SureSilencing shrna Plasmids
|
|
|
- Suzan Daniels
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 User Manual BIOMOL GmbH Waidmannstr Hamburg Phone: or (D) Fax: or (D) SureSilencing shrna Plasmids Genome-Wide Plasmid-Based RNA Interference See Purchaser Notification for limited use license and warranty information (pages 2 and 3). Part #1019A Version /29/2008
2 SureSilencing shrna Plasmids Genome-Wide Plasmid-Based RNA Interference User Manual (For Catalog Numbers KX#####G/N/P) Ordering and Technical Service Contact Information: Tel: (US) (outside US) Fax: (US) (outside US) On-line Order: (to place an order) (for technical support) You may place orders by fax, or from our website. Each order should include the following information: Your contact information (name, phone, address) Product name, catalog number and quantity Purchase order number or credit card information (Visa or MasterCard) Shipping address Billing address For more information, visit us at NOTICE TO PURCHASER I This product is made under license from The Carnegie Institution of Washington. However, the purchase of this material by a nonacademic or for-profit organization will require a license to use the material from Carnegie. License queries may be directed to Gloria Brienza or Gary Kowalczyk at The Carnegie Institution of Washington, 1530 P Street NW, Washington, DC LIMITED PRODUCT WARRANTY This product is intended for research purposes only and is not intended for drug or diagnostic purposes or for human use. This warranty limits our liability to replace this product in the event the product fails to perform due to any manufacturing defect. SABiosciences Corporation makes no other warranties of any kind, expressed or implied, including without limitation, warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose. SABiosciences Corporation shall not be liable for any direct, indirect, consequential or incidental damages arising out of the use, the results of use or the inability to use this product. NOTICE TO PURCHASER II The purchase of SureSilencing shrna Plasmids includes a limited, nonexclusive license to use the kit components for research use only. This license does not grant rights to use the kit components for reproduction of any shrna, to modify kit components for resale or to use SureSilencing shrna Plasmids to manufacture commercial products without written approval of SABiosciences Corporation. No other license, expressed, implied or by estoppel, is granted. U.S. patents may cover certain isolated DNA sequences included in the SureSilencing shrna Plasmids. Presently, it is not clear under U.S. laws whether commercial users must obtain licenses from the owners of the rights to these U.S. patents before using SureSilencing shrna Plasmids. SABiosciences Corporation 6951 Executive Way; Frederick, MD 21703; USA BIOMOL GmbH Waidmannstr Hamburg [email protected] Phone: or (D) Fax: or (D) 2
3 CONTENTS I. Background and Introduction 4 II. Kit Contents and Vector Information 6 III. Additional Materials Required 7 IV. Protocol 9 A. E. coli Transformation 9 B. Plasmid Purification 9 C. Transfection 11 D. Selection or Enrichment 12 E. Real-time RT-PCR Protocol for Verifying Suppression 16 F. Assay Effects of Silencing Gene Expression 20 V. SureSilencing shrna Plasmid FAQ 21 VI. Troubleshooting Guide 23 Appendix A: Neomycin Parent Vector Sequence Information 27 Appendix B: GFP Parent Vector Sequence Information 30 Appendix C: Puromycin Parent Vector Sequence Information 33 Technical Support: [email protected] 3
4 SureSilencing shrna Plasmids I. Background and Introduction RNA Interference, a now commonplace and popular method for exploring gene function, suppresses the expression of a specific gene of interest in transformed mammalian cell culture. Upon suppression, missing or altered activities in the cell can be attributed to the function of the affected gene. However, the most commonly used technique, small interfering RNA (sirna), proves useful for some applications but not all. This technique works optimally with cells known to be easily and readily transfected with nucleic acid, but not in cells with low transfection efficiencies. Small interfering RNA does not allow transfected cells to be identified, preventing both enrichment and determination of transfection efficiency. Additionally, due to a lack of selection markers, sirna only works under transient and not stable transfection conditions, preventing the exploration of longterm gene-suppression effects. The SureSilencing shrna plasmids are designed using an experimentally validated algorithm. These constructs specifically knock down the expression of specific genes by RNA interference and allow for enrichment or selection of transfected cells. Each vector expresses a short hairpin RNA, or shrna, under control of the U1 promoter and either the neomycin resistance gene, the puromycin resistance gene, or the GFP gene. Neomycin and puromycin resistance permit selection of stably transfected cells. GFP helps estimate transfection efficiencies, tracks transfected cells by fluorescence microscopy, and permits FACS-based enrichment of transiently transfected cells. The ability to select or track and enrich shrna-expressing cells brings RNA interference to cell lines with lower transfection efficiencies. Unlike sirna, plasmid-based shrna also provides a renewable source of RNA interference. Our experimentally verified shrna design algorithm assures gene-specificity and efficacy. An advanced specificity search in addition to BLAST built into the algorithm helps to reduce the potential off-target effects. At least two of the provided SureSilencing shrna Plasmids is guaranteed to knock down expression of the targeted gene at the RNA level by at least 70 percent in transfected cells upon selection for neomycin resistance or FACSbased enrichment for GFP expression. Benefits of the SureSilencing shrna Plasmids: Enrich or Select: Plasmids are available with either GFP Marker, Neomycin, or Puromycin Resistance enabling either enrichment and short-term studies or selection and the study of the long-term effects of gene suppression. GUARANTEED!*: Knock down expression of any targeted human gene by at least 70 percent. Control for non-specific and off-target effects. Convenient & Cost-Effective: Use standard plasmid-based and lipid-mediated transfection methods. Plasmids provide a renewable source of RNA Interference. * At least two of the four provided pre-designed SureSilencing shrna Plasmids are guaranteed to knock down expression of the targeted gene at the RNA level by at least 70 percent as measured by real-time qrt- PCR in transfected cells upon FACS-based enrichment for GFP expression or selection for neomycin or puromycin resistance as described in this User Manual. Technical Support: [email protected] 4
5 Version 1.7 Figure 1: Overview of SureSilencing shrna Plasmid Procedure. Technical Support: (US)
6 SureSilencing shrna Plasmids II. Kit Contents and Vector Information A. Kit Contents: Component Specification Quantity shrna SureSilencing shrna vector Four (4) Pre-Designed NC Negative Control shrna* vector One (1) * The negative control shrna is a scrambled artificial sequence which does not match any human, mouse, or rat gene. NOTE: These plasmids are transformation-grade ONLY and are prepared and meant for introduction and amplification in bacteria FIRST. These plasmids ARE NOT transfectiongrade and ARE NOT provided in a large amount or of high enough quality for direct introduction into a mammalian cell line of interest. Storage Conditions: All components included with this catalog number are shipped with cold ice packs. The plasmids must be stored at -20 C and are guaranteed for 6 months from the date received. B. Vector Information: Plasmids contain either one of three markers identifiable by the catalog number scheme: 1. Plasmids with catalog numbers ending in the letter N contain the neomycin resistance gene for selection of stably transfected cells. 2. Plasmids with catalog numbers ending in the letter P contain the puromycin resistance gene for selection of stably transfected cells. 3. Plasmids with catalog numbers ending in the letter G contain a gene encoding a Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP) for fluorescence microscopy-based tracking or FACS-based enrichment of transiently transfected cells. The shrna sequences and the negative control sequence are provided with each product information sheet included with the plasmid set. The sequences were cloned downstream of the U1 promoter of the plasmid. For detailed information about the parent vectors including vector maps and sequences, see Appendixes A, B, and C for the neomycin resistance, GFP, and puromycin resistance plasmid formats, respectively. Technical Support: [email protected] 6
7 Version 1.7 III. Additional Materials Required: A. For Transformation and Plasmid Purification: 1. Competent E. coli cells: In general, any strain designed for the amplification of plasmid may be used. We recommend JM109 competent cells (Promega Cat No L1001 or 2001). 2. Ampicillin: Molecular Biology grade from any source. 3. LB medium and agar (Gibco) Recipe for LB-ampicillin agar plates: Add 15 g agar to 1 liter of LB medium. Autoclave. Allow the medium to cool to 50 C before adding ampicillin (50 μg/ml, final concentration). Pour ml of medium into 85 mm Petri dishes. Let the agar solidify. Store at 4 C for up to 1 month or at room temperature for up to 1 week. 4. Plasmid Purification Kit, such as: a. EndoFree Plasmid Maxi Kit Qiagen Catalog Number For purification of up to 500 μg transfection-grade plasmid DNA OR b. QIAfilter Plasmid Midi Kit Qiagen Catalog Number For fast purification of up to 100 μg transfection-grade plasmid DNA PLUS EndoFree Plasmid Buffer Set Qiagen Catalog Number Endotoxin-free buffer set for 10 mega- or 5 giga- transfection grade plasmid DNA preps NOTE: Because plasmid DNA purity and quality are crucial for optimal transfection efficiencies and therefore the success of the shrna-based gene suppression, we do not recommend using mini-preparation of plasmid DNA for transfection. B. For Transfection: 1. Whichever Transfection Reagent and Protocol that you have already optimized for transfecting plasmids into your cell line of interest. 2. Neomycin (Molecular Biology and Tissue Culture Grade), also known as G Puromycin (Molecular Biology and Tissue Culture Grade) Technical Support: (US)
8 SureSilencing shrna Plasmids C. For Real-Time RT-PCR Verification of Gene Suppression: 1. RT 2 PCR Array First Strand Kit Catalog Number C SABiosciences RT 2 Real-Time SYBR Green PCR Master Mix Be sure to pick the correct one for the instrumentation in your laboratory. RT 2 Real-Time SYBR Green / ROX: Specifically designed for: All ABI and Stratagene Instrumentation Eppendorf Mastercycler ep realplex Instruments with ROX filter set Catalog Number Size PA-012 For 2 RT 2 Profiler PCR Arrays PA For 12 RT 2 Profiler PCR Arrays PA For 24 RT 2 Profiler PCR Arrays RT 2 Real-Time SYBR Green / Fluorescein: Specifically designed for BioRad icylcer, MyiQ, and iq5 Instrumentation Catalog Number Size PA-011 For 2 RT 2 Profiler PCR Arrays PA For 12 RT 2 Profiler PCR Arrays PA For 24 RT 2 Profiler PCR Arrays RT 2 Real-Time SYBR Green: Specifically designed for instrumentation that does not require a reference dye: BioRad (MJ Research) Opticon, Opticon 2, and Chromo 4 Roche LightCycler 480 System Eppendorf Mastercycler ep realplex Instruments without ROX filter set Catalog Number Size PA-010 For 2 RT 2 Profiler PCR Arrays PA For 12 RT 2 Profiler PCR Arrays PA For 24 RT 2 Profiler PCR Arrays 3. RT 2 PCR Primer Set targeting the suppressed target gene of interest and a housekeeping gene, such as ACTB of GAPD, to normalize the real-time PCR results Technical Support: [email protected] 8
9 Version 1.7 IV. Protocol: A. E. coli Transformation: 1. Use 2 μl of each stock plasmid solution to separately transform competent E. coli cells following the manufacturer s protocol. Store the remaining stock plasmid at - 20 C. NOTE: In order to amplify a known amount of plasmid, the E. coli cells do not need to be extremely competent. 2. Plate each transformation onto separate LB agar plates containing ampicillin. Grow overnight at 37 C. B. Plasmid Purification: 1. Pick one colony for each plate with a sterile loop or toothpick and inoculate separate 2.5 ml cultures of LB medium containing 50 μg/ml ampicillin. Incubate with shaking at 37 C until just a hint of turbidity is observed in the culture (3 to 6 h). 2. Use the small cultures to inoculate 250 ml cultures of LB medium containing 50 μg/ml ampicillin. Incubate with shaking at 37 C, overnight. 3. Isolate the cells and purify plasmid DNA according to the Plasmid Purification Kit manufacturer s instructions for high copy number plasmids. NOTE: Save the remaining stocks of the plasmids provided by SABiosciences for future transformations and amplifications. However, use these remaining stocks only if your amplified plasmid preparation is compromised. When the amplified stocks become depleted, use your amplified preparation as the working stock solution, both for transfections and for new transformations and amplifications. Technical Support: (US)
10 SureSilencing shrna Plasmids 4. Plasmid Quality Control and Diagnostic Restriction Digest: To verify that you have purified plasmids containing shrna insert, you may perform a Pst I restriction enzyme digestion of a small aliquot of each plasmid preparation. All three plasmid types, with either neomycin resistance or puromycin resistance or GFP, will generate a diagnostic pair of bands on an agarose gel upon Pst I digestion: Parent Vector SureSilencing Neomycin Vector SureSilencing Puromycin Vector SureSilencing GFP Vector Pst I Fragments 3827 bp and 991 bp 3209 bp and 1402 bp 4130 bp and 1197 bp To insure optimal (especially transient) transfection efficiency, also characterize a small aliquot of each undigested plasmid on the same agarose gel. The DNA should be predominantly supercoiled and not extensively nicked. NOTE: To avoid nicking the plasmid, make sure the NaOH/SDS lysis (Solution II) step of the plasmid preparation protocol does not proceed for any longer than the time specified. 1 kb ladder uncut Pst I cut uncut Pst I cut Figure 2: Example of Plasmid Preparation Quality Control Two SureSilencing shrna Plasmids with GFP and their Pst I digests are characterized side-by-side on an agarose gel along with a 1-kb ladder. The Pst I digests contain the two diagnostic bands indicating the presence of shrna insert. The uncut plasmid preparations predominantly contain the faster migrating supercoiled form and very small amounts of slower migrating nicked plasmid or plasmid concatamers. 5. Optional Linearization of Plasmid for Stable Transfections To increase the likelihood of integration and shorten the time needed to isolate stable transfectants, you may wish to linearize the plasmid containing the neomycin or puromycin resistance markers prior to transfection as described below: a. Perform a restriction enzyme digest on enough of your plasmid preparation for the necessary transfections with either Sca I, Bsa I, or Dra III for the neomycin plasmids or with either Sca I, EclHK I, Nae I, or NgoM IV for the puromycin plasmids, in order of preference. b. Re-purify the DNA according to a standard phenol extraction procedure. c. Use the purified linearized plasmid DNA material to setup the stable transfection. Technical Support: [email protected] 10
