Allium Triangular Prostatic Urethral Stent System (TPS) Instructions For Use
|
|
|
- Todd Lang
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Allium Triangular Prostatic Urethral Stent System (TPS) Instructions For Use Manufactured by Allium Ltd.
2 Device Name: Allium Triangular Prostatic Urethral Stent (TPS) Allium Triangular Prostatic Urethral Stent (TPS) has a triangular cross section body to fit the prostatic urethral lumen occluded by enlarged prostate lobes. This stent has a bulbar anchoring segment for preventing migration. Device Description: The TPS is a temporary device intended for transurethral insertion into the male urethra diagnosed with Bladder Outlet Obstruction (BOO), caused by an enlarged prostate gland (benign or malignant). It is a single use device intended to remain in the urethra up to 1 year, to open the occluded urethral passage and allow spontaneous urination. The stent is comprised of a coiled super-elastic structure covered with a co-polymer. Once inserted into the urethra with the aid of its special inserter, the stent is released to allow its selfexpansion. The TPS System includes: 1. A delivery tool containing the TPS crimped into a 19 Fr tube mounted on a deployment handle (Figures 1a and 1b) 2. A Foley-type catheter with markings (for indicating the landmarks) (Figure 2) Figure 1 a - The Delivery Tool for Deploying the TPS (note the Tiemann-type distal end with its non-inflated balloon) Figure 1 b - The Delivery Tool for Deploying the TPS (note the Tiemann-type distal end with its inflated balloon) The Foley-type Marking Catheter (accompanying the TPS Kit as an accessory) has markers at 1 cm intervals, starting below the balloon for marking the distance between the bladder-neck and the veru montanum (the length of the prostatic urethra) Figure 2 - The Foley-type Marking Catheter Pre Treatment Evaluation of BOO: It is recommended to perform the following basic evaluation prior to initiation of treatment for BOO with a stent: history, physical examination, PVR (post-void residual urine), DRE (digital rectal examination), prostate sonography (abdominal and/or trans-rectal), uroflowmetry, PSA (prostate specific antigen), urethrography and urinalysis. If indicated by the results of the basic evaluation, a more extensive workup may be required. Indications for Use: The use of TPS System is indicated for the management of BOO in adult males (18 years or older). It is intended for use in the following obstructions to provide temporary relief of the obstructions: prostatic enlargement (benign or malignant), or for use after minimally invasive 2
3 treatments (MIT) based on thermal tissue damage of the prostate (by heating: microwave, RF thermotherapy, laser coagulation surgery, hot water etc; by freezing: cryotherapy); or interstitial irradiation (brachytherapy) for prostate cancer, which may cause post-procedural temporary edema and severe voiding difficulties or urine retention. The TPS is not intended for definitive treatment of prostatic disease or of the complications of prostatic disease or urethral strictures. Contraindications: The insertion of a TPS is contraindicated in men who: 1. Are younger than Have an acute infection of the prostate or urethra. 3. Have an acute upper urinary tract infection. 4. Are immuno-compromised, have a prosthetic heart valve or other implanted device, or have any other conditions in which the patient is at significant risk from urinary tract infection. 5. Cannot tolerate any form of antibiotic treatment. 6. Are currently receiving anticoagulation therapy. 7. Have irreversible atonic / acontractile bladder. 8. Have a urethro-cutaneous or urethro rectal fistule. 9. Cystolithiasis. 10. A history of any illness, medications or surgery that may affect the efficacy of the stent. 11. Patients who use constriction rings and/or vacuum erection devices. 12. Patients who use injectable medications to obtain erection. 13. Patients with penile implants and / or implanted artificial urinary sphincters. Precautions: Checking the device: The constricted stent and delivery system should be inspected for damage prior to use. Prior to delivery, the physician should ensure that the stent is covered by the over-tube. Training: Proper training is required to position and deploy the TPS. Prior to its use, the technical information supplied with the device should be carefully reviewed. Device Related Warnings: Single use device: The TPS is intended for Single Use Only-DO NOT RESTERILIZE. Reuse, reprocessing, resterilization or repackaging may compromise the structural integrity and/or essential material and design characteristics that are critical to the overall performance of the device and may lead to device failure which may result in injury to the patient. Reuse, reprocessing, resterilization or repackaging may also create a risk of contamination of the device and/or cause patient infection or cross infection, including, but not limited to, transmission of infectious diseases from one patient to another. Contamination of the device may lead to injury, illness or death of the patient or end user. The device should not be used if the package is open or damaged, or if the device has been contaminated prior to insertion. Re-use of any of the components of the TPS system or the entire system can seriously damage the health of the patient. The stent and delivery system should be inspected for damage prior its use. Remounting of a stent into the delivery system should not be attempted, since this will damage the cover of the stent. The delivery system of the TPS contains natural latex which may cause allergic reactions. Positioning of the main body or the anchoring segment of the stent across the external sphincter may render the patient incontinent. The stent is intended to be used for a period of up to 1 year and is not intended as a permanent option to treat urethral obstructions. 3
4 Main Body The Foley-type Marking Catheter (supplied as an accessory) should be used to mark the distances between the identified landmarks to determine the appropriate stent length. Bladder catheterization with an implanted stent is not recommended. Introduction and passage of a catheter through the stented urethra into the bladder may dislodge the stent and/or damage the polymeric cover. The use of transurethral instrumentation while the stent is in place is not recommended because longitudinal compression of the stent by instrumentation could dislodge the stent. The stent should be inserted and positioned only according the Instructions for Use (IFU) accompanying the device. Under-vision insertion should not be attempted in patients in whom bleeding may impede the visualization process. The stent should not be used in patients with bladder stones. The stent may migrate during and after placement. If this occurs, the stent should be removed and a new one inserted. INSERTION INSTRUCTIONS FOR THE Triangular Prostatic urethral Stent (TPS) The TPS is a temporary device intended for transurethral insertion into the male urethra diagnosed with BOO, caused by an enlarged prostate gland (benign or malignant). The TPS once inserted into the prostatic urethra with the aid of its insertion tool, is released to allow its self-expansion. The TPS is available in 5 lengths: Catalogue No. Body Length [mm] TPS TPS TPS TPS TPS Trans-Sphincteric Segment Length [cm] Anchoring Segment Length [cm] Main Body Caliber Equivalent to 45 Fr Sphincteric Segment Trans-Sphincteric Segment Anchoring Segment Figure 3 - TPS segments and their correlation with the posterior urethral anatomy Note: The "body" of the stent is composed of the high radial force "Main Body" and the "Sphincteric Segment" having a gradually decreasing radial force. The overall length of the stent and its various segments are identical in both the crimped and expanded state. 4
