Nerve tissue. Development and function of the nervous system Neuron Membrane potentials Synaptic communication
|
|
|
- Jasmine O’Neal’
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Nerve tissue Development and function of the nervous system Neuron Membrane potentials Synaptic communication
2 Development neuroectoderm neural plate neural tube: brain vesicles spinal cord neural crest sensory ganglia ganglia of cranial nerves, spinal ganglia adrenal medulla melanocytes meningeal layers
3 Function highly specialized processing and transmission of cellular signals excitable and irritable: propagation of the action potential divisions sensory somatic sensory: skin, skeletal muscles, joints visceral sensory: intestines and other visceral organs motor somatic: voluntary control of skeletal muscles visceral motor: involuntary smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, glands memory cognitive homeostasis and neuroendocrine function
4 Nerve tissue cells neurons = nerve cells cell body (soma) = perikaryon neurite = axon dendrites glia cells (neuroglia) oligodendrocyte astrocyte ependyma Schwann cell = neurolemmocyte microglia matter neuropil = dense network pro processes of neurons and glia grey matter: accumulated neuronal cell bodies, glia, capillaries white matter: mainly processes and glia cells
5 Neurons classified according to the processes apolar: embryonic neuroblasts unipolar: retinal amacrine and horizontal cells pseudounipolar: sensory neurons of the spinal ganglia bipolar: retinal bipolar neurons multipolar: single axon, more dendrites cells Golgi I: long-projecting axonal processes pyramidal cells Purkinje cells anterior horn motor neurons Golgi II: axonal process projects locally granullar cells of the cerebellum Camillo Golgi 1906 Nobel Laureate
6 Purkinje cells large inhibitory projection neurons of the cerebellar cortex up to 120 x 60 x 30 µm up to dendritic spines with synapses Czech anatomist Jan Evangelista Purkyně 1837 Purkinje cells 1839 Pukrinje fibres Purkinje images Purkinje color shift cell theory + M. Schleiden, T. Schwann
7 Neurons classified according to their function sensory = afferent neurons - convey information from tissues and organs into the CNS motor = efferent neurons - transmit signals from the CNS to the effector cells muscle glands interneurons - connect neurons with other neurons
8 Morphology of neuron cell body = perikaryon µm trophic center of the cell nucleus with euchromatin prominent nucleolus GER = Nissl bodies neurofilaments (intermediate f.) and microtubules pigments neuromelanin: related to catecholamines lipofuscin: residual from lysosomal digestion dendrites tree-like branching = arborization receive synapses on dendritic spines axon = neurite perikaryon axon hillock the initial segment axon axolemma axoplasm: no GER collateral branches transport anterograde: cell body synaptic terminals; kinesin (ATP-ase) retrograde: towards the perikaryon: dynein (ATP-ase) fast: mm/day slow: mm/day
9 Axon carries the membrane potentials from the soma to the periphery axonal transport length up to 100 cm single axons, but branched a number of target cells axon hillock = arising from the perikaryon followed by the initial segment the greatest density of voltage-dependent Na+ channels the most easily-excited part of the neuron receives inputs from other neurons the axon terminal contains synapses neurotransmitters are released in order to communicate with target neurons the membrane of the vesicle fuses with the presynaptic membrane at the synapse the vesicle membrane is recycled
10 Membrane potentials Na+/K+ ATP-ase 3Na+ out of the cytoplasm/2k+ into the cell potential difference (voltage) across the axolemma approx. -70 mv = resting membrane potential inside negative outside positive stimulus opening ion channels Na+ influx +30mV depolarization = action potential approx. 5 ms recovery
11 Synaptic communication transmission of nerve impulses between neurons between neurons and other cells (muscle, glands) presynaptic cell membrane synaptic cleft postsynaptic cell membrane chemical synapse converting electrical signal into a chemical signal using neurotransmitters and cell adhesion proteins synaptic cleft nm approx within the brain electrical synapse transmit ionic signals through gap junctions direct electrical coupling, 3-4 nm neurons, cardiac and smooth muscle
12 Types of synapses according to morphology axo-dendritic axo-somatic axo-axonic neuromuscular and neuro-glandular junctions act as chemical synapses motor end plate varicosities of autonomic nerve system the effect of the neurotransmitters on the postsynaptic membrane excitatory depolarization; e.g., glutamate inhibitory hyperpolarization; e.g., GABA neuromodulation = modulating sensitivity
13 Synapses and drugs organophosphates (insecticides, nerve agents/weapons) inactivate acetylcholinesterase succinylcholine inhibits the action or acetylcholine, myorelaxation in anaesthesia botulinum toxin blocking the release of acetylcholine muscle paralysis nicotine stimulates nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (autonomic ganglia and CNS) SSRI selective serotonin re-uptake inhibitors antidepressants etc.
Nervous Tissue Dr. Archana Rani Associate Professor Department of Anatomy KGMU UP, Lucknow
 13.01.2015 Nervous Tissue Dr. Archana Rani Associate Professor Department of Anatomy KGMU UP, Lucknow Introduction Property of irritability and conductivity Respond to various types of stimuli Distributed
13.01.2015 Nervous Tissue Dr. Archana Rani Associate Professor Department of Anatomy KGMU UP, Lucknow Introduction Property of irritability and conductivity Respond to various types of stimuli Distributed
NEURONS NEUROGLIAL CELLS.
