Inborn Errors of Metabolism
|
|
|
- Cody Harrington
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 351 Inborn Errors of Metabolism Definition/ cut-off value Inherited metabolic disorders caused by a defect in the enzymes or their cofactors that metabolize protein, carbohydrate, or fat. Inborn errors of metabolism (IEM) generally refer to gene mutations or gene deletions that alter metabolism in the body, including but not limited to: Inborn errors of Metabolism* Amino Acid Disorders Organic Acid Metabolism Disorders Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders Lysosomal Storage Diseases Urea Cycle Disorders Carbohydrate Disorders Peroxisomal Disorders Mitochondrial Disorders *For information about additional IEM, please see Clarification. Presence of condition diagnosed, documented, or reported by a physician or someone working under physician s orders, or as self- reported by applicant/participant/caregiver. See Clarifications for more information about self-reporting a diagnosis. Participant category and priority level Category Pregnant Woman Breastfeeding Woman Non-breastfeeding Woman Infants Children Priority Justification The inheritance of most metabolic disorders is rare. IEM disorders may manifest at any stage of life, from infancy to adulthood. Early identification of IEM correlates with significant reduction in morbidity, mortality, and associated disabilities for those affected (1). All States screen newborns for IEM, although the type and number of IEM screened for may vary from State to State. Typically, infants are screened for amino acid disorders, urea cycle disorders, organic acid disorders, and fatty acid oxidation defects. A few States are working toward including lysosomal storage diseases and peroxisomal disorders among their newborn screening panels (2). In most states, treatment of an IEM is referred to a specialized metabolic treatment facility. Please see Clarification for contact information for treatment facilities. IEM treatment is based on symptomatic therapy which may include
2 the following strategies: substrate restriction; stimulation or stabilization of residual enzyme activity; replacement of deficient products; removal of toxic metabolites or blocking their production; and enzyme replacement therapy (3). Avoidance of catabolism is essential at all treatment stages. Nutrition therapy is integral to the treatment of IEM. Nutrition therapy should both correct the metabolic imbalance and ensure adequate energy, protein, and nutrients for normal growth and development among affected individuals. Continual monitoring of nutrient intake, laboratory values, and the individual s growth are needed for evaluation of the adequacy of the prescribed diet (4). It is important that caregivers of infants and children with IEM ensure that the patient follows the prescribed dietary regimen. The below embedded links provide the most up-to-date information about the disease state as well as treatment. Amino Acid Metabolism Disorders (3) Phenylketonuria (includes clinically significant hyperphenylalaninemia variants) Maple syrup urine disease Homocystinuria Tyrosinemia Amino Acid Metabolism Disorders are characterized by the inability to metabolize a certain essential amino acid. The build-up of the amino acid that is not metabolized can be toxic. Treatment of amino acid disorders involves restricting one or more essential amino acids to the minimum required for growth and development and supplying the missing product due to the blocked reaction. Carbohydrate Disorders (5) Galactosemia Glycogen storage disease type I Glycogen storage disease type II (See also Pompe disease) Glycogen storage disease type III Glycogen storage disease type IV (Andersen Disease) Glycogen storage disease type V Glycogen storage disease type VI Hereditary Fructose Intolerance (Fructose 1-phosphate aldolase deficiency, Fructose 1, 6, biphosphatase deficiency, fructose kinase deficiency) This group of disorders includes an enzyme deficiency or its cofactor that affects the catabolism or anabolism of carbohydrate. Carbohydrate disorders are complex and affect neurological, physical, and nutritional status.
3 Fatty Acid Oxidation Defects (5) Medium-chain acyl-coa dehydrogenase deficiency Long-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency Trifunctional protein deficiency type 1 (LCHAD deficiency) Trifunctional protein deficiency type 2 (mitochondrial trifunctional protein deficiency) Carnitine uptake defect (primary carnitine deficiency) Very long-chain acyl-coa dehydrogenase deficiency Fatty acid oxidation defects include any enzyme defect in the process of mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation (FAO) system. The biochemical characteristic of all FAO defects is abnormal low ketone production as a result of the increased energy demands. This results in fasting hypoglycemia with severe acidosis secondary to the abnormal accumulation of intermediate metabolites of FAO, which can result in death. Organic Acid Disorders (AKA organic aciduria or organic acidemia) (6) Isovaleric acidemia 3-Methylcrotonyl-CoA carboxylase deficiency Glutaric acidemia type I Glutaric acidemia type II 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A lyase deficiency Multiple carboxylase deficiency (Biotinidase deficiency, Holocarboxylase synthetase deficiency) Methylmalonic acidemia Propionic acidemia Beta-ketothiolase deficiency Organic Acid Disorders are characterized by the excretion of non-amino organic acids in the urine. Most of the disorders are caused by a deficient enzyme involving the catabolism of specific amino acid(s). As a result, the non-metabolized substance accumulates due to the blockage of the specific metabolic pathway, which is toxic to certain organs and may also cause damage to the brain (7). Lysosomal Storage Diseases (6, 8) Fabry disease (α-galactosidase A deficiency) Gauchers disease (glucocerebrosidase deficiency) Pompe disease (glycogen storage disease Type II, or acid α-glucosidase deficiency) Lysosomal storage diseases are a group of related conditions characterized by
4 increased storage of undigested large molecule in lysosomes. Lysosome is a cellular organelle responsible for intracellular degradation and recycling of macromolecules. Due to a defect in a specific lysosomal enzyme, the macromolecule that normally would be metabolized is not broken down; instead, it accumulates in the lysosomes. This leads to tissue damage, organ failures and premature death. Common clinical features include bone abnormalities, organomegaly, developmental impairment and central, peripheral nervous system disorders. Mitochondrial Disorders (6, 8) Leber hereditary optic neuropathy Mitochondrial encephalomyopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like episodes (MELAS) Mitochondrial neurogastrointestinal encephalopathy disease (MNGIE) Myoclonic epilepsy with ragged-red fibers (MERRF) Neuropathy, ataxia, and retinitis pigmentosa (NARP) Pyruvate carboxylase deficiency Mitochondrial Disorders are caused by the dysfunction of the mitochondrial respiratory chain, or electron transport chain (ETC). Mitochondria play an essential role in energy production. The ETC dysfunction increases free radical production, which causes mitochondrial cellular damage, cell death and tissue necrosis and further worsens ETC dysfunction and thus forms a vicious cycle. The disorders can affect almost all organ systems. However, the organs and cells that have the highest energy demand, such as the brain and muscles (skeletal and cardiac) are most affected. The clinical features vary greatly among this group of disorders, but most have multiple organ dysfunctions with severe neuropathy and myopathy. Peroxisomal Disorders (6, 8, 9) Zellweger Syndrome Spectrum Adrenoleukodystrophy (x-ald) There are two types of peroxisomal disorders: single peroxisomal enzyme deficiencies and peroxisomal biogenesis disorders. These disorders cause severe seizures and psychomotor retardation (9). Peroxisomes are small organelles found in cytoplasm of all cells. They carry out oxidative reactions which generate hydrogen peroxides. They also contain catalase (peroxidase), which is important in detoxifying ethanol, formic acid and other toxins. Single peroxisomal enzyme deficiencies are diseases with dysfunction of a specific enzyme, such as acyl coenzyme A oxidase deficiency. Peroxisomal biogenesis disorders are caused by multiple peroxisome enzymes such as Zellweger syndrome and neonatal adrenoleukodystrophy.