5 Sphincter Prostate Bladder Posterior Urethra Bulbar Urethra Figure 4 - Choosing the correct stent length and its appropriate position [All dimensions in millimeters] Pre-procedural preparation A broad-spectrum antibiotic for prophylaxis should be started at least 3 hours before the procedure and continued according to the endoscopic transurethral procedures protocol used in your institution. It is recommended to prescribe an oral or rectal non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug to be started the evening before the procedure and continued for 3-4 days thereafter. The following equipment should be prepared for insertion of the TPS: # Cystoscope for measuring the prostatic urethral length # TPS kit + accompanying accessory Marking Catheter # Rigid or strong flexible endoscopic foreign body forceps It is important to have a complete kit with all the lengths of stents in the OR or in the office to choose the accurate stent size after measuring the prostatic urethral length. Measurement of the Prostatic Urethra Endoscopic Measurement: Insert the Marking Catheter until it reaches the bladder and inflate its balloon with 10ml saline. Pull the balloon until it touches the bladder neck. Insert a small caliber cystoscope (up to 17 Fr) with a 0, 5 or 30 lens beside the catheter enabling vision of the bladder neck. Measure the prostatic urethral length by counting the marks on the Marking Catheter from the bladder neck to the down-stream end of the Veru Montanum (prostatic apex). The measured length is the length of the prostatic urethra. Measurement by Trans-Rectal Ultrasound (TRUS): Using TRUS measure the length of the prostatic urethra (on the sagittal axis of the gland - the distance between the bladder-neck and the apex). Choosing the Appropriate Stent Length Appropriate length of the stent to be chosen is based upon the length of the measured prostatic urethral length. Since the Body of the TPS will be situated in the prostatic urethra above the external sphincter the "Body" segment of the stent should fit the measured prostatic urethral length (±0.5 cm.). If the measured prostatic urethral length is 4 cm a TPS 40 is chosen. IMPORTANT Since the apex of the triangular stent should be positioned at 12 o'clock position of the bladder neck it is a must to keep the deployment tool with its handle between the legs of the patient in downward position. Do not try to pull back the partially released stent into the delivery tool. This may cause irreparable damage to the stent. 5
6 MRI INFO TPS MRI Information MR Conditional The Triangular Prostatic Stent was determined to be MR-conditional. Non-clinical testing demonstrated that the Triangular Prostatic Stent is MR Conditional. A patient with this device can be scanned safely, immediately after placement under the following conditions: Static Magnetic Field -Static magnetic field of 3-Tesla or less -Maximum spatial gradient magnetic field of 720-Gauss/cm or less MRI-Related Heating In non-clinical testing, the Triangular Prostatic Stent produced the following temperature rises during MRI performed for 15-min of scanning (i.e., per pulse sequence) in 1.5- Tesla/64-MHz (Magnetom, Siemens Medical Solutions, Malvern, PA. Software Numaris/4, Version Syngo MR 2002B DHHS Active-shielded, horizontal field scanner) and 3-Tesla (3- Tesla/128-MHz, Excite, HDx, Software 14X.M5, General Electric Healthcare, Milwaukee, WI) MR systems: 1.5-Tesla 3-Tesla MR system reported, whole body averaged SAR 2.9-W/kg 2.9-W/kg Calorimetry measured values, whole body averaged SAR 2.1-W/kg 2.7-W/kg Highest temperature change +2.5 C +3.0 C These temperature changes will not pose a hazard to a human subject under the conditions indicated above. Artifact Information MR image quality may be compromised if the area of interest is in the exact same area or relatively close to the position of the Triangular Prostatic Stent. Therefore, optimization of MR imaging parameters to compensate for the presence of this device may be necessary. The maximum artifact size (i.e., as seen on the gradient echo pulse sequence) extends approximately 5-mm relative to the size and shape of this implant. Pulse Sequence T1-SE T1-SE GRE GRE Signal Void Size 1,770-mm2 293-mm2 2,293-mm2 372-mm2 Plane Orientation Parallel Perpendicular Parallel Perpendicular Stent Deployment The delivery system is intended for inserting the TPS either directly or under fluoroscopic control. It is recommended to insert the stent with at least full bladder. Inform the patient to drink 2-3 glasses of liquid 1-2 hours before the procedure. If the bladder is not full, saline can be filled through the deployment system. Caution: Remove the protective cover by pulling from its ring! Direct insertion: Take an Endoscopic Measurement of the Prostatic Urethra as described above. Choose the appropriate stent length mounted on the delivery system. After generously lubricating the urethra insert the delivery system as inserting a Tiemann tip Foley catheter until its tip reaches the bladder (urine will appear through 6
7 the end of the device). Then insert the device 3-4 cm further. If the bladder is not full inject ml saline to fill it. Inflate the balloon of the deployment device with 10 ml saline and gently pull the device outward until the balloon reaches the bladder neck. For accurate positioning of the stent, keeping the gentle traction during the delivery is important. This will assure that the bladder end of the stent is at the bladder neck. Assure that the handle of the deployment device is at 6 o'clock position between the legs of the patient. This will assure that the apex of the triangular stent is at 12 o'clock position of the prostatic urethra Unlock to release the trigger by sliding the lock downward before starting the release. Release of the stent: The total length of the stent is composed of Body Length (30 to 65 mm, in 5 mm increments) + Trans-sphincteric wire (20 mm) + Anchoring segment (14 mm). Pull the trigger minimum 14 times (depending on the length of the stent) to release the stent. Each full pull of the trigger releases approximately mm of the stent and its anchor. Deflate the balloon gently and assure that the saline is completely withdrawn from the balloon. In case of difficulty in retrieving all the saline, gently push the insertion device 2-3 cm toward the bladder and continue evacuating the balloon. With small rotating maneuvers gently remove the deployment device from the urethra. Incomplete balloon deflation or hasty removal of the delivery tool may pull the stent outward and cause its malpositioning. After removing the deployment device, ask the patient to pass urine and stop the stream voluntarily to check the integrity of the sphincter. Fluoroscopic Insertion: After taking an accurate measurement of the prostatic urethral length (as described in Measurement of the Prostatic Urethra) perform a retrograde urethrogram and mark the place of the sphincter using a metallic skin marker. Choose the appropriate stent length mounted on the delivery system. After generously lubricating the urethra insert the delivery system as inserting a Tiemann tip Foley catheter until its tip reaches the bladder (urine will appear through the end of the deployment device) and insert the device 3-4 cm further. If the bladder is not full inject ml saline to fill it. Inflate the balloon of the deployment device with 10 ml saline containing 1-2 cc of contrast and gently pull the device outward until the balloon reaches the bladder neck. Verify fluoroscopically that the balloon is at the bladder neck. This will assure that the bladder end of the stent is positioned at the bladder neck. Under fluoroscopy verify that the trans-sphincteric wire is at the level of the skin marker Assure that the handle of the deployment device is at 6 o'clock position between the legs of the patient. This will assure that the apex of the triangular stent is at 12 o'clock position of the prostatic urethra. Unlock to release the trigger by sliding the lock downward before starting the release. Insertion and release of the TPS can be followed also by TRUS. Release of the stent: The total length of the stent is composed of Body Length (30 to 65 mm, in 5 mm increments) + Trans-sphincteric wire (20 mm) + Anchoring segment (14 mm). Pull the trigger minimum 14 times (depending on the length of the stent) to release the stent. Each full pull of the trigger releases approximately mm of the stent and its anchor. The TPS has 2 radiopaque markers at its bladder end: one at the apex of the last loop at the bladder end and the second at the middle of its base loop. Verify fluoroscopically that the 2 markers are one over the other or very near to each other. This will verify that the apex of the triangular stent is at 12 o'clock position of the prostatic urethra Deflate the balloon (assure that the saline is completely withdrawn from the balloon by fluroscopy) and with small rotating maneuvers gently remove the deployment device from the urethra. Removal of the deployment device can be followed fluoroscopically. Incomplete balloon deflation or hasty removal of the delivery tool may pull the stent outward and cause its malpositioning. 7
