Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Shoulder
|
|
|
- Abraham Marshall
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Shoulder Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the shoulder uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to produce detailed pictures of the bones, tendons, muscles and blood vessels within the shoulder joint. It is primarily used to assess injuries. Tell your doctor about any health problems, recent surgeries or allergies and whether there s a possibility you are pregnant. The magnetic field is not harmful, but it may cause some medical devices to malfunction. Most orthopedic implants pose no risk, but you should always tell the technologist if you have any devices or metal in your body. Guidelines about eating and drinking before your exam vary between facilities. Unless you are told otherwise, take your regular medications as usual. Leave jewelry at home and wear loose, comfortable clothing. You may be asked to wear a gown. If you have claustrophobia or anxiety, you may want to ask your doctor for a mild sedative prior to the exam. What is MRI of the shoulder? MRI of the shoulder provides detailed images of structures within the shoulder joint, including bones, tendons, muscles and vessels, from any angle. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a noninvasive medical test that physicians use to diagnose and treat medical conditions. MRI uses a powerful magnetic field, radio frequency pulses and a computer to produce detailed pictures of organs, soft tissues, bone and virtually all other internal body structures. MRI does not use ionizing radiation (x-rays). Detailed MR images allow physicians to evaluate various parts of the body and determine the presence of certain diseases. The images can then be examined on a computer monitor, transmitted electronically, printed or copied to a CD. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Shoulder Page 1 of 8
2 What are some common uses of the MRI procedure? MRI is an excellent choice for examining the shoulder joint. MRI gives clear views of rotator cuff tears, injuries to the biceps tendon and damage to the glenoid labrum, the soft fibrous tissue rim that helps stabilize the joint. MR imaging of the shoulder is typically performed to diagnose or evaluate: degenerative joint disorders such as arthritis and labral tears fractures (in selected patients) rotator cuff disorders, including tears and impingement, which are the major cause of shoulder pain in patients older than 40 years joint abnormalities due to trauma, such as tears of ligaments and tendons sports-related injuries and work-related disorders caused by repeated strain, forceful impact or vibration from using certain hand-held tools infections (such as osteomyelitis) tumors (primary tumors and metastases) involving bones and joints pain, swelling or bleeding in the tissues in and around the joint unexplained shoulder pain that does not get better with treatment decreased motion of the shoulder joint progress after shoulder surgery A special form of MRI called magnetic resonance arthrography involves the injection of a contrast material into the joint so that the radiologist can get a better look at structures within the shoulder. How should I prepare? You may be asked to wear a gown during the exam or you may be allowed to wear your own clothing if it is loose-fitting and has no metal fasteners. Guidelines about eating and drinking before an MRI exam vary with the specific exam and also with the imaging facility. Unless you are told otherwise, you may follow your regular daily routine and take food and medications as usual. Some MRI examinations may require you to receive an injection of contrast material into the bloodstream. The radiologist, technologist or a nurse may ask if you have allergies of any kind, such as an allergy to iodine or x-ray contrast material, drugs, food, or the environment, or if you have asthma. The contrast material most commonly used for an MRI exam contains a metal called gadolinium. Gadolinium can be used in patients with iodine contrast allergy, but may require pre-medication. It is far less common for a patient to have an allergy to a gadolinium-based contrast agent used for MRI than the iodine-containing contrast for CT. However, even if it is known that the patient has an allergy to the gadolinium contrast, it may still be possible to use it after appropriate pre-medication. Patient consent will be requested in this instance. For more information on adverse reactions to gadolinium-based contrast agents, please consult the ACR Manual on Contrast Media. You should also let the radiologist know if you have any serious health problems, or if you have had any Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Shoulder Page 2 of 8
3 recent surgeries. Some conditions, such as severe kidney disease, may prevent you from being given gadolinium contrast for an MRI. If you have a history of kidney disease or liver transplant, it will be necessary to perform a blood test to determine whether the kidneys are functioning adequately. Women should always inform their physician or technologist if there is any possibility that they are pregnant. MRI has been used for scanning patients since the 1980s with no reports of any ill effects on pregnant women or their unborn babies. However, because the unborn baby will be in a strong magnetic field, pregnant women should not have this exam in the first trimester of pregnancy unless the potential benefit from the MRI exam is assumed to outweigh the potential risks. Pregnant women should not receive injections of gadolinium contrast material except when absolutely necessary for medical treatment. See the Safety page for more information about pregnancy and MRI. If you have claustrophobia (fear of enclosed spaces) or anxiety, you may want to ask your physician for a prescription for a mild sedative prior to your scheduled examination. Infants and young children usually require sedation or anesthesia to complete an MRI exam without moving. Whether a child requires sedation depends on the child's age and the type of exam. Moderate and conscious sedation can be provided at many facilities. A physician or nurse specializing in sedation or anesthesia for children should be available during the exam for your child's safety. You will be given special instructions for how to prepare your child for the sedation or anesthesia. Jewelry and other accessories should be left at home if possible, or removed prior to the MRI scan. Because they can interfere with the magnetic field of the MRI unit, metal and electronic items are not allowed in the exam room. These items include: jewelry, watches, credit cards and hearing aids, all of which can be damaged pins, hairpins, metal zippers and similar metallic items, which can distort MRI images removable dental work pens, pocket knives and eyeglasses body piercings In most cases, an MRI exam is safe for patients with metal implants, except for a few types. People with the following implants cannot be scanned and should not enter the MRI scanning area: cochlear (ear) implant some types of clips used for brain aneurysms some types of metal coils placed within blood vessels nearly all cardiac defibrillators and pacemakers You should tell the technologist if you have medical or electronic devices in your body. These objects may interfere with the exam or potentially pose a risk, depending on their nature and the strength of the MRI magnet. Many implanted devices will have a pamphlet explaining the MRI risks for that particular device. If you have the pamphlet, it is useful to bring that to the attention of the technologist or scheduler before the exam. Some implanted devices require a short period of time after placement (usually six weeks) before being safe for MRI examinations. Examples include but are not limited to: artificial heart valves implanted drug infusion ports artificial limbs or metallic joint prostheses Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Shoulder Page 3 of 8
