Significance of Data Warehousing and Data Mining in Business Applications
|
|
|
- Moris Greer
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
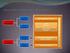
1 International Journal of Soft Computing and Engineering (IJSCE) Significance of Data Warehousing and Data Mining in Business Applications Madhuri V. Joseph Abstract-Information technology is now required in every aspect of our lives which help business and enterprise to make use of applications like decision support system, query and reporting online analytical processing, predictive analysis and business performance management. In this aspect this paper focuses on the significance and role of Data Warehousing and Data Mining technology in business. A Data Warehouse is a central repository of relational database designed for query and analysis. If helps the business organization to consolidate data from different varying sources. These warehouses are analyzed by the latest technique known as Data Mining. In Data Mining data sets will be explored to yield hidden and unknown predictions which can be used in future for the efficient decision making. Now companies use techniques of Data Mining that involves pattern recognition, mathematical and statistical techniques to search Data Warehouses and help the analyst in recognizing significant trends, facts relationships and anomalies. Index Terms: Data Warehousing, Data Mining, OLAP, OLTP, CART & CHAID. I. INTRODUCTION Since Data Warehouses are gaining enormous ground in Business Intelligence (BI), every organization gives highest priority to maintain a corporate Data Warehouse. Most business applications like online analytical processing, statistical/predictive analysis, complex query processing and critical business decisions are based on the data available in the Data Warehouse. Data Warehouse (DW) is a system that extracts, cleans, confirms and source data into a dimensional data store and then supports and implements querying and analysis for the purpose of decision making. Sophisticated OLAP and Data Mining tools are used to facilitate multinational analysis and complex business models. Inmon W.H defines the Data Warehouse as a subject oriented, integrated, time variant andnon-volatile collection of data in support of management s decision making process [1]. BI applications in enterprises provide reports for the strategic management of business by collaborating the business data and electronic data interchange. This ensures competitive intelligence and thereby helps in good decision making [2]. According to B de Ville, BI refers to the technologies and application for collecting, storing and analyzing business data that helps the enterprise to make better decisions [3]. Data Marts were used to analyze the data and it s a complex task that is time consuming. Thus for the improved analysis if data, Data Mining methodologies is used. The Data Mining process involves computer assisted analysis and extraction of large volume of business data. Frawley, Piatetsky and Mathues defined Data Mining as a nontrivial extraction of implicit, previously unknown and potentially useful information from data [4]. The combination of data warehousing and Data Mining technology has become an innovative idea in many business areas through the automation of routine tasks and simplification of administrative procedures. II. DATA WAREHOUSE: DEFINITION Data Warehouse is a repository of enterprise or business databases which provides a clear picture of current and historical operations of organizations [5]. Since it provides a coherent picture of the business conditions at a particular point of time, it is used for the efficient decision making process. it involves the development of system that helps the extraction of data in flexible ways. Data Mining describes the process of designing how the data is stored in order to improve the reporting and analysis. Data Warehouse experts consider that the various stores of data are connected and related to each other conceptually as well as physically. A business s data is usually stored across a number of Databases. However, to be able to analyze the broadest range of data, each of these databases needs to be connected in some way. This means that the data within them need a way of being related to other relevant data and that the physical databases themselves have a connection so their data can be looked at together for reporting purposes.. Manuscript received March, Madhuri V. Joseph, Sr.Lecturer, Dept. of Computing, Muscat College, Muscat, Sultanate of Oman. Fig 1: Data Warehouse [6] Multiple data stores are integrated by the Data Warehouses and this information is used by the mangers for better decision making. Data warehousing environment includes the Extraction of relational database, Transformation, Loading (ETL process), Online Analytical Processing (OLAP) engine and client analysis tools. 329
2 Significance of Data Warehousing And Data Mining in Business Applications As a business grows globally, the parameters and complexities involved in analysis and decision making become more complex. Data access portion which is available in the form of products is the most visible part of a Data Warehouse project. Data warehousing process involves transformation of data from original format to a dimensional data store which consumes a greater percentage of effort, time and expenses. Since e implementation of a data warehousing is expensive and critical, there are a number of data extraction and data cleaning tools and load and fresh utilities are available for the same. One of the most important characteristic of the Data Warehouse is data integration. A. Example of Data warehousing Facebook A great example of data warehousing is what Facebook does. Facebook gathers al your data such as your friends, your likes, your groups etc. All these data are stored into one central repository. Although Facebook is storing all these information into separate databases, they store the most relevant and significant information into one central aggregated database. This is because of many reasons like to make sure that you see the most relevant ads that you are most likely to click on or the friends that they suggest are the most relevant to you. B. Relevance of Data Warehouse. Data Warehouse is a subject oriented, time variant, integrated and non-volatilecollection of data. Data cleansing, data integration and Online Analytical Processing (OLAP) are a part of the data warehousing technology. It provides a complete and consistent data store from multiple sources which can be easily understood and used in business applications. Some of the application areas include: Integration of data across the enterprise. Quick decisions on current & historical data Provide ad-hoc information for loosely-defined system Manage & control businesses Solving what-if analysis. C. Data Warehousing: Process Data warehousing is the process of centralizing or aggregating data from multiple sources into one common repository. Data warehousing occurs before Data Mining takes place. Data warehousing involves a strict engineering phase, where no business users are involved. In data warehousing, data stored in different databases are combined into one comprehensive and easily accessible database. This is available to business professionals or managers who use the data for Data Mining and to create forecasts. Data is fed from a variety of disparate sources into the Data Warehouse which is again converted, reformatted, summarized and used for managerial decision making. The process of data warehousing acts as a guideline to identify the business requirements, develop the business plan and create Data Warehouse also includes project management, startup and wrap-up activities. D. Data Warehouse: Architecture Data Warehouse architecture is based on the various business processes associated with an organization. Some other considerations while going for the architecture of a Data Warehouse include data modeling, adequate security, metadata management, extent of query requirement and utilization of full technology. Metadata is data about data which is stored either as a unstructured or semi-structured form. These summary data are very useful in Data Warehouses. For example simple Data Warehouse query can be used to retrieve January sales. Data Warehouse architecture can be shown with the materialized view in Oracle 9i as below. III. Fig 2: Data Warehouse Architecture[7] FROM DATA WAREHOUSE TO DATA MINING It is necessary to choose adequate Data Mining algorithms for making Data Warehouse more useful. Data Mining algorithms are used for transforming data into business information and thereby improving decision making process. Data Mining is a set of methods used for data analysis, created with the aim to find out specific dependence, relations and rules related to data and making them out in the new higher level quality information [8]. Data Mining gives results that show the interdependence and relations of data. These dependences are mainly based on various mathematical and statistical relations [9]. Data are collected from internal database and converted into various documents, reports, list etc. which can be further used in decision making processes. After selecting the data for analysis, Data Mining is applied to the appropriate rules of behavior and patterns. That is the reasons why Data Mining is also known as extraction of knowledge, data archeology or pattern analysis. Fig 3: The process of knowledge recovery from database by using Data Warehousing and Data Mining technologies. [10]. 330
