Interpretable Fuzzy Modeling using Multi-Objective Immune- Inspired Optimization Algorithms
|
|
|
- Bryan Lucas
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Interpretable Fuzzy Modeling using Multi-Objetive Immune- Inspired Optimization Algorithms Jun Chen, Mahdi Mahfouf Abstrat In this paper, an immune inspired multi-objetive fuzzy modeling (IMOFM) mehanism is proposed speifially for high-dimensional regression problems. For suh problems, high preditive auray is often the paramount requirement. With suh a requirement in mind, however, one should also put onsiderable efforts in making the eliited model as interpretable as possible, whih leads to a diffiult optimization problem. The proposed modeling approah adopts a multistage modeling proedure and a variable length oding sheme to aount for the enlarged searh spae due to the simultaneous optimization of the rule-base struture and its assoiated parameters. IMOFM an aount for both Singleton and Mamdani Fuzzy Rule-Based Systems (FRBS) due to the arefully hosen output membership funtions, the inferene and the defuzzifiation methods. The proposed algorithm has been ompared with other representatives using a simple benhmark problem, and has also been applied to a highdimensional problem whih models mehanial properties of hot rolled steels. Results onfirm that IMOFM an eliit aurate and yet transparent FRBSs from quantitative data. T I. INTRODUCTION RADITIONALLY, modeling tasks involve the building of mathematial equations whih an best desribe the underlying proess. Suh a modeling pratie normally requires a deep understanding of the systems under investigation, hene the reason why it is often referred to as knowledge-driven Modeling. On the ontrary, Data-Driven Modeling (DDM), inspired prinipally from artifiial intelligene tehniques, is based on limited knowledge of the modeling proess and relies on the data desribing the input and output mapping. DDM is able to make abstration and generalizations of the proess and plays often a omplementary role to knowledge-based models. For omplex systems, the linear regression may not be suffiient, whih leads to the need of the non-linear regression tehniques. Among many of these tehniques, Artifiial Neural Networks (ANN), fuzzy rule-based systems (FRBS) and Neural-Fuzzy Systems (NFS) have been reeiving more attention during the last two deades due to the fats of not only being able to approximate pratially any given funtion to an arbitrary auray [1], but also being able to Manusript reeived January 1, 010. This work was supported in part by the EPSRC under Grant EP/F0464/1. Jun Chen is with the Department of Automati Control and Systems Engineering, University of Sheffield, Sheffield, S1 JD, UK (phone: +44 (0) ; [email protected]). Mahdi Mahfouf is with the Department of Automati Control and Systems Engineering, University of Sheffield, Sheffield, S1 JD, UK (phone: +44 (0) ; fax: +44 (0) ; [email protected]). generalize reasonably well for any previously unseen situations. The prevalene of these nonlinear regression tehniques is largely attributed to the breakthrough in the nonlinear optimization tehniques, suh as the Bak-Error Propagation (BEP) algorithm [, p. 46-5] and the bioinspired optimization []-[4]. Sine the first introdution of fuzzy logi, FRBSs have been widely used in systems and ontrol engineering []. However, the predominant approah in the traditional design of FRBS highly relies on human experts. Although learning omponents an be further inorporated into the proedures of oarse model induement [5] and its further refinement [, p. 46-5], it may suffer from two serious problems, viz. the deterioration of the model s interpretability and the over-fitting to the training patterns. Taking this into aount, one an find that bio-inspired optimization, in partiular Generi Algorithms (GAs), has a long history of being inorporated into fuzzy logi [6] and demonstrate a possible route to the remedy for the mentioned two problems. The main aim of this paper is to present a systemati immune-inspired multi-objetive fuzzy modeling approah whih an simultaneously aount for the interpretability of the rule-base and its preditive auray for regression problems. The paper is organized as follows: Setion II disusses the formation of the multi-objetive fuzzy modeling problems and the FRBSs used in this work; Setion III shortly reviews the existing evolutionary based approahes for improving FRBS s interpretability; IMOFM whih represents an alternative tati to solve interpretability issues will be introdued in Setion IV; in Setion V, in order to evaluate the performanes of IMOFM, the algorithm is tested using a simple benhmark problem and is applied to the predition of the mehanial properties of alloy steels; finally, onlusions are given in Setion VI. II. FUZZY RULE BASED SYSTEMS AND THE FORMATION OF THE MULTI-OBJECTIVE FUZZY MODELING PROBLEM A. Fuzzy Rule Based Systems (FRBS) Two fuzzy modeling paradigms, viz. Singleton [7] and Mamdani [8] FRBSs, are employed in this work due to their abilities of expressing linguisti meanings in both of their anteedents and onsequents. Generally speaking, a FRBS an be formulated as follows: where, is the ith linguisti value (fuzzy set) for the jth
2 linguisti variable defined over the universe of disourse ; the funtion assoiated with that maps to [ ] is the orresponding membership funtion; R i represents the ith rule in the rule base, and is the output of the ith rule. Typially, an be the funtion of the inputs or the linguisti value of the output, whih differentiate FRBS into Singleton (the former) and Mamdani (the latter) FRBS. It is worth noting that Singleton FRBS is a speial ase of TSK FRBS [7] when is the zero order funtion of the inputs. In some sense, Singleton FRBS shares the basi feature of Mamdani FRBS if one onsiders singleton onsequents as a speial type of fuzzy sets. B. Formation of the Multi-objetive Fuzzy Modeling Problem As Casillas et al. pointed out in [9], modeling is the task that simplifies a real system or omplex reality with the aim of easing its understanding. Hene, the development of reliable and omprehensible models must be the main theme of any modeling tasks. By reliable it is meant the model s apability of faithfully representing the real systems, in other words the model auray. By omprehensible it is meant the model s apability of expressing the behavior of the real systems in a omprehensible way, in other words the model interpretability. However, as Zadeh onjetured in his Priniple of Inompatibility [10], it is very likely that auray and interpretability may well be exlusive requirements in a modeling proess. The refletion of these in a fuzzy modeling senario represents a dilemma of designing FRBS. The auray vs. interpretability issue in a fuzzy modeling ontext an also be formulated as a multi-objetive optimization problem. Fig. 1 shows the front in a biobjetive fuzzy modeling senario where two ompeting objetives, viz. the preditive error (auray) and the rule base omplexity (interpretability), are minimized simultaneously. The aim is to find a set of approximate FRBSs as lose to the true front as possible. Fig. 1. front in a bi-objetive fuzzy modeling ase. By finding a set of solutions, human an understand the underlying problem in a muh greater depth, and finally a single optimal solution to a speifi senario is finally seleted and applied. In the ase shown in Fig. 1, if one requires ertain interpretability (transpareny) of the FRBS along with its good preditive auray the middle irle ould be the one that fulfils the user s need. As already stated in [11], this should result in a minimal human intervention during the modeling proess. III. LITERATURE REVIEW OF PREVIOUS WORKS Originated from Karr s work [6], the GA approah in fuzzy systems was initially utilized to adjust the parameters of membership funtions, whih leads to no signifiant differene when ompared to other learning paradigms. The real signifiane of employing evolutionary algorithms (EAs) for optimizing FRBSs omes from EAs flexibility in terms of being able to enode and evolve almost every omponent of the FRBS [1]. Suh a flexibility offers a solution so that one an take into aount the interpretability (struture) and the preditive performane of the FRBS in a more oherent way. Broadly speaking, there urrently exist two different EA-based streams to takle the interpretability issues: 1) The first stream is mainly onerned with the linguisti modeling using a Mamdani type of FRBSs, in whih a set of pre-speified fuzzy partitions (linguisti terms) are given a priori by experts or users (grid partition). These linguisti terms are fixed during the ourse of the evolution [1]-[15] so that their physial meanings are retained. Only the fuzzy rules are subjet to the seletion via GAs so that a ompat rule-base an be evolved from a large number of andidate rules, whih should lead to a more interpretable FRBS. Sine the seletion proess removes irrelevant and inonsistent rules, the auray is also improved. Further relevant researhes inlude those in [16]-[17], apart from the rule seletion, these works also tuned the linguisti terms by a modified GA. However, suh tuning is only operated in a restrained spae in order to maintain their original semantis. ) the seond stream generally uses an approximate fuzzy model as the starting point (in suh a ase, fuzzy partitions are extrated via some automati learning proedures; hene, there is not a global data-base a priori); the task is then to improve the model s explanatory ability, whih may have been lost during the automati learning proess, through a set of similarity-driven simplifiation and parameter adjusting operations [18]-[1]. Under this stream, a similarity measure is taken so that similar fuzzy sets an be merged. Consequently, similar rules are merged as well. Hene, the distinguishability of membership funtions and the ompatness of the rule-base are improved. Comparing the two streams leads to the following: 1) in the linguisti modeling stream, the target problems are normally assoiated with lassifiations and lowdimensional regression problems; this is beause that, for suh problems, the effet of the urse of dimensionality due to the grid partition and the need for the parameter tuning due to the preditive auray requirement are not serious issues; only very reently, suh a linguisti modeling framework has been adopted for high-dimensional
