tumors
MRI of Bone Marrow Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation
 MRI of Bone Marrow Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel, M.D. Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology Washington University School of Medicine St. Louis, MO and Visiting Scientist, AFIP, Washington,
MRI of Bone Marrow Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel, M.D. Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology Washington University School of Medicine St. Louis, MO and Visiting Scientist, AFIP, Washington,
Part I Failure to Thrive
 Part I Failure to Thrive Emma and Jacob Miller were so excited at the birth of their baby Matthew. Jacob, he s just so perfect! Just one problem though, it looks like he has your hairline! Emma teased
Part I Failure to Thrive Emma and Jacob Miller were so excited at the birth of their baby Matthew. Jacob, he s just so perfect! Just one problem though, it looks like he has your hairline! Emma teased
Genetic Aspects of Mental Retardation and Developmental Disabilities
 Prepared by: Chahira Kozma, MD Associate Professor of Pediatrics Medical Director/DCHRP [email protected] [email protected] Genetic Aspects of Mental Retardation and Developmental Disabilities
Prepared by: Chahira Kozma, MD Associate Professor of Pediatrics Medical Director/DCHRP [email protected] [email protected] Genetic Aspects of Mental Retardation and Developmental Disabilities
Sheep Brain Dissection
 Sheep Brain Dissection http://www.carolina.com/product/preserved+organisms/preserved+animals+%28mammal s%29/sheep+organs/preserved+sheep+dissection.do Michigan State University Neuroscience Program Brain
Sheep Brain Dissection http://www.carolina.com/product/preserved+organisms/preserved+animals+%28mammal s%29/sheep+organs/preserved+sheep+dissection.do Michigan State University Neuroscience Program Brain
2401 : Anatomy/Physiology
 Dr. Chris Doumen Week 7 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology The Brain Central Nervous System TextBook Readings Pages 431 through 435 and 463-467 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
Dr. Chris Doumen Week 7 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology The Brain Central Nervous System TextBook Readings Pages 431 through 435 and 463-467 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
Inborn Errors of Metabolism
 351 Inborn Errors of Metabolism Definition/ cut-off value Inherited metabolic disorders caused by a defect in the enzymes or their cofactors that metabolize protein, carbohydrate, or fat. Inborn errors
351 Inborn Errors of Metabolism Definition/ cut-off value Inherited metabolic disorders caused by a defect in the enzymes or their cofactors that metabolize protein, carbohydrate, or fat. Inborn errors
Cerebral Palsy. 1995-2014, The Patient Education Institute, Inc. www.x-plain.com nr200105 Last reviewed: 06/17/2014 1
 Cerebral Palsy Introduction Cerebral palsy, or CP, can cause serious neurological symptoms in children. Thousands of children are diagnosed with cerebral palsy every year. This reference summary explains
Cerebral Palsy Introduction Cerebral palsy, or CP, can cause serious neurological symptoms in children. Thousands of children are diagnosed with cerebral palsy every year. This reference summary explains
C CS. California Children Services Alameda County
 C CS California Children Services Alameda County The California Children Services (CCS) Program strives to assure access to medical services essential to the health and well-being of children with catastrophic
C CS California Children Services Alameda County The California Children Services (CCS) Program strives to assure access to medical services essential to the health and well-being of children with catastrophic
3) Cerebral Cortex & Functions of the 4 LOBES. 5) Cranial Nerves (Nerves In the Cranium, i.e., Head)
 Lecture 5 (Oct 8 th ): ANATOMY and FUNCTION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Lecture Outline 1) Basic Divisions (CNS vs. PNS, Somatic vs. Autonomic) and Directional Terms 2) The Brain (Hindbrain/ Midbrain/ Forebrain)
Lecture 5 (Oct 8 th ): ANATOMY and FUNCTION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Lecture Outline 1) Basic Divisions (CNS vs. PNS, Somatic vs. Autonomic) and Directional Terms 2) The Brain (Hindbrain/ Midbrain/ Forebrain)
Cerebral Palsy. In order to function, the brain needs a continuous supply of oxygen.
