Hemodynamic Disorders Edema, Hyperemia/Congestion, Hemorrhage
|
|
|
- Augustus Mason
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Michele D. Raible, M.D., Pharm.D. UIC College of Medicine Deputy Head for Pathology Education M2 Pathology Course Assistant Professor of Clinical Pathology,UIC Lecture #12 Phone: Monday, September 8, :30 9:20 Reading assignment: Robbins Pathologic Basis of Disease, 6 th Edition, Chapter 5, pp Lecture and Reading Objectives 1. Describe the distribution of fluid in the normal human body. 2. Define edema, anasarca, pitting edema, nonpitting edema, hyperemia, congestion, petechiae, purpura, ecchymosis. 3. Compare and contrast transudate and exudate. 4. List the pathophysiologic categories of edema and give examples of each. 5. Describe the sequence of events that leads to edema in patients with congestive heart failure, protein malnutrition, liver disease, renal disease/nephrotic syndrome, and ascites (Figure 5-2, page 115). 6. Describe why lymphatic obstruction leads to edema. 7. Explain the term dependent edema and its significance. 8. Describe the gross findings in lungs with pulmonary edema. 9. Explain the general clinical significance of subcutaneous edema. Why is pulmonary edema clinically important? What are the potential consequences of severe brain edema? 10. Compare and contrast hyperemia and congestion. 11. Explain the relationship of congestion and edema. 12. Outline the consequences of long-standing congestion (chronic passive congestion). 13. Describe the morphologic appearance (gross and microscopic) of tissues with congestion. 14. Discuss the clinical significance of hemorrhage. Page 1 of 7
2 Why is it important that a patient comes to clinic because her eyelids are suddenly puffy or her legs are swollen? Normal fluid homeostasis is critical to orderly cellular functioning, and although mild edema may be simply annoying, pulmonary or cerebral edema may be rapidly fatal. I. Fluid distribution ~60% of lean body weight is water ~2/3 is intracellular ~1/3 is extracellular (mostly interstitial) ~5% of total body water is in blood plasma II. Edema increased fluid in the interstitial tissue spaces A. Fluid collections in different body cavities may have various designations Hydrothorax (pleural effusion) Hydropericardium Hydroperitoneum (usually called ascites) Anasarca is severe, generalized edema with profound subcutaneous tissue swelling B. Etiologies of Edema Categories of Edema Table 5-1 Increased Hydrostatic Pressure Reduced Plasma Osmotic Pressure Lymphatic Obstruction Sodium Retention Inflammation largely related to local increases in vascular permeability (Edema occurring in hydrodynamic derangements is usually a transudate: protein-poor, specific gravity < ~1.012 to 1.015, usually with few cells. Edema occurring in inflammatory conditions is usually an exudate: protein-rich, specific gravity >~1.015 to 1.020, often with inflammatory components such as leucocytes, fibrin, etc. What are some examples of situations in which a transudate occurs versus an exudate?) Page 2 of 7
3 1. Increased Hydrostatic Pressure a. Local e.g., Impaired venous outflow, such as in deep venous thrombosis, or lower extremity inactivity with prolonged dependency b. Generalized e.g., Congestive heart failure, affecting right ventricular function (Figure 5-2, page 115) 2. Reduced Plasma Osmotic Pressure a. Excessive loss or reduced synthesis of albumin (which is the serum protein most responsible for maintaining colloid osmotic pressure) i. Nephrotic syndrome - Leaky glomerular capillary wall, albumin loss, and generalized edema ii. Diffuse liver pathology or protein malnutrition - Reduced albumin synthesis b. Decreased albumin leads to reduced plasma osmotic pressure, with subsequent net movement of fluid into interstitial tissues and resultant plasma volume contraction. In spite of sodium and water retention, plasma volume deficit cannot be corrected because low serum protein persists. 3. Lymphatic obstruction usually localized; inflammatory versus neoplastic a. Filariasis elephantiasis b. Carcinoma i. Obstruction ii. Secondary to therapy e.g., axillary node dissection at time of diagnosis (as with breast carcinoma) or post-irradiation 4. Sodium and water retention although a secondary factor in many forms of edema, salt retention may also be primary Page 3 of 7
4 Increased salt (with accompanying water) causes: a. Increased hydrostatic pressure due to intravascular fluid volume expansion b. Diminished vascular colloid osmotic pressure C. Morphology of Edema 1. Usually recognized grossly rather than microscopically, in which edema is seen as subtle cell swelling with clearing and separation of extracellular matrix elements 2. Subcutaneous tissues Different distributions depending on etiology of edema a. Diffuse distribution e.g., renal dysfunction, nephrotic syndrome i. Affects all parts of body equally ii. Initially may be more obvious in tissues with loose connective tissue matrix such as eyelids (periorbital edema) b. More conspicuous in site of higher hydrostatic pressure dependent Prominent feature of congestive heart failure (particularly right heart failure) c. Pitting edema versus nonpitting edema 3. Pulmonary edema a. Typical in left heart failure, but also in renal failure, adult respiratory distress syndrome, infection (pneumonia), hypersensitivity reactions b. Grossly, lungs are heavy with frothy, blood-tinged fluid that is mixture of air, edema fluid, and red blood cells 4. Brain edema a. Localized to sites of injury i. Abscess ii. Neoplasm Page 4 of 7
5 b. Generalized brain is grossly swollen with narrowed sulci and distended, flattened gyri i. Encephalitis ii. Hypertensive crises iii. Obstruction to venous outflow D. Clinical correlations c. Trauma may cause localized or generalized edema May be annoying; may signal underlying disease; may be life-threatening III. Hyperemia and Congestion local increased volume of blood in a particular tissue or area A. Hyperemia active process resulting from augmented tissue inflow because of arteriolar dilation; tissue is redder than surrounding areas because of engorgement with oxygenated blood 1. Skeletal muscle during exercise 2. Sites of inflammation B. Congestion passive process resulting from impaired outflow; systemic or local; tissue becomes blue-red (cyanotic), as worsening congestion leads to accumulation of deoxygenated hemoglobin 1. Systemic 2. Local C. Congestion and edema commonly occur together: congestion of capillary beds is related to development of edema D. Long-standing congestion (chronic passive congestion) results in stasis of poorly oxygenated blood and chronic hypoxia 1. May result in parenchymal cell degeneration, cell death, microscopic scarring 2. Capillary rupture may cause small hemorrhagic foci 3. Breakdown and phagocytosis of red cell debris may result in hemosiderin-laden macrophages Page 5 of 7