3 regression problems [17]; ) for high-dimensional regression problems, an approximate FRBS may represent a better hoie to start with due to the auray and ompatness requirement. However, to the best of our knowledge, majority of the works within the seond modeling stream were using TSK FRBS, whih breah the original intention of eliiting an interpretable FRBS. It is rather triky to deide whih modeling stream is more suitable. Both modeling streams have their limitations: 1) although linguisti modeling often leads to well distributed membership funtions more rules are required to ahieve similar preditive performanes as those provided by the seond modeling stream with fewer rules, this being due to the restrition imposed on the membership funtion searh spae; ) although the seond modeling stream often leads to a ompat rule-base and higher preditive auray, the membership funtions are not well distributed even after interpretability improvement; furthermore, if TSK FRBS is employed the transpareny in the onsequents will be lost. In the light of the above onsiderations, the proposed algorithm sits in the middle of the two modeling streams by using a ompat FRBS with ertain interpretability for highdimensional regression problems. Although a Singleton/Mamdani FRBS is used in this work, unlike those whih use similar types of FRBS within the first modeling stream, the membership funtions of the proposed method an move freely within the variable intervals. Hene, it is still within the seond modeling stream. However, it greatly improves the interpretability of the eliited FRBS, and an be viewed as a omplement to [17] due to the fat that more ompat and higher aurate FRBSs an be eliited. IV. AN IMMUNE INSPIRED MULTI-OBJECTIVE FUZZY MODELING (IMOFM) MECHANISM An immune inspired multi-objetive fuzzy modeling (IMOFM) proedure onsists of three stages whih follow priniples of vaination and the seondary response of the immune systems. Furthermore, the third modeling stage utilizes a Population Adaptive Immune Algorithm (PAIA) [], [] as the searh engine in searh of the optimal struture and parameters. In the following spae, Artifiial Immune Systems (AIS), in partiular PAIA, are first introdued followed by the desription of IMOFM. A. AIS for Multi-objetive Optimization The basi idea of using AIS for optimization is emanated from the Clonal Seletion Priniple and Network Hypothesis [4]. The Clonal Seletion Priniple desribes the basi features of an immune response to an antigeni stimulus, and establishes the idea that only those antibodies that reognize the antigen are seleted to proliferate. The analogies of this in AIS are omposed of the followings: 1) Ativation alulates the affinity (fitness) for eah antibody (solution) so that an adaptive number of lones an be seleted and produed; ) Affinity Maturation mutates the seleted good lones so that more searh spae an be explored; ) Reseletion selets good andidate solutions from the ombined parents and lones to provide seletion pressure to effetively drive the andidate solutions towards the front. The Network Hypothesis states that antibodies an be stimulated by reognizing other antibodies, and for the same reason an be suppressed by being reognized. Suh a suppression mehanism allows the regulation of the overstimulated antibodies to maintain a stable memory. The refletion of this in AIS is the so-alled Network Suppression whih is used to regulate the population so that it is adaptive to the searh proess. By synergizing all the above omponents, PAIA is proposed in [], []. In [4], the authors further proposed a multi-stage optimization proedure by inorporating the onept of vaination. The idea is to first use a single objetive optimization stage, ating as the vaination proess, to effiiently find any one of the solutions resting on the front. Then, PAIA an at as a post-proessing proedure to expand suh a solution along the front. For fuzzy modeling, small modifiations of the Ativation step are needed and will be disussed aordingly in Part B. Details regarding PAIA and multi-stage optimization are referred to [] and [4, h. ]. B. IMOFM for Obtaining a Set of FRBSs IMOFM is a three-stage modeling proedure. The first two stages are equivalent to the vaination proess in the first stage of the multi-stage optimization proedure. The aim is to first extrat an initial approximate FRBS and then to refine it in terms of its preditive auray. By doing so, an initial vaine model with the over-estimated number of rules an effiiently be eliited. Another reason of inluding the first two modeling stages, espeially the seond one (refinement), is that by doing so the most omplex rule-base an survive under the pressure of seletion. Without inluding the refining step, the rule-base with a omplex struture may be regarded inferior to the less omplex rulebase in a sense even if both them are inaurate in the early evolutionary stages. Hene, one may lose the hane of evolving the most aurate FRBS, whih normally omes with a omplex struture. The vaine model is then used in the third stage to seed the initial population of PAIA in order to obtain a set of fuzzy models with improved interpretability. To takle the problem of simultaneously optimizing the rule-base struture and parameters, a variable length oding sheme is adopted, and a new distane index is proposed to ope with the variablelength individuals, whih should improve the effiieny of the searh. For model struture optimization, a Model Simplifiation module is added after the Affinity Maturation in a bid to find transparent FRBSs. Fig. represents a shemati diagram of suh a modeling framework. 1) Eliitation of the Initial Singleton/Mamdani FRBSs Firstly, an evolutionary based K-means lustering algorithm [5] is used to group the available data into a predefined number of lusters. In order to onvert the obtained lusters into FRBSs, a ertain mehanism has to be
4 Yes First Stage: Extrating The Initial FRBS Seond Stage: Refining The Initial FRBS The Initial FRBS An Immune Algorithm Based Fuzzy Preditive Modeling Mehanism For Singleton FRBS, is equal to. If Centroid of Area (COA) defuzzifiation method is employed, the risp output of the initial Singleton FRBS an be omputed as below: (4) where, ( Third Stage: Multi-objetive Fuzzy Modelling A Set of Fuzzy Models No Initial Population Pool Ativation Clone Variable Length Coding Affinity Maturation Clone ( ) ), and ( ) is the parameter vetor whih is subjet to further tuning in the seond modeling stage. For Mamdani FRBS, the bell-shape membership funtions are used for : ( ) (5) established so that and the orresponding output (refer to Setion II) an be linked with the extrated lusters. Gaussian membership funtions are used for the inputs of FRBSs. In suh a ase, the ith identified luster entre in the input spae orresponds diretly to the entroids of the Gaussian membership funtions responsible for the ith rule. The spreads of the orresponding Gaussian funtions are obtained by first alulating the matrix as follows: ( ) (1) where, are k luster enters in the input spae, is the Eulidean distane, and speifies the degree of data point belonging to the ith luster. Spread is thus dedued as follows: ( ( ) ) ( ) ( ) Model Simplifiation Reseletion Network Suppression [ ]( ) where, j indiates the dimension of the spread in the input spae for the ith luster, N is the total number of data points. The maximum value of is piked to ensure a ertain degree of overlap between different lusters. This also ensures a smooth transition of the preditions over different regions. is used to adjust the degree of overlap, and is set to 0.95 in this work without any loss of generality. Hene, the Gaussian membership funtion on eah dimension an be speified using (): Stop Fig.. The proposed IMOFM framework. () ( ) ( ( ) ) () where, is obtained by using (1) and () but in the output spae. Unlike traditional Mamdani FRBS where defuzzifiation is normally applied on the overall implied fuzzy set [, p. 64], IMOFM employs the enter of gravity (COG) defuzzifiaiton on the implied fuzzy set as below: (6) Instead of using minimum and maximum, IMOFM hooses to use produt and plus for the T-norm and S-norm respetively. All these modifiations are done to ensure omputational effiieny, and more importantly, to ensure that an analytial solution desribed in (7) an be deduted. (7) where, is the enter of area of the membership funtion and is the peak ( ) if is symmetri; is the final defuzzified output of the FRBS. ( ) is the parameter vetor whih is subjet to further fine-tuning in a bid to improve the model s preditive performane. denotes the area under over the output interval [ ] and is alulated using (8). [ ( ) ( )] (8) Hene, after the first stage, a Singleton/Mamdani FRBS with the pre-speified number of rules is extrated from the numerial data, whih is analytial and an be refined further using the seond modeling stage. ) Refinement of Initial FRBSs In the seond modeling stage, a BEP with momentum terms algorithm [, p. 46-5] is developed to first improve the auray of the initial FRBS by adjusting the parameters in so that the rule-base with the over-estimated number of rules an also survive under the pressure of
5 seletion. By taking the partial derivatives of (4) and (7) with respet to eah parameter inluded in, one an obtain a set of parameter updating laws (due to the spae, interested readers are referred to [4]). One problem assoiated with the BEP updating formulas is that they inlude no onstraints with respet to the update mehanism of these parameters. Hene, during the ourse of the optimization, the enters of the membership funtions are likely to be plaed outside the boundaries. Hene, in this work a simple onstraint handling sheme is added, whih heks the boundary violation for enters during eah iteration step and drives any violated enters bak to the boundaries. ) Multi-objetive Fuzzy Modeling a) Forming Objetive funtions Two onfliting objetive funtions are formulated with the first fousing on the predition auray and the seond on the struture simplifiation as desribed in (9); and are th predited and real outputs; Nrule is the number of fuzzy rules in FRBS; Nset is the total number of fuzzy sets; RL is the summation of the rule length of eah rule ( Don t are is not inluded in the rule length). (a) (b) FRBS1 Rule1 q: ( 1 FRBS Rule1 Rule 1 1 ; ; b 1 ; Rule Singleton FRBS: q: ( 1 Mamdani FRBS: Rule ; b Rule 1 1 ; ; b 1 ; original vaine FRBS extrated from the first two modelling stages. and are the entre and the spread of the ith rule s onsequent. is a random number within [0, 1]. defines the minimum interval between the entre and its orresponding upper and lower limits of the input (or the output) variable, whihever is smaller. and are the user speified parameters whih define how muh different the newly generated FRBSs are from the original vaine one, and are set to 0. and 0.1 respetively. Rule4 ; b y y Rule5 Rule6 Fig.. Variable length oding sheme for: (a) a three-rule Singleton/Mamdani FRBS; (b) a six-rule Singleton/Mamdani FRBS. ) ) ( ) (10) b) Variable Length Coding Sheme and Initial Population As far as the multi-objetive fuzzy modeling is onerned, different enoding shemes have been proposed and an be broadly divided into two ategories: 1) enoding based on the global data-base; ) enoding based on the effetive rule parameters. The former is mainly found in the linguisti modeling stream [1]-[15], in whih a string or a rule matrix is formed as the hromosome in order to selet the effetive rules and linguisti terms from the andidate set. [17] represents the variant of the first enoding sheme, in whih the enoding omprised the struture oding and the parameter (data-base) oding. Key to the first enoding sheme is that the global data-base is usually kept unhanged or only varied in a onstrained searh spae. The latter is mainly found in the approximate modeling stream due to the lak of global data-base. Sine only the effetive rule parameters are inluded in the oding, a variable length oding sheme is inevitable and is used in this work. Fig. gives an example of how to enode FRBSs. As shown in Fig., the inrease of the ode length is only linear to the variable s dimension, whih effetively takles the effiieny of the searh and the urse of dimensionality. The initial population is obtained with all individuals generated around the vaine model using (10) and (11). Where, and are the entre and spread of the ith rule and the jth input membership funtion in the (11) Suh a forming approah only aquires the knowledge about the maximum allowable number of rules (i.e. the prespeified number of lusters) and the data so that emphasis of the third modeling stage is plaed on the automati eliitation of a set of FRBSs in the sense. The size of the initial population in this work is set to 7. ) Variation Operators and a New Distane Index The variation operator used in PAIA is Affinity Maturation whih mutates the seleted good solutions aording to their affinity values ( as desribed in (1). Suh a variation operator is used in IMOFM to optimize the assoiated parameters enoded in q (see Fig. ). (1) where N(0, 1) is a Gaussian random variable with zero mean and standard deviation 1. is a dimension index within the length of that has been hosen to mutate. One problem in using (1) is assoiated with whih is originally alulated based on the distane between two fixed-length individuals. Given the variable length oding sheme and the unonstrained optimization used in this work, a onomitant effet of the so-alled unordered sets of rules [6] may our. As pointed in [6], variations
