Procedures/risks: Radiology (CT, DXA, MRI, ultrasound, X-ray)
|
|
|
- Garry Hunter
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Procedures/risks: Radiology (CT, DXA, MRI, ultrasound, X-ray) Computerized Axial Tomography (CT): Procedure: A Computerized Axial Tomography (CT) scan [of your heart] involves holding your breath for a brief period of time (usually a few seconds) after a small dose of contrast/dye is injected into an intravenous line. You will have an intravenous catheter placed in your arm to administer the contrast agent. You will lie on a flat table that slides into a short, round CT scanner that detects the presence of dye in the heart and the arteries supplying the heart. A computer connected to the scanner makes images of the heart and arteries. The CT Scan [of the abdomen] is a standard procedure to measure structures inside the body/ of the body [e.g., total body fat of the abdomen]. You will lie flat on your back on the CT Scan table with your shoes off and minimal clothing. The machine will take one picture of your body [abdominal area]. At the completion of the test, the computer of the machine will generate images or pictures of your body [the fat content in your abdomen]. The x-ray emitted as part of the CT Scanning is 6 times that of a chest x-ray. Risks: Lying on a flat table for a few minutes may be uncomfortable. Occasionally, during a CT scan, some patients have experienced a feeling of being closed in or rarely, claustrophobia. The radiation exposure of an abdominal CT scan is about 6 times the amount of exposure of a chest x-ray. [For the purposes of this study, there will only be one (1) slice or picture of the abodmen taken, rather than a full abdominal CT Scan.] In order to see the blood vessels better during the CT scan, contrast agent must be injected. Any time a contrast agent is injected, there is the rare possibility of affecting the kidney. This is more likely if kidney function is already abnormal. If your kidney function is abnormal, then you will not be enrolled in this research study. There is also a chance that you may experience an allergic reaction to the contrast agent that will be used for the CT. Such a reaction is unlikely to occur especially if you have never had a reaction to this type of contrast agent in the past. There is about a 1 in 40,000 risk that anaphylactic shock (a serious and possibly life threatening allergic reaction) may result from the use of the CT contrast agent. The injection of the contrast agent may result in some discomfort as well as the possibilities of a general feeling of warmth, coolness or a sensation of local pressure or pain at the injection site. Less frequently reported side effects include dizziness, nausea, headache and a metallic taste in the mouth. Rare reactions include vomiting, drowsiness, visual disturbances, difficulty breathing, chest pain, increased heart rate, or allergy-like symptoms such as hives, itching or an irritation in the throat. Severe allergy-like reactions, if not treated, may result in death. However, for this study all CT scans will be performed where the necessary emergency medical equipment is immediately available should the need arise. In addition, you will be in continuous contact with a technologist and a physician and/or nurse who is readily available.
2 If you have a contrast allergy or any other factors that would prohibit you from safely and effectively participating in this study, please give this information to any member of the research team before you decide to participate in the study. For your safety you would not be eligible to participate in this study. When the contrast dye is injected during the CT scan, you may have a feeling of warmth spread throughout my body. You may have a salty taste in my mouth. You could have an allergic reaction to the dye and may feel nauseated (like the need to throw up), vomit (throw up), sneeze, get hives on your skin, or have itchy skin. The most common contrast dye contains iodine. If you know that you are allergic to contrast dye or iodine, you are to tell the study doctor. A rare but very serious allergic reaction to contrast dye is known as anaphylaxis (a life threatening swelling of the airway). If you begin to feel short of breath after the contrast dye is injected into your vein, then you should immediately tell the person taking the scan. If this rare reaction does take place, the procedure will be stopped, and you will be monitored by a physician. You must not move during the test; just relax and breathe normally. You might be uncomfortable while you are in the tunnel-shaped machine. Some people have felt claustrophobic during the test (feeling of being closed in because the space feels too small). If you become uncomfortable and feel like you are closed in, you are to tell the person taking the scan right away so that person can help you. If you know that you are claustrophobic, then tell your study doctor. There may be medication that can help you feel more relaxed during the procedure. The total body CT scan exposes you to a limited amount of radiation. The amount is similar to that from 100 chest x-rays and is similar to that received during a diagnostic cardiac catheterization procedure. It is also about one-third the amount received during a nuclear medicine stress test. It is unsafe for a pregnant women to undergo a CT scan. Therefore pregnant women will not be recruited nor be eligible to participate in this study. For all women of childbearing potential, a urine or serum pregnancy test will be performed [at the beginning of the study]. The cost of the pregnancy test, if indicated, will be performed at no cost to you. Results of the pregnancy test will be given to you. Contrast Dye (iohexol) Procedure: A small (1 teaspoon) dose of intravenous (IV) dye (iohexol, which is used for many radiological procedures, e.g. x-rays, CT scans, etc.) will be given intravenously in order to better measure your body s functions [name specific function(s)]. Risks: You will be given some dye. Some people develop allergic reactions to this dye. If you have a history of this, or a history of an allergic reaction to iodine or seafood, you will not be given the dye. However, there is a small chance that you may have a reaction to the dye. Such a reaction may be minor, for example itching and/or skin rash. Rarely, an allergic reaction can be severe, requiring emergency treatment with medications, hospitalization, or even death. X-ray dye can cause temporary kidney damage, but the amount of X-ray dye used in this study is at least only one-fifth of the amount that has been reported to cause this kind of kidney damage.
