The Autonomic Nervous System and Toxic Syndromes
|
|
|
- Karen Bridges
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Autonomic Nervous System and Toxic Syndromes S. Rutherfoord Rose Virginia Poison Center Division of Clinical Toxicology Department of Emergency Medicine VCU Health System
2 Objectives Review the anatomy and physiology of the autonomic nervous system Improve understanding of medications that affect the autonomic nervous system Use clinical findings to predict potential causes of toxic syndromes Go over a bunch of tox cases and make this lecture slightly more enjoyable than a hernia
3
4 Autonomic Nervous System Temperature regulation Fluid and electrolyte balance Metabolism rate Digestion and excretion Cardiovascular function
5 Autonomic Nervous System Responsible for control of involuntary responses Two functional divisions: Sympathetic (adrenergic) Parasympathetic (cholinergic) Preganglionic fibers from spinal cord to ganglia Postganglionic fibers from ganglia to target organs Synapses space between nerve cells (endings) Neurotransmitters chemical messengers Norepinephrine (NE) Acetylcholine (Ach)
6
7
8 Autonomic Nervous System A. Sympathetic (thoracolumbar) Peripheral neurotransmitter = norepinephrine Receptors: alpha (1 and 2) & beta (1 and 2) B. Parasympathetic (craniosacral) Peripheral neurotransmitter = acetylcholine Cholinergic receptors: muscarinic and nicotinic
9
10
11
12 Physiologic Receptors in the Autonomic Nervous System CHOLINERGIC (Acetylcholine) Nicotinic: autonomic ganglia, adrenal medulla, striated muscle Muscarinic: heart, smooth muscle, glands ADRENERGIC (epinephrine, norepinephrine) Alpha 1: blood vessels, eyes, reproductive organs Alpha 2: regulate neurotransmitter release Beta 1: heart and kidneys Beta 2: salivary glands, eyes, lungs, GI tract, arterioles of hear, lungs, skin, skeletal muscle DOPAMINERGIC CNS and renal vasculature
13 Adrenergic Transmission
14 Parasympathetic Receptors
15
16 Autonomic NS Receptors
17 Autonomic Pharmacology Sympathetic Agonist: sympathomimetic / adrenergic (epinephrine) Antagonist: sympatholytic Alpha receptor blockers (phentolamine) Beta blockers (propranolol, metoprolol) Parasympathetic Agonist: cholinergic (acetylcholine) Antagonist: parasympatholytic, anticholinergic Muscarinic receptor blocker (atropine) Nicotinic antagonist (neuromuscular blockers, ganglionic blockers)
18 Toxic Syndromes Physical signs Patient symptoms Characteristic odors, color Laboratory findings Suggests, but does not confirm, a diagnosis
19 TOXIC SYNDROMES CASE 1 A 34 y/o female presents with confusion, disorientation and somnolence HR 140 BP 130/80 RR 16 T Pupils widely dilated, reactive Skin hot, dry Bowel sounds decreased Mouth dry Speech slurred CLUE: depressed, took sleeping pills
20 Diagnosis???
21 ANTICHOLINERGIC SYNDROME Antihistamines: pyrilamine, doxylamine, diphenhydramine, dimenhydrinate Phenothiazines, cyclic antidepressants Antiparkinson agents: benztropine, trihexiphenidyl Plants Jimson weed (Datura stramonium) Deadly nightshade (Atropa belladonna) Some Mushrooms (muscimol, ibotenic acid) Atropine, scopalamine Antispasmodics (belladonna, hyoscamine)
22 ANTICHOLINERGIC SYNDROME Blind as a bat Dry as a bone Red as a beet Hot as Hades Mad as a hatter
23 TOXIC SYNDROMES CASE 2 A 24 y/o male presents with seizures and coma. HR 160 BP 190/100 RR 24 T 102 Pupils, dilated, reactive Marked diaphoresis Bowel sound hypoactive CLUE 1: EKG narrow complex sinus tach CLUE 2: Drug abuser CLUE 3: HR & BP return to normal within 60 minutes
24 SYMPATHOMIMETIC SYNDROME Mixed alpha and beta adrenergic effects Clinical effects: Tachycardia Hypertension CNS stimulation Diaphoresis Decreased GI motility Miosis/Mydriasis
25 SYMPATHOMIMETIC SYNDROME Dx: cocaine toxicity Other agents: Amphetamines Ephedrine Pseudoephedrine Anoretics (Fen-Phen) Propylhexadrine Tyramine
26
27 TOXIC SYNDROMES CASE 3 A 22 y/o male presents with lethargy, confusion, and complaining of severe crampy abdominal pain, vomiting and severe diarrhea. HR 60 BP 110/70 RR 28, labored T 99 Diaphoretic, cyanotic, drooling Marked respiratory distress with rales Bowel sounds hyperactive Incontinent of bowel and bladder CLUE: depressed Orkin Man recently broke up with his girlfriend
28 CHOLINERGIC SYNDROME Excess acetylcholine at muscarinic and nicotinic receptors Dx: Organophosphate insecticide Other Agents: Carbamate insecticides Physostigmine Nicotine insecticides Tobacco Mushroom (Clitocybe, Inocybe)
29 CHOLINERGIC SYNDROME D U M B B E L S diarrhea, diaphoresis urination miosis bradycardia bronchorrhea emesis lacrimation salivation, sweating
30 TOXIC SYNDROMES CASE 4 A 19 y/o male presents with headache and lethargy. No history of vomiting or diarrhea. HR 60 BP 210/120 RR 16 T 99.9 Pupils dilated, sluggishly reactive Skin slightly moist Bowels sounds decreased CLUE: 30 min later he develops LOC and hemiparesis. Hx of street speed.
31 ALPHA ADRENERGIC SYNDROME Dx: Phenylpropanolamine (PPA) Overdose Other agents: Phenylephrine Methoxamine Imidazolines Tetrahydrozaline (Visine) Oxymetazoline Naphazoline Xylometazoline
32 Alpha Adrenergic Drugs ALPHA AGONISTS Dobutamine Dopamine Ephedrine Epinephrine Ergot alkaloids Methoxamine (Vasoxyl) Phenylephrine (Neo-synephrine) Phenylpropanolamine (PPA) Pseudoephedrine (Sudafed) ALPHA ANTAGONISTS Doxazosin (Cardura) Prazosin (Minipress) Terazosin (Hytrin) Phentolamine (Regitine) Phenoxybenzamine Tolazoline (Priscoline) Induramine (Baratol) Urapidil Labetalol (alpha & beta)
33 TOXIC SYNDROMES CASE 5 A 2 y/o male presents with agitation and bizarre behavior. HR 190 BP 80/60 RR 24 T 99.8 Tremulous, irritable Pupils normal size, reactive Skin and bowel sounds normal CLUE: older sibling takes liquid medicine for asthma
34 BETA-ADRENERGIC SYNDROME Dx: Albuterol overdose Other agents: Terbutaline Metaproterenol Isoproterenol Theophylline Caffeine
35 Beta Adrenergic Drugs BETA AGONISTS Albuterol (Proventil, Ventolin) Bitolterol (Tornalate) Dobutamine Dopamine Epinephrine Isoetharine (Bronkosol) Isoproterenol (Isuprel) Metaproterenol (Alupent) Norepinephrine Ritodrine (Yutopar)] Salmeterol (Serevent) Terbutaline (Bricanyl, Brethrine) BETA BLOCKERS Acebutolol (Sectral) Atenolol (Tenormin) Betaxolol (Kerlone) Bisoprolol (Zebeta) Esmolol (Brevibloc) Metoprolol (Lopressor) Carteolol (Cartrol) Nadolol (Corgard) Penbutolol (Levatol) Pindolol (Visken) Propranolol (Inderal) Sotalol (Betapace) Timolol (Blocadren) Labetalol (Normodyne, Trandate)
36 Beta Blocker Toxicity Bradycardia Hypotension A-V block Heart failure CNS depression Seizures
37 TOXIC SYNDROMES CASE 6 A 2 y/o female presents with extreme lethargy. HR 72 Dusky appearance BP 70/50 Lips cyanotic RR 10 Shallow respirations T 98 Skin Dry Bowel sounds decreased, present CLUE 1: The child improves somewhat after a 2mg dose of naloxone CLUE 2: Grandfather, visiting at child s house, takes blood pressure medicine
38 SYMPATHOLYTIC SYNDROME Clonidine Methyldopa Guanabenz Sedative / hypnotics Opioids Alcohol
39 Imidazolines Antihypertensives: Guanfacine (Tenex) Guanabenz (Wytensin) Decongestants Tetrahydrozoline (Visine) Oxymetazoline (Afrin) Naphazoline (Clear Eyes)
40 TOXIC SYNDROMES CASE 7 A 45 y/o male presents comatose and cyanotic. HR 68 BP 110/60 RR 8, shallow T 97.8 Pupils constricted Needle marks on left arm Bowel sounds decreased CLUE:wakes up after IV naloxone
41 OPIOID SYNDROME Dx: Heroin Overdose Triad: coma, respiratory depression, miosis Other agents Opiates Clonidine GHB or analogue
42 TOXIC SYNDROMES CASE 8 A 35 y/o female presents with confusion and lethargy. No nausea or vomiting. HR 110 BP 120/80 PE unremarkable except for drowsy, RR 32 confusion and tachypnea. T 99 Labs: Na 142 Cl 96 BUN 27 Glucose 100 K 4.1 Bicarb 8 Cr 2.2 Other labs? ABG: 7.02 / 96 / 25 Measured osmolality = 380. ETOH = 0. CLUE 1: Ca oxylate crystals in urine CLUE 2: Empty container of radiator antifreeze found in trash can at home.