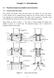
6 over unordered individuals are equivalent to ombing the mother s gen for good vision and father s gen for urly hair, whih does not make muh sense. To takle this problem, a new distane index is proposed for the alulation of. The basi idea is to align the losest rules from different individuals in order to have a meaningful variation. ( ) ( ) ( ) (1) where, and are two FRBSs with and rules; is the length of the rule; ( represents the losest rule in ) with respet to the rule in ; is the absolute value of. d) Model Simplifiation A model simplifiation step is added as shown in Fig.. The aim is to remove the redundany both in the rules and in the fuzzy sets. On the rule level: 1) one of the insignifiant rules (rules that ontribute the least to any predition error inrease when not inlude these rules) is removed unless the rule base reahes the fewest rules designated by the user; ) one of singleton rules [1] (rules whose omprising fuzzy sets are similar to singleton set) is removed; ) the most similar pair of rules based on the Similarity of Rule Premise (SRP) [0] are merged. On the fuzzy sets level: 1) one fuzzy set that is the most similar to the universal fuzzy set is labeled as Don t are ; ) two most similar fuzzy sets from the inputs and output dimensions are merged to form a single fuzzy set based on the similarity measure [0]. It is worth mentioning that the above operations are exeuted for eah loned FRBS at eah iteration step. A set of thresholds whih ontrol the various similarity measures are speified by the users. Interested readers are referred to [4, h.5] for more details. During the experiments, it is found that the thresholds are not the ritial parameters due to the following two reasons: 1) only one fuzzy rule or two fuzzy sets are removed or merged at eah iteration step; ) elitism is adopted to reord any non-dominated solution found at eah iteration step. modeling stage using (10) and (11). The initial population size is set to 7. The number of iterations in the third stage is set to 100. Table I summarizes suh omparative results fousing on their preditive performanes and the number of rules. The results in Table I inlude the average values of 0 runs. Fig. 4 shows the membership funtion distribution of input (x ) through the three modeling stages. TABLE I COMPARISONS OF THE PREDICTIVE PERFORMANCE OF THE DIFFERENT MODELING METHODS FOR THE BENCHMARK PROBLEM Modeling Methods (Ref.) No. of rules No. of fuzzy sets & The type of FRBS Performane (RMSE training) [5] 6 1 Mamdani * [7] 5 10 Singleton * IMOFM_S (IMOFM for Singleton FRBS): Initial FRBS 5 10 Singleton * FRBS1(0 times) 5 9 Singleton # FRBS(0 times) 5 8 Singleton # FRBS(9 times) 4 8 Singleton # FRBS4(9 times) 6 Singleton # FRBS5(5 times) (5 T ) 4 Singleton # IMOFM_M (IMOFM for Mamdani FRBS): Initial FRBS 5 15 Mamdani * FRBS1(5 times) 5 14 Mamdani # FRBS( times) 5 1 Mamdani # FRBS(6 times) 4 11 Mamdani # FRBS4(8 times) 9 Mamdani # FRBS5(8 times) (5 T ) 5 Mamdani # &: For IMOFM_S, it is the number of fuzzy sets in its inputs; for IMOFM_M, it is the number of fuzzy sets in its inputs and output. *: Initial model extrated diretly from data using lustering algorithms or grid partition Refined model or the onsequents are omputed through the estimation methods. #: Simplified model after model simplifiation and parameter fine tuning. T: Total number of rule length. : Stardard deviation of the results obtained from 0 runs. Input (x) of a 5-rule initial Mamdani FRBS Input (x) of a 5-rule refined Mamdani FRBS Input (x) of a 4-rule simplified Mamdani FRBS A. A Benhmark Problem V. EXPERIMENTS The benhmark example used in this setion is a nonlinear stati system with two inputs and one output, whih has been studied in [7]. The system is defined as follows: (14) Although this problem is a simple low-dimensional problem, it is a very good example in terms of demonstrating how IMOFM works. The same 50 input-output data pairs as those used in [5] and [7] are olleted. The number of lusters is set to 5 in the first modeling stage. The refined 5-rule initial FRBS is used to seed the initial population in the third Input (x) First Modeling Stage Seond Modeling Stage Third Modeling Stage Fig. 4. The membership funtion distribution of input. Sine different runs will lead to slightly different FRBS onfigurations, Table I also reords the number of eah FRBS onfiguration found within the 0 runs. Most onfigurations are found more than 0 times within 0 runs, whih suggests that IMOFM is robust and onsistent. The Comparing to other Singleton and Mamdani modeling approahes, IMOFM was found to represent the most aurate results with simpler rule-base struture.
7 In order to test the influenes of the eah modeling stages, two variants of the proposed IMOFM are investigated: 1) the ombination of the first stage and the third stage; ) only the third stage. In the latter ase, the initial 5-rule FRBS is randomly generated within the variable domains. Table II summarizes the results of the two variants. It is worth mentioning that for the two variants, the thresholds for the model simplifiation are set at higher values so that the merging operation only happens when the fuzzy sets or rules are very similar. This is to ensure that the FRBSs with more rules are given a better hane of surviving in the early stages of the evolution. In [19], a nihe onept is used to maintain a set of FRBSs with the same number of rules. A substitution only happens within eah nihe so that one an evolve a set of FRBSs with the different number of rules without the worry of losing individuals with more rules. The proposed three-stage proedure does not need the aforementioned nihe onept if all the stages work as a unified proedure. In suh a ase, the most aurate FRBS is always the one with the number of rules lose to the maximum value. More importantly, this aurate FRBS will diret the searh from the most omplex struture (the more aurate one) to the simplest ones (the less aurate ones). This ensures the oexistene of FRBSs with various omplexities during the seletion. TABLE II COMPARISONS OF THE PREDICTIVE PERFORMANCE OF THE DIFFERENT MODELING STAGES FOR THE BENCHMARK PROBLEM Modeling Methods (Ref.) No. of rules No. of fuzzy sets & The type of FRBS Performane (RMSE training) IMOFM (the first stage and the third stage); numbeer of iterations: 000 Initial FRBS 5 10 Singleton * FRBS1 5 6 Singleton # FRBS 4 6 Singleton # FRBS 5 Singleton # FRBS4 4 Singleton # FRBS5 (4 T ) Singleton 0.75 # IMOFM (only the third stage); number of iterations: 4000 Initial FRBS 5 10 Singleton 1.06 * FRBS1 4 7 Singleton # FRBS 4 6 Singleton 0.1 # FRBS 5 Singleton # FRBS4 (8 T ) 4 Singleton # FRBS5 (7 T ) 4 Singleton 0.11 # *: Initial model extrated diretly from data using lustering algorithms or grid partition methods; T: Total number of rule length; #: Simplified model after model simplifiation and parameter fine tuning.. As shown in Table II, more iterations are needed for the two variants to ahieve a similar preditive performane as that obtained using the three-stage modeling proedure (refer to Table I), and only a few FRBSs are obtained. The most omplex struture whih is supposed to evolve to the most aurate FRBS is disarded during the optimization for the reasons already desribed. All these justified the inlusion of the first two stages. B. Real World Appliations In this setion, the problem of prediting the Ultimate Tensile Strength (UTS) of heat-treated steel is studied, whih features a high dimensional, nonlinear and sparse data spae. The UTS data set onsists of 760 data samples and inludes 15 inputs and 1 output whih is the UTS with the values between 516. and 184. In order to ompare with the work in [8], the data set is randomly divided into two parts: 75% of the data are used for training and the remaining data are used for testing. Another 1 unseen examples are also inluded. All the parameter settings related to IMOFM are the same as those used for the benhmark problem exept that the initial number of rules is set to 1. The results presented in Table III inlude the average values of 10 independent runs and only a few FRBS are presented due to the onstraints on spae. TABLE III COMPARISONS OF THE PREDICTIVE PERFORMANCE FOR THE DIFFERENT MODELING METHODS USING THE UTS DATA Modeling First Stage (lustering algorithm) Seond Stage (single objetive refining) Methods Training Testing Training Testing Validation [8] IMOFM_S IMOFM_M Third Stage (multi-objetive fuzzy modeling) Modeling Methods [8] FRBS1 FRBS IMOFM_S FRBS1 FRBS FRBS IMOFM_M FRBS1 FRBS FRBS No. of rules No. of Fuzzy sets in inputs Inputs: [ ] Output: 10 Inputs: [ ], Output: 9 Inputs: [ ], Outputs: 10 Modeling performane Training Testing/ Validation / / /41.01 Inputs: [ ], Output: /1.54 Inputs: [ ], Output: 7 10 Inputs: [ ], Output: Inputs: [ ], Output: 5 Inputs: [ ], Output: / / / /49.87 As shown in Table III, the problem of over-fitting speifially related to the seond modeling stage (vaine FRBS) under unseen situations is revealed in Table III. Suh over-fitting is mainly attributed to the omplex strutures involved in the first two modeling stages. However, the simplified fuzzy models an predit well even under unknown senarios. Fig. 5 shows the snapshot of the obtained approximate fronts at different iterations. The evolution starts from the most aurate FRBS and expands the front during the ourse of the optimization. Table IV summarizes the results of the UTS modeling problem using IMOFM with and without the
