Thermal gelation of whey protein at different ph values
|
|
|
- Milton Flowers
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Thermal gelation of whey protein at different ph values Suzana Rimac Brnčić, Vesna Lelas, Mladen Brnčić, Tomislav Bosiljkov, Damir Ježek, Marija Badanjak Faculty of Food Technology and Biotechnology, Pierottijeva 6, Zagreb, Croatia Gelation is an important functional property of whey proteins. Their ability to form heat induced gels and provide appropriate texture is determined by its molecular structure (primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary), interactions with other components (salts, acids, urea) and processing conditions (ph, ionic strength, heating temperature, heating and cooling rate). The objective of this work was to define gel texture changes of whey protein isolates (WPI) at various ph values in function of following processing operations: tribomechanical activation and enzymatic hydrolysis. Whey protein gels were prepared by heating dispersions of two commercial powdered whey protein isolates before and after tribomechanical activation and enzymatic hydrolysis, respectively. The results obtained showed that tribomechanical activation as well as enzymatic hydrolysis influenced the gelation ability. Texture of gels was affected by ph. Gels prepared at ph 3 showed higher hardness than gels at ph 7. This work suggests that desired modification of gel texture can be achieved in order to enhance the suitability of WPI for incorporation into various processed and formulated food products. 1. Introduction Whey is liquid by-product of the cheese making process which can be further processed into spray dried products like for instance whey protein concentrates (WPC), whey protein isolates (WPI) or whey protein hydrolysates (WPH)). Characteristics of different types of whey protein powder available on the market are related to the chemical composition and processing technique. Whey proteins are widely used as important ingredients in different foods (dairy, meat and bakery products) due to their unique nutritional and functional properties. Processing steps can alter the characteristics of whey protein products which can result in the modification of whey protein structure and functionality (i.e. foaming, emulsification, gelation). The two major whey proteins are β-lactoglobulin (β-lg) and α-lactalbumin (α-lac). β- lactoglobulin is primary gelling agent while α-lactalbumin has got good emulsifying properties. (Gezimati et al., 1997; Rojas et al., 1997).The gelling properties of thermally induced gels are influenced by concentration, heating rate, extent of denaturation, ionic strength, ph and the presence of specific ions.
2 Gelation is generated by the action of heat, pressure and by divalent cations (Schmidt, 1984.). Most protein gels are prepared by heating. Thermal gelation of whey proteins is a two step mechanism. First step involves an initial denaturation-unfolding of whey protein molecules, followed by rearrangements and aggregation of functional groups which become available for intermolecular interactions under appropriate conditions, resulting in a three-dimensional gel network (Krešić et al., 2008). This phenomenon is important in food industry due to strong effect on rheological and textural properties of food. 2. Materials and methods In this work research was conducted with whey protein isolate BiPRO (Manufacturer: Davisco Foods International, Le Suer, SAD), whey protein isolate RT- 90 (Manufacturer: Main Street Ingredients, La Crosse, SAD), commercial whey protein hydrolysate BioZate 5 (Manufacturer: Davisco Foods International, Le Suer, SAD) and commercial whey protein hydrolysate RT-80 as well (Manufacturer: Main Street Ingredients, La Crosse, SAD). Chemical composition of each sample was declared by manufacturer and is presented in table 1. Table 1: Chemical composition of whey protein isolates and whey protein hydrolysates Sample Protein Lactose Fat Water Ash Whey protein isolate 92,0 1,0 0,3 5,0 2,0 BiPRO Whey protein isolate 90,0 0,8 0,5 4,2 2,5 RT-90 Whey protein hydrolysate Biozate 5 90,0 0,1 0,5 5,0 4,5 Whey protein hydrolysate RT-80 81,0 5,0 6,0 4,0 4,0 Tribomechanical activation Samples were treated in the laboratory using the equipment devised for tribomechanical activation (figure 1).The treatment was carried out at rotor speed r.p.m. and at ambient temperature. TMA equipment is made up of housing and two rotor disks.the disks rotate in opposite directions at the same angular rate. The particles are accelerated and, because of the repeated change of direction of motion, are in constant collision, which causes friction in short time intervals (less than s).
3 Figure 1. Laboratory equipment for tribomechanical activation (Herceg et al., 2004a) Gel preparation Whey protein solutions were prepared by dissolution of the powder in deionised distilled water and stirring with a magnetic stirrer for 90 min at room temperature in beakers at a concentration of 10wt%. The ph of the solutions was adjusted using 1 N HCl and 1 N NaOH. Beakers were placed in a water bath heated at 80 C for 30 minutes. After the heat treatment, the solutions were rapidly cooled to 10 C in an ice bath and stored in a refrigerator overnight. Gels were placed at room temperature 2h before texture analysis. Gel texture properties Gel texture parameters were determined by a Texture analyzer HD+ (Stable Micro System, UK). The gels were penetrated with a xx-mm diameter cylinder probe. A force-time curve was obtained at a crosshead speed of 0.5 mm/s. Hardness at fracture was determined from the texture analysis of the gels. 3. Results and discussion The whey proteins are compact globular proteins with a relatively uniform distribution of a chain of polar (hydrophobic), non-polar (neutral) and uncharged and charged remains of amino acids. The wrinkled intramolecular structure of these proteins is a result of the disulfide bonds (S S) between the remains of cisteine inside the molecules, mainly covered with hydrophobic remains (Tratnik, 1998). During tribomechanical treatment of the whey proteins, the protein globules were mechanically divided, producing a larger number of protein fragments and peptides (Herceg et al., 2004b).
4 During hydrolysis proteins are broken down into peptides of different sizes and free amino acids, Consequently, the extent of the interactions amongst the exposed functional groups of whey proteins after tribomechanical treatment and enzymatic hydrolysis increases. This interactions are responsible for the network strength. Also, an important factor in the gelation process of whey proteins and characteristics of the obtained gels is ph. Namely, ph affects the net charge carried by the protein. Textural properties of gels obtained by heating (80 C/30 min) of 10% solutions of whey protein isolates with different ph values (3,0; 7,0 i 9,0) are presented in figures 2-5. At ph value 3 the harder gels were formed in compliance with gels at ph 7. However, at ph values 7 harder gels were formed by hydrolisates, and with ph value 3 substantially greater hardness of the gels were prove to be from untreated proteins. No gels formation was established at ph 9. Figure 2. Hardness of treated and untreated whey isolate protein gels Bipro at ph 3
5 Figure 3. Hardness of treated and untreated whey isolate protein gels Bipro at ph 7 Figure 4. Hardness of treated and untreated whey isolate protein gels RT at ph 3
6 Figure 5. Hardness of treated and untreated whey isolate protein gels RT at ph 7 References Gezimati, J., Creamer, L.K., Singh, H. (1997) Heat induced interaction and gelation of mixtures of β-lactoglobulin and α-lactalbumin. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 45, Herceg, Z., Lelas, V., Brnčić, M., Tripalo, B. Ježek, D Fine milling and micronization of organic and inorganic materials under dynamic conditions. Powder technology, 139, Herceg, Z., Lelas, V., Brnčić, M., Tripalo, B., Ježek, D Tribomechanical micronization and activation of whey protein concentrate and zeolite, Sadhana 29, part 1, Krešić, G., Lelas, V., Režek Jambrak, A., Herceg, Z., Rimac Brnčić,S., 2008, Influence of novel food processing techologies on the rheological and thermophysical properties of whey proteins, Journal of Food Engineering, 87, Rojas, S.A., Goff, H.D., Senaratne, V., Dalgliesh, D.G., Flores, A. (1997) Gelation of commercial fractions of β-lactoglobulin and α-lactalbumin. International Dairy Journal, 7, Schmidt, R.H. (1984) Effect of processing on whey protein functionality. Journal of Dairy Science, 67, Tratnik, Lj Milk-technology, biochemistry and microbiology. (pp ). Zagreb, Croatia: Croatian Milk Society.
