Enthalpy of Combustion via Calorimetry
|
|
|
- Joel Leonard
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Enthalpy of Combustion via Calorimetry Introduction This experiment measures the enthalpy change when a system consisting of a known amount of a substance in the presence of excess oxygen is quantitatively reacted to form simple oxides, i.e., when the substance is burned. For example, benzoic acid, which is the reference material for this experiment, undergoes the exothermic reaction C 6 H 5 COOH(s) + 15/2 O 2 (g) 7 CO 2 (g) + 3 H 2 O(l) For this reaction, the isothermal conversion of one mole of benzoic acid to these products at K liberates 3, ± 0.24 kj of internal energy. Since this energy left the system, (i.e., U(final) < U(initial)), we write the molar internal energy change of combustion, U m,comb, as U m,comb = 3, ± 0.24 kj/mol. The emphasis initially is on the U value, because the reaction is carried out experimentally in a closed, constant-volume apparatus and the experimentally measured quantity is the heat associated with the process. Since U = q V, a measurement of q V gives U directly. If we measure the mass of benzoic acid at the start of the experiment, we can calculate the number of moles reacted (since the reaction goes to completion) and thus calculate the molar quantity U m,comb. These values can be turned into enthalpy changes, yielding standard enthalpies of combustion, (often called heats of combustion in the older literature) by the definition of enthalpy: H = U + PV so that H = U + (PV), and, since V is constant and P changes only from a change in the amount of gas in the calorimeter, we can write H = U + (nrt) = U + RT( n) where n = (# moles of product gases) (# moles of reactant gases). Note that this argument assumes that the reaction is carried out isothermally and that the gases are ideal. In the lab, the experiment is done adiabatically, and the primary data of any one measurement give the temperature rise of the apparatus that accompanies the combustion. Thus, a small correction must be made to bring the system along the hypothetical path from the experimental final temperature back to the experimental initial temperature. Enthalpy of Combustion 1
2 This calculation will involve the heat capacity of the apparatus, a quantity which is measured by burning benzoic acid, which has the internal energy of combustion value quoted above. Once the benzoic acid calibration run is performed satisfactorily, you will then measure H m, comb for one of the following solid hydrocarbons: (1) polyethylene, ( CH 2 ) x (2) phenanthrene (3) anthracene These latter two are C 14 H 10 isomeric aromatic hydrocarbons: Phenanthrene Anthracene Enthalpy of Combustion 2
3 Laboratory Procedure We will be using a Parr calorimeter (shown on this lab s web page). You will make one calibration measurement using benzoic acid (do two if you have extra time at the end of the lab) and duplicate runs on your choice of the other three solids. (You may want to make your choice based on the calculations and problems at the end of this writeup. All three are equally informative experiments, but each reveals a different aspect of the type of molecular information to be gleaned from calorimetric data.) Since data from the calibration measurement are used in subsequent experiments, it is worth performing the calibration measurement as carefully as you can. You will be using compressed O 2 gas at high (30 atm) pressures in this experiment. The calorimeter is called a Bomb calorimeter for just this reason! Follow the detailed steps below carefully. Have an instructor check your gas connections at the appropriate time as indicated below. Directions for use of the Parr Bomb Calorimeter 1. Cut and weigh a piece of Fe ignition wire 9 to 10 cm long, seeing to it that there is at least an 8 cm portion in the middle which is free of kinks. (A piece of wire attached so there is a kink between the leads will burn through at the kink rather than ignite your sample.) The specific internal energy of combustion of Fe is J mg 1. (Note the units; the word specific is often used to mean per unit mass rather than per mole. ) 2. Press a pellet of mass 0.8 ± 0.1 g for benzoic acid (or use a pre-pressed pellet, if available). For the other solids, press a pellet of mass 0.5 ± 0.1 g. 3. Attach the wire to the DC power supply, then slowly raise the voltage while pressing the wire onto the pellet. Keep increasing the voltage until the wire gets hot enough to melt the pellet slightly around the wire, then turn off the supply. The wire should now be stuck to the pellet, insuring good mechanical contact inside the bomb. Weigh the pellet/wire sample. 4. Place the pellet into the pan, attach the ignition wire to the calorimeter lead connections so that there are no kinks or sharp bends, and slide the fasteners over the ignition wire to secure it to the calorimeter leads. Make sure that the wire does not touch the pan, or else it will short circuit and burn through rather than ignite your sample. This is the critical step. Test for electrical continuity between the calorimeter lead connections using a digital ohmmeter, and note the electrical resistance reading. 5. Close the bomb, and screw on the cap until it is hand-tight note that there is Enthalpy of Combustion 3
4 no need to go beyond hand-tightening the screw cap. Re-test for electrical continuity between the calorimeter lead connections. (If this electrical resistance reading is very different from that obtained in step 4, open the bomb, and recheck the position of the pellet and the ignition wire.) 6. Hand-tighten the knurled venting nut. Attach the bomb to the oxygen filling line. Consult an instructor at this point. 7. Pressurize the bomb to 400 psi (about 30 atm). 8. Unscrew the knurled venting nut carefully to release the pressure and thus flush most of the air out of the bomb. When the bomb pressure has fallen back to the ambient pressure, hand-tighten the knurled venting nut, and repeat this procedure (steps 7 and 8) to flush the bomb a second time. 9. Hand-tighten the knurled venting nut, and pressurize the bomb again to 400 psi. Open the venting valve to depressurize the filling line, and detach the bomb from the oxygen filling line. Re-test for electrical continuity between the calorimeter lead connections. If this electrical resistance reading is very different from those obtained in steps 4 and 5, unscrew the knurled venting nut carefully to release the pressure, open the bomb and recheck the position of the pellet and the ignition wire. Make any required adjustments, and repeat steps 6 through Seat the water pail in the calorimeter jacket and the bomb in the pail. Attach the ignition leads to the bomb and again test for electrical continuity across the ignition contacts on the side of the jacket. If this resistance reading differs appreciably from those measured in previous steps, consult an instructor. Fill the pail with 2000 ml of water at 25 C, using a volumetric flask. Mix hot and cold water in the flask to reach the desired 25 C. 11. Put the calorimeter lid in place and insert the precision thermometer so that its bulb is near the mid-point of the water depth. Be careful! This thermometer has a thin glass bulb at its end containing mercury. Go slowly and carefully to ensure that you do not break the thermometer. Attach the thermometer viewer to the thermometer, and practice taking temperature measurements. 12. Turn the stirrer shaft by hand to ensure that the stirrer blades are not obstructed. Attach the stirrer motor to the stirrer blade with the motor belt, plug in the motor, and start the stirrer. 13. Attach the ignition wires to the leads marked 10 cm on the ignition box. 14. Begin measuring temperature as a function of time, making a reading every Enthalpy of Combustion 4
5 30 s. Read the temperature to the nearest C. You will continue these readings until the entire run is over. 15. After you have observed a steady but small rate of temperature change on the order of 0.01 C/min for at least 5 minutes, push the black button on the ignition box. The red light on the box should light briefly, and then fade, indicating an ignition current flowing through the Fe wire, followed by an open circuit due to the wire's consumption. A notable temperature rise should begin within 20 to 30 s. Follow the temperature for an additional 10 to 15 min, until the rate of change is again about as slow as before ignition. 16. Unplug the stirrer, disassemble the apparatus, release the bomb pressure carefully, and open the bomb. If the inside of the bomb is coated with soot, then there was insufficient O 2 present to give complete combustion, and the run will have to be repeated. If not, weigh any unburnt wire. Clean and dry all bomb parts before you begin a new run and after your last run. Questions and Calculations Your primary data for each run are the various (time, temperature) measurements you recorded. From these data, we need an accurate a value for the overall temperature change, T, that was caused by the burning reaction. You should plot these data for each of your runs, and when you do, you should find plots that look somewhat like the lefthand schematic plot below. Our T = T 1 T 0, and thus we need to know these initial and final temperatures as accurately as we can. To that end, make a second plot of your data in the vicinity of the ignition time in which you expand the temperature scale, as shown on the right-hand plot below. Extrapolate the temperatures on either side of the ignition time in order to obtain the best T 1 and T 0 values that you can. 28 Raw Data Plot 27.4 Raw Data on Expanded and Interrupted Temperature Plot 27 T T 1 T/ C T/ C T 0 25 T time time Enthalpy of Combustion 5
6 Next, calculate the system heat capacity, C, as determined by your benzoic acid calibration run(s), and calculate the absolute uncertainty associated with this quantity. (See the discussion on Propagation of Errors in the handout distributed in class.) This heat capacity is simply the total internal energy change associated with burning your sample of benzoic acid (of known mass) and the segment of Fe wire that burned (also of known mass) divided by the observed temperature change. For the other substance, find the molar internal energy change of combustion, U m,comb, using C, the mass of the burned substance (what about the Fe wire that burned, too? how should you account for that?), and the observed temperature change. Write a balanced combustion reaction for the oxidation of your substance to CO 2 and H 2 O. From the stoichiometry of this reaction and the amount of sample you used, find (PV) and thus calculate H m,comb and its associated uncertainty. Compare your value of H m,comb with the literature value. Continue with the calculations outlined below for the appropriate substance. Polyethylene A table of standard enthalpy of formation data is at the end of this handout. Use these H f,m data and your experimental results to calculate: and (1) the standard enthalpy of formation of solid polyethylene, per mole of CH 2 units, (2) the reaction enthalpy change for the polymerization reaction C 2 H 4 (g) (2/x) ( CH 2 ) x (s). Next, find the C C bond energy in the polymer chain. (Recall that a bond energy is really an enthalpy.) In the present case, H for the reaction ( CH 2 ) x (g) x C(g) + 2x H(g) is the sum of (x 1) times the molar C C bond energy plus (2x) times the molar energy of a C H bond. Use 413 kj/mol for the C H bond energy. Note that the reaction above is written for gaseous polyethylene. To take the solid-to-gas transition into account (i.e., the process of sublimation), use the value of 9 kj/mol per CH 2 group for the enthalpy of sublimation of polyethylene. The standard molar enthalpies of formation of C(g) and H(g) are tabulated below. How does your answer compare to (i) the accepted average C C single bond energy of 348 kj/mol, and (ii) to the ethane C C bond energy of 368 kj/mol? Enthalpy of Combustion 6
7 Phenanthrene and Anthracene 1. Using the value of H m,comb you determined experimentally, and the standard molar enthalpy of formation ( H f,m ) data tabulated below, calculate the standard molar enthalpy of formation ( H f,m ) of phenanthrene or anthracene (C 14 H 10 (s) hereinafter) and its associated uncertainty. Compare your value of H f,m with the literature value: 121. ± 10. kj/mol for anthracene and ± 2.2 kj/mol for phenanthrene. 2. Calculate the standard molar enthalpy change to break C 14 H 10 (g) apart into its atomic constituents, i.e., H m,atom, the molar enthalpy of atomization of (gas phase) C 14 H 10 : C 14 H 10 (g) 14 C(g) + 10 H(g). You will need to use your value of H f,m for C 14 H 10 (s), the tabulated values for the enthalpies of formation of C(g) and H(g), and the molar enthalpy of sublimation of C 14 H 10 (s): which is 91 kj/mol for phenanthrene and 102 kj/mol for anthracene. 3. Compare the value of H m,atom calculated in 2 with a sum of the appropriate number of C C, C=C, and C H bond energies, based on the Kekulé structures given earlier in the writeup, using 348 kj/mol for C C, 614 kj/mol for C=C, and 413 kj/mol for C H. This sum should be a smaller number than your calculated H m,atom ; the difference is the stabilization energy associated with delocalization of the electron system in these aromatic hydrocarbons. The literature values for these energies are 351 kj/mol for anthracene and 385 kj/mol for phenanthrene. How does your value compare? The resonance energy for benzene is about 151 kj/mol. What does this tell you about the additional stability induced by the center ring system in your substance? Acknowledgements: The figure of data plots is based on a similar figure in Experiments in Physical Chemistry, C. W. Garland, J. W. Nibler, and D. P. Shoemaker, 8 th Edition, McGraw Hill, New York, 2009, page 148. Enthalpies of formation of anthracene and phenanthrene taken from the NIST Chemistry WebBook, NIST Standard Reference Database Number 69, National Institute of Standards and Technology, accessed December, Enthalpy of Combustion 7
8 Standard Molar Enthalpies of Formation/kJ mol 1 H(g) C(g) O(g) H 2 O(g) CO 2 (g) C 2 H 4 (g) O 2 (g) 0 H 2 O(l) Enthalpy of Combustion 8
Adiabatic Bomb Calorimetry
 CHEM 366 II-1 Adiabatic Bomb Calorimetry Introduction Obtaining energy in the form of heat from the combustion or oxidation of thermodynamically unstable (and often kinetically inert) hydrocarbons and
CHEM 366 II-1 Adiabatic Bomb Calorimetry Introduction Obtaining energy in the form of heat from the combustion or oxidation of thermodynamically unstable (and often kinetically inert) hydrocarbons and
Experiment 1: Adiabatic Bomb Calorimeter (Dated: September 27, 2010)
 Experiment 1: Adiabatic Bomb Calorimeter (Dated: September 27, 2010) I. INTRODUCTION Heat released in a chemical reaction can be determined experimentally by using an adiabatic calorimeter. The reaction
Experiment 1: Adiabatic Bomb Calorimeter (Dated: September 27, 2010) I. INTRODUCTION Heat released in a chemical reaction can be determined experimentally by using an adiabatic calorimeter. The reaction
Determination of the enthalpy of combustion using a bomb calorimeter TEC
 Determination of the enthalpy of TEC Related concepts First law of thermodynamics, Hess s law of constant heat summation, enthalpy of combustion, enthalpy of formation, heat capacity. Principle The bomb
Determination of the enthalpy of TEC Related concepts First law of thermodynamics, Hess s law of constant heat summation, enthalpy of combustion, enthalpy of formation, heat capacity. Principle The bomb
Bomb Calorimetry and Heat of Combustion
 UC Berkeley College of Chemistry Chemistry 125 Physical Chemistry Laboratory Bomb Calorimetry and Heat of Combustion Author: Jonathan Melville Collaborators: David Gygi and Effie Zhou Graduate Student
UC Berkeley College of Chemistry Chemistry 125 Physical Chemistry Laboratory Bomb Calorimetry and Heat of Combustion Author: Jonathan Melville Collaborators: David Gygi and Effie Zhou Graduate Student
Combustion Calorimetry
 ombustion alorimetry 1 Please Note: Each lab group will be required to pick the compound they use in this experiment. The compound must contain only carbon and hydrogen or carbon, hydrogen and oxygen.
ombustion alorimetry 1 Please Note: Each lab group will be required to pick the compound they use in this experiment. The compound must contain only carbon and hydrogen or carbon, hydrogen and oxygen.
DETERMINING THE ENTHALPY OF FORMATION OF CaCO 3
 DETERMINING THE ENTHALPY OF FORMATION OF CaCO 3 Standard Enthalpy Change Standard Enthalpy Change for a reaction, symbolized as H 0 298, is defined as The enthalpy change when the molar quantities of reactants
DETERMINING THE ENTHALPY OF FORMATION OF CaCO 3 Standard Enthalpy Change Standard Enthalpy Change for a reaction, symbolized as H 0 298, is defined as The enthalpy change when the molar quantities of reactants
Heat of Combustion PCh 6-99
 UMR ChemLabs Heat of Combustion PCh 6-99 Gary L. Bertrand, Professor of Chemistry A calorimeter (calor L = heat + metron Gr = measure) should be literally a device to measure heat. In reality, most calorimeters
UMR ChemLabs Heat of Combustion PCh 6-99 Gary L. Bertrand, Professor of Chemistry A calorimeter (calor L = heat + metron Gr = measure) should be literally a device to measure heat. In reality, most calorimeters
Thermochemistry: Calorimetry and Hess s Law
 Thermochemistry: Calorimetry and Hess s Law Some chemical reactions are endothermic and proceed with absorption of heat while others are exothermic and proceed with an evolution of heat. The magnitude
Thermochemistry: Calorimetry and Hess s Law Some chemical reactions are endothermic and proceed with absorption of heat while others are exothermic and proceed with an evolution of heat. The magnitude
Introductory Laboratory EST - Experiment 9 Calorimetry - 1 - Introductory Laboratory Energy Science and Technology. Experiment 9. Physical Chemistry
 Introductory Laboratory EST - Experiment 9 Calorimetry - 1 - Introductory Laboratory Energy Science and Technology Experiment 9 Physical Chemistry Calorimetry Abstract The heat of combustion of Naphthalene
Introductory Laboratory EST - Experiment 9 Calorimetry - 1 - Introductory Laboratory Energy Science and Technology Experiment 9 Physical Chemistry Calorimetry Abstract The heat of combustion of Naphthalene
Determination of the enthalpy of combustion using a bomb calorimeter TEC. Safety precautions
 Safety precautions Naphthalene is harmful if swallowed. May cause cancer. Is further very toxic to aquatic organisms and can have long-term harmful effects in bodies of water. Equipment 1 Bomb calorimeter
Safety precautions Naphthalene is harmful if swallowed. May cause cancer. Is further very toxic to aquatic organisms and can have long-term harmful effects in bodies of water. Equipment 1 Bomb calorimeter
Transfer of heat energy often occurs during chemical reactions. A reaction
 Chemistry 111 Lab: Thermochemistry Page I-3 THERMOCHEMISTRY Heats of Reaction The Enthalpy of Formation of Magnesium Oxide Transfer of heat energy often occurs during chemical reactions. A reaction may
Chemistry 111 Lab: Thermochemistry Page I-3 THERMOCHEMISTRY Heats of Reaction The Enthalpy of Formation of Magnesium Oxide Transfer of heat energy often occurs during chemical reactions. A reaction may
Module 5: Combustion Technology. Lecture 34: Calculation of calorific value of fuels
 1 P age Module 5: Combustion Technology Lecture 34: Calculation of calorific value of fuels 2 P age Keywords : Gross calorific value, Net calorific value, enthalpy change, bomb calorimeter 5.3 Calculation
1 P age Module 5: Combustion Technology Lecture 34: Calculation of calorific value of fuels 2 P age Keywords : Gross calorific value, Net calorific value, enthalpy change, bomb calorimeter 5.3 Calculation
Bomb Calorimetry. Electrical leads. Stirrer
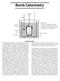 Bomb Calorimetry Stirrer Electrical leads Oxygen inlet valve Bomb Fuse Calorimeter Outer jacket Not shown: heating and cooling system for outer jacket, and controls that keep the outer jacket at the same
Bomb Calorimetry Stirrer Electrical leads Oxygen inlet valve Bomb Fuse Calorimeter Outer jacket Not shown: heating and cooling system for outer jacket, and controls that keep the outer jacket at the same
Molar Mass of Butane
 Cautions Butane is toxic and flammable. No OPEN Flames should be used in this experiment. Purpose The purpose of this experiment is to determine the molar mass of butane using Dalton s Law of Partial Pressures
Cautions Butane is toxic and flammable. No OPEN Flames should be used in this experiment. Purpose The purpose of this experiment is to determine the molar mass of butane using Dalton s Law of Partial Pressures
Determining Equivalent Weight by Copper Electrolysis
 Purpose The purpose of this experiment is to determine the equivalent mass of copper based on change in the mass of a copper electrode and the volume of hydrogen gas generated during an electrolysis reaction.
Purpose The purpose of this experiment is to determine the equivalent mass of copper based on change in the mass of a copper electrode and the volume of hydrogen gas generated during an electrolysis reaction.
PREPARATION FOR CHEMISTRY LAB: COMBUSTION
 1 Name: Lab Instructor: PREPARATION FOR CHEMISTRY LAB: COMBUSTION 1. What is a hydrocarbon? 2. What products form in the complete combustion of a hydrocarbon? 3. Combustion is an exothermic reaction. What
1 Name: Lab Instructor: PREPARATION FOR CHEMISTRY LAB: COMBUSTION 1. What is a hydrocarbon? 2. What products form in the complete combustion of a hydrocarbon? 3. Combustion is an exothermic reaction. What
HEAT OF FORMATION OF AMMONIUM NITRATE
 303 HEAT OF FORMATION OF AMMONIUM NITRATE OBJECTIVES FOR THE EXPERIMENT The student will be able to do the following: 1. Calculate the change in enthalpy (heat of reaction) using the Law of Hess. 2. Find
303 HEAT OF FORMATION OF AMMONIUM NITRATE OBJECTIVES FOR THE EXPERIMENT The student will be able to do the following: 1. Calculate the change in enthalpy (heat of reaction) using the Law of Hess. 2. Find
HEAT OF COMBUSTION BY OXYGEN BOMB CALORIMETER. References: See relevant chapters in undergraduate text.
 HEAT OF COMBUSTION BY OXYGEN BOMB CALORIMETER References: See relevant chapters in undergraduate text. Background: Study text sections on calorimetry and "thermochemistry" carefully. Know definitions of
HEAT OF COMBUSTION BY OXYGEN BOMB CALORIMETER References: See relevant chapters in undergraduate text. Background: Study text sections on calorimetry and "thermochemistry" carefully. Know definitions of
Bomb Calorimetry. Example 4. Energy and Enthalpy
 Bomb Calorimetry constant volume often used for combustion reactions heat released by reaction is absorbed by calorimeter contents need heat capacity of calorimeter q cal = q rxn = q bomb + q water Example
Bomb Calorimetry constant volume often used for combustion reactions heat released by reaction is absorbed by calorimeter contents need heat capacity of calorimeter q cal = q rxn = q bomb + q water Example
The Molar Mass of a Gas
 The Molar Mass of a Gas Goals The purpose of this experiment is to determine the number of grams per mole of a gas by measuring the pressure, volume, temperature, and mass of a sample. Terms to Know Molar
The Molar Mass of a Gas Goals The purpose of this experiment is to determine the number of grams per mole of a gas by measuring the pressure, volume, temperature, and mass of a sample. Terms to Know Molar
Reaction of Magnesium with Hydrochloric Acid (Gas Laws) Chemicals Needed:
 Reaction of Magnesium with Hydrochloric Acid (Gas Laws) Your Name: Date: Partner(s) Names: Objectives: React magnesium metal with hydrochloric acid, collecting the hydrogen over water. Calculate the grams
Reaction of Magnesium with Hydrochloric Acid (Gas Laws) Your Name: Date: Partner(s) Names: Objectives: React magnesium metal with hydrochloric acid, collecting the hydrogen over water. Calculate the grams
SUPPLEMENTARY TOPIC 3 ENERGY AND CHEMICAL REACTIONS
 SUPPLEMENTARY TOPIC 3 ENERGY AND CHEMICAL REACTIONS Rearranging atoms. In a chemical reaction, bonds between atoms in one or more molecules (reactants) break and new bonds are formed with other atoms to
SUPPLEMENTARY TOPIC 3 ENERGY AND CHEMICAL REACTIONS Rearranging atoms. In a chemical reaction, bonds between atoms in one or more molecules (reactants) break and new bonds are formed with other atoms to
BLOWING UP BALLOONS, chemically
 BLOWING UP BALLOONS, chemically PRE LAB DISCUSSION: Today we will be using a closed system. A closed system does not permit matter to enter or exit the apparatus. Lavoisier's classic 12-day experiment,
BLOWING UP BALLOONS, chemically PRE LAB DISCUSSION: Today we will be using a closed system. A closed system does not permit matter to enter or exit the apparatus. Lavoisier's classic 12-day experiment,
Determination of the Empirical Formula of Magnesium Oxide
 Determination of the Empirical Formula of Magnesium Oxide GOAL AND OVERVIEW The quantitative stoichiometric relationships governing mass and amount will be studied using the combustion reaction of magnesium
Determination of the Empirical Formula of Magnesium Oxide GOAL AND OVERVIEW The quantitative stoichiometric relationships governing mass and amount will be studied using the combustion reaction of magnesium
UNIT 1 THERMOCHEMISTRY
 UNIT 1 THERMOCHEMISTRY THERMOCHEMISTRY LEARNING OUTCOMES Students will be expected to: THERMOCHEMISTRY STSE analyse why scientific and technological activities take place in a variety individual and group
UNIT 1 THERMOCHEMISTRY THERMOCHEMISTRY LEARNING OUTCOMES Students will be expected to: THERMOCHEMISTRY STSE analyse why scientific and technological activities take place in a variety individual and group
Experiment 2: Using Bomb Calorimetry to Determine the Resonance Energy of Benzene
 Experiment 2: Using Bomb Calorimetry to Determine the Resonance Energy of Benzene Reading: SGN: p.145-151 (152-157 may also be useful) Quanta: Benzene, Resonance Benzene was historically a very difficult
Experiment 2: Using Bomb Calorimetry to Determine the Resonance Energy of Benzene Reading: SGN: p.145-151 (152-157 may also be useful) Quanta: Benzene, Resonance Benzene was historically a very difficult
1 Exercise 2.19a pg 86
 In this solution set, an underline is used to show the last significant digit of numbers. For instance in x = 2.51693 the 2,5,1, and 6 are all significant. Digits to the right of the underlined digit,
In this solution set, an underline is used to show the last significant digit of numbers. For instance in x = 2.51693 the 2,5,1, and 6 are all significant. Digits to the right of the underlined digit,
EXPERIMENT 15: Ideal Gas Law: Molecular Weight of a Vapor
 EXPERIMENT 15: Ideal Gas Law: Molecular Weight of a Vapor Purpose: In this experiment you will use the ideal gas law to calculate the molecular weight of a volatile liquid compound by measuring the mass,
EXPERIMENT 15: Ideal Gas Law: Molecular Weight of a Vapor Purpose: In this experiment you will use the ideal gas law to calculate the molecular weight of a volatile liquid compound by measuring the mass,
1. Thermite reaction 2. Enthalpy of reaction, H 3. Heating/cooling curves and changes in state 4. More thermite thermodynamics
 Chem 105 Fri 10-23-09 1. Thermite reaction 2. Enthalpy of reaction, H 3. Heating/cooling curves and changes in state 4. More thermite thermodynamics 10/23/2009 1 Please PICK UP your graded EXAM in front.
Chem 105 Fri 10-23-09 1. Thermite reaction 2. Enthalpy of reaction, H 3. Heating/cooling curves and changes in state 4. More thermite thermodynamics 10/23/2009 1 Please PICK UP your graded EXAM in front.
Chapter 6 Thermodynamics: The First Law
 Key Concepts 6.1 Systems Chapter 6 Thermodynamics: The First Law Systems, States, and Energy (Sections 6.1 6.8) thermodynamics, statistical thermodynamics, system, surroundings, open system, closed system,
Key Concepts 6.1 Systems Chapter 6 Thermodynamics: The First Law Systems, States, and Energy (Sections 6.1 6.8) thermodynamics, statistical thermodynamics, system, surroundings, open system, closed system,
Apparatus error for each piece of equipment = 100 x margin of error quantity measured
 1) Error Analysis Apparatus Errors (uncertainty) Every time you make a measurement with a piece of apparatus, there is a small margin of error (i.e. uncertainty) in that measurement due to the apparatus
1) Error Analysis Apparatus Errors (uncertainty) Every time you make a measurement with a piece of apparatus, there is a small margin of error (i.e. uncertainty) in that measurement due to the apparatus
Austin Peay State University Department of Chemistry CHEM 1111. Empirical Formula of a Compound
 Cautions Magnesium ribbon is flammable. Nitric acid (HNO 3 ) is toxic, corrosive and contact with eyes or skin may cause severe burns. Ammonia gas (NH 3 ) is toxic and harmful. Hot ceramic crucibles and
Cautions Magnesium ribbon is flammable. Nitric acid (HNO 3 ) is toxic, corrosive and contact with eyes or skin may cause severe burns. Ammonia gas (NH 3 ) is toxic and harmful. Hot ceramic crucibles and
87 16 70 20 58 24 44 32 35 40 29 48 (a) graph Y versus X (b) graph Y versus 1/X
 HOMEWORK 5A Barometer; Boyle s Law 1. The pressure of the first two gases below is determined with a manometer that is filled with mercury (density = 13.6 g/ml). The pressure of the last two gases below
HOMEWORK 5A Barometer; Boyle s Law 1. The pressure of the first two gases below is determined with a manometer that is filled with mercury (density = 13.6 g/ml). The pressure of the last two gases below
Molar Mass and the Ideal Gas Law Prelab
 Molar Mass and the Ideal Gas Law Prelab Name Total /10 SHOW ALL WORK NO WORK = NO CREDIT 1. What is the purpose of this experiment? 2. Determine the mass (in grams) of magnesium metal required to produce
Molar Mass and the Ideal Gas Law Prelab Name Total /10 SHOW ALL WORK NO WORK = NO CREDIT 1. What is the purpose of this experiment? 2. Determine the mass (in grams) of magnesium metal required to produce
Enthalpy of Reaction and Calorimetry worksheet
 Enthalpy of Reaction and Calorimetry worksheet 1. Calcium carbonate decomposes at high temperature to form carbon dioxide and calcium oxide, calculate the enthalpy of reaction. CaCO 3 CO 2 + CaO 2. Carbon
Enthalpy of Reaction and Calorimetry worksheet 1. Calcium carbonate decomposes at high temperature to form carbon dioxide and calcium oxide, calculate the enthalpy of reaction. CaCO 3 CO 2 + CaO 2. Carbon
AP CHEMISTRY 2009 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B)
 AP CHEMISTRY 2009 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B) Question 3 (10 points) 2 H 2 O 2 (aq) 2 H 2 O(l) + O 2 (g) The mass of an aqueous solution of H 2 O 2 is 6.951 g. The H 2 O 2 in the solution decomposes completely
AP CHEMISTRY 2009 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B) Question 3 (10 points) 2 H 2 O 2 (aq) 2 H 2 O(l) + O 2 (g) The mass of an aqueous solution of H 2 O 2 is 6.951 g. The H 2 O 2 in the solution decomposes completely
Energy and Chemical Reactions. Characterizing Energy:
 Energy and Chemical Reactions Energy: Critical for virtually all aspects of chemistry Defined as: We focus on energy transfer. We observe energy changes in: Heat Transfer: How much energy can a material
Energy and Chemical Reactions Energy: Critical for virtually all aspects of chemistry Defined as: We focus on energy transfer. We observe energy changes in: Heat Transfer: How much energy can a material
2. The percent yield is the maximum amount of product that can be produced from the given amount of limiting reactant.
 UNIT 6 stoichiometry practice test True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. moles F 1. The mole ratio is a comparison of how many grams of one substance are required to participate in
UNIT 6 stoichiometry practice test True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. moles F 1. The mole ratio is a comparison of how many grams of one substance are required to participate in
Chemistry 112 Laboratory Experiment 6: The Reaction of Aluminum and Zinc with Hydrochloric Acid
 Chemistry 112 Laboratory Experiment 6: The Reaction of Aluminum and Zinc with Hydrochloric Acid Introduction Many metals react with acids to form hydrogen gas. In this experiment, you will use the reactions
Chemistry 112 Laboratory Experiment 6: The Reaction of Aluminum and Zinc with Hydrochloric Acid Introduction Many metals react with acids to form hydrogen gas. In this experiment, you will use the reactions
EXPERIMENT 13: THE IDEAL GAS LAW AND THE MOLECULAR WEIGHT OF GASES
 Name Section EXPERIMENT 13: THE IDEAL GAS LAW AND THE MOLECULAR WEIGHT OF GASES PRE-LABORATORY QUESTIONS The following preparatory questions should be answered before coming to lab. They are intended to
Name Section EXPERIMENT 13: THE IDEAL GAS LAW AND THE MOLECULAR WEIGHT OF GASES PRE-LABORATORY QUESTIONS The following preparatory questions should be answered before coming to lab. They are intended to
IB Chemistry. DP Chemistry Review
 DP Chemistry Review Topic 1: Quantitative chemistry 1.1 The mole concept and Avogadro s constant Assessment statement Apply the mole concept to substances. Determine the number of particles and the amount
DP Chemistry Review Topic 1: Quantitative chemistry 1.1 The mole concept and Avogadro s constant Assessment statement Apply the mole concept to substances. Determine the number of particles and the amount
Chemical Equations & Stoichiometry
 Chemical Equations & Stoichiometry Chapter Goals Balance equations for simple chemical reactions. Perform stoichiometry calculations using balanced chemical equations. Understand the meaning of the term
Chemical Equations & Stoichiometry Chapter Goals Balance equations for simple chemical reactions. Perform stoichiometry calculations using balanced chemical equations. Understand the meaning of the term
Standard Free Energies of Formation at 298 K. Average Bond Dissociation Energies at 298 K
 1 Thermodynamics There always seems to be at least one free response question that involves thermodynamics. These types of question also show up in the multiple choice questions. G, S, and H. Know what
1 Thermodynamics There always seems to be at least one free response question that involves thermodynamics. These types of question also show up in the multiple choice questions. G, S, and H. Know what
IDEAL AND NON-IDEAL GASES
 2/2016 ideal gas 1/8 IDEAL AND NON-IDEAL GASES PURPOSE: To measure how the pressure of a low-density gas varies with temperature, to determine the absolute zero of temperature by making a linear fit to
2/2016 ideal gas 1/8 IDEAL AND NON-IDEAL GASES PURPOSE: To measure how the pressure of a low-density gas varies with temperature, to determine the absolute zero of temperature by making a linear fit to
Heat of Solution. Purpose To calculate the heat of solution for sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and ammonium nitrate (NH 4 NO 3 )
 Heat of Solution Purpose To calculate the heat of solution for sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and ammonium nitrate (NH 4 NO 3 ) Background For a given solute, the heat of solution is the change in enerrgy that
Heat of Solution Purpose To calculate the heat of solution for sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and ammonium nitrate (NH 4 NO 3 ) Background For a given solute, the heat of solution is the change in enerrgy that
Thermodynamics and Equilibrium
 Chapter 19 Thermodynamics and Equilibrium Concept Check 19.1 You have a sample of 1.0 mg of solid iodine at room temperature. Later, you notice that the iodine has sublimed (passed into the vapor state).
Chapter 19 Thermodynamics and Equilibrium Concept Check 19.1 You have a sample of 1.0 mg of solid iodine at room temperature. Later, you notice that the iodine has sublimed (passed into the vapor state).
Chapter 3: Stoichiometry
 Chapter 3: Stoichiometry Key Skills: Balance chemical equations Predict the products of simple combination, decomposition, and combustion reactions. Calculate formula weights Convert grams to moles and
Chapter 3: Stoichiometry Key Skills: Balance chemical equations Predict the products of simple combination, decomposition, and combustion reactions. Calculate formula weights Convert grams to moles and
EXPERIMENT 7 Reaction Stoichiometry and Percent Yield
 EXPERIMENT 7 Reaction Stoichiometry and Percent Yield INTRODUCTION Stoichiometry calculations are about calculating the amounts of substances that react and form in a chemical reaction. The word stoichiometry
EXPERIMENT 7 Reaction Stoichiometry and Percent Yield INTRODUCTION Stoichiometry calculations are about calculating the amounts of substances that react and form in a chemical reaction. The word stoichiometry
CHEM 36 General Chemistry EXAM #1 February 13, 2002
 CHEM 36 General Chemistry EXAM #1 February 13, 2002 Name: Serkey, Anne INSTRUCTIONS: Read through the entire exam before you begin. Answer all of the questions. For questions involving calculations, show
CHEM 36 General Chemistry EXAM #1 February 13, 2002 Name: Serkey, Anne INSTRUCTIONS: Read through the entire exam before you begin. Answer all of the questions. For questions involving calculations, show
Part One: Mass and Moles of Substance. Molecular Mass = sum of the Atomic Masses in a molecule
 CHAPTER THREE: CALCULATIONS WITH CHEMICAL FORMULAS AND EQUATIONS Part One: Mass and Moles of Substance A. Molecular Mass and Formula Mass. (Section 3.1) 1. Just as we can talk about mass of one atom of
CHAPTER THREE: CALCULATIONS WITH CHEMICAL FORMULAS AND EQUATIONS Part One: Mass and Moles of Substance A. Molecular Mass and Formula Mass. (Section 3.1) 1. Just as we can talk about mass of one atom of
In this experiment, we will use three properties to identify a liquid substance: solubility, density and boiling point..
 Identification of a Substance by Physical Properties 2009 by David A. Katz. All rights reserved. Permission for academic use provided the original copyright is included Every substance has a unique set
Identification of a Substance by Physical Properties 2009 by David A. Katz. All rights reserved. Permission for academic use provided the original copyright is included Every substance has a unique set
MEMORANDUM GRADE 11. PHYSICAL SCIENCES: CHEMISTRY Paper 2
 MEMORANDUM GRADE 11 PHYSICAL SCIENCES: CHEMISTRY Paper 2 MARKS: 150 TIME: 3 hours Learning Outcomes and Assessment Standards LO1 LO2 LO3 AS 11.1.1: Plan and conduct a scientific investigation to collect
MEMORANDUM GRADE 11 PHYSICAL SCIENCES: CHEMISTRY Paper 2 MARKS: 150 TIME: 3 hours Learning Outcomes and Assessment Standards LO1 LO2 LO3 AS 11.1.1: Plan and conduct a scientific investigation to collect
SUGGESTION ANSWER SCHEME CHAPTER 8: THERMOCHEMISTRY. 1 (a) Use the data in the table below to answer the following questions:
 SUGGESTION ANSWER SCHEME CHAPTER 8: THERMOCHEMISTRY ANSWER SCHEME UPS 2004/2005 SK027 1 (a) Use the data in the table below to answer the following questions: Enthalpy change ΔH (kj/mol) Atomization energy
SUGGESTION ANSWER SCHEME CHAPTER 8: THERMOCHEMISTRY ANSWER SCHEME UPS 2004/2005 SK027 1 (a) Use the data in the table below to answer the following questions: Enthalpy change ΔH (kj/mol) Atomization energy
Introductory Chemistry, 3 rd Edition Nivaldo Tro. Roy Kennedy Massachusetts Bay Community College Wellesley Hills, Maqqwertd ygoijpk[l
 Introductory Chemistry, 3 rd Edition Nivaldo Tro Quantities in Car an octane and oxygen molecules and carbon dioxide and water Chemical Reactions Roy Kennedy Massachusetts Bay Community College Wellesley
Introductory Chemistry, 3 rd Edition Nivaldo Tro Quantities in Car an octane and oxygen molecules and carbon dioxide and water Chemical Reactions Roy Kennedy Massachusetts Bay Community College Wellesley
Chem 1A Exam 2 Review Problems
 Chem 1A Exam 2 Review Problems 1. At 0.967 atm, the height of mercury in a barometer is 0.735 m. If the mercury were replaced with water, what height of water (in meters) would be supported at this pressure?
Chem 1A Exam 2 Review Problems 1. At 0.967 atm, the height of mercury in a barometer is 0.735 m. If the mercury were replaced with water, what height of water (in meters) would be supported at this pressure?
Experiment 3 Limiting Reactants
 3-1 Experiment 3 Limiting Reactants Introduction: Most chemical reactions require two or more reactants. Typically, one of the reactants is used up before the other, at which time the reaction stops. The
3-1 Experiment 3 Limiting Reactants Introduction: Most chemical reactions require two or more reactants. Typically, one of the reactants is used up before the other, at which time the reaction stops. The
The first law: transformation of energy into heat and work. Chemical reactions can be used to provide heat and for doing work.
 The first law: transformation of energy into heat and work Chemical reactions can be used to provide heat and for doing work. Compare fuel value of different compounds. What drives these reactions to proceed
The first law: transformation of energy into heat and work Chemical reactions can be used to provide heat and for doing work. Compare fuel value of different compounds. What drives these reactions to proceed
Exp 13 Volumetric Analysis: Acid-Base titration
 Exp 13 Volumetric Analysis: Acid-Base titration Exp. 13 video (time: 47:17 minutes) Titration - is the measurement of the volume of a standard solution required to completely react with a measured volume
Exp 13 Volumetric Analysis: Acid-Base titration Exp. 13 video (time: 47:17 minutes) Titration - is the measurement of the volume of a standard solution required to completely react with a measured volume
CHEM 105 HOUR EXAM III 28-OCT-99. = -163 kj/mole determine H f 0 for Ni(CO) 4 (g) = -260 kj/mole determine H f 0 for Cr(CO) 6 (g)
 CHEM 15 HOUR EXAM III 28-OCT-99 NAME (please print) 1. a. given: Ni (s) + 4 CO (g) = Ni(CO) 4 (g) H Rxn = -163 k/mole determine H f for Ni(CO) 4 (g) b. given: Cr (s) + 6 CO (g) = Cr(CO) 6 (g) H Rxn = -26
CHEM 15 HOUR EXAM III 28-OCT-99 NAME (please print) 1. a. given: Ni (s) + 4 CO (g) = Ni(CO) 4 (g) H Rxn = -163 k/mole determine H f for Ni(CO) 4 (g) b. given: Cr (s) + 6 CO (g) = Cr(CO) 6 (g) H Rxn = -26
DETERMINING THE MOLAR MASS OF CARBON DIOXIDE
 DETERMINING THE MOLAR MASS OF CARBON DIOXIDE PURPOSE: The goal of the experiment is to determine the molar mass of carbon dioxide and compare the experimentally determined value to the theoretical value.
DETERMINING THE MOLAR MASS OF CARBON DIOXIDE PURPOSE: The goal of the experiment is to determine the molar mass of carbon dioxide and compare the experimentally determined value to the theoretical value.
Honors Chemistry: Unit 6 Test Stoichiometry PRACTICE TEST ANSWER KEY Page 1. A chemical equation. (C-4.4)
 Honors Chemistry: Unit 6 Test Stoichiometry PRACTICE TEST ANSWER KEY Page 1 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Question What is a symbolic representation of a chemical reaction? What 3 things (values) is a mole of a chemical
Honors Chemistry: Unit 6 Test Stoichiometry PRACTICE TEST ANSWER KEY Page 1 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Question What is a symbolic representation of a chemical reaction? What 3 things (values) is a mole of a chemical
= 1.038 atm. 760 mm Hg. = 0.989 atm. d. 767 torr = 767 mm Hg. = 1.01 atm
 Chapter 13 Gases 1. Solids and liquids have essentially fixed volumes and are not able to be compressed easily. Gases have volumes that depend on their conditions, and can be compressed or expanded by
Chapter 13 Gases 1. Solids and liquids have essentially fixed volumes and are not able to be compressed easily. Gases have volumes that depend on their conditions, and can be compressed or expanded by
INTI COLLEGE MALAYSIA A? LEVEL PROGRAMME CHM 111: CHEMISTRY MOCK EXAMINATION: DECEMBER 2000 SESSION. 37 74 20 40 60 80 m/e
 CHM111(M)/Page 1 of 5 INTI COLLEGE MALAYSIA A? LEVEL PROGRAMME CHM 111: CHEMISTRY MOCK EXAMINATION: DECEMBER 2000 SESSION SECTION A Answer ALL EIGHT questions. (52 marks) 1. The following is the mass spectrum
CHM111(M)/Page 1 of 5 INTI COLLEGE MALAYSIA A? LEVEL PROGRAMME CHM 111: CHEMISTRY MOCK EXAMINATION: DECEMBER 2000 SESSION SECTION A Answer ALL EIGHT questions. (52 marks) 1. The following is the mass spectrum
Experiment 6 Coffee-cup Calorimetry
 6-1 Experiment 6 Coffee-cup Calorimetry Introduction: Chemical reactions involve the release or consumption of energy, usually in the form of heat. Heat is measured in the energy units, Joules (J), defined
6-1 Experiment 6 Coffee-cup Calorimetry Introduction: Chemical reactions involve the release or consumption of energy, usually in the form of heat. Heat is measured in the energy units, Joules (J), defined
Problem Solving. Stoichiometry of Gases
 Skills Worksheet Problem Solving Stoichiometry of Gases Now that you have worked with relationships among moles, mass, and volumes of gases, you can easily put these to work in stoichiometry calculations.
Skills Worksheet Problem Solving Stoichiometry of Gases Now that you have worked with relationships among moles, mass, and volumes of gases, you can easily put these to work in stoichiometry calculations.
DATE PERFORMED: DATE DUE:
 Sample lab report The first page is the cover page for the report. Title: Experiment #12 Determination of the Atomic Mass of Zinc ( p 117, Hunt and Block) YOUR NAME: PARTNER(S) NAME: DATE PERFORMED: DATE
Sample lab report The first page is the cover page for the report. Title: Experiment #12 Determination of the Atomic Mass of Zinc ( p 117, Hunt and Block) YOUR NAME: PARTNER(S) NAME: DATE PERFORMED: DATE
The Empirical Formula of a Compound
 The Empirical Formula of a Compound Lab #5 Introduction A look at the mass relationships in chemistry reveals little order or sense. The ratio of the masses of the elements in a compound, while constant,
The Empirical Formula of a Compound Lab #5 Introduction A look at the mass relationships in chemistry reveals little order or sense. The ratio of the masses of the elements in a compound, while constant,
Evaluation copy. Titration of a Diprotic Acid: Identifying an Unknown. Computer
 Titration of a Diprotic Acid: Identifying an Unknown Computer 25 A diprotic acid is an acid that yields two H + ions per acid molecule. Examples of diprotic acids are sulfuric acid, H 2 SO 4, and carbonic
Titration of a Diprotic Acid: Identifying an Unknown Computer 25 A diprotic acid is an acid that yields two H + ions per acid molecule. Examples of diprotic acids are sulfuric acid, H 2 SO 4, and carbonic
EXPERIMENT 9 Evaluation of the Universal Gas Constant, R
 Outcomes EXPERIMENT 9 Evaluation of the Universal Gas Constant, R After completing this experiment, the student should be able to: 1. Determine universal gas constant using reaction of an acid with a metal.
Outcomes EXPERIMENT 9 Evaluation of the Universal Gas Constant, R After completing this experiment, the student should be able to: 1. Determine universal gas constant using reaction of an acid with a metal.
Chapter 6 Chemical Calculations
 Chapter 6 Chemical Calculations 1 Submicroscopic Macroscopic 2 Chapter Outline 1. Formula Masses (Ch 6.1) 2. Percent Composition (supplemental material) 3. The Mole & Avogadro s Number (Ch 6.2) 4. Molar
Chapter 6 Chemical Calculations 1 Submicroscopic Macroscopic 2 Chapter Outline 1. Formula Masses (Ch 6.1) 2. Percent Composition (supplemental material) 3. The Mole & Avogadro s Number (Ch 6.2) 4. Molar
Thermodynamics. Thermodynamics 1
 Thermodynamics 1 Thermodynamics Some Important Topics First Law of Thermodynamics Internal Energy U ( or E) Enthalpy H Second Law of Thermodynamics Entropy S Third law of Thermodynamics Absolute Entropy
Thermodynamics 1 Thermodynamics Some Important Topics First Law of Thermodynamics Internal Energy U ( or E) Enthalpy H Second Law of Thermodynamics Entropy S Third law of Thermodynamics Absolute Entropy
EXPERIMENT 12: Empirical Formula of a Compound
 EXPERIMENT 12: Empirical Formula of a Compound INTRODUCTION Chemical formulas indicate the composition of compounds. A formula that gives only the simplest ratio of the relative number of atoms in a compound
EXPERIMENT 12: Empirical Formula of a Compound INTRODUCTION Chemical formulas indicate the composition of compounds. A formula that gives only the simplest ratio of the relative number of atoms in a compound
Chemistry B11 Chapter 4 Chemical reactions
 Chemistry B11 Chapter 4 Chemical reactions Chemical reactions are classified into five groups: A + B AB Synthesis reactions (Combination) H + O H O AB A + B Decomposition reactions (Analysis) NaCl Na +Cl
Chemistry B11 Chapter 4 Chemical reactions Chemical reactions are classified into five groups: A + B AB Synthesis reactions (Combination) H + O H O AB A + B Decomposition reactions (Analysis) NaCl Na +Cl
CHEMISTRY. Matter and Change. Section 13.1 Section 13.2 Section 13.3. The Gas Laws The Ideal Gas Law Gas Stoichiometry
 CHEMISTRY Matter and Change 13 Table Of Contents Chapter 13: Gases Section 13.1 Section 13.2 Section 13.3 The Gas Laws The Ideal Gas Law Gas Stoichiometry State the relationships among pressure, temperature,
CHEMISTRY Matter and Change 13 Table Of Contents Chapter 13: Gases Section 13.1 Section 13.2 Section 13.3 The Gas Laws The Ideal Gas Law Gas Stoichiometry State the relationships among pressure, temperature,
COMMON LABORATORY APPARATUS
 COMMON LABORATORY APPARATUS Beakers are useful as a reaction container or to hold liquid or solid samples. They are also used to catch liquids from titrations and filtrates from filtering operations. Bunsen
COMMON LABORATORY APPARATUS Beakers are useful as a reaction container or to hold liquid or solid samples. They are also used to catch liquids from titrations and filtrates from filtering operations. Bunsen
TA INSTRUMENTS DIFFERENTIAL SCANNING CALORIMETER (DSC) Insert Nickname Here. Operating Instructions
 TA INSTRUMENTS DIFFERENTIAL SCANNING CALORIMETER (DSC) Insert Nickname Here Operating Instructions Table of Contents 1 INTRODUCTION Safety 2 Sample Preparation 3 2 BACKGROUND Background Information 4 Resources
TA INSTRUMENTS DIFFERENTIAL SCANNING CALORIMETER (DSC) Insert Nickname Here Operating Instructions Table of Contents 1 INTRODUCTION Safety 2 Sample Preparation 3 2 BACKGROUND Background Information 4 Resources
Gas Laws. The kinetic theory of matter states that particles which make up all types of matter are in constant motion.
 Name Period Gas Laws Kinetic energy is the energy of motion of molecules. Gas state of matter made up of tiny particles (atoms or molecules). Each atom or molecule is very far from other atoms or molecules.
Name Period Gas Laws Kinetic energy is the energy of motion of molecules. Gas state of matter made up of tiny particles (atoms or molecules). Each atom or molecule is very far from other atoms or molecules.
General Chemistry I (FC, 09-10) Lab #3: The Empirical Formula of a Compound. Introduction
 General Chemistry I (FC, 09-10) Introduction A look at the mass relationships in chemistry reveals little order or sense. The ratio of the masses of the elements in a compound, while constant, does not
General Chemistry I (FC, 09-10) Introduction A look at the mass relationships in chemistry reveals little order or sense. The ratio of the masses of the elements in a compound, while constant, does not
Formulas, Equations and Moles
 Chapter 3 Formulas, Equations and Moles Interpreting Chemical Equations You can interpret a balanced chemical equation in many ways. On a microscopic level, two molecules of H 2 react with one molecule
Chapter 3 Formulas, Equations and Moles Interpreting Chemical Equations You can interpret a balanced chemical equation in many ways. On a microscopic level, two molecules of H 2 react with one molecule
Thermochemistry. r2 d:\files\courses\1110-20\99heat&thermorans.doc. Ron Robertson
 Thermochemistry r2 d:\files\courses\1110-20\99heat&thermorans.doc Ron Robertson I. What is Energy? A. Energy is a property of matter that allows work to be done B. Potential and Kinetic Potential energy
Thermochemistry r2 d:\files\courses\1110-20\99heat&thermorans.doc Ron Robertson I. What is Energy? A. Energy is a property of matter that allows work to be done B. Potential and Kinetic Potential energy
Physical Properties of a Pure Substance, Water
 Physical Properties of a Pure Substance, Water The chemical and physical properties of a substance characterize it as a unique substance, and the determination of these properties can often allow one to
Physical Properties of a Pure Substance, Water The chemical and physical properties of a substance characterize it as a unique substance, and the determination of these properties can often allow one to
Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations
 Chapter 3 Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations Concept Check 3.1 You have 1.5 moles of tricycles. a. How many moles of seats do you have? b. How many moles of tires do you have? c. How could
Chapter 3 Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations Concept Check 3.1 You have 1.5 moles of tricycles. a. How many moles of seats do you have? b. How many moles of tires do you have? c. How could
thermometer as simple as a styrofoam cup and a thermometer. In a calorimeter the reactants are placed into the
 Thermochemistry Readin assinment: Chan, Chemistry 10 th edition, pp. 249-258. Goals We will become familiar with the principles of calorimetry in order to determine the heats of reaction for endothermic
Thermochemistry Readin assinment: Chan, Chemistry 10 th edition, pp. 249-258. Goals We will become familiar with the principles of calorimetry in order to determine the heats of reaction for endothermic
Where the exp subscripts refer to the experimental temperature and pressure acquired in the laboratory.
 Molar Volume of Carbon Dioxide Reading assignment: Julia Burdge, Chemistry 3rd edition, Chapter 10. Goals To determine the molar volume of carbon dioxide gas and the amount of sodium carbonate in a sample.
Molar Volume of Carbon Dioxide Reading assignment: Julia Burdge, Chemistry 3rd edition, Chapter 10. Goals To determine the molar volume of carbon dioxide gas and the amount of sodium carbonate in a sample.
Thermodynamics Worksheet I also highly recommend Worksheets 13 and 14 in the Lab Manual
 Thermodynamics Worksheet I also highly recommend Worksheets 13 and 14 in the Lab Manual 1. Predict the sign of entropy change in the following processes a) The process of carbonating water to make a soda
Thermodynamics Worksheet I also highly recommend Worksheets 13 and 14 in the Lab Manual 1. Predict the sign of entropy change in the following processes a) The process of carbonating water to make a soda
7. 1.00 atm = 760 torr = 760 mm Hg = 101.325 kpa = 14.70 psi. = 0.446 atm. = 0.993 atm. = 107 kpa 760 torr 1 atm 760 mm Hg = 790.
 CHATER 3. The atmosphere is a homogeneous mixture (a solution) of gases.. Solids and liquids have essentially fixed volumes and are not able to be compressed easily. have volumes that depend on their conditions,
CHATER 3. The atmosphere is a homogeneous mixture (a solution) of gases.. Solids and liquids have essentially fixed volumes and are not able to be compressed easily. have volumes that depend on their conditions,
Appendix D. Reaction Stoichiometry D.1 INTRODUCTION
 Appendix D Reaction Stoichiometry D.1 INTRODUCTION In Appendix A, the stoichiometry of elements and compounds was presented. There, the relationships among grams, moles and number of atoms and molecules
Appendix D Reaction Stoichiometry D.1 INTRODUCTION In Appendix A, the stoichiometry of elements and compounds was presented. There, the relationships among grams, moles and number of atoms and molecules
Thermochemistry I: Endothermic & Exothermic Reactions
 THERMOCHEMISTRY I 77 Thermochemistry I: Endothermic & Exothermic Reactions OBJECTIVES: Learn elementary concepts of calorimetry and thermochemistry Practice techniques of careful temperature, mass, and
THERMOCHEMISTRY I 77 Thermochemistry I: Endothermic & Exothermic Reactions OBJECTIVES: Learn elementary concepts of calorimetry and thermochemistry Practice techniques of careful temperature, mass, and
F321 MOLES. Example If 1 atom has a mass of 1.241 x 10-23 g 1 mole of atoms will have a mass of 1.241 x 10-23 g x 6.02 x 10 23 = 7.
 Moles 1 MOLES The mole the standard unit of amount of a substance (mol) the number of particles in a mole is known as Avogadro s constant (N A ) Avogadro s constant has a value of 6.02 x 10 23 mol -1.
Moles 1 MOLES The mole the standard unit of amount of a substance (mol) the number of particles in a mole is known as Avogadro s constant (N A ) Avogadro s constant has a value of 6.02 x 10 23 mol -1.
Oxidation States of Copper Two forms of copper oxide are found in nature, copper(i) oxide and copper(ii) oxide.
 The Empirical Formula of a Copper Oxide Reading assignment: Chang, Chemistry 10 th edition, pp. 55-58. Goals The reaction of hydrogen gas with a copper oxide compound will be studied quantitatively. By
The Empirical Formula of a Copper Oxide Reading assignment: Chang, Chemistry 10 th edition, pp. 55-58. Goals The reaction of hydrogen gas with a copper oxide compound will be studied quantitatively. By
Chapter 3. Chemical Reactions and Reaction Stoichiometry. Lecture Presentation. James F. Kirby Quinnipiac University Hamden, CT
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 3 Chemical Reactions and Reaction James F. Kirby Quinnipiac University Hamden, CT The study of the mass relationships in chemistry Based on the Law of Conservation of Mass
Lecture Presentation Chapter 3 Chemical Reactions and Reaction James F. Kirby Quinnipiac University Hamden, CT The study of the mass relationships in chemistry Based on the Law of Conservation of Mass
STANDARDIZATION OF A SODIUM HYDROXIDE SOLUTION EXPERIMENT 14
 STANDARDIZATION OF A SODIUM HYDROXIDE SOLUTION EXPERIMENT 14 OBJECTIVE The objective of this experiment will be the standardization of sodium hydroxide using potassium hydrogen phthalate by the titration
STANDARDIZATION OF A SODIUM HYDROXIDE SOLUTION EXPERIMENT 14 OBJECTIVE The objective of this experiment will be the standardization of sodium hydroxide using potassium hydrogen phthalate by the titration
Thermochemical equations allow stoichiometric calculations.
 CHEM 1105 THERMOCHEMISTRY 1. Change in Enthalpy ( H) Heat is evolved or absorbed in all chemical reactions. Exothermic reaction: heat evolved - heat flows from reaction mixture to surroundings; products
CHEM 1105 THERMOCHEMISTRY 1. Change in Enthalpy ( H) Heat is evolved or absorbed in all chemical reactions. Exothermic reaction: heat evolved - heat flows from reaction mixture to surroundings; products
Phys222 W11 Quiz 1: Chapters 19-21 Keys. Name:
 Name:. In order for two objects to have the same temperature, they must a. be in thermal equilibrium.
Name:. In order for two objects to have the same temperature, they must a. be in thermal equilibrium.
AP Chemistry 2005 Scoring Guidelines Form B
 AP Chemistry 2005 Scoring Guidelines Form B The College Board: Connecting Students to College Success The College Board is a not-for-profit membership association whose mission is to connect students to
AP Chemistry 2005 Scoring Guidelines Form B The College Board: Connecting Students to College Success The College Board is a not-for-profit membership association whose mission is to connect students to
COMBUSTION. In order to operate a heat engine we need a hot source together with a cold sink
 COMBUSTION In order to operate a heat engine we need a hot source together with a cold sink Occasionally these occur together in nature eg:- geothermal sites or solar powered engines, but usually the heat
COMBUSTION In order to operate a heat engine we need a hot source together with a cold sink Occasionally these occur together in nature eg:- geothermal sites or solar powered engines, but usually the heat
CSUS Department of Chemistry Experiment 8 Chem.1A
 EXPERIMENT #8 Name: PRE-LABORATORY ASSIGNMENT: Lab Section 1. The alkali metals are so reactive that they react directly with water in the absence of acid. For example, potassium reacts with water as follows:
EXPERIMENT #8 Name: PRE-LABORATORY ASSIGNMENT: Lab Section 1. The alkali metals are so reactive that they react directly with water in the absence of acid. For example, potassium reacts with water as follows:
EXPERIMENT 1 (Organic Chemistry I)
 EXPERIMENT 1 (Organic Chemistry I) Melting Point Determination Purpose a) Determine the purity of a substance using melting point as physical property b) Identify an unknown compound using its melting
EXPERIMENT 1 (Organic Chemistry I) Melting Point Determination Purpose a) Determine the purity of a substance using melting point as physical property b) Identify an unknown compound using its melting
CHEMICAL REACTIONS OF COPPER AND PERCENT YIELD KEY
 CHEMICAL REACTIONS OF COPPER AND PERCENT YIELD Objective To gain familiarity with basic laboratory procedures, some chemistry of a typical transition element, and the concept of percent yield. Apparatus
CHEMICAL REACTIONS OF COPPER AND PERCENT YIELD Objective To gain familiarity with basic laboratory procedures, some chemistry of a typical transition element, and the concept of percent yield. Apparatus
Chemistry 101 Generating Hydrogen Gas
 Chemistry 101 Generating Hydrogen Gas Objectives To experimentally verify the molar volume of hydrogen gas at STP To gain experience in collecting gas over water Discussion The molar volume of a gas is
Chemistry 101 Generating Hydrogen Gas Objectives To experimentally verify the molar volume of hydrogen gas at STP To gain experience in collecting gas over water Discussion The molar volume of a gas is
