CHAPTER 20: URINARY SYSTEM
|
|
|
- Garey Hodge
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 OBJECTIVES: 1. Name the major function of the urinary system, and name and locate (on a diagram) the organs that compose the system. 2. Explain what the term renal refers to. 3. Define the term retroperitoneal. 4. Using a cross-section diagram of a kidney, locate the renal capsule, renal cortex, renal medulla, renal pyramids, minor calyces, major calyces, renal sinus, renal pelvis, and ureter. 5. Discuss the many ways in which the kidney maintains the blood. 6. Name the functional unit of the kidney. 7. Distinguish between a renal corpuscle and renal tubule, and identify each component on a microscopic section of the kidney. 8. Trace a drop of blood from the heart through a nephron and back to the heart. 9. Explain what is meant by, the components of, and the significance of the juxtaglomerular apparatus. 10. List the three major steps involved in urine formation, name the portion of the nephron where each occurs, and discuss each process fully. 11. Explain why proteins are not filtered out of the blood in the glomerulus. 12. Name the force responsible for glomerular filtration. 13. Discuss the negative feedback mechanisms involved in the regulation of the glomerular filtration rate (GFR). Include the names of detection sites (cells), enzymes, hormones, target organs, and effects. 14. Explain the process by which most reabsorption occurs in the PCT, and list the substances that are reabsorbed here. 396
2 15. Explain the significance of anti-diuretic hormone (ADH) and which portion of the nephron it targets. 397
3 Objectives (continued) 16. List the wastes excreted in urine, and explain what metabolic processes these by-products result from. 17. Explain the structure, location, and function of the ureters, urinary bladder, and ureters. 18. Define the term micturition. 19. Discuss the differences between male and female urethras. 20. Trace a drop of urine from its initial collection point as the "glomerular filtrate". 398
4 I. INTRODUCTION The major function of the urinary system to remove metabolic wastes from blood, and direct them out of the body. The organs of the urinary system include the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. See Fig and Fig 20.2, page 780. II. URINARY ORGANS A. Kidney (Renal) 1. Location: Fig 20.1, page 780 and Fig 20.3, page 781. a. high on posterior abdominal wall; b. retroperitoneal; c. right kidney lies just below left. Why? 2. Structure: (Fig 20.4c, page 782) a. renal capsule = tough fibrous shell around kidney; b. renal cortex = outer portion of kidney; c. renal medulla = inner portion of kidney; d. renal pyramids = cone shaped masses of tissue in renal medulla; e. ureter = tube leading from kidney; f. renal pelvis = superior end of ureter which is expanded to form a funnel shape; g. major calyces = divisions of renal pelvis (2-3 tubes); h. minor calyces = divisions of major calyces. 3. Functions of Kidney: a. to remove metabolic wastes from blood & excrete them to outside (urine). b. Maintenance of blood: regulation of RBC formation (hormone erythropoietin); blood pressure (enzyme renin); 399
5 blood volume (hormone ADH); blood composition; blood ph. 400
6 II. URINARY ORGANS A. Kidney (Renal) 4. The functional unit of a kidney = the nephron. a. Structure: (Fig 20.4a, page 782) A nephron is composed of a renal corpuscle and a renal tubule. Renal Corpuscle = glomerulus (filtration unit) within Bowman's capsule. Renal Tubule = 1. proximal convoluted tubule; 2. descending loop of Henle 3. ascending loop of Henle; 4. distal convoluted tubule; (5. collecting duct). Each collecting duct empties into a minor calyx which leads to a major calyx and into the renal pelvis. Refer to Fig 20.7 page 785 to see electron micrograph of glomeruli within the renal tubules. 5. Blood flow: Macroscopic = Fig 20.6, page 784; Microscopic = Fig page 786; Summary Fig 20.14, page 790. Aorta > Renal Artery (to each kidney) > Interlobar arteries (between each pyramid) > Arciform arteries (between medulla & cortex) > Interlobular arteries (within cortex) > Afferent arteriole (leading to glomerulus) > Glomerular capillaries (site of filtration) > Efferent arteriole (leading away from glom) > Peritubular capillaries (around renal tubule) > 401
7 Interlobular veins > Arciform veins > Interlobar veins > Renal vein >IVC. 402
8 II. URINARY ORGANS A. Kidney (Renal) 6. Juxtaglomerular Apparatus (JGA) = point of contact between the afferent arteriole and distal convoluted tubule (DCT). See Fig , page 788. a. Macula Densa = cells in DCT in contact with afferent arteriole. b. Juxtaglomerular cells = smooth muscle cells in afferent arteriole. c. The JGA is very important in the regulation of glomerular filtration (see below)! 7. Urine Formation: The nephrons function to remove wastes from blood and regulate water & electrolyte concentrations. Urine is the end-product of these functions. Urine formation involves three major steps including glomerular filtration, tubular reabsorption, and tubular secretion. a. Glomerular Filtration (Fig 20.15, page 791) The fenestrated glomerular capillaries filter water & dissolved materials (remember plasma components) from blood. This "filtrate" is collected in Bowman's Capsule. Proteins are not filtered out of blood! Filtration is due to a force called hydrostatic pressure inside glomerular capillaries mmhg in glomerular capillaries; mmhg in Bowman s capsule Kidneys produce 125 ml fluid per minute; (most of this is reabsorbed in tubule). 403
9 II. Urinary Organs (continued) A. The kidney (continued) 7. Urine Formation (continued) a. Glomerular Filtration (continued) Regulation of Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) 1. involves juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA); 2. directly affected by blood pressure: 404