3 There is no evidence that the small amount of x-ray dye used for this testing is damaging to the kidney. Due to the unknown risks and potential harm to the unborn fetus, women who may become pregnant should not receive the dye. If you are a woman of childbearing potential you will undergo a pregnancy test prior to receiving the dye for the test at time that this procedure is scheduled during this research study. D[E]XA Procedure: Dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA or DEXA) is a standard procedure to measure body composition. It measures whole body fat, lean body mass (muscle) and bone density as well as regional body fat. After a technician has explained the procedure to you, you will lie flat on the DEXA table. X-rays from the machine will be introduced into your body. The absorption of the x-rays of your body tissue will be determined by the computer in the machine. Your muscle mass will be measured using a low dose x-ray machine (dual energy x-ray absorptiometry or D[E]XA). We will ask you to lie still for about 5-10 minutes while the D[E]XA machine scans over your body. This procedure is not painful, but there could be some minor discomfort from lying in the same position. Risk: The radiation emitted from the D[E]XA is less than that of a chest x-ray. The radiation exposure from the bone density machine (DEXA) is usually compared to the amount of exposure from one chest x-ray. Therefore, risks associated with DEXA are similar to exposure from a chest x-ray. Similarly, the bioelectrical impedance analyzer (BIA) is associated with minimal electrical current similar to that of electrocardiogram (EKG), a machine that is routinely used to measure heart beat and heart rhythm. During the DEXA scanning, you will be exposed to a tiny amount of radioactivity. The amount of radioactivity is equivalent to the amount you are exposed to when you are outside for five hours. There may be some minor discomfort from lying in the same position for 5 to 10 minutes while having the DEXA scan. The amount of radiation you will be exposed to from the DEXA scan is extremely small. This is a standard test that is performed in the study exactly the same as it is for regular patient care. The exposures for the DEXA are as follows: about 0.04 mrem (mrem is the standard unit of radiation exposure) from the whole body; 3.7 mrem (average adult) each from the hip and spine and 0.2 mrem from the forearm. In comparison, a typical airplane flight from Columbus to Los Angeles would expose your whole body to about 30 mrem of radiation and the annual natural exposure of radiation in Columbus is about 300 mrem per year. Any dose of radiation could be potentially harmful, but the risks that you will be exposed to are so small that they are difficult to measure. If you have had more than 5-10 x-ray procedures in the last year, you should discuss this with the investigator.
4 DEXA scans expose your body to radiation. Although it can vary from person to person, your whole-body radiation exposure is equivalent to approximately 3% of the amount of exposure a person in the U.S. receives from natural background radiation. The risk of harm from this amount of radiation is low and no harmful health effects are expected; however, your risk of harmful effects may increase if you are exposed to more procedures that involve radiation. You may experience a small amount of discomfort while being placed on the examination table or while lying down for the D[E]XA. This discomfort will be minimized by keeping the time involved in making the measurements as short as possible, and by allowing you a break if necessary. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Procedure: You will undergo a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan. Instead of using radiation (x-rays), MRI uses a powerful magnetic field (1.5 Tesla) and radio frequency waves. Many changes in body tissues can be evaluated by MRI. [The body is made up of atoms. These atoms have a magnetic charge. When the body is placed in a magnetic field, these atoms tend to line up with the magnetic field. Radio waves (similar to those used for TV) are then sent into the body, which alters the alignment of the atoms. When the radio waves are stopped, the atoms generate a weak radio signal that the machine detects. These radio signals are then processed by a computer. The result is an image that looks like the structures of the human body.] For the specifics of this study, the image will look like XXXX. [Since different tissues (heart muscle, arteries, etc.) have different magnetic properties, they will appear different on MRI images resulting in pictures of these structures.] You will be asked to remove all metal objects from your person. You may be asked to remove clothing and put on a hospital gown. You will lie on a flat table that slides into a round, full body clinical MRI scanner. Risks: Risks of having a MRI are much the same as the risks for having a CT scan. But in addition to those risks, you are not allowed to have any metal objects in or on your body because a MRI uses a powerful magnet that could cause a damaging pull on the objects. For example, you cannot have a MRI if you have a pacemaker or a metal pin in your body. You are to tell the study doctor if you have any metal objects in or on your body. It is possible that you could feel stress and/or claustrophobia (fear of enclosed spaces) during the MRI scans. Excessive levels of stress can pose risks to your health. The scans may take a long period of time (up to one hour) and it is possible that you may feel some discomfort related to lying on your back for that period of time. You may also experience fatigue during completion of the tasks presented to you. If you feel fatigue you can ask for a break. If you feel claustrophobic you can ask to end the study and you will be taken out of the MRI scanner. You will be able to speak to investigators and/or technician(s) at any time during the procedures if you have any concerns or difficulties.
5 As is common for routine clinical MRI exams, you will be asked to wear earplugs in order to reduce noise from the MRI system. The MRI magnet itself has been classified by the United States Food & Drug Administration (FDA) as a device with non-significant risk, and the MRI systems used in this experiment are all FDA approved for routine clinical use. Exposures to magnetic fields and radio waves will be within the FDA approved limits. If you have metallic objects in your body, you must inform the research team, since the magnetic field may affect this object in a significant manner that can harm you. Possible discomforts associated with being in the MRI scanner include noise from the magnet, which can be minimized with soft earplugs. You may also experience a sense of claustrophobia (a feeling of being closed in or trapped in a small space). Subjects with metallic foreign bodies, a cardiac pacemaker, an electronic stimulator, cerebral aneurysm clips or any metallic implant that is not compatible with the MRI machine, will not be allowed to be enrolled in the study. Subjects with coronary (around the heart) stents are candidates if they fall within the approved manufacturer MR safety guidelines and recommendations. There is a risk of movement or dislodgment of metal objects if overlooked during the screening process. In addition, an increase in the temperature of the object may occur. Although there have been no demonstrated effects of MRI in pregnancy, its safety remains unproven. Therefore pregnant females will not be recruited. Females of childbearing potential will be questioned as to whether or not they are pregnant, if there is any doubt a urine/serum pregnancy test will be performed. If a pregnancy test is conducted, then you will be notified of the results. MRI (cardiac): Procedure: You will undergo a cardiac magnetic resonance imaging scan (CMR), also known as heart MRI. Instead of using radiation (x rays), MRI uses a powerful magnetic field (1.5 Tesla) and radio frequency waves. Many changes in tissue can be evaluated by MRI. The result is an image that looks like the body s anatomy, for the specifics of this study, the image will look at your heart. [Since different tissues (arteries, muscle, etc.) have different magnetic properties, they will appear different on MRI images resulting in very clear pictures of the heart and heart arteries.] You will be asked to remove all metal objects. You may be asked to remove clothing and put on a hospital gown. An intravenous catheter (IV) will be placed in your arm or hand vein to deliver contrast material and/or medication during the scan. You will lie on a flat table that slides into a round, full body clinical MRI scanner. For this study, a contrast agent (material used to make tissue more visible, sometimes referred to dye) will be used in addition to routine cardiac MRI techniques. Risk: (see Magnetic Resonance Imaging) There is very small chance that you may have an allergic reaction to the contrast agent (gadolinium) that will be administered through the IV [for the CMR exam]. Other risks include headache, nausea, local pain, or hypotension (low blood pressure). Only about 3 out of 10,000
6 people experience any type of reaction to the [CMR] contrast agent. Severe allergy-like reaction, if not treated, may result in death. The MRI facility is equipped with all the necessary equipment and personnel to handle this situation, if it should it arise. If you have a known contrast allergy or any other factors that would prohibit you from safely and effectively participating in this study, you will not be enrolled. You will be monitored at all times by a nurse, physician and technologist during the administration of medications. The staff have immediate access to the emergency equipment should the need arise. Ultrasound Procedure: An ultrasound is a test that uses sound waves to get a picture of your insides, in this case your [anatomical structure]. You will lie on a table and the doctor or nurse will use a transducer (hand-held device) and gel that is applied to your skin, running the transducer over the skin of your abdomen. Ultrasound waves cause no sensation, and the only thing you will feel is the pressure of the transducer on your skin. Risks: There are no known risks to you [or to the developing fetus] from the use of ultrasound. X-Ray Procedure: You will have a chest X-ray to [check the placement of the central venous catheter]. [Additional X-rays may be done at any time if we think there is a problem with the catheter]. The chest X-ray will expose you to 8 millirem (mrem) of radiation. A millirem (mrem) is the the amount of radiation is measured. This amount of radiation is equal to about 3% of the annual radiation one is usually exposed to each year from the earth and the sky. Risks: When you have a chest x-ray, you will be exposed to low levels of radiation. There is a very slight chance of damage to cells or tissues from radiation.
