MPC107 PCI Bridge/Memory Controller Technical Summary
|
|
|
- Meagan Blankenship
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 nc. Order Number: MPC107TS/D Rev. 0, 9/1999 Semiconductor Products Sector Advance Information MPC107 PCI Bridge/Memory Controller Technical Summary This document provides an overview of the MPC107 PCI bridge/memory controller (PCIB/ MC) for high-performance embedded systems. The MPC107 is a cost-effective, generalpurpose PCI bridge/memory controller for applications using PCI in networking infrastructure, telecommunications, and other embedded markets. It can be used in applications such as network routers and switches, mass storage subsystems, network appliances, and print and imaging systems. For errata or revisions to this document, refer to the website at powerpc. 1.1 MPC107 PCI Bridge/Memory Controller Features The MPC107 provides an integrated high-bandwidth, high-performance interface between up to two 60x processors, the PCI bus, and main memory. This section summarizes the features of the MPC107. Major features of the MPC107 are as follows: Memory interface 64-/32-bit 100-MHz bus Programmable timing supporting either FPM DRAM, EDO DRAM or SDRAM High-bandwidth bus (32-/64-bit data bus) to DRAM This document contains information on a new product under development by Motorola. Motorola reserves the right to change or discontinue this product without notice. Motorola, Inc., All rights reserved.
2 MPC107 PCI Bridge/Memory Controller Features nc. Supports one to eight banks of 4-, 16-, 64-, or 128-Mbit memory devices, and up to four banks of 256-Mbit SDRAM devices Supports 1-Mbyte to 1-Gbyte DRAM memory 144 Mbytes of ROM space 8-, 32-, or 64-bit ROM Write buffering for PCI and processor accesses Supports normal parity, read-modify-write (RMW), or ECC Data-path buffering between memory interface and processor Low-voltage TTL logic (LVTTL) interfaces Port X: 8-, 32-, or 64-bit general-purpose I/O port using ROM controller interface with programmable address strobe timing 32-bit PCI interface operating up to 66 MHz PCI 2.1-compliant PCI 5.0-V tolerance Support for PCI locked accesses to memory Support for accesses to PCI memory, I/O, and configuration spaces Selectable big- or little-endian operation Store gathering of processor-to-pci write and PCI-to-memory write accesses Memory prefetching of PCI read accesses Selectable hardware-enforced coherency PCI bus arbitration unit (five request/grant pairs) PCI agent mode capability Address translation unit Some internal configuration registers accessible from PCI Two-channel integrated DMA controller (writes to ROM/Port X not supported) Supports direct mode or chaining mode (automatic linking of DMA transfers) Supports scatter gathering read or write discontinuous memory Interrupt on completed segment, chain, and error Local-to-local memory PCI-to-PCI memory PCI-to-local memory PCI memory-to-local memory 2 MPC107 PCI Bridge/Memory Controller Technical Summary
3 nc. MPC107 PCI/MC Applications Message unit Two doorbell registers An extended doorbell register mechanism that facilitates interprocessor communication through interrupts in a dual-local-processor system Two inbound and two outbound messaging registers I 2 O message controller I 2 C controller with full master/slave support (except broadcast all) Embedded programmable interrupt controller (EPIC) Five hardware interrupts (IRQs) or 16 serial interrupts Four programmable timers Integrated PCI bus, CPU, and SDRAM clock generation Programmable PCI bus, 60x, and memory interface output drivers Dynamic power management Supports 60x nap, doze, sleep, and suspend modes Programmable input and output signals with watchpoint capability Built-in PCI bus performance monitor facility Debug features Error injection/capture on data path IEEE (JTAG)/test interface Processor interface Supports up to two PowerPC microprocessors with 60x bus interface Supports various operating frequencies and bus divider ratios 32-bit address bus, 64/32-bit data bus supported at 100 MHz Supports full memory coherency Supports optional local bus slave Decoupled address and data buses for pipelining of 60x accesses Store gathering on 60x-to-PCI writes Concurrent transactions on 60x and PCI buses supported 1.2 MPC107 PCI/MC Applications The MPC107 can be used in either a system host configuration or as a peripheral device. For system applications where cost, space, and power consumption are critical parameters, yet performance cannot be sacrificed, the MPC107 provides a complete solution. The MPC107 is shown in Figure 1-1 as a host bridge. MPC107 PCI Bridge/Memory Controller Technical Summary 3
4 MPC107 PCI/MC Applications nc. MPC107 DMA PowerPC Microprocessor MU(I 2 O) I 2 C EPIC Peripheral Logic ROM / Port X Data CTRL Local Memory: DRAM, EDO, SDRAM PCI Bus up to 66 MHz Peripheral Peripheral Peripheral PCI to PCI Bridge PCI Bus Figure 1-1. System Using MPC107 as a Host Bridge With the embedded enhancements provided in the MPC107, it is possible to use it in distributed I/O processor applications as shown in Figure 1-2. Periph. 2 MPC107 PCI Bus DMA MU(I 2 O) I 2 C EPIC Peripheral Logic Host Processor Host Bridge CTRL Data Host Memory up to 66 MHz Peripheral Peripheral System I/O PCI to PCI 1 3 Controller Bridge PCI Bus PowerPC Microprocessor ROM / Port X Local Memory: DRAM, EDO, SDRAM Figure 1-2. Embedded System Using the MPC107 as a Bridge to a Distributed I/O Processor 4 MPC107 PCI Bridge/Memory Controller Technical Summary
5 nc. MPC107 PCI/MC Applications The MPC107 can also be used with a peripheral processing device as shown in Figure 1-3. In this case, the PCI-to-PCI bridge shown Figure 1-3 could be of the PCI type 0 variety. The MPC107 would not be part of the system configuration map. This configuration is useful in applications such as RAID controllers or multi-port network controllers where the I/O devices shown are SCSI controllers or Ethernet controllers, respectively. Host Processor Host Bridge Host Memory Peripheral 1 Peripheral 2 PCI Bus Local PCI Bus MPC107 DMA MU(I 2 O) I 2 C EPIC PCI-to-PCI Bridge Peripheral Logic PowerPC Microprocessor up to 66 MHz CTRL ROM / Port X I/O Device Local Memory: DRAM, EDO, SDRAM Figure 1-3. Embedded System Using MPC107 with a Peripheral Processor The processor bus interface (60x) of the MPC107 contains all of the necessary arbitration and control logic to communicate with up to two PowerPC microprocessors in a symmetric multiprocessing environment. In addition, the MPC107 also has a side-band mode to allow an alternate bus slave to capture address tenures. This application is show in Figure 1-4. Data I/O Device Peripheral 3 System I/O Controller MPC107 PCI Bridge/Memory Controller Technical Summary 5
6 MPC107 Major Functional Blocks nc. PowerPC Microprocessor PowerPC Microprocessor 60x Bus Local Bus Slave MPC107 DMA MU(I 2 O) I 2 C EPIC PCI Bus Peripheral Logic ROM / Port X Data CTRL Local Memory: DRAM, EDO, SDRAM Figure 1-4. Multiprocessor System Using the MPC107 and a Local Bus Slave 1.3 MPC107 Major Functional Blocks The MPC107 integrates a PCI bridge, memory controller, DMA controller, EPIC interrupt controller/timers, a message unit with an Intelligent Input/Output (I 2 O) message controller, and an Inter-Integrated Circuit (I 2 C) controller. The integration reduces the overall packaging requirements and the number of discrete devices required for an embedded system. Figure 1-5 shows the major functional units within the MPC107. Note that this is a conceptual block diagram intended to show the basic features rather than an attempt to show how these features are physically implemented. 6 MPC107 PCI Bridge/Memory Controller Technical Summary
7 nc. MPC107 Major Functional Blocks MPC107 60x Bus Interface (64- or 32-Bit Data Bus) Additional features: Programmable I/O with Watchpoint JTAG/COP Interface Power Management I 2 C 5 IRQs/ 16 Serial Interrupts Peripheral Logic Block Message Unit (with I 2 O) DMA Controller I 2 C Controller EPIC Interrupt Controller /Timers Address (32-Bit) Central Control Unit PCI Bus Interface Unit Address Translator 32-Bit PCI Interface Data (64-Bit) PCI Arbiter x Processor Interface Configuration Registers Five Request/Grant Pairs Data Path ECC Controller Memory Controller Figure 1-5. MPC107 Block Diagram The MPC107 supports a programmable interface to a variety of PowerPC microprocessors operating at select bus speeds. The 60x address bus is 32 bits wide and the data bus is configurable to be 64 or 32 bits wide. The 60x processor interface of the MPC107 uses a subset of the 60x bus protocol, supporting single-beat and burst data transfers. The address and data buses are decoupled to support pipelined transactions. In this document, the term 60x is used to denote a 32-bit microprocessor from the PowerPC architecture family that conforms to the bus interface of the MPC603e, MPC740, MPC750, or MPC7400 microprocessors. 60x processors implement the PowerPC architecture as it is specified for 32-bit addressing, which provides 32-bit effective (logical) addresses, integer data types of 8, 16, and 32 bits, and floating-point data types of 32 and 64 bits (single-precision and double-precision). DLL PLL Fanout Buffers OSC_IN Data Bus (64- or 32-bit) with 8-bit Parity or ECC Memory/ROM/ Port X Control/ Address SDRAM_SYNC_IN SDRAM Clocks CPU Clocks PCI_SYNC_IN PCI Bus Clocks Two signals on the MPC107, local bus slave claim (LBCLAIM) and data bus grant local bus slave (DBGLB), are provided for an optional local bus slave. However, the local bus slave must be capable of generating the transfer acknowledge (TA) signal to interact with the 60x processor(s). MPC107 PCI Bridge/Memory Controller Technical Summary 7
