Recovering Articulated Motion with a Hierarchical Factorization Method
|
|
|
- Marvin Sanders
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Reovering Artiulated Motion with a Hierarhial Fatorization Method Hanning Zhou and Thomas S Huang University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 405 North Mathews Avenue, Urbana, IL 680, USA {hzhou, huang}@ifpuiuedu Abstrat Reovering artiulated human motion is an important task in many appliations inluding surveillane and human-omputer interation In this paper, a hierarhial fatorization method is proposed for reovering artiulated human motion (suh as hand gesture) from a sequene of images aptured under weak perspetive projetion It is robust against missing feature points due to self-olusion, and various observation noises The auray of our algorithm is verified by experiments on syntheti data Introdution Hand gesture an be a more natural way for human to interat with omputers For instane, one an use his or her hands to manipulate virtual objets diretly in virtual environments However, apturing human hand motion is inherently diffiult due to its artiulation and variability One way to solve the problem is to deompose the hand into linked objets, trak them hierarhially and derive the onfiguration afterwards This kind of deomposition method was first used in human motion analysis by Webb et al[5] Holt and Huang [7] proposed a more general approah whih used perspetive (instead of orthogonal) projetion They found a losed form solution using an algebrai geometry method [6] In this paper, a hierarhial fatorization method is proposed for reovering artiulated hand motion from a image sequene Both global motion and loal artiulation are reovered simultaneously Setion 2 summaries previous work on the fatorization methods, espeially for multiple objet and non-rigid objet Setion 3 desribes the extension of the fatorization method to artiulated objet Setion 4 introdues the hierarhial fatorization method to handle olusion and feature point orrespondenes Setion 5 provides experimental results in both quantitative and visual forms Setion 6 onludes with appliable situations, the limitation of this approah and future diretions for extension and improvement The appendix gives some omputational details
2 2 Previous Work in Fatorization Methods Fatorization-based struture from motion of a single objet under orthographi projetion was introdued by Tomasi et al [4], and later extended to paraperspetive projetion model [2] A sequential version was proposed in [] Attempts were made to generalize the tehnique for full perspetive [3], but due to the inherent nonlinearity of amera projetion, some preproessing (espeially depth estimation) is neessary, whih leads to a sub-optimal solution Costeira et al proposed an algorithm for multi-body segmentation based on fatorization tehnique [2] Similar approahes were later developed for linearly moving objets [5] and for deformable objets [] Costeira [2] based their segmentation algorithm on a so-alled shape interation matrix Q (see below) If two features belong to two different objets, their orresponding element in Q should be zero; otherwise, the value should be non-zero They then grouped feature points into objets by thresholding and sorting Q Gear [4] formulated the task as a graph mathing problem by plaing appropriate weights on the graph edges Unfortunately, the performane of both tehniques degrades quikly when data points are orrupted with noise, beause the relationship between data noise and the oeffiients of Q (or weights of the graph edges) is so ompliated that it is hard to determine an appropriate threshold Ihimura [8] proposed an improved algorithm by applying a disriminant riterion for thresholding, but the disriminant analysis is still performed on the elements of Q, resulting a similar degradation with noise To avoid this problem, Kanatani [9] proposed to work in the original data spae by inorporating suh tehniques as dimension orretion (fitting a subspae to a group of points and replaing them with their projetions onto the fitted subspae) and model seletion (using a geometri information riterion to determine whether two subspaes an be merged) Wu and Huang in [6] proposed a new grouping tehnique based on orthogonal subspae deomposition, whih introdues the shape signal subspae distane matrix D, for shape spae grouping, based on a distane measure defined over the subspaes Robust segmentation results are ahieved Following the exploration of multi-body fatorization, it is natural to extend the multi-body fatorization method to artiulated objets, whih an be treated as a group of linked rigid bodies This paper mainly disusses the integration of kinemati onstraints into the multi-body fatorization method 3 Fatorization Method for Artiulated Objets Although the fatorization method here an be applied to arbitrary artiulated objets, we desribe the algorithm using human hand as an example The kinemati hand model has 2 degrees of freedom (DOF) for joint angles and 6 DOF for global pose Figure shows a kinemati hand model The distal interphalangeal (DIP) joint and proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joint eah of the four fingers has one DOF and the metaarpophalangeal(mcp) joint has two DOF due to flexion and abdution The thumb has a different struture from the
3 other four fingers and has five DOF, one for the interphalangeal (IP) joint and two for eah of the thumb MCP joint and trapeziometaarpal (TM) joint both due to flexion and abdution The palm is approximated by a rigid polygon Fig Kinemati hand model and joint notations 3 Rank onstraints for Artiulated Motion Aording to the kinemati model, we treat the hand as 6 linked objets (5 phalanxes and palm) Upon the F images of hand artiulation, we trak P (at least four non-oplanar) feature points on the -th objet Given the P = N = P feature points and their pixel oordinates (u f,p, v f,p ) in eah frame f, we ollet all the image measurements into matrix W 2F P = [ W W N ] () u, u,p u where W2F P = F, u F,P ζ and ζ is the foal length Applying the v, v,p vf, v F,P multi-body fatorization method [3] without onsidering the kinemati on-
4 straints, W an be fatorized as: W 2F P = [ M M N ] S S S N S N (2) Where onsists of and M2F 4 = t i z, t i F z,f t z, j t j F z,f i x,f t x, t z, t x,f t z,f t y, t z, t y,f t z,f (3) i f = i y,f (4) i z,f j x,f j f = jy,f (5) jz,f whih are the axes of the amera oordinate frame expressed in the objet s frame t x,f, t y,f, t z,f represent the translation from the origin of the objet s frame to that of the amera frame x x P S4 P = y yp z zp (6) is the homogeneous 3D oordinates of the feature points in phalanx s frame It is obvious that W 2F P has at most rank 4N The motion estimation problem is formulated as finding the orresponding sequene of rotation-translation matries M f = [R f T f ] with respet to the initial pose 32 Solving Motion [R f T f ] by Fatorization Singular value deomposition is proved to be a robust method for reovering M matrix W = UΣV T (7)