8 After removing the deployment device, ask the patient to pass urine and stop the stream voluntarily to check the integrity of the sphincter. Voiding Function Assessment If the patient feels that his bladder is full after removing the delivery tool, ask him to pass urine and stop the stream voluntarily to re-assure that the sphincteric function is intact. If the patient cannot voluntarily stop the stream check the position of the stent endoscopically. If the stent appears to be compromising the function of the external sphincter a repositioning maneuver can be tried. In case this maneuver is not successful, the stent should be removed and another one inserted. Repositioning Maneuver Never try to reposition the Allium Urethral Stents with a foreign body forceps. The forceps can damage the polymeric cover. If the main body of the stent is seen in the external sphincter the stent should be pushed forward, toward the bladder. For doing this : Fill the urethra with 20 ml of lubricating jelly. Gently insert a 12 Fr Foley Catheter through the stent until it reaches the bladder (urine will appear from its port). Do not inflate the balloon. Insert a small caliber cystoscope (up to 17 Fr) beside the catheter up to the sphincteric segment of the main body of the stent. Slowly pull back the catheter until the lower edge of its empty balloon is seen. Fill the balloon which is in the lumen of the body of the stent with 5-6 ml saline solution. Under vision, with the tip of the cystoscope gently push the balloon of the catheter toward the bladder. This pushing will move the stent inward. Pull back the cystoscope about 1-2 cm and check if the sphincteric segment entered the prostatic urethra. If not continue to push gently the balloon. If the repositioning is satisfactory evacuate the balloon and under vision gently pull out the catheter and then the cystoscope. If the anchoring bulbar segment of the stent is seen in or above the external sphincter the stent should be pulled outward. For doing this the same maneuvers described above are done, but instead of pushing the main body toward the bladder, the catheter with its inflated balloon in the main body of the stent, is gently pulled outward, until the entire bulbar segment enters the bulbar urethra. Do not inflate the balloon in the anchoring bulbar segment and try to pull it or use a forceps for pulling this segment. This will cause unraveling of the main body and the bulbar segment and will not move the stent outward. Removing the Stent The Stent is a single use device and is designed to be removed at the end of its intended indwelling time. The stent can be removed under vision using a rigid endoscopic or a strong flexible endoscopic foreign body forceps. Under vision insert a Fr cystoscope until the down-stream anchoring end of the stent is seen in the bulbar urethra. Insert the foreign body forceps through the cystoscope. Engage the metal wire of the anchor with the forceps or catch one of the distal loops of the stent main body with the forceps. Disconnect the sheath from the bridge of the cystoscope together with the flexible forceps, and start pulling the loop toward the sheath. This may initiate tearing the polymeric cover. Continue to pull outward the metal wire together with the endoscope sheath. Do not try to remove the stent by pulling the wire through the sheath, this might cause the stent to tangle and get caught in the sheath or breakage of the stent wire. Verify that the entire stent came out by checking that the second small loop at the upstream end of the stent came out. 8
9 DISCLAIMER OF WARRANTIES Allium, Ltd. warrants that reasonable care has been used in the manufacture of this device. This warranty is exclusive and in lieu of all other warranties whether expressed, implied, written or oral, including but not limited to any warranties of merchantability of fitness for a particular purpose. As a result of biological differences in individuals, no product is 100% effective under all circumstances. Because of this fact, and since Allium, Ltd. has no control over the conditions under which the device is used, diagnosis of the patient, methods of administration or its handling after the device leaves our possession, Allium, Ltd. does not warrant either a good effect or against any ill effect following its use. Allium, Ltd. shall not be liable for any incidental or consequential loss, damage, or expense arising directly or indirectly from the use of this device. Allium, Ltd. will replace any device that we feel was defective at the time of shipment. No representative of Allium, Ltd. may change any of the foregoing or assume any additional liability or responsibility with this device. 9
10 Labeling Information Symbol This Symbol Means Do Not Reuse Use By Batch Code Sterilization Using Ethylene Oxide Catalog Number Caution, Consult Accompanying Documents Manufacturer Authorized Representative in the European Committee Consult Instructions for Use Store in Dry Place at Room Temperature Do Not Use if Package is Damaged For further questions or information, please contact the manufacturer: Allium, Ltd. Ha-Eshel 2 P.O.BOX 3081 Caesarea Industrial Park Israel Phone: Fax: info@allium-medical.com REF: AUTHORIZED REPRESENTATIVE MEDNET GmbH Borkstrasse 10 D Munster Germany 10
Allium Bulbar Urethral Stent System (BUS) Instructions For Use
 Allium Bulbar Urethral Stent System (BUS) Instructions For Use Manufactured by Allium Ltd. Device Name: Allium Bulbar Urethral Stent (BUS) Device Description: The BUS is a temporary device intended for
Allium Bulbar Urethral Stent System (BUS) Instructions For Use Manufactured by Allium Ltd. Device Name: Allium Bulbar Urethral Stent (BUS) Device Description: The BUS is a temporary device intended for
Allium Ureteral Stent (URS)
 Allium Ureteral Stent (URS) Instructions For Use Manufactured by Allium Ltd. DEVICE NAME: ALLIUM Ureteral Stent (URS) is intended to be inserted into the lower ureter to allow free flow of urine from the
Allium Ureteral Stent (URS) Instructions For Use Manufactured by Allium Ltd. DEVICE NAME: ALLIUM Ureteral Stent (URS) is intended to be inserted into the lower ureter to allow free flow of urine from the
Contraindications: Malign or benign strictures in the upper part of esophagus close to the cricopharyngeal muscle.
 Manufactured by: ELLA CS, s.r.o. Milady Horákové 504 500 06 Hradec Králové 6 Czech Republic Phone: +420 49 527 91 11 Fax: +420 49 526 56 55 E-mail: volenec@ellacs.cz Instructions for Use FerX-ELLA Esophageal
Manufactured by: ELLA CS, s.r.o. Milady Horákové 504 500 06 Hradec Králové 6 Czech Republic Phone: +420 49 527 91 11 Fax: +420 49 526 56 55 E-mail: volenec@ellacs.cz Instructions for Use FerX-ELLA Esophageal
LifeStent XL Biliary Stent System
 B05688 Rev.2/07-13 LifeStent XL Biliary Stent System Recommended Guidewire Length Table Catheter Working Length Recommended Guidewire Length 130 cm 300 cm 80 cm 260 cm 130 cm & 80 cm 160 cm & 110 cm Figure
B05688 Rev.2/07-13 LifeStent XL Biliary Stent System Recommended Guidewire Length Table Catheter Working Length Recommended Guidewire Length 130 cm 300 cm 80 cm 260 cm 130 cm & 80 cm 160 cm & 110 cm Figure
Bard LifeStar Biliary Stent System
 Bard LifeStar Biliary Stent System Instructions For Use (IFU) Bard LifeStar Biliary Stent System Delivery System Diagram B05686 Vers.1/08-11 1 Information for use Read the Bard LifeStar Biliary Stent System
Bard LifeStar Biliary Stent System Instructions For Use (IFU) Bard LifeStar Biliary Stent System Delivery System Diagram B05686 Vers.1/08-11 1 Information for use Read the Bard LifeStar Biliary Stent System
Instructions for Use. Device Description The AMPLATZER Vascular Plug II is a self-expandable nitinol mesh occlusion device (see Figure 1).
 Vascular Plug II Instructions for Use Device Description The AMPLATZER Vascular Plug II is a self-expandable nitinol mesh occlusion device (see Figure 1). A B Figure 1. AMPLATZER Vascular Plug II A. Nitinol
Vascular Plug II Instructions for Use Device Description The AMPLATZER Vascular Plug II is a self-expandable nitinol mesh occlusion device (see Figure 1). A B Figure 1. AMPLATZER Vascular Plug II A. Nitinol
Foley Catheter Placement
 Foley Catheter Placement Indications for a Foley Catheter Retention of urine leading to urinary hesitancy, straining to urinate, decrease in size and force of the urinary stream, interruption of urinary
Foley Catheter Placement Indications for a Foley Catheter Retention of urine leading to urinary hesitancy, straining to urinate, decrease in size and force of the urinary stream, interruption of urinary
surg urin Surgery: Urinary System 1
 Surgery: Urinary System 1 This section contains information to assist providers in billing for surgical procedures related to the urinary system. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy Medi-Cal covers Extracorporeal
Surgery: Urinary System 1 This section contains information to assist providers in billing for surgical procedures related to the urinary system. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy Medi-Cal covers Extracorporeal
AERO. Tracheobronchial Stent Technology System
 AERO Tracheobronchial Stent Technology System Review Instructions For Use Before Using This System. Single Use Non-sterile MR Conditional CONTENTS Instructions For Use.............................. 3 IMPORTANT
AERO Tracheobronchial Stent Technology System Review Instructions For Use Before Using This System. Single Use Non-sterile MR Conditional CONTENTS Instructions For Use.............................. 3 IMPORTANT
