DiNP Dose-Response Studies:
|
|
|
- Allison Craig
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DiNP Dose-Response Studies: Gestation PK and Developmental Effects Postnatal Effects Final Project Summary October 2011 Rebecca Clewell, PhD Research Investigator Institute for Chemical Safety Sciences Funding provided by ExxonMobil Chemical Company
2 Assessing endocrine susceptibility Life cycle assessment e.g. rodent multigeneration study Study start F 0 Mating F 0 and F 1 Birth F 1 and F 2 Six Androgen mediated endpoint assessments in males Decreased Testosterone Synthesis Cryptorchidism and Hypospadias Ano-genital Distance Nipple Retention Sexual maturity F 1 Parents Removed F 0 and F 1 Weaning F 1 and F 2 Sexual Organ Weight Changes Decreased Sperm Production Greatest androgen susceptibility Parental generation (F 0 ) First generation (F 1 ) Second generation (F 2 ) Study end F 2 1
3 DiNP studies cover window of susceptibility life cycle (rodent) Mating Developmental toxicity Waterman et al. Reproductive Toxicology, Vol. 13, No. 2, pp , 1999 Birth DiNP Kinetics & Effects Study 1 End of life DiNP Extended Effects Study 1 (evaluation phase continues beyond dosing window, to PND 49) Weaning Sexual maturity = timepoint to assess androgen endpoint = window of susceptibility 1 New studies conducted by The Hamner Institutes for Health Sciences 2
4 Gestation Study Design Objective: comprehensively evaluate effect of fetal exposure to DiNP on the developing male rat reproductive system, determine DiNP kinetics in maternal and fetal compartments and to develop a physiologically based pharmacokinetic model DiNP exposure Oral gavage GD , 50, 250, and 750 mg/kg/day Time-points: 0.5, 1, 2, 6, 12, 24 hrs after final dose Animals 144 pregnant Sprague-Dawley rats (Charles River) ~ 1,700 pups n = 4 dams/time-point/dose (kinetic data) n = 8 dams/time-point/dose (effect data) Developmental Endpoints Hormone Testes testosterone Morphology AGD, testis histopathology 3
5 Gestation Study 1) Developmental Effects GD 19, 20; 2hr, 24 hr post-dose 2) Pharmacokinetics GD 19; hr post-dose 3) PBPK Model for maternal and fetal dosimetry 4
6 Developmental Effects- Testosterone 2 hr post-dose 24 hr post-dose * Versus concurrent controls * Versus concurrent controls Clear no-observed effect level for DiNP-induced decrease in testosterone at 50 mg/kg/day Calculated ED 50 DiNP = 389 mg/kg/day DBP = 39 mg/kg/day 1 DEHP = 100 mg/kg/day 2 1 DBP data from Mylchreest et al., 1999 (PND 2) 2 DEHP data from Borch et al., 2004; Gray et al., 2009 (PND 2) 5
7 Developmental Effects- Anogenital Distance (AGD) Absolute AGD Scaled AGD No change in absolute or scaled AGD up to 750 mg/kg/day DiNP NOEL DiNP = >750 mg/kg/day DBP = 100 mg/kg/day 1 DEHP = 100 mg/kg/day 2 LOEL DiNP = no LOEL identified DBP = 250 mg/kg/day 1 DEHP = 300 mg/kg/day 2 1 DBP data from Mylchreest et al., 1999 (PND 2) 2 DEHP data from Gray et al., 2009 (PND 2) 6
8 Developmental Effects- Testis Histopathology Seminiferous Tubule (ST) Diameter a Multinucleated Gonocytes b No change in ST diameter ST diameter NOEL DiNP = >750 mg/kg/day NOEL DBP = 30 mg/kg/day LOEL DBP = 50 mg/kg/day a Evaluated quantitatively using ImagePro Software at The Hamner Institutes b Evaluated by Gabrielle Willson, Experimental Pathology Laboratories, Inc. Increase in #MNGs/section at 250 and 750 mg/kg/day DiNP Unclear biological significance, although not testosterone dependent Multinucleated Gonocytes NOEL DiNP = 50 mg/kg/day LOEL DiNP = 250 mg/kg/day NOEL DBP = 50 mg/kg/day LOEL DBP = 100 mg/kg/day 7
9 Developmental Effects- Testis Histopathology* DiNP Dose (mg/kg/day) Control Number of animals examined # Animals with MNGs * # Animals with large Leydig cell aggregates # Animals with increased number of gonocytes * Statistically significant increase in the number of animals with multinucleated gonocytes (MNGs) with 750 mg/kg/day based on mouse studies, effect not considered testosterone dependent Statistically significant increase in the number of animals with large leydig cell aggregates with 750 mg/kg/day DiNP * Evaluated in blinded manner by Dr. Dianne Creasy, Huntingdon Life Sciences, Inc. 8
10 PPAR Effects- Fractional Liver Weight (Maternal Rat) As expected, increase in fractional liver weight observed with 250 and 750 mg/kg/day DiNP likely due to peroxisome proliferation 1 NOEL DiNP = 50 mg/kg/day DBP = 200 mg/kg/day 2 DEHP = 50 mg/kg/day 2 LOEL DiNP = 250 mg/kg/day DBP = 1000 mg/kg/day 1 DEHP = 200 mg/kg/day 1 1 Mode of action (i.e. activation of peroxisome proliferator activated receptor alpha (PPARα)) in development of rodent liver tumors has been characterized and demonstrated not active in humans 2 DBP and DEHP data from Seo et al., 2004 (male SD) 9
11 Gestation Study DiNP Pharmacokinetics Preparation of MiNP-glucuronide standard Glucuronide conjugation performed using human liver microsomes Isolation of glucuronide by liquid chromatography Confirmation of MiNP-G by NMR spectroscopy Measure MiNP-G concentration by HPLC-UV/Vis Metabolite Analysis LC-MS/MS Atmospheric pressure ionization Selective ion monitoring/product ion identification Quantitation by isotope dilution, using 13 C-internal standards Tissues evaluated Maternal plasma Pup plasma Urine Maternal liver, placenta Fetal testes, amniotic fluid 10
12 Maternal Plasma Fetal Plasma Concentration of metabolites in maternal plasma: MCiOP> MiNP> MHiNP> MOiNP> MiNP-G MiNP-G detected at all doses indicating that glucuronideconjugation occurs in the rat Concentration of metabolites in fetal plasma: MCiOP> MiNP> MHiNP, MOiNP,and MiNP-G MiNP-G generally higher than the maternal plasma 11
13 Plasma PK Analysis - MiNP Cmax AUC Cmax ( M) Maternal Plasma Fetal Plasma AUC inf ( M*hr) DiNP Dose (mg/kg/day) DiNP Dose (mg/kg/day) 5.0 T 1/ Ke T 1/2 (hr) 4.0 k e (hr -r ) DiNP Dose (mg/kg/day) DiNP Dose (mg/kg/day) Non-linearity in C MAX and AUC, but not K e or T 1/2, suggests absorption limitation 12
14 Maternal Urine Metabolites MCiOP >> MHiNP > MOiNP >>> MiNP, MiNP-G MiNP and MiNP-G are present Account for < 0.1% of dose. 13
15 PBPK Model for DiNP Preliminary Analysis DEHP Model Structure Glucuronidation turned off Combined oxidative metabolites (MiNP-OX = MHiNP + MOiNP + MCiNP) First run used DEHP parameters No adjustments other than molecular weight Assume similar partitioning for MiNP and MiNP-OX Parameter adjustments for: Oral absorption: water emulsion (DEHP) vs. corn oil (DiNP) Placental transfer of ox metabolites (not measured with DEHP) 14
16 Phthalate PBPK Model Structure MiNP-OX MiNP-G MiNP-G MiNP Liver GI Wall GI Lumen DiNP DiNP Feces Richly Perfused Slowly Perfused MiNP-G Placenta Fetus Amniotic Fluid Testes Maternal Plasma DiNP Urine 15
