Ohm s Law. Ohmic relationship V=IR. Electric Power. Non Ohmic devises. Schematic representation. Electric Power
|
|
|
- Ginger Morrison
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Ohm Law Ohmic relationhip V=IR Ohm law tate that current through the conductor i directly proportional to the voltage acro it if temperature and other phyical condition do not change. In many material, the voltage and reitance are connected by Ohm' Law: Ohm' Law : V = IR Conductor which obey Ohm law are made up of metal, carbon and ome alloy. hey are called ohmic conductor. V/volt I/ampere R/ohm V(v) V = IR Slope = V/I = R I(A) Non Ohmic devie Electric Power he connection between voltage and reitance can be more complicated in ome material. hee material are called non-ohmic (e.g. emiconductor device uch a tranitor). We'll focu mainly on ohmic material for now, thoe obeying Ohm' Law. Semiconductor will be covered later on. Worked Example:what i the voltage acro a reitor of K5 when a current of ma flow? V = IR = 500*0.00 =0.V = 00mV Self Aement Quetion: A copper wire ha a length of 60m and a diameter of mm. If the wire i connected to a.5v battery, how much current flow through the wire? Power i the rate at which work i done. It ha unit of Watt. W = J/ Electric power i given by the equation: P =VI. Batterie and power upplie upply power to a circuit, and thi power i ued up by anything that ha reitance. he power diipated in a reitor goe into heating the reitor. In many cae, thi i wated energy. In ome cae, however, the heating i exploited a a ource of heat, uch a in a toater or an electric heater. P = I R ( ince V =IR) Electric Power Schematic repreentation Worked Example: A current of 0mA flow through a reitor when the potential difference acro it i.5v. How much power i diipated in the reitor. P = VI = 0e-*.5 =5mw. Self-aement Quetion: If a light bulb operating at full power of 00W ha a potential difference of 5V acro it. What i the reitance of the bulb. An. R Reitor Battery Reitive circuit Prepared by Dr Yona M Gebremichael, 005
2 Reitor in a circuit Serie configuration Serie connection of reitor Equivalent reitance R Serie connection of reitor he arrow in the above circuit how direction of current flow, by convention the arrow end i at the poitive end. hu the potential at the left end of each reitor i more poitive than at the right, becaue the current i flowing from left to right. In a erie configuration, the ame current flow through each component in the circuit. Reitor in erie Reitor in erie hu we can calculate the voltage drop (potential difference) cro each reitor uing ohm relationhip. V =IR, V =IR, V =IR he total voltage drop acro all the reitor i V +V +V and thi mut be equal to the applied e.m.f auming ideal ource. Hence V V V V V IR IR IR V I ( R ) If V IR IR I ( R ) R i the combinedreitan ce Worked Example: What are the voltage acro R and R? R = R+R = 5k I = V/R = 0/5k = ma hu V = R*I =0k*mA =0v. And V = R*I = 5k*mA =0v. Note that V + V = 0v+0v=0V. Reitor in erie Summary of reitor in erie Self-aement quetion: hree reitor R, R & R of reitance value 00Ω, 00Ω, and 500Ωrepectively are connected in erie acro a 0V e.m.f. ource of negligible internal reitance. By firt drawing a chematic diagram of the circuit, calculate (a) the equivalent reitance, (b)the current flowing in the circuit, (c) the potential difference acro each reitor (d) the power diipated in each reitor and (e) the power taken from the e.m.f. ource. An. a) 800Ω, b).5ma c).5v,.5v, 6.5V d)5.6mw,.mw, 78.mw e)5mw. he reitance equivalent to n number of reitor connected in erie i the um of the individual reitance. Alway check the equivalent reitance i larger than every individual reitor value. Same current flow through each reitor in erie. he voltage drop acro each erie reitor i proportional to it reitance. he um of all the voltage drop acro all the erie reitor i equal to the ource voltage. Prepared by Dr Yona M Gebremichael, 005
3 Reitor in parallel Reitor in parallel Note that the combined reitance i le that either reitance Putting reitor in parallel provide alternative path for the current and lower the effective reitance. Reitor R and R are in parallel he ame voltage act acro each reitor he total current I from the upply equal the um of the eparate current I and I through each reitor. Worked Example: wo reitor of value 0K and 0K are connected in parallel acro a voltage of 5V. What i the value of the current flowing through each reitor. Draw a fully labelled chematic of the circuit. Parallel network Summary of reitor in parallel Self-aement quetion. In the circuit hown below, find the voltage drop acro each reitor. What ingle reitor would replace the network. An. V =.88, V = 0.V, V = V, 840K he reitance equivalent to n number of reitor connected in parallel i the invere of the um of the reciprocal of the individual reitance. Alway check the equivalent reitance i maller than the mallet reitance value in the network. he voltage acro each reitor i the ame for all the reitor in the parallel network. he current through each reitor in parallel i inverely proportional to it reitance. he um of all the current through each reitor i equal to the total current drawn from the ource. he Voltage divider he current divider he potential divider arrangement provide convenient way of getting a variable voltage from a fixed voltage upply. Conider two reitor R and R connected acro emf V. he voltage divider rule tate that the voltage V divide between R and R in the ration of their reitance. he current divider arrangement divide the current between the reitor branche in proportion to their conductance. In the circuit hown I and I are divided in proportion to the conductance of R and R. Prepared by Dr Yona M Gebremichael, 005
4 Variable Reitor Voltage and Current divider Worked Example: Variable reitor alo called pot (hort for potential divider). Unlike the uual reitor (two terminal), thee device have three terminal. wo end terminal are connected and the centre connection, alo called wiper, move the output voltage of the pot from zero to the value of the voltage upplied acro the end of the whole reitive track. A 0k linear pot i ued a a potential divider for a 9V upply. If the wiper i et halfway round the track, what i the voltage when the load reitance i: A. very large B 00K C. 0K Voltage and current divider Meaurement of R,I,V Self-aement quetion: A.5k linear pot i ued a a potential divider for a 9V upply a hown in the figure below. he wiper i et at B 4/5 of the way round from end C of the track. what i the reitance of the length BC of the track? What i the voltage acro BC. If a reitor i connected a a load to X and Y, what doe the voltage become acro BC when the load reitance i (i) 0k (ii) 0k. Comment on the reult. An. k, 0.5k, 7.V, (I) 7V (II) 6V Voltmeter: to meaure the voltage acro a circuit component, the voltmeter i connected acro