F. Morgan, J.-J. Maugas
 Whey, the natural source for a broad range of food ingredients F. Morgan, J.-J. Maugas LACTALIS R&D Whey Skim milk Milk Casein production Cheese production Acid Rennet Fresh cheeses Soft cheeses Semi-hard
Whey, the natural source for a broad range of food ingredients F. Morgan, J.-J. Maugas LACTALIS R&D Whey Skim milk Milk Casein production Cheese production Acid Rennet Fresh cheeses Soft cheeses Semi-hard
Dairy Proteins. Table of Contents. Section Page. Cheese Milk Protein Review 2. Basic Flows and Definitions of Milk Products 4
 Dairy Proteins This document, prepared by the Wisconsin Center for Dairy Research and the Wisconsin Milk Marketing Board, is intended to help clarify the present dairy protein issue. It can also be used
Dairy Proteins This document, prepared by the Wisconsin Center for Dairy Research and the Wisconsin Milk Marketing Board, is intended to help clarify the present dairy protein issue. It can also be used
Rennet coagulation of milk. Tiiu-Maie Laht
 Rennet coagulation of milk Tiiu-Maie Laht Cheese Coagulation of casein and trapping fat globules in the formed structure is one of the most important technological ideas of the food fermentations Coagulation
Rennet coagulation of milk Tiiu-Maie Laht Cheese Coagulation of casein and trapping fat globules in the formed structure is one of the most important technological ideas of the food fermentations Coagulation
WHEY PRODUCTS. Demineralised whey powder is made by removing dissolved salts and water.
 WHEY PRDUCTS Whey is the portion of milk left after cheese or casein is made. Whey is about 96% water but contains some valuable protein, much lactose (milk sugar) and various dissolved salts. Years ago,
WHEY PRDUCTS Whey is the portion of milk left after cheese or casein is made. Whey is about 96% water but contains some valuable protein, much lactose (milk sugar) and various dissolved salts. Years ago,
18.2 Protein Structure and Function: An Overview
 18.2 Protein Structure and Function: An Overview Protein: A large biological molecule made of many amino acids linked together through peptide bonds. Alpha-amino acid: Compound with an amino group bonded
18.2 Protein Structure and Function: An Overview Protein: A large biological molecule made of many amino acids linked together through peptide bonds. Alpha-amino acid: Compound with an amino group bonded
Separation of Amino Acids by Paper Chromatography
 Separation of Amino Acids by Paper Chromatography Chromatography is a common technique for separating chemical substances. The prefix chroma, which suggests color, comes from the fact that some of the
Separation of Amino Acids by Paper Chromatography Chromatography is a common technique for separating chemical substances. The prefix chroma, which suggests color, comes from the fact that some of the
Chapter 5 Classification of Organic Compounds by Solubility
 Chapter 5 Classification of Organic Compounds by Solubility Deductions based upon interpretation of simple solubility tests can be extremely useful in organic structure determination. Both solubility and
Chapter 5 Classification of Organic Compounds by Solubility Deductions based upon interpretation of simple solubility tests can be extremely useful in organic structure determination. Both solubility and
Introduction. Emulsify with water. Asphalt Emulsions 101. Asphalt Binder Properties. Why Heat Asphalt? So It Can Be:
 Asphalt Emulsions 101 Introduction Chris Lubbers Technical Sales and Marketing Mgr Kraton Polymers, LLC 50 TH Annual Idaho Asphalt Conference Moscow, ID October 28, 2010 Semi Solid Liquid Asphalt Binder
Asphalt Emulsions 101 Introduction Chris Lubbers Technical Sales and Marketing Mgr Kraton Polymers, LLC 50 TH Annual Idaho Asphalt Conference Moscow, ID October 28, 2010 Semi Solid Liquid Asphalt Binder
DNA SPOOLING 1 ISOLATION OF DNA FROM ONION
 DNA SPOOLING 1 ISOLATION OF DNA FROM ONION INTRODUCTION This laboratory protocol will demonstrate several basic steps required for isolation of chromosomal DNA from cells. To extract the chromosomal DNA,
DNA SPOOLING 1 ISOLATION OF DNA FROM ONION INTRODUCTION This laboratory protocol will demonstrate several basic steps required for isolation of chromosomal DNA from cells. To extract the chromosomal DNA,
Organic Chemistry Lab Experiment 4 Preparation and Properties of Soap
 Organic Chemistry Lab Experiment 4 Preparation and Properties of Soap Introduction A soap is the sodium or potassium salt of a long-chain fatty acid. The fatty acid usually contains 12 to 18 carbon atoms.
Organic Chemistry Lab Experiment 4 Preparation and Properties of Soap Introduction A soap is the sodium or potassium salt of a long-chain fatty acid. The fatty acid usually contains 12 to 18 carbon atoms.