17 DiNP PBPK Model Initial fits MiNP MiNP-Ox Maternal Plasma Fetal Plasma Using DEHP parameters 16
18 Summary DiNP Gestation Study NOEL for DiNP effects 50 mg/kg/day: T inhibition, MNG, increased liver weight >750 mg/kg/day: AGD, ST diameter DiNP metabolites are present in the fetal testes Apparent saturation of oral absorption at highest dose (750 mg/kg/day) Evidenced by tissue metabolite data Causes plateau in liver wt and T inhibition Likely result of oral gavage administration DiNP is consistently less potent than DBP and DEHP where there is equivalent D-R data Similar kinetics to DEHP, indicates reduced potency of DiNP is due to pharmacodynamic differences 17
19 Postnatal Effects Study A Objective: determine a NOEL for effects on the developing male rat reproductive tract for di-isononyl phthalate (DiNP). Study Design Very large n for statistical significance: litters per treatment group Begin dietary dosing GD 12 Weigh dams and food 4x per week All necropsies and observations completely BLINDED PND 2: necropsy 1 male, cull to 8 pups/litter PND 21: euthanize all females PND 49: necropsy all males Endpoints PND 2 AGD, testes testosterone, testis/epididymis histopathology PND 14 AGD, nipple retention PND 49 AGD, nipple retention, testes testosterone Hypospadias (phallus malformation), preputial separation Morphology/tissue weight of 10 reprod. tissues, liver, kidney A Note: Results in this presentation are revised from previous presentationfollowing completed QA/QC review by The Hamner Quality Assurance Unit. Finalized results will be provided in the signed final report. 18
20 DiNP Dose Calculated from DiNP concentration (measured) and food consumption (measured) Target Dose 19
21 Postnatal Effects Study PND 2 Body Weight (males) Pup body weights were reduced in the ppm DiNP group on PND 2 20
22 Postnatal Effects Study PND 2 No statistically significant change in testicular testosterone content with DiNP No change in absolute or scaled AGD or seminiferous tubule diameter with DiNP Absolute and scaled AGD reduced with DBP AGD (scaled by BW 1/3 ) No change in relative testes or epididymis weights Multinucleated Gonocytes Increase in number of multinucleated gonocytes/section Incidence rate was low compared to DBP Unclear biological significance, although not testosterone dependent 21
23 Postnatal Effects- PND 2 Testis Histopathology* Control DiNP 760 ppm DiNP 3800 ppm DiNP ppm DBP 7600 ppm Number of animals examined # Animals with MNGs 1 2 7* 18** 21** # Animals with large Leydig cell aggregates # Animals with increased number of gonocytes ** 18** * Statistically significant increase in the number of animals with multinucleated gonocytes (MNGs) at 250 and 750 mg/kg/day DiNP based on mouse studies, effect not considered testosterone dependent Statistically significant increase in the number of animals with large leydig cell aggregates at 750 mg/kg/day DiNP * Evaluated in blinded manner by Dr. Dianne Creasy, Huntingdon Life Sciences, Inc. 22
24 Postnatal Effects Study Histopathology LC MNG MNG LC LC MNG MNG Control ppm DiNP 7600 ppm DBP MNG = Multinucleated gonocytes LC = Large Leydig cell aggregates 23
25 Postnatal Effects Study PND 14 Body Weight (males) Pup body weights were reduced in the 3800 and ppm DiNP groups on PND 14 24
26 Postnatal Effects Study PND 14 A Reduced AGD with ppm DiNP and DBP A AGD (scaled by BW 1/3 ) No increase in nipple retention with DiNP Increased nipples with DBP Nipples/Areolae A Revised from July 2011 slides Mean values shown for all control (n = 24) and DiNP (n = 20) or DBP (n = 21)exposed litters. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, *** p < 0.001, 1-way ANOVA with Dunnett s post-test, using the litter as the statistical unit 25
27 Postnatal Effects Study PND 49 AGD (scaled by BW 1/3 ) Nipple Retention Preputial Separation No effect on absolute or scaled AGD for either DiNP or DBP No increase in nipple retention with DiNP clear increase observed with DBP No effect on preputial separation with DiNP decrease in preputial separation with DBP 26
28 Postnatal Effects Study PND 49 Testis Histopathology* Control DiNP 760 ppm DiNP 3800 ppm DiNP ppm DBP 7600 ppm Number examined Tubular/rete dilation a Occasional atrophic tubules Tubular dysplasia a Multinucleate germ cells No statistically significant histopathologic alterations of the male rat testis were seen with DiNP A NOEL of ppm DiNP was established for alterations in male rat testis histopathology a Includes testes sampled for gross abnormalities (3 rats with tubular dilation, 1 rat with tubular dysplasia) *Evaluated in blinded manner by Dr. Dianne Creasy, Huntingdon Life Sciences, Inc. 27
29 Postnatal Effects Study PND 49 A Control 760 ppm DiNP 3800 ppm DiNP ppm DiNP 7600 ppm DBP Body Wt (g) Testes Pair Wt (% BW) Epididymides Pair Wt (%BW) Seminal Vesicles Wt (%BW) ** Ventral Prostate Wt (% BW) * Glans Penis Wt (%BW) LABC Wt (%BW) ** Cowpers Glands Wt (% BW) Adrenals Wt (% BW) Kidney Pair Wt (% BW) * Liver Wt (%BW) Ave Gubernacular Cord (mm) * A Table revised from July 2011 slides Mean values shown for all control (n = 25) and DiNP (n = 20) or DBP ( n = 21) exposed litters. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, 1-way ANOVA with Dunnett s post-test, using the litter as the statistical unit. 28
30 Postnatal Effects Study PND 49 Control 760 ppm DiNP 3800 ppm DiNP ppm DiNP 7600 ppm DBP Epididymal Agenesis (Incidence, total litters) 0/24 0/20 0/20 0/20 2/21 Incomplete Epididymis (Incidence, total litters) 0/24 2/20 0/20 0/20 8/21** Flaccid Epididymis (Incidence, total litters) 2/24 2/20 4/20 3/20 7/21* Undescended Testes (Incidence, total litters) 0/24 1/20 1/20 0/20 1/21 Atropic Testis/Epididymis (Incidence, total litters) 0/24 0/20 0/20 0/20 1/21 Mild/Slight Hypospadias (Incidence, total litters) 1/24 0/20 0/20 1/20 5/21 Exposed Os Penis (Incidence, total litters) 0/24 0/20 0/20 0/20 1/21 DiNP did not induce significant permanent alterations in epididymal development A NOEL of ppm DiNP was established for alterations in epididymal histopathology *p<0.05 using nesting approach to account for incidence data in multiple pups per litter (Haseman, 1979). 29
31 Comparison of effects - DiNP Postnatal Study A 500 mg/kg/day DBP No body weight effects > 250 mg/kg/day DiNP PND 2 body weight (750 mg/kg) PND 14 body weight ( 250 mg/kg) Nipple retention AGD (absolute and scaled) PND Phallus development Epididymal development Preputial separation Weight of 4 reproductive organs PND 14 reduced AGD (750 mg/kg) PND 2 ST some enlarged tubules PND 2 #MNG/section, large LC aggregates Effects were seen to be transient (not observed at PND 49) A Table revised from July 2011 slides No change in ST diameter PND 2 # MNG/section ( 250 mg/kg), large LC aggregates (750 mg/kg) Effects were seen to be transient (not observed at PND 49) 30
