Subject specific vocabulary
|
|
|
- Lewis Dorsey
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Subject specific vocabulary The following subject specific vocabulary provides definitions of key terms used in our GCSE Physical Education specification (8582). Students should be familiar with, and gain understanding of, these terms. Ability Inherited, stable traits that determine an individual s potential to learn or acquire a skill. Adaptability The potential to change with ease. Adrenaline Natural hormone released to speed heart rate up. Aerobic With oxygen. When exercise is not too fast and is steady, the heart can supply all the oxygen that the working muscles need. Summarised as: glucose + oxygen energy + carbon dioxide + water. Aerobic training zone The aerobic training zone allows the aerobic system to be trained. To define aerobic training zone: Aggression 1. Calculate maximum heart rate (220 bpm) minus age: 220-age 2. Work at 60-80% of maximum heart rate. A deliberate intent to harm or injure another person, which can be physical or mental (see direct and indirect aggression). Agility The ability to move and change direction quickly (at speed) whilst maintaining control.
2 Agonist (prime mover) Muscle or group responsible for the movement. Altitude A geographical area (of land) which is over 2,000 m above sea level. Altitude training (traditional) Training at altitude where there is less oxygen. The body adapts by making more red blood cells to carry oxygen. The additional oxygen carrying red blood cells is an advantage for endurance athletes returning to sea level to compete. Altitude sickness Nausea caused by training at altitude. Alveoli Air sacs in the lungs. Amateur This term defines someone who: takes part in an activity as a hobby, rather than for financial gain has another main job outside of sport takes part for fun could be at a lower level. Anabolic steroids Artificially produced male hormones mimicking testosterone. They promote muscle and bone growth, and reduce recovery time. Often used by power athletes, eg sprinters. Anaerobic Without oxygen. When exercise duration is short and at high intensity, the heart and lungs cannot supply blood and oxygen to muscles as fast as the respiring cells need them. Summarised as: glucose energy + lactic acid. Antagonist Acts to produce the opposite action to the agonist. They work in antagonistic pairs.
3 Arousal A physical and mental (physiological and psychological) state of alertness/readiness, varying from deep sleep to intense excitement/alertness. Articulating bones Where two or more bones meet to allow movement at a joint. Axis Imaginary line through the body around which it rotates. Types of axis: longitudinal (or vertical) head to toe transverse through the hips sagittal through the belly button. Backflow The flowing backwards of blood. Valves in the veins prevent this from happening. Balance The maintenance of the centre of mass over the base of support. Reference can be made to whilst static (still) or dynamic (whilst moving). Balanced diet It is defined as eating: the right amount (for energy expended) the right amount of calories according to how much you exercise different food types to provide suitable nutrients, vitamins and minerals. Beta blockers Drugs that are used to steady nerves by controlling heart rate. They have a calming and relaxing effect. (Blood) doping Defined by World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) as the misuse of techniques and/or substances to increase one's red blood cell count.
4 Blood pressure The pressure that blood is under. Types of pressure: systolic - when the heart is contracting diastolic - when the heart is relaxed. Body composition The percentage of body weight which is fat and non-fat (muscle and bone). Calorie A unit which measures heat or energy production in the body, normally expressed as Kcal. Carbohydrate The body's preferred energy source. Cardiac cycle The process of the heart going through the stages of systole and diastole (see Blood pressure) in the atria and ventricles (see Heart chambers). Cardiac output The amount of blood ejected from the heart in one minute or stroke volume x heart rate. Cardio-vascular endurance (aerobic power) The ability of the heart and lungs to supply oxygen to the working muscles. Circuit training A series of exercise stations whereby periods of work are interspersed with periods of rest. Closed season Post (transition). It is defined as: period of rest to recuperate players doing gentle aerobic exercise to maintain general fitness fully rested and ready for pre-season training.