3 International Journal of Soft Computing and Engineering (IJSCE) A. Example of Data Mining: Fraud detection of credit card usage Credit card companies will alert you when they think your credit card is fraudulently used by someone other than you. Companies will have a history of the customer s purchases and know geographically where the purchases have been made. If a purchase is made in a city far away from where you live, the companies will put an alert to possible fraud since their Data Mining shows that you don t normally make purchases in that city. Companies can either disable the card for that transaction or put a flag for suspicious activity. B. Data Mining Process. The process of Data Mining provides ways to make best use of data through rapid computerization [11]. Data Mining software uses modeling techniques to make a model that is a set of examples or a mathematical relationship based on data from situations where the answer is known and then applying the same model to other situations where answers are hidden. [12] The 3 main stages involved in the process of Data Mining are: 1) Exploration: data preparation, cleaning and transformations are involved in this stage. A subset of records will be selected to reduce the number of variables to a manageable range. This depends on the complexity of analysis of graphical and statistical data. 2) Model building and validation: in this stage the best model will be taken based on their predictive performance. Various techniques used for comparison of models include bagging, boosting, stacking and Meta learning. 3) Dependent: in this final stage the best model is selected and it is applied to the new data sets to generate predictions of the expected outcome. One simple example for this is the online shopping site doing e-commerce transactions through credit card deploys neural networks and Meta learner to identify fraud. Data Mining process involves use of various techniques and methods. Most common techniques are: 1) Classification: stored data will be grouped into different classes. This allows locating data into pre-determined groups. 2) Clustering: Data items are grouped into clusters of similar groups. It may be of It may be of hierarchical or non-hierarchical. 3) Regression: this method uses a numerical data set to develop a best fit mathematical formula. This formula can be used to feed new data sets and get a better prediction. This is suitable for continuous quantitative data. 4) Association: it is a rule X->Y such that X and Y are data items sets. 5) Sequential pattern matching: it allows predicting behavior patterns and trends based on the sequential rule A->B which implies that event B will always be followed by A. C. Next Generation Data Mining Techniques Data Mining uses black box approach to explore data and discovered knowledge using Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA) techniques. The techniques used in Data Mining are a blend of statistics, database research and artificial intelligence [13]. Next generation Data Mining techniques include artificial neural networks, decision trees, induction rules and genetic algorithms. 1) Artificial neural networks: This technique uses non-linear predictive models to enable learning through training. Computers are trained to think, act and take decision similar to humans. These models are quite complex to use even by the experts because it is packed as a complete solution[14]. It determines relevant prediction for a model. 2) Rule induction: This technique enables knowledge discovery and unsupervised learning. It extracts useful patterns from database based on accuracy and statistical significance. Prediction will be more correct and has better logic by neural network. It creates a certain confusions to select the best rule from a pool of rules. Normally rule induction is used on databases with many columns of binary fields or fields with higher cardinality in order to collect the suitable patterns for making a better prediction, a bottom to top approach is chosen. 3) Decision trees: Decision tree is a Data Mining technique where tree shapes structures are representing the set if decision generating rules for a data set classifications. The starting node or the top node is known as the root. Depending results of test, the root partitioned into two or more nodes. It is a fast Data Mining technique since its required less or no pre-processing of business data. It is used for both exploration and prediction using Classification And Regression Trees (CART) and Chi Square Automatic Interactions detection (CHAID). CART generates two way splits from data set segmentation which needs less preparation of data than CHAID which generates a multi-way split. Rules are mutually exclusive and relatively exhaustive. 4) Genetic algorithms: This optimized technique of Data Mining is based on genetics and natural selections, combination and mutation [15]. Genetic algorithms are used in patterns recognition either as classifier or as an optimization tool. According to Chuck Kelly (2002), genetic algorithms support the survival of the fittest using heuristic functions even by posing the problems [16]. IV. INFRASTRUCTURE FOR IMPLEMENTING DATA WAREHOUSE AND DATA MINING Data Warehouse and Data Mining application are quite divorced in size and storage capacities. Enterprise applications range from 10 GBs to higher. Data Warehouse is a very flexible solution that can explore database more efficiently than any other Online Transaction Processing (OLTP) environment. The major advantage of this is that the user does not have to possess knowledge of relational model and complex query languages. A. Data ware house implementation phases. According to Barry D & Addison Wesley, 1997 Data Warehouse implementation phases include [17]: 1) Analysis of current situations: this is a very important phase in the Data Warehouse design, since at this phase a possibility of realization and solution of the problems can be seen. Since the users will have a better knowledge about the problems than the designers, their opinion is very crucial for a good warehouse design. 2) Selecting the most appropriate data for analysis from the existing data: instead of using the entire OLTP database, 331
