Adjusting and Closing Entries
|
|
|
- Brittany Tucker
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Adjusting and Closing Entries Adjusting and Closing entries tend to be difficult to grasp at first. A reason for this might be due to the type of transactions requiring adjustment, which tend to be unfamiliar. The key feature of this type of transaction is that they involve time. In one way or another, adjusting entries tend to have an initial transaction being made, but then things occur later for which entries will need to be made. In addition, the adjustments tend to be forced upon the accountant because the accounting cycle is coming to an end and the financial statements need to be prepared. Closing entries occur at the end of the accounting cycle as well. These entries are made in order to prepare for a new accounting cycle. For example, we do not want to carry over the amounts in cost of goods sold expense account into the next cycle. Rather, we want that account to start fresh from a zero balance. This is true for all of the accounts on the income statement (recall, this statement is a record of what happened during a period of time) as well as the dividend account. Accounts on the balance sheet, however, do not start over at the beginning of an accounting cycle. These accounts are termed real accounts and keeping a running balance of their activity during the entire life of the organization.
2 Assume you keep the books for a small engineering firm. Make the following journal entries for each transaction on the date it occurred and the adjusting entry at the end of the accounting period (e.g, Dec. 31) (1) On July 1, the firm signs a contract with a city planning department for $60,000 to design a bridge. The design work will be done in equal monthly installments and last one year. The city pays the full amount in advance on July 1. On July 1, the following would be recorded. Cash 60,000 Unearned Revenue 60,000 Unearned Revenue 30,000 Revenue 30,000 Six months have gone by and we ll assume the work has been occurring as planned. The firm is earning revenue of $5,000 per month.
3 (2) On Oct. 1, the firm pays the insurance premiums on its fleet of cars for the next 6 months. The monthly premiums run $300. On Oct. 1, the following would be recorded. Pre-Paid Insurance (an asset!) 1,800 Cash 1,800 Insurance Expense 900 Pre-Paid Insurance 900 Three months have past and the firm has incurred half the insurance expense it has previously paid for.
4 (3) On July 1, the firm pays the yearly dues of its 20 employees to the Academy of American Engineers. The yearly dues per employee are $100. On July 1, the following would be recorded. Pre-Paid Dues 2,000 Cash 2,000 Dues Expense 1,000 Pre-Paid Dues 1,000 Six months have passed and we want to show the dues as an expense for the firm.
5 (4) On May 15th, the firm purchases office supplies on credit in the amount of $5000. The inventory of office supplies on December 31st comes to $500. On May 15, the following would be recorded. Supplies (an asset!!) 5,000 Accounts Payable 5,000 Supplies Expense (or, SGA expense) 4,500 Supplies (asset) 4,500 Showing that $4,500 of our supplies (asset) are gone. Notice, the new balance sheet will have a $500 line item for supplies (asset).
6 The transactions in this section relate to a financial counseling service ( URMoney ) 1. URMoney pays salaries on the 15th of every month. The salaries amount to $1,000 each month. What will be the required adjusting entry on December 31? [I ll show more than is really required here to demonstrate the logic of the Dec. 31 entry] On Dec. 15 th 2008 (for example), the following would be recorded. Salaries (expense) 1,000 Cash 1,000 Salaries (expense) 500 Accounts Payable (or, salary payable) 500 Now, take a look at what will happen on the next 15 th of the month, when they actually pay the salary.
7 On Jan. 15 th 2009, the following would be recorded Salaries (expense) 500 Accounts Payable (or, salary payable) 500 Cash 1,000 We had already shown half the expense on Dec. 31 in order to make sure our income statement was correct. In addition, we had shown a $500 liability (accounts payable) for the salary expense. On Jan. 15 th we have made the full payment and meet the liability, and we are showing the salary expense incurred from Jan. 1 to Jan. 15 th.
8 2. On Oct. 1, URMoney received $4,000 to provide counseling services for the next four months. What will be the required adjusting entry on December 31? On Oct.. 1, the following would be recorded. Cash 4,000 Unearned Revenue 4,000 Unearned Revenue 3,000 Revenue 3,000 Consider what will show up on the firm s income statement and balance sheet. It will show additional revenue of $3,000 now (it has earned it). Also, the balance sheet will show only a $1,000 unearned revenue liability (it still has to perform these services). Hence, we have decreased the liability by $3,000 on Dec. 31. What is the balancing account? The recognition of revenue also increased the Retained Earnings account within the Equity on the balance sheet. Thus, liabilities went down by $3,000 and equity has increased by $3,000 the balance sheet should balance just fine.
9 3. On October 1, URMoney paid the yearly $1,200 premium for fire & theft insurance (or, $100 monthly premium). What will be the required adjusting entry on December 31? On Oct. 1, the following would be recorded. Pre-Paid Insurance (an asset!) 1,200 Cash 1,200 Insurance Expense 300 Pre-Paid Insurance 300
10 4. URMoney publishes financial statements on December 31. The statements indicate the following account balances: Cash $10,000; Building $50,000; Revenue $5,000; Notes Payable $12,000; Accounts Payable $2,000; Salary expenses $3,000; Accounts Receivable $500; Retained Earnings $100,000; Dividends $1,000. What are the closing entries required to prepare for the next accounting cycle? Revenue 5,000 Retained Earnings 5,000 Retained Earnings 3,000 Salary Expense 3,000 Retained Earnings 1,000 Dividends 1,000 So, all of this may appear quite strange debits/credits seem to be recorded wrong. However, keep in mind the purpose of these entries. We are attempting to prepare the income statement for the next year. We want the Revenue account to begin the new year (or, new accounting cycle) with a zero balance, same for the expense account and dividends. Revenues, expenses, and dividends are a record of things that have happened during a period of time (e.g., the accounting cycle, a year, a quarter, etc.). By debiting the full amount of revenues that had been earned, we are reducing the balance to zero for the new year. Where should the revenues go? We know that revenues add to equity (specifically, the retained earnings account). This is what we have done, same for expenses and dividends. Notice, on net, the retained earnings will go up by a $1,000 balance!!! A little more practice on this might be helpful.