2. Does the patient have one of the following appropriate indications for placing indwelling urinary catheters?
 A. Decision to Insert a Urinary Catheter: 1. Before placing an indwelling catheter, please consider if these alternatives would be more appropriate: Bladder scanner: to assess and confirm urinary retention,
A. Decision to Insert a Urinary Catheter: 1. Before placing an indwelling catheter, please consider if these alternatives would be more appropriate: Bladder scanner: to assess and confirm urinary retention,
INTERDISCIPLINARY CLINICAL MANUAL Practice Guideline
 INTERDISCIPLINARY CLINICAL MANUAL Practice Guideline TITLE: Insertion of a curved tip Urinary Catheter (Coude/Tiemann) NUMBER: CC 50-013 Effective Date: August 2015 Page 1 of 5 Applies To: All Preamble:
INTERDISCIPLINARY CLINICAL MANUAL Practice Guideline TITLE: Insertion of a curved tip Urinary Catheter (Coude/Tiemann) NUMBER: CC 50-013 Effective Date: August 2015 Page 1 of 5 Applies To: All Preamble:
URINARY CATHETER CARE
 URINARY CATHETER CARE INTRODUCTION Urinary catheter care is a very important skill, and it is a skill that many certified nursing assistants (CNAs) must know. Competence at providing urinary catheter care
URINARY CATHETER CARE INTRODUCTION Urinary catheter care is a very important skill, and it is a skill that many certified nursing assistants (CNAs) must know. Competence at providing urinary catheter care
Long-term result of Memokath urethral sphincter stent in. spinal cord injury patients
 1 Long-term result of Memokath urethral sphincter stent in spinal cord injury patients Subramanian Vaidyanathan 1 E-mail: vaidyanathansiu@hotmail.com Bakul M Soni 1 E-mail: Bakul.Soni@mail.soh-tr.nwest.nhs.uk
1 Long-term result of Memokath urethral sphincter stent in spinal cord injury patients Subramanian Vaidyanathan 1 E-mail: vaidyanathansiu@hotmail.com Bakul M Soni 1 E-mail: Bakul.Soni@mail.soh-tr.nwest.nhs.uk
Subject: Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Information on Sorin Group Heart Valve Prostheses and Annuloplasty Devices
 Saluggia, 18 December 2013 Subject: Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Information on Sorin Group Heart Prostheses and Annuloplasty Devices To whom it may concern This letter summarizes the required MRI
Saluggia, 18 December 2013 Subject: Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Information on Sorin Group Heart Prostheses and Annuloplasty Devices To whom it may concern This letter summarizes the required MRI
URINARY CATHETER INSERTION - STRAIGHT OR INDWELLING CATHETER
 URINARY CATHETER INSERTION - STRAIGHT OR INDWELLING CATHETER PURPOSE To obtain a sterile urine specimen. To facilitate emptying bladder. To relieve bladder distention. To irrigate bladder. To measure residual
URINARY CATHETER INSERTION - STRAIGHT OR INDWELLING CATHETER PURPOSE To obtain a sterile urine specimen. To facilitate emptying bladder. To relieve bladder distention. To irrigate bladder. To measure residual
MANAGEMENT OF PROSTATE ENLARGEMENT/BPH
 MANAGEMENT OF PROSTATE ENLARGEMENT/BPH J E S S I C A E. P A O N E S S A, M. D. A S S I S T A N T P R O F E S S O R D E P A R T M E N T O F U R O L O G Y S U N Y U P S T A T E M E D I C A L U N I V E R
MANAGEMENT OF PROSTATE ENLARGEMENT/BPH J E S S I C A E. P A O N E S S A, M. D. A S S I S T A N T P R O F E S S O R D E P A R T M E N T O F U R O L O G Y S U N Y U P S T A T E M E D I C A L U N I V E R
BARD MEDICAL DIVISION UROLOGICAL DRAINAGE. Foley Catheter Care & Maintenance. Patient Education Guide
 BARD MEDICAL DIVISION Foley Catheter Care & Maintenance Patient Education Guide WHAT IS A FOLEY CATHETER? Because of your medical problem, your body is having trouble completely emptying your bladder of
BARD MEDICAL DIVISION Foley Catheter Care & Maintenance Patient Education Guide WHAT IS A FOLEY CATHETER? Because of your medical problem, your body is having trouble completely emptying your bladder of
Spinal Cord and Bladder Management Male: Intermittent Catheter
 Spinal Cord and Bladder Management Male: Intermittent Catheter The 5 parts of the urinary system work together to get rid of waste and make urine. Urine is made in your kidneys and travels down 2 thin
Spinal Cord and Bladder Management Male: Intermittent Catheter The 5 parts of the urinary system work together to get rid of waste and make urine. Urine is made in your kidneys and travels down 2 thin
HELPFUL STEP-BY-STEP ILLUSTRATIONS ARE LOCATED IN THIS BOOKLET
 HELPFUL STEP-BY-STEP ILLUSTRATIONS ARE LOCATED IN THIS BOOKLET DESCRIPTION The Vet Sent Ureter comes as a sterile stent system comprised of two components: 1) the radioopaque, double pigtail multi-fenestrated
HELPFUL STEP-BY-STEP ILLUSTRATIONS ARE LOCATED IN THIS BOOKLET DESCRIPTION The Vet Sent Ureter comes as a sterile stent system comprised of two components: 1) the radioopaque, double pigtail multi-fenestrated
Medical Tests for Prostate Problems
 Medical Tests for Prostate Problems National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is the prostate? The
Medical Tests for Prostate Problems National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is the prostate? The
CATHETERISATION. East Lancashire Hospitals NHS Trust Eileen Whitehead 2010
 CATHETERISATION East Lancashire Hospitals NHS Trust Eileen Whitehead 2010 1 Indications for catheterisation: A person is unable to void naturally due to injury or a disease process Diagnostic or therapeutic
CATHETERISATION East Lancashire Hospitals NHS Trust Eileen Whitehead 2010 1 Indications for catheterisation: A person is unable to void naturally due to injury or a disease process Diagnostic or therapeutic
Achieving Independence
 Bard: Intermittent Self-Catheterization A Guide to Self-Catheterization Achieving Independence Introduction This brochure is provided by Bard, a leading provider of urology products since 1907. The best
Bard: Intermittent Self-Catheterization A Guide to Self-Catheterization Achieving Independence Introduction This brochure is provided by Bard, a leading provider of urology products since 1907. The best
Aspira* Peritoneal Drainage Catheter
 Aspira* Peritoneal Drainage Catheter Instructions For Use Access Systems Product Description: The Aspira* Peritoneal Drainage Catheter is a tunneled, long-term catheter used to drain accumulated fluid
Aspira* Peritoneal Drainage Catheter Instructions For Use Access Systems Product Description: The Aspira* Peritoneal Drainage Catheter is a tunneled, long-term catheter used to drain accumulated fluid
150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 2. Patient Information. Freedom From an Enlarged Prostate
 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 2 Patient Information Freedom From an Enlarged Prostate 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 3 GreenLight Laser Therapy 1 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page
150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 2 Patient Information Freedom From an Enlarged Prostate 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page 3 GreenLight Laser Therapy 1 150640_Brochure_B 4/12/07 2:58 PM Page
Bard: Prostate Cancer Treatment. Bard: Pelvic Organ Prolapse. Prostate Cancer. An overview of. Treatment. Prolapse. Information and Answers
 Bard: Prostate Cancer Treatment Bard: Pelvic Organ Prolapse Prostate Cancer An overview of Pelvic Treatment Organ Prolapse Information and Answers A Brief Overview Prostate Anatomy The prostate gland,
Bard: Prostate Cancer Treatment Bard: Pelvic Organ Prolapse Prostate Cancer An overview of Pelvic Treatment Organ Prolapse Information and Answers A Brief Overview Prostate Anatomy The prostate gland,
Urinary Incontinence FAQ Sheet
 Urinary Incontinence FAQ Sheet Are you reluctant to talk to your doctor about your bladder control problem? Don t be. There is help. Loss of bladder control is called urinary incontinence. It can happen
Urinary Incontinence FAQ Sheet Are you reluctant to talk to your doctor about your bladder control problem? Don t be. There is help. Loss of bladder control is called urinary incontinence. It can happen
Cook Celect and Günther Tulip Vena Cava Filter Patient Guide
 Cook Celect and Günther Tulip Vena Cava Filter Patient Guide www.cookmedical.com Filter patient guide Contents Pulmonary embolism 4 5 What is pulmonary embolism? What causes it? What are the symptoms of
Cook Celect and Günther Tulip Vena Cava Filter Patient Guide www.cookmedical.com Filter patient guide Contents Pulmonary embolism 4 5 What is pulmonary embolism? What causes it? What are the symptoms of
Location: Clinical Practice Manual
 Subject: Area: Classification: Relevant to: Bladder Management Clinical Practice All Clinical Staff Implementation Date: March 2001 Review Date: March 2004 Responsible for Review: Approved by: Distribution:
Subject: Area: Classification: Relevant to: Bladder Management Clinical Practice All Clinical Staff Implementation Date: March 2001 Review Date: March 2004 Responsible for Review: Approved by: Distribution:
PERCUTANEOUS PD CATHETER IMPLANTATION SYSTEM
 Place on Patient s Cranial Border of the Pubic Symphysis IMPLANTATION STENCIL Classic Exit Cuff Site PERCUTANEOUS PD CATHETER IMPLANTATION SYSTEM INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE VP 511 and VP-511M Implantation System
Place on Patient s Cranial Border of the Pubic Symphysis IMPLANTATION STENCIL Classic Exit Cuff Site PERCUTANEOUS PD CATHETER IMPLANTATION SYSTEM INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE VP 511 and VP-511M Implantation System
Prostate Cancer Screening. A Decision Guide
 Prostate Cancer Screening A Decision Guide This booklet was developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Is screening right for you?