8 MPC107 Major Functional Blocks nc. Depending on the system implementation, the processor bus may operate at the PCI bus clock rate, or at a multiple of the PCI bus clock rate (determined at reset). The 60x processor bus is synchronous, with all timing relative to the rising edge of the 60x bus clock. When two 60x processors are used, the two sets of bus request, bus grant, and data bus grant signals allow for arbitration between the 60x processors. The 60x processors share all 60x interface signals of the MPC107, except the bus arbitration signals Memory System Interface The MPC107 memory interface controls processor and PCI interactions to main memory. It supports a variety of DRAM, and flash or ROM configurations as main memory. The MPC107 supports fast page mode (FPM), extended data out (EDO) and synchronous DRAM (SDRAM). The maximum supported memory size is 1 Gbyte of DRAM or SDRAM and 144 Mbytes of ROM/flash. SDRAM must comply with the JEDEC SDRAM specification. The MPC107 implements Port X, a memory bus interface that facilitates the connection of general-purpose I/O devices. The Port X functionality allows the designer to connect external registers, communication devices, and other such devices directly to the MPC107. Some devices may require a small amount of external logic to properly generate address strobes, chip selects, and other signals. The MPC107 is designed to control a 32-bit or 64-bit data path to main memory DRAM or SDRAM. For a 32-bit data path, the MPC107 can be configured to check and generate byte parity using four parity bits. For a 64-bit data path, the MPC107 can be configured to support parity or ECC checking and generation with eight parity/syndrome bits checked and generated. Note that the data bus width (32- or 64-bit) chosen at reset for the 60x bus interface is also used for the memory interface. The MPC107 supports DRAM bank sizes from 1 to 128 Mbytes, SDRAM bank sizes of 1 to 256 Mbytes, and provides bank start address and end address configuration registers. Note that the MPC107 does not support mixed DRAM/SDRAM configurations. The MPC107 can be configured so that appropriate row and column address multiplexing occurs according to the accessed memory bank. Addresses are provided to DRAM and SDRAM through a 13-bit interface for DRAM and a 15-bit interface for SDRAM. The memory bus width is configured at reset as 32- or 64-bits wide, depending on the setting of the MDL0 reset configuration signal. Four chip selects, one write enable, one output enable, and up to 21 address signals are provided for ROM/flash systems Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) Interface The PCI interface for the MPC107 is compliant with the Peripheral Component Interconnect Specification Revision 2.1. The PCI interface provides mode-selectable, bigto little-endian conversion. The MPC107 provides an interface to the PCI bus running at speeds up to 66 MHz. 8 MPC107 PCI Bridge/Memory Controller Technical Summary
9 MPC107 Major Functional Blocks The MPC107 s PCI interface can be configured as host or agent. In host mode, the interface acts as the main memory controller for the system and responds to all host memory transactions. In agent mode, the MPC107 can be configured to respond to a programmed window of PCI memory space. A variety of initialization modes are provided to boot the device PCI Bus Arbitration Unit nc. The MPC107 contains a PCI bus arbitration unit, which eliminates the need for an external unit, thus lowering system complexity and cost. It has the following features: Five external arbitration signal pairs. The MPC107 is the sixth member of the arbitration pool. The bus arbitration unit allows fairness as well as a priority mechanism. A two-level round-robin scheme is used in which each device can be programmed within a pool of a high- or low-priority arbitration. One member of the low-priority pool is promoted to the high-priority pool. As soon as it is granted the bus, it returns to the low-priority pool. The unit can be disabled to allow a remote arbitration unit to be used Address Maps and Translation The MPC107 s processor bus interface supports memory-mapped accesses. The address space is divided between memory and PCI according to one of two allowable address maps map A and map B. Note that the support of map A is provided for backward compatibility only. It is strongly recommended that new designs use map B because map A may not be supported in future devices. An inbound and outbound PCI address translation mechanism is provided to support the use of the MPC107 in agent mode. Note that address translation is supported only for agent mode; it is not supported when the MPC107 is operating in host mode. Also note that since agent mode is supported only for address map B, address translation is supported only for address map B. When the MPC107 is configured to be a PCI agent, the amount of local memory visible to the system is programmable. In addition, it may be necessary to map the local memory to a different system memory address space. The address translation unit handles the mapping of both inbound and outbound transactions for these cases Byte Ordering The MPC107 allows the processor to run in either big- or little-endian mode (except for the initial boot code which must run in big-endian mode). MPC107 PCI Bridge/Memory Controller Technical Summary 9
10 MPC107 Major Functional Blocks PCI Agent Capability nc. In certain applications, the embedded system architecture dictates that the MPC107 bridges to a peripheral processor. In this case, the peripheral logic must not act like a host bridge for the PCI bus. Instead it functions as a configurable device that is accessed by a host bridge. This capability allows multiple MPC107 devices to coexist with other PCI peripheral devices on a single PCI bus. The MPC107 has PCI 2.1- compliant configuration capabilities DMA Controller The integrated DMA controller contains two independent units. Note that the DMA writing capability for local memory is available for DRAM and SDRAM, but writing is not available for the ROM/Port X interface. Each DMA unit is capable of performing the following types of transfers: PCI-to-local memory Local-to-PCI memory PCI-to-PCI memory Local-to-local memory The DMA controller allows chaining through local memory-mapped chain descriptors. Transfers can be scatter gathered and misaligned. Interrupts are provided on completed segment, chain, and error conditions Message Unit (MU) Many embedded applications require handshake algorithms to pass control, status, and data information from one owner to another. This is made easier with doorbell and message registers. The MPC107 has a message unit (MU) that implements doorbell and message registers as well as an I 2 O interface. The MU has many conditions that can cause interrupts and uses the EPIC unit to signal interrupts to the PCI interface and interrupts to the processor Doorbell Registers The MPC107 MU contains one 32-bit inbound doorbell register and one 32-bit outbound doorbell register. The inbound doorbell register allows a remote processor to set a bit in the register from the PCI bus. This, in turn, generates an interrupt to the local processor. The local processor can write to the outbound register, causing the outbound interrupt signal INTA to assert, thus interrupting the host processor. Once INTA is generated, it can be cleared only by the host processor by writing ones to the bits that are set in the outbound doorbell register. 10 MPC107 PCI Bridge/Memory Controller Technical Summary
11 nc. MPC107 Major Functional Blocks Extended Doorbell Register Facility The MPC107 MU also contains an extended doorbell register mechanism that facilitates interprocessor communication through interrupts in a dual-local-processor system. For example, processor 0 can write to the EDBW1S register to generate an interrupt to processor 1. Processor 1 can then clear the interrupt by writing to the EDBW1C register. The same process can be used if processor 1 needs to interrupt processor 0. Use of this facility requires that the rest of the MU be disabled Inbound and Outbound Message Registers The MPC107 contains two 32-bit inbound message registers and two 32-bit outbound message registers. The inbound registers allow a remote host or PCI master to write a 32- bit value, causing an interrupt to the local processor. The outbound registers allow the local processor to write an outbound message which causes the outbound interrupt signal INTA to assert Intelligent Input/Output Controller (I 2 O) The intelligent I/O specification is an open standard that defines an abstraction layer interface between the OS and subsystem drivers. Messages are passed between the message abstraction layer from one device to another. The I 2 O specification describes a system as being made up of host processors and input/ output platforms (IOPs). The host processor is a single processor or a collection of processors working together to execute a homogenous operating system. An IOP consists of a processor, memory, and I/O interfaces. The IOP functions separately from other processors within the system to handle system I/O functions. The I 2 O controller of the MU enhances communication between hosts and IOPs within a system. There are two paths for messages an inbound queue is used to transfer messages from a remote host or IOP to the local processor, and an outbound queue is used to transfer messages from the local processor to the remote host. Each queue is implemented as a pair of FIFOs. The inbound and outbound message queues each consists of a free_list FIFO and a post_list FIFO. Messages are transferred between the host and the IOP using PCI memory-mapped registers. The MPC107 s I 2 O controller facilitates moving the messages to and from the inbound and outbound registers and local IOP memory. Interrupts signal the host and IOP to indicate the arrival of new messages Inter-Integrated Circuit (I 2 C) Controller The I 2 C serial interface has become an industry de facto standard for communicating with low-speed peripherals. Typically, it is used for system management functions and EEPROM support. The MPC107 contains an I 2 C controller with full master and slave functionality. MPC107 PCI Bridge/Memory Controller Technical Summary 11