Thom Huppertz Inge Gazi
 Thom Huppertz Principal Scientist, Dairy and Ingredient Technology, NIZO food research Inge Gazi Project Manager, NIZO food research Milk protein concentrate functionality through optimised product-process
Thom Huppertz Principal Scientist, Dairy and Ingredient Technology, NIZO food research Inge Gazi Project Manager, NIZO food research Milk protein concentrate functionality through optimised product-process
8/20/2012 H C OH H R. Proteins
 Proteins Rubisco monomer = amino acids 20 different amino acids polymer = polypeptide protein can be one or more polypeptide chains folded & bonded together large & complex 3-D shape hemoglobin Amino acids
Proteins Rubisco monomer = amino acids 20 different amino acids polymer = polypeptide protein can be one or more polypeptide chains folded & bonded together large & complex 3-D shape hemoglobin Amino acids
Biological Molecules
 Biological Molecules I won t lie. This is probably the most boring topic you have ever done in any science. It s pretty much as simple as this: learn the material deal with it. Enjoy don t say I didn t
Biological Molecules I won t lie. This is probably the most boring topic you have ever done in any science. It s pretty much as simple as this: learn the material deal with it. Enjoy don t say I didn t
New Processes for New Products. Impact of protein modification designed functionalities as food ingredients
 New Processes for New Products Impact of protein modification designed functionalities as food ingredients E. Allen Foegeding Department of Food, Bioprocessing and Nutrition Sciences North Carolina State
New Processes for New Products Impact of protein modification designed functionalities as food ingredients E. Allen Foegeding Department of Food, Bioprocessing and Nutrition Sciences North Carolina State
LAB 3: DIGESTION OF ORGANIC MACROMOLECULES
 LAB 3: DIGESTION OF ORGANIC MACROMOLECULES INTRODUCTION Enzymes are a special class of proteins that lower the activation energy of biological reactions. These biological catalysts change the rate of chemical
LAB 3: DIGESTION OF ORGANIC MACROMOLECULES INTRODUCTION Enzymes are a special class of proteins that lower the activation energy of biological reactions. These biological catalysts change the rate of chemical
Built from 20 kinds of amino acids
 Built from 20 kinds of amino acids Each Protein has a three dimensional structure. Majority of proteins are compact. Highly convoluted molecules. Proteins are folded polypeptides. There are four levels
Built from 20 kinds of amino acids Each Protein has a three dimensional structure. Majority of proteins are compact. Highly convoluted molecules. Proteins are folded polypeptides. There are four levels
6 Characterization of Casein and Bovine Serum Albumin
 6 Characterization of Casein and Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) Objectives: A) To separate a mixture of casein and bovine serum albumin B) to characterize these proteins based on their solubilities as a function
6 Characterization of Casein and Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) Objectives: A) To separate a mixture of casein and bovine serum albumin B) to characterize these proteins based on their solubilities as a function
Catalase Enzyme Lab. Background information
 Catalase Enzyme Lab Background information Liver and other living tissues contain the enzyme catalase. This enzyme breaks down hydrogen peroxide, which is a harmful by-product of the process of cellular
Catalase Enzyme Lab Background information Liver and other living tissues contain the enzyme catalase. This enzyme breaks down hydrogen peroxide, which is a harmful by-product of the process of cellular
ETHYL LAUROYL ARGINATE Chemical and Technical Assessment. Prepared by Yoko Kawamura, Ph.D. and Brian Whitehouse, Ph.D., for the 69 th JECFA
 ETHYL LAURYL ARGINATE Chemical and Technical Assessment Prepared by Yoko Kawamura, Ph.D. and Brian Whitehouse, Ph.D., for the 69 th JECFA 1. Summary Ethyl lauroyl arginate is synthesized by esterifying
ETHYL LAURYL ARGINATE Chemical and Technical Assessment Prepared by Yoko Kawamura, Ph.D. and Brian Whitehouse, Ph.D., for the 69 th JECFA 1. Summary Ethyl lauroyl arginate is synthesized by esterifying
Chemical Processes of Digestion
 Chemical Processes of Digestion Objective: To explain in short essays or diagrams how carbohydrates, proteins, and fats are digested into end products that can be absorbed into the blood, at the level
Chemical Processes of Digestion Objective: To explain in short essays or diagrams how carbohydrates, proteins, and fats are digested into end products that can be absorbed into the blood, at the level
Analysis of Casein and Whey Protein in Whole, 2%, and Skim Milk by Capillary Gel Electrophoresis
 Analysis of Casein and Whey Protein in Whole, 2%, and Skim Milk by Capillary Gel Electrophoresis Marcia Santos, Staff Applications Scientist, Beckman Coulter Life Sciences, Brea, CA USA Mark Lies, Marketing
Analysis of Casein and Whey Protein in Whole, 2%, and Skim Milk by Capillary Gel Electrophoresis Marcia Santos, Staff Applications Scientist, Beckman Coulter Life Sciences, Brea, CA USA Mark Lies, Marketing
Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes. Primary and Secondary Structure Tertiary and Quaternary Structure Protein Hydrolysis and Denaturation
 Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Primary and Secondary Structure Tertiary and Quaternary Structure Protein Hydrolysis and Denaturation 1 Primary Structure of Proteins H 3 N The particular sequence of
Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Primary and Secondary Structure Tertiary and Quaternary Structure Protein Hydrolysis and Denaturation 1 Primary Structure of Proteins H 3 N The particular sequence of
A. A peptide with 12 amino acids has the following amino acid composition: 2 Met, 1 Tyr, 1 Trp, 2 Glu, 1 Lys, 1 Arg, 1 Thr, 1 Asn, 1 Ile, 1 Cys
 Questions- Proteins & Enzymes A. A peptide with 12 amino acids has the following amino acid composition: 2 Met, 1 Tyr, 1 Trp, 2 Glu, 1 Lys, 1 Arg, 1 Thr, 1 Asn, 1 Ile, 1 Cys Reaction of the intact peptide
Questions- Proteins & Enzymes A. A peptide with 12 amino acids has the following amino acid composition: 2 Met, 1 Tyr, 1 Trp, 2 Glu, 1 Lys, 1 Arg, 1 Thr, 1 Asn, 1 Ile, 1 Cys Reaction of the intact peptide
Effect of temperature and ph on the enzymatic activity of salivary amylase
 Effect of temperature and ph on the enzymatic activity of salivary amylase Gae Khalil Rodillas, Nonia Carla Ysabel Samson, Raphael Jaime Santos* and Brylle Tabora Department of Biological Sciences, College
Effect of temperature and ph on the enzymatic activity of salivary amylase Gae Khalil Rodillas, Nonia Carla Ysabel Samson, Raphael Jaime Santos* and Brylle Tabora Department of Biological Sciences, College
Enzyme Lab. DEFINITIONS: 1. Enzyme: 2. Catalase: 3. Catalyze: 4. Hydrolysis: 5. Monomer: 6. Digestion: BACKGROUND INFORMATION
 Enzyme Lab DEFINITIONS: 1. Enzyme: 2. Catalase: 3. Catalyze: 4. Hydrolysis: 5. Monomer: 6. Digestion: BACKGROUND INFORMATION Many living tissues contain the enzyme catalase. This enzyme breaks down hydrogen
Enzyme Lab DEFINITIONS: 1. Enzyme: 2. Catalase: 3. Catalyze: 4. Hydrolysis: 5. Monomer: 6. Digestion: BACKGROUND INFORMATION Many living tissues contain the enzyme catalase. This enzyme breaks down hydrogen
[email protected] 1. Enzyme Function
 [email protected] 1 Enzyme Function National Science Standards Science as Inquiry: Content Standard A: As a result of activities in grades 9-12, all students should develop: Abilities
[email protected] 1 Enzyme Function National Science Standards Science as Inquiry: Content Standard A: As a result of activities in grades 9-12, all students should develop: Abilities
Chapter 2 Chemical Principles
 Chapter 2 Chemical Principles I. Chemistry. [Students should read this section on their own]. a. Chemistry is the study of the interactions between atoms and molecules. b. The atom is the smallest unit
Chapter 2 Chemical Principles I. Chemistry. [Students should read this section on their own]. a. Chemistry is the study of the interactions between atoms and molecules. b. The atom is the smallest unit