43
44 TOXIC SYNDROMES- CASE 9 The police bring in a 28 y/o female with drowsiness who says she just wants to die. There is a suicide note. HR 130 Skin warm and dry BP 120/80 Bowel sounds decreased RR 16 Pupils slightly,reactive T 98
45 15 minutes later:
46 TOXIC SYNDROMES- CASE 9 The police bring in a 28 y/o female with drowsiness who says she just wants to die. There is a suicide note. HR 130 Skin warm and dry BP 120/80 Bowel sounds decreased RR 16 Pupils slightly,reactive T 98 CLUE: 15 minutes later she has a seizure lasting 2 minutes, after which she is deeply comatose with agonal respirations. Cardiac monitor shows wide complex tachycardia with a rate of 160. BP 60/40.
47 TCA Clinical Toxicity Lethargy ± agitation Sinus tachycardia Then: Seizures, hypotension, ventricular dysrhythmias
48 Cyclic Antidepressants Inhibit catecholamine reuptake NE, 5-HT, DA Block ACH receptors M Block fast Na + cardiac channels Block alpha- adrenergic receptors Block K + efflux from cardiac cells Indirect GABA antagonist Block H 1 and H 2 receptors
49 TOXIC SYNDROMES CASE 10 A 22 y/o female presents with a severe toothache for one week, and mild nausea and vomiting for 3 days. She is seeking pain medication for the persistent toothache. Her friends told her that her eyes were turning yellow. Vital signs normal Mild scleral icterus Right upper quadrant tenderness Severely abcessed tooth CLUE: taking 4-5 OTC pain pills at a time every 3 4 hours.
50
51 TOXIC SYNDROMES CASE 11 A depressed 17 y/o female presents with acute onset of nausea, abdominal pain, hematemesis and diarrhea. HR 115 BP initially normal but falls to 80/50 Anion gap metabolic acidosis is present CLUE 1: pregnant CLUE 2: X-ray shows radiopaque pills in stomach and proximal small bowel
52
53 Iron Poisoning Direct GI irritant corrosive Decreased venous return fall in CO Elevated lactate, release of protons as Fe++ converted to Fe+++ Catalyzes free radical formation and lipid peroxidation (hepatotoxicity) Hyperglycemia, leukocytosis
54
55 TOXIC SYNDROMES CASE 12 A 44 y/o female presents with dyspnea, nausea, vomiting and lethargy. It is difficult to obtain a history because the patient is hard of hearing. HR 96 BP 130/90 RR 28 T PE: consistent with advanced rheumatoid arthritis CLUE: ABG: 7.48 / 98 / 22 Na 142 Cl 106 Bicarb 14 K 3.5
56 Salicylates Analgesics ASA, Fiorinal Goody, BC powders Pepto-Bismol Topical liniment analgesics (Ben Gay) Suppositories Chewing gum Flavorings (oil of wintergreen) Plants (acacia, hyacinth, calycanthus) Chinese / herbal products
57 Salicylates GI irritant Stimulates respiratory center Hyperventilation/respiratory alkalosis May alter capillary permeability Cerebral/pulmonary edema Uncouples oxidative phosphorylation Causing lactic acidosis, ketoacidosis Inhibits cyclo-oxygenase Loss of gastric mucosal barrier Platelet dysfunction
58 TOXIC SYNDROME CASE 13 A 44 y/o female presents with severe nausea and vomiting. HR 140, irregular BP 110/70 RR 18 Agitated, tremulous T 99 Skin, pupils, bowel sounds are normal Cardiac monitor shows sinus tach with narrow QRS complex and occasional PADS and PVDS. Before any further information can be obtained the patient has a seizure which is not controlled with diazepam and phenytoin. CLUE: husband had asthma Hypokalemia
59 Theophylline Mechanism of Action Inhibition of phosphodieterase Adenosine receptor antagonism Release of catecholamines Clinical Effects Gastric acid and pepsin secretion Stimulation of respiratory & vomiting centers in medulla Positive inotropic and chronotropic effects Reduction of peripheral arteriolar resistance Relaxation of bronchial smooth muscle Increase GFR and RBF CNS stimulation
60 TOXIC SYNDROMES CASE 14 A 48 y/o male alcoholic presents with confusion and blurred vision. HR 100 BP 140/90 RR 32 T 99 Confused, lethargic, disoriented Labs: Na 144 Cl 100 Bicarb 10 K 3.9 Glu 100 BUN 18 Cr 1.2 ETOH = 0 Measured osmolality = 350 CLUE: emesis has a bluish tint; urinalysis is normal
61
62 TOXIC SYNDROMES CASE 15 A 19 y/o male is brought in by 6 policemen for severe agitation and disruptive behavior. Hypertensive Nystagmus Severe agitation alternating with coma
63 TOXIC SYNDROMES CASE 16 A 55 y/o male alcoholic presents with lethargy, confusion, nausea, vomiting and abdominal pain. HR Mild epigastric tenderness 95 remainder of vital signs normal Labs: Na 140 Cl 110 Bicarb 24 K 3.8 BUN 21 Cr 1.2 Glucose 100 ETOH = 0 Measured osmolality = 372 CLUE: urine is positive for acetone
64 A 4 y/o girl is found comatose in a closet in her home. She is dressed in her mother s clothes, shoes and jewelry. Also in the closet are her doll, several suitcases and several cans of cleaning fluids and pesticides. In the ED, she is comatose, with a regular HR of 108 bpm and BP 80 mm Hg by palpation. She has pinpoint pupils, dry skin and clear lungs. No bowel sounds are audible. The parents are certain that all medications in the home are secured in a medicine cabinet, and all other toxic chemicals are locked under the kitchen sink
65 The child is stabilized in the ED. The HR decreases to 96 and the BP rises to 90 mm Hg. She becomes awake, alert and her pupils dilate to normal size after receiving a dose of 2 mg naloxone IV. The parents still emphatically deny the use of any natural or synthetic opiates at home. Upon returning home, the father, while searching through the closet, discovers an open bottle of Lomotil tablets in an open suitcase. The antidiarrheal medication had been left there after a foreign trip.
66 Lomotil Diphenoxylate 2.5mg + atropine 0.025mg Lethargy reported after ingestion of 1 tablet CNS depression may be delayed up to 18 hours Treatment is supportive Naloxone for opioid effects Physostigmine has been used for anticholinergic toxicity
67 A mother runs into your office with her 2 yearold son, anxiously stating that he is difficult to arouse. He awoke that morning and had breakfast as usual, then fell asleep two hours later. The child has now been sleeping for about an hour. No one witnessed trauma. Only medications in the house are APAP and ASA both stored in the bathroom medicine cabinet. No history of previous similar episodes. No family history of metabolic disorders.