11 Version 1.7 C. Transfection: 1. If you have already optimized a transfection reagent and protocol for your cell line of interest, you may use that protocol to transfect the SureSilencing shrna Plasmids into the same cell line. Just be sure that the original protocol optimization used plasmids and counted transfected cells (rather than relying on a reporter s activity). 2. If you have NOT optimized a reagent and protocol for transfecting plasmids into your cell line of interest, review the literature and availability of transfection reagents from other manufacturers. Chose one or more that may work with your cell line and optimize a protocol that maximizes transfection efficiency while minimizing toxicity. Refer to manufacturers recommendations for the chosen transfection reagents and the Troubleshooting Guide of this User Manual. The following procedure, utilizing HEK 293 cells and Lipofectamine2000 in a 24-well format, ONLY means to provide an example of a starting point and a guideline for optimizing the transfection of the plasmids into a cell line of interest. a. One day before transfection, seed 3 x 10 4 cells in each well of 24-well plate (for roughly 30 to 35 percent confluence) with 400 μl of growth medium. b. On the day of transfection, add 0.50 μg of each gene-specific shrna plasmid and the negative control shrna plasmid into separate 50 μl aliquots of Opti- MEM I Reduced-Serum Medium (Gibco). Mix gently. Prepare separate mixtures for each replicate well of cells to be transfected with the same plasmid. c. For each well, add 1.0 μl of Lipofectamine2000 into 50 μl of Opti-MEM (that is, 2 μl of Lipofectamine2000 per μg of plasmid). Mix gently and incubate all mixtures for 10 min at room temperature. d. Add 50 μl of Lipofectamine2000 mix to each 50 μl shrna mix. Mix gently and incubate for 20 min at room temperature. e. Add each 100 μl mixture of shrna and Lipofectamine2000 in medium to the appropriate well containing cells and 400 μl of normal growth medium. Mix gently. f. Incubate the cells at 37 C in a CO 2 incubator for 24 to 48 hours. g. Determine the transfection efficiency as the number of transfected cells divided by the total number of cells. 3. Set up three (3) replicate transfections for each of the four gene-specific and the negative control SureSilencing shrna Plasmids using your optimized protocol. Our rigorous real-time RT-PCR protocol for verifying suppression by RNA interference relies on triplicate transfections for each gene-specific shrna design and the negative control shrna for statistically significant results. See the appropriate section of this User Manual for more details. 4. Allow the transfection to occur for 24 to 48 hours, and then proceed immediately to the appropriate selection or enrichment process below. Technical Support: (US)
12 SureSilencing shrna Plasmids D. Selection or Enrichment: NOTE: Unless your transfection efficiency is routinely greater than 90%, we strongly recommend enriching the transfected cell population. If you chose plasmids containing the neomycin resistance gene, select for transfected cells using neomycin (or G418). If you chose plasmids containing the puromycin resistance gene, select for transfected cells using puromycin. If you chose GFP-containing plasmids, enrich the transfected cells by Fluorescence Activated Cell Sorting (FACS). 1. Selection for Neomycin Resistance NOTE: Different cell lines normally have different levels of neomycin resistance. Before transfection, the minimum G418 concentration necessary to kill untransfected cells must be determined by generating a dose response curve. The minimum concentration needed to kill untransfected cells is known as the effective concentration. The effective concentration will depend on the cell line, growth rate, and state of confluence during growth. In general, more confluent cells tolerate higher concentrations of G418; therefore, maintain the cells in a sub-confluent state during selection. To generate a dose response curve for G418 selection: a. Plate untransfected cells at a low density (< 10% confluence) in normal growth medium containing different G418 concentrations in separate wells: 0, 100, 200, 400, 600, 800 and 1000 µg ml -1 b. Allow the cells to grow until the 0 concentration point reaches confluence. c. Replace the media every 2 days during the selection process. d. Count the number of cells in each well, and plot the cell number versus the G418 concentration. e. The minimum concentration of G418 that kills all of the cells is the effective concentration used for selection. Technical Support: [email protected] 12
13 Version 1.7 To select transfected cells for neomycin resistance in each plasmid transfection: a. After transfection, re-plate the cells at a low cell density (< 10% confluence). b. Grow cells in medium containing the effective concentration of G418. c. Prepare control plates for all selection experiments to ensure that the selection conditions are still working as previously observed: i. Plate untransfected cells at the same density in medium containing the effective concentration of G418. No growth should be observed from these plates. ii. Plate transfected cells at the same density in medium without G418. Uninhibited growth should be observed from these plates. d. Replace the medium every 2 to 3 days with fresh medium. Re-plate cells every week. Continue the selection for up to two weeks or until enough cells are available for generating a frozen stock and for isolating total RNA. e. As soon as possible, be sure to freeze a stock of the stably transfected cells. Be sure to generate stable transfections for each gene-specific shrna plasmid and the negative control shrna plasmid. f. Once such a population is available, continue to grow these cells in media containing a reduced or maintenance concentration of G418, typically 25 to 50% of the effective concentration. Technical Support: (US)
14 SureSilencing shrna Plasmids 2. Selection for Puromycin Resistance NOTE: Different cell lines normally have different levels of puromycin resistance. Before transfection, the minimum puromycin concentration necessary to kill untransfected cells must be determined by generating a dose response curve. The minimum concentration needed to kill untransfected cells is known as the effective concentration. The effective concentration will depend on the cell line, growth rate, and state of confluence during growth. In general, more confluent cells tolerate higher concentrations of puromycin; therefore, maintain the cells in a sub-confluent state during selection. To generate a dose response curve for puromycin selection: a. Plate untransfected cells at a low density (<10% confluence) in normal growth medium containing different puromycin concentrations in separate wells: 0, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8 and 10 µg ml -1 b. Allow the cells to grow until 0 reaches confluence. c. Replace the media every 2 days during the selection process. d. Count the number of cells in each well, and plot the cell number versus the puromycin concentration. e. The minimum concentration of puromycin that kills all of the cells is the effective concentration used for selection. To select transfected cells for puromycin resistance in each plasmid transfection: a. After transfection, re-plate the cells at a low cell density (<10% confluence). b. Grow cells in medium containing the effective concentration of puromycin. c. Prepare control plates for all selection experiments to ensure that the selection conditions are still working as previously observed: i. Plate untransfected cells at the same density in medium containing the effective concentration of puromycin. No growth should be observed from these plates. ii. Plate transfected cells at the same density in medium without puromycin. Uninhibited growth should be observed from these plates. d. Replace the medium every 2 to 3 days with fresh medium. Re-plate cells every week. Continue the selection for up to two weeks or until enough cells are available for generating a frozen stock and for isolating total RNA. e. As soon as possible, be sure to freeze a stock of the stably transfected cells. Be sure to generate stable transfections for each gene-specific shrna plasmid and the negative control shrna plasmid. f. Once such a population is available, continue to grow these cells in media containing a reduced or maintenance concentration of G418, typically 25 to 50% of the effective concentration. Technical Support: [email protected] 14
15 Version Enrichment for GFP a. Consult with your FACS instrument manufacturer or your local FACS core facility for details on enriching GFP-expressing cells using this method. Peak excitation of the GFP from the SureSilencing plasmids occurs at 505 nm, with a shoulder at 480 nm, and peak emission occurs at 515 nm. b. Please note that these peak excitation and peak emission wavelengths differ from those of other sources of GFP. c. Save the sort parameters as well as an image of the flow cytometer or FACS analysis trace for troubleshooting purposes. d. Be sure to enrich all cell populations: those transfected with each gene-specific shrna plasmid and those transfected with the negative control shrna. e. Target gene suppression may also be analyzed at the individual cell level, for example by immunofluorescence or morphology scoring. The expression of the GFP from the SureSilencing plasmids can be monitored by fluorescence microscopy using an excitation filter of 470 ± 20nm (470 / 40 nm) and an emission filter of 515 nm (long pass). Technical Support: (US)
16 SureSilencing shrna Plasmids E. Real-time RT-PCR Protocol for Verifying Suppression: A detailed description of the theory behind RNA interference validation using real-time PCR may be found in our white paper entitled: Did Your RNAi Experiment Work?! Reliably Validating RNA Interference with Real-Time PCR It may be downloaded from our website at the following address: For statistically significant results, the method relies on triplicate transfections for each gene-specific shrna design and the negative control shrna. It also requires triplicate real-time PCR reactions to characterize the targeted gene of interest (GOI) and a housekeeping gene (HKG) to normalize the results using the total RNA sample from each transfection. (Typical housekeeping genes include β-actin and GAPDH.) Figure 3: Setting up real-time PCR validation of suppression The triplicate reactions for each gene in all five triplicate transfections may be conveniently setup in a 96-well PCR plate as depicted in this figure. The table represents half of a 96-well plate. The reactions in the first set of six numbered columns will characterize expression of the GOI in the indicated RNA samples, while the second set of six numbered columns will characterize expression of the HKG in the corresponding RNA samples. A B C D E F G H 1 = GOI 7 = HKG Construct 1 Transfection 1 Replicate 1 Construct 1 Transfection 2 Replicate 1 Construct 1 Transfection 3 Replicate 1 Construct 2 Transfection 1 Replicate 1 Construct 2 Transfection 2 Replicate 1 Construct 2 Transfection 3 Replicate 1 NC Construct Transfection 1 Replicate 1 NC Construct Transfection 2 Replicate 1 2 = GOI 8 = HKG Construct 1 Transfection 1 Replicate 2 Construct 1 Transfection 2 Replicate 2 Construct 1 Transfection 3 Replicate 2 Construct 2 Transfection 1 Replicate 2 Construct 2 Transfection 2 Replicate 2 Construct 2 Transfection 3 Replicate 2 NC Construct Transfection 1 Replicate 2 NC Construct Transfection 2 Replicate 2 3 = GOI 9 = HKG Construct 1 Transfection 1 Replicate 3 Construct 1 Transfection 2 Replicate 3 Construct 1 Transfection 3 Replicate 3 Construct 2 Transfection 1 Replicate 3 Construct 2 Transfection 2 Replicate 3 Construct 2 Transfection 3 Replicate 3 NC Construct Transfection 1 Replicate 3 NC Construct Transfection 2 Replicate 3 4 = GOI 10 = HKG NC Construct Transfection 3 Replicate 1 Construct 3 Transfection 1 Replicate 1 Construct 3 Transfection 2 Replicate 1 Construct 3 Transfection 3 Replicate 1 Construct 4 Transfection 1 Replicate 1 Construct 4 Transfection 2 Replicate 1 Construct 4 Transfection 3 Replicate 1 5 = GOI 11 = HKG NC Construct Transfection 3 Replicate 2 Construct 3 Transfection 1 Replicate 2 Construct 3 Transfection 2 Replicate 2 Construct 3 Transfection 3 Replicate 2 Construct 4 Transfection 1 Replicate 2 Construct 4 Transfection 2 Replicate 2 Construct 4 Transfection 3 Replicate 2 6 = GOI 12 = HKG NC Construct Transfection 3 Replicate 3 Construct 3 Transfection 1 Replicate 3 Construct 3 Transfection 2 Replicate 3 Construct 3 Transfection 3 Replicate 3 Construct 4 Transfection 1 Replicate 3 Construct 4 Transfection 2 Replicate 3 Construct 4 Transfection 3 Replicate 3 Blank Blank Blank Technical Support: [email protected] 16
17 Version 1.7 Unless otherwise indicated, follow the protocols described in the RT 2 Gene Expression Assays User Manual included with the SABiosciences RT 2 PCR Primer Sets 1. RNA Isolation a. Isolate total RNA from each of the 15 transfections. b. For cultured cells, use the Qiagen RNeasy Mini Kit (Catalog # 74104). Be sure to include the recommended DNase treatment step. c. Also, make sure to perform the RNA quality control described in the RT 2 Gene Expression Assays User Manual. 2. Reverse Transcription (First Strand cdna Template Synthesis) a. Perform one reverse transfection for each of the 15 total RNA samples (one per transfection). b. Follow the instructions in the RT 2 Gene Expression Assays User Manual included with the RT 2 PCR Primer Sets. c. For convenient pipetting below, dilute each completed 20-μl RT reaction 10-fold by adding 180 μl of ddh 2 O. 3. Primer Set and Master Mix Cocktail For real-time PCR, prepare two separate cocktails, one for the GOI and one for the HKG, using the following recipe: Component 2X SABiosciences Real-Time PCR Master Mix ddh 2 O RT² primer set for GOI OR HKG Final Volume Volume 600 μl 72 μl 48 μl 720 μl 4. Set Up the Reactions Add 15 μl of the appropriate primer set and master mix cocktail and 10 μl of the appropriate diluted cdna template (RT reaction) to the appropriate PCR wells as outlined in Figure Perform Real-Time PCR Perform PCR as described in RT 2 Gene Expression Assays User Manual included with the RT 2 PCR Primer Sets. Technical Support: (US)