5 Urea Cycle Disorders (6, 5) Citrullinemia Argininosuccinic aciduria Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I deficiency Urea Cycle Disorders occur when any defect or total absence of any of the enzymes or the cofactors used in the urea cycle results in the accumulation of ammonia in the blood. The urea cycle converts waste nitrogen into urea and excretes it from the kidneys. Since there are no alternate pathways to clear the ammonia, dysfunction of the urea cycle results in neurologic damages. Implications For WIC Nutrition Services WIC can provide exempt infant formulas and WIC-eligible medical foods, including those specifically formulated for IEM. Most of the dietary regimens for IEM require a combination of medical food (special formula in most cases) and standard infant formula or prescribed conventional foods. For example, participants with IEM related to essential amino acid metabolism (such as PKU, MSUD), who are not developmentally ready for conventional foods; require both medical food without the offending amino acid(s), and human milk or standard infant formula. It is recommended that WIC nutritionists collaborate with the clinical dietitians at the metabolic treatment facility, where available, to prescribe WIC food packages (Food Package III) according to the therapeutic diet ordered by the metabolic team, monitor the compliance of the restricted diet, and follow up on the growth and developmental status of the participants with IEM. Note: Infants with classic galactosemia cannot be breastfed due to lactose in human milk References 1. Metabolic backgrounder: The Ross metabolic formula system for meeting special nutrition needs. Columbus, OH: Ross Products Division; Levy PA. Inborn Errors of Metabolism: part 1: Overview. Pediatr Rev. 2009Apr; 30(4): Wilcken B. An introduction to nutritional treatment in Inborn errors of metabolism different disorders, different approaches. Southeast Asian J Trop med Public Health. 2003; 34 Suppl 3: Hendricks KM, Duggan C. Manual of pediatric nutrition, 4th ed. 2005; Ekval S, Ekvall, VK, editors. Pediatric nutrition in chronic diseases and developmental disorders: prevention, assessment and treatment. 2nd ed. Oxford University Press; Part III. Chapters GeneReviews are expert-authored, peer-reviewed, current disease descriptions that apply genetic testing to the diagnosis, management, and genetic counseling of patients and families with specific inherited conditions. Available at:
6 (last accessed 8/5/2010). 7. Stanley CA. Disorders of fatty acid oxidation. In: Fernandes J, et al editors. Inborn metabolic diseases. Berlin Springer; p Agamanolis D. Inherited metabolic disorders in neuropathology: an illustrated interactive course for medical students and residents. Akron OH: Akron Children s Hospital, Northeastern Ohio University College of Medicine. Available at: 9. Van Veldhoven, PP, Leuven KU. Biochemistry and genetic disorders of inherited disorders of peroxisomal fatty acid metabolism. J Lipid Res June. Available at: Clarification IEM not listed within this write-up may be found under: Please keep in mind these additional resources are not meant for medical advice nor to suggest treatment. Self-reporting of a diagnosis by a medical professional should not be confused with self-diagnosis, where a person simply claims to have or to have had a medical condition without any reference to professional diagnosis. A selfreported medical diagnosis ( My doctor says that I have/my son or daughter has ) should prompt the CPA to validate the presence of the condition by asking more pointed questions related to that diagnosis. The link below lists newborn screening coordinators. The coordinator can direct families to appropriate metabolic treatment facilities based on the newborn screening result: 10/2012
Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders Galactosemia Biotinidase Deficiency
 Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders Galactosemia Biotinidase Deficiency Dr. Kathy Grange, MD Division of Genetics and Genomic Medicine Department of Pediatrics Washington University School of Medicine What
Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders Galactosemia Biotinidase Deficiency Dr. Kathy Grange, MD Division of Genetics and Genomic Medicine Department of Pediatrics Washington University School of Medicine What
Newborn Screening in Saskatchewan Information for Health Care Providers
 Newborn Screening in Saskatchewan Information for Health Care Providers 2 Newborn screening: a healthy start leads to a healthier life Since the mid-1960s, health care providers have offered newborn screening
Newborn Screening in Saskatchewan Information for Health Care Providers 2 Newborn screening: a healthy start leads to a healthier life Since the mid-1960s, health care providers have offered newborn screening
Newborn Screening in Manitoba. Information for Health Care Providers
 Newborn Screening in Manitoba Information for Health Care Providers Newborn screening: a healthy start leads to a healthier life Health care professionals have provided newborn screening for phenylketonuria
Newborn Screening in Manitoba Information for Health Care Providers Newborn screening: a healthy start leads to a healthier life Health care professionals have provided newborn screening for phenylketonuria
Inborn Errors of Metabolism
 Intensive Care Nursery House Staff Manual Inborn Errors of Metabolism INTRODUCTION and PATHOPHYSIOLOGY: Inborn Errors of Metabolism (IEM) comprise a group of disorders in which a single gene defect causes
Intensive Care Nursery House Staff Manual Inborn Errors of Metabolism INTRODUCTION and PATHOPHYSIOLOGY: Inborn Errors of Metabolism (IEM) comprise a group of disorders in which a single gene defect causes
NORD Guides for Physicians #1. Physician s Guide to. Tyrosinemia. Type 1
 NORD Guides for Physicians #1 The National Organization for Rare Disorders Physician s Guide to Tyrosinemia Type 1 The original version of this booklet was made possible by donations in honor of Danielle
NORD Guides for Physicians #1 The National Organization for Rare Disorders Physician s Guide to Tyrosinemia Type 1 The original version of this booklet was made possible by donations in honor of Danielle
Organisation of Biochemical Genetic Testing in Estonia
 Organisation of Biochemical Genetic Testing in Estonia Katrin Õunap Department of Pediatrics, University of Tartu Department of Genetics, Tartu University Hospital Basel, 09 th May 2008 ESTONIA 1,35 million
Organisation of Biochemical Genetic Testing in Estonia Katrin Õunap Department of Pediatrics, University of Tartu Department of Genetics, Tartu University Hospital Basel, 09 th May 2008 ESTONIA 1,35 million
How To Treat The Sando Syndrome
 Consultation on Drugs for Rare Diseases Rare Disease Day Symposium Hannover Medical School (MHH), Solidarity Rare but Strong Together Roland Seifert, MHH @ Dear Sir, I am writing hoping that there might
Consultation on Drugs for Rare Diseases Rare Disease Day Symposium Hannover Medical School (MHH), Solidarity Rare but Strong Together Roland Seifert, MHH @ Dear Sir, I am writing hoping that there might