68 Pulse 110, BP 90/60, RR 8, T 36 (96.8) Obtunded, responding only to painful stimuli by crying and moving purposelessly. Skin cool, slightly diphoretic. Pupils midsize, neuro exam non-focal and symmetric, with slight hyporeflexia in all extremities. At the end of the exam the child has a generalized, tonic-clonic seizure.
69 Chem-strip blood sugar = 20 mg% Further history reveals that the parents had hosted a party the night before that had continued late into the night.
70 Summary
71
72
73
74 Conclusions Safe use of cardiovascular and other resuscitation drugs requires understanding of autonomic nervous system Assessment for toxidromes can assist in diagnosis of intoxication when lab testing is not available Call the Poison Center it s a free call and not a sign of weakness!!
Adrenergic, Adrenergic Blockers, Cholinergic and Cholinergic Blockers
 Adrenergic, Adrenergic Blockers, Cholinergic and Cholinergic Blockers Objective 1: Explain the difference between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems Autonomic Nervous System Sympathetic
Adrenergic, Adrenergic Blockers, Cholinergic and Cholinergic Blockers Objective 1: Explain the difference between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems Autonomic Nervous System Sympathetic
ADRENERGIC RECEPTOR AGONIST,CLASSIFICATION AND MECHANISM OF ACTION.
 ADRENERGIC RECEPTOR AGONIST,CLASSIFICATION AND MECHANISM OF ACTION. LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of lecture students should be able to know, Adrenergic receptor agonist, Classification and mechanism
ADRENERGIC RECEPTOR AGONIST,CLASSIFICATION AND MECHANISM OF ACTION. LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of lecture students should be able to know, Adrenergic receptor agonist, Classification and mechanism
Key Points. Autonomic Nervous System Drugs. Autonomic effects Sympathetic. Drugs can modify ANS activity by: Autonomic Nervous System
 Key Points Autonomic Nervous System Drugs Autonomic drugs work at the synapses, Drugs either suppress or magnify the sympathetic or parasympathetic effect, Drugs don t work on a single target organ so
Key Points Autonomic Nervous System Drugs Autonomic drugs work at the synapses, Drugs either suppress or magnify the sympathetic or parasympathetic effect, Drugs don t work on a single target organ so
Chapter 15: The Autonomic Nervous System
 Chapter 15: The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Objectives COMPARISON OF SOMATIC AND AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEMS 1. List the structural and functional characteristics of the autonomic nervous system. 2.
Chapter 15: The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Objectives COMPARISON OF SOMATIC AND AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEMS 1. List the structural and functional characteristics of the autonomic nervous system. 2.
Chapter 13. Sympathetic Nervous System. Basic Functions of the Nervous System. Divisions of the Peripheral Nervous System
 Chapter 13 Drugs Affecting the Autonomic Basic Functions of the Recognizing changes in Internal environment External environment Processing and integrating changes Reacting to changes Upper Saddle River,
Chapter 13 Drugs Affecting the Autonomic Basic Functions of the Recognizing changes in Internal environment External environment Processing and integrating changes Reacting to changes Upper Saddle River,
Pharmacology - Problem Drill 06: Autonomic Pharmacology - Adrenergic System
 Pharmacology - Problem Drill 06: Autonomic Pharmacology - Adrenergic System Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as 1. What
Pharmacology - Problem Drill 06: Autonomic Pharmacology - Adrenergic System Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as 1. What
Mammalian Physiology. Autonomic Nervous System UNLV. PHYSIOLOGY, Chapter 11 Berne, Levy, Koeppen, Stanton UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA LAS VEGAS
 Mammalian Physiology Autonomic Nervous System UNLV 1 UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA LAS VEGAS PHYSIOLOGY, Chapter 11 Berne, Levy, Koeppen, Stanton Objectives Describe the organization of the autonomic nervous system
Mammalian Physiology Autonomic Nervous System UNLV 1 UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA LAS VEGAS PHYSIOLOGY, Chapter 11 Berne, Levy, Koeppen, Stanton Objectives Describe the organization of the autonomic nervous system
ADRENERGIC AND ANTI-ADRENERGIC DRUGS. Mr. D.Raju, M.pharm, Lecturer
 ADRENERGIC AND ANTI-ADRENERGIC DRUGS Mr. D.Raju, M.pharm, Lecturer SYMPATHETIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Fight or flight response results in: 1. Increased BP 2. Increased blood flow to brain, heart and skeletal muscles
ADRENERGIC AND ANTI-ADRENERGIC DRUGS Mr. D.Raju, M.pharm, Lecturer SYMPATHETIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Fight or flight response results in: 1. Increased BP 2. Increased blood flow to brain, heart and skeletal muscles
Drugs affecting the autonomic nervous system. Objectives. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) 12/23/2014
 Drugs affecting the autonomic nervous system N231 Nursing Pharmacology Objectives Analyze the implementation of the nursing process in the promotion and maintenance of system stability for individuals
Drugs affecting the autonomic nervous system N231 Nursing Pharmacology Objectives Analyze the implementation of the nursing process in the promotion and maintenance of system stability for individuals
PHARMACOLOGY OF VNS VARIANT 1 1) Anti-ChEs: contraindications and precautions. 2) Examples of Cholinesterase reactivators. 3) Cholinoblockers-natural
 VARIANT 1 Anti-ChEs: contraindications and precautions. Examples of Cholinesterase reactivators. Cholinoblockers-natural alkaloids (examples). 4) GIT-effects of Atropine. 5) Pharmacologic characteristic
VARIANT 1 Anti-ChEs: contraindications and precautions. Examples of Cholinesterase reactivators. Cholinoblockers-natural alkaloids (examples). 4) GIT-effects of Atropine. 5) Pharmacologic characteristic
D.U.C. Assist. Lec. Faculty of Dentistry General Physiology Ihsan Dhari. The Autonomic Nervous System
 The Autonomic Nervous System The portion of the nervous system that controls most visceral functions of the body is called the autonomic nervous system. This system helps to control arterial pressure,
The Autonomic Nervous System The portion of the nervous system that controls most visceral functions of the body is called the autonomic nervous system. This system helps to control arterial pressure,
Adrenergic agonists. R. A. Nimmi Dilsha Department of pharmacy Faculty of Health Sciences The Open University of Sri Lanka
 Adrenergic agonists R. A. Nimmi Dilsha Department of pharmacy Faculty of Health Sciences The Open University of Sri Lanka Outline Recall Introduction to adrenergic agonists Classification of adrenergic
Adrenergic agonists R. A. Nimmi Dilsha Department of pharmacy Faculty of Health Sciences The Open University of Sri Lanka Outline Recall Introduction to adrenergic agonists Classification of adrenergic
Chapter 15. The Autonomic Nervous. The Autonomic Nervous System. Autonomic Motor Pathways. ANS vs. SNS
 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter 15 The subconscious involuntary nervous system Regulates activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle & certain glands The Autonomic Nervous System 1 2 ANS vs. SNS Somatic
The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter 15 The subconscious involuntary nervous system Regulates activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle & certain glands The Autonomic Nervous System 1 2 ANS vs. SNS Somatic
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture
 1 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 2 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and certain
1 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 2 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and certain
Chapter 15. Neurotransmitters of the ANS
 Chapter 15 Neurotransmitters of the ANS Neurotransmitters and Receptors How can the same ANS neurons create different effects on different target tissue? Variety of neurotransmitters Secondly, different
Chapter 15 Neurotransmitters of the ANS Neurotransmitters and Receptors How can the same ANS neurons create different effects on different target tissue? Variety of neurotransmitters Secondly, different
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. 7-4. Given a group of statements, select the best definition of the term adrenergic (sympathomimetic) drug.