Prostate Cancer Screening A Decision Guide This booklet was developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Is screening right for you?
Prostate Cancer Screening. A Decision Guide for African Americans
 Prostate Cancer Screening A Decision Guide for African Americans This booklet was developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Published
Prostate Cancer Screening A Decision Guide for African Americans This booklet was developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Published
Bladder Catheterization
 Approved by: Bladder Catheterization Gail Cameron Senior Director, Operations, Maternal, Neonatal & Child Health Programs Dr. Ensenat Medical Director, Neonatology Neonatal Nursery Policy & Procedures
Approved by: Bladder Catheterization Gail Cameron Senior Director, Operations, Maternal, Neonatal & Child Health Programs Dr. Ensenat Medical Director, Neonatology Neonatal Nursery Policy & Procedures
Mini-led spotlight with magnetic base
 Mini-led spotlight with magnetic base Model 95799 Assembly And Operation Instructions Due to continuing improvements, actual product may differ slightly from the product described herein. 3491 Mission
Mini-led spotlight with magnetic base Model 95799 Assembly And Operation Instructions Due to continuing improvements, actual product may differ slightly from the product described herein. 3491 Mission
Learning Resource Guide. Understanding Incontinence. 2000 Prism Innovations, Inc. All Rights Reserved
 Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence 2000 Prism Innovations, Inc. All Rights Reserved ElderCare Online s Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence Table of Contents Introduction
Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence 2000 Prism Innovations, Inc. All Rights Reserved ElderCare Online s Learning Resource Guide Understanding Incontinence Table of Contents Introduction
III-701 Urinary Catheterization/Bladder Irrigation Original Date: 3/1/1977 Last Review Date: 10/28/2004
 III-701 Urinary Catheterization/Bladder Irrigation Original Date: 3/1/1977 Last Review Date: 10/28/2004 Purpose A. Allow for precise measurement of urine output. B. Collect a sterile urine specimen. C.
III-701 Urinary Catheterization/Bladder Irrigation Original Date: 3/1/1977 Last Review Date: 10/28/2004 Purpose A. Allow for precise measurement of urine output. B. Collect a sterile urine specimen. C.
Aspira* Pleural Drainage Catheter
 Aspira* Pleural Drainage Catheter Instructions For Use Access Systems Product Description: The Aspira* Pleural Drainage Catheter is a tunneled, long-term catheter used to drain accumulated fluid from the
Aspira* Pleural Drainage Catheter Instructions For Use Access Systems Product Description: The Aspira* Pleural Drainage Catheter is a tunneled, long-term catheter used to drain accumulated fluid from the
PREVENTION OF CATHETER ASSOCIATED URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS. (CAUTIs)
 PREVENTION OF CATHETER ASSOCIATED URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS (CAUTIs) CAUTIs A UTI where an indwelling urinary catheter was in place for >2 calendar days on the date of event. OR If an indwelling urinary
PREVENTION OF CATHETER ASSOCIATED URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS (CAUTIs) CAUTIs A UTI where an indwelling urinary catheter was in place for >2 calendar days on the date of event. OR If an indwelling urinary
VaPro Touch Free Hydrophilic Intermittent Catheter
 7202 What healthcare practitioners are saying about the catheter:4 Easy to explain to patients how to use the product. Medical Assistant 72102 72122 72142 7204 72104 72124 72144 724 73124 73144 734 Advance
7202 What healthcare practitioners are saying about the catheter:4 Easy to explain to patients how to use the product. Medical Assistant 72102 72122 72142 7204 72104 72124 72144 724 73124 73144 734 Advance
Placement of an indwelling urinary catheter in female dogs
 Female Dog Urinary Catheterization 1 of 6 Placement of an indwelling urinary catheter in female dogs Bernie Hansen DVM MS North Carolina State University College of Veterinary Medicine Materials Needed
Female Dog Urinary Catheterization 1 of 6 Placement of an indwelling urinary catheter in female dogs Bernie Hansen DVM MS North Carolina State University College of Veterinary Medicine Materials Needed
To decrease and/or prevent the incidence of catheter associated infections and other complications associated with IUC.
 Patient Care Manual Standardized Procedure Number: PC-SP.115 Latest Revision Date: 01/27/2015 Effective Date: 10/10/2011 Standardized Procedure: Urethral Catheter (IUC), Adult, Discontinuance of FUNCTION
Patient Care Manual Standardized Procedure Number: PC-SP.115 Latest Revision Date: 01/27/2015 Effective Date: 10/10/2011 Standardized Procedure: Urethral Catheter (IUC), Adult, Discontinuance of FUNCTION
Urinary tract and perineum
 9 Urinary tract and perineum Key Points 9.1 9.1 THE URINARY BLADDER URINARY RETENTION Acute retention of urine is an indication for emergency drainage of the bladder The common causes of acute retention
9 Urinary tract and perineum Key Points 9.1 9.1 THE URINARY BLADDER URINARY RETENTION Acute retention of urine is an indication for emergency drainage of the bladder The common causes of acute retention
Fact Sheet. Caring for and Changing your Supra-Pubic Catheter (SPC) Queensland Spinal Cord Injuries Service
 and Caring for and Changing your Supra-Pubic Catheter (SPC) What is a Suprapubic Catheter? A supra-pubic catheter is a tube that goes into your bladder through your abdominal wall which continuously drains
and Caring for and Changing your Supra-Pubic Catheter (SPC) What is a Suprapubic Catheter? A supra-pubic catheter is a tube that goes into your bladder through your abdominal wall which continuously drains
1.5 Tesla and 3 Tesla Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Guidelines for the Senza System
 1.5 Tesla and 3 Tesla Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Guidelines for the Senza System NEVRO CORP. All questions or concerns about Nevro products should be forwarded to: Nevro Corp. 1800 Bridge Parkway
1.5 Tesla and 3 Tesla Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Guidelines for the Senza System NEVRO CORP. All questions or concerns about Nevro products should be forwarded to: Nevro Corp. 1800 Bridge Parkway
PCA3 DETECTION TEST FOR PROSTATE CANCER DO YOU KNOW YOUR RISK OF HAVING CANCER?
 PCA3 DETECTION TEST FOR PROSTATE CANCER DO YOU KNOW YOUR RISK OF HAVING CANCER? PCA3 DETECTION TEST FOR PROSTATE CANCER There is a range of methods available to your healthcare professional to verify the
PCA3 DETECTION TEST FOR PROSTATE CANCER DO YOU KNOW YOUR RISK OF HAVING CANCER? PCA3 DETECTION TEST FOR PROSTATE CANCER There is a range of methods available to your healthcare professional to verify the
Refer to Coaptite Injectable Implant Instructions for Use provided with product for complete instructions for use.
 Questions for my Doctor Refer to Coaptite Injectable Implant Instructions for Use provided with product for complete instructions for use. INDICATIONS: Coaptite Injectable Implant is indicated for soft
Questions for my Doctor Refer to Coaptite Injectable Implant Instructions for Use provided with product for complete instructions for use. INDICATIONS: Coaptite Injectable Implant is indicated for soft
Instructions for Use
 Pleural Effusion Shunt with External Pump Chamber Catalog No. 42-9005 Instructions for Use Denver Biomedical, Inc. Table of Contents Description 2 Indications 2 Contraindications 2 Warnings 4 Cautions
Pleural Effusion Shunt with External Pump Chamber Catalog No. 42-9005 Instructions for Use Denver Biomedical, Inc. Table of Contents Description 2 Indications 2 Contraindications 2 Warnings 4 Cautions
Normal bladder function requires a coordinated effort between the brain, spinal cord, and the bladder.