11 More on Closing Entries (different company) Ledgers allow us to keep track of individual accounts. Your checking register (where you hopefully record when you write checks and receive money into your account) is a ledger for your checking account. If you are faithful in recording all checks written and deposits, then at any time you know your true balance (even if the check hasn t cleared yet). You could create ledgers for all sorts of accounts. For example, you could keep a Food Ledger in which you record all purchases of food. Thus, at the end of the month or year, you could go back and see just how much you spent on food. Moreover, at any specific time, you could see how much you have spent on food. Organizations will have ledgers for nearly all of their accounts. For example, the following could be a two ledgers for a small business actually, the ledgers would probably have a little more detail, but I want a simplified presentation. Accounts Cash: Receivable: Debit Credit Balance Debit Credit Balance $26,000 $4,500 $45,000 $71,000 $3,000 $7,500 $40,000 $31,000 $500 $8,000 $5,000 $36,000 $3,000 $5,000 $1,000 $37,000 $1,000 $36,000 $4,900 $31,100 $3,000 $34,100 $2,000 $32,100 The $26,000 balance on the first line of the Cash Ledger indicates what we started with, then each row is showing an individual transactions involving cash. Thus, we received $45,000 in cash at some point. All that is happening is that in addition to our normal recording transaction (debit cash $45,000) we are also putting each entry into a separate ledger. If we were at the end of the accounting cycle, then we could begin constructing the balance sheet quite easily. We just go to the Cash Ledger and see the current balance ($32,100 in this case), then put this on the balance sheet. Finally, notice that $3,000 entry for both ledgers. What might have happened? We received payment from a person that owed us ---- we have seen that when this occurs we Debit cash for the amount ($3,000) and Credit the accounts receivable account ($3,000). We could have ledgers for all of our asset account
12 ASSETS Cash: A/R: Supplies: Inventory: Land: Debit Credit Balance Debit Credit Balance Debit Credit Balance Debit Credit Balance Debit Credit Balance $26,000 $4,500 $0 $0 $0 $45,000 $71,000 $3,000 $7,500 $300 $300 $800 $800 $40,000 $40,000 $40,000 $31,000 $500 $8,000 $800 $0 $5,000 $36,000 $3,000 $5,000 $1,000 $37,000 $1,000 $36,000 $4,900 $31,100 $3,000 $34,100 $2,000 $32,100 and our liability accounts LIABILITIES Accounts Payable: Long-Term Debt: Debit Credit Balance Debit Credit Balance $2,000 $0 $300 $2,300 $45,000 $45,000 $800 $3,100 $1,000 $2,100 $200 $2,300 I have drawn a few arrows to indicate matching transactions. Thus, we must have borrowed $45,000 (debit cash, credit long-term debt). We must have purchased $300 worth of supplied but not paid for them at the time (debit supplies, credit accounts payable). We must have purchased $800 in inventory and not paid at the time (debit inventory, credit accounts payable). If we had included dates and names in the ledgers then we could reconstruct all the individual transaction, but this is not really the point of the ledgers. The ledgers show the balance on each account at any given point in time. Now, we return to the issue of closing entries. We need to look at the revenue, expense, dividends, and equity ledgers.
13 Prior to making an closing entries we have the following account balances at the end of the year (or, accounting cycle). Owners' Equity Revenue: Expenses: Dividends: Debit Credit Balance Debit Credit Balance Debit Credit Balance $0 $0 $0 $5,000 $5,000 $800 $800 $2,000 $2,000 $3,000 $8,000 $3,000 $3,800 $1,500 $9,500 $1,500 $5,300 $400 $5,700 $200 $5,900 Retained Earnings: Capital Stock: Debit Credit Balance Debit Credit Balance $18,500 $10,000 Before continuing, consider two questions? (1) What was the profit (or, net income) for the year? (2) What should be the balance of the retained earnings account on the ending balance sheet? (1) NET INCOME = Revenue Expenses = $9,500 - $5,900 = $3,600 (2) Ending Retained Earnings = Beginning Retained Earnings + Net Income Dividends = $18,500 + $3,600 - $2,000 = $20,100 How do we get to this retained earnings? Let s make the closing entries.
14 Revenue 9,500 Retained Earnings 9,500 Retained Earnings 5,900 Expenses 5,900 Retained Earnings 2,000 Dividends 2,000 Now, post each of the above to the ledgers.
15 Owners' Equity Revenue: Expenses: Dividends: Debit Credit Balance Debit Credit Balance Debit Credit Balance $0 $0 $0 $5,000 $5,000 $800 $800 $2,000 $2,000 $3,000 $8,000 $3,000 $3,800 $2,000 $0 $1,500 $9,500 $1,500 $5,300 $9,500 $0 $400 $5,700 $200 $5,900 $5,900 $0 Retained Earnings: Capital Stock: Debit Credit Balance Debit Credit Balance $18,500 $10,000 $9,500 $28,000 $5,900 $22,100 $2,000 $20,100 The $9,500 debit to revenue made the balance zero. Thus, we are ready to start recording new revenue for the coming year. We matched the $9,500 debit with a $9,500 credit to Retained Earnings, this increased our retained earnings. We performed similar operations with the expenses and dividends. Notice, the ending balance on the Retained Earnings account, we had calculated based on the net income and dividends that the company should have ending retained earnings of $20,100 and it does!!! This is the amount that will go on the new balance sheet.
TRANSACTIONS ANALYSIS EXAMPLE. Maxwell Partners Medical Diagnostic Services report the following information for 2011, their first year of operations:
 TRANSACTIONS ANALYSIS EXAMPLE Maxwell Partners Medical Diagnostic Services report the following information for 2011, their first year of operations: 1. Billings to clients for services provided: $350,000
TRANSACTIONS ANALYSIS EXAMPLE Maxwell Partners Medical Diagnostic Services report the following information for 2011, their first year of operations: 1. Billings to clients for services provided: $350,000
Vol. 1, Chapter 3 - Accounting Adjustments
 Vol. 1, Chapter 3 - Accounting Adjustments Problem 1 1. ($20,000 2,000) 48 = $375 per month 2. Jan. 31 Depreciation Expense $375 Accumulated Depreciation Van $375 To record depreciation expense for January
Vol. 1, Chapter 3 - Accounting Adjustments Problem 1 1. ($20,000 2,000) 48 = $375 per month 2. Jan. 31 Depreciation Expense $375 Accumulated Depreciation Van $375 To record depreciation expense for January
Accounting Cycle. Matching Principle
 CHAPTER 3 Accounting Cycle Analyze and record the transactions Post the transactions and prepare trial balance Adjust the accounts and prepare trial balance Prepare the financial statements Close the accounts
CHAPTER 3 Accounting Cycle Analyze and record the transactions Post the transactions and prepare trial balance Adjust the accounts and prepare trial balance Prepare the financial statements Close the accounts
Chapter 4. Completing the accounting cycle
 1 Chapter 4 Completing the accounting cycle 2 Learning objectives 1. Prepare an accounting worksheet and describe its purpose 2. Prepare a classified balance sheet and explain the major headings 3. Explain
1 Chapter 4 Completing the accounting cycle 2 Learning objectives 1. Prepare an accounting worksheet and describe its purpose 2. Prepare a classified balance sheet and explain the major headings 3. Explain
Chapter 3. Adjusting the accounts. Appendix 3A: An alternative method of recording deferrals
 1 Chapter 3 Adjusting the accounts Appendix 3A: An alternative method of recording deferrals 2 Learning objectives 1. Prepare adjusting entries for prepaid expenses originally recorded in an expense account
1 Chapter 3 Adjusting the accounts Appendix 3A: An alternative method of recording deferrals 2 Learning objectives 1. Prepare adjusting entries for prepaid expenses originally recorded in an expense account
Authored for ENMU Tutoring Services. By Jessica Huff
 By Jessica Huff The standard accounting equation is Assets=Liabilities + Stockholders Equity. Depending on which item someone is looking at will determine what the normal balance is. The normal balance
By Jessica Huff The standard accounting equation is Assets=Liabilities + Stockholders Equity. Depending on which item someone is looking at will determine what the normal balance is. The normal balance