6 E. Morphology 1. Cut surfaces of affected tissues hemorrhagic and wet 2. Pulmonary a. Acute congestion engorged alveolar capillaries, alveolar septal edema, intra-alveolar hemorrhage b. Chronic congestion thickened and/or fibrotic septae, hemosiderin-laden macrophages 3. Hepatic a. Acute congestion central vein/sinusoids distended with blood, may see central hepatocyte degeneration. Periportal hepatocytes suffer less severe hypoxia. b. Chronic congestion central regions of lobules grossly redbrown and slightly depressed (loss of cells) Nutmeg liver : microscopically, centrilobular necrosis with hepatocyte dropout, hemorrhage, hemosiderin-laden macrophages. Severe, longstanding hepatic congestion may lead to hepatic fibrosis (often associated with heart failure: cardiac cirrhosis ). Central portion of lobule is last to receive blood, so centrilobular necrosis can occur whenever there is reduced hepatic blood flow. IV. Hemorrhage extravasation of blood because of vessel rupture Capillary bleeding can occur under conditions of chronic congestion. Hemorrhagic diatheses variety of clinical disorders with increased tendency to hemorrhage from usually insignificant injury. A. Rupture of large artery or vein is usually due to vascular injury such as trauma, atherosclerosis, erosion. 1. Hemorrhage may be external or may be enclosed within a tissue. Accumulation of blood is called a hematoma. Hematomas may be insignificant, such as a bruise, or may result in death, such as massive retroperitoneal hematomas. Page 6 of 7
7 2. Petechiae 1- to 2-mm hemorrhages into skin, mucous membranes, or serosal surfaces Typically associated with locally increased intravascular pressure, low platelet counts, platelet function defects, clotting factor deficits 3. Purpura Slightly larger hemorrhages ( 3mm) Typically associated with similar pathologies as petechiae, as well as trauma, vasculitis, increased vascular fragility 4. Ecchymoses Larger hemorrhages (>1 to 2 cm), typical after traumas Red blood cells are degraded and phagocytized by macrophages, hemoglobin degraded into bilirubin, then hemosiderin 5. Larger accumulations of blood in a body cavity called hemoperitoneum, hemothorax, etc. Jaundice may develop from blood breakdown. B. Clinical significance 1. Depends on volume and rate of blood loss 2. Site of hemorrhage is also important 3. Loss of iron and subsequent iron-deficiency anemia may become a diagnostic consideration Page 7 of 7
Inflammation and Healing. Review of Normal Defenses. Review of Normal Capillary Exchange. BIO 375 Pathophysiology
 Inflammation and Healing BIO 375 Pathophysiology Review of Normal Defenses Review of Normal Capillary Exchange 1 Inflammation Inflammation is a biochemical and cellular process that occurs in vascularized
Inflammation and Healing BIO 375 Pathophysiology Review of Normal Defenses Review of Normal Capillary Exchange 1 Inflammation Inflammation is a biochemical and cellular process that occurs in vascularized
Provided by the American Venous Forum: veinforum.org
 CHAPTER 1 NORMAL VENOUS CIRCULATION Original author: Frank Padberg Abstracted by Teresa L.Carman Introduction The circulatory system is responsible for circulating (moving) blood throughout the body. The
CHAPTER 1 NORMAL VENOUS CIRCULATION Original author: Frank Padberg Abstracted by Teresa L.Carman Introduction The circulatory system is responsible for circulating (moving) blood throughout the body. The
Ischemia and Infarction
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.035: Principle and Practice of Human Pathology Dr. Badizadegan Ischemia and Infarction HST.035 Spring 2003 In the US: ~50% of deaths are due to
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.035: Principle and Practice of Human Pathology Dr. Badizadegan Ischemia and Infarction HST.035 Spring 2003 In the US: ~50% of deaths are due to
Diseases of peritoneum Lect. Al Qassim University, Faculty of Medicine Phase II Year III, CMD 332 Pathology Department 31-32
 Diseases of peritoneum Lect Al Qassim University, Faculty of Medicine Phase II Year III, CMD 332 Pathology Department 31-32 Describe the etiology, pathogenesis and types of peritonitis Define ascites and
Diseases of peritoneum Lect Al Qassim University, Faculty of Medicine Phase II Year III, CMD 332 Pathology Department 31-32 Describe the etiology, pathogenesis and types of peritonitis Define ascites and
2161-1 - Page 1. Name: 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. Questions 10 and 11 refer to the following:
 Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
Congestive Heart Failure
 William Herring, M.D. 2002 Congestive Heart Failure In Slide Show mode, to advance slides, press spacebar or click left mouse button Congestive Heart Failure Causes of Coronary artery disease Hypertension
William Herring, M.D. 2002 Congestive Heart Failure In Slide Show mode, to advance slides, press spacebar or click left mouse button Congestive Heart Failure Causes of Coronary artery disease Hypertension
Influenza (Flu) Influenza is a viral infection that may affect both the upper and lower respiratory tracts. There are three types of flu virus:
 Respiratory Disorders Bio 375 Pathophysiology General Manifestations of Respiratory Disease Sneezing is a reflex response to irritation in the upper respiratory tract and is associated with inflammation
Respiratory Disorders Bio 375 Pathophysiology General Manifestations of Respiratory Disease Sneezing is a reflex response to irritation in the upper respiratory tract and is associated with inflammation
Pulmonary interstitium. Interstitial Lung Disease. Interstitial lung disease. Interstitial lung disease. Causes.