the component. Voltmeter i connected in parallel. Connecting the voltmeter acro R hould not affect the the quantity under meaurement. In thi cae the voltage drop acro R will not change by connecting the Voltmeter o long a the voltmeter doe not draw any current. hu an ideal voltmeter will have an infinite reitance! Meaurement of V, I & R Which meaurement, V or I? Meauring Current o meaure current, the circuit ha to be broken and an ammeter inerted in the path of the current to be meaured. Ammeter i connected in erie. Addition of the ammeter to the circuit hould not change the quantity to be meaured, in thi cae current. herefore an ideal ammeter mut have zero reitance o it doe not drop and voltage acro it. Which meaurement technique do you think will be the more ueful? Voltage meaurement are ued much more often than current meaurement. he proceing of electronic ignal i uually thought of in voltage term. It i an added advantage that a voltage meaurement i eaier to make. he original circuit doe not need to be changed. Often, the meter probe are connected imply by touching them to the point of interet. 4 Prepared by Dr Yona M Gebremichael, 005
5 Meauring V, I & R Ohm meter: meaure reitance. Ohmmeter work by paing a mall current through the component and meauring the voltage produced. An ohmmeter doe not function with a circuit connected to a power upply. If you want to meaure the reitance of a particular component, you mut take it out of the circuit altogether and tet it eparately. If you try thi with the component connected into a circuit with a power upply, the mot likely reult i that the meter will be damaged. Mot multimeter have a fue to help protect againt miue. he reading will not be accurate. Multimeter Meauring V, I & R A multimeter i a general purpoe electrical meauring intrument which i capable of meauring current and voltage (a.c. and d.c.) and reitance. It ha everal range for each of thee quantitie. Each range ha a different full cale value which can be et by witche. Modern multimeter have auto ranging capability. Moving coil multimeter: diplay the quantity a a mechanical deflection of the pointer acro a graduated cale. Digital multimeter diplay the meaured value a a decimal digit. 5 Prepared by Dr Yona M Gebremichael, 005
Experiment #3, Ohm s Law
 Experiment #3, Ohm s Law 1 Purpose Physics 182 - Summer 2013 - Experiment #3 1 To investigate the -oltage, -, characteristics of a carbon resistor at room temperature and at liquid nitrogen temperature,
Experiment #3, Ohm s Law 1 Purpose Physics 182 - Summer 2013 - Experiment #3 1 To investigate the -oltage, -, characteristics of a carbon resistor at room temperature and at liquid nitrogen temperature,
PHYSICS 111 LABORATORY Experiment #3 Current, Voltage and Resistance in Series and Parallel Circuits
 PHYSCS 111 LABORATORY Experiment #3 Current, Voltage and Resistance in Series and Parallel Circuits This experiment is designed to investigate the relationship between current and potential in simple series
PHYSCS 111 LABORATORY Experiment #3 Current, Voltage and Resistance in Series and Parallel Circuits This experiment is designed to investigate the relationship between current and potential in simple series
Experiment #5, Series and Parallel Circuits, Kirchhoff s Laws
 Physics 182 Summer 2013 Experiment #5 1 Experiment #5, Series and Parallel Circuits, Kirchhoff s Laws 1 Purpose Our purpose is to explore and validate Kirchhoff s laws as a way to better understanding
Physics 182 Summer 2013 Experiment #5 1 Experiment #5, Series and Parallel Circuits, Kirchhoff s Laws 1 Purpose Our purpose is to explore and validate Kirchhoff s laws as a way to better understanding
Resistance, Ohm s Law, and the Temperature of a Light Bulb Filament
 Resistance, Ohm s Law, and the Temperature of a Light Bulb Filament Name Partner Date Introduction Carbon resistors are the kind typically used in wiring circuits. They are made from a small cylinder of
Resistance, Ohm s Law, and the Temperature of a Light Bulb Filament Name Partner Date Introduction Carbon resistors are the kind typically used in wiring circuits. They are made from a small cylinder of
Experiment NO.3 Series and parallel connection
 Experiment NO.3 Series and parallel connection Object To study the properties of series and parallel connection. Apparatus 1. DC circuit training system 2. Set of wires. 3. DC Power supply 4. Digital A.V.O.
Experiment NO.3 Series and parallel connection Object To study the properties of series and parallel connection. Apparatus 1. DC circuit training system 2. Set of wires. 3. DC Power supply 4. Digital A.V.O.
Simple Modular Half-Bridge
 Simple Modular HalfBridge Shane Colton Email: [email protected] Maachuett Intitute of Technology Rev.1.1 13 March, 2009 Simple Modular HalfBridge Module Overview V i V i Iolated DCDC Supply: Supplied by 12V
Simple Modular HalfBridge Shane Colton Email: [email protected] Maachuett Intitute of Technology Rev.1.1 13 March, 2009 Simple Modular HalfBridge Module Overview V i V i Iolated DCDC Supply: Supplied by 12V
Electrical Fundamentals Module 3: Parallel Circuits
 Electrical Fundamentals Module 3: Parallel Circuits PREPARED BY IAT Curriculum Unit August 2008 Institute of Applied Technology, 2008 ATE310- Electrical Fundamentals 2 Module 3 Parallel Circuits Module
Electrical Fundamentals Module 3: Parallel Circuits PREPARED BY IAT Curriculum Unit August 2008 Institute of Applied Technology, 2008 ATE310- Electrical Fundamentals 2 Module 3 Parallel Circuits Module
6. Friction, Experiment and Theory
 6. Friction, Experiment and Theory The lab thi wee invetigate the rictional orce and the phyical interpretation o the coeicient o riction. We will mae ue o the concept o the orce o gravity, the normal
6. Friction, Experiment and Theory The lab thi wee invetigate the rictional orce and the phyical interpretation o the coeicient o riction. We will mae ue o the concept o the orce o gravity, the normal
Lab 3 - DC Circuits and Ohm s Law
 Lab 3 DC Circuits and Ohm s Law L3-1 Name Date Partners Lab 3 - DC Circuits and Ohm s Law OBJECTIES To learn to apply the concept of potential difference (voltage) to explain the action of a battery in
Lab 3 DC Circuits and Ohm s Law L3-1 Name Date Partners Lab 3 - DC Circuits and Ohm s Law OBJECTIES To learn to apply the concept of potential difference (voltage) to explain the action of a battery in
Lab E1: Introduction to Circuits
 E1.1 Lab E1: Introduction to Circuits The purpose of the this lab is to introduce you to some basic instrumentation used in electrical circuits. You will learn to use a DC power supply, a digital multimeter
E1.1 Lab E1: Introduction to Circuits The purpose of the this lab is to introduce you to some basic instrumentation used in electrical circuits. You will learn to use a DC power supply, a digital multimeter
Physics Equation List :Form 5 Wave