8 variable length oding and the new distane index. Muh bigger improvements have been registered for the FRBS with fewer rules sine they are more prone to suffering from the problem of unordered set of rules. Fig. 5. The FRBSs at different iterations. TABLE IV THE COMPARISON OF THE MODELING APPROACHES WITH AND WITHOUT VARIABLE LENGTH CODING SCHEME FRBS Configurations No. of rules IMOFM_S (without VLC) (Training RMSE) VI. CONCLUSION The main novelty of IMOFM is onsidered to be as follows: 1) the initial number of rules in the rule-base is not an important fator anymore sine in the third stage a set of FRBS with different struture are eliited; only the maximum allowable number of rules is required a priori; ) due to the vaination proess, the effiieny and preditive auray of the modelling are improved; ) by using the variable length oding sheme, the problem of the unordered set of rules is resolved, whih leads to a more effiient parameter optimisation; 4)the proposed method represents one of the first attempts whih uses an approximate Mamdani FRBS for high-dimensional regression problems, and an be viewed as a omplement to the linguisti Mamdani fuzzy modeling approah. REFERENCES IMOFM_S (with VLC) (Training RMSE) Improvement (%) FRBS % FRBS % FRBS % FRBS % [1] B. Kosko, Fuzzy Systems as Universal Approximators, IEEE Transations on Computers, vol. 4(11), pp. 19-1, [] K. M. Passino, S. Yurkovih, Fuzzy Control, MA: Addison-Wesley, 1998, pp [] J. H. Holland, Adaptation in Natural and Artifiial Systems, MI: The University of Mihigan Press, [4] J. D. Farmer, N. H. Pakard, The Immune System, Adaptation, and Mahine Learning, Physia, vol. D, pp , [5] M. Delgado, F. G mez-skarmeta Antonio, F. Martin, A Fuzzy Clustering-Based Rapid Prototyping for Fuzzy Rule-Based Modelling, IEEE Transations on Fuzzy Systems, vol. 5(), pp. -, [6] C. L. Karr, Geneti Algorithms for Fuzzy Controllers, AI Expert, vol. 6 (), pp. 6-, 1991 [7] T. Takagi, M. Sugeno, Fuzzy Identifiation of Systems and Its Appliations to Modelling and Control, IEEE Transations on Systems, Man, and Cybernetis, vol. 15, pp , [8] E. H. Mamdani, Appliations of Fuzzy Algorithm for Control a Simple Dynami Plant, Pro. Inst. Eletr. Eng., vol. 11 (1), pp , [9] J. Casillas, O. Cordon, J. Del Jesus Mara, F. Herrera, Geneti Tuning of Fuzzy Rule Deep Strutures for Linguisti Modelling, IEEE Transations on Fuzzy Systems, vol. 1, pp. 1-9, 001. [10] L. Zadeh, Outline of A New Approah to the Analysis of Complex Systems and Deision Proesses, IEEE Transations on Systems, Man, and Cybernetis, vol., pp. 8-44, 197. [11] F. Jiménez, A. F. Gómez-Skarmeta, H. Roubos, R. Babuška, Aurate, Transparent, and Compat Fuzzy Models for Funtion Approximation and Dynami Modeling through Multi-Objetive Evolutionary Optimisation, in E. Zitzler et al. (Eds.): EMO 001, LNCS 199, pp [1] F. Herrera, Geneti Fuzzy Systems: Taxonomy, Current Researh Treads and Prospets, Evol. Intel., vol. 1 (1), pp. 7-46, 008. [1] H. Ishibuhi, K. Nozaki, N. Yamamoto, H. Tanaka, Seleting Fuzzy If-Then Rules for Classifiation Problems Using Geneti Algorithms, IEEE Transations on Fuzzy Systems, vol. (), pp.60-70, [14] H. Ishibuhi, T. Nakashima, T. Murata, Three-objetive Genetisbased Mahine Learning for Linguisti Rule Extration, Information Sienes, vol. 16, pp , 001. [15] H. Ishibuhi, T. Yamamoto, Fuzzy Rule Seletion by Multi- Objetive Geneti Loal Searh Algorithms and Rule Evaluation Measures in Data Mining, Fuzzy Sets and Systems, vol. 141, pp , 004. [16] M. J. Gato, R. Alalά, F. Herrera, Adaptation and Appliation of Multi-objetive Evolutionary Algorithms for Rule Redution and Parameter Tuning of Fuzzy Rule-based Systems, Soft Computing, vol. 1 (5), pp , 009. [17] R. Alalά, P. Duange, F. Herrera, B. Lazzerini, A Multiobjetive Evolutionary Approah to Conurrently Learn Rule and Data Bases of Linguisti Fuzzy-Rule-Based Systems, IEEE Transations on Fuzzy Systems, vol. 17(5), pp , 009. [18] M. Setnes, R. Babuška, U. Kaymak, H. Lemke, Similarity Measures in Fuzzy Rule Base Simplifiation, IEEE Transations on Systems, Man, and Cybernetis-Part B, vol. 8 (), pp , [19] F. Jiménez, G. Sánhez, A. F. Gómez-Skarmeta, H. Roubos, R. Babuška, Fuzzy Modeling with Multi-Objetive Neuro-Evolutionary Algorithms, IEEE International Conferene on Systems, Man, and Cybernetis, vol., 00. [0] Y. Jin, W. Von Seelen, B. Sendhoff, On Generating FC Fuzzy Rule Systems From Data Using Evolution Strategies, IEEE Transations on Systems, Man, and Cybernetis, vol. 9 (6), pp , [1] H. L. Wang, S. Kwong, Y. C. Jin, W. Wei, K. F. Man, Multiobjetive Hierarhial Geneti Algorithm for Interpretable Fuzzy Rule-based Knowledge Extration, Fuzzy Sets and Systems, Vol. 149 (1), pp , 005. [] J. Chen, M. Mahfouf, A Population Adaptive Based Immune Algorithm for Solving Multi-objetive Optimisation Problems, in H. Bersini & J. Carneiro (Eds.): ICARIS 006, LNCS 416, pp. 80-9, 006. [] J. Chen, M. Mahfouf, Artifiial Immune Systems as a Bio-inspired Optimisation Tehnique and Its Engineering Appliations, in H. W. Mo (Eds.): Artifiial Immune Systems and Natural Computing: Applying Complex Adaptive Tehnologies, pp. -48, 008. [4] J. Chen, Biologially Inspired Optimisation Algorithms for Transparent Knowledge Extration Allied to Engineering Materials Proessing, The University of Sheffield, Ph.D. Thesis, 009, h.. [5] J. Chen, M. Mahfouf, An Immune Algorithm Based Fuzzy Preditive Modeling Mehanism using Variable Length Coding and Multiobjetive Optimisation Allied to Engineering Materials Proessing, in proeedings of the 008 IEEE International Conferene on Granule Computation (GrC008), pp.6-8, 008. [6] M. G. Cooper, J. J. Vidal, Geneti Design of Fuzzy Controllers: The Cart and Jointed-Pole Problem, in Proeedings of the Third IEEE Conferene on Fuzzy Systems, vol., pp. 1-17, [7] M. Sugeno, T. Yasukawa, A Fuzzy-Logi-Based Approah to Qualitative Modeling, IEEE Transations on Fuzzy Systems, vol. 1 (1), pp. 7-1, 199. [8] Q. Zhang, Nature-Inspired Multi-Objetive Optimisation and Transparent Knowledge Disovery via Hierarhial Fuzzy Modelling, Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Sheffield, U.K, 009, h.6.
A Holistic Method for Selecting Web Services in Design of Composite Applications
 A Holisti Method for Seleting Web Servies in Design of Composite Appliations Mārtiņš Bonders, Jānis Grabis Institute of Information Tehnology, Riga Tehnial University, 1 Kalu Street, Riga, LV 1658, Latvia,
A Holisti Method for Seleting Web Servies in Design of Composite Appliations Mārtiņš Bonders, Jānis Grabis Institute of Information Tehnology, Riga Tehnial University, 1 Kalu Street, Riga, LV 1658, Latvia,
The Application of Mamdani Fuzzy Model for Auto Zoom Function of a Digital Camera
 (IJCSIS) International Journal of Computer Siene and Information Seurity, Vol. 6, No. 3, 2009 The Appliation of Mamdani Fuzzy Model for Auto Funtion of a Digital Camera * I. Elamvazuthi, P. Vasant Universiti
(IJCSIS) International Journal of Computer Siene and Information Seurity, Vol. 6, No. 3, 2009 The Appliation of Mamdani Fuzzy Model for Auto Funtion of a Digital Camera * I. Elamvazuthi, P. Vasant Universiti
Hierarchical Clustering and Sampling Techniques for Network Monitoring
 S. Sindhuja Hierarhial Clustering and Sampling Tehniques for etwork Monitoring S. Sindhuja ME ABSTRACT: etwork monitoring appliations are used to monitor network traffi flows. Clustering tehniques are
S. Sindhuja Hierarhial Clustering and Sampling Tehniques for etwork Monitoring S. Sindhuja ME ABSTRACT: etwork monitoring appliations are used to monitor network traffi flows. Clustering tehniques are
Granular Problem Solving and Software Engineering
 Granular Problem Solving and Software Engineering Haibin Zhu, Senior Member, IEEE Department of Computer Siene and Mathematis, Nipissing University, 100 College Drive, North Bay, Ontario, P1B 8L7, Canada
Granular Problem Solving and Software Engineering Haibin Zhu, Senior Member, IEEE Department of Computer Siene and Mathematis, Nipissing University, 100 College Drive, North Bay, Ontario, P1B 8L7, Canada
Improved SOM-Based High-Dimensional Data Visualization Algorithm
 Computer and Information Siene; Vol. 5, No. 4; 2012 ISSN 1913-8989 E-ISSN 1913-8997 Published by Canadian Center of Siene and Eduation Improved SOM-Based High-Dimensional Data Visualization Algorithm Wang
Computer and Information Siene; Vol. 5, No. 4; 2012 ISSN 1913-8989 E-ISSN 1913-8997 Published by Canadian Center of Siene and Eduation Improved SOM-Based High-Dimensional Data Visualization Algorithm Wang
Sebastián Bravo López
 Transfinite Turing mahines Sebastián Bravo López 1 Introdution With the rise of omputers with high omputational power the idea of developing more powerful models of omputation has appeared. Suppose that
Transfinite Turing mahines Sebastián Bravo López 1 Introdution With the rise of omputers with high omputational power the idea of developing more powerful models of omputation has appeared. Suppose that
A Keyword Filters Method for Spam via Maximum Independent Sets
 Vol. 7, No. 3, May, 213 A Keyword Filters Method for Spam via Maximum Independent Sets HaiLong Wang 1, FanJun Meng 1, HaiPeng Jia 2, JinHong Cheng 3 and Jiong Xie 3 1 Inner Mongolia Normal University 2
Vol. 7, No. 3, May, 213 A Keyword Filters Method for Spam via Maximum Independent Sets HaiLong Wang 1, FanJun Meng 1, HaiPeng Jia 2, JinHong Cheng 3 and Jiong Xie 3 1 Inner Mongolia Normal University 2
FIRE DETECTION USING AUTONOMOUS AERIAL VEHICLES WITH INFRARED AND VISUAL CAMERAS. J. Ramiro Martínez-de Dios, Luis Merino and Aníbal Ollero
 FE DETECTION USING AUTONOMOUS AERIAL VEHICLES WITH INFRARED AND VISUAL CAMERAS. J. Ramiro Martínez-de Dios, Luis Merino and Aníbal Ollero Robotis, Computer Vision and Intelligent Control Group. University
FE DETECTION USING AUTONOMOUS AERIAL VEHICLES WITH INFRARED AND VISUAL CAMERAS. J. Ramiro Martínez-de Dios, Luis Merino and Aníbal Ollero Robotis, Computer Vision and Intelligent Control Group. University
Discovering Trends in Large Datasets Using Neural Networks
 Disovering Trends in Large Datasets Using Neural Networks Khosrow Kaikhah, Ph.D. and Sandesh Doddameti Department of Computer Siene Texas State University San Maros, Texas 78666 Abstrat. A novel knowledge
Disovering Trends in Large Datasets Using Neural Networks Khosrow Kaikhah, Ph.D. and Sandesh Doddameti Department of Computer Siene Texas State University San Maros, Texas 78666 Abstrat. A novel knowledge
A Context-Aware Preference Database System
 J. PERVASIVE COMPUT. & COMM. (), MARCH 005. TROUBADOR PUBLISHING LTD) A Context-Aware Preferene Database System Kostas Stefanidis Department of Computer Siene, University of Ioannina,, [email protected] Evaggelia
J. PERVASIVE COMPUT. & COMM. (), MARCH 005. TROUBADOR PUBLISHING LTD) A Context-Aware Preferene Database System Kostas Stefanidis Department of Computer Siene, University of Ioannina,, [email protected] Evaggelia
Channel Assignment Strategies for Cellular Phone Systems
 Channel Assignment Strategies for Cellular Phone Systems Wei Liu Yiping Han Hang Yu Zhejiang University Hangzhou, P. R. China Contat: [email protected] 000 Mathematial Contest in Modeling (MCM) Meritorious
Channel Assignment Strategies for Cellular Phone Systems Wei Liu Yiping Han Hang Yu Zhejiang University Hangzhou, P. R. China Contat: [email protected] 000 Mathematial Contest in Modeling (MCM) Meritorious
Deadline-based Escalation in Process-Aware Information Systems
 Deadline-based Esalation in Proess-Aware Information Systems Wil M.P. van der Aalst 1,2, Mihael Rosemann 2, Marlon Dumas 2 1 Department of Tehnology Management Eindhoven University of Tehnology, The Netherlands