4 Significance of Data Warehousing And Data Mining in Business Applications the data subset which includes all the interesting data related to the subject will be chosen. 3) Filtering data interesting for analysis: data analysis does not need all the data. Because of this the filtering of data will be done related to certain time period or some specific area. 4) Extracting data in staging database: after reducing and filtering of data, data are being extracted in staging database from which the Data Warehouse is being built. Data Transformation Services (DTS) package is written in SQL server Package writing is very significant in Data Warehouse implementation because packages can be arranged to function automatically so that the users can fresh and prompted data. 5) Selecting fact table, dimensional tables and appropriate schemas: entity-relationship model commonly used in the design of relational databases. This is suitable for OLTP. A Data Warehouse requires a concise, subject oriented schema that facilitates online data analysis. The simplest scheme is a single table scheme which consists of redundant fact table. Data Warehouse contains a large central fact table containing the bulk of data with no redundancy and a set of smaller dimension tables. 6) Selecting measurement, percentage of aggregations and warehouse models: the next step in designing Data Warehouse is selecting measurements. It needs calculated measurements that are attained from 7) Various arithmetic operations with other measurements. Data Warehouse solutions also use aggregations through which they solve the queries very fast. The increasing of the percentage of aggregated data speeds up the user defined queries. 8) Creating and using the cube: the cube is being created on either client or server computer. Basic factors for selecting the place for cube s storehouse are size of the cube, performance of the client s and server s computers, number of the cube users and throughput of the system. The cube created can be used by the support of various client tools. B. Data Mining Implementations Microsoft Decision Tree (MDT) algorithms are based on possibility of various attributes and it is when prediction is necessary. These algorithms also generate rules. MDT also enables the user to analyze a large number of Data Mining problems. Fig 4: Scheme of Data Warehouse and Data Mining implementation [18]. Database size and query complexity are the 2 critical technological drivers for Data Mining. New hardware architectures like Massively Parallel Processors (MPP) are used which can link hundreds of speed processors to achieve better performance. Data Mining is now aggressively used in various industries [19]. All the major database vendors are using various Data Mining techniques in their platforms. Some of them are: 1) SQL server: it is Microsoft database platform that allows Data Mining through the use of clustering and classification algorithms. 2) SAS, SPSS and S-PLUS are advanced statistical packages for implementing Data Mining algorithms. 3) Darwin: is an Oracle Data Mining suite for implementing classification and decision trees, K-nearest neighbors, regression analysis, clustering algorithms and neural networks. V. DATA WAREHOUSE AND DATA MINING: APPLICATION AREAS IN BUSINESS Data warehousing and Data Mining has gained improved popularity in multiple areas of business to analyze the large databases quickly which would be too complex and time consuming. Some of these application areas are listed below. 1) Government: for searching terrorist profile and threat assessments. 2) Finance: analysis and forecasting of business performance, for stock and bond analysis. 3) Banking: to learn underwriting, mortgage approval etc. 4) Direct marketing: for identifying prospects that are included in mailing list so as to obtain highest response time. 5) Medicine: for drug analysis, diagnosis, quality control and epidemiological studies. 6) Manufacturing: for improved quality control and maintenance. 7) Churn analysis: to predict customers who are likely to quit the company and move to a competitor company. 8) Market segmentation: to identify customer s common characteristics and behavior that purchases the same products of a company [20]. 9) Trend analysis: to analyze the difference between the customer s behavior over consecutive months. 10) Fraud detection: to identify the fraud users in telecommunication industry as well as credit card usage. 11) Web marketing: for advertisements and personalization opportunities. VI. CONCLUSION Data Warehouse and Data Mining technologies have bright future in business applications as it helps to generate new possibilities by automated prediction of trends and behaviors in a large database. Data Mining techniques help to automatically discover the unknown patterns like identifying anomalous data that highlight errors generated during the data entry. Data Warehouse & Data Mining technologies have become a hit with various industries like sales & marketing, healthcare organization, financial institutions and many more. These technologies have a lot of benefits in varying fields. It can be said with pleasure that these technologies help the quick analysis of data and thereby improving the quality of decision making process. Both Data Mining and Data Warehousing are business intelligence tools that are used to turn information or data into actionable knowledge. Data Warehouse experts design data storage 332
5 system that connects relevant data in different databases where as a Data miner run more meaningful and efficient queries to improve business. The immense data volumes and extremely complex knowledge discovery procedures associated with business organizations make the Data Warehouse with its OLAP and Data Mining tools a very significant technology supporting decision making. Thus Data Warehouse & Data Mining are very essential components in business operations to gain competitive intelligence. These technologies allow statistical multidimensional analysis of data to evaluate relationships, correlations and trends in business. REFERENCES [1] Inmon W.H., Building the Data Warehouse, Second Edition, JWiley and Sons, New York, [2] P. Bergeron, C. A. Hiller, (2002), Competitive intelligence, in B. Cronin, Annual Review of Information Science and Technology, zedford, N.J.: Information Today, vol. 36, chapter 8 [3] B. de Ville, (2001), Microsoft Data Mining: Integrated Business Intelligence for e-commerce and Knowledge Management, Boston: Digital press. [4] Frawley W., Piatetsky Shapiro G. and Matheus C., Knowledge Discovery in Databases: An Overview, Al Magazine, Fall 1992, pgs [5] C. Date, (2003), Introduction to Database Systems, 8th ed., Upper Saddle River, N.J.: Pearson Addison Wesley. [6] Han Jiawei, Kamber Micheline, Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques, 2nd edition, Morgan Kaufman Publishers, March ISBN [7] Oracle9i Data Warehousing Guide Release 2 (9.2), Part No. A , March [8] Berry, M.J.A., and Linoff, G., "Mastering data mining", The Art and Science of Customer Relationship Management, [9] Bhavani, T., Data Mining: Technologies, Techniques, Tools and Trends, [10] Jiwei, H., and Micheline, K., Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques, Simon Fraser. [11] D. Pyle, (2003), Business Modeling and Data Mining, Morgan Kaufmann, San Francisco, CA. [12] M.H. Dunham, (2005), Data Mining Introductory and Advanced Topics, Prentice Hall. [13] Berson Alex, Smith J. Stephen, Thearling Kurt, (1999), Building Data Mining Applications for CRM, McGraw-Hill Companies. [14] Gilman Michael, (2004), Nuggets and Data Mining, Data Mining Technologies Inc. Melville, NY 11714, (631) [15] Chen, S. H, (2002), Genetic Algorithms and Genetic Programming in Computational Finance, Boston, A: Kluwer. [16] Kelly Chuck, (2002), What is the role of Genetic Algorithms in Data Mining, Information Management: How your Business Works,Electronic Newsletter, [17] Barry, D., Data Warehouse from Architecture to Implementation, Addison-Wesley, [18] Krulj, D., "Design and implementation of data warehouse systems", M Sc. Thesis, Faculty oforganizational Sciences, Belgrade, [19] Chapple Mike, Data Mining: An Introduction, (2011), /databases.about. com/od/datamining/a/datamining.htm. [20] Alexander Doug, Data Mining, (2000), /course.mat/alex/, electronic article. International Journal of Soft Computing and Engineering (IJSCE) 333
Importance or the Role of Data Warehousing and Data Mining in Business Applications
 Journal of The International Association of Advanced Technology and Science Importance or the Role of Data Warehousing and Data Mining in Business Applications ATUL ARORA ANKIT MALIK Abstract Information
Journal of The International Association of Advanced Technology and Science Importance or the Role of Data Warehousing and Data Mining in Business Applications ATUL ARORA ANKIT MALIK Abstract Information
Data Warehousing and Data Mining in Business Applications
 133 Data Warehousing and Data Mining in Business Applications Eesha Goel CSE Deptt. GZS-PTU Campus, Bathinda. Abstract Information technology is now required in all aspect of our lives that helps in business
133 Data Warehousing and Data Mining in Business Applications Eesha Goel CSE Deptt. GZS-PTU Campus, Bathinda. Abstract Information technology is now required in all aspect of our lives that helps in business
Data Mining Solutions for the Business Environment
 Database Systems Journal vol. IV, no. 4/2013 21 Data Mining Solutions for the Business Environment Ruxandra PETRE University of Economic Studies, Bucharest, Romania [email protected] Over