 .. Urinary Incontinence Urinary incontinence is not an inevitable part of aging, and it is not a disease. The loss of bladder control - called urinary incontinence - affects between 13 and 17 million adult
.. Urinary Incontinence Urinary incontinence is not an inevitable part of aging, and it is not a disease. The loss of bladder control - called urinary incontinence - affects between 13 and 17 million adult
WallFlex Biliary RX Stent. Fully, Partially and Uncovered Self-Expanding Metal Stents
 WallFlex Biliary RX Stent Fully, Partially and Uncovered Self-Expanding Metal Stents WallFlex Biliary RX Stent Fully, Partially and Uncovered Self-Expanding Metal Stents The WallFlex Biliary RX Stent is
WallFlex Biliary RX Stent Fully, Partially and Uncovered Self-Expanding Metal Stents WallFlex Biliary RX Stent Fully, Partially and Uncovered Self-Expanding Metal Stents The WallFlex Biliary RX Stent is
Ureteroscopy with Laser Lithotripsy
 Ureteroscopy with Laser Lithotripsy Introduction Kidney stones are fairly common. Although kidney stones can be very painful, they are treatable, and in many cases preventable. Your doctor may recommend
Ureteroscopy with Laser Lithotripsy Introduction Kidney stones are fairly common. Although kidney stones can be very painful, they are treatable, and in many cases preventable. Your doctor may recommend
Prevention of catheter associated urinary tract infections
 Prevention of catheter associated urinary tract infections Dr. Suzan Sanavi, Nephrologist, M.D University of Social Welfare and Rehabilitation Akhavan Physical Spine Center INTRODUCTION Urinary bladder
Prevention of catheter associated urinary tract infections Dr. Suzan Sanavi, Nephrologist, M.D University of Social Welfare and Rehabilitation Akhavan Physical Spine Center INTRODUCTION Urinary bladder
Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test
 TO PROVIDE THE VERY BEST CARE FOR EACH PATIENT ON EVERY OCCASION Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test An information guide Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA)
TO PROVIDE THE VERY BEST CARE FOR EACH PATIENT ON EVERY OCCASION Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test An information guide Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA)
Adult Urodynamics: American Urological Association (AUA)/Society of Urodynamics, Female Pelvic Medicine & Urogenital Reconstruction (SUFU) Guideline
 Adult Urodynamics: American Urological Association (AUA)/Society of Urodynamics, Female Pelvic Medicine & Urogenital Reconstruction (SUFU) Guideline RECOMMENDATIONS 1 Conditional: Clinicians who are making
Adult Urodynamics: American Urological Association (AUA)/Society of Urodynamics, Female Pelvic Medicine & Urogenital Reconstruction (SUFU) Guideline RECOMMENDATIONS 1 Conditional: Clinicians who are making
A PRINTED copy of this guideline may not be the most recent version. The OFFICIAL version is located on IHNET at the Policies & Procedures Home Page
 A PRINTED copy of this guideline may not be the most recent version. The OFFICIAL version is located on IHNET at the Policies & Procedures Home Page IX0200: Prevention & Control of Catheter Associated
A PRINTED copy of this guideline may not be the most recent version. The OFFICIAL version is located on IHNET at the Policies & Procedures Home Page IX0200: Prevention & Control of Catheter Associated
SAMPLE Policy and Procedure Insertion, Removal and Care of an Indwelling Foley Catheter
 SAMPLE Policy and Procedure Insertion, Removal and Care of an Indwelling Foley Catheter Approved by: Policy and Procedure Committee Effective: x/xx Revised: x/xx Description: This policy provides the procedure
SAMPLE Policy and Procedure Insertion, Removal and Care of an Indwelling Foley Catheter Approved by: Policy and Procedure Committee Effective: x/xx Revised: x/xx Description: This policy provides the procedure
Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal
 Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal What is Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal? An inferior vena cava filter placement procedure involves an interventional radiologist (a specialist doctor)
Inferior Vena Cava filter and removal What is Inferior Vena Cava Filter Placement and Removal? An inferior vena cava filter placement procedure involves an interventional radiologist (a specialist doctor)
Care of the Catheterised Patient and Urinalysis
 Care of the Catheterised Patient and Urinalysis Male Pelvic Anatomy Female Pelvic Anatomy What does a urinary catheter do? Urinary Catheters Urinary Catheters Urinary Catheters Why do patients have catheters?
Care of the Catheterised Patient and Urinalysis Male Pelvic Anatomy Female Pelvic Anatomy What does a urinary catheter do? Urinary Catheters Urinary Catheters Urinary Catheters Why do patients have catheters?
HEALTH NEWS PROSTATE CANCER THE PROSTATE
 HEALTH NEWS PROSTATE CANCER THE PROSTATE Prostate comes from the Greek meaning to stand in front of ; this is very different than prostrate which means to lie down flat. The prostate is a walnut-sized
HEALTH NEWS PROSTATE CANCER THE PROSTATE Prostate comes from the Greek meaning to stand in front of ; this is very different than prostrate which means to lie down flat. The prostate is a walnut-sized
ATI Skills Modules Checklist for Urinary Catheter Care
 For faculty use only Educator s name Score Date ATI Skills Modules Checklist for Urinary Catheter Care Student s name Date Verify order Patient record Assess for procedure need Identify, gather, and prepare
For faculty use only Educator s name Score Date ATI Skills Modules Checklist for Urinary Catheter Care Student s name Date Verify order Patient record Assess for procedure need Identify, gather, and prepare
Prostate Cancer. What is prostate cancer?