 Cerebral Palsy Introduction Cerebral palsy, or CP, can cause serious neurological symptoms in children. Up to 5000 children in the United States are diagnosed with cerebral palsy every year. This reference
Cerebral Palsy Introduction Cerebral palsy, or CP, can cause serious neurological symptoms in children. Up to 5000 children in the United States are diagnosed with cerebral palsy every year. This reference
CLINICAL NEUROPHYSIOLOGY
 CLINICAL NEUROPHYSIOLOGY Barry S. Oken, MD, Carter D. Wray MD Objectives: 1. Know the role of EMG/NCS in evaluating nerve and muscle function 2. Recognize common EEG findings and their significance 3.
CLINICAL NEUROPHYSIOLOGY Barry S. Oken, MD, Carter D. Wray MD Objectives: 1. Know the role of EMG/NCS in evaluating nerve and muscle function 2. Recognize common EEG findings and their significance 3.
Objectives Role of Medical Genetics in Hearing Loss Evaluation. 5 y.o. boy with severe SNHL
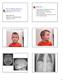 Objectives Role of Medical Genetics in Hearing Loss Evaluation Millan Patel, MD UBC Dept. of Medical Genetics October 22, 2010 Case presentation to illustrate importance of defining syndromic hearing loss
Objectives Role of Medical Genetics in Hearing Loss Evaluation Millan Patel, MD UBC Dept. of Medical Genetics October 22, 2010 Case presentation to illustrate importance of defining syndromic hearing loss
Neurofibromatosis Type 2: Information for Patients & Families by Mia MacCollin, M.D., Catherine Bove, R.N. Ed. & M. Priscilla Short, M.D.
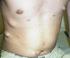 Neurofibromatosis Type 2: Information for Patients & Families by Mia MacCollin, M.D., Catherine Bove, R.N. Ed. & M. Priscilla Short, M.D. Neurofibromatosis Type 2 is a rare genetic disease, which causes
Neurofibromatosis Type 2: Information for Patients & Families by Mia MacCollin, M.D., Catherine Bove, R.N. Ed. & M. Priscilla Short, M.D. Neurofibromatosis Type 2 is a rare genetic disease, which causes
MRI for Paediatric Surgeons
 MRI for Paediatric Surgeons Starship David Perry Paediatric Radiologist Starship Children s Hospital CHILDREN S HEALTH What determines the brightness of a pixel in MRI? i.e. What determines the strength
MRI for Paediatric Surgeons Starship David Perry Paediatric Radiologist Starship Children s Hospital CHILDREN S HEALTH What determines the brightness of a pixel in MRI? i.e. What determines the strength
FastTest. You ve read the book... ... now test yourself
 FastTest You ve read the book...... now test yourself To ensure you have learned the key points that will improve your patient care, read the authors questions below. The answers will refer you back to
FastTest You ve read the book...... now test yourself To ensure you have learned the key points that will improve your patient care, read the authors questions below. The answers will refer you back to
A Rare Image. Dean M. Cestari, MD Fred Jakobiec, MD Fred Hochberg, MD Joseph F. Rizzo III, MD Rebecca C. Stacy, MD PhD
 A Rare Image Dean M. Cestari, MD Fred Jakobiec, MD Fred Hochberg, MD Joseph F. Rizzo III, MD Rebecca C. Stacy, MD PhD Harvard Neuro-ophthalmology Service Boston, Massachusetts 51 year-old male financial
A Rare Image Dean M. Cestari, MD Fred Jakobiec, MD Fred Hochberg, MD Joseph F. Rizzo III, MD Rebecca C. Stacy, MD PhD Harvard Neuro-ophthalmology Service Boston, Massachusetts 51 year-old male financial
Organisation of Biochemical Genetic Testing in Estonia
 Organisation of Biochemical Genetic Testing in Estonia Katrin Õunap Department of Pediatrics, University of Tartu Department of Genetics, Tartu University Hospital Basel, 09 th May 2008 ESTONIA 1,35 million
Organisation of Biochemical Genetic Testing in Estonia Katrin Õunap Department of Pediatrics, University of Tartu Department of Genetics, Tartu University Hospital Basel, 09 th May 2008 ESTONIA 1,35 million
Muscular Dystrophy. By. Tina Strauss