4 implanted nerve stimulators metal pins, screws, plates, stents or surgical staples If there is any question of their presence, an x-ray may be taken to detect and identify any metal objects. In general, metal objects used in orthopedic surgery pose no risk during MRI. However, a recently placed artificial joint may require the use of another imaging procedure. Patients who might have metal objects in certain parts of their bodies may also require an x-ray prior to an MRI. You should notify the technologist or radiologist of any shrapnel, bullets, or other pieces of metal which may be present in your body due to prior accidents. Foreign bodies near and especially lodged in the eyes are particularly important. Dyes used in tattoos may contain iron and could heat up during MRI, but this is rarely a problem. Tooth fillings and braces usually are not affected by the magnetic field, but they may distort images of the facial area or brain, so the radiologist should be aware of them. Parents or family members who accompany patients into the scanning room also need to remove metal objects and notify the technologist of any medical or electronic devices they may have. What does the equipment look like? The traditional MRI unit is a large cylinder-shaped tube surrounded by a circular magnet. You will lie on a moveable examination table that slides into the center of the magnet. Some MRI units, called short-bore systems, are designed so that the magnet does not completely surround you. Some newer MRI machines have a larger diameter bore which can be more comfortable for larger size patients or patients with claustrophobia. Other MRI machines are open on the sides (open MRI). Open units are especially helpful for examining larger patients or those with claustrophobia. Newer open MRI units provide very high quality images for many types of exams; however, older open MRI units may not provide this same image quality. Certain types of exams cannot be performed using open MRI. For more information, consult your radiologist. The computer workstation that processes the imaging information is located in a separate room from the scanner. How does the procedure work? Unlike conventional x-ray examinations and computed tomography (CT) scans, MRI does not utilize ionizing radiation. Instead, radio waves redirect alignment of hydrogen atoms that naturally exist within the body while you are in the scanner without causing any chemical changes in the tissues. As the hydrogen atoms return to their usual alignment, they emit energy that varies according to the type of body tissue from which they come. The MR scanner captures this energy and creates a picture of the tissues scanned based on this information. The magnetic field is produced by passing an electric current through wire coils in most MRI units. Other coils, located in the machine and in some cases, placed around the part of the body being imaged, send and receive radio waves, producing signals that are detected by the coils. The electric current does not Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Shoulder Page 4 of 8
5 come in contact with the patient. A computer then processes the signals and generates a series of images, each of which shows a thin slice of the body. The images can then be studied from different angles by the interpreting radiologist. Frequently, the differentiation of abnormal (diseased) tissue from normal tissues is better with MRI than with other imaging modalities such as x-ray, CT and ultrasound. How is the procedure performed? MRI examinations may be performed on outpatients or inpatients. You will be positioned on the moveable examination table. Straps and bolsters may be used to help you stay still and maintain the correct position during imaging. Small devices that contain coils capable of sending and receiving radio waves may be placed around your shoulder to improve image quality. If a contrast material will be used in the MRI exam, a physician, nurse or technologist will insert an intravenous (IV) catheter, also known as an IV line, into a vein in your hand or arm. A saline solution may be used to inject the contrast material. The solution will drip through the IV to prevent blockage of the IV catheter until the contrast material is injected. You will be placed into the magnet of the MRI unit and the radiologist and technologist will perform the examination while working at a computer outside of the room. If a contrast material is used during the examination, it will be injected into the intravenous line (IV) after an initial series of scans. Additional series of images will be taken during or following the injection. When the examination is complete, you may be asked to wait until the technologist or radiologist checks the images in case additional images are needed. Your intravenous line will be removed. MRI exams generally include multiple runs (sequences), some of which may last several minutes. Depending on the type of exam and the equipment used, the entire exam is usually completed in 15 to 45 minutes. If your child requires sedation to complete the MRI, you may be asked to come early for the exam in order for your child to be evaluated prior to sedation. Sedation may add 15 to 30 minutes to the procedure. Your child may need to stay additional time to be monitored as the sedation wears off. In selected patients, arthrography will be performed first. During that procedure, contrast material may be injected into the shoulder joint before MRI in order to image the joint structures in more detail. Arthrography may require imaging guidance to place a needle into the shoulder joint. See the Conventional Arthrography page for more information. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Shoulder Page 5 of 8
6 What will I experience during and after the procedure? Most MRI exams are painless. However, some patients find it uncomfortable to remain still during MR imaging. Others experience a sense of being closed-in (claustrophobia). Therefore, sedation can be arranged for those patients who anticipate anxiety, but fewer than one in 20 require medication. It is normal for the area of your body being imaged to feel slightly warm, but if it bothers you, notify the radiologist or technologist. It is important that you remain perfectly still while the images are being obtained, which is typically only a few seconds to a few minutes at a time. You will know when images are being recorded because you will hear and feel loud tapping or thumping sounds when the coils that generate the radiofrequency pulses are activated. Some centers provide earplugs, while others use headphones to reduce the intensity of the sounds made by the MRI machine. You will be able to relax between imaging sequences, but will be asked to maintain your position without movement as much as possible. You will usually be alone in the exam room during the MRI procedure. However, the technologist will be able to see, hear and speak with you at all times using a two-way intercom. Many MRI centers allow a friend or parent to stay in the room as long as they are also screened for safety in the magnetic environment. Children will be given appropriately sized earplugs or headphones during the exam. MRI scanners are air-conditioned and well-lit. Music may be played through the headphones to help you pass the time. In some cases, intravenous injection of contrast material may be performed. The intravenous needle may cause you some discomfort when it is inserted and you may experience some bruising. There is also a very small chance of irritation of your skin at the site of the IV tube insertion. Some patients may sense a temporary metallic taste in their mouth after the contrast injection. If you have not been sedated, no recovery period is necessary. You may resume your usual activities and normal diet immediately after the exam. On very rare occasions, a few patients experience side effects from the contrast material, including nausea and local pain. Similarly, patients are very rarely allergic to the contrast material and experience hives, itchy eyes or other reactions. If you experience allergic symptoms, notify the technologist. A radiologist or other physician will be available for immediate assistance. There is no recovery time from an MRI scan, unless you received sedation. After the scan, you can resume your normal diet, activity and medications. Who interprets the results and how do I get them? A radiologist, a physician specifically trained to supervise and interpret radiology examinations, will analyze the images and send a signed report to your primary care or referring physician, who will share the results with you. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Shoulder Page 6 of 8
7 What are the benefits vs. risks? Benefits Risks MRI is a noninvasive imaging technique that does not involve exposure to ionizing radiation. MRI has proven valuable in diagnosing a broad range of conditions, including muscle and bone abnormalities. MRI can help determine which patients with shoulder injuries require surgery. MRI may help diagnose a bone fracture when results from x-rays and other tests are not clear. MRI enables the discovery of abnormalities that might be obscured by bone with other imaging methods. The contrast material used in MRI exams is less likely to produce an allergic reaction than the iodine-based contrast materials used for conventional x-rays and CT scanning. MRI may provide a noninvasive alternative to x-ray, angiography and CT for diagnosing problems of the blood vessels. The MRI examination poses almost no risk to the average patient when appropriate safety guidelines are followed. If sedation is used, there are risks of excessive sedation. However, the technologist or nurse monitors your vital signs to minimize this risk. Although the strong magnetic field is not harmful in itself, implanted medical devices that contain metal may malfunction or cause problems during an MRI exam. Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis is currently a recognized, but rare, complication of MRI believed to be caused by the injection of high doses of gadolinium-based contrast material in patients with very poor kidney function. Careful assessment of kidney function before considering a contrast injection minimizes the risk of this very rare complication. There is a very slight risk of an allergic reaction if contrast material is injected. Such reactions usually are mild and easily controlled by medication. If you experience allergic symptoms, a radiologist or other physician will be available for immediate assistance. Manufacturers of intravenous contrast indicate mothers should not breastfeed their babies for hours after contrast medium is given. However, both the American College of Radiology (ACR) and the European Society of Urogenital Radiology note that the available data suggest that it is safe to continue breastfeeding after receiving intravenous contrast. For further information please consult the ACR Manual on Contrast Media and its references. What are the limitations of a shoulder MRI? High-quality images are assured only if you are able to remain perfectly still and follow breath-holding instructions while the images are being recorded. If you are anxious, confused or in severe pain, you may find it difficult to lie still during imaging. A person who is very large may not fit into the opening of certain types of MRI machines. The presence of an implant or other metallic object sometimes makes it difficult to obtain clear images. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Shoulder Page 7 of 8