Deadline-based Esalation in Proess-Aware Information Systems Wil M.P. van der Aalst 1,2, Mihael Rosemann 2, Marlon Dumas 2 1 Department of Tehnology Management Eindhoven University of Tehnology, The Netherlands
Behavior Analysis-Based Learning Framework for Host Level Intrusion Detection
 Behavior Analysis-Based Learning Framework for Host Level Intrusion Detetion Haiyan Qiao, Jianfeng Peng, Chuan Feng, Jerzy W. Rozenblit Eletrial and Computer Engineering Department University of Arizona
Behavior Analysis-Based Learning Framework for Host Level Intrusion Detetion Haiyan Qiao, Jianfeng Peng, Chuan Feng, Jerzy W. Rozenblit Eletrial and Computer Engineering Department University of Arizona
Henley Business School at Univ of Reading. Pre-Experience Postgraduate Programmes Chartered Institute of Personnel and Development (CIPD)
 MS in International Human Resoure Management For students entering in 2012/3 Awarding Institution: Teahing Institution: Relevant QAA subjet Benhmarking group(s): Faulty: Programme length: Date of speifiation:
MS in International Human Resoure Management For students entering in 2012/3 Awarding Institution: Teahing Institution: Relevant QAA subjet Benhmarking group(s): Faulty: Programme length: Date of speifiation:
A novel active mass damper for vibration control of bridges
 IABMAS 08, International Conferene on Bridge Maintenane, Safety and Management, 3-7 July 008, Seoul, Korea A novel ative mass damper for vibration ontrol of bridges U. Starossek & J. Sheller Strutural
IABMAS 08, International Conferene on Bridge Maintenane, Safety and Management, 3-7 July 008, Seoul, Korea A novel ative mass damper for vibration ontrol of bridges U. Starossek & J. Sheller Strutural
Capacity at Unsignalized Two-Stage Priority Intersections
 Capaity at Unsignalized Two-Stage Priority Intersetions by Werner Brilon and Ning Wu Abstrat The subjet of this paper is the apaity of minor-street traffi movements aross major divided four-lane roadways
Capaity at Unsignalized Two-Stage Priority Intersetions by Werner Brilon and Ning Wu Abstrat The subjet of this paper is the apaity of minor-street traffi movements aross major divided four-lane roadways
Pattern Recognition Techniques in Microarray Data Analysis
 Pattern Reognition Tehniques in Miroarray Data Analysis Miao Li, Biao Wang, Zohreh Momeni, and Faramarz Valafar Department of Computer Siene San Diego State University San Diego, California, USA [email protected]
Pattern Reognition Tehniques in Miroarray Data Analysis Miao Li, Biao Wang, Zohreh Momeni, and Faramarz Valafar Department of Computer Siene San Diego State University San Diego, California, USA [email protected]
An integrated optimization model of a Closed- Loop Supply Chain under uncertainty
 ISSN 1816-6075 (Print), 1818-0523 (Online) Journal of System and Management Sienes Vol. 2 (2012) No. 3, pp. 9-17 An integrated optimization model of a Closed- Loop Supply Chain under unertainty Xiaoxia
ISSN 1816-6075 (Print), 1818-0523 (Online) Journal of System and Management Sienes Vol. 2 (2012) No. 3, pp. 9-17 An integrated optimization model of a Closed- Loop Supply Chain under unertainty Xiaoxia
Supply chain coordination; A Game Theory approach
 aepted for publiation in the journal "Engineering Appliations of Artifiial Intelligene" 2008 upply hain oordination; A Game Theory approah Jean-Claude Hennet x and Yasemin Arda xx x LI CNR-UMR 668 Université
aepted for publiation in the journal "Engineering Appliations of Artifiial Intelligene" 2008 upply hain oordination; A Game Theory approah Jean-Claude Hennet x and Yasemin Arda xx x LI CNR-UMR 668 Université
Neural network-based Load Balancing and Reactive Power Control by Static VAR Compensator
 nternational Journal of Computer and Eletrial Engineering, Vol. 1, No. 1, April 2009 Neural network-based Load Balaning and Reative Power Control by Stati VAR Compensator smail K. Said and Marouf Pirouti
nternational Journal of Computer and Eletrial Engineering, Vol. 1, No. 1, April 2009 Neural network-based Load Balaning and Reative Power Control by Stati VAR Compensator smail K. Said and Marouf Pirouti
An Enhanced Critical Path Method for Multiple Resource Constraints
 An Enhaned Critial Path Method for Multiple Resoure Constraints Chang-Pin Lin, Hung-Lin Tai, and Shih-Yan Hu Abstrat Traditional Critial Path Method onsiders only logial dependenies between related ativities
An Enhaned Critial Path Method for Multiple Resoure Constraints Chang-Pin Lin, Hung-Lin Tai, and Shih-Yan Hu Abstrat Traditional Critial Path Method onsiders only logial dependenies between related ativities
Open and Extensible Business Process Simulator
 UNIVERSITY OF TARTU FACULTY OF MATHEMATICS AND COMPUTER SCIENCE Institute of Computer Siene Karl Blum Open and Extensible Business Proess Simulator Master Thesis (30 EAP) Supervisors: Luiano Garía-Bañuelos,
UNIVERSITY OF TARTU FACULTY OF MATHEMATICS AND COMPUTER SCIENCE Institute of Computer Siene Karl Blum Open and Extensible Business Proess Simulator Master Thesis (30 EAP) Supervisors: Luiano Garía-Bañuelos,
An Efficient Network Traffic Classification Based on Unknown and Anomaly Flow Detection Mechanism
 An Effiient Network Traffi Classifiation Based on Unknown and Anomaly Flow Detetion Mehanism G.Suganya.M.s.,B.Ed 1 1 Mphil.Sholar, Department of Computer Siene, KG College of Arts and Siene,Coimbatore.
An Effiient Network Traffi Classifiation Based on Unknown and Anomaly Flow Detetion Mehanism G.Suganya.M.s.,B.Ed 1 1 Mphil.Sholar, Department of Computer Siene, KG College of Arts and Siene,Coimbatore.
Context-Sensitive Adjustments of Cognitive Control: Conflict-Adaptation Effects Are Modulated by Processing Demands of the Ongoing Task
 Journal of Experimental Psyhology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition 2008, Vol. 34, No. 3, 712 718 Copyright 2008 by the Amerian Psyhologial Assoiation 0278-7393/08/$12.00 DOI: 10.1037/0278-7393.34.3.712
Journal of Experimental Psyhology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition 2008, Vol. 34, No. 3, 712 718 Copyright 2008 by the Amerian Psyhologial Assoiation 0278-7393/08/$12.00 DOI: 10.1037/0278-7393.34.3.712
Chapter 1 Microeconomics of Consumer Theory
 Chapter 1 Miroeonomis of Consumer Theory The two broad ategories of deision-makers in an eonomy are onsumers and firms. Eah individual in eah of these groups makes its deisions in order to ahieve some
Chapter 1 Miroeonomis of Consumer Theory The two broad ategories of deision-makers in an eonomy are onsumers and firms. Eah individual in eah of these groups makes its deisions in order to ahieve some
Recovering Articulated Motion with a Hierarchical Factorization Method
 Reovering Artiulated Motion with a Hierarhial Fatorization Method Hanning Zhou and Thomas S Huang University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 405 North Mathews Avenue, Urbana, IL 680, USA {hzhou, huang}@ifpuiuedu
Reovering Artiulated Motion with a Hierarhial Fatorization Method Hanning Zhou and Thomas S Huang University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 405 North Mathews Avenue, Urbana, IL 680, USA {hzhou, huang}@ifpuiuedu
Big Data Analysis and Reporting with Decision Tree Induction
 Big Data Analysis and Reporting with Deision Tree Indution PETRA PERNER Institute of Computer Vision and Applied Computer Sienes, IBaI Postbox 30 11 14, 04251 Leipzig GERMANY [email protected],
Big Data Analysis and Reporting with Deision Tree Indution PETRA PERNER Institute of Computer Vision and Applied Computer Sienes, IBaI Postbox 30 11 14, 04251 Leipzig GERMANY [email protected],
RATING SCALES FOR NEUROLOGISTS
 RATING SCALES FOR NEUROLOGISTS J Hobart iv22 WHY Correspondene to: Dr Jeremy Hobart, Department of Clinial Neurosienes, Peninsula Medial Shool, Derriford Hospital, Plymouth PL6 8DH, UK; Jeremy.Hobart@
RATING SCALES FOR NEUROLOGISTS J Hobart iv22 WHY Correspondene to: Dr Jeremy Hobart, Department of Clinial Neurosienes, Peninsula Medial Shool, Derriford Hospital, Plymouth PL6 8DH, UK; Jeremy.Hobart@
A Three-Hybrid Treatment Method of the Compressor's Characteristic Line in Performance Prediction of Power Systems
 A Three-Hybrid Treatment Method of the Compressor's Charateristi Line in Performane Predition of Power Systems A Three-Hybrid Treatment Method of the Compressor's Charateristi Line in Performane Predition
A Three-Hybrid Treatment Method of the Compressor's Charateristi Line in Performane Predition of Power Systems A Three-Hybrid Treatment Method of the Compressor's Charateristi Line in Performane Predition
Weighting Methods in Survey Sampling
 Setion on Survey Researh Methods JSM 01 Weighting Methods in Survey Sampling Chiao-hih Chang Ferry Butar Butar Abstrat It is said that a well-designed survey an best prevent nonresponse. However, no matter
Setion on Survey Researh Methods JSM 01 Weighting Methods in Survey Sampling Chiao-hih Chang Ferry Butar Butar Abstrat It is said that a well-designed survey an best prevent nonresponse. However, no matter
WORKFLOW CONTROL-FLOW PATTERNS A Revised View
 WORKFLOW CONTROL-FLOW PATTERNS A Revised View Nik Russell 1, Arthur H.M. ter Hofstede 1, 1 BPM Group, Queensland University of Tehnology GPO Box 2434, Brisbane QLD 4001, Australia {n.russell,a.terhofstede}@qut.edu.au
WORKFLOW CONTROL-FLOW PATTERNS A Revised View Nik Russell 1, Arthur H.M. ter Hofstede 1, 1 BPM Group, Queensland University of Tehnology GPO Box 2434, Brisbane QLD 4001, Australia {n.russell,a.terhofstede}@qut.edu.au
AUDITING COST OVERRUN CLAIMS *
 AUDITING COST OVERRUN CLAIMS * David Pérez-Castrillo # University of Copenhagen & Universitat Autònoma de Barelona Niolas Riedinger ENSAE, Paris Abstrat: We onsider a ost-reimbursement or a ost-sharing
AUDITING COST OVERRUN CLAIMS * David Pérez-Castrillo # University of Copenhagen & Universitat Autònoma de Barelona Niolas Riedinger ENSAE, Paris Abstrat: We onsider a ost-reimbursement or a ost-sharing
SLA-based Resource Allocation for Software as a Service Provider (SaaS) in Cloud Computing Environments
 2 th IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Cluster, Cloud and Grid Computing SLA-based Resoure Alloation for Software as a Servie Provider (SaaS) in Cloud Computing Environments Linlin Wu, Saurabh Kumar
2 th IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Cluster, Cloud and Grid Computing SLA-based Resoure Alloation for Software as a Servie Provider (SaaS) in Cloud Computing Environments Linlin Wu, Saurabh Kumar
Henley Business School at Univ of Reading. Chartered Institute of Personnel and Development (CIPD)
 MS in International Human Resoure Management (full-time) For students entering in 2015/6 Awarding Institution: Teahing Institution: Relevant QAA subjet Benhmarking group(s): Faulty: Programme length: Date
MS in International Human Resoure Management (full-time) For students entering in 2015/6 Awarding Institution: Teahing Institution: Relevant QAA subjet Benhmarking group(s): Faulty: Programme length: Date
Intelligent Measurement Processes in 3D Optical Metrology: Producing More Accurate Point Clouds
 Intelligent Measurement Proesses in 3D Optial Metrology: Produing More Aurate Point Clouds Charles Mony, Ph.D. 1 President Creaform in. [email protected] Daniel Brown, Eng. 1 Produt Manager Creaform in.