 Pulmonary interstitium Interstitial Lung Disease Alveolar lining cells (types 1 and 2) Thin elastin-rich connective component containing capillary blood vessels Interstitial lung disease Increase in interstitial
Pulmonary interstitium Interstitial Lung Disease Alveolar lining cells (types 1 and 2) Thin elastin-rich connective component containing capillary blood vessels Interstitial lung disease Increase in interstitial
Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back
 Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back to the left atria from the left ventricle, blood is pumped
Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back to the left atria from the left ventricle, blood is pumped
Dehydration & Overhydration. Waseem Jerjes
 Dehydration & Overhydration Waseem Jerjes Dehydration 3 Major Types Isotonic - Fluid has the same osmolarity as plasma Hypotonic -Fluid has fewer solutes than plasma Hypertonic-Fluid has more solutes than
Dehydration & Overhydration Waseem Jerjes Dehydration 3 Major Types Isotonic - Fluid has the same osmolarity as plasma Hypotonic -Fluid has fewer solutes than plasma Hypertonic-Fluid has more solutes than
Diseases. Inflammations Non-inflammatory pleural effusions Pneumothorax Tumours
 Pleura Visceral pleura covers lungs and extends into fissures Parietal pleura limits mediastinum and covers dome of diaphragm and inner aspect of chest wall. Two layers between them (pleural cavity) contains
Pleura Visceral pleura covers lungs and extends into fissures Parietal pleura limits mediastinum and covers dome of diaphragm and inner aspect of chest wall. Two layers between them (pleural cavity) contains
37 2 Blood and the Lymphatic System Slide 1 of 34
 1 of 34 Blood is a connective tissue that contains both dissolved substances and specialized cells. 2 of 34 The functions of blood include: collecting oxygen from the lungs, nutrients from the digestive
1 of 34 Blood is a connective tissue that contains both dissolved substances and specialized cells. 2 of 34 The functions of blood include: collecting oxygen from the lungs, nutrients from the digestive
Circulatory System Review
 Circulatory System Review 1. Draw a table to describe the similarities and differences between arteries and veins? Anatomy Direction of blood flow: Oxygen concentration: Arteries Thick, elastic smooth
Circulatory System Review 1. Draw a table to describe the similarities and differences between arteries and veins? Anatomy Direction of blood flow: Oxygen concentration: Arteries Thick, elastic smooth
Tired, Aching Legs? Swollen Ankles? Varicose Veins?
 Tired, Aching Legs? Swollen Ankles? Varicose Veins? Healthy Legs 2006 http://healthylegs.com Page 1 Venous disorders are widespread Leg problems are widespread throughout the world, but what most people
Tired, Aching Legs? Swollen Ankles? Varicose Veins? Healthy Legs 2006 http://healthylegs.com Page 1 Venous disorders are widespread Leg problems are widespread throughout the world, but what most people
Edema. Brad Anawalt, MD VA Puget Sound University of Washington
 Edema Brad Anawalt, MD VA Puget Sound University of Washington Types of edema Dependent bilateral edema (usually pitting ) Lymphedema Localized edema Myxedema 2 Pitting dependent edema: causes Decreased
Edema Brad Anawalt, MD VA Puget Sound University of Washington Types of edema Dependent bilateral edema (usually pitting ) Lymphedema Localized edema Myxedema 2 Pitting dependent edema: causes Decreased
Chapter 19 Ci C r i cula l t a i t o i n
 Chapter 19 Circulation A closed system Circulatory System Consisting of Heart, Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, Blood & the Lymphatic system Blood Make up The blood is made up of Plasma and three main types
Chapter 19 Circulation A closed system Circulatory System Consisting of Heart, Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, Blood & the Lymphatic system Blood Make up The blood is made up of Plasma and three main types
INFLAMMATORY PLEURAL EFFUSION
 PLEURA- LESIONS LESIONS OF PLEURA Primary Intra pleural bacterial infections Neoplasm (mesothelioma) Secondary A complication of some underlying disease PLEURAL EFFUSION Common manifestation of both primary
PLEURA- LESIONS LESIONS OF PLEURA Primary Intra pleural bacterial infections Neoplasm (mesothelioma) Secondary A complication of some underlying disease PLEURAL EFFUSION Common manifestation of both primary
Chapter 16: Circulation
 Section 1 (The Body s Transport System) Chapter 16: Circulation 7 th Grade Cardiovascular system (the circulatory system) includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood carries needed substances to the cells
Section 1 (The Body s Transport System) Chapter 16: Circulation 7 th Grade Cardiovascular system (the circulatory system) includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood carries needed substances to the cells
12.1: The Function of Circulation page 478
 12.1: The Function of Circulation page 478 Key Terms: Circulatory system, heart, blood vessel, blood, open circulatory system, closed circulatory system, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein, aorta, atrioventricular
12.1: The Function of Circulation page 478 Key Terms: Circulatory system, heart, blood vessel, blood, open circulatory system, closed circulatory system, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein, aorta, atrioventricular
Lymph capillaries, Lymphatic collecting vessels, Valves, Lymph Duct, Lymph node, Vein
 WLHS/A&P/Oppelt Name Lymphatic System Practice 1. Figure 12-1 provides an overview of the lymphatic vessels. First color code the following structures. Color code in Figure 12-1 Heart Veins Lymphatic vessels/lymph
WLHS/A&P/Oppelt Name Lymphatic System Practice 1. Figure 12-1 provides an overview of the lymphatic vessels. First color code the following structures. Color code in Figure 12-1 Heart Veins Lymphatic vessels/lymph
Ventilation Perfusion Relationships
 Ventilation Perfusion Relationships VENTILATION PERFUSION RATIO Ideally, each alveolus in the lungs would receive the same amount of ventilation and pulmonary capillary blood flow (perfusion). In reality,
Ventilation Perfusion Relationships VENTILATION PERFUSION RATIO Ideally, each alveolus in the lungs would receive the same amount of ventilation and pulmonary capillary blood flow (perfusion). In reality,
Functions of Blood System. Blood Cells
 Functions of Blood System Transport: to and from tissue cells Nutrients to cells: amino acids, glucose, vitamins, minerals, lipids (as lipoproteins). Oxygen: by red blood corpuscles (oxyhaemoglobin - 4
Functions of Blood System Transport: to and from tissue cells Nutrients to cells: amino acids, glucose, vitamins, minerals, lipids (as lipoproteins). Oxygen: by red blood corpuscles (oxyhaemoglobin - 4
The Circulatory System. Chapter 17 Lesson 1
 The Circulatory System Chapter 17 Lesson 1 Functions of the Circulatory System Your circulatory system maintains an internal environment in which all the cells in your body are nourished. As your heart
The Circulatory System Chapter 17 Lesson 1 Functions of the Circulatory System Your circulatory system maintains an internal environment in which all the cells in your body are nourished. As your heart
ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME (ARDS) S. Agarwal, MD, S. Kache MD
 ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME (ARDS) S. Agarwal, MD, S. Kache MD Definition ARDS is a clinical syndrome of lung injury with hypoxic respiratory failure caused by intense pulmonary inflammation that
ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME (ARDS) S. Agarwal, MD, S. Kache MD Definition ARDS is a clinical syndrome of lung injury with hypoxic respiratory failure caused by intense pulmonary inflammation that
Functions of Blood. Collects O 2 from lungs, nutrients from digestive tract, and waste products from tissues Helps maintain homeostasis
 Blood Objectives Describe the functions of blood Describe blood plasma Explain the functions of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets Summarize the process of blood clotting What is Blood?