8 The presence of an implant or other metallic object sometimes makes it difficult to obtain clear images. Patient movement can have the same effect. A very irregular heartbeat may affect the quality of images obtained using techniques that time the imaging based on the electrical activity of the heart, such as electrocardiography (EKG). Although there is no reason to believe that magnetic resonance imaging harms the fetus, pregnant women usually are advised not to have an MRI exam during the first trimester unless medically necessary. MRI typically costs more and may take more time to perform than other imaging modalities. Disclaimer This information is copied from the RadiologyInfo Web site ( which is dedicated to providing the highest quality information. To ensure that, each section is reviewed by a physician with expertise in the area presented. All information contained in the Web site is further reviewed by an ACR (American College of Radiology) - RSNA (Radiological Society of North America) committee, comprising physicians with expertise in several radiologic areas. However, it is not possible to assure that this Web site contains complete, up-to-date information on any particular subject. Therefore, ACR and RSNA make no representations or warranties about the suitability of this information for use for any particular purpose. All information is provided "as is" without express or implied warranty. Please visit the RadiologyInfo Web site at to view or download the latest information. Note: Images may be shown for illustrative purposes. Do not attempt to draw conclusions or make diagnoses by comparing these images to other medical images, particularly your own. Only qualified physicians should interpret images; the radiologist is the physician expert trained in medical imaging. Copyright This material is copyrighted by either the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA), 820 Jorie Boulevard, Oak Brook, IL or the American College of Radiology (ACR), 1891 Preston White Drive, Reston, VA Commercial reproduction or multiple distribution by any traditional or electronically based reproduction/publication method is prohibited. Copyright 2016 Radiological Society of North America, Inc. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Shoulder Page 8 of 8
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Knee
 Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Knee Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the knee uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to produce detailed pictures of the
Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Knee Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the knee uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to produce detailed pictures of the
Magnetic Resonance, Functional (fmri) - Brain
 Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance, Functional (fmri) - Brain Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fmri) measures the metabolic changes that occur within the brain. It may be used to examine the
Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance, Functional (fmri) - Brain Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fmri) measures the metabolic changes that occur within the brain. It may be used to examine the
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Musculoskeletal
 Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Musculoskeletal Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to produce detailed pictures of joints,
Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Musculoskeletal Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to produce detailed pictures of joints,
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Spine
 Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Spine Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the spine uses radio waves, a magnetic field and a computer to produce detailed pictures of the spine
Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Spine Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the spine uses radio waves, a magnetic field and a computer to produce detailed pictures of the spine
Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography (MRCP)
 Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography or MRCP uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to evaluate the liver,
Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography or MRCP uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to evaluate the liver,
MRI of the Breast. What is MRI of the Breast?
 MRI of the Breast What is MRI of the Breast? Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a noninvasive, usually painless medical test that helps physicians diagnose and treat medical conditions. MRI uses a powerful
MRI of the Breast What is MRI of the Breast? Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a noninvasive, usually painless medical test that helps physicians diagnose and treat medical conditions. MRI uses a powerful
X-ray (Radiography) - Bone
 Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Bone Bone x-ray uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of any bone in the body. It is commonly used to diagnose fractured bones or
Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Bone Bone x-ray uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of any bone in the body. It is commonly used to diagnose fractured bones or
Ureteral Stenting and Nephrostomy
 Scan for mobile link. Ureteral Stenting and Nephrostomy Ureteral stenting and nephrostomy help restore urine flow through blocked ureters and return the kidney to normal function. Ureters are long, narrow
Scan for mobile link. Ureteral Stenting and Nephrostomy Ureteral stenting and nephrostomy help restore urine flow through blocked ureters and return the kidney to normal function. Ureters are long, narrow
X-ray (Radiography) - Abdomen
 Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Abdomen Abdominal x-ray uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of the inside of the abdominal cavity. It is used to evaluate the stomach,
Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Abdomen Abdominal x-ray uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of the inside of the abdominal cavity. It is used to evaluate the stomach,
Percutaneous Abscess Drainage
 Scan for mobile link. Percutaneous Abscess Drainage An abscess is an infected fluid collection within the body. Percutaneous abscess drainage uses imaging guidance to place a thin needle through the skin
Scan for mobile link. Percutaneous Abscess Drainage An abscess is an infected fluid collection within the body. Percutaneous abscess drainage uses imaging guidance to place a thin needle through the skin
Computed Tomography (CT) - Sinuses
 Scan for mobile link. Computed Tomography (CT) - Sinuses Computed tomography (CT) of the sinuses uses special x-ray equipment to evaluate the paranasal sinus cavities hollow, air-filled spaces within the
Scan for mobile link. Computed Tomography (CT) - Sinuses Computed tomography (CT) of the sinuses uses special x-ray equipment to evaluate the paranasal sinus cavities hollow, air-filled spaces within the
X-ray (Radiography) - Chest
 Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Chest What is a Chest X-ray (Chest Radiography)? The chest x-ray is the most commonly performed diagnostic x-ray examination. A chest x-ray produces images of
Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Chest What is a Chest X-ray (Chest Radiography)? The chest x-ray is the most commonly performed diagnostic x-ray examination. A chest x-ray produces images of
X-ray (Radiography), Chest
 X-ray (Radiography), Chest What is a Chest X-ray (Chest Radiography)? The chest x-ray is the most commonly performed diagnostic x-ray examination. A chest x-ray makes images of the heart, lungs, airways,
X-ray (Radiography), Chest What is a Chest X-ray (Chest Radiography)? The chest x-ray is the most commonly performed diagnostic x-ray examination. A chest x-ray makes images of the heart, lungs, airways,
Nerve Blocks. What is a Nerve Block? What are some common uses of the procedure?