10 II. URINARY ORGANS A. Kidney (Renal) 7. Urine Formation (continued) b. Tubular reabsorption: See Fig 20.19, page 794. Definition = the process by which substances are transported from the glomerular filtrate (through the walls of the renal tubule) to blood in the peritubular caps. Most occurs in the PCT through the process of active transport; Reabsorption of water = osmosis. Reabsorbed substances pass from the lumen of the renal tubule through the epithelial cells (PCT) and into the lumen of a peritubular capillary where they are returned to bloodstream. Reabsorbed substances include: 1. glucose 2. amino acids 3. water 4. ions (sodium, chloride, phosphate, sulfate, potassium) 5. others (creatine, lactic acid. citric acid, urea, uric acid, ascorbic acid) Substances that remain in filtrate become concentrated as water is reabsorbed. c. Tubular secretion: See Fig 20.25, page 800. Definition = the process by which substances are transported from the blood in the peritubular caps into the DCT. 405
11 Maintains ion concentrations in blood (i.e. if the blood is high in K +, K + will be secreted into urine). 406
12 II. URINARY ORGANS A. Kidney (Renal) 7. Urine Formation (continued) d. Regulation of urine concentration & volume hormone anti-diuretic hormone (ADH) promotes the reabsorption of water through the DCT, when excessive amounts of water are being lost in the urine. This negative feedback mechanism prevents dehydration. See Table 20.2, page 799. e. Excretion of wastes (Urea & Uric Acid) Wastes are by-products of metabolism: 1. urea from amino acid metabolism; 2. uric acid from nucleotide metabolism) Wastes are reabsorbed by tubules, but are then secreted back into urine & excreted. f. Composition of Urine See Table 20.1, page % water; other 5% includes: 1. urea, 2. uric acid, 3. trace amino acids 4 electrolytes. 7. Use Chart 20.1, page 791 to compare the levels of various 407
13 substances present in plasma, the glomerular filtrate, and urine. 408
14 II. URINARY ORGANS A. Kidney (Renal) 7. Urine Formation (continued) SUMMARY TABLE (Keyed on page of this outline 408) Major Step in Urine Formation Location in Nephron Substances Transported and Mode of Transport From where to where? (i.e. from blood to glomerular filtrate) 409
15 II. Urinary Organs (continued) B. Ureters are small tubes that carry urine from each to kidney to the urinary bladder through peristaltic movements cm in length; 2. retroperitoneal; 3. Three layers: a. Inner mucosa = transitional epithelium; b. Middle muscularis = inner circular layer of smooth muscle and outer longitudinal layer (peristalsis); c. Outer serosa = fibrous CT. See Fig 20.27, page 803. C. Urinary Bladder (See Fig and Fig 20.29, page 804). 1. Location: within pelvic cavity, behind symphysis pubis; 2. Structure: a. hollow, distensible, muscular organ; b. lined by transitional epithelium; c. detrusor muscle = 3 layers of smooth muscle; d. covered by fibrous CT. 3. Function: storage of urine. * Micturition = the process by which urine is expelled from urinary bladder to outside. D. The urethra is a tube that carries urine from the urinary bladder to the outside. See Figures on page Length depends on sex: a. female = 4 cm; 410
16 b. male = 20 cm. 2. Histology depends of sex: a. female = 3 layers; b. males = 2 layers. CHAPTER 20: URINARY SYSTEM III. Elimination of Urine Starts at glomerulus where glomerular filtrate is collected in Bowman's capsule PCT loop of Henle DCT collecting duct (urine) minor calyx major calyx renal pelvis ureter (peristalsis) urinary bladder (micturition) 411
17 urethra outside Use this flow chart as a review by adding key points where they belong (i.e. reabsorption, reabsorption of water under influence of ADH, secretion, etc.) 412
18 IV. Homeostatic Imbalances/Disorder of the Urinary System 1. Hemolytic uremic anemia (See intro on page 779) B. Inherited kidney abnormalities (see page 780) C. Chronic Renal Failure (See CA 20.1, page 783) D. Glomerulonephritis (See CA 20.2, page 787) E. Nephrotic Syndrome (See CA 20.3, page 795) 6. Gout (page 799) 7. Cystitis/Ureteritis (page 803) 8. Kidney Stones (page 803) 9. Bladder Cancer (page 804) V. Other Interesting Topics Concerning the Urinary System A. Dialysis (page 781) B. Renal Clearance (see CA 20.4, page 802) C. Urinalysis (see CA 20.5, page 806) VI. Innerconnections of the Urinary System: See page
19 Urine Formation SUMMARY TABLE (outline page 404) Major Step in Urine Formation glomerular filtration tubular reabsorption tubular secretion Location in Nephron glomerulus primarily through proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) primarily through distal convoluted tubule (DCT) Substances Transported and Mode of Transport All plasma constituents except proteins (i.e. glucose, amino acids, water, ions, creatine, lactic acid, urea, uric aid, ascorbic acid, etc) glucose, amino acids, water, ions, creatine, lactic acid, urea, uric acid, ascorbic acid, etc) excess ions, urea, uric acid From where to where? (i.e. from blood to glomerular filtrate) from blood in glomerulus to filtrate in Bowman s capsule from filtrate in PCT to blood in peritubular capillaries from blood in peritubular capillaries to urine in DCT 414
20 415
The digestive system eliminated waste from the digestive tract. But we also need a way to eliminate waste from the rest of the body.
 Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system 1
Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system 1
LECTURE 1 RENAL FUNCTION
 LECTURE 1 RENAL FUNCTION Components of the Urinary System 2 Kidneys 2 Ureters Bladder Urethra Refer to Renal System Vocabulary in your notes Figure 2-1,page10 Kidney Composition Cortex Outer region Contains
LECTURE 1 RENAL FUNCTION Components of the Urinary System 2 Kidneys 2 Ureters Bladder Urethra Refer to Renal System Vocabulary in your notes Figure 2-1,page10 Kidney Composition Cortex Outer region Contains
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology. Chapter 15. The Urinary System. Slides 15.1 15.20. Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L.