Energy Production In A Cell (Chapter 25 Metabolism)
 Energy Production In A Cell (Chapter 25 Metabolism) Large food molecules contain a lot of potential energy in the form of chemical bonds but it requires a lot of work to liberate the energy. Cells need
Energy Production In A Cell (Chapter 25 Metabolism) Large food molecules contain a lot of potential energy in the form of chemical bonds but it requires a lot of work to liberate the energy. Cells need
Newborn screening policy and guidelines
 Newborn screening policy and guidelines 2011 Newborn screening policy and guidelines 2011 Newborn screening policy and guidelines 2011 Contacts Detailed newborn screening program information including
Newborn screening policy and guidelines 2011 Newborn screening policy and guidelines 2011 Newborn screening policy and guidelines 2011 Contacts Detailed newborn screening program information including
The Urea Cycle. April 11, 2003 Bryant Miles
 The Urea ycle April 11, 2003 Bryant Miles I. Ammonia Toxicity Every amino acid contains at least one amino group. Therefore every amino acid degradation pathway has a key step where the amino group is
The Urea ycle April 11, 2003 Bryant Miles I. Ammonia Toxicity Every amino acid contains at least one amino group. Therefore every amino acid degradation pathway has a key step where the amino group is
STATE STATUTES AND REGULATIONS ON DIETARY TREATMENT OF DISORDERS IDENTIFIED THROUGH NEWBORN SCREENING JURISDICTION AND CITATION
 Alabama AC 22 20 3 AAC 40 20 10.01 et seq. PKU, CH, GALT, CAH, hearing loss, hemoglobinopathy, BD, CF, AAD, FAOD, OAD, and other heritable diseases Statutes authorize board of health to create regulations
Alabama AC 22 20 3 AAC 40 20 10.01 et seq. PKU, CH, GALT, CAH, hearing loss, hemoglobinopathy, BD, CF, AAD, FAOD, OAD, and other heritable diseases Statutes authorize board of health to create regulations
Chapter 9 Mitochondrial Structure and Function
 Chapter 9 Mitochondrial Structure and Function 1 2 3 Structure and function Oxidative phosphorylation and ATP Synthesis Peroxisome Overview 2 Mitochondria have characteristic morphologies despite variable
Chapter 9 Mitochondrial Structure and Function 1 2 3 Structure and function Oxidative phosphorylation and ATP Synthesis Peroxisome Overview 2 Mitochondria have characteristic morphologies despite variable
1. What has a higher stored energy potential per gram, glycogen or triglycerides? Explain.
 Lipid Metabolism 1. What has a higher stored energy potential per gram, glycogen or triglycerides? Explain. 2. How can excess acetyl CoA trapped in the mitochondria, be utilized as a substrate for fatty
Lipid Metabolism 1. What has a higher stored energy potential per gram, glycogen or triglycerides? Explain. 2. How can excess acetyl CoA trapped in the mitochondria, be utilized as a substrate for fatty
Lactic Acid Dehydrogenase
 Lactic Acid Dehydrogenase Pyruvic Acid Dehydrogenase Complex Pyruvate to ACETYL coa CC CoA + CO 2 Mitochondria 3 carbon Pyruvate to 2 carbon ACETYL Coenzyme A Pyruvate Acetyl CoA + CO 2 + NADH + H + CO2
Lactic Acid Dehydrogenase Pyruvic Acid Dehydrogenase Complex Pyruvate to ACETYL coa CC CoA + CO 2 Mitochondria 3 carbon Pyruvate to 2 carbon ACETYL Coenzyme A Pyruvate Acetyl CoA + CO 2 + NADH + H + CO2
Newborn Screening Test
 Important Information for Parents about the Newborn Screening Test Newborn Screening Branch Genetic Disease Screening Program http://cdph.ca.gov/nbs California Department of Public Health Publication Date:
Important Information for Parents about the Newborn Screening Test Newborn Screening Branch Genetic Disease Screening Program http://cdph.ca.gov/nbs California Department of Public Health Publication Date:
AP BIOLOGY CHAPTER 7 Cellular Respiration Outline
 AP BIOLOGY CHAPTER 7 Cellular Respiration Outline I. How cells get energy. A. Cellular Respiration 1. Cellular respiration includes the various metabolic pathways that break down carbohydrates and other
AP BIOLOGY CHAPTER 7 Cellular Respiration Outline I. How cells get energy. A. Cellular Respiration 1. Cellular respiration includes the various metabolic pathways that break down carbohydrates and other
Alabama Newborn Screening Program
 Alabama Newborn Screening Program Blood Spot Screening Hearing Screening Pulse Oximetry Screening Delivering You the Facts Alabama Department of Public Health Newborn Screening Program www.adph.org/newbornscreening
Alabama Newborn Screening Program Blood Spot Screening Hearing Screening Pulse Oximetry Screening Delivering You the Facts Alabama Department of Public Health Newborn Screening Program www.adph.org/newbornscreening
Genetics in Family Medicine: The Australian Handbook for General Practitioners. Newborn screening
 Genetics in Family Medicine: The Australian Handbook for General Practitioners GP s role 3 The newborn screening process 3 Storage of newborn screening cards 3 results 5 Where no further testing is required
Genetics in Family Medicine: The Australian Handbook for General Practitioners GP s role 3 The newborn screening process 3 Storage of newborn screening cards 3 results 5 Where no further testing is required
FORMULA & SPECIALIZED FOOD
 FORMULA & SPECIALIZED FOOD ADMINISTRATIVE POLICY Policy Number: HOME 005.16 T2 Effective Date: December 1, 2014 Table of Contents CONDITIONS OF COVERAGE... COVERAGE RATIONALE BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS...
FORMULA & SPECIALIZED FOOD ADMINISTRATIVE POLICY Policy Number: HOME 005.16 T2 Effective Date: December 1, 2014 Table of Contents CONDITIONS OF COVERAGE... COVERAGE RATIONALE BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS...
MEDICAL NUTRITION FOR INHERITED METABOLIC DISEASE Corporate Medical Policy
 MEDICAL NUTRITION FOR INHERITED METABOLIC DISEASE Corporate Medical Policy File name: Medical Nutrition for Inherited Metabolic Disease File code: UM.NUT.02 Origination: 10/1998 Last Review: 11/2013 Next
MEDICAL NUTRITION FOR INHERITED METABOLIC DISEASE Corporate Medical Policy File name: Medical Nutrition for Inherited Metabolic Disease File code: UM.NUT.02 Origination: 10/1998 Last Review: 11/2013 Next
The diagram below summarizes the effects of the compounds that cells use to regulate their own metabolism.
 Regulation of carbohydrate metabolism Intracellular metabolic regulators Each of the control point steps in the carbohydrate metabolic pathways in effect regulates itself by responding to molecules that
Regulation of carbohydrate metabolism Intracellular metabolic regulators Each of the control point steps in the carbohydrate metabolic pathways in effect regulates itself by responding to molecules that
Chapter 16 The Citric Acid Cycle
 Chapter 16 The Citric Acid Cycle Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which of the following is not true of the reaction catalyzed by the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex? A) Biotin participates in the decarboxylation.
Chapter 16 The Citric Acid Cycle Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which of the following is not true of the reaction catalyzed by the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex? A) Biotin participates in the decarboxylation.