Database Systems Journal vol. IV, no. 4/2013 21 Data Mining Solutions for the Business Environment Ruxandra PETRE University of Economic Studies, Bucharest, Romania [email protected] Over
DATA MINING TECHNIQUES SUPPORT TO KNOWLEGDE OF BUSINESS INTELLIGENT SYSTEM
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN COMPUTER APPLICATIONS AND ROBOTICS ISSN 2320-7345 DATA MINING TECHNIQUES SUPPORT TO KNOWLEGDE OF BUSINESS INTELLIGENT SYSTEM M. Mayilvaganan 1, S. Aparna 2 1 Associate
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN COMPUTER APPLICATIONS AND ROBOTICS ISSN 2320-7345 DATA MINING TECHNIQUES SUPPORT TO KNOWLEGDE OF BUSINESS INTELLIGENT SYSTEM M. Mayilvaganan 1, S. Aparna 2 1 Associate
A Review of Data Mining Techniques
 Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology IJCSMC, Vol. 3, Issue. 4, April 2014,
Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology IJCSMC, Vol. 3, Issue. 4, April 2014,
Fluency With Information Technology CSE100/IMT100
 Fluency With Information Technology CSE100/IMT100 ),7 Larry Snyder & Mel Oyler, Instructors Ariel Kemp, Isaac Kunen, Gerome Miklau & Sean Squires, Teaching Assistants University of Washington, Autumn 1999
Fluency With Information Technology CSE100/IMT100 ),7 Larry Snyder & Mel Oyler, Instructors Ariel Kemp, Isaac Kunen, Gerome Miklau & Sean Squires, Teaching Assistants University of Washington, Autumn 1999
Subject Description Form
 Subject Description Form Subject Code Subject Title COMP417 Data Warehousing and Data Mining Techniques in Business and Commerce Credit Value 3 Level 4 Pre-requisite / Co-requisite/ Exclusion Objectives
Subject Description Form Subject Code Subject Title COMP417 Data Warehousing and Data Mining Techniques in Business and Commerce Credit Value 3 Level 4 Pre-requisite / Co-requisite/ Exclusion Objectives
An Overview of Knowledge Discovery Database and Data mining Techniques
 An Overview of Knowledge Discovery Database and Data mining Techniques Priyadharsini.C 1, Dr. Antony Selvadoss Thanamani 2 M.Phil, Department of Computer Science, NGM College, Pollachi, Coimbatore, Tamilnadu,
An Overview of Knowledge Discovery Database and Data mining Techniques Priyadharsini.C 1, Dr. Antony Selvadoss Thanamani 2 M.Phil, Department of Computer Science, NGM College, Pollachi, Coimbatore, Tamilnadu,
DATA MINING TECHNIQUES AND APPLICATIONS
 DATA MINING TECHNIQUES AND APPLICATIONS Mrs. Bharati M. Ramageri, Lecturer Modern Institute of Information Technology and Research, Department of Computer Application, Yamunanagar, Nigdi Pune, Maharashtra,
DATA MINING TECHNIQUES AND APPLICATIONS Mrs. Bharati M. Ramageri, Lecturer Modern Institute of Information Technology and Research, Department of Computer Application, Yamunanagar, Nigdi Pune, Maharashtra,
DATA MINING AND WAREHOUSING CONCEPTS
 CHAPTER 1 DATA MINING AND WAREHOUSING CONCEPTS 1.1 INTRODUCTION The past couple of decades have seen a dramatic increase in the amount of information or data being stored in electronic format. This accumulation
CHAPTER 1 DATA MINING AND WAREHOUSING CONCEPTS 1.1 INTRODUCTION The past couple of decades have seen a dramatic increase in the amount of information or data being stored in electronic format. This accumulation
Data Mining for Successful Healthcare Organizations
 Data Mining for Successful Healthcare Organizations For successful healthcare organizations, it is important to empower the management and staff with data warehousing-based critical thinking and knowledge
Data Mining for Successful Healthcare Organizations For successful healthcare organizations, it is important to empower the management and staff with data warehousing-based critical thinking and knowledge
The Role of Data Warehousing Concept for Improved Organizations Performance and Decision Making
 Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology IJCSMC, Vol. 3, Issue. 10, October 2014,
Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology IJCSMC, Vol. 3, Issue. 10, October 2014,
Course 803401 DSS. Business Intelligence: Data Warehousing, Data Acquisition, Data Mining, Business Analytics, and Visualization
 Oman College of Management and Technology Course 803401 DSS Business Intelligence: Data Warehousing, Data Acquisition, Data Mining, Business Analytics, and Visualization CS/MIS Department Information Sharing
Oman College of Management and Technology Course 803401 DSS Business Intelligence: Data Warehousing, Data Acquisition, Data Mining, Business Analytics, and Visualization CS/MIS Department Information Sharing
IMPROVING DATA INTEGRATION FOR DATA WAREHOUSE: A DATA MINING APPROACH
 IMPROVING DATA INTEGRATION FOR DATA WAREHOUSE: A DATA MINING APPROACH Kalinka Mihaylova Kaloyanova St. Kliment Ohridski University of Sofia, Faculty of Mathematics and Informatics Sofia 1164, Bulgaria
IMPROVING DATA INTEGRATION FOR DATA WAREHOUSE: A DATA MINING APPROACH Kalinka Mihaylova Kaloyanova St. Kliment Ohridski University of Sofia, Faculty of Mathematics and Informatics Sofia 1164, Bulgaria
Data Mining: Motivations and Concepts
 POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY Department of Computer Science / Finance and Risk Engineering Data Mining: Motivations and Concepts K. Ming Leung Abstract: We discuss here the need, the goals, and the primary tasks
POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY Department of Computer Science / Finance and Risk Engineering Data Mining: Motivations and Concepts K. Ming Leung Abstract: We discuss here the need, the goals, and the primary tasks
A STUDY ON DATA MINING INVESTIGATING ITS METHODS, APPROACHES AND APPLICATIONS
 A STUDY ON DATA MINING INVESTIGATING ITS METHODS, APPROACHES AND APPLICATIONS Mrs. Jyoti Nawade 1, Dr. Balaji D 2, Mr. Pravin Nawade 3 1 Lecturer, JSPM S Bhivrabai Sawant Polytechnic, Pune (India) 2 Assistant
A STUDY ON DATA MINING INVESTIGATING ITS METHODS, APPROACHES AND APPLICATIONS Mrs. Jyoti Nawade 1, Dr. Balaji D 2, Mr. Pravin Nawade 3 1 Lecturer, JSPM S Bhivrabai Sawant Polytechnic, Pune (India) 2 Assistant
Foundations of Business Intelligence: Databases and Information Management
 Foundations of Business Intelligence: Databases and Information Management Problem: HP s numerous systems unable to deliver the information needed for a complete picture of business operations, lack of
Foundations of Business Intelligence: Databases and Information Management Problem: HP s numerous systems unable to deliver the information needed for a complete picture of business operations, lack of
Digging for Gold: Business Usage for Data Mining Kim Foster, CoreTech Consulting Group, Inc., King of Prussia, PA
 Digging for Gold: Business Usage for Data Mining Kim Foster, CoreTech Consulting Group, Inc., King of Prussia, PA ABSTRACT Current trends in data mining allow the business community to take advantage of
Digging for Gold: Business Usage for Data Mining Kim Foster, CoreTech Consulting Group, Inc., King of Prussia, PA ABSTRACT Current trends in data mining allow the business community to take advantage of
An Overview of Database management System, Data warehousing and Data Mining
 An Overview of Database management System, Data warehousing and Data Mining Ramandeep Kaur 1, Amanpreet Kaur 2, Sarabjeet Kaur 3, Amandeep Kaur 4, Ranbir Kaur 5 Assistant Prof., Deptt. Of Computer Science,
An Overview of Database management System, Data warehousing and Data Mining Ramandeep Kaur 1, Amanpreet Kaur 2, Sarabjeet Kaur 3, Amandeep Kaur 4, Ranbir Kaur 5 Assistant Prof., Deptt. Of Computer Science,
Chapter 5 Business Intelligence: Data Warehousing, Data Acquisition, Data Mining, Business Analytics, and Visualization
 Turban, Aronson, and Liang Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Seventh Edition Chapter 5 Business Intelligence: Data Warehousing, Data Acquisition, Data Mining, Business Analytics, and Visualization
Turban, Aronson, and Liang Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Seventh Edition Chapter 5 Business Intelligence: Data Warehousing, Data Acquisition, Data Mining, Business Analytics, and Visualization
What is Customer Relationship Management? Customer Relationship Management Analytics. Customer Life Cycle. Objectives of CRM. Three Types of CRM
 Relationship Management Analytics What is Relationship Management? CRM is a strategy which utilises a combination of Week 13: Summary information technology policies processes, employees to develop profitable