 1 THE NERVOUS TISSUE Definition: The nervous tissue is an assemblage of cells and supportive elements (materials) in which there is a predominance of cells which are highly specialized in the property
1 THE NERVOUS TISSUE Definition: The nervous tissue is an assemblage of cells and supportive elements (materials) in which there is a predominance of cells which are highly specialized in the property
12. Nervous System: Nervous Tissue
 12. Nervous System: Nervous Tissue I. Introduction to the Nervous System General functions of the nervous system The nervous system has three basic functions: 1. Gather sensory input from the environment
12. Nervous System: Nervous Tissue I. Introduction to the Nervous System General functions of the nervous system The nervous system has three basic functions: 1. Gather sensory input from the environment
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
 Chapter 7: The Nervous System Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways involved in a withdraw reflex Define
Chapter 7: The Nervous System Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways involved in a withdraw reflex Define
CELLS IN THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
 NEURONS AND GLIA CELLS IN THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Glia Insulates, supports, and nourishes neurons Neurons Process information Sense environmental changes Communicate changes to other neurons Command body response
NEURONS AND GLIA CELLS IN THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Glia Insulates, supports, and nourishes neurons Neurons Process information Sense environmental changes Communicate changes to other neurons Command body response
Nerves and Nerve Impulse
 Nerves and Nerve Impulse Terms Absolute refractory period: Period following stimulation during which no additional action potential can be evoked. Acetylcholine: Chemical transmitter substance released
Nerves and Nerve Impulse Terms Absolute refractory period: Period following stimulation during which no additional action potential can be evoked. Acetylcholine: Chemical transmitter substance released
Chapter 11: Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue
 Chapter 11: Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue Multiple Choice 1. The nervous system A) monitors internal and external stimuli. B) transmits information in the form of action potentials. C) interprets
Chapter 11: Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue Multiple Choice 1. The nervous system A) monitors internal and external stimuli. B) transmits information in the form of action potentials. C) interprets
Anatomy & Physiology Bio 2401 Lecture. Instructor: Daryl Beatty Nervous System Introduction Part 1
 Anatomy & Physiology Bio 2401 Lecture Instructor: Daryl Beatty Nervous System Introduction Part 1 Nervous System Introduction Chapter 11 Section A Sequence 4.1 DB Nervous system 1 Intro Presentations 4.2,
Anatomy & Physiology Bio 2401 Lecture Instructor: Daryl Beatty Nervous System Introduction Part 1 Nervous System Introduction Chapter 11 Section A Sequence 4.1 DB Nervous system 1 Intro Presentations 4.2,
Biology Slide 1 of 38
 Biology 1 of 38 2 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System What are the functions of the nervous system? 3 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System 1. Nervous system: a. controls and coordinates functions throughout the body
Biology 1 of 38 2 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System What are the functions of the nervous system? 3 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System 1. Nervous system: a. controls and coordinates functions throughout the body
Name: Teacher: Olsen Hour:
 Name: Teacher: Olsen Hour: The Nervous System: Part 1 Textbook p216-225 41 In all exercises, quizzes and tests in this class, always answer in your own words. That is the only way that you can show that
Name: Teacher: Olsen Hour: The Nervous System: Part 1 Textbook p216-225 41 In all exercises, quizzes and tests in this class, always answer in your own words. That is the only way that you can show that
FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM 1. Sensory input. Sensory receptors detects external and internal stimuli.
 FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM 1. Sensory input. Sensory receptors detects external and internal stimuli. 2. Integration. The brain and spinal cord process sensory input and produce responses. 3. Homeostasis.
FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM 1. Sensory input. Sensory receptors detects external and internal stimuli. 2. Integration. The brain and spinal cord process sensory input and produce responses. 3. Homeostasis.
The Neuron and the Synapse. The Neuron. Parts of the Neuron. Functions of the neuron:
 The Neuron and the Synapse The Neuron Functions of the neuron: Transmit information from one point in the body to another. Process the information in various ways (that is, compute). The neuron has a specialized
The Neuron and the Synapse The Neuron Functions of the neuron: Transmit information from one point in the body to another. Process the information in various ways (that is, compute). The neuron has a specialized
U N IT 10 NE RVOUS SYS TE M REVIEW 1. Which of the following is controlled by the somatic nervous system? A. rate of heartbeat B.
 U N IT 10 NE RVOUS SYS TE M REVIEW 1. Which of the following is controlled by the somatic nervous system? A. rate of heartbeat B. contraction of skeletal muscles C. increased blood flow to muscle tissue
U N IT 10 NE RVOUS SYS TE M REVIEW 1. Which of the following is controlled by the somatic nervous system? A. rate of heartbeat B. contraction of skeletal muscles C. increased blood flow to muscle tissue
AP Biology I. Nervous System Notes
 AP Biology I. Nervous System Notes 1. General information: passage of information occurs in two ways: Nerves - process and send information fast (eg. stepping on a tack) Hormones - process and send information
AP Biology I. Nervous System Notes 1. General information: passage of information occurs in two ways: Nerves - process and send information fast (eg. stepping on a tack) Hormones - process and send information
Resting membrane potential ~ -70mV - Membrane is polarized
 Resting membrane potential ~ -70mV - Membrane is polarized (ie) Electrical charge on the outside of the membrane is positive while the electrical charge on the inside of the membrane is negative Changes
Resting membrane potential ~ -70mV - Membrane is polarized (ie) Electrical charge on the outside of the membrane is positive while the electrical charge on the inside of the membrane is negative Changes
Nervous Tissue Chapter 12
 Nervous Tissue Chapter 12 Overview of the Nervous System Cells of the Nervous System Electrophysiology of Neurons Synapses Subdivisions of the Nervous System Two major anatomical subdivisions: Central
Nervous Tissue Chapter 12 Overview of the Nervous System Cells of the Nervous System Electrophysiology of Neurons Synapses Subdivisions of the Nervous System Two major anatomical subdivisions: Central