12 MPC107 Major Functional Blocks Embedded Programmable Interrupt Controller (EPIC) The integrated embedded programmable interrupt controller (EPIC) of the MPC107 reduces the overall component count in embedded applications. The EPIC unit is designed to collect external and internal hardware interrupts, prioritize them, and deliver them to the local processor. The module operates in one of three modes: nc. In direct mode, five level- or edge-triggered interrupts can be connected directly to an MPC107. In pass-through mode, interrupts detected at the IRQ0 input are passed directly (with logic inversion) to the INT output signal. Also in this case, interrupts generated by the I 2 O, I 2 C, and DMA controllers are passed to the L_INT output signal. The MPC107 provides a serial delivery mechanism for when more than five external interrupt sources are needed. The serial mechanism allows for up to 16 interrupts to be serially scanned into the MPC107. This mechanism increases the number of interrupts without increasing the number of pins. The outbound interrupt request signal, L_INT, is used to signal interrupts to the host processor when the MPC107 is configured for agent mode. The MPC107 EPIC includes four programmable timers that can be used for system timing or for generating periodic interrupts Integrated PCI Bus, CPU, and SDRAM Clock Generation There are two PCI bus clocking solutions directed towards different system requirements. For systems where the MPC107 is the host controller with a minimum number of clock loads, five clock fanout buffers are provided on-chip. For systems requiring more clock fan out or where the MPC107 is an agent device, external clock buffers may be used. The MPC107 provides an on-chip delay-locked loop (DLL) that supplies the external memory bus clock signals to SDRAM banks and also supplies three CPU clock outputs that are synchronized to the SDRAM clocks. The memory bus clock signals are of the same frequency and synchronous with the processor clock signals. The four SDRAM clock outputs are generated by the internal DLL and can account for the trace length between SDRAM_SYNC_OUT signal and the SDRAM_SYNC_IN signal. The MPC107 requires a single clock input signal, PCI_SYNC_IN, which can be driven by the PCI clock fan-out buffers specifically the PCI_SYNC_OUT output. PCI_SYNC_IN can also be driven by an external clock driver. 12 MPC107 PCI Bridge/Memory Controller Technical Summary
13 nc. Power Management PCI_SYNC_IN is driven by the PCI bus frequency. An internal PLL, using PCI_SYNC_IN as a reference, generates an internal sys-logic-clk signal that is used for the internal logic. The processor (60x) bus clock frequency on the CPU_CLK[0:2] outputs is configured at reset (by the MPC107 PLL configuration signals (PLL_CFG[0:3])) to be a multiple of the PCI_SYNC_IN frequency. 1.4 Power Management The MPC107 provides program-controllable power reduction modes for progressive reduction of power consumption and a system hardware mechanism for further power reduction. The MPC107 provides hardware support for three levels of programmable power reduction doze, nap, and sleep modes; each is invoked by programming configuration registers. The MPC107 also has a fourth power reduction mode invoked by the assertion of the external SUSPEND signal. In suspend mode, the MPC107 may have its clock input and PLL shut down for additional power savings. Memory refresh can be accomplished in two ways either by using self-refresh mode DRAMs or by using the RTC input. To exit the suspend mode, the system clock must be turned on in sufficient time to restart the PLL. After this time, SUSPEND may be negated. In suspend mode, all bidirectional and output signals (except the memory refresh-related signals if RTC refresh is being used) are at high impedance and all input signals except the PLL_CFG[0:3] signals, HRST, and SUSPEND, are ignored. Note that the SUSPEND signal is monitored for negation during suspend mode. The MPC107 is fully static, allowing internal logic states to be preserved during all powersaving modes. Table 1-1 summarizes the programmable power-saving modes for the MPC107.. PM Mode Table 1-1. MPC107 Power Modes Summary Functioning Units Activation Method Full-Power Wake Up Method Full power All units active Doze PCI address decoding and bus arbiter System RAM refreshing 60x bus request and NMI monitoring EPIC unit I 2 C unit PLL Controlled by software (write to PMCR1) PCI access to memory 60x bus request Assertion of NMI 1 Hard Reset MPC107 PCI Bridge/Memory Controller Technical Summary 13
14 Programmable I/O Signals with Watchpoint nc. Table 1-1. MPC107 Power Modes Summary (Continued) PM Mode Nap Sleep Functioning Units PCI address decoding and bus arbiter System RAM refreshing 60x bus request and NMI monitoring EPIC unit I 2 C unit PLL PCI bus arbiter System RAM refreshing (can be disabled) 60x bus request and NMI monitoring EPIC unit I 2 C unit PLL (can be disabled) 1.5 Programmable I/O Signals with Watchpoint The MPC107 programmable I/O facility allows the system designer to monitor the 60x bus. Up to two watchpoints and their respective 4-bit countdown values can be programmed. When the programmed threshold of the selected watchpoint is reached, an external trigger signal is generated and the states of the 60x address, control, and data buses are latched into user-readable registers. 1.6 Debug Features The MPC107 includes the following debug features: Activation Method Controlled by software (write to PMCR1) and processor in nap or sleep mode (QREQ asserted) Controlled by software (write to PMCR1) and processor in nap or sleep mode (QREQ asserted) Full-Power Wake Up Method PCI access to memory 2 60x bus request 3 Assertion of NMI 1 Hard Reset 60x bus request 3 Assertion of NMI 1 Hard Reset Suspend System RAM refreshing (can be disabled) PLL (can be disabled) Assertion of SUSPEND SUSPEND negation Hard Reset SUSPEND, PLL_CFG[0:3], and HRST signal monitoring 1 Programmable option based on value of PICR1[MCP_EN] = 1. 2 A PCI access to memory in nap mode causes QACK to negate while the MPC107 services the access. Additionally, some 60x processors (MPC740, MPC750, and MPC7400) will wake up and respond to the snoop transaction. After servicing the PCI access, the MPC107 automatically returns to the nap mode. 3 Programmable option for recognition of BR1 (bus request from second local processor in a dual processor system) based on PMCR1[BR1_WAKE] Error injection/capture on data path IEEE (JTAG)/test interface 14 MPC107 PCI Bridge/Memory Controller Technical Summary
15 nc. Debug Features Error Injection/Capture on Data Path The MPC107 provides hardware to exercise and debug the ECC and parity logic by allowing the user to inject multi-bit stuck-at faults onto the peripheral logic or memory data/parity buses and to capture the data/parity output on receipt of an ECC or parity error IEEE (JTAG)/Test Interface To facilitate system testing, the MPC107 provides a JTAG test access port that complies with the IEEE boundary-scan specification. MPC107 PCI Bridge/Memory Controller Technical Summary 15
16 nc. Mfax is a trademark of Motorola, Inc. The PowerPC name, the PowerPC logotype, PowerPC 603e, PowerPC 740, and PowerPC 750 are trademarks of International Business Machines Corporation used by Motorola under license from International Business Machines Corporation. Information in this document is provided solely to enable system and software implementers to use PowerPC microprocessors. There are no express or implied copyright licenses granted hereunder to design or fabricate PowerPC integrated circuits or integrated circuits based on the information in this document. Motorola reserves the right to make changes without further notice to any products herein. Motorola makes no warranty, representation or guarantee regarding the suitability of its products for any particular purpose, nor does Motorola assume any liability arising out of the application or use of any product or circuit, and specifically disclaims any and all liability, including without limitation consequential or incidental damages. Typical parameters can and do vary in different applications. All operating parameters, including Typicals must be validated for each customer application by customer s technical experts. Motorola does not convey any license under its patent rights nor the rights of others. Motorola products are not designed, intended, or authorized for use as components in systems intended for surgical implant into the body, or other applications intended to support or sustain life, or for any other application in which the failure of the Motorola product could create a situation where personal injury or death may occur. Should Buyer purchase or use Motorola products for any such unintended or unauthorized application, Buyer shall indemnify and hold Motorola and its officers, employees, subsidiaries, affiliates, and distributors harmless against all claims, costs, damages, and expenses, and reasonable attorney fees arising out of, directly or indirectly, any claim of personal injury or death associated with such unintended or unauthorized use, even if such claim alleges that Motorola was negligent regarding the design or manufacture of the part. Motorola and are registered trademarks of Motorola, Inc. Motorola, Inc. is an Equal Opportunity/Affirmative Action Employer. Motorola Literature Distribution Centers: USA/EUROPE: Motorola Literature Distribution; P.O. Box 5405; Denver, Colorado 80217; Tel.: or ; World Wide Web Address: JAPAN: Nippon Motorola Ltd SPD, Strategic Planning Office , Nishi-Gotanda Shinagawa-ku, Tokyo 141, Japan Tel.: ASIA/PACIFIC: Motorola Semiconductors H.K. Ltd Silicon Harbour Centre 2, Dai King Street Tai Po Industrial Estate Tai Po, New Territories, Hong Kong Mfax : RMFAX0@ .sps.mot.com; TOUCHTONE ; US & Canada ONLY (800) ; World Wide Web Address: INTERNET: Technical Information: Motorola Inc. SPS Customer Support Center ; electronic mail address: [email protected]. Document Comments: FAX (512) , Attn: RISC Applications Engineering. World Wide Web Addresses: MPC107TS/D
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. Product Brief Integrated Portable System Processor DragonBall ΤΜ
 nc. Order this document by MC68328/D Microprocessor and Memory Technologies Group MC68328 MC68328V Product Brief Integrated Portable System Processor DragonBall ΤΜ As the portable consumer market grows