5 Take the largest 4N singular values in Σ to form diagonal matrix ˆΣ We define ˆM = U ˆΣ 2 (8) Ŝ = ˆΣ 2 V T This fatorization is unique up to a nonsingular matrix A 4 4, sine MS = ( ˆMA)(A Ŝ) For a single rigid body, if we hoose the entroid of the objet as the origin of the world oordinate, we an solve A using the onstrains on M (as given in the appendix) However, in the ase of artiulated objet, different onstraints must be applied, whih will be disussed in Setion 4 Given M = ˆMA, the two axes of the amera frame at instant f in objet s frame are given by i f and j f And the third axis (9) k f = i f j f (0) The Full rotation matrix from objet s frame to the amera frame is 33 Reovering Loal and Global Motion R f 3 3 = [i f j f k f ] () Reovering of 20 joint angles of the hand model equivalent to solve the rotation matrix between adjaent phalanxes Assuming phalanxes, 2 are adjaent, we an solve the relative rotation at instant f as R f (, 2 ) = R f R 2 f, and reover the joint angles from R f (, 2 ) If we define the world oordinates as that of the palm (objet 0 ), the global hand pose is R f = R 0 f 4 Hierarhial Fatorization The ideal solution in Setion 3 has two diffiulties in pratie First it is very hard to trak all the feature points reliably and measure their loal oordinates, due to self-olusion and observation noise The feature points of different objets will be randomly mixed in matrix W There have been many methods to address this problem as listed in Setion 2 The seond diffiulty is more speifi for artiulated objet: sine we treated eah objet as independent objets, there is no guarantee that the ends of onseutive objets are linked in the reovered motion We propose a hierarhial fatorization method to solve this problem Given F images with P = N = P feature points and their pixel oordinates (u f,p, v f,p ) in eah frame f, we ollet all the image measurements into matrix u, u,p W 2F P = u F, u F,P ζ v, v,p (2) vf, v F,P
6 Using the multi-body fatorization method in [2], W 2F P an be fatorized as following Ŝ 0 0 W 2F P = [ ˆM N ˆM ] 0 Ŝ (3) 0 ŜN Ŝ N Where and where A is a full rank 4 4 matrix In the matrix M 2 f = t 2 i 2 f z,f t 2 j 2 f z,f ˆM 2F 4 = M A (4) Ŝ 4 P = (A ) S (5) t 2 x,f t 2 z,f t 2 y,f t 2 z,f i 2 f, we have j2 f (6) i 2 f = (7) j 2 f = (8) Denote the 4 4 matrix A as the onatenation of two bloks A = [A R a t] (9) A R is the first 4 3 submatrix related to rotational omponent And a t is a 4 vetor related to translations From Equation (6)(7)(8), A R an be solved (the details are given in the appendix) To reover a t, [2] used the entroid of the feature points on objet, that is, the average of eah row of W : w P u,p [ ] s P = [ ˆMA R ˆMa t] (20) p= vf,p x p where s = P y p P p= zp is the 3D entroid of the objet The traditional method [2] assumes the entroid of the objet to be the origin of the objet, that is s = 0 Then w = M ˆ a t and a t is solved to be a t = ( M ˆT ˆM) Mˆ T w = Σ 2 U T w However, if we solve a t this way, the results will usually violate the linked-ends onstraints
7 Step(): Solving motion of the palm as the root objet Trak at least 4 feature points in general position on the palm; solving transformation matrix for palm M as desribed in Setion 3 Step(2): Solving motion of the five proximal phalanxes Based on M, we an solve the M matries for the five proximal phalanxes (the phalanxes attahed to the palm) Step(3): Solving the motion of the five medial phalanxes (the seond row) Step(4): Solving the motion of the five distal phalanxes (on the third row) Fig 2 The hierarhial fatorization algorithm To solve this problem, we propose the hierarhial fatorization algorithm for solving A ( = N) as shown in Figure 2 In eah step, the solution for A R is still the same as the multi-body fatorization method desribed in the appendix, but for a t, we introdue the translational onstraint as shown in Figure 3 Fig 3 An example of two linked phalanxes and 2 (the medial phalanx and the distal phalanx) and the translational relation between their loal oordinates Table lists the notations used in Figure 3 As M is solved from the previous step, we an express the translational onstraint due to the linked-ends of and 2 as: t x,f t2 x,f T f = t y,f t2 y,f t z,f t 2 z,f (2)
8 Table Notations used in Figure 3 notation physial meaning medial phalanx 2 distal phalanx T translation between the loal oordinates of and 2 in the amera frame T translation between the loal oordinates of and 2 in sub objet s frame where f = F Aording to the kinemati hand model T = 0 l (22) 0 where l is the length of T f = t y,f t z,f [ ] i f j f k f T (23) where i, j and k are defined in Equation (4), (5) and (0) Therefore, [t 2 satisfies t x,f [ ] = i f j f k 0 f l 0 x,f t 2 y,f t 2 z,f ]T (24) From Equation (24), we obtain the origin of objet s loal oordinates, whih is not the entroid of the feature points, but the joint where urrent objet is linked with the previous one We take the ratio between their x-y oordinates t x, t z, t x,f and the oordinates and stak them into vetor t t z,f =, whih is the fourth t y, t z, t y,f t z,f olumn of M Therefore ˆMa t = t and a t an be solved as: a t = ( M ˆT M ˆ ) M ˆ T t = Σ 2 U T t (25) 5 Experimental Results Figure 4 shows a syntheti sequene of hand motion rendered with OpenGL The joint angle data is olleted with CyberGlove T M
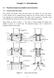
9 Fig 4 Syntheti image sequene of hand motion Fig 5 Hand motion reovered with the hierarhial fatorization method Figure 5 shows Hand motion reovered with hierarhial fatorization method, rendered from the same view point It an be seen that the metaarpophalangeal (MCP) abdution angle is a bit off, whih also shows in the first subplot in Figure 6 Finger 6 shows the omparison between the original joint angles and the reovered joint angles of the index finger The blue urves show the original joints angles over 38 frames The red urves show the reovered joint angles The 4 subplots orresponds to 4 angles, ie MCP Abdution (MCPA), MCP Flexion (MCPF), PIP Flexion (PIPF) and DIP Flexion (DIPF) respetively, at 3 joints of the index finger All the values shown in the plots are in degree angle Table 2 RMSE, std, range of motion(rom) and rrmse between the ground truth and reovered joint angles joint angle RMSE std ROM rrmse MCPA % MCPF % PIPF % DIPF % In Table 2, RMSE denotes the rooted mean square error between the ground truth joint angles and the reovered ones, the mean is taken aross all the frames within the test sequene And std denotes the standard deviation of the absolute differene between the ground truth joint angles and the reovered ones, taken aross all the frames within the test sequene ROM denotes the range of motion, that is, the differene between the joint angle in the first frame and that in the last frame rrmse is the ratio between RMSE and ROM As the table shows,
10 MCP Abdution MCP Flexion PIP Flexion [deg] DIP Flexion Index Finger: Original joint angles (blue urves), reoverd joint angles (red dashed urves) time instant Fig 6 Original joint angles and joint angles reovered with hierarhial fatorization method the results for MCPF are the best, while the relative MSE for MCPA is the largest among all joint angles, whih shows that most of the noise is in MCPA and the noise is hanging dramatially with the motion This is due to the fat that most sample points are hosen at similar relative depth Nearly oplanar struture matrix will ause rank defiieny in singular value deomposition and thus ause majority of the noise in z diretion: the main diretion of MCPA As for PIPF, the MSE is 60, the standard deviation of the differene is very small (only 2), whih shows there is an almost onstant offset between the original angle and reovered angle This suggests that the noise is global and irrelevant to the partiular motion By inreasing the feature points on the medial and proximal phalanxes, this error an be redued For DIPF, both ROM and MSE are very small 6 Conlusions In this paper, we propose a hierarhial fatorization method for reovering the artiulated human motion The kinematial onstraints are utilized to grantee the ends of onseutive objets are linked The limitation for this algorithm is that at least 4 non-oplanar feature points on the palm must be traked reliably in order to reover the global pose and initiate the hierarhial algorithm After fatorization-based segmentation, labelling of eah objet is also nontrivial In the future we will onentrate on integrate more onstraints into the fatorization method For example, in eah proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joint
