Ureteral Stenting and Nephrostomy
|
|
|
- Amice Hunter
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Scan for mobile link. Ureteral Stenting and Nephrostomy Ureteral stenting and nephrostomy help restore urine flow through blocked ureters and return the kidney to normal function. Ureters are long, narrow tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder. They can become obstructed and urine flow blocked as a result of various conditions. Your doctor may use image guidance to place a thin, flexible tube called a stent into the ureter to restore urine flow. If a stent cannot be placed, he may perform a nephrostomy, during which a tube is placed through the skin into the kidney and connected to either an external drainage bag or the bladder. Tell your doctor if there s a possibility you are pregnant and discuss any recent illnesses, medical conditions, allergies and medications you re taking. Your doctor may advise you to stop taking aspirin, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or blood thinners several days prior to your procedure and instruct you not to eat or drink anything after midnight the night before. Take regular medication with sips of water. Leave jewelry at home and wear loose, comfortable clothing. You may be asked to wear a gown. If you are not to be admitted to the hospital, plan to have someone drive you home afterward. What are Ureteral Stenting and Nephrostomy? Urine is normally carried from the kidneys to the bladder through long, narrow tubes called ureters. The ureter can become obstructed due to conditions such as kidney stones, tumors, infection, or blood clots. When this happens, physicians can use image guidance to place stents or tubes in the ureter to restore the flow of urine to the bladder. A ureteral stent is a thin, flexible tube threaded into the ureter. When it is not possible to insert a ureteral stent, nephrostomy is performed. During this procedure, a tube is placed through the skin on the patient's back into the kidney. The tube is connected to an external drainage bag or from the kidney to the bladder. How should I prepare? Ureteral Stenting and Nephrostomy Page 1 of 6
2 You might have blood drawn prior to your procedure. Prior to your procedure, your blood may be tested to determine how well your kidneys are functioning and whether your blood clots normally. You should report to your doctor all medications that you are taking, including herbal supplements, and if you have any allergies, especially to local anesthetic medications, general anesthesia or to contrast materials containing iodine (sometimes referred to as "dye" or "x-ray dye"). Your physician may advise you to stop taking aspirin, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or blood thinners for a specified period of time before your procedure. Also inform your doctor about recent illnesses or other medical conditions. Women should always inform their physician and x-ray technologist if there is any possibility that they are pregnant. Many imaging tests are not performed during pregnancy so as not to expose the fetus to radiation. If an x-ray is necessary, precautions will be taken to minimize radiation exposure to the baby. See the Safety page for more information about pregnancy and x-rays. In general, you should not eat or drink anything after midnight the day of your procedure. However, you may take your routine medications with sips of water. If you are diabetic and take insulin, you should talk to your doctor as your usual insulin dose may need to be adjusted. You will be given a gown to wear during the procedure. You should plan to have a relative or friend drive you home after your procedure. What does the equipment look like? During ureteral stenting, a fluoroscope and a guide wire are used to place a stent into the ureter. A guide wire may be inserted with the aid of a fluoroscope, an imaging device that uses x-rays to see structures on a fluorescent screen. A stent is 10 to 15 inches long and less than a quarter inch thick. During a nephrostomy, a fluoroscope, or an ultrasound, and a needle are used to place a catheter in the kidney. A catheter is a long, thin plastic tube that is considerably smaller than a "pencil lead", or approximately 1/8 inch in diameter. Ultrasound scanners consist of a console containing a computer and electronics, a video display screen and a transducer that is used to do the scanning. The transducer is a small hand-held device that resembles a microphone, attached to the scanner by a cord. Some exams may use different transducers (with different capabilities) during a single exam. The transducer sends out inaudible, high frequency sound waves into the body and then listens for the returning echoes from the tissues in the body. The principles are similar to sonar used by boats and submarines. The ultrasound image is immediately visible on a video display screen that looks like a computer or Ureteral Stenting and Nephrostomy Page 2 of 6
3 The ultrasound image is immediately visible on a video display screen that looks like a computer or television monitor. The image is created based on the amplitude (loudness), frequency (pitch) and time it takes for the ultrasound signal to return from the area within the patient that is being examined to the transducer (the device used to examine the patient), as well as the type of body structure and composition of body tissue through which the sound travels. A small amount of gel is put on the skin to allow the sound waves to best travel from the transducer to the examined area within the body and then back again. Ultrasound is an excellent modality for some areas of the body while other areas, especially the lungs, are poorly suited for ultrasound. Other equipment that may be used during the procedure includes an intravenous line (IV), ultrasound machine and devices that monitor your heart beat and blood pressure. How are these procedures performed? Image-guided, minimally invasive procedures such as ureteral stenting and nephrostomy are most often performed by a specially trained interventional radiologist in an interventional radiology suite or occasionally in the operating room. This procedure is often done on an outpatient basis. However, some patients may require admission following the procedure. Please consult with your physician as to whether or not you will be admitted. Prior to your procedure, ultrasound, computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be performed. You may be given medications to help prevent nausea and pain, and antibiotics to help prevent infection. You may be connected to monitors that track your heart rate, blood pressure and pulse during the procedure. A nurse or technologist will insert an intravenous (IV) line into a vein in your hand or arm so that sedative medication can be given intravenously. Moderate sedation may be used. As an alternative, you may receive general anesthesia. If you receive moderate sedation, you will be asleep but have the ability to be awakened. The sedation will be administered and monitored by your physician and nursing staff. If you receive a general anesthetic, you will be unconscious for the entire procedure, and you will be monitored by an anesthesiologist. The area of your body where the catheter is to be inserted (usually in a groin region) will be shaved, sterilized and covered with a surgical drape. Your physician will numb the area with a local anesthetic. The interventional radiologist will use x-rays and/or ultrasound to locate your kidney and a needle will be inserted through your skin into the kidneys. Contrast dye will be injected through the needle. During ureteral stenting, you are positioned on your stomach. Using a fluoroscope to see the ureter, a guide wire is inserted into the ureter. The stent is run over the guide wire and placed in its permanent Ureteral Stenting and Nephrostomy Page 3 of 6