18 SureSilencing shrna Plasmids 6. Data Analysis: An Excel-based data analysis template that automatically performs the calculations below is available for download from our website at the following address: a. Separately determine the average of the technical triplicate PCR C t values and their standard deviations for both genes in each of the replicate transfections of each design and the negative control. b. Separately calculate individual ΔC t values for each biological replicate transfection of each design and the negative control: GOI-Specific shrna C t = AVG GOI-Specific shrna C t (GOI) AVG GOI-Specific shrna C t (HKG) 2 2 GOI-Specific shrna ΔC t STDEV = STDEV GOI + STDEV HKG Negative Control shrna C t = AVG Negative Control shrna C t (GOI) AVG Negative Control shrna C t (HKG) 2 2 Negative Control shrna ΔC t STDEV = STDEV + GOI STDEV HKG c. Calculate the average ΔC t and its standard deviation across the biological replicates for each design. d. Calculate the average ΔΔC t and its standard deviation for each design: C t = Gene-Specific shrna C t - Negative Control shrna C t 2 2 ΔΔ C t STDEV = STDEV STDEV Gene Specific ΔCt + NegativeControl ΔCt e. Calculate the average knockdown and its 95 % confidence interval: Percent Knockdown = 100 (100 x 2^ (- C t )) Lower 95 % Confidence Interval Boundary = 100 (100 2^ (- ΔΔC t + ΔΔ C t STDEV)) Upper 95 % Confidence Interval Boundary = 100 (100 2^ (- ΔΔC t - ΔΔ C t STDEV)) f. Interpretation Successful Design: Observed KD > 70 % and an upper 95 % C.I. boundary > 55.5 % Failed Design: Observed KD < 33.3 and a lower 95 % C.I. boundary < 55.5 % Two out of the four designs should be successful. Use at least two of the four pre-designed plasmids that demonstrate the greatest percent knock-down in your subsequent gene function assays and studies. Technical Support: [email protected] 18
19 Version 1.7 Special Note for Stable Transfection Applications: Achieving a high level of knockdown in the initial population of stably transfected cells can be difficult. The plasmid integrates into the cell line genome randomly, and the initial polyclonal population represents several such integration sites. Each integration site affects the relative level of expression of the shrna construct differently and therefore the effectiveness of the knockdown. Some sites provide more expression of shrna and better knockdown of the GOI than others. The level of knockdown in the polyclonal population represents the weighted average knockdown of all of the integration sites. To obtain an even greater and more consistent level of knockdown, this polyclonal population of stably transfected cells can be cloned by limiting dilution to generate separate populations of stably transfected cells. Each new clone (or monoclonal population) will represent a single integration site, its level of shrna expression, and its level of GOI knockdown. Screen for the clone or clones that provides the greatest level of knockdown using a real-time qrt-pcr procedure similar to the one described above. For example: 1. Separately suspend a stock culture of the polyclonal populations of cells stably transfected with the two shrna designs with the greatest apparent level of knockdown. Determine their concentrations. Choose one of the replicate transfections at random. 2. Serially dilute each suspended stock down to a concentration of roughly 1 cell per 400 μl. 3. Plate 200 μl of each dilution per well of separate 96-well cell culture plates so that roughly every other well will receive one cell. 4. Allow the cells to grow to large colonies in medium containing the maintenance concentration of the same antibiotic drug used for the first stage of selection (neomycin or puromycin). 5. Re-plate the each cell population separately into a larger well. Allow them to grow to a larger number. Re-plate them again into an even larger well. Continue this process iteratively until enough cells are available for generating a frozen stock and for isolating total RNA. 6. Repeat the real-time qrt-pcr-based validation of shrna knockdown on selected clones from each plate. 7. Use one or more clones that demonstrate the greatest percent knock-down from each of the two best designs in your subsequent gene function assays and studies. Technical Support: (US)
20 SureSilencing shrna Plasmids F. Assay Effects of Silencing Gene Expression There are many ways to characterize the effects on cells brought on by a decrease in the expression of a gene meditated by RNA Interference. The following is a brief list of possibilities. Your experiments need not be limited to these suggestions, however. Cells may be harvested, and RNA isolated for gene expression analysis using: SABiosciences' RT 2 Profiler PCR Arrays SABiosciences' RT 2 Real-Time PCR Primer Sets and SYBR Green Master Mixes As in for the verification of suppression above SABiosciences' GEArray Focused DNA Microarrays Cells may be harvested, and protein isolated for: SDS-PAGE and Western Verification SABiosciences' Multi-Analyte Profiler ELISArray Kits SABiosciences' Single Analyte ELISA Kits Biochemical Assays Cells may be left in wells or plates for: SABiosciences' Cellular Activation Signaling ELISA (CASE ) Kits Cell biological assays such as morphology and immunofluorescence (GFP only) Steady-state labeling or uptake assays (neomycin or puromycin recommended) Technical Support: [email protected] 20
21 Version 1.7 V. SureSilencing FAQs What is the SureSilencing shrna Plasmids guarantee? We guarantee that at least two of the set of four SureSilencing shrna Plasmids will knock down the expression of the target gene by at least 70 percent in transfected cells by realtime qrt-pcr in target shrna-transfected cells relative to negative control shrnatransfected cells upon FACS-based enrichment for GFP expression or selection for neomycin or puromycin resistance. Please follow the recommendations in this User Manual in order to insure the optimal level of knockdown from these plasmids and the best method for detecting knockdown. If you can demonstrate each plasmid's failure to knock down gene expression as described, please contact a Technical Support representative to discuss your results and be prepared to provide the results as an Excel file in an attachment. If a product failure is verified, we will send you another set of plasmids with four pre-designed shrna constructs for free. Should I use the SureSilencing shrna Plasmids with the GFP, neomycin resistance, or puromycin resistance marker? Use the SureSilencing shrna Plasmids with the neomycin or puromycin resistance marker for stable transfection to achieve long-term knockdown (a cell line permanently knocking down the gene of interest) and to perform gene function assays involving the cell for a long period of time (anything greater than a day). Neomycin tends to be the more popular choice, but some researchers prefer puromycin because the time needed for selection of puromycin resistance is typically shorter than neomycin resistance. Puromycin resistance may also be used to stably transfect SureSilencing shrna into cells that are already neomycin resistant due to a previous stable transfection with other exogenous nucleic acid. Use the SureSilencing shrna Plasmids with GFP for transient transfections and gene function assays that can be performed with the cells quickly (in less than a day), but only if you have access and the resources to use a flow cytometry core facility. What transfection method should I use with the SureSilencing shrna Plasmids? If you have previously optimized a transfection method for plasmids into your cell line that counts cells and does not use a biochemical assay from cell lysate, you may use that method to transfect the SureSilencing shrna Plasmids. If you have never optimized transfection of your cell line of interest before, we recommend trying lipid-based methods, such as the LipofectAMINE 2000 reagent from Invitrogen and others, first. Follow the manufacturer's instructions and recommendations for optimizing your transfection protocol. Use either the GFP-based SureSilencing shrna plasmids or another plasmid system that has an easily screened marker that allows you to count cells, such as GFP or betagalactosidase. If your cells do not tolerate lipid-based transfection methods, electroporation via methods such as those provided by Amaxa may be a useful alternative. Technical Support: (US)
22 SureSilencing shrna Plasmids Can I use the SureSilencing shrna Plasmids with primary cells or macrophages or for injection into live animals? No, we do not recommend using the SureSilencing shrna Plasmids with primary cells or macrophages or other cell lines that tend to be difficult to transfect with expression plasmids by traditional methods. For these applications, we instead recommend finding a viral-based delivery system. Similarly, we do not recommend using the SureSilencing shrna Plasmids for RNA interference in live animals. The SureSilencing shrna Plasmids are meant for in vitro use only. The delivery of any method of RNA interference into live animals to specific target tissues or organs is a difficult procedure for which no manufacturer has a viable solution. Can the SureSilencing shrna Plasmids be use for viral-based delivery? The SureSilencing shrna plasmids cannot be directly used for viral delivery, nor do they have convenient restriction sites to re-clone the U1-based shrna expression cassette into another vector or viral expression system. In fact, the U1 transcription termination sequence necessary for proper expression of the shrna can disrupt the process of viral production. Inserts for shrna are more easily synthesized as oligonucleotides and then cloned into an appropriate expression system. So instead, we recommend screening the set of four shrna sequences in another model system amenable to lipid-mediated transfection to find the best sequence. Then, use the shrna insert sequence information provided with the purchase of our plasmids to have the necessary oligonucleotides synthesized for cloning into your viral-based delivery system of choice. Do the SureSilencing shrna Plasmids contain inducible promoters? No, SureSilencing shrna Plasmids with inducible promoters are not available. These promoters are meant to control the timing of silencing particularly for stable shrna transfections for essential genes or for differentiation model systems. However, they tend to be too leaky for RNA interference. That is, they still express a certain amount of the shrna of interest even under repressed conditions. We do not recommend a specific vector system for this application. However, you are welcome to screen our shrna sequences in another cell model system, and then use the shrna insert sequence information provided with the purchase of our plasmids to have the necessary oligonucleotides synthesize for cloning into your inducible expression system of choice. Technical Support: [email protected] 22
23 Version 1.7 VI. Troubleshooting Guide A. Poor plasmid transformation efficiency into E. coli Consult the manufacturer s instructions for the component E. coli cells. B. Poor yield of plasmid from transformed E. coli Consult the manufacturer s instructions for the plasmid DNA purification kit. C. How to optimize or improve low transfection efficiencies 1. Use guidelines provided by the transfection reagent or method manufacturer. These usually include the density of the cells at the time of transfection and the nucleic acid to transfection reagent mass ratio. 2. Do not use a transfection method optimized for sirna, and do not use sirna to optimize transfection efficiency. 3. If using the GFP-containing SureSilencing shrna Plasmid: Stain the cells with a nuclear DNA stain to count both transfected (GFP-positive) cells and the total number of cells (nuclear DNA stain) in the same fluorescent view of the same microscope field. Be sure to obtain numbers from several different randomly-chosen microscope fields in the interior (not toward the edges) of the cell culture well. NOTE: DO NOT try to use the phase (cell) and fluorescence (GFP) views separately to estimate or count the total number of cells and the number of transfected cells, respectively. 4. If using the neomycin-containing SureSilencing shrna Plasmid: Use another plasmid instead with a reporter gene that allows you count transfected cells. Do not use one that relies on the total activity of reporter assay (e.g., CAT) in the entire cell population. For example, if using beta-galactosidase, fix and stain the cells with X-gal to visualize and count the total number of cells and the number of transfected (blue-stained) cells rather than assaying activity in total cell lysate. D. Interpreting knock-down results from low transfection efficiencies 1. Select for neomycin resistance or puromycin resistance, or enrich by FACS for GFP expression to obtain a pure population of transfected cells. 2. For the GFP-containing SureSilencing shrna Plasmids ONLY: The approximate apparent level of suppression in transfected cells is equal to the observed percent knockdown divided by the experimentally determined transfection efficiency. For example, eighty (80) percent transfection efficiency and seventy (70) percent observed knockdown (30 percent of control) means an approximate percent suppression in transfected cells of (70 / 0.8) Technical Support: (US)
24 SureSilencing shrna Plasmids E. No stably-transfected cell population obtained after selection 1. Low transfection efficiency: a. Determine the observed transfection efficiency and optimize again, if necessary. b. If you have not done so already, repeat the plasmid purification using an endotoxin-free plasmid purification kit, particularly if excessive mammalian cell toxicity is observed upon transfection. c. Attempt to linearize the plasmid before transfection as described in this User Manual to help facilitate integration into your cell line s genome. 2. Antibiotic concentration too high: Only use the minimum neomycin (G418) concentration necessary to kill untransfected cells as defined by your kill curve. 3. Cells plated at too low a density during selection: Plating cells at extremely low densities may inhibit growth due to the effective dilution of autocrine growth factors. Conditioned medium may be used to promote growth, or repeat the transfection and then the selection at a higher cell density. 4. Suppressed gene is an essential gene for viability: The shrna successfully suppressed the expression of the target gene, but the target gene is required for the survival of the cells. In other words, the very act of suppressing the gene of interest itself killed the stably transfected cells. To explore the function of essential genes, you may need to develop and optimize an inducible promoter system for shrna in you laboratory or seek other alternatives. F. Selection completed but low level of knockdown or stable transfection 1. Cells plated at too high a density during selection: The use of too many cells during the selection reduces the effective concentration of neomycin. Repeat the transfection and then repeat the selection at a lower cell density. Preserve all of the transfected cells by dividing the entire population across a greater number of plates. Conditioned medium may be used to promote growth at these lower densities. 2. Neomycin concentration too low: Be sure to use at least the minimum neomycin (G418) concentration necessary to kill untransfected cells as defined by your kill curve. 3. Isolation of individual clones from pooled population is required to achieve maximal knockdown: Choose the two pooled populations which exhibit the greatest level of knockdown. Sub-clone to select for single integration events. Briefly, dilute the cells such that a concentration of 0.5 cells per well of a 384 well dish is achieved. Select 10 colonies from each of the pooled population to assay for knockdown. Technical Support: [email protected] 24