11 and eah distal interphalangeal (DIP) joint, there are only DOF in the rotation matrix R, while for MCP joints, there are only 2 DOF in R By projeting the orresponding rotation matrix the subspae of SO() and SO(2) [0], we an get more aurate reovering results Referenes C Bregler, A Hertzmann, and H Biermann Reovering non-rigid 3D shape from image streams In Pro IEEE Conf on Computer Vision and Pattern Reognition, pages , Hilton Head Island, SC, June J Costeira and T Kanade A multibody fatorization method for independently moving objets International Journal of Computer Vision, 29:59 79, Joao Costeira and Takeo Kanade A multibody fatorization method for motion analysis Tehnial Report CMU-CS-TR , Computer Siene Department, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA, September C Gear Multibody grouping from motion images International Journal of Computer Vision, 29:33 50, M Han and T Kanade Reonstrution of a sene with multiple linearly moving objets In Pro IEEE Conf on Computer Vision and Pattern Reognition, volume II, pages , Hilton Head Island, SC, June R J Holt and T S Huang Algebrai methods for image proessing and omputer vision IEEE Transations on Image Proessing, 5: , R J Holt, T S Huang, A N Netravali, and R J Qian Determining artiulated motion from perspetive views: A deomposition approah Pattern Reognition, 30: , N Ihimura Motion segmentation based on fatorization method and disriminant riterion In Pro IEEE International Conferene on Computer Vision, pages , Greee, Sept K Kanatani Motion segmentation by subspae separation and model seletion In Pro IEEE International Conferene on Computer Vision, Vanouver, Canada, July Yi Ma, Jana Koseka, Stefano Soatto, and Shankar Sastry An Invitation to 3-D Vision Springer-Verlag, New York, 2002 T Morita and T Kanade A sequential fatorization method for reovering shape and motion from image streams IEEE Transations on Pattern Analysis and Mahine Intelligene, 9: , C Poelman and T Kanade A paraperspetive fatorization method for shape and motion reovery IEEE Transations on Pattern Analysis and Mahine Intelligene, 9:206 28, P Sturm and B Triggs A fatorization based algorithm for multi-image projetive struture and motion In Pro European Conferene on Computer Vision, volume II, pages , C Tomasi and T Kanade Shape and motion from image streams under orthography a fatorized method International Journal of Computer Vision, 9:37 54, J A Webb and J K Aggarwal Struture from motion of rigid and jointed objets Artifiial Intelligene, 9:07 30, Y Wu, Z Zhang, T S Huang, and J Y Lin Multibody grouping via orthogonal subspae deomposition In IEEE Conf on Computer Vision and Pattern Reognition, volume II, pages , Kauai, Hawaii, De 200
12 Appendix: Solving A R The following equations hold for all, so the supersript are omitted Define l l 2 l 3 l 2 l 4 l 5 = L = A T R A R (26) l 3 l 5 l 6 m,f = [ ˆM(, ) f ˆM(, 2)f ˆM(, 3)f ] (27) m 2,f = [ ˆM(2, ) f ˆM(2, 2)f ˆM(2, 3)f ] (28) Aording to Equation (6) (7)(8), we have ˆm T,f L ˆm 2,f = 0 (29) ˆm T,f L ˆm,f = t z (30) ˆm T 2,f L ˆm 2,f = t z (3) Aording to [], for eah, there are 3 F equations and they an be rewritten as Gl = (32) where and g(m,, m, ) g(m,f, m,f ) g(m 2,, m 2, ) l G =, l = (33) g(m 2,F, m 2,F ) l 6 g(m,, m 2, ) g(m,f, m 2,F ) T = [ } {{ } 2F 0 } {{ 0 } ] T (34) F g(a, b) = [a b 2a b 2 2a b 3 a 2 b 2 2a 2 b 3 a 3 b 3 ] (35) Using Least Square Method, l an be solved l = (G T G) G T (36) The eigen-deomposition of matrix L gives matrix A R
Marker Tracking and HMD Calibration for a Video-based Augmented Reality Conferencing System
 Marker Traking and HMD Calibration for a Video-based Augmented Reality Conferening System Hirokazu Kato 1 and Mark Billinghurst 2 1 Faulty of Information Sienes, Hiroshima City University 2 Human Interfae
Marker Traking and HMD Calibration for a Video-based Augmented Reality Conferening System Hirokazu Kato 1 and Mark Billinghurst 2 1 Faulty of Information Sienes, Hiroshima City University 2 Human Interfae
A Holistic Method for Selecting Web Services in Design of Composite Applications
 A Holisti Method for Seleting Web Servies in Design of Composite Appliations Mārtiņš Bonders, Jānis Grabis Institute of Information Tehnology, Riga Tehnial University, 1 Kalu Street, Riga, LV 1658, Latvia,
A Holisti Method for Seleting Web Servies in Design of Composite Appliations Mārtiņš Bonders, Jānis Grabis Institute of Information Tehnology, Riga Tehnial University, 1 Kalu Street, Riga, LV 1658, Latvia,
FIRE DETECTION USING AUTONOMOUS AERIAL VEHICLES WITH INFRARED AND VISUAL CAMERAS. J. Ramiro Martínez-de Dios, Luis Merino and Aníbal Ollero
 FE DETECTION USING AUTONOMOUS AERIAL VEHICLES WITH INFRARED AND VISUAL CAMERAS. J. Ramiro Martínez-de Dios, Luis Merino and Aníbal Ollero Robotis, Computer Vision and Intelligent Control Group. University
FE DETECTION USING AUTONOMOUS AERIAL VEHICLES WITH INFRARED AND VISUAL CAMERAS. J. Ramiro Martínez-de Dios, Luis Merino and Aníbal Ollero Robotis, Computer Vision and Intelligent Control Group. University
Granular Problem Solving and Software Engineering
 Granular Problem Solving and Software Engineering Haibin Zhu, Senior Member, IEEE Department of Computer Siene and Mathematis, Nipissing University, 100 College Drive, North Bay, Ontario, P1B 8L7, Canada
Granular Problem Solving and Software Engineering Haibin Zhu, Senior Member, IEEE Department of Computer Siene and Mathematis, Nipissing University, 100 College Drive, North Bay, Ontario, P1B 8L7, Canada
Intelligent Measurement Processes in 3D Optical Metrology: Producing More Accurate Point Clouds
 Intelligent Measurement Proesses in 3D Optial Metrology: Produing More Aurate Point Clouds Charles Mony, Ph.D. 1 President Creaform in. [email protected] Daniel Brown, Eng. 1 Produt Manager Creaform in.
Intelligent Measurement Proesses in 3D Optial Metrology: Produing More Aurate Point Clouds Charles Mony, Ph.D. 1 President Creaform in. [email protected] Daniel Brown, Eng. 1 Produt Manager Creaform in.
Algorithm of Removing Thin Cloud-fog Cover from Single Remote Sensing Image
 Journal of Information & Computational Siene 11:3 (2014 817 824 February 10, 2014 Available at http://www.jois.om Algorithm of Removing Thin Cloud-fog Cover from Single Remote Sensing Image Yinqi Xiong,
Journal of Information & Computational Siene 11:3 (2014 817 824 February 10, 2014 Available at http://www.jois.om Algorithm of Removing Thin Cloud-fog Cover from Single Remote Sensing Image Yinqi Xiong,
Channel Assignment Strategies for Cellular Phone Systems
 Channel Assignment Strategies for Cellular Phone Systems Wei Liu Yiping Han Hang Yu Zhejiang University Hangzhou, P. R. China Contat: [email protected] 000 Mathematial Contest in Modeling (MCM) Meritorious
Channel Assignment Strategies for Cellular Phone Systems Wei Liu Yiping Han Hang Yu Zhejiang University Hangzhou, P. R. China Contat: [email protected] 000 Mathematial Contest in Modeling (MCM) Meritorious
The Application of Mamdani Fuzzy Model for Auto Zoom Function of a Digital Camera
 (IJCSIS) International Journal of Computer Siene and Information Seurity, Vol. 6, No. 3, 2009 The Appliation of Mamdani Fuzzy Model for Auto Funtion of a Digital Camera * I. Elamvazuthi, P. Vasant Universiti
(IJCSIS) International Journal of Computer Siene and Information Seurity, Vol. 6, No. 3, 2009 The Appliation of Mamdani Fuzzy Model for Auto Funtion of a Digital Camera * I. Elamvazuthi, P. Vasant Universiti