4 guide wire is inserted into the ureter. The stent is run over the guide wire and placed in its permanent position within the ureter. Once the stent has been placed, the guide wire may be removed, or a nephrostomy catheter may be left in place for a day or two and then removed. At the end of the procedure, the catheter will be removed and pressure will be applied to stop any bleeding. The opening in the skin is then covered with a dressing. No sutures are needed. During nephrostomy, you are positioned on your stomach. Using a fluoroscope to see the kidney, a guide wire is inserted into the kidney, followed by a catheter. This will be left in place until a ureteral stent can be placed or the ureteral blockage is resolved. Most commonly, the nephrostomy catheter is connected to an external bag that collects urine. You will be instructed on how to empty and care for the drainage bag prior to leaving the hospital. Your intravenous line will be removed. Both procedures are usually completed within one hour. What will I experience during and after the procedure? Devices to monitor your heart rate and blood pressure will be attached to your body. You will feel a slight pin prick when the needle is inserted into your vein for the intravenous line (IV) and when the local anesthetic is injected. Most of the sensation is at the skin incision site which is numbed using local anesthetic. You may feel pressure when the catheter is inserted into the vein or artery. If the procedure is done with sedation, the intravenous (IV) sedative will make you feel relaxed and sleepy. You may or may not remain awake, depending on how deeply you are sedated. You may feel slight pressure as the catheter is inserted into the kidney and down the ureter. During placement of a ureteral stent, until the stent is positioned, you may feel pressure as the guide wire is inserted into the bladder. You will remain in the recovery room until you are completely awake and ready to return home. You will not feel when the contrast is excreted into the urine. You should be able to resume your normal activities within a few days. Who interprets the results and how do I get them? The interventional radiologist can advise you as to whether the procedure was a technical success when it is completed. Your interventional radiologist may recommend a follow-up visit after your procedure or treatment is complete. The visit may include a physical check-up, imaging procedure(s) and blood or other lab tests. During Ureteral Stenting and Nephrostomy Page 4 of 6
5 your follow-up visit, you may discuss with your doctor any changes or side effects you have experienced since your procedure or treatment. What are the benefits vs. risks? Benefits Risks A ureteral stent or nephrostomy catheter will allow urine to flow again from the kidney and permit the kidney to function normally. Any procedure where the skin is penetrated carries a risk of infection. The chance of infection requiring antibiotic treatment appears to be less than one in 1,000. Rarely, you may experience ongoing spasm of the bladder after placement of a ureteral stent. If this happens, notify you doctor. This spasm may be treated with medication. Because the kidney is an organ with a substantial amount of blood flow to it, bleeding is a possible but rare complication. There is also a small risk of damage to surrounding organs. Imaging guidance is used to minimize this risk. There is a very slight risk of an allergic reaction if contrast material is injected. Disclaimer This information is copied from the RadiologyInfo Web site ( which is dedicated to providing the highest quality information. To ensure that, each section is reviewed by a physician with expertise in the area presented. All information contained in the Web site is further reviewed by an ACR (American College of Radiology) - RSNA (Radiological Society of North America) committee, comprising physicians with expertise in several radiologic areas. However, it is not possible to assure that this Web site contains complete, up-to-date information on any particular subject. Therefore, ACR and RSNA make no representations or warranties about the suitability of this information for use for any particular purpose. All information is provided "as is" without express or implied warranty. Please visit the RadiologyInfo Web site at to view or download the latest information. Note: Images may be shown for illustrative purposes. Do not attempt to draw conclusions or make diagnoses by comparing these images to other medical images, particularly your own. Only qualified physicians should interpret images; the radiologist is the physician expert trained in medical imaging. Copyright This material is copyrighted by either the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA), 820 Jorie Boulevard, Oak Brook, IL or the American College of Radiology (ACR), 1891 Preston White Drive, Reston, VA Commercial reproduction or multiple distribution by any traditional or electronically based reproduction/publication method is prohibited. Copyright 2016 Radiological Society of North America, Inc. Ureteral Stenting and Nephrostomy Page 5 of 6
6 Ureteral Stenting and Nephrostomy Page 6 of 6
Percutaneous Abscess Drainage
 Scan for mobile link. Percutaneous Abscess Drainage An abscess is an infected fluid collection within the body. Percutaneous abscess drainage uses imaging guidance to place a thin needle through the skin
Scan for mobile link. Percutaneous Abscess Drainage An abscess is an infected fluid collection within the body. Percutaneous abscess drainage uses imaging guidance to place a thin needle through the skin
Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal
 Scan for mobile link. Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal What is Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal? In an inferior vena cava filter placement procedure, interventional radiologists
Scan for mobile link. Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal What is Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal? In an inferior vena cava filter placement procedure, interventional radiologists
Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal
 Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal What is Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal? An inferior vena cava filter placement procedure involves an interventional radiologist (a specialist doctor)
Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal What is Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal? An inferior vena cava filter placement procedure involves an interventional radiologist (a specialist doctor)
Varicose Vein Treatment (Endovenous Ablation of Varicose Veins)
 Scan for mobile link. Varicose Vein Treatment (Endovenous Ablation of Varicose Veins) Varicose vein treatment, also known as endovenous ablation, uses radiofrequency or laser energy to cauterize and close
Scan for mobile link. Varicose Vein Treatment (Endovenous Ablation of Varicose Veins) Varicose vein treatment, also known as endovenous ablation, uses radiofrequency or laser energy to cauterize and close
Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA) of Liver Tumors
 Scan for mobile link. Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA) of Liver Tumors Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is a treatment that uses imaging guidance to place a needle electrode through the skin into a liver tumor.
Scan for mobile link. Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA) of Liver Tumors Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is a treatment that uses imaging guidance to place a needle electrode through the skin into a liver tumor.