Blood Objectives Describe the functions of blood Describe blood plasma Explain the functions of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets Summarize the process of blood clotting What is Blood?
The Body s Transport System
 Circulation Name Date Class The Body s Transport System This section describes how the heart, blood vessels, and blood work together to carry materials throughout the body. Use Target Reading Skills As
Circulation Name Date Class The Body s Transport System This section describes how the heart, blood vessels, and blood work together to carry materials throughout the body. Use Target Reading Skills As
Francine Lortie-Monette, MD, MSc, CSPQ, MBA Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics University of Western Ontario 2003
 ASBESTOS Francine Lortie-Monette, MD, MSc, CSPQ, MBA Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics University of Western Ontario 2003 Asbestosis Asbestosis is a model for other dust diseases as well as
ASBESTOS Francine Lortie-Monette, MD, MSc, CSPQ, MBA Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics University of Western Ontario 2003 Asbestosis Asbestosis is a model for other dust diseases as well as
Consent for Treatment/Procedure Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy
 Patient's Name: Today's Date: / / The purpose of this document is to confirm, in the presence of witnesses, your informed request to have Surgery for obesity. You are asked to read the following document
Patient's Name: Today's Date: / / The purpose of this document is to confirm, in the presence of witnesses, your informed request to have Surgery for obesity. You are asked to read the following document
Emergency Fluid Therapy in Companion Animals
 Emergency Fluid Therapy in Companion Animals Paul Pitney BVSc [email protected] The administration of appropriate types and quantities of intravenous fluids is the cornerstone of emergency therapy
Emergency Fluid Therapy in Companion Animals Paul Pitney BVSc [email protected] The administration of appropriate types and quantities of intravenous fluids is the cornerstone of emergency therapy
Circulatory System and Blood
 Circulatory System and Blood 1. Identify the arteries in the diagram and give one function for each. Y: Common carotid artery: sends oxygenated blood to the brain, provide nutrients. X: Subclavian artery:
Circulatory System and Blood 1. Identify the arteries in the diagram and give one function for each. Y: Common carotid artery: sends oxygenated blood to the brain, provide nutrients. X: Subclavian artery:
Tired, Aching Legs? Swollen Ankles? Varicose Veins? An informative guide for patients
 Tired, Aching Legs? Swollen Ankles? Varicose Veins? An informative guide for patients Are You at Risk? Leg problems are widespread throughout the world, but what most people don t know is that approximately
Tired, Aching Legs? Swollen Ankles? Varicose Veins? An informative guide for patients Are You at Risk? Leg problems are widespread throughout the world, but what most people don t know is that approximately
Certified Clinical Documentation Specialist Examination Content Outline - 2016
 Certified Clinical Documentation Specialist Examination Content Outline - 2016 1. Healthcare Regulations, Reimbursement, and Documentation Requirements Related to the Inpatient Prospective Payment System
Certified Clinical Documentation Specialist Examination Content Outline - 2016 1. Healthcare Regulations, Reimbursement, and Documentation Requirements Related to the Inpatient Prospective Payment System
Leukocytoclastic Vasculitis and Stasis Dermatitis With Id Reaction
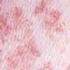 Id Reaction December 01, 2007 By David L. Kaplan, MD [1] A Photo Quiz to Hone Dermatologic Skills Case 1: A slightly pruritic eruption developed on the lower legs of a 39-year-old woman after she had an
Id Reaction December 01, 2007 By David L. Kaplan, MD [1] A Photo Quiz to Hone Dermatologic Skills Case 1: A slightly pruritic eruption developed on the lower legs of a 39-year-old woman after she had an
Hepatitis C. Laboratory Tests and Hepatitis C
 Hepatitis C Laboratory Tests and Hepatitis C If you have hepatitis C, your doctor will use laboratory tests to check your health. This handout will help you understand what the major tests are and what
Hepatitis C Laboratory Tests and Hepatitis C If you have hepatitis C, your doctor will use laboratory tests to check your health. This handout will help you understand what the major tests are and what
Section B: Epithelial Tissue 1. Where are epithelial tissues found within the body? 2. What are the functions of the epithelial tissues?
 Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Liver Failure. Nora Aziz. www.3bv.org. Bones, Brains & Blood Vessels
 Liver Failure Nora Aziz www.3bv.org Bones, Brains & Blood Vessels Severe deterioration in liver function Looses ability to regenerate/repair decompensated Liver extensively damaged before it fails Equal
Liver Failure Nora Aziz www.3bv.org Bones, Brains & Blood Vessels Severe deterioration in liver function Looses ability to regenerate/repair decompensated Liver extensively damaged before it fails Equal
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley. Practice Exam 1
 Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam 1 1. Which definition is the best definition of the term gross anatomy? a. The study of cells. b. The study of tissues. c. The study of structures
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam 1 1. Which definition is the best definition of the term gross anatomy? a. The study of cells. b. The study of tissues. c. The study of structures
Johanna Kruckeberg Human Anatomy and Physiology CASTLE Case Study Analysis Questions July 28, 2006
 Johanna Kruckeberg Human Anatomy and Physiology CASTLE Case Study Analysis Questions July 28, 2006 1. What are the important teaching/learning issues in this case? Some students in Human Anatomy and Physiology
Johanna Kruckeberg Human Anatomy and Physiology CASTLE Case Study Analysis Questions July 28, 2006 1. What are the important teaching/learning issues in this case? Some students in Human Anatomy and Physiology
Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Accofil (filgrastim)
 EMA/475472/2014 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Accofil (filgrastim) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Accofil, which details the measures to be taken in order to ensure
EMA/475472/2014 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Accofil (filgrastim) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Accofil, which details the measures to be taken in order to ensure
Diagnostics: Page 2 of 5
 Proteinuria Proteinuria is a condition in which there are increased amounts of protein in the urine. There are a number of different diseases which can result in proteinuria. In the early stages of the
Proteinuria Proteinuria is a condition in which there are increased amounts of protein in the urine. There are a number of different diseases which can result in proteinuria. In the early stages of the
Practical class 3 THE HEART
 Practical class 3 THE HEART OBJECTIVES By the time you have completed this assignment and any necessary further reading or study you should be able to:- 1. Describe the fibrous pericardium and serous pericardium,
Practical class 3 THE HEART OBJECTIVES By the time you have completed this assignment and any necessary further reading or study you should be able to:- 1. Describe the fibrous pericardium and serous pericardium,
The State of the Liver in the Adult Patient after Fontan Palliation
 The State of the Liver in the Adult Patient after Fontan Palliation Fred Wu, M.D. Boston Adult Congenital Heart Service Boston Children s Hospital/Brigham & Women s Hospital 7 th National Adult Congenital
The State of the Liver in the Adult Patient after Fontan Palliation Fred Wu, M.D. Boston Adult Congenital Heart Service Boston Children s Hospital/Brigham & Women s Hospital 7 th National Adult Congenital
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT
 CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING PLANTS Function of heart Wilting Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Transpiration: function
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING PLANTS Function of heart Wilting Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Transpiration: function
Pattern Identification According to Qi and Blood
 CHAPTER EIGHT Pattern Identification According to Qi and Blood Pattern identification according to qi and blood is a commonly used method for pattern identification which analyzes manifestations obtained
CHAPTER EIGHT Pattern Identification According to Qi and Blood Pattern identification according to qi and blood is a commonly used method for pattern identification which analyzes manifestations obtained
Immunohistochemistry on cytology specimens from pleural and peritoneal fluid
 Immunohistochemistry on cytology specimens from pleural and peritoneal fluid Dr Naveena Singh Consultant Pathologist Bart health NHS Trust London United Kingdom Disclosures and Acknowledgements I have
Immunohistochemistry on cytology specimens from pleural and peritoneal fluid Dr Naveena Singh Consultant Pathologist Bart health NHS Trust London United Kingdom Disclosures and Acknowledgements I have
Acute heart failure may be de novo or it may be a decompensation of chronic heart failure.
 Management of Acute Left Ventricular Failure Acute left ventricular failure presents as pulmonary oedema due to increased pressure in the pulmonary capillaries. It is important to realise though that left
Management of Acute Left Ventricular Failure Acute left ventricular failure presents as pulmonary oedema due to increased pressure in the pulmonary capillaries. It is important to realise though that left
The Structure and Function of the Lymphatic System
 The Structure and Function of the Lymphatic System The lymphatic system runs though the body and is made up of organs and lymphatic tissue, this includes organs like the spleen and thymus and also lymphatic
The Structure and Function of the Lymphatic System The lymphatic system runs though the body and is made up of organs and lymphatic tissue, this includes organs like the spleen and thymus and also lymphatic
MECHINICAL VENTILATION S. Kache, MD
 MECHINICAL VENTILATION S. Kache, MD Spontaneous respiration vs. Mechanical ventilation Natural spontaneous ventilation occurs when the respiratory muscles, diaphragm and intercostal muscles pull on the
MECHINICAL VENTILATION S. Kache, MD Spontaneous respiration vs. Mechanical ventilation Natural spontaneous ventilation occurs when the respiratory muscles, diaphragm and intercostal muscles pull on the
CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Lung cancer affects a life-sustaining system of the body, the respiratory system. The respiratory system is responsible for one of the essential
CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Lung cancer affects a life-sustaining system of the body, the respiratory system. The respiratory system is responsible for one of the essential
Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Ofev (nintedanib)
 EMA/738120/2014 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Ofev (nintedanib) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Ofev, which details the measures to be taken in order to ensure that
EMA/738120/2014 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Ofev (nintedanib) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Ofev, which details the measures to be taken in order to ensure that
Introduction Hemophilia is a rare bleeding disorder in which the blood does not clot normally. About 1 in 10,000 people are born with hemophilia.
 Hemophilia Introduction Hemophilia is a rare bleeding disorder in which the blood does not clot normally. About 1 in 10,000 people are born with hemophilia. Hemophilia can be mild, moderate, or severe.
Hemophilia Introduction Hemophilia is a rare bleeding disorder in which the blood does not clot normally. About 1 in 10,000 people are born with hemophilia. Hemophilia can be mild, moderate, or severe.
Albumin. Prothrombin time. Total protein
 Hepatitis C Fact Sheet February 2016 www.hepatitis.va.gov Laboratory Tests and Hepatitis If you have hepatitis C, your doctor will use laboratory tests to about learn more about your individual hepatitis
Hepatitis C Fact Sheet February 2016 www.hepatitis.va.gov Laboratory Tests and Hepatitis If you have hepatitis C, your doctor will use laboratory tests to about learn more about your individual hepatitis
UNIT 3 : MAINTAINING DYNAMIC EQUILIBRIUM
 BIOLOGY - 2201 UNIT 3 : MAINTAINING DYNAMIC EQUILIBRIUM What happens to your body as you run? Breathing, heart rate, temperature, muscle pain, thirsty... Homeotasis Homeostasis is the process of maintaining
BIOLOGY - 2201 UNIT 3 : MAINTAINING DYNAMIC EQUILIBRIUM What happens to your body as you run? Breathing, heart rate, temperature, muscle pain, thirsty... Homeotasis Homeostasis is the process of maintaining
Coronary Artery Disease leading cause of morbidity & mortality in industrialised nations.