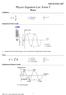 Ocillation Phyic Equation Lit :Form 5 Wave f 1 T f frequency (Hz or -1 ) T Period () Dilacement-Time Grah Amlitude, Period and Frequency can be found from a Dilacement-Time Grah Wave v f λ v velocity (m
Ocillation Phyic Equation Lit :Form 5 Wave f 1 T f frequency (Hz or -1 ) T Period () Dilacement-Time Grah Amlitude, Period and Frequency can be found from a Dilacement-Time Grah Wave v f λ v velocity (m
Fig. 1 Analogue Multimeter Fig.2 Digital Multimeter
 ELECTRICAL INSTRUMENT AND MEASUREMENT Electrical measuring instruments are devices used to measure electrical quantities such as electric current, voltage, resistance, electrical power and energy. MULTIMETERS
ELECTRICAL INSTRUMENT AND MEASUREMENT Electrical measuring instruments are devices used to measure electrical quantities such as electric current, voltage, resistance, electrical power and energy. MULTIMETERS
Objectives 200 CHAPTER 4 RESISTANCE
 Objectives Explain the differences among conductors, insulators, and semiconductors. Define electrical resistance. Solve problems using resistance, voltage, and current. Describe a material that obeys
Objectives Explain the differences among conductors, insulators, and semiconductors. Define electrical resistance. Solve problems using resistance, voltage, and current. Describe a material that obeys
On Reference RIAA Networks by Jim Hagerman
 On eference IAA Network by Jim Hagerman You d think there would be nothing left to ay. Everything you need to know about IAA network ha already been publihed. However, a few year back I came acro an intereting
On eference IAA Network by Jim Hagerman You d think there would be nothing left to ay. Everything you need to know about IAA network ha already been publihed. However, a few year back I came acro an intereting
CLASS TEST GRADE 11. PHYSICAL SCIENCES: PHYSICS Test 3: Electricity and magnetism
 CLASS TEST GRADE 11 PHYSICAL SCIENCES: PHYSICS Test 3: Electricity and magnetism MARKS: 45 TIME: 1 hour INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION 1. Answer ALL the questions. 2. You may use non-programmable calculators.
CLASS TEST GRADE 11 PHYSICAL SCIENCES: PHYSICS Test 3: Electricity and magnetism MARKS: 45 TIME: 1 hour INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION 1. Answer ALL the questions. 2. You may use non-programmable calculators.
Current, Resistance and Electromotive Force. Young and Freedman Chapter 25
 Current, Resistance and Electromotive Force Young and Freedman Chapter 25 Electric Current: Analogy, water flowing in a pipe H 2 0 gallons/minute Flow Rate is the NET amount of water passing through a
Current, Resistance and Electromotive Force Young and Freedman Chapter 25 Electric Current: Analogy, water flowing in a pipe H 2 0 gallons/minute Flow Rate is the NET amount of water passing through a
STUDY MATERIAL FOR CLASS 10+2 - Physics- CURRENT ELECTRICITY. The flow of electric charges in a particular direction constitutes electric current.
 Chapter : 3 Current Electricity Current Electricity The branch of Physics which deals with the study of electric charges in motion is called current electricity. Electric current The flow of electric charges
Chapter : 3 Current Electricity Current Electricity The branch of Physics which deals with the study of electric charges in motion is called current electricity. Electric current The flow of electric charges
Student Exploration: Circuits
 Name: Date: Student Exploration: Circuits Vocabulary: ammeter, circuit, current, ohmmeter, Ohm s law, parallel circuit, resistance, resistor, series circuit, voltage Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these
Name: Date: Student Exploration: Circuits Vocabulary: ammeter, circuit, current, ohmmeter, Ohm s law, parallel circuit, resistance, resistor, series circuit, voltage Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these
People s Physics Book
 The Big Ideas: The name electric current is given to the phenomenon that occurs when an electric field moves down a wire at close to the speed of light. Voltage is the electrical energy density (energy
The Big Ideas: The name electric current is given to the phenomenon that occurs when an electric field moves down a wire at close to the speed of light. Voltage is the electrical energy density (energy
Bob York. Simple FET DC Bias Circuits
 Bob York Simple FET DC Bia Circuit Loa-Line an Q-point Conier the effect of a rain reitor in the comnon-ource configuration: Smaller + g D out KL: Thi i the equation of a line that can be uperimpoe on
Bob York Simple FET DC Bia Circuit Loa-Line an Q-point Conier the effect of a rain reitor in the comnon-ource configuration: Smaller + g D out KL: Thi i the equation of a line that can be uperimpoe on
Lab 1: DC Circuits. Student 1, [email protected] Partner : Student 2, [email protected]
 Lab Date Lab 1: DC Circuits Student 1, [email protected] Partner : Student 2, [email protected] I. Introduction The purpose of this lab is to allow the students to become comfortable with the use of lab
Lab Date Lab 1: DC Circuits Student 1, [email protected] Partner : Student 2, [email protected] I. Introduction The purpose of this lab is to allow the students to become comfortable with the use of lab
MECH 2110 - Statics & Dynamics
 Chapter D Problem 3 Solution 1/7/8 1:8 PM MECH 11 - Static & Dynamic Chapter D Problem 3 Solution Page 7, Engineering Mechanic - Dynamic, 4th Edition, Meriam and Kraige Given: Particle moving along a traight
Chapter D Problem 3 Solution 1/7/8 1:8 PM MECH 11 - Static & Dynamic Chapter D Problem 3 Solution Page 7, Engineering Mechanic - Dynamic, 4th Edition, Meriam and Kraige Given: Particle moving along a traight
Series and Parallel Circuits
 Series and Parallel Circuits Components in a circuit can be connected in series or parallel. A series arrangement of components is where they are inline with each other, i.e. connected end-to-end. A parallel
Series and Parallel Circuits Components in a circuit can be connected in series or parallel. A series arrangement of components is where they are inline with each other, i.e. connected end-to-end. A parallel
Tutorial 12 Solutions
 PHYS000 Tutorial 2 solutions Tutorial 2 Solutions. Two resistors, of 00 Ω and 200 Ω, are connected in series to a 6.0 V DC power supply. (a) Draw a circuit diagram. 6 V 00 Ω 200 Ω (b) What is the total
PHYS000 Tutorial 2 solutions Tutorial 2 Solutions. Two resistors, of 00 Ω and 200 Ω, are connected in series to a 6.0 V DC power supply. (a) Draw a circuit diagram. 6 V 00 Ω 200 Ω (b) What is the total
AP Physics Electricity and Magnetism #4 Electrical Circuits, Kirchoff s Rules
 Name Period AP Physics Electricity and Magnetism #4 Electrical Circuits, Kirchoff s Rules Dr. Campbell 1. Four 240 Ω light bulbs are connected in series. What is the total resistance of the circuit? What