25 Version 1.7 G. Knockdown not distinguishable by real-time PCR 1. Poor transfection efficiency and/or no selection or enrichment: Make sure that your transfection efficiency is optimized and that you have selected or enriched the cell population for transfected cells. You must be looking at a population of cells that is nearly 100 percent transfected for an accurate determination of knockdown. 2. Poor real-time PCR reproducibility: Make sure that your triplicate real-time PCR determinations of threshold cycle values demonstrate a high degree of reproducibility with a standard deviation of roughly 0.25 to 0.33 cycles. A seventy (70) percent knockdown of expression will be observed as only a 1.74 difference in normalized C t values for the gene of interest between pure populations of negative control and gene-specific shrna transfected cells. This specific level of reproducibility is required to reliably detect such a difference. 3. Low level of expression of gene of interest: To accurately determine knockdown by real-time PCR, the level of expression of the gene of interest in control- or un-transfected cells should be at least reasonably expressed with a C t value less than 30. Real-time PCR cannot determine the relative expression of genes expressed at a lower level (C t > 30) with enough reproducibility to detect a seventy (70) percent knockdown of expression. Try using more input RNA (up to 5 μg) in the reverse transcription reaction and only dilute the completed reaction by four-fold, adding 60 instead of 100 μl of ddh 2 O, but still use 10 μl of the dilution to setup PCR. 4. Real-time PCR analysis not performed properly: Make sure that real-time PCR analysis was set up and performed properly. Consult the Troubleshooting Guide of the RT 2 Gene Expression Assay User Manual if using the RT 2 PCR Primer Sets and RT 2 Real-Time SYBR Green PCR Master Mixes from SABiosciences. If using other reagents for real-time PCR, consult the original manufacturers recommendations and suggestions. Note: Only use real-time PCR to determine the extent of knock-down. No other RNA detection method (e.g. Northern analysis or conventional PCR) will be quantitative enough to observe a 70 percent knockdown. Western analysis is also unreliable because the success of knockdown at the protein level also depends on the quality of the antibody and the biological half-life of the protein, whereas RNA interference specifically acts at the RNA level. (See below.) Technical Support: (US)
26 SureSilencing shrna Plasmids H. Real-time PCR decrease in expression at RNA level observed but no effect seen at the level of protein or biochemical assay The RT-PCR verification will confirm that expression has been decreased at the level of messenger RNA and that the SureSilencing shrna Plasmids functioned correctly. A change in the RNA level for a particular gene product does not necessarily immediately correlate with a change in the amount of protein in the cell. If the protein has a long half-life, then changes in protein level will take much longer to occur than changes in the RNA level. The protein level changes may therefore not be observed in a GFPbased transient transfection experiment, but should be detected in a longer term stable transfection based on neomycin or puromycin selection. Note: Most mammalian expression plasmids, like the SureSilencing shrna Plasmids, do not replicate in mammalian cells. They are eventually lost due to dilution caused by cell growth and division causing random distribution to daughter cells. The use of a selectable marker (such as antibiotic resistance) on the same or another plasmid (at one-tenth the amount) selects for the very rare incorporation of the plasmid DNA into cell line genome by an unknown mechanism. Once integrated, the plasmid sequence is replicated with the rest of the genome and passed to both daughter cells. Selection for the expression of GFP in such a fashion is not possible, meaning that GFP may only be used for transient transfection experiments. For any other troubleshooting or technical questions about the SureSilencing shrna Plasmids, please call one of our Technical Support representatives at or or at [email protected]. Technical Support: [email protected] 26
27 Version 1.7 Appendix A: Neomycin Parent Vector Sequence pgeneclip Neomycin Vector This vector can be obtained from Promega Corporation, Madison, WI. Call one of the following numbers for ordering or technical information: ; Outside U.S pgeneclip Neomycin Vector sequence reference points: Base pairs 4758 T7 RNA polymerase transcription initiation site 1 U1 promoter (human, -392 to +1) bp spacer U1 termination sequence SP6 RNA polymerase promoter (-17 to +3) SP6 RNA polymerase promoter primer binding site Binding region of puc/m13 reverse sequencing primer SV40 early enhancer/promoter SV40 minimum origin of replication Coding region of neomycin phosphotransferase Synthetic poly(a) signal Beta-lactamase (Ampr) coding region Binding region of puc/m13 forward sequencing primer T7 RNA polymerase promoter (-17 to +3) Insert Sequence: The sense strand of the insert for each provided plasmid will read as follows: 1. G - only if the shrna specific sequence does not already start with a G 2. The shrna sequence listed on the individual product information sheet 3. CTTCCTGTCA - the loop of the short hairpin RNA structure 4. The complementary sequence to the above shrna sequence 5. CT - to engineer a new diagnostic Pst I site indicating the presence of insert This sequence is inserted between positions 438 and 439 in the plasmid sequence below directly in the middle of the bold, underlined sequence of TCTC^GCAG. Technical Support: (US)
28 SureSilencing shrna Plasmids 1 GGGCGAATTG GGCCCGATAT CTCTAGAGTC GACGAATTCG GATCCCTAAG 51 GACCAGCTTC TTTGGGAGAG AACAGACGCA GGGGCGGGAG GGAAAAAGGG 101 AGAGGCAGAC GTCACTTCCC CTTGGCGGCT CTGGCAGCAG ATTGGTCGGT 151 TGAGTGGCAG AAAGGCAGAC GGGGACTGGG CAAGGCACTG TCGGTGACAT 201 CACGGACAGG GCGACTTCTA TGTAGATGAG GCAGCGCAGA GGCTGCTGCT 251 TCGCCACTTG CTGCTTCACC ACGAAGGAGT TCCCGTGCCC TGGGAGCGGG 301 TTCAGGACCG CTGATCGGAA GTGAGAATCC CAGCTGTGTG TCAGGGCTGG 351 AAAGGGCTCG GGAGTGCGCG GGGCAAGTGA CCGTGTGTGT AAAGAGTGAG 401 GCGTATGAGG CTGTGTCGGG GCAGAGGCCC AAGATCTCGC AGTCTGGAGT 451 TTCAAAAGTA GACTGGGCGG CCGCATCGAT GTTAACCTCG AGGAGCTCCC 501 AACGCGTTGG ATGCATAGCT TGAGTATTCT ATAGTGTCAC CTAAATAGCT 551 TGGCGTAATC ATGGTCATAG CTGTTTCCTG TGTGAAATTG TTATCCGCTC 601 ACAATTCCAC ACAACATACG AGCCGGAAGC ATAAAGTGTA AAGCCTGGGG 651 TGCCTAATGA GTGAGCTAAC TCACATTAAT TGCGTTGCGC TCACTGCCCG 701 CTTTCCAGTC GGGAAACCTG TCGTGCCAGC TGCATTAATG AATCGGCCAA 751 CGCGCGGGGA GAGGCGGTTT GCGTATTGGG CGCTCTTCCG CTGATCTGCG 801 CAGCACCATG GCCTGAAATA ACCTCTGAAA GAGGAACTTG GTTAGGTACC 851 TTCTGAGGCG GAAAGAACCA GCTGTGGAAT GTGTGTCAGT TAGGGTGTGG 901 AAAGTCCCCA GGCTCCCCAG CAGGCAGAAG TATGCAAAGC ATGCATCTCA 951 ATTAGTCAGC AACCAGGTGT GGAAAGTCCC CAGGCTCCCC AGCAGGCAGA 1001 AGTATGCAAA GCATGCATCT CAATTAGTCA GCAACCATAG TCCCGCCCCT 1051 AACTCCGCCC ATCCCGCCCC TAACTCCGCC CAGTTCCGCC CATTCTCCGC 1101 CCCATGGCTG ACTAATTTTT TTTATTTATG CAGAGGCCGA GGCCGCCTCG 1151 GCCTCTGAGC TATTCCAGAA GTAGTGAGGA GGCTTTTTTG GAGGCCTAGG 1201 CTTTTGCAAA AAGCTTGATT CTTCTGACGC TAGCGATCGC CCGGGCCACC 1251 ATGATTGAAC AAGATGGATT GCACGCAGGT TCTCCGGCCG CTTGGGTGGA 1301 GAGGCTATTC GGCTATGACT GGGCACAACA GACAATCGGC TGCTCTGATG 1351 CCGCCGTGTT CCGGCTGTCA GCGCAGGGGC GCCCGGTTCT TTTTGTCAAG 1401 ACCGACCTGT CCGGTGCCCT GAATGAACTG CAGGACGAGG CAGCGCGGCT 1451 ATCGTGGCTG GCCACGACGG GCGTTCCTTG CGCAGCTGTG CTCGACGTTG 1501 TCACTGAAGC GGGAAGGGAC TGGCTGCTAT TGGGCGAAGT GCCGGGGCAG 1551 GATCTCCTGT CATCTCACCT TGCTCCTGCC GAGAAAGTAT CCATCATGGC 1601 TGATGCAATG CGGCGGCTGC ATACGCTTGA TCCGGCTACC TGCCCATTCG 1651 ACCACCAAGC GAAACATCGC ATCGAGCGAG CACGTACTCG GATGGAAGCC 1701 GGTCTTGTCG ATCAGGATGA TCTGGACGAA GAGCATCAGG GGCTCGCGCC 1751 AGCCGAACTG TTCGCCAGGC TCAAGGCGCG CATGCCCGAC GGCGAGGATC 1801 TCGTCGTGAC CCATGGCGAT GCCTGCTTGC CGAATATCAT GGTGGAAAAT 1851 GGCCGCTTTT CTGGATTCAT CGACTGTGGC CGGCTGGGTG TGGCGGACCG 1901 CTATCAGGAC ATAGCGTTGG CTACCCGTGA TATTGCTGAA GAGCTTGGCG 1951 GCGAATGGGC TGACCGCTTC CTCGTGCTTT ACGGTATCGC CGCTCCCGAT 2001 TCGCAGCGCA TCGCCTTCTA TCGCCTTCTT GACGAGTTCT TCTGACTCGA 2051 GTTTAAACTC TAGAACCGGT CATGGCCGCA ATAAAATATC TTTATTTTCA 2101 TTACATCTGT GTGTTGGTTT TTTGTGTGTT CGAACTAGAA GCTTGCTTCC 2151 TCGCTCACTG ACTCGCTGCG CTCGGTCGTT CGGCTGCGGC GAGCGGTATC 2201 AGCTCACTCA AAGGCGGTAA TACGGTTATC CACAGAATCA GGGGATAACG 2251 CAGGAAAGAA CATGTGAGCA AAAGGCCAGC AAAAGGCCAG GAACCGTAAA 2301 AAGGCCGCGT TGCTGGCGTT TTTCCATAGG CTCCGCCCCC CTGACGAGCA 2351 TCACAAAAAT CGACGCTCAA GTCAGAGGTG GCGAAACCCG ACAGGACTAT 2401 AAAGATACCA GGCGTTTCCC CCTGGAAGCT CCCTCGTGCG CTCTCCTGTT 2451 CCGACCCTGC CGCTTACCGG ATACCTGTCC GCCTTTCTCC CTTCGGGAAG 2501 CGTGGCGCTT TCTCATAGCT CACGCTGTAG GTATCTCAGT TCGGTGTAGG 2551 TCGTTCGCTC CAAGCTGGGC TGTGTGCACG AACCCCCCGT TCAGCCCGAC 2601 CGCTGCGCCT TATCCGGTAA CTATCGTCTT GAGTCCAACC CGGTAAGACA 2651 CGACTTATCG CCACTGGCAG CAGCCACTGG TAACAGGATT AGCAGAGCGA 2701 GGTATGTAGG CGGTGCTACA GAGTTCTTGA AGTGGTGGCC TAACTACGGC 2751 TACACTAGAA GAACAGTATT TGGTATCTGC GCTCTGCTGA AGCCAGTTAC 2801 CTTCGGAAAA AGAGTTGGTA GCTCTTGATC CGGCAAACAA ACCACCGCTG 2851 GTAGCGGTGG TTTTTTTGTT TGCAAGCAGC AGATTACGCG CAGAAAAAAA 2901 GGATCTCAAG AAGATCCTTT GATCTTTTCT ACGGGGTCTG ACGCTCAGTG Technical Support: [email protected] 28
29 Version GAACGAAAAC TCACGTTAAG GGATTTTGGT CATGAGATTA TCAAAAAGGA 3001 TCTTCACCTA GATCCTTTTA AATTAAAAAT GAAGTTTTAA ATCAATCTAA 3051 AGTATATATG AGTAAACTTG GTCTGACAGT TACCAATGCT TAATCAGTGA 3101 GGCACCTATC TCAGCGATCT GTCTATTTCG TTCATCCATA GTTGCCTGAC 3151 TCCCCGTCGT GTAGATAACT ACGATACGGG AGGGCTTACC ATCTGGCCCC 3201 AGTGCTGCAA TGATACCGCG AGACCCACGC TCACCGGCTC CAGATTTATC 3251 AGCAATAAAC CAGCCAGCCG GAAGGGCCGA GCGCAGAAGT GGTCCTGCAA 3301 CTTTATCCGC CTCCATCCAG TCTATTAATT GTTGCCGGGA AGCTAGAGTA 3351 AGTAGTTCGC CAGTTAATAG TTTGCGCAAC GTTGTTGCCA TTGCTACAGG 3401 CATCGTGGTG TCACGCTCGT CGTTTGGTAT GGCTTCATTC AGCTCCGGTT 3451 CCCAACGATC AAGGCGAGTT ACATGATCCC CCATGTTGTG CAAAAAAGCG 3501 GTTAGCTCCT TCGGTCCTCC GATCGTTGTC AGAAGTAAGT TGGCCGCAGT 3551 GTTATCACTC ATGGTTATGG CAGCACTGCA TAATTCTCTT ACTGTCATGC 3601 CATCCGTAAG ATGCTTTTCT GTGACTGGTG AGTACTCAAC CAAGTCATTC 3651 TGAGAATAGT GTATGCGGCG ACCGAGTTGC TCTTGCCCGG CGTCAATACG 3701 GGATAATACC GCGCCACATA GCAGAACTTT AAAAGTGCTC ATCATTGGAA 3751 AACGTTCTTC GGGGCGAAAA CTCTCAAGGA TCTTACCGCT GTTGAGATCC 3801 AGTTCGATGT AACCCACTCG TGCACCCAAC TGATCTTCAG CATCTTTTAC 3851 TTTCACCAGC GTTTCTGGGT GAGCAAAAAC AGGAAGGCAA AATGCCGCAA 3901 AAAAGGGAAT AAGGGCGACA CGGAAATGTT GAATACTCAT ACTCTTCCTT 3951 TTTCAATATT ATTGAAGCAT TTATCAGGGT TATTGTCTCA TGAGCGGATA 4001 CATATTTGAA TGTATTTAGA AAAATAAACA AATAGGGGTT CCGCGCACAT 4051 TTCCCCGAAA AGTGCCACCT GATGCGGTGT GAAATACCGC ACAGATGCGT 4101 AAGGAGAAAA TACCGCATCA GGAAATTGTA AGCGTTAATA TTTTGTTAAA 4151 ATTCGCGTTA AATTTTTGTT AAATCAGCTC ATTTTTTAAC CAATAGGCCG 4201 AAATCGGCAA AATCCCTTAT AAATCAAAAG AATAGACCGA GATAGGGTTG 4251 AGTGTTGTTC CAGTTTGGAA CAAGAGTCCA CTATTAAAGA ACGTGGACTC 4301 CAACGTCAAA GGGCGAAAAA CCGTCTATCA GGGCGATGGC CCACTACGTG 4351 AACCATCACC CTAATCAAGT TTTTTGGGGT CGAGGTGCCG TAAAGCACTA 4401 AATCGGAACC CTAAAGGGAG CCCCCGATTT AGAGCTTGAC GGGGAAAGCC 4451 GGCGAACGTG GCGAGAAAGG AAGGGAAGAA AGCGAAAGGA GCGGGCGCTA 4501 GGGCGCTGGC AAGTGTAGCG GTCACGCTGC GCGTAACCAC CACACCCGCC 4551 GCGCTTAATG CGCCGCTACA GGGCGCGTCC ATTCGCCATT CAGGCTGCGC 4601 AACTGTTGGG AAGGGCGATC GGTGCGGGCC TCTTCGCTAT TACGCCAGCT 4651 GGCGAAAGGG GGATGTGCTG CAAGGCGATT AAGTTGGGTA ACGCCAGGGT 4701 TTTCCCAGTC ACGACGTTGT AAAACGACGG CCAGTGAATT GTAATACGAC 4751 TCACTATA Sequence file prepared 5-Oct-04. Technical Support: (US)
30 SureSilencing shrna Plasmids Appendix B: GFP Parent Vector Sequence pgeneclip hmgfp Vector This vector can be obtained from Promega Corporation, Madison, WI. Call one of the following numbers for ordering or technical information: ; Outside U.S pgeneclip hmgfp Vector sequence reference points: Base pairs 5267 T7 RNA polymerase transcription initiation site 1 U1 promoter (human, -392 to +1) bp spacer U1 termination sequence SP6 RNA polymerase promoter (-17 to +3) SP6 RNA polymerase promoter primer binding site Binding region of puc/m13 reverse sequencing primer CMV enhancer/promoter Chimeric intron hmgfp open reading frame Synthetic poly(a) signal Beta-lactamase (Ampr) coding region Binding region of puc/m13 forward sequencing primer T7 RNA polymerase promoter (-17 to +3) Insert Sequence: The sense strand of the insert for each provided plasmid will read as follows: 1. G - only if the shrna specific sequence does not already start with a G 2. The shrna sequence listed on the individual product information sheet 3. CTTCCTGTCA - the loop of the short hairpin RNA structure 4. The complementary sequence to the above shrna sequence 5. CT - to engineer a new diagnostic Pst I site indicating the presence of insert This sequence is inserted between positions 438 and 439 in the plasmid sequence below directly in the middle of the bold, underlined sequence of TCTC^GCAG. Technical Support: [email protected] 30