Chapter 25: Metabolism and Nutrition
 Chapter 25: Metabolism and Nutrition Chapter Objectives INTRODUCTION 1. Generalize the way in which nutrients are processed through the three major metabolic fates in order to perform various energetic
Chapter 25: Metabolism and Nutrition Chapter Objectives INTRODUCTION 1. Generalize the way in which nutrients are processed through the three major metabolic fates in order to perform various energetic
1- Fatty acids are activated to acyl-coas and the acyl group is further transferred to carnitine because:
 Section 10 Multiple Choice 1- Fatty acids are activated to acyl-coas and the acyl group is further transferred to carnitine because: A) acyl-carnitines readily cross the mitochondrial inner membrane, but
Section 10 Multiple Choice 1- Fatty acids are activated to acyl-coas and the acyl group is further transferred to carnitine because: A) acyl-carnitines readily cross the mitochondrial inner membrane, but
An introduction to metabolic disorders
 12 An introduction to metabolic disorders Individual inborn or congenital errors of metabolism are very rare. However, more than 1400 inherited metabolic diseases have been described. Many of these disorders
12 An introduction to metabolic disorders Individual inborn or congenital errors of metabolism are very rare. However, more than 1400 inherited metabolic diseases have been described. Many of these disorders
NURSING GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF CHILDREN WITH FATTY ACID OXIDATION DEFECT
 NURSING GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF CHILDREN WITH FATTY ACID OXIDATION DEFECT National Centre for Inherited Metabolic Disorders 2.1 NURSING GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF CHILDREN WITH FATTY ACID OXIDATION
NURSING GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF CHILDREN WITH FATTY ACID OXIDATION DEFECT National Centre for Inherited Metabolic Disorders 2.1 NURSING GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF CHILDREN WITH FATTY ACID OXIDATION
State of Board of Health Agenda March 23, 2012 9:00 a.m. Perimeter Center 9960 Mayland Drive Richmond, Virginia 23233
 State of Board of Health Agenda March 23, 2012 9:00 a.m. Perimeter Center 9960 Mayland Drive Richmond, Virginia 23233 Welcome and Introductions Review of Agenda Approval of December 2011 Minutes Commissioner
State of Board of Health Agenda March 23, 2012 9:00 a.m. Perimeter Center 9960 Mayland Drive Richmond, Virginia 23233 Welcome and Introductions Review of Agenda Approval of December 2011 Minutes Commissioner
Organic Acid Disorders
 Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Organic Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues
Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Organic Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues
Newborn Screening Update for Health Care Practitioners
 Newborn Screening Update for Health Care Practitioners Changes in regulations affecting your practice for newborns transferred to neonatal intensive care units. Changes for newborn screening of premature,
Newborn Screening Update for Health Care Practitioners Changes in regulations affecting your practice for newborns transferred to neonatal intensive care units. Changes for newborn screening of premature,
ENTERAL FORMULAE AND PARENTERAL NUTRITIONAL SOLUTIONS, DME
 ENTERAL FORMULAE AND PARENTERAL NUTRITIONAL SOLUTIONS, DME Policy NHP only reimburses participating DME vendors for the provision of medically necessary enteral and parenteral formulae and nutritional
ENTERAL FORMULAE AND PARENTERAL NUTRITIONAL SOLUTIONS, DME Policy NHP only reimburses participating DME vendors for the provision of medically necessary enteral and parenteral formulae and nutritional
Regulation of Metabolism. By Dr. Carmen Rexach Physiology Mt San Antonio College
 Regulation of Metabolism By Dr. Carmen Rexach Physiology Mt San Antonio College Energy Constant need in living cells Measured in kcal carbohydrates and proteins = 4kcal/g Fats = 9kcal/g Most diets are
Regulation of Metabolism By Dr. Carmen Rexach Physiology Mt San Antonio College Energy Constant need in living cells Measured in kcal carbohydrates and proteins = 4kcal/g Fats = 9kcal/g Most diets are
008 Chapter 8. Student:
 008 Chapter 8 Student: 1. Some bacteria are strict aerobes and others are strict anaerobes. Some bacteria, however, are facultative anaerobes and can live with or without oxygen. If given the choice of
008 Chapter 8 Student: 1. Some bacteria are strict aerobes and others are strict anaerobes. Some bacteria, however, are facultative anaerobes and can live with or without oxygen. If given the choice of
CHAPTER 15: ANSWERS TO SELECTED PROBLEMS
 CHAPTER 15: ANSWERS T SELECTED PRBLEMS SAMPLE PRBLEMS ( Try it yourself ) 15.1 ur bodies can carry out the second reaction, because it requires less energy than we get from breaking down a molecule of
CHAPTER 15: ANSWERS T SELECTED PRBLEMS SAMPLE PRBLEMS ( Try it yourself ) 15.1 ur bodies can carry out the second reaction, because it requires less energy than we get from breaking down a molecule of
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter Twenty Three 1
 23.2 Glucose Metabolism: An Overview When glucose enters a cell from the bloodstream, it is immediately converted to glucose 6- phosphate. Once this phosphate is formed, glucose is trapped within the cell
23.2 Glucose Metabolism: An Overview When glucose enters a cell from the bloodstream, it is immediately converted to glucose 6- phosphate. Once this phosphate is formed, glucose is trapped within the cell
10.1 The function of Digestion pg. 402
 10.1 The function of Digestion pg. 402 Macromolecules and Living Systems The body is made up of more than 60 % water. The water is found in the cells cytoplasm, the interstitial fluid and the blood (5
10.1 The function of Digestion pg. 402 Macromolecules and Living Systems The body is made up of more than 60 % water. The water is found in the cells cytoplasm, the interstitial fluid and the blood (5
Ammonia (plasma, blood)
 Ammonia (plasma, blood) 1 Name and description of analyte 1.1 Name of analyte Ammonia 1.2 Alternative names None 1.3 NLMC code 1.4 Description of analyte Ammonia has the formula NH 3. At physiological
Ammonia (plasma, blood) 1 Name and description of analyte 1.1 Name of analyte Ammonia 1.2 Alternative names None 1.3 NLMC code 1.4 Description of analyte Ammonia has the formula NH 3. At physiological
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 17 Nutrition and Metabolism. Multiple-Choice Questions
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 17 Nutrition and Metabolism Multiple-Choice Questions 1) The sum of all of the biochemical processes going on within the human body at any
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 17 Nutrition and Metabolism Multiple-Choice Questions 1) The sum of all of the biochemical processes going on within the human body at any
COLLECTION OF NEWBORN SCREENING SPECIMENS
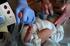 COLLECTION OF NEWBORN SCREENING SPECIMENS Newborn Screening is Mandatory Newborn screening has the potential to save or greatly improve the life of a newborn; therefore, Newborn Screening is mandatory
COLLECTION OF NEWBORN SCREENING SPECIMENS Newborn Screening is Mandatory Newborn screening has the potential to save or greatly improve the life of a newborn; therefore, Newborn Screening is mandatory
Integration of Metabolism
 I. Central Themes of Metabolism 1. ATP is the universal energy carrier. Integration of Metabolism Bryant Miles 2. ATP is generated by the oxidation of metabolic fuels Glucose Fatty Acids Amino Acids 3.