Name Period AP Physics Electricity and Magnetism #4 Electrical Circuits, Kirchoff s Rules Dr. Campbell 1. Four 240 Ω light bulbs are connected in series. What is the total resistance of the circuit? What
Basic voltmeter use. Resources and methods for learning about these subjects (list a few here, in preparation for your research):
 Basic voltmeter use This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons ttribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/,
Basic voltmeter use This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons ttribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/,
7. What is the current in a circuit if 15 coulombs of electric charge move past a given point in 3 seconds? (1) 5 A (3) 18 A (2) 12 A (4) 45 A
 1. Compared to the number of free electrons in a conductor, the number of free electrons in an insulator of the same volume is less the same greater 2. Most metals are good electrical conductors because
1. Compared to the number of free electrons in a conductor, the number of free electrons in an insulator of the same volume is less the same greater 2. Most metals are good electrical conductors because
EXPERIMENT 7 OHM S LAW, RESISTORS IN SERIES AND PARALLEL
 260 7- I. THEOY EXPEIMENT 7 OHM S LAW, ESISTOS IN SEIES AND PAALLEL The purposes of this experiment are to test Ohm's Law, to study resistors in series and parallel, and to learn the correct use of ammeters
260 7- I. THEOY EXPEIMENT 7 OHM S LAW, ESISTOS IN SEIES AND PAALLEL The purposes of this experiment are to test Ohm's Law, to study resistors in series and parallel, and to learn the correct use of ammeters
Series and Parallel Circuits
 Direct Current (DC) Direct current (DC) is the unidirectional flow of electric charge. The term DC is used to refer to power systems that use refer to the constant (not changing with time), mean (average)
Direct Current (DC) Direct current (DC) is the unidirectional flow of electric charge. The term DC is used to refer to power systems that use refer to the constant (not changing with time), mean (average)
A technical guide to 2014 key stage 2 to key stage 4 value added measures
 A technical guide to 2014 key tage 2 to key tage 4 value added meaure CONTENTS Introduction: PAGE NO. What i value added? 2 Change to value added methodology in 2014 4 Interpretation: Interpreting chool
A technical guide to 2014 key tage 2 to key tage 4 value added meaure CONTENTS Introduction: PAGE NO. What i value added? 2 Change to value added methodology in 2014 4 Interpretation: Interpreting chool
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
 aachuett Intitute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.685 Electric achinery Cla Note 10: Induction achine Control and Simulation c 2003 Jame L. Kirtley Jr. 1 Introduction
aachuett Intitute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.685 Electric achinery Cla Note 10: Induction achine Control and Simulation c 2003 Jame L. Kirtley Jr. 1 Introduction
Chapter 7 Direct-Current Circuits
 Chapter 7 Direct-Current Circuits 7. Introduction...7-7. Electromotive Force...7-3 7.3 Resistors in Series and in Parallel...7-5 7.4 Kirchhoff s Circuit Rules...7-7 7.5 Voltage-Current Measurements...7-9
Chapter 7 Direct-Current Circuits 7. Introduction...7-7. Electromotive Force...7-3 7.3 Resistors in Series and in Parallel...7-5 7.4 Kirchhoff s Circuit Rules...7-7 7.5 Voltage-Current Measurements...7-9
Physics 111. Exam #1. January 24, 2014
 Phyic 111 Exam #1 January 24, 2014 Name Pleae read and follow thee intruction carefully: Read all problem carefully before attempting to olve them. Your work mut be legible, and the organization clear.
Phyic 111 Exam #1 January 24, 2014 Name Pleae read and follow thee intruction carefully: Read all problem carefully before attempting to olve them. Your work mut be legible, and the organization clear.
TRANSFORM AND ITS APPLICATION
 LAPLACE TRANSFORM AND ITS APPLICATION IN CIRCUIT ANALYSIS C.T. Pan. Definition of the Laplace Tranform. Ueful Laplace Tranform Pair.3 Circuit Analyi in S Domain.4 The Tranfer Function and the Convolution
LAPLACE TRANSFORM AND ITS APPLICATION IN CIRCUIT ANALYSIS C.T. Pan. Definition of the Laplace Tranform. Ueful Laplace Tranform Pair.3 Circuit Analyi in S Domain.4 The Tranfer Function and the Convolution
Lecture Notes: ECS 203 Basic Electrical Engineering Semester 1/2010. Dr.Prapun Suksompong 1 June 16, 2010
 Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology Thammasat University School of Information, Computer and Communication Technology Lecture Notes: ECS 203 Basic Electrical Engineering Semester 1/2010 Dr.Prapun
Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology Thammasat University School of Information, Computer and Communication Technology Lecture Notes: ECS 203 Basic Electrical Engineering Semester 1/2010 Dr.Prapun
Series and Parallel Resistive Circuits Physics Lab VIII
 Series and Parallel Resistive Circuits Physics Lab VIII Objective In the set of experiments, the theoretical expressions used to calculate the total resistance in a combination of resistors will be tested
Series and Parallel Resistive Circuits Physics Lab VIII Objective In the set of experiments, the theoretical expressions used to calculate the total resistance in a combination of resistors will be tested
Electronics. Basic Concepts. Yrd. Doç. Dr. Aytaç GÖREN Yrd. Doç. Dr. Levent ÇETİN
 Electronics Basic Concepts Electric charge Ordinary matter is made up of atoms which have positively charged nuclei and negatively charged electrons surrounding them. Charge is quantized as the subtraction
Electronics Basic Concepts Electric charge Ordinary matter is made up of atoms which have positively charged nuclei and negatively charged electrons surrounding them. Charge is quantized as the subtraction
12.4 Problems. Excerpt from "Introduction to Geometry" 2014 AoPS Inc. Copyrighted Material CHAPTER 12. CIRCLES AND ANGLES
 HTER 1. IRLES N NGLES Excerpt from "Introduction to Geometry" 014 os Inc. onider the circle with diameter O. all thi circle. Why mut hit O in at leat two di erent point? (b) Why i it impoible for to hit
HTER 1. IRLES N NGLES Excerpt from "Introduction to Geometry" 014 os Inc. onider the circle with diameter O. all thi circle. Why mut hit O in at leat two di erent point? (b) Why i it impoible for to hit
Lab 2: Resistance, Current, and Voltage
 2 Lab 2: Resistance, Current, and Voltage I. Before you come to la.. A. Read the following chapters from the text (Giancoli): 1. Chapter 25, sections 1, 2, 3, 5 2. Chapter 26, sections 1, 2, 3 B. Read
2 Lab 2: Resistance, Current, and Voltage I. Before you come to la.. A. Read the following chapters from the text (Giancoli): 1. Chapter 25, sections 1, 2, 3, 5 2. Chapter 26, sections 1, 2, 3 B. Read
Unit 11 Using Linear Regression to Describe Relationships