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 15 The Urinary System Slides 15.1 15.20 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Functions of the Urinary System Elimination
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 15 The Urinary System Slides 15.1 15.20 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Functions of the Urinary System Elimination
Structure of the Kidney Laboratory Exercise 56
 Structure of the Kidney Laboratory Exercise 56 Background The two kidneys are the primary organs of the urinary system. They are located in the upper quadrants of the abdominal cavity, against the posterior
Structure of the Kidney Laboratory Exercise 56 Background The two kidneys are the primary organs of the urinary system. They are located in the upper quadrants of the abdominal cavity, against the posterior
Chapter 26: The Urinary System
 Chapter 26: The Urinary System Chapter Objectives OVERVIEW OF KIDNEY FUNCTION 1. List and describe the functions of the kidneys. NEPHRONS 2. Describe the two major portions of a nephron and the capillaries
Chapter 26: The Urinary System Chapter Objectives OVERVIEW OF KIDNEY FUNCTION 1. List and describe the functions of the kidneys. NEPHRONS 2. Describe the two major portions of a nephron and the capillaries
Components. Urinary System. Formation of Urine. Functions of Kidney. Pathway of Urine. Kidney. Major functions of the kidneys include:
 Components Urinary System To Accompany: Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part of this publication can be used for any commercial
Components Urinary System To Accompany: Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part of this publication can be used for any commercial
Urinary System Lab Guide
 Urinary System Lab Guide I. Prelab Questions Name 1. Describe the location of the kidneys. 2. Describe the following structures: a. renal cortex b. renal pyramid c. renal column d. minor calyx e. renal
Urinary System Lab Guide I. Prelab Questions Name 1. Describe the location of the kidneys. 2. Describe the following structures: a. renal cortex b. renal pyramid c. renal column d. minor calyx e. renal
Urinary System. And Adrenal Function
 Urinary System And Adrenal Function Overview Kidney anatomy and physiology Urine Ureters, Bladder and Urethra Adrenal Function Functions of the Kidney Filter fluids from the blood Regulate volume and composition
Urinary System And Adrenal Function Overview Kidney anatomy and physiology Urine Ureters, Bladder and Urethra Adrenal Function Functions of the Kidney Filter fluids from the blood Regulate volume and composition
Select the one that is the best answer:
 MQ Kidney 1 Select the one that is the best answer: 1) n increase in the concentration of plasma potassium causes increase in: a) release of renin b) secretion of aldosterone c) secretion of H d) release
MQ Kidney 1 Select the one that is the best answer: 1) n increase in the concentration of plasma potassium causes increase in: a) release of renin b) secretion of aldosterone c) secretion of H d) release
Urinary System! (Chapter 26)! Lecture Materials! for! Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D.! Suffolk County Community College! Eastern Campus!
 Urinary System! (Chapter 26)! Lecture Materials! for! Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D.! Suffolk County Community College! Eastern Campus! Urinary System Components:! -Kidneys! -Ureters! -Urinary Bladder!! -Urethra!
Urinary System! (Chapter 26)! Lecture Materials! for! Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D.! Suffolk County Community College! Eastern Campus! Urinary System Components:! -Kidneys! -Ureters! -Urinary Bladder!! -Urethra!
Kidney Structure and Function.
 Kidney Structure and Function. Learning Objectives. At the end of this section, you should be able to : 1. describe the structure of the kidney; 2. understand the vascular organisation of the kidneys;
Kidney Structure and Function. Learning Objectives. At the end of this section, you should be able to : 1. describe the structure of the kidney; 2. understand the vascular organisation of the kidneys;
Chapter 23. Urine Formation I Glomerular Filtration
 Chapter 23 Urine Formation I Glomerular Filtration Urine Formation I: Glomerular Filtration kidneys convert blood plasma to urine in three stages glomerular filtration tubular reabsorption and secretion
Chapter 23 Urine Formation I Glomerular Filtration Urine Formation I: Glomerular Filtration kidneys convert blood plasma to urine in three stages glomerular filtration tubular reabsorption and secretion
UNIT 11 - URINARY SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES
 UNIT 11 - URINARY SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 11.01 FUNCTIONS OF THE URINARY SYSTEM A. Regulate the composition and volume of the blood by removing and restoring selected amounts of water and solutes. B. Excretes
UNIT 11 - URINARY SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 11.01 FUNCTIONS OF THE URINARY SYSTEM A. Regulate the composition and volume of the blood by removing and restoring selected amounts of water and solutes. B. Excretes
Sign up to receive ATOTW weekly - email [email protected]
 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY - PART 1 ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 273 5 th NOVEMBER 2012 Dr Matthew Gwinnutt Mersey Deanery, UK Dr Jennifer Gwinnutt Mersey Deanery, UK Correspondence to: [email protected]
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY - PART 1 ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 273 5 th NOVEMBER 2012 Dr Matthew Gwinnutt Mersey Deanery, UK Dr Jennifer Gwinnutt Mersey Deanery, UK Correspondence to: [email protected]
Body Fluids. Physiology of Fluid. Body Fluids, Kidneys & Renal Physiology
 Pc Remember arterioles have more smooth muscle So SNS effects are greater on arterioles than on venules Net effects: SNS P c (vasoconstriction > venoconstriction) SNS P c (vasodilation > venodilation)
Pc Remember arterioles have more smooth muscle So SNS effects are greater on arterioles than on venules Net effects: SNS P c (vasoconstriction > venoconstriction) SNS P c (vasodilation > venodilation)
Renal Topics 1) renal function 2) renal system 3) urine formation 4) urine & urination 5) renal diseases
 Renal Topics 1) renal function 2) renal system 3) urine formation 4) urine & urination 5) renal diseases 1/9/2015 Renal Biology - Sandra Hsu 1 Renal Functions 1) excrete metabolic wastes (blood cleaning)
Renal Topics 1) renal function 2) renal system 3) urine formation 4) urine & urination 5) renal diseases 1/9/2015 Renal Biology - Sandra Hsu 1 Renal Functions 1) excrete metabolic wastes (blood cleaning)
Water Homeostasis. Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.