Chapter 9 Nervous System
 Chapter 9 Nervous System Nervous System function: The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. at the ends of peripheral nerves gather information and convert it into nerve impulses. When sensory
Chapter 9 Nervous System Nervous System function: The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. at the ends of peripheral nerves gather information and convert it into nerve impulses. When sensory
Name Date Hour. Nerve Histology Microscope Lab
 Name Date Hour Nerve Histology Microscope Lab PRE-LAB: Answer the following questions using your reading and class notes before starting the microscope lab. 1. What is the difference between the functions
Name Date Hour Nerve Histology Microscope Lab PRE-LAB: Answer the following questions using your reading and class notes before starting the microscope lab. 1. What is the difference between the functions
Parts of the Nerve Cell and Their Functions
 Parts of the Nerve Cell and Their Functions Silvia Helena Cardoso, PhD [ 1. Cell body] [2. Neuronal membrane] [3. Dendrites] [4. Axon] [5. Nerve ending] 1. Cell body The cell body (soma) is the factory
Parts of the Nerve Cell and Their Functions Silvia Helena Cardoso, PhD [ 1. Cell body] [2. Neuronal membrane] [3. Dendrites] [4. Axon] [5. Nerve ending] 1. Cell body The cell body (soma) is the factory
Biology/ANNB 261 Exam 1 Name Fall, 2006
 Biology/ANNB 261 Exam 1 Name Fall, 2006 * = correct answer. 1. The Greek philosopher Aristotle hypothesized that the brain was a) A radiator for cooling the blood.* b) The seat of the soul. c) The organ
Biology/ANNB 261 Exam 1 Name Fall, 2006 * = correct answer. 1. The Greek philosopher Aristotle hypothesized that the brain was a) A radiator for cooling the blood.* b) The seat of the soul. c) The organ
Neurophysiology. 2.1 Equilibrium Potential
 2 Neurophysiology 2.1 Equilibrium Potential An understanding of the concepts of electrical and chemical forces that act on ions, electrochemical equilibrium, and equilibrium potential is a powerful tool
2 Neurophysiology 2.1 Equilibrium Potential An understanding of the concepts of electrical and chemical forces that act on ions, electrochemical equilibrium, and equilibrium potential is a powerful tool
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz
 Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz 1. The term central nervous system refers to the: A) autonomic and peripheral nervous systems B) brain, spinal cord, and cranial nerves
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz 1. The term central nervous system refers to the: A) autonomic and peripheral nervous systems B) brain, spinal cord, and cranial nerves
Nervous System: Nervous Tissue! (Chapter 12)! Lecture Materials! for! Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D.! Suffolk County Community College! Eastern Campus!
 Nervous System: Nervous Tissue! (Chapter 12)! Lecture Materials! for! Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D.! Suffolk County Community College! Eastern Campus! Neural Tissue! -3% of body mass! -cellular, ~20% extracellular
Nervous System: Nervous Tissue! (Chapter 12)! Lecture Materials! for! Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D.! Suffolk County Community College! Eastern Campus! Neural Tissue! -3% of body mass! -cellular, ~20% extracellular
Chapter 15. The Autonomic Nervous. The Autonomic Nervous System. Autonomic Motor Pathways. ANS vs. SNS
 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter 15 The subconscious involuntary nervous system Regulates activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle & certain glands The Autonomic Nervous System 1 2 ANS vs. SNS Somatic
The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter 15 The subconscious involuntary nervous system Regulates activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle & certain glands The Autonomic Nervous System 1 2 ANS vs. SNS Somatic
The Nervous System, Part I.Unlecture
 The Nervous System, Part I.Unlecture Review basic nervous system anatomy before you begin this lecture. The lecture touches on a few of the major characteristics, but you are expected to have already been
The Nervous System, Part I.Unlecture Review basic nervous system anatomy before you begin this lecture. The lecture touches on a few of the major characteristics, but you are expected to have already been
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
NERVOUS SYSTEM B 1. Which of the following is controlled by the somatic nervous system? A. rate of heartbeat B. contraction of skeletal muscles C.
 NERVOUS SYSTEM B 1. Which of the following is controlled by the somatic nervous system? A. rate of heartbeat B. contraction of skeletal muscles C. increased blood flow to muscle tissue D. movement of food
NERVOUS SYSTEM B 1. Which of the following is controlled by the somatic nervous system? A. rate of heartbeat B. contraction of skeletal muscles C. increased blood flow to muscle tissue D. movement of food
Biology/ANNB 261 Exam 1 Spring, 2006
 Biology/ANNB 261 Exam 1 Spring, 2006 Name * = correct answer Multiple Choice: 1. Axons and dendrites are two types of a) Neurites * b) Organelles c) Synapses d) Receptors e) Golgi cell components 2. The
Biology/ANNB 261 Exam 1 Spring, 2006 Name * = correct answer Multiple Choice: 1. Axons and dendrites are two types of a) Neurites * b) Organelles c) Synapses d) Receptors e) Golgi cell components 2. The
CHAPTER 5 SIGNALLING IN NEURONS
 5.1. SYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION CHAPTER 5 SIGNALLING IN NEURONS One of the main functions of neurons is to communicate with other neurons. An individual neuron may receive information from many different sources.
5.1. SYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION CHAPTER 5 SIGNALLING IN NEURONS One of the main functions of neurons is to communicate with other neurons. An individual neuron may receive information from many different sources.
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
 Chapter 7: The Nervous System I. Organization of the Nervous System Objectives: List the general functions of the nervous system Explain the structural and functional classifications of the nervous system
Chapter 7: The Nervous System I. Organization of the Nervous System Objectives: List the general functions of the nervous system Explain the structural and functional classifications of the nervous system
Structure and Function of Neurons
 CHPTER 1 Structure and Function of Neurons Varieties of neurons General structure Structure of unique neurons Internal operations and the functioning of a neuron Subcellular organelles Protein synthesis
CHPTER 1 Structure and Function of Neurons Varieties of neurons General structure Structure of unique neurons Internal operations and the functioning of a neuron Subcellular organelles Protein synthesis
Please read chapter 15, The Autonomic Nervous System, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class.