 Unit 11 Uing Linear Regreion to Decribe Relationhip Objective: To obtain and interpret the lope and intercept of the leat quare line for predicting a quantitative repone variable from a quantitative explanatory
Unit 11 Uing Linear Regreion to Decribe Relationhip Objective: To obtain and interpret the lope and intercept of the leat quare line for predicting a quantitative repone variable from a quantitative explanatory
Chapter 13: Electric Circuits
 Chapter 13: Electric Circuits 1. A household circuit rated at 120 Volts is protected by a fuse rated at 15 amps. What is the maximum number of 100 watt light bulbs which can be lit simultaneously in parallel
Chapter 13: Electric Circuits 1. A household circuit rated at 120 Volts is protected by a fuse rated at 15 amps. What is the maximum number of 100 watt light bulbs which can be lit simultaneously in parallel
MATLAB/Simulink Based Modelling of Solar Photovoltaic Cell
 MATLAB/Simulink Baed Modelling of Solar Photovoltaic Cell Tarak Salmi *, Mounir Bouzguenda **, Adel Gatli **, Ahmed Mamoudi * *Reearch Unit on Renewable Energie and Electric Vehicle, National Engineering
MATLAB/Simulink Baed Modelling of Solar Photovoltaic Cell Tarak Salmi *, Mounir Bouzguenda **, Adel Gatli **, Ahmed Mamoudi * *Reearch Unit on Renewable Energie and Electric Vehicle, National Engineering
Parallel DC circuits
 Parallel DC circuits This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/,
Parallel DC circuits This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/,
CHAPTER 28 ELECTRIC CIRCUITS
 CHAPTER 8 ELECTRIC CIRCUITS 1. Sketch a circuit diagram for a circuit that includes a resistor R 1 connected to the positive terminal of a battery, a pair of parallel resistors R and R connected to the
CHAPTER 8 ELECTRIC CIRCUITS 1. Sketch a circuit diagram for a circuit that includes a resistor R 1 connected to the positive terminal of a battery, a pair of parallel resistors R and R connected to the
Measuring Electric Phenomena: the Ammeter and Voltmeter
 Measuring Electric Phenomena: the Ammeter and Voltmeter 1 Objectives 1. To understand the use and operation of the Ammeter and Voltmeter in a simple direct current circuit, and 2. To verify Ohm s Law for
Measuring Electric Phenomena: the Ammeter and Voltmeter 1 Objectives 1. To understand the use and operation of the Ammeter and Voltmeter in a simple direct current circuit, and 2. To verify Ohm s Law for
The Electrical Properties of Materials: Resistivity
 The Electrical Properties of Materials: Resistivity 1 Objectives 1. To understand the properties of resistance and resistivity in conductors, 2. To measure the resistivity and temperature coefficient of
The Electrical Properties of Materials: Resistivity 1 Objectives 1. To understand the properties of resistance and resistivity in conductors, 2. To measure the resistivity and temperature coefficient of
Essential Electrical Concepts
 Essential Electrical Concepts Introduction Modern vehicles incorporate many electrical and electronic components and systems: Audio Lights Navigation Engine control Transmission control Braking and traction
Essential Electrical Concepts Introduction Modern vehicles incorporate many electrical and electronic components and systems: Audio Lights Navigation Engine control Transmission control Braking and traction
13.10: How Series and Parallel Circuits Differ pg. 571
 13.10: How Series and Parallel Circuits Differ pg. 571 Key Concepts: 5. Connecting loads in series and parallel affects the current, potential difference, and total resistance. - Using your knowledge of
13.10: How Series and Parallel Circuits Differ pg. 571 Key Concepts: 5. Connecting loads in series and parallel affects the current, potential difference, and total resistance. - Using your knowledge of
Solutions to Bulb questions
 Solutions to Bulb questions Note: We did some basic circuits with bulbs in fact three main ones I can think of I have summarized our results below. For the final exam, you must have an understanding of
Solutions to Bulb questions Note: We did some basic circuits with bulbs in fact three main ones I can think of I have summarized our results below. For the final exam, you must have an understanding of
Course description: Introduces the student to basic electricity with an emphasis on Ohms Law.
 The following is presented for information purposes only and comes with no warranty. See http://www.bristolwatch.com/ Course Title: Basic Electricity and Ohms Law Course description: Introduces the student
The following is presented for information purposes only and comes with no warranty. See http://www.bristolwatch.com/ Course Title: Basic Electricity and Ohms Law Course description: Introduces the student
T-test for dependent Samples. Difference Scores. The t Test for Dependent Samples. The t Test for Dependent Samples. s D
 The t Tet for ependent Sample T-tet for dependent Sample (ak.a., Paired ample t-tet, Correlated Group eign, Within- Subject eign, Repeated Meaure,.. Repeated-Meaure eign When you have two et of core from
The t Tet for ependent Sample T-tet for dependent Sample (ak.a., Paired ample t-tet, Correlated Group eign, Within- Subject eign, Repeated Meaure,.. Repeated-Meaure eign When you have two et of core from
Experiment 4 ~ Resistors in Series & Parallel
 Experiment 4 ~ Resistors in Series & Parallel Objective: In this experiment you will set up three circuits: one with resistors in series, one with resistors in parallel, and one with some of each. You
Experiment 4 ~ Resistors in Series & Parallel Objective: In this experiment you will set up three circuits: one with resistors in series, one with resistors in parallel, and one with some of each. You
CHAPTER 5 BROADBAND CLASS-E AMPLIFIER
 CHAPTER 5 BROADBAND CLASS-E AMPLIFIER 5.0 Introduction Cla-E amplifier wa firt preented by Sokal in 1975. The application of cla- E amplifier were limited to the VHF band. At thi range of frequency, cla-e
CHAPTER 5 BROADBAND CLASS-E AMPLIFIER 5.0 Introduction Cla-E amplifier wa firt preented by Sokal in 1975. The application of cla- E amplifier were limited to the VHF band. At thi range of frequency, cla-e
Heat transfer to or from a fluid flowing through a tube
 Heat tranfer to or from a fluid flowing through a tube R. Shankar Subramanian A common ituation encountered by the chemical engineer i heat tranfer to fluid flowing through a tube. Thi can occur in heat
Heat tranfer to or from a fluid flowing through a tube R. Shankar Subramanian A common ituation encountered by the chemical engineer i heat tranfer to fluid flowing through a tube. Thi can occur in heat
AP1 Electricity. 1. A student wearing shoes stands on a tile floor. The students shoes do not fall into the tile floor due to
 1. A student wearing shoes stands on a tile floor. The students shoes do not fall into the tile floor due to (A) a force of repulsion between the shoes and the floor due to macroscopic gravitational forces.