32 Conclusions The current studies on DiNP are the most well designed, comprehensive studies available for testing the effects of DiNP on the male reproductive tract A clear NOEL for effects on the developing male rat reproductive tract was established for DiNP of 760 ppm (50 mg/kg/day) A LOEL of 3800 ppm DiNP (250 mg/kg/day) based on the significant increase in MNGs on GD 20/PND 2, testosterone reduction on GD 19, and decreased pup body weight on PND 14 All effects were recoverable at later time points No evidence for DiNP-induced effects attributed to the rat phthalate syndrome at doses up to 750 mg/kg/day using global statistical analysis The role of testosterone as part of the mechanism leading to each of the male reproductive effects is unclear Data indicate that decreased testosterone may be necessary for the induction of some effects, but is clearly not sufficient at doses up to 750 mg DiNP/kg/day Although the kinetics of DiNP are similar to DEHP, the mechanism and/or potency of DiNP is different 31
Chemical Name: Acetone CAS: 67-64-1 Synonyms: propanone, β-ketopropane, dimethyl ketone, dimethylformaldehyde, DMK, 2-propanone, propan-2-one
 2011 Health Risk Limits for Groundwater Health Risk Assessment Unit, Environmental Health Division 651-201-4899 651-201-5797 TDD Web Publication Date: March 21, 2011 Chemical Name: Acetone CAS: 67-64-1
2011 Health Risk Limits for Groundwater Health Risk Assessment Unit, Environmental Health Division 651-201-4899 651-201-5797 TDD Web Publication Date: March 21, 2011 Chemical Name: Acetone CAS: 67-64-1
Rodent Toxicity/Carcinogenicity Studies on Cell Phone Radio Frequency Radiation in Reverberation Chambers
 Rodent Toxicity/Carcinogenicity Studies on Cell Phone Radio Frequency Radiation in Reverberation Chambers Ronald L. Melnick, Christopher Portier National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences National
Rodent Toxicity/Carcinogenicity Studies on Cell Phone Radio Frequency Radiation in Reverberation Chambers Ronald L. Melnick, Christopher Portier National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences National
Anatomy of Male Reproductive System
 Anatomy of Male Reproductive System A. Reproductive Systems 1. Gonads: primary sex organs a. Produce gametes b. Produce hormones c. Male Gonads: testes d. Female Gonads: ovaries 2. Gametes: sex cells a.
Anatomy of Male Reproductive System A. Reproductive Systems 1. Gonads: primary sex organs a. Produce gametes b. Produce hormones c. Male Gonads: testes d. Female Gonads: ovaries 2. Gametes: sex cells a.
Exercise Day 3-13 A PBPK Model for Methyl Mercury
 Exercise Day 3-13 A PBPK Model for Methyl Mercury Interpretation of biomonitoring data using physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling Center for Human Health Assessment September 25-29, 29, 2006
Exercise Day 3-13 A PBPK Model for Methyl Mercury Interpretation of biomonitoring data using physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling Center for Human Health Assessment September 25-29, 29, 2006
FACT SHEET TESTETROL, A NOVEL ORALLY BIOACTIVE ANDROGEN
 FACT SHEET TESTETROL, A NOVEL ORALLY BIOACTIVE ANDROGEN General Pantarhei Bioscience B.V. is an emerging specialty pharmaceutical company with a creative approach towards drug development. The Company
FACT SHEET TESTETROL, A NOVEL ORALLY BIOACTIVE ANDROGEN General Pantarhei Bioscience B.V. is an emerging specialty pharmaceutical company with a creative approach towards drug development. The Company
Health Effects Test Guidelines OPPTS 870.3800 Reproduction and Fertility Effects
 United States Prevention, Pesticides EPA 712 C 98 208 Environmental Protection and Toxic Substances August 1998 Agency (7101) Health Effects Test Guidelines OPPTS 870.3800 Reproduction and Fertility Effects
United States Prevention, Pesticides EPA 712 C 98 208 Environmental Protection and Toxic Substances August 1998 Agency (7101) Health Effects Test Guidelines OPPTS 870.3800 Reproduction and Fertility Effects
Introduction. MassDEP, Office of Research and Standards 1 Tetrachloroethylene
 Summary of the Basis of Cancer Risk Values for Massachusetts Department of Environmental Protection (MassDEP) Office of Research and Standards January 22, 2014 Introduction In February 2012 the United
Summary of the Basis of Cancer Risk Values for Massachusetts Department of Environmental Protection (MassDEP) Office of Research and Standards January 22, 2014 Introduction In February 2012 the United
Appendix I: Summary of Human Health Effects Data for Iprodione
 Appendix I: Summary of Human Health Effects Data for Iprodione MEMORANDUM Subject: Toxicology Review for the Reregistration Eligibility Document on IPRODIONE - UPDATE From: Thru: To: Linda L. Taylor, Ph.D.
Appendix I: Summary of Human Health Effects Data for Iprodione MEMORANDUM Subject: Toxicology Review for the Reregistration Eligibility Document on IPRODIONE - UPDATE From: Thru: To: Linda L. Taylor, Ph.D.
Page 1. 1. The production of monoploid cells by spermatogenesis occurs in (1) zygotes (3) ovaries (2) testes (4) meristems
 1. The production of monoploid cells by spermatogenesis occurs in (1) zygotes (3) ovaries (2) testes (4) meristems Base your answers to questions 2 and 3 on the diagram below of the female reproductive
1. The production of monoploid cells by spermatogenesis occurs in (1) zygotes (3) ovaries (2) testes (4) meristems Base your answers to questions 2 and 3 on the diagram below of the female reproductive
Bifenthrin 41 5.2 BIFENTHRIN (178)
 Bifenthrin 41 5.2 BIFENTHRIN (178) TOXICOLOGY Bifenthrin is the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) approved name for 2-methyl-3- phenylphenyl) methyl (1RS, 3RS)-3-[(Z)-2-chloro-3, 3,
Bifenthrin 41 5.2 BIFENTHRIN (178) TOXICOLOGY Bifenthrin is the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) approved name for 2-methyl-3- phenylphenyl) methyl (1RS, 3RS)-3-[(Z)-2-chloro-3, 3,
Reproduction Multiple Choice questions
 Reproduction Multiple Choice questions 1. In mammals that are seasonal breeders, females are receptive only once a year. This is called A) a follicular cycle B) an estrous cycle C) a menstrual cycle D)
Reproduction Multiple Choice questions 1. In mammals that are seasonal breeders, females are receptive only once a year. This is called A) a follicular cycle B) an estrous cycle C) a menstrual cycle D)
How to Find Out What s Wrong A BASIC GUIDE TO MALE. A doctor s guide for patients developed by the American Urological Association, Inc.