Capacity at Unsignalized Two-Stage Priority Intersections
 Capaity at Unsignalized Two-Stage Priority Intersetions by Werner Brilon and Ning Wu Abstrat The subjet of this paper is the apaity of minor-street traffi movements aross major divided four-lane roadways
Capaity at Unsignalized Two-Stage Priority Intersetions by Werner Brilon and Ning Wu Abstrat The subjet of this paper is the apaity of minor-street traffi movements aross major divided four-lane roadways
Superpixel Tracking. Shu Wang 1, Huchuan Lu 1, Fan Yang 1, and Ming-Hsuan Yang 2. Abstract. 1. Introduction
 Superpixel Traking Shu Wang 1, Huhuan Lu 1, Fan Yang 1, and Ming-Hsuan Yang 2 1 Shool of Information and Communiation Engineering, Dalian University of Tehnology, China 2 Eletrial Engineering and Computer
Superpixel Traking Shu Wang 1, Huhuan Lu 1, Fan Yang 1, and Ming-Hsuan Yang 2 1 Shool of Information and Communiation Engineering, Dalian University of Tehnology, China 2 Eletrial Engineering and Computer
Chapter 5 Single Phase Systems
 Chapter 5 Single Phase Systems Chemial engineering alulations rely heavily on the availability of physial properties of materials. There are three ommon methods used to find these properties. These inlude
Chapter 5 Single Phase Systems Chemial engineering alulations rely heavily on the availability of physial properties of materials. There are three ommon methods used to find these properties. These inlude
Big Data Analysis and Reporting with Decision Tree Induction
 Big Data Analysis and Reporting with Deision Tree Indution PETRA PERNER Institute of Computer Vision and Applied Computer Sienes, IBaI Postbox 30 11 14, 04251 Leipzig GERMANY [email protected],
Big Data Analysis and Reporting with Deision Tree Indution PETRA PERNER Institute of Computer Vision and Applied Computer Sienes, IBaI Postbox 30 11 14, 04251 Leipzig GERMANY [email protected],
Chapter 1 Microeconomics of Consumer Theory
 Chapter 1 Miroeonomis of Consumer Theory The two broad ategories of deision-makers in an eonomy are onsumers and firms. Eah individual in eah of these groups makes its deisions in order to ahieve some
Chapter 1 Miroeonomis of Consumer Theory The two broad ategories of deision-makers in an eonomy are onsumers and firms. Eah individual in eah of these groups makes its deisions in order to ahieve some
Static Fairness Criteria in Telecommunications
 Teknillinen Korkeakoulu ERIKOISTYÖ Teknillisen fysiikan koulutusohjelma 92002 Mat-208 Sovelletun matematiikan erikoistyöt Stati Fairness Criteria in Teleommuniations Vesa Timonen, e-mail: vesatimonen@hutfi
Teknillinen Korkeakoulu ERIKOISTYÖ Teknillisen fysiikan koulutusohjelma 92002 Mat-208 Sovelletun matematiikan erikoistyöt Stati Fairness Criteria in Teleommuniations Vesa Timonen, e-mail: vesatimonen@hutfi
Scalable Hierarchical Multitask Learning Algorithms for Conversion Optimization in Display Advertising
 Salable Hierarhial Multitask Learning Algorithms for Conversion Optimization in Display Advertising Amr Ahmed Google [email protected] Abhimanyu Das Mirosoft Researh [email protected] Alexander J. Smola
Salable Hierarhial Multitask Learning Algorithms for Conversion Optimization in Display Advertising Amr Ahmed Google [email protected] Abhimanyu Das Mirosoft Researh [email protected] Alexander J. Smola
arxiv:astro-ph/0304006v2 10 Jun 2003 Theory Group, MS 50A-5101 Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory One Cyclotron Road Berkeley, CA 94720 USA
 LBNL-52402 Marh 2003 On the Speed of Gravity and the v/ Corretions to the Shapiro Time Delay Stuart Samuel 1 arxiv:astro-ph/0304006v2 10 Jun 2003 Theory Group, MS 50A-5101 Lawrene Berkeley National Laboratory
LBNL-52402 Marh 2003 On the Speed of Gravity and the v/ Corretions to the Shapiro Time Delay Stuart Samuel 1 arxiv:astro-ph/0304006v2 10 Jun 2003 Theory Group, MS 50A-5101 Lawrene Berkeley National Laboratory
Sebastián Bravo López
 Transfinite Turing mahines Sebastián Bravo López 1 Introdution With the rise of omputers with high omputational power the idea of developing more powerful models of omputation has appeared. Suppose that
Transfinite Turing mahines Sebastián Bravo López 1 Introdution With the rise of omputers with high omputational power the idea of developing more powerful models of omputation has appeared. Suppose that
Supply chain coordination; A Game Theory approach
 aepted for publiation in the journal "Engineering Appliations of Artifiial Intelligene" 2008 upply hain oordination; A Game Theory approah Jean-Claude Hennet x and Yasemin Arda xx x LI CNR-UMR 668 Université
aepted for publiation in the journal "Engineering Appliations of Artifiial Intelligene" 2008 upply hain oordination; A Game Theory approah Jean-Claude Hennet x and Yasemin Arda xx x LI CNR-UMR 668 Université
Hierarchical Clustering and Sampling Techniques for Network Monitoring
 S. Sindhuja Hierarhial Clustering and Sampling Tehniques for etwork Monitoring S. Sindhuja ME ABSTRACT: etwork monitoring appliations are used to monitor network traffi flows. Clustering tehniques are
S. Sindhuja Hierarhial Clustering and Sampling Tehniques for etwork Monitoring S. Sindhuja ME ABSTRACT: etwork monitoring appliations are used to monitor network traffi flows. Clustering tehniques are
Pattern Recognition Techniques in Microarray Data Analysis
 Pattern Reognition Tehniques in Miroarray Data Analysis Miao Li, Biao Wang, Zohreh Momeni, and Faramarz Valafar Department of Computer Siene San Diego State University San Diego, California, USA [email protected]
Pattern Reognition Tehniques in Miroarray Data Analysis Miao Li, Biao Wang, Zohreh Momeni, and Faramarz Valafar Department of Computer Siene San Diego State University San Diego, California, USA [email protected]
Improved SOM-Based High-Dimensional Data Visualization Algorithm
 Computer and Information Siene; Vol. 5, No. 4; 2012 ISSN 1913-8989 E-ISSN 1913-8997 Published by Canadian Center of Siene and Eduation Improved SOM-Based High-Dimensional Data Visualization Algorithm Wang
Computer and Information Siene; Vol. 5, No. 4; 2012 ISSN 1913-8989 E-ISSN 1913-8997 Published by Canadian Center of Siene and Eduation Improved SOM-Based High-Dimensional Data Visualization Algorithm Wang
How To Fator
 CHAPTER hapter 4 > Make the Connetion 4 INTRODUCTION Developing seret odes is big business beause of the widespread use of omputers and the Internet. Corporations all over the world sell enryption systems
CHAPTER hapter 4 > Make the Connetion 4 INTRODUCTION Developing seret odes is big business beause of the widespread use of omputers and the Internet. Corporations all over the world sell enryption systems
Computer Networks Framing
 Computer Networks Framing Saad Mneimneh Computer Siene Hunter College of CUNY New York Introdution Who framed Roger rabbit? A detetive, a woman, and a rabbit in a network of trouble We will skip the physial
Computer Networks Framing Saad Mneimneh Computer Siene Hunter College of CUNY New York Introdution Who framed Roger rabbit? A detetive, a woman, and a rabbit in a network of trouble We will skip the physial
An Enhanced Critical Path Method for Multiple Resource Constraints
 An Enhaned Critial Path Method for Multiple Resoure Constraints Chang-Pin Lin, Hung-Lin Tai, and Shih-Yan Hu Abstrat Traditional Critial Path Method onsiders only logial dependenies between related ativities
An Enhaned Critial Path Method for Multiple Resoure Constraints Chang-Pin Lin, Hung-Lin Tai, and Shih-Yan Hu Abstrat Traditional Critial Path Method onsiders only logial dependenies between related ativities
AUTOMATED VISUAL TRAFFIC MONITORING AND SURVEILLANCE THROUGH A NETWORK OF DISTRIBUTED UNITS