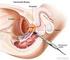 Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam, prostate-specific
Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam, prostate-specific
Bladder Health Promotion
 Bladder Health Promotion Community Awareness Presentation Content contributions provided by the Society of Urologic Nurses (SUNA) National Association for Continence (NAFC) Simon Foundation for Continence
Bladder Health Promotion Community Awareness Presentation Content contributions provided by the Society of Urologic Nurses (SUNA) National Association for Continence (NAFC) Simon Foundation for Continence
Catheter Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Prevention. System CAUTI Prevention Team
 Catheter Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Prevention System CAUTI Prevention Team 1 Objectives At the end of this module, the participant will be able to: Identify risk factors for CAUTI Explain
Catheter Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Prevention System CAUTI Prevention Team 1 Objectives At the end of this module, the participant will be able to: Identify risk factors for CAUTI Explain
Simple Urinary Techniques to Diagnose and Treat Complex Urinary Conditions
 Simple Urinary Techniques to Diagnose and Treat Complex Urinary Conditions Jody P. Lulich, DVM,PhD, The Minnesota Urolith Center, St Paul MN 55108 USA NONSURGICAL STONE REMOVAL: VOIDING UROHYDROPROPULSION
Simple Urinary Techniques to Diagnose and Treat Complex Urinary Conditions Jody P. Lulich, DVM,PhD, The Minnesota Urolith Center, St Paul MN 55108 USA NONSURGICAL STONE REMOVAL: VOIDING UROHYDROPROPULSION
to Know About Your Partner s
 What You Need to Know About Your Partner s Prostate Cancer. A Guide for Wives, Partners, and the Men They Love. Providing Support for Your Partner Prostate cancer can be a physical and emotional challenge
What You Need to Know About Your Partner s Prostate Cancer. A Guide for Wives, Partners, and the Men They Love. Providing Support for Your Partner Prostate cancer can be a physical and emotional challenge
Case Based Urology Learning Program
 Case Based Urology Learning Program Resident s Corner: UROLOGY Case Number 21 CBULP 2011 068 Case Based Urology Learning Program Editor: Associate Editors: Manager: Case Contributors: Steven C. Campbell,
Case Based Urology Learning Program Resident s Corner: UROLOGY Case Number 21 CBULP 2011 068 Case Based Urology Learning Program Editor: Associate Editors: Manager: Case Contributors: Steven C. Campbell,
Overactive Bladder (OAB)
 Overactive Bladder (OAB) Overactive bladder is a problem with bladder storage function that causes a sudden urge to urinate. The urge may be difficult to suppress, and overactive bladder can lead to the
Overactive Bladder (OAB) Overactive bladder is a problem with bladder storage function that causes a sudden urge to urinate. The urge may be difficult to suppress, and overactive bladder can lead to the
EVALUATION OF SUPRAPUBIC CATHETERISATION OF URINARY BLADDER IN CALVES. İbrahim Canpolat * and Cihan Günay*
 EVALUATION OF SUPRAPUBIC CATHETERISATION OF URINARY BLADDER IN CALVES. İbrahim Canpolat * and Cihan Günay* * Department of Surgery, Veterinary Faculty, Firat University, Elazig,23119, Turkey SUMMARY In
EVALUATION OF SUPRAPUBIC CATHETERISATION OF URINARY BLADDER IN CALVES. İbrahim Canpolat * and Cihan Günay* * Department of Surgery, Veterinary Faculty, Firat University, Elazig,23119, Turkey SUMMARY In
AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options
 AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options INTRODUCTION This booklet describes how prostate cancer develops, how it affects the body and the current treatment methods. Although
AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options INTRODUCTION This booklet describes how prostate cancer develops, how it affects the body and the current treatment methods. Although
Instruction Guide to Sterile Self-Catheterization for Women Using the Cure Catheter Closed System
 Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Bladder Health Promotion
 Bladder Health Promotion Community Awareness Presentation endorsed by the Society of Urologic Nurses (SUNA) National Association for Continence( NAFC) Simon Foundation for Continence This presentation
Bladder Health Promotion Community Awareness Presentation endorsed by the Society of Urologic Nurses (SUNA) National Association for Continence( NAFC) Simon Foundation for Continence This presentation
Managing your bladder with a suprapubic catheter at home
 Managing your bladder with a suprapubic catheter at home Gateshead Primary Care Trust South Tyneside Primary Care Trust Sunderland Teaching Primary Care Trust What is a suprapubic catheter? A suprapubic
Managing your bladder with a suprapubic catheter at home Gateshead Primary Care Trust South Tyneside Primary Care Trust Sunderland Teaching Primary Care Trust What is a suprapubic catheter? A suprapubic
Having a urinary catheter information for men
 Having a urinary catheter information for men This leaflet explains what a catheter is, why you need it and how you should look after it. If you have any further questions, please contact your district
Having a urinary catheter information for men This leaflet explains what a catheter is, why you need it and how you should look after it. If you have any further questions, please contact your district
Achieving Independence. A Guide to Self-Catheterization with the Bard Touchless Plus Intermittent Catheter System
 Bard: Intermittent Self-Catheterization A Guide to Self-Catheterization with the Bard Touchless Plus Intermittent Catheter System Achieving Independence Introducing the Bard Touchless Plus Catheter One
Bard: Intermittent Self-Catheterization A Guide to Self-Catheterization with the Bard Touchless Plus Intermittent Catheter System Achieving Independence Introducing the Bard Touchless Plus Catheter One
AMS Sphincter 800 Urinary Prosthesis
 AMS Sphincter 800 Urinary Prosthesis AMS Sphincter 800 AMS Sphincter 800 AMS Sphincter 800 The device is implanted in the body and cannot be seen. The cuff can be placed at the bulbous urethra or at the
AMS Sphincter 800 Urinary Prosthesis AMS Sphincter 800 AMS Sphincter 800 AMS Sphincter 800 The device is implanted in the body and cannot be seen. The cuff can be placed at the bulbous urethra or at the
CMScript. Member of a medical scheme? Know your guaranteed benefits! Issue 7 of 2014
 Background CMScript Member of a medical scheme? Know your guaranteed benefits! Issue 7 of 2014 Prostate cancer is second only to lung cancer as the leading cause of cancer-related deaths in men. It is
Background CMScript Member of a medical scheme? Know your guaranteed benefits! Issue 7 of 2014 Prostate cancer is second only to lung cancer as the leading cause of cancer-related deaths in men. It is
FAQ About Prostate Cancer Treatment and SpaceOAR System
 FAQ About Prostate Cancer Treatment and SpaceOAR System P. 4 Prostate Cancer Background SpaceOAR Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) 1. What is prostate cancer? The vast majority of prostate cancers develop
FAQ About Prostate Cancer Treatment and SpaceOAR System P. 4 Prostate Cancer Background SpaceOAR Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) 1. What is prostate cancer? The vast majority of prostate cancers develop
Ureteral Stenting and Nephrostomy
 Scan for mobile link. Ureteral Stenting and Nephrostomy Ureteral stenting and nephrostomy help restore urine flow through blocked ureters and return the kidney to normal function. Ureters are long, narrow
Scan for mobile link. Ureteral Stenting and Nephrostomy Ureteral stenting and nephrostomy help restore urine flow through blocked ureters and return the kidney to normal function. Ureters are long, narrow
Guy s, King s and St Thomas Cancer Centre The Cancer Outpatient Clinic Central venous catheter: Peripherally inserted central catheter
 Guy s, King s and St Thomas Cancer Centre The Cancer Outpatient Clinic Central venous catheter: Peripherally inserted central catheter This information leaflet aims to help answer some of the questions
Guy s, King s and St Thomas Cancer Centre The Cancer Outpatient Clinic Central venous catheter: Peripherally inserted central catheter This information leaflet aims to help answer some of the questions
Incontinence. What is incontinence?
 Incontinence What is incontinence? Broadly speaking, the medical term incontinence refers to any involuntary release of bodily fluids, but many people associate it strongly with the inability to control
Incontinence What is incontinence? Broadly speaking, the medical term incontinence refers to any involuntary release of bodily fluids, but many people associate it strongly with the inability to control
STAY-PUT Nasojejunal Feeding Tubes. Nursing Manual/ Patient Information
 SPECIALTY FEEDING TUBES STAY-PUT Nasojejunal Feeding Tubes Nursing Manual/ Patient Information Manual contains important care and maintenance information and should accompany patient NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
SPECIALTY FEEDING TUBES STAY-PUT Nasojejunal Feeding Tubes Nursing Manual/ Patient Information Manual contains important care and maintenance information and should accompany patient NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
Radiation therapy involves using many terms you may have never heard before. Below is a list of words you could hear during your treatment.
 Dictionary Radiation therapy involves using many terms you may have never heard before. Below is a list of words you could hear during your treatment. Applicator A device used to hold a radioactive source
Dictionary Radiation therapy involves using many terms you may have never heard before. Below is a list of words you could hear during your treatment. Applicator A device used to hold a radioactive source
SECTION 12.1 URINARY CATHETERS
 SECTION 12.1 URINARY CATHETERS Introduction Summary of Recommendations taken from Guidelines for the Prevention of Catheter-associated Urinary Tract Infection, Published on behalf of SARI by HSE Health
SECTION 12.1 URINARY CATHETERS Introduction Summary of Recommendations taken from Guidelines for the Prevention of Catheter-associated Urinary Tract Infection, Published on behalf of SARI by HSE Health
LAP-BAND System Calibration Tube DIRECTIONS FOR USE (DFU)
 LAP-BAND System Calibration Tube DIRECTIONS FOR USE (DFU) LAP-BAND System Calibration Tube The LAP-BAND System Calibration Tube is a flexible gastric tube designed to be used in gastric and bariatric surgical
LAP-BAND System Calibration Tube DIRECTIONS FOR USE (DFU) LAP-BAND System Calibration Tube The LAP-BAND System Calibration Tube is a flexible gastric tube designed to be used in gastric and bariatric surgical
Anatomy of Male Reproductive System
 Anatomy of Male Reproductive System A. Reproductive Systems 1. Gonads: primary sex organs a. Produce gametes b. Produce hormones c. Male Gonads: testes d. Female Gonads: ovaries 2. Gametes: sex cells a.
Anatomy of Male Reproductive System A. Reproductive Systems 1. Gonads: primary sex organs a. Produce gametes b. Produce hormones c. Male Gonads: testes d. Female Gonads: ovaries 2. Gametes: sex cells a.