CT Scan Thorax and Upper Abdomen. Respiratory Unit Patient Information Leaflet
 CT Scan Thorax and Upper Abdomen Respiratory Unit Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet gives you general information about your CT (computerised tomography) scan. It does not replace the
CT Scan Thorax and Upper Abdomen Respiratory Unit Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet gives you general information about your CT (computerised tomography) scan. It does not replace the
Positron Emission Tomography - For Patients
 Positron Emission Tomography - For Patients A physician s written order is required for any PET-CT tests. How should I prepare for my PET-CT? PET-CT is more complicated than most other tests you may be
Positron Emission Tomography - For Patients A physician s written order is required for any PET-CT tests. How should I prepare for my PET-CT? PET-CT is more complicated than most other tests you may be
Percutaneous Abscess Drainage
 Scan for mobile link. Percutaneous Abscess Drainage An abscess is an infected fluid collection within the body. Percutaneous abscess drainage uses imaging guidance to place a thin needle through the skin
Scan for mobile link. Percutaneous Abscess Drainage An abscess is an infected fluid collection within the body. Percutaneous abscess drainage uses imaging guidance to place a thin needle through the skin
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)? Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a valuable diagnostic study that has been used
Magnetic Resonance Imaging North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)? Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a valuable diagnostic study that has been used
X-Rays Benefits and Risks. Techniques that use x-rays
 X-Rays Benefits and Risks X-rays are a form of electromagnetic radiation, just like light waves and radiowaves. Because X-rays have higher energy than light waves, they can pass through the body. X-rays
X-Rays Benefits and Risks X-rays are a form of electromagnetic radiation, just like light waves and radiowaves. Because X-rays have higher energy than light waves, they can pass through the body. X-rays
Magnetic Resonance, Functional (fmri) - Brain
 Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance, Functional (fmri) - Brain Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fmri) measures the metabolic changes that occur within the brain. It may be used to examine the
Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance, Functional (fmri) - Brain Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fmri) measures the metabolic changes that occur within the brain. It may be used to examine the
Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal
 Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal What is Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal? An inferior vena cava filter placement procedure involves an interventional radiologist (a specialist doctor)
Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal What is Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal? An inferior vena cava filter placement procedure involves an interventional radiologist (a specialist doctor)
How To Prepare For A Ct Scan
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Radiology Department Information for patients having a CT scan page 2 The radiology department has received a request for you to have a CT scan. This leaflet tells
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Radiology Department Information for patients having a CT scan page 2 The radiology department has received a request for you to have a CT scan. This leaflet tells
Ureteral Stenting and Nephrostomy
 Scan for mobile link. Ureteral Stenting and Nephrostomy Ureteral stenting and nephrostomy help restore urine flow through blocked ureters and return the kidney to normal function. Ureters are long, narrow
Scan for mobile link. Ureteral Stenting and Nephrostomy Ureteral stenting and nephrostomy help restore urine flow through blocked ureters and return the kidney to normal function. Ureters are long, narrow
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Knee
 Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Knee Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the knee uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to produce detailed pictures of the
Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Knee Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the knee uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to produce detailed pictures of the
CT Scan UHN. Information for patients and families
 CT Scan UHN Information for patients and families Read this information to learn: what a CT scan is how to prepare for the scan what to expect who to contact if you have any questions Joint Department
CT Scan UHN Information for patients and families Read this information to learn: what a CT scan is how to prepare for the scan what to expect who to contact if you have any questions Joint Department
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Shoulder
 Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Shoulder Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the shoulder uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to produce detailed pictures
Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Shoulder Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the shoulder uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to produce detailed pictures
MRI of the Breast. What is MRI of the Breast?