 Muscular Dystrophy By. Tina Strauss Story Outline for Presentation on Muscular Dystrophy What is Muscular Dystrophy? Signs & Symptoms Types When to seek medical attention? Screening and Diagnosis Treatment
Muscular Dystrophy By. Tina Strauss Story Outline for Presentation on Muscular Dystrophy What is Muscular Dystrophy? Signs & Symptoms Types When to seek medical attention? Screening and Diagnosis Treatment
95% of childhood kidney cancer cases are Wilms tumours. Childhood kidney cancer is extremely rare, with only 90 cases a year in
 James Whale Fund for Kidney Cancer Childhood kidney cancer factsheet Kidney cancer rarely afflicts children and about 90 paediatric cases are diagnosed in the UK each year. About 75% of childhood kidney
James Whale Fund for Kidney Cancer Childhood kidney cancer factsheet Kidney cancer rarely afflicts children and about 90 paediatric cases are diagnosed in the UK each year. About 75% of childhood kidney
Genetic Mutations Cause Many Birth Defects:
 Genetic Mutations Cause Many Birth Defects: What We Learned from the FORGE Canada Project Jan M. Friedman, MD, PhD University it of British Columbia Vancouver, Canada I have no conflicts of interest related
Genetic Mutations Cause Many Birth Defects: What We Learned from the FORGE Canada Project Jan M. Friedman, MD, PhD University it of British Columbia Vancouver, Canada I have no conflicts of interest related
How To Treat Wolman S Disease
 Case Presentation in Genetics and Ethics By Julie A. Nelson, R.N.C., W.H.C.N.P-B.C. Wolman s Disease 1 Definition: It is a lysosomal storage disorder which causes a buildup of lipids in body organs and
Case Presentation in Genetics and Ethics By Julie A. Nelson, R.N.C., W.H.C.N.P-B.C. Wolman s Disease 1 Definition: It is a lysosomal storage disorder which causes a buildup of lipids in body organs and
Cerebral Cortical and White Matter Lesions in Chronic Hepatic Encephalopathy: MR-Pathologic Correlations
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:347 351, February 2005 Case Report Cerebral Cortical and White Matter Lesions in Chronic Hepatic Encephalopathy: MR-Pathologic Correlations Eiji Matsusue, Toshibumi Kinoshita,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:347 351, February 2005 Case Report Cerebral Cortical and White Matter Lesions in Chronic Hepatic Encephalopathy: MR-Pathologic Correlations Eiji Matsusue, Toshibumi Kinoshita,
Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain Organization
 Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain Organization Jeanette J. Norden, Ph.D. Professor Emerita Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Course Outline Lecture 1: Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain
Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain Organization Jeanette J. Norden, Ph.D. Professor Emerita Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Course Outline Lecture 1: Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain
Key Facts about Influenza (Flu) & Flu Vaccine
 Key Facts about Influenza (Flu) & Flu Vaccine mouths or noses of people who are nearby. Less often, a person might also get flu by touching a surface or object that has flu virus on it and then touching
Key Facts about Influenza (Flu) & Flu Vaccine mouths or noses of people who are nearby. Less often, a person might also get flu by touching a surface or object that has flu virus on it and then touching
Static Encephalopathy A Basis Explanation for Parents
 Static Encephalopathy A Basis Explanation for Parents Nancy J. Hitzfelder, M.D. Medical Director July 1999 This article may not be copied without the express written permission of Easter Seals of Greater
Static Encephalopathy A Basis Explanation for Parents Nancy J. Hitzfelder, M.D. Medical Director July 1999 This article may not be copied without the express written permission of Easter Seals of Greater
Obstetrical Ultrasound and Prenatal Diagnostic Center
 Obstetrical Ultrasound and Prenatal Diagnostic Center Prenatal Diagnosis: Options and Opportunities Learn about various screening options including Early Risk Assessment (ERA), now available to women of