 A BASIC GUIDE TO MALE How to Find Out What s Wrong A doctor s guide for patients developed by the American Urological Association, Inc. Based on the AUA Best Practice Policy and ASRM Practice Committee
A BASIC GUIDE TO MALE How to Find Out What s Wrong A doctor s guide for patients developed by the American Urological Association, Inc. Based on the AUA Best Practice Policy and ASRM Practice Committee
EVERY LIVING THING has a number of
 Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproductive Systems EVERY LIVING THING has a number of organ systems operating to perform specific functions. If you were to examine one of these systems, you would observe
Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproductive Systems EVERY LIVING THING has a number of organ systems operating to perform specific functions. If you were to examine one of these systems, you would observe
COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
 The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Evaluation of Medicines for Veterinary Use EMEA/MRL/717/99-FINAL December 1999 COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS TOLDIMFOS SUMMARY
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Evaluation of Medicines for Veterinary Use EMEA/MRL/717/99-FINAL December 1999 COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS TOLDIMFOS SUMMARY
Methamphetamine induces abnormal sperm morphology, low sperm concentration and apoptosis in the testis of male rats
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Methamphetamine induces abnormal sperm morphology, low sperm concentration and apoptosis in the testis of male rats S. Nudmamud-Thanoi & S. Thanoi Department of Anatomy, Faculty of Medical
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Methamphetamine induces abnormal sperm morphology, low sperm concentration and apoptosis in the testis of male rats S. Nudmamud-Thanoi & S. Thanoi Department of Anatomy, Faculty of Medical
5.7 CHLOROTHALONIL (081)
 Chlorothalonil 89 5.7 CHLOROTHALONIL (081) TOXICOLOGY Chlorothalonil is the ISO approved common name for tetrachloroisophthalonitrile. Chlorothalonil (CAS No. 1897-45-6) is a non-systemic foliar fungicide
Chlorothalonil 89 5.7 CHLOROTHALONIL (081) TOXICOLOGY Chlorothalonil is the ISO approved common name for tetrachloroisophthalonitrile. Chlorothalonil (CAS No. 1897-45-6) is a non-systemic foliar fungicide
Lesson Plan Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I
 Lesson Plan Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I TOPIC: Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I SUBJECT: Life Skills TARGET AGE RANGE: 9 15 TIME: 45 minutes IDEAL NUMBER OF LEARNERS:
Lesson Plan Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I TOPIC: Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I SUBJECT: Life Skills TARGET AGE RANGE: 9 15 TIME: 45 minutes IDEAL NUMBER OF LEARNERS:
Lead optimization services
 Lead optimization services The WIL Research Company (WRC) has extensive experience in fast track tailor-made screening strategies to help you with the challenging task of selecting your best candidate
Lead optimization services The WIL Research Company (WRC) has extensive experience in fast track tailor-made screening strategies to help you with the challenging task of selecting your best candidate
Issues Relevant to Endocrine Disruptor Screening
 Concepts of Endocrinology: Issues Relevant to Endocrine Disruptor Screening Raphael J. Witorsch, Ph.D. Professor Emeritus Physiology and Biophysics School of Medicine Virginia i i Commonwealth University
Concepts of Endocrinology: Issues Relevant to Endocrine Disruptor Screening Raphael J. Witorsch, Ph.D. Professor Emeritus Physiology and Biophysics School of Medicine Virginia i i Commonwealth University
Sex Hormone Testing by Mass Spectrometry
 Sex Hormone Testing by Mass Spectrometry Robert L. Fitzgerald, PhD, DABCC Professor of Pathology University of California-San Diego San Diego, CA, 92161 [email protected] Learning Objectives After this
Sex Hormone Testing by Mass Spectrometry Robert L. Fitzgerald, PhD, DABCC Professor of Pathology University of California-San Diego San Diego, CA, 92161 [email protected] Learning Objectives After this
General toxicity study designs
 General toxicity study designs Jan Willem van der Laan Section on Safety of Medicines and Teratology Centre for Biological Medicines and Medical Technology National Institute for Public Health and the
General toxicity study designs Jan Willem van der Laan Section on Safety of Medicines and Teratology Centre for Biological Medicines and Medical Technology National Institute for Public Health and the
Sweet-taste receptors, glucose absorption and insulin release: Are LCS nutritionally active?
 Sweet-taste receptors, glucose absorption and insulin release: Are LCS nutritionally active? Samuel V. Molinary, Ph.D. Consultant, Scientific & Regulatory Affairs ILSI/NA April 6, 2011 Washington, DC Why
Sweet-taste receptors, glucose absorption and insulin release: Are LCS nutritionally active? Samuel V. Molinary, Ph.D. Consultant, Scientific & Regulatory Affairs ILSI/NA April 6, 2011 Washington, DC Why
FRENCH AGENCY FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS DECENTRALISED PROCEDURE PUBLICLY AVAILABLE ASSESSMENT REPORT FOR A VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCT
 FRENCH AGENCY FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS DECENTRALISED PROCEDURE FOR A VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCT EMEDOG, 1 mg/ml, solution for injection for dogs Date: 20/08/2015 French agency for food, environnemental
FRENCH AGENCY FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS DECENTRALISED PROCEDURE FOR A VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCT EMEDOG, 1 mg/ml, solution for injection for dogs Date: 20/08/2015 French agency for food, environnemental
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON HARMONISATION OF TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR REGISTRATION OF PHARMACEUTICALS FOR HUMAN USE M3(R2)
 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON HARMONISATION OF TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR REGISTRATION OF PHARMACEUTICALS FOR HUMAN USE ICH HARMONISED TRIPARTITE GUIDELINE GUIDANCE ON NONCLINICAL SAFETY STUDIES FOR THE
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON HARMONISATION OF TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR REGISTRATION OF PHARMACEUTICALS FOR HUMAN USE ICH HARMONISED TRIPARTITE GUIDELINE GUIDANCE ON NONCLINICAL SAFETY STUDIES FOR THE
Guidance for Industry
 Guidance for Industry S9 Nonclinical Evaluation for Anticancer Pharmaceuticals U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) Center
Guidance for Industry S9 Nonclinical Evaluation for Anticancer Pharmaceuticals U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) Center
OUTCOMES BASED LEARNING MATRIX
 OUTCOMES BASED LEARNING MATRIX Course: BIOL 206 Vertebrate Anatomy and Physiology II Department: Biology Course Description: This is the second part of an introductory course sequence in the comparative
OUTCOMES BASED LEARNING MATRIX Course: BIOL 206 Vertebrate Anatomy and Physiology II Department: Biology Course Description: This is the second part of an introductory course sequence in the comparative
Teriflunomide is the active metabolite of Leflunomide, a drug employed since 1994 for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (Baselt, 2011).