 Scan for mobile link. Nerve Blocks A nerve block is an injection to decrease inflammation or "turn off" a pain signal along a specific distribution of nerve. Imaging guidance may be used to place the needle
Scan for mobile link. Nerve Blocks A nerve block is an injection to decrease inflammation or "turn off" a pain signal along a specific distribution of nerve. Imaging guidance may be used to place the needle
Cardiac CT for Calcium Scoring
 Scan for mobile link. Cardiac CT for Calcium Scoring Cardiac computed tomography (CT) for Calcium Scoring uses special x-ray equipment to produce pictures of the coronary arteries to determine if they
Scan for mobile link. Cardiac CT for Calcium Scoring Cardiac computed tomography (CT) for Calcium Scoring uses special x-ray equipment to produce pictures of the coronary arteries to determine if they
Hysterosalpingography
 Scan for mobile link. Hysterosalpingography Hysterosalpingography uses a real-time form of x-ray called fluoroscopy to examine the uterus and fallopian tubes of a woman who is having difficulty becoming
Scan for mobile link. Hysterosalpingography Hysterosalpingography uses a real-time form of x-ray called fluoroscopy to examine the uterus and fallopian tubes of a woman who is having difficulty becoming
Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal
 Scan for mobile link. Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal What is Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal? In an inferior vena cava filter placement procedure, interventional radiologists
Scan for mobile link. Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal What is Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal? In an inferior vena cava filter placement procedure, interventional radiologists
An abdominal ultrasound produces a picture of the organs and other structures in the upper abdomen.
 Scan for mobile link. Ultrasound - Abdomen Ultrasound imaging of the abdomen uses sound waves to produce pictures of the structures within the upper abdomen. It is used to help diagnose pain or distention
Scan for mobile link. Ultrasound - Abdomen Ultrasound imaging of the abdomen uses sound waves to produce pictures of the structures within the upper abdomen. It is used to help diagnose pain or distention
YOUR MRI EXAM: QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
 YOUR MRI EXAM: QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS What is MRI? MRI is short for Magnetic Resonance Imaging. MRI is an advanced technology that lets your doctor see internal organs, blood vessels, muscles, joints, tumors,
YOUR MRI EXAM: QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS What is MRI? MRI is short for Magnetic Resonance Imaging. MRI is an advanced technology that lets your doctor see internal organs, blood vessels, muscles, joints, tumors,
Lymphoscintigraphy is a special type of nuclear medicine imaging that provides pictures called scintigrams of the lymphatic system.
 Scan for mobile link. Lymphoscintigraphy Lymphoscintigraphy helps evaluate your body s lymphatic system for disease using small amounts of radioactive materials called radiotracers that are typically injected
Scan for mobile link. Lymphoscintigraphy Lymphoscintigraphy helps evaluate your body s lymphatic system for disease using small amounts of radioactive materials called radiotracers that are typically injected
CT Angiography (CTA) What is CT Angiography?
 Scan for mobile link. CT Angiography (CTA) Computed tomography angiography (CTA) uses an injection of iodine-rich contrast material and CT scanning to help diagnose and evaluate blood vessel disease or
Scan for mobile link. CT Angiography (CTA) Computed tomography angiography (CTA) uses an injection of iodine-rich contrast material and CT scanning to help diagnose and evaluate blood vessel disease or
Computed Tomography (CT) - Spine
 Scan for mobile link. Computed Tomography (CT) - Spine Computed tomography (CT) of the spine is a diagnostic imaging test used to help diagnose or rule out spinal column damage in injured patients. CT
Scan for mobile link. Computed Tomography (CT) - Spine Computed tomography (CT) of the spine is a diagnostic imaging test used to help diagnose or rule out spinal column damage in injured patients. CT
Procedures/risks: Radiology (CT, DXA, MRI, ultrasound, X-ray)
 Procedures/risks: Radiology (CT, DXA, MRI, ultrasound, X-ray) Computerized Axial Tomography (CT): Procedure: A Computerized Axial Tomography (CT) scan [of your heart] involves holding your breath for a
Procedures/risks: Radiology (CT, DXA, MRI, ultrasound, X-ray) Computerized Axial Tomography (CT): Procedure: A Computerized Axial Tomography (CT) scan [of your heart] involves holding your breath for a
Ultrasound - Vascular
 Scan for mobile link. Ultrasound - Vascular Vascular ultrasound uses sound waves to evaluate the body s circulatory system and help identify blockages and detect blood clots. A Doppler ultrasound study
Scan for mobile link. Ultrasound - Vascular Vascular ultrasound uses sound waves to evaluate the body s circulatory system and help identify blockages and detect blood clots. A Doppler ultrasound study
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)? Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a valuable diagnostic study that has been used
Magnetic Resonance Imaging North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)? Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a valuable diagnostic study that has been used
Computed Tomography (CT) - Chest
 Scan for mobile link. Computed Tomography (CT) - Chest Computed tomography (CT) of the chest uses special x-ray equipment to examine abnormalities found in other imaging tests and to help diagnose the
Scan for mobile link. Computed Tomography (CT) - Chest Computed tomography (CT) of the chest uses special x-ray equipment to examine abnormalities found in other imaging tests and to help diagnose the
Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA) of Liver Tumors
 Scan for mobile link. Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA) of Liver Tumors Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is a treatment that uses imaging guidance to place a needle electrode through the skin into a liver tumor.