1. If the assets owned by a business total $100,000 and liabilities total $70,000, stockholders' equity totals $30,000.
 Rallis Page 1 Name: _ Date: 1. If the assets owned by a business total $100,000 and liabilities total $70,000, stockholders' equity totals $30,000. A) True B) False 2. If total liabilities decreased by
Rallis Page 1 Name: _ Date: 1. If the assets owned by a business total $100,000 and liabilities total $70,000, stockholders' equity totals $30,000. A) True B) False 2. If total liabilities decreased by
The Basics of Accounting ACCT 201
 The Basics of Accounting ACCT 201 Content Accounting definition Accounting equation Accounting elements Asset, Liabilities, & Equity Transactions Accounts Receivable vs Accounts Payable Retained Earnings
The Basics of Accounting ACCT 201 Content Accounting definition Accounting equation Accounting elements Asset, Liabilities, & Equity Transactions Accounts Receivable vs Accounts Payable Retained Earnings
EXERCISES. Does not normally require adjustment. Normally requires adjustment (AE).
 EXERCISES Ex. 3 1 1. Prepaid expense 2. Accrued revenue 3. Unearned revenue 4. Accrued expense 5. Unearned revenue 6. Prepaid expense 7. Accrued expense 8. Accrued expense Ex. 3 2 Account Accounts Receivable...
EXERCISES Ex. 3 1 1. Prepaid expense 2. Accrued revenue 3. Unearned revenue 4. Accrued expense 5. Unearned revenue 6. Prepaid expense 7. Accrued expense 8. Accrued expense Ex. 3 2 Account Accounts Receivable...
b. Do not recognize revenue until steel is shipped. c. Do not recognize revenue until next year after the games are played.
 CHAPTER FOUR SE4-2 Revenue recognition a. Recognize revenue from car sales for 12,000. Notes receivable $12,000 Sales revenue $12,000 b. Do not recognize revenue until steel is shipped. c. Do not recognize
CHAPTER FOUR SE4-2 Revenue recognition a. Recognize revenue from car sales for 12,000. Notes receivable $12,000 Sales revenue $12,000 b. Do not recognize revenue until steel is shipped. c. Do not recognize
CHAPTER 3: PREPARING FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
 CHAPTER 3: PREPARING FINANCIAL STATEMENTS I. TIMING AND REPORTING A. The Accounting Period Time period assumption an organization s activities can be divided into specific time periods. Examples: a month,
CHAPTER 3: PREPARING FINANCIAL STATEMENTS I. TIMING AND REPORTING A. The Accounting Period Time period assumption an organization s activities can be divided into specific time periods. Examples: a month,
Chapter 6 Statement of Cash Flows
 Chapter 6 Statement of Cash Flows The Statement of Cash Flows describes the cash inflows and outflows for the firm based upon three categories of activities. Operating Activities: Generally include transactions
Chapter 6 Statement of Cash Flows The Statement of Cash Flows describes the cash inflows and outflows for the firm based upon three categories of activities. Operating Activities: Generally include transactions
Chapter 4. Completing the accounting cycle. Appendix 4A: Reversing entries
 1 Chapter 4 Completing the accounting cycle Appendix 4A: Reversing entries 2 Learning objective 1. Prepare reversing entries and describe their purpose 3 Reversing entries Reversing entries are optional
1 Chapter 4 Completing the accounting cycle Appendix 4A: Reversing entries 2 Learning objective 1. Prepare reversing entries and describe their purpose 3 Reversing entries Reversing entries are optional
Learn Accounting Understand Business: Course Review Answers
 Learn Accounting Understand Business: Course Review Answers 1. What type of accounting measures the activity of the company by looking at economic events regardless of when cash transactions occur? A.
Learn Accounting Understand Business: Course Review Answers 1. What type of accounting measures the activity of the company by looking at economic events regardless of when cash transactions occur? A.
Accounting Skills Assessment Practice Exam Page 1 of 10
 NAU ACCOUNTING SKILLS ASSESSMENT PRACTICE EXAM & KEY 1. A company received cash and issued common stock. What was the effect on the accounting equation? Assets Liabilities Stockholders Equity A. + NE +
NAU ACCOUNTING SKILLS ASSESSMENT PRACTICE EXAM & KEY 1. A company received cash and issued common stock. What was the effect on the accounting equation? Assets Liabilities Stockholders Equity A. + NE +
Study Guide - Final Exam Accounting I
 Study Guide - Final Exam Accounting I True/False Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. 1. Entries in a sales journal affect account balances in both the accounts receivable ledger
Study Guide - Final Exam Accounting I True/False Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. 1. Entries in a sales journal affect account balances in both the accounts receivable ledger
Financial Statement Consolidation
 Financial Statement Consolidation We will consolidate the previously completed worksheets in this financial plan. In order to complete this section of the plan, you must have already completed all of the
Financial Statement Consolidation We will consolidate the previously completed worksheets in this financial plan. In order to complete this section of the plan, you must have already completed all of the
(a) (i) Marking Scheme: 1 mark for definition and 1 mark for example.
 T A S M A N I A N Accounting C E R T I F I C A T E Subject Code ACC5C O F E D U C A T I O N Question 1 T A S M A N I A N Q U A L I F I C A T I O N S A U T H O R I T Y (a) (i) Marking Scheme: 1 mark for
T A S M A N I A N Accounting C E R T I F I C A T E Subject Code ACC5C O F E D U C A T I O N Question 1 T A S M A N I A N Q U A L I F I C A T I O N S A U T H O R I T Y (a) (i) Marking Scheme: 1 mark for
> DO IT! Chapter 3 Adjusting the Accounts. Timing Concepts. Adjusting Entries for Deferrals D-12. Solution
 Chapter 3 Adjusting the Accounts Timing Concepts Review the glossary terms. Study carefully the revenue recognition principle, the expense recognition principle, and the time period assumption. Several
Chapter 3 Adjusting the Accounts Timing Concepts Review the glossary terms. Study carefully the revenue recognition principle, the expense recognition principle, and the time period assumption. Several
Review of Accounting Principles
 Appendix A Review of Accounting Principles Appendix A is a review of basic accounting principles and procedures. Standard accounting procedures are based on the double-entry system. This means that each
Appendix A Review of Accounting Principles Appendix A is a review of basic accounting principles and procedures. Standard accounting procedures are based on the double-entry system. This means that each
Basic Accounting Principles
 Basic Accounting Principles Basic Accounting Model The basic accounting model represents the relationship between assets (what the company owns), liabilities (what the company owes), and owner s equity
Basic Accounting Principles Basic Accounting Model The basic accounting model represents the relationship between assets (what the company owns), liabilities (what the company owes), and owner s equity
Accounting Basics. (Explanation)
 Accounting Basics (Explanation) Your AccountingCoach PRO membership includes lifetime access to all of our materials. Take a quick tour by visiting www.accountingcoach.com/quicktour. Introduction to Accounting
Accounting Basics (Explanation) Your AccountingCoach PRO membership includes lifetime access to all of our materials. Take a quick tour by visiting www.accountingcoach.com/quicktour. Introduction to Accounting
State of Idaho - Public Works Contractor Licensing MULTI-PURPOSE BALANCE SHEET (For Class D and C Licenses Only)
 State of Idaho - Public Works Contractor Licensing MULTI-PURPOSE SHEET (For Class D and C Licenses Only) Instructions: Complete only the sections that pertain to your company structure. Do not include
State of Idaho - Public Works Contractor Licensing MULTI-PURPOSE SHEET (For Class D and C Licenses Only) Instructions: Complete only the sections that pertain to your company structure. Do not include
CHAPTER 2 ACCOUNTING FOR TRANSACTIONS
 CHAPTER 2 ACCOUNTING FOR TRANSACTIONS Key Terms and Concepts to Know Double entry accounting: Debits and Credits Total debits must always equal total credits Accounting Books: Accounts General Journal
CHAPTER 2 ACCOUNTING FOR TRANSACTIONS Key Terms and Concepts to Know Double entry accounting: Debits and Credits Total debits must always equal total credits Accounting Books: Accounts General Journal
CHAPTER 3. BE3-2 Advertising. Dec. 31 Advertising Supplies Expense 7200 Advertising Supplies 7200 to adjust. BE3-3 Bere Co.