 Water Homeostasis Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) 1. Water Homeostasis The body maintains a balance of water intake
Water Homeostasis Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) 1. Water Homeostasis The body maintains a balance of water intake
Chapter 23. Composition and Properties of Urine
 Chapter 23 Composition and Properties of Urine Composition and Properties of Urine urinalysis the examination of the physical and chemical properties of urine appearance - clear, almost colorless to deep
Chapter 23 Composition and Properties of Urine Composition and Properties of Urine urinalysis the examination of the physical and chemical properties of urine appearance - clear, almost colorless to deep
CHAPTER 11: URINARY SYSTEM. At the end of this chapter, student will be able to:
 CHAPTER 11: URINARY SYSTEM At the end of this chapter, student will be able to: a) Describe the location and general function of each organ of the urinary system. b) Name the parts of a nephron and the
CHAPTER 11: URINARY SYSTEM At the end of this chapter, student will be able to: a) Describe the location and general function of each organ of the urinary system. b) Name the parts of a nephron and the
Pathophysiology Introduction/ Renal Anatomy and Function
 Pathophysiology Introduction/ Renal Anatomy and Function I. Functions of the kidney A. Maintaining homeostasis of a large number of solutes and water is the main job of the kidney. Total body contents
Pathophysiology Introduction/ Renal Anatomy and Function I. Functions of the kidney A. Maintaining homeostasis of a large number of solutes and water is the main job of the kidney. Total body contents
Regulating the Internal Environment Water Balance & Nitrogenous Waste Removal
 Regulating the Internal Environment Water Balance & Nitrogenous Waste Removal 2006-2007 Animal systems evolved to support multicellular life CH CHO O 2 O 2 NH 3 CH CHO O 2 CO 2 NH NH 3 O 2 3 NH 3 intracellular
Regulating the Internal Environment Water Balance & Nitrogenous Waste Removal 2006-2007 Animal systems evolved to support multicellular life CH CHO O 2 O 2 NH 3 CH CHO O 2 CO 2 NH NH 3 O 2 3 NH 3 intracellular
THE URINARY SYSTEM THE URINARY SYSTEM 2012
 THE URINARY SYSTEM KIDNEYS A. Location: a. under the back muscles b. behind the parietal peritoneum c. just above the waistline d. right kidney a little lower than the left B. internal structure a. cortex:
THE URINARY SYSTEM KIDNEYS A. Location: a. under the back muscles b. behind the parietal peritoneum c. just above the waistline d. right kidney a little lower than the left B. internal structure a. cortex:
April 18, 2008 Dr. Alan H. Stephenson Pharmacological and Physiological Science
 Renal Mechanisms for Regulating Urine Concentration April 18, 2008 Dr. Alan H. Stephenson Pharmacological and Physiological Science Amount Filtered Reabsorption is selective Examples of substances that
Renal Mechanisms for Regulating Urine Concentration April 18, 2008 Dr. Alan H. Stephenson Pharmacological and Physiological Science Amount Filtered Reabsorption is selective Examples of substances that
Kidneys, Nephrons, and Urine Production
 Valerie ovelace Kidneys, Nephrons, and rine Production Part of the urinary system, our kidneys are vital organs that serve to remove waste from the bloodstream through ultrafiltration and the formation
Valerie ovelace Kidneys, Nephrons, and rine Production Part of the urinary system, our kidneys are vital organs that serve to remove waste from the bloodstream through ultrafiltration and the formation
Chapter 48. Nutrients in Food. Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids. Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids, continued
 Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids The three nutrients needed by the body in the greatest amounts are carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Nutrients in Food All of these nutrients are called organic compounds,
Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids The three nutrients needed by the body in the greatest amounts are carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Nutrients in Food All of these nutrients are called organic compounds,
Renal Blood Flow GFR. Glomerulus Fluid Flow and Forces. Renal Blood Flow (cont d)
 GFR Glomerular filtration rate: about 120 ml /minute (180 L a day) Decreases with age (about 10 ml/min for each decade over 40) GFR = Sum of the filtration of two million glomeruli Each glomerulus probably
GFR Glomerular filtration rate: about 120 ml /minute (180 L a day) Decreases with age (about 10 ml/min for each decade over 40) GFR = Sum of the filtration of two million glomeruli Each glomerulus probably
Blood Pressure Regulation
 Blood Pressure Regulation Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction There are two basic mechanisms for regulating
Blood Pressure Regulation Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction There are two basic mechanisms for regulating
Eating, pooping, and peeing THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Ingested food is not technically in the body until it is absorbed so it needs to be: Mechanically and chemically reduced Transported by the blood to the cells Large portions are not
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Ingested food is not technically in the body until it is absorbed so it needs to be: Mechanically and chemically reduced Transported by the blood to the cells Large portions are not
The Urinary System. Anatomy of Urinary System. Urine production and elimination are one of the most important mechanisms of body homeostasis
 The Urinary System Urine production and elimination are one of the most important mechanisms of body homeostasis all body systems are directly or indirectly affected by kidney function eg. composition
The Urinary System Urine production and elimination are one of the most important mechanisms of body homeostasis all body systems are directly or indirectly affected by kidney function eg. composition
23. The Urinary System Text The McGraw Hill Companies, 2003 CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 23 The kidneys (green), ureters, and urinary bladder (red) of a healthy person (colorized X ray) The Urinary System CHAPTER OUTLINE Functions of the Urinary System 880 Functions of the Kidneys
CHAPTER 23 The kidneys (green), ureters, and urinary bladder (red) of a healthy person (colorized X ray) The Urinary System CHAPTER OUTLINE Functions of the Urinary System 880 Functions of the Kidneys
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab
 BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
Quiz Urinary System. 1. The kidneys help regulate blood volume. help control blood pressure. help control ph. All of the above are correct.
 Quiz Urinary System 1. The kidneys help regulate blood volume. help control blood pressure. help control ph. All of the above are correct. 2. The location of the kidneys in relationship to the peritoneal
Quiz Urinary System 1. The kidneys help regulate blood volume. help control blood pressure. help control ph. All of the above are correct. 2. The location of the kidneys in relationship to the peritoneal
The Urinary System Urine (pp. 984 985)
 Kidney Anatomy (pp. 961 969) Location and External Anatomy (pp. 961 962) Internal Anatomy (pp. 962 963) Blood and Nerve Supply (pp. 963 964) Nephrons (pp. 964 969) Kidney Physiology: Mechanisms of Urine
Kidney Anatomy (pp. 961 969) Location and External Anatomy (pp. 961 962) Internal Anatomy (pp. 962 963) Blood and Nerve Supply (pp. 963 964) Nephrons (pp. 964 969) Kidney Physiology: Mechanisms of Urine
Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 8; Lecture 1; Monday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida. Excretory Physiology
 Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 8; Lecture 1; Monday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Excretory Physiology The following ELEVEN slides are review. They will not be covered in lecture, but will be
Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 8; Lecture 1; Monday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Excretory Physiology The following ELEVEN slides are review. They will not be covered in lecture, but will be
Acid/Base Homeostasis (Part 3)
 Acid/Base Homeostasis (Part 3) Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) 27. Effect of Hypoventilation Now let's look at how the
Acid/Base Homeostasis (Part 3) Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) 27. Effect of Hypoventilation Now let's look at how the
Pathophysiology Renal Anatomy and Function II
 Pathophysiology Renal Anatomy and Function II I. Effects of blood volume on the filtration fraction (FF) {Altered Volume Effects in syllabus A. Under normal conditions, ~20% of renal plasma flow becomes
Pathophysiology Renal Anatomy and Function II I. Effects of blood volume on the filtration fraction (FF) {Altered Volume Effects in syllabus A. Under normal conditions, ~20% of renal plasma flow becomes
AORN A.CARDARELLI NAPOLI dr.e.di Florio III SAR
 AORN A.CARDARELLI NAPOLI dr.e.di Florio III SAR Renal Anatomy Renal Artery & Veins 6 cm 3cm Cortex 11cm Pelvis of the ureter Capsule Ureter To the bladder Medulla Medulary Pyramid Renal Anatomy and Physiology
AORN A.CARDARELLI NAPOLI dr.e.di Florio III SAR Renal Anatomy Renal Artery & Veins 6 cm 3cm Cortex 11cm Pelvis of the ureter Capsule Ureter To the bladder Medulla Medulary Pyramid Renal Anatomy and Physiology
2. Understand the structure of the kidney, and how this structure facilitates its function
 Objectives 1. Understand the roles of the kidney 2. Understand the structure of the kidney, and how this structure facilitates its function 3. Begin to appreciate the inter-dependence of regulatory mechanisms
Objectives 1. Understand the roles of the kidney 2. Understand the structure of the kidney, and how this structure facilitates its function 3. Begin to appreciate the inter-dependence of regulatory mechanisms
RENAL WATER REGULATION page 1
 page 1 INTRODUCTION TO WATER EXCRETION A. Role of the Kidney: to adjust urine formation rate and urine concentration to maintain 1. body fluid osmolar concentration 2. body fluid volume 3. intravascular
page 1 INTRODUCTION TO WATER EXCRETION A. Role of the Kidney: to adjust urine formation rate and urine concentration to maintain 1. body fluid osmolar concentration 2. body fluid volume 3. intravascular
Chapter 26: The Urinary System Kidney
 Chapter 26: The Urinary System Kidney --Overview of Kidney Function a. Regulation of blood ionic composition b. Regulation of blood ph and osmolarity c. Regulate blood glucose level (gluconeogenesis) d.