nc. Order this document by MC68328/D Microprocessor and Memory Technologies Group MC68328 MC68328V Product Brief Integrated Portable System Processor DragonBall ΤΜ As the portable consumer market grows
PowerQUICC II Pro (MPC83xx) PCI Agent Initialization
 Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN3373 Rev. 0, 04/2007 PowerQUICC II Pro (MPC83xx) PCI Agent Initialization by: David Smith Field Application Engineering Raleigh, NC In many designs,
Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN3373 Rev. 0, 04/2007 PowerQUICC II Pro (MPC83xx) PCI Agent Initialization by: David Smith Field Application Engineering Raleigh, NC In many designs,
MPC603/MPC604 Evaluation System
 nc. MPC105EVB/D (Motorola Order Number) 7/94 Advance Information MPC603/MPC604 Evaluation System Big Bend Technical Summary This document describes an evaluation system that demonstrates the capabilities
nc. MPC105EVB/D (Motorola Order Number) 7/94 Advance Information MPC603/MPC604 Evaluation System Big Bend Technical Summary This document describes an evaluation system that demonstrates the capabilities
Spreadsheet Estimation of CPU-DRAM Subsystem Power Consumption
 AN1272 2196 Application Note Spreadsheet Estimation of CPU-DRAM Subsystem Power Consumption As the energy efficiency of computers becomes more important to consumers, the early estimation, preferably during
AN1272 2196 Application Note Spreadsheet Estimation of CPU-DRAM Subsystem Power Consumption As the energy efficiency of computers becomes more important to consumers, the early estimation, preferably during
MPC8245/MPC8241 Memory Clock Design Guidelines: Part 1
 Freescale Semiconductor AN2164 Rev. 4.1, 03/2007 MPC8245/MPC8241 Memory Clock Design Guidelines: Part 1 by Esther C. Alexander RISC Applications, CPD Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. Austin, TX This application
Freescale Semiconductor AN2164 Rev. 4.1, 03/2007 MPC8245/MPC8241 Memory Clock Design Guidelines: Part 1 by Esther C. Alexander RISC Applications, CPD Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. Austin, TX This application
Programming Audio Applications in the i.mx21 MC9328MX21
 Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN2628 Rev. 1, 10/2005 Programming Audio Applications in the MC9328MX21 by: Alfred Sin 1 Abstract The MC9328MX21 () processor has two dedicated
Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN2628 Rev. 1, 10/2005 Programming Audio Applications in the MC9328MX21 by: Alfred Sin 1 Abstract The MC9328MX21 () processor has two dedicated
etpu Host Interface by:
 Freescale Semiconductor Application Note AN2821 Rev. 2, 08/2007 etpu Host Interface by: David Paterson Ming Li MCD Applications 1 Introduction This application note discusses the enhanced Time Processing
Freescale Semiconductor Application Note AN2821 Rev. 2, 08/2007 etpu Host Interface by: David Paterson Ming Li MCD Applications 1 Introduction This application note discusses the enhanced Time Processing
Data Movement Between Big-Endian and Little-Endian Devices
 Freescale Semiconductor Application Note AN2285 Rev. 2.2, 3/2008 Data Movement Between Big-Endian and Little-Endian Devices by Kyle Aubrey, Field Technical Leader Ashan Kabir, System Engineering Freescale
Freescale Semiconductor Application Note AN2285 Rev. 2.2, 3/2008 Data Movement Between Big-Endian and Little-Endian Devices by Kyle Aubrey, Field Technical Leader Ashan Kabir, System Engineering Freescale
Flexible Active Shutter Control Interface using the MC1323x
 Freescale Semiconductor Document Number: AN4353 Application Note Rev. 0, 9/2011 Flexible Active Shutter Control Interface using the MC1323x by: Dennis Lui Freescale Hong Kong 1 Introduction This application
Freescale Semiconductor Document Number: AN4353 Application Note Rev. 0, 9/2011 Flexible Active Shutter Control Interface using the MC1323x by: Dennis Lui Freescale Hong Kong 1 Introduction This application
Initializing the TSEC Controller
 Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN2925 Rev. 0, 11/2005 Initializing the TSEC Controller by Ahsan Kabir Digital Systems Division Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. Austin, TX This application
Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN2925 Rev. 0, 11/2005 Initializing the TSEC Controller by Ahsan Kabir Digital Systems Division Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. Austin, TX This application
Understanding LCD Memory and Bus Bandwidth Requirements ColdFire, LCD, and Crossbar Switch
 Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN3606 Rev. 0, 03/2008 Understanding LCD Memory and Bus Bandwidth Requirements ColdFire, LCD, and Crossbar Switch by: Melissa Hunter TSPG Applications
Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN3606 Rev. 0, 03/2008 Understanding LCD Memory and Bus Bandwidth Requirements ColdFire, LCD, and Crossbar Switch by: Melissa Hunter TSPG Applications
AND8336. Design Examples of On Board Dual Supply Voltage Logic Translators. Prepared by: Jim Lepkowski ON Semiconductor. http://onsemi.
 Design Examples of On Board Dual Supply Voltage Logic Translators Prepared by: Jim Lepkowski ON Semiconductor Introduction Logic translators can be used to connect ICs together that are located on the
Design Examples of On Board Dual Supply Voltage Logic Translators Prepared by: Jim Lepkowski ON Semiconductor Introduction Logic translators can be used to connect ICs together that are located on the
21152 PCI-to-PCI Bridge
 Product Features Brief Datasheet Intel s second-generation 21152 PCI-to-PCI Bridge is fully compliant with PCI Local Bus Specification, Revision 2.1. The 21152 is pin-to-pin compatible with Intel s 21052,
Product Features Brief Datasheet Intel s second-generation 21152 PCI-to-PCI Bridge is fully compliant with PCI Local Bus Specification, Revision 2.1. The 21152 is pin-to-pin compatible with Intel s 21052,
Genesi Pegasos II Setup
 Freescale Semiconductor Application Note AN2666 Rev. 0, 07/2004 Genesi Pegasos II Setup by Maurie Ommerman CPD Applications Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. Austin, TX This application note is the first in
Freescale Semiconductor Application Note AN2666 Rev. 0, 07/2004 Genesi Pegasos II Setup by Maurie Ommerman CPD Applications Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. Austin, TX This application note is the first in
Local Interconnect Network (LIN) Physical Interface
 Freescale Semiconductor Engineering Bulletin EB215 Rev. 1.0, 03/2005 Local Interconnect Network (LIN) Physical Interface Difference Between MC33399 and MC33661 Introduction This engineering bulletin highlights
Freescale Semiconductor Engineering Bulletin EB215 Rev. 1.0, 03/2005 Local Interconnect Network (LIN) Physical Interface Difference Between MC33399 and MC33661 Introduction This engineering bulletin highlights
MCF54418 NAND Flash Controller
 Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN4348 Rev. 0, 09/2011 MCF54418 NAND Flash Controller by: Liew Tsi Chung Applications Engineer 1 Introduction The ColdFire MCF5441x family is the
Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN4348 Rev. 0, 09/2011 MCF54418 NAND Flash Controller by: Liew Tsi Chung Applications Engineer 1 Introduction The ColdFire MCF5441x family is the
OpenSPARC T1 Processor
 OpenSPARC T1 Processor The OpenSPARC T1 processor is the first chip multiprocessor that fully implements the Sun Throughput Computing Initiative. Each of the eight SPARC processor cores has full hardware
OpenSPARC T1 Processor The OpenSPARC T1 processor is the first chip multiprocessor that fully implements the Sun Throughput Computing Initiative. Each of the eight SPARC processor cores has full hardware
PowerPC Microprocessor Clock Modes
 nc. Freescale Semiconductor AN1269 (Freescale Order Number) 1/96 Application Note PowerPC Microprocessor Clock Modes The PowerPC microprocessors offer customers numerous clocking options. An internal phase-lock
nc. Freescale Semiconductor AN1269 (Freescale Order Number) 1/96 Application Note PowerPC Microprocessor Clock Modes The PowerPC microprocessors offer customers numerous clocking options. An internal phase-lock
LOW POWER NARROWBAND FM IF
 Order this document by MC336B/D The MC336B includes an Oscillator, Mixer, Limiting Amplifier, Quadrature Discriminator, Active Filter, Squelch, Scan Control and Mute Switch. This device is designed for
Order this document by MC336B/D The MC336B includes an Oscillator, Mixer, Limiting Amplifier, Quadrature Discriminator, Active Filter, Squelch, Scan Control and Mute Switch. This device is designed for
Detecting a CPM Overload on the PowerQUICC II
 Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN2547 Rev. 1, 11/2006 Detecting a CPM Overload on the PowerQUICC II by Qiru Zou NCSD Applications Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. Austin, TX This
Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN2547 Rev. 1, 11/2006 Detecting a CPM Overload on the PowerQUICC II by Qiru Zou NCSD Applications Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. Austin, TX This
User Guide. Introduction. HCS12PLLCALUG/D Rev. 0, 12/2002. HCS12 PLL Component Calculator
 User Guide HCS12PLLCALUG/D Rev. 0, 12/2002 HCS12 PLL Component Calculator by Stuart Robb Applications Engineering Motorola, East Kilbride Introduction The MC9S12D amily o MCUs includes a Phase-Locked Loop
User Guide HCS12PLLCALUG/D Rev. 0, 12/2002 HCS12 PLL Component Calculator by Stuart Robb Applications Engineering Motorola, East Kilbride Introduction The MC9S12D amily o MCUs includes a Phase-Locked Loop
3-Phase BLDC Motor Control with Hall Sensors Using 56800/E Digital Signal Controllers
 Freescale Semiconductor Application Note AN1916 Rev. 2.0, 11/2005 3-Phase BLDC Motor Control with Hall Sensors Using 56800/E Digital Signal Controllers Leonard N. Elevich Contents 1. Application Benefits...1
Freescale Semiconductor Application Note AN1916 Rev. 2.0, 11/2005 3-Phase BLDC Motor Control with Hall Sensors Using 56800/E Digital Signal Controllers Leonard N. Elevich Contents 1. Application Benefits...1
NOTE: The Flatpak version has the same pinouts (Connection Diagram) as the Dual In-Line Package.