 CHAPTER 3 BE3-2 Advertising Advertising Supplies Supplies Expense 8700 7200 7200 1500 7200 Dec. Advertising Supplies Expense 7200 Advertising Supplies 7200 BE3-3 Bere Co. Prepaid Insurance Insurance Expense
CHAPTER 3 BE3-2 Advertising Advertising Supplies Supplies Expense 8700 7200 7200 1500 7200 Dec. Advertising Supplies Expense 7200 Advertising Supplies 7200 BE3-3 Bere Co. Prepaid Insurance Insurance Expense
COMPLETION OF THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE - Closing Entries -
 COMPLETION OF THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE - Closing Entries - Worksheet Overview Trial Balance Adjustments Adjusted Trial Balance Income Statement Balance Sheet Account Titles Debit Credit Debit Credit Debit
COMPLETION OF THE ACCOUNTING CYCLE - Closing Entries - Worksheet Overview Trial Balance Adjustments Adjusted Trial Balance Income Statement Balance Sheet Account Titles Debit Credit Debit Credit Debit
Statement of Change in Working Capital & Inflows/Outflows of Working Capital
 HOSP 2110 (Management Acct) Learning Centre Statement of Change in Working Capital & Inflows/Outflows of Working Capital The statement of changes in working capital shows the net change in working capital
HOSP 2110 (Management Acct) Learning Centre Statement of Change in Working Capital & Inflows/Outflows of Working Capital The statement of changes in working capital shows the net change in working capital
ACS-1803 Introduction to Information Systems. Functional Area Systems. Lecture 4
 ACS-1803 Introduction to Information Systems Instructor: David Tenjo Functional Area Systems Lecture 4 1 Overview Overview of Functional Areas in the organization Functional Area: Accounting Accounting
ACS-1803 Introduction to Information Systems Instructor: David Tenjo Functional Area Systems Lecture 4 1 Overview Overview of Functional Areas in the organization Functional Area: Accounting Accounting
Financial Statements Tutorial
 Financial Statement Review: Financial Statements Tutorial There are four major financial statements used to communicate information to external users (creditors, investors, suppliers, etc.) - 1. Balance
Financial Statement Review: Financial Statements Tutorial There are four major financial statements used to communicate information to external users (creditors, investors, suppliers, etc.) - 1. Balance
HERE'S A TIP. Double Entry Accounting. Debits and Credits
 Double Entry Accounting Because every business transaction affects at least two accounts, our accounting system is known as a double entry system. (You can refer to the company's chart of accounts to select
Double Entry Accounting Because every business transaction affects at least two accounts, our accounting system is known as a double entry system. (You can refer to the company's chart of accounts to select
Learning Module 3 Journal Entries
 Learning Module 3 Journal Entries The Accounting Equation Balance Sheet Income Statement = + + - Assets Liabilities Owners' Equity Revenue Expenses Dr. Cr. Dr. Cr. Dr. Cr. Dr. Cr. Dr. Cr. Recording journal
Learning Module 3 Journal Entries The Accounting Equation Balance Sheet Income Statement = + + - Assets Liabilities Owners' Equity Revenue Expenses Dr. Cr. Dr. Cr. Dr. Cr. Dr. Cr. Dr. Cr. Recording journal
A Simple Model. The Accounting Equation
 An introduction to the accounting equation in the context of building a financial model. This series introduces the financial statements in the context of a financial model. NOTES TO ACCOMPANY VIDEOS These
An introduction to the accounting equation in the context of building a financial model. This series introduces the financial statements in the context of a financial model. NOTES TO ACCOMPANY VIDEOS These
How To Account For Revenue Under Accrual Accounting
 BAT 4M: Chapter 3 ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS 01. (a) Under the time period assumption, an accountant is required to determine the relevance of each business transaction to specific accounting periods, and its
BAT 4M: Chapter 3 ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS 01. (a) Under the time period assumption, an accountant is required to determine the relevance of each business transaction to specific accounting periods, and its
Adjusting the Accounts
 HOSP 1210 (Financial Acct) Learning Centre Adjusting the Accounts Anytime we prepare financial statements or reach the end of an accounting period, there are account adjustments that need to be made to
HOSP 1210 (Financial Acct) Learning Centre Adjusting the Accounts Anytime we prepare financial statements or reach the end of an accounting period, there are account adjustments that need to be made to
Accrual Accounting Process
 Accrual Accounting Process 15.501 Accounting Spring 2004 Professor S. Roychowdhury Sloan School of Management Massachusetts Institute of Technology Feb 17/18, 2004 1 An accountant s functions include Classifying
Accrual Accounting Process 15.501 Accounting Spring 2004 Professor S. Roychowdhury Sloan School of Management Massachusetts Institute of Technology Feb 17/18, 2004 1 An accountant s functions include Classifying
In the event of a tie, the score on the last ten questions will be used as a tie-breaker.