Stabilizer Blends and their importance in Ice cream Industry A Review
 New Zealand Food Magazine, 2006 Stabilizer Blends and their importance in Ice cream Industry A Review ABSTRACT Naresh L and Shailaja U. Merchant Lucid Colloids Limited, B 5/7, MIA, Basni, Phase I, Jodhpur,
New Zealand Food Magazine, 2006 Stabilizer Blends and their importance in Ice cream Industry A Review ABSTRACT Naresh L and Shailaja U. Merchant Lucid Colloids Limited, B 5/7, MIA, Basni, Phase I, Jodhpur,
Sample Liver Enzyme Lab
 Sample Liver Enzyme Lab Design Aspect 1: Research Question This lab will be driven by the research question, Do changes in temperature have an effect on the activity of the enzyme catalase? Pearson Baccalaureate:
Sample Liver Enzyme Lab Design Aspect 1: Research Question This lab will be driven by the research question, Do changes in temperature have an effect on the activity of the enzyme catalase? Pearson Baccalaureate:
Prentice Hall. Chemistry (Wilbraham) 2008, National Student Edition - South Carolina Teacher s Edition. High School. High School
 Prentice Hall Chemistry (Wilbraham) 2008, National Student Edition - South Carolina Teacher s Edition High School C O R R E L A T E D T O High School C-1.1 Apply established rules for significant digits,
Prentice Hall Chemistry (Wilbraham) 2008, National Student Edition - South Carolina Teacher s Edition High School C O R R E L A T E D T O High School C-1.1 Apply established rules for significant digits,
Carbohydrates, proteins and lipids
 Carbohydrates, proteins and lipids Chapter 3 MACROMOLECULES Macromolecules: polymers with molecular weights >1,000 Functional groups THE FOUR MACROMOLECULES IN LIFE Molecules in living organisms: proteins,
Carbohydrates, proteins and lipids Chapter 3 MACROMOLECULES Macromolecules: polymers with molecular weights >1,000 Functional groups THE FOUR MACROMOLECULES IN LIFE Molecules in living organisms: proteins,
P Havea & P Watkinson
 Whey protein a realistic approach designed products for the food industry P Havea & P Watkinson Fonterra Research Centre, Palmerston North, New Zealand Introduction Use of whey protein so far dominated
Whey protein a realistic approach designed products for the food industry P Havea & P Watkinson Fonterra Research Centre, Palmerston North, New Zealand Introduction Use of whey protein so far dominated
The Organic Chemistry of Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
 Essential rganic Chemistry Chapter 16 The rganic Chemistry of Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins Amino Acids a-amino carboxylic acids. The building blocks from which proteins are made. H 2 N C 2 H Note:
Essential rganic Chemistry Chapter 16 The rganic Chemistry of Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins Amino Acids a-amino carboxylic acids. The building blocks from which proteins are made. H 2 N C 2 H Note:
http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/h.alshehri
 http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/h.alshehri Definition: Proteins are macromolecules with a backbone formed by polymerization of amino acids. Proteins carry out a number of functions in living organisms: - They
http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/h.alshehri Definition: Proteins are macromolecules with a backbone formed by polymerization of amino acids. Proteins carry out a number of functions in living organisms: - They
CHEMISTRY STANDARDS BASED RUBRIC ATOMIC STRUCTURE AND BONDING
 CHEMISTRY STANDARDS BASED RUBRIC ATOMIC STRUCTURE AND BONDING Essential Standard: STUDENTS WILL UNDERSTAND THAT THE PROPERTIES OF MATTER AND THEIR INTERACTIONS ARE A CONSEQUENCE OF THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER,
CHEMISTRY STANDARDS BASED RUBRIC ATOMIC STRUCTURE AND BONDING Essential Standard: STUDENTS WILL UNDERSTAND THAT THE PROPERTIES OF MATTER AND THEIR INTERACTIONS ARE A CONSEQUENCE OF THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER,
Chemical Basis of Life Module A Anchor 2
 Chemical Basis of Life Module A Anchor 2 Key Concepts: - Water is a polar molecule. Therefore, it is able to form multiple hydrogen bonds, which account for many of its special properties. - Water s polarity
Chemical Basis of Life Module A Anchor 2 Key Concepts: - Water is a polar molecule. Therefore, it is able to form multiple hydrogen bonds, which account for many of its special properties. - Water s polarity
Chem 100 Lab Experiment #9 - ACID/BASE INDICATORS
 Lab #9 Chem 100 Lab Experiment #9 - ACID/BASE INDICATORS Name: Purpose: In this laboratory we will investigate how indicators can be used to test for the presence of acids or bases in a number of common
Lab #9 Chem 100 Lab Experiment #9 - ACID/BASE INDICATORS Name: Purpose: In this laboratory we will investigate how indicators can be used to test for the presence of acids or bases in a number of common
Chapter 3. Protein Structure and Function
 Chapter 3 Protein Structure and Function Broad functional classes So Proteins have structure and function... Fine! -Why do we care to know more???? Understanding functional architechture gives us POWER
Chapter 3 Protein Structure and Function Broad functional classes So Proteins have structure and function... Fine! -Why do we care to know more???? Understanding functional architechture gives us POWER
Enzyme Action: Testing Catalase Activity
 Enzyme Action: Testing Catalase Activity Experiment 6A Many organisms can decompose hydrogen peroxide (H 2 O 2 ) enzymatically. Enzymes are globular proteins, responsible for most of the chemical activities
Enzyme Action: Testing Catalase Activity Experiment 6A Many organisms can decompose hydrogen peroxide (H 2 O 2 ) enzymatically. Enzymes are globular proteins, responsible for most of the chemical activities
Chapter 12 - Proteins
 Roles of Biomolecules Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins 1) Catalytic 2) Transport 3) Regulatory 4) Structural 5) Contractile 6) Protective 7) Storage Nucleic Acids 12.1 -Amino Acids Chapter 12 - Proteins Amino
Roles of Biomolecules Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins 1) Catalytic 2) Transport 3) Regulatory 4) Structural 5) Contractile 6) Protective 7) Storage Nucleic Acids 12.1 -Amino Acids Chapter 12 - Proteins Amino
Sensors 2007, 7 372. 1. Introduction
 Sensors 2007, 7, 371-383 sensors ISSN 1424-8220 2007 by MDPI www.mdpi.org/sensors Full Research Paper SDS-PAGE Analysis of Soluble Proteins in Reconstituted Milk Exposed to Different Heat Treatments Snezana
Sensors 2007, 7, 371-383 sensors ISSN 1424-8220 2007 by MDPI www.mdpi.org/sensors Full Research Paper SDS-PAGE Analysis of Soluble Proteins in Reconstituted Milk Exposed to Different Heat Treatments Snezana
BIOLOGICAL MEMBRANES: FUNCTIONS, STRUCTURES & TRANSPORT
 BIOLOGICAL MEMBRANES: FUNCTIONS, STRUCTURES & TRANSPORT UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY BMLS II / B Pharm II / BDS II VJ Temple
BIOLOGICAL MEMBRANES: FUNCTIONS, STRUCTURES & TRANSPORT UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY BMLS II / B Pharm II / BDS II VJ Temple
A. Types of Mixtures:
 I. MIXTURES: SOLUTIONS 1) mixture = a blend of two or more kinds of matter, each of which retains its own identity and properties a) homogeneous mixture = a mixture that is uniform in composition throughout
I. MIXTURES: SOLUTIONS 1) mixture = a blend of two or more kinds of matter, each of which retains its own identity and properties a) homogeneous mixture = a mixture that is uniform in composition throughout
BOND TYPES: THE CLASSIFICATION OF SUBSTANCES
 BOND TYPES: THE CLASSIFICATION OF SUBSTANCES Every (pure) substance has a unique set of intrinsic properties which distinguishes it from all other substances. What inferences, if any can be made from a
BOND TYPES: THE CLASSIFICATION OF SUBSTANCES Every (pure) substance has a unique set of intrinsic properties which distinguishes it from all other substances. What inferences, if any can be made from a
AP BIOLOGY 2008 SCORING GUIDELINES
 AP BIOLOGY 2008 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 1 1. The physical structure of a protein often reflects and affects its function. (a) Describe THREE types of chemical bonds/interactions found in proteins.