 AUTOMATED VISUAL TRAFFIC MOITORIG AD SURVEILLACE THROUGH A ETWORK OF DISTRIBUTED UITS A. Koutsia a, T. Semertzidis a, K. Dimitropoulos a,. Grammalidis a and K. Georgouleas b a Informatis and Telematis
AUTOMATED VISUAL TRAFFIC MOITORIG AD SURVEILLACE THROUGH A ETWORK OF DISTRIBUTED UITS A. Koutsia a, T. Semertzidis a, K. Dimitropoulos a,. Grammalidis a and K. Georgouleas b a Informatis and Telematis
Computational Analysis of Two Arrangements of a Central Ground-Source Heat Pump System for Residential Buildings
 Computational Analysis of Two Arrangements of a Central Ground-Soure Heat Pump System for Residential Buildings Abstrat Ehab Foda, Ala Hasan, Kai Sirén Helsinki University of Tehnology, HVAC Tehnology,
Computational Analysis of Two Arrangements of a Central Ground-Soure Heat Pump System for Residential Buildings Abstrat Ehab Foda, Ala Hasan, Kai Sirén Helsinki University of Tehnology, HVAC Tehnology,
Classical Electromagnetic Doppler Effect Redefined. Copyright 2014 Joseph A. Rybczyk
 Classial Eletromagneti Doppler Effet Redefined Copyright 04 Joseph A. Rybzyk Abstrat The lassial Doppler Effet formula for eletromagneti waves is redefined to agree with the fundamental sientifi priniples
Classial Eletromagneti Doppler Effet Redefined Copyright 04 Joseph A. Rybzyk Abstrat The lassial Doppler Effet formula for eletromagneti waves is redefined to agree with the fundamental sientifi priniples
A novel active mass damper for vibration control of bridges
 IABMAS 08, International Conferene on Bridge Maintenane, Safety and Management, 3-7 July 008, Seoul, Korea A novel ative mass damper for vibration ontrol of bridges U. Starossek & J. Sheller Strutural
IABMAS 08, International Conferene on Bridge Maintenane, Safety and Management, 3-7 July 008, Seoul, Korea A novel ative mass damper for vibration ontrol of bridges U. Starossek & J. Sheller Strutural
1.3 Complex Numbers; Quadratic Equations in the Complex Number System*
 04 CHAPTER Equations and Inequalities Explaining Conepts: Disussion and Writing 7. Whih of the following pairs of equations are equivalent? Explain. x 2 9; x 3 (b) x 29; x 3 () x - 2x - 22 x - 2 2 ; x
04 CHAPTER Equations and Inequalities Explaining Conepts: Disussion and Writing 7. Whih of the following pairs of equations are equivalent? Explain. x 2 9; x 3 (b) x 29; x 3 () x - 2x - 22 x - 2 2 ; x
A Context-Aware Preference Database System
 J. PERVASIVE COMPUT. & COMM. (), MARCH 005. TROUBADOR PUBLISHING LTD) A Context-Aware Preferene Database System Kostas Stefanidis Department of Computer Siene, University of Ioannina,, [email protected] Evaggelia
J. PERVASIVE COMPUT. & COMM. (), MARCH 005. TROUBADOR PUBLISHING LTD) A Context-Aware Preferene Database System Kostas Stefanidis Department of Computer Siene, University of Ioannina,, [email protected] Evaggelia
) ( )( ) ( ) ( )( ) ( ) ( ) (1)
 OPEN CHANNEL FLOW Open hannel flow is haraterized by a surfae in ontat with a gas phase, allowing the fluid to take on shapes and undergo behavior that is impossible in a pipe or other filled onduit. Examples
OPEN CHANNEL FLOW Open hannel flow is haraterized by a surfae in ontat with a gas phase, allowing the fluid to take on shapes and undergo behavior that is impossible in a pipe or other filled onduit. Examples
Neural network-based Load Balancing and Reactive Power Control by Static VAR Compensator
 nternational Journal of Computer and Eletrial Engineering, Vol. 1, No. 1, April 2009 Neural network-based Load Balaning and Reative Power Control by Stati VAR Compensator smail K. Said and Marouf Pirouti
nternational Journal of Computer and Eletrial Engineering, Vol. 1, No. 1, April 2009 Neural network-based Load Balaning and Reative Power Control by Stati VAR Compensator smail K. Said and Marouf Pirouti
CIS570 Lecture 4 Introduction to Data-flow Analysis 3
 Introdution to Data-flow Analysis Last Time Control flow analysis BT disussion Today Introdue iterative data-flow analysis Liveness analysis Introdue other useful onepts CIS570 Leture 4 Introdution to
Introdution to Data-flow Analysis Last Time Control flow analysis BT disussion Today Introdue iterative data-flow analysis Liveness analysis Introdue other useful onepts CIS570 Leture 4 Introdution to
Weighting Methods in Survey Sampling
 Setion on Survey Researh Methods JSM 01 Weighting Methods in Survey Sampling Chiao-hih Chang Ferry Butar Butar Abstrat It is said that a well-designed survey an best prevent nonresponse. However, no matter
Setion on Survey Researh Methods JSM 01 Weighting Methods in Survey Sampling Chiao-hih Chang Ferry Butar Butar Abstrat It is said that a well-designed survey an best prevent nonresponse. However, no matter
THE PERFORMANCE OF TRANSIT TIME FLOWMETERS IN HEATED GAS MIXTURES
 Proeedings of FEDSM 98 998 ASME Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting June 2-25, 998 Washington DC FEDSM98-529 THE PERFORMANCE OF TRANSIT TIME FLOWMETERS IN HEATED GAS MIXTURES John D. Wright Proess
Proeedings of FEDSM 98 998 ASME Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting June 2-25, 998 Washington DC FEDSM98-529 THE PERFORMANCE OF TRANSIT TIME FLOWMETERS IN HEATED GAS MIXTURES John D. Wright Proess
A Three-Hybrid Treatment Method of the Compressor's Characteristic Line in Performance Prediction of Power Systems
 A Three-Hybrid Treatment Method of the Compressor's Charateristi Line in Performane Predition of Power Systems A Three-Hybrid Treatment Method of the Compressor's Charateristi Line in Performane Predition
A Three-Hybrid Treatment Method of the Compressor's Charateristi Line in Performane Predition of Power Systems A Three-Hybrid Treatment Method of the Compressor's Charateristi Line in Performane Predition
 Chapter 6 A N ovel Solution Of Linear Congruenes Proeedings NCUR IX. (1995), Vol. II, pp. 708{712 Jerey F. Gold Department of Mathematis, Department of Physis University of Utah Salt Lake City, Utah 84112
Chapter 6 A N ovel Solution Of Linear Congruenes Proeedings NCUR IX. (1995), Vol. II, pp. 708{712 Jerey F. Gold Department of Mathematis, Department of Physis University of Utah Salt Lake City, Utah 84112
Interpretable Fuzzy Modeling using Multi-Objective Immune- Inspired Optimization Algorithms
 Interpretable Fuzzy Modeling using Multi-Objetive Immune- Inspired Optimization Algorithms Jun Chen, Mahdi Mahfouf Abstrat In this paper, an immune inspired multi-objetive fuzzy modeling (IMOFM) mehanism
Interpretable Fuzzy Modeling using Multi-Objetive Immune- Inspired Optimization Algorithms Jun Chen, Mahdi Mahfouf Abstrat In this paper, an immune inspired multi-objetive fuzzy modeling (IMOFM) mehanism
Performance Analysis of IEEE 802.11 in Multi-hop Wireless Networks
 Performane Analysis of IEEE 80.11 in Multi-hop Wireless Networks Lan Tien Nguyen 1, Razvan Beuran,1, Yoihi Shinoda 1, 1 Japan Advaned Institute of Siene and Tehnology, 1-1 Asahidai, Nomi, Ishikawa, 93-19
Performane Analysis of IEEE 80.11 in Multi-hop Wireless Networks Lan Tien Nguyen 1, Razvan Beuran,1, Yoihi Shinoda 1, 1 Japan Advaned Institute of Siene and Tehnology, 1-1 Asahidai, Nomi, Ishikawa, 93-19
An integrated optimization model of a Closed- Loop Supply Chain under uncertainty
 ISSN 1816-6075 (Print), 1818-0523 (Online) Journal of System and Management Sienes Vol. 2 (2012) No. 3, pp. 9-17 An integrated optimization model of a Closed- Loop Supply Chain under unertainty Xiaoxia
ISSN 1816-6075 (Print), 1818-0523 (Online) Journal of System and Management Sienes Vol. 2 (2012) No. 3, pp. 9-17 An integrated optimization model of a Closed- Loop Supply Chain under unertainty Xiaoxia
User s Guide VISFIT: a computer tool for the measurement of intrinsic viscosities