I. Central Themes of Metabolism 1. ATP is the universal energy carrier. Integration of Metabolism Bryant Miles 2. ATP is generated by the oxidation of metabolic fuels Glucose Fatty Acids Amino Acids 3.
NUTRITION OF THE BODY
 5 Training Objectives:! Knowledge of the most important function of nutrients! Description of both, mechanism and function of gluconeogenesis! Knowledge of the difference between essential and conditionally
5 Training Objectives:! Knowledge of the most important function of nutrients! Description of both, mechanism and function of gluconeogenesis! Knowledge of the difference between essential and conditionally
Neonatal Hypotonia. Clinical Approach to Floppy Baby
 Neonatal Hypotonia Clinical Approach to Floppy Baby Hypotonia in the newborn is a common presenting feature of systemic illness or neurologic dysfunction at any level of the central or peripheral nervous
Neonatal Hypotonia Clinical Approach to Floppy Baby Hypotonia in the newborn is a common presenting feature of systemic illness or neurologic dysfunction at any level of the central or peripheral nervous
Chapter 16 The Citric Acid Cycle
 Chapter 16 The Citric Acid Cycle Multiple Choice Questions 1. Production of acetyl-coa (activated acetate) Page: 603 Difficulty: 2 Ans: A Which of the following is not true of the reaction catalyzed by
Chapter 16 The Citric Acid Cycle Multiple Choice Questions 1. Production of acetyl-coa (activated acetate) Page: 603 Difficulty: 2 Ans: A Which of the following is not true of the reaction catalyzed by
Course Curriculum for Master Degree in Food Science and Technology/ Department of Nutrition and Food Technology
 Course Curriculum for Master Degree in Food Science and Technology/ Department of Nutrition and Food Technology The Master Degree in Food Science and Technology / Department of Nutrition and Food Technology,
Course Curriculum for Master Degree in Food Science and Technology/ Department of Nutrition and Food Technology The Master Degree in Food Science and Technology / Department of Nutrition and Food Technology,
Copyright 2000-2003 Mark Brandt, Ph.D. 54
 Pyruvate Oxidation Overview of pyruvate metabolism Pyruvate can be produced in a variety of ways. It is an end product of glycolysis, and can be derived from lactate taken up from the environment (or,
Pyruvate Oxidation Overview of pyruvate metabolism Pyruvate can be produced in a variety of ways. It is an end product of glycolysis, and can be derived from lactate taken up from the environment (or,
Nutritional Support of the Burn Patient
 Nutritional Support of the Burn Patient Objectives To understand the principles of normal nutrient utilization and the abnormalities caused by burn injury To be able to assess nutrient needs To be able
Nutritional Support of the Burn Patient Objectives To understand the principles of normal nutrient utilization and the abnormalities caused by burn injury To be able to assess nutrient needs To be able
MOLECULAR CELL BIOLOGY: ESSAY OUTLINE. What are peroxisomes? What do they do? And, how are proteins targeted to them?
 MOLECULAR CELL BIOLOGY: ESSAY OUTLINE What are peroxisomes? What do they do? And, how are proteins targeted to them? Are they related to the ER/Golgi? Are they more like mitochondria? Or, are they completely
MOLECULAR CELL BIOLOGY: ESSAY OUTLINE What are peroxisomes? What do they do? And, how are proteins targeted to them? Are they related to the ER/Golgi? Are they more like mitochondria? Or, are they completely
Spotlight: Improved Services for Clients with Qualifying Conditions
 Spotlight: Improved Services for Clients with Qualifying Conditions The new food package for clients with s provides a unique opportunity to coordinate better services for clients. Not only does it improve
Spotlight: Improved Services for Clients with Qualifying Conditions The new food package for clients with s provides a unique opportunity to coordinate better services for clients. Not only does it improve
DIETARY TREATMENT FOR PHENYLKETONURIA (PKU)
 DIETARY TREATMENT FOR PHENYLKETONURIA (PKU) Policy Number: 2015M0062A Effective Date: August 1, 2015 Table of Contents: Page: Cross Reference Policy: POLICY DESCRIPTION 2 Not Available COVERAGE RATIONALE/CLINICAL
DIETARY TREATMENT FOR PHENYLKETONURIA (PKU) Policy Number: 2015M0062A Effective Date: August 1, 2015 Table of Contents: Page: Cross Reference Policy: POLICY DESCRIPTION 2 Not Available COVERAGE RATIONALE/CLINICAL
GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS-II: An Overview
 GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS-II: An Overview University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences, Division of Basic Medical Sciences Discipline of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology, M Med Part I
GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS-II: An Overview University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences, Division of Basic Medical Sciences Discipline of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology, M Med Part I
Summary of Metabolism. Mechanism of Enzyme Action
 Summary of Metabolism Mechanism of Enzyme Action 1. The substrate contacts the active site 2. The enzyme-substrate complex is formed. 3. The substrate molecule is altered (atoms are rearranged, or the
Summary of Metabolism Mechanism of Enzyme Action 1. The substrate contacts the active site 2. The enzyme-substrate complex is formed. 3. The substrate molecule is altered (atoms are rearranged, or the
ETIOLOGIC CLASSIFICATION. Type I diabetes Type II diabetes
 DIABETES MELLITUS DEFINITION It is a common, chronic, metabolic syndrome characterized by hyperglycemia as a cardinal biochemical feature. Resulting from absolute lack of insulin. Abnormal metabolism of
DIABETES MELLITUS DEFINITION It is a common, chronic, metabolic syndrome characterized by hyperglycemia as a cardinal biochemical feature. Resulting from absolute lack of insulin. Abnormal metabolism of
MICHIGAN NEWBORN SCREENING PROGRAM
 Michigan Department of Community Health MICHIGAN NEWBORN SCREENING PROGRAM Annual Report 2011 Acknowledgements State of Michigan Governor Rick Snyder Michigan Department of Community Health Director James
Michigan Department of Community Health MICHIGAN NEWBORN SCREENING PROGRAM Annual Report 2011 Acknowledgements State of Michigan Governor Rick Snyder Michigan Department of Community Health Director James
Copyright 2000-2003 Mark Brandt, Ph.D. 35
 Amino acid breakdown Amino acids comprise one of the three major energy sources for animals. They are an especially important energy source for carnivorous animals, and for all animals during early starvation
Amino acid breakdown Amino acids comprise one of the three major energy sources for animals. They are an especially important energy source for carnivorous animals, and for all animals during early starvation
Graduate and Postdoctoral Affairs School of Biomedical Sciences College of Medicine. Graduate Certificate. Metabolic & Nutritional Medicine
 Graduate and Postdoctoral Affairs School of Biomedical Sciences College of Medicine Graduate Certificate in Metabolic & Nutritional Medicine Graduate Certificate Metabolic & Nutritional Medicine Purpose