AP BIOLOGY 2008 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 1 1. The physical structure of a protein often reflects and affects its function. (a) Describe THREE types of chemical bonds/interactions found in proteins.
Protein Physics. A. V. Finkelstein & O. B. Ptitsyn LECTURE 1
 Protein Physics A. V. Finkelstein & O. B. Ptitsyn LECTURE 1 PROTEINS Functions in a Cell MOLECULAR MACHINES BUILDING BLOCKS of a CELL ARMS of a CELL ENZYMES - enzymatic catalysis of biochemical reactions
Protein Physics A. V. Finkelstein & O. B. Ptitsyn LECTURE 1 PROTEINS Functions in a Cell MOLECULAR MACHINES BUILDING BLOCKS of a CELL ARMS of a CELL ENZYMES - enzymatic catalysis of biochemical reactions
Chemistry 20 Chapters 15 Enzymes
 Chemistry 20 Chapters 15 Enzymes Enzymes: as a catalyst, an enzyme increases the rate of a reaction by changing the way a reaction takes place, but is itself not changed at the end of the reaction. An
Chemistry 20 Chapters 15 Enzymes Enzymes: as a catalyst, an enzyme increases the rate of a reaction by changing the way a reaction takes place, but is itself not changed at the end of the reaction. An
Hands-On Labs SM-1 Lab Manual
 EXPERIMENT 4: Separation of a Mixture of Solids Read the entire experiment and organize time, materials, and work space before beginning. Remember to review the safety sections and wear goggles when appropriate.
EXPERIMENT 4: Separation of a Mixture of Solids Read the entire experiment and organize time, materials, and work space before beginning. Remember to review the safety sections and wear goggles when appropriate.
The Endless Possibilities of Whey: Still Many Opportunities for Innovation. Prof. Dr. Ernst H. Reimerdes FoodInfoTec (FIT)
 The Endless Possibilities of Whey: Still Many Opportunities for Innovation Prof. Dr. Ernst H. Reimerdes FoodInfoTec (FIT) Food and Nutrition: Yesterday, Today, Tomorrow Industrialisation of traditional
The Endless Possibilities of Whey: Still Many Opportunities for Innovation Prof. Dr. Ernst H. Reimerdes FoodInfoTec (FIT) Food and Nutrition: Yesterday, Today, Tomorrow Industrialisation of traditional
A disaccharide is formed when a dehydration reaction joins two monosaccharides. This covalent bond is called a glycosidic linkage.
 CH 5 Structure & Function of Large Molecules: Macromolecules Molecules of Life All living things are made up of four classes of large biological molecules: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic
CH 5 Structure & Function of Large Molecules: Macromolecules Molecules of Life All living things are made up of four classes of large biological molecules: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic
Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
 1 Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins Introduction Amino Acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. In class you learned the structures of the 20 common amino acids that make up proteins. All
1 Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins Introduction Amino Acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. In class you learned the structures of the 20 common amino acids that make up proteins. All
International Whey Market Overview
 International Whey Market Overview 2009 ADPI/ABI Annual Conference Tage Affertsholt, 1 Agenda 1 2 3 4 5 Introduction Whey market overview Lactose market overview NPD overview Market dynamics & outlook
International Whey Market Overview 2009 ADPI/ABI Annual Conference Tage Affertsholt, 1 Agenda 1 2 3 4 5 Introduction Whey market overview Lactose market overview NPD overview Market dynamics & outlook
Quality Advantages of Food Grade Soybeans from the Upper Midwest: storage perspective. Sam K. C. Chang. Ph.D., Professor; IFT Fellow
 Quality Advantages of Food Grade Soybeans from the Upper Midwest: storage perspective Sam K. C. Chang Ph.D., Professor; IFT Fellow Department of Cereal and Food Sciences North Dakota State University Fargo,
Quality Advantages of Food Grade Soybeans from the Upper Midwest: storage perspective Sam K. C. Chang Ph.D., Professor; IFT Fellow Department of Cereal and Food Sciences North Dakota State University Fargo,
STUDY GUIDE AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES GRADE 11
 STUDY GUIDE AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES GRADE 11 A publication of Impak Onderwysdiens (Pty) Ltd Copyright reserved. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of research, criticism or review as permitted under
STUDY GUIDE AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES GRADE 11 A publication of Impak Onderwysdiens (Pty) Ltd Copyright reserved. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of research, criticism or review as permitted under
List the 3 main types of subatomic particles and indicate the mass and electrical charge of each.
 Basic Chemistry Why do we study chemistry in a biology course? All living organisms are composed of chemicals. To understand life, we must understand the structure, function, and properties of the chemicals
Basic Chemistry Why do we study chemistry in a biology course? All living organisms are composed of chemicals. To understand life, we must understand the structure, function, and properties of the chemicals
Chapter 6. Solution, Acids and Bases
 Chapter 6 Solution, Acids and Bases Mixtures Two or more substances Heterogeneous- different from place to place Types of heterogeneous mixtures Suspensions- Large particles that eventually settle out
Chapter 6 Solution, Acids and Bases Mixtures Two or more substances Heterogeneous- different from place to place Types of heterogeneous mixtures Suspensions- Large particles that eventually settle out
Experiment #10: Liquids, Liquid Mixtures and Solutions
 Experiment #10: Liquids, Liquid Mixtures and Solutions Objectives: This experiment is a broad survey of the physical properties of liquids. We will investigate solvent/solute mixtures. We will study and
Experiment #10: Liquids, Liquid Mixtures and Solutions Objectives: This experiment is a broad survey of the physical properties of liquids. We will investigate solvent/solute mixtures. We will study and
Acids & Bases: Using Purple Cabbage as a ph indicator. Grade 9 Activity Plan
 Acids & Bases: Using Purple Cabbage as a ph indicator Grade 9 Activity Plan 1 Acids, Bases & Purple Cabbage Objectives: 1. To demonstrate the basic physical and chemical properties of acids and bases.