 File:UserVisfit_2.do User s Guide VISFIT: a omputer tool for the measurement of intrinsi visosities Version 2.a, September 2003 From: Multiple Linear Least-Squares Fits with a Common Interept: Determination
File:UserVisfit_2.do User s Guide VISFIT: a omputer tool for the measurement of intrinsi visosities Version 2.a, September 2003 From: Multiple Linear Least-Squares Fits with a Common Interept: Determination
Discovering Trends in Large Datasets Using Neural Networks
 Disovering Trends in Large Datasets Using Neural Networks Khosrow Kaikhah, Ph.D. and Sandesh Doddameti Department of Computer Siene Texas State University San Maros, Texas 78666 Abstrat. A novel knowledge
Disovering Trends in Large Datasets Using Neural Networks Khosrow Kaikhah, Ph.D. and Sandesh Doddameti Department of Computer Siene Texas State University San Maros, Texas 78666 Abstrat. A novel knowledge
A Keyword Filters Method for Spam via Maximum Independent Sets
 Vol. 7, No. 3, May, 213 A Keyword Filters Method for Spam via Maximum Independent Sets HaiLong Wang 1, FanJun Meng 1, HaiPeng Jia 2, JinHong Cheng 3 and Jiong Xie 3 1 Inner Mongolia Normal University 2
Vol. 7, No. 3, May, 213 A Keyword Filters Method for Spam via Maximum Independent Sets HaiLong Wang 1, FanJun Meng 1, HaiPeng Jia 2, JinHong Cheng 3 and Jiong Xie 3 1 Inner Mongolia Normal University 2
REDUCTION FACTOR OF FEEDING LINES THAT HAVE A CABLE AND AN OVERHEAD SECTION
 C I E 17 th International Conferene on Eletriity istriution Barelona, 1-15 May 003 EUCTION FACTO OF FEEING LINES THAT HAVE A CABLE AN AN OVEHEA SECTION Ljuivoje opovi J.. Elektrodistriuija - Belgrade -
C I E 17 th International Conferene on Eletriity istriution Barelona, 1-15 May 003 EUCTION FACTO OF FEEING LINES THAT HAVE A CABLE AN AN OVEHEA SECTION Ljuivoje opovi J.. Elektrodistriuija - Belgrade -
Relativity in the Global Positioning System
 Relativity in the Global Positioning System Neil Ashby Department of Physis,UCB 390 University of Colorado, Boulder, CO 80309-00390 NIST Affiliate Email: [email protected] July 0, 006 AAPT workshop
Relativity in the Global Positioning System Neil Ashby Department of Physis,UCB 390 University of Colorado, Boulder, CO 80309-00390 NIST Affiliate Email: [email protected] July 0, 006 AAPT workshop
Behavior Analysis-Based Learning Framework for Host Level Intrusion Detection
 Behavior Analysis-Based Learning Framework for Host Level Intrusion Detetion Haiyan Qiao, Jianfeng Peng, Chuan Feng, Jerzy W. Rozenblit Eletrial and Computer Engineering Department University of Arizona
Behavior Analysis-Based Learning Framework for Host Level Intrusion Detetion Haiyan Qiao, Jianfeng Peng, Chuan Feng, Jerzy W. Rozenblit Eletrial and Computer Engineering Department University of Arizona
A Robust Optimization Approach to Dynamic Pricing and Inventory Control with no Backorders
 A Robust Optimization Approah to Dynami Priing and Inventory Control with no Bakorders Elodie Adida and Georgia Perakis July 24 revised July 25 Abstrat In this paper, we present a robust optimization formulation
A Robust Optimization Approah to Dynami Priing and Inventory Control with no Bakorders Elodie Adida and Georgia Perakis July 24 revised July 25 Abstrat In this paper, we present a robust optimization formulation
Open and Extensible Business Process Simulator
 UNIVERSITY OF TARTU FACULTY OF MATHEMATICS AND COMPUTER SCIENCE Institute of Computer Siene Karl Blum Open and Extensible Business Proess Simulator Master Thesis (30 EAP) Supervisors: Luiano Garía-Bañuelos,
UNIVERSITY OF TARTU FACULTY OF MATHEMATICS AND COMPUTER SCIENCE Institute of Computer Siene Karl Blum Open and Extensible Business Proess Simulator Master Thesis (30 EAP) Supervisors: Luiano Garía-Bañuelos,
In order to be able to design beams, we need both moments and shears. 1. Moment a) From direct design method or equivalent frame method
 BEAM DESIGN In order to be able to design beams, we need both moments and shears. 1. Moment a) From diret design method or equivalent frame method b) From loads applied diretly to beams inluding beam weight
BEAM DESIGN In order to be able to design beams, we need both moments and shears. 1. Moment a) From diret design method or equivalent frame method b) From loads applied diretly to beams inluding beam weight
i_~f e 1 then e 2 else e 3
 A PROCEDURE MECHANISM FOR BACKTRACK PROGRAMMING* David R. HANSON + Department o Computer Siene, The University of Arizona Tuson, Arizona 85721 One of the diffiulties in using nondeterministi algorithms
A PROCEDURE MECHANISM FOR BACKTRACK PROGRAMMING* David R. HANSON + Department o Computer Siene, The University of Arizona Tuson, Arizona 85721 One of the diffiulties in using nondeterministi algorithms
Optimal Online Buffer Scheduling for Block Devices *
 Optimal Online Buffer Sheduling for Blok Devies * ABSTRACT Anna Adamaszek Department of Computer Siene and Centre for Disrete Mathematis and its Appliations (DIMAP) University of Warwik, Coventry, UK [email protected]
Optimal Online Buffer Sheduling for Blok Devies * ABSTRACT Anna Adamaszek Department of Computer Siene and Centre for Disrete Mathematis and its Appliations (DIMAP) University of Warwik, Coventry, UK [email protected]
Deadline-based Escalation in Process-Aware Information Systems
 Deadline-based Esalation in Proess-Aware Information Systems Wil M.P. van der Aalst 1,2, Mihael Rosemann 2, Marlon Dumas 2 1 Department of Tehnology Management Eindhoven University of Tehnology, The Netherlands
Deadline-based Esalation in Proess-Aware Information Systems Wil M.P. van der Aalst 1,2, Mihael Rosemann 2, Marlon Dumas 2 1 Department of Tehnology Management Eindhoven University of Tehnology, The Netherlands
A Survey of Usability Evaluation in Virtual Environments: Classi cation and Comparison of Methods
 Doug A. Bowman [email protected] Department of Computer Siene Virginia Teh Joseph L. Gabbard Deborah Hix [ jgabbard, hix]@vt.edu Systems Researh Center Virginia Teh A Survey of Usability Evaluation in Virtual
Doug A. Bowman [email protected] Department of Computer Siene Virginia Teh Joseph L. Gabbard Deborah Hix [ jgabbard, hix]@vt.edu Systems Researh Center Virginia Teh A Survey of Usability Evaluation in Virtual
Programming Basics - FORTRAN 77 http://www.physics.nau.edu/~bowman/phy520/f77tutor/tutorial_77.html
 CWCS Workshop May 2005 Programming Basis - FORTRAN 77 http://www.physis.nau.edu/~bowman/phy520/f77tutor/tutorial_77.html Program Organization A FORTRAN program is just a sequene of lines of plain text.
CWCS Workshop May 2005 Programming Basis - FORTRAN 77 http://www.physis.nau.edu/~bowman/phy520/f77tutor/tutorial_77.html Program Organization A FORTRAN program is just a sequene of lines of plain text.
On Some Mathematics for Visualizing High Dimensional Data
 On Some Mathematis for Visualizing High Dimensional Data Edward J. Wegman Jeffrey L. Solka Center for Computational Statistis George Mason University Fairfax, VA 22030 This paper is dediated to Professor
On Some Mathematis for Visualizing High Dimensional Data Edward J. Wegman Jeffrey L. Solka Center for Computational Statistis George Mason University Fairfax, VA 22030 This paper is dediated to Professor
An Efficient Network Traffic Classification Based on Unknown and Anomaly Flow Detection Mechanism
 An Effiient Network Traffi Classifiation Based on Unknown and Anomaly Flow Detetion Mehanism G.Suganya.M.s.,B.Ed 1 1 Mphil.Sholar, Department of Computer Siene, KG College of Arts and Siene,Coimbatore.
An Effiient Network Traffi Classifiation Based on Unknown and Anomaly Flow Detetion Mehanism G.Suganya.M.s.,B.Ed 1 1 Mphil.Sholar, Department of Computer Siene, KG College of Arts and Siene,Coimbatore.