 PRESETTABLE BCD/DECADE UP/DOWN COUNTERS PRESETTABLE 4-BIT BINARY UP/DOWN COUNTERS The SN54/74LS190 is a synchronous UP/DOWN BCD Decade (8421) Counter and the SN54/74LS191 is a synchronous UP/DOWN Modulo-
PRESETTABLE BCD/DECADE UP/DOWN COUNTERS PRESETTABLE 4-BIT BINARY UP/DOWN COUNTERS The SN54/74LS190 is a synchronous UP/DOWN BCD Decade (8421) Counter and the SN54/74LS191 is a synchronous UP/DOWN Modulo-
White Paper. Freescale s Embedded Hypervisor for QorIQ P4 Series Communications Platform
 White Paper Freescale s Embedded for QorIQ P4 Series Communications Platform Document Number: EMHYPQIQTP4CPWP Rev 1 10/2008 Overview Freescale Semiconductor s QorIQ communications platform P4 series processors
White Paper Freescale s Embedded for QorIQ P4 Series Communications Platform Document Number: EMHYPQIQTP4CPWP Rev 1 10/2008 Overview Freescale Semiconductor s QorIQ communications platform P4 series processors
SN54/74LS682 SN54/74LS684 8-BIT MAGNITUDE COMPARATORS SN54/74LS688 8-BIT MAGNITUDE COMPARATORS FAST AND LS TTL DATA 5-603
 8-BIT MAGNITUDE COMPARATORS The SN54/ 74LS682, 684, 688 are 8-bit magnitude comparators. These device types are designed to perform compariso between two eight-bit binary or BCD words. All device types
8-BIT MAGNITUDE COMPARATORS The SN54/ 74LS682, 684, 688 are 8-bit magnitude comparators. These device types are designed to perform compariso between two eight-bit binary or BCD words. All device types
Hardware Configurations for the i.mx Family USB Modules
 Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN4136 Rev. 0, 06/2010 Hardware Configurations for the i.mx Family USB Modules by Multimedia Applications Division Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN4136 Rev. 0, 06/2010 Hardware Configurations for the i.mx Family USB Modules by Multimedia Applications Division Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
White Paper Utilizing Leveling Techniques in DDR3 SDRAM Memory Interfaces
 White Paper Introduction The DDR3 SDRAM memory architectures support higher bandwidths with bus rates of 600 Mbps to 1.6 Gbps (300 to 800 MHz), 1.5V operation for lower power, and higher densities of 2
White Paper Introduction The DDR3 SDRAM memory architectures support higher bandwidths with bus rates of 600 Mbps to 1.6 Gbps (300 to 800 MHz), 1.5V operation for lower power, and higher densities of 2
PQ-MDS-T1 Module. HW Getting Started Guide. Contents. About This Document. Required Reading. Definitions, Acronyms, and Abbreviations
 HW Getting Started Guide PQ-MDS-T1 Module April 2006: Rev. 0.3 Contents Contents................................................................................. 1 About This Document.......................................................................
HW Getting Started Guide PQ-MDS-T1 Module April 2006: Rev. 0.3 Contents Contents................................................................................. 1 About This Document.......................................................................
Software Real Time Clock Implementation on MC9S08LG32
 Freescale Semiconductor Document Number: AN4478 Rev. 0, 03/2012 Software Real Time Clock Implementation on MC9S08LG32 by: Nitin Gupta Automotive and Industrial Solutions Group 1 Introduction The MC9S08LG32
Freescale Semiconductor Document Number: AN4478 Rev. 0, 03/2012 Software Real Time Clock Implementation on MC9S08LG32 by: Nitin Gupta Automotive and Industrial Solutions Group 1 Introduction The MC9S08LG32
Performance Monitor on PowerQUICC II Pro Processors
 Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN3359 Rev. 0, 05/2007 Performance Monitor on PowerQUICC II Pro Processors by Harinder Rai Network Computing Systems Group Freescale Semiconductor,
Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN3359 Rev. 0, 05/2007 Performance Monitor on PowerQUICC II Pro Processors by Harinder Rai Network Computing Systems Group Freescale Semiconductor,
AN10850. LPC1700 timer triggered memory to GPIO data transfer. Document information. LPC1700, GPIO, DMA, Timer0, Sleep Mode
 LPC1700 timer triggered memory to GPIO data transfer Rev. 01 16 July 2009 Application note Document information Info Keywords Abstract Content LPC1700, GPIO, DMA, Timer0, Sleep Mode This application note
LPC1700 timer triggered memory to GPIO data transfer Rev. 01 16 July 2009 Application note Document information Info Keywords Abstract Content LPC1700, GPIO, DMA, Timer0, Sleep Mode This application note
Digitale Signalverarbeitung mit FPGA (DSF) Soft Core Prozessor NIOS II Stand Mai 2007. Jens Onno Krah
 (DSF) Soft Core Prozessor NIOS II Stand Mai 2007 Jens Onno Krah Cologne University of Applied Sciences www.fh-koeln.de [email protected] NIOS II 1 1 What is Nios II? Altera s Second Generation
(DSF) Soft Core Prozessor NIOS II Stand Mai 2007 Jens Onno Krah Cologne University of Applied Sciences www.fh-koeln.de [email protected] NIOS II 1 1 What is Nios II? Altera s Second Generation
Switch Fabric Implementation Using Shared Memory
 Order this document by /D Switch Fabric Implementation Using Shared Memory Prepared by: Lakshmi Mandyam and B. Kinney INTRODUCTION Whether it be for the World Wide Web or for an intra office network, today
Order this document by /D Switch Fabric Implementation Using Shared Memory Prepared by: Lakshmi Mandyam and B. Kinney INTRODUCTION Whether it be for the World Wide Web or for an intra office network, today
MVME162P2. VME Embedded Controller with Two IP Slots
 MVME162P2 VME Embedded Controller with Two IP Slots [Advantages] [Details] [Specifications] [Ordering Info] [.pdf version ] 25 MHz MC68040 with floating point coprocessor or 25 MHz MC68LC040 High-performance
MVME162P2 VME Embedded Controller with Two IP Slots [Advantages] [Details] [Specifications] [Ordering Info] [.pdf version ] 25 MHz MC68040 with floating point coprocessor or 25 MHz MC68LC040 High-performance
SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA
 SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA Order this document by MPX5050/D The MPX5050 series piezoresistive transducer is a state of the art monolithic silicon pressure sensor designed for a wide range of applications,
SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA Order this document by MPX5050/D The MPX5050 series piezoresistive transducer is a state of the art monolithic silicon pressure sensor designed for a wide range of applications,
AND8326/D. PCB Design Guidelines for Dual Power Supply Voltage Translators
 PCB Design Guidelines for Dual Power Supply Voltage Translators Jim Lepkowski ON Semiconductor Introduction The design of the PCB is an important factor in maximizing the performance of a dual power supply
PCB Design Guidelines for Dual Power Supply Voltage Translators Jim Lepkowski ON Semiconductor Introduction The design of the PCB is an important factor in maximizing the performance of a dual power supply
PD 40 0.23 Storage Temperature Range Tstg 65 to +150 C Junction Temperature TJ 200 C
 SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA Order this document by MRF228/D The RF Line... designed for. volt VHF large signal power amplifiers in commercial and industrial FM equipment. Compact.28 Stud Package Specified.
SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA Order this document by MRF228/D The RF Line... designed for. volt VHF large signal power amplifiers in commercial and industrial FM equipment. Compact.28 Stud Package Specified.
ES_LPC4357/53/37/33. Errata sheet LPC4357/53/37/33. Document information
 Rev. 1.1 8 August 2012 Errata sheet Document information Info Keywords Abstract Content LPC4357FET256; LPC4357FET180; LPC4357FBD208; LPC4353FET256; LPC4353FET180; LPC4353FBD208; LPC4337FET256; LPC4337FET180;
Rev. 1.1 8 August 2012 Errata sheet Document information Info Keywords Abstract Content LPC4357FET256; LPC4357FET180; LPC4357FBD208; LPC4353FET256; LPC4353FET180; LPC4353FBD208; LPC4337FET256; LPC4337FET180;
Chapter 13. PIC Family Microcontroller
 Chapter 13 PIC Family Microcontroller Lesson 01 PIC Characteristics and Examples PIC microcontroller characteristics Power-on reset Brown out reset Simplified instruction set High speed execution Up to
Chapter 13 PIC Family Microcontroller Lesson 01 PIC Characteristics and Examples PIC microcontroller characteristics Power-on reset Brown out reset Simplified instruction set High speed execution Up to
ULN2803A ULN2804A OCTAL PERIPHERAL DRIVER ARRAYS
 Order this document by ULN283/D The eight NPN Darlington connected transistors in this family of arrays are ideally suited for interfacing between low logic level digital circuitry (such as TTL, CMOS or
Order this document by ULN283/D The eight NPN Darlington connected transistors in this family of arrays are ideally suited for interfacing between low logic level digital circuitry (such as TTL, CMOS or
150127-Microprocessor & Assembly Language
 Chapter 3 Z80 Microprocessor Architecture The Z 80 is one of the most talented 8 bit microprocessors, and many microprocessor-based systems are designed around the Z80. The Z80 microprocessor needs an
Chapter 3 Z80 Microprocessor Architecture The Z 80 is one of the most talented 8 bit microprocessors, and many microprocessor-based systems are designed around the Z80. The Z80 microprocessor needs an
Cyclic Redundant Checker Calculation on Power Architecture Technology and Comparison of Big-Endian Versus Little-Endian
 Freescale Semiconductor Document Number:AN4657 Application Note Rev. 0, 01/2013 Cyclic Redundant Checker Calculation on Power Architecture Technology and Comparison of Big-Endian Versus Little-Endian by:
Freescale Semiconductor Document Number:AN4657 Application Note Rev. 0, 01/2013 Cyclic Redundant Checker Calculation on Power Architecture Technology and Comparison of Big-Endian Versus Little-Endian by:
Improving Embedded Software Test Effectiveness in Automotive Applications
 Improving Embedded Software Test Effectiveness in Automotive Applications Author, D Brook Document Number: CODETESTTECHWP Rev. 0 11/2005 As the automotive industry introduces more and more safety-critical,
Improving Embedded Software Test Effectiveness in Automotive Applications Author, D Brook Document Number: CODETESTTECHWP Rev. 0 11/2005 As the automotive industry introduces more and more safety-critical,
Enhanced Serial Interface Mapping
 Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN3536 Rev. 1, 11/2007 Enhanced Serial Interface Mapping 16 E1/T1 QUICC Engine Solution for TDM Connectivity by Netcomm Applications Networking
Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN3536 Rev. 1, 11/2007 Enhanced Serial Interface Mapping 16 E1/T1 QUICC Engine Solution for TDM Connectivity by Netcomm Applications Networking
NOTE: The Flatpak version has the same pinouts (Connection Diagram) as the Dual In-Line Package.