Acids & Bases: Using Purple Cabbage as a ph indicator Grade 9 Activity Plan 1 Acids, Bases & Purple Cabbage Objectives: 1. To demonstrate the basic physical and chemical properties of acids and bases.
Warm-Up 9/9. 1. Define the term matter. 2. Name something in this room that is not matter.
 Warm-Up 9/9 1. Define the term matter. 2. Name something in this room that is not matter. Warm-Up 9/16 1. List the three most important rules of lab safety. 2. Would you classify jello as a solid or a
Warm-Up 9/9 1. Define the term matter. 2. Name something in this room that is not matter. Warm-Up 9/16 1. List the three most important rules of lab safety. 2. Would you classify jello as a solid or a
Recap. Lecture 2. Protein conformation. Proteins. 8 types of protein function 10/21/10. Proteins.. > 50% dry weight of a cell
 Lecture 2 Protein conformation ecap Proteins.. > 50% dry weight of a cell ell s building blocks and molecular tools. More important than genes A large variety of functions http://www.tcd.ie/biochemistry/courses/jf_lectures.php
Lecture 2 Protein conformation ecap Proteins.. > 50% dry weight of a cell ell s building blocks and molecular tools. More important than genes A large variety of functions http://www.tcd.ie/biochemistry/courses/jf_lectures.php
Proteins Functionality & Application. Anneke Martin
 Proteins Functionality & Application Anneke Martin Content Functionality Techno-functionality of proteins Interfacial properties Gelation properties Type of protein networks Water holding Texturizing of
Proteins Functionality & Application Anneke Martin Content Functionality Techno-functionality of proteins Interfacial properties Gelation properties Type of protein networks Water holding Texturizing of
Agarose Gel Electrophoresis with Food Color- Teacher Guide
 Page 1 of 7 Project Home Gateway to the Project Laboratory Activities What the Project can do in the classroom Biotechnology Resources Favorite resources online and in print Agarose Gel Electrophoresis
Page 1 of 7 Project Home Gateway to the Project Laboratory Activities What the Project can do in the classroom Biotechnology Resources Favorite resources online and in print Agarose Gel Electrophoresis
This laboratory explores the affects ph has on a reaction rate. The reaction
 Joy Paul Enzyme Catalyst lab Abstract: This laboratory explores the affects ph has on a reaction rate. The reaction studied was the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide catalyzed by the enzyme peroxidase. Three
Joy Paul Enzyme Catalyst lab Abstract: This laboratory explores the affects ph has on a reaction rate. The reaction studied was the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide catalyzed by the enzyme peroxidase. Three
Ch. 57 MILK AND DAIRY PRODUCTS 7 CHAPTER 57. MILK AND DAIRY PRODUCTS GENERAL PROVISIONS
 Ch. 57 MILK AND DAIRY PRODUCTS 7 CHAPTER 57. MILK AND DAIRY PRODUCTS GENERAL PROVISIONS Subchap. Sec. A. MILK AND DAIRY PRODUCTS DEFINITIONS AND STANDARDS... 57.1 B. LABELING... 57.41 C. OTHER DAIRY PRODUCTS...
Ch. 57 MILK AND DAIRY PRODUCTS 7 CHAPTER 57. MILK AND DAIRY PRODUCTS GENERAL PROVISIONS Subchap. Sec. A. MILK AND DAIRY PRODUCTS DEFINITIONS AND STANDARDS... 57.1 B. LABELING... 57.41 C. OTHER DAIRY PRODUCTS...
Taking Apart the Pieces
 Lab 4 Taking Apart the Pieces How does starting your morning out right relate to relief from a headache? I t is a lazy Saturday morning and you ve just awakened to your favorite cereal Morning Trails and
Lab 4 Taking Apart the Pieces How does starting your morning out right relate to relief from a headache? I t is a lazy Saturday morning and you ve just awakened to your favorite cereal Morning Trails and
10-ml Graduated cylinder 40 ml 3% Hydrogen peroxide solution (found in stores) Straight-edged razor blade Scissors and Forceps (tweezers)
 Name: Class: Date: Objectives * Measure the effects of changes in temperature, ph, and enzyme concentration on reaction rates of an enzyme catalyzed reaction in a controlled experiment. * Explain how environmental
Name: Class: Date: Objectives * Measure the effects of changes in temperature, ph, and enzyme concentration on reaction rates of an enzyme catalyzed reaction in a controlled experiment. * Explain how environmental
Chapter 2. The Chemistry of Life Worksheets
 Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Life Worksheets (Opening image courtesy of David Iberri, http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/file:camkii.png, and under the Creative Commons license CC-BY-SA 3.0.) Lesson 2.1: Matter
Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Life Worksheets (Opening image courtesy of David Iberri, http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/file:camkii.png, and under the Creative Commons license CC-BY-SA 3.0.) Lesson 2.1: Matter
Whey Protein Characteristics
 Technical Report: Written by: Kimberlee (K.J.) Burrington Reviewed by: Shantanu Agarwal As part of a growing health and wellness trend, food and beverage manufacturers are boosting the protein content
Technical Report: Written by: Kimberlee (K.J.) Burrington Reviewed by: Shantanu Agarwal As part of a growing health and wellness trend, food and beverage manufacturers are boosting the protein content
Modes of Membrane Transport
 Modes of Membrane Transport Transmembrane Transport movement of small substances through a cellular membrane (plasma, ER, mitochondrial..) ions, fatty acids, H 2 O, monosaccharides, steroids, amino acids
Modes of Membrane Transport Transmembrane Transport movement of small substances through a cellular membrane (plasma, ER, mitochondrial..) ions, fatty acids, H 2 O, monosaccharides, steroids, amino acids
catalase 2H 2 O 2 (l) ----> 2H 2 O (l) + O 2 (g)
 ENZYME POST LAB QUIZ STUDY GUIDE Below are the answers to the post-lab (Data Analysis) questions. Make sure you UNDERSTAND all of these questions. The post-lab questions will, of course, be different,
ENZYME POST LAB QUIZ STUDY GUIDE Below are the answers to the post-lab (Data Analysis) questions. Make sure you UNDERSTAND all of these questions. The post-lab questions will, of course, be different,
Chapter 13 - LIQUIDS AND SOLIDS
 Chapter 13 - LIQUIDS AND SOLIDS Problems to try at end of chapter: Answers in Appendix I: 1,3,5,7b,9b,15,17,23,25,29,31,33,45,49,51,53,61 13.1 Properties of Liquids 1. Liquids take the shape of their container,
Chapter 13 - LIQUIDS AND SOLIDS Problems to try at end of chapter: Answers in Appendix I: 1,3,5,7b,9b,15,17,23,25,29,31,33,45,49,51,53,61 13.1 Properties of Liquids 1. Liquids take the shape of their container,
About us. SNF has 40% market share, 1 B sales and manufactures 300 000 tons of polymers on a world wide base.