Intelligent Measurement Proesses in 3D Optial Metrology: Produing More Aurate Point Clouds Charles Mony, Ph.D. 1 President Creaform in. [email protected] Daniel Brown, Eng. 1 Produt Manager Creaform in.
Static Fairness Criteria in Telecommunications
 Teknillinen Korkeakoulu ERIKOISTYÖ Teknillisen fysiikan koulutusohjelma 92002 Mat-208 Sovelletun matematiikan erikoistyöt Stati Fairness Criteria in Teleommuniations Vesa Timonen, e-mail: vesatimonen@hutfi
Teknillinen Korkeakoulu ERIKOISTYÖ Teknillisen fysiikan koulutusohjelma 92002 Mat-208 Sovelletun matematiikan erikoistyöt Stati Fairness Criteria in Teleommuniations Vesa Timonen, e-mail: vesatimonen@hutfi
RISK-BASED IN SITU BIOREMEDIATION DESIGN JENNINGS BRYAN SMALLEY. A.B., Washington University, 1992 THESIS. Urbana, Illinois
 RISK-BASED IN SITU BIOREMEDIATION DESIGN BY JENNINGS BRYAN SMALLEY A.B., Washington University, 1992 THESIS Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Siene in Environmental
RISK-BASED IN SITU BIOREMEDIATION DESIGN BY JENNINGS BRYAN SMALLEY A.B., Washington University, 1992 THESIS Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Siene in Environmental
arxiv:astro-ph/0304006v2 10 Jun 2003 Theory Group, MS 50A-5101 Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory One Cyclotron Road Berkeley, CA 94720 USA
 LBNL-52402 Marh 2003 On the Speed of Gravity and the v/ Corretions to the Shapiro Time Delay Stuart Samuel 1 arxiv:astro-ph/0304006v2 10 Jun 2003 Theory Group, MS 50A-5101 Lawrene Berkeley National Laboratory
LBNL-52402 Marh 2003 On the Speed of Gravity and the v/ Corretions to the Shapiro Time Delay Stuart Samuel 1 arxiv:astro-ph/0304006v2 10 Jun 2003 Theory Group, MS 50A-5101 Lawrene Berkeley National Laboratory
Scalable Hierarchical Multitask Learning Algorithms for Conversion Optimization in Display Advertising
 Salable Hierarhial Multitask Learning Algorithms for Conversion Optimization in Display Advertising Amr Ahmed Google [email protected] Abhimanyu Das Mirosoft Researh [email protected] Alexander J. Smola
Salable Hierarhial Multitask Learning Algorithms for Conversion Optimization in Display Advertising Amr Ahmed Google [email protected] Abhimanyu Das Mirosoft Researh [email protected] Alexander J. Smola
FOOD FOR THOUGHT Topical Insights from our Subject Matter Experts
 FOOD FOR THOUGHT Topial Insights from our Sujet Matter Experts DEGREE OF DIFFERENCE TESTING: AN ALTERNATIVE TO TRADITIONAL APPROACHES The NFL White Paper Series Volume 14, June 2014 Overview Differene
FOOD FOR THOUGHT Topial Insights from our Sujet Matter Experts DEGREE OF DIFFERENCE TESTING: AN ALTERNATIVE TO TRADITIONAL APPROACHES The NFL White Paper Series Volume 14, June 2014 Overview Differene
A Survey of Usability Evaluation in Virtual Environments: Classi cation and Comparison of Methods
 Doug A. Bowman [email protected] Department of Computer Siene Virginia Teh Joseph L. Gabbard Deborah Hix [ jgabbard, hix]@vt.edu Systems Researh Center Virginia Teh A Survey of Usability Evaluation in Virtual
Doug A. Bowman [email protected] Department of Computer Siene Virginia Teh Joseph L. Gabbard Deborah Hix [ jgabbard, hix]@vt.edu Systems Researh Center Virginia Teh A Survey of Usability Evaluation in Virtual
International Journal of Supply and Operations Management. Mathematical modeling for EOQ inventory system with advance payment and fuzzy Parameters
 nternational Journal of Supply and Operations Management JSOM November 0, Volume, ssue 3, pp. 60-78 SSN-Print: 383-359 SSN-Online: 383-55 www.ijsom.om Mathematial modeling for EOQ inventory system with
nternational Journal of Supply and Operations Management JSOM November 0, Volume, ssue 3, pp. 60-78 SSN-Print: 383-359 SSN-Online: 383-55 www.ijsom.om Mathematial modeling for EOQ inventory system with
Chapter 1: Introduction
 Chapter 1: Introdution 1.1 Pratial olumn base details in steel strutures 1.1.1 Pratial olumn base details Every struture must transfer vertial and lateral loads to the supports. In some ases, beams or
Chapter 1: Introdution 1.1 Pratial olumn base details in steel strutures 1.1.1 Pratial olumn base details Every struture must transfer vertial and lateral loads to the supports. In some ases, beams or
Findings and Recommendations
 Contrating Methods and Administration Findings and Reommendations Finding 9-1 ESD did not utilize a formal written pre-qualifiations proess for seleting experiened design onsultants. ESD hose onsultants
Contrating Methods and Administration Findings and Reommendations Finding 9-1 ESD did not utilize a formal written pre-qualifiations proess for seleting experiened design onsultants. ESD hose onsultants
Chapter 5 Single Phase Systems
 Chapter 5 Single Phase Systems Chemial engineering alulations rely heavily on the availability of physial properties of materials. There are three ommon methods used to find these properties. These inlude
Chapter 5 Single Phase Systems Chemial engineering alulations rely heavily on the availability of physial properties of materials. There are three ommon methods used to find these properties. These inlude
Learning Curves and Stochastic Models for Pricing and Provisioning Cloud Computing Services
 T Learning Curves and Stohasti Models for Priing and Provisioning Cloud Computing Servies Amit Gera, Cathy H. Xia Dept. of Integrated Systems Engineering Ohio State University, Columbus, OH 4310 {gera.,
T Learning Curves and Stohasti Models for Priing and Provisioning Cloud Computing Servies Amit Gera, Cathy H. Xia Dept. of Integrated Systems Engineering Ohio State University, Columbus, OH 4310 {gera.,
MATE: MPLS Adaptive Traffic Engineering
 MATE: MPLS Adaptive Traffi Engineering Anwar Elwalid Cheng Jin Steven Low Indra Widjaja Bell Labs EECS Dept EE Dept Fujitsu Network Communiations Luent Tehnologies Univ. of Mihigan Calteh Pearl River,
MATE: MPLS Adaptive Traffi Engineering Anwar Elwalid Cheng Jin Steven Low Indra Widjaja Bell Labs EECS Dept EE Dept Fujitsu Network Communiations Luent Tehnologies Univ. of Mihigan Calteh Pearl River,
Performance Analysis of IEEE 802.11 in Multi-hop Wireless Networks
 Performane Analysis of IEEE 80.11 in Multi-hop Wireless Networks Lan Tien Nguyen 1, Razvan Beuran,1, Yoihi Shinoda 1, 1 Japan Advaned Institute of Siene and Tehnology, 1-1 Asahidai, Nomi, Ishikawa, 93-19
Performane Analysis of IEEE 80.11 in Multi-hop Wireless Networks Lan Tien Nguyen 1, Razvan Beuran,1, Yoihi Shinoda 1, 1 Japan Advaned Institute of Siene and Tehnology, 1-1 Asahidai, Nomi, Ishikawa, 93-19
i_~f e 1 then e 2 else e 3
 A PROCEDURE MECHANISM FOR BACKTRACK PROGRAMMING* David R. HANSON + Department o Computer Siene, The University of Arizona Tuson, Arizona 85721 One of the diffiulties in using nondeterministi algorithms
A PROCEDURE MECHANISM FOR BACKTRACK PROGRAMMING* David R. HANSON + Department o Computer Siene, The University of Arizona Tuson, Arizona 85721 One of the diffiulties in using nondeterministi algorithms
Recommending Questions Using the MDL-based Tree Cut Model
 WWW 2008 / Refereed Trak: Data Mining - Learning April 2-25, 2008 Beijing, China Reommending Questions Using the MDL-based Tree Cut Model Yunbo Cao,2, Huizhong Duan, Chin-Yew Lin 2, Yong Yu, and Hsiao-Wuen
WWW 2008 / Refereed Trak: Data Mining - Learning April 2-25, 2008 Beijing, China Reommending Questions Using the MDL-based Tree Cut Model Yunbo Cao,2, Huizhong Duan, Chin-Yew Lin 2, Yong Yu, and Hsiao-Wuen
Trade Information, Not Spectrum: A Novel TV White Space Information Market Model
 Trade Information, Not Spetrum: A Novel TV White Spae Information Market Model Yuan Luo, Lin Gao, and Jianwei Huang 1 Abstrat In this paper, we propose a novel information market for TV white spae networks,
Trade Information, Not Spetrum: A Novel TV White Spae Information Market Model Yuan Luo, Lin Gao, and Jianwei Huang 1 Abstrat In this paper, we propose a novel information market for TV white spae networks,
Software Ecosystems: From Software Product Management to Software Platform Management
 Software Eosystems: From Software Produt Management to Software Platform Management Slinger Jansen, Stef Peeters, and Sjaak Brinkkemper Department of Information and Computing Sienes Utreht University,
Software Eosystems: From Software Produt Management to Software Platform Management Slinger Jansen, Stef Peeters, and Sjaak Brinkkemper Department of Information and Computing Sienes Utreht University,
Srinivas Bollapragada GE Global Research Center. Abstract
 Sheduling Commerial Videotapes in Broadast Television Srinivas Bollapragada GE Global Researh Center Mihael Bussiek GAMS Development Corporation Suman Mallik University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign
Sheduling Commerial Videotapes in Broadast Television Srinivas Bollapragada GE Global Researh Center Mihael Bussiek GAMS Development Corporation Suman Mallik University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign
Computer Networks Framing
 Computer Networks Framing Saad Mneimneh Computer Siene Hunter College of CUNY New York Introdution Who framed Roger rabbit? A detetive, a woman, and a rabbit in a network of trouble We will skip the physial
Computer Networks Framing Saad Mneimneh Computer Siene Hunter College of CUNY New York Introdution Who framed Roger rabbit? A detetive, a woman, and a rabbit in a network of trouble We will skip the physial
 Chapter 6 A N ovel Solution Of Linear Congruenes Proeedings NCUR IX. (1995), Vol. II, pp. 708{712 Jerey F. Gold Department of Mathematis, Department of Physis University of Utah Salt Lake City, Utah 84112
Chapter 6 A N ovel Solution Of Linear Congruenes Proeedings NCUR IX. (1995), Vol. II, pp. 708{712 Jerey F. Gold Department of Mathematis, Department of Physis University of Utah Salt Lake City, Utah 84112
Optimal Sales Force Compensation
 Optimal Sales Fore Compensation Matthias Kräkel Anja Shöttner Abstrat We analyze a dynami moral-hazard model to derive optimal sales fore ompensation plans without imposing any ad ho restritions on the
Optimal Sales Fore Compensation Matthias Kräkel Anja Shöttner Abstrat We analyze a dynami moral-hazard model to derive optimal sales fore ompensation plans without imposing any ad ho restritions on the
) ( )( ) ( ) ( )( ) ( ) ( ) (1)
 OPEN CHANNEL FLOW Open hannel flow is haraterized by a surfae in ontat with a gas phase, allowing the fluid to take on shapes and undergo behavior that is impossible in a pipe or other filled onduit. Examples
OPEN CHANNEL FLOW Open hannel flow is haraterized by a surfae in ontat with a gas phase, allowing the fluid to take on shapes and undergo behavior that is impossible in a pipe or other filled onduit. Examples
Customer Efficiency, Channel Usage and Firm Performance in Retail Banking
 Customer Effiieny, Channel Usage and Firm Performane in Retail Banking Mei Xue Operations and Strategi Management Department The Wallae E. Carroll Shool of Management Boston College 350 Fulton Hall, 140
Customer Effiieny, Channel Usage and Firm Performane in Retail Banking Mei Xue Operations and Strategi Management Department The Wallae E. Carroll Shool of Management Boston College 350 Fulton Hall, 140
AUTOMATED VISUAL TRAFFIC MONITORING AND SURVEILLANCE THROUGH A NETWORK OF DISTRIBUTED UNITS
 AUTOMATED VISUAL TRAFFIC MOITORIG AD SURVEILLACE THROUGH A ETWORK OF DISTRIBUTED UITS A. Koutsia a, T. Semertzidis a, K. Dimitropoulos a,. Grammalidis a and K. Georgouleas b a Informatis and Telematis
AUTOMATED VISUAL TRAFFIC MOITORIG AD SURVEILLACE THROUGH A ETWORK OF DISTRIBUTED UITS A. Koutsia a, T. Semertzidis a, K. Dimitropoulos a,. Grammalidis a and K. Georgouleas b a Informatis and Telematis
REDUCTION FACTOR OF FEEDING LINES THAT HAVE A CABLE AND AN OVERHEAD SECTION
 C I E 17 th International Conferene on Eletriity istriution Barelona, 1-15 May 003 EUCTION FACTO OF FEEING LINES THAT HAVE A CABLE AN AN OVEHEA SECTION Ljuivoje opovi J.. Elektrodistriuija - Belgrade -
C I E 17 th International Conferene on Eletriity istriution Barelona, 1-15 May 003 EUCTION FACTO OF FEEING LINES THAT HAVE A CABLE AN AN OVEHEA SECTION Ljuivoje opovi J.. Elektrodistriuija - Belgrade -
A Game Theoretical Approach to Gateway Selections in Multi-domain Wireless Networks
 1 A Game Theoretial Approah to Gateway Seletions in Multi-domain Wireless Networks Yang Song, Starsky H.Y. Wong and Kang-Won Lee IBM Researh, Hawthorne, NY Email: {yangsong, hwong, kangwon}@us.ibm.om Abstrat
1 A Game Theoretial Approah to Gateway Seletions in Multi-domain Wireless Networks Yang Song, Starsky H.Y. Wong and Kang-Won Lee IBM Researh, Hawthorne, NY Email: {yangsong, hwong, kangwon}@us.ibm.om Abstrat
Price-based versus quantity-based approaches for stimulating the development of renewable electricity: new insights in an old debate
 Prie-based versus -based approahes for stimulating the development of renewable eletriity: new insights in an old debate uthors: Dominique FINON, Philippe MENNTEU, Marie-Laure LMY, Institut d Eonomie et
Prie-based versus -based approahes for stimulating the development of renewable eletriity: new insights in an old debate uthors: Dominique FINON, Philippe MENNTEU, Marie-Laure LMY, Institut d Eonomie et
Soft-Edge Flip-flops for Improved Timing Yield: Design and Optimization
 Soft-Edge Flip-flops for Improved Timing Yield: Design and Optimization Abstrat Parameter variations ause high yield losses due to their large impat on iruit delay. In this paper, we propose the use of
Soft-Edge Flip-flops for Improved Timing Yield: Design and Optimization Abstrat Parameter variations ause high yield losses due to their large impat on iruit delay. In this paper, we propose the use of
Lemon Signaling in Cross-Listings Michal Barzuza*
 Lemon Signaling in Cross-Listings Mihal Barzuza* This paper analyzes the deision to ross-list by managers and ontrolling shareholders assuming that they have private information with respet to the amount
Lemon Signaling in Cross-Listings Mihal Barzuza* This paper analyzes the deision to ross-list by managers and ontrolling shareholders assuming that they have private information with respet to the amount
A Comparison of Service Quality between Private and Public Hospitals in Thailand
 International Journal of Business and Soial Siene Vol. 4 No. 11; September 2013 A Comparison of Servie Quality between Private and Hospitals in Thailand Khanhitpol Yousapronpaiboon, D.B.A. Assistant Professor
International Journal of Business and Soial Siene Vol. 4 No. 11; September 2013 A Comparison of Servie Quality between Private and Hospitals in Thailand Khanhitpol Yousapronpaiboon, D.B.A. Assistant Professor
UNIVERSITY AND WORK-STUDY EMPLOYERS WEB SITE USER S GUIDE
 UNIVERSITY AND WORK-STUDY EMPLOYERS WEB SITE USER S GUIDE September 8, 2009 Table of Contents 1 Home 2 University 3 Your 4 Add 5 Managing 6 How 7 Viewing 8 Closing 9 Reposting Page 1 and Work-Study Employers
UNIVERSITY AND WORK-STUDY EMPLOYERS WEB SITE USER S GUIDE September 8, 2009 Table of Contents 1 Home 2 University 3 Your 4 Add 5 Managing 6 How 7 Viewing 8 Closing 9 Reposting Page 1 and Work-Study Employers
How To Fator
 CHAPTER hapter 4 > Make the Connetion 4 INTRODUCTION Developing seret odes is big business beause of the widespread use of omputers and the Internet. Corporations all over the world sell enryption systems
CHAPTER hapter 4 > Make the Connetion 4 INTRODUCTION Developing seret odes is big business beause of the widespread use of omputers and the Internet. Corporations all over the world sell enryption systems
Dynamic and Competitive Effects of Direct Mailings
 Dynami and Competitive Effets of Diret Mailings Merel van Diepen, Bas Donkers and Philip Hans Franses ERIM REPORT SERIES RESEARCH IN MANAGEMENT ERIM Report Series referene number ERS-2006-050-MKT Publiation
Dynami and Competitive Effets of Diret Mailings Merel van Diepen, Bas Donkers and Philip Hans Franses ERIM REPORT SERIES RESEARCH IN MANAGEMENT ERIM Report Series referene number ERS-2006-050-MKT Publiation
5.2 The Master Theorem
 170 CHAPTER 5. RECURSION AND RECURRENCES 5.2 The Master Theorem Master Theorem In the last setion, we saw three different kinds of behavior for reurrenes of the form at (n/2) + n These behaviors depended
170 CHAPTER 5. RECURSION AND RECURRENCES 5.2 The Master Theorem Master Theorem In the last setion, we saw three different kinds of behavior for reurrenes of the form at (n/2) + n These behaviors depended
User s Guide VISFIT: a computer tool for the measurement of intrinsic viscosities
 File:UserVisfit_2.do User s Guide VISFIT: a omputer tool for the measurement of intrinsi visosities Version 2.a, September 2003 From: Multiple Linear Least-Squares Fits with a Common Interept: Determination
File:UserVisfit_2.do User s Guide VISFIT: a omputer tool for the measurement of intrinsi visosities Version 2.a, September 2003 From: Multiple Linear Least-Squares Fits with a Common Interept: Determination
THE PERFORMANCE OF TRANSIT TIME FLOWMETERS IN HEATED GAS MIXTURES
 Proeedings of FEDSM 98 998 ASME Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting June 2-25, 998 Washington DC FEDSM98-529 THE PERFORMANCE OF TRANSIT TIME FLOWMETERS IN HEATED GAS MIXTURES John D. Wright Proess
Proeedings of FEDSM 98 998 ASME Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting June 2-25, 998 Washington DC FEDSM98-529 THE PERFORMANCE OF TRANSIT TIME FLOWMETERS IN HEATED GAS MIXTURES John D. Wright Proess