Scan for mobile link. Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA) of Liver Tumors Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is a treatment that uses imaging guidance to place a needle electrode through the skin into a liver tumor.
How To Use An Ultrasound For Medical Research
 Scan for mobile link. General Ultrasound What is General Ultrasound Imaging? Ultrasound is safe and painless, and produces pictures of the inside of the body using sound waves. Ultrasound imaging, also
Scan for mobile link. General Ultrasound What is General Ultrasound Imaging? Ultrasound is safe and painless, and produces pictures of the inside of the body using sound waves. Ultrasound imaging, also
Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal
 Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal What is Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal? An inferior vena cava filter placement procedure involves an interventional radiologist (a specialist doctor)
Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal What is Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal? An inferior vena cava filter placement procedure involves an interventional radiologist (a specialist doctor)
Stereotactic Breast Biopsy
 Scan for mobile link. Stereotactic Breast Biopsy Stereotactic breast biopsy uses mammography a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to help locate a breast lump or abnormality and
Scan for mobile link. Stereotactic Breast Biopsy Stereotactic breast biopsy uses mammography a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to help locate a breast lump or abnormality and
What are contrast materials and how do they work? Contrast materials enter the body in one of three ways. They can be:
 Scan for mobile link. Contrast Materials What are contrast materials and how do they work? Contrast materials, also called contrast agents or contrast media, are used to improve pictures of the inside
Scan for mobile link. Contrast Materials What are contrast materials and how do they work? Contrast materials, also called contrast agents or contrast media, are used to improve pictures of the inside
Computed Tomography (CT) - Body
 Scan for mobile link. Computed Tomography (CT) - Body Computed tomography (CT) of the body uses special x-ray equipment to help detect a variety of diseases and conditions. CT scanning is fast, painless,
Scan for mobile link. Computed Tomography (CT) - Body Computed tomography (CT) of the body uses special x-ray equipment to help detect a variety of diseases and conditions. CT scanning is fast, painless,
CONSENT FOR MRI SCAN WITH INTRAVENOUS CONTRAST
 CONSENT FOR MRI SCAN WITH INTRAVENOUS CONTRAST Your Doctor has asked that an MRI scan be performed using intravenous contrast. This contrast may give the radiologist additional information that may not
CONSENT FOR MRI SCAN WITH INTRAVENOUS CONTRAST Your Doctor has asked that an MRI scan be performed using intravenous contrast. This contrast may give the radiologist additional information that may not
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) Arthrogram
 MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) Arthrogram MRI is a safe way for your doctor to take pictures of soft tissues and bones in the body. Using radio waves and a magnet field, the pictures provide information
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) Arthrogram MRI is a safe way for your doctor to take pictures of soft tissues and bones in the body. Using radio waves and a magnet field, the pictures provide information
Mammography. What is Mammography?
 Scan for mobile link. Mammography Mammography is a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to detect cancer early before women experience symptoms when it is most treatable. Tell your
Scan for mobile link. Mammography Mammography is a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to detect cancer early before women experience symptoms when it is most treatable. Tell your
Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT)
 Scan for mobile link. Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) Intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) uses linear accelerators to safely and painlessly deliver precise radiation doses to a tumor while
Scan for mobile link. Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) Intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) uses linear accelerators to safely and painlessly deliver precise radiation doses to a tumor while
X-ray (Radiography), Lower GI Tract
 Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography), Lower GI Tract What is Lower GI Tract X-ray Radiography (Barium Enema)? Lower gastrointestinal (GI) tract radiography, also called a lower GI or barium enema,
Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography), Lower GI Tract What is Lower GI Tract X-ray Radiography (Barium Enema)? Lower gastrointestinal (GI) tract radiography, also called a lower GI or barium enema,
Video Fluoroscopic Swallowing Exam (VFSE)
 Scan for mobile link. Video Fluoroscopic Swallowing Exam (VFSE) A video fluoroscopic swallowing exam (VFSE) uses a form of real-time x-ray called fluoroscopy to evaluate a patient s ability to swallow
Scan for mobile link. Video Fluoroscopic Swallowing Exam (VFSE) A video fluoroscopic swallowing exam (VFSE) uses a form of real-time x-ray called fluoroscopy to evaluate a patient s ability to swallow
Varicose Vein Treatment (Endovenous Ablation of Varicose Veins)
 Scan for mobile link. Varicose Vein Treatment (Endovenous Ablation of Varicose Veins) Varicose vein treatment, also known as endovenous ablation, uses radiofrequency or laser energy to cauterize and close
Scan for mobile link. Varicose Vein Treatment (Endovenous Ablation of Varicose Veins) Varicose vein treatment, also known as endovenous ablation, uses radiofrequency or laser energy to cauterize and close
X-ray (Radiography), Upper GI Tract
 Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography), Upper GI Tract What is Upper Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract Radiography? Upper gastrointestinal tract radiography, also called an upper GI, is an x-ray examination
Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography), Upper GI Tract What is Upper Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract Radiography? Upper gastrointestinal tract radiography, also called an upper GI, is an x-ray examination
Positron Emission Tomography - For Patients
 Positron Emission Tomography - For Patients A physician s written order is required for any PET-CT tests. How should I prepare for my PET-CT? PET-CT is more complicated than most other tests you may be
Positron Emission Tomography - For Patients A physician s written order is required for any PET-CT tests. How should I prepare for my PET-CT? PET-CT is more complicated than most other tests you may be
Proton Therapy. What is proton therapy and how is it used?
 Scan for mobile link. Proton Therapy Proton therapy delivers radiation to tumor tissue in a much more confined way than conventional photon therapy thus allowing the radiation oncologist to use a greater
Scan for mobile link. Proton Therapy Proton therapy delivers radiation to tumor tissue in a much more confined way than conventional photon therapy thus allowing the radiation oncologist to use a greater
Bone Densitometry. What is a Bone Density Scan (DXA)?