Graduate and Postdoctoral Affairs School of Biomedical Sciences College of Medicine Graduate Certificate in Metabolic & Nutritional Medicine Graduate Certificate Metabolic & Nutritional Medicine Purpose
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Ch23_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following statements concerning digestion are correct except A) The major physical
Ch23_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following statements concerning digestion are correct except A) The major physical
Inborn Errors of Metabolism Presenting in Neonates
 Inborn Errors of Metabolism Presenting in Neonates Inborn errors of metabolism (IEM) are disorders in which there is a block at some point in the normal metabolic pathway caused by a genetic defect of
Inborn Errors of Metabolism Presenting in Neonates Inborn errors of metabolism (IEM) are disorders in which there is a block at some point in the normal metabolic pathway caused by a genetic defect of
Urea cycle disorders and organic acidurias For younger people
 Urea cycle disorders and organic acidurias For younger people www.e-imd.org What is a Urea cycle disorder/organic aciduria? The food we eat gets broken down by the body with the help of thousands of chemical
Urea cycle disorders and organic acidurias For younger people www.e-imd.org What is a Urea cycle disorder/organic aciduria? The food we eat gets broken down by the body with the help of thousands of chemical
X-Plain Hypoglycemia Reference Summary
 X-Plain Hypoglycemia Reference Summary Introduction Hypoglycemia is a condition that causes blood sugar level to drop dangerously low. It mostly shows up in diabetic patients who take insulin. When recognized
X-Plain Hypoglycemia Reference Summary Introduction Hypoglycemia is a condition that causes blood sugar level to drop dangerously low. It mostly shows up in diabetic patients who take insulin. When recognized
Chapter 7 Active Reading Guide Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
 Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 7 Active Reading Guide Cellular Respiration and Fermentation Overview: Before getting involved with the details of cellular respiration and photosynthesis, take a second
Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 7 Active Reading Guide Cellular Respiration and Fermentation Overview: Before getting involved with the details of cellular respiration and photosynthesis, take a second
Endocrine System: Practice Questions #1
 Endocrine System: Practice Questions #1 1. Removing part of gland D would most likely result in A. a decrease in the secretions of other glands B. a decrease in the blood calcium level C. an increase in
Endocrine System: Practice Questions #1 1. Removing part of gland D would most likely result in A. a decrease in the secretions of other glands B. a decrease in the blood calcium level C. an increase in
The correct answer is d C. Answer c is incorrect. Reliance on the energy produced by others is a characteristic of heterotrophs.
 1. An autotroph is an organism that a. extracts energy from organic sources b. converts energy from sunlight into chemical energy c. relies on the energy produced by other organisms as an energy source
1. An autotroph is an organism that a. extracts energy from organic sources b. converts energy from sunlight into chemical energy c. relies on the energy produced by other organisms as an energy source
Biochemistry of Cells
 Biochemistry of Cells 1 Carbon-based Molecules Although a cell is mostly water, the rest of the cell consists mostly of carbon-based molecules Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds Carbon
Biochemistry of Cells 1 Carbon-based Molecules Although a cell is mostly water, the rest of the cell consists mostly of carbon-based molecules Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds Carbon
Metabolic Disorders in Pediatric Neurology
 NEUROLOGY BOARD REVIEW MANUAL STATEMENT OF EDITORIAL PURPOSE The Hospital Physician Neurology Board Review Manual is a study guide for residents and practicing physicians preparing for board examinations
NEUROLOGY BOARD REVIEW MANUAL STATEMENT OF EDITORIAL PURPOSE The Hospital Physician Neurology Board Review Manual is a study guide for residents and practicing physicians preparing for board examinations
Work and Energy in Muscles
 Work and Energy in Muscles Why can't I sprint forever? I'll start this section with that silly question. What lies behind the undisputable observation that we must reduce speed if we want to run longer
Work and Energy in Muscles Why can't I sprint forever? I'll start this section with that silly question. What lies behind the undisputable observation that we must reduce speed if we want to run longer
Hepatic Encephalopathy, Hyperammonemia, and Current Treatment in ICU Room
 Hepatic Encephalopathy, Hyperammonemia, and Current Treatment in ICU Room Assoc.Prof. Chan Sovandy Chairman by : Prof.So Saphy and Assoc Prof, Kim chhoung Hepatic Encephalopathy Hepatic (portal systemic
Hepatic Encephalopathy, Hyperammonemia, and Current Treatment in ICU Room Assoc.Prof. Chan Sovandy Chairman by : Prof.So Saphy and Assoc Prof, Kim chhoung Hepatic Encephalopathy Hepatic (portal systemic
1. Explain the difference between fermentation and cellular respiration.
 : Harvesting Chemical Energy Name Period Overview: Before getting involved with the details of cellular respiration and photosynthesis, take a second to look at the big picture. Photosynthesis and cellular
: Harvesting Chemical Energy Name Period Overview: Before getting involved with the details of cellular respiration and photosynthesis, take a second to look at the big picture. Photosynthesis and cellular
Unsaturated and Odd-Chain Fatty Acid Catabolism
 Unsaturated and dd-hain Fatty Acid atabolism March 24, 2003 Bryant Miles The complete oxidation of saturated fatty acids containing an even number of carbon atoms is accomplished by the β-oxidation pathway.
Unsaturated and dd-hain Fatty Acid atabolism March 24, 2003 Bryant Miles The complete oxidation of saturated fatty acids containing an even number of carbon atoms is accomplished by the β-oxidation pathway.
Curriculum Overview:
 Curriculum Overview: The following courses must be completed by all Certified Nutrition Specialist candidates. Courses cannot fulfill multiple curriculum requirements, however, excess nutrition science
Curriculum Overview: The following courses must be completed by all Certified Nutrition Specialist candidates. Courses cannot fulfill multiple curriculum requirements, however, excess nutrition science
Your newborn baby s blood test
 Newborn Screening Free health checks for your baby Your newborn baby s blood test The Newborn Metabolic Screening Programme All babies are checked at birth to see that all is well. Some of your baby s
Newborn Screening Free health checks for your baby Your newborn baby s blood test The Newborn Metabolic Screening Programme All babies are checked at birth to see that all is well. Some of your baby s
FAILURE TO THRIVE What Is Failure to Thrive?