 MRI of the Breast What is MRI of the Breast? Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a noninvasive, usually painless medical test that helps physicians diagnose and treat medical conditions. MRI uses a powerful
MRI of the Breast What is MRI of the Breast? Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a noninvasive, usually painless medical test that helps physicians diagnose and treat medical conditions. MRI uses a powerful
University College Hospital. Contrast agent for radiotherapy CT (computed tomography) scans. Radiotherapy Department Patient information series
 University College Hospital Contrast agent for radiotherapy CT (computed tomography) scans Radiotherapy Department Patient information series 11 2 If you need a large print, audio or translated copy of
University College Hospital Contrast agent for radiotherapy CT (computed tomography) scans Radiotherapy Department Patient information series 11 2 If you need a large print, audio or translated copy of
What are contrast materials and how do they work? Contrast materials enter the body in one of three ways. They can be:
 Scan for mobile link. Contrast Materials What are contrast materials and how do they work? Contrast materials, also called contrast agents or contrast media, are used to improve pictures of the inside
Scan for mobile link. Contrast Materials What are contrast materials and how do they work? Contrast materials, also called contrast agents or contrast media, are used to improve pictures of the inside
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) Arthrogram
 MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) Arthrogram MRI is a safe way for your doctor to take pictures of soft tissues and bones in the body. Using radio waves and a magnet field, the pictures provide information
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) Arthrogram MRI is a safe way for your doctor to take pictures of soft tissues and bones in the body. Using radio waves and a magnet field, the pictures provide information
Patient Prep Information
 Stereotactic Breast Biopsy Patient Prep Information Imaging Services Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center Table Weight Limits for each facility Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center
Stereotactic Breast Biopsy Patient Prep Information Imaging Services Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center Table Weight Limits for each facility Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center
X-ray (Radiography) - Abdomen
 Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Abdomen Abdominal x-ray uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of the inside of the abdominal cavity. It is used to evaluate the stomach,
Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Abdomen Abdominal x-ray uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of the inside of the abdominal cavity. It is used to evaluate the stomach,
First floor, Main Hospital North Services provided 24/7 365 days per year
 First floor, Main Hospital North Services provided 24/7 365 days per year General Radiology (X-ray) Fluoroscopy Ultrasound (Sonography) Nuclear Medicine P.E.T. imaging Computed Tomography (CT scan) Magnetic
First floor, Main Hospital North Services provided 24/7 365 days per year General Radiology (X-ray) Fluoroscopy Ultrasound (Sonography) Nuclear Medicine P.E.T. imaging Computed Tomography (CT scan) Magnetic
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Musculoskeletal
 Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Musculoskeletal Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to produce detailed pictures of joints,
Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Musculoskeletal Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to produce detailed pictures of joints,
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Spine
 Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Spine Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the spine uses radio waves, a magnetic field and a computer to produce detailed pictures of the spine
Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Spine Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the spine uses radio waves, a magnetic field and a computer to produce detailed pictures of the spine
Suspected pulmonary embolism (PE) in pregnant women
 Suspected pulmonary embolism (PE) in pregnant women What is a pulmonary embolus? A deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot that forms in one of the deep veins of the leg. If the clot moves to the lung,
Suspected pulmonary embolism (PE) in pregnant women What is a pulmonary embolus? A deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot that forms in one of the deep veins of the leg. If the clot moves to the lung,
YOUR MRI EXAM: QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
 YOUR MRI EXAM: QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS What is MRI? MRI is short for Magnetic Resonance Imaging. MRI is an advanced technology that lets your doctor see internal organs, blood vessels, muscles, joints, tumors,
YOUR MRI EXAM: QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS What is MRI? MRI is short for Magnetic Resonance Imaging. MRI is an advanced technology that lets your doctor see internal organs, blood vessels, muscles, joints, tumors,
Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography (MRCP)
 Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography or MRCP uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to evaluate the liver,
Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography or MRCP uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to evaluate the liver,
Computed Tomography (CT) - Sinuses
 Scan for mobile link. Computed Tomography (CT) - Sinuses Computed tomography (CT) of the sinuses uses special x-ray equipment to evaluate the paranasal sinus cavities hollow, air-filled spaces within the
Scan for mobile link. Computed Tomography (CT) - Sinuses Computed tomography (CT) of the sinuses uses special x-ray equipment to evaluate the paranasal sinus cavities hollow, air-filled spaces within the
X-ray (Radiography) - Chest
 Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Chest What is a Chest X-ray (Chest Radiography)? The chest x-ray is the most commonly performed diagnostic x-ray examination. A chest x-ray produces images of
Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Chest What is a Chest X-ray (Chest Radiography)? The chest x-ray is the most commonly performed diagnostic x-ray examination. A chest x-ray produces images of
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
CT Angiography (CTA) What is CT Angiography?
 Scan for mobile link. CT Angiography (CTA) Computed tomography angiography (CTA) uses an injection of iodine-rich contrast material and CT scanning to help diagnose and evaluate blood vessel disease or
Scan for mobile link. CT Angiography (CTA) Computed tomography angiography (CTA) uses an injection of iodine-rich contrast material and CT scanning to help diagnose and evaluate blood vessel disease or
Nerve Blocks. What is a Nerve Block? What are some common uses of the procedure?
 Scan for mobile link. Nerve Blocks A nerve block is an injection to decrease inflammation or "turn off" a pain signal along a specific distribution of nerve. Imaging guidance may be used to place the needle
Scan for mobile link. Nerve Blocks A nerve block is an injection to decrease inflammation or "turn off" a pain signal along a specific distribution of nerve. Imaging guidance may be used to place the needle
CARDIAC REHABILITATION PROGRAM
 CARDIAC REHABILITATION PROGRAM Preparation for the Cardiac Rehabilitation Program After your heart problem is stable, your physician or cardiologist will refer you to the Cardiac Rehabilitation program.
CARDIAC REHABILITATION PROGRAM Preparation for the Cardiac Rehabilitation Program After your heart problem is stable, your physician or cardiologist will refer you to the Cardiac Rehabilitation program.
Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal
 Scan for mobile link. Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal What is Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal? In an inferior vena cava filter placement procedure, interventional radiologists
Scan for mobile link. Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal What is Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal? In an inferior vena cava filter placement procedure, interventional radiologists
An abdominal ultrasound produces a picture of the organs and other structures in the upper abdomen.
 Scan for mobile link. Ultrasound - Abdomen Ultrasound imaging of the abdomen uses sound waves to produce pictures of the structures within the upper abdomen. It is used to help diagnose pain or distention
Scan for mobile link. Ultrasound - Abdomen Ultrasound imaging of the abdomen uses sound waves to produce pictures of the structures within the upper abdomen. It is used to help diagnose pain or distention
Lymphoscintigraphy is a special type of nuclear medicine imaging that provides pictures called scintigrams of the lymphatic system.