Relationship Management Analytics What is Relationship Management? CRM is a strategy which utilises a combination of Week 13: Summary information technology policies processes, employees to develop profitable
A Knowledge Management Framework Using Business Intelligence Solutions
 www.ijcsi.org 102 A Knowledge Management Framework Using Business Intelligence Solutions Marwa Gadu 1 and Prof. Dr. Nashaat El-Khameesy 2 1 Computer and Information Systems Department, Sadat Academy For
www.ijcsi.org 102 A Knowledge Management Framework Using Business Intelligence Solutions Marwa Gadu 1 and Prof. Dr. Nashaat El-Khameesy 2 1 Computer and Information Systems Department, Sadat Academy For
A STUDY OF DATA MINING ACTIVITIES FOR MARKET RESEARCH
 205 A STUDY OF DATA MINING ACTIVITIES FOR MARKET RESEARCH ABSTRACT MR. HEMANT KUMAR*; DR. SARMISTHA SARMA** *Assistant Professor, Department of Information Technology (IT), Institute of Innovation in Technology
205 A STUDY OF DATA MINING ACTIVITIES FOR MARKET RESEARCH ABSTRACT MR. HEMANT KUMAR*; DR. SARMISTHA SARMA** *Assistant Professor, Department of Information Technology (IT), Institute of Innovation in Technology
International Journal of Computer Science Trends and Technology (IJCST) Volume 2 Issue 3, May-Jun 2014
 RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS A Survey of Data Mining: Concepts with Applications and its Future Scope Dr. Zubair Khan 1, Ashish Kumar 2, Sunny Kumar 3 M.Tech Research Scholar 2. Department of Computer
RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS A Survey of Data Mining: Concepts with Applications and its Future Scope Dr. Zubair Khan 1, Ashish Kumar 2, Sunny Kumar 3 M.Tech Research Scholar 2. Department of Computer
Database Marketing, Business Intelligence and Knowledge Discovery
 Database Marketing, Business Intelligence and Knowledge Discovery Note: Using material from Tan / Steinbach / Kumar (2005) Introduction to Data Mining,, Addison Wesley; and Cios / Pedrycz / Swiniarski
Database Marketing, Business Intelligence and Knowledge Discovery Note: Using material from Tan / Steinbach / Kumar (2005) Introduction to Data Mining,, Addison Wesley; and Cios / Pedrycz / Swiniarski
Chapter 5. Warehousing, Data Acquisition, Data. Visualization
 Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Seventh Edition Chapter 5 Business Intelligence: Data Warehousing, Data Acquisition, Data Mining, Business Analytics, and Visualization 5-1 Learning Objectives
Decision Support Systems and Intelligent Systems, Seventh Edition Chapter 5 Business Intelligence: Data Warehousing, Data Acquisition, Data Mining, Business Analytics, and Visualization 5-1 Learning Objectives
A HOLISTIC FRAMEWORK FOR KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT
 A HOLISTIC FRAMEWORK FOR KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT Dr. Shamsul Chowdhury, Roosevelt University, [email protected] ABSTRACT Knowledge management refers to the set of processes developed in an organization
A HOLISTIC FRAMEWORK FOR KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT Dr. Shamsul Chowdhury, Roosevelt University, [email protected] ABSTRACT Knowledge management refers to the set of processes developed in an organization
Data Mining System, Functionalities and Applications: A Radical Review
 Data Mining System, Functionalities and Applications: A Radical Review Dr. Poonam Chaudhary System Programmer, Kurukshetra University, Kurukshetra Abstract: Data Mining is the process of locating potentially
Data Mining System, Functionalities and Applications: A Radical Review Dr. Poonam Chaudhary System Programmer, Kurukshetra University, Kurukshetra Abstract: Data Mining is the process of locating potentially
5.5 Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall. Figure 5-2
 Class Announcements TIM 50 - Business Information Systems Lecture 15 Database Assignment 2 posted Due Tuesday 5/26 UC Santa Cruz May 19, 2015 Database: Collection of related files containing records on
Class Announcements TIM 50 - Business Information Systems Lecture 15 Database Assignment 2 posted Due Tuesday 5/26 UC Santa Cruz May 19, 2015 Database: Collection of related files containing records on
A Brief Tutorial on Database Queries, Data Mining, and OLAP
 A Brief Tutorial on Database Queries, Data Mining, and OLAP Lutz Hamel Department of Computer Science and Statistics University of Rhode Island Tyler Hall Kingston, RI 02881 Tel: (401) 480-9499 Fax: (401)
A Brief Tutorial on Database Queries, Data Mining, and OLAP Lutz Hamel Department of Computer Science and Statistics University of Rhode Island Tyler Hall Kingston, RI 02881 Tel: (401) 480-9499 Fax: (401)
Data Mining for Fun and Profit
 Data Mining for Fun and Profit Data mining is the extraction of implicit, previously unknown, and potentially useful information from data. - Ian H. Witten, Data Mining: Practical Machine Learning Tools
Data Mining for Fun and Profit Data mining is the extraction of implicit, previously unknown, and potentially useful information from data. - Ian H. Witten, Data Mining: Practical Machine Learning Tools
Introduction to Data Mining
 Introduction to Data Mining Jay Urbain Credits: Nazli Goharian & David Grossman @ IIT Outline Introduction Data Pre-processing Data Mining Algorithms Naïve Bayes Decision Tree Neural Network Association
Introduction to Data Mining Jay Urbain Credits: Nazli Goharian & David Grossman @ IIT Outline Introduction Data Pre-processing Data Mining Algorithms Naïve Bayes Decision Tree Neural Network Association
SPATIAL DATA CLASSIFICATION AND DATA MINING
 , pp.-40-44. Available online at http://www. bioinfo. in/contents. php?id=42 SPATIAL DATA CLASSIFICATION AND DATA MINING RATHI J.B. * AND PATIL A.D. Department of Computer Science & Engineering, Jawaharlal
, pp.-40-44. Available online at http://www. bioinfo. in/contents. php?id=42 SPATIAL DATA CLASSIFICATION AND DATA MINING RATHI J.B. * AND PATIL A.D. Department of Computer Science & Engineering, Jawaharlal
DATA WAREHOUSING AND OLAP TECHNOLOGY
 DATA WAREHOUSING AND OLAP TECHNOLOGY Manya Sethi MCA Final Year Amity University, Uttar Pradesh Under Guidance of Ms. Shruti Nagpal Abstract DATA WAREHOUSING and Online Analytical Processing (OLAP) are
DATA WAREHOUSING AND OLAP TECHNOLOGY Manya Sethi MCA Final Year Amity University, Uttar Pradesh Under Guidance of Ms. Shruti Nagpal Abstract DATA WAREHOUSING and Online Analytical Processing (OLAP) are
A Survey on Web Research for Data Mining
 A Survey on Web Research for Data Mining Gaurav Saini 1 [email protected] 1 Abstract Web mining is the application of data mining techniques to extract knowledge from web data, including web documents,
A Survey on Web Research for Data Mining Gaurav Saini 1 [email protected] 1 Abstract Web mining is the application of data mining techniques to extract knowledge from web data, including web documents,
Building Data Warehousing and Data Mining from Course Management Systems: A Case Study of FUTA Course Management Information Systems
 Building Data Warehousing and Data Mining from Course Management Systems: A Case Study of FUTA Course Management Information Systems *Akintola K.G., ** Adetunmbi A.O. **Adeola O.S. *Computer Science Department,
Building Data Warehousing and Data Mining from Course Management Systems: A Case Study of FUTA Course Management Information Systems *Akintola K.G., ** Adetunmbi A.O. **Adeola O.S. *Computer Science Department,
CONCEPTUALIZING BUSINESS INTELLIGENCE ARCHITECTURE MOHAMMAD SHARIAT, Florida A&M University ROSCOE HIGHTOWER, JR., Florida A&M University
 CONCEPTUALIZING BUSINESS INTELLIGENCE ARCHITECTURE MOHAMMAD SHARIAT, Florida A&M University ROSCOE HIGHTOWER, JR., Florida A&M University Given today s business environment, at times a corporate executive
CONCEPTUALIZING BUSINESS INTELLIGENCE ARCHITECTURE MOHAMMAD SHARIAT, Florida A&M University ROSCOE HIGHTOWER, JR., Florida A&M University Given today s business environment, at times a corporate executive
Data Mart/Warehouse: Progress and Vision
 Data Mart/Warehouse: Progress and Vision Institutional Research and Planning University Information Systems What is data warehousing? A data warehouse: is a single place that contains complete, accurate
Data Mart/Warehouse: Progress and Vision Institutional Research and Planning University Information Systems What is data warehousing? A data warehouse: is a single place that contains complete, accurate
131-1. Adding New Level in KDD to Make the Web Usage Mining More Efficient. Abstract. 1. Introduction [1]. 1/10