 Please read chapter 15,, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class. I. Introduction to the autonomic nervous system: Briefly describe the autonomic nervous system.
Please read chapter 15,, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class. I. Introduction to the autonomic nervous system: Briefly describe the autonomic nervous system.
Introduction to Psychology, 7th Edition, Rod Plotnik Module 3: Brain s Building Blocks. Module 3. Brain s Building Blocks
 Module 3 Brain s Building Blocks Structure of the Brain Genes chains of chemicals that are arranged like rungs on a twisting ladder there are about 100,000 genes that contain chemical instructions that
Module 3 Brain s Building Blocks Structure of the Brain Genes chains of chemicals that are arranged like rungs on a twisting ladder there are about 100,000 genes that contain chemical instructions that
18. What is limbic system? A. The inner parts of cerebral hemispheres associated with deep structures and from a complex structure. 19.
 CHAPTER 21 NEURAL CONTROL AND COORDINATION One mark Questions: 1. Name the structural and functional unit of nervous system? A. Neuron. 2. What does central Nervous System consists of? A. Brain and spinal
CHAPTER 21 NEURAL CONTROL AND COORDINATION One mark Questions: 1. Name the structural and functional unit of nervous system? A. Neuron. 2. What does central Nervous System consists of? A. Brain and spinal
NEURON AND NEURAL TRAMSMISSION: ANATOMY OF A NEURON. created by Dr. Joanne Hsu
 NEURON AND NEURAL TRAMSMISSION: ANATOMY OF A NEURON NEURON AND NEURAL TRAMSMISSION: MICROSCOPIC VIEW OF NEURONS A photograph taken through a light microscope (500x) of neurons in the spinal cord. NEURON
NEURON AND NEURAL TRAMSMISSION: ANATOMY OF A NEURON NEURON AND NEURAL TRAMSMISSION: MICROSCOPIC VIEW OF NEURONS A photograph taken through a light microscope (500x) of neurons in the spinal cord. NEURON
Nerves and Conduction of Nerve Impulses
 A. Introduction 1. Innovation in Cnidaria - Nerve net a. We need to talk more about nerves b. Cnidaria have simple nerve net - 2 way conduction c. Basis for more complex system in Vertebrates B. Vertebrate
A. Introduction 1. Innovation in Cnidaria - Nerve net a. We need to talk more about nerves b. Cnidaria have simple nerve net - 2 way conduction c. Basis for more complex system in Vertebrates B. Vertebrate
You can t turn on the television or radio, much less go online, without seeing something
 11 Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue You can t turn on the television or radio, much less go online, without seeing something to remind you of the nervous system. From advertisements
11 Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue You can t turn on the television or radio, much less go online, without seeing something to remind you of the nervous system. From advertisements
What is the basic component of the brain and spinal cord communication system?
 EXPLORING PSYCHOLOGY David Myers The Biology of Mind Chapter 2 Neural Communication Neurons How Neurons Communicate How Neurotransmitters Influence Us The Nervous System The Peripheral Nervous System The
EXPLORING PSYCHOLOGY David Myers The Biology of Mind Chapter 2 Neural Communication Neurons How Neurons Communicate How Neurotransmitters Influence Us The Nervous System The Peripheral Nervous System The
3. The neuron has many branch-like extensions called that receive input from other neurons. a. glia b. dendrites c. axons d.
 Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer: A difficulty: 1 factual
Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer: A difficulty: 1 factual
ANIMATED NEUROSCIENCE
 ANIMATED NEUROSCIENCE and the Action of Nicotine, Cocaine, and Marijuana in the Brain Te a c h e r s G u i d e Films for the Humanities & Sciences Background Information This program, made entirely of
ANIMATED NEUROSCIENCE and the Action of Nicotine, Cocaine, and Marijuana in the Brain Te a c h e r s G u i d e Films for the Humanities & Sciences Background Information This program, made entirely of
http://abcnews.go.com/politics/video/obama-says-brain-initiative-will-be-transformative-18861944
 http://abcnews.go.com/politics/video/obama-says-brain-initiative-will-be-transformative-18861944 What are the nervous system s functions? The nervous system organizes and controls an individual s appropriate
http://abcnews.go.com/politics/video/obama-says-brain-initiative-will-be-transformative-18861944 What are the nervous system s functions? The nervous system organizes and controls an individual s appropriate
Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture
 1 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 2 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and certain
1 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 2 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and certain
Bi 360: Midterm Review
 Bi 360: Midterm Review Basic Neurobiology 1) Many axons are surrounded by a fatty insulating sheath called myelin, which is interrupted at regular intervals at the Nodes of Ranvier, where the action potential
Bi 360: Midterm Review Basic Neurobiology 1) Many axons are surrounded by a fatty insulating sheath called myelin, which is interrupted at regular intervals at the Nodes of Ranvier, where the action potential
PHYSIOLOGICAL PSYCHOLOGY
 UNIVERSITY OF CALICUT SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION B Sc COUNSELLING PSYCHOLOGY (2011 Admission Onwards) I Semester Complementary Course PHYSIOLOGICAL PSYCHOLOGY QUESTION BANK 1. are the basic units of
UNIVERSITY OF CALICUT SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION B Sc COUNSELLING PSYCHOLOGY (2011 Admission Onwards) I Semester Complementary Course PHYSIOLOGICAL PSYCHOLOGY QUESTION BANK 1. are the basic units of
Mammalian Physiology. Autonomic Nervous System UNLV. PHYSIOLOGY, Chapter 11 Berne, Levy, Koeppen, Stanton UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA LAS VEGAS
 Mammalian Physiology Autonomic Nervous System UNLV 1 UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA LAS VEGAS PHYSIOLOGY, Chapter 11 Berne, Levy, Koeppen, Stanton Objectives Describe the organization of the autonomic nervous system
Mammalian Physiology Autonomic Nervous System UNLV 1 UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA LAS VEGAS PHYSIOLOGY, Chapter 11 Berne, Levy, Koeppen, Stanton Objectives Describe the organization of the autonomic nervous system
Chapter 13. The Nature of Somatic Reflexes
 Chapter 13 The Nature of Somatic Reflexes Nature of Reflexes (1 of 3) A reflex is an involuntary responses initiated by a sensory input resulting in a change in a gland or muscle tissue occur without our
Chapter 13 The Nature of Somatic Reflexes Nature of Reflexes (1 of 3) A reflex is an involuntary responses initiated by a sensory input resulting in a change in a gland or muscle tissue occur without our
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
 AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Somatic efferent and ANS Somatic Efferent Control is over skeletal muscles. External environment This division of the PNS responds to some change in the external environment. single
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Somatic efferent and ANS Somatic Efferent Control is over skeletal muscles. External environment This division of the PNS responds to some change in the external environment. single
Anatomy Review. Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.