 FAILURE TO THRIVE The first few years of life are a time when most children gain weight and grow much more rapidly than they will later on. Sometimes, however, babies and children don't meet expected standards
FAILURE TO THRIVE The first few years of life are a time when most children gain weight and grow much more rapidly than they will later on. Sometimes, however, babies and children don't meet expected standards
School of Kinesiology Faculty of Health Sciences Western University. EXERCISE BIOCHEMISTRY Kin 3360B Winter, 2015
 2014-15 School of Kinesiology Faculty of Health Sciences Western University EXERCISE BIOCHEMISTRY Kin 3360B Winter, 2015 Instructor: J.M. Kowalchuk Office: HSB 411C Location: SH 3317 Office Hours: by appointment
2014-15 School of Kinesiology Faculty of Health Sciences Western University EXERCISE BIOCHEMISTRY Kin 3360B Winter, 2015 Instructor: J.M. Kowalchuk Office: HSB 411C Location: SH 3317 Office Hours: by appointment
Louise Simmons Clinical Nurse Specialist Inherited Metabolic Disorders (IMD) Birmingham Children s Hospital
 Louise Simmons Clinical Nurse Specialist Inherited Metabolic Disorders (IMD) Birmingham Children s Hospital Individually rare Collectively not uncommon - 1:700 - Childhood cancer 1:500 Genetically inherited
Louise Simmons Clinical Nurse Specialist Inherited Metabolic Disorders (IMD) Birmingham Children s Hospital Individually rare Collectively not uncommon - 1:700 - Childhood cancer 1:500 Genetically inherited
Cellular Energy: ATP & Enzymes. What is it? Where do organism s get it? How do they use it?
 Cellular Energy: ATP & Enzymes What is it? Where do organism s get it? How do they use it? Where does Energy come from? Ultimately, from the sun. It is transferred between organisms in the earth s lithosphere,
Cellular Energy: ATP & Enzymes What is it? Where do organism s get it? How do they use it? Where does Energy come from? Ultimately, from the sun. It is transferred between organisms in the earth s lithosphere,
Do mitochondria play a role in ME/CFS?
 Do mitochondria play a role in ME/CFS? Karl Morten Nuffield Dept of Obstetrics & Gynaecology University of Oxford ME/CFS Awareness Week May 10 th 2016 Mitochondrial dysfunction associates with many chronic
Do mitochondria play a role in ME/CFS? Karl Morten Nuffield Dept of Obstetrics & Gynaecology University of Oxford ME/CFS Awareness Week May 10 th 2016 Mitochondrial dysfunction associates with many chronic
1. The diagram below represents a biological process
 1. The diagram below represents a biological process 5. The chart below indicates the elements contained in four different molecules and the number of atoms of each element in those molecules. Which set
1. The diagram below represents a biological process 5. The chart below indicates the elements contained in four different molecules and the number of atoms of each element in those molecules. Which set
Methyl groups, like vitamins, are
 Methyl groups are essential for the body to function properly and must be obtained from the diet The need for methyl groups increases under stress Chapter 11 Betaine a new B vitamin Methyl groups reduce
Methyl groups are essential for the body to function properly and must be obtained from the diet The need for methyl groups increases under stress Chapter 11 Betaine a new B vitamin Methyl groups reduce
Expanded newborn screening and confirmatory follow-up testing for inborn errors of metabolism detected by tandem mass spectrometry
 DOI 10.1515/cclm-2012-0472 Clin Chem Lab Med 2013; 51(1): 157 176 Review Tomris Ozben * Expanded newborn screening and confirmatory follow-up testing for inborn errors of metabolism detected by tandem
DOI 10.1515/cclm-2012-0472 Clin Chem Lab Med 2013; 51(1): 157 176 Review Tomris Ozben * Expanded newborn screening and confirmatory follow-up testing for inborn errors of metabolism detected by tandem
Oxygen Metabolism and Oxygen Toxicity
 xygen Metabolism and xygen Toxicity February 26, 2003 Bryant Miles Chemiosmotic Theory Chemiosomitic Theory state that the free energy of electron transport is coupled to the pumping of protons from the
xygen Metabolism and xygen Toxicity February 26, 2003 Bryant Miles Chemiosmotic Theory Chemiosomitic Theory state that the free energy of electron transport is coupled to the pumping of protons from the
4. Which carbohydrate would you find as part of a molecule of RNA? a. Galactose b. Deoxyribose c. Ribose d. Glucose
 1. How is a polymer formed from multiple monomers? a. From the growth of the chain of carbon atoms b. By the removal of an OH group and a hydrogen atom c. By the addition of an OH group and a hydrogen
1. How is a polymer formed from multiple monomers? a. From the growth of the chain of carbon atoms b. By the removal of an OH group and a hydrogen atom c. By the addition of an OH group and a hydrogen
Genetic Testing in Research & Healthcare
 We Innovate Healthcare Genetic Testing in Research & Healthcare We Innovate Healthcare Genetic Testing in Research and Healthcare Human genetic testing is a growing science. It is used to study genes
We Innovate Healthcare Genetic Testing in Research & Healthcare We Innovate Healthcare Genetic Testing in Research and Healthcare Human genetic testing is a growing science. It is used to study genes
NUTRITION IN LIVER DISEASES
 NUTRITION IN LIVER DISEASES 1. HEPATITIS: Definition: - Viral inflammation of liver cells. Types: a. HAV& HEV, transmitted by fecal-oral route. b. HBV & HCV, transmitted by blood and body fluids. c. HDV
NUTRITION IN LIVER DISEASES 1. HEPATITIS: Definition: - Viral inflammation of liver cells. Types: a. HAV& HEV, transmitted by fecal-oral route. b. HBV & HCV, transmitted by blood and body fluids. c. HDV
Insurance coverage of medical foods for treatment of inherited metabolic disorders
 May 18, 2012 Insurance coverage of medical foods for treatment of inherited metabolic disorders Secretary s Advisory Committee on Heritable Disorders in Newborns and Children (SACHDNC) Susan A. Berry,
May 18, 2012 Insurance coverage of medical foods for treatment of inherited metabolic disorders Secretary s Advisory Committee on Heritable Disorders in Newborns and Children (SACHDNC) Susan A. Berry,
Cells & Cell Organelles
 Cells & Cell Organelles The Building Blocks of Life H Biology Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell
Cells & Cell Organelles The Building Blocks of Life H Biology Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell
CITRIC ACID (KREB S, TCA) CYCLE
 ITRI AID (KREB S, TA) YLE Date: September 2, 2005 * Time: 10:40 am 11:30 am * Room: G202 Biomolecular Building Lecturer: Steve haney 515A Mary Ellen Jones Building stephen_chaney@med.unc.edu 9663286 *Please
ITRI AID (KREB S, TA) YLE Date: September 2, 2005 * Time: 10:40 am 11:30 am * Room: G202 Biomolecular Building Lecturer: Steve haney 515A Mary Ellen Jones Building stephen_chaney@med.unc.edu 9663286 *Please
EFFIMET 1000 XR Metformin Hydrochloride extended release tablet
 BRAND NAME: Effimet XR. THERAPEUTIC CATEGORY: Anti-Diabetic PHARMACOLOGIC CLASS: Biguanides EFFIMET 1000 XR Metformin Hydrochloride extended release tablet COMPOSITION AND PRESENTATION Composition Each