 Page 1 of 10 ANALYTE NAME AND STRUCTURE TERIFLUNOMIDE Teriflunomide TRADE NAME Aubagio CATEGORY Antimetabolite TEST CODE PURPOSE Therapeutic Drug Monitoring GENERAL RELEVANCY BACKGROUND sclerosis. The
Page 1 of 10 ANALYTE NAME AND STRUCTURE TERIFLUNOMIDE Teriflunomide TRADE NAME Aubagio CATEGORY Antimetabolite TEST CODE PURPOSE Therapeutic Drug Monitoring GENERAL RELEVANCY BACKGROUND sclerosis. The
14/11/2014. Copper supply affects growth performance and health in growing pigs. Outline. Copper as essential trace elements
 Copper supply affects growth performance and health in growing pigs Themamiddag 4 november 2014 Outline Introduction Copper as essential trace element Paul Bikker, Jurgen van Baal, Roselinde Goselink Presence:
Copper supply affects growth performance and health in growing pigs Themamiddag 4 november 2014 Outline Introduction Copper as essential trace element Paul Bikker, Jurgen van Baal, Roselinde Goselink Presence:
2. What muscle pulls the testis down into the scrotum during development?
 Anatomy & Physiology Reproductive System Worksheet Male 1. Put the following structures in order from testis to urethra: ductus deferens, rete testis, epididymus, seminiferous tubules 1) 2) 3) 4) 2. What
Anatomy & Physiology Reproductive System Worksheet Male 1. Put the following structures in order from testis to urethra: ductus deferens, rete testis, epididymus, seminiferous tubules 1) 2) 3) 4) 2. What
Chapter 12: SPECIFIC TARGET ORGAN SYSTEMIC TOXICITY (TOST) FOLLOWING A SINGLE EXPOSURE
 Chapter 12: SPECIFIC TARGET ORGAN SYSTEMIC TOXICITY (TOST) FOLLOWING A SINGLE EXPOSURE DEFINITIONS 1. Classification identifies the chemical substance as being a specific target organ/systemic toxicant
Chapter 12: SPECIFIC TARGET ORGAN SYSTEMIC TOXICITY (TOST) FOLLOWING A SINGLE EXPOSURE DEFINITIONS 1. Classification identifies the chemical substance as being a specific target organ/systemic toxicant
Overview: Human Health Effects of Environmental Contaminants
 Overview: Human Health Effects of Environmental Contaminants 1 1 OVERVIEW: HUMAN HEALTH EFFECTS OF ENVIRONMENTAL CONTAMINANTS Human activity has led to the production and release into the environment of
Overview: Human Health Effects of Environmental Contaminants 1 1 OVERVIEW: HUMAN HEALTH EFFECTS OF ENVIRONMENTAL CONTAMINANTS Human activity has led to the production and release into the environment of
Anatomy and Physiology of Human Reproduction. Module 10a
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
Absorption of Drugs. Transport of a drug from the GI tract
 Absorption of Drugs Absorption is the transfer of a drug from its site of administration to the bloodstream. The rate and efficiency of absorption depend on the route of administration. For IV delivery,
Absorption of Drugs Absorption is the transfer of a drug from its site of administration to the bloodstream. The rate and efficiency of absorption depend on the route of administration. For IV delivery,
NONCLINICAL EVALUATION FOR ANTICANCER PHARMACEUTICALS
 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON HARMONISATION OF TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR REGISTRATION OF PHARMACEUTICALS FOR HUMAN USE ICH HARMONISED TRIPARTITE GUIDELINE NONCLINICAL EVALUATION FOR ANTICANCER PHARMACEUTICALS
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON HARMONISATION OF TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR REGISTRATION OF PHARMACEUTICALS FOR HUMAN USE ICH HARMONISED TRIPARTITE GUIDELINE NONCLINICAL EVALUATION FOR ANTICANCER PHARMACEUTICALS
EUROPEAN COMMISSION HEALTH & CONSUMER PROTECTION DIRECTORATE-GENERAL
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION HEALTH & CONSUMER PROTECTION DIRECTORATE-GENERAL Directorate C - Scientific Opinions C2 - Management of scientific committees II; scientific co-operation and networks Revision of the
EUROPEAN COMMISSION HEALTH & CONSUMER PROTECTION DIRECTORATE-GENERAL Directorate C - Scientific Opinions C2 - Management of scientific committees II; scientific co-operation and networks Revision of the
September 19, 1984 FOOD PRODUCTION AND DIRECTION GÉNÉRALE, SECTION INSPECTION BRANCH PRODUCTION ET INSPECTION PESTICIDES DES ALIMENTS TRADE MEMORANDUM
 Agriculture Canada September 19, 1984 T-1-245 FOOD PRODUCTION AND DIRECTION GÉNÉRALE, SECTION INSPECTION BRANCH PRODUCTION ET INSPECTION PESTICIDES DES ALIMENTS TRADE MEMORANDUM RE: Guidelines for Developing
Agriculture Canada September 19, 1984 T-1-245 FOOD PRODUCTION AND DIRECTION GÉNÉRALE, SECTION INSPECTION BRANCH PRODUCTION ET INSPECTION PESTICIDES DES ALIMENTS TRADE MEMORANDUM RE: Guidelines for Developing
Part C. Hazard Assessment and Review of Available Studies
 Part C Hazard Assessment and Review of Available Studies List of Contents 10. Possible Effects of Atrazine Exposure on Testosterone Metabolism... 3 11. Epidemiology... 4 11.1 IUGR in Iowa Communities...
Part C Hazard Assessment and Review of Available Studies List of Contents 10. Possible Effects of Atrazine Exposure on Testosterone Metabolism... 3 11. Epidemiology... 4 11.1 IUGR in Iowa Communities...
What Do We Learn about Hepatotoxicity Using Coumarin-Treated Rat Model?
 What Do We Learn about Hepatotoxicity Using Coumarin-Treated Rat Model? authors M. David Ho 1, Bob Xiong 1, S. Stellar 2, J. Proctor 2, J. Silva 2, H.K. Lim 2, Patrick Bennett 1, and Lily Li 1 Tandem Labs,
What Do We Learn about Hepatotoxicity Using Coumarin-Treated Rat Model? authors M. David Ho 1, Bob Xiong 1, S. Stellar 2, J. Proctor 2, J. Silva 2, H.K. Lim 2, Patrick Bennett 1, and Lily Li 1 Tandem Labs,
Manual: Policies Document ID: PI013 Date Created: Jun 08 Section: Investigator No. Pages: 7 Review Date: Aug 15 Future Review Date: Aug 17
 P0LICYI013 PREGNANCY AND SEXUAL HEALTH POLICY Manual: Policies Document ID: PI013 Date Created: Jun 08 Section: Investigator No. Pages: 7 Review Date: Aug 15 Future Review Date: Aug 17 PURPOSE To describe
P0LICYI013 PREGNANCY AND SEXUAL HEALTH POLICY Manual: Policies Document ID: PI013 Date Created: Jun 08 Section: Investigator No. Pages: 7 Review Date: Aug 15 Future Review Date: Aug 17 PURPOSE To describe
Effect of occupational exposures on male fertility: literature review, Ind Health. 2003 Apr;41(2):55-62.
 The most recent statistics show that 2 out of every 10 couples trying to achieve pregnancy will be diagnosed with infertility. For many, this can be an extremely difficult diagnosis to accept and to understand.
The most recent statistics show that 2 out of every 10 couples trying to achieve pregnancy will be diagnosed with infertility. For many, this can be an extremely difficult diagnosis to accept and to understand.