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 7 Adrenergic Agents. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 7-1 through 7-6. LESSON OBJECTIVES 7-1. Given a group of statements, select the mechanism(s) of action of drugs which stimulate
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 7 Adrenergic Agents. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 7-1 through 7-6. LESSON OBJECTIVES 7-1. Given a group of statements, select the mechanism(s) of action of drugs which stimulate
Case 1: Anticholinesterase
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.151: Principles of Pharmocology Instructor: Dr. Carl Rosow, Dr. David Standaert and Prof. Gary Strichartz Case 1: Anticholinesterase February
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.151: Principles of Pharmocology Instructor: Dr. Carl Rosow, Dr. David Standaert and Prof. Gary Strichartz Case 1: Anticholinesterase February
Autonomic Nervous System
 MOST FREQUENTLY USED DRUG CATEGORIES FOR AUTONOMIC SYSTEM THERAPY Beta 1 Adrenergic Blockers (Anatgonists) - Work on the Heart Beta 1 Adrenergic receptors are typically found on the heart and is a means
MOST FREQUENTLY USED DRUG CATEGORIES FOR AUTONOMIC SYSTEM THERAPY Beta 1 Adrenergic Blockers (Anatgonists) - Work on the Heart Beta 1 Adrenergic receptors are typically found on the heart and is a means
The Autonomic Nervous System Physiology Study Guide, Chapter 9
 Name: The Autonomic Nervous System Physiology Study Guide, Chapter 9 Lab Time: 1 Part I. Clinical Applications and Short Essay 1. After surgery, patients are often temporarily unable to urinate, and bowel
Name: The Autonomic Nervous System Physiology Study Guide, Chapter 9 Lab Time: 1 Part I. Clinical Applications and Short Essay 1. After surgery, patients are often temporarily unable to urinate, and bowel
CHAPTER 16: THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
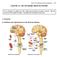 Unit 4: The Autonomic Nervous System 254 CHAPTER 16: THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Read: Chapter 16, pages 517-534. Read only the topics covered in lecture. We will not cover this chapter in detail. Complete
Unit 4: The Autonomic Nervous System 254 CHAPTER 16: THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Read: Chapter 16, pages 517-534. Read only the topics covered in lecture. We will not cover this chapter in detail. Complete
1. The potential sites of action for sympathomimetics and the difference between a direct and indirect acting agonist.
 1 OBI 836 The Autonomic Nervous System-Sympathomimetics M.T. Piascik August 29, 2012 Learning Objectives Lecture II The student should be able to explain or describe 1. The potential sites of action for
1 OBI 836 The Autonomic Nervous System-Sympathomimetics M.T. Piascik August 29, 2012 Learning Objectives Lecture II The student should be able to explain or describe 1. The potential sites of action for
Pharmacology 260 Online Course Schedule Spring 2012
 Pharmacology 260 Online Course Spring 2012 The topics listed below do not necessarily correspond to a 1 - hour lecture period. You should cover the topics for each week at some time during that week. Readings
Pharmacology 260 Online Course Spring 2012 The topics listed below do not necessarily correspond to a 1 - hour lecture period. You should cover the topics for each week at some time during that week. Readings
Please read chapter 15, The Autonomic Nervous System, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class.
 Please read chapter 15,, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class. I. Introduction to the autonomic nervous system: Briefly describe the autonomic nervous system.
Please read chapter 15,, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class. I. Introduction to the autonomic nervous system: Briefly describe the autonomic nervous system.
Chapter 15. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes. general properties Anatomy. Autonomic effects on target organs
 Chapter 15 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes general properties Anatomy Autonomic effects on target organs Central control of autonomic function 15-1 Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Chapter 15 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes general properties Anatomy Autonomic effects on target organs Central control of autonomic function 15-1 Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies,
The somatic nervous system regulates conscious movements via efferent nerves exit from the CNS to skeletal muscles.
 Lecture 1 Nervous system The nervous system is divided into the central nervous system (CNS; brain and spinal cord) and peripheral nervous system (somatic and autonomic nervous systems; comprised of nerves
Lecture 1 Nervous system The nervous system is divided into the central nervous system (CNS; brain and spinal cord) and peripheral nervous system (somatic and autonomic nervous systems; comprised of nerves
Adrenergic receptors lec 9, part 2. 16/10/2014 Dr. Laila M. Matalqah Rama Kamal Ali Treany
 Adrenergic receptors lec 9, part 2 16/10/2014 Dr. Laila M. Matalqah Rama Kamal Ali Treany Pharmacology of ANS Adrenergic Agonists Adrenergic receptors:- - It is a receptor which is located in the peripheral
Adrenergic receptors lec 9, part 2 16/10/2014 Dr. Laila M. Matalqah Rama Kamal Ali Treany Pharmacology of ANS Adrenergic Agonists Adrenergic receptors:- - It is a receptor which is located in the peripheral
Autonomic Receptor Functions
 Part II Autonomic Receptor Functions Summary of ANS overview Pharmacological classification of ANS is based on neurotransmitters: cholinergic, adrenergic, and dopaminergic. Major sites for pharmacological
Part II Autonomic Receptor Functions Summary of ANS overview Pharmacological classification of ANS is based on neurotransmitters: cholinergic, adrenergic, and dopaminergic. Major sites for pharmacological
Autonomic (ANS) Pharmacology. Sympathetic Nervous System
 Autonomic (ANS) Pharmacology Sympathetic Nervous System Autonomic and Somatic Innervation Skeletal muscle is innervated by somatic nerves, controlling voluntary actions All other innervated structures
Autonomic (ANS) Pharmacology Sympathetic Nervous System Autonomic and Somatic Innervation Skeletal muscle is innervated by somatic nerves, controlling voluntary actions All other innervated structures
Adrenergic agonists:-
 Adrenergic agonists:- A.) Catecholamines They are called catecholamines because they contain a catechol group, they are water-soluble and are 50% bound to plasma proteins, so they circulate in the bloodstream.
Adrenergic agonists:- A.) Catecholamines They are called catecholamines because they contain a catechol group, they are water-soluble and are 50% bound to plasma proteins, so they circulate in the bloodstream.
Physiology and Pharmacology
 Pharmacokinetics Physiology and Pharmacology Pharmacokinetics of Local Anesthetics Uptake Oral Route Topical Route Injection Distribution Metabolism (Biotransformation) Excretion Uptake So what? Vasoactivity
Pharmacokinetics Physiology and Pharmacology Pharmacokinetics of Local Anesthetics Uptake Oral Route Topical Route Injection Distribution Metabolism (Biotransformation) Excretion Uptake So what? Vasoactivity
ACLS PHARMACOLOGY 2011 Guidelines
 ACLS PHARMACOLOGY 2011 Guidelines ADENOSINE Narrow complex tachycardias or wide complex tachycardias that may be supraventricular in nature. It is effective in treating 90% of the reentry arrhythmias.
ACLS PHARMACOLOGY 2011 Guidelines ADENOSINE Narrow complex tachycardias or wide complex tachycardias that may be supraventricular in nature. It is effective in treating 90% of the reentry arrhythmias.
PHC 313 The 7 th. Lecture. Adrenergic Agents
 PHC 313 The 7 th. Lecture Adrenergic Agents Introduction Introduction Adrenergic agents are a broad class of agents employed in the treatment of many disorders. They are those chemical agents that exert
PHC 313 The 7 th. Lecture Adrenergic Agents Introduction Introduction Adrenergic agents are a broad class of agents employed in the treatment of many disorders. They are those chemical agents that exert
Safety issues. Any stress test may have some risks, and you should consult with your physician prior to the test if you have any concerns.
 Instructions for Nuclear Cardiology Stress Tests An intravenous catheter (I.V.) will be placed in your arm. Several electrodes will also be placed on your chest in order to record your heart rhythm (as
Instructions for Nuclear Cardiology Stress Tests An intravenous catheter (I.V.) will be placed in your arm. Several electrodes will also be placed on your chest in order to record your heart rhythm (as
Arrest. What s a Nurse to do?