1. A student wearing shoes stands on a tile floor. The students shoes do not fall into the tile floor due to (A) a force of repulsion between the shoes and the floor due to macroscopic gravitational forces.
Light Bulbs in Parallel Circuits
 Light Bulbs in Parallel Circuits In the last activity, we analyzed several different series circuits. In a series circuit, there is only one complete pathway for the charge to travel. Here are the basic
Light Bulbs in Parallel Circuits In the last activity, we analyzed several different series circuits. In a series circuit, there is only one complete pathway for the charge to travel. Here are the basic
Ammeter design. Resources and methods for learning about these subjects (list a few here, in preparation for your research):
 Ammeter design This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/,
Ammeter design This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/,
Ohm's Law and Circuits
 2. Conductance, Insulators and Resistance A. A conductor in electricity is a material that allows electrons to flow through it easily. Metals, in general, are good conductors. Why? The property of conductance
2. Conductance, Insulators and Resistance A. A conductor in electricity is a material that allows electrons to flow through it easily. Metals, in general, are good conductors. Why? The property of conductance
An Automatic Noise-Figure Meter
 An Automatic Noie-Figure Meter Here i a project that will automatically meaure the noie figure of your preamplifier project. It ha an operating range from 3 MHz to over 400 MHz. Jim Koehler, Introduction
An Automatic Noie-Figure Meter Here i a project that will automatically meaure the noie figure of your preamplifier project. It ha an operating range from 3 MHz to over 400 MHz. Jim Koehler, Introduction
v = x t = x 2 x 1 t 2 t 1 The average speed of the particle is absolute value of the average velocity and is given Distance travelled t
 Chapter 2 Motion in One Dimenion 2.1 The Important Stuff 2.1.1 Poition, Time and Diplacement We begin our tudy of motion by conidering object which are very mall in comparion to the ize of their movement
Chapter 2 Motion in One Dimenion 2.1 The Important Stuff 2.1.1 Poition, Time and Diplacement We begin our tudy of motion by conidering object which are very mall in comparion to the ize of their movement
HOW TO USE MULTIMETER. COMPILE BY: Dzulautotech
 HOW TO USE MULTIMETER COMPILE BY: Dzulautotech 1. GENERAL Electricity is absolutely necessary for an automobile. It is indispensable when the engine is started, the air fuel mixture is ignited and exploded,
HOW TO USE MULTIMETER COMPILE BY: Dzulautotech 1. GENERAL Electricity is absolutely necessary for an automobile. It is indispensable when the engine is started, the air fuel mixture is ignited and exploded,
Module 8. Three-phase Induction Motor. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 8 Three-phae Induction Motor Verion EE IIT, Kharagpur Leon 33 Different Type of Starter for Induction Motor (IM Verion EE IIT, Kharagpur Inructional Objective Need of uing arter for Induction motor
Module 8 Three-phae Induction Motor Verion EE IIT, Kharagpur Leon 33 Different Type of Starter for Induction Motor (IM Verion EE IIT, Kharagpur Inructional Objective Need of uing arter for Induction motor
Current Electricity Lab Series/Parallel Circuits. Safety and Equipment Precautions!
 Current Electricity Lab Series/Parallel Circuits Name Safety and Equipment Precautions! Plug in your power supply and use ONLY the D.C. terminals of the power source, NOT the A. C. terminals. DO NOT touch
Current Electricity Lab Series/Parallel Circuits Name Safety and Equipment Precautions! Plug in your power supply and use ONLY the D.C. terminals of the power source, NOT the A. C. terminals. DO NOT touch
σ m using Equation 8.1 given that σ
 8. Etimate the theoretical fracture trength of a brittle material if it i known that fracture occur by the propagation of an elliptically haped urface crack of length 0.8 mm and having a tip radiu of curvature
8. Etimate the theoretical fracture trength of a brittle material if it i known that fracture occur by the propagation of an elliptically haped urface crack of length 0.8 mm and having a tip radiu of curvature
Parallel and Series Resistors, Kirchoff s Law
 Experiment 2 31 Kuwait University Physics 107 Physics Department Parallel and Series Resistors, Kirchoff s Law Introduction In this experiment the relations among voltages, currents and resistances for
Experiment 2 31 Kuwait University Physics 107 Physics Department Parallel and Series Resistors, Kirchoff s Law Introduction In this experiment the relations among voltages, currents and resistances for
Lecture 14: Transformers. Ideal Transformers
 White, EE 3 Lecture 14 Page 1 of 9 Lecture 14: Tranforer. deal Tranforer n general, a tranforer i a ultiort ac device that convert voltage, current and iedance fro one value to another. Thi device only
White, EE 3 Lecture 14 Page 1 of 9 Lecture 14: Tranforer. deal Tranforer n general, a tranforer i a ultiort ac device that convert voltage, current and iedance fro one value to another. Thi device only
Physics, Chapter 27: Direct-Current Circuits
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Robert Katz Publications Research Papers in Physics and Astronomy 1-1-1958 Physics, Chapter 27: Direct-Current Circuits
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Robert Katz Publications Research Papers in Physics and Astronomy 1-1-1958 Physics, Chapter 27: Direct-Current Circuits
Chapter 1. Fundamental Electrical Concepts
 Chapter 1 Fundamental Electrical Concepts Charge, current, voltage, power circuits, nodes, branches Branch and node voltages, Kirchhoff Laws Basic circuit elements, combinations 01 fundamental 1 1.3 Electrical
Chapter 1 Fundamental Electrical Concepts Charge, current, voltage, power circuits, nodes, branches Branch and node voltages, Kirchhoff Laws Basic circuit elements, combinations 01 fundamental 1 1.3 Electrical
STUDY GUIDE: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM
 319 S. Naperville Road Wheaton, IL 60187 www.questionsgalore.net Phone: (630) 580-5735 E-Mail: [email protected] Fax: (630) 580-5765 STUDY GUIDE: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM An atom is made of three
319 S. Naperville Road Wheaton, IL 60187 www.questionsgalore.net Phone: (630) 580-5735 E-Mail: [email protected] Fax: (630) 580-5765 STUDY GUIDE: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM An atom is made of three