 Anatomy Review Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction The structure of neurons reflects their function.
Anatomy Review Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction The structure of neurons reflects their function.
Anatomy Review Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.com/bc).
 Page 1. Introduction The structure of neurons reflects their function. One part of the cell receives incoming signals. Another part generates outgoing signals. Anatomy Review Graphics are used with permission
Page 1. Introduction The structure of neurons reflects their function. One part of the cell receives incoming signals. Another part generates outgoing signals. Anatomy Review Graphics are used with permission
Chapter 9 - Nervous System
 Chapter 9 - Nervous System 9.1 Introduction (p. 215; Fig. 9.1) A. The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. 1. Neurons transmit nerve impulses along nerve fibers to other neurons. 2. Nerves
Chapter 9 - Nervous System 9.1 Introduction (p. 215; Fig. 9.1) A. The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. 1. Neurons transmit nerve impulses along nerve fibers to other neurons. 2. Nerves
Questions on The Nervous System and Gas Exchange
 Name: Questions on The Nervous System and Gas Exchange Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on Topics 6.4 (Gas Exchange) and 6.5 (Nerves, hormones and homeostasis).
Name: Questions on The Nervous System and Gas Exchange Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on Topics 6.4 (Gas Exchange) and 6.5 (Nerves, hormones and homeostasis).
Origin of Electrical Membrane Potential
 Origin of Electrical Membrane Potential parti This book is about the physiological characteristics of nerve and muscle cells. As we shall see, the ability of these cells to generate and conduct electricity
Origin of Electrical Membrane Potential parti This book is about the physiological characteristics of nerve and muscle cells. As we shall see, the ability of these cells to generate and conduct electricity
Chapter 15. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes. general properties Anatomy. Autonomic effects on target organs
 Chapter 15 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes general properties Anatomy Autonomic effects on target organs Central control of autonomic function 15-1 Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Chapter 15 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes general properties Anatomy Autonomic effects on target organs Central control of autonomic function 15-1 Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Nervous System: PNS and CNS
 Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
PART I: Neurons and the Nerve Impulse
 PART I: Neurons and the Nerve Impulse Identify each of the labeled structures of the neuron below. A. B. C. D. E. F. G. Identify each of the labeled structures of the neuron below. A. dendrites B. nucleus
PART I: Neurons and the Nerve Impulse Identify each of the labeled structures of the neuron below. A. B. C. D. E. F. G. Identify each of the labeled structures of the neuron below. A. dendrites B. nucleus
Introduction to the Nervous System
 SENSORY PROCESSES Introduction to the Nervous System Introduction to the Nervous System he world is mostly unknown. This statement immediately emphasizes the point that we are not conscious of most of
SENSORY PROCESSES Introduction to the Nervous System Introduction to the Nervous System he world is mostly unknown. This statement immediately emphasizes the point that we are not conscious of most of
31.1 The Neuron. BUILD Vocabulary. Lesson Objectives
 Name Class Date 31.1 The Neuron Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the nervous system. Describe the function of neurons. Describe how a nerve impulse is transmitted. BUILD Vocabulary A. The chart
Name Class Date 31.1 The Neuron Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the nervous system. Describe the function of neurons. Describe how a nerve impulse is transmitted. BUILD Vocabulary A. The chart
Human Physiology Study Questions-2
 Human Physiology Study Questions-2 Action potentials: Handout-8, Chapter 8 1. Explain the positive feedback component of an action potential that is, how the opening of one voltage-gated sodium (or calcium)
Human Physiology Study Questions-2 Action potentials: Handout-8, Chapter 8 1. Explain the positive feedback component of an action potential that is, how the opening of one voltage-gated sodium (or calcium)
Chapter 15. Sympathetic Nervous System
 Chapter 15 Sympathetic Nervous System Somatic versus Autonomic Pathways Somatic efferent innervation ACh Myelinated fiber Somatic effectors (skeletal muscles) Autonomic efferent innervation ACh ACh or
Chapter 15 Sympathetic Nervous System Somatic versus Autonomic Pathways Somatic efferent innervation ACh Myelinated fiber Somatic effectors (skeletal muscles) Autonomic efferent innervation ACh ACh or
Nervous System Organization. PNS and CNS. Nerves. Peripheral Nervous System. Peripheral Nervous System. Motor Component.