 Benzo s, Blockers, Coma & Cardiac Arrest What s a Nurse to do? Objectives Review of ACLS Algorithms for Cardiac Arrest Management Discuss the toxicology of Beta Blocker Poisoning Describe the clinical
Benzo s, Blockers, Coma & Cardiac Arrest What s a Nurse to do? Objectives Review of ACLS Algorithms for Cardiac Arrest Management Discuss the toxicology of Beta Blocker Poisoning Describe the clinical
Opioid Analgesics. Week 19
 Opioid Analgesics Week 19 Analgesic Vocabulary Analgesia Narcotic Opiate Opioid Agonist Antagonist Narcotic Analgesics Controlled substances Opioid analgesics derived from poppy Opiates include morphine,
Opioid Analgesics Week 19 Analgesic Vocabulary Analgesia Narcotic Opiate Opioid Agonist Antagonist Narcotic Analgesics Controlled substances Opioid analgesics derived from poppy Opiates include morphine,
Naloxone treatment of opioid overdose
 Naloxone treatment of opioid overdose Opioids Chemicals that act in the brain to relieve pain, often use to suppress cough, treat addiction, and provide comfort After prolonged use of opioids, increasing
Naloxone treatment of opioid overdose Opioids Chemicals that act in the brain to relieve pain, often use to suppress cough, treat addiction, and provide comfort After prolonged use of opioids, increasing
The Autonomic Nervous System Part II - Basic Pharmacology
 Dr Oliver Pratt, Specialist Registrar Dr Carl Gwinnutt, Consultant Department of Anaesthesia, Hope Hospital, Salford M6 8HD, UK. e mail: carl.gwinnutt@srht.nhs.uk Tutorial Of The Week The Autonomic Nervous
Dr Oliver Pratt, Specialist Registrar Dr Carl Gwinnutt, Consultant Department of Anaesthesia, Hope Hospital, Salford M6 8HD, UK. e mail: carl.gwinnutt@srht.nhs.uk Tutorial Of The Week The Autonomic Nervous
Diabetic Emergencies. David Hill, D.O.
 Diabetic Emergencies David Hill, D.O. Class Outline Diabetic emergency/glucometer training Identify the different signs of insulin shock Diabetic coma, and HHNK Participants will understand the treatment
Diabetic Emergencies David Hill, D.O. Class Outline Diabetic emergency/glucometer training Identify the different signs of insulin shock Diabetic coma, and HHNK Participants will understand the treatment
Share the important information in this Medication Guide with members of your household.
 MEDICATION GUIDE BUPRENORPHINE (BUE-pre-NOR-feen) Sublingual Tablets, CIII IMPORTANT: Keep buprenorphine sublingual tablets in a secure place away from children. Accidental use by a child is a medical
MEDICATION GUIDE BUPRENORPHINE (BUE-pre-NOR-feen) Sublingual Tablets, CIII IMPORTANT: Keep buprenorphine sublingual tablets in a secure place away from children. Accidental use by a child is a medical
ANNE ARUNDEL MEDICAL CENTER CRITICAL CARE MEDICATION MANUAL DEPARTMENT OF NURSING AND PHARMACY. Guidelines for Use of Intravenous Isoproterenol
 ANNE ARUNDEL MEDICAL CENTER CRITICAL CARE MEDICATION MANUAL DEPARTMENT OF NURSING AND PHARMACY Guidelines for Use of Intravenous Isoproterenol Major Indications Status Asthmaticus As a last resort for
ANNE ARUNDEL MEDICAL CENTER CRITICAL CARE MEDICATION MANUAL DEPARTMENT OF NURSING AND PHARMACY Guidelines for Use of Intravenous Isoproterenol Major Indications Status Asthmaticus As a last resort for
STAGES OF SHOCK. IRREVERSIBLE SHOCK Heart deteriorates until it can no longer pump and death occurs.
 STAGES OF SHOCK SHOCK : A profound disturbance of circulation and metabolism, which leads to inadequate perfusion of all organs which are needed to maintain life. COMPENSATED NONPROGRESSIVE SHOCK 30 sec
STAGES OF SHOCK SHOCK : A profound disturbance of circulation and metabolism, which leads to inadequate perfusion of all organs which are needed to maintain life. COMPENSATED NONPROGRESSIVE SHOCK 30 sec
KAP Keys. For Physicians. Based on TIP 40 Clinical Guidelines for the Use of Buprenorphine in the Treatment. of Opioid Addiction
 Clinical Guidelines for the Use of Buprenorphine in the Treatment of Opioid Addiction Knowledge Application Program KAP Keys For Physicians Based on TIP 40 Clinical Guidelines for the Use of Buprenorphine
Clinical Guidelines for the Use of Buprenorphine in the Treatment of Opioid Addiction Knowledge Application Program KAP Keys For Physicians Based on TIP 40 Clinical Guidelines for the Use of Buprenorphine
Inotropes/Vasoactive Agents Hina N. Patel, Pharm.D., BCPS Cathy Lawson, Pharm.D., BCPS
 Inotropes/Vasoactive Agents Hina N. Patel, Pharm.D., BCPS Cathy Lawson, Pharm.D., BCPS 1. Definition -an agent that affects the contractility of the heart -may be positive (increases contractility) or
Inotropes/Vasoactive Agents Hina N. Patel, Pharm.D., BCPS Cathy Lawson, Pharm.D., BCPS 1. Definition -an agent that affects the contractility of the heart -may be positive (increases contractility) or
OTC Abuse. Dr. Eman Said Abd-Elkhalek Lecturer of Pharmacology & Toxicology Faculty of Pharmacy Mansoura University
 OTC Abuse Dr. Eman Said Abd-Elkhalek Lecturer of Pharmacology & Toxicology Faculty of Pharmacy Mansoura University Opiates Abuse Opioids are a group of natural, partially synthetic, or synthetic drugs
OTC Abuse Dr. Eman Said Abd-Elkhalek Lecturer of Pharmacology & Toxicology Faculty of Pharmacy Mansoura University Opiates Abuse Opioids are a group of natural, partially synthetic, or synthetic drugs
DRUG INTERACTIONS: WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW. Council on Family Health
 DRUG INTERACTIONS: WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW Council on Family Health Drug Interactions There are more opportunities today than ever before to learn about your health and to take better care of yourself. It
DRUG INTERACTIONS: WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW Council on Family Health Drug Interactions There are more opportunities today than ever before to learn about your health and to take better care of yourself. It
Chapter 16. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives 9/11/2012. Shock. Explain difference between compensated and uncompensated shock
 Chapter 16 Shock Learning Objectives Explain difference between compensated and uncompensated shock Differentiate among 5 causes and types of shock: Hypovolemic Cardiogenic Neurogenic Septic Anaphylactic
Chapter 16 Shock Learning Objectives Explain difference between compensated and uncompensated shock Differentiate among 5 causes and types of shock: Hypovolemic Cardiogenic Neurogenic Septic Anaphylactic
UNIT VIII NARCOTIC ANALGESIA
 UNIT VIII NARCOTIC ANALGESIA Objective Review the definitions of Analgesic, Narcotic and Antagonistic. List characteristics of Opioid analgesics in terms of mechanism of action, indications for use and
UNIT VIII NARCOTIC ANALGESIA Objective Review the definitions of Analgesic, Narcotic and Antagonistic. List characteristics of Opioid analgesics in terms of mechanism of action, indications for use and
ACID-BASE DISORDER. Presenter: NURUL ATIQAH AWANG LAH Preceptor: PN. KHAIRUL BARIAH JOHAN
 ACID-BASE DISORDER Presenter: NURUL ATIQAH AWANG LAH Preceptor: PN. KHAIRUL BARIAH JOHAN OBJECTIVES OF PRESENTATION 1. To refresh knowledge of acid-base disorders 2. To evaluate acid-base disorders using
ACID-BASE DISORDER Presenter: NURUL ATIQAH AWANG LAH Preceptor: PN. KHAIRUL BARIAH JOHAN OBJECTIVES OF PRESENTATION 1. To refresh knowledge of acid-base disorders 2. To evaluate acid-base disorders using
Like cocaine, heroin is a drug that is illegal in some areas of the world. Heroin is highly addictive.
 Heroin Introduction Heroin is a powerful drug that affects the brain. People who use it can form a strong addiction. Addiction is when a drug user can t stop taking a drug, even when he or she wants to.
Heroin Introduction Heroin is a powerful drug that affects the brain. People who use it can form a strong addiction. Addiction is when a drug user can t stop taking a drug, even when he or she wants to.
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
 AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Somatic efferent and ANS Somatic Efferent Control is over skeletal muscles. External environment This division of the PNS responds to some change in the external environment. single
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Somatic efferent and ANS Somatic Efferent Control is over skeletal muscles. External environment This division of the PNS responds to some change in the external environment. single
Routes of Use. Overdose and EMS. Injection. Ingestion. Inhalation. Absorption 1/2/2013. Injection Ingestion Inhalation Absorption.