Chapter 26: The Urinary System Kidney --Overview of Kidney Function a. Regulation of blood ionic composition b. Regulation of blood ph and osmolarity c. Regulate blood glucose level (gluconeogenesis) d.
Introduction to the kidneys + urinary system Dr Vikram Khullar ([email protected])
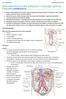 Introduction to the kidneys + urinary system Dr Vikram Khullar ([email protected]) 1. Draw a simple diagram of the urinary system including the following: kidney, renal pelvis, ureter, bladder,
Introduction to the kidneys + urinary system Dr Vikram Khullar ([email protected]) 1. Draw a simple diagram of the urinary system including the following: kidney, renal pelvis, ureter, bladder,
KIDNEY Locate the following structures on the sheep kidney and human kidney models:
 Laboratory Handouts 163 Lab 11: Urinary System Anatomy and Physiology, Reproductive System Anatomy Unit 15: Urinary System Unit 16: Reproductive Systems Cat Dissection: Photo Atlas, Chapter 19 Ex. 15-1:
Laboratory Handouts 163 Lab 11: Urinary System Anatomy and Physiology, Reproductive System Anatomy Unit 15: Urinary System Unit 16: Reproductive Systems Cat Dissection: Photo Atlas, Chapter 19 Ex. 15-1:
The kidneys play a dominant role in regulating the composition
 PART VI RENAL PHYSIOLOGY AND BODY FLUIDS C H A P T E R 22 Kidney Function George A. Tanner, Ph.D. LEARNING OBJECTIVES Upon mastering the material in this chapter you should be able to: Summarize the functions
PART VI RENAL PHYSIOLOGY AND BODY FLUIDS C H A P T E R 22 Kidney Function George A. Tanner, Ph.D. LEARNING OBJECTIVES Upon mastering the material in this chapter you should be able to: Summarize the functions
30.3 The Digestive System
 30.3 The Digestive System Lesson Objectives Describe the organs of the digestive system and explain their functions. Explain what happens during digestion. Describe how nutrients are absorbed into the
30.3 The Digestive System Lesson Objectives Describe the organs of the digestive system and explain their functions. Explain what happens during digestion. Describe how nutrients are absorbed into the
Anatomy and Physiology
 Learning Activities It is important that you do not lecture all of the time. If you employ a variety of teaching styles, your students will stay focused better and they will find it easier to process the
Learning Activities It is important that you do not lecture all of the time. If you employ a variety of teaching styles, your students will stay focused better and they will find it easier to process the
The Respiratory System
 Human Anatomy III: Respiratory, Urinary & Digestive Systems The Respiratory System Major functions include: Obtaining oxygen Removing carbon dioxide Maintenance of ph balance Respiration may be accomplished
Human Anatomy III: Respiratory, Urinary & Digestive Systems The Respiratory System Major functions include: Obtaining oxygen Removing carbon dioxide Maintenance of ph balance Respiration may be accomplished
Drug Excretion. Renal Drug Clearance. Drug Clearance and Half-Life. Glomerular Filtration II. Glomerular Filtration I. Drug Excretion and Clearance
 t/.drugexcretion AINTRAVENOUSDOSE 36848765430TIME(hours) t/ Drug Excretion Dr. Robert G. Lamb Professor Pharmacology & Toxicology Drug Excretion and Clearance Drug Excretion: is the movement of drug from
t/.drugexcretion AINTRAVENOUSDOSE 36848765430TIME(hours) t/ Drug Excretion Dr. Robert G. Lamb Professor Pharmacology & Toxicology Drug Excretion and Clearance Drug Excretion: is the movement of drug from
Acid-Base Balance and Renal Acid Excretion
 AcidBase Balance and Renal Acid Excretion Objectives By the end of this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Cite the basic principles of acidbase physiology. 2. Understand the bicarbonatecarbon dioxide
AcidBase Balance and Renal Acid Excretion Objectives By the end of this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Cite the basic principles of acidbase physiology. 2. Understand the bicarbonatecarbon dioxide
1. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled A on the diagram. 2. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled B on the diagram.