31 Version GGGCGAATTG GGCCCGATAT CTCTAGAGTC GACGAATTCG GATCCCTAAG 51 GACCAGCTTC TTTGGGAGAG AACAGACGCA GGGGCGGGAG GGAAAAAGGG 101 AGAGGCAGAC GTCACTTCCC CTTGGCGGCT CTGGCAGCAG ATTGGTCGGT 151 TGAGTGGCAG AAAGGCAGAC GGGGACTGGG CAAGGCACTG TCGGTGACAT 201 CACGGACAGG GCGACTTCTA TGTAGATGAG GCAGCGCAGA GGCTGCTGCT 251 TCGCCACTTG CTGCTTCACC ACGAAGGAGT TCCCGTGCCC TGGGAGCGGG 301 TTCAGGACCG CTGATCGGAA GTGAGAATCC CAGCTGTGTG TCAGGGCTGG 351 AAAGGGCTCG GGAGTGCGCG GGGCAAGTGA CCGTGTGTGT AAAGAGTGAG 401 GCGTATGAGG CTGTGTCGGG GCAGAGGCCC AAGATCTCGC AGTCTGGAGT 451 TTCAAAAGTA GACTGGGCGG CCGCATCGAT GTTAACCTCG AGGAGCTCCC 501 AACGCGTTGG ATGCATAGCT TGAGTATTCT ATAGTGTCAC CTAAATAGCT 551 TGGCGTAATC ATGGTCATAG CTGTTTCCTG TGTGAAATTG TTATCCGCTC 601 ACAATTCCAC ACAACATACG AGCCGGAAGC ATAAAGTGTA AAGCCTGGGG 651 TGCCTAATGA GTGAGCTAAC TCACATTAAT TGCGTTGCGC TCACTGCCCG 701 CTTTCCAGTC GGGAAACCTG TCGTGCCAGC TGCATTAATG AATCGGCCAA 751 CGCGCGGGGA GAGGCGGTTT GCGTATTGGG CGCTCTTCCG CTCTTCCGCT 801 TCAATATTGG CCATTAGCCA TATTATTCAT TGGTTATATA GCATAAATCA 851 ATATTGGCTA TTGGCCATTG CATACGTTGT ATCTATATCA TAATATGTAC 901 ATTTATATTG GCTCATGTCC AATATGACCG CCATGTTGGC ATTGATTATT 951 GACTAGTTAT TAATAGTAAT CAATTACGGG GTCATTAGTT CATAGCCCAT 1001 ATATGGAGTT CCGCGTTACA TAACTTACGG TAAATGGCCC GCCTGGCTGA 1051 CCGCCCAACG ACCCCCGCCC ATTGACGTCA ATAATGACGT ATGTTCCCAT 1101 AGTAACGCCA ATAGGGACTT TCCATTGACG TCAATGGGTG GAGTATTTAC 1151 GGTAAACTGC CCACTTGGCA GTACATCAAG TGTATCATAT GCCAAGTCCG 1201 CCCCCTATTG ACGTCAATGA CGGTAAATGG CCCGCCTGGC ATTATGCCCA 1251 GTACATGACC TTACGGGACT TTCCTACTTG GCAGTACATC TACGTATTAG 1301 TCATCGCTAT TACCATGGTG ATGCGGTTTT GGCAGTACAC CAATGGGCGT 1351 GGATAGCGGT TTGACTCACG GGGATTTCCA AGTCTCCACC CCATTGACGT 1401 CAATGGGAGT TTGTTTTGGC ACCAAAATCA ACGGGACTTT CCAAAATGTC 1451 GTAACAACTG CGATCGCCCG CCCCGTTGAC GCAAATGGGC GGTAGGCGTG 1501 TACGGTGGGA GGTCTATATA AGCAGAGCTC GTTTAGTGAA CCGTCAGATC 1551 ACTAGAAGCT TTATTGCGGT AGTTTATCAC AGTTAAATTG CTAACGCAGT 1601 CAGTGCTTCT GACACAACAG TCTCGAACTT AAGCTGCAGT GACTCTCTTA 1651 AGGTAGCCTT GCAGAAGTTG GTCGTGAGGC ACTGGGCAGG TAAGTATCAA 1701 GGTTACAAGA CAGGTTTAAG GAGACCAATA GAAACTGGGC TTGTCGAGAC 1751 AGAGAAGACT CTTGCGTTTC TGATAGGCAC CTATTGGTCT TACTGACATC 1801 CACTTTGCCT TTCTCTCCAC AGGTGTCCAC TCCCAGTTCA ATTACAGCTC 1851 GCTAGCGATC GCCCGGGGAT ATCGCCACCA TGGGCGTGAT CAAGCCCGAC 1901 ATGAAGATCA AGCTGCGGAT GGAGGGCGCC GTGAACGGCC ACAAATTCGT 1951 GATCGAGGGC GACGGGAAAG GCAAGCCCTT TGAGGGTAAG CAGACTATGG 2001 ACCTGACCGT GATCGAGGGC GCCCCCCTGC CCTTCGCTTA TGACATTCTC 2051 ACCACCGTGT TCGACTACGG TAACCGTGTC TTCGCCAAGT ACCCCAAGGA 2101 CATCCCTGAC TACTTCAAGC AGACCTTCCC CGAGGGCTAC TCGTGGGAGC 2151 GAAGCATGAC ATACGAGGAC CAGGGAATCT GTATCGCTAC AAACGACATC 2201 ACCATGATGA AGGGTGTGGA CGACTGCTTC GTGTACAAAA TCCGCTTCGA 2251 CGGGGTCAAC TTCCCTGCTA ATGGCCCGGT GATGCAGCGC AAGACCCTAA 2301 AGTGGGAGCC CAGTACCGAG AAGATGTACG TGCGGGACGG CGTACTGAAG 2351 GGCGATGTTA ATATGGCACT GCTCTTGGAG GGAGGCGGCC ACTACCGCTG 2401 CGACTTCAAG ACCACCTACA AAGCCAAGAA GGTGGTGCAG CTTCCCGACT 2451 ACCACTTCGT GGACCACCGC ATCGAGATCG TGAGCCACGA CAAGGACTAC 2501 AACAAAGTCA AGCTGTACGA GCACGCCGAA GCCCACAGCG GACTACCCCG 2551 CCAGGCCGGC TAATAGTTCT AGAACCGGTC ATGGCCGCAA TAAAATATCT 2601 TTATTTTCAT TACATCTGTG TGTTGGTTTT TTGTGTGTTC GAACTAGAAG 2651 CTTGCTTCCT CGCTCACTGA CTCGCTGCGC TCGGTCGTTC GGCTGCGGCG 2701 AGCGGTATCA GCTCACTCAA AGGCGGTAAT ACGGTTATCC ACAGAATCAG 2751 GGGATAACGC AGGAAAGAAC ATGTGAGCAA AAGGCCAGCA AAAGGCCAGG 2801 AACCGTAAAA AGGCCGCGTT GCTGGCGTTT TTCCATAGGC TCCGCCCCCC 2851 TGACGAGCAT CACAAAAATC GACGCTCAAG TCAGAGGTGG CGAAACCCGA 2901 CAGGACTATA AAGATACCAG GCGTTTCCCC CTGGAAGCTC CCTCGTGCGC Technical Support: (US)
32 SureSilencing shrna Plasmids 2951 TCTCCTGTTC CGACCCTGCC GCTTACCGGA TACCTGTCCG CCTTTCTCCC 3001 TTCGGGAAGC GTGGCGCTTT CTCATAGCTC ACGCTGTAGG TATCTCAGTT 3051 CGGTGTAGGT CGTTCGCTCC AAGCTGGGCT GTGTGCACGA ACCCCCCGTT 3101 CAGCCCGACC GCTGCGCCTT ATCCGGTAAC TATCGTCTTG AGTCCAACCC 3151 GGTAAGACAC GACTTATCGC CACTGGCAGC AGCCACTGGT AACGGGATTA 3201 GCAGAGCGAG GTATGTAGGC GGTGCTACAG AGTTCTTGAA GTGGTGGCCT 3251 AACTACGGCT ACACTAGAAG AACAGTATTT GGTATCTGCG CTCTGCTGAA 3301 GCCAGTTACC TTCGGAAAAA GAGTTGGTAG CTCTTGATCC GGCAAACAAA 3351 CCACCGCTGG TAGCGGTGGT TTTTTTGTTT GCAAGCAGCA GATTACGCGC 3401 AGAAAAAAAG GATCTCAAGA AGATCCTTTG ATCTTTTCTA CGGGGTCTGA 3451 CGCTCAGTGG AACGAAAACT CACGTTAAGG GATTTTGGTC ATGAGATTAT 3501 CAAAAAGGAT CTTCACCTAG ATCCTTTTAA ATTAAAAATG AAGTTTTAAA 3551 TCAATCTAAA GTATATATGA GTAAACTTGG TCTGACAGTT ACCAATGCTT 3601 AATCAGTGAG GCACCTATCT CAGCGATCTG TCTATTTCGT TCATCCATAG 3651 TTGCCTGACT CCCCGTCGTG TAGATAACTA CGATACGGGA GGGCTTACCA 3701 TCTGGCCCCA GTGCTGCAAT GATACCGCGA GACCCACGCT CACCGGCTCC 3751 AGATTTATCA GCAATAAACC AGCCAGCCGG AAGGGCCGAG CGCAGAAGTG 3801 GTCCTGCAAC TTTATCCGCC TCCATCCAGT CTATTAATTG TTGCCGGGAA 3851 GCTAGAGTAA GTAGTTCGCC AGTTAATAGT TTGCGCAACG TTGTTGCCAT 3901 TGCTACAGGC ATCGTGGTGT CACGCTCGTC GTTTGGTATG GCTTCATTCA 3951 GCTCCGGTTC CCAACGATCA AGGCGAGTTA CATGATCCCC CATGTTGTGC 4001 AAAAAAGCGG TTAGCTCCTT CGGTCCTCCG ATCGTTGTCA GAAGTAAGTT 4051 GGCCGCAGTG TTATCACTCA TGGTTATGGC AGCACTGCAT AATTCTCTTA 4101 CTGTCATGCC ATCCGTAAGA TGCTTTTCTG TGACTGGTGA GTACTCAACC 4151 AAGTCATTCT GAGAATAGTG TATGCGGCGA CCGAGTTGCT CTTGCCCGGC 4201 GTCAATACGG GATAATACCG CGCCACATAG CAGAACTTTA AAAGTGCTCA 4251 TCATTGGAAA ACGTTCTTCG GGGCGAAAAC TCTCAAGGAT CTTACCGCTG 4301 TTGAGATCCA GTTCGATGTA ACCCACTCGT GCACCCAACT GATCTTCAGC 4351 ATCTTTTACT TTCACCAGCG TTTCTGGGTG AGCAAAAACA GGAAGGCAAA 4401 ATGCCGCAAA AAAGGGAATA AGGGCGACAC GGAAATGTTG AATACTCATA 4451 CTCTTCCTTT TTCAATATTA TTGAAGCATT TATCAGGGTT ATTGTCTCAT 4501 GAGCGGATAC ATATTTGAAT GTATTTAGAA AAATAAACAA ATAGGGGTTC 4551 CGCGCACATT TCCCCGAAAA GTGCCACCTG ATGCGGTGTG AAATACCGCA 4601 CAGATGCGTA AGGAGAAAAT ACCGCATCAG GAAATTGTAA GCGTTAATAT 4651 TTTGTTAAAA TTCGCGTTAA ATTTTTGTTA AATCAGCTCA TTTTTTAACC 4701 AATAGGCCGA AATCGGCAAA ATCCCTTATA AATCAAAAGA ATAGACCGAG 4751 ATAGGGTTGA GTGTTGTTCC AGTTTGGAAC AAGAGTCCAC TATTAAAGAA 4801 CGTGGACTCC AACGTCAAAG GGCGAAAAAC CGTCTATCAG GGCGATGGCC 4851 CACTACGTGA ACCATCACCC TAATCAAGTT TTTTGGGGTC GAGGTGCCGT 4901 AAAGCACTAA ATCGGAACCC TAAAGGGAGC CCCCGATTTA GAGCTTGACG 4951 GGGAAAGCCG GCGAACGTGG CGAGAAAGGA AGGGAAGAAA GCGAAAGGAG 5001 CGGGCGCTAG GGCGCTGGCA AGTGTAGCGG TCACGCTGCG CGTAACCACC 5051 ACACCCGCCG CGCTTAATGC GCCGCTACAG GGCGCGTCCA TTCGCCATTC 5101 AGGCTGCGCA ACTGTTGGGA AGGGCGATCG GTGCGGGCCT CTTCGCTATT 5151 ACGCCAGCTG GCGAAAGGGG GATGTGCTGC AAGGCGATTA AGTTGGGTAA 5201 CGCCAGGGTT TTCCCAGTCA CGACGTTGTA AAACGACGGC CAGTGAATTG 5251 TAATACGACT CACTATA Sequence file prepared 5-Oct-04. Technical Support: 32
33 Appendix C: Puromycin Parent Vector Sequence Version 1.7 pgeneclip Puromycin Vector This vector can be obtained from Promega Corporation, Madison, WI. Call one of the following numbers for ordering or technical information: ; Outside U.S pgeneclip(tm) Puromycin Vector sequence reference points: Base pairs 4561 T7 RNA polymerase transcription initiation site 1 U1 promoter (human, -392 to +1) bp spacer U1 termination sequence SP6 RNA polymerase promoter (-17 to +3) SP6 RNA polymerase promoter primer binding site Binding region of puc/m13 reverse sequencing primer SV40 early enhancer/promoter SV40 minimum origin of replication Puromycine-N-acetyltransferase coding region Synthetic poly(a) signal Beta-lactamase (Ampr) coding region Binding region of puc/m13 forward sequencing primer T7 RNA polymerase promoter (-17 to +3) Insert Sequence: The sense strand of the insert for each provided plasmid will read as follows: 1. G - only if the shrna specific sequence does not already start with a G 2. The shrna sequence listed on the individual product information sheet 3. CTTCCTGTCA - the loop of the short hairpin RNA structure 4. The complementary sequence to the above shrna sequence 5. CT - to engineer a new diagnostic Pst I site indicating the presence of insert This sequence is inserted between positions 438 and 439 in the plasmid sequence below directly in the middle of the bold, underlined sequence of TCTC^GCAG. Technical Support: (US)
34 SureSilencing shrna Plasmids 1 GGGCGAATTG GGCCCGATAT CTCTAGAGTC GACGAATTCG GATCCCTAAG 51 GACCAGCTTC TTTGGGAGAG AACAGACGCA GGGGCGGGAG GGAAAAAGGG 101 AGAGGCAGAC GTCACTTCCC CTTGGCGGCT CTGGCAGCAG ATTGGTCGGT 151 TGAGTGGCAG AAAGGCAGAC GGGGACTGGG CAAGGCACTG TCGGTGACAT 201 CACGGACAGG GCGACTTCTA TGTAGATGAG GCAGCGCAGA GGCTGCTGCT 251 TCGCCACTTG CTGCTTCACC ACGAAGGAGT TCCCGTGCCC TGGGAGCGGG 301 TTCAGGACCG CTGATCGGAA GTGAGAATCC CAGCTGTGTG TCAGGGCTGG 351 AAAGGGCTCG GGAGTGCGCG GGGCAAGTGA CCGTGTGTGT AAAGAGTGAG 401 GCGTATGAGG CTGTGTCGGG GCAGAGGCCC AAGATCTCGC AGTCTGGAGT 451 TTCAAAAGTA GACTGGGCGG CCGCATCGAT GTTAACCTCG AGGAGCTCCC 501 AACGCGTTGG ATGCATAGCT TGAGTATTCT ATAGTGTCAC CTAAATAGCT 551 TGGCGTAATC ATGGTCATAG CTGTTTCCTG TGTGAAATTG TTATCCGCTC 601 ACAATTCCAC ACAACATACG AGCCGGAAGC ATAAAGTGTA AAGCCTGGGG 651 TGCCTAATGA GTGAGCTAAC TCACATTAAT TGCGTTGCGC TCACTGCCCG 701 CTTTCCAGTC GGGAAACCTG TCGTGCCAGC TGCATTAATG AATCGGCCAA 751 CGCGCGGGGA GAGGCGGTTT GCGTATTGGG CGCTCTTCCG CTGATCTGCG 801 CAGCACCATG GCCTGAAATA ACCTCTGAAA GAGGAACTTG GTTAGGTACC 851 TTCTGAGGCG GAAAGAACCA GCTGTGGAAT GTGTGTCAGT TAGGGTGTGG 901 AAAGTCCCCA GGCTCCCCAG CAGGCAGAAG TATGCAAAGC ATGCATCTCA 951 ATTAGTCAGC AACCAGGTGT GGAAAGTCCC CAGGCTCCCC AGCAGGCAGA 1001 AGTATGCAAA GCATGCATCT CAATTAGTCA GCAACCATAG TCCCGCCCCT 1051 AACTCCGCCC ATCCCGCCCC TAACTCCGCC CAGTTCCGCC CATTCTCCGC 1101 CCCATGGCTG ACTAATTTTT TTTATTTATG CAGAGGCCGA GGCCGCCTCG 1151 GCCTCTGAGC TATTCCAGAA GTAGTGAGGA GGCTTTTTTG GAGGCCTAGG 1201 CTTTTGCAAA AAGCTTGATT CTTCTGACGC TAGCCACCAT GACCGAGTAC 1251 AAGCCCACGG TGCGCCTCGC CACCCGCGAC GACGTCCCCC GGGCCGTACG 1301 CACCCTCGCC GCCGCGTTCG CCGACTACCC CGCCACGCGC CACACCGTCG 1351 ACCCGGACCG CCACATCGAG CGGGTCACCG AGCTGCAAGA ACTCTTCCTC 1401 ACGCGCGTCG GGCTCGACAT CGGCAAGGTG TGGGTCGCGG ACGACGGCGC 1451 CGCGGTGGCG GTCTGGACCA CGCCGGAGAG CGTCGAAGCG GGGGCGGTGT 1501 TCGCCGAGAT CGGCCCGCGC ATGGCCGAGT TGAGCGGTTC CCGGCTGGCC 1551 GCGCAGCAAC AGATGGAAGG CCTCCTGGCG CCGCACCGGC CCAAGGAGCC 1601 CGCGTGGTTC CTGGCCACCG TCGGCGTGTC GCCCGACCAC CAGGGCAAGG 1651 GTCTGGGCAG CGCCGTCGTG CTCCCCGGAG TGGAGGCGGC CGAGCGCGCC 1701 GGGGTGCCCG CCTTCCTGGA GACCTCCGCG CCCCGCAACC TCCCCTTCTA 1751 CGAGCGGCTC GGCTTCACCG TCACCGCCGA CGTCGAGGTG CCCGAAGGAC 1801 CGCGCACCTG GTGCATGACC CGCAAGCCCG GTGCCTGACT GCAGGATCCT 1851 CGAGTTTAAA CTCTAGAACC GGTCATGGCC GCAATAAAAT ATCTTTATTT 1901 TCATTACATC TGTGTGTTGG TTTTTTGTGT GTTCGAACTA GAAGCTTGCT 1951 TCCTCGCTCA CTGACTCGCT GCGCTCGGTC GTTCGGCTGC GGCGAGCGGT 2001 ATCAGCTCAC TCAAAGGCGG TAATACGGTT ATCCACAGAA TCAGGGGATA 2051 ACGCAGGAAA GAACATGTGA GCAAAAGGCC AGCAAAAGGC CAGGAACCGT 2101 AAAAAGGCCG CGTTGCTGGC GTTTTTCCAT AGGCTCCGCC CCCCTGACGA 2151 GCATCACAAA AATCGACGCT CAAGTCAGAG GTGGCGAAAC CCGACAGGAC 2201 TATAAAGATA CCAGGCGTTT CCCCCTGGAA GCTCCCTCGT GCGCTCTCCT 2251 GTTCCGACCC TGCCGCTTAC CGGATACCTG TCCGCCTTTC TCCCTTCGGG 2301 AAGCGTGGCG CTTTCTCATA GCTCACGCTG TAGGTATCTC AGTTCGGTGT 2351 AGGTCGTTCG CTCCAAGCTG GGCTGTGTGC ACGAACCCCC CGTTCAGCCC 2401 GACCGCTGCG CCTTATCCGG TAACTATCGT CTTGAGTCCA ACCCGGTAAG 2451 ACACGACTTA TCGCCACTGG CAGCAGCCAC TGGTAACAGG ATTAGCAGAG 2501 CGAGGTATGT AGGCGGTGCT ACAGAGTTCT TGAAGTGGTG GCCTAACTAC 2551 GGCTACACTA GAAGAACAGT ATTTGGTATC TGCGCTCTGC TGAAGCCAGT 2601 TACCTTCGGA AAAAGAGTTG GTAGCTCTTG ATCCGGCAAA CAAACCACCG 2651 CTGGTAGCGG TGGTTTTTTT GTTTGCAAGC AGCAGATTAC GCGCAGAAAA 2701 AAAGGATCTC AAGAAGATCC TTTGATCTTT TCTACGGGGT CTGACGCTCA 2751 GTGGAACGAA AACTCACGTT AAGGGATTTT GGTCATGAGA TTATCAAAAA 2801 GGATCTTCAC CTAGATCCTT TTAAATTAAA AATGAAGTTT TAAATCAATC 2851 TAAAGTATAT ATGAGTAAAC TTGGTCTGAC AGTTACCAAT GCTTAATCAG 2901 TGAGGCACCT ATCTCAGCGA TCTGTCTATT TCGTTCATCC ATAGTTGCCT Technical Support: [email protected] 34
35 2951 GACTCCCCGT CGTGTAGATA ACTACGATAC GGGAGGGCTT ACCATCTGGC 3001 CCCAGTGCTG CAATGATACC GCGAGACCCA CGCTCACCGG CTCCAGATTT 3051 ATCAGCAATA AACCAGCCAG CCGGAAGGGC CGAGCGCAGA AGTGGTCCTG 3101 CAACTTTATC CGCCTCCATC CAGTCTATTA ATTGTTGCCG GGAAGCTAGA 3151 GTAAGTAGTT CGCCAGTTAA TAGTTTGCGC AACGTTGTTG CCATTGCTAC 3201 AGGCATCGTG GTGTCACGCT CGTCGTTTGG TATGGCTTCA TTCAGCTCCG 3251 GTTCCCAACG ATCAAGGCGA GTTACATGAT CCCCCATGTT GTGCAAAAAA 3301 GCGGTTAGCT CCTTCGGTCC TCCGATCGTT GTCAGAAGTA AGTTGGCCGC 3351 AGTGTTATCA CTCATGGTTA TGGCAGCACT GCATAATTCT CTTACTGTCA 3401 TGCCATCCGT AAGATGCTTT TCTGTGACTG GTGAGTACTC AACCAAGTCA 3451 TTCTGAGAAT AGTGTATGCG GCGACCGAGT TGCTCTTGCC CGGCGTCAAT 3501 ACGGGATAAT ACCGCGCCAC ATAGCAGAAC TTTAAAAGTG CTCATCATTG 3551 GAAAACGTTC TTCGGGGCGA AAACTCTCAA GGATCTTACC GCTGTTGAGA 3601 TCCAGTTCGA TGTAACCCAC TCGTGCACCC AACTGATCTT CAGCATCTTT 3651 TACTTTCACC AGCGTTTCTG GGTGAGCAAA AACAGGAAGG CAAAATGCCG 3701 CAAAAAAGGG AATAAGGGCG ACACGGAAAT GTTGAATACT CATACTCTTC 3751 CTTTTTCAAT ATTATTGAAG CATTTATCAG GGTTATTGTC TCATGAGCGG 3801 ATACATATTT GAATGTATTT AGAAAAATAA ACAAATAGGG GTTCCGCGCA 3851 CATTTCCCCG AAAAGTGCCA CCTGATGCGG TGTGAAATAC CGCACAGATG 3901 CGTAAGGAGA AAATACCGCA TCAGGAAATT GTAAGCGTTA ATATTTTGTT 3951 AAAATTCGCG TTAAATTTTT GTTAAATCAG CTCATTTTTT AACCAATAGG 4001 CCGAAATCGG CAAAATCCCT TATAAATCAA AAGAATAGAC CGAGATAGGG 4051 TTGAGTGTTG TTCCAGTTTG GAACAAGAGT CCACTATTAA AGAACGTGGA 4101 CTCCAACGTC AAAGGGCGAA AAACCGTCTA TCAGGGCGAT GGCCCACTAC 4151 GTGAACCATC ACCCTAATCA AGTTTTTTGG GGTCGAGGTG CCGTAAAGCA 4201 CTAAATCGGA ACCCTAAAGG GAGCCCCCGA TTTAGAGCTT GACGGGGAAA 4251 GCCGGCGAAC GTGGCGAGAA AGGAAGGGAA GAAAGCGAAA GGAGCGGGCG 4301 CTAGGGCGCT GGCAAGTGTA GCGGTCACGC TGCGCGTAAC CACCACACCC 4351 GCCGCGCTTA ATGCGCCGCT ACAGGGCGCG TCCATTCGCC ATTCAGGCTG 4401 CGCAACTGTT GGGAAGGGCG ATCGGTGCGG GCCTCTTCGC TATTACGCCA 4451 GCTGGCGAAA GGGGGATGTG CTGCAAGGCG ATTAAGTTGG GTAACGCCAG 4501 GGTTTTCCCA GTCACGACGT TGTAAAACGA CGGCCAGTGA ATTGTAATAC 4551 GACTCACTAT A Sequence file prepared 5-Oct-04 Version 1.7 Technical Support: (US)
36 SureSilencing shrna Plasmids Part #1019A Version /29/2008 BIOMOL GmbH Waidmannstr Hamburg Phone: or (D) Fax: or (D)
MystiCq microrna cdna Synthesis Mix Catalog Number MIRRT Storage Temperature 20 C
 microrna cdna Synthesis Mix Catalog Number MIRRT Storage Temperature 20 C Product Description The microrna cdna Synthesis Mix has been designed to easily convert micrornas into cdna templates for qpcr
microrna cdna Synthesis Mix Catalog Number MIRRT Storage Temperature 20 C Product Description The microrna cdna Synthesis Mix has been designed to easily convert micrornas into cdna templates for qpcr
Introduction To Real Time Quantitative PCR (qpcr)
 Introduction To Real Time Quantitative PCR (qpcr) SABiosciences, A QIAGEN Company www.sabiosciences.com The Seminar Topics The advantages of qpcr versus conventional PCR Work flow & applications Factors
Introduction To Real Time Quantitative PCR (qpcr) SABiosciences, A QIAGEN Company www.sabiosciences.com The Seminar Topics The advantages of qpcr versus conventional PCR Work flow & applications Factors
Essentials of Real Time PCR. About Sequence Detection Chemistries
 Essentials of Real Time PCR About Real-Time PCR Assays Real-time Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is the ability to monitor the progress of the PCR as it occurs (i.e., in real time). Data is therefore collected
Essentials of Real Time PCR About Real-Time PCR Assays Real-time Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is the ability to monitor the progress of the PCR as it occurs (i.e., in real time). Data is therefore collected
TransIT -2020 Transfection Reagent
 Quick Reference Protocol, MSDS and Certificate of Analysis available at mirusbio.com/5400 INTRODUCTION TransIT -2020 Transfection Reagent is a high-performance, animal-origin free, broad spectrum reagent
Quick Reference Protocol, MSDS and Certificate of Analysis available at mirusbio.com/5400 INTRODUCTION TransIT -2020 Transfection Reagent is a high-performance, animal-origin free, broad spectrum reagent
Thermo Scientific DyNAmo cdna Synthesis Kit for qrt-pcr Technical Manual
 Thermo Scientific DyNAmo cdna Synthesis Kit for qrt-pcr Technical Manual F- 470S 20 cdna synthesis reactions (20 µl each) F- 470L 100 cdna synthesis reactions (20 µl each) Table of contents 1. Description...