5 Closed skill A skill which is not affected by the environment or performers within it. The skill tends to be done the same way each time. Commercialisation To manage or exploit (an organisation, activity, etc) in a way designed to make a profit. The specification refers to commercialised activity as being sponsorship and the media only. Coordination The ability to use different (two or more) parts of the body together, smoothly and efficiently. Competition season (peak) It is defined as: playing season taking part in matches every week maintenance of fitness related to the activity but not too much training as it may cause fatigue, which would decrease performance concentration on skills/set plays to improve team performance. Continuous training Involves working for a sustained period of time without rest. It improves cardiovascular fitness. Sometimes referred to as a steady state training. Contract to compete Unwritten agreement to follow and abide by the written and unwritten rules. Deep breathing Slow, deep breaths whilst relaxed. Dehydration Excessive loss of body water interrupting the function of the body. Hydration Having enough water to enable normal functioning of the body.
6 Rehydration Consuming water to restore hydration. Direct aggression Aggressive act which involves physical contact with others, eg a punch. Diuretic drugs Drugs that remove fluid from the body, elevating the rate of bodily urine excretion. Delayed onset of muscle soreness (DOMS) The pain felt in the muscles the day after exercise. Ectomorph A somatotype characterised by being tall and thin. Individuals with narrow shoulders and narrow hips. Embolism Blockage of a blood vessel. Endomorph A somatotype, characterised by a pear shaped body/fatness. Individuals with wide hips and narrow shoulders. Excess post-exercise oxygen consumption (EPOC) Sometimes referred to as oxygen debt (now an outdated term), EPOC refers to the amount of oxygen needed to recover after exercise. EPOC enables lactic acid to be converted to glucose, carbon dioxide and water (using oxygen). It explains why we continue to breathe deeply and quickly after exercise. Erythropoietin (EPO) A type of peptide hormone that increases the red blood cell count. Etiquette A convention or unwritten rule in an activity. It is not an enforceable rule but it is usually observed. Expire Breathe out.
7 Externally-paced skill The skill that is started because of an external factor. The speed, rate or pace of the skill is controlled by external factors, eg an opponent. Extrinsic feedback Received from outside of the performer, eg from a coach. See Kinaesthetic feedback for a comparison. Extrovert Sociable, active, talkative, out-going personality type usually associated with team sports players. Fartlek training Swedish for speed play. Periods of fast work with intermittent periods of slower work. Often used in running, ie sprint, jog, walk, jog, sprint, etc. Fatigue Either physical or mental, fatigue is a feeling of extreme or severe tiredness due to a build-up of lactic acid or working for long periods of time. Feedback Information a performer receives about their performance. Feedback can be given during and/or after performance. Fine movement (skill classification) Small and precise movement, showing high levels of accuracy and coordination. It involves the use of a small group of muscles. Fitness The ability to meet/cope with the demands of the environment. FITT FITT is used to increase the amount of work the body does, in order to achieve overload (see SPORT). FITT stands for: frequency how often you train intensity how hard you train time the length of the training session type the specific method, eg continuous training.
8 Flexibility The range of movements possible at a joint. Gamesmanship Attempting to gain an advantage by stretching the rules to their limit, eg time wasting. Goal setting (SMART goals) A method to increase motivation and reduce anxiety. Goals should be SMART: specific specific to the demands of the sport/muscles used/movements used measureable it must be possible to measure whether they have been met accepted they must be accepted by the performer and others involved, eg coach realistic they are actually possible to complete time bound over a set period of time. Goal types (performance goals and outcome goals) Performance goals Personal standards to be achieved. Performers compare themselves against what they have already done or suggest what they are going to do. There is no comparison with other performers. Outcome goals Focus on end result/winning. Gross movement (skill classification) Using large muscle groups to perform big, strong, powerful movements. Guidance A method to convey information to a performer. Guidance methods: visual (seeing) verbal (hearing) manual (assist movement physical) mechanical (use of objects/aids).
9 Haemoglobin The substance in the red blood cells which transports oxygen (as oxyhaemoglobin) and carbon dioxide. Health A state of complete physical, mental and social well-being, and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity (as per the World Health Organisation- WHO). Ill health refers to being in a state of poor physical, mental and/or social wellbeing. Heart attack It occurs when the flow of oxygen-rich blood to a section of heart muscle suddenly becomes blocked. Heart chambers They include the right and left atria and ventricles. Heart rate The number of times the heart beats (usually measured per minute). High intensity interval training (HITT) It s an exercise strategy alternating periods of short intense anaerobic exercise with less intense recovery periods (see Interval training). Hooliganism Disorderly, aggressive and often violent behaviour by spectators at sporting events. Home field advantage Gaining an advantage in a sporting event from being in familiar surroundings, with the majority of the spectators supporting you. Hypertension High blood pressure in the arteries. Hypertrophy The enlargement of an organ or tissue from the increase in the size of its cells.