 NEW YORK STATE ASSOCIATION FUTURE BUSINESS LEADERS OF AMERICA SPRING DISTRICT MEETING ACCOUNTING II 2010 TEST DIRECTIONS 1. Complete the information requested on the answer sheet. PRINT your name on the
NEW YORK STATE ASSOCIATION FUTURE BUSINESS LEADERS OF AMERICA SPRING DISTRICT MEETING ACCOUNTING II 2010 TEST DIRECTIONS 1. Complete the information requested on the answer sheet. PRINT your name on the
Periodicity Assumption... Time Period Assumption... Chapter 4 Accrual Accounting Concepts
 Financial Accounting: Tools for Business Decision Making, 4th Ed. CHAPTER 4 Kimmel, Weygandt, Kieso Chapter 4 Accrual Accounting Concepts KEY THINGS WE LL DO: Refresh and expand Ch.3 concepts. Differentiate
Financial Accounting: Tools for Business Decision Making, 4th Ed. CHAPTER 4 Kimmel, Weygandt, Kieso Chapter 4 Accrual Accounting Concepts KEY THINGS WE LL DO: Refresh and expand Ch.3 concepts. Differentiate
Do it! Chapter 11. Current Liabilities
 Chapter 11 Do it! You and several classmates are studying for the next accounting examination. They ask you to answer the following questions. 1. If cash is borrowed on a $50,000, 6-month, 12% note on
Chapter 11 Do it! You and several classmates are studying for the next accounting examination. They ask you to answer the following questions. 1. If cash is borrowed on a $50,000, 6-month, 12% note on
CH 23 STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS SELF-STUDY QUESTIONS
 C H 2 3, P a g e 1 CH 23 STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS SELF-STUDY QUESTIONS (note from Dr. N: I have deleted questions for you to omit, but did not renumber the remaining questions) 1. The primary purpose of
C H 2 3, P a g e 1 CH 23 STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS SELF-STUDY QUESTIONS (note from Dr. N: I have deleted questions for you to omit, but did not renumber the remaining questions) 1. The primary purpose of
ACCT1115. Review Package - Midterm SOLUTION Fall 2013
 ACCT1115 Review Package - Midterm SOLUTION Fall 2013 Part I Multiple Choice 1) How should you record the purchase of an expensive automobile? a) Decrease cash, increase assets b) Decrease cash, increase
ACCT1115 Review Package - Midterm SOLUTION Fall 2013 Part I Multiple Choice 1) How should you record the purchase of an expensive automobile? a) Decrease cash, increase assets b) Decrease cash, increase
Chapter 1. Introduction to Accounting and Business
 1 Chapter 1 Introduction to Accounting and Business Learning Objective 1 Describe the nature of a business, the role of accounting, and ethics in business. Nature of Business and Accounting A business
1 Chapter 1 Introduction to Accounting and Business Learning Objective 1 Describe the nature of a business, the role of accounting, and ethics in business. Nature of Business and Accounting A business
The Statement of Cash Flows Direct Method
 23 The Statement of Cash Flows Direct Method DEMONSTRATION PROBLEM The financial statements of Bolero Corporation follow. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 1 Bolero Corporation Income
23 The Statement of Cash Flows Direct Method DEMONSTRATION PROBLEM The financial statements of Bolero Corporation follow. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 1 Bolero Corporation Income
Chapter 2. Analyzing transactions
 1 Chapter 2 Analyzing transactions 2 Learning objectives 1. Explain the steps in the accounting cycle and each step s supporting documentation 2. Explain the purpose of source documents 3. Describe an
1 Chapter 2 Analyzing transactions 2 Learning objectives 1. Explain the steps in the accounting cycle and each step s supporting documentation 2. Explain the purpose of source documents 3. Describe an
Exam 1 chapters 1-4 Needles 10ed
 Exam 1 chapters 1-4 Needles 10ed Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is the most appropriate definition of accounting?
Exam 1 chapters 1-4 Needles 10ed Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is the most appropriate definition of accounting?
3 Accrual Accounting & Income
 29366_10_ch3_p125-196 12/12/07 5:50 PM Page 125 3 Accrual Accounting & Income SPOTLIGHT STARBUCKS CORPORATION Starbucks has changed coffee from a breakfast drink to an experience. The corporation began
29366_10_ch3_p125-196 12/12/07 5:50 PM Page 125 3 Accrual Accounting & Income SPOTLIGHT STARBUCKS CORPORATION Starbucks has changed coffee from a breakfast drink to an experience. The corporation began
COMPONENTS OF THE STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS
 ILLUSTRATION 24-1 OPERATING, INVESTING, AND FINANCING ACTIVITIES COMPONENTS OF THE STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES + Sales and Service Revenue Received Cost of Sales Paid Selling
ILLUSTRATION 24-1 OPERATING, INVESTING, AND FINANCING ACTIVITIES COMPONENTS OF THE STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES + Sales and Service Revenue Received Cost of Sales Paid Selling
Fundamentals of Financial Accounting
 Fundamentals of Financial Accounting CHAPTER I Accounting in action. What is accounting? Accounting is the recording of financial transactions plus storing, sorting, retrieving, summarizing, and presenting
Fundamentals of Financial Accounting CHAPTER I Accounting in action. What is accounting? Accounting is the recording of financial transactions plus storing, sorting, retrieving, summarizing, and presenting
Statement of Cash Flows
 THE CONTENT AND VALUE OF THE STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS The cash flow statement reconciles beginning and ending cash by presenting the cash receipts and cash disbursements of an enterprise for an accounting
THE CONTENT AND VALUE OF THE STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS The cash flow statement reconciles beginning and ending cash by presenting the cash receipts and cash disbursements of an enterprise for an accounting
ILLUSTRATION 3-1 DOUBLE-ENTRY ACCOUNTING SYSTEM
 ILLUSTRATION 3-1 DOUBLE-ENTRY ACCOUNTING SYSTEM ASSETS Increase Decrease + DOUBLE-ENTRY ACCOUNTING REAL (PERMANENT) ACCOUNTS = LIABILITIES + Rules of Thumb + If the "normal balance" for an account is a
ILLUSTRATION 3-1 DOUBLE-ENTRY ACCOUNTING SYSTEM ASSETS Increase Decrease + DOUBLE-ENTRY ACCOUNTING REAL (PERMANENT) ACCOUNTS = LIABILITIES + Rules of Thumb + If the "normal balance" for an account is a
Marist College ACCT 203 Financial Accounting Quiz Prep Chapter 3
 Marist College ACCT 203 Financial Accounting Quiz Prep Chapter 3 The Accounting Cycle: Capturing Economic Events Peter Rivera August 2011 Disclaimer This Quiz Prep is provided as an outline of the key
Marist College ACCT 203 Financial Accounting Quiz Prep Chapter 3 The Accounting Cycle: Capturing Economic Events Peter Rivera August 2011 Disclaimer This Quiz Prep is provided as an outline of the key
A = L + OE. Transaction 1 Assets = Liabilitites + Owners equity + 1,000,000 Cash + 1,000,000 Common stock
 FINANCIAL STATEMENT ANALYSIS Henry Jarva Aalto University, Spring 2015 Student name: EXERCISE 1. Provide journal entries for Transactions 5 8, Adjusting Entries 2 7, and prepare Exhibit 1. 2. Calculate
FINANCIAL STATEMENT ANALYSIS Henry Jarva Aalto University, Spring 2015 Student name: EXERCISE 1. Provide journal entries for Transactions 5 8, Adjusting Entries 2 7, and prepare Exhibit 1. 2. Calculate
2 Transaction Analysis
 29366_06_ch2_p053-110 12/12/07 5:50 PM Page 53 2 Transaction Analysis SPOTLIGHT A P P L E C O M P U T E R, I N C. How do you manage your music library? You may use Apple Computer s itunes, which along
29366_06_ch2_p053-110 12/12/07 5:50 PM Page 53 2 Transaction Analysis SPOTLIGHT A P P L E C O M P U T E R, I N C. How do you manage your music library? You may use Apple Computer s itunes, which along
How To Calculate A Trial Balance For A Company
 THE BASIC MODEL The accounting information system is designed to collect and organize data into information that is useful for stakeholders. The Accounting Equation The basic accounting equation is what
THE BASIC MODEL The accounting information system is designed to collect and organize data into information that is useful for stakeholders. The Accounting Equation The basic accounting equation is what
Transaction Analysis SPOTLIGHT. 2 Chapter 40878 Page 53 09/25/07 jhr APPLE COMPUTER, INC.