 2013 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Sample Tournament Station A: Use the diagram in answering Questions 1-5. 1. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled A on the diagram. 2. Give the name and functions
2013 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Sample Tournament Station A: Use the diagram in answering Questions 1-5. 1. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled A on the diagram. 2. Give the name and functions
Respiratory Gaseous Exchange and Elimination of Body Wastes
 : 204 : Respiratory Gaseous Exchange and Elimination of Body Wastes 27 Respiratory Gaseous Exchange and Elimination of Body Wastes We can live without food for several days but we cannot live without breathing
: 204 : Respiratory Gaseous Exchange and Elimination of Body Wastes 27 Respiratory Gaseous Exchange and Elimination of Body Wastes We can live without food for several days but we cannot live without breathing
Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back
 Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back to the left atria from the left ventricle, blood is pumped
Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back to the left atria from the left ventricle, blood is pumped
Renal Acid/Base. Acid Base Homeostasis... 2 H+ Balance... 2
 Renal Acid/Base By Adam Hollingworth Table of Contents Acid Base Homeostasis... 2 H+ Balance... 2 Acid Base Homeostasis... 2 Role of Kidneys in Acid- Base Homeostasis... 3 Renal H+ Secretion... 3 Proximal
Renal Acid/Base By Adam Hollingworth Table of Contents Acid Base Homeostasis... 2 H+ Balance... 2 Acid Base Homeostasis... 2 Role of Kidneys in Acid- Base Homeostasis... 3 Renal H+ Secretion... 3 Proximal
HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY MAINTENANCE 30
 Curriculum Development In the Fairfield Public Schools FAIRFIELD PUBLIC SCHOOLS FAIRFIELD, CONNECTICUT HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY MAINTENANCE 30 Board of Education Approved 05/22/2007 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY
Curriculum Development In the Fairfield Public Schools FAIRFIELD PUBLIC SCHOOLS FAIRFIELD, CONNECTICUT HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY MAINTENANCE 30 Board of Education Approved 05/22/2007 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY
Acid-Base Balance and the Anion Gap
 Acid-Base Balance and the Anion Gap 1. The body strives for electrical neutrality. a. Cations = Anions b. One of the cations is very special, H +, and its concentration is monitored and regulated very
Acid-Base Balance and the Anion Gap 1. The body strives for electrical neutrality. a. Cations = Anions b. One of the cations is very special, H +, and its concentration is monitored and regulated very
REGULATION OF FLUID & ELECTROLYTE BALANCE
 REGULATION OF FLUID & ELECTROLYTE BALANCE 1 REGULATION OF FLUID & ELECTROLYTE BALANCE The kidney is the primary organ that maintains the total volume, ph, and osmolarity of the extracellular fluid within
REGULATION OF FLUID & ELECTROLYTE BALANCE 1 REGULATION OF FLUID & ELECTROLYTE BALANCE The kidney is the primary organ that maintains the total volume, ph, and osmolarity of the extracellular fluid within
2012 Anatomy & Physiology C Division. National Competition-Science
 2012 Anatomy & Physiology C Division National Competition-Science Olympiad 1. The alimentary canal includes 8 different parts and 4 accessory organs. Name 5 parts from the alimentary canal and 3 accessory
2012 Anatomy & Physiology C Division National Competition-Science Olympiad 1. The alimentary canal includes 8 different parts and 4 accessory organs. Name 5 parts from the alimentary canal and 3 accessory
Histology. Epithelial Tissue
 Histology Epithelial Tissue Epithelial Tissue Lines internal and external body surfaces Forms glands Epithelial Tissue Little extracellular matrix Attached on one side Avascular Basement membrane Apical
Histology Epithelial Tissue Epithelial Tissue Lines internal and external body surfaces Forms glands Epithelial Tissue Little extracellular matrix Attached on one side Avascular Basement membrane Apical
Part I Clinical Chemistry of the Kidney and Renal-Associated Physiology
 Part I Clinical Chemistry of the Kidney and Renal-Associated Physiology 1 Kidney Anatomy and Function (Lecture 1) 2 Functions of Kidney A) Regulation of water B) Regulation of electrolytes C) Acid-base
Part I Clinical Chemistry of the Kidney and Renal-Associated Physiology 1 Kidney Anatomy and Function (Lecture 1) 2 Functions of Kidney A) Regulation of water B) Regulation of electrolytes C) Acid-base
2161-1 - Page 1. Name: 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. Questions 10 and 11 refer to the following:
 Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
The first vertebrates evolved in seawater, and the physiology
 58 Maintaining the Internal Environment Concept Outline 58.1 The regulatory systems of the body maintain homeostasis. The Need to Maintain Homeostasis. Regulatory mechanisms maintain homeostasis through
58 Maintaining the Internal Environment Concept Outline 58.1 The regulatory systems of the body maintain homeostasis. The Need to Maintain Homeostasis. Regulatory mechanisms maintain homeostasis through
CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Lung cancer affects a life-sustaining system of the body, the respiratory system. The respiratory system is responsible for one of the essential
CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Lung cancer affects a life-sustaining system of the body, the respiratory system. The respiratory system is responsible for one of the essential
Your Kidneys: Master Chemists of the Body
 Your Kidneys: Master Chemists of the Body www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes
Your Kidneys: Master Chemists of the Body www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes
DIALYSIS COMPACT. The function, diseases and treatments for the human kidney.
 DIALYSIS COMPACT The function, diseases and treatments for the human kidney. Content 3 Editorial 4 What do healthy kidneys accomplish? 5 What causes kidney disease? 6 What effects does kidney disease have?
DIALYSIS COMPACT The function, diseases and treatments for the human kidney. Content 3 Editorial 4 What do healthy kidneys accomplish? 5 What causes kidney disease? 6 What effects does kidney disease have?
What is creatinine? The kidneys maintain the blood creatinine in a normal range. Creatinine has been found to be a fairly reliable indicator of kidney
 What is creatinine? Creatinine is a chemical waste molecule that is generated from muscle metabolism. Creatinine is produced from creatine, a molecule of major importance for energy production in muscles.
What is creatinine? Creatinine is a chemical waste molecule that is generated from muscle metabolism. Creatinine is produced from creatine, a molecule of major importance for energy production in muscles.