10 Indirect aggression Aggression which does not involve physical contact. The aggression is taken out on an object to gain advantage, eg hitting a tennis ball hard during a rally. Information processing Making decisions. Gathering data from the display (senses), prioritising the most important stimuli to make a suitable decision. Inspire Breathe in. Interval training Periods of training/work that are followed by periods of rest, eg work, rest, work, rest (see High intensity interval training). Intrinsic feedback See Kinaesthetic feedback. Introvert A quiet, passive, reserved, shy personality type, usually associated with individual sports performance. Isometric contraction Muscle contraction where the length of the muscle does not alter. The contraction is constant, ie pushing against a load. Isotonic contraction Muscle contraction that results in limb movement: concentric contraction - shortening of the muscle eccentric contraction - lengthening of the muscle. Kinaesthetic feedback It's a type of intrinsic feedback, received via receptors in the muscles. Sensations that are felt by the performer, providing information from movement. Level playing field The same for all competitors.
11 Lever A rigid bar (bone) that turns about an axis to create movement. The force to move the lever comes from the muscle(s). Each lever contains: a fulcrum - fixed point, effort (from the muscle(s) to move it) load/resistance (from gravity). Lifestyle See sedentary lifestyle. Masculinity Displaying masculine (male) stereotypical behaviour. Maximal heart rate Calculated by: 220-age Mechanical advantage The efficiency of a working lever, calculated by: effort weight (resistance) arm Media Diversified technologies which act as the main means of mass communication. These include: printed media (eg newspapers) broadcast media (eg TV and radio) internet/social media (eg Facebook) outdoor media (eg billboards). Mental health and well-being A state of well-being in which every individual realises his/her own potential, can cope with the normal stresses of life, can work productively and fruitfully, and is able to make a contribution to her or his community (as per WHO). It works in conjunction with physical and social health. Mental rehearsal/visualisation/imagery Cognitive relaxation techniques involving control of mental thoughts and imagining positive outcomes.
12 Mesomorph A somatotype, characterised by a muscular appearance. Individuals with wide shoulders and narrow hips. Minerals Inorganic substances which assist the body with many of its functions, eg bone formation (Calcium). Motivation (intrinsic motivation and extrinsic motivation) The drive to succeed or the desire (want) to achieve something/to be inspired to do something. This can be: or intrinsic the drive that comes from within (eg for pride, satisfaction, a sense of accomplishment, self-worth) extrinsic the drive to perform well or to win in order to gain external rewards (eg prizes, money, praise). Movement at a joint Classified into: flexion decrease in the angle of the bones at a joint extension increasing the angle of bones at a joint abduction movement away from the midline of the body adduction movement towards the midline of the body rotation movement around an axis plantar flexion pointing the toes at the ankle/increasing the ankle angle dorsi flexion toes up at the ankle/decreasing the ankle angle. Muscular endurance (similar to dynamic strength) Ability of a muscle or muscle group to undergo repeated contractions, avoiding fatigue. Narcotic analgesics Drugs that can be used to reduce the feeling of pain.
13 Nutrition The intake of food, considered in relation to the body s dietary needs. Good nutrition is an adequate, well balanced diet, combined with regular physical activity. Obese A term used to describe people with a large fat content, caused by an imbalance of calories consumed to energy expenditure. A body mass index (BMI) of over 30 or over 20% above standard weight for height ratio. One rep max The maximal amount that can be lifted in one repetition by a muscle/group of muscles (with the correct technique). Open skill A skill which is performed in a certain way to deal with a changing or unstable environment, eg to outwit an opponent. Peptide hormones Drugs that stimulate the production of naturally occurring hormones (eg EPO), which increase red blood cell count/oxygen carrying capacity. Physical health and well-being All body systems working well, free from illness and injury. Ability to carry out everyday tasks. It works in conjunction with social and mental health. Physiology Study of how our cells, muscles and organs work together, and how they interact. Plane Imaginary lines depicting the direction of movement. Types of planes: sagittal - forwards and backwards frontal - left or right transverse - rotation around the longitudinal axis. Positive self-talk Developing cognitive positive thoughts about your own performance.