![131-1. Adding New Level in KDD to Make the Web Usage Mining More Efficient. Abstract. 1. Introduction [1]. 1/10 131-1. Adding New Level in KDD to Make the Web Usage Mining More Efficient. Abstract. 1. Introduction [1]. 1/10](/thumbs/25/4963058.jpg) 1/10 131-1 Adding New Level in KDD to Make the Web Usage Mining More Efficient Mohammad Ala a AL_Hamami PHD Student, Lecturer m_ah_1@yahoocom Soukaena Hassan Hashem PHD Student, Lecturer soukaena_hassan@yahoocom
1/10 131-1 Adding New Level in KDD to Make the Web Usage Mining More Efficient Mohammad Ala a AL_Hamami PHD Student, Lecturer m_ah_1@yahoocom Soukaena Hassan Hashem PHD Student, Lecturer soukaena_hassan@yahoocom
Data Mining Algorithms Part 1. Dejan Sarka
 Data Mining Algorithms Part 1 Dejan Sarka Join the conversation on Twitter: @DevWeek #DW2015 Instructor Bio Dejan Sarka ([email protected]) 30 years of experience SQL Server MVP, MCT, 13 books 7+ courses
Data Mining Algorithms Part 1 Dejan Sarka Join the conversation on Twitter: @DevWeek #DW2015 Instructor Bio Dejan Sarka ([email protected]) 30 years of experience SQL Server MVP, MCT, 13 books 7+ courses
www.ijreat.org Published by: PIONEER RESEARCH & DEVELOPMENT GROUP (www.prdg.org) 28
 Data Warehousing - Essential Element To Support Decision- Making Process In Industries Ashima Bhasin 1, Mr Manoj Kumar 2 1 Computer Science Engineering Department, 2 Associate Professor, CSE Abstract SGT
Data Warehousing - Essential Element To Support Decision- Making Process In Industries Ashima Bhasin 1, Mr Manoj Kumar 2 1 Computer Science Engineering Department, 2 Associate Professor, CSE Abstract SGT
OLAP and Data Mining. Data Warehousing and End-User Access Tools. Introducing OLAP. Introducing OLAP
 Data Warehousing and End-User Access Tools OLAP and Data Mining Accompanying growth in data warehouses is increasing demands for more powerful access tools providing advanced analytical capabilities. Key
Data Warehousing and End-User Access Tools OLAP and Data Mining Accompanying growth in data warehouses is increasing demands for more powerful access tools providing advanced analytical capabilities. Key
Data Warehousing and Data Mining
 Data Warehousing and Data Mining Part I: Data Warehousing Gao Cong [email protected] Slides adapted from Man Lung Yiu and Torben Bach Pedersen Course Structure Business intelligence: Extract knowledge
Data Warehousing and Data Mining Part I: Data Warehousing Gao Cong [email protected] Slides adapted from Man Lung Yiu and Torben Bach Pedersen Course Structure Business intelligence: Extract knowledge
Managing Big Data with Hadoop & Vertica. A look at integration between the Cloudera distribution for Hadoop and the Vertica Analytic Database
 Managing Big Data with Hadoop & Vertica A look at integration between the Cloudera distribution for Hadoop and the Vertica Analytic Database Copyright Vertica Systems, Inc. October 2009 Cloudera and Vertica
Managing Big Data with Hadoop & Vertica A look at integration between the Cloudera distribution for Hadoop and the Vertica Analytic Database Copyright Vertica Systems, Inc. October 2009 Cloudera and Vertica
Hexaware E-book on Predictive Analytics
 Hexaware E-book on Predictive Analytics Business Intelligence & Analytics Actionable Intelligence Enabled Published on : Feb 7, 2012 Hexaware E-book on Predictive Analytics What is Data mining? Data mining,
Hexaware E-book on Predictive Analytics Business Intelligence & Analytics Actionable Intelligence Enabled Published on : Feb 7, 2012 Hexaware E-book on Predictive Analytics What is Data mining? Data mining,
B.Sc (Computer Science) Database Management Systems UNIT-V
 1 B.Sc (Computer Science) Database Management Systems UNIT-V Business Intelligence? Business intelligence is a term used to describe a comprehensive cohesive and integrated set of tools and process used
1 B.Sc (Computer Science) Database Management Systems UNIT-V Business Intelligence? Business intelligence is a term used to describe a comprehensive cohesive and integrated set of tools and process used
Enterprise Resource Planning Analysis of Business Intelligence & Emergence of Mining Objects
 Enterprise Resource Planning Analysis of Business Intelligence & Emergence of Mining Objects Abstract: Build a model to investigate system and discovering relations that connect variables in a database
Enterprise Resource Planning Analysis of Business Intelligence & Emergence of Mining Objects Abstract: Build a model to investigate system and discovering relations that connect variables in a database
Lection 3-4 WAREHOUSING
 Lection 3-4 DATA WAREHOUSING Learning Objectives Understand d the basic definitions iti and concepts of data warehouses Understand data warehousing architectures Describe the processes used in developing
Lection 3-4 DATA WAREHOUSING Learning Objectives Understand d the basic definitions iti and concepts of data warehouses Understand data warehousing architectures Describe the processes used in developing
Predicting the Risk of Heart Attacks using Neural Network and Decision Tree
 Predicting the Risk of Heart Attacks using Neural Network and Decision Tree S.Florence 1, N.G.Bhuvaneswari Amma 2, G.Annapoorani 3, K.Malathi 4 PG Scholar, Indian Institute of Information Technology, Srirangam,
Predicting the Risk of Heart Attacks using Neural Network and Decision Tree S.Florence 1, N.G.Bhuvaneswari Amma 2, G.Annapoorani 3, K.Malathi 4 PG Scholar, Indian Institute of Information Technology, Srirangam,
Dr. U. Devi Prasad Associate Professor Hyderabad Business School GITAM University, Hyderabad Email: [email protected]
 96 Business Intelligence Journal January PREDICTION OF CHURN BEHAVIOR OF BANK CUSTOMERS USING DATA MINING TOOLS Dr. U. Devi Prasad Associate Professor Hyderabad Business School GITAM University, Hyderabad
96 Business Intelligence Journal January PREDICTION OF CHURN BEHAVIOR OF BANK CUSTOMERS USING DATA MINING TOOLS Dr. U. Devi Prasad Associate Professor Hyderabad Business School GITAM University, Hyderabad
Information Management course
 Università degli Studi di Milano Master Degree in Computer Science Information Management course Teacher: Alberto Ceselli Lecture 01 : 06/10/2015 Practical informations: Teacher: Alberto Ceselli ([email protected])
Università degli Studi di Milano Master Degree in Computer Science Information Management course Teacher: Alberto Ceselli Lecture 01 : 06/10/2015 Practical informations: Teacher: Alberto Ceselli ([email protected])
Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques. Jiawei Han. Micheline Kamber. Simon Fräser University К MORGAN KAUFMANN PUBLISHERS. AN IMPRINT OF Elsevier
 Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques Jiawei Han Micheline Kamber Simon Fräser University К MORGAN KAUFMANN PUBLISHERS AN IMPRINT OF Elsevier Contents Foreword Preface xix vii Chapter I Introduction I I.
Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques Jiawei Han Micheline Kamber Simon Fräser University К MORGAN KAUFMANN PUBLISHERS AN IMPRINT OF Elsevier Contents Foreword Preface xix vii Chapter I Introduction I I.
Data Mining and Business Intelligence CIT-6-DMB. http://blackboard.lsbu.ac.uk. Faculty of Business 2011/2012. Level 6
 Data Mining and Business Intelligence CIT-6-DMB http://blackboard.lsbu.ac.uk Faculty of Business 2011/2012 Level 6 Table of Contents 1. Module Details... 3 2. Short Description... 3 3. Aims of the Module...
Data Mining and Business Intelligence CIT-6-DMB http://blackboard.lsbu.ac.uk Faculty of Business 2011/2012 Level 6 Table of Contents 1. Module Details... 3 2. Short Description... 3 3. Aims of the Module...
2.1. Data Mining for Biomedical and DNA data analysis
 Applications of Data Mining Simmi Bagga Assistant Professor Sant Hira Dass Kanya Maha Vidyalaya, Kala Sanghian, Distt Kpt, India (Email: [email protected]) Dr. G.N. Singh Department of Physics and
Applications of Data Mining Simmi Bagga Assistant Professor Sant Hira Dass Kanya Maha Vidyalaya, Kala Sanghian, Distt Kpt, India (Email: [email protected]) Dr. G.N. Singh Department of Physics and
OLAP Theory-English version
 OLAP Theory-English version On-Line Analytical processing (Business Intelligence) [Ing.J.Skorkovský,CSc.] Department of corporate economy Agenda The Market Why OLAP (On-Line-Analytic-Processing Introduction
OLAP Theory-English version On-Line Analytical processing (Business Intelligence) [Ing.J.Skorkovský,CSc.] Department of corporate economy Agenda The Market Why OLAP (On-Line-Analytic-Processing Introduction
DATA MINING TECHNOLOGY. Keywords: data mining, data warehouse, knowledge discovery, OLAP, OLAM.