 INTRODUCTION Coronary Artery Disease leading cause of morbidity & mortality in industrialised nations. Although decrease in cardiovascular mortality still major cause of morbidity & burden of disease.
INTRODUCTION Coronary Artery Disease leading cause of morbidity & mortality in industrialised nations. Although decrease in cardiovascular mortality still major cause of morbidity & burden of disease.
MRI of Bone Marrow Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation
 MRI of Bone Marrow Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel, M.D. Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology Washington University School of Medicine St. Louis, MO and Visiting Scientist, AFIP, Washington,
MRI of Bone Marrow Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel, M.D. Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology Washington University School of Medicine St. Louis, MO and Visiting Scientist, AFIP, Washington,
Determinants of Blood Oxygen Content Instructor s Guide
 Determinants of Blood Oxygen Content Instructor s Guide Time to Complete This activity will take approximately 75 minutes, but can be shortened depending on how much time the instructor takes to review
Determinants of Blood Oxygen Content Instructor s Guide Time to Complete This activity will take approximately 75 minutes, but can be shortened depending on how much time the instructor takes to review
Exchange solutes and water with cells of the body
 Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
MANAGEMENT OF LIVER CIRRHOSIS
 MANAGEMENT OF LIVER CIRRHOSIS Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What is cirrhosis? Cirrhosis is a result of long-term, continuous damage to the liver and may be due to many different
MANAGEMENT OF LIVER CIRRHOSIS Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What is cirrhosis? Cirrhosis is a result of long-term, continuous damage to the liver and may be due to many different
Diagram showing Systemic and Portal Circulation
 Diagram showing Systemic and Portal Circulation The Lymphatic System The Lymphatic System comprises of lymphatic capillaries, lymphatic vessels, nodes and ducts. Lymph fluid is not blood plasma, it contains
Diagram showing Systemic and Portal Circulation The Lymphatic System The Lymphatic System comprises of lymphatic capillaries, lymphatic vessels, nodes and ducts. Lymph fluid is not blood plasma, it contains
What Is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)?
 What Is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D., Chair 1 What
What Is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D., Chair 1 What
Bleeding disorders or haemorrhagic diatheses are a group of disorders characterised by defective haemostasis with abnormal bleeding.
 Bleeding disorders or haemorrhagic diatheses are a group of disorders characterised by defective haemostasis with abnormal bleeding. Bleeding may be spontaneous in the form of small haemorrhages into the
Bleeding disorders or haemorrhagic diatheses are a group of disorders characterised by defective haemostasis with abnormal bleeding. Bleeding may be spontaneous in the form of small haemorrhages into the
BLOOD-Chp. Chp.. 6 What are the functions of blood? What is the composition of blood? 3 major types of plasma proteins
 6.1 Blood: An overview BLOOD-Chp Chp.. 6 What are the functions of blood? Transportation: oxygen, nutrients, wastes, carbon dioxide and hormones Defense: against invasion by pathogens Regulatory functions:
6.1 Blood: An overview BLOOD-Chp Chp.. 6 What are the functions of blood? Transportation: oxygen, nutrients, wastes, carbon dioxide and hormones Defense: against invasion by pathogens Regulatory functions:
Suffering from varicose veins? Patient Information. ELVeS Radial Minimally invasive laser therapy of venous insufficiency
 Suffering from varicose veins? Patient Information ELVeS Radial Minimally invasive laser therapy of venous insufficiency Do you suffer from heavy legs or visible veins? This makes diseases of the veins
Suffering from varicose veins? Patient Information ELVeS Radial Minimally invasive laser therapy of venous insufficiency Do you suffer from heavy legs or visible veins? This makes diseases of the veins
STAGES OF SHOCK. IRREVERSIBLE SHOCK Heart deteriorates until it can no longer pump and death occurs.
 STAGES OF SHOCK SHOCK : A profound disturbance of circulation and metabolism, which leads to inadequate perfusion of all organs which are needed to maintain life. COMPENSATED NONPROGRESSIVE SHOCK 30 sec
STAGES OF SHOCK SHOCK : A profound disturbance of circulation and metabolism, which leads to inadequate perfusion of all organs which are needed to maintain life. COMPENSATED NONPROGRESSIVE SHOCK 30 sec
Department of Surgery
 What is emphysema? 2004 Regents of the University of Michigan Emphysema is a chronic disease of the lungs characterized by thinning and overexpansion of the lung-like blisters (bullae) in the lung tissue.
What is emphysema? 2004 Regents of the University of Michigan Emphysema is a chronic disease of the lungs characterized by thinning and overexpansion of the lung-like blisters (bullae) in the lung tissue.
Liver Function Essay
 Liver Function Essay Name: Quindoline Ntui Date: April 20, 2009 Professor: Dr. Danil Hammoudi Class: Anatomy and Physiology 2 Liver function The human body consist of many highly organize part working
Liver Function Essay Name: Quindoline Ntui Date: April 20, 2009 Professor: Dr. Danil Hammoudi Class: Anatomy and Physiology 2 Liver function The human body consist of many highly organize part working
Provided by the American Venous Forum: veinforum.org
 CHAPTER 20 LYMPHEDEMA DIAGNOSIS AND THERAPY Original authors: Audrea Cheville, Cindy Felty, Gail L. Gamble, Peter Gloviczki, Thom W. Rooke, David Strick Abstracted by Raghu Motaganahalli Introduction Lymphedema
CHAPTER 20 LYMPHEDEMA DIAGNOSIS AND THERAPY Original authors: Audrea Cheville, Cindy Felty, Gail L. Gamble, Peter Gloviczki, Thom W. Rooke, David Strick Abstracted by Raghu Motaganahalli Introduction Lymphedema