 FLOCARE 2 About us SNF, a French company with headquarter in Andrézieux, is a leading producer of acrylamide based polymers with manufacturing sites in Andrézieux France, Savannah USA and Taixing China.
FLOCARE 2 About us SNF, a French company with headquarter in Andrézieux, is a leading producer of acrylamide based polymers with manufacturing sites in Andrézieux France, Savannah USA and Taixing China.
Chemical Bonds. Chemical Bonds. The Nature of Molecules. Energy and Metabolism < < Covalent bonds form when atoms share 2 or more valence electrons.
 The Nature of Molecules Chapter 2 Energy and Metabolism Chapter 6 Chemical Bonds Molecules are groups of atoms held together in a stable association. Compounds are molecules containing more than one type
The Nature of Molecules Chapter 2 Energy and Metabolism Chapter 6 Chemical Bonds Molecules are groups of atoms held together in a stable association. Compounds are molecules containing more than one type
1. The diagram below represents a biological process
 1. The diagram below represents a biological process 5. The chart below indicates the elements contained in four different molecules and the number of atoms of each element in those molecules. Which set
1. The diagram below represents a biological process 5. The chart below indicates the elements contained in four different molecules and the number of atoms of each element in those molecules. Which set
Lecture 13-14 Conformation of proteins Conformation of a protein three-dimensional structure native state. native condition
 Lecture 13-14 Conformation of proteins Conformation of a protein refers to the three-dimensional structure in its native state. There are many different possible conformations for a molecule as large as
Lecture 13-14 Conformation of proteins Conformation of a protein refers to the three-dimensional structure in its native state. There are many different possible conformations for a molecule as large as
Molecular Cell Biology
 Harvey Lodish Arnold Berk Paul Matsudaira Chris A. Kaiser Monty Krieger Matthew P. Scott Lawrence Zipursky James Darnell Molecular Cell Biology Fifth Edition Chapter 2: Chemical Foundations Copyright 2004
Harvey Lodish Arnold Berk Paul Matsudaira Chris A. Kaiser Monty Krieger Matthew P. Scott Lawrence Zipursky James Darnell Molecular Cell Biology Fifth Edition Chapter 2: Chemical Foundations Copyright 2004
Peptide Bond Amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds to form polypepetide chain.
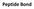 Peptide Bond Peptide Bond Amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds to form polypepetide chain. + H 2 O 2 Peptide bonds are strong and not broken by conditions that denature proteins, such as heating.
Peptide Bond Peptide Bond Amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds to form polypepetide chain. + H 2 O 2 Peptide bonds are strong and not broken by conditions that denature proteins, such as heating.
It is an important tool to assess factors that affect the bioavailability of a drug from a solid preparartion.
 Quality control of tablets Dissolution It is an important tool to assess factors that affect the bioavailability of a drug from a solid preparartion. To ensure that the preparation comply with product
Quality control of tablets Dissolution It is an important tool to assess factors that affect the bioavailability of a drug from a solid preparartion. To ensure that the preparation comply with product
INTERMOLECULAR FORCES
 INTERMOLECULAR FORCES Intermolecular forces- forces of attraction and repulsion between molecules that hold molecules, ions, and atoms together. Intramolecular - forces of chemical bonds within a molecule
INTERMOLECULAR FORCES Intermolecular forces- forces of attraction and repulsion between molecules that hold molecules, ions, and atoms together. Intramolecular - forces of chemical bonds within a molecule
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD [email protected] www.facebook.com/natarboush
 Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD [email protected] www.facebook.com/natarboush α-keratins, bundles of α- helices Contain polypeptide chains organized approximately parallel along a single axis: Consist
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD [email protected] www.facebook.com/natarboush α-keratins, bundles of α- helices Contain polypeptide chains organized approximately parallel along a single axis: Consist
Amino Acids. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. All AA s have the same basic structure: Side Chain. Alpha Carbon. Carboxyl. Group.
 Protein Structure Amino Acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. All AA s have the same basic structure: Side Chain Alpha Carbon Amino Group Carboxyl Group Amino Acid Properties There are
Protein Structure Amino Acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. All AA s have the same basic structure: Side Chain Alpha Carbon Amino Group Carboxyl Group Amino Acid Properties There are
5s Solubility & Conductivity
 5s Solubility & Conductivity OBJECTIVES To explore the relationship between the structures of common household substances and the kinds of solvents in which they dissolve. To demonstrate the ionic nature
5s Solubility & Conductivity OBJECTIVES To explore the relationship between the structures of common household substances and the kinds of solvents in which they dissolve. To demonstrate the ionic nature
CAKE EMULSIFIERS NEW DEVELOPMENTS- ALPHA CRYSTALLINE GELS DRAFT-AMERICAN SOCIETY OF BAKING MEETING- 2001
 CAKE EMULSIFIERS NEW DEVELOPMENTS- ALPHA CRYSTALLINE GELS DRAFT-AMERICAN SOCIETY OF BAKING MEETING- 2001 Emulsion & Emulsifiers Oil and water are immiscible since the interaction results in high energy
CAKE EMULSIFIERS NEW DEVELOPMENTS- ALPHA CRYSTALLINE GELS DRAFT-AMERICAN SOCIETY OF BAKING MEETING- 2001 Emulsion & Emulsifiers Oil and water are immiscible since the interaction results in high energy
Enzymes: Practice Questions #1
 Enzymes: Practice Questions #1 1. Compound X increases the rate of the reaction below. Compound X is most likely A. an enzyme B. a lipid molecule C. an indicator D. an ADP molecule 2. The equation below
Enzymes: Practice Questions #1 1. Compound X increases the rate of the reaction below. Compound X is most likely A. an enzyme B. a lipid molecule C. an indicator D. an ADP molecule 2. The equation below
Proteins and Nucleic Acids
 Proteins and Nucleic Acids Chapter 5 Macromolecules: Proteins Proteins Most structurally & functionally diverse group of biomolecules. : o Involved in almost everything o Enzymes o Structure (keratin,
Proteins and Nucleic Acids Chapter 5 Macromolecules: Proteins Proteins Most structurally & functionally diverse group of biomolecules. : o Involved in almost everything o Enzymes o Structure (keratin,
KINETIC MOLECULAR THEORY OF MATTER
 KINETIC MOLECULAR THEORY OF MATTER The kinetic-molecular theory is based on the idea that particles of matter are always in motion. The theory can be used to explain the properties of solids, liquids,
KINETIC MOLECULAR THEORY OF MATTER The kinetic-molecular theory is based on the idea that particles of matter are always in motion. The theory can be used to explain the properties of solids, liquids,
Enzymes: Amylase Activity in Starch-degrading Soil Isolates
 Enzymes: Amylase Activity in Starch-degrading Soil Isolates Introduction This week you will continue our theme of industrial microbiologist by characterizing the enzyme activity we selected for (starch
Enzymes: Amylase Activity in Starch-degrading Soil Isolates Introduction This week you will continue our theme of industrial microbiologist by characterizing the enzyme activity we selected for (starch
Amino Acids and Proteins
 Amino Acids and Proteins Proteins are composed of amino acids. There are 20 amino acids commonly found in proteins. All have: N2 C α R COO Amino acids at neutral p are dipolar ions (zwitterions) because
Amino Acids and Proteins Proteins are composed of amino acids. There are 20 amino acids commonly found in proteins. All have: N2 C α R COO Amino acids at neutral p are dipolar ions (zwitterions) because
Lab 3 Organic Molecules of Biological Importance
 Name Biology 3 ID Number Lab 3 Organic Molecules of Biological Importance Section 1 - Organic Molecules Section 2 - Functional Groups Section 3 - From Building Blocks to Macromolecules Section 4 - Carbohydrates
Name Biology 3 ID Number Lab 3 Organic Molecules of Biological Importance Section 1 - Organic Molecules Section 2 - Functional Groups Section 3 - From Building Blocks to Macromolecules Section 4 - Carbohydrates
Proteins. Proteins. Amino Acids. Most diverse and most important molecule in. Functions: Functions (cont d)
 Proteins Proteins Most diverse and most important molecule in living i organisms Functions: 1. Structural (keratin in hair, collagen in ligaments) 2. Storage (casein in mother s milk) 3. Transport (HAEMOGLOBIN!)