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON DEPENDABLE AND SECURE COMPUTING, VOL. 9, NO. 3, MAY/JUNE 2012 401
 IEEE TRASACTIOS O DEPEDABLE AD SECURE COMPUTIG, VOL. 9, O. 3, MAY/JUE 2012 401 Mitigating Distributed Denial of Servie Attaks in Multiparty Appliations in the Presene of Clok Drifts Zhang Fu, Marina Papatriantafilou,
IEEE TRASACTIOS O DEPEDABLE AD SECURE COMPUTIG, VOL. 9, O. 3, MAY/JUE 2012 401 Mitigating Distributed Denial of Servie Attaks in Multiparty Appliations in the Presene of Clok Drifts Zhang Fu, Marina Papatriantafilou,
' R ATIONAL. :::~i:. :'.:::::: RETENTION ':: Compliance with the way you work PRODUCT BRIEF
 ' R :::i:. ATIONAL :'.:::::: RETENTION ':: Compliane with the way you work, PRODUCT BRIEF In-plae Management of Unstrutured Data The explosion of unstrutured data ombined with new laws and regulations
' R :::i:. ATIONAL :'.:::::: RETENTION ':: Compliane with the way you work, PRODUCT BRIEF In-plae Management of Unstrutured Data The explosion of unstrutured data ombined with new laws and regulations
Impedance Method for Leak Detection in Zigzag Pipelines
 10.478/v10048-010-0036-0 MEASUREMENT SCIENCE REVIEW, Volume 10, No. 6, 010 Impedane Method for Leak Detetion in igzag Pipelines A. Lay-Ekuakille 1, P. Vergallo 1, A. Trotta 1 Dipartimento d Ingegneria
10.478/v10048-010-0036-0 MEASUREMENT SCIENCE REVIEW, Volume 10, No. 6, 010 Impedane Method for Leak Detetion in igzag Pipelines A. Lay-Ekuakille 1, P. Vergallo 1, A. Trotta 1 Dipartimento d Ingegneria
Availability, Reliability, Maintainability, and Capability
 Availability, Reliability, Maintainability, and Capability H. Paul Barringer, P.E. Barringer & Assoiates, In. Humble, TX Triplex Chapter Of The Vibrations Institute Hilton Hotel Beaumont, Texas February
Availability, Reliability, Maintainability, and Capability H. Paul Barringer, P.E. Barringer & Assoiates, In. Humble, TX Triplex Chapter Of The Vibrations Institute Hilton Hotel Beaumont, Texas February
protection p1ann1ng report
 f1re~~ protetion p1ann1ng report BUILDING CONSTRUCTION INFORMATION FROM THE CONCRETE AND MASONRY INDUSTRIES Signifiane of Fire Ratings for Building Constrution NO. 3 OF A SERIES The use of fire-resistive
f1re~~ protetion p1ann1ng report BUILDING CONSTRUCTION INFORMATION FROM THE CONCRETE AND MASONRY INDUSTRIES Signifiane of Fire Ratings for Building Constrution NO. 3 OF A SERIES The use of fire-resistive
Classical Electromagnetic Doppler Effect Redefined. Copyright 2014 Joseph A. Rybczyk
 Classial Eletromagneti Doppler Effet Redefined Copyright 04 Joseph A. Rybzyk Abstrat The lassial Doppler Effet formula for eletromagneti waves is redefined to agree with the fundamental sientifi priniples
Classial Eletromagneti Doppler Effet Redefined Copyright 04 Joseph A. Rybzyk Abstrat The lassial Doppler Effet formula for eletromagneti waves is redefined to agree with the fundamental sientifi priniples
Green Cloud Computing
 International Journal of Information and Computation Tehnology. ISSN 0974-2239 Volume 4, Number 4 (2014), pp. 431-436 International Researh Publiations House http://www. irphouse.om /ijit.htm Green Cloud
International Journal of Information and Computation Tehnology. ISSN 0974-2239 Volume 4, Number 4 (2014), pp. 431-436 International Researh Publiations House http://www. irphouse.om /ijit.htm Green Cloud
TRENDS IN EXECUTIVE EDUCATION: TOWARDS A SYSTEMS APPROACH TO EXECUTIVE DEVELOPMENT PLANNING
 INTERMAN 7 TRENDS IN EXECUTIVE EDUCATION: TOWARDS A SYSTEMS APPROACH TO EXECUTIVE DEVELOPMENT PLANNING by Douglas A. Ready, Albert A. Viere and Alan F. White RECEIVED 2 7 MAY 1393 International Labour
INTERMAN 7 TRENDS IN EXECUTIVE EDUCATION: TOWARDS A SYSTEMS APPROACH TO EXECUTIVE DEVELOPMENT PLANNING by Douglas A. Ready, Albert A. Viere and Alan F. White RECEIVED 2 7 MAY 1393 International Labour
Measurement of Powder Flow Properties that relate to Gravity Flow Behaviour through Industrial Processing Lines
 Measurement of Powder Flow Properties that relate to Gravity Flow ehaviour through Industrial Proessing Lines A typial industrial powder proessing line will inlude several storage vessels (e.g. bins, bunkers,
Measurement of Powder Flow Properties that relate to Gravity Flow ehaviour through Industrial Proessing Lines A typial industrial powder proessing line will inlude several storage vessels (e.g. bins, bunkers,
State of Maryland Participation Agreement for Pre-Tax and Roth Retirement Savings Accounts
 State of Maryland Partiipation Agreement for Pre-Tax and Roth Retirement Savings Aounts DC-4531 (08/2015) For help, please all 1-800-966-6355 www.marylandd.om 1 Things to Remember Complete all of the setions
State of Maryland Partiipation Agreement for Pre-Tax and Roth Retirement Savings Aounts DC-4531 (08/2015) For help, please all 1-800-966-6355 www.marylandd.om 1 Things to Remember Complete all of the setions
On the Characteristics of Spectrum-Agile Communication Networks
 1 On the Charateristis of Spetrum-Agile Communiation Networks Xin Liu Wei Wang Department of Computer Siene University of California, Davis, CA 95616 Email:{liu,wangw}@s.udavis.edu Abstrat Preliminary
1 On the Charateristis of Spetrum-Agile Communiation Networks Xin Liu Wei Wang Department of Computer Siene University of California, Davis, CA 95616 Email:{liu,wangw}@s.udavis.edu Abstrat Preliminary
DSP-I DSP-I DSP-I DSP-I
 DSP-I DSP-I DSP-I DSP-I Digital Signal Proessing I (8-79) Fall Semester, 005 IIR FILER DESIG EXAMPLE hese notes summarize the design proedure for IIR filters as disussed in lass on ovember. Introdution:
DSP-I DSP-I DSP-I DSP-I Digital Signal Proessing I (8-79) Fall Semester, 005 IIR FILER DESIG EXAMPLE hese notes summarize the design proedure for IIR filters as disussed in lass on ovember. Introdution:
REVISTA INVESTIGACIÓN OPERACIONAL Vol. 28, No.1, 4-16, 2007
 REVISTA INVESTIGACIÓN OPERACIONAL Vol. 28 No.1 4-16 2007 ALGORITHMS FOR MEAN-RISK STOCHASTIC INTEGER PROGRAMS IN ENERGY Rüdiger Shultz Frederike Neise Department of Mathematis University of Duisburg-Essen
REVISTA INVESTIGACIÓN OPERACIONAL Vol. 28 No.1 4-16 2007 ALGORITHMS FOR MEAN-RISK STOCHASTIC INTEGER PROGRAMS IN ENERGY Rüdiger Shultz Frederike Neise Department of Mathematis University of Duisburg-Essen
Electrician'sMathand BasicElectricalFormulas
 Eletriian'sMathand BasiEletrialFormulas MikeHoltEnterprises,In. 1.888.NEC.CODE www.mikeholt.om Introdution Introdution This PDF is a free resoure from Mike Holt Enterprises, In. It s Unit 1 from the Eletrial
Eletriian'sMathand BasiEletrialFormulas MikeHoltEnterprises,In. 1.888.NEC.CODE www.mikeholt.om Introdution Introdution This PDF is a free resoure from Mike Holt Enterprises, In. It s Unit 1 from the Eletrial
Deduplication with Block-Level Content-Aware Chunking for Solid State Drives (SSDs)
 23 IEEE International Conferene on High Performane Computing and Communiations & 23 IEEE International Conferene on Embedded and Ubiquitous Computing Dedupliation with Blok-Level Content-Aware Chunking
23 IEEE International Conferene on High Performane Computing and Communiations & 23 IEEE International Conferene on Embedded and Ubiquitous Computing Dedupliation with Blok-Level Content-Aware Chunking
Computational Analysis of Two Arrangements of a Central Ground-Source Heat Pump System for Residential Buildings
 Computational Analysis of Two Arrangements of a Central Ground-Soure Heat Pump System for Residential Buildings Abstrat Ehab Foda, Ala Hasan, Kai Sirén Helsinki University of Tehnology, HVAC Tehnology,
Computational Analysis of Two Arrangements of a Central Ground-Soure Heat Pump System for Residential Buildings Abstrat Ehab Foda, Ala Hasan, Kai Sirén Helsinki University of Tehnology, HVAC Tehnology,
Using Live Chat in your Call Centre
 Using Live Chat in your Call Centre Otober Key Highlights Yesterday's all entres have beome today's ontat entres where agents deal with multiple queries from multiple hannels. Live Chat hat is one now
Using Live Chat in your Call Centre Otober Key Highlights Yesterday's all entres have beome today's ontat entres where agents deal with multiple queries from multiple hannels. Live Chat hat is one now
In order to be able to design beams, we need both moments and shears. 1. Moment a) From direct design method or equivalent frame method
 BEAM DESIGN In order to be able to design beams, we need both moments and shears. 1. Moment a) From diret design method or equivalent frame method b) From loads applied diretly to beams inluding beam weight
BEAM DESIGN In order to be able to design beams, we need both moments and shears. 1. Moment a) From diret design method or equivalent frame method b) From loads applied diretly to beams inluding beam weight