 Scan for mobile link. Lymphoscintigraphy Lymphoscintigraphy helps evaluate your body s lymphatic system for disease using small amounts of radioactive materials called radiotracers that are typically injected
Scan for mobile link. Lymphoscintigraphy Lymphoscintigraphy helps evaluate your body s lymphatic system for disease using small amounts of radioactive materials called radiotracers that are typically injected
Epidural Continuous Infusion. Patient information Leaflet
 Epidural Continuous Infusion Patient information Leaflet April 2015 Introduction You may already know that epidural s are often used to treat pain during childbirth. This same technique can also used as
Epidural Continuous Infusion Patient information Leaflet April 2015 Introduction You may already know that epidural s are often used to treat pain during childbirth. This same technique can also used as
X-ray (Radiography), Chest
 X-ray (Radiography), Chest What is a Chest X-ray (Chest Radiography)? The chest x-ray is the most commonly performed diagnostic x-ray examination. A chest x-ray makes images of the heart, lungs, airways,
X-ray (Radiography), Chest What is a Chest X-ray (Chest Radiography)? The chest x-ray is the most commonly performed diagnostic x-ray examination. A chest x-ray makes images of the heart, lungs, airways,
How can I be sure it will be performed to a high standard?
 FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS (About ultrasound scans at Derriford) What is an Ultrasound Scan? How does it work? What are the dangers? What are the advantages? Who will perform my scan? How can I be sure
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS (About ultrasound scans at Derriford) What is an Ultrasound Scan? How does it work? What are the dangers? What are the advantages? Who will perform my scan? How can I be sure
Epinephrine Administration Training for Unlicensed School Personnel
 Epinephrine Administration Training for Unlicensed School Personnel Management of Life-Threatening Allergies in the School Setting Dover and Sherborn Schools EpiPen Administration This program is designed
Epinephrine Administration Training for Unlicensed School Personnel Management of Life-Threatening Allergies in the School Setting Dover and Sherborn Schools EpiPen Administration This program is designed
Oxford Centre for Respiratory Medicine Bronchial-Artery Embolisation Information for patients
 Oxford Centre for Respiratory Medicine Bronchial-Artery Embolisation Information for patients This leaflet tells you about the bronchial-artery embolisation procedure. It explains what is involved and
Oxford Centre for Respiratory Medicine Bronchial-Artery Embolisation Information for patients This leaflet tells you about the bronchial-artery embolisation procedure. It explains what is involved and
A Patient s Guide to Minimally Invasive Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair
 A Patient s Guide to Minimally Invasive Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair Table of Contents The AFX Endovascular AAA System............................................ 1 What is an Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
A Patient s Guide to Minimally Invasive Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair Table of Contents The AFX Endovascular AAA System............................................ 1 What is an Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
The science of medicine. The compassion to heal.
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES OF THE HEART The science of medicine. The compassion to heal. This teaching booklet is designed to introduce you to electrophysiology studies of the heart.
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES OF THE HEART The science of medicine. The compassion to heal. This teaching booklet is designed to introduce you to electrophysiology studies of the heart.
Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty (PTA) and Stenting For PVS Patients
 Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty (PTA) and Stenting For PVS Patients There are two types of blood vessels in the body arteries and veins. Arteries carry blood rich in oxygen from the heart to all
Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty (PTA) and Stenting For PVS Patients There are two types of blood vessels in the body arteries and veins. Arteries carry blood rich in oxygen from the heart to all
University College Hospital. Having an MRI scan Imaging Department
 University College Hospital Having an MRI scan Imaging Department If you would like this leaflet in another format, for example: large print or audio, or in translation please contact us on 020 3456 7002.
University College Hospital Having an MRI scan Imaging Department If you would like this leaflet in another format, for example: large print or audio, or in translation please contact us on 020 3456 7002.
Who can have an MRI scan?
 i MRI Scan Contents What is an MRI scan? 1 Why am I having an MRI scan? 1 Who can have an MRI scan? 1 What preparation will I need? 2 What happens when I come for the scan? 2 Who will I see when I have
i MRI Scan Contents What is an MRI scan? 1 Why am I having an MRI scan? 1 Who can have an MRI scan? 1 What preparation will I need? 2 What happens when I come for the scan? 2 Who will I see when I have
CONSENT FOR MRI SCAN WITH INTRAVENOUS CONTRAST
 CONSENT FOR MRI SCAN WITH INTRAVENOUS CONTRAST Your Doctor has asked that an MRI scan be performed using intravenous contrast. This contrast may give the radiologist additional information that may not
CONSENT FOR MRI SCAN WITH INTRAVENOUS CONTRAST Your Doctor has asked that an MRI scan be performed using intravenous contrast. This contrast may give the radiologist additional information that may not
RADIOLOGY SERVICES. By Dr Lim Eng Kok 1
 INTRODUCTION RADIOLOGY SERVICES By Dr Lim Eng Kok 1 Radiology is the branch of medicine that deals with the use of ionising (e.g. x- rays and radio-isotopes) and non-ionising radiation (e.g. ultrasound
INTRODUCTION RADIOLOGY SERVICES By Dr Lim Eng Kok 1 Radiology is the branch of medicine that deals with the use of ionising (e.g. x- rays and radio-isotopes) and non-ionising radiation (e.g. ultrasound
CT scan. Useful information. Contents. This information is about CT scans. There are sections on
 CT scan Useful information Contents This information is about CT scans. There are sections on How a CT scanner works What happens Preparation for the scan Abdominal CT scans CT scans of the head CT scans
CT scan Useful information Contents This information is about CT scans. There are sections on How a CT scanner works What happens Preparation for the scan Abdominal CT scans CT scans of the head CT scans
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Aortic Stenosis. What is heart valve disease? What is aortic stenosis?