 QUA FLIP-FLOP SN54/LS75 The LSTTL /SI SN54 /LS75 is a high speed Quad Flip-Flop. The device is useful for general flip-flop requirements where clock and clear inputs are common. The information on the
QUA FLIP-FLOP SN54/LS75 The LSTTL /SI SN54 /LS75 is a high speed Quad Flip-Flop. The device is useful for general flip-flop requirements where clock and clear inputs are common. The information on the
7a. System-on-chip design and prototyping platforms
 7a. System-on-chip design and prototyping platforms Labros Bisdounis, Ph.D. Department of Computer and Communication Engineering 1 What is System-on-Chip (SoC)? System-on-chip is an integrated circuit
7a. System-on-chip design and prototyping platforms Labros Bisdounis, Ph.D. Department of Computer and Communication Engineering 1 What is System-on-Chip (SoC)? System-on-chip is an integrated circuit
VGA Output using TV-Out Extension Solution i.mx21
 Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN3378 Rev. 0, 11/2006 VGA Output using TV-Out Extension Solution i.mx21 by: Tatiana Orofino 1 Abstract Freescale first thought of a TV-Out Extension
Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN3378 Rev. 0, 11/2006 VGA Output using TV-Out Extension Solution i.mx21 by: Tatiana Orofino 1 Abstract Freescale first thought of a TV-Out Extension
MC33064DM 5 UNDERVOLTAGE SENSING CIRCUIT
 Order this document by MC3464/D The MC3464 is an undervoltage sensing circuit specifically designed for use as a reset controller in microprocessor-based systems. It offers the designer an economical solution
Order this document by MC3464/D The MC3464 is an undervoltage sensing circuit specifically designed for use as a reset controller in microprocessor-based systems. It offers the designer an economical solution
TECHNOLOGY BRIEF. Compaq RAID on a Chip Technology EXECUTIVE SUMMARY CONTENTS
 TECHNOLOGY BRIEF August 1999 Compaq Computer Corporation Prepared by ISSD Technology Communications CONTENTS Executive Summary 1 Introduction 3 Subsystem Technology 3 Processor 3 SCSI Chip4 PCI Bridge
TECHNOLOGY BRIEF August 1999 Compaq Computer Corporation Prepared by ISSD Technology Communications CONTENTS Executive Summary 1 Introduction 3 Subsystem Technology 3 Processor 3 SCSI Chip4 PCI Bridge
ColdFire Security SEC and Hardware Encryption Acceleration Overview
 Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN2788 Rev. 1, 05/2008 ColdFire Security SEC and Hardware Encryption Acceleration Overview by: Melissa Hunter MSG Applications This application
Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN2788 Rev. 1, 05/2008 ColdFire Security SEC and Hardware Encryption Acceleration Overview by: Melissa Hunter MSG Applications This application
Blood Pressure Monitor Using Flexis QE128 Gabriel Sanchez RTAC Americas
 Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN3500 Rev. 0, 08/2007 Blood Pressure Monitor Using Flexis QE128 by: Gabriel Sanchez RTAC Americas 1 Introduction Product designers and developers
Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN3500 Rev. 0, 08/2007 Blood Pressure Monitor Using Flexis QE128 by: Gabriel Sanchez RTAC Americas 1 Introduction Product designers and developers
Using the Performance Monitor Unit on the e200z760n3 Power Architecture Core
 Freescale Semiconductor Document Number: AN4341 Application Note Rev. 1, 08/2011 Using the Performance Monitor Unit on the e200z760n3 Power Architecture Core by: Inga Harris MSG Application Engineering
Freescale Semiconductor Document Number: AN4341 Application Note Rev. 1, 08/2011 Using the Performance Monitor Unit on the e200z760n3 Power Architecture Core by: Inga Harris MSG Application Engineering
How To Improve Performance On A P4080 Processor
 QorIQ Advanced Multiprocessing (AMP) Series Delivers More than Moore Freescale s new QorIQ AMP series pushes the compute and energy performance envelope beyond the P4080 processor such that its performance
QorIQ Advanced Multiprocessing (AMP) Series Delivers More than Moore Freescale s new QorIQ AMP series pushes the compute and energy performance envelope beyond the P4080 processor such that its performance
P D 215 1.25 Operating Junction Temperature T J 200 C Storage Temperature Range T stg 65 to +150 C
 SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA Order this document by /D The RF Line The is designed for output stages in band IV and V TV transmitter amplifiers. It incorporates high value emitter ballast resistors, gold
SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA Order this document by /D The RF Line The is designed for output stages in band IV and V TV transmitter amplifiers. It incorporates high value emitter ballast resistors, gold
LOW POWER SCHOTTKY. http://onsemi.com GUARANTEED OPERATING RANGES ORDERING INFORMATION
 The TTL/MSI SN74LS151 is a high speed 8-input Digital Multiplexer. It provides, in one package, the ability to select one bit of data from up to eight sources. The LS151 can be used as a universal function
The TTL/MSI SN74LS151 is a high speed 8-input Digital Multiplexer. It provides, in one package, the ability to select one bit of data from up to eight sources. The LS151 can be used as a universal function
Freescale Semiconductor, I
 nc. SEMICONDUCTOR APPLICATION NOTE ARCHIVED BY FREESCALE SEMICONDUCTOR, INC. 00 Order this document by AN8/D by: Eric Jacobsen and Jeff Baum Systems Engineering Group Sensor Products Division Motorola
nc. SEMICONDUCTOR APPLICATION NOTE ARCHIVED BY FREESCALE SEMICONDUCTOR, INC. 00 Order this document by AN8/D by: Eric Jacobsen and Jeff Baum Systems Engineering Group Sensor Products Division Motorola
IRTC Compensation and 1 Hz Clock Generation
 Freescale Semiconductor Document Number: AN4257 Application Note Rev. 0, January 2011 IRTC Compensation and 1 Hz Clock Generation by: Derek Liu Applications Engineering Shanghai 1 Introduction The MC9S08GW64
Freescale Semiconductor Document Number: AN4257 Application Note Rev. 0, January 2011 IRTC Compensation and 1 Hz Clock Generation by: Derek Liu Applications Engineering Shanghai 1 Introduction The MC9S08GW64
10-/100-Mbps Ethernet Media Access Controller (MAC) Core
 10-/100-Mbps Ethernet Media Access Controller (MAC) Core Preliminary Product Brief December 1998 Description The Ethernet Media Access Controller (MAC) core is a high-performance core with a low gate count,
10-/100-Mbps Ethernet Media Access Controller (MAC) Core Preliminary Product Brief December 1998 Description The Ethernet Media Access Controller (MAC) core is a high-performance core with a low gate count,
Installing Service Pack Updater Archive for CodeWarrior Tools (Windows and Linux) Quick Start
 Installing Service Pack Updater Archive for CodeWarrior Tools (Windows and Linux) Quick Start SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS Processor Windows OS: Intel Pentium 4 processor, 2 GHz or faster, Intel Xeon, Intel Core,
Installing Service Pack Updater Archive for CodeWarrior Tools (Windows and Linux) Quick Start SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS Processor Windows OS: Intel Pentium 4 processor, 2 GHz or faster, Intel Xeon, Intel Core,
USB Thumb Drive. Designer Reference Manual. HCS12 Microcontrollers. freescale.com. DRM061 Rev. 0 9/2004
 USB Thumb Drive Designer Reference Manual HCS12 Microcontrollers DRM061 Rev. 0 9/2004 freescale.com USB Thumb Drive Designer Reference Manual by: Kenny Lam, Derek Lau, and Dennis Lui Applications Engineering
USB Thumb Drive Designer Reference Manual HCS12 Microcontrollers DRM061 Rev. 0 9/2004 freescale.com USB Thumb Drive Designer Reference Manual by: Kenny Lam, Derek Lau, and Dennis Lui Applications Engineering
AND9015. A Solution for Peak EMI Reduction with Spread Spectrum Clock Generators APPLICATION NOTE. Prepared by: Apps Team, BIDC ON Semiconductor
 A Solution for Peak EMI Reduction with Spread Spectrum Clock Generators Prepared by: Apps Team, BIDC ON Semiconductor APPLICATION NOTE Introduction This application note will outline Spread Spectrum Clock
A Solution for Peak EMI Reduction with Spread Spectrum Clock Generators Prepared by: Apps Team, BIDC ON Semiconductor APPLICATION NOTE Introduction This application note will outline Spread Spectrum Clock
Technical Note. Micron NAND Flash Controller via Xilinx Spartan -3 FPGA. Overview. TN-29-06: NAND Flash Controller on Spartan-3 Overview
 Technical Note TN-29-06: NAND Flash Controller on Spartan-3 Overview Micron NAND Flash Controller via Xilinx Spartan -3 FPGA Overview As mobile product capabilities continue to expand, so does the demand