An abdominal ultrasound produces a picture of the organs and other structures in the upper abdomen.
 Scan for mobile link. Ultrasound - Abdomen Ultrasound imaging of the abdomen uses sound waves to produce pictures of the structures within the upper abdomen. It is used to help diagnose pain or distention
Scan for mobile link. Ultrasound - Abdomen Ultrasound imaging of the abdomen uses sound waves to produce pictures of the structures within the upper abdomen. It is used to help diagnose pain or distention
Nerve Blocks. What is a Nerve Block? What are some common uses of the procedure?
 Scan for mobile link. Nerve Blocks A nerve block is an injection to decrease inflammation or "turn off" a pain signal along a specific distribution of nerve. Imaging guidance may be used to place the needle
Scan for mobile link. Nerve Blocks A nerve block is an injection to decrease inflammation or "turn off" a pain signal along a specific distribution of nerve. Imaging guidance may be used to place the needle
Stereotactic Breast Biopsy
 Scan for mobile link. Stereotactic Breast Biopsy Stereotactic breast biopsy uses mammography a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to help locate a breast lump or abnormality and
Scan for mobile link. Stereotactic Breast Biopsy Stereotactic breast biopsy uses mammography a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to help locate a breast lump or abnormality and
Hysterosalpingography
 Scan for mobile link. Hysterosalpingography Hysterosalpingography uses a real-time form of x-ray called fluoroscopy to examine the uterus and fallopian tubes of a woman who is having difficulty becoming
Scan for mobile link. Hysterosalpingography Hysterosalpingography uses a real-time form of x-ray called fluoroscopy to examine the uterus and fallopian tubes of a woman who is having difficulty becoming
X-ray (Radiography) - Abdomen
 Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Abdomen Abdominal x-ray uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of the inside of the abdominal cavity. It is used to evaluate the stomach,
Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Abdomen Abdominal x-ray uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of the inside of the abdominal cavity. It is used to evaluate the stomach,
Ultrasound - Vascular
 Scan for mobile link. Ultrasound - Vascular Vascular ultrasound uses sound waves to evaluate the body s circulatory system and help identify blockages and detect blood clots. A Doppler ultrasound study
Scan for mobile link. Ultrasound - Vascular Vascular ultrasound uses sound waves to evaluate the body s circulatory system and help identify blockages and detect blood clots. A Doppler ultrasound study
How To Use An Ultrasound For Medical Research
 Scan for mobile link. General Ultrasound What is General Ultrasound Imaging? Ultrasound is safe and painless, and produces pictures of the inside of the body using sound waves. Ultrasound imaging, also
Scan for mobile link. General Ultrasound What is General Ultrasound Imaging? Ultrasound is safe and painless, and produces pictures of the inside of the body using sound waves. Ultrasound imaging, also
Lymphoscintigraphy is a special type of nuclear medicine imaging that provides pictures called scintigrams of the lymphatic system.
 Scan for mobile link. Lymphoscintigraphy Lymphoscintigraphy helps evaluate your body s lymphatic system for disease using small amounts of radioactive materials called radiotracers that are typically injected
Scan for mobile link. Lymphoscintigraphy Lymphoscintigraphy helps evaluate your body s lymphatic system for disease using small amounts of radioactive materials called radiotracers that are typically injected
Computed Tomography (CT) - Sinuses
 Scan for mobile link. Computed Tomography (CT) - Sinuses Computed tomography (CT) of the sinuses uses special x-ray equipment to evaluate the paranasal sinus cavities hollow, air-filled spaces within the
Scan for mobile link. Computed Tomography (CT) - Sinuses Computed tomography (CT) of the sinuses uses special x-ray equipment to evaluate the paranasal sinus cavities hollow, air-filled spaces within the
X-ray (Radiography) - Chest
 Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Chest What is a Chest X-ray (Chest Radiography)? The chest x-ray is the most commonly performed diagnostic x-ray examination. A chest x-ray produces images of
Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Chest What is a Chest X-ray (Chest Radiography)? The chest x-ray is the most commonly performed diagnostic x-ray examination. A chest x-ray produces images of
X-ray (Radiography), Chest
 X-ray (Radiography), Chest What is a Chest X-ray (Chest Radiography)? The chest x-ray is the most commonly performed diagnostic x-ray examination. A chest x-ray makes images of the heart, lungs, airways,
X-ray (Radiography), Chest What is a Chest X-ray (Chest Radiography)? The chest x-ray is the most commonly performed diagnostic x-ray examination. A chest x-ray makes images of the heart, lungs, airways,
X-ray (Radiography) - Bone
 Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Bone Bone x-ray uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of any bone in the body. It is commonly used to diagnose fractured bones or
Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Bone Bone x-ray uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of any bone in the body. It is commonly used to diagnose fractured bones or
Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT)
 Scan for mobile link. Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) Intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) uses linear accelerators to safely and painlessly deliver precise radiation doses to a tumor while
Scan for mobile link. Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) Intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) uses linear accelerators to safely and painlessly deliver precise radiation doses to a tumor while
Video Fluoroscopic Swallowing Exam (VFSE)
 Scan for mobile link. Video Fluoroscopic Swallowing Exam (VFSE) A video fluoroscopic swallowing exam (VFSE) uses a form of real-time x-ray called fluoroscopy to evaluate a patient s ability to swallow
Scan for mobile link. Video Fluoroscopic Swallowing Exam (VFSE) A video fluoroscopic swallowing exam (VFSE) uses a form of real-time x-ray called fluoroscopy to evaluate a patient s ability to swallow
Cardiac CT for Calcium Scoring
 Scan for mobile link. Cardiac CT for Calcium Scoring Cardiac computed tomography (CT) for Calcium Scoring uses special x-ray equipment to produce pictures of the coronary arteries to determine if they
Scan for mobile link. Cardiac CT for Calcium Scoring Cardiac computed tomography (CT) for Calcium Scoring uses special x-ray equipment to produce pictures of the coronary arteries to determine if they
X-ray (Radiography), Lower GI Tract
 Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography), Lower GI Tract What is Lower GI Tract X-ray Radiography (Barium Enema)? Lower gastrointestinal (GI) tract radiography, also called a lower GI or barium enema,
Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography), Lower GI Tract What is Lower GI Tract X-ray Radiography (Barium Enema)? Lower gastrointestinal (GI) tract radiography, also called a lower GI or barium enema,
Catheter Embolization and YOU
 Catheter Embolization and YOU What is catheter embolization? Embolization therapy is a minimally invasive (non-surgical) treatment that occludes or blocks one or more blood vessels or vascular channels
Catheter Embolization and YOU What is catheter embolization? Embolization therapy is a minimally invasive (non-surgical) treatment that occludes or blocks one or more blood vessels or vascular channels
X-ray (Radiography), Upper GI Tract
 Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography), Upper GI Tract What is Upper Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract Radiography? Upper gastrointestinal tract radiography, also called an upper GI, is an x-ray examination
Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography), Upper GI Tract What is Upper Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract Radiography? Upper gastrointestinal tract radiography, also called an upper GI, is an x-ray examination
CT Angiography (CTA) What is CT Angiography?