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA UNIT 5 - ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES NQF LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 4 - ALTERNATING CURRENT
 EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA UNIT 5 - ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES NQF LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 4 - ALTERNATING CURRENT 4 Understand single-phase alternating current (ac) theory Single phase AC
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA UNIT 5 - ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES NQF LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 4 - ALTERNATING CURRENT 4 Understand single-phase alternating current (ac) theory Single phase AC
Module 2. DC Circuit. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module DC Circuit Lesson 4 Loop Analysis of resistive circuit in the context of dc voltages and currents Objectives Meaning of circuit analysis; distinguish between the terms mesh and loop. To provide
Module DC Circuit Lesson 4 Loop Analysis of resistive circuit in the context of dc voltages and currents Objectives Meaning of circuit analysis; distinguish between the terms mesh and loop. To provide
FLUID MECHANICS. TUTORIAL No.4 FLOW THROUGH POROUS PASSAGES
 FLUID MECHANICS TUTORIAL No.4 FLOW THROUGH POROUS PASSAGES In thi tutorial you will continue the work on laminar flow and develop Poieuille' equation to the form known a the Carman - Kozeny equation. Thi
FLUID MECHANICS TUTORIAL No.4 FLOW THROUGH POROUS PASSAGES In thi tutorial you will continue the work on laminar flow and develop Poieuille' equation to the form known a the Carman - Kozeny equation. Thi
Solar Energy Discovery Lab
 Solar Energy Discovery Lab Objective Set up circuits with solar cells in series and parallel and analyze the resulting characteristics. Introduction A photovoltaic solar cell converts radiant (solar) energy
Solar Energy Discovery Lab Objective Set up circuits with solar cells in series and parallel and analyze the resulting characteristics. Introduction A photovoltaic solar cell converts radiant (solar) energy
I = V/r P = VI. I = P/V = 100 W / 6 V = 16.66 amps. What would happen if you use a 12-volt battery and a 12-volt light bulb to get 100 watts of power?
 Volts, Amps and Ohms Measuring Electricity The three most basic units in electricity are voltage (V), current (I) and resistance (r). Voltage is measured in volts, current is measured in amps and resistance
Volts, Amps and Ohms Measuring Electricity The three most basic units in electricity are voltage (V), current (I) and resistance (r). Voltage is measured in volts, current is measured in amps and resistance
Basic Principles of. Electricity. Basic Principles of Electricity. by Prof. Dr. Osman SEVAİOĞLU Electrical and Electronics Engineering Department
 Basic Principles of Electricity METU by Prof. Dr. Osman SEVAİOĞLU Electrical and Electronics Engineering Department EE 209 Fundamentals of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Prof. Dr. O. SEVAİOĞLU,
Basic Principles of Electricity METU by Prof. Dr. Osman SEVAİOĞLU Electrical and Electronics Engineering Department EE 209 Fundamentals of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Prof. Dr. O. SEVAİOĞLU,
REDUCTION OF TOTAL SUPPLY CHAIN CYCLE TIME IN INTERNAL BUSINESS PROCESS OF REAMER USING DOE AND TAGUCHI METHODOLOGY. Abstract. 1.
 International Journal of Advanced Technology & Engineering Reearch (IJATER) REDUCTION OF TOTAL SUPPLY CHAIN CYCLE TIME IN INTERNAL BUSINESS PROCESS OF REAMER USING DOE AND Abtract TAGUCHI METHODOLOGY Mr.
International Journal of Advanced Technology & Engineering Reearch (IJATER) REDUCTION OF TOTAL SUPPLY CHAIN CYCLE TIME IN INTERNAL BUSINESS PROCESS OF REAMER USING DOE AND Abtract TAGUCHI METHODOLOGY Mr.
Objectives. Electric Current
 Objectives Define electrical current as a rate. Describe what is measured by ammeters and voltmeters. Explain how to connect an ammeter and a voltmeter in an electrical circuit. Explain why electrons travel
Objectives Define electrical current as a rate. Describe what is measured by ammeters and voltmeters. Explain how to connect an ammeter and a voltmeter in an electrical circuit. Explain why electrons travel
MSc Financial Economics: International Finance. Bubbles in the Foreign Exchange Market. Anne Sibert. Revised Spring 2013. Contents
 MSc Financial Economic: International Finance Bubble in the Foreign Exchange Market Anne Sibert Revied Spring 203 Content Introduction................................................. 2 The Mone Market.............................................
MSc Financial Economic: International Finance Bubble in the Foreign Exchange Market Anne Sibert Revied Spring 203 Content Introduction................................................. 2 The Mone Market.............................................
Chapter 7. DC Circuits
 Chapter 7 DC Circuits 7.1 Introduction... 7-3 Example 7.1.1: Junctions, branches and loops... 7-4 7.2 Electromotive Force... 7-5 7.3 Electrical Energy and Power... 7-9 7.4 Resistors in Series and in Parallel...
Chapter 7 DC Circuits 7.1 Introduction... 7-3 Example 7.1.1: Junctions, branches and loops... 7-4 7.2 Electromotive Force... 7-5 7.3 Electrical Energy and Power... 7-9 7.4 Resistors in Series and in Parallel...
CURRENT ELECTRICITY - I
 CURRNT LCTRCTY - 1. lectric Current 2. Conventional Current 3. Drift elocity of electrons and current 4. Current Density 5. Ohm s Law 6. Resistance, Resistivity, Conductance & Conductivity 7. Temperature
CURRNT LCTRCTY - 1. lectric Current 2. Conventional Current 3. Drift elocity of electrons and current 4. Current Density 5. Ohm s Law 6. Resistance, Resistivity, Conductance & Conductivity 7. Temperature
ELECTRIC FIELD LINES AND EQUIPOTENTIAL SURFACES
 ELECTRIC FIELD LINES AND EQUIPOTENTIAL SURFACES The purpose of this lab session is to experimentally investigate the relation between electric field lines of force and equipotential surfaces in two dimensions.
ELECTRIC FIELD LINES AND EQUIPOTENTIAL SURFACES The purpose of this lab session is to experimentally investigate the relation between electric field lines of force and equipotential surfaces in two dimensions.
FB-DC3 Electric Circuits: Series and Parallel Circuits
 CREST Foundation Electrical Engineering: DC Electric Circuits Kuphaldt FB-DC3 Electric Circuits: Series and Parallel Circuits Contents 1. What are "series" and "parallel"? 2. Simple series circuits 3.