1 The diagram shows blood as seen under a microscope. Which identifies parts P, Q, R and S of the blood?
 1 1 The diagram shows blood as seen under a microscope. Which identifies parts P, Q, R and S of the blood? 2 The plan shows the blood system of a mammal. What does the part labelled X represent? A heart
1 1 The diagram shows blood as seen under a microscope. Which identifies parts P, Q, R and S of the blood? 2 The plan shows the blood system of a mammal. What does the part labelled X represent? A heart
Intravenous Fluid Selection
 BENNMC03_0131186116.qxd 3/9/05 18:24 Page 20 seema Seema-3:Desktop Folder:PQ731: CHAPTER 3 Intravenous Fluid Selection LEARNING OBJECTIVES By the end of this chapter, you should be able to: Describe and
BENNMC03_0131186116.qxd 3/9/05 18:24 Page 20 seema Seema-3:Desktop Folder:PQ731: CHAPTER 3 Intravenous Fluid Selection LEARNING OBJECTIVES By the end of this chapter, you should be able to: Describe and
Venous Reflux Disease and Current Treatments VN20-87-A 01/06
 Venous Reflux Disease and Current Treatments Leg Vein Anatomy Your legs are made up of a network of veins and vessels that carry blood back to the heart The venous system is comprised of: Deep veins Veins
Venous Reflux Disease and Current Treatments Leg Vein Anatomy Your legs are made up of a network of veins and vessels that carry blood back to the heart The venous system is comprised of: Deep veins Veins
3. The Circulatory System
 3. The Circulatory System A. Introduction B. Blood 1. Circulatory system transports water, electrolytes, hormones, enzymes, antibodies, cell, gases and nutrients to all cells and carries away metabolic
3. The Circulatory System A. Introduction B. Blood 1. Circulatory system transports water, electrolytes, hormones, enzymes, antibodies, cell, gases and nutrients to all cells and carries away metabolic
The largest clinical study of Bayer's Xarelto (rivaroxaban) Wednesday, 14 November 2012 07:38
 Bayer HealthCare has announced the initiation of the COMPASS study, the largest clinical study of its oral anticoagulant Xarelto (rivaroxaban) to date, investigating the prevention of major adverse cardiac
Bayer HealthCare has announced the initiation of the COMPASS study, the largest clinical study of its oral anticoagulant Xarelto (rivaroxaban) to date, investigating the prevention of major adverse cardiac
Approach to Abnormal Liver Tests
 Approach to Abnormal Liver Tests Naga P. Chalasani, MD, FACG Professor of Medicine and Cellular & Integrative Physiology Director, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Indiana University School
Approach to Abnormal Liver Tests Naga P. Chalasani, MD, FACG Professor of Medicine and Cellular & Integrative Physiology Director, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Indiana University School
Protein electrophoresis is used to categorize globulins into the following four categories:
 Globulin Globulin is one of the two types of serum proteins, the other being albumin. This generic term encompasses a heterogeneous series of families of proteins, with larger molecules and less soluble
Globulin Globulin is one of the two types of serum proteins, the other being albumin. This generic term encompasses a heterogeneous series of families of proteins, with larger molecules and less soluble
Blood Transfusion. Red Blood Cells White Blood Cells Platelets
 Blood Transfusion Introduction Blood transfusions are very common. Each year, almost 5 million Americans need a blood transfusion. Blood transfusions are given to replace blood lost during surgery or serious
Blood Transfusion Introduction Blood transfusions are very common. Each year, almost 5 million Americans need a blood transfusion. Blood transfusions are given to replace blood lost during surgery or serious
Blood. Functions of Blood. Components of Blood. Transporting. Distributing body heat. A type of connective tissue. Formed elements.
 Blood Functions of Blood Transporting nutrients respiratory gases waste products Distributing body heat Components of Blood A type of connective tissue Formed elements Living blood cells Plasma Nonliving
Blood Functions of Blood Transporting nutrients respiratory gases waste products Distributing body heat Components of Blood A type of connective tissue Formed elements Living blood cells Plasma Nonliving
Sepsis: Identification and Treatment
 Sepsis: Identification and Treatment Daniel Z. Uslan, MD Associate Clinical Professor Division of Infectious Diseases Medical Director, UCLA Sepsis Task Force Severe Sepsis: A Significant Healthcare Challenge
Sepsis: Identification and Treatment Daniel Z. Uslan, MD Associate Clinical Professor Division of Infectious Diseases Medical Director, UCLA Sepsis Task Force Severe Sepsis: A Significant Healthcare Challenge
33.1 The Circulatory System
 33.1 The Circulatory System Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the human circulatory system. Describe the structure of the heart and explain how it pumps blood through the body. Name three types
33.1 The Circulatory System Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the human circulatory system. Describe the structure of the heart and explain how it pumps blood through the body. Name three types
Lumbar Laminectomy and Interspinous Process Fusion
 Lumbar Laminectomy and Interspinous Process Fusion Introduction Low back and leg pain caused by pinched nerves in the back is a common condition that limits your ability to move, walk, and work. This condition
Lumbar Laminectomy and Interspinous Process Fusion Introduction Low back and leg pain caused by pinched nerves in the back is a common condition that limits your ability to move, walk, and work. This condition
Common types of congenital heart defects
 Common types of congenital heart defects Congenital heart defects are abnormalities that develop before birth. They can occur in the heart's chambers, valves or blood vessels. A baby may be born with only
Common types of congenital heart defects Congenital heart defects are abnormalities that develop before birth. They can occur in the heart's chambers, valves or blood vessels. A baby may be born with only
Supplemental Material CBE Life Sciences Education. Su et al.