14 Post season (transition) Period of rest/active recovery/light aerobic work after the competition period (season). Power/explosive strength (anaerobic power) The product of strength and speed, ie strength x speed. Pre-season (preparation) It is defined as: period leading up to competition usually using continuous/fartlek/interval training sessions to increase aerobic fitness weight training to build up strength and muscular endurance developing techniques specific to the sport in order to be fully prepared for matches at start of season and therefore be more successful. Principles of overload Frequency, intensity, time and type (see FITT). Principles of training Specificity, progressive overload, reversibility and tedium (see SPORT). Prime mover (agonist) Muscle or muscle group responsible for the movement. Pulse raiser Any activity that raises heart rate. Usually as part of a warm up, eg light jog. Qualitative More of a subjective than an objective appraisal. Involving opinions relating to the quality of a performance rather than the quantity (eg score, placing, number). Quantitative A measurement which can be quantified as a number, eg time in seconds or goals scored. There is no opinion expressed (qualitative). It is a fact.
15 Reaction time The time taken to initiate a response to a stimulus, ie the time from the initiation of the stimulus (eg starting gun in 100 m) to starting to initiate a response (eg starting to move out of the blocks in 100 m). Recovery Time required to repair the damage to the body caused by training or competition. Reliability Relating to the consistency and repeatability of a test (ie to produce same or similar scores). Repetitions The number of times an individual action is performed. A set is a group of repetitions. Residual volume Volume of air left in the lungs after maximal expiration. Role model A person looked to by others as an example to be imitated. Season A period of time during which competition takes place or training seasons, dividing the year up into sectional parts for pre-determined benefits. Training seasons include: pre-season (preparation) competition season (peak) post-season (transition). See these terms for definitions. Sedentary lifestyle A lifestyle with irregular or no physical activity. Self-paced skill The skill is started when the performer decides to start it. The speed, rate or pace of the skill is controlled by the performer.
16 Skeletal system Skeletal system provides a framework of bones for movement, in conjunction with the muscular system. Skill A learned action/learned behaviour with the intention of bringing about predetermined results, with maximum certainty and minimum outlay of time and energy. Skill classification Categorisation of sporting skills in accordance with set continua. These include: simple/complex continua open/closed continua self-paced/externally-paced continua gross/fine continua. Social health and well-being Basic human needs are being met (food, shelter and clothing). The individual has friendship and support, some value in society, is socially active and has little stress in social circumstances. It works in conjunction with physical and mental health. Somatotype A method of classifying body type. Body types: ectomorph endomorph mesomorph See these terms for definitions of individual somatotypes. Speed The maximum rate at which an individual is able to perform a movement or cover a distance in a period of time, putting the body parts into action as quickly as possible. Calculated by: distance time
17 Spirometer trace A measure of lung volumes, which includes: tidal volume volume of air inspired or expired/exchanged per breath inspiratory reserve volume the amount of air that could be breathed in after tidal volume expiratory reserve volume the amount of air that could be breathed out after tidal volume residual volume the amount of air left in the lungs after maximal expiration. Sponsor An individual or group that provides financial support to an event, activity, person, or organisation. SPORT (the principles of training) Specificity Making training specific to the sport being played/movements used/muscles used/energy system(s) used. Progressive overload Gradual increase of the amount of overload so that fitness gains occur, but without potential for injury. Overload is the gradual increase of stress placed upon the body during exercise training (more than normal). Reversibility Losing fitness levels when you stop exercising. Tedium Boredom that can occur from training the same way every time. Variety is needed. Sponsorship Provision of funds or other forms of support to an individual or event in return for some commercial return. Sportsmanship Conforming to the rules, spirit and etiquette of a sport.