 2 Chapter 40878 9/25/07 3:18 PM Page 53 2 Transaction Analysis 2 Chapter 40878 Page 53 09/25/07 jhr SPOTLIGHT APPLE COMPUTER, INC. How do you manage your music library? You may use Apple Computer s itunes,
2 Chapter 40878 9/25/07 3:18 PM Page 53 2 Transaction Analysis 2 Chapter 40878 Page 53 09/25/07 jhr SPOTLIGHT APPLE COMPUTER, INC. How do you manage your music library? You may use Apple Computer s itunes,
Accruals and prepayments
 5 Accruals and prepayments this chapter covers... In the last chapter we have looked at the preparation of financial statements or final accounts using the extended trial balance, or spreadsheet, approach.
5 Accruals and prepayments this chapter covers... In the last chapter we have looked at the preparation of financial statements or final accounts using the extended trial balance, or spreadsheet, approach.
Gold Run Snowmobile. Adjusting Entries and Closing Entries For The Quarter Ended December 31. Final Project Evaluation. 5 th Edition.
 Gold Run Snowmobile 5 th Edition Adjusting Entries and Closing Entries For The Quarter Ended December 31 and the Final Project Evaluation Page 1 ADJUSTING ENTRIES FOR THE QUARTER Using a copy of the December
Gold Run Snowmobile 5 th Edition Adjusting Entries and Closing Entries For The Quarter Ended December 31 and the Final Project Evaluation Page 1 ADJUSTING ENTRIES FOR THE QUARTER Using a copy of the December
TOPIC LEARNING OBJECTIVE
 Topic Mapping 1 Transaction Analysis Understand the effect of various types of transactions on the accounting equation, accounting journal and accounting ledger. Concepts and Skills Accounting Equation
Topic Mapping 1 Transaction Analysis Understand the effect of various types of transactions on the accounting equation, accounting journal and accounting ledger. Concepts and Skills Accounting Equation
The Accounting Equation & Transaction Analysis
 HOSP 1860 (Financial Acct) Learning Centre The Accounting Equation & Transaction Analysis A business must always have a balance between what it owns and what it owes. This is shown by the basic accounting
HOSP 1860 (Financial Acct) Learning Centre The Accounting Equation & Transaction Analysis A business must always have a balance between what it owns and what it owes. This is shown by the basic accounting
SOLUTIONS. Learning Goal 15
 Learning Goal 15: Prepare a Classified S1 Learning Goal 15 Multiple Choice 1. b 2. c 3. a 4. b 5. d 6. a 7. c Their importance in paying current liabilities is the main reason current assets are shown
Learning Goal 15: Prepare a Classified S1 Learning Goal 15 Multiple Choice 1. b 2. c 3. a 4. b 5. d 6. a 7. c Their importance in paying current liabilities is the main reason current assets are shown
Plan and Track Your Finances
 Plan and Track Your Finances 9.1 Financing Your Business 9.2 Pro Forma Financial Statements 9.3 Recordkeeping for Businesses Lesson 9.1 Financing Your Business Goals Estimate your startup costs and personal
Plan and Track Your Finances 9.1 Financing Your Business 9.2 Pro Forma Financial Statements 9.3 Recordkeeping for Businesses Lesson 9.1 Financing Your Business Goals Estimate your startup costs and personal
William B. Pollard, Appalachian State University, Boone, NC 28608, [email protected] INTRODUCTION
 TEACHING PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTING: HELPING STUDENTS IDENTIFY TEN DIFFERENCES WHEN COMPARING A TRIAL BALANCE, AN ADJUSTED TRIAL BALANCE AND A BALANCE SHEET William B. Pollard, Appalachian State University,
TEACHING PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTING: HELPING STUDENTS IDENTIFY TEN DIFFERENCES WHEN COMPARING A TRIAL BALANCE, AN ADJUSTED TRIAL BALANCE AND A BALANCE SHEET William B. Pollard, Appalachian State University,
LIABILITIES. Liabilities are claims against your Assets. They are something that you have to repay to someone else.
 Accounting 101 ASSETS An Asset is something that you own, that has value, and will generate a future benefit. Assets are good. Eg.) Cash, accounts receivable, GST receivable, inventory, equipment, land,
Accounting 101 ASSETS An Asset is something that you own, that has value, and will generate a future benefit. Assets are good. Eg.) Cash, accounts receivable, GST receivable, inventory, equipment, land,
The Accounting Process
 GAAP LITERATURE The Accounting Process Chapter 3 TRADITIONAL: Original pronouncements, issued by the FASB. SEPT. 2009 CHANGE: Codification issued by the FASB. DIFFERENCE: Codification is listed by topic
GAAP LITERATURE The Accounting Process Chapter 3 TRADITIONAL: Original pronouncements, issued by the FASB. SEPT. 2009 CHANGE: Codification issued by the FASB. DIFFERENCE: Codification is listed by topic
CHAPTER II GENERAL LEDGER ACCOUNTS
 CHAPTER II GENERAL LEDGER ACCOUNTS A general ledger is basic to an accounting system. The General Ledger of a fund is a summary record containing the balance of assets, liabilities, deferred revenues,
CHAPTER II GENERAL LEDGER ACCOUNTS A general ledger is basic to an accounting system. The General Ledger of a fund is a summary record containing the balance of assets, liabilities, deferred revenues,
Statement of Cash Flows
 HOSP 2110 (Management Acct) Learning Centre Statement of Cash Flows The Statement of Cash Flows (or cash flow statement) is one of the main financial statements used by investors. It shows the cash generated
HOSP 2110 (Management Acct) Learning Centre Statement of Cash Flows The Statement of Cash Flows (or cash flow statement) is one of the main financial statements used by investors. It shows the cash generated
Chapter 5 Accrual Adjustments and Financial Statement Preparation. Revenue recognition Matching expenses to revenues Expenses related to periods
 Chapter 5 Accrual Adjustments and Financial Statement Preparation Revenue recognition Matching expenses to revenues Expenses related to periods 1 The Measurement of Income major function of accounting
Chapter 5 Accrual Adjustments and Financial Statement Preparation Revenue recognition Matching expenses to revenues Expenses related to periods 1 The Measurement of Income major function of accounting
Sample Test for entrance into Acct 3110 and Acct 3310
 Sample Test for entrance into Acct 3110 and Acct 3310 1. Which of the following financial statements could properly have the following in the date line: For the Year Ended December 31, 2010"? a. Balance
Sample Test for entrance into Acct 3110 and Acct 3310 1. Which of the following financial statements could properly have the following in the date line: For the Year Ended December 31, 2010"? a. Balance
Chapter Review Problems
 Chapter Review Problems Unit 17.1 Income statements 1. When revenues exceed expenses, is the result (a) net income or (b) net loss? (a) net income 2. Do income statements reflect profits of a business
Chapter Review Problems Unit 17.1 Income statements 1. When revenues exceed expenses, is the result (a) net income or (b) net loss? (a) net income 2. Do income statements reflect profits of a business
CHAPTER 2 REVIEW OF THE ACCOUNTING PROCESS. Lecture Outline
 CHAPTER 2 REVIEW OF THE ACCOUNTING PROCESS Overview Chapter 1 explained that the primary means of conveying financial information to investors, creditors, and other external users is through financial
CHAPTER 2 REVIEW OF THE ACCOUNTING PROCESS Overview Chapter 1 explained that the primary means of conveying financial information to investors, creditors, and other external users is through financial
SMART TOUCH LEARNING Balance Sheet May 31, 2013 $ 4,800. $ 48,700 Accounts receivable 2,600. 900 Inventory 30,500. 100 Supplies.