Obstetrical Ultrasound and Prenatal Diagnostic Center Prenatal Diagnosis: Options and Opportunities Learn about various screening options including Early Risk Assessment (ERA), now available to women of
CMS CLINICAL ELIGIBILITY ATTESTATION
 CMS CLINICAL ELIGIBILITY ATTESTATION Patient Name: DOB: Medicaid and/or KidCare ID: Parent/Legal Guardian Name: Phone number: Initial all that Apply: Initials ICD 10 Descriptor Certain infectious and parasitic
CMS CLINICAL ELIGIBILITY ATTESTATION Patient Name: DOB: Medicaid and/or KidCare ID: Parent/Legal Guardian Name: Phone number: Initial all that Apply: Initials ICD 10 Descriptor Certain infectious and parasitic
Chapter 3 The Anatomy of the Nervous System
 Chapter 3 The Anatomy of the Nervous System Systems, Structures, and Cells That Make Up Your Nervous System 1 General Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain (in the skull) Spinal
Chapter 3 The Anatomy of the Nervous System Systems, Structures, and Cells That Make Up Your Nervous System 1 General Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain (in the skull) Spinal
Normal Postnatal Development of the Corpus Callosum as Demonstrated by MR Imaging
 487 Normal Postnatal Development of the Corpus Callosum as Demonstrated by MR Imaging A. James Barkovich 1, 2 Bent 0, Kjos2,3 Sixty-three patients, 3 days to 12 months old, were examined by MR imaging
487 Normal Postnatal Development of the Corpus Callosum as Demonstrated by MR Imaging A. James Barkovich 1, 2 Bent 0, Kjos2,3 Sixty-three patients, 3 days to 12 months old, were examined by MR imaging
Inborn Errors of Metabolism
 Intensive Care Nursery House Staff Manual Inborn Errors of Metabolism INTRODUCTION and PATHOPHYSIOLOGY: Inborn Errors of Metabolism (IEM) comprise a group of disorders in which a single gene defect causes
Intensive Care Nursery House Staff Manual Inborn Errors of Metabolism INTRODUCTION and PATHOPHYSIOLOGY: Inborn Errors of Metabolism (IEM) comprise a group of disorders in which a single gene defect causes
DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN
 DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the threedimensional structure of the brain and teach you one of the great methods of studying
DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the threedimensional structure of the brain and teach you one of the great methods of studying
Optic Neuritis. The optic nerve fibers are coated with myelin to help them conduct the electrical signals back to your brain.
 Optic Neuritis Your doctor thinks that you have had an episode of optic neuritis. This is the most common cause of sudden visual loss in a young patient. It is often associated with discomfort in or around
Optic Neuritis Your doctor thinks that you have had an episode of optic neuritis. This is the most common cause of sudden visual loss in a young patient. It is often associated with discomfort in or around
Metabolic Disorders in Pediatric Neurology
 NEUROLOGY BOARD REVIEW MANUAL STATEMENT OF EDITORIAL PURPOSE The Hospital Physician Neurology Board Review Manual is a study guide for residents and practicing physicians preparing for board examinations
NEUROLOGY BOARD REVIEW MANUAL STATEMENT OF EDITORIAL PURPOSE The Hospital Physician Neurology Board Review Manual is a study guide for residents and practicing physicians preparing for board examinations
Slide 4: Forebrain Structures. Slide 5: 4 Lobes of the Cerebral Cortex. Slide 6: The Cerebral Hemispheres (L & R)
 Slide 1: [Film Clip: The Brain #2- Phineas Gage] Integrated Bodily Communications Within Brain (Hemispheres and structures) The remaining Nervous System Endocrine System (Hormonal communication) Our bodies-
Slide 1: [Film Clip: The Brain #2- Phineas Gage] Integrated Bodily Communications Within Brain (Hemispheres and structures) The remaining Nervous System Endocrine System (Hormonal communication) Our bodies-