 DATA MINING TECHNOLOGY Georgiana Marin 1 Abstract In terms of data processing, classical statistical models are restrictive; it requires hypotheses, the knowledge and experience of specialists, equations,
DATA MINING TECHNOLOGY Georgiana Marin 1 Abstract In terms of data processing, classical statistical models are restrictive; it requires hypotheses, the knowledge and experience of specialists, equations,
Data Mining Techniques
 15.564 Information Technology I Business Intelligence Outline Operational vs. Decision Support Systems What is Data Mining? Overview of Data Mining Techniques Overview of Data Mining Process Data Warehouses
15.564 Information Technology I Business Intelligence Outline Operational vs. Decision Support Systems What is Data Mining? Overview of Data Mining Techniques Overview of Data Mining Process Data Warehouses
Data Warehouse: Introduction
 Base and Mining Group of Base and Mining Group of Base and Mining Group of Base and Mining Group of Base and Mining Group of Base and Mining Group of Base and Mining Group of base and data mining group,
Base and Mining Group of Base and Mining Group of Base and Mining Group of Base and Mining Group of Base and Mining Group of Base and Mining Group of Base and Mining Group of base and data mining group,
A Critical Review of Data Warehouse
 Global Journal of Business Management and Information Technology. Volume 1, Number 2 (2011), pp. 95-103 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com A Critical Review of Data Warehouse Sachin
Global Journal of Business Management and Information Technology. Volume 1, Number 2 (2011), pp. 95-103 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com A Critical Review of Data Warehouse Sachin
Data warehousing and data mining an overview
 Data warehousing and data mining an overview Abstract Dr. Suman Bhusan Bhattacharyya MBBS, ADHA, MBA With continuous advances in technology, increasing number of clinicians are using electronic medical
Data warehousing and data mining an overview Abstract Dr. Suman Bhusan Bhattacharyya MBBS, ADHA, MBA With continuous advances in technology, increasing number of clinicians are using electronic medical
Dimensional Modeling for Data Warehouse
 Modeling for Data Warehouse Umashanker Sharma, Anjana Gosain GGS, Indraprastha University, Delhi Abstract Many surveys indicate that a significant percentage of DWs fail to meet business objectives or
Modeling for Data Warehouse Umashanker Sharma, Anjana Gosain GGS, Indraprastha University, Delhi Abstract Many surveys indicate that a significant percentage of DWs fail to meet business objectives or
Business Intelligence
 Business Intelligence Data Mining and Data Warehousing Dominik Ślęzak [email protected] www.infobright.com Research Interests Data Warehouses, Knowledge Discovery, Rough Sets Machine Intelligence,
Business Intelligence Data Mining and Data Warehousing Dominik Ślęzak [email protected] www.infobright.com Research Interests Data Warehouses, Knowledge Discovery, Rough Sets Machine Intelligence,
A New Approach for Evaluation of Data Mining Techniques
 181 A New Approach for Evaluation of Data Mining s Moawia Elfaki Yahia 1, Murtada El-mukashfi El-taher 2 1 College of Computer Science and IT King Faisal University Saudi Arabia, Alhasa 31982 2 Faculty
181 A New Approach for Evaluation of Data Mining s Moawia Elfaki Yahia 1, Murtada El-mukashfi El-taher 2 1 College of Computer Science and IT King Faisal University Saudi Arabia, Alhasa 31982 2 Faculty
Lost in Space? Methodology for a Guided Drill-Through Analysis Out of the Wormhole
 Paper BB-01 Lost in Space? Methodology for a Guided Drill-Through Analysis Out of the Wormhole ABSTRACT Stephen Overton, Overton Technologies, LLC, Raleigh, NC Business information can be consumed many
Paper BB-01 Lost in Space? Methodology for a Guided Drill-Through Analysis Out of the Wormhole ABSTRACT Stephen Overton, Overton Technologies, LLC, Raleigh, NC Business information can be consumed many
Introduction. A. Bellaachia Page: 1
 Introduction 1. Objectives... 3 2. What is Data Mining?... 4 3. Knowledge Discovery Process... 5 4. KD Process Example... 7 5. Typical Data Mining Architecture... 8 6. Database vs. Data Mining... 9 7.
Introduction 1. Objectives... 3 2. What is Data Mining?... 4 3. Knowledge Discovery Process... 5 4. KD Process Example... 7 5. Typical Data Mining Architecture... 8 6. Database vs. Data Mining... 9 7.
Business Intelligence Solutions for Gaming and Hospitality
 Business Intelligence Solutions for Gaming and Hospitality Prepared by: Mario Perkins Qualex Consulting Services, Inc. Suzanne Fiero SAS Objective Summary 2 Objective Summary The rise in popularity and
Business Intelligence Solutions for Gaming and Hospitality Prepared by: Mario Perkins Qualex Consulting Services, Inc. Suzanne Fiero SAS Objective Summary 2 Objective Summary The rise in popularity and
Nagarjuna College Of
 Nagarjuna College Of Information Technology (Bachelor in Information Management) TRIBHUVAN UNIVERSITY Project Report on World s successful data mining and data warehousing projects Submitted By: Submitted
Nagarjuna College Of Information Technology (Bachelor in Information Management) TRIBHUVAN UNIVERSITY Project Report on World s successful data mining and data warehousing projects Submitted By: Submitted
14. Data Warehousing & Data Mining
 14. Data Warehousing & Data Mining Data Warehousing Concepts Decision support is key for companies wanting to turn their organizational data into an information asset Data Warehouse "A subject-oriented,
14. Data Warehousing & Data Mining Data Warehousing Concepts Decision support is key for companies wanting to turn their organizational data into an information asset Data Warehouse "A subject-oriented,
Chapter 6 Basics of Data Integration. Fundamentals of Business Analytics RN Prasad and Seema Acharya
 Chapter 6 Basics of Data Integration Fundamentals of Business Analytics Learning Objectives and Learning Outcomes Learning Objectives 1. Concepts of data integration 2. Needs and advantages of using data
Chapter 6 Basics of Data Integration Fundamentals of Business Analytics Learning Objectives and Learning Outcomes Learning Objectives 1. Concepts of data integration 2. Needs and advantages of using data
Data Mining: Overview. What is Data Mining?
 Data Mining: Overview What is Data Mining? Recently * coined term for confluence of ideas from statistics and computer science (machine learning and database methods) applied to large databases in science,
Data Mining: Overview What is Data Mining? Recently * coined term for confluence of ideas from statistics and computer science (machine learning and database methods) applied to large databases in science,
OLAP and OLTP. AMIT KUMAR BINDAL Associate Professor M M U MULLANA
 OLAP and OLTP AMIT KUMAR BINDAL Associate Professor Databases Databases are developed on the IDEA that DATA is one of the critical materials of the Information Age Information, which is created by data,
OLAP and OLTP AMIT KUMAR BINDAL Associate Professor Databases Databases are developed on the IDEA that DATA is one of the critical materials of the Information Age Information, which is created by data,
Data Warehousing: A Technology Review and Update Vernon Hoffner, Ph.D., CCP EntreSoft Resouces, Inc.
 Warehousing: A Technology Review and Update Vernon Hoffner, Ph.D., CCP EntreSoft Resouces, Inc. Introduction Abstract warehousing has been around for over a decade. Therefore, when you read the articles
Warehousing: A Technology Review and Update Vernon Hoffner, Ph.D., CCP EntreSoft Resouces, Inc. Introduction Abstract warehousing has been around for over a decade. Therefore, when you read the articles
Ezgi Dinçerden. Marmara University, Istanbul, Turkey
 Economics World, Mar.-Apr. 2016, Vol. 4, No. 2, 60-65 doi: 10.17265/2328-7144/2016.02.002 D DAVID PUBLISHING The Effects of Business Intelligence on Strategic Management of Enterprises Ezgi Dinçerden Marmara
Economics World, Mar.-Apr. 2016, Vol. 4, No. 2, 60-65 doi: 10.17265/2328-7144/2016.02.002 D DAVID PUBLISHING The Effects of Business Intelligence on Strategic Management of Enterprises Ezgi Dinçerden Marmara
Foundations of Business Intelligence: Databases and Information Management
 Chapter 5 Foundations of Business Intelligence: Databases and Information Management 5.1 Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Student Learning Objectives How does a relational database organize data,
Chapter 5 Foundations of Business Intelligence: Databases and Information Management 5.1 Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Student Learning Objectives How does a relational database organize data,
Chapter 6 - Enhancing Business Intelligence Using Information Systems
 Chapter 6 - Enhancing Business Intelligence Using Information Systems Managers need high-quality and timely information to support decision making Copyright 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Chapter 6 Learning
Chapter 6 - Enhancing Business Intelligence Using Information Systems Managers need high-quality and timely information to support decision making Copyright 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Chapter 6 Learning