 Routes of Use Overdose and EMS Injection Ingestion Inhalation Absorption Shaun Pitts, AEMT Venomous bites Common drugs Heroin Cocaine Meth Injection Ingestion Cleaning solutions Household plants Medications
Routes of Use Overdose and EMS Injection Ingestion Inhalation Absorption Shaun Pitts, AEMT Venomous bites Common drugs Heroin Cocaine Meth Injection Ingestion Cleaning solutions Household plants Medications
RESIDENT ASSESSMENT TOOL
 RESIDENT ASSESSMENT TOOL To be completed by a physician, certified nurse practitioner, registered nurse, or physician assistant within 30 days prior to admission, at least annually, & within 48 hours after
RESIDENT ASSESSMENT TOOL To be completed by a physician, certified nurse practitioner, registered nurse, or physician assistant within 30 days prior to admission, at least annually, & within 48 hours after
1. According to recent US national estimates, which of the following substances is associated
 1 Chapter 36. Substance-Related, Self-Assessment Questions 1. According to recent US national estimates, which of the following substances is associated with the highest incidence of new drug initiates
1 Chapter 36. Substance-Related, Self-Assessment Questions 1. According to recent US national estimates, which of the following substances is associated with the highest incidence of new drug initiates
DIPHENHYDRAMINE (Benadryl)
 DIPHENHYDRAMINE (Benadryl) Classification: Antihistamine (H1 blocker) Antihistamine; appear to compete with histamine for cell receptor sites on effector cells. Therapeutic Relieves effects of histamine
DIPHENHYDRAMINE (Benadryl) Classification: Antihistamine (H1 blocker) Antihistamine; appear to compete with histamine for cell receptor sites on effector cells. Therapeutic Relieves effects of histamine
Philip Moore DO, Toxicology Fellow, PinnacleHealth Toxicology Center Joanne Konick-McMahan RN MSRN, Staff RN, PinnacleHealth
 Philip Moore DO, Toxicology Fellow, PinnacleHealth Toxicology Center Joanne Konick-McMahan RN MSRN, Staff RN, PinnacleHealth I. II. Background A. AWS can occur in anyone who consumes alcohol B. Risk correlates
Philip Moore DO, Toxicology Fellow, PinnacleHealth Toxicology Center Joanne Konick-McMahan RN MSRN, Staff RN, PinnacleHealth I. II. Background A. AWS can occur in anyone who consumes alcohol B. Risk correlates
PHEOCHROMOCYTOMA. Pheochromocytoma. Pheochromocytoma. Signs and Symptoms. Extra-Adrenal Sites. Factors associated with pheochromocytoma include:
 Pheochromocytoma PHEOCHROMOCYTOMA By: Belkys Cota, Priscilla Carpio, Melissa Houchin, Leslie N. Beltran. Rare neuroendocrine tumor of the medulla of the adrenal glands (originating in the chromaffin cells),
Pheochromocytoma PHEOCHROMOCYTOMA By: Belkys Cota, Priscilla Carpio, Melissa Houchin, Leslie N. Beltran. Rare neuroendocrine tumor of the medulla of the adrenal glands (originating in the chromaffin cells),
Milwaukee School of Engineering Gerrits@msoe.edu. Case Study: Factors that Affect Blood Pressure Instructor Version
 Case Study: Factors that Affect Blood Pressure Instructor Version Goal This activity (case study and its associated questions) is designed to be a student-centered learning activity relating to the factors
Case Study: Factors that Affect Blood Pressure Instructor Version Goal This activity (case study and its associated questions) is designed to be a student-centered learning activity relating to the factors
8/6/2010. Name of medication Concentration (1:1,000 or 1mg/1ml) Expiration date
 Learning Objectives: Anaphylaxis & Epinephrine Administration by the EMT Adapted with permission from the Pilot Project for the Administration of Epinephrine by Washington EMTs With successful completion
Learning Objectives: Anaphylaxis & Epinephrine Administration by the EMT Adapted with permission from the Pilot Project for the Administration of Epinephrine by Washington EMTs With successful completion
MEDICATION GUIDE SUBOXONE (Sub-OX-own) (buprenorphine and naloxone) Sublingual Film for sublingual or buccal administration (CIII)
 MEDICATION GUIDE SUBOXONE (Sub-OX-own) (buprenorphine and naloxone) Sublingual Film for sublingual or buccal administration (CIII) IMPORTANT: Keep SUBOXONE in a secure place away from children. Accidental
MEDICATION GUIDE SUBOXONE (Sub-OX-own) (buprenorphine and naloxone) Sublingual Film for sublingual or buccal administration (CIII) IMPORTANT: Keep SUBOXONE in a secure place away from children. Accidental
Procedure for Inotrope Administration in the home
 Procedure for Inotrope Administration in the home Purpose This purpose of this procedure is to define the care used when administering inotropic agents intravenously in the home This includes: A. Practice
Procedure for Inotrope Administration in the home Purpose This purpose of this procedure is to define the care used when administering inotropic agents intravenously in the home This includes: A. Practice
Integration and Coordination of the Human Body. Nervous System
 I. General Info Integration and Coordination of the Human Body A. Both the and system are responsible for maintaining 1. Homeostasis is the process by which organisms keep internal conditions despite changes
I. General Info Integration and Coordination of the Human Body A. Both the and system are responsible for maintaining 1. Homeostasis is the process by which organisms keep internal conditions despite changes
Elements for a public summary. VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology. VI.2.2 Summary of treatment benefits
 VI.2 Elements for a public summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Pain is one of the most common reasons for a patient to seek medical attention. Moderate or severe intensity pain can be acute
VI.2 Elements for a public summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Pain is one of the most common reasons for a patient to seek medical attention. Moderate or severe intensity pain can be acute
MEDICATION GUIDE. What is Morphine Sulfate Oral Solution?