 Scan for mobile link. CT Angiography (CTA) Computed tomography angiography (CTA) uses an injection of iodine-rich contrast material and CT scanning to help diagnose and evaluate blood vessel disease or
Scan for mobile link. CT Angiography (CTA) Computed tomography angiography (CTA) uses an injection of iodine-rich contrast material and CT scanning to help diagnose and evaluate blood vessel disease or
Oxford Centre for Respiratory Medicine Bronchial-Artery Embolisation Information for patients
 Oxford Centre for Respiratory Medicine Bronchial-Artery Embolisation Information for patients This leaflet tells you about the bronchial-artery embolisation procedure. It explains what is involved and
Oxford Centre for Respiratory Medicine Bronchial-Artery Embolisation Information for patients This leaflet tells you about the bronchial-artery embolisation procedure. It explains what is involved and
Nephrostomy &/or Ureteric Stent Insertion PROCEDURAL CONSENT FORM. A. Interpreter / cultural needs. B. Procedure. C. Risks of the procedure
 DO NOT WRITE IN THIS BINDING MARGIN v2.00-03/2011 SW9231 Facility: Nephrostomy &/or Ureteric Stent Insertion A. Interpreter / cultural needs An Interpreter Service is required? Yes No If Yes, is a qualified
DO NOT WRITE IN THIS BINDING MARGIN v2.00-03/2011 SW9231 Facility: Nephrostomy &/or Ureteric Stent Insertion A. Interpreter / cultural needs An Interpreter Service is required? Yes No If Yes, is a qualified
What are some common uses of the procedure?
 Scan for mobile link. Cardiac Nuclear Medicine Cardiac nuclear medicine imaging evaluates the heart for coronary artery disease and cardiomyopathy. It also may be used to help determine whether the heart
Scan for mobile link. Cardiac Nuclear Medicine Cardiac nuclear medicine imaging evaluates the heart for coronary artery disease and cardiomyopathy. It also may be used to help determine whether the heart
Positron Emission Tomography - For Patients
 Positron Emission Tomography - For Patients A physician s written order is required for any PET-CT tests. How should I prepare for my PET-CT? PET-CT is more complicated than most other tests you may be
Positron Emission Tomography - For Patients A physician s written order is required for any PET-CT tests. How should I prepare for my PET-CT? PET-CT is more complicated than most other tests you may be
A GUIDE TO HAVING A URETERIC STENT INSERTED
 A GUIDE TO HAVING A URETERIC STENT INSERTED WHAT IS A URETERIC STENT? A ureteric stent is a thin plastic tube which can be inserted into your ureters (tubes that carry urine from your kidney to your bladder)
A GUIDE TO HAVING A URETERIC STENT INSERTED WHAT IS A URETERIC STENT? A ureteric stent is a thin plastic tube which can be inserted into your ureters (tubes that carry urine from your kidney to your bladder)
Proton Therapy. What is proton therapy and how is it used?
 Scan for mobile link. Proton Therapy Proton therapy delivers radiation to tumor tissue in a much more confined way than conventional photon therapy thus allowing the radiation oncologist to use a greater
Scan for mobile link. Proton Therapy Proton therapy delivers radiation to tumor tissue in a much more confined way than conventional photon therapy thus allowing the radiation oncologist to use a greater
Computed Tomography (CT) - Spine
 Scan for mobile link. Computed Tomography (CT) - Spine Computed tomography (CT) of the spine is a diagnostic imaging test used to help diagnose or rule out spinal column damage in injured patients. CT
Scan for mobile link. Computed Tomography (CT) - Spine Computed tomography (CT) of the spine is a diagnostic imaging test used to help diagnose or rule out spinal column damage in injured patients. CT
Computed Tomography (CT) - Chest
 Scan for mobile link. Computed Tomography (CT) - Chest Computed tomography (CT) of the chest uses special x-ray equipment to examine abnormalities found in other imaging tests and to help diagnose the
Scan for mobile link. Computed Tomography (CT) - Chest Computed tomography (CT) of the chest uses special x-ray equipment to examine abnormalities found in other imaging tests and to help diagnose the
Cardiac catheterization Information for patients
 Cardiac catheterization Information for patients You have been scheduled for a cardiac catheterization. Your procedure is scheduled for:. Someone will call you the day before your procedure to tell you
Cardiac catheterization Information for patients You have been scheduled for a cardiac catheterization. Your procedure is scheduled for:. Someone will call you the day before your procedure to tell you
Spinal Injections. North American Spine Society Public Education Series
 Spinal Injections North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Spinal Injection? Your doctor has suggested that you have a spinal injection to help reduce pain and improve function. This
Spinal Injections North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Spinal Injection? Your doctor has suggested that you have a spinal injection to help reduce pain and improve function. This
Airport Scanner Safety
 Scan for mobile link. Airport Scanner Safety Airport scanners When it comes to airport scanner safety, there are four questions you should consider, including: What are airport scanners? Are there different
Scan for mobile link. Airport Scanner Safety Airport scanners When it comes to airport scanner safety, there are four questions you should consider, including: What are airport scanners? Are there different
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO CARDIAC CATHETERIZATION
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO CARDIAC CATHETERIZATION The science of medicine. The compassion to heal. This teaching booklet is designed to introduce you to cardiac catheterization. In the following pages, we will
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO CARDIAC CATHETERIZATION The science of medicine. The compassion to heal. This teaching booklet is designed to introduce you to cardiac catheterization. In the following pages, we will
Children's (Pediatric) CT (Computed Tomography)
 Scan for mobile link. Children's (Pediatric) CT (Computed Tomography) Pediatric computed tomography (CT) is a fast, painless exam that uses special x-ray equipment to create detailed images of your child
Scan for mobile link. Children's (Pediatric) CT (Computed Tomography) Pediatric computed tomography (CT) is a fast, painless exam that uses special x-ray equipment to create detailed images of your child
Liver Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE) Cancer treatment
 Patient Education Liver Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE) Cancer treatment This handout explains what liver transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) is and what to expect with this cancer treatment.