Fexinidazole a new oral treatment for sleeping sickness update of development
 Fexinidazole a new oral treatment for sleeping sickness update of development SMe O 2 Me CH 2 O Antoine TARRAL Olaf Valverde Séverine Blesson Clélia Bardonneau Wilfried Mutumbo September 2011 Fexinidazole
Fexinidazole a new oral treatment for sleeping sickness update of development SMe O 2 Me CH 2 O Antoine TARRAL Olaf Valverde Séverine Blesson Clélia Bardonneau Wilfried Mutumbo September 2011 Fexinidazole
CENTER FOR DRUG EVALUATION AND RESEARCH
 CENTER FOR DRUG EVALUATION AND RESEARCH APPLICATION NUMBER: 204042Orig1s000 PHARMACOLOGY REVIEW(S) Tertiary Pharmacology/Toxicology Review From: Paul C. Brown, Ph.D., ODE Associate Director for Pharmacology
CENTER FOR DRUG EVALUATION AND RESEARCH APPLICATION NUMBER: 204042Orig1s000 PHARMACOLOGY REVIEW(S) Tertiary Pharmacology/Toxicology Review From: Paul C. Brown, Ph.D., ODE Associate Director for Pharmacology
Safe Nano Design Molecule Manufacturing Market
 August 14 16, 212 College of Nanoscale Science & Engineering (CNSE) of the University at Albany National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) Prevention through Design Program Safe Nano
August 14 16, 212 College of Nanoscale Science & Engineering (CNSE) of the University at Albany National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) Prevention through Design Program Safe Nano
Introduction. Pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes
 Introduction Type 2 diabetes mellitus (t2dm) is the most prevalent form of diabetes worldwide. It is characterised by high fasting and high postprandial blood glucose concentrations (hyperglycemia). Chronic
Introduction Type 2 diabetes mellitus (t2dm) is the most prevalent form of diabetes worldwide. It is characterised by high fasting and high postprandial blood glucose concentrations (hyperglycemia). Chronic
MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET
 Page 1 of 7 1. IDENTIFICATION OF THE SUBSTANCE/PREPARATION AND THE COMPANY/UNDERTAKING Pfizer Inc Pfizer Pharmaceuticals Group 235 East 42nd Street New York, New York 10017 1-212-573-2222 Emergency telephone
Page 1 of 7 1. IDENTIFICATION OF THE SUBSTANCE/PREPARATION AND THE COMPANY/UNDERTAKING Pfizer Inc Pfizer Pharmaceuticals Group 235 East 42nd Street New York, New York 10017 1-212-573-2222 Emergency telephone
Basic Overview of Preclinical Toxicology Animal Models
 Basic Overview of Preclinical Toxicology Animal Models Charles D. Hebert, Ph.D., D.A.B.T. December 5, 2013 Outline Background In Vitro Toxicology In Vivo Toxicology Animal Models What is Toxicology? Background
Basic Overview of Preclinical Toxicology Animal Models Charles D. Hebert, Ph.D., D.A.B.T. December 5, 2013 Outline Background In Vitro Toxicology In Vivo Toxicology Animal Models What is Toxicology? Background
3-Nitro-1,2,4-Triazol-5-One (2014)
 WORKPLACE ENVIRONMENTAL EXPOSURE LEVEL 3-Nitro-1,2,4-Triazol-5-One (2014) I. IDENTIFICATION (1,2) Chemical Name: 3-NITRO-1,2,4-TRIAZOL-5-ONE Synonyms: (NTO) CAS Number: 932-64-9 Molecular Formula: C 2
WORKPLACE ENVIRONMENTAL EXPOSURE LEVEL 3-Nitro-1,2,4-Triazol-5-One (2014) I. IDENTIFICATION (1,2) Chemical Name: 3-NITRO-1,2,4-TRIAZOL-5-ONE Synonyms: (NTO) CAS Number: 932-64-9 Molecular Formula: C 2
Testosterone Therapy for Women
 Testosterone Therapy for Women The Facts You Need Contents 2 INTRODUCTION: The Facts You Need... 3-4 CHAPTER 1: Testosterone and Women... 5-9 CHAPTER 2: Testosterone Therapy for Women... 10-14 CONCLUSION:
Testosterone Therapy for Women The Facts You Need Contents 2 INTRODUCTION: The Facts You Need... 3-4 CHAPTER 1: Testosterone and Women... 5-9 CHAPTER 2: Testosterone Therapy for Women... 10-14 CONCLUSION:
Evaluation of Human Relevance and Mode of Action for Tunica. Vaginalis Mesotheliomas Resulting from Oral Exposure to. Acrylamide
 Evaluation of Human Relevance and Mode of Action for Tunica Vaginalis Mesotheliomas Resulting from Oral Exposure to Acrylamide Lynne T. Haber a*, Andrew Maier a, Oliver L. Kroner a, and Melissa J. Kohrman
Evaluation of Human Relevance and Mode of Action for Tunica Vaginalis Mesotheliomas Resulting from Oral Exposure to Acrylamide Lynne T. Haber a*, Andrew Maier a, Oliver L. Kroner a, and Melissa J. Kohrman
Guidance for Industry Safety Testing of Drug Metabolites
 Guidance for Industry Safety Testing of Drug Metabolites U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) February 2008 Pharmacology
Guidance for Industry Safety Testing of Drug Metabolites U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) February 2008 Pharmacology
Section 4. Toxicology
 Section 4 Toxicology Occupational Health Any chemical you use incorrectly can result in over-exposure leading to adverse health effects immediately or in the future. All hazardous materials can be handled
Section 4 Toxicology Occupational Health Any chemical you use incorrectly can result in over-exposure leading to adverse health effects immediately or in the future. All hazardous materials can be handled
Risk Assessment Report on (3-CHLORO-2-HYDROXYPROPYL)TRIMETHYLAMMONIUM CHLORIDE (CHPTAC)
 Scientific Committee on Health and Environmental Risks SCHER Risk Assessment Report on (3-CHLORO-2-HYDROXYPROPYL)TRIMETHYLAMMONIUM CHLORIDE (CHPTAC) Human Health Part CAS No.: 3327-22-8 EINECS No.: 222-048-3
Scientific Committee on Health and Environmental Risks SCHER Risk Assessment Report on (3-CHLORO-2-HYDROXYPROPYL)TRIMETHYLAMMONIUM CHLORIDE (CHPTAC) Human Health Part CAS No.: 3327-22-8 EINECS No.: 222-048-3
Kalamazoo River Oil Spill Health Hazards
 Kalamazoo River Oil Spill Health Hazards This document provides information on the health hazards of crude oil to help people understand the health risks of crude oil exposure. The information is provided
Kalamazoo River Oil Spill Health Hazards This document provides information on the health hazards of crude oil to help people understand the health risks of crude oil exposure. The information is provided
Pleural Mesotheliomas in Sprague-D~wley Rats by Erionite: First Experimental Evidence
 ENVIRONMENTAL RESEARCH 29, 238-244 (1982) Pleural Mesotheliomas in Sprague-D~wley Rats by Erionite: First Experimental Evidence CESARE MALTONI, FRANCO MINARDI, AND LEONILDO MORISI Institute oj Oncology,
ENVIRONMENTAL RESEARCH 29, 238-244 (1982) Pleural Mesotheliomas in Sprague-D~wley Rats by Erionite: First Experimental Evidence CESARE MALTONI, FRANCO MINARDI, AND LEONILDO MORISI Institute oj Oncology,
HUMAN SEMEN QUALITY IN THE NEW MILLENIUM: A MATTER OF CONCERN?