 MEDICATION GUIDE Morphine Sulfate (mor-pheen) (CII) Oral Solution IMPORTANT: Keep Morphine Sulfate Oral Solution in a safe place away from children. Accidental use by a child is a medical emergency and
MEDICATION GUIDE Morphine Sulfate (mor-pheen) (CII) Oral Solution IMPORTANT: Keep Morphine Sulfate Oral Solution in a safe place away from children. Accidental use by a child is a medical emergency and
PREP for Boards Substance Abuse. Jeremy Jones, DO Oklahoma State University Center for Health Sciences
 PREP for Boards Substance Abuse Jeremy Jones, DO Oklahoma State University Center for Health Sciences Table of Contents Questions And Then Answers Resources 2 1. PREP 2008 Question 133 A 15-year-old high
PREP for Boards Substance Abuse Jeremy Jones, DO Oklahoma State University Center for Health Sciences Table of Contents Questions And Then Answers Resources 2 1. PREP 2008 Question 133 A 15-year-old high
DRUG USE. 1300 136 588 ndss.com.au AND TYPE 1 DIABETES
 DRUG USE AND TYPE 1 DIABETES 1300 136 588 ndss.com.au The National Diabetes Services Scheme (NDSS) is an initiative of the Australian Government administered by Diabetes Australia. Contents Topic Page
DRUG USE AND TYPE 1 DIABETES 1300 136 588 ndss.com.au The National Diabetes Services Scheme (NDSS) is an initiative of the Australian Government administered by Diabetes Australia. Contents Topic Page
SUBSTANCE USE DISORDERS EMERGENCIES AND MANAGEMENT
 SUBSTANCE USE DISORDERS EMERGENCIES AND MANAGEMENT Objectives Review importance of substance use disorders (SUDs) Identify emergencies related to SUDs Discuss general principles of management Discuss management
SUBSTANCE USE DISORDERS EMERGENCIES AND MANAGEMENT Objectives Review importance of substance use disorders (SUDs) Identify emergencies related to SUDs Discuss general principles of management Discuss management
And the. Two types of orders:
 1 PHARMACOLOGY And the EMT-B 2 MEDICAL DIRECTION Must have Dr. s orders to administer any drug to a Pt Local medical director can override any state set protocols Two types of orders: On-line : verbal
1 PHARMACOLOGY And the EMT-B 2 MEDICAL DIRECTION Must have Dr. s orders to administer any drug to a Pt Local medical director can override any state set protocols Two types of orders: On-line : verbal
Here is a drug list that you need to know before taking the NREMT-P exam!! Taken from the book EMS NOTES.com
 Here is a drug list that you need to know before taking the NREMT-P exam!! Taken from the book EMS NOTES.com Special thanks to the number #1 internet training site id44.com and also to (NOTE) Please remember
Here is a drug list that you need to know before taking the NREMT-P exam!! Taken from the book EMS NOTES.com Special thanks to the number #1 internet training site id44.com and also to (NOTE) Please remember
Alcohol Withdrawal. Introduction. Blood Alcohol Concentration. DSM-IV Criteria/Alcohol Abuse. Pharmacologic Effects of Alcohol
 Pharmacologic Effects of Alcohol Alcohol Withdrawal Kristi Theobald, Pharm.D., BCPS Therapeutics III Fall 2003 Inhibits glutamate receptor function (NMDA receptor) Inhibits excitatory neurotransmission
Pharmacologic Effects of Alcohol Alcohol Withdrawal Kristi Theobald, Pharm.D., BCPS Therapeutics III Fall 2003 Inhibits glutamate receptor function (NMDA receptor) Inhibits excitatory neurotransmission
Naloxone Hydrochloride Injection PRODUCT INFORMATION
 Naloxone Hydrochloride Injection PRODUCT INFORMATION DESCRIPTION Naloxone hydrochloride is 17-allyl-4,5α-epoxy-3,14-dihydroxymorphinan-6-one hydrochloride; C 19 H 21 NO 4.HCl. It is an off-white powder
Naloxone Hydrochloride Injection PRODUCT INFORMATION DESCRIPTION Naloxone hydrochloride is 17-allyl-4,5α-epoxy-3,14-dihydroxymorphinan-6-one hydrochloride; C 19 H 21 NO 4.HCl. It is an off-white powder
Dr.Karima Elshamy Faculty of Nursing Mansoura University Egypt
 Body Temperature ١ Dr.Karima Elshamy Faculty of Nursing Mansoura University Egypt ٢ Learning objectives: At the end of this lecture the student should be able to: Define body temperature. Identify sites
Body Temperature ١ Dr.Karima Elshamy Faculty of Nursing Mansoura University Egypt ٢ Learning objectives: At the end of this lecture the student should be able to: Define body temperature. Identify sites
ALCOHOL WITHDRAWAL SYNDROME
 ALCOHOL WITHDRAWAL SYNDROME INTRODUCTION Alcohol is the most commonly abused drug in the United States and when someone who chronically abuses alcohol does not drink, that person is at risk for developing
ALCOHOL WITHDRAWAL SYNDROME INTRODUCTION Alcohol is the most commonly abused drug in the United States and when someone who chronically abuses alcohol does not drink, that person is at risk for developing
Drug addiction. These factors increase the likelihood of your having an addiction to a legal or an illegal drug:
 Drug addiction You may be hooked emotionally and psychologically. You may have a physical dependence, too. If you're addicted to a drug whether it's legal or illegal you have intense cravings for it. You
Drug addiction You may be hooked emotionally and psychologically. You may have a physical dependence, too. If you're addicted to a drug whether it's legal or illegal you have intense cravings for it. You
Pharmacology Drug Chart
 Pharmacology Drug Chart Cholinergic Agonists Acetylcholine Muscarinic HR, CO and BP Salivary Secretions Secretions and Motility in the GIT Bronchiolar Secretions Miosis (Constriction of the Pupil) Pharmacology
Pharmacology Drug Chart Cholinergic Agonists Acetylcholine Muscarinic HR, CO and BP Salivary Secretions Secretions and Motility in the GIT Bronchiolar Secretions Miosis (Constriction of the Pupil) Pharmacology
4/13/15. Case 1. COWS = Clinical Opioid Withdrawal Scale. Special Populations
 Special Populations ACMT Addiction Academy Faculty Panelists 1 Case 1 The Toxicology service is consulted from the ED as the county jail has brought in a 21 year-old Hispanic woman who is 18 weeks pregnant.
Special Populations ACMT Addiction Academy Faculty Panelists 1 Case 1 The Toxicology service is consulted from the ED as the county jail has brought in a 21 year-old Hispanic woman who is 18 weeks pregnant.
Drug Abuse/Overdose. By : Dr. Ragia M Hegazy, M.D. Assistant professor of Clinical Toxicology
 Drug Abuse/Overdose By : Dr. Ragia M Hegazy, M.D. Assistant professor of Clinical Toxicology OPIATES DESIRED EFFECTS OF USE The Rush Sedation Euphoria Analgesia OPIUM COMES FROM THE POPPY PLANT PAPAVER
Drug Abuse/Overdose By : Dr. Ragia M Hegazy, M.D. Assistant professor of Clinical Toxicology OPIATES DESIRED EFFECTS OF USE The Rush Sedation Euphoria Analgesia OPIUM COMES FROM THE POPPY PLANT PAPAVER
Additional Supplements
 Additional Supplements The following additional supplements are included here because they are the most popular at this time. This section is not intended as an endorsement to take these products, but
Additional Supplements The following additional supplements are included here because they are the most popular at this time. This section is not intended as an endorsement to take these products, but
Management in the pre-hospital setting
 Management in the pre-hospital setting Inflammation of the joints Two main types: Osteoarthritis - cartilage loss from wear and tear Rheumatoid arthritis - autoimmune disorder Affects all age groups,
Management in the pre-hospital setting Inflammation of the joints Two main types: Osteoarthritis - cartilage loss from wear and tear Rheumatoid arthritis - autoimmune disorder Affects all age groups,
Diabetes Expert Witness on: Diabetic Hypoglycemia in Nursing Homes
 Diabetes Expert Witness on: Diabetic Hypoglycemia in Nursing Homes Nursing home patients with diabetes treated with insulin and certain oral diabetes medications (i.e. sulfonylureas and glitinides) are
Diabetes Expert Witness on: Diabetic Hypoglycemia in Nursing Homes Nursing home patients with diabetes treated with insulin and certain oral diabetes medications (i.e. sulfonylureas and glitinides) are
CBT/OTEP 937 Street Medicine Street Drugs
 Seattle-King County EMS Seattle-King County Emergency Medical Services Division Public Health - Seattle/King County 401 5th Avenue, Suite 1200 Seattle, WA 98104 February 2009 CBT/OTEP 937 Street Medicine
Seattle-King County EMS Seattle-King County Emergency Medical Services Division Public Health - Seattle/King County 401 5th Avenue, Suite 1200 Seattle, WA 98104 February 2009 CBT/OTEP 937 Street Medicine
Heat Production and Loss. Environmental Emergencies. Heat Regulation. Body Temperature Ranges. Focused Assessment: Your Patient: Heat Production
 Heat Production and Loss Environmental Emergencies Messing with Mother Nature Heat Production Basal Metabolism processes in the body that generate heat through nominal functions Activity, fever, metabolic
Heat Production and Loss Environmental Emergencies Messing with Mother Nature Heat Production Basal Metabolism processes in the body that generate heat through nominal functions Activity, fever, metabolic
Pesticide Poisonings. Chapter 9. In This Chapter. Keywords. Pesticide Poisonings in Canada. How do Accidental Poisonings Occur?