Patient Education Liver Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE) Cancer treatment This handout explains what liver transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) is and what to expect with this cancer treatment.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Knee
 Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Knee Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the knee uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to produce detailed pictures of the
Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Knee Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the knee uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to produce detailed pictures of the
Mammography. What is Mammography?
 Scan for mobile link. Mammography Mammography is a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to detect cancer early before women experience symptoms when it is most treatable. Tell your
Scan for mobile link. Mammography Mammography is a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to detect cancer early before women experience symptoms when it is most treatable. Tell your
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Shoulder
 Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Shoulder Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the shoulder uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to produce detailed pictures
Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Shoulder Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the shoulder uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to produce detailed pictures
Bone Densitometry. What is a Bone Density Scan (DXA)?
 Scan for mobile link. Bone Densitometry Bone densitometry, also called dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry or DEXA, uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of the inside of the body
Scan for mobile link. Bone Densitometry Bone densitometry, also called dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry or DEXA, uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of the inside of the body
Radiation Exposure in X-ray and CT Examinations
 Patient Safety-Xray: Radiation Exposure in X-ray and CT Examinations What are x-rays and what do they do? X-rays are forms of radiant energy, like light or radio waves. Unlike light, x-rays can penetrate
Patient Safety-Xray: Radiation Exposure in X-ray and CT Examinations What are x-rays and what do they do? X-rays are forms of radiant energy, like light or radio waves. Unlike light, x-rays can penetrate
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Cardiac (Heart)
 Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Cardiac (Heart) Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to produce detailed pictures
Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Cardiac (Heart) Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to produce detailed pictures
Procedures/risks: Radiology (CT, DXA, MRI, ultrasound, X-ray)
 Procedures/risks: Radiology (CT, DXA, MRI, ultrasound, X-ray) Computerized Axial Tomography (CT): Procedure: A Computerized Axial Tomography (CT) scan [of your heart] involves holding your breath for a
Procedures/risks: Radiology (CT, DXA, MRI, ultrasound, X-ray) Computerized Axial Tomography (CT): Procedure: A Computerized Axial Tomography (CT) scan [of your heart] involves holding your breath for a
Computed Tomography (CT) - Body
 Scan for mobile link. Computed Tomography (CT) - Body Computed tomography (CT) of the body uses special x-ray equipment to help detect a variety of diseases and conditions. CT scanning is fast, painless,
Scan for mobile link. Computed Tomography (CT) - Body Computed tomography (CT) of the body uses special x-ray equipment to help detect a variety of diseases and conditions. CT scanning is fast, painless,
Having denervation of the renal arteries for treatment of high blood pressure
 Having denervation of the renal arteries for treatment of high blood pressure The aim of this information sheet is to help answer some of the questions you may have about having denervation of the renal
Having denervation of the renal arteries for treatment of high blood pressure The aim of this information sheet is to help answer some of the questions you may have about having denervation of the renal
X-Plain Preparing For Surgery Reference Summary
 X-Plain Preparing For Surgery Reference Summary Introduction More than 25 million surgical procedures are performed each year in the US. This reference summary will help you prepare for surgery. By understanding
X-Plain Preparing For Surgery Reference Summary Introduction More than 25 million surgical procedures are performed each year in the US. This reference summary will help you prepare for surgery. By understanding
Magnetic Resonance, Functional (fmri) - Brain
 Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance, Functional (fmri) - Brain Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fmri) measures the metabolic changes that occur within the brain. It may be used to examine the
Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance, Functional (fmri) - Brain Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fmri) measures the metabolic changes that occur within the brain. It may be used to examine the
RENAL ANGIOMYOLIPOMA EMBOLIZATION
 RENAL ANGIOMYOLIPOMA EMBOLIZATION The information about renal angiomyolipomas on the next several pages includes questions commonly asked about the embolization procedure. Please take a few moments to
RENAL ANGIOMYOLIPOMA EMBOLIZATION The information about renal angiomyolipomas on the next several pages includes questions commonly asked about the embolization procedure. Please take a few moments to
Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) for Outpatient
 Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) for Outpatient Introduction A Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter, or PICC line, is a thin, long, soft plastic tube inserted into a vein of the arm. It
Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) for Outpatient Introduction A Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter, or PICC line, is a thin, long, soft plastic tube inserted into a vein of the arm. It
Yttrium-90 Radiotherapy Treatment for liver tumors
 Patient Education Yttrium-90 Radiotherapy Treatment for liver tumors This handout explains what Yttrium-90 radiotherapy is and what to expect when you have it done. Why do I need this treatment? Your doctors
Patient Education Yttrium-90 Radiotherapy Treatment for liver tumors This handout explains what Yttrium-90 radiotherapy is and what to expect when you have it done. Why do I need this treatment? Your doctors
Image-guided abdominal drain insertion Information for patients
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Image-guided abdominal drain insertion Information for patients What is an image-guided abdominal drain insertion? A drain is a thin plastic tube which is inserted
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Image-guided abdominal drain insertion Information for patients What is an image-guided abdominal drain insertion? A drain is a thin plastic tube which is inserted