18 Static stretching Holding a stretch still/held/isometric. Stimulants Drugs that have an effect on the central nervous system, ie they increase mental and/or physical alertness. Strength The ability to overcome a resistance. This can be explosive, static or dynamic: explosive see Power static static ability to hold a body part (limb) in a static position. Muscle length stays the same/maximum force that can be applied to an immoveable object dynamic see Muscular endurance for similarity. Stroke volume The volume of blood pumped out of the heart by each ventricle during one contraction. Sub-maximal Working below maximal intensity level. Suppleness As with flexibility, the range of movement possible at a joint. Synovial joint An area of the body where two or more bones meet (articulate) to allow a range of movements. The ends of the bones are covered in articular cartilage and are enclosed in a capsule filled with fluid. For the purposes of this specification, the following structural features and roles should be known: synovial membrane secretes synovial fluid synovial fluid provides lubrication joint capsule encloses/supports bursae (sacks of fluid) reduce friction cartilage prevents friction/bones rubbing together ligaments attach bone to bone.
19 Tangible Something that can be seen and touched, eg a trophy. Target zone The range within which athletes need to work for aerobic training to take place (60-80% of maximum heart rate). Training A well-planned programme which uses scientific principles to improve performance, skill, game ability, motor and physical fitness. Training thresholds The actual boundaries of the target zone. Validity The extent to which a test or method measures what it sets out to measure. Viscosity Thickening of the blood. Vitamins Organic substances that are required for many essential processes in the body, eg Vitamin A for structure and function of the skin. Weight training The use of weights/resistance to cause adaptation of the muscles. Well-being Involves physical, mental and social well-being. The dynamic process that gives people a sense of being comfortable, healthy or happy.
GCSE PE REVISION QUESTIONS 2011
 GCSE PE REVISION QUESTIONS 2011 Tick off list of revision topics Section 1 Reasons for taking part physical, social, mental Influences people, image, cultural, resources, health and well-being, socio-economic
GCSE PE REVISION QUESTIONS 2011 Tick off list of revision topics Section 1 Reasons for taking part physical, social, mental Influences people, image, cultural, resources, health and well-being, socio-economic
GCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION PE2 UNIT GUIDE. Content Title: Methods of training. Practical Application/Explanation. Fartlek training. Continuous training
 Content Title: Methods of training Key points GCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION Different methods of training How to design specific training sessions How to design a training programme PE2 UNIT GUIDE Practical Application/Explanation
Content Title: Methods of training Key points GCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION Different methods of training How to design specific training sessions How to design a training programme PE2 UNIT GUIDE Practical Application/Explanation
General Certificate of Secondary Education (Short Course) June 2011. Unit 1: Knowledge and Understanding for the Active Participant (Short Course)
 Version 1 General Certificate of Secondary Education (Short Course) June 2011 Physical Education 48901 (Specification 4891) Unit 1: Knowledge and Understanding for the Active Participant (Short Course)
Version 1 General Certificate of Secondary Education (Short Course) June 2011 Physical Education 48901 (Specification 4891) Unit 1: Knowledge and Understanding for the Active Participant (Short Course)
SAMPLE ASSESSMENT TASKS PHYSICAL EDUCATION STUDIES GENERAL YEAR 11
 SAMPLE ASSESSMENT TASKS PHYSICAL EDUCATION STUDIES GENERAL YEAR 11 Copyright School Curriculum and Standards Authority, 2014 This document apart from any third party copyright material contained in it
SAMPLE ASSESSMENT TASKS PHYSICAL EDUCATION STUDIES GENERAL YEAR 11 Copyright School Curriculum and Standards Authority, 2014 This document apart from any third party copyright material contained in it
9 TH GRADE KINETIC WELLNESS
 Teacher: Mr. Hartung 9 TH GRADE KINETIC WELLNESS Introduction to 9 th Grade Physical Education Introduction/Overview Chapter 1 10 reasons to get and stay in shape - Key terms you should be able to define
Teacher: Mr. Hartung 9 TH GRADE KINETIC WELLNESS Introduction to 9 th Grade Physical Education Introduction/Overview Chapter 1 10 reasons to get and stay in shape - Key terms you should be able to define