 Chapter 9 Pesticide Poisonings In This Chapter Keywords After learning the information in this chapter, you will be able to: 1. Explain the 4 ways pesticide poisonings can occur. 2. List the symptoms of
Chapter 9 Pesticide Poisonings In This Chapter Keywords After learning the information in this chapter, you will be able to: 1. Explain the 4 ways pesticide poisonings can occur. 2. List the symptoms of
Alabama Medications. Christopher J. Colvin January 2010
 Alabama Medications Christopher J. Colvin p January 2010 Activated Charcoal Used to absorb toxins ingested before they can be absorbed in the GI system. Contraindicated in AMS patients who cannot control
Alabama Medications Christopher J. Colvin p January 2010 Activated Charcoal Used to absorb toxins ingested before they can be absorbed in the GI system. Contraindicated in AMS patients who cannot control
Chapter 28. Drug Treatment of Parkinson s Disease
 Chapter 28 Drug Treatment of Parkinson s Disease 1. Introduction Parkinsonism Tremors hands and head develop involuntary movements when at rest; pin rolling sign (finger and thumb) Muscle rigidity arthritis
Chapter 28 Drug Treatment of Parkinson s Disease 1. Introduction Parkinsonism Tremors hands and head develop involuntary movements when at rest; pin rolling sign (finger and thumb) Muscle rigidity arthritis
Required when distributed (EMR, EMT, AEMT)
 Required when distributed (EMR, EMT, AEMT) Objectives At the completion of this education module, the provider will have: An understanding of scene safety and assuring responder safety. An understanding
Required when distributed (EMR, EMT, AEMT) Objectives At the completion of this education module, the provider will have: An understanding of scene safety and assuring responder safety. An understanding
MEDICATION GUIDE Trokendi XR (tro-ken-dee eks ahr) (topiramate) Extended-release Capsules
 Page 1 MEDICATION GUIDE Trokendi XR (tro-ken-dee eks ahr) (topiramate) Extended-release Capsules Read this Medication Guide before you start taking Trokendi XR and each time you get a refill. There may
Page 1 MEDICATION GUIDE Trokendi XR (tro-ken-dee eks ahr) (topiramate) Extended-release Capsules Read this Medication Guide before you start taking Trokendi XR and each time you get a refill. There may
The Family Library. Understanding Diabetes
 The Family Library Understanding Diabetes What is Diabetes? Diabetes is caused when the body has a problem in making or using insulin. Insulin is a hormone secreted by the pancreas and is needed for the
The Family Library Understanding Diabetes What is Diabetes? Diabetes is caused when the body has a problem in making or using insulin. Insulin is a hormone secreted by the pancreas and is needed for the
Nassau Regional EMS Council Basic Life Support Protocols and Supplements to State BLS Protocol Manual Table of Contents
 Nassau Regional EMS Council Basic Life Support Protocols and Supplements to State BLS Protocol Manual Table of Contents Approved/ Revised Effective BLS Adult Nerve Agent/Organophosphate Poisoning Antidote
Nassau Regional EMS Council Basic Life Support Protocols and Supplements to State BLS Protocol Manual Table of Contents Approved/ Revised Effective BLS Adult Nerve Agent/Organophosphate Poisoning Antidote
Adrenergic receptors: Anatomy, physiology, and pharmacological interactions
 Adrenergic receptors: Anatomy, physiology, and pharmacological interactions SANDRA M. MAREE, BS, CRNA Winston-Salem, North Carolina The author presents a review of the peripheral autonomic nervous system
Adrenergic receptors: Anatomy, physiology, and pharmacological interactions SANDRA M. MAREE, BS, CRNA Winston-Salem, North Carolina The author presents a review of the peripheral autonomic nervous system
BENZODIAZEPINES. Benzodiazepines may be habit-forming (causing mental or physical dependence), especially when taken for a long time or in high doses.
 Some commonly used brand names are: BENZODIAZEPINES Ativan (lorazepam), Dalmane (flurazepam), Diastat or Valium (diazepam),, Doral (quazepam), Halcion (triazolam), Klonopin (clonazepam), Librium (chlordiazepoxide),
Some commonly used brand names are: BENZODIAZEPINES Ativan (lorazepam), Dalmane (flurazepam), Diastat or Valium (diazepam),, Doral (quazepam), Halcion (triazolam), Klonopin (clonazepam), Librium (chlordiazepoxide),
1-3.20 Defend medication administration by an EMT-Intermediate to effect positive therapeutic affect. (A-3)
 UNIT TERMINAL OBJECTIVE 1-3 At the completion of this unit, the EMT-Intermediate student will be able to understand the basic principles of pharmacology and be able to develop a drug profile for common
UNIT TERMINAL OBJECTIVE 1-3 At the completion of this unit, the EMT-Intermediate student will be able to understand the basic principles of pharmacology and be able to develop a drug profile for common
Update and Review of Medication Assisted Treatments
 Update and Review of Medication Assisted Treatments for Opiate and Alcohol Use Disorders Richard N. Whitney, MD Medical Director Addiction Services Shepherd Hill Newark, Ohio Medication Assisted Treatment
Update and Review of Medication Assisted Treatments for Opiate and Alcohol Use Disorders Richard N. Whitney, MD Medical Director Addiction Services Shepherd Hill Newark, Ohio Medication Assisted Treatment
Hospital Management of Opioid Dependence. Dependence. Disclosure. Pharmacologic Management. Methadone Utilization. Hospital Management of Opioid
 Disclosure Hospital Management of Opioid Dependence Attended Buprenorphine advisory board meeting (Schering Canada) May 2007, but personal honorarium/compensation was declined Dr. Alex Chan alexchchan@hotmail.com
Disclosure Hospital Management of Opioid Dependence Attended Buprenorphine advisory board meeting (Schering Canada) May 2007, but personal honorarium/compensation was declined Dr. Alex Chan alexchchan@hotmail.com
Acid-Base Disorders. Jai Radhakrishnan, MD, MS. Objectives. Diagnostic Considerations. Step 1: Primary Disorder. Formulae. Step 2: Compensation
 Objectives Diagnostic approach to acid base disorders Common clinical examples of acidoses and alkaloses Acid-Base Disorders Jai Radhakrishnan 1 2 Diagnostic Considerations Data points required: ABG: ph,
Objectives Diagnostic approach to acid base disorders Common clinical examples of acidoses and alkaloses Acid-Base Disorders Jai Radhakrishnan 1 2 Diagnostic Considerations Data points required: ABG: ph,
Anaphylaxis and the Role of Diphenhydramine, Epinephrine and Ventolin
 Anaphylaxis and the Role of Diphenhydramine, Epinephrine and Ventolin Dwayne Cottel Regional Paramedic Educator Matthew Davis Medical Director of Education Learning Objectives Describe the pathophysiology
Anaphylaxis and the Role of Diphenhydramine, Epinephrine and Ventolin Dwayne Cottel Regional Paramedic Educator Matthew Davis Medical Director of Education Learning Objectives Describe the pathophysiology
Diuretics: You may get diuretic medicine to help decrease swelling in your brain. This may help your brain get better blood flow.
 Hemorrhagic Stroke GENERAL INFORMATION: What is a hemorrhagic stroke? A hemorrhagic stroke happens when a blood vessel in the brain bursts. This may happen if the blood vessel wall is weak, or sometimes
Hemorrhagic Stroke GENERAL INFORMATION: What is a hemorrhagic stroke? A hemorrhagic stroke happens when a blood vessel in the brain bursts. This may happen if the blood vessel wall is weak, or sometimes
MEDICATION GUIDE KOMBIGLYZE XR (kom-be-glyze X-R) (saxagliptin and metformin HCl extended-release) tablets
 MEDICATION GUIDE KOMBIGLYZE XR (kom-be-glyze X-R) (saxagliptin and metformin HCl extended-release) tablets Read this Medication Guide carefully before you start taking KOMBIGLYZE XR and each time you get
MEDICATION GUIDE KOMBIGLYZE XR (kom-be-glyze X-R) (saxagliptin and metformin HCl extended-release) tablets Read this Medication Guide carefully before you start taking KOMBIGLYZE XR and each time you get
Does This Hospital Serve Cocktails? Alcohol Withdrawal: A Nursing Perspective. Written and presented by: Susan Laffan, RN, CCHP-RN, CCHP-A
 Does This Hospital Serve Cocktails? Alcohol Withdrawal: A Nursing Perspective Written and presented by: Susan Laffan, RN, CCHP-RN, CCHP-A Disclaimer: This speaker has no financial disclaimers to report.
Does This Hospital Serve Cocktails? Alcohol Withdrawal: A Nursing Perspective Written and presented by: Susan Laffan, RN, CCHP-RN, CCHP-A Disclaimer: This speaker has no financial disclaimers to report.
Prescription Drugs: Abuse and Addiction
 EAP Drug Free Workplace Newsletter March 2014 Prescription Drugs: Abuse and Addiction What are some of the commonly abused prescription drugs? Although many prescription drugs can be abused or misused,
EAP Drug Free Workplace Newsletter March 2014 Prescription Drugs: Abuse and Addiction What are some of the commonly abused prescription drugs? Although many prescription drugs can be abused or misused,