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Spine
 Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Spine Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the spine uses radio waves, a magnetic field and a computer to produce detailed pictures of the spine
Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Spine Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the spine uses radio waves, a magnetic field and a computer to produce detailed pictures of the spine
The degree of liver inflammation or damage (grade) Presence and extent of fatty liver or other metabolic liver diseases
 ilearning about your health Liver Biopsy www.cpmc.org/learning What is a Liver Biopsy? A liver biopsy is a procedure where a specially trained doctor (typically a hepatologist, radiologist, or gastroenterologist)
ilearning about your health Liver Biopsy www.cpmc.org/learning What is a Liver Biopsy? A liver biopsy is a procedure where a specially trained doctor (typically a hepatologist, radiologist, or gastroenterologist)
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Prostate
 Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Prostate Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the prostate uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to produce detailed pictures
Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Prostate Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the prostate uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to produce detailed pictures
Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography (MRCP)
 Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography or MRCP uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to evaluate the liver,
Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography or MRCP uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to evaluate the liver,
Colorectal Cancer Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Colorectal Cancer Treatment Colorectal cancer overview Colorectal cancer, also called large bowel cancer, is the term used to describe malignant tumors found in the colon and rectum.
Scan for mobile link. Colorectal Cancer Treatment Colorectal cancer overview Colorectal cancer, also called large bowel cancer, is the term used to describe malignant tumors found in the colon and rectum.
Mesenteric Angiography
 Information for patients Mesenteric Angiography Sheffield Vascular Institute Northern General Hospital You have been given this leaflet because you need a procedure known as a Mesenteric Angiogram. This
Information for patients Mesenteric Angiography Sheffield Vascular Institute Northern General Hospital You have been given this leaflet because you need a procedure known as a Mesenteric Angiogram. This
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Musculoskeletal
 Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Musculoskeletal Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to produce detailed pictures of joints,
Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Musculoskeletal Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to produce detailed pictures of joints,
Fecal Incontinence. What is fecal incontinence?
 Scan for mobile link. Fecal Incontinence Fecal incontinence is the inability to control the passage of waste material from the body. It may be associated with constipation or diarrhea and typically occurs
Scan for mobile link. Fecal Incontinence Fecal incontinence is the inability to control the passage of waste material from the body. It may be associated with constipation or diarrhea and typically occurs
Patient & Family Guide. Fistuloplasty. www.nshealth.ca
 Patient & Family Guide Fistuloplasty 2016 www.nshealth.ca Fistuloplasty What is a fistuloplasty? A fistuloplasty is a non-surgical procedure used to open blocked or narrowed blood vessels in your fistula.
Patient & Family Guide Fistuloplasty 2016 www.nshealth.ca Fistuloplasty What is a fistuloplasty? A fistuloplasty is a non-surgical procedure used to open blocked or narrowed blood vessels in your fistula.
Chest Port Port-a-cath
 Patient Education Port-a-cath This handout explains what a chest port is and what to expect when you have one. What is a chest port? Your doctor has asked us to insert a chest port (also called a port-acath)
Patient Education Port-a-cath This handout explains what a chest port is and what to expect when you have one. What is a chest port? Your doctor has asked us to insert a chest port (also called a port-acath)
What are contrast materials and how do they work? Contrast materials enter the body in one of three ways. They can be:
 Scan for mobile link. Contrast Materials What are contrast materials and how do they work? Contrast materials, also called contrast agents or contrast media, are used to improve pictures of the inside
Scan for mobile link. Contrast Materials What are contrast materials and how do they work? Contrast materials, also called contrast agents or contrast media, are used to improve pictures of the inside
How To Prepare For A Ct Scan
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Radiology Department Information for patients having a CT scan page 2 The radiology department has received a request for you to have a CT scan. This leaflet tells
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Radiology Department Information for patients having a CT scan page 2 The radiology department has received a request for you to have a CT scan. This leaflet tells
Femoral artery bypass graft (Including femoral crossover graft)
 Femoral artery bypass graft (Including femoral crossover graft) Why do I need the operation? You have a blockage or narrowing of the arteries supplying blood to your leg. This reduces the blood flow to
Femoral artery bypass graft (Including femoral crossover graft) Why do I need the operation? You have a blockage or narrowing of the arteries supplying blood to your leg. This reduces the blood flow to
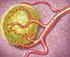
Prostate Cancer. What is prostate cancer?
 Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam, prostate-specific
Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam, prostate-specific
Cardiac Catheterization
 Thank you for choosing Rose Medical Center for your cardiac care. Our goal is to make your stay as comfortable and pleasant as possible. Please let our knowledgeable and friendly staff know if there is
Thank you for choosing Rose Medical Center for your cardiac care. Our goal is to make your stay as comfortable and pleasant as possible. Please let our knowledgeable and friendly staff know if there is
An Informative Guide for Heart Catheterization Patients & Families
 An Informative Guide for Heart Catheterization Patients & Families What is a Cardiac Cath? Cardiac catheterization is a procedure used to diagnose and treat patients who have various forms of heart disease.
An Informative Guide for Heart Catheterization Patients & Families What is a Cardiac Cath? Cardiac catheterization is a procedure used to diagnose and treat patients who have various forms of heart disease.