Technical Note TN-29-06: NAND Flash Controller on Spartan-3 Overview Micron NAND Flash Controller via Xilinx Spartan -3 FPGA Overview As mobile product capabilities continue to expand, so does the demand
Adding SDIO Wi-Fi Solution to i.mx Windows CE 5.0/Windows CE 6.0
 Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN3981 Rev. 0, 04/2010 Adding SDIO Wi-Fi Solution to i.mx Windows CE 5.0/Windows CE 6.0 by Multimedia Applications Division Freescale Semiconductor,
Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN3981 Rev. 0, 04/2010 Adding SDIO Wi-Fi Solution to i.mx Windows CE 5.0/Windows CE 6.0 by Multimedia Applications Division Freescale Semiconductor,
I/O Products IC697VSC096
 I/O Products IC697VSC096 Single-Slot Celeron Socket 370 Processor-Based 814-000431-000 VMEbus Single-Board Computer January 2010 Features Celeron socket 370-based Single-Board Computer (SBC) with operating
I/O Products IC697VSC096 Single-Slot Celeron Socket 370 Processor-Based 814-000431-000 VMEbus Single-Board Computer January 2010 Features Celeron socket 370-based Single-Board Computer (SBC) with operating
Using eflexpwm Module for ADC Synchronization in MC56F82xx and MC56F84xx Family of Digital Signal Controllers
 Freescale Semiconductor Document Number:AN4675 Application Note Rev. 0, 01/2013 Using eflexpwm Module for ADC Synchronization in MC56F82xx and MC56F84xx Family of Digital Signal Controllers by: Pavel Grasblum
Freescale Semiconductor Document Number:AN4675 Application Note Rev. 0, 01/2013 Using eflexpwm Module for ADC Synchronization in MC56F82xx and MC56F84xx Family of Digital Signal Controllers by: Pavel Grasblum
Design of a High Speed Communications Link Using Field Programmable Gate Arrays
 Customer-Authored Application Note AC103 Design of a High Speed Communications Link Using Field Programmable Gate Arrays Amy Lovelace, Technical Staff Engineer Alcatel Network Systems Introduction A communication
Customer-Authored Application Note AC103 Design of a High Speed Communications Link Using Field Programmable Gate Arrays Amy Lovelace, Technical Staff Engineer Alcatel Network Systems Introduction A communication
Applying the Benefits of Network on a Chip Architecture to FPGA System Design
 Applying the Benefits of on a Chip Architecture to FPGA System Design WP-01149-1.1 White Paper This document describes the advantages of network on a chip (NoC) architecture in Altera FPGA system design.
Applying the Benefits of on a Chip Architecture to FPGA System Design WP-01149-1.1 White Paper This document describes the advantages of network on a chip (NoC) architecture in Altera FPGA system design.
The I2C Bus. NXP Semiconductors: UM10204 I2C-bus specification and user manual. 14.10.2010 HAW - Arduino 1
 The I2C Bus Introduction The I2C-bus is a de facto world standard that is now implemented in over 1000 different ICs manufactured by more than 50 companies. Additionally, the versatile I2C-bus is used
The I2C Bus Introduction The I2C-bus is a de facto world standard that is now implemented in over 1000 different ICs manufactured by more than 50 companies. Additionally, the versatile I2C-bus is used
Using XGATE to Implement LIN Communication on HCS12X Daniel Malik 8/16-Bit Products Division East Kilbride, Scotland
 Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN2732 Rev. 0, 05/2004 Using XGATE to Implement LIN Communication on HCS12X By Daniel Malik 8/16-Bit Products Division East Kilbride, Scotland
Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN2732 Rev. 0, 05/2004 Using XGATE to Implement LIN Communication on HCS12X By Daniel Malik 8/16-Bit Products Division East Kilbride, Scotland
Eureka Technology. Understanding SD, SDIO and MMC Interface. by Eureka Technology Inc. May 26th, 2011. Copyright (C) All Rights Reserved
 Understanding SD, SDIO and MMC Interface by Eureka Technology Inc. May 26th, 2011 Copyright (C) All Rights Reserved Copyright by Eureka Technology Inc. All Rights Reserved Introduction This white paper
Understanding SD, SDIO and MMC Interface by Eureka Technology Inc. May 26th, 2011 Copyright (C) All Rights Reserved Copyright by Eureka Technology Inc. All Rights Reserved Introduction This white paper
Handling Freescale Pressure Sensors
 Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Rev 3, 11/2006 Handling Freescale Pressure by: William McDonald INTRODUCTION Smaller package outlines and higher board densities require the need for automated
Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Rev 3, 11/2006 Handling Freescale Pressure by: William McDonald INTRODUCTION Smaller package outlines and higher board densities require the need for automated
MC13783 Buck and Boost Inductor Sizing
 Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN3294 Rev. 0.1, 01/2010 MC13783 Buck and Boost Inductor Sizing by: Power Management Application Team 1 Introduction The purpose of this application
Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN3294 Rev. 0.1, 01/2010 MC13783 Buck and Boost Inductor Sizing by: Power Management Application Team 1 Introduction The purpose of this application
i.mx Applications Processors with Hantro's Multimedia Framework
 Freescale Semiconductor White Paper IMXHANTROWP/D Rev. 2, 09/2004 i.mx Applications Processors with Hantro's Multimedia Framework By: Clint Powell, Freescale Semiconductor Inc. Marko Nurro, Hantro Products
Freescale Semiconductor White Paper IMXHANTROWP/D Rev. 2, 09/2004 i.mx Applications Processors with Hantro's Multimedia Framework By: Clint Powell, Freescale Semiconductor Inc. Marko Nurro, Hantro Products
DS1104 R&D Controller Board
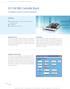 DS1104 R&D Controller Board Cost-effective system for controller development Highlights Single-board system with real-time hardware and comprehensive I/O Cost-effective PCI hardware for use in PCs Application
DS1104 R&D Controller Board Cost-effective system for controller development Highlights Single-board system with real-time hardware and comprehensive I/O Cost-effective PCI hardware for use in PCs Application
Semiconductor Device Technology for Implementing System Solutions: Memory Modules
 Hitachi Review Vol. 47 (1998), No. 4 141 Semiconductor Device Technology for Implementing System Solutions: Memory Modules Toshio Sugano Atsushi Hiraishi Shin ichi Ikenaga ABSTRACT: New technology is producing
Hitachi Review Vol. 47 (1998), No. 4 141 Semiconductor Device Technology for Implementing System Solutions: Memory Modules Toshio Sugano Atsushi Hiraishi Shin ichi Ikenaga ABSTRACT: New technology is producing
Architectures, Processors, and Devices
 Architectures, Processors, and Devices Development Article Copyright 2009 ARM Limited. All rights reserved. ARM DHT 0001A Development Article Copyright 2009 ARM Limited. All rights reserved. Release Information
Architectures, Processors, and Devices Development Article Copyright 2009 ARM Limited. All rights reserved. ARM DHT 0001A Development Article Copyright 2009 ARM Limited. All rights reserved. Release Information
Avalon Interface Specifications
 Avalon Interface Specifications Subscribe MNL-AVABUSREF 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com TOC-2 Contents 1. Introduction to the Avalon Interface Specifications... 1-1 1.1 Avalon Properties
Avalon Interface Specifications Subscribe MNL-AVABUSREF 101 Innovation Drive San Jose, CA 95134 www.altera.com TOC-2 Contents 1. Introduction to the Avalon Interface Specifications... 1-1 1.1 Avalon Properties
Windows 7: Using USB TAP on a Classic CodeWarrior Installation (MGT V9.2 DSC V8.3)
 Freescale Semiconductor Document Number: AN4338 Application Note Rev. 1.0, 12/2011 Windows 7: Using USB TAP on a Classic CodeWarrior Installation (MGT V9.2 DSC V8.3) Technical Information & Commercial
Freescale Semiconductor Document Number: AN4338 Application Note Rev. 1.0, 12/2011 Windows 7: Using USB TAP on a Classic CodeWarrior Installation (MGT V9.2 DSC V8.3) Technical Information & Commercial
Production Flash Programming Best Practices for Kinetis K- and L-series MCUs
 Freescale Semiconductor Document Number:AN4835 Application Note Rev 1, 05/2014 Production Flash Programming Best Practices for Kinetis K- and L-series MCUs by: Melissa Hunter 1 Introduction This application
Freescale Semiconductor Document Number:AN4835 Application Note Rev 1, 05/2014 Production Flash Programming Best Practices for Kinetis K- and L-series MCUs by: Melissa Hunter 1 Introduction This application
The Orca Chip... Heart of IBM s RISC System/6000 Value Servers
 The Orca Chip... Heart of IBM s RISC System/6000 Value Servers Ravi Arimilli IBM RISC System/6000 Division 1 Agenda. Server Background. Cache Heirarchy Performance Study. RS/6000 Value Server System Structure.