CREST Foundation Electrical Engineering: DC Electric Circuits Kuphaldt FB-DC3 Electric Circuits: Series and Parallel Circuits Contents 1. What are "series" and "parallel"? 2. Simple series circuits 3.
Experiment #4, Ohmic Heat
 Experiment #4, Ohmic Heat 1 Purpose Physics 18 - Fall 013 - Experiment #4 1 1. To demonstrate the conversion of the electric energy into heat.. To demonstrate that the rate of heat generation in an electrical
Experiment #4, Ohmic Heat 1 Purpose Physics 18 - Fall 013 - Experiment #4 1 1. To demonstrate the conversion of the electric energy into heat.. To demonstrate that the rate of heat generation in an electrical
Using voltage regulator to convert 5-12V range to 3.3V. Huan Lin
 Using voltage regulator to convert 5-12V range to 3.3V Huan Lin 4/2/2010 1 Table of Contents 1. Introduction... Error! Bookmark not defined. 2. Objective... Error! Bookmark not defined. 3. Implementation...
Using voltage regulator to convert 5-12V range to 3.3V Huan Lin 4/2/2010 1 Table of Contents 1. Introduction... Error! Bookmark not defined. 2. Objective... Error! Bookmark not defined. 3. Implementation...
Circuit symbol. Each of the cells has a potential difference of 1.5 volts. Figure 1. Use the correct answer from the box to complete the sentence.
 Q.(a) Draw one line from each circuit symbol to its correct name. Circuit symbol Name Diode Light-dependent resistor (LDR) Lamp Light-emitting diode (LED) (3) Figure shows three circuits. The resistors
Q.(a) Draw one line from each circuit symbol to its correct name. Circuit symbol Name Diode Light-dependent resistor (LDR) Lamp Light-emitting diode (LED) (3) Figure shows three circuits. The resistors
Progress 8 measure in 2016, 2017, and 2018. Guide for maintained secondary schools, academies and free schools
 Progre 8 meaure in 2016, 2017, and 2018 Guide for maintained econdary chool, academie and free chool July 2016 Content Table of figure 4 Summary 5 A ummary of Attainment 8 and Progre 8 5 Expiry or review
Progre 8 meaure in 2016, 2017, and 2018 Guide for maintained econdary chool, academie and free chool July 2016 Content Table of figure 4 Summary 5 A ummary of Attainment 8 and Progre 8 5 Expiry or review
Project Management Basics
 Project Management Baic A Guide to undertanding the baic component of effective project management and the key to ucce 1 Content 1.0 Who hould read thi Guide... 3 1.1 Overview... 3 1.2 Project Management
Project Management Baic A Guide to undertanding the baic component of effective project management and the key to ucce 1 Content 1.0 Who hould read thi Guide... 3 1.1 Overview... 3 1.2 Project Management
Resistors. Some substances are insulators. A battery will not make detectible current flow through them.
 Resistors Some substances are insulators. A battery will not make detectible current flow through them. Many substances (lead, iron, graphite, etc.) will let current flow. For most substances that are
Resistors Some substances are insulators. A battery will not make detectible current flow through them. Many substances (lead, iron, graphite, etc.) will let current flow. For most substances that are
ELECTRICAL FUNDAMENTALS
 General Electricity is a form of energy called electrical energy. It is sometimes called an "unseen" force because the energy itself cannot be seen, heard, touched, or smelled. However, the effects of
General Electricity is a form of energy called electrical energy. It is sometimes called an "unseen" force because the energy itself cannot be seen, heard, touched, or smelled. However, the effects of
After completing this chapter, the student should be able to:
 DC Circuits OBJECTIVES After completing this chapter, the student should be able to: Solve for all unknown values (current, voltage, resistance, and power) in a series, parallel, or series-parallel circuit.
DC Circuits OBJECTIVES After completing this chapter, the student should be able to: Solve for all unknown values (current, voltage, resistance, and power) in a series, parallel, or series-parallel circuit.
Physics 3330 Experiment #2 Fall 1999. DC techniques, dividers, and bridges R 2 =(1-S)R P R 1 =SR P. R P =10kΩ 10-turn pot.
 Physics 3330 Experiment #2 Fall 1999 DC techniques, dividers, and bridges Purpose You will gain a familiarity with the circuit board and work with a variety of DC techniques, including voltage dividers,
Physics 3330 Experiment #2 Fall 1999 DC techniques, dividers, and bridges Purpose You will gain a familiarity with the circuit board and work with a variety of DC techniques, including voltage dividers,
ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS. Electrical Circuits
 Electrical Circuits A complete path, or circuit, is needed before voltage can cause a current flow through resistances to perform work. There are several types of circuits, but all require the same basic
Electrical Circuits A complete path, or circuit, is needed before voltage can cause a current flow through resistances to perform work. There are several types of circuits, but all require the same basic
Figure 2.1. a. Block diagram representation of a system; b. block diagram representation of an interconnection of subsystems
 Figure. a. Block diagram repreentation o a ytem; b. block diagram repreentation o an interconnection o ubytem REVIEW OF THE LAPLACE TRANSFORM Table. Laplace tranorm table Table. Laplace tranorm theorem
Figure. a. Block diagram repreentation o a ytem; b. block diagram repreentation o an interconnection o ubytem REVIEW OF THE LAPLACE TRANSFORM Table. Laplace tranorm table Table. Laplace tranorm theorem
DIRECT CURRENT GENERATORS
 DIRECT CURRENT GENERATORS Revision 12:50 14 Nov 05 INTRODUCTION A generator is a machine that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy by using the principle of magnetic induction. This principle
DIRECT CURRENT GENERATORS Revision 12:50 14 Nov 05 INTRODUCTION A generator is a machine that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy by using the principle of magnetic induction. This principle
Review of Multiple Regression Richard Williams, University of Notre Dame, http://www3.nd.edu/~rwilliam/ Last revised January 13, 2015
 Review of Multiple Regreion Richard William, Univerity of Notre Dame, http://www3.nd.edu/~rwilliam/ Lat revied January 13, 015 Aumption about prior nowledge. Thi handout attempt to ummarize and yntheize
Review of Multiple Regreion Richard William, Univerity of Notre Dame, http://www3.nd.edu/~rwilliam/ Lat revied January 13, 015 Aumption about prior nowledge. Thi handout attempt to ummarize and yntheize

 a FEATURE Low On Resistance 2.5 Max
a FEATURE Low On Resistance 2.5 Max