 Scan for mobile link. Bone Densitometry Bone densitometry, also called dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry or DEXA, uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of the inside of the body
Scan for mobile link. Bone Densitometry Bone densitometry, also called dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry or DEXA, uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of the inside of the body
LOW BACK PAIN: SHOULD I HAVE AN MRI?
 DATE: / / HG SY EH CQ RL AS JZ Name: (Last, First, M.I.) M F DOB: / / Decision Point LOW BACK PAIN: SHOULD I HAVE AN MRI? You may want to have a say in this decision, or you may simply want to follow your
DATE: / / HG SY EH CQ RL AS JZ Name: (Last, First, M.I.) M F DOB: / / Decision Point LOW BACK PAIN: SHOULD I HAVE AN MRI? You may want to have a say in this decision, or you may simply want to follow your
Who can have an MRI scan?
 i MRI Scan Contents What is an MRI scan? 1 Why am I having an MRI scan? 1 Who can have an MRI scan? 1 What preparation will I need? 2 What happens when I come for the scan? 2 Who will I see when I have
i MRI Scan Contents What is an MRI scan? 1 Why am I having an MRI scan? 1 Who can have an MRI scan? 1 What preparation will I need? 2 What happens when I come for the scan? 2 Who will I see when I have
Fecal Incontinence. What is fecal incontinence?
 Scan for mobile link. Fecal Incontinence Fecal incontinence is the inability to control the passage of waste material from the body. It may be associated with constipation or diarrhea and typically occurs
Scan for mobile link. Fecal Incontinence Fecal incontinence is the inability to control the passage of waste material from the body. It may be associated with constipation or diarrhea and typically occurs
Radiation Exposure in X-ray and CT Examinations
 Patient Safety-Xray: Radiation Exposure in X-ray and CT Examinations What are x-rays and what do they do? X-rays are forms of radiant energy, like light or radio waves. Unlike light, x-rays can penetrate
Patient Safety-Xray: Radiation Exposure in X-ray and CT Examinations What are x-rays and what do they do? X-rays are forms of radiant energy, like light or radio waves. Unlike light, x-rays can penetrate
University College Hospital. Contrast agent for radiotherapy CT (computed tomography) scans. Radiotherapy Department Patient information series
 University College Hospital Contrast agent for radiotherapy CT (computed tomography) scans Radiotherapy Department Patient information series 11 2 If you need a large print, audio or translated copy of
University College Hospital Contrast agent for radiotherapy CT (computed tomography) scans Radiotherapy Department Patient information series 11 2 If you need a large print, audio or translated copy of
Mesenteric Angiography
 Information for patients Mesenteric Angiography Sheffield Vascular Institute Northern General Hospital You have been given this leaflet because you need a procedure known as a Mesenteric Angiogram. This
Information for patients Mesenteric Angiography Sheffield Vascular Institute Northern General Hospital You have been given this leaflet because you need a procedure known as a Mesenteric Angiogram. This
How To Prepare For A Ct Scan
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Radiology Department Information for patients having a CT scan page 2 The radiology department has received a request for you to have a CT scan. This leaflet tells
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Radiology Department Information for patients having a CT scan page 2 The radiology department has received a request for you to have a CT scan. This leaflet tells
Brain Tumor Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Brain Tumor Treatment Brain Tumors Overview A brain tumor is a group of abnormal cells that grows in or around the brain. Tumors can directly destroy healthy brain cells. They can
Scan for mobile link. Brain Tumor Treatment Brain Tumors Overview A brain tumor is a group of abnormal cells that grows in or around the brain. Tumors can directly destroy healthy brain cells. They can
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
Prostate Cancer. What is prostate cancer?
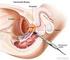 Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam, prostate-specific
Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam, prostate-specific
University College Hospital. Your child is having an MRI scan under sedation. Imaging Department
 University College Hospital Your child is having an MRI scan under sedation Imaging Department If you would like this document in another language or format, or require the services of an interpreter,
University College Hospital Your child is having an MRI scan under sedation Imaging Department If you would like this document in another language or format, or require the services of an interpreter,
CT Scan UHN. Information for patients and families
 CT Scan UHN Information for patients and families Read this information to learn: what a CT scan is how to prepare for the scan what to expect who to contact if you have any questions Joint Department
CT Scan UHN Information for patients and families Read this information to learn: what a CT scan is how to prepare for the scan what to expect who to contact if you have any questions Joint Department
Colorectal Cancer Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Colorectal Cancer Treatment Colorectal cancer overview Colorectal cancer, also called large bowel cancer, is the term used to describe malignant tumors found in the colon and rectum.
Scan for mobile link. Colorectal Cancer Treatment Colorectal cancer overview Colorectal cancer, also called large bowel cancer, is the term used to describe malignant tumors found in the colon and rectum.