Alexander Nikov. 5. Database Systems and Managing Data Resources. Learning Objectives. RR Donnelley Tries to Master Its Data
 INFO 1500 Introduction to IT Fundamentals 5. Database Systems and Managing Data Resources Learning Objectives 1. Describe how the problems of managing data resources in a traditional file environment are
INFO 1500 Introduction to IT Fundamentals 5. Database Systems and Managing Data Resources Learning Objectives 1. Describe how the problems of managing data resources in a traditional file environment are
Practical Considerations for Real-Time Business Intelligence. Donovan Schneider Yahoo! September 11, 2006
 Practical Considerations for Real-Time Business Intelligence Donovan Schneider Yahoo! September 11, 2006 Outline Business Intelligence (BI) Background Real-Time Business Intelligence Examples Two Requirements
Practical Considerations for Real-Time Business Intelligence Donovan Schneider Yahoo! September 11, 2006 Outline Business Intelligence (BI) Background Real-Time Business Intelligence Examples Two Requirements
An Introduction to Data Warehousing. An organization manages information in two dominant forms: operational systems of
 An Introduction to Data Warehousing An organization manages information in two dominant forms: operational systems of record and data warehouses. Operational systems are designed to support online transaction
An Introduction to Data Warehousing An organization manages information in two dominant forms: operational systems of record and data warehouses. Operational systems are designed to support online transaction
THE INTELLIGENT BUSINESS INTELLIGENCE SOLUTIONS
 THE INTELLIGENT BUSINESS INTELLIGENCE SOLUTIONS ADRIAN COJOCARIU, CRISTINA OFELIA STANCIU TIBISCUS UNIVERSITY OF TIMIŞOARA, FACULTY OF ECONOMIC SCIENCE, DALIEI STR, 1/A, TIMIŞOARA, 300558, ROMANIA [email protected],
THE INTELLIGENT BUSINESS INTELLIGENCE SOLUTIONS ADRIAN COJOCARIU, CRISTINA OFELIA STANCIU TIBISCUS UNIVERSITY OF TIMIŞOARA, FACULTY OF ECONOMIC SCIENCE, DALIEI STR, 1/A, TIMIŞOARA, 300558, ROMANIA [email protected],
How To Use Data Mining For Loyalty Based Management
 Data Mining for Loyalty Based Management Petra Hunziker, Andreas Maier, Alex Nippe, Markus Tresch, Douglas Weers, Peter Zemp Credit Suisse P.O. Box 100, CH - 8070 Zurich, Switzerland [email protected],
Data Mining for Loyalty Based Management Petra Hunziker, Andreas Maier, Alex Nippe, Markus Tresch, Douglas Weers, Peter Zemp Credit Suisse P.O. Box 100, CH - 8070 Zurich, Switzerland [email protected],
A Technical Review on On-Line Analytical Processing (OLAP)
 A Technical Review on On-Line Analytical Processing (OLAP) K. Jayapriya 1., E. Girija 2,III-M.C.A., R.Uma. 3,M.C.A.,M.Phil., Department of computer applications, Assit.Prof,Dept of M.C.A, Dhanalakshmi
A Technical Review on On-Line Analytical Processing (OLAP) K. Jayapriya 1., E. Girija 2,III-M.C.A., R.Uma. 3,M.C.A.,M.Phil., Department of computer applications, Assit.Prof,Dept of M.C.A, Dhanalakshmi
SQL Server 2005 Features Comparison
 Page 1 of 10 Quick Links Home Worldwide Search Microsoft.com for: Go : Home Product Information How to Buy Editions Learning Downloads Support Partners Technologies Solutions Community Previous Versions
Page 1 of 10 Quick Links Home Worldwide Search Microsoft.com for: Go : Home Product Information How to Buy Editions Learning Downloads Support Partners Technologies Solutions Community Previous Versions
Foundations of Business Intelligence: Databases and Information Management
 Chapter 6 Foundations of Business Intelligence: Databases and Information Management 6.1 2010 by Prentice Hall LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe how the problems of managing data resources in a traditional
Chapter 6 Foundations of Business Intelligence: Databases and Information Management 6.1 2010 by Prentice Hall LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe how the problems of managing data resources in a traditional
Moving Large Data at a Blinding Speed for Critical Business Intelligence. A competitive advantage
 Moving Large Data at a Blinding Speed for Critical Business Intelligence A competitive advantage Intelligent Data In Real Time How do you detect and stop a Money Laundering transaction just about to take
Moving Large Data at a Blinding Speed for Critical Business Intelligence A competitive advantage Intelligent Data In Real Time How do you detect and stop a Money Laundering transaction just about to take
Introduction to Data Mining
 Introduction to Data Mining José Hernández ndez-orallo Dpto.. de Systems Informáticos y Computación Universidad Politécnica de Valencia, Spain [email protected] Horsens, Denmark, 26th September 2005
Introduction to Data Mining José Hernández ndez-orallo Dpto.. de Systems Informáticos y Computación Universidad Politécnica de Valencia, Spain [email protected] Horsens, Denmark, 26th September 2005
Data Mining with SAS. Mathias Lanner [email protected]. Copyright 2010 SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved.
 Data Mining with SAS Mathias Lanner [email protected] Copyright 2010 SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved. Agenda Data mining Introduction Data mining applications Data mining techniques SEMMA
Data Mining with SAS Mathias Lanner [email protected] Copyright 2010 SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved. Agenda Data mining Introduction Data mining applications Data mining techniques SEMMA
Data Mining. Vera Goebel. Department of Informatics, University of Oslo
 Data Mining Vera Goebel Department of Informatics, University of Oslo 2011 1 Lecture Contents Knowledge Discovery in Databases (KDD) Definition and Applications OLAP Architectures for OLAP and KDD KDD
Data Mining Vera Goebel Department of Informatics, University of Oslo 2011 1 Lecture Contents Knowledge Discovery in Databases (KDD) Definition and Applications OLAP Architectures for OLAP and KDD KDD
Course 103402 MIS. Foundations of Business Intelligence
 Oman College of Management and Technology Course 103402 MIS Topic 5 Foundations of Business Intelligence CS/MIS Department Organizing Data in a Traditional File Environment File organization concepts Database:
Oman College of Management and Technology Course 103402 MIS Topic 5 Foundations of Business Intelligence CS/MIS Department Organizing Data in a Traditional File Environment File organization concepts Database:
Week 3 lecture slides
 Week 3 lecture slides Topics Data Warehouses Online Analytical Processing Introduction to Data Cubes Textbook reference: Chapter 3 Data Warehouses A data warehouse is a collection of data specifically
Week 3 lecture slides Topics Data Warehouses Online Analytical Processing Introduction to Data Cubes Textbook reference: Chapter 3 Data Warehouses A data warehouse is a collection of data specifically
TIM 50 - Business Information Systems
 TIM 50 - Business Information Systems Lecture 15 UC Santa Cruz March 1, 2015 The Database Approach to Data Management Database: Collection of related files containing records on people, places, or things.
TIM 50 - Business Information Systems Lecture 15 UC Santa Cruz March 1, 2015 The Database Approach to Data Management Database: Collection of related files containing records on people, places, or things.
Jagir Singh, Greeshma, P Singh University of Northern Virginia. Abstract
 224 Business Intelligence Journal July DATA WAREHOUSING Ofori Boateng, PhD Professor, University of Northern Virginia BMGT531 1900- SU 2011 Business Intelligence Project Jagir Singh, Greeshma, P Singh
224 Business Intelligence Journal July DATA WAREHOUSING Ofori Boateng, PhD Professor, University of Northern Virginia BMGT531 1900- SU 2011 Business Intelligence Project Jagir Singh, Greeshma, P Singh
University of Gaziantep, Department of Business Administration
 University of Gaziantep, Department of Business Administration The extensive use of information technology enables organizations to collect huge amounts of data about almost every aspect of their businesses.
University of Gaziantep, Department of Business Administration The extensive use of information technology enables organizations to collect huge amounts of data about almost every aspect of their businesses.
KNOWLEDGE BASE DATA MINING FOR BUSINESS INTELLIGENCE
 KNOWLEDGE BASE DATA MINING FOR BUSINESS INTELLIGENCE Dr. Ruchira Bhargava 1 and Yogesh Kumar Jakhar 2 1 Associate Professor, Department of Computer Science, Shri JagdishPrasad Jhabarmal Tibrewala University,
KNOWLEDGE BASE DATA MINING FOR BUSINESS INTELLIGENCE Dr. Ruchira Bhargava 1 and Yogesh Kumar Jakhar 2 1 Associate Professor, Department of Computer Science, Shri JagdishPrasad Jhabarmal Tibrewala University,
Data Mining as Part of Knowledge Discovery in Databases (KDD)
 Mining as Part of Knowledge Discovery in bases (KDD) Presented by Naci Akkøk as part of INF4180/3180, Advanced base Systems, fall 2003 (based on slightly modified foils of Dr. Denise Ecklund from 6 November
Mining as Part of Knowledge Discovery in bases (KDD) Presented by Naci Akkøk as part of INF4180/3180, Advanced base Systems, fall 2003 (based on slightly modified foils of Dr. Denise Ecklund from 6 November