NOMCLUST: AN R PACKAGE FOR HIERARCHICAL CLUSTERING OF OBJECTS CHARACTERIZED BY NOMINAL VARIABLES
 The 9 th International Days of Statistis and Eonomis, Prague, September 10-1, 015 NOMCLUST: AN R PACKAGE FOR HIERARCHICAL CLUSTERING OF OBJECTS CHARACTERIZED BY NOMINAL VARIABLES Zdeněk Šul Hana Řezanková
The 9 th International Days of Statistis and Eonomis, Prague, September 10-1, 015 NOMCLUST: AN R PACKAGE FOR HIERARCHICAL CLUSTERING OF OBJECTS CHARACTERIZED BY NOMINAL VARIABLES Zdeněk Šul Hana Řezanková
Impedance Method for Leak Detection in Zigzag Pipelines
 10.478/v10048-010-0036-0 MEASUREMENT SCIENCE REVIEW, Volume 10, No. 6, 010 Impedane Method for Leak Detetion in igzag Pipelines A. Lay-Ekuakille 1, P. Vergallo 1, A. Trotta 1 Dipartimento d Ingegneria
10.478/v10048-010-0036-0 MEASUREMENT SCIENCE REVIEW, Volume 10, No. 6, 010 Impedane Method for Leak Detetion in igzag Pipelines A. Lay-Ekuakille 1, P. Vergallo 1, A. Trotta 1 Dipartimento d Ingegneria
Agile ALM White Paper: Redefining ALM with Five Key Practices
 Agile ALM White Paper: Redefining ALM with Five Key Praties by Ethan Teng, Cyndi Mithell and Chad Wathington 2011 ThoughtWorks ln. All rights reserved www.studios.thoughtworks.om Introdution The pervasiveness
Agile ALM White Paper: Redefining ALM with Five Key Praties by Ethan Teng, Cyndi Mithell and Chad Wathington 2011 ThoughtWorks ln. All rights reserved www.studios.thoughtworks.om Introdution The pervasiveness
CHAPTER J DESIGN OF CONNECTIONS
 J-1 CHAPTER J DESIGN OF CONNECTIONS INTRODUCTION Chapter J of the addresses the design and heking of onnetions. The hapter s primary fous is the design of welded and bolted onnetions. Design requirements
J-1 CHAPTER J DESIGN OF CONNECTIONS INTRODUCTION Chapter J of the addresses the design and heking of onnetions. The hapter s primary fous is the design of welded and bolted onnetions. Design requirements
SLA-based Resource Allocation for Software as a Service Provider (SaaS) in Cloud Computing Environments
 2 th IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Cluster, Cloud and Grid Computing SLA-based Resoure Alloation for Software as a Servie Provider (SaaS) in Cloud Computing Environments Linlin Wu, Saurabh Kumar
2 th IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Cluster, Cloud and Grid Computing SLA-based Resoure Alloation for Software as a Servie Provider (SaaS) in Cloud Computing Environments Linlin Wu, Saurabh Kumar
Trade Information, Not Spectrum: A Novel TV White Space Information Market Model
 Trade Information, Not Spetrum: A Novel TV White Spae Information Market Model Yuan Luo, Lin Gao, and Jianwei Huang 1 Abstrat In this paper, we propose a novel information market for TV white spae networks,
Trade Information, Not Spetrum: A Novel TV White Spae Information Market Model Yuan Luo, Lin Gao, and Jianwei Huang 1 Abstrat In this paper, we propose a novel information market for TV white spae networks,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON DEPENDABLE AND SECURE COMPUTING, VOL. 9, NO. 3, MAY/JUNE 2012 401
 IEEE TRASACTIOS O DEPEDABLE AD SECURE COMPUTIG, VOL. 9, O. 3, MAY/JUE 2012 401 Mitigating Distributed Denial of Servie Attaks in Multiparty Appliations in the Presene of Clok Drifts Zhang Fu, Marina Papatriantafilou,
IEEE TRASACTIOS O DEPEDABLE AD SECURE COMPUTIG, VOL. 9, O. 3, MAY/JUE 2012 401 Mitigating Distributed Denial of Servie Attaks in Multiparty Appliations in the Presene of Clok Drifts Zhang Fu, Marina Papatriantafilou,
To the Graduate Council:
 o the Graduate Counil: I am submitting herewith a dissertation written by Yan Xu entitled A Generalized Instantaneous Nonative Power heory for Parallel Nonative Power Compensation. I have examined the
o the Graduate Counil: I am submitting herewith a dissertation written by Yan Xu entitled A Generalized Instantaneous Nonative Power heory for Parallel Nonative Power Compensation. I have examined the
10.1 The Lorentz force law
 Sott Hughes 10 Marh 2005 Massahusetts Institute of Tehnology Department of Physis 8.022 Spring 2004 Leture 10: Magneti fore; Magneti fields; Ampere s law 10.1 The Lorentz fore law Until now, we have been
Sott Hughes 10 Marh 2005 Massahusetts Institute of Tehnology Department of Physis 8.022 Spring 2004 Leture 10: Magneti fore; Magneti fields; Ampere s law 10.1 The Lorentz fore law Until now, we have been
Chapter 1: Introduction
 Chapter 1: Introdution 1.1 Pratial olumn base details in steel strutures 1.1.1 Pratial olumn base details Every struture must transfer vertial and lateral loads to the supports. In some ases, beams or
Chapter 1: Introdution 1.1 Pratial olumn base details in steel strutures 1.1.1 Pratial olumn base details Every struture must transfer vertial and lateral loads to the supports. In some ases, beams or
Soft-Edge Flip-flops for Improved Timing Yield: Design and Optimization
 Soft-Edge Flip-flops for Improved Timing Yield: Design and Optimization Abstrat Parameter variations ause high yield losses due to their large impat on iruit delay. In this paper, we propose the use of
Soft-Edge Flip-flops for Improved Timing Yield: Design and Optimization Abstrat Parameter variations ause high yield losses due to their large impat on iruit delay. In this paper, we propose the use of
Findings and Recommendations
 Contrating Methods and Administration Findings and Reommendations Finding 9-1 ESD did not utilize a formal written pre-qualifiations proess for seleting experiened design onsultants. ESD hose onsultants
Contrating Methods and Administration Findings and Reommendations Finding 9-1 ESD did not utilize a formal written pre-qualifiations proess for seleting experiened design onsultants. ESD hose onsultants
Context-Sensitive Adjustments of Cognitive Control: Conflict-Adaptation Effects Are Modulated by Processing Demands of the Ongoing Task
 Journal of Experimental Psyhology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition 2008, Vol. 34, No. 3, 712 718 Copyright 2008 by the Amerian Psyhologial Assoiation 0278-7393/08/$12.00 DOI: 10.1037/0278-7393.34.3.712
Journal of Experimental Psyhology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition 2008, Vol. 34, No. 3, 712 718 Copyright 2008 by the Amerian Psyhologial Assoiation 0278-7393/08/$12.00 DOI: 10.1037/0278-7393.34.3.712
tr(a + B) = tr(a) + tr(b) tr(ca) = c tr(a)
 Chapter 3 Determinant 31 The Determinant Funtion We follow an intuitive approah to introue the efinition of eterminant We alreay have a funtion efine on ertain matries: the trae The trae assigns a numer
Chapter 3 Determinant 31 The Determinant Funtion We follow an intuitive approah to introue the efinition of eterminant We alreay have a funtion efine on ertain matries: the trae The trae assigns a numer
Learning Curves and Stochastic Models for Pricing and Provisioning Cloud Computing Services
 T Learning Curves and Stohasti Models for Priing and Provisioning Cloud Computing Servies Amit Gera, Cathy H. Xia Dept. of Integrated Systems Engineering Ohio State University, Columbus, OH 4310 {gera.,
T Learning Curves and Stohasti Models for Priing and Provisioning Cloud Computing Servies Amit Gera, Cathy H. Xia Dept. of Integrated Systems Engineering Ohio State University, Columbus, OH 4310 {gera.,
Software Ecosystems: From Software Product Management to Software Platform Management
 Software Eosystems: From Software Produt Management to Software Platform Management Slinger Jansen, Stef Peeters, and Sjaak Brinkkemper Department of Information and Computing Sienes Utreht University,
Software Eosystems: From Software Produt Management to Software Platform Management Slinger Jansen, Stef Peeters, and Sjaak Brinkkemper Department of Information and Computing Sienes Utreht University,
Relativistic Kinematics -a project in Analytical mechanics Karlstad University
 Relativisti Kinematis -a projet in Analytial mehanis Karlstad University Carl Stigner 1th January 6 Abstrat The following text is a desription of some of the ontent in hapter 7 in the textbook Classial
Relativisti Kinematis -a projet in Analytial mehanis Karlstad University Carl Stigner 1th January 6 Abstrat The following text is a desription of some of the ontent in hapter 7 in the textbook Classial