Thermo Scientific DyNAmo cdna Synthesis Kit for qrt-pcr Technical Manual F- 470S 20 cdna synthesis reactions (20 µl each) F- 470L 100 cdna synthesis reactions (20 µl each) Table of contents 1. Description...
Validating Microarray Data Using RT 2 Real-Time PCR Products
 Validating Microarray Data Using RT 2 Real-Time PCR Products Introduction: Real-time PCR monitors the amount of amplicon as the reaction occurs. Usually, the amount of product is directly related to the
Validating Microarray Data Using RT 2 Real-Time PCR Products Introduction: Real-time PCR monitors the amount of amplicon as the reaction occurs. Usually, the amount of product is directly related to the
CompleteⅡ 1st strand cdna Synthesis Kit
 Instruction Manual CompleteⅡ 1st strand cdna Synthesis Kit Catalog # GM30401, GM30402 Green Mountain Biosystems. LLC Web: www.greenmountainbio.com Tel: 800-942-1160 Sales: Sales@ greenmountainbio.com Support:
Instruction Manual CompleteⅡ 1st strand cdna Synthesis Kit Catalog # GM30401, GM30402 Green Mountain Biosystems. LLC Web: www.greenmountainbio.com Tel: 800-942-1160 Sales: Sales@ greenmountainbio.com Support:
Instructions. Torpedo sirna. Material. Important Guidelines. Specifications. Quality Control
 is a is a state of the art transfection reagent, specifically designed for the transfer of sirna and mirna into a variety of eukaryotic cell types. is a state of the art transfection reagent, specifically
is a is a state of the art transfection reagent, specifically designed for the transfer of sirna and mirna into a variety of eukaryotic cell types. is a state of the art transfection reagent, specifically
mircute mirna qpcr Detection Kit (SYBR Green)
 mircute mirna qpcr Detection Kit (SYBR Green) For detection of mirna using real-time RT-PCR (SYBR Green I) www.tiangen.com QP110302 mircute mirna qpcr Detection Kit (SYBR Green) Kit Contents Cat. no. FP401
mircute mirna qpcr Detection Kit (SYBR Green) For detection of mirna using real-time RT-PCR (SYBR Green I) www.tiangen.com QP110302 mircute mirna qpcr Detection Kit (SYBR Green) Kit Contents Cat. no. FP401
sirna Duplexes & RNAi Explorer
 P r o d u c t S p e c i f i c a t i o n s Guaranteed RNAi Explorer kit with Fl/Dabcyl Molecular Beacon Catalog No.:27-6402-01 Guaranteed RNAi Explorer kit with Fluorescein/Tamra TaqMan Catalog No.:27-6402-01
P r o d u c t S p e c i f i c a t i o n s Guaranteed RNAi Explorer kit with Fl/Dabcyl Molecular Beacon Catalog No.:27-6402-01 Guaranteed RNAi Explorer kit with Fluorescein/Tamra TaqMan Catalog No.:27-6402-01
TransformAid Bacterial Transformation Kit
 Home Contacts Order Catalog Support Search Alphabetical Index Numerical Index Restriction Endonucleases Modifying Enzymes PCR Kits Markers Nucleic Acids Nucleotides & Oligonucleotides Media Transfection
Home Contacts Order Catalog Support Search Alphabetical Index Numerical Index Restriction Endonucleases Modifying Enzymes PCR Kits Markers Nucleic Acids Nucleotides & Oligonucleotides Media Transfection
Real-Time PCR Vs. Traditional PCR
 Real-Time PCR Vs. Traditional PCR Description This tutorial will discuss the evolution of traditional PCR methods towards the use of Real-Time chemistry and instrumentation for accurate quantitation. Objectives
Real-Time PCR Vs. Traditional PCR Description This tutorial will discuss the evolution of traditional PCR methods towards the use of Real-Time chemistry and instrumentation for accurate quantitation. Objectives
All-in-One mirna qrt-pcr Reagent Kits For quantitative detection of mature mirna
 All-in-One mirna qrt-pcr Reagent Kits For quantitative detection of mature mirna All-in-One TM mirna First-Strand cdna Synthesis Kit AMRT-0020 (20 RT reactions), AMRT-0060 (60 RT reactions) Used in combination
All-in-One mirna qrt-pcr Reagent Kits For quantitative detection of mature mirna All-in-One TM mirna First-Strand cdna Synthesis Kit AMRT-0020 (20 RT reactions), AMRT-0060 (60 RT reactions) Used in combination
Reprogramming, Screening and Validation of ipscs and Terminally Differentiated Cells using the qbiomarker PCR Array System
 Reprogramming, Screening and Validation of ipscs and Terminally Differentiated Cells using the qbiomarker PCR Array System Outline of Webinar What are induced pluripotent Stem Cells (ips Cells or ipscs)?
Reprogramming, Screening and Validation of ipscs and Terminally Differentiated Cells using the qbiomarker PCR Array System Outline of Webinar What are induced pluripotent Stem Cells (ips Cells or ipscs)?
HiPerFect Transfection Reagent Handbook
 Fifth Edition October 2010 HiPerFect Transfection Reagent Handbook For transfection of eukaryotic cells with sirna and mirna Sample & Assay Technologies QIAGEN Sample and Assay Technologies QIAGEN is the
Fifth Edition October 2010 HiPerFect Transfection Reagent Handbook For transfection of eukaryotic cells with sirna and mirna Sample & Assay Technologies QIAGEN Sample and Assay Technologies QIAGEN is the
Mouse ES Cell Nucleofector Kit
 page 1 of 7 Mouse ES Cell Nucleofector Kit for Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells Cell type Origin Cells derived from mouse blastocysts. Morphology Round cells growing in clumps. Important remarks! 1. This protocol
page 1 of 7 Mouse ES Cell Nucleofector Kit for Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells Cell type Origin Cells derived from mouse blastocysts. Morphology Round cells growing in clumps. Important remarks! 1. This protocol
Molecular Biology Techniques: A Classroom Laboratory Manual THIRD EDITION
 Molecular Biology Techniques: A Classroom Laboratory Manual THIRD EDITION Susan Carson Heather B. Miller D.Scott Witherow ELSEVIER AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK OXFORD PARIS SAN DIEGO SAN
Molecular Biology Techniques: A Classroom Laboratory Manual THIRD EDITION Susan Carson Heather B. Miller D.Scott Witherow ELSEVIER AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK OXFORD PARIS SAN DIEGO SAN
Genomic DNA Extraction Kit INSTRUCTION MANUAL
 Genomic DNA Extraction Kit INSTRUCTION MANUAL Table of Contents Introduction 3 Kit Components 3 Storage Conditions 4 Recommended Equipment and Reagents 4 Introduction to the Protocol 4 General Overview
Genomic DNA Extraction Kit INSTRUCTION MANUAL Table of Contents Introduction 3 Kit Components 3 Storage Conditions 4 Recommended Equipment and Reagents 4 Introduction to the Protocol 4 General Overview
RT 2 Profiler PCR Array: Web-Based Data Analysis Tutorial
 RT 2 Profiler PCR Array: Web-Based Data Analysis Tutorial Samuel J. Rulli, Jr., Ph.D. qpcr-applications Scientist [email protected] Pathway Focused Research from Sample Prep to Data Analysis! -2-
RT 2 Profiler PCR Array: Web-Based Data Analysis Tutorial Samuel J. Rulli, Jr., Ph.D. qpcr-applications Scientist [email protected] Pathway Focused Research from Sample Prep to Data Analysis! -2-
RealStar HBV PCR Kit 1.0 11/2012
 RealStar HBV PCR Kit 1.0 11/2012 RealStar HBV PCR Kit 1.0 For research use only! (RUO) Product No.: 201003 96 rxns INS-201000-GB-02 Store at -25 C... -15 C November 2012 altona Diagnostics GmbH Mörkenstraße
RealStar HBV PCR Kit 1.0 11/2012 RealStar HBV PCR Kit 1.0 For research use only! (RUO) Product No.: 201003 96 rxns INS-201000-GB-02 Store at -25 C... -15 C November 2012 altona Diagnostics GmbH Mörkenstraße
Mir-X mirna First-Strand Synthesis Kit User Manual
 User Manual Mir-X mirna First-Strand Synthesis Kit User Manual United States/Canada 800.662.2566 Asia Pacific +1.650.919.7300 Europe +33.(0)1.3904.6880 Japan +81.(0)77.543.6116 Clontech Laboratories, Inc.
User Manual Mir-X mirna First-Strand Synthesis Kit User Manual United States/Canada 800.662.2566 Asia Pacific +1.650.919.7300 Europe +33.(0)1.3904.6880 Japan +81.(0)77.543.6116 Clontech Laboratories, Inc.
Description: Molecular Biology Services and DNA Sequencing
 Description: Molecular Biology s and DNA Sequencing DNA Sequencing s Single Pass Sequencing Sequence data only, for plasmids or PCR products Plasmid DNA or PCR products Plasmid DNA: 20 100 ng/μl PCR Product:
Description: Molecular Biology s and DNA Sequencing DNA Sequencing s Single Pass Sequencing Sequence data only, for plasmids or PCR products Plasmid DNA or PCR products Plasmid DNA: 20 100 ng/μl PCR Product:
First Strand cdna Synthesis
 380PR 01 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 [email protected] A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name First Strand cdna Synthesis (Cat. # 786 812) think proteins! think G-Biosciences
380PR 01 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 [email protected] A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name First Strand cdna Synthesis (Cat. # 786 812) think proteins! think G-Biosciences
Real-time PCR: Understanding C t
 APPLICATION NOTE Real-Time PCR Real-time PCR: Understanding C t Real-time PCR, also called quantitative PCR or qpcr, can provide a simple and elegant method for determining the amount of a target sequence
APPLICATION NOTE Real-Time PCR Real-time PCR: Understanding C t Real-time PCR, also called quantitative PCR or qpcr, can provide a simple and elegant method for determining the amount of a target sequence
Stratagene QPCR Mouse Reference Total RNA
 Stratagene QPCR Mouse Reference Total RNA Instruction Manual Catalog #750600 Revision C.0 For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. 750600-12 LIMITED PRODUCT WARRANTY This warranty limits
Stratagene QPCR Mouse Reference Total RNA Instruction Manual Catalog #750600 Revision C.0 For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. 750600-12 LIMITED PRODUCT WARRANTY This warranty limits
Transfection reagent for visualizing lipofection with DNA. For ordering information, MSDS, publications and application notes see www.biontex.