Homework 5: Differential Diagnosis of Multiple Sclerosis
 Homework 5: Differential Diagnosis of Multiple Sclerosis Due Wednesday, 3/3/99 1.0 Background Multiple Sclerosis affects approximately 350 K Americans and is the leading nontraumatic source of neurologic
Homework 5: Differential Diagnosis of Multiple Sclerosis Due Wednesday, 3/3/99 1.0 Background Multiple Sclerosis affects approximately 350 K Americans and is the leading nontraumatic source of neurologic
A Note to Physical, Occupational and Speech Therapists
 D Page 1 of 5 A Note to Physical, Occupational and Speech Therapists Treating Children with Hurler Syndrome Because Hurler syndrome is such a rare disease, we have provided some basic information to assist
D Page 1 of 5 A Note to Physical, Occupational and Speech Therapists Treating Children with Hurler Syndrome Because Hurler syndrome is such a rare disease, we have provided some basic information to assist
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab
 BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
Case Report. Central Neurocytoma. Fotis Souslian, MD; Dino Terzic, MD; Ramachandra Tummala, MD. Department of Neurosurgery, University of Minnesota
 1 Case Report Central Neurocytoma Fotis, MD; Dino Terzic, MD; Ramachandra Tummala, MD Department of Neurosurgery, University of Minnesota Case This is a previously healthy 20 year old female, with 3 months
1 Case Report Central Neurocytoma Fotis, MD; Dino Terzic, MD; Ramachandra Tummala, MD Department of Neurosurgery, University of Minnesota Case This is a previously healthy 20 year old female, with 3 months
About The Causes of Hearing Loss
 About 1 in 500 infants is born with or develops hearing loss during early childhood. Hearing loss has many causes: some are genetic (that is, caused by a baby s genes) or non-genetic (such as certain infections
About 1 in 500 infants is born with or develops hearing loss during early childhood. Hearing loss has many causes: some are genetic (that is, caused by a baby s genes) or non-genetic (such as certain infections
Neurology Clerkship Learning Objectives
 Neurology Clerkship Learning Objectives Clinical skills Perform a neurological screening examination of the cranial nerves, motor system, reflexes, and sensory system under the observation and guidance
Neurology Clerkship Learning Objectives Clinical skills Perform a neurological screening examination of the cranial nerves, motor system, reflexes, and sensory system under the observation and guidance
Module 1: The Somato-Motor System: Tendon Tap reflex
 Module 1: The Somato-Motor System: Tendon Tap reflex Module Objectives: 1. Describe the anatomic pathway of a tendon tap reflex. 2. Explain how a tendon tap reflex assessment assists in diagnosis of a
Module 1: The Somato-Motor System: Tendon Tap reflex Module Objectives: 1. Describe the anatomic pathway of a tendon tap reflex. 2. Explain how a tendon tap reflex assessment assists in diagnosis of a
The Nuts and Bolts of Multiple Sclerosis. Rebecca Milholland, M.D., Ph.D. Center for Neurosciences
 The Nuts and Bolts of Multiple Sclerosis Rebecca Milholland, M.D., Ph.D. Center for Neurosciences Objectives Discuss which patients are at risk for Multiple Sclerosis Discuss the diagnostic criteria for
The Nuts and Bolts of Multiple Sclerosis Rebecca Milholland, M.D., Ph.D. Center for Neurosciences Objectives Discuss which patients are at risk for Multiple Sclerosis Discuss the diagnostic criteria for
Clinical features. Chapter 2. Clinical manifestations. Course
 Chapter 2 Clinical features Clinical manifestations The wide range of symptoms and signs of multiple sclerosis (MS) reflect multifocal lesions in the central nervous system (CNS), including in the afferent
Chapter 2 Clinical features Clinical manifestations The wide range of symptoms and signs of multiple sclerosis (MS) reflect multifocal lesions in the central nervous system (CNS), including in the afferent
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz
 Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz 1. The term central nervous system refers to the: A) autonomic and peripheral nervous systems B) brain, spinal cord, and cranial nerves
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz 1. The term central nervous system refers to the: A) autonomic and peripheral nervous systems B) brain, spinal cord, and cranial nerves
Spinal Cord Diseases in Bernese Mountain Dogs
 Spinal Cord Diseases in Bernese Mountain Dogs 0 A N O V E R V I E W F O R BERNER O W N E R S O R G A N I Z E D B Y N A N C Y M E L O N E, P H. D. Based on materials obtained from the Berner Garde Foundation
Spinal Cord Diseases in Bernese Mountain Dogs 0 A N O V E R V I E W F O R BERNER O W N E R S O R G A N I Z E D B Y N A N C Y M E L O N E, P H. D. Based on materials obtained from the Berner Garde Foundation
DISABILITY-RELATED DEFINITIONS
 DISABILITY-RELATED DEFINITIONS 1. The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) of 1990 is a civil rights law, which makes it unlawful to discriminate on the basis of disability. It covers employment in the
DISABILITY-RELATED DEFINITIONS 1. The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) of 1990 is a civil rights law, which makes it unlawful to discriminate on the basis of disability. It covers employment in the
HEADACHES AND THE THIRD OCCIPITAL NERVE
 HEADACHES AND THE THIRD OCCIPITAL NERVE Edward Babigumira M.D. FAAPMR. Interventional Pain Management, Lincoln. B. Pain Clinic, Ltd. Diplomate ABPMR. Board Certified Pain Medicine No disclosures Disclosure
HEADACHES AND THE THIRD OCCIPITAL NERVE Edward Babigumira M.D. FAAPMR. Interventional Pain Management, Lincoln. B. Pain Clinic, Ltd. Diplomate ABPMR. Board Certified Pain Medicine No disclosures Disclosure
ICD-9-CM coding for patients with Spinal Cord Injury*
 ICD-9-CM coding for patients with Spinal Cord Injury* indicates intervening codes have been left out of this list. OTHER DISORDERS OF THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM (340-349) 344 Other paralytic syndromes
ICD-9-CM coding for patients with Spinal Cord Injury* indicates intervening codes have been left out of this list. OTHER DISORDERS OF THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM (340-349) 344 Other paralytic syndromes
Primary Motor Pathway
 Understanding Eye Movements Abdullah Moh. El-Menaisy, MD, FRCS Chief, Neuro-ophthalmology ophthalmology & Investigation Units, Dhahran Eye Specialist Hospital, Dhahran, Saudi Arabia Primary Motor Pathway
Understanding Eye Movements Abdullah Moh. El-Menaisy, MD, FRCS Chief, Neuro-ophthalmology ophthalmology & Investigation Units, Dhahran Eye Specialist Hospital, Dhahran, Saudi Arabia Primary Motor Pathway
Paraneoplastic Antibodies in Clinical Practice. Mohammed El lahawi New Cross Hospital Wolverhampton
 Paraneoplastic Antibodies in Clinical Practice Mohammed El lahawi New Cross Hospital Wolverhampton 1 Effects of Neoplasm Direct mass ( pressure ) effect Metastasis effect Remote effect 2 The Nervous System
Paraneoplastic Antibodies in Clinical Practice Mohammed El lahawi New Cross Hospital Wolverhampton 1 Effects of Neoplasm Direct mass ( pressure ) effect Metastasis effect Remote effect 2 The Nervous System
1: Motor neurone disease (MND)
 1: Motor neurone disease (MND) This section provides basic facts about motor neurone disease (MND) and its diagnosis. The following information is an extracted section from our full guide Living with motor
1: Motor neurone disease (MND) This section provides basic facts about motor neurone disease (MND) and its diagnosis. The following information is an extracted section from our full guide Living with motor
Oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy (OPMD)
 Oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy (OPMD) The term muscular dystrophy is used to cover a wide range of conditions which have in common progressive muscle weakness due to an inherited genetic defect (mutation).
Oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy (OPMD) The term muscular dystrophy is used to cover a wide range of conditions which have in common progressive muscle weakness due to an inherited genetic defect (mutation).
Multiple System Atrophy
 Multiple System Atrophy U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Public Health Service National Institutes of Health Multiple System Atrophy What is multiple system atrophy? Multiple system atrophy
Multiple System Atrophy U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Public Health Service National Institutes of Health Multiple System Atrophy What is multiple system atrophy? Multiple system atrophy
Classification of Cerebral Palsy and Major Causes Physiologic Topographic Etiologic Function. trauma, infection)
 Cerebral palsy (CP) It is a diagnostic term used to describe a group of motor syndromes. a static encephalopathy, a term previously used, is now inaccurate because of the recognition that the neurologic
Cerebral palsy (CP) It is a diagnostic term used to describe a group of motor syndromes. a static encephalopathy, a term previously used, is now inaccurate because of the recognition that the neurologic
Effective SLP Interventions for Children with Cerebral Palsy
 Effective SLP Interventions for Children with Cerebral Palsy NDT/Traditional/Eclectic, PhD, CCC-SLP, C/NDT Contents Preface Acknowledgments Contributors ix x xi Chapter 1. The Development in Neurodevelopmental
Effective SLP Interventions for Children with Cerebral Palsy NDT/Traditional/Eclectic, PhD, CCC-SLP, C/NDT Contents Preface Acknowledgments Contributors ix x xi Chapter 1. The Development in Neurodevelopmental
Patient Information. for Childhood
 Patient Information Genetic Testing for Childhood Hearing Loss Introduction This document describes the most common genetic cause of childhood hearing loss and explains the role of genetic testing. Childhood
Patient Information Genetic Testing for Childhood Hearing Loss Introduction This document describes the most common genetic cause of childhood hearing loss and explains the role of genetic testing. Childhood
Things You Don t Want to Miss in Multiple Myeloma
 Things You Don t Want to Miss in Multiple Myeloma Sreenivasa Chandana, MD, PhD Attending Hematologist and Medical Oncologist West Michigan Cancer Center Assistant Professor, Western Michigan University
Things You Don t Want to Miss in Multiple Myeloma Sreenivasa Chandana, MD, PhD Attending Hematologist and Medical Oncologist West Michigan Cancer Center Assistant Professor, Western Michigan University
Usher Syndrome Genetics
 Usher Syndrome Genetics October 2012 Page 1 of 20 Introduction Usher syndrome is a genetic or inherited condition that affects hearing, vision and balance The sight loss is caused by an eye condition known
Usher Syndrome Genetics October 2012 Page 1 of 20 Introduction Usher syndrome is a genetic or inherited condition that affects hearing, vision and balance The sight loss is caused by an eye condition known
EMG and the Electrodiagnostic Consultation for the Family Physician
 EMG and the Electrodiagnostic Consultation for the Family Physician Stephanie Kopey, D.O., P.T. 9/27/15 The American Association of Neuromuscular & Electrodiagnostic Medicine (AANEM) Marketing Committee
EMG and the Electrodiagnostic Consultation for the Family Physician Stephanie Kopey, D.O., P.T. 9/27/15 The American Association of Neuromuscular & Electrodiagnostic Medicine (AANEM) Marketing Committee
Module 1: The Brain and the Central Nervous System (CNS)
 Module 1: The Brain and the Central Nervous System (CNS) By the end of this unit, the learner will be able to: Describe the anatomy of the brain and the central nervous system Identify regions of the brain
Module 1: The Brain and the Central Nervous System (CNS) By the end of this unit, the learner will be able to: Describe the anatomy of the brain and the central nervous system Identify regions of the brain
Newborn Screening in Manitoba. Information for Health Care Providers
 Newborn Screening in Manitoba Information for Health Care Providers Newborn screening: a healthy start leads to a healthier life Health care professionals have provided newborn screening for phenylketonuria
Newborn Screening in Manitoba Information for Health Care Providers Newborn screening: a healthy start leads to a healthier life Health care professionals have provided newborn screening for phenylketonuria