BRAND NAME: Effimet XR. THERAPEUTIC CATEGORY: Anti-Diabetic PHARMACOLOGIC CLASS: Biguanides EFFIMET 1000 XR Metformin Hydrochloride extended release tablet COMPOSITION AND PRESENTATION Composition Each
Enzyme Replacement Therapies for UCD (Liver/ Liver Cell / Stem Cell Transplantation) Pat McKiernan Birmingham Children s Hospital
 Enzyme Replacement Therapies for UCD (Liver/ Liver Cell / Stem Cell Transplantation) Pat McKiernan Birmingham Children s Hospital Survival following liver transplantation for Biliary Atresia at BCH (n=195)
Enzyme Replacement Therapies for UCD (Liver/ Liver Cell / Stem Cell Transplantation) Pat McKiernan Birmingham Children s Hospital Survival following liver transplantation for Biliary Atresia at BCH (n=195)
Newborn Screening Issues
 Newborn Screening Issues - The Public Health Aspect - Dr. Helmut Brand Msc, MFPHM Institute of Public Health NRW, Bielefeld Public Health Genetics is like Mr Tur Tur, the phantom giant: the further you
Newborn Screening Issues - The Public Health Aspect - Dr. Helmut Brand Msc, MFPHM Institute of Public Health NRW, Bielefeld Public Health Genetics is like Mr Tur Tur, the phantom giant: the further you
1. Enzymes. Biochemical Reactions. Chapter 5: Microbial Metabolism. 1. Enzymes. 2. ATP Production. 3. Autotrophic Processes
 Chapter 5: Microbial Metabolism 1. Enzymes 2. ATP Production 3. Autotrophic Processes 1. Enzymes Biochemical Reactions All living cells depend on biochemical reactions to maintain homeostasis. All of the
Chapter 5: Microbial Metabolism 1. Enzymes 2. ATP Production 3. Autotrophic Processes 1. Enzymes Biochemical Reactions All living cells depend on biochemical reactions to maintain homeostasis. All of the
Regulation of the Citric Acid Cycle
 Regulation of the itric Acid ycle I. hanges in Free Energy February 17, 2003 Bryant Miles kj/mol 40 20 0 20 40 60 80 Reaction DGo' DG TA Free Energy hanges 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1.) itrate Synthase 2.) Aconitase
Regulation of the itric Acid ycle I. hanges in Free Energy February 17, 2003 Bryant Miles kj/mol 40 20 0 20 40 60 80 Reaction DGo' DG TA Free Energy hanges 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1.) itrate Synthase 2.) Aconitase
Pantesin Effective support for heart healthy cholesterol levels*
 Pantesin Effective support for heart healthy cholesterol levels* { Pantesin Effective support for heart healthy cholesterol levels* Many health-conscious adults keeping a watchful eye on their cholesterol
Pantesin Effective support for heart healthy cholesterol levels* { Pantesin Effective support for heart healthy cholesterol levels* Many health-conscious adults keeping a watchful eye on their cholesterol
NUTRITIONAL COUNSELING Corporate Medical Policy
 NUTRITIONAL COUNSELING Corporate Medical Policy File name: Nutritional Counseling File code: RB.NC.01 Origination: 4/2002 Last Review: 06/2015 Next Review: 06/2016 Effective Date: 01/01/2016 Description
NUTRITIONAL COUNSELING Corporate Medical Policy File name: Nutritional Counseling File code: RB.NC.01 Origination: 4/2002 Last Review: 06/2015 Next Review: 06/2016 Effective Date: 01/01/2016 Description
Cell Injury, Adaptation and Death
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.035: Principle and Practice of Human Pathology Dr. Badizadegan Cell Injury, Adaptation and Death HST.035 Spring 2003 Overview of Cell Injury Cells
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.035: Principle and Practice of Human Pathology Dr. Badizadegan Cell Injury, Adaptation and Death HST.035 Spring 2003 Overview of Cell Injury Cells
Carbon Hydrogen Oxygen Nitrogen
 Concept 1 - Thinking Practice 1. If the following molecules were to undergo a dehydration synthesis reaction, what molecules would result? Circle the parts of each amino acid that will interact and draw
Concept 1 - Thinking Practice 1. If the following molecules were to undergo a dehydration synthesis reaction, what molecules would result? Circle the parts of each amino acid that will interact and draw
Comprehensive Fatty Acids Panel - Serum
 Date of Collection: 2/11/2011 Patient Age: 48 Time of Collection: 03:20 PM Sex: F Print Date: 2/25/2015 Common Name Lipid Name Patient Result Units Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Series 1 alpha-linolenic Acid
Date of Collection: 2/11/2011 Patient Age: 48 Time of Collection: 03:20 PM Sex: F Print Date: 2/25/2015 Common Name Lipid Name Patient Result Units Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Series 1 alpha-linolenic Acid
INTRODUCTION TO THE UK CURRICULUM IN CLINICAL GENETICS
 INTRODUCTION TO THE UK CURRICULUM IN CLINICAL GENETICS Clinical Geneticists work in multidisciplinary regional genetic centres in the UK, in close collaboration with laboratory scientists, clinical co-workers
INTRODUCTION TO THE UK CURRICULUM IN CLINICAL GENETICS Clinical Geneticists work in multidisciplinary regional genetic centres in the UK, in close collaboration with laboratory scientists, clinical co-workers
Cellular Energy. 1. Photosynthesis is carried out by which of the following?
 Cellular Energy 1. Photosynthesis is carried out by which of the following? A. plants, but not animals B. animals, but not plants C. bacteria, but neither animals nor plants D. all living organisms 2.
Cellular Energy 1. Photosynthesis is carried out by which of the following? A. plants, but not animals B. animals, but not plants C. bacteria, but neither animals nor plants D. all living organisms 2.
Introduction. Pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes
 Introduction Type 2 diabetes mellitus (t2dm) is the most prevalent form of diabetes worldwide. It is characterised by high fasting and high postprandial blood glucose concentrations (hyperglycemia). Chronic
Introduction Type 2 diabetes mellitus (t2dm) is the most prevalent form of diabetes worldwide. It is characterised by high fasting and high postprandial blood glucose concentrations (hyperglycemia). Chronic
Chapter 2 Phosphorus in the Organic Life: Cells, Tissues, Organisms
 Chapter 2 Phosphorus in the Organic Life: Cells, Tissues, Organisms As already mentioned (see Chap. 1 ), in the living cell phosphorus plays a decisive role in three different essential structures: In
Chapter 2 Phosphorus in the Organic Life: Cells, Tissues, Organisms As already mentioned (see Chap. 1 ), in the living cell phosphorus plays a decisive role in three different essential structures: In
H.W. 1 Bio 101 Prof. Fournier
 H.W. 1 Bio 101 Prof. Fournier 1. What is a similarity between all bacteria and plants? A) They both have a nucleus B) They are both composed of cells C) They both have chloroplasts D) They both lack a
H.W. 1 Bio 101 Prof. Fournier 1. What is a similarity between all bacteria and plants? A) They both have a nucleus B) They are both composed of cells C) They both have chloroplasts D) They both lack a
B12 & Cobalamin. Learning objectives
 Learning objectives B12 & Cobalamin Define vitamins Classify fat soluble and water soluble vitamins. Study chemical structure and biological active coenzyme form of vitamin B12. List the dietary sources
Learning objectives B12 & Cobalamin Define vitamins Classify fat soluble and water soluble vitamins. Study chemical structure and biological active coenzyme form of vitamin B12. List the dietary sources