 METAFECTENE FluoR Transfection reagent for visualizing lipofection with DNA For ordering information, MSDS, publications and application notes see www.biontex.com Description Cat. No. Size METAFECTENE
METAFECTENE FluoR Transfection reagent for visualizing lipofection with DNA For ordering information, MSDS, publications and application notes see www.biontex.com Description Cat. No. Size METAFECTENE
Cloning GFP into Mammalian cells
 Protocol for Cloning GFP into Mammalian cells Studiepraktik 2013 Molecular Biology and Molecular Medicine Aarhus University Produced by the instructors: Tobias Holm Bønnelykke, Rikke Mouridsen, Steffan
Protocol for Cloning GFP into Mammalian cells Studiepraktik 2013 Molecular Biology and Molecular Medicine Aarhus University Produced by the instructors: Tobias Holm Bønnelykke, Rikke Mouridsen, Steffan
Transformation Protocol
 To make Glycerol Stocks of Plasmids ** To be done in the hood and use RNase/DNase free tips** 1. In a 10 ml sterile tube add 3 ml autoclaved LB broth and 1.5 ul antibiotic (@ 100 ug/ul) or 3 ul antibiotic
To make Glycerol Stocks of Plasmids ** To be done in the hood and use RNase/DNase free tips** 1. In a 10 ml sterile tube add 3 ml autoclaved LB broth and 1.5 ul antibiotic (@ 100 ug/ul) or 3 ul antibiotic
RevertAid Premium First Strand cdna Synthesis Kit
 RevertAid Premium First Strand cdna Synthesis Kit #K1651, #K1652 CERTIFICATE OF ANALYSIS #K1651 Lot QUALITY CONTROL RT-PCR using 100 fg of control GAPDH RNA and GAPDH control primers generated a prominent
RevertAid Premium First Strand cdna Synthesis Kit #K1651, #K1652 CERTIFICATE OF ANALYSIS #K1651 Lot QUALITY CONTROL RT-PCR using 100 fg of control GAPDH RNA and GAPDH control primers generated a prominent
User Manual. CelluLyser Lysis and cdna Synthesis Kit. Version 1.4 Oct 2012 From cells to cdna in one tube
 User Manual CelluLyser Lysis and cdna Synthesis Kit Version 1.4 Oct 2012 From cells to cdna in one tube CelluLyser Lysis and cdna Synthesis Kit Table of contents Introduction 4 Contents 5 Storage 5 Additionally
User Manual CelluLyser Lysis and cdna Synthesis Kit Version 1.4 Oct 2012 From cells to cdna in one tube CelluLyser Lysis and cdna Synthesis Kit Table of contents Introduction 4 Contents 5 Storage 5 Additionally
Gene Expression Assays
 APPLICATION NOTE TaqMan Gene Expression Assays A mpl i fic ationef ficienc yof TaqMan Gene Expression Assays Assays tested extensively for qpcr efficiency Key factors that affect efficiency Efficiency
APPLICATION NOTE TaqMan Gene Expression Assays A mpl i fic ationef ficienc yof TaqMan Gene Expression Assays Assays tested extensively for qpcr efficiency Key factors that affect efficiency Efficiency
Highly specific and sensitive quantitation
 PRODUCT ULLETIN SYR Select Master Mix SYR Select Master Mix Highly specific and sensitive quantitation SYR Select Master Mix offers advanced performance at an affordable price. SYR Select Master Mix is
PRODUCT ULLETIN SYR Select Master Mix SYR Select Master Mix Highly specific and sensitive quantitation SYR Select Master Mix offers advanced performance at an affordable price. SYR Select Master Mix is
PicoMaxx High Fidelity PCR System
 PicoMaxx High Fidelity PCR System Instruction Manual Catalog #600420 (100 U), #600422 (500 U), and #600424 (1000 U) Revision C Research Use Only. Not for Use in Diagnostic Procedures. 600420-12 LIMITED
PicoMaxx High Fidelity PCR System Instruction Manual Catalog #600420 (100 U), #600422 (500 U), and #600424 (1000 U) Revision C Research Use Only. Not for Use in Diagnostic Procedures. 600420-12 LIMITED
MEF Nucleofector Kit 1 and 2
 page 1 of 7 MEF Nucleofector Kit 1 and 2 for Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts (MEF) MEF display significant phenotypic variations which depend on the strain, the genetic background of the they are isolated
page 1 of 7 MEF Nucleofector Kit 1 and 2 for Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts (MEF) MEF display significant phenotypic variations which depend on the strain, the genetic background of the they are isolated
AffinityScript QPCR cdna Synthesis Kit
 AffinityScript QPCR cdna Synthesis Kit INSTRUCTION MANUAL Catalog #600559 Revision C.01 For In Vitro Use Only 600559-12 LIMITED PRODUCT WARRANTY This warranty limits our liability to replacement of this
AffinityScript QPCR cdna Synthesis Kit INSTRUCTION MANUAL Catalog #600559 Revision C.01 For In Vitro Use Only 600559-12 LIMITED PRODUCT WARRANTY This warranty limits our liability to replacement of this
Path-ID Multiplex One-Step RT-PCR Kit
 USER GUIDE Path-ID Multiplex One-Step RT-PCR Kit TaqMan probe-based multiplex one-step real-time RT-PCR detection of RNA targets Catalog Numbers 4428206, 4428207, 4440022 Publication Part Number 4440907
USER GUIDE Path-ID Multiplex One-Step RT-PCR Kit TaqMan probe-based multiplex one-step real-time RT-PCR detection of RNA targets Catalog Numbers 4428206, 4428207, 4440022 Publication Part Number 4440907
SYBR Green Realtime PCR Master Mix -Plus-
 Instruction manual SYBR Green Realtime PCR Master Mix -Plus- 0810 F0925K SYBR Green Realtime PCR Master Mix -Plus- Contents QPK-212T 1mLx1 QPK-212 1mLx5 Store at -20 C, protected from light [1] Introduction
Instruction manual SYBR Green Realtime PCR Master Mix -Plus- 0810 F0925K SYBR Green Realtime PCR Master Mix -Plus- Contents QPK-212T 1mLx1 QPK-212 1mLx5 Store at -20 C, protected from light [1] Introduction
Integrated Protein Services
 Integrated Protein Services Custom protein expression & purification Version DC04-0012 Expression strategy The first step in the recombinant protein generation process is to design an appropriate expression
Integrated Protein Services Custom protein expression & purification Version DC04-0012 Expression strategy The first step in the recombinant protein generation process is to design an appropriate expression
Mir-X mirna First-Strand Synthesis and SYBR qrt-pcr
 User Manual Mir-X mirna First-Strand Synthesis and SYBR qrt-pcr User Manual United States/Canada 800.662.2566 Asia Pacific +1.650.919.7300 Europe +33.(0)1.3904.6880 Japan +81.(0)77.543.6116 Clontech Laboratories,
User Manual Mir-X mirna First-Strand Synthesis and SYBR qrt-pcr User Manual United States/Canada 800.662.2566 Asia Pacific +1.650.919.7300 Europe +33.(0)1.3904.6880 Japan +81.(0)77.543.6116 Clontech Laboratories,
RNA Extraction and Quantification, Reverse Transcription, and Real-time PCR (q-pcr)
 RNA Extraction and Quantification, Reverse Transcription, and Real-time Preparation of Samples Cells: o Remove media and wash cells 2X with cold PBS. (2 ml for 6 well plate or 3 ml for 6cm plate) Keep
RNA Extraction and Quantification, Reverse Transcription, and Real-time Preparation of Samples Cells: o Remove media and wash cells 2X with cold PBS. (2 ml for 6 well plate or 3 ml for 6cm plate) Keep
MEF Starter Nucleofector Kit
 page 1 of 7 MEF Starter Nucleofector Kit for Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts (MEF) MEF display significant phenotypic variations which depend on the strain, the genetic background of the mice they are isolated
page 1 of 7 MEF Starter Nucleofector Kit for Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts (MEF) MEF display significant phenotypic variations which depend on the strain, the genetic background of the mice they are isolated
Application Guide... 2
 Protocol for GenomePlex Whole Genome Amplification from Formalin-Fixed Parrafin-Embedded (FFPE) tissue Application Guide... 2 I. Description... 2 II. Product Components... 2 III. Materials to be Supplied
Protocol for GenomePlex Whole Genome Amplification from Formalin-Fixed Parrafin-Embedded (FFPE) tissue Application Guide... 2 I. Description... 2 II. Product Components... 2 III. Materials to be Supplied
HiPer RT-PCR Teaching Kit
 HiPer RT-PCR Teaching Kit Product Code: HTBM024 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5 Duration of Experiment: Protocol: 4 hours Agarose Gel Electrophoresis: 45 minutes Storage Instructions: The
HiPer RT-PCR Teaching Kit Product Code: HTBM024 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5 Duration of Experiment: Protocol: 4 hours Agarose Gel Electrophoresis: 45 minutes Storage Instructions: The
FastLine cell cdna Kit
 1. FastLine cell cdna Kit For high-speed preparation of first-strand cdna directly from cultured cells without RNA purification www.tiangen.com RT100701 FastLine cell cdna Kit Cat. no. KR105 Kit Contents
1. FastLine cell cdna Kit For high-speed preparation of first-strand cdna directly from cultured cells without RNA purification www.tiangen.com RT100701 FastLine cell cdna Kit Cat. no. KR105 Kit Contents
Classic Immunoprecipitation
 292PR 01 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 [email protected] A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name Classic Immunoprecipitation Utilizes Protein A/G Agarose for Antibody Binding (Cat.
292PR 01 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 [email protected] A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name Classic Immunoprecipitation Utilizes Protein A/G Agarose for Antibody Binding (Cat.
Table of Contents. I. Description... 2. II. Kit Components... 2. III. Storage... 2. IV. 1st Strand cdna Synthesis Reaction... 3
 Table of Contents I. Description... 2 II. Kit Components... 2 III. Storage... 2 IV. 1st Strand cdna Synthesis Reaction... 3 V. RT-PCR, Real-time RT-PCR... 4 VI. Application... 5 VII. Preparation of RNA
Table of Contents I. Description... 2 II. Kit Components... 2 III. Storage... 2 IV. 1st Strand cdna Synthesis Reaction... 3 V. RT-PCR, Real-time RT-PCR... 4 VI. Application... 5 VII. Preparation of RNA
2.1.2 Characterization of antiviral effect of cytokine expression on HBV replication in transduced mouse hepatocytes line
 i 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Human Hepatitis B virus (HBV) 1 1.1.1 Pathogenesis of Hepatitis B 1 1.1.2 Genome organization of HBV 3 1.1.3 Structure of HBV virion 5 1.1.4 HBV life cycle 5 1.1.5 Experimental models
i 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Human Hepatitis B virus (HBV) 1 1.1.1 Pathogenesis of Hepatitis B 1 1.1.2 Genome organization of HBV 3 1.1.3 Structure of HBV virion 5 1.1.4 HBV life cycle 5 1.1.5 Experimental models
HighPure Maxi Plasmid Kit
 HighPure Maxi Plasmid Kit For purification of high pure plasmid DNA with high yields www.tiangen.com PP120109 HighPure Maxi Plasmid Kit Kit Contents Storage Cat.no. DP116 Contents RNaseA (100 mg/ml) Buffer
HighPure Maxi Plasmid Kit For purification of high pure plasmid DNA with high yields www.tiangen.com PP120109 HighPure Maxi Plasmid Kit Kit Contents Storage Cat.no. DP116 Contents RNaseA (100 mg/ml) Buffer
Taq98 Hot Start 2X Master Mix
 Taq98 Hot Start 2X Master Mix Optimized for 98C Denaturation Lucigen Corporation 2905 Parmenter St, Middleton, WI 53562 USA Toll Free: (888) 575-9695 (608) 831-9011 FAX: (608) 831-9012 [email protected]
Taq98 Hot Start 2X Master Mix Optimized for 98C Denaturation Lucigen Corporation 2905 Parmenter St, Middleton, WI 53562 USA Toll Free: (888) 575-9695 (608) 831-9011 FAX: (608) 831-9012 [email protected]
Fast, easy and effective transfection reagent for mammalian cells
 METAFECTENE EASY + Fast, easy and effective transfection reagent for mammalian cells For ordering information, MSDS, publications and application notes see www.biontex.com Description Cat. No. Size METAFECTENE
METAFECTENE EASY + Fast, easy and effective transfection reagent for mammalian cells For ordering information, MSDS, publications and application notes see www.biontex.com Description Cat. No. Size METAFECTENE
Quando si parla di PCR quantitativa si intende:
 Quando si parla di PCR quantitativa si intende: A. Una PCR che produce grandi quantità di DNA B. Una PCR che emette quanti di luce C. Una PCR che quantifica il numero di molecole stampo presenti all inizio
Quando si parla di PCR quantitativa si intende: A. Una PCR che produce grandi quantità di DNA B. Una PCR che emette quanti di luce C. Una PCR che quantifica il numero di molecole stampo presenti all inizio
DyNAmo cdna Synthesis Kit for qrt-pcr
 DyNAmo cdna Synthesis Kit for qrt-pcr Instruction manual F- 470S Sufficient for 20 cdna synthesis reactions (20 µl each) F- 470L Sufficient for 100 cdna synthesis reactions (20 µl each) Description...
DyNAmo cdna Synthesis Kit for qrt-pcr Instruction manual F- 470S Sufficient for 20 cdna synthesis reactions (20 µl each) F- 470L Sufficient for 100 cdna synthesis reactions (20 µl each) Description...
Integrated Protein Services
 Integrated Protein Services Custom protein expression & purification Last date of revision June 2015 Version DC04-0013 www.iba-lifesciences.com Expression strategy The first step in the recombinant protein
Integrated Protein Services Custom protein expression & purification Last date of revision June 2015 Version DC04-0013 www.iba-lifesciences.com Expression strategy The first step in the recombinant protein
MGC premier Expression-Ready cdna clones TCH1103, TCM1104, TCR1105, TCB1106, TCH1203, TCM1204, TCR1205, TCB1206, TCH1303, TCM1304, TCR1305
 MGC premier Expression-Ready cdna clones TCH1103, TCM1104, TCR1105, TCB1106, TCH1203, TCM1204, TCR1205, TCB1206, TCH1303, TCM1304, TCR1305 The MGC premier Expression-Ready collection has the high quality,
MGC premier Expression-Ready cdna clones TCH1103, TCM1104, TCR1105, TCB1106, TCH1203, TCM1204, TCR1205, TCB1206, TCH1303, TCM1304, TCR1305 The MGC premier Expression-Ready collection has the high quality,
Bacterial Transformation and Plasmid Purification. Chapter 5: Background
 Bacterial Transformation and Plasmid Purification Chapter 5: Background History of Transformation and Plasmids Bacterial methods of DNA transfer Transformation: when bacteria take up DNA from their environment
Bacterial Transformation and Plasmid Purification Chapter 5: Background History of Transformation and Plasmids Bacterial methods of DNA transfer Transformation: when bacteria take up DNA from their environment
Manual for: sirna-trans Maximo Reagent
 Manual for: sirna-trans Maximo Reagent Contact: [email protected]; www.geneon.net GeneON GmbH Germany GeneON GmbH / Protocol sirna-trans reagent vs. 1.3 / www.geneon.net / - 0 - sirna-trans reagent Instruction
Manual for: sirna-trans Maximo Reagent Contact: [email protected]; www.geneon.net GeneON GmbH Germany GeneON GmbH / Protocol sirna-trans reagent vs. 1.3 / www.geneon.net / - 0 - sirna-trans reagent Instruction
Especially developed for the transfection of mammalian cells with sirna or mirna
 METAFECTENE SI Especially developed for the transfection of mammalian cells with sirna or mirna For ordering information, MSDS, publications and application notes see www.biontex.com Description Cat. No.
METAFECTENE SI Especially developed for the transfection of mammalian cells with sirna or mirna For ordering information, MSDS, publications and application notes see www.biontex.com Description Cat. No.
1.Gene Synthesis. 2.Peptide & Phospho-P. Assembly PCR. Design & Synthesis. Advantages. Specifications. Advantages
 1.Gene Synthesis Assembly PCR Looking for a cdna for your research but could not fish out the gene through traditional cloning methods or a supplier? Abnova provides a gene synthesis service via assembly
1.Gene Synthesis Assembly PCR Looking for a cdna for your research but could not fish out the gene through traditional cloning methods or a supplier? Abnova provides a gene synthesis service via assembly
mirnaselect pep-mir Cloning and Expression Vector
 Product Data Sheet mirnaselect pep-mir Cloning and Expression Vector CATALOG NUMBER: MIR-EXP-C STORAGE: -80ºC QUANTITY: 2 vectors; each contains 100 µl of bacterial glycerol stock Components 1. mirnaselect
Product Data Sheet mirnaselect pep-mir Cloning and Expression Vector CATALOG NUMBER: MIR-EXP-C STORAGE: -80ºC QUANTITY: 2 vectors; each contains 100 µl of bacterial glycerol stock Components 1. mirnaselect
TOOLS sirna and mirna. User guide
 TOOLS sirna and mirna User guide Introduction RNA interference (RNAi) is a powerful tool for suppression gene expression by causing the destruction of specific mrna molecules. Small Interfering RNAs (sirnas)
TOOLS sirna and mirna User guide Introduction RNA interference (RNAi) is a powerful tool for suppression gene expression by causing the destruction of specific mrna molecules. Small Interfering RNAs (sirnas)
SmartFlare RNA Detection Probes: Principles, protocols and troubleshooting
 Technical Guide SmartFlare RNA Detection Probes: Principles, protocols and troubleshooting Principles of SmartFlare technology RNA detection traditionally requires transfection, laborious sample prep,
Technical Guide SmartFlare RNA Detection Probes: Principles, protocols and troubleshooting Principles of SmartFlare technology RNA detection traditionally requires transfection, laborious sample prep,
Proto col. GoClone Repor ter Construc ts: Sample Protocol for Adherent Cells. Tech support: 877-994-8240. Luciferase Assay System
 Luciferase Assay System Proto col GoClone Repor ter Construc ts: Sample Protocol for Adherent Cells LightSwitch Luciferase Assay System GoClone Reporter Assay Workflow Step 1: Seed cells in plate format.
Luciferase Assay System Proto col GoClone Repor ter Construc ts: Sample Protocol for Adherent Cells LightSwitch Luciferase Assay System GoClone Reporter Assay Workflow Step 1: Seed cells in plate format.
HCS604.03 Exercise 1 Dr. Jones Spring 2005. Recombinant DNA (Molecular Cloning) exercise:
 HCS604.03 Exercise 1 Dr. Jones Spring 2005 Recombinant DNA (Molecular Cloning) exercise: The purpose of this exercise is to learn techniques used to create recombinant DNA or clone genes. You will clone
HCS604.03 Exercise 1 Dr. Jones Spring 2005 Recombinant DNA (Molecular Cloning) exercise: The purpose of this exercise is to learn techniques used to create recombinant DNA or clone genes. You will clone
pcas-guide System Validation in Genome Editing
 pcas-guide System Validation in Genome Editing Tagging HSP60 with HA tag genome editing The latest tool in genome editing CRISPR/Cas9 allows for specific genome disruption and replacement in a flexible
pcas-guide System Validation in Genome Editing Tagging HSP60 with HA tag genome editing The latest tool in genome editing CRISPR/Cas9 allows for specific genome disruption and replacement in a flexible
The fastest spin-column based procedure for purifying up to 10 mg of ultra-pure endotoxin-free transfection-grade plasmid DNA.