CURRICULUM OVERVIEW. Please contact your child s subject teacher or Head of Department for answers to subject related questions
 CURRICULUM OVERVIEW Please contact your child s subject teacher or Head of Department for answers to subject related questions SUBJECT SHORT COURSE GCSE PE YEAR GROUP Y9 &10 This course is for students
CURRICULUM OVERVIEW Please contact your child s subject teacher or Head of Department for answers to subject related questions SUBJECT SHORT COURSE GCSE PE YEAR GROUP Y9 &10 This course is for students
GCSE PHYSICAL EDUCATION
 GCSE PHYSICAL EDUCATION 48901: Knowledge and Understanding for the Active Participant (Short Course) Mark scheme June 2014 Version: 1.0 Final Mark schemes are prepared by the Lead Assessment Writer and
GCSE PHYSICAL EDUCATION 48901: Knowledge and Understanding for the Active Participant (Short Course) Mark scheme June 2014 Version: 1.0 Final Mark schemes are prepared by the Lead Assessment Writer and
A1 Reasons for taking part in activity. A2 Health, fitness, exercise and performance
 Centre No. Paper Reference (complete below) Candidate No. / Surname Signature Initials Paper Reference 1827/01 Edexcel GCSE Physical Education End Of Unit Test SECTION 1: FITNESS A1 Reasons for taking
Centre No. Paper Reference (complete below) Candidate No. / Surname Signature Initials Paper Reference 1827/01 Edexcel GCSE Physical Education End Of Unit Test SECTION 1: FITNESS A1 Reasons for taking
Final. Mark Scheme. Physical Education. (Specification 4890)
 Version 1 General Certificate of Secondary Education June 2012 Physical Education 48903 (Specification 4890) Unit 3: Knowledge and Understanding for the Active Participant (Full Course and Double Award)
Version 1 General Certificate of Secondary Education June 2012 Physical Education 48903 (Specification 4890) Unit 3: Knowledge and Understanding for the Active Participant (Full Course and Double Award)
Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology
 Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology These questions have been compiled based on the information available for the above qualification and unit. This mock should be
Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology These questions have been compiled based on the information available for the above qualification and unit. This mock should be
What is Physical Fitness?
 What is Physical Fitness? Physical fitness is made up of two components: Skill-related fitness and Health related fitness. Skill related fitness items are factors, which relate to the possibility of you
What is Physical Fitness? Physical fitness is made up of two components: Skill-related fitness and Health related fitness. Skill related fitness items are factors, which relate to the possibility of you
5TH GRADE FITNESS STUDY GUIDE
 PHYSICAL EDUCATION 5 TH GRADE FITNESS STUDY GUIDE PART I. Revised 5-13 DIRECTIONS: Review the following terms and concepts. Do not try to memorize the definitions, rather think about and understand: 1)
PHYSICAL EDUCATION 5 TH GRADE FITNESS STUDY GUIDE PART I. Revised 5-13 DIRECTIONS: Review the following terms and concepts. Do not try to memorize the definitions, rather think about and understand: 1)
Strength and Conditioning Program
 Strength and Conditioning Program Guidelines All speed work must be performed when the body is fully rested. Proper sprinting techniques must be taught and mastered by the player. Adequate rest must follow
Strength and Conditioning Program Guidelines All speed work must be performed when the body is fully rested. Proper sprinting techniques must be taught and mastered by the player. Adequate rest must follow
THE BADMINTON ASSOCIATION OF ENGLAND MISSION STATEMENT
 THE BADMINTON ASSOCIATION OF ENGLAND MISSION STATEMENT Badminton is an Olympic Sport It is played by groups, families and individuals of all ages and it provides a healthy, lifelong sport activity that
THE BADMINTON ASSOCIATION OF ENGLAND MISSION STATEMENT Badminton is an Olympic Sport It is played by groups, families and individuals of all ages and it provides a healthy, lifelong sport activity that
Final. Mark Scheme. Physical Education. (Specification 4891) Unit 1: Knowledge and Understanding for the Active Participant (Short Course)
 Version 2 General Certificate of Secondary Education (Short Course) June 203 Physical Education 4890 (Specification 489) Unit : Knowledge and Understanding for the Active Participant (Short Course) Final
Version 2 General Certificate of Secondary Education (Short Course) June 203 Physical Education 4890 (Specification 489) Unit : Knowledge and Understanding for the Active Participant (Short Course) Final
This very important area is often the least understood or completely ignored by some coaches when designing a fitness program for their athletes.