Proteins Proteins Most diverse and most important molecule in living i organisms Functions: 1. Structural (keratin in hair, collagen in ligaments) 2. Storage (casein in mother s milk) 3. Transport (HAEMOGLOBIN!)
Enzyme Action: Testing Catalase Activity
 Enzyme Action: Testing Catalase Activity Experiment 6A Many organisms can decompose hydrogen peroxide (H 2 O 2 ) enzymatically. Enzymes are globular proteins, responsible for most of the chemical activities
Enzyme Action: Testing Catalase Activity Experiment 6A Many organisms can decompose hydrogen peroxide (H 2 O 2 ) enzymatically. Enzymes are globular proteins, responsible for most of the chemical activities
CHAPTER 6 AN INTRODUCTION TO METABOLISM. Section B: Enzymes
 CHAPTER 6 AN INTRODUCTION TO METABOLISM Section B: Enzymes 1. Enzymes speed up metabolic reactions by lowering energy barriers 2. Enzymes are substrate specific 3. The active site in an enzyme s catalytic
CHAPTER 6 AN INTRODUCTION TO METABOLISM Section B: Enzymes 1. Enzymes speed up metabolic reactions by lowering energy barriers 2. Enzymes are substrate specific 3. The active site in an enzyme s catalytic
Chapter 13 Solution Dynamics. An Introduction to Chemistry by Mark Bishop
 Chapter 13 Solution Dynamics An Introduction to Chemistry by Mark Bishop Chapter Map Why Changes Happen Consider a system that can switch freely between two states, A and B. Probability helps us to predict
Chapter 13 Solution Dynamics An Introduction to Chemistry by Mark Bishop Chapter Map Why Changes Happen Consider a system that can switch freely between two states, A and B. Probability helps us to predict
The Molecules of Cells
 The Molecules of Cells I. Introduction A. Most of the world s population cannot digest milk-based foods. 1. These people are lactose intolerant because they lack the enzyme lactase. 2. This illustrates
The Molecules of Cells I. Introduction A. Most of the world s population cannot digest milk-based foods. 1. These people are lactose intolerant because they lack the enzyme lactase. 2. This illustrates
IV. -Amino Acids: carboxyl and amino groups bonded to -Carbon. V. Polypeptides and Proteins
 IV. -Amino Acids: carboxyl and amino groups bonded to -Carbon A. Acid/Base properties 1. carboxyl group is proton donor! weak acid 2. amino group is proton acceptor! weak base 3. At physiological ph: H
IV. -Amino Acids: carboxyl and amino groups bonded to -Carbon A. Acid/Base properties 1. carboxyl group is proton donor! weak acid 2. amino group is proton acceptor! weak base 3. At physiological ph: H
Chapter 5. The Structure and Function of Macromolecule s
 Chapter 5 The Structure and Function of Macromolecule s Most Macromolecules are polymers: Polymer: (poly: many; mer: part) Large molecules consisting of many identical or similar subunits connected together.
Chapter 5 The Structure and Function of Macromolecule s Most Macromolecules are polymers: Polymer: (poly: many; mer: part) Large molecules consisting of many identical or similar subunits connected together.
Lecture Overview. Hydrogen Bonds. Special Properties of Water Molecules. Universal Solvent. ph Scale Illustrated. special properties of water
 Lecture Overview special properties of water > water as a solvent > ph molecules of the cell > properties of carbon > carbohydrates > lipids > proteins > nucleic acids Hydrogen Bonds polarity of water
Lecture Overview special properties of water > water as a solvent > ph molecules of the cell > properties of carbon > carbohydrates > lipids > proteins > nucleic acids Hydrogen Bonds polarity of water
Chapter 5: The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules
 Name Period Concept 5.1 Macromolecules are polymers, built from monomers 1. The large molecules of all living things fall into just four main classes. Name them. 2. Circle the three classes that are called
Name Period Concept 5.1 Macromolecules are polymers, built from monomers 1. The large molecules of all living things fall into just four main classes. Name them. 2. Circle the three classes that are called
TEACHER ACTIVITY GUIDE
 Page 1/5 TEACHER ACTIVITY GUIDE EFFECT OF HEAT & ph ON COLOR & TEXTURE OF GREEN VEGETABLES Taken from IFT Experiments in Food Science Series Color plays a key role in establishing consumer acceptability
Page 1/5 TEACHER ACTIVITY GUIDE EFFECT OF HEAT & ph ON COLOR & TEXTURE OF GREEN VEGETABLES Taken from IFT Experiments in Food Science Series Color plays a key role in establishing consumer acceptability
Study the following diagrams of the States of Matter. Label the names of the Changes of State between the different states.
 Describe the strength of attractive forces between particles. Describe the amount of space between particles. Can the particles in this state be compressed? Do the particles in this state have a definite
Describe the strength of attractive forces between particles. Describe the amount of space between particles. Can the particles in this state be compressed? Do the particles in this state have a definite