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZymoPURE Plasmid Gigaprep Kit Catalog Nos. D4204 (Patent Pending) Highlights The fastest spin-column based procedure for purifying up to 10 mg of ultra-pure endotoxin-free transfection-grade
INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZymoPURE Plasmid Gigaprep Kit Catalog Nos. D4204 (Patent Pending) Highlights The fastest spin-column based procedure for purifying up to 10 mg of ultra-pure endotoxin-free transfection-grade
TaqMan Fast Advanced Master Mix. Protocol
 TaqMan Fast Advanced Master Mix Protocol For Research Use Only. Not intended for any animal or human therapeutic or diagnostic use. Information in this document is subject to change without notice. APPLIED
TaqMan Fast Advanced Master Mix Protocol For Research Use Only. Not intended for any animal or human therapeutic or diagnostic use. Information in this document is subject to change without notice. APPLIED
2.500 Threshold. 2.000 1000e - 001. Threshold. Exponential phase. Cycle Number
 application note Real-Time PCR: Understanding C T Real-Time PCR: Understanding C T 4.500 3.500 1000e + 001 4.000 3.000 1000e + 000 3.500 2.500 Threshold 3.000 2.000 1000e - 001 Rn 2500 Rn 1500 Rn 2000
application note Real-Time PCR: Understanding C T Real-Time PCR: Understanding C T 4.500 3.500 1000e + 001 4.000 3.000 1000e + 000 3.500 2.500 Threshold 3.000 2.000 1000e - 001 Rn 2500 Rn 1500 Rn 2000
Cloning Blunt-End Pfu DNA Polymerase- Generated PCR Fragments into pgem -T Vector Systems
 Promega Notes Number 71, 1999, p. 10 Blunt-End Pfu DNA Polymerase- Generated PCR Fragments into pgem -T Vector Systems By Kimberly Knoche, Ph.D., and Dan Kephart, Ph.D. Promega Corporation Corresponding
Promega Notes Number 71, 1999, p. 10 Blunt-End Pfu DNA Polymerase- Generated PCR Fragments into pgem -T Vector Systems By Kimberly Knoche, Ph.D., and Dan Kephart, Ph.D. Promega Corporation Corresponding
Bacterial Transformation with Green Fluorescent Protein. Table of Contents Fall 2012
 Bacterial Transformation with Green Fluorescent Protein pglo Version Table of Contents Bacterial Transformation Introduction..1 Laboratory Exercise...3 Important Laboratory Practices 3 Protocol...... 4
Bacterial Transformation with Green Fluorescent Protein pglo Version Table of Contents Bacterial Transformation Introduction..1 Laboratory Exercise...3 Important Laboratory Practices 3 Protocol...... 4
NIH Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)
 USER GUIDE NIH Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC) Catalog number FL1002 Revision date 28 November 2011 Publication Part number 25-0610 MAN0000351 For Research Use Only. Not for diagnostic procedures. ii Table
USER GUIDE NIH Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC) Catalog number FL1002 Revision date 28 November 2011 Publication Part number 25-0610 MAN0000351 For Research Use Only. Not for diagnostic procedures. ii Table
GRS Plasmid Purification Kit Transfection Grade GK73.0002 (2 MaxiPreps)
 1 GRS Plasmid Purification Kit Transfection Grade GK73.0002 (2 MaxiPreps) (FOR RESEARCH ONLY) Sample : Expected Yield : Endotoxin: Format : Operation Time : Elution Volume : 50-400 ml of cultured bacterial
1 GRS Plasmid Purification Kit Transfection Grade GK73.0002 (2 MaxiPreps) (FOR RESEARCH ONLY) Sample : Expected Yield : Endotoxin: Format : Operation Time : Elution Volume : 50-400 ml of cultured bacterial
restriction enzymes 350 Home R. Ward: Spring 2001
 restriction enzymes 350 Home Restriction Enzymes (endonucleases): molecular scissors that cut DNA Properties of widely used Type II restriction enzymes: recognize a single sequence of bases in dsdna, usually
restriction enzymes 350 Home Restriction Enzymes (endonucleases): molecular scissors that cut DNA Properties of widely used Type II restriction enzymes: recognize a single sequence of bases in dsdna, usually
PrimeSTAR HS DNA Polymerase
 Cat. # R010A For Research Use PrimeSTAR HS DNA Polymerase Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description...3 II. III. IV. Components...3 Storage...3 Features...3 V. General Composition of PCR Reaction
Cat. # R010A For Research Use PrimeSTAR HS DNA Polymerase Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description...3 II. III. IV. Components...3 Storage...3 Features...3 V. General Composition of PCR Reaction
All-in-One First-Strand cdna Synthesis Kit
 All-in-One First-Strand cdna Synthesis Kit For reliable first-strand cdna synthesis from all RNA sources Cat. No. AORT-0020 (20 synthesis reactions) Cat. No. AORT-0050 (50 synthesis reactions) User Manual
All-in-One First-Strand cdna Synthesis Kit For reliable first-strand cdna synthesis from all RNA sources Cat. No. AORT-0020 (20 synthesis reactions) Cat. No. AORT-0050 (50 synthesis reactions) User Manual
PyroPhage 3173 DNA Polymerase, Exonuclease Minus (Exo-)
 PyroPhage 3173 DNA Polymerase, Exonuclease Minus (Exo-) FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. NOT FOR HUMAN OR DIAGNOSTIC USE Lucigen Corporation 2905 Parmenter St, Middleton, WI 53562 USA Toll Free: (888) 575-9695 (608)
PyroPhage 3173 DNA Polymerase, Exonuclease Minus (Exo-) FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. NOT FOR HUMAN OR DIAGNOSTIC USE Lucigen Corporation 2905 Parmenter St, Middleton, WI 53562 USA Toll Free: (888) 575-9695 (608)
ab185916 Hi-Fi cdna Synthesis Kit
 ab185916 Hi-Fi cdna Synthesis Kit Instructions for Use For cdna synthesis from various RNA samples This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Version 1 Last Updated 1
ab185916 Hi-Fi cdna Synthesis Kit Instructions for Use For cdna synthesis from various RNA samples This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Version 1 Last Updated 1
BacReady TM Multiplex PCR System
 BacReady TM Multiplex PCR System Technical Manual No. 0191 Version 10112010 I Description.. 1 II Applications 2 III Key Features.. 2 IV Shipping and Storage. 2 V Simplified Procedures. 2 VI Detailed Experimental
BacReady TM Multiplex PCR System Technical Manual No. 0191 Version 10112010 I Description.. 1 II Applications 2 III Key Features.. 2 IV Shipping and Storage. 2 V Simplified Procedures. 2 VI Detailed Experimental
FOR REFERENCE PURPOSES
 BIOO LIFE SCIENCE PRODUCTS FOR REFERENCE PURPOSES This manual is for Reference Purposes Only. DO NOT use this protocol to run your assays. Periodically, optimizations and revisions are made to the kit
BIOO LIFE SCIENCE PRODUCTS FOR REFERENCE PURPOSES This manual is for Reference Purposes Only. DO NOT use this protocol to run your assays. Periodically, optimizations and revisions are made to the kit
Speed Matters - Fast ways from template to result
 qpcr Symposium 2007 - Weihenstephan Speed Matters - Fast ways from template to result March 28, 2007 Dr. Thorsten Traeger Senior Scientist, Research and Development - 1 - Overview Ạgenda Fast PCR The Challenges
qpcr Symposium 2007 - Weihenstephan Speed Matters - Fast ways from template to result March 28, 2007 Dr. Thorsten Traeger Senior Scientist, Research and Development - 1 - Overview Ạgenda Fast PCR The Challenges
Fighting the Battles: Conducting a Clinical Assay
 Fighting the Battles: Conducting a Clinical Assay 6 Vocabulary: In Vitro: studies in biology that are conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated from their usual biological surroundings
Fighting the Battles: Conducting a Clinical Assay 6 Vocabulary: In Vitro: studies in biology that are conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated from their usual biological surroundings
RealLine HCV PCR Qualitative - Uni-Format
 Instructions for use PCR KIT FOR EXTRACTION OF RNA AND REAL TIME PCR DETECTION KIT FOR HEPATITIS C VIRUS RNA Research Use Only Qualitative Uni Format VBD0798 48 tests valid from: December 2013 Rev11122013
Instructions for use PCR KIT FOR EXTRACTION OF RNA AND REAL TIME PCR DETECTION KIT FOR HEPATITIS C VIRUS RNA Research Use Only Qualitative Uni Format VBD0798 48 tests valid from: December 2013 Rev11122013
DNA Integrity Number (DIN) For the Assessment of Genomic DNA Samples in Real-Time Quantitative PCR (qpcr) Experiments
 DNA Integrity Number () For the Assessment of Genomic DNA Samples in Real-Time Quantitative PCR (qpcr) Experiments Application Note Nucleic Acid Analysis Author Arunkumar Padmanaban Agilent Technologies,
DNA Integrity Number () For the Assessment of Genomic DNA Samples in Real-Time Quantitative PCR (qpcr) Experiments Application Note Nucleic Acid Analysis Author Arunkumar Padmanaban Agilent Technologies,
qstar mirna qpcr Detection System
 qstar mirna qpcr Detection System Table of Contents Table of Contents...1 Package Contents and Storage Conditions...2 For mirna cdna synthesis kit...2 For qstar mirna primer pairs...2 For qstar mirna qpcr
qstar mirna qpcr Detection System Table of Contents Table of Contents...1 Package Contents and Storage Conditions...2 For mirna cdna synthesis kit...2 For qstar mirna primer pairs...2 For qstar mirna qpcr
QIAGEN Transfection Technologies
 QIAGEN Transfection Technologies Efficient and robust transfection for all your applications Sample & Assay Technologies Table of contents QIAGEN solutions for efficient transfection Transfection is a
QIAGEN Transfection Technologies Efficient and robust transfection for all your applications Sample & Assay Technologies Table of contents QIAGEN solutions for efficient transfection Transfection is a
Transfection-Transfer of non-viral genetic material into eukaryotic cells. Infection/ Transduction- Transfer of viral genetic material into cells.
 Transfection Key words: Transient transfection, Stable transfection, transfection methods, vector, plasmid, origin of replication, reporter gene/ protein, cloning site, promoter and enhancer, signal peptide,
Transfection Key words: Transient transfection, Stable transfection, transfection methods, vector, plasmid, origin of replication, reporter gene/ protein, cloning site, promoter and enhancer, signal peptide,
ChIP TROUBLESHOOTING TIPS
 ChIP TROUBLESHOOTING TIPS Creative Diagnostics Abstract ChIP dissects the spatial and temporal dynamics of the interactions between chromatin and its associated factors CD Creative Diagnostics info@creative-
ChIP TROUBLESHOOTING TIPS Creative Diagnostics Abstract ChIP dissects the spatial and temporal dynamics of the interactions between chromatin and its associated factors CD Creative Diagnostics info@creative-
Intended Use: The kit is designed to detect the 5 different mutations found in Asian population using seven different primers.
 Unzipping Genes MBPCR014 Beta-Thalassemia Detection Kit P r o d u c t I n f o r m a t i o n Description: Thalassemia is a group of genetic disorders characterized by quantitative defects in globin chain
Unzipping Genes MBPCR014 Beta-Thalassemia Detection Kit P r o d u c t I n f o r m a t i o n Description: Thalassemia is a group of genetic disorders characterized by quantitative defects in globin chain
All-in-One mirna qrt-pcr Detection System Handbook
 All-in-One mirna qrt-pcr Detection System Handbook For quantitative detection of mature mirna All-in-One mirna First-Strand cdna Synthesis Kit Cat. No. AMRT-0020 (20 mirna reverse transcription reactions)
All-in-One mirna qrt-pcr Detection System Handbook For quantitative detection of mature mirna All-in-One mirna First-Strand cdna Synthesis Kit Cat. No. AMRT-0020 (20 mirna reverse transcription reactions)
Qubit dsdna HS Assay Kits
 Qubit dsdna HS Assay Kits For use with the Qubit 2.0 Fluorometer Table 1. Contents and storage information. Material Amount Concentration Storage Stability Qubit dsdna HS Reagent (Component A) 250 µl or
Qubit dsdna HS Assay Kits For use with the Qubit 2.0 Fluorometer Table 1. Contents and storage information. Material Amount Concentration Storage Stability Qubit dsdna HS Reagent (Component A) 250 µl or
Real-time quantitative RT -PCR (Taqman)
 Real-time quantitative RT -PCR (Taqman) Author: SC, Patti Lab, 3/03 This is performed as a 2-step reaction: 1. cdna synthesis from DNase 1-treated total RNA 2. PCR 1. cdna synthesis (Advantage RT-for-PCR
Real-time quantitative RT -PCR (Taqman) Author: SC, Patti Lab, 3/03 This is performed as a 2-step reaction: 1. cdna synthesis from DNase 1-treated total RNA 2. PCR 1. cdna synthesis (Advantage RT-for-PCR
BaculoDirect Baculovirus Expression System Free your hands with the BaculoDirect Baculovirus Expression System
 BaculoDirect Baculovirus Expression System Free your hands with the BaculoDirect Baculovirus Expression System The BaculoDirect Baculovirus Expression System gives you: Unique speed and simplicity High-throughput
BaculoDirect Baculovirus Expression System Free your hands with the BaculoDirect Baculovirus Expression System The BaculoDirect Baculovirus Expression System gives you: Unique speed and simplicity High-throughput
UltraClean PCR Clean-Up Kit
 UltraClean PCR Clean-Up Kit Catalog No. Quantity 12500-50 50 Preps 12500-100 100 Preps 12500-250 250 Preps Instruction Manual Please recycle Version: 02212013 1 Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Protocol
UltraClean PCR Clean-Up Kit Catalog No. Quantity 12500-50 50 Preps 12500-100 100 Preps 12500-250 250 Preps Instruction Manual Please recycle Version: 02212013 1 Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Protocol
DNA Sequencing Troubleshooting Guide
 DNA Sequencing Troubleshooting Guide Successful DNA Sequencing Read Peaks are well formed and separated with good quality scores. There is a small area at the beginning of the run before the chemistry
DNA Sequencing Troubleshooting Guide Successful DNA Sequencing Read Peaks are well formed and separated with good quality scores. There is a small area at the beginning of the run before the chemistry
UltraClean Soil DNA Isolation Kit
 PAGE 1 UltraClean Soil DNA Isolation Kit Catalog # 12800-50 50 preps New improved PCR inhibitor removal solution (IRS) included Instruction Manual (New Alternative Protocol maximizes yields) Introduction
PAGE 1 UltraClean Soil DNA Isolation Kit Catalog # 12800-50 50 preps New improved PCR inhibitor removal solution (IRS) included Instruction Manual (New Alternative Protocol maximizes yields) Introduction
Technical Note. Roche Applied Science. No. LC 19/2004. Color Compensation
 Roche Applied Science Technical Note No. LC 19/2004 Purpose of this Note Color The LightCycler System is able to simultaneously detect and analyze more than one color in each capillary. Due to overlap
Roche Applied Science Technical Note No. LC 19/2004 Purpose of this Note Color The LightCycler System is able to simultaneously detect and analyze more than one color in each capillary. Due to overlap
Lab 10: Bacterial Transformation, part 2, DNA plasmid preps, Determining DNA Concentration and Purity
 Lab 10: Bacterial Transformation, part 2, DNA plasmid preps, Determining DNA Concentration and Purity Today you analyze the results of your bacterial transformation from last week and determine the efficiency
Lab 10: Bacterial Transformation, part 2, DNA plasmid preps, Determining DNA Concentration and Purity Today you analyze the results of your bacterial transformation from last week and determine the efficiency
STOP. Before using this product, please read the Limited Use License statement below:
 STOP Before using this product, please read the Limited Use License statement below: Important Limited Use License information for pdrive5lucia-rgfap The purchase of the pdrive5lucia-rgfap vector conveys
STOP Before using this product, please read the Limited Use License statement below: Important Limited Use License information for pdrive5lucia-rgfap The purchase of the pdrive5lucia-rgfap vector conveys
Investigating the role of a Cryptosporidium parum apyrase in infection
 Investigating the role of a Cryptosporidium parum apyrase in infection David Riccardi and Patricio Manque Abstract This project attempted to characterize the function of a Cryptosporidium parvum apyrase
Investigating the role of a Cryptosporidium parum apyrase in infection David Riccardi and Patricio Manque Abstract This project attempted to characterize the function of a Cryptosporidium parvum apyrase
One Shot TOP10 Competent Cells
 USER GUIDE One Shot TOP10 Competent Cells Catalog Numbers C4040-10, C4040-03, C4040-06, C4040-50, and C4040-52 Document Part Number 280126 Publication Number MAN0000633 Revision A.0 For Research Use Only.
USER GUIDE One Shot TOP10 Competent Cells Catalog Numbers C4040-10, C4040-03, C4040-06, C4040-50, and C4040-52 Document Part Number 280126 Publication Number MAN0000633 Revision A.0 For Research Use Only.
Optimized Protocol sirna Test Kit for Cell Lines and Adherent Primary Cells
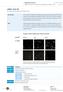 page 1 of 8 sirna Test Kit for Cell Lines and Adherent Primary Cells Kit principle Co-transfection of pmaxgfp, encoding the green fluorescent protein (GFP) from Pontellina p. with an sirna directed against
page 1 of 8 sirna Test Kit for Cell Lines and Adherent Primary Cells Kit principle Co-transfection of pmaxgfp, encoding the green fluorescent protein (GFP) from Pontellina p. with an sirna directed against