 Supplemental Material CBE Life Sciences Education Su et al. APPENDIX Human Body's Immune System Test This test consists of 31 questions, with only 1 answer to be selected for each question. Please select
Supplemental Material CBE Life Sciences Education Su et al. APPENDIX Human Body's Immune System Test This test consists of 31 questions, with only 1 answer to be selected for each question. Please select
Heart Diseases and their Complications
 Heart Diseases and their Complications Health Promotion and Education Program Rev. 2014 2014, MMM Healthcare, Inc. - PMC Medicare Choice, Inc. Reproduction of this material is prohibited. MP-HEP-PPT-252-01-021914-E
Heart Diseases and their Complications Health Promotion and Education Program Rev. 2014 2014, MMM Healthcare, Inc. - PMC Medicare Choice, Inc. Reproduction of this material is prohibited. MP-HEP-PPT-252-01-021914-E
Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide
 Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Define the terms anatomy and physiology. List and discuss in order of increasing complexity, the body from the cell to the whole organism. Define the
Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Define the terms anatomy and physiology. List and discuss in order of increasing complexity, the body from the cell to the whole organism. Define the
Pharmacology of the Respiratory Tract: COPD and Steroids
 Pharmacology of the Respiratory Tract: COPD and Steroids Dr. Tillie-Louise Hackett Department of Anesthesiology, Pharmacology and Therapeutics University of British Columbia Associate Head, Centre of Heart
Pharmacology of the Respiratory Tract: COPD and Steroids Dr. Tillie-Louise Hackett Department of Anesthesiology, Pharmacology and Therapeutics University of British Columbia Associate Head, Centre of Heart
PULMONARY HYPERTENSION. Charles A. Thompson, M.D., FACC, FSCAI Cardiovascular Institute of the South Zachary, Louisiana
 PULMONARY HYPERTENSION Charles A. Thompson, M.D., FACC, FSCAI Cardiovascular Institute of the South Zachary, Louisiana What is Pulmonary Hypertension? What is normal? Pulmonary artery systolic pressure
PULMONARY HYPERTENSION Charles A. Thompson, M.D., FACC, FSCAI Cardiovascular Institute of the South Zachary, Louisiana What is Pulmonary Hypertension? What is normal? Pulmonary artery systolic pressure
Wound and Skin Assessment. Mary Carvalho RN, BSN, MBA Clinical Coordinator Johnson Creek Wound and Edema Center
 Wound and Skin Assessment Mary Carvalho RN, BSN, MBA Clinical Coordinator Johnson Creek Wound and Edema Center Skin The largest Organ Weighs between 6 and 8 pounds Covers over 20 square feet Thickness
Wound and Skin Assessment Mary Carvalho RN, BSN, MBA Clinical Coordinator Johnson Creek Wound and Edema Center Skin The largest Organ Weighs between 6 and 8 pounds Covers over 20 square feet Thickness
A. All cells need oxygen and release carbon dioxide why?
 I. Introduction: Describe how the cardiovascular and respiratory systems interact to supply O 2 and eliminate CO 2. A. All cells need oxygen and release carbon dioxide why? B. Two systems that help to
I. Introduction: Describe how the cardiovascular and respiratory systems interact to supply O 2 and eliminate CO 2. A. All cells need oxygen and release carbon dioxide why? B. Two systems that help to
Cardiovascular diseases. pathology
 Cardiovascular diseases pathology Atherosclerosis Vascular diseases A disease that results in arterial wall thickens as a result of build- up of fatty materials such cholesterol, resulting in acute and
Cardiovascular diseases pathology Atherosclerosis Vascular diseases A disease that results in arterial wall thickens as a result of build- up of fatty materials such cholesterol, resulting in acute and
Mosby s PATHOLOGY for Massage Therapists. Lesson 9.1 Objectives. Chapter 9 Lymphatic and Immune Pathologies. Lymphatic System Overview
 Mosby s PATHOLOGY for Massage Therapists Chapter 9 Lymphatic and Immune Pathologies Lesson 9.1 Objectives Discuss anatomic structures and physiologic processes related to the lymphatic system. Describe
Mosby s PATHOLOGY for Massage Therapists Chapter 9 Lymphatic and Immune Pathologies Lesson 9.1 Objectives Discuss anatomic structures and physiologic processes related to the lymphatic system. Describe
ENTITLEMENT ELIGIBILITY GUIDELINES VARICOSE VEINS AND SUPERFICIAL THROMBOPHLEBITIS
 ENTITLEMENT ELIGIBILITY GUIDELINES VARICOSE VEINS AND SUPERFICIAL THROMBOPHLEBITIS 1. VARICOSE VEINS MPC 00727 ICD-9 454 DEFINITION Varicose Veins of the lower extremities are a dilatation, lengthening
ENTITLEMENT ELIGIBILITY GUIDELINES VARICOSE VEINS AND SUPERFICIAL THROMBOPHLEBITIS 1. VARICOSE VEINS MPC 00727 ICD-9 454 DEFINITION Varicose Veins of the lower extremities are a dilatation, lengthening
We have made the following changes to the Critical Illness events covered under our group critical illness policy.
 We have made the following changes to the Critical Illness events covered under our group critical illness policy. March 2015 Because everyone needs a back-up plan 7 New critical illness events added to
We have made the following changes to the Critical Illness events covered under our group critical illness policy. March 2015 Because everyone needs a back-up plan 7 New critical illness events added to
INFORMED CONSENT - CARPAL TUNNEL RELEASE
 . Purchasers of the Patient Consultation Resource Book are given a limited license to modify documents contained herein and reproduce the modified version for use in the Purchaser's own practice only.
. Purchasers of the Patient Consultation Resource Book are given a limited license to modify documents contained herein and reproduce the modified version for use in the Purchaser's own practice only.
Pulmonary Diseases. Lung Disease: Pathophysiology, Medical and Exercise Programming. Overview of Pathophysiology
 Lung Disease: Pathophysiology, Medical and Exercise Programming Overview of Pathophysiology Ventilatory Impairments Increased airway resistance Reduced compliance Increased work of breathing Ventilatory
Lung Disease: Pathophysiology, Medical and Exercise Programming Overview of Pathophysiology Ventilatory Impairments Increased airway resistance Reduced compliance Increased work of breathing Ventilatory
EXHIBIT H SETTLEMENT ELIGIBILITY CRITERIA. a) pharmacy records reflecting the dispensing of Bextra and/or Celebrex to the Class Member; or
 EXHIBIT H SETTLEMENT ELIGIBILITY CRITERIA 1. PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION DOCUMENTATION In order to be eligible for compensation under the Settlement Agreement, each Claimant must provide evidence of the Class
EXHIBIT H SETTLEMENT ELIGIBILITY CRITERIA 1. PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION DOCUMENTATION In order to be eligible for compensation under the Settlement Agreement, each Claimant must provide evidence of the Class