 HUMAN SEMEN QUALITY IN THE NEW MILLENIUM: A MATTER OF CONCERN? Niels Jørgensen, Ulla N. Joensen, Tina K. Jensen, Martin B. Jensen, Kristian Almstrup, Inge A. Olesen, Elisabeth Carlsen, Jørgen H. Petersen,
HUMAN SEMEN QUALITY IN THE NEW MILLENIUM: A MATTER OF CONCERN? Niels Jørgensen, Ulla N. Joensen, Tina K. Jensen, Martin B. Jensen, Kristian Almstrup, Inge A. Olesen, Elisabeth Carlsen, Jørgen H. Petersen,
Management of Pregnancy. Opioid Addiction Treatment
 Management of Pregnancy Opioid Addiction Treatment Perinatal Opioid Addiction Pharmacotherapy and co-ordination of care are essential elements in the comprehensive care of pregnant patients with opioid
Management of Pregnancy Opioid Addiction Treatment Perinatal Opioid Addiction Pharmacotherapy and co-ordination of care are essential elements in the comprehensive care of pregnant patients with opioid
ANS 431 - Reproductive Physiology of Domestic Animals (Spring 2015)
 1 ANS 431 - Reproductive Physiology of Domestic Animals (Spring 2015) Instructor: Dr. Eduardo L. Gastal, DVM, MS, PhD Room: AG 129; Phone: 453-1774; E-mail: [email protected] Office hours: MWF 11-12 a.m.;
1 ANS 431 - Reproductive Physiology of Domestic Animals (Spring 2015) Instructor: Dr. Eduardo L. Gastal, DVM, MS, PhD Room: AG 129; Phone: 453-1774; E-mail: [email protected] Office hours: MWF 11-12 a.m.;
Statistics and Pharmacokinetics in Clinical Pharmacology Studies
 Paper ST03 Statistics and Pharmacokinetics in Clinical Pharmacology Studies ABSTRACT Amy Newlands, GlaxoSmithKline, Greenford UK The aim of this presentation is to show how we use statistics and pharmacokinetics
Paper ST03 Statistics and Pharmacokinetics in Clinical Pharmacology Studies ABSTRACT Amy Newlands, GlaxoSmithKline, Greenford UK The aim of this presentation is to show how we use statistics and pharmacokinetics
Male Health Issues. Survivorship Clinic
 Male Health Issues The effects of cancer therapy on male reproductive function depend on many factors, including the boy s age at the time of cancer therapy, the specific type and location of the cancer,
Male Health Issues The effects of cancer therapy on male reproductive function depend on many factors, including the boy s age at the time of cancer therapy, the specific type and location of the cancer,
Guidance for Industry
 Guidance for Industry M3(R2) Nonclinical Safety Studies for the Conduct of Human Clinical Trials and Marketing Authorization for Pharmaceuticals U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug
Guidance for Industry M3(R2) Nonclinical Safety Studies for the Conduct of Human Clinical Trials and Marketing Authorization for Pharmaceuticals U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug
Trends in Male Reproductive Health
 Trends in Male Reproductive Health Paul A.L. Lancaster University of New South Wales Thanks very much Prof. Hirahara, and I would like to add my thanks to the Ministry of the Environment and especially
Trends in Male Reproductive Health Paul A.L. Lancaster University of New South Wales Thanks very much Prof. Hirahara, and I would like to add my thanks to the Ministry of the Environment and especially
Anatomy and Physiology of the Boar. W.L. Flowers Department of Animal Science North Carolina State University Raleigh, N.C.
 Anatomy and Physiology of the Boar W.L. Flowers Department of Animal Science North Carolina State University Raleigh, N.C. 27695-7621 Introduction The boar has a tremendous impact on the reproductive efficiency
Anatomy and Physiology of the Boar W.L. Flowers Department of Animal Science North Carolina State University Raleigh, N.C. 27695-7621 Introduction The boar has a tremendous impact on the reproductive efficiency
SAFETY PHARMACOLOGY STUDIES FOR HUMAN PHARMACEUTICALS S7A
 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON HARMONISATION OF TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR REGISTRATION OF PHARMACEUTICALS FOR HUMAN USE ICH HARMONISED TRIPARTITE GUIDELINE SAFETY PHARMACOLOGY STUDIES FOR HUMAN PHARMACEUTICALS
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON HARMONISATION OF TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR REGISTRATION OF PHARMACEUTICALS FOR HUMAN USE ICH HARMONISED TRIPARTITE GUIDELINE SAFETY PHARMACOLOGY STUDIES FOR HUMAN PHARMACEUTICALS
Biological importance of metabolites. Safety and efficacy aspects
 Biological importance of metabolites Safety and efficacy aspects Bernard Walther Technologie Servier Biological importance of metabolites Safety testing of drug metabolites Bioanalytical strategy Structural
Biological importance of metabolites Safety and efficacy aspects Bernard Walther Technologie Servier Biological importance of metabolites Safety testing of drug metabolites Bioanalytical strategy Structural
EHP Student Edition, January 2006, p. A671 A677 http://ehp.niehs.nih.gov/docs/2005/113-10/focus-abs.html
 ehp LESSON: Are EDCs Blurring Issues of Summary: Gender? Students read the article Are EDCs Blurring Issues of Gender? and identify and summarize the research cited within the article. Students then decide
ehp LESSON: Are EDCs Blurring Issues of Summary: Gender? Students read the article Are EDCs Blurring Issues of Gender? and identify and summarize the research cited within the article. Students then decide
D. Vitamin D. 1. Two main forms; vitamin D2 and D3
 D. Vitamin D. Two main forms; vitamin D2 and D3 H H D3 - Cholecalciferol D2 - Ergocalciferol Technically, vitamin D is not a vitamin. It is the name given to a group of fat-soluble prohormones (substances
D. Vitamin D. Two main forms; vitamin D2 and D3 H H D3 - Cholecalciferol D2 - Ergocalciferol Technically, vitamin D is not a vitamin. It is the name given to a group of fat-soluble prohormones (substances
STUDENT S WORKSHEETS. Eva M. Zamudio Zamudio
 STUDENT S WORKSHEETS January April 2009 HUMAN LIFE CYCLE HANDOUT 1 1. Write the name of each stage in the right order: retirement adolescence babyhood adulthood - childhood 2. What stage does it belong
STUDENT S WORKSHEETS January April 2009 HUMAN LIFE CYCLE HANDOUT 1 1. Write the name of each stage in the right order: retirement adolescence babyhood adulthood - childhood 2. What stage does it belong
Treating Thyroid Cancer using I-131 Maximum Tolerable Dose Method
 Treating Thyroid Cancer using I-131 Maximum Tolerable Dose Method Christopher Martel, M.Sc., CHP Lisa Thornhill,, NRRPT, RT(NM) Boston University Medical Center Thyroid Carcinoma New cases and deaths in
Treating Thyroid Cancer using I-131 Maximum Tolerable Dose Method Christopher Martel, M.Sc., CHP Lisa Thornhill,, NRRPT, RT(NM) Boston University Medical Center Thyroid Carcinoma New cases and deaths in
In Vivo and In Vitro Screening for Thyroid Hormone Disruptors
 In Vivo and In Vitro Screening for Thyroid Hormone Disruptors Kevin M. Crofton National lhealth and Environmental Research Laboratory California Environmental Protection Agency Human Health Hazard Indicators
In Vivo and In Vitro Screening for Thyroid Hormone Disruptors Kevin M. Crofton National lhealth and Environmental Research Laboratory California Environmental Protection Agency Human Health Hazard Indicators
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY
 ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
UNIVERSIDAD DE GUAYAQUIL DEPARTMENT OF CHEMICAL SCIENCES
 CODE: 38/05 TITLE: Establishment of the potential anti-inflammatory effect of the product known as CUMANDA, originating from NutraMedix Laboratories, LLC, Florida OBJECTIVES: To study the possible anti-inflammatory
CODE: 38/05 TITLE: Establishment of the potential anti-inflammatory effect of the product known as CUMANDA, originating from NutraMedix Laboratories, LLC, Florida OBJECTIVES: To study the possible anti-inflammatory
LEARNER OUTCOME 1 W-5.3:
 GRADE 5 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY LESSON 4 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Lesson 4 GRADE 5 LEARNER OUTCOME W-5.3: Identify the basic components of the human reproductive system, and describe the basic functions of the
GRADE 5 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY LESSON 4 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Lesson 4 GRADE 5 LEARNER OUTCOME W-5.3: Identify the basic components of the human reproductive system, and describe the basic functions of the