CT Scan Thorax and Upper Abdomen. Respiratory Unit Patient Information Leaflet
 CT Scan Thorax and Upper Abdomen Respiratory Unit Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet gives you general information about your CT (computerised tomography) scan. It does not replace the
CT Scan Thorax and Upper Abdomen Respiratory Unit Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet gives you general information about your CT (computerised tomography) scan. It does not replace the
What You Should Know About Cerebral Aneurysms
 What You Should Know About Cerebral Aneurysms From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Interventions Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Radiology Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D.,
What You Should Know About Cerebral Aneurysms From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Interventions Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Radiology Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D.,
X-Rays Benefits and Risks. Techniques that use x-rays
 X-Rays Benefits and Risks X-rays are a form of electromagnetic radiation, just like light waves and radiowaves. Because X-rays have higher energy than light waves, they can pass through the body. X-rays
X-Rays Benefits and Risks X-rays are a form of electromagnetic radiation, just like light waves and radiowaves. Because X-rays have higher energy than light waves, they can pass through the body. X-rays
Information for adults having an MRI scan of the gallbladder and biliary tree (an MRCP scan)
 South Tyneside NHS Foundation Trust Information for adults having an MRI scan of the gallbladder and biliary tree (an MRCP scan) Department: Radiology Providing a range of NHS services in Gateshead, South
South Tyneside NHS Foundation Trust Information for adults having an MRI scan of the gallbladder and biliary tree (an MRCP scan) Department: Radiology Providing a range of NHS services in Gateshead, South
NeuroStar TMS Therapy Patient Guide for Treating Depression
 NeuroStar TMS Therapy Patient Guide for Treating Depression This NeuroStar TMS Therapy Patient Guide for Treating Depression provides important safety and use information for you to consider about treating
NeuroStar TMS Therapy Patient Guide for Treating Depression This NeuroStar TMS Therapy Patient Guide for Treating Depression provides important safety and use information for you to consider about treating
Having denervation of the renal arteries for treatment of high blood pressure
 Having denervation of the renal arteries for treatment of high blood pressure The aim of this information sheet is to help answer some of the questions you may have about having denervation of the renal
Having denervation of the renal arteries for treatment of high blood pressure The aim of this information sheet is to help answer some of the questions you may have about having denervation of the renal
Airport Scanner Safety
 Scan for mobile link. Airport Scanner Safety Airport scanners When it comes to airport scanner safety, there are four questions you should consider, including: What are airport scanners? Are there different
Scan for mobile link. Airport Scanner Safety Airport scanners When it comes to airport scanner safety, there are four questions you should consider, including: What are airport scanners? Are there different
CT scan. Useful information. Contents. This information is about CT scans. There are sections on
 CT scan Useful information Contents This information is about CT scans. There are sections on How a CT scanner works What happens Preparation for the scan Abdominal CT scans CT scans of the head CT scans
CT scan Useful information Contents This information is about CT scans. There are sections on How a CT scanner works What happens Preparation for the scan Abdominal CT scans CT scans of the head CT scans
1 of 6 1/22/2015 10:06 AM
 1 of 6 1/22/2015 10:06 AM 2 of 6 1/22/2015 10:06 AM This cross-section view of the shoulder socket shows a typical SLAP tear. Injuries to the superior labrum can be caused by acute trauma or by repetitive
1 of 6 1/22/2015 10:06 AM 2 of 6 1/22/2015 10:06 AM This cross-section view of the shoulder socket shows a typical SLAP tear. Injuries to the superior labrum can be caused by acute trauma or by repetitive
First floor, Main Hospital North Services provided 24/7 365 days per year
 First floor, Main Hospital North Services provided 24/7 365 days per year General Radiology (X-ray) Fluoroscopy Ultrasound (Sonography) Nuclear Medicine P.E.T. imaging Computed Tomography (CT scan) Magnetic
First floor, Main Hospital North Services provided 24/7 365 days per year General Radiology (X-ray) Fluoroscopy Ultrasound (Sonography) Nuclear Medicine P.E.T. imaging Computed Tomography (CT scan) Magnetic
Oxford Centre for Respiratory Medicine Bronchial-Artery Embolisation Information for patients
 Oxford Centre for Respiratory Medicine Bronchial-Artery Embolisation Information for patients This leaflet tells you about the bronchial-artery embolisation procedure. It explains what is involved and
Oxford Centre for Respiratory Medicine Bronchial-Artery Embolisation Information for patients This leaflet tells you about the bronchial-artery embolisation procedure. It explains what is involved and
.org. Shoulder Pain and Common Shoulder Problems. Anatomy. Cause
 Shoulder Pain and Common Shoulder Problems Page ( 1 ) What most people call the shoulder is really several joints that combine with tendons and muscles to allow a wide range of motion in the arm from scratching
Shoulder Pain and Common Shoulder Problems Page ( 1 ) What most people call the shoulder is really several joints that combine with tendons and muscles to allow a wide range of motion in the arm from scratching
The science of medicine. The compassion to heal.
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES OF THE HEART The science of medicine. The compassion to heal. This teaching booklet is designed to introduce you to electrophysiology studies of the heart.
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES OF THE HEART The science of medicine. The compassion to heal. This teaching booklet is designed to introduce you to electrophysiology studies of the heart.
Clinical Trials and Screening: What You Need to Know
 Scan for mobile link. Clinical Trials and Screening: What You Need to Know What is a Clinical Trial? At A Glance A clinical trial is a research study that tests how well new medical techniques work in
Scan for mobile link. Clinical Trials and Screening: What You Need to Know What is a Clinical Trial? At A Glance A clinical trial is a research study that tests how well new medical techniques work in
ASSESSMENT OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING PROTOCOLS WITH HEALTHY VOLUNTEERS
 SHEFC BRAIN IMAGING RESEARCH CENTRE FOR SCOTLAND Department of Clinical Neurosciences The University of Edinburgh Western General Hospital Crewe Road Edinburgh EH4 2XU Tel: 0131 537 2664 Fax: 0131 537
SHEFC BRAIN IMAGING RESEARCH CENTRE FOR SCOTLAND Department of Clinical Neurosciences The University of Edinburgh Western General Hospital Crewe Road Edinburgh EH4 2XU Tel: 0131 537 2664 Fax: 0131 537
Catheter Embolization and YOU
 Catheter Embolization and YOU What is catheter embolization? Embolization therapy is a minimally invasive (non-surgical) treatment that occludes or blocks one or more blood vessels or vascular channels
Catheter Embolization and YOU What is catheter embolization? Embolization therapy is a minimally invasive (non-surgical) treatment that occludes or blocks one or more blood vessels or vascular channels
Prostate Cancer Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Treatment Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam,
Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Treatment Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam,
Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) for Outpatient
 Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) for Outpatient Introduction A Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter, or PICC line, is a thin, long, soft plastic tube inserted into a vein of the arm. It
Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) for Outpatient Introduction A Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter, or PICC line, is a thin, long, soft plastic tube inserted into a vein of the arm. It
Lung cancer forms in tissues of the lung, usually in the cells lining air passages.