The Orca Chip... Heart of IBM s RISC System/6000 Value Servers Ravi Arimilli IBM RISC System/6000 Division 1 Agenda. Server Background. Cache Heirarchy Performance Study. RS/6000 Value Server System Structure.
Computer Systems Structure Input/Output
 Computer Systems Structure Input/Output Peripherals Computer Central Processing Unit Main Memory Computer Systems Interconnection Communication lines Input Output Ward 1 Ward 2 Examples of I/O Devices
Computer Systems Structure Input/Output Peripherals Computer Central Processing Unit Main Memory Computer Systems Interconnection Communication lines Input Output Ward 1 Ward 2 Examples of I/O Devices
Freescale Embedded GUI Converter Utility 2.0 Quick User Guide
 Freescale Semiconductor User Guide Document Number: EGUICUG Rev. 1, 08/2010 Freescale Embedded GUI Converter Utility 2.0 Quick User Guide 1 Introduction The Freescale Embedded GUI Converter Utility 2.0
Freescale Semiconductor User Guide Document Number: EGUICUG Rev. 1, 08/2010 Freescale Embedded GUI Converter Utility 2.0 Quick User Guide 1 Introduction The Freescale Embedded GUI Converter Utility 2.0
Am186ER/Am188ER AMD Continues 16-bit Innovation
 Am186ER/Am188ER AMD Continues 16-bit Innovation 386-Class Performance, Enhanced System Integration, and Built-in SRAM Problem with External RAM All embedded systems require RAM Low density SRAM moving
Am186ER/Am188ER AMD Continues 16-bit Innovation 386-Class Performance, Enhanced System Integration, and Built-in SRAM Problem with External RAM All embedded systems require RAM Low density SRAM moving
Software engineering for real-time systems
 Introduction Software engineering for real-time systems Objectives To: Section 1 Introduction to real-time systems Outline the differences between general-purpose applications and real-time systems. Give
Introduction Software engineering for real-time systems Objectives To: Section 1 Introduction to real-time systems Outline the differences between general-purpose applications and real-time systems. Give
Intel StrongARM SA-110 Microprocessor
 Intel StrongARM SA-110 Microprocessor Product Features Brief Datasheet The Intel StrongARM SA-110 Microprocessor (SA-110), the first member of the StrongARM family of high-performance, low-power microprocessors,
Intel StrongARM SA-110 Microprocessor Product Features Brief Datasheet The Intel StrongARM SA-110 Microprocessor (SA-110), the first member of the StrongARM family of high-performance, low-power microprocessors,
Computer Organization & Architecture Lecture #19
 Computer Organization & Architecture Lecture #19 Input/Output The computer system s I/O architecture is its interface to the outside world. This architecture is designed to provide a systematic means of
Computer Organization & Architecture Lecture #19 Input/Output The computer system s I/O architecture is its interface to the outside world. This architecture is designed to provide a systematic means of
SoC-Based Microcontroller Bus Design In High Bandwidth Embedded Applications
 SoC-Based Microcontroller Bus Design In High Bandwidth Embedded Applications White Paper Abstract 32-bit embedded designs increasingly require real-time control of highbandwidth data streams over a network.
SoC-Based Microcontroller Bus Design In High Bandwidth Embedded Applications White Paper Abstract 32-bit embedded designs increasingly require real-time control of highbandwidth data streams over a network.
Open Flow Controller and Switch Datasheet
 Open Flow Controller and Switch Datasheet California State University Chico Alan Braithwaite Spring 2013 Block Diagram Figure 1. High Level Block Diagram The project will consist of a network development
Open Flow Controller and Switch Datasheet California State University Chico Alan Braithwaite Spring 2013 Block Diagram Figure 1. High Level Block Diagram The project will consist of a network development
What is a bus? A Bus is: Advantages of Buses. Disadvantage of Buses. Master versus Slave. The General Organization of a Bus
 Datorteknik F1 bild 1 What is a bus? Slow vehicle that many people ride together well, true... A bunch of wires... A is: a shared communication link a single set of wires used to connect multiple subsystems
Datorteknik F1 bild 1 What is a bus? Slow vehicle that many people ride together well, true... A bunch of wires... A is: a shared communication link a single set of wires used to connect multiple subsystems
Real Time Development of MC Applications using the PC Master Software Visualization Tool. 1. Introduction. 2. Development of Motor Control.
 Freescale Semiconductor Application Note AN1948 Rev. 1, 11/2005 Real Time Development of MC Applications using the PC Master Software Visualization Tool The PC Master Software Visualization Tool Simplifies
Freescale Semiconductor Application Note AN1948 Rev. 1, 11/2005 Real Time Development of MC Applications using the PC Master Software Visualization Tool The PC Master Software Visualization Tool Simplifies
MICROPROCESSOR. Exclusive for IACE Students www.iace.co.in iacehyd.blogspot.in Ph: 9700077455/422 Page 1
 MICROPROCESSOR A microprocessor incorporates the functions of a computer s central processing unit (CPU) on a single Integrated (IC), or at most a few integrated circuit. It is a multipurpose, programmable
MICROPROCESSOR A microprocessor incorporates the functions of a computer s central processing unit (CPU) on a single Integrated (IC), or at most a few integrated circuit. It is a multipurpose, programmable
SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA
 SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA The B Series logic gates are constructed with P and N channel enhancement mode devices in a single monolithic structure (Complementary MOS). Their primary use is where low
SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA The B Series logic gates are constructed with P and N channel enhancement mode devices in a single monolithic structure (Complementary MOS). Their primary use is where low
Comparison of MC9S08QE128 and MCF51QE128 Microcontrollers Scott Pape and Eduardo Montanez Systems Engineering, Freescale Microcontroller Division
 Freescale Semiconductor White Paper Document Number: QE128COMPWP Rev. 0, 05/2007 Comparison of MC9S08QE128 and MCF51QE128 Microcontrollers by: Scott Pape and Eduardo Montanez Systems Engineering, Freescale
Freescale Semiconductor White Paper Document Number: QE128COMPWP Rev. 0, 05/2007 Comparison of MC9S08QE128 and MCF51QE128 Microcontrollers by: Scott Pape and Eduardo Montanez Systems Engineering, Freescale
Techniques and Tools for Software Analysis
 Techniques and Tools for Software Analysis Freescale Semiconductor Document Number: CODETESTTECHWP Rev. 0 11/2005 Understanding how software development can be optimized through the use of software analysis
Techniques and Tools for Software Analysis Freescale Semiconductor Document Number: CODETESTTECHWP Rev. 0 11/2005 Understanding how software development can be optimized through the use of software analysis
User Interface Design using CGI Programming and Boa Web Server on M5249C3 Board
 Freescale Semiconductor Application Note AN3238 Rev. 0, 02/2006 User Interface Design using CGI Programming and Boa Web Server on M5249C3 Board by: H.K. Au MCD Applications 1 Introduction This application
Freescale Semiconductor Application Note AN3238 Rev. 0, 02/2006 User Interface Design using CGI Programming and Boa Web Server on M5249C3 Board by: H.K. Au MCD Applications 1 Introduction This application
PC Base Adapter Daughter Card UART GPIO. Figure 1. ToolStick Development Platform Block Diagram
 TOOLSTICK VIRTUAL TOOLS USER S GUIDE RELEVANT DEVICES 1. Introduction The ToolStick development platform consists of a ToolStick Base Adapter and a ToolStick Daughter card. The ToolStick Virtual Tools
TOOLSTICK VIRTUAL TOOLS USER S GUIDE RELEVANT DEVICES 1. Introduction The ToolStick development platform consists of a ToolStick Base Adapter and a ToolStick Daughter card. The ToolStick Virtual Tools
How To Control A Motor Control On An Hvac Platform
 Freescale Semiconductor Document Number:AN4616 Application Note Rev. 0, 10/2012 Flap Motor Control Based On HVAC Platform by: Shawn Shi, Albert Chen, Alex Liu 1 Introduction According to the world market
Freescale Semiconductor Document Number:AN4616 Application Note Rev. 0, 10/2012 Flap Motor Control Based On HVAC Platform by: Shawn Shi, Albert Chen, Alex Liu 1 Introduction According to the world market
Von der Hardware zur Software in FPGAs mit Embedded Prozessoren. Alexander Hahn Senior Field Application Engineer Lattice Semiconductor
 Von der Hardware zur Software in FPGAs mit Embedded Prozessoren Alexander Hahn Senior Field Application Engineer Lattice Semiconductor AGENDA Overview Mico32 Embedded Processor Development Tool Chain HW/SW
Von der Hardware zur Software in FPGAs mit Embedded Prozessoren Alexander Hahn Senior Field Application Engineer Lattice Semiconductor AGENDA Overview Mico32 Embedded Processor Development Tool Chain HW/SW
http://onsemi.com MARKING DIAGRAMS LOGIC DIAGRAM PDIP 16 P SUFFIX CASE 648 DIP PIN ASSIGNMENT ORDERING INFORMATION CDIP 16 L SUFFIX CASE 620
 The MC10 is a dual master slave dc coupled J K flip flop. Asynchro nous set (S) and reset (R) are provided. The set and reset inputs override the clock. A common clock is provided with separate J K inputs.
The MC10 is a dual master slave dc coupled J K flip flop. Asynchro nous set (S) and reset (R) are provided. The set and reset inputs override the clock. A common clock is provided with separate J K inputs.