Visual Acuity. Hearing. Height and Weight. Blood Pressure MEASURED VALUE
 TEST ITEM DESCRIPTION STANDARD LEVEL Standard level varies among different examination methods. Please check with your medical facility about normal level. MEASURED VALUE Visual Acuity You look at rings
TEST ITEM DESCRIPTION STANDARD LEVEL Standard level varies among different examination methods. Please check with your medical facility about normal level. MEASURED VALUE Visual Acuity You look at rings
2015 RN.ORG, S.A., RN.ORG, LLC
 Renal Function Tests WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed December, 2015, Expires December, 2017 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2015 RN.ORG, S.A., RN.ORG,
Renal Function Tests WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed December, 2015, Expires December, 2017 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2015 RN.ORG, S.A., RN.ORG,
Introduction to Animal Systems
 Human Body Systems Introduction to Animal Systems Recurring Themes in Biology 1. Correlation between structure and function( seen at many levels) 2. Life is organized at many levels from Smallest ----
Human Body Systems Introduction to Animal Systems Recurring Themes in Biology 1. Correlation between structure and function( seen at many levels) 2. Life is organized at many levels from Smallest ----
12.1: The Function of Circulation page 478
 12.1: The Function of Circulation page 478 Key Terms: Circulatory system, heart, blood vessel, blood, open circulatory system, closed circulatory system, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein, aorta, atrioventricular
12.1: The Function of Circulation page 478 Key Terms: Circulatory system, heart, blood vessel, blood, open circulatory system, closed circulatory system, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein, aorta, atrioventricular
Dr. Johnson PA Renal Winter 2010
 1 Renal Control of Acid/Base Balance Dr. Johnson PA Renal Winter 2010 Acid/Base refers to anything having to do with the concentrations of H + ions in aqueous solutions. In medical physiology, we are concerned
1 Renal Control of Acid/Base Balance Dr. Johnson PA Renal Winter 2010 Acid/Base refers to anything having to do with the concentrations of H + ions in aqueous solutions. In medical physiology, we are concerned
Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide
 Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Define the terms anatomy and physiology. List and discuss in order of increasing complexity, the body from the cell to the whole organism. Define the
Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Define the terms anatomy and physiology. List and discuss in order of increasing complexity, the body from the cell to the whole organism. Define the
Course Specification (Master in Urology/Physiology)
 Course Specification (Master in Urology/Physiology) ١ University/ Academy: Al-Azhar University Faculty/ Institute: Faculty of Medicine (Assuit) Department: physiology Course Specification (Master in Urology/Physiology)
Course Specification (Master in Urology/Physiology) ١ University/ Academy: Al-Azhar University Faculty/ Institute: Faculty of Medicine (Assuit) Department: physiology Course Specification (Master in Urology/Physiology)
Animal Tissues. I. Epithelial Tissue
 Animal Tissues There are four types of tissues found in animals: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. In this lab you will learn the major characteristics of each tissue
Animal Tissues There are four types of tissues found in animals: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. In this lab you will learn the major characteristics of each tissue
The Digestive System. Chapter 16. Introduction. Histological Organization. Overview of Digestive System. Movement and Mixing of Digestive Materials
 The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
1 The diagram shows blood as seen under a microscope. Which identifies parts P, Q, R and S of the blood?
 1 1 The diagram shows blood as seen under a microscope. Which identifies parts P, Q, R and S of the blood? 2 The plan shows the blood system of a mammal. What does the part labelled X represent? A heart
1 1 The diagram shows blood as seen under a microscope. Which identifies parts P, Q, R and S of the blood? 2 The plan shows the blood system of a mammal. What does the part labelled X represent? A heart
Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology Course Outline, Objectives and Accreditation Information
 201 Webster Building 3411 Silverside Road Wilmington, DE 19810 Phone: 1-888-658-6641 Fax: 1-302-477-9744 [email protected] www.corexcel.com Course Outline, Objectives and Accreditation Information Chapter
201 Webster Building 3411 Silverside Road Wilmington, DE 19810 Phone: 1-888-658-6641 Fax: 1-302-477-9744 [email protected] www.corexcel.com Course Outline, Objectives and Accreditation Information Chapter
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg. Automation: Introduction. Urine Automation. published by Bayer. Unit 3. Chemical Examination of Urine
 Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 3 Chemical Examination of Urine Part 7, Automation, Function Tests, and Calculi Automation: Introduction Advantages Saves time Allows for standardization of procedures
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 3 Chemical Examination of Urine Part 7, Automation, Function Tests, and Calculi Automation: Introduction Advantages Saves time Allows for standardization of procedures
Excretion & Osmoregulation
 CHAPTER 22 Excretion & Osmoregulation Introduction Excretion is the elimination to waste products from the body. Waste products are unwanted and toxic byproducts which are removed to maintain homeostasis
CHAPTER 22 Excretion & Osmoregulation Introduction Excretion is the elimination to waste products from the body. Waste products are unwanted and toxic byproducts which are removed to maintain homeostasis
Lesson Aim To explain the human body at a microscopic level, including the structure and function of cells, tissues and membranes.
 LESSON 1. CELLS & TISSUES Lesson Aim To explain the human body at a microscopic level, including the structure and function of cells, tissues and membranes. THE CELL All living matter is composed of functional
LESSON 1. CELLS & TISSUES Lesson Aim To explain the human body at a microscopic level, including the structure and function of cells, tissues and membranes. THE CELL All living matter is composed of functional
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY
 ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
MANITOBA NEPHROLOGY NURSING COURSE
 MANITOBA NEPHROLOGY NURSING COURSE Introduction to the Manitoba Renal Program 3 The Renal Education Department 6 WRHA Renal Education Department 6 Site Educators 7 Philosophy Statement of MRP Education
MANITOBA NEPHROLOGY NURSING COURSE Introduction to the Manitoba Renal Program 3 The Renal Education Department 6 WRHA Renal Education Department 6 Site Educators 7 Philosophy Statement of MRP Education
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES
 BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
OUTCOMES BASED LEARNING MATRIX
 OUTCOMES BASED LEARNING MATRIX Course: BIOL 206 Vertebrate Anatomy and Physiology II Department: Biology Course Description: This is the second part of an introductory course sequence in the comparative
OUTCOMES BASED LEARNING MATRIX Course: BIOL 206 Vertebrate Anatomy and Physiology II Department: Biology Course Description: This is the second part of an introductory course sequence in the comparative
Functions of Blood System. Blood Cells
 Functions of Blood System Transport: to and from tissue cells Nutrients to cells: amino acids, glucose, vitamins, minerals, lipids (as lipoproteins). Oxygen: by red blood corpuscles (oxyhaemoglobin - 4
Functions of Blood System Transport: to and from tissue cells Nutrients to cells: amino acids, glucose, vitamins, minerals, lipids (as lipoproteins). Oxygen: by red blood corpuscles (oxyhaemoglobin - 4
Keystone Review Practice Test Module A Cells and Cell Processes. 1. Which characteristic is shared by all prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
 Keystone Review Practice Test Module A Cells and Cell Processes 1. Which characteristic is shared by all prokaryotes and eukaryotes? a. Ability to store hereditary information b. Use of organelles to control
Keystone Review Practice Test Module A Cells and Cell Processes 1. Which characteristic is shared by all prokaryotes and eukaryotes? a. Ability to store hereditary information b. Use of organelles to control
Problem 24. Pathophysiology of the diabetes insipidus
 Problem 24. Pathophysiology of the diabetes insipidus In order to workout this problem, study pages 240 6, 249 51, 318 9, 532 3 and 886 7 of the Pathophysiology, 5 th Edition. (This problem was based on
Problem 24. Pathophysiology of the diabetes insipidus In order to workout this problem, study pages 240 6, 249 51, 318 9, 532 3 and 886 7 of the Pathophysiology, 5 th Edition. (This problem was based on
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley. Practice Exam 1
 Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam 1 1. Which definition is the best definition of the term gross anatomy? a. The study of cells. b. The study of tissues. c. The study of structures
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam 1 1. Which definition is the best definition of the term gross anatomy? a. The study of cells. b. The study of tissues. c. The study of structures