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Aortic Stenosis Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment This handout describes aortic stenosis, a narrowing of the aortic valve in your heart. It also explains how this
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Aortic Stenosis Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment This handout describes aortic stenosis, a narrowing of the aortic valve in your heart. It also explains how this
Cardiac CT for Calcium Scoring
 Scan for mobile link. Cardiac CT for Calcium Scoring Cardiac computed tomography (CT) for Calcium Scoring uses special x-ray equipment to produce pictures of the coronary arteries to determine if they
Scan for mobile link. Cardiac CT for Calcium Scoring Cardiac computed tomography (CT) for Calcium Scoring uses special x-ray equipment to produce pictures of the coronary arteries to determine if they
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. Radiology Tech
 From the: U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics Radiology Tech What They Do Radiologic technologists (RTs) perform diagnostic imaging examinations, such as x rays, on patients. Duties RTs typically do the following:
From the: U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics Radiology Tech What They Do Radiologic technologists (RTs) perform diagnostic imaging examinations, such as x rays, on patients. Duties RTs typically do the following:
X-ray (Radiography) - Bone
 Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Bone Bone x-ray uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of any bone in the body. It is commonly used to diagnose fractured bones or
Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Bone Bone x-ray uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of any bone in the body. It is commonly used to diagnose fractured bones or
BROCKTON AREA MULTI-SERVICES, INC. MEDICAL PROCEDURE GUIDE. Date(s) Reviewed/Revised:
 Page 1 of 5 PROCEDURE FOR: MAP-certified staff and RN/LPN MAP-certified staff are to be trained in the use of epinephrine administration via pre-filled autoinjector devices(s) annually. Certified staff
Page 1 of 5 PROCEDURE FOR: MAP-certified staff and RN/LPN MAP-certified staff are to be trained in the use of epinephrine administration via pre-filled autoinjector devices(s) annually. Certified staff
Chemotherapy Side Effects Worksheet
 Page 1 of 6 Chemotherapy Side Effects Worksheet Medicines or drugs that destroy cancer cells are called cancer chemotherapy. It is sometimes the first choice for treating many cancers. Chemotherapy differs
Page 1 of 6 Chemotherapy Side Effects Worksheet Medicines or drugs that destroy cancer cells are called cancer chemotherapy. It is sometimes the first choice for treating many cancers. Chemotherapy differs
University College Hospital. Your child is having an MRI scan under sedation. Imaging Department
 University College Hospital Your child is having an MRI scan under sedation Imaging Department If you would like this document in another language or format, or require the services of an interpreter,
University College Hospital Your child is having an MRI scan under sedation Imaging Department If you would like this document in another language or format, or require the services of an interpreter,
This handout is for informational purposes only. Talk with your doctor or health care team if you have any questions about your care.
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu PET stands for Positron Emission Tomography. The scan looks at metabolic activity (cell activity) inside the body. Your doctor uses this information to help
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu PET stands for Positron Emission Tomography. The scan looks at metabolic activity (cell activity) inside the body. Your doctor uses this information to help
Nephrostomy &/or Ureteric Stent Insertion PROCEDURAL CONSENT FORM. A. Interpreter / cultural needs. B. Procedure. C. Risks of the procedure
 DO NOT WRITE IN THIS BINDING MARGIN v2.00-03/2011 SW9231 Facility: Nephrostomy &/or Ureteric Stent Insertion A. Interpreter / cultural needs An Interpreter Service is required? Yes No If Yes, is a qualified
DO NOT WRITE IN THIS BINDING MARGIN v2.00-03/2011 SW9231 Facility: Nephrostomy &/or Ureteric Stent Insertion A. Interpreter / cultural needs An Interpreter Service is required? Yes No If Yes, is a qualified
THORACIC DIAGNOSTIC ASSESMENT PROGRAM (DAP) PATIENT INFORMATION FOR:
 central east regional cancer program in partnership with cancer care ontario THORACIC DIAGNOSTIC ASSESMENT PROGRAM (DAP) PATIENT INFORMATION FOR: Thoracic dap booklet March2012.indd 1 SCHEDULED TESTS YOUR
central east regional cancer program in partnership with cancer care ontario THORACIC DIAGNOSTIC ASSESMENT PROGRAM (DAP) PATIENT INFORMATION FOR: Thoracic dap booklet March2012.indd 1 SCHEDULED TESTS YOUR
Small cell lung cancer
 Small cell lung cancer Small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing organs that are found within
Small cell lung cancer Small cell lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing organs that are found within
University of Pennsylvania RESEARCH Subject Informed Consent Form AND RESEARCH SUBJECT HIPAA AUTHORIZATION
 University of Pennsylvania RESEARCH Subject Informed Consent Form AND RESEARCH SUBJECT HIPAA AUTHORIZATION Protocol Title: Evaluating the impact of cocaine use and HIV infection in arterial wall inflammation
University of Pennsylvania RESEARCH Subject Informed Consent Form AND RESEARCH SUBJECT HIPAA AUTHORIZATION Protocol Title: Evaluating the impact of cocaine use and HIV infection in arterial wall inflammation
Yttrium-90 Radiotherapy Treatment for liver tumors
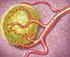 Patient Education Yttrium-90 Radiotherapy Treatment for liver tumors This handout explains what Yttrium-90 radiotherapy is and what to expect when you have it done. Why do I need this treatment? Your doctors
Patient Education Yttrium-90 Radiotherapy Treatment for liver tumors This handout explains what Yttrium-90 radiotherapy is and what to expect when you have it done. Why do I need this treatment? Your doctors
Patient Information Booklet. Endovascular Stent Grafts: A Treatment for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms
 Patient Information Booklet Endovascular Stent Grafts: A Treatment for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction 1 Glossary 2 Abdominal Aorta 4 Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm 5 Causes 6 Symptoms
Patient Information Booklet Endovascular Stent Grafts: A Treatment for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction 1 Glossary 2 Abdominal Aorta 4 Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm 5 Causes 6 Symptoms
EMERGENCY TREATMENT OF ANAPHYLAXIS EPINEPHRINE AUTO-INJECTOR
 I. GENERAL GUIDELINES EMERGENCY TREATMENT OF ANAPHYLAXIS EPINEPHRINE AUTO-INJECTOR A. PURPOSE To counteract a severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis) to a foreign substance as prescribed by the licensed
I. GENERAL GUIDELINES EMERGENCY TREATMENT OF ANAPHYLAXIS EPINEPHRINE AUTO-INJECTOR A. PURPOSE To counteract a severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis) to a foreign substance as prescribed by the licensed
Having denervation of the renal arteries for treatment of high blood pressure
 Having denervation of the renal arteries for treatment of high blood pressure The aim of this information sheet is to help answer some of the questions you may have about having denervation of the renal
Having denervation of the renal arteries for treatment of high blood pressure The aim of this information sheet is to help answer some of the questions you may have about having denervation of the renal
MEDICATION GUIDE mitoxantrone (mito-xan-trone) for injection concentrate
 MEDICATION GUIDE mitoxantrone (mito-xan-trone) for injection concentrate Read this Medication Guide before you start receiving mitoxantrone and each time you receive mitoxantrone. There may be new information.
MEDICATION GUIDE mitoxantrone (mito-xan-trone) for injection concentrate Read this Medication Guide before you start receiving mitoxantrone and each time you receive mitoxantrone. There may be new information.
Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) for Outpatient
 Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) for Outpatient Introduction A Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter, or PICC line, is a thin, long, soft plastic tube inserted into a vein of the arm. It
Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) for Outpatient Introduction A Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter, or PICC line, is a thin, long, soft plastic tube inserted into a vein of the arm. It
Mesothelioma. 1995-2013, The Patient Education Institute, Inc. www.x-plain.com ocft0101 Last reviewed: 03/21/2013 1
 Mesothelioma Introduction Mesothelioma is a type of cancer. It starts in the tissue that lines your lungs, stomach, heart, and other organs. This tissue is called mesothelium. Most people who get this
Mesothelioma Introduction Mesothelioma is a type of cancer. It starts in the tissue that lines your lungs, stomach, heart, and other organs. This tissue is called mesothelium. Most people who get this
PICC- Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter PROCEDURAL CONSENT FORM. A. Interpreter / cultural needs. B. Procedure. C. Risks of the procedure
 DO NOT WRITE IN THIS BINDING MARGIN v3.00-03/2011 SW9266 Facility: PICC- Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter A. Interpreter / cultural needs An Interpreter Service is required? Yes No If Yes, is a qualified
DO NOT WRITE IN THIS BINDING MARGIN v3.00-03/2011 SW9266 Facility: PICC- Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter A. Interpreter / cultural needs An Interpreter Service is required? Yes No If Yes, is a qualified
Radiation Exposure in X-ray and CT Examinations
 Patient Safety-Xray: Radiation Exposure in X-ray and CT Examinations What are x-rays and what do they do? X-rays are forms of radiant energy, like light or radio waves. Unlike light, x-rays can penetrate
Patient Safety-Xray: Radiation Exposure in X-ray and CT Examinations What are x-rays and what do they do? X-rays are forms of radiant energy, like light or radio waves. Unlike light, x-rays can penetrate
APPENDIX I-A: INFORMED CONSENT BB IND 11184 Protocol CDC IRB #4167
 APPENDIX I-A: INFORMED CONSENT BB IND 11184 Protocol CDC IRB #4167 INFORMED CONSENT FOR USE OF DIPHTHERIA ANTITOXIN (DAT) FOR SUSPECTED DIPHTHERIA CASES Investigational New Drug (IND) BB 11184 Protocol
APPENDIX I-A: INFORMED CONSENT BB IND 11184 Protocol CDC IRB #4167 INFORMED CONSENT FOR USE OF DIPHTHERIA ANTITOXIN (DAT) FOR SUSPECTED DIPHTHERIA CASES Investigational New Drug (IND) BB 11184 Protocol
LOW BACK PAIN: SHOULD I HAVE AN MRI?
 DATE: / / HG SY EH CQ RL AS JZ Name: (Last, First, M.I.) M F DOB: / / Decision Point LOW BACK PAIN: SHOULD I HAVE AN MRI? You may want to have a say in this decision, or you may simply want to follow your
DATE: / / HG SY EH CQ RL AS JZ Name: (Last, First, M.I.) M F DOB: / / Decision Point LOW BACK PAIN: SHOULD I HAVE AN MRI? You may want to have a say in this decision, or you may simply want to follow your
PERIPHERAL STEM CELL TRANSPLANT INTRODUCTION
 PERIPHERAL STEM CELL TRANSPLANT INTRODUCTION This booklet was designed to help you and the important people in your life understand the treatment of high dose chemotherapy with stem cell support: a procedure
PERIPHERAL STEM CELL TRANSPLANT INTRODUCTION This booklet was designed to help you and the important people in your life understand the treatment of high dose chemotherapy with stem cell support: a procedure
Ultrasound - Vascular
 Scan for mobile link. Ultrasound - Vascular Vascular ultrasound uses sound waves to evaluate the body s circulatory system and help identify blockages and detect blood clots. A Doppler ultrasound study
Scan for mobile link. Ultrasound - Vascular Vascular ultrasound uses sound waves to evaluate the body s circulatory system and help identify blockages and detect blood clots. A Doppler ultrasound study
X-Plain Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer - Adriamycin, Cytoxan, and Tamoxifen Reference Summary
 X-Plain Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer - Adriamycin, Cytoxan, and Tamoxifen Reference Summary Introduction Breast cancer is a common condition that affects one out of every 11 women. Your doctor has recommended
X-Plain Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer - Adriamycin, Cytoxan, and Tamoxifen Reference Summary Introduction Breast cancer is a common condition that affects one out of every 11 women. Your doctor has recommended
RENAL ANGIOMYOLIPOMA EMBOLIZATION
 RENAL ANGIOMYOLIPOMA EMBOLIZATION The information about renal angiomyolipomas on the next several pages includes questions commonly asked about the embolization procedure. Please take a few moments to
RENAL ANGIOMYOLIPOMA EMBOLIZATION The information about renal angiomyolipomas on the next several pages includes questions commonly asked about the embolization procedure. Please take a few moments to
Society of Nuclear Medicine 1850 Samuel Morse Drive Reston, VA 20190-5316 www.snm.org
 What is nuclear medicine? Nuclear medicine is a medical specialty that is used to diagnose and treat diseases in a safe and painless way. Nuclear medicine procedures permit the determination of medical
What is nuclear medicine? Nuclear medicine is a medical specialty that is used to diagnose and treat diseases in a safe and painless way. Nuclear medicine procedures permit the determination of medical
How To Prepare For An Imaging Test
 Imaging (Radiology) Tests What are imaging tests? An imaging test is a way to let doctors see what s going on inside your body. These tests send forms of energy (x-rays, sound waves, radioactive particles,
Imaging (Radiology) Tests What are imaging tests? An imaging test is a way to let doctors see what s going on inside your body. These tests send forms of energy (x-rays, sound waves, radioactive particles,
Mammography. What is Mammography?