 This very important area is often the least understood or completely ignored by some coaches when designing a fitness program for their athletes. An understanding of the various energy systems of our body
This very important area is often the least understood or completely ignored by some coaches when designing a fitness program for their athletes. An understanding of the various energy systems of our body
Functions of Blood System. Blood Cells
 Functions of Blood System Transport: to and from tissue cells Nutrients to cells: amino acids, glucose, vitamins, minerals, lipids (as lipoproteins). Oxygen: by red blood corpuscles (oxyhaemoglobin - 4
Functions of Blood System Transport: to and from tissue cells Nutrients to cells: amino acids, glucose, vitamins, minerals, lipids (as lipoproteins). Oxygen: by red blood corpuscles (oxyhaemoglobin - 4
GCSE PHYSICAL EDUCATION PAPER 2
 GCSE PHYSICAL EDUCATION PAPER 2 SOCIO-CULTURAL INFLUENCES AND WELL-BEING IN PHYSICAL ACTIVITY AND SPORT Mark scheme Specimen Material V1.0 aqa.org.uk Copyright 2016 AQA and its licensors. All rights reserved.
GCSE PHYSICAL EDUCATION PAPER 2 SOCIO-CULTURAL INFLUENCES AND WELL-BEING IN PHYSICAL ACTIVITY AND SPORT Mark scheme Specimen Material V1.0 aqa.org.uk Copyright 2016 AQA and its licensors. All rights reserved.
MUSCLES G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION. Unit 1. Factors Affecting Participation and Performance. G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:.
 G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1 Factors Affecting Participation and Performance MUSCLES Name: G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:. By the end of this booklet you should: Be able to describe and explain how muscles
G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1 Factors Affecting Participation and Performance MUSCLES Name: G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:. By the end of this booklet you should: Be able to describe and explain how muscles
USCGA Health and Physical Education Fitness Preparation Guidelines
 USCGA Health and Physical Education Fitness Preparation Guidelines MUSCULAR STRENGTH Muscular strength and endurance can be improved by systematically increasing the load (resistance) that you are using.
USCGA Health and Physical Education Fitness Preparation Guidelines MUSCULAR STRENGTH Muscular strength and endurance can be improved by systematically increasing the load (resistance) that you are using.
IFA Senior Fitness Certification Test Answer Form
 IFA Senior Fitness Certification Test Answer Form In order to receive your certification card, take the following test and mail this single page answer sheet in with your check or money order in US funds.
IFA Senior Fitness Certification Test Answer Form In order to receive your certification card, take the following test and mail this single page answer sheet in with your check or money order in US funds.
GCSE P.E. REVISION BOOKLET
 GCSE P.E. Short Course REVISION BOOKLET Name: How many mice, like the one above, can you find in this revision booklet?! 2 GCSE PE Revision! Dear Student, Here are a few ideas to help you to revise in
GCSE P.E. Short Course REVISION BOOKLET Name: How many mice, like the one above, can you find in this revision booklet?! 2 GCSE PE Revision! Dear Student, Here are a few ideas to help you to revise in
1.1.1 To include: Body language - facial expressions, gestures, eye contact and posture
 Unit 415 Delivering Personal Training Sessions Recommended Guided Learning Hours: 58 Credit value 9 QCF Unit Number J/600/9053 1. Understand how to instruct exercise during personal training sessions 1.1
Unit 415 Delivering Personal Training Sessions Recommended Guided Learning Hours: 58 Credit value 9 QCF Unit Number J/600/9053 1. Understand how to instruct exercise during personal training sessions 1.1
Module F SKELETAL SYSTEM & ARTICULATIONS
 Module F SKELETAL SYSTEM & ARTICULATIONS Topic from General functions of bone & the skeletal system Structural components microscopic anatomy Structural components gross anatomy Physiology of embryonic
Module F SKELETAL SYSTEM & ARTICULATIONS Topic from General functions of bone & the skeletal system Structural components microscopic anatomy Structural components gross anatomy Physiology of embryonic
Circulatory System Review