 3 The Adjusting Process Are these balances correctly showing everything the company OWNS? SMART TOUCH LEARNING ance Sheet May 31, 2013 Are these balances correctly showing everything the company OWES?
3 The Adjusting Process Are these balances correctly showing everything the company OWNS? SMART TOUCH LEARNING ance Sheet May 31, 2013 Are these balances correctly showing everything the company OWES?
ACCOUNTING COMPETENCY EXAM SAMPLE EXAM. 2. The financial statement or statements that pertain to a stated period of time is (are) the:
 ACCOUNTING COMPETENCY EXAM SAMPLE EXAM 1. The accounting process does not include: a. interpreting d. observing b. reporting e. classifying c. purchasing 2. The financial statement or statements that pertain
ACCOUNTING COMPETENCY EXAM SAMPLE EXAM 1. The accounting process does not include: a. interpreting d. observing b. reporting e. classifying c. purchasing 2. The financial statement or statements that pertain
A Simple Model. Introduction to Financial Statements
 Introduction to Financial Statements NOTES TO ACCOMPANY VIDEOS These notes are intended to supplement the videos on ASimpleModel.com. They are not to be used as stand alone study aids, and are not written
Introduction to Financial Statements NOTES TO ACCOMPANY VIDEOS These notes are intended to supplement the videos on ASimpleModel.com. They are not to be used as stand alone study aids, and are not written
GBA 521 Midterm Review Dr. Markelevich
 GBA 521 Midterm Review Dr. Markelevich Multiple Choice (3 points for each question) Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Wynn Corp. Wynn Corp. reported
GBA 521 Midterm Review Dr. Markelevich Multiple Choice (3 points for each question) Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Wynn Corp. Wynn Corp. reported
Midterm Fall 2012 Solution
 Midterm Fall 2012 Solution Instructions: 1) Answers for the multiple-choice questions must be recorded on the UW answer card. All other questions must be answered in the space provided on the examination
Midterm Fall 2012 Solution Instructions: 1) Answers for the multiple-choice questions must be recorded on the UW answer card. All other questions must be answered in the space provided on the examination
Time Period Assumption
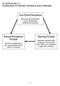 ILLUSTRATION 3-1 GUIDELINES TO REPORT REVENUE AND EXPENSES Time Period Assumption Economic life of business can be divided into artificial time periods Revenue Recognition Principle Revenue recognized
ILLUSTRATION 3-1 GUIDELINES TO REPORT REVENUE AND EXPENSES Time Period Assumption Economic life of business can be divided into artificial time periods Revenue Recognition Principle Revenue recognized
The Nature of Accounting Systems
 Basic Accounting & Budgeting February 4, 2009 The Nature of Accounting Systems Accounting is the process of recording, classifying, summarizing, reporting and interpreting information about the economic
Basic Accounting & Budgeting February 4, 2009 The Nature of Accounting Systems Accounting is the process of recording, classifying, summarizing, reporting and interpreting information about the economic
EXERCISES. The cash from operating activities detail is provided as follows for class discussion:
 EXERCISES Ex. 14 1 There were net additions, such as depreciation and amortization of intangible assets of $389 million, to the net loss reported on the income statement to convert the net loss from the
EXERCISES Ex. 14 1 There were net additions, such as depreciation and amortization of intangible assets of $389 million, to the net loss reported on the income statement to convert the net loss from the
Accounting Principles Dr. Mishari Alfraih. Adjusting the Accounts
 Accrual- vs. Cash-Basis Accounting Accrual-Basis Accounting Adjusting the Accounts Transactions recorded in the periods in which the events occur Revenues are recognized when earned, rather than when cash
Accrual- vs. Cash-Basis Accounting Accrual-Basis Accounting Adjusting the Accounts Transactions recorded in the periods in which the events occur Revenues are recognized when earned, rather than when cash
CHAPTER 16. Non-current assets: Revaluation, disposal and other aspects CONTENTS
 CHAPTER 16 Non-current assets: Revaluation, disposal and other aspects CONTENTS 16.1 Non-current asset disposals 16.2 Revaluation and disposal 16.3 Intangibles and natural resources 16.4 Goodwill and discount
CHAPTER 16 Non-current assets: Revaluation, disposal and other aspects CONTENTS 16.1 Non-current asset disposals 16.2 Revaluation and disposal 16.3 Intangibles and natural resources 16.4 Goodwill and discount
Bookkeeping Proficiency
 Bookkeeping Proficiency (Exam) Your AccountingCoach PRO membership includes lifetime access to all of our materials. Take a quick tour by visiting www.accountingcoach.com/quicktour. Table of Contents (click
Bookkeeping Proficiency (Exam) Your AccountingCoach PRO membership includes lifetime access to all of our materials. Take a quick tour by visiting www.accountingcoach.com/quicktour. Table of Contents (click
Accounts Payable are the total amounts your business owes its suppliers for goods and services purchased.
 Accounts Payable are the total amounts your business owes its suppliers for goods and services purchased. Accounts Receivable are the total amounts customers owe your business for goods or services sold
Accounts Payable are the total amounts your business owes its suppliers for goods and services purchased. Accounts Receivable are the total amounts customers owe your business for goods or services sold
Learning Objectives: Quick answer key: Question # Multiple Choice True/False. 14.1 Describe the important of accounting and financial information.