 Nervous System Organization PNS and CNS Chapters 8 and 9 Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) connects CNS to sensory receptors, muscles and glands Central Nervous System (CNS) control/integrating center brain
Nervous System Organization PNS and CNS Chapters 8 and 9 Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) connects CNS to sensory receptors, muscles and glands Central Nervous System (CNS) control/integrating center brain
of computational neuroscience. The chapter is organized as follows. Section 1 describes the
 Chapter 1 This chapter presents elements of neurobiology that form the necessary preparation for a student of computational neuroscience. The chapter is organized as follows. Section 1 describes the biology
Chapter 1 This chapter presents elements of neurobiology that form the necessary preparation for a student of computational neuroscience. The chapter is organized as follows. Section 1 describes the biology
Chapter 3 The Anatomy of the Nervous System
 Chapter 3 The Anatomy of the Nervous System Systems, Structures, and Cells That Make Up Your Nervous System 1 General Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain (in the skull) Spinal
Chapter 3 The Anatomy of the Nervous System Systems, Structures, and Cells That Make Up Your Nervous System 1 General Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain (in the skull) Spinal
D.U.C. Assist. Lec. Faculty of Dentistry General Physiology Ihsan Dhari. The Autonomic Nervous System
 The Autonomic Nervous System The portion of the nervous system that controls most visceral functions of the body is called the autonomic nervous system. This system helps to control arterial pressure,
The Autonomic Nervous System The portion of the nervous system that controls most visceral functions of the body is called the autonomic nervous system. This system helps to control arterial pressure,
REVIEW SHEET EXERCISE 3 Neurophysiology of Nerve Impulses Name Lab Time/Date. The Resting Membrane Potential
 REVIEW SHEET EXERCISE 3 Neurophysiology of Nerve Impulses Name Lab Time/Date ACTIVITY 1 The Resting Membrane Potential 1. Explain why increasing extracellular K + reduces the net diffusion of K + out of
REVIEW SHEET EXERCISE 3 Neurophysiology of Nerve Impulses Name Lab Time/Date ACTIVITY 1 The Resting Membrane Potential 1. Explain why increasing extracellular K + reduces the net diffusion of K + out of
The Action Potential, Synaptic Transmission, and Maintenance of Nerve Function
 C H A P T E R 3 The Action Potential, Synaptic Transmission, and Maintenance of Nerve Function Cynthia J. Forehand, Ph.D. CHAPTER OUTLINE PASSIVE MEMBRANE PROPERTIES, THE ACTION POTENTIAL, AND ELECTRICAL
C H A P T E R 3 The Action Potential, Synaptic Transmission, and Maintenance of Nerve Function Cynthia J. Forehand, Ph.D. CHAPTER OUTLINE PASSIVE MEMBRANE PROPERTIES, THE ACTION POTENTIAL, AND ELECTRICAL
Chapter 4. The Brain
 Chapter 4 The Brain The Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) receives, processes, interprets and stores info (taste, sound, smell, color etc.) Sends information to muscles, glands and internal organs
Chapter 4 The Brain The Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) receives, processes, interprets and stores info (taste, sound, smell, color etc.) Sends information to muscles, glands and internal organs
Integration and Coordination of the Human Body. Nervous System
 I. General Info Integration and Coordination of the Human Body A. Both the and system are responsible for maintaining 1. Homeostasis is the process by which organisms keep internal conditions despite changes
I. General Info Integration and Coordination of the Human Body A. Both the and system are responsible for maintaining 1. Homeostasis is the process by which organisms keep internal conditions despite changes
Explore the Neuroscience for Kids Web Site (ANSWERS) Start at: http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/neurok.html
 NAME Explore the Neuroscience for Kids Web Site (ANSWERS) Start at: http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/neurok.html On the left side, click on Explore, then click on The Neuron, then click on Millions
NAME Explore the Neuroscience for Kids Web Site (ANSWERS) Start at: http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/neurok.html On the left side, click on Explore, then click on The Neuron, then click on Millions
1. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled A on the diagram. 2. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled B on the diagram.
 2013 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Sample Tournament Station A: Use the diagram in answering Questions 1-5. 1. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled A on the diagram. 2. Give the name and functions
2013 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Sample Tournament Station A: Use the diagram in answering Questions 1-5. 1. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled A on the diagram. 2. Give the name and functions
Brain & Mind. Bicester Community College Science Department
 B6 Brain & Mind B6 Key Questions How do animals respond to changes in their environment? How is information passed through the nervous system? What can we learn through conditioning? How do humans develop
B6 Brain & Mind B6 Key Questions How do animals respond to changes in their environment? How is information passed through the nervous system? What can we learn through conditioning? How do humans develop
Barbara St. Marie, PhD Candidate Nurse Practitioner Supervisor Pain and Palliative Care Fairview Ridges Hospital Minneapolis, MN
 Barbara St. Marie, PhD Candidate Nurse Practitioner Supervisor Pain and Palliative Care Fairview Ridges Hospital Minneapolis, MN Pain Physiology Objectives: Explain how pain is transmitted through the
Barbara St. Marie, PhD Candidate Nurse Practitioner Supervisor Pain and Palliative Care Fairview Ridges Hospital Minneapolis, MN Pain Physiology Objectives: Explain how pain is transmitted through the
Slide 4: Forebrain Structures. Slide 5: 4 Lobes of the Cerebral Cortex. Slide 6: The Cerebral Hemispheres (L & R)
 Slide 1: [Film Clip: The Brain #2- Phineas Gage] Integrated Bodily Communications Within Brain (Hemispheres and structures) The remaining Nervous System Endocrine System (Hormonal communication) Our bodies-
Slide 1: [Film Clip: The Brain #2- Phineas Gage] Integrated Bodily Communications Within Brain (Hemispheres and structures) The remaining Nervous System Endocrine System (Hormonal communication) Our bodies-
Reflex Physiology. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi. 2009 Ebneshahidi
 Reflex Physiology Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Reflex Physiology Reflexes are automatic, subconscious response to changes within or outside the body. a. Reflexes maintain homeostasis (autonomic reflexes) heart
Reflex Physiology Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Reflex Physiology Reflexes are automatic, subconscious response to changes within or outside the body. a. Reflexes maintain homeostasis (autonomic reflexes) heart
Standards Alignment Minnesota Science Standards Alignment Matrix www.brainu.org/resources/mnstds
 Lesson Summary: Neurons transfer information by releasing neurotransmitters across the synapse or space between neurons. Students model the chemical communication between pre-synaptic and post-synaptic
Lesson Summary: Neurons transfer information by releasing neurotransmitters across the synapse or space between neurons. Students model the chemical communication between pre-synaptic and post-synaptic
Activity 5: The Action Potential: Measuring Its Absolute and Relative Refractory Periods. 250 20 Yes. 125 20 Yes. 60 20 No. 60 25 No.