 Circulatory System Review 1. Draw a table to describe the similarities and differences between arteries and veins? Anatomy Direction of blood flow: Oxygen concentration: Arteries Thick, elastic smooth
Circulatory System Review 1. Draw a table to describe the similarities and differences between arteries and veins? Anatomy Direction of blood flow: Oxygen concentration: Arteries Thick, elastic smooth
Endocrine System: Practice Questions #1
 Endocrine System: Practice Questions #1 1. Removing part of gland D would most likely result in A. a decrease in the secretions of other glands B. a decrease in the blood calcium level C. an increase in
Endocrine System: Practice Questions #1 1. Removing part of gland D would most likely result in A. a decrease in the secretions of other glands B. a decrease in the blood calcium level C. an increase in
Tymikia S. Glenn, BS ACSM CPT Fitness and Membership Director Milan Family YMCA
 Tymikia S. Glenn, BS ACSM CPT Fitness and Membership Director Milan Family YMCA Benefits of Starting an Exercise Program 1. Helps build and maintain healthy bones, muscles and joints 2. Reduces feelings
Tymikia S. Glenn, BS ACSM CPT Fitness and Membership Director Milan Family YMCA Benefits of Starting an Exercise Program 1. Helps build and maintain healthy bones, muscles and joints 2. Reduces feelings
Fitness Training A Sensible Guide to Preparing for Selection in the Gurkhas
 Fitness Training A Sensible Guide to Preparing for Selection in the Gurkhas Background Physical fitness has a number of components: aerobic endurance (stamina), strength, speed, flexibility, muscle endurance,
Fitness Training A Sensible Guide to Preparing for Selection in the Gurkhas Background Physical fitness has a number of components: aerobic endurance (stamina), strength, speed, flexibility, muscle endurance,
How To Train For Flexibility
 FLEXIBILITY It has been proven that participating in a flexibility program will have numerous benefits. A flexibility-training program is a planned and deliberate program of specific stretching exercises
FLEXIBILITY It has been proven that participating in a flexibility program will have numerous benefits. A flexibility-training program is a planned and deliberate program of specific stretching exercises
Chapter 4 Exercise Metabolism and Bioenergetics:
 CPT Study Guide, Version 4 On the actual exam, you will be tested in the following subject areas (exam breakdown): Basic and Applied Sciences Assessment Exercise Technique and Training Instruction Program
CPT Study Guide, Version 4 On the actual exam, you will be tested in the following subject areas (exam breakdown): Basic and Applied Sciences Assessment Exercise Technique and Training Instruction Program
CPT. Content Outline and Domain Weightings
 Appendix J CPT Content Outline and Domain Weightings National Academy of Sports Medicine (NASM) Page 147 National Academy of Sports Medicine - Certified Personal Trainer (CPT) Content Outline Domain I:
Appendix J CPT Content Outline and Domain Weightings National Academy of Sports Medicine (NASM) Page 147 National Academy of Sports Medicine - Certified Personal Trainer (CPT) Content Outline Domain I:
Flyball Dogs and Injury Prevention Conditioning, warm-up and cool-down
 Flyball Dogs and Injury Prevention Conditioning, warm-up and cool-down Carol J. Helfer, D.V.M. Canine Peak Performance www.caninepeakperformance.com Most injuries seen in flyball and agility dogs are repetitive
Flyball Dogs and Injury Prevention Conditioning, warm-up and cool-down Carol J. Helfer, D.V.M. Canine Peak Performance www.caninepeakperformance.com Most injuries seen in flyball and agility dogs are repetitive
Heart Monitor Training for the Compleat Idiot By John L. Parker, Jr.
 Estimating Your Max Heart Rate There are a number of ways to estimate your maximum heart rate. The best way is to get on a treadmill and slowly increase the speed or the incline until your heart rate is
Estimating Your Max Heart Rate There are a number of ways to estimate your maximum heart rate. The best way is to get on a treadmill and slowly increase the speed or the incline until your heart rate is
The type of cancer Your specific treatment Your pre training levels before diagnose (your current strength and fitness levels)
 Exercise and Breast Cancer: Things you can do! Cancