Lecture 20: Transmission (ABCD) Matrix.
|
|
|
- Joan Williamson
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Whites, EE 48/58 Lecture 0 Page of 7 Lecture 0: Transmission (ABC) Matrix. Concerning the equivalent port representations of networks we ve seen in this course:. Z parameters are useful for series connected networks,. Y parameters are useful for parallel connected networks,. S parameters are useful for describing interactions of voltage and current waves with a network. There is another set of network parameters particularly suited for cascading twoport networks. This set is called the ABC matrix or, equivalently, the transmission matrix. Consider this twoport network (Fig. 4.a): A C B Unlike in the definition used for Z and Y parameters, notice that is directed away from the port. This is an important point and we ll discover the reason for it shortly. The ABC matrix is defined as A B C (4.69),() 05 Keith W. Whites
2 Whites, EE 48/58 Lecture 0 Page of 7 t is easy to show that, A 0 C 0, B 0 0 Note that not all of these parameters have the same units. The usefulness of the ABC matrix is that cascaded twoport networks can be characterized by simply multiplying their ABC matrices. Nice! To see this, consider the following twoport networks: A C B A C B n matrix form and A B C A B C (4.70a),() () When these twoports are cascaded,
3 Whites, EE 48/58 Lecture 0 Page of 7 A C B A C B it is apparent that and. (The latter is the reason for assuming out of the port.) Consequently, substituting () into () yields A B A B C C (4.7),(4) We can consider the matrixmatrix product in this equation as describing the cascade of the two networks. That is, let A B A B A B C C C (5) so that A B C (6) where A C B n other words, a cascaded connection of twoport networks is equivalent to a single twoport network containing a product of the ABC matrices. t is important to note that the order of matrix multiplication must be the same as the order in which the two ports are
4 Whites, EE 48/58 Lecture 0 Page 4 of 7 arranged in the circuit from signal input to output. Matrix multiplication is not commutative, in general. That is, A B B A. Text example 4.6 shows the derivation of the ABC parameters for a series (i.e., floating ) impedance, which is the first entry in Table 4. on p. 90 of the text. n your homework, you ll derive the ABC parameters for the next three entries in the table. n the following example, we ll derive the last entry in this table. Example N0. erive the ABC parameters for the T network: Z Z Z A Z in, Recall from () that by definition A B and C To determine A: A 0
5 Whites, EE 48/58 Lecture 0 Page 5 of 7 we need to opencircuit port so that 0. Hence, Z A Z Z which yields, Z A Z 0 To determine B: B 0 we need to shortcircuit port so that 0. Then, using current division: Z Z Z Substituting this into the expression for B above we find Z Z B ZZ Z Z Z 0 Z in, 0 ZZ Z Z Z Z Z Z ZZ ZZ Z Z Z Z Z Z Z ZZ Therefore, BZZ Z
6 Whites, EE 48/58 Lecture 0 Page 6 of 7 To determine C: C 0 we need to opencircuit port, from which we find Z Therefore, A C 0 Z To determine : 0 we need to shortcircuit port. Using current division, as above, Z Z Z Therefore, Z Z 0 These ABC parameters agree with those listed in the last entry of Table 4.. Properties of ABC parameters As shown on p. 9 of the text, the ABC parameters can be expressed in terms of the Z parameters. (Actually, there are
7 Whites, EE 48/58 Lecture 0 Page 7 of 7 interrelationships between all the network parameters, which are conveniently listed in Table 4. on p. 9.) From this relationship, we can show that for a reciprocal network A B et C or A BC f the network is lossless, there are no really outstanding features of the ABC matrix. Rather, using the relationship to the Z parameters we can see that if the network is lossless, then From (4.7a): Z A A real Z From (4.7b): ZZ ZZ B B imaginary Z From (4.7c): C Z C imaginary From (4.7d): Z real Z n other words, the diagonal elements are real while the offdiagonal elements are imaginary for an ABC matrix representation of a lossless network.
Lecture 27: Mixers. Gilbert Cell
 Whites, EE 322 Lecture 27 Page 1 of 9 Lecture 27: Mixers. Gilbert Cell Mixers shift the frequency spectrum of an input signal. This is an essential component in electrical communications (wireless or otherwise)
Whites, EE 322 Lecture 27 Page 1 of 9 Lecture 27: Mixers. Gilbert Cell Mixers shift the frequency spectrum of an input signal. This is an essential component in electrical communications (wireless or otherwise)
Agilent AN 154 S-Parameter Design Application Note
 Agilent AN 154 S-Parameter Design Application Note Introduction The need for new high-frequency, solid-state circuit design techniques has been recognized both by microwave engineers and circuit designers.
Agilent AN 154 S-Parameter Design Application Note Introduction The need for new high-frequency, solid-state circuit design techniques has been recognized both by microwave engineers and circuit designers.
Basic Laws Circuit Theorems Methods of Network Analysis Non-Linear Devices and Simulation Models
 EE Modul 1: Electric Circuits Theory Basic Laws Circuit Theorems Methods of Network Analysis Non-Linear Devices and Simulation Models EE Modul 1: Electric Circuits Theory Current, Voltage, Impedance Ohm
EE Modul 1: Electric Circuits Theory Basic Laws Circuit Theorems Methods of Network Analysis Non-Linear Devices and Simulation Models EE Modul 1: Electric Circuits Theory Current, Voltage, Impedance Ohm
Experiment 7: Familiarization with the Network Analyzer
 Experiment 7: Familiarization with the Network Analyzer Measurements to characterize networks at high frequencies (RF and microwave frequencies) are usually done in terms of scattering parameters (S parameters).
Experiment 7: Familiarization with the Network Analyzer Measurements to characterize networks at high frequencies (RF and microwave frequencies) are usually done in terms of scattering parameters (S parameters).
Chapter 6. Orthogonality
 6.3 Orthogonal Matrices 1 Chapter 6. Orthogonality 6.3 Orthogonal Matrices Definition 6.4. An n n matrix A is orthogonal if A T A = I. Note. We will see that the columns of an orthogonal matrix must be
6.3 Orthogonal Matrices 1 Chapter 6. Orthogonality 6.3 Orthogonal Matrices Definition 6.4. An n n matrix A is orthogonal if A T A = I. Note. We will see that the columns of an orthogonal matrix must be
Lecture 10: TEM, TE, and TM Modes for Waveguides. Rectangular Waveguide.
 Whites, EE 481/581 Lecture 10 Page 1 of 10 Lecture 10: TEM, TE, and TM Modes for Waveguides. Rectangular Waveguide. We will now generalie our discussion of transmission lines by considering EM waveguides.
Whites, EE 481/581 Lecture 10 Page 1 of 10 Lecture 10: TEM, TE, and TM Modes for Waveguides. Rectangular Waveguide. We will now generalie our discussion of transmission lines by considering EM waveguides.
PHY3128 / PHYM203 (Electronics / Instrumentation) Transmission Lines. Repeated n times I L
 Transmission Lines Introduction A transmission line guides energy from one place to another. Optical fibres, waveguides, telephone lines and power cables are all electromagnetic transmission lines. are
Transmission Lines Introduction A transmission line guides energy from one place to another. Optical fibres, waveguides, telephone lines and power cables are all electromagnetic transmission lines. are
Lecture 24: Oscillators. Clapp Oscillator. VFO Startup
 Whites, EE 322 Lecture 24 Page 1 of 10 Lecture 24: Oscillators. Clapp Oscillator. VFO Startup Oscillators are circuits that produce periodic output voltages, such as sinusoids. They accomplish this feat
Whites, EE 322 Lecture 24 Page 1 of 10 Lecture 24: Oscillators. Clapp Oscillator. VFO Startup Oscillators are circuits that produce periodic output voltages, such as sinusoids. They accomplish this feat
Similar matrices and Jordan form
 Similar matrices and Jordan form We ve nearly covered the entire heart of linear algebra once we ve finished singular value decompositions we ll have seen all the most central topics. A T A is positive
Similar matrices and Jordan form We ve nearly covered the entire heart of linear algebra once we ve finished singular value decompositions we ll have seen all the most central topics. A T A is positive
SECTION 2 Transmission Line Theory
 SEMICONDUCTOR DESIGN GUIDE Transmission Line Theory SECTION 2 Transmission Line Theory Introduction The ECLinPS family has pushed the world of ECL into the realm of picoseconds. When output transitions
SEMICONDUCTOR DESIGN GUIDE Transmission Line Theory SECTION 2 Transmission Line Theory Introduction The ECLinPS family has pushed the world of ECL into the realm of picoseconds. When output transitions
Engineering Sciences 151. Electromagnetic Communication Laboratory Assignment 3 Fall Term 1998-99
 Engineering Sciences 151 Electromagnetic Communication Laboratory Assignment 3 Fall Term 1998-99 WAVE PROPAGATION II: HIGH FREQUENCY SLOTTED LINE AND REFLECTOMETER MEASUREMENTS OBJECTIVES: To build greater
Engineering Sciences 151 Electromagnetic Communication Laboratory Assignment 3 Fall Term 1998-99 WAVE PROPAGATION II: HIGH FREQUENCY SLOTTED LINE AND REFLECTOMETER MEASUREMENTS OBJECTIVES: To build greater
Ver 3537 E1.1 Analysis of Circuits (2014) E1.1 Circuit Analysis. Problem Sheet 1 (Lectures 1 & 2)
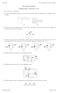 Ver 3537 E. Analysis of Circuits () Key: [A]= easy... [E]=hard E. Circuit Analysis Problem Sheet (Lectures & ). [A] One of the following circuits is a series circuit and the other is a parallel circuit.
Ver 3537 E. Analysis of Circuits () Key: [A]= easy... [E]=hard E. Circuit Analysis Problem Sheet (Lectures & ). [A] One of the following circuits is a series circuit and the other is a parallel circuit.
December 4, 2013 MATH 171 BASIC LINEAR ALGEBRA B. KITCHENS
 December 4, 2013 MATH 171 BASIC LINEAR ALGEBRA B KITCHENS The equation 1 Lines in two-dimensional space (1) 2x y = 3 describes a line in two-dimensional space The coefficients of x and y in the equation
December 4, 2013 MATH 171 BASIC LINEAR ALGEBRA B KITCHENS The equation 1 Lines in two-dimensional space (1) 2x y = 3 describes a line in two-dimensional space The coefficients of x and y in the equation
Lecture 7 Circuit analysis via Laplace transform
 S. Boyd EE12 Lecture 7 Circuit analysis via Laplace transform analysis of general LRC circuits impedance and admittance descriptions natural and forced response circuit analysis with impedances natural
S. Boyd EE12 Lecture 7 Circuit analysis via Laplace transform analysis of general LRC circuits impedance and admittance descriptions natural and forced response circuit analysis with impedances natural
Lecture 18: Common Emitter Amplifier. Maximum Efficiency of Class A Amplifiers. Transformer Coupled Loads.
 Whites, EE 3 Lecture 18 Page 1 of 10 Lecture 18: Common Emitter Amplifier. Maximum Efficiency of Class A Amplifiers. Transformer Coupled Loads. We discussed using transistors as switches in the last lecture.
Whites, EE 3 Lecture 18 Page 1 of 10 Lecture 18: Common Emitter Amplifier. Maximum Efficiency of Class A Amplifiers. Transformer Coupled Loads. We discussed using transistors as switches in the last lecture.
Lecture N -1- PHYS 3330. Microcontrollers
 Lecture N -1- PHYS 3330 Microcontrollers If you need more than a handful of logic gates to accomplish the task at hand, you likely should use a microcontroller instead of discrete logic gates 1. Microcontrollers
Lecture N -1- PHYS 3330 Microcontrollers If you need more than a handful of logic gates to accomplish the task at hand, you likely should use a microcontroller instead of discrete logic gates 1. Microcontrollers
Solving Systems of Linear Equations
 LECTURE 5 Solving Systems of Linear Equations Recall that we introduced the notion of matrices as a way of standardizing the expression of systems of linear equations In today s lecture I shall show how
LECTURE 5 Solving Systems of Linear Equations Recall that we introduced the notion of matrices as a way of standardizing the expression of systems of linear equations In today s lecture I shall show how
LS.6 Solution Matrices
 LS.6 Solution Matrices In the literature, solutions to linear systems often are expressed using square matrices rather than vectors. You need to get used to the terminology. As before, we state the definitions
LS.6 Solution Matrices In the literature, solutions to linear systems often are expressed using square matrices rather than vectors. You need to get used to the terminology. As before, we state the definitions
4 SENSORS. Example. A force of 1 N is exerted on a PZT5A disc of diameter 10 mm and thickness 1 mm. The resulting mechanical stress is:
 4 SENSORS The modern technical world demands the availability of sensors to measure and convert a variety of physical quantities into electrical signals. These signals can then be fed into data processing
4 SENSORS The modern technical world demands the availability of sensors to measure and convert a variety of physical quantities into electrical signals. These signals can then be fed into data processing
Lecture 22: Class C Power Amplifiers
 Whites, EE 322 Lecture 22 Page 1 of 13 Lecture 22: lass Power Amplifiers We discovered in Lecture 18 (Section 9.2) that the maximum efficiency of lass A amplifiers is 25% with a resistive load and 50%
Whites, EE 322 Lecture 22 Page 1 of 13 Lecture 22: lass Power Amplifiers We discovered in Lecture 18 (Section 9.2) that the maximum efficiency of lass A amplifiers is 25% with a resistive load and 50%
Example: Determine the power supplied by each of the sources, independent and dependent, in this circuit:
 Example: Determine the power supplied by each of the sources, independent and dependent, in this circuit: Solution: We ll begin by choosing the bottom node to be the reference node. Next we ll label the
Example: Determine the power supplied by each of the sources, independent and dependent, in this circuit: Solution: We ll begin by choosing the bottom node to be the reference node. Next we ll label the
Chapter 19 Operational Amplifiers
 Chapter 19 Operational Amplifiers The operational amplifier, or op-amp, is a basic building block of modern electronics. Op-amps date back to the early days of vacuum tubes, but they only became common
Chapter 19 Operational Amplifiers The operational amplifier, or op-amp, is a basic building block of modern electronics. Op-amps date back to the early days of vacuum tubes, but they only became common
LINES AND PLANES CHRIS JOHNSON
 LINES AND PLANES CHRIS JOHNSON Abstract. In this lecture we derive the equations for lines and planes living in 3-space, as well as define the angle between two non-parallel planes, and determine the distance
LINES AND PLANES CHRIS JOHNSON Abstract. In this lecture we derive the equations for lines and planes living in 3-space, as well as define the angle between two non-parallel planes, and determine the distance
Lecture 24. Inductance and Switching Power Supplies (how your solar charger voltage converter works)
 Lecture 24 Inductance and Switching Power Supplies (how your solar charger voltage converter works) Copyright 2014 by Mark Horowitz 1 Roadmap: How Does This Work? 2 Processor Board 3 More Detailed Roadmap
Lecture 24 Inductance and Switching Power Supplies (how your solar charger voltage converter works) Copyright 2014 by Mark Horowitz 1 Roadmap: How Does This Work? 2 Processor Board 3 More Detailed Roadmap
Chapter 12 Modal Decomposition of State-Space Models 12.1 Introduction The solutions obtained in previous chapters, whether in time domain or transfor
 Lectures on Dynamic Systems and Control Mohammed Dahleh Munther A. Dahleh George Verghese Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Massachuasetts Institute of Technology 1 1 c Chapter
Lectures on Dynamic Systems and Control Mohammed Dahleh Munther A. Dahleh George Verghese Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Massachuasetts Institute of Technology 1 1 c Chapter
Preamble. Kirchoff Voltage Law (KVL) Series Resistors. In this section of my lectures we will be. resistor arrangements; series and
 Preamble Series and Parallel Circuits Physics, 8th Edition Custom Edition Cutnell & Johnson Chapter 0.6-0.8, 0.0 Pages 60-68, 69-6 n this section of my lectures we will be developing the two common types
Preamble Series and Parallel Circuits Physics, 8th Edition Custom Edition Cutnell & Johnson Chapter 0.6-0.8, 0.0 Pages 60-68, 69-6 n this section of my lectures we will be developing the two common types
6. Cholesky factorization
 6. Cholesky factorization EE103 (Fall 2011-12) triangular matrices forward and backward substitution the Cholesky factorization solving Ax = b with A positive definite inverse of a positive definite matrix
6. Cholesky factorization EE103 (Fall 2011-12) triangular matrices forward and backward substitution the Cholesky factorization solving Ax = b with A positive definite inverse of a positive definite matrix
Solution to Homework 2
 Solution to Homework 2 Olena Bormashenko September 23, 2011 Section 1.4: 1(a)(b)(i)(k), 4, 5, 14; Section 1.5: 1(a)(b)(c)(d)(e)(n), 2(a)(c), 13, 16, 17, 18, 27 Section 1.4 1. Compute the following, if
Solution to Homework 2 Olena Bormashenko September 23, 2011 Section 1.4: 1(a)(b)(i)(k), 4, 5, 14; Section 1.5: 1(a)(b)(c)(d)(e)(n), 2(a)(c), 13, 16, 17, 18, 27 Section 1.4 1. Compute the following, if
Question 2: How do you solve a matrix equation using the matrix inverse?
 Question : How do you solve a matrix equation using the matrix inverse? In the previous question, we wrote systems of equations as a matrix equation AX B. In this format, the matrix A contains the coefficients
Question : How do you solve a matrix equation using the matrix inverse? In the previous question, we wrote systems of equations as a matrix equation AX B. In this format, the matrix A contains the coefficients
CHAPTER 6 Frequency Response, Bode Plots, and Resonance
 ELECTRICAL CHAPTER 6 Frequency Response, Bode Plots, and Resonance 1. State the fundamental concepts of Fourier analysis. 2. Determine the output of a filter for a given input consisting of sinusoidal
ELECTRICAL CHAPTER 6 Frequency Response, Bode Plots, and Resonance 1. State the fundamental concepts of Fourier analysis. 2. Determine the output of a filter for a given input consisting of sinusoidal
zcable Model for Frequency Dependent Modelling of Cable Transmission Systems
 zcable Model for Frequency Dependent Modelling of Cable Transmission Systems T. C. Yu Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of British Columbia 356 Main Mall, Vancouver, B.C., Canada
zcable Model for Frequency Dependent Modelling of Cable Transmission Systems T. C. Yu Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of British Columbia 356 Main Mall, Vancouver, B.C., Canada
Matrix Calculations: Applications of Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors; Inner Products
 Matrix Calculations: Applications of Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors; Inner Products H. Geuvers Institute for Computing and Information Sciences Intelligent Systems Version: spring 2015 H. Geuvers Version:
Matrix Calculations: Applications of Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors; Inner Products H. Geuvers Institute for Computing and Information Sciences Intelligent Systems Version: spring 2015 H. Geuvers Version:
Lecture 30: Biasing MOSFET Amplifiers. MOSFET Current Mirrors.
 Whites, EE 320 Lecture 30 Page 1 of 8 Lecture 30: Biasing MOSFET Amplifiers. MOSFET Current Mirrors. There are two different environments in which MOSFET amplifiers are found, (1) discrete circuits and
Whites, EE 320 Lecture 30 Page 1 of 8 Lecture 30: Biasing MOSFET Amplifiers. MOSFET Current Mirrors. There are two different environments in which MOSFET amplifiers are found, (1) discrete circuits and
DETERMINANTS TERRY A. LORING
 DETERMINANTS TERRY A. LORING 1. Determinants: a Row Operation By-Product The determinant is best understood in terms of row operations, in my opinion. Most books start by defining the determinant via formulas
DETERMINANTS TERRY A. LORING 1. Determinants: a Row Operation By-Product The determinant is best understood in terms of row operations, in my opinion. Most books start by defining the determinant via formulas
RF Engineering Basic Concepts
 RF Engineering Basic Concepts Fritz Caspers, Peter McIntosh, Tom Kroyer CAS 2007, Daresbury Contents S parameters Signal flow graph Properties of the S matrix of an N-port Basic properties of striplines,
RF Engineering Basic Concepts Fritz Caspers, Peter McIntosh, Tom Kroyer CAS 2007, Daresbury Contents S parameters Signal flow graph Properties of the S matrix of an N-port Basic properties of striplines,
SYNCHRONOUS MACHINES
 SYNCHRONOUS MACHINES The geometry of a synchronous machine is quite similar to that of the induction machine. The stator core and windings of a three-phase synchronous machine are practically identical
SYNCHRONOUS MACHINES The geometry of a synchronous machine is quite similar to that of the induction machine. The stator core and windings of a three-phase synchronous machine are practically identical
[1] Diagonal factorization
![[1] Diagonal factorization [1] Diagonal factorization](/thumbs/40/21671034.jpg) 8.03 LA.6: Diagonalization and Orthogonal Matrices [ Diagonal factorization [2 Solving systems of first order differential equations [3 Symmetric and Orthonormal Matrices [ Diagonal factorization Recall:
8.03 LA.6: Diagonalization and Orthogonal Matrices [ Diagonal factorization [2 Solving systems of first order differential equations [3 Symmetric and Orthonormal Matrices [ Diagonal factorization Recall:
Agilent De-embedding and Embedding S-Parameter Networks Using a Vector Network Analyzer. Application Note 1364-1
 Agilent De-embedding and Embedding S-Parameter Networks Using a Vector Network Analyzer Application Note 1364-1 Introduction Traditionally RF and microwave components have been designed in packages with
Agilent De-embedding and Embedding S-Parameter Networks Using a Vector Network Analyzer Application Note 1364-1 Introduction Traditionally RF and microwave components have been designed in packages with
Lecture 23: Common Emitter Amplifier Frequency Response. Miller s Theorem.
 Whites, EE 320 ecture 23 Page 1 of 17 ecture 23: Common Emitter mplifier Frequency Response. Miller s Theorem. We ll use the high frequency model for the BJT we developed the previous lecture and compute
Whites, EE 320 ecture 23 Page 1 of 17 ecture 23: Common Emitter mplifier Frequency Response. Miller s Theorem. We ll use the high frequency model for the BJT we developed the previous lecture and compute
Direct Methods for Solving Linear Systems. Matrix Factorization
 Direct Methods for Solving Linear Systems Matrix Factorization Numerical Analysis (9th Edition) R L Burden & J D Faires Beamer Presentation Slides prepared by John Carroll Dublin City University c 2011
Direct Methods for Solving Linear Systems Matrix Factorization Numerical Analysis (9th Edition) R L Burden & J D Faires Beamer Presentation Slides prepared by John Carroll Dublin City University c 2011
Lecture 21: Junction Field Effect Transistors. Source Follower Amplifier
 Whites, EE 322 Lecture 21 Page 1 of 8 Lecture 21: Junction Fiel Effect Transistors. Source Follower Amplifier As mentione in Lecture 16, there are two major families of transistors. We ve worke with BJTs
Whites, EE 322 Lecture 21 Page 1 of 8 Lecture 21: Junction Fiel Effect Transistors. Source Follower Amplifier As mentione in Lecture 16, there are two major families of transistors. We ve worke with BJTs
Keysight Technologies Understanding the Fundamental Principles of Vector Network Analysis. Application Note
 Keysight Technologies Understanding the Fundamental Principles of Vector Network Analysis Application Note Introduction Network analysis is the process by which designers and manufacturers measure the
Keysight Technologies Understanding the Fundamental Principles of Vector Network Analysis Application Note Introduction Network analysis is the process by which designers and manufacturers measure the
Solving Systems of Linear Equations
 LECTURE 5 Solving Systems of Linear Equations Recall that we introduced the notion of matrices as a way of standardizing the expression of systems of linear equations In today s lecture I shall show how
LECTURE 5 Solving Systems of Linear Equations Recall that we introduced the notion of matrices as a way of standardizing the expression of systems of linear equations In today s lecture I shall show how
Network Theory Question Bank
 Network Theory Question Bank Unit-I JNTU SYLLABUS: Three Phase Circuits Three phase circuits: Phase sequence Star and delta connection Relation between line and phase voltages and currents in balanced
Network Theory Question Bank Unit-I JNTU SYLLABUS: Three Phase Circuits Three phase circuits: Phase sequence Star and delta connection Relation between line and phase voltages and currents in balanced
Solving Equations by the Multiplication Property
 2.2 Solving Equations by the Multiplication Property 2.2 OBJECTIVES 1. Determine whether a given number is a solution for an equation 2. Use the multiplication property to solve equations. Find the mean
2.2 Solving Equations by the Multiplication Property 2.2 OBJECTIVES 1. Determine whether a given number is a solution for an equation 2. Use the multiplication property to solve equations. Find the mean
Using row reduction to calculate the inverse and the determinant of a square matrix
 Using row reduction to calculate the inverse and the determinant of a square matrix Notes for MATH 0290 Honors by Prof. Anna Vainchtein 1 Inverse of a square matrix An n n square matrix A is called invertible
Using row reduction to calculate the inverse and the determinant of a square matrix Notes for MATH 0290 Honors by Prof. Anna Vainchtein 1 Inverse of a square matrix An n n square matrix A is called invertible
Circuit Analysis using the Node and Mesh Methods
 Circuit Analysis using the Node and Mesh Methods We have seen that using Kirchhoff s laws and Ohm s law we can analyze any circuit to determine the operating conditions (the currents and voltages). The
Circuit Analysis using the Node and Mesh Methods We have seen that using Kirchhoff s laws and Ohm s law we can analyze any circuit to determine the operating conditions (the currents and voltages). The
Topic Suggested Teaching Suggested Resources
 Lesson 1 & 2: DC Networks Learning Outcome: Be able to apply electrical theorems to solve DC network problems Electrical theorems and DC network problems Introduction into the unit contents, aims & objectives
Lesson 1 & 2: DC Networks Learning Outcome: Be able to apply electrical theorems to solve DC network problems Electrical theorems and DC network problems Introduction into the unit contents, aims & objectives
Transistor Characteristics and Single Transistor Amplifier Sept. 8, 1997
 Physics 623 Transistor Characteristics and Single Transistor Amplifier Sept. 8, 1997 1 Purpose To measure and understand the common emitter transistor characteristic curves. To use the base current gain
Physics 623 Transistor Characteristics and Single Transistor Amplifier Sept. 8, 1997 1 Purpose To measure and understand the common emitter transistor characteristic curves. To use the base current gain
by the matrix A results in a vector which is a reflection of the given
 Eigenvalues & Eigenvectors Example Suppose Then So, geometrically, multiplying a vector in by the matrix A results in a vector which is a reflection of the given vector about the y-axis We observe that
Eigenvalues & Eigenvectors Example Suppose Then So, geometrically, multiplying a vector in by the matrix A results in a vector which is a reflection of the given vector about the y-axis We observe that
Similarity and Diagonalization. Similar Matrices
 MATH022 Linear Algebra Brief lecture notes 48 Similarity and Diagonalization Similar Matrices Let A and B be n n matrices. We say that A is similar to B if there is an invertible n n matrix P such that
MATH022 Linear Algebra Brief lecture notes 48 Similarity and Diagonalization Similar Matrices Let A and B be n n matrices. We say that A is similar to B if there is an invertible n n matrix P such that
Differential Amplifier Common & Differential Modes
 Differential Amplifier Common & Differential Modes Common & Differential Modes BJT Differential Amplifier Diff. Amp Voltage Gain and Input Impedance Small Signal Analysis Differential Mode Small Signal
Differential Amplifier Common & Differential Modes Common & Differential Modes BJT Differential Amplifier Diff. Amp Voltage Gain and Input Impedance Small Signal Analysis Differential Mode Small Signal
Solving Systems of Linear Equations Using Matrices
 Solving Systems of Linear Equations Using Matrices What is a Matrix? A matrix is a compact grid or array of numbers. It can be created from a system of equations and used to solve the system of equations.
Solving Systems of Linear Equations Using Matrices What is a Matrix? A matrix is a compact grid or array of numbers. It can be created from a system of equations and used to solve the system of equations.
Measurement of Multi-Port S-Parameters using Four-Port Network Analyzer
 JOURNAL OF SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNOLOGY AND SCIENCE, VOL.13, NO.6, DECEMBER, 2013 http://dx.doi.org/10.5573/jsts.2013.13.6.589 Measurement of Multi-Port S-Parameters using Four-Port Network Analyzer Jongmin
JOURNAL OF SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNOLOGY AND SCIENCE, VOL.13, NO.6, DECEMBER, 2013 http://dx.doi.org/10.5573/jsts.2013.13.6.589 Measurement of Multi-Port S-Parameters using Four-Port Network Analyzer Jongmin
The Membrane Equation
 The Membrane Equation Professor David Heeger September 5, 2000 RC Circuits Figure 1A shows an RC (resistor, capacitor) equivalent circuit model for a patch of passive neural membrane. The capacitor represents
The Membrane Equation Professor David Heeger September 5, 2000 RC Circuits Figure 1A shows an RC (resistor, capacitor) equivalent circuit model for a patch of passive neural membrane. The capacitor represents
Mixed-mode S-parameters and Conversion Techniques
 Mixed-mode S-parameters and Conversion Techniques 1 x 1 Mixed-mode S-parameters and Conversion Techniques Allan Huynh, Magnus Karlsson and Shaofang Gong Linköping University Sweden 1. Introduction Differential
Mixed-mode S-parameters and Conversion Techniques 1 x 1 Mixed-mode S-parameters and Conversion Techniques Allan Huynh, Magnus Karlsson and Shaofang Gong Linköping University Sweden 1. Introduction Differential
Lecture L3 - Vectors, Matrices and Coordinate Transformations
 S. Widnall 16.07 Dynamics Fall 2009 Lecture notes based on J. Peraire Version 2.0 Lecture L3 - Vectors, Matrices and Coordinate Transformations By using vectors and defining appropriate operations between
S. Widnall 16.07 Dynamics Fall 2009 Lecture notes based on J. Peraire Version 2.0 Lecture L3 - Vectors, Matrices and Coordinate Transformations By using vectors and defining appropriate operations between
2. The Vector Network Analyzer
 ECE 584 Laboratory Experiments 2. The Vector Network Analyzer Introduction: In this experiment we will learn to use a Vector Network Analyzer to measure the magnitude and phase of reflection and transmission
ECE 584 Laboratory Experiments 2. The Vector Network Analyzer Introduction: In this experiment we will learn to use a Vector Network Analyzer to measure the magnitude and phase of reflection and transmission
Operation Count; Numerical Linear Algebra
 10 Operation Count; Numerical Linear Algebra 10.1 Introduction Many computations are limited simply by the sheer number of required additions, multiplications, or function evaluations. If floating-point
10 Operation Count; Numerical Linear Algebra 10.1 Introduction Many computations are limited simply by the sheer number of required additions, multiplications, or function evaluations. If floating-point
MATRIX ALGEBRA AND SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS
 MATRIX ALGEBRA AND SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS Systems of Equations and Matrices Representation of a linear system The general system of m equations in n unknowns can be written a x + a 2 x 2 + + a n x n b a
MATRIX ALGEBRA AND SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS Systems of Equations and Matrices Representation of a linear system The general system of m equations in n unknowns can be written a x + a 2 x 2 + + a n x n b a
Three-phase analysis of unbalanced systems
 Exercises of course ELEC0029 - Electric power systems analysis and operation Three-phase analysis of unbalanced systems Thierry Van Cutsem [email protected] www.montefiore.ulg.ac.be/~vct March 205
Exercises of course ELEC0029 - Electric power systems analysis and operation Three-phase analysis of unbalanced systems Thierry Van Cutsem [email protected] www.montefiore.ulg.ac.be/~vct March 205
BALANCED THREE-PHASE CIRCUITS
 BALANCED THREE-PHASE CIRCUITS The voltages in the three-phase power system are produced by a synchronous generator (Chapter 6). In a balanced system, each of the three instantaneous voltages have equal
BALANCED THREE-PHASE CIRCUITS The voltages in the three-phase power system are produced by a synchronous generator (Chapter 6). In a balanced system, each of the three instantaneous voltages have equal
Experiment 4 ~ Resistors in Series & Parallel
 Experiment 4 ~ Resistors in Series & Parallel Objective: In this experiment you will set up three circuits: one with resistors in series, one with resistors in parallel, and one with some of each. You
Experiment 4 ~ Resistors in Series & Parallel Objective: In this experiment you will set up three circuits: one with resistors in series, one with resistors in parallel, and one with some of each. You
Measurement of Capacitance
 Measurement of Capacitance Pre-Lab Questions Page Name: Class: Roster Number: Instructor:. A capacitor is used to store. 2. What is the SI unit for capacitance? 3. A capacitor basically consists of two
Measurement of Capacitance Pre-Lab Questions Page Name: Class: Roster Number: Instructor:. A capacitor is used to store. 2. What is the SI unit for capacitance? 3. A capacitor basically consists of two
Notes on Orthogonal and Symmetric Matrices MENU, Winter 2013
 Notes on Orthogonal and Symmetric Matrices MENU, Winter 201 These notes summarize the main properties and uses of orthogonal and symmetric matrices. We covered quite a bit of material regarding these topics,
Notes on Orthogonal and Symmetric Matrices MENU, Winter 201 These notes summarize the main properties and uses of orthogonal and symmetric matrices. We covered quite a bit of material regarding these topics,
Antenna Cable Attenuation at very high SWR
 Antenna Cable Attenuation at very high SWR Gerald Schuller, DL5BBN July 19, 2014 Abstract This article describes the additional losses that are incurred in antenna cables if the SWR at the antenna is very
Antenna Cable Attenuation at very high SWR Gerald Schuller, DL5BBN July 19, 2014 Abstract This article describes the additional losses that are incurred in antenna cables if the SWR at the antenna is very
A Mathematical Model for Online Electrical Characterization of Thermoelectric Generators using the P-I Curves at Different Temperatures
 A Mathematical Model for Online Electrical Characterization of Thermoelectric Generators using the P-I Curves at Different Temperatures Eduardo I. Ortiz-Rivera, Member IEEE Email: [email protected]
A Mathematical Model for Online Electrical Characterization of Thermoelectric Generators using the P-I Curves at Different Temperatures Eduardo I. Ortiz-Rivera, Member IEEE Email: [email protected]
APPLICATION NOTES POWER DIVIDERS. Things to consider
 Internet Copy Rev A Overview Various RF applications require power to be distributed among various paths. The simplest way this can be done is by using a power splitter/divider. Power dividers are reciprocal
Internet Copy Rev A Overview Various RF applications require power to be distributed among various paths. The simplest way this can be done is by using a power splitter/divider. Power dividers are reciprocal
Physics 623 Transistor Characteristics and Single Transistor Amplifier Sept. 13, 2006
 Physics 623 Transistor Characteristics and Single Transistor Amplifier Sept. 13, 2006 1 Purpose To measure and understand the common emitter transistor characteristic curves. To use the base current gain
Physics 623 Transistor Characteristics and Single Transistor Amplifier Sept. 13, 2006 1 Purpose To measure and understand the common emitter transistor characteristic curves. To use the base current gain
(Refer Slide Time: 2:03)
 Control Engineering Prof. Madan Gopal Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 11 Models of Industrial Control Devices and Systems (Contd.) Last time we were
Control Engineering Prof. Madan Gopal Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 11 Models of Industrial Control Devices and Systems (Contd.) Last time we were
High Voltage Transient Analysis
 High Voltage Transient Analysis 4. Surges on Transmission Lines Due to a variety of reasons, such as a direct stroke of lightning on the line, or by indirect strokes, or by switching operations or by faults,
High Voltage Transient Analysis 4. Surges on Transmission Lines Due to a variety of reasons, such as a direct stroke of lightning on the line, or by indirect strokes, or by switching operations or by faults,
Basic Electrical Technology Dr. L. Umanand Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore. Lecture - 33 3 phase System 4
 Basic Electrical Technology Dr. L. Umanand Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Lecture - 33 3 phase System 4 Hello everybody. So, in the last class we have been
Basic Electrical Technology Dr. L. Umanand Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Lecture - 33 3 phase System 4 Hello everybody. So, in the last class we have been
SOLVING COMPLEX SYSTEMS USING SPREADSHEETS: A MATRIX DECOMPOSITION APPROACH
 SOLVING COMPLEX SYSTEMS USING SPREADSHEETS: A MATRIX DECOMPOSITION APPROACH Kenneth E. Dudeck, Associate Professor of Electrical Engineering Pennsylvania State University, Hazleton Campus Abstract Many
SOLVING COMPLEX SYSTEMS USING SPREADSHEETS: A MATRIX DECOMPOSITION APPROACH Kenneth E. Dudeck, Associate Professor of Electrical Engineering Pennsylvania State University, Hazleton Campus Abstract Many
Factoring Polynomials and Solving Quadratic Equations
 Factoring Polynomials and Solving Quadratic Equations Math Tutorial Lab Special Topic Factoring Factoring Binomials Remember that a binomial is just a polynomial with two terms. Some examples include 2x+3
Factoring Polynomials and Solving Quadratic Equations Math Tutorial Lab Special Topic Factoring Factoring Binomials Remember that a binomial is just a polynomial with two terms. Some examples include 2x+3
School of Engineering Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 1 School of Engineering Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering 332:223 Principles of Electrical Engineering I Laboratory Experiment #4 Title: Operational Amplifiers 1 Introduction Objectives
1 School of Engineering Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering 332:223 Principles of Electrical Engineering I Laboratory Experiment #4 Title: Operational Amplifiers 1 Introduction Objectives
Transmission Lines. Smith Chart
 Smith Chart The Smith chart is one of the most useful graphical tools for high frequency circuit applications. The chart provides a clever way to visualize complex functions and it continues to endure
Smith Chart The Smith chart is one of the most useful graphical tools for high frequency circuit applications. The chart provides a clever way to visualize complex functions and it continues to endure
Power measurement in balanced 3 phase circuits and power factor improvement. 1 Power in Single Phase Circuits. Experiment no 1
 Experiment no 1 Power measurement in balanced 3 phase circuits and power factor improvement 1 Power in Single Phase Circuits Let v = m cos(ωt) = cos(ωt) is the voltage applied to a R-L circuit and i =
Experiment no 1 Power measurement in balanced 3 phase circuits and power factor improvement 1 Power in Single Phase Circuits Let v = m cos(ωt) = cos(ωt) is the voltage applied to a R-L circuit and i =
Section 1.1 Linear Equations: Slope and Equations of Lines
 Section. Linear Equations: Slope and Equations of Lines Slope The measure of the steepness of a line is called the slope of the line. It is the amount of change in y, the rise, divided by the amount of
Section. Linear Equations: Slope and Equations of Lines Slope The measure of the steepness of a line is called the slope of the line. It is the amount of change in y, the rise, divided by the amount of
Understanding the Fundamental Principles of Vector Network Analysis. Application Note 1287-1. Table of Contents. Page
 Understanding the Fundamental Principles of Vector Network Analysis Application Note 1287-1 Table of Contents Page Introduction 2 Measurements in Communications Systems 2 Importance of Vector Measurements
Understanding the Fundamental Principles of Vector Network Analysis Application Note 1287-1 Table of Contents Page Introduction 2 Measurements in Communications Systems 2 Importance of Vector Measurements
Lecture 3: Finding integer solutions to systems of linear equations
 Lecture 3: Finding integer solutions to systems of linear equations Algorithmic Number Theory (Fall 2014) Rutgers University Swastik Kopparty Scribe: Abhishek Bhrushundi 1 Overview The goal of this lecture
Lecture 3: Finding integer solutions to systems of linear equations Algorithmic Number Theory (Fall 2014) Rutgers University Swastik Kopparty Scribe: Abhishek Bhrushundi 1 Overview The goal of this lecture
Experiments Using the HP8714 RF Network Analyzer
 Experiments Using the HP8714 RF Network Analyzer Purpose: The purpose of this set of experiments is two folded: to get familiar with the basic operation of a RF network analyzer, and to gain a physical
Experiments Using the HP8714 RF Network Analyzer Purpose: The purpose of this set of experiments is two folded: to get familiar with the basic operation of a RF network analyzer, and to gain a physical
Transistor Amplifiers
 Physics 3330 Experiment #7 Fall 1999 Transistor Amplifiers Purpose The aim of this experiment is to develop a bipolar transistor amplifier with a voltage gain of minus 25. The amplifier must accept input
Physics 3330 Experiment #7 Fall 1999 Transistor Amplifiers Purpose The aim of this experiment is to develop a bipolar transistor amplifier with a voltage gain of minus 25. The amplifier must accept input
Solving Linear Systems, Continued and The Inverse of a Matrix
 , Continued and The of a Matrix Calculus III Summer 2013, Session II Monday, July 15, 2013 Agenda 1. The rank of a matrix 2. The inverse of a square matrix Gaussian Gaussian solves a linear system by reducing
, Continued and The of a Matrix Calculus III Summer 2013, Session II Monday, July 15, 2013 Agenda 1. The rank of a matrix 2. The inverse of a square matrix Gaussian Gaussian solves a linear system by reducing
IV. ALGEBRAIC CONCEPTS
 IV. ALGEBRAIC CONCEPTS Algebra is the language of mathematics. Much of the observable world can be characterized as having patterned regularity where a change in one quantity results in changes in other
IV. ALGEBRAIC CONCEPTS Algebra is the language of mathematics. Much of the observable world can be characterized as having patterned regularity where a change in one quantity results in changes in other
Dependent Sources: Introduction and analysis of circuits containing dependent sources.
 Dependent Sources: Introduction and analysis of circuits containing dependent sources. So far we have explored timeindependent (resistive) elements that are also linear. We have seen that two terminal
Dependent Sources: Introduction and analysis of circuits containing dependent sources. So far we have explored timeindependent (resistive) elements that are also linear. We have seen that two terminal
ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING The master degree programme of Teacher Training in Electronical Engineering is designed to develop graduates competencies in the field of Curriculum Development and Instructional
ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING The master degree programme of Teacher Training in Electronical Engineering is designed to develop graduates competencies in the field of Curriculum Development and Instructional
Copyright 2000 IEEE. Reprinted from IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium 2000
 Copyright 2000 IEEE Reprinted from IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium 2000 This material is posted here with permission of the IEEE. Such permission of the IEEE does not in any way imply IEEE
Copyright 2000 IEEE Reprinted from IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium 2000 This material is posted here with permission of the IEEE. Such permission of the IEEE does not in any way imply IEEE
RLC Resonant Circuits
 C esonant Circuits Andrew McHutchon April 20, 203 Capacitors and Inductors There is a lot of inconsistency when it comes to dealing with reactances of complex components. The format followed in this document
C esonant Circuits Andrew McHutchon April 20, 203 Capacitors and Inductors There is a lot of inconsistency when it comes to dealing with reactances of complex components. The format followed in this document
3. Solve the equation containing only one variable for that variable.
 Question : How do you solve a system of linear equations? There are two basic strategies for solving a system of two linear equations and two variables. In each strategy, one of the variables is eliminated
Question : How do you solve a system of linear equations? There are two basic strategies for solving a system of two linear equations and two variables. In each strategy, one of the variables is eliminated
= (0.400 A) (4.80 V) = 1.92 W = (0.400 A) (7.20 V) = 2.88 W
 Physics 2220 Module 06 Homework 0. What are the magnitude and direction of the current in the 8 Ω resister in the figure? Assume the current is moving clockwise. Then use Kirchhoff's second rule: 3.00
Physics 2220 Module 06 Homework 0. What are the magnitude and direction of the current in the 8 Ω resister in the figure? Assume the current is moving clockwise. Then use Kirchhoff's second rule: 3.00
Revised Version of Chapter 23. We learned long ago how to solve linear congruences. ax c (mod m)
 Chapter 23 Squares Modulo p Revised Version of Chapter 23 We learned long ago how to solve linear congruences ax c (mod m) (see Chapter 8). It s now time to take the plunge and move on to quadratic equations.
Chapter 23 Squares Modulo p Revised Version of Chapter 23 We learned long ago how to solve linear congruences ax c (mod m) (see Chapter 8). It s now time to take the plunge and move on to quadratic equations.
Linear algebra and the geometry of quadratic equations. Similarity transformations and orthogonal matrices
 MATH 30 Differential Equations Spring 006 Linear algebra and the geometry of quadratic equations Similarity transformations and orthogonal matrices First, some things to recall from linear algebra Two
MATH 30 Differential Equations Spring 006 Linear algebra and the geometry of quadratic equations Similarity transformations and orthogonal matrices First, some things to recall from linear algebra Two
8.2. Solution by Inverse Matrix Method. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 Solution by Inverse Matrix Method 8.2 Introduction The power of matrix algebra is seen in the representation of a system of simultaneous linear equations as a matrix equation. Matrix algebra allows us
Solution by Inverse Matrix Method 8.2 Introduction The power of matrix algebra is seen in the representation of a system of simultaneous linear equations as a matrix equation. Matrix algebra allows us
How To Calculate The Power Gain Of An Opamp
 A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EE 100 / 42 Lecture 8 p. 1/23 EE 42/100 Lecture 8: Op-Amps ELECTRONICS Rev C 2/8/2012 (9:54 AM) Prof. Ali M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley
A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EE 100 / 42 Lecture 8 p. 1/23 EE 42/100 Lecture 8: Op-Amps ELECTRONICS Rev C 2/8/2012 (9:54 AM) Prof. Ali M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley
Lecture 3: DC Analysis of Diode Circuits.
 Whites, EE 320 Lecture 3 Page 1 of 10 Lecture 3: DC Analysis of Diode Circuits. We ll now move on to the DC analysis of diode circuits. Applications will be covered in following lectures. Let s consider
Whites, EE 320 Lecture 3 Page 1 of 10 Lecture 3: DC Analysis of Diode Circuits. We ll now move on to the DC analysis of diode circuits. Applications will be covered in following lectures. Let s consider
Part 1 Expressions, Equations, and Inequalities: Simplifying and Solving
 Section 7 Algebraic Manipulations and Solving Part 1 Expressions, Equations, and Inequalities: Simplifying and Solving Before launching into the mathematics, let s take a moment to talk about the words
Section 7 Algebraic Manipulations and Solving Part 1 Expressions, Equations, and Inequalities: Simplifying and Solving Before launching into the mathematics, let s take a moment to talk about the words
Math 115A HW4 Solutions University of California, Los Angeles. 5 2i 6 + 4i. (5 2i)7i (6 + 4i)( 3 + i) = 35i + 14 ( 22 6i) = 36 + 41i.
 Math 5A HW4 Solutions September 5, 202 University of California, Los Angeles Problem 4..3b Calculate the determinant, 5 2i 6 + 4i 3 + i 7i Solution: The textbook s instructions give us, (5 2i)7i (6 + 4i)(
Math 5A HW4 Solutions September 5, 202 University of California, Los Angeles Problem 4..3b Calculate the determinant, 5 2i 6 + 4i 3 + i 7i Solution: The textbook s instructions give us, (5 2i)7i (6 + 4i)(
Reciprocal Cost Allocations for Many Support Departments Using Spreadsheet Matrix Functions
 Reciprocal Cost Allocations for Many Support Departments Using Spreadsheet Matrix Functions Dennis Togo University of New Mexico The reciprocal method for allocating costs of support departments is the
Reciprocal Cost Allocations for Many Support Departments Using Spreadsheet Matrix Functions Dennis Togo University of New Mexico The reciprocal method for allocating costs of support departments is the