 0 Learning Objectives: 14.1 Describe the important of accounting and financial information. 14.2 Differentiate between managerial and financial accounting. 14.3 Identify the six steps of the accounting
0 Learning Objectives: 14.1 Describe the important of accounting and financial information. 14.2 Differentiate between managerial and financial accounting. 14.3 Identify the six steps of the accounting
Statement of Cash Flow
 Management Accounting 337 Statement of Cash Flow Cash is obviously an important asset to all, both individually and in business. A shortage or lack of cash may mean an inability to purchase needed inventory
Management Accounting 337 Statement of Cash Flow Cash is obviously an important asset to all, both individually and in business. A shortage or lack of cash may mean an inability to purchase needed inventory
CHAPTER 3 Solutions MEASURING BUSINESS INCOME
 CHAPTER 3 Solutions MEASURING BUSINESS INCOME Chapter 3, SE 1. 1. 2. 3. 4. c b d a Chapter 3, SE 2. Dec. 31 Insurance Expense 800 Prepaid Insurance To record insurance expired during the year $460 + $1,040
CHAPTER 3 Solutions MEASURING BUSINESS INCOME Chapter 3, SE 1. 1. 2. 3. 4. c b d a Chapter 3, SE 2. Dec. 31 Insurance Expense 800 Prepaid Insurance To record insurance expired during the year $460 + $1,040
Completing the Accounting Cycle
 C H A P T E R 4 Completing the Accounting Cycle Financial Accounting 14e Warren Reeve Duchac human/istock/360/getty Images Flow of Accounting Information (slide 1 of 5) End-of-Period Spreadsheet (Work
C H A P T E R 4 Completing the Accounting Cycle Financial Accounting 14e Warren Reeve Duchac human/istock/360/getty Images Flow of Accounting Information (slide 1 of 5) End-of-Period Spreadsheet (Work
Chapter 2 Balance sheets - what a company owns and what it owes
 Chapter 2 Balance sheets - what a company owns and what it owes SharePad is packed full of useful financial data. This data holds the key to understanding the financial health and value of any company
Chapter 2 Balance sheets - what a company owns and what it owes SharePad is packed full of useful financial data. This data holds the key to understanding the financial health and value of any company
ACS 1803 Accounting SUPPLEMENTARY NOTES prepared by E. Kaluzniacky & K. Augustine. Computerized Accounting - The General Ledger System
 ACS 1803 Accounting SUPPLEMENTARY NOTES prepared by E. Kaluzniacky & K. Augustine Computerized Accounting - The General Ledger System Every business must keep track of financial information that relates
ACS 1803 Accounting SUPPLEMENTARY NOTES prepared by E. Kaluzniacky & K. Augustine Computerized Accounting - The General Ledger System Every business must keep track of financial information that relates
Accounting Notes. Cash - includes money and any medium of exchange that a bank accepts at face value
 Asset Accounts: Cash - includes money and any medium of exchange that a bank accepts at face value Accounts Receivable - a record of an oral or implied promise of future cash receipts in exchange for goods
Asset Accounts: Cash - includes money and any medium of exchange that a bank accepts at face value Accounts Receivable - a record of an oral or implied promise of future cash receipts in exchange for goods
Assuming office supplies are charged to the Office Supplies inventory account when purchased:
 Adjusting Entries Prepaid Expenses Second Bullet Example - Assuming office supplies are charged to the Office Supplies inventory account when purchased: Office supplies expense 7,800 Office supplies 7,800
Adjusting Entries Prepaid Expenses Second Bullet Example - Assuming office supplies are charged to the Office Supplies inventory account when purchased: Office supplies expense 7,800 Office supplies 7,800
ACCOUNTING ENTRANCE EXAMINATION PRACTICE QUESTION SET J.M. TULL SCHOOL OF ACCOUNTING ENTRANCE EXAMINATION PRACTICE QUESTION SET
 ACCOUNTING ENTRANCE EXAMINATION PRACTICE QUESTION SET J.M. TULL SCHOOL OF ACCOUNTING ENTRANCE EXAMINATION PRACTICE QUESTION SET Important: PRINT your response (A,B,C,D or E) that best completes the statement
ACCOUNTING ENTRANCE EXAMINATION PRACTICE QUESTION SET J.M. TULL SCHOOL OF ACCOUNTING ENTRANCE EXAMINATION PRACTICE QUESTION SET Important: PRINT your response (A,B,C,D or E) that best completes the statement
SESSION 3: COMPANIES FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (THE BALANCE SHEET)
 SESSION 3: COMPANIES FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (THE BALANCE SHEET) KEY CONCEPTS: In this session we will look at: - The Balance Sheet - Notes to the Financial Statements Trading Business X-PLANATION THE BALANCE
SESSION 3: COMPANIES FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (THE BALANCE SHEET) KEY CONCEPTS: In this session we will look at: - The Balance Sheet - Notes to the Financial Statements Trading Business X-PLANATION THE BALANCE
PROFESSOR S NAME ACC 255 FALL 2011 COVER SHEET FOR COMPREHENSIVE PROBLEM 2 (CHAPTERS 2, 5-8)
 COMPREHENSIVE PROBLEM 2 (CHAPTERS 2, 5-8) Page 137 NAME ANSWER KEY PROFESSOR S NAME SECTION SCORE ACC 255 FALL 2011 COVER SHEET FOR COMPREHENSIVE PROBLEM 2 (CHAPTERS 2, 5-8) INSTRUCTIONS: COMPLETE ALL
COMPREHENSIVE PROBLEM 2 (CHAPTERS 2, 5-8) Page 137 NAME ANSWER KEY PROFESSOR S NAME SECTION SCORE ACC 255 FALL 2011 COVER SHEET FOR COMPREHENSIVE PROBLEM 2 (CHAPTERS 2, 5-8) INSTRUCTIONS: COMPLETE ALL
CASH FLOW STATEMENT & BALANCE SHEET GUIDE
 CASH FLOW STATEMENT & BALANCE SHEET GUIDE The Agriculture Development Council requires the submission of a cash flow statement and balance sheet that provide annual financial projections for the business
CASH FLOW STATEMENT & BALANCE SHEET GUIDE The Agriculture Development Council requires the submission of a cash flow statement and balance sheet that provide annual financial projections for the business
The Matching Concept and the Adjusting Process
 The Matching Concept and the Adjusting Process o b j e c t i v e s After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 4 Explain how the matching concept relates to the accrual basis of accounting. Explain
The Matching Concept and the Adjusting Process o b j e c t i v e s After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 4 Explain how the matching concept relates to the accrual basis of accounting. Explain
Advanced Accounting. Chapter 4: Financial Reporting for a Departmentalized Business
 Advanced Accounting Chapter 4: Financial Reporting for a Departmentalized Business Financial statements are used to summarize financial info and then are used to evaluate the financial position and progress
Advanced Accounting Chapter 4: Financial Reporting for a Departmentalized Business Financial statements are used to summarize financial info and then are used to evaluate the financial position and progress
The Double-Entry System EFFECTS OF TRANSACTIONS ON THE BALANCE SHEET. Initial Paid-in Capital. An Example Entity. Transaction 2.
 The Double-Entry System EFFECTS OF TRANSACTIONS ON THE BALANCE SHEET 2001 Richard S. Barr Transaction: Any event that affects the entity's financial position and requires recording Every accounting transaction
The Double-Entry System EFFECTS OF TRANSACTIONS ON THE BALANCE SHEET 2001 Richard S. Barr Transaction: Any event that affects the entity's financial position and requires recording Every accounting transaction