RISK-BASED IN SITU BIOREMEDIATION DESIGN JENNINGS BRYAN SMALLEY. A.B., Washington University, 1992 THESIS. Urbana, Illinois
 RISK-BASED IN SITU BIOREMEDIATION DESIGN BY JENNINGS BRYAN SMALLEY A.B., Washington University, 1992 THESIS Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Siene in Environmental
RISK-BASED IN SITU BIOREMEDIATION DESIGN BY JENNINGS BRYAN SMALLEY A.B., Washington University, 1992 THESIS Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Siene in Environmental
From a strategic view to an engineering view in a digital enterprise
 Digital Enterprise Design & Management 2013 February 11-12, 2013 Paris From a strategi view to an engineering view in a digital enterprise The ase of a multi-ountry Telo Hervé Paault Orange Abstrat In
Digital Enterprise Design & Management 2013 February 11-12, 2013 Paris From a strategi view to an engineering view in a digital enterprise The ase of a multi-ountry Telo Hervé Paault Orange Abstrat In
OpenSession: SDN-based Cross-layer Multi-stream Management Protocol for 3D Teleimmersion
 : SN-based ross-layer Multi-stream Management Protool for 3 Teleimmersion hsan refin Raoul Rivas Rehana Tabassum Klara Nahrstedt University of Illinois at Urbana-hampaign, Urbana, IL {marefin2, trivas,
: SN-based ross-layer Multi-stream Management Protool for 3 Teleimmersion hsan refin Raoul Rivas Rehana Tabassum Klara Nahrstedt University of Illinois at Urbana-hampaign, Urbana, IL {marefin2, trivas,
university of illinois library AT URBANA-CHAMPAIGN BOOKSTACKS
 university of illinois library AT URBANA-CHAMPAIGN BOOKSTACKS CENTRAL CIRCULATION BOOKSTACKS The person harging this material is responsible for its renewal or its return to the library from whih it was
university of illinois library AT URBANA-CHAMPAIGN BOOKSTACKS CENTRAL CIRCULATION BOOKSTACKS The person harging this material is responsible for its renewal or its return to the library from whih it was
International Journal of Supply and Operations Management. Mathematical modeling for EOQ inventory system with advance payment and fuzzy Parameters
 nternational Journal of Supply and Operations Management JSOM November 0, Volume, ssue 3, pp. 60-78 SSN-Print: 383-359 SSN-Online: 383-55 www.ijsom.om Mathematial modeling for EOQ inventory system with
nternational Journal of Supply and Operations Management JSOM November 0, Volume, ssue 3, pp. 60-78 SSN-Print: 383-359 SSN-Online: 383-55 www.ijsom.om Mathematial modeling for EOQ inventory system with
Asymmetric Error Correction and Flash-Memory Rewriting using Polar Codes
 1 Asymmetri Error Corretion and Flash-Memory Rewriting using Polar Codes Eyal En Gad, Yue Li, Joerg Kliewer, Mihael Langberg, Anxiao (Andrew) Jiang and Jehoshua Bruk Abstrat We propose effiient oding shemes
1 Asymmetri Error Corretion and Flash-Memory Rewriting using Polar Codes Eyal En Gad, Yue Li, Joerg Kliewer, Mihael Langberg, Anxiao (Andrew) Jiang and Jehoshua Bruk Abstrat We propose effiient oding shemes
Research on Virtual Vehicle Driven with Vision
 I.J. Information Tehnolog and Computer Siene, 2011, 4, 29-35 Published Online August 2011 in MECS http://.mes-press.org/) Researh on Virtual Vehile Driven ith Vision Youquan Liu and Yu Cui Shool of Information
I.J. Information Tehnolog and Computer Siene, 2011, 4, 29-35 Published Online August 2011 in MECS http://.mes-press.org/) Researh on Virtual Vehile Driven ith Vision Youquan Liu and Yu Cui Shool of Information
RATING SCALES FOR NEUROLOGISTS
 RATING SCALES FOR NEUROLOGISTS J Hobart iv22 WHY Correspondene to: Dr Jeremy Hobart, Department of Clinial Neurosienes, Peninsula Medial Shool, Derriford Hospital, Plymouth PL6 8DH, UK; Jeremy.Hobart@
RATING SCALES FOR NEUROLOGISTS J Hobart iv22 WHY Correspondene to: Dr Jeremy Hobart, Department of Clinial Neurosienes, Peninsula Medial Shool, Derriford Hospital, Plymouth PL6 8DH, UK; Jeremy.Hobart@
Deduplication with Block-Level Content-Aware Chunking for Solid State Drives (SSDs)
 23 IEEE International Conferene on High Performane Computing and Communiations & 23 IEEE International Conferene on Embedded and Ubiquitous Computing Dedupliation with Blok-Level Content-Aware Chunking
23 IEEE International Conferene on High Performane Computing and Communiations & 23 IEEE International Conferene on Embedded and Ubiquitous Computing Dedupliation with Blok-Level Content-Aware Chunking
To Coordinate Or Not To Coordinate? Wide-Area Traffic Management for Data Centers
 To Coordinate Or Not To Coordinate? Wide-Area Traffi Management for Data Centers Srinivas Narayana, Joe Wenjie Jiang, Jennifer Rexford, Mung Chiang Department of Computer Siene, and Department of Eletrial
To Coordinate Or Not To Coordinate? Wide-Area Traffi Management for Data Centers Srinivas Narayana, Joe Wenjie Jiang, Jennifer Rexford, Mung Chiang Department of Computer Siene, and Department of Eletrial
Outline. Planning. Search vs. Planning. Search vs. Planning Cont d. Search vs. planning. STRIPS operators Partial-order planning.
 Outline Searh vs. planning Planning STRIPS operators Partial-order planning Chapter 11 Artifiial Intelligene, lp4 2005/06, Reiner Hähnle, partly based on AIMA Slides Stuart Russell and Peter Norvig, 1998
Outline Searh vs. planning Planning STRIPS operators Partial-order planning Chapter 11 Artifiial Intelligene, lp4 2005/06, Reiner Hähnle, partly based on AIMA Slides Stuart Russell and Peter Norvig, 1998
SHAFTS: TORSION LOADING AND DEFORMATION
 ECURE hird Edition SHAFS: ORSION OADING AND DEFORMAION A. J. Clark Shool of Engineering Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering 6 Chapter 3.1-3.5 by Dr. Ibrahim A. Assakkaf SPRING 2003 ENES 220
ECURE hird Edition SHAFS: ORSION OADING AND DEFORMAION A. J. Clark Shool of Engineering Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering 6 Chapter 3.1-3.5 by Dr. Ibrahim A. Assakkaf SPRING 2003 ENES 220
Measurement of Powder Flow Properties that relate to Gravity Flow Behaviour through Industrial Processing Lines
 Measurement of Powder Flow Properties that relate to Gravity Flow ehaviour through Industrial Proessing Lines A typial industrial powder proessing line will inlude several storage vessels (e.g. bins, bunkers,
Measurement of Powder Flow Properties that relate to Gravity Flow ehaviour through Industrial Proessing Lines A typial industrial powder proessing line will inlude several storage vessels (e.g. bins, bunkers,
THE EFFECT OF WATER VAPOR ON COUNTERFLOW DIFFUSION FLAMES
 THE EFFECT OF WATER VAPOR ON COUNTERFLOW DIFFUSION FLAMES by Jaeil Suh and Arvind Atreya Combustion and Heat Tkansfer Laboratory Department of Mehanial Engineering and Applied Mehanis The University of
THE EFFECT OF WATER VAPOR ON COUNTERFLOW DIFFUSION FLAMES by Jaeil Suh and Arvind Atreya Combustion and Heat Tkansfer Laboratory Department of Mehanial Engineering and Applied Mehanis The University of
REVISTA INVESTIGACIÓN OPERACIONAL Vol. 28, No.1, 4-16, 2007
 REVISTA INVESTIGACIÓN OPERACIONAL Vol. 28 No.1 4-16 2007 ALGORITHMS FOR MEAN-RISK STOCHASTIC INTEGER PROGRAMS IN ENERGY Rüdiger Shultz Frederike Neise Department of Mathematis University of Duisburg-Essen
REVISTA INVESTIGACIÓN OPERACIONAL Vol. 28 No.1 4-16 2007 ALGORITHMS FOR MEAN-RISK STOCHASTIC INTEGER PROGRAMS IN ENERGY Rüdiger Shultz Frederike Neise Department of Mathematis University of Duisburg-Essen
A Comparison of Service Quality between Private and Public Hospitals in Thailand
 International Journal of Business and Soial Siene Vol. 4 No. 11; September 2013 A Comparison of Servie Quality between Private and Hospitals in Thailand Khanhitpol Yousapronpaiboon, D.B.A. Assistant Professor
International Journal of Business and Soial Siene Vol. 4 No. 11; September 2013 A Comparison of Servie Quality between Private and Hospitals in Thailand Khanhitpol Yousapronpaiboon, D.B.A. Assistant Professor
HEAT CONDUCTION. q A q T
 HEAT CONDUCTION When a temperature gradient eist in a material, heat flows from the high temperature region to the low temperature region. The heat transfer mehanism is referred to as ondution and the
HEAT CONDUCTION When a temperature gradient eist in a material, heat flows from the high temperature region to the low temperature region. The heat transfer mehanism is referred to as ondution and the