Presence and extent of fatty liver or other metabolic liver diseases
 UC San Diego Health System Patient Information Sheet: Liver Biopsy What is a Liver Biopsy? A liver biopsy is a procedure where a qualified doctor (typically a hepatologist, radiologist or gastroenterologist)
UC San Diego Health System Patient Information Sheet: Liver Biopsy What is a Liver Biopsy? A liver biopsy is a procedure where a qualified doctor (typically a hepatologist, radiologist or gastroenterologist)
X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary
 X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary Introduction A Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter, or subclavian line, is a long thin hollow tube inserted in a vein under the
X-Plain Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter (SICC Line) Reference Summary Introduction A Subclavian Inserted Central Catheter, or subclavian line, is a long thin hollow tube inserted in a vein under the
Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty (PTA) and Stenting For PVS Patients
 Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty (PTA) and Stenting For PVS Patients There are two types of blood vessels in the body arteries and veins. Arteries carry blood rich in oxygen from the heart to all
Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty (PTA) and Stenting For PVS Patients There are two types of blood vessels in the body arteries and veins. Arteries carry blood rich in oxygen from the heart to all
Ultrasound or Computed Tomography. PATIENT GUIDE and PREPARATION. Liver Biopsy
 Ultrasound or Computed Tomography PATIENT GUIDE and PREPARATION Liver Biopsy What is a Liver Biopsy? A Liver Biopsy is a procedure that involves taking a specimen ( a small amount of tissue) from within
Ultrasound or Computed Tomography PATIENT GUIDE and PREPARATION Liver Biopsy What is a Liver Biopsy? A Liver Biopsy is a procedure that involves taking a specimen ( a small amount of tissue) from within
Patient Prep Information
 Stereotactic Breast Biopsy Patient Prep Information Imaging Services Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center Table Weight Limits for each facility Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center
Stereotactic Breast Biopsy Patient Prep Information Imaging Services Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center Table Weight Limits for each facility Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center
The science of medicine. The compassion to heal.
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES OF THE HEART The science of medicine. The compassion to heal. This teaching booklet is designed to introduce you to electrophysiology studies of the heart.
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES OF THE HEART The science of medicine. The compassion to heal. This teaching booklet is designed to introduce you to electrophysiology studies of the heart.
Clinical Trials and Screening: What You Need to Know
 Scan for mobile link. Clinical Trials and Screening: What You Need to Know What is a Clinical Trial? At A Glance A clinical trial is a research study that tests how well new medical techniques work in
Scan for mobile link. Clinical Trials and Screening: What You Need to Know What is a Clinical Trial? At A Glance A clinical trial is a research study that tests how well new medical techniques work in
Thyroid Surgery at Massachusetts General Hospital Frequently Asked Questions
 Thyroid Surgery at Massachusetts General Hospital Frequently Asked Questions Q: What is the thyroid gland? A: The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the front of the neck. It is one of the
Thyroid Surgery at Massachusetts General Hospital Frequently Asked Questions Q: What is the thyroid gland? A: The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the front of the neck. It is one of the
Breast Augmentation. If you are dissatisfied with your breast size, augmentation surgery is a choice to consider. Breast augmentation can:
 Breast Augmentation What is Breast Augmentation? Also known as augmentation mammaplasty, breast augmentation involves using implants to fulfill your desire for fuller breasts or to restore breast volume
Breast Augmentation What is Breast Augmentation? Also known as augmentation mammaplasty, breast augmentation involves using implants to fulfill your desire for fuller breasts or to restore breast volume
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Aortic Stenosis. What is heart valve disease? What is aortic stenosis?
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Aortic Stenosis Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment This handout describes aortic stenosis, a narrowing of the aortic valve in your heart. It also explains how this
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Aortic Stenosis Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment This handout describes aortic stenosis, a narrowing of the aortic valve in your heart. It also explains how this
Biliary Drain. What is a biliary drain?
 Biliary Drain What is a biliary drain? A biliary drain is a tube to drain bile from your liver. It is put in by a doctor called an Interventional Radiologist. The tube or catheter is placed through your
Biliary Drain What is a biliary drain? A biliary drain is a tube to drain bile from your liver. It is put in by a doctor called an Interventional Radiologist. The tube or catheter is placed through your
CT Colonography. What is CT Colonography?
 Scan for mobile link. CT Colonography Computed tomography (CT) colonography or virtual colonoscopy uses special x-ray equipment to examine the large intestine for cancer and growths called polyps. During
Scan for mobile link. CT Colonography Computed tomography (CT) colonography or virtual colonoscopy uses special x-ray equipment to examine the large intestine for cancer and growths called polyps. During
What You Need to Know About Your Nephrostomy Tube
 What You Need to Know About Your Nephrostomy Tube Information for patients and families UHN Read this information to learn about: what a nephrostomy tube is and why you may need one how to prepare for
What You Need to Know About Your Nephrostomy Tube Information for patients and families UHN Read this information to learn about: what a nephrostomy tube is and why you may need one how to prepare for
Cardiac Catheterization
 Page 1 Cardiac Catheterization What Other Terms Are Used To Describe Cardiac Catheterization? Heart Cath (catheter) Angiogram What Is Cardiac Catheterization? This procedure is nonsurgical and is performed
Page 1 Cardiac Catheterization What Other Terms Are Used To Describe Cardiac Catheterization? Heart Cath (catheter) Angiogram What Is Cardiac Catheterization? This procedure is nonsurgical and is performed
ANESTHESIA. Anesthesia for Ambulatory Surgery
 ANESTHESIA & YOU Anesthesia for Ambulatory Surgery T oday the majority of patients who undergo surgery or diagnostic tests do not need to stay overnight in the hospital. In most cases, you will be well
ANESTHESIA & YOU Anesthesia for Ambulatory Surgery T oday the majority of patients who undergo surgery or diagnostic tests do not need to stay overnight in the hospital. In most cases, you will be well
Having a kidney biopsy
 Having a kidney biopsy Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm Introduction
Having a kidney biopsy Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm Introduction
Esophageal Cancer Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Esophageal Cancer Treatment What is Esophageal Cancer? Esophageal cancer occurs when cancer cells develop in the esophagus, a long, tube-like structure that connects the throat and
Scan for mobile link. Esophageal Cancer Treatment What is Esophageal Cancer? Esophageal cancer occurs when cancer cells develop in the esophagus, a long, tube-like structure that connects the throat and
Prostate Cancer Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Treatment Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam,
Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Treatment Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam,
CT Scan Thorax and Upper Abdomen. Respiratory Unit Patient Information Leaflet
 CT Scan Thorax and Upper Abdomen Respiratory Unit Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet gives you general information about your CT (computerised tomography) scan. It does not replace the
CT Scan Thorax and Upper Abdomen Respiratory Unit Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet gives you general information about your CT (computerised tomography) scan. It does not replace the
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) Arthrogram
 MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) Arthrogram MRI is a safe way for your doctor to take pictures of soft tissues and bones in the body. Using radio waves and a magnet field, the pictures provide information
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) Arthrogram MRI is a safe way for your doctor to take pictures of soft tissues and bones in the body. Using radio waves and a magnet field, the pictures provide information
Cardiac Catheterization Lab Procedures
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Cardiac Catheterization Lab Procedures This handout describes how cardiac catheterization works. It also explains how to prepare for your procedure and the self-care needed
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Cardiac Catheterization Lab Procedures This handout describes how cardiac catheterization works. It also explains how to prepare for your procedure and the self-care needed
Lung cancer forms in tissues of the lung, usually in the cells lining air passages.