5. Secretion: release of water, acids. Enzymes, buffers by digestive tract.
 Digestive System CH-16 Lecture topics Functions of the digestive system: p. 488. 1. Ingestion: Taking food in 2. Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal p.490. voluntary: swalloing : skeletal
Digestive System CH-16 Lecture topics Functions of the digestive system: p. 488. 1. Ingestion: Taking food in 2. Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal p.490. voluntary: swalloing : skeletal
Renal syndromes leading to abnormal kidney function:
 Renal syndromes leading to abnormal kidney function: An abnormality in kidney function can be detected by the following: 1) changes in serum creatinine concentration, reflecting changes in GFR 2) abnormalities
Renal syndromes leading to abnormal kidney function: An abnormality in kidney function can be detected by the following: 1) changes in serum creatinine concentration, reflecting changes in GFR 2) abnormalities
KEY CHAPTER 14: BLOOD OBJECTIVES. 1. Describe blood according to its tissue type and major functions.
 KEY CHAPTER 14: BLOOD OBJECTIVES 1. Describe blood according to its tissue type and major functions. TISSUE TYPE? MAJOR FUNCTIONS connective Transport Maintenance of body temperature 2. Define the term
KEY CHAPTER 14: BLOOD OBJECTIVES 1. Describe blood according to its tissue type and major functions. TISSUE TYPE? MAJOR FUNCTIONS connective Transport Maintenance of body temperature 2. Define the term
Anatomy and Physiology of the Bowel and Urinary Systems
 PMS /26/05 0:52 AM Page Anatomy and Physiology of the Bowel and Urinary Systems Anthony McGrath INTRODUCTION The aim of this chapter is to increase the reader s understanding of the small and large bowel
PMS /26/05 0:52 AM Page Anatomy and Physiology of the Bowel and Urinary Systems Anthony McGrath INTRODUCTION The aim of this chapter is to increase the reader s understanding of the small and large bowel
Clinical Aspects of Hyponatremia & Hypernatremia
 Clinical Aspects of Hyponatremia & Hypernatremia Case Presentation: History 62 y/o male is admitted to the hospital with a 3 month history of excessive urination (polyuria) and excess water intake up to
Clinical Aspects of Hyponatremia & Hypernatremia Case Presentation: History 62 y/o male is admitted to the hospital with a 3 month history of excessive urination (polyuria) and excess water intake up to
Hormonal Cycles. 1. Briefly describe each component of an endocrine feedback loop: Stimulus. Production Cell. Hormone. Target Cell. Target Cell Action
 Hormonal Cycles Directions: a. Click the Contents button. b. Open the Endocrine System File. c. Click Animations. d. Click Hormonal Cycles. 1. Briefly describe each component of an endocrine feedback loop:
Hormonal Cycles Directions: a. Click the Contents button. b. Open the Endocrine System File. c. Click Animations. d. Click Hormonal Cycles. 1. Briefly describe each component of an endocrine feedback loop:
Elaboration of an artificial model for filtering of spam based on Human Renal Function
 Elaboration of an artificial model for filtering of spam based on Human Renal Function Reda Mohamed HAMOU 1, Mohamed Amine BOUDIA 3, Abdelmalek AMINE 3 Dr. Moulay Tahar University SAÏDA Department of Computer
Elaboration of an artificial model for filtering of spam based on Human Renal Function Reda Mohamed HAMOU 1, Mohamed Amine BOUDIA 3, Abdelmalek AMINE 3 Dr. Moulay Tahar University SAÏDA Department of Computer
Chronic Kidney Disease
 Page 1 of 6 Chronic Kidney Disease Chronic kidney disease (CKD) means that your kidneys are not working as well as they once did. Various conditions can cause CKD. Severity can vary but most cases are:
Page 1 of 6 Chronic Kidney Disease Chronic kidney disease (CKD) means that your kidneys are not working as well as they once did. Various conditions can cause CKD. Severity can vary but most cases are:
Anatomy & Physiology Bio 2401 Lecture. Instructor: Daryl Beatty Day 1 Intro to Lecture 1
 Anatomy & Physiology Bio 2401 Lecture Instructor: Daryl Beatty Day 1 Intro to Lecture 1 Introduction: Daryl Beatty M.S. Microbiology 28 Years Dow, Research & TS&D. Family BC since 2007 More importantly:
Anatomy & Physiology Bio 2401 Lecture Instructor: Daryl Beatty Day 1 Intro to Lecture 1 Introduction: Daryl Beatty M.S. Microbiology 28 Years Dow, Research & TS&D. Family BC since 2007 More importantly:
THE PHYSICAL EXAMINATION AND THE URINARY SYSTEM. 156 The Body Systems: Clinical and Applied Topics
 56 The Body Systems: Clinical and Applied Topics The Urinary System The urinary system consists of the kidneys, where urine production occurs, and the conducting system that transports and stores urine
56 The Body Systems: Clinical and Applied Topics The Urinary System The urinary system consists of the kidneys, where urine production occurs, and the conducting system that transports and stores urine