 3: Neurophysiology of Nerve Impulses (Part 2) Activity 5: The Action Potential: Measuring Its Absolute and Relative Refractory Periods Interval between stimuli Stimulus voltage (mv) Second action potential?
3: Neurophysiology of Nerve Impulses (Part 2) Activity 5: The Action Potential: Measuring Its Absolute and Relative Refractory Periods Interval between stimuli Stimulus voltage (mv) Second action potential?
THE SPINAL CORD AND THE INFLUENCE OF ITS DAMAGE ON THE HUMAN BODY
 THE SPINAL CORD AND THE INFLUENCE OF ITS DAMAGE ON THE HUMAN BODY THE SPINAL CORD. A part of the Central Nervous System The nervous system is a vast network of cells, which carry information in the form
THE SPINAL CORD AND THE INFLUENCE OF ITS DAMAGE ON THE HUMAN BODY THE SPINAL CORD. A part of the Central Nervous System The nervous system is a vast network of cells, which carry information in the form
Nervous System sensor input integration motor output sensory organs central nervous system
 Nervous System Nervous system performs three overlapping functions of sensor input, integration, and motor output. This process is generally the same even at a very primitive level of nervous system, but
Nervous System Nervous system performs three overlapping functions of sensor input, integration, and motor output. This process is generally the same even at a very primitive level of nervous system, but
Chapter 15. Neurotransmitters of the ANS
 Chapter 15 Neurotransmitters of the ANS Neurotransmitters and Receptors How can the same ANS neurons create different effects on different target tissue? Variety of neurotransmitters Secondly, different
Chapter 15 Neurotransmitters of the ANS Neurotransmitters and Receptors How can the same ANS neurons create different effects on different target tissue? Variety of neurotransmitters Secondly, different
Andrew Rosen - Chapter 3: The Brain and Nervous System Intro:
 Intro: Brain is made up of numerous, complex parts Frontal lobes by forehead are the brain s executive center Parietal lobes wave sensory information together (maps feeling on body) Temporal lobes interpret
Intro: Brain is made up of numerous, complex parts Frontal lobes by forehead are the brain s executive center Parietal lobes wave sensory information together (maps feeling on body) Temporal lobes interpret
Ion Channels. Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com)
 Ion Channels Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) ** There are a number of ion channels introducted in this topic which you
Ion Channels Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) ** There are a number of ion channels introducted in this topic which you
The Autonomic Nervous System Physiology Study Guide, Chapter 9
 Name: The Autonomic Nervous System Physiology Study Guide, Chapter 9 Lab Time: 1 Part I. Clinical Applications and Short Essay 1. After surgery, patients are often temporarily unable to urinate, and bowel
Name: The Autonomic Nervous System Physiology Study Guide, Chapter 9 Lab Time: 1 Part I. Clinical Applications and Short Essay 1. After surgery, patients are often temporarily unable to urinate, and bowel
EXCITABILITY & ACTION POTENTIALS page 1
 page 1 INTRODUCTION A. Excitable Tissue: able to generate Action Potentials (APs) (e.g. neurons, muscle cells) B. Neurons (nerve cells) a. components 1) soma (cell body): metabolic center (vital, always
page 1 INTRODUCTION A. Excitable Tissue: able to generate Action Potentials (APs) (e.g. neurons, muscle cells) B. Neurons (nerve cells) a. components 1) soma (cell body): metabolic center (vital, always
Diagram 2(i): Structure of the Neuron
 Diagram 2(i): Structure of the Neuron Generally speaking, we can divide the nervous system into different parts, according to location and function. So far we have mentioned the central nervous system
Diagram 2(i): Structure of the Neuron Generally speaking, we can divide the nervous system into different parts, according to location and function. So far we have mentioned the central nervous system
Nerve Cell Communication
 Nerve Cell Communication Core Concept: Nerve cells communicate using electrical and chemical signals. Class time required: Approximately 2 forty minute class periods Teacher Provides: For each student
Nerve Cell Communication Core Concept: Nerve cells communicate using electrical and chemical signals. Class time required: Approximately 2 forty minute class periods Teacher Provides: For each student
Peripheral Nervous System
 Nervous system consists of: Peripheral Nervous System CNS = brain and spinal cord ~90% (90 Bil) of all neurons in body are in CNS PNS = Cranial nerves and spinal nerves, nerve plexuses & ganglia ~10% (10
Nervous system consists of: Peripheral Nervous System CNS = brain and spinal cord ~90% (90 Bil) of all neurons in body are in CNS PNS = Cranial nerves and spinal nerves, nerve plexuses & ganglia ~10% (10
Nervous System: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves (Chapter 13) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College
 Nervous System: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves (Chapter 13) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Primary Sources for figures and content: Eastern Campus Marieb,
Nervous System: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves (Chapter 13) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Primary Sources for figures and content: Eastern Campus Marieb,
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. Sensory Pathway (PNS) OVERVIEW OF SPINAL CORD ANATOMY OF THE SPINAL CORD FUNCTIONS OF THE SPINAL CORD
 CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Central nervous system (CNS) brain and spinal cord enclosed in bony coverings Functions of the spinal cord spinal cord reflexes integration ti (summation of inhibitory and excitatory)