 Scan for mobile link. Lung Cancer Lung cancer usually forms in the tissue cells lining the air passages within the lungs. The two main types are small-cell lung cancer (usually found in cigarette smokers)
Scan for mobile link. Lung Cancer Lung cancer usually forms in the tissue cells lining the air passages within the lungs. The two main types are small-cell lung cancer (usually found in cigarette smokers)
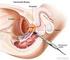
A GUIDE TO HAVING PERCUTANEOUS TRANSHEPATIC CHOLANGIOGRAM (PTC) AND BILIARY DRAIN/DILATATION/STENTING
 A GUIDE TO HAVING PERCUTANEOUS TRANSHEPATIC CHOLANGIOGRAM (PTC) AND BILIARY DRAIN/DILATATION/STENTING WHAT IS PERCUTANEOUS TRANSHEPATIC CHOLANGIOGRAM (PTC) AND BILIARY DRAIN/ DILATATION/STENTING? A percutaneous
A GUIDE TO HAVING PERCUTANEOUS TRANSHEPATIC CHOLANGIOGRAM (PTC) AND BILIARY DRAIN/DILATATION/STENTING WHAT IS PERCUTANEOUS TRANSHEPATIC CHOLANGIOGRAM (PTC) AND BILIARY DRAIN/ DILATATION/STENTING? A percutaneous
PICC- Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter PROCEDURAL CONSENT FORM. A. Interpreter / cultural needs. B. Procedure. C. Risks of the procedure
 DO NOT WRITE IN THIS BINDING MARGIN v3.00-03/2011 SW9266 Facility: PICC- Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter A. Interpreter / cultural needs An Interpreter Service is required? Yes No If Yes, is a qualified
DO NOT WRITE IN THIS BINDING MARGIN v3.00-03/2011 SW9266 Facility: PICC- Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter A. Interpreter / cultural needs An Interpreter Service is required? Yes No If Yes, is a qualified
University College Hospital. Contrast agent for radiotherapy CT (computed tomography) scans. Radiotherapy Department Patient information series
 University College Hospital Contrast agent for radiotherapy CT (computed tomography) scans Radiotherapy Department Patient information series 11 2 If you need a large print, audio or translated copy of
University College Hospital Contrast agent for radiotherapy CT (computed tomography) scans Radiotherapy Department Patient information series 11 2 If you need a large print, audio or translated copy of
Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter
 Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) by Patricia Griffin Kellicker, BSN En Español (Spanish Version) Definition A peripherally inserted central catheter is a long, thin tube that is inserted through
Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) by Patricia Griffin Kellicker, BSN En Español (Spanish Version) Definition A peripherally inserted central catheter is a long, thin tube that is inserted through
X-Rays Benefits and Risks. Techniques that use x-rays
 X-Rays Benefits and Risks X-rays are a form of electromagnetic radiation, just like light waves and radiowaves. Because X-rays have higher energy than light waves, they can pass through the body. X-rays
X-Rays Benefits and Risks X-rays are a form of electromagnetic radiation, just like light waves and radiowaves. Because X-rays have higher energy than light waves, they can pass through the body. X-rays
Brachytherapy: Low Dose Rate (LDR) Radiation Interstitial Implant
 Brachytherapy: Low Dose Rate (LDR) Radiation Interstitial Implant Goal of the Procedure Brachytherapy, or internal radiation therapy, is a way of giving a higher dose of radiation to the tumor area while
Brachytherapy: Low Dose Rate (LDR) Radiation Interstitial Implant Goal of the Procedure Brachytherapy, or internal radiation therapy, is a way of giving a higher dose of radiation to the tumor area while
Biliary Stone Disease
 Biliary Stone Disease Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm You have
Biliary Stone Disease Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm You have
Preparing for your laparoscopic pyeloplasty
 Preparing for your laparoscopic pyeloplasty Welcome We look forward to welcoming you to The Royal London Hospital. You have been referred to us for a laparoscopic pyeloplasty, which is an operation using
Preparing for your laparoscopic pyeloplasty Welcome We look forward to welcoming you to The Royal London Hospital. You have been referred to us for a laparoscopic pyeloplasty, which is an operation using
Having a RIG tube inserted
 Having a RIG tube inserted Information for patients and carers Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Having a RIG tube inserted Information for patients and carers Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