 Scan for mobile link. Mammography Mammography is a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to detect cancer early before women experience symptoms when it is most treatable. Tell your
Scan for mobile link. Mammography Mammography is a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to detect cancer early before women experience symptoms when it is most treatable. Tell your
Liver Disease & Hepatitis Program Providers: Brian McMahon, MD, Steve Livingston, MD, Lisa Townshend, ANP. Primary Care Provider:
 Liver Disease & Hepatitis Program Providers: Brian McMahon, MD, Steve Livingston, MD, Lisa Townshend, ANP Primary Care Provider: If you are considering hepatitis C treatment, please read this treatment
Liver Disease & Hepatitis Program Providers: Brian McMahon, MD, Steve Livingston, MD, Lisa Townshend, ANP Primary Care Provider: If you are considering hepatitis C treatment, please read this treatment
Liver Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE) Cancer treatment
 Patient Education Liver Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE) Cancer treatment This handout explains what liver transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) is and what to expect with this cancer treatment.
Patient Education Liver Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE) Cancer treatment This handout explains what liver transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) is and what to expect with this cancer treatment.
Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT)
 Scan for mobile link. Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) Intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) uses linear accelerators to safely and painlessly deliver precise radiation doses to a tumor while
Scan for mobile link. Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) Intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) uses linear accelerators to safely and painlessly deliver precise radiation doses to a tumor while
The degree of liver inflammation or damage (grade) Presence and extent of fatty liver or other metabolic liver diseases
 ilearning about your health Liver Biopsy www.cpmc.org/learning What is a Liver Biopsy? A liver biopsy is a procedure where a specially trained doctor (typically a hepatologist, radiologist, or gastroenterologist)
ilearning about your health Liver Biopsy www.cpmc.org/learning What is a Liver Biopsy? A liver biopsy is a procedure where a specially trained doctor (typically a hepatologist, radiologist, or gastroenterologist)
Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too.
 Male Breast Cancer Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too. Many people do not know that men can get breast
Male Breast Cancer Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too. Many people do not know that men can get breast
Prolia 2 shots a year proven to help strengthen bones.
 Ask your doctor if Prolia (denosumab) is right for you and visit us at www.prolia.com For women with postmenopausal osteoporosis at high risk for fracture: there s Prolia. Prolia 2 shots a year proven
Ask your doctor if Prolia (denosumab) is right for you and visit us at www.prolia.com For women with postmenopausal osteoporosis at high risk for fracture: there s Prolia. Prolia 2 shots a year proven
Smoking and misuse of certain pain medicines can affect the risk of developing renal cell cancer.
 Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
Presenting the SUTENT Patient Call Center.
 Presenting the SUTENT Patient Call Center. Please see patient Medication Guide and full prescribing information attached. We re here to support you. Dealing with cancer is a journey. Along the way, you
Presenting the SUTENT Patient Call Center. Please see patient Medication Guide and full prescribing information attached. We re here to support you. Dealing with cancer is a journey. Along the way, you
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Xofigo Therapy. For metastatic prostate cancer. What is Xofigo? How does it work?
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Xofigo Therapy For metastatic prostate cancer This handout explains how the drug Xofigo is used to treat metastatic prostate cancer. What is Xofigo? Xofigo is a radioactive
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Xofigo Therapy For metastatic prostate cancer This handout explains how the drug Xofigo is used to treat metastatic prostate cancer. What is Xofigo? Xofigo is a radioactive
Heart Attack: What You Need to Know
 A WorkLife4You Guide Heart Attack: What You Need to Know What is a Heart Attack? The heart works 24 hours a day, pumping oxygen and nutrient-rich blood to the body. Blood is supplied to the heart through
A WorkLife4You Guide Heart Attack: What You Need to Know What is a Heart Attack? The heart works 24 hours a day, pumping oxygen and nutrient-rich blood to the body. Blood is supplied to the heart through
What You Should Know About Cerebral Aneurysms
 What You Should Know About Cerebral Aneurysms From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Interventions Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Radiology Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D.,
What You Should Know About Cerebral Aneurysms From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Interventions Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Radiology Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D.,
Computed Tomography (CT) - Chest
 Scan for mobile link. Computed Tomography (CT) - Chest Computed tomography (CT) of the chest uses special x-ray equipment to examine abnormalities found in other imaging tests and to help diagnose the
Scan for mobile link. Computed Tomography (CT) - Chest Computed tomography (CT) of the chest uses special x-ray equipment to examine abnormalities found in other imaging tests and to help diagnose the
MEDICATION GUIDE ACTOPLUS MET (ak-tō-plus-met) (pioglitazone hydrochloride and metformin hydrochloride) tablets
 MEDICATION GUIDE (ak-tō-plus-met) (pioglitazone hydrochloride and metformin hydrochloride) tablets Read this Medication Guide carefully before you start taking and each time you get a refill. There may
MEDICATION GUIDE (ak-tō-plus-met) (pioglitazone hydrochloride and metformin hydrochloride) tablets Read this Medication Guide carefully before you start taking and each time you get a refill. There may
Mitoxantrone. For multiple sclerosis. InfoNEURO INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS. Montreal Neurological Hospital
 i InfoNEURO Montreal Neurological Hospital INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS Mitoxantrone For multiple sclerosis Centre universitaire de santé McGill McGill University Health Centre Collaborators: D. Lowden Clinical
i InfoNEURO Montreal Neurological Hospital INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS Mitoxantrone For multiple sclerosis Centre universitaire de santé McGill McGill University Health Centre Collaborators: D. Lowden Clinical
Information for adults having an MRI scan of the gallbladder and biliary tree (an MRCP scan)
 South Tyneside NHS Foundation Trust Information for adults having an MRI scan of the gallbladder and biliary tree (an MRCP scan) Department: Radiology Providing a range of NHS services in Gateshead, South
South Tyneside NHS Foundation Trust Information for adults having an MRI scan of the gallbladder and biliary tree (an MRCP scan) Department: Radiology Providing a range of NHS services in Gateshead, South
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma)
 Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
Electroconvulsive Therapy - ECT
 Electroconvulsive Therapy - ECT Introduction Electroconvulsive therapy, or ECT, is a safe and effective treatment that may reduce symptoms related to depression or mental illness. During ECT, certain parts
Electroconvulsive Therapy - ECT Introduction Electroconvulsive therapy, or ECT, is a safe and effective treatment that may reduce symptoms related to depression or mental illness. During ECT, certain parts
Horton General Hospital Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Information for patients
 Horton General Hospital Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Information for patients What is a Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)? A DVT is a blood clot which forms in a deep vein, usually in
Horton General Hospital Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Information for patients What is a Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)? A DVT is a blood clot which forms in a deep vein, usually in