Nursing 113. Pharmacology Principles
 Nursing 113 Pharmacology Principles 1. The study of how drugs enter the body, reach the site of action, and are removed from the body is called a. pharmacotherapeutics b. pharmacology c. pharmacodynamics
Nursing 113 Pharmacology Principles 1. The study of how drugs enter the body, reach the site of action, and are removed from the body is called a. pharmacotherapeutics b. pharmacology c. pharmacodynamics
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System
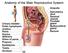 Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System External genitalia (can be seen on the body surface) penis scrotum Internal genitalia (can t be seen on the body surface)
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System External genitalia (can be seen on the body surface) penis scrotum Internal genitalia (can t be seen on the body surface)
ZOVIRAX Cold Sore Cream
 Data Sheet ZOVIRAX Cold Sore Cream Aciclovir 5% w/w Presentation Topical cream Indications ZOVIRAX Cold Sore Cream is indicated for the treatment of Herpes simplex virus infections of the lips and face
Data Sheet ZOVIRAX Cold Sore Cream Aciclovir 5% w/w Presentation Topical cream Indications ZOVIRAX Cold Sore Cream is indicated for the treatment of Herpes simplex virus infections of the lips and face
UNIVERSIDAD DE GUAYAQUIL DEPARTMENT OF CHEMICAL SCIENCES
 CODE: 38/05 TITLE: Establishment of the potential anti-inflammatory effect of the product known as SAMENTO, originating from NutraMedix Laboratories, LLC, Florida OBJECTIVES: To study the possible anti-inflammatory
CODE: 38/05 TITLE: Establishment of the potential anti-inflammatory effect of the product known as SAMENTO, originating from NutraMedix Laboratories, LLC, Florida OBJECTIVES: To study the possible anti-inflammatory
Endocrine Glands and the General Principles of Hormone Action
 Endocrine Glands and the General Principles of Hormone Action Cai Li, Ph.D. Assistant professor Touchstone Center for Diabetes Research Departments of Physiology and Internal Medicine The University of
Endocrine Glands and the General Principles of Hormone Action Cai Li, Ph.D. Assistant professor Touchstone Center for Diabetes Research Departments of Physiology and Internal Medicine The University of
M110.726 The Nucleus M110.727 The Cytoskeleton M340.703 Cell Structure and Dynamics
 of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 1. Master the knowledge base of current biochemistry, molecular biology, and cellular physiology Describe current knowledge in metabolic transformations conducted
of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 1. Master the knowledge base of current biochemistry, molecular biology, and cellular physiology Describe current knowledge in metabolic transformations conducted
Men s Health: Testicular & Breast. September 2012
 Men s Health: Testicular & Breast September 2012 Objectives: You will learn: How to perform a testicular self-exam and breast self-exam. You will know when to perform testicular and breast self-exams.
Men s Health: Testicular & Breast September 2012 Objectives: You will learn: How to perform a testicular self-exam and breast self-exam. You will know when to perform testicular and breast self-exams.
Human Biomonitoring of Mercury Exposure
 Human Biomonitoring of Mercury Exposure The main objective of this workshop is to familiarize the participants with the choice and measurement of biomarkers for different chemical forms of mercury exposure.
Human Biomonitoring of Mercury Exposure The main objective of this workshop is to familiarize the participants with the choice and measurement of biomarkers for different chemical forms of mercury exposure.
QSAR. The following lecture has drawn many examples from the online lectures by H. Kubinyi
 QSAR The following lecture has drawn many examples from the online lectures by H. Kubinyi LMU Institut für Informatik, LFE Bioinformatik, Cheminformatics, Structure independent methods J. Apostolakis 1
QSAR The following lecture has drawn many examples from the online lectures by H. Kubinyi LMU Institut für Informatik, LFE Bioinformatik, Cheminformatics, Structure independent methods J. Apostolakis 1
Reproductive System. Anatomy of Male Reproductive System
 Function: producing offspring Reproductive System propagation of the species in terms of evolution the only reason all the other systems exist only major system that doesn t work continuously only activated
Function: producing offspring Reproductive System propagation of the species in terms of evolution the only reason all the other systems exist only major system that doesn t work continuously only activated
Newsletter. WntResearch AB, Medeon Science Park, Per Albin Hanssons väg 41, 205 12 Malmö, Sweden. Primary Objective:
 Newsletter This resume of the results from the phase 1 study with Foxy-5 is based on clinical and laboratory data from the study, and these data have now been locked into the database. The full report
Newsletter This resume of the results from the phase 1 study with Foxy-5 is based on clinical and laboratory data from the study, and these data have now been locked into the database. The full report
Initial Risk Assessment Report of Chemical Substances (Extract) Ver.1.0 No. 56. Decabromodiphenyl ether
 Initial Risk Assessment Report of Chemical Substances (Extract) Ver.1.0 No. 56 Decabromodiphenyl ether Government Ordinance Number in the PRTR Law: 1-197 CAS Registry Number: 1163-19-5 July 2005 New Energy
Initial Risk Assessment Report of Chemical Substances (Extract) Ver.1.0 No. 56 Decabromodiphenyl ether Government Ordinance Number in the PRTR Law: 1-197 CAS Registry Number: 1163-19-5 July 2005 New Energy
Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1
 Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1 1. Which two glands in the diagram produce gametes? A. glands A and B B. glands B and E C. glands C and F D. glands E and F 2. Base your answer
Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1 1. Which two glands in the diagram produce gametes? A. glands A and B B. glands B and E C. glands C and F D. glands E and F 2. Base your answer
DRAFT RISK ASSESSMENT OF THE POTENTIAL HUMAN HEALTH EFFECTS ASSOCIATED WITH EXPOSURE TO PERFLUOROOCTANOIC ACID AND ITS SALTS
 DRAFT RISK ASSESSMENT OF THE POTENTIAL HUMAN HEALTH EFFECTS ASSOCIATED WITH EXPOSURE TO PERFLUOROOCTANOIC ACID AND ITS SALTS U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Office of Pollution Prevention and Toxics
DRAFT RISK ASSESSMENT OF THE POTENTIAL HUMAN HEALTH EFFECTS ASSOCIATED WITH EXPOSURE TO PERFLUOROOCTANOIC ACID AND ITS SALTS U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Office of Pollution Prevention and Toxics
Summary and conclusion 2013
 The work presented in the thesis is focused on the problems related to the prostate gland. Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and prostate cancer (PCa) are the two major problems associated with prostate.
The work presented in the thesis is focused on the problems related to the prostate gland. Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and prostate cancer (PCa) are the two major problems associated with prostate.
X-Plain Low Testosterone Reference Summary
 X-Plain Low Testosterone Reference Summary Introduction Testosterone is the most important male sex hormone. It helps the body produce and maintain adult male features. Low levels of testosterone affect
X-Plain Low Testosterone Reference Summary Introduction Testosterone is the most important male sex hormone. It helps the body produce and maintain adult male features. Low levels of testosterone affect
Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS AND THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE
 Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS AND THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE Learning Objectives By the end of this unit, the learner should be able to: Explain the importance of understanding the male and female reproductive
Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS AND THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE Learning Objectives By the end of this unit, the learner should be able to: Explain the importance of understanding the male and female reproductive