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Central nervous system (CNS) brain and spinal cord enclosed in bony coverings Functions of the spinal cord spinal cord reflexes integration ti (summation of inhibitory and excitatory)
Exploring Creation with Advanced Biology ~ Schedule for 2015-2016 Apologia ~ Exploring Creation with Biology ~ Module 1 (Week 1) Date:
 Apologia ~ Exploring Creation with Biology ~ Module 1 (Week 1) Mon., Aug. 31 Tue., Sep. 1 Wed., Sept. 2 Thurs., Sept. 3 Fri., Sept. 4 Reading Pgs. 1-4; Introduction, Heart of the matter, Pgs. 5-8; Organization
Apologia ~ Exploring Creation with Biology ~ Module 1 (Week 1) Mon., Aug. 31 Tue., Sep. 1 Wed., Sept. 2 Thurs., Sept. 3 Fri., Sept. 4 Reading Pgs. 1-4; Introduction, Heart of the matter, Pgs. 5-8; Organization
Muscle Tissue. Muscle Physiology. Skeletal Muscle. Types of Muscle. Skeletal Muscle Organization. Myofibril Structure
 Muscle Tissue Muscle Physiology Chapter 12 Specially designed to contract Generates mechanical force Functions locomotion and external movements internal movement (circulation, digestion) heat generation
Muscle Tissue Muscle Physiology Chapter 12 Specially designed to contract Generates mechanical force Functions locomotion and external movements internal movement (circulation, digestion) heat generation
Chapter 15: The Autonomic Nervous System
 Chapter 15: The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Objectives COMPARISON OF SOMATIC AND AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEMS 1. List the structural and functional characteristics of the autonomic nervous system. 2.
Chapter 15: The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Objectives COMPARISON OF SOMATIC AND AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEMS 1. List the structural and functional characteristics of the autonomic nervous system. 2.
CHAPTER 16: THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
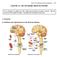 Unit 4: The Autonomic Nervous System 254 CHAPTER 16: THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Read: Chapter 16, pages 517-534. Read only the topics covered in lecture. We will not cover this chapter in detail. Complete
Unit 4: The Autonomic Nervous System 254 CHAPTER 16: THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Read: Chapter 16, pages 517-534. Read only the topics covered in lecture. We will not cover this chapter in detail. Complete
Drugs, The Brain, and Behavior
 Drugs, The Brain, and Behavior John Nyby Department of Biological Sciences Lehigh University What is a drug? Difficult to define Know it when you see it Neuroactive vs Non-Neuroactive drugs Two major categories
Drugs, The Brain, and Behavior John Nyby Department of Biological Sciences Lehigh University What is a drug? Difficult to define Know it when you see it Neuroactive vs Non-Neuroactive drugs Two major categories
North Bergen School District Benchmarks
 Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Chapter 2. The Biological Bases of Psychological Functioning
 Chapter 2 The Biological Bases of Psychological Functioning Outline I. Neurons: The Building Blocks of the Nervous System A. A neuron is a nerve cell that transmits information from one part of the body
Chapter 2 The Biological Bases of Psychological Functioning Outline I. Neurons: The Building Blocks of the Nervous System A. A neuron is a nerve cell that transmits information from one part of the body
What role does the nucleolus have in cell functioning? Glial cells
 Nervous System Lab The nervous system of vertebrates can be divided into the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which contains nerves,
Nervous System Lab The nervous system of vertebrates can be divided into the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which contains nerves,
Neurotransmission: Muscle Messages
 2 Neurotransmission: Muscle Messages GOAL The goal of this unit is to reinforce the process of neuromuscular transmission with hands-on materials. Set-up: -Reaction Time poster -Nerve-muscle poster -Synapse
2 Neurotransmission: Muscle Messages GOAL The goal of this unit is to reinforce the process of neuromuscular transmission with hands-on materials. Set-up: -Reaction Time poster -Nerve-muscle poster -Synapse
CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS SYSTEM II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system.
 CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system. NERVOUS CENTRAL NERVOUS (BRAIN & SPINAL CORD) (INTERNEURONS) PERIPHERAL NERVOUS (CRANIAL
CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system. NERVOUS CENTRAL NERVOUS (BRAIN & SPINAL CORD) (INTERNEURONS) PERIPHERAL NERVOUS (CRANIAL
BIOPHYSICS OF NERVE CELLS & NETWORKS
 UNIVERSITY OF LONDON MSci EXAMINATION May 2007 for Internal Students of Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine This paper is also taken for the relevant Examination for the Associateship
UNIVERSITY OF LONDON MSci EXAMINATION May 2007 for Internal Students of Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine This paper is also taken for the relevant Examination for the Associateship
NERVOUS SYSTEM PLEASE LABEL THIS DIAGRAM F G H
 BIOLOGY 12 - THE NERVOUS SYSTEM CHAPTER NOTES The nervous system is our processing system, and the system that keeps us in contact with the outside world. It tells us that we exist, and along with the
BIOLOGY 12 - THE NERVOUS SYSTEM CHAPTER NOTES The nervous system is our processing system, and the system that keeps us in contact with the outside world. It tells us that we exist, and along with the