 Scan for mobile link. Lung Cancer Lung cancer usually forms in the tissue cells lining the air passages within the lungs. The two main types are small-cell lung cancer (usually found in cigarette smokers)
Scan for mobile link. Lung Cancer Lung cancer usually forms in the tissue cells lining the air passages within the lungs. The two main types are small-cell lung cancer (usually found in cigarette smokers)
Esophageal Cancer Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Esophageal Cancer Treatment What is Esophageal Cancer? Esophageal cancer occurs when cancer cells develop in the esophagus, a long, tube-like structure that connects the throat and
Scan for mobile link. Esophageal Cancer Treatment What is Esophageal Cancer? Esophageal cancer occurs when cancer cells develop in the esophagus, a long, tube-like structure that connects the throat and
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO ABLATION THERAPY
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO ABLATION THERAPY THE DIVISION OF VASCULAR/INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGY THE ROBERT WOOD JOHNSON UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL Treatment options for patients with cancer continue to expand, providing
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO ABLATION THERAPY THE DIVISION OF VASCULAR/INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGY THE ROBERT WOOD JOHNSON UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL Treatment options for patients with cancer continue to expand, providing
Image-guided abdominal drain insertion Information for patients
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Image-guided abdominal drain insertion Information for patients What is an image-guided abdominal drain insertion? A drain is a thin plastic tube which is inserted
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Image-guided abdominal drain insertion Information for patients What is an image-guided abdominal drain insertion? A drain is a thin plastic tube which is inserted
Liver Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE) Cancer treatment
 Patient Education Liver Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE) Cancer treatment This handout explains what liver transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) is and what to expect with this cancer treatment.
Patient Education Liver Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE) Cancer treatment This handout explains what liver transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) is and what to expect with this cancer treatment.
Patient Prep Information
 Stereotactic Breast Biopsy Patient Prep Information Imaging Services Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center Table Weight Limits for each facility Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center
Stereotactic Breast Biopsy Patient Prep Information Imaging Services Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center Table Weight Limits for each facility Cannon Memorial Hospital Watauga Medical Center
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Aortic Stenosis. What is heart valve disease? What is aortic stenosis?
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Aortic Stenosis Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment This handout describes aortic stenosis, a narrowing of the aortic valve in your heart. It also explains how this
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Aortic Stenosis Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment This handout describes aortic stenosis, a narrowing of the aortic valve in your heart. It also explains how this
X-Plain Preparing For Surgery Reference Summary
 X-Plain Preparing For Surgery Reference Summary Introduction More than 25 million surgical procedures are performed each year in the US. This reference summary will help you prepare for surgery. By understanding
X-Plain Preparing For Surgery Reference Summary Introduction More than 25 million surgical procedures are performed each year in the US. This reference summary will help you prepare for surgery. By understanding
A Patient s Guide to Minimally Invasive Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair
 A Patient s Guide to Minimally Invasive Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair Table of Contents The AFX Endovascular AAA System............................................ 1 What is an Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
A Patient s Guide to Minimally Invasive Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair Table of Contents The AFX Endovascular AAA System............................................ 1 What is an Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
CT Virtual Colonoscopy
 CT Virtual Colonoscopy Ladywell Building Radiology 2 0161 206 1233 All Rights Reserved 2015. Document for issue as handout. This information booklet tells you about virtual colonoscopy, which is a test
CT Virtual Colonoscopy Ladywell Building Radiology 2 0161 206 1233 All Rights Reserved 2015. Document for issue as handout. This information booklet tells you about virtual colonoscopy, which is a test
PERIPHERAL STEM CELL TRANSPLANT INTRODUCTION
 PERIPHERAL STEM CELL TRANSPLANT INTRODUCTION This booklet was designed to help you and the important people in your life understand the treatment of high dose chemotherapy with stem cell support: a procedure
PERIPHERAL STEM CELL TRANSPLANT INTRODUCTION This booklet was designed to help you and the important people in your life understand the treatment of high dose chemotherapy with stem cell support: a procedure
University College Hospital. Having an MRI scan Imaging Department
 University College Hospital Having an MRI scan Imaging Department If you would like this leaflet in another format, for example: large print or audio, or in translation please contact us on 020 3456 7002.
University College Hospital Having an MRI scan Imaging Department If you would like this leaflet in another format, for example: large print or audio, or in translation please contact us on 020 3456 7002.
Spinal Injections. North American Spine Society Public Education Series
 Spinal Injections North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Spinal Injection? Your doctor has suggested that you have a spinal injection to help reduce pain and improve function. This
Spinal Injections North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Spinal Injection? Your doctor has suggested that you have a spinal injection to help reduce pain and improve function. This
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma)
 Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
Epidurals for pain relief after surgery
 Epidurals for pain relief after surgery This information leaflet is for anyone who may benefit from an epidural for pain relief after surgery. We hope it will help you to ask questions and direct you to
Epidurals for pain relief after surgery This information leaflet is for anyone who may benefit from an epidural for pain relief after surgery. We hope it will help you to ask questions and direct you to
Nephrostomy &/or Ureteric Stent Insertion PROCEDURAL CONSENT FORM. A. Interpreter / cultural needs. B. Procedure. C. Risks of the procedure
 DO NOT WRITE IN THIS BINDING MARGIN v2.00-03/2011 SW9231 Facility: Nephrostomy &/or Ureteric Stent Insertion A. Interpreter / cultural needs An Interpreter Service is required? Yes No If Yes, is a qualified
DO NOT WRITE IN THIS BINDING MARGIN v2.00-03/2011 SW9231 Facility: Nephrostomy &/or Ureteric Stent Insertion A. Interpreter / cultural needs An Interpreter Service is required? Yes No If Yes, is a qualified
Patient Information Booklet. Endovascular Stent Grafts: A Treatment for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms
 Patient Information Booklet Endovascular Stent Grafts: A Treatment for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction 1 Glossary 2 Abdominal Aorta 4 Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm 5 Causes 6 Symptoms
Patient Information Booklet Endovascular Stent Grafts: A Treatment for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction 1 Glossary 2 Abdominal Aorta 4 Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm 5 Causes 6 Symptoms
X-Plain Temporomandibular Joint Disorders Reference Summary
 X-Plain Temporomandibular Joint Disorders Reference Summary Introduction Temporomandibular joint disorders, or TMJ disorders, are a group of medical problems related to the jaw joint. TMJ disorders can
X-Plain Temporomandibular Joint Disorders Reference Summary Introduction Temporomandibular joint disorders, or TMJ disorders, are a group of medical problems related to the jaw joint. TMJ disorders can
General Nuclear Medicine
 Scan for mobile link. General Nuclear Medicine Nuclear medicine imaging uses small amounts of radioactive materials called radiotracers that are typically injected into the bloodstream, inhaled or swallowed.
Scan for mobile link. General Nuclear Medicine Nuclear medicine imaging uses small amounts of radioactive materials called radiotracers that are typically injected into the bloodstream, inhaled or swallowed.