Male Urinary Catheterisation & Catheter Care
 Male Urinary Catheterisation & Catheter Care Mark Jones, Martin Steggall & Marsh Gelbart City University, London. Good practice Consent gain informed consent. Who can catheterise any Registered Nurse who
Male Urinary Catheterisation & Catheter Care Mark Jones, Martin Steggall & Marsh Gelbart City University, London. Good practice Consent gain informed consent. Who can catheterise any Registered Nurse who
FEMALE INCONTINENCE REVIEW
 200 S. Wenona Suite 298 Steven L. Jensen, M.D. 5400 Mackinaw, Suite 4302 Bay City, MI 48706 Frank H. Kim, M.D. Saginaw, MI 48604 Telephone (989) 895-2634 Adult & Pediatric Urologists (989) 791-4020 Fax
200 S. Wenona Suite 298 Steven L. Jensen, M.D. 5400 Mackinaw, Suite 4302 Bay City, MI 48706 Frank H. Kim, M.D. Saginaw, MI 48604 Telephone (989) 895-2634 Adult & Pediatric Urologists (989) 791-4020 Fax
A Guide for Patients Living with a Biliary Metal Stent
 A Guide for Patients Living with a Biliary Metal Stent What is a biliary metal stent? A biliary metal stent (also known as a bile duct stent ) is a flexible metallic tube specially designed to hold your
A Guide for Patients Living with a Biliary Metal Stent What is a biliary metal stent? A biliary metal stent (also known as a bile duct stent ) is a flexible metallic tube specially designed to hold your
LOSS OF BLADDER CONTROL IS TREATABLE TAKE CONTROL AND RESTORE YOUR LIFESTYLE
 LOSS OF BLADDER CONTROL IS TREATABLE TAKE CONTROL AND RESTORE YOUR LIFESTYLE TALKING ABOUT STRESS INCONTINENCE (SUI) Millions of women suffer from stress incontinence (SUI). This condition results in accidental
LOSS OF BLADDER CONTROL IS TREATABLE TAKE CONTROL AND RESTORE YOUR LIFESTYLE TALKING ABOUT STRESS INCONTINENCE (SUI) Millions of women suffer from stress incontinence (SUI). This condition results in accidental
URINARY INCONTINENCE
 URINARY INCONTINENCE What is urinary incontinence? Urinary incontinence is the uncontrollable loss of urine. The amount of urine leaked can vary from only a few drops when you cough or sneeze to entirely
URINARY INCONTINENCE What is urinary incontinence? Urinary incontinence is the uncontrollable loss of urine. The amount of urine leaked can vary from only a few drops when you cough or sneeze to entirely
Patient Information Booklet. Endovascular Stent Grafts: A Treatment for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms
 Patient Information Booklet Endovascular Stent Grafts: A Treatment for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction 1 Glossary 2 Abdominal Aorta 4 Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm 5 Causes 6 Symptoms
Patient Information Booklet Endovascular Stent Grafts: A Treatment for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction 1 Glossary 2 Abdominal Aorta 4 Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm 5 Causes 6 Symptoms
MEDICAL POLICY No. 91502-R1 INCONTINENCE SUPPLIES FOR MEDICAID MEMBERS
 INCONTINENCE SUPPLIES FOR MEDICAID MEMBERS Effective Date: December 23, 2013 Review Dates: 1/05, 12/05, 12/06, 12/07, 12/08, 12/09, 12/10, 12/11, 12/12, 12/13, 2/15 Date Of Origin: January 19, 2005 Status:
INCONTINENCE SUPPLIES FOR MEDICAID MEMBERS Effective Date: December 23, 2013 Review Dates: 1/05, 12/05, 12/06, 12/07, 12/08, 12/09, 12/10, 12/11, 12/12, 12/13, 2/15 Date Of Origin: January 19, 2005 Status:
Patient Information. PORT-A-CATH Implantable Venous Access Systems
 Patient Information PORT-A-CATH Implantable Venous Access Systems Your doctor has prescribed treatment that requires the frequent administration of medications or other fluids directly into your bloodstream
Patient Information PORT-A-CATH Implantable Venous Access Systems Your doctor has prescribed treatment that requires the frequent administration of medications or other fluids directly into your bloodstream
Catheter Care. What you need to know. Jacinta Stewart Continence Nurse
 Catheter Care What you need to know Jacinta Stewart Continence Nurse Indications for Long Term Catheter Use Long term urinary catheters should only be used with clients who cannot satisfactorily be managed
Catheter Care What you need to know Jacinta Stewart Continence Nurse Indications for Long Term Catheter Use Long term urinary catheters should only be used with clients who cannot satisfactorily be managed
CARE PROCESS STEP EXPECTATIONS RATIONALE
 URINARY INCONTINENCE CARE PROCESS STEP EXPECTATIONS RATIONALE ASSESSMENT/PROBLEM RECOGNITION 1. Did the staff and physician seek and document risk factors for urinary incontinence and any history of urinary
URINARY INCONTINENCE CARE PROCESS STEP EXPECTATIONS RATIONALE ASSESSMENT/PROBLEM RECOGNITION 1. Did the staff and physician seek and document risk factors for urinary incontinence and any history of urinary
Male Continence Training. AMS 800 Artificial Urinary Sphincter
 Male Continence Training AMS 800 Artificial Urinary Sphincter The AMS Sphincter 800 is the Gold Standard, time-tested surgical solution for control of moderate to severe stress urinary incontinence. Patient
Male Continence Training AMS 800 Artificial Urinary Sphincter The AMS Sphincter 800 is the Gold Standard, time-tested surgical solution for control of moderate to severe stress urinary incontinence. Patient
Spine University s Guide to Cauda Equina Syndrome
 Spine University s Guide to Cauda Equina Syndrome 2 Introduction Your spine is a very complicated part of your body. It s made up of the bones (vertebrae) that keep it aligned, nerves that channel down
Spine University s Guide to Cauda Equina Syndrome 2 Introduction Your spine is a very complicated part of your body. It s made up of the bones (vertebrae) that keep it aligned, nerves that channel down
Prostate Cancer. There is no known association with an enlarged prostate or benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
 Prostate Cancer Definition Prostate cancer is cancer that starts in the prostate gland. The prostate is a small, walnut-sized structure that makes up part of a man's reproductive system. It wraps around
Prostate Cancer Definition Prostate cancer is cancer that starts in the prostate gland. The prostate is a small, walnut-sized structure that makes up part of a man's reproductive system. It wraps around
The Captivator II Snares are the first line of stiff and rounded snares available in multiple sizes with both a hot and cold snaring indication.
 Captivator II Single-Use Snares The Captivator II Snares are the first line of stiff and rounded snares available in multiple sizes with both a hot and cold snaring indication. The Captivator II Snare
Captivator II Single-Use Snares The Captivator II Snares are the first line of stiff and rounded snares available in multiple sizes with both a hot and cold snaring indication. The Captivator II Snare
Kaiser Oakland Urology
 Kaiser Oakland Urology The Main Purpose of Bladder Catheterization Complete Bladder Emptying! Help maintain a healthy bladder Help maintain healthy kidneys Reduce the chances of significant urinary tract
Kaiser Oakland Urology The Main Purpose of Bladder Catheterization Complete Bladder Emptying! Help maintain a healthy bladder Help maintain healthy kidneys Reduce the chances of significant urinary tract
Possible Side Effects of Radiation Therapy on the Prostate Gland
 Possible Side Effects of Radiation Therapy on the Prostate Gland Information compiled by Daniel J. Faber, Coordinator of the Warriors+one, a Breakout Group of the Prostate Cancer Canada Network- Ottawa,
Possible Side Effects of Radiation Therapy on the Prostate Gland Information compiled by Daniel J. Faber, Coordinator of the Warriors+one, a Breakout Group of the Prostate Cancer Canada Network- Ottawa,
A Patient s Guide to Minimally Invasive Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair
 A Patient s Guide to Minimally Invasive Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair Table of Contents The AFX Endovascular AAA System............................................ 1 What is an Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
A Patient s Guide to Minimally Invasive Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair Table of Contents The AFX Endovascular AAA System............................................ 1 What is an Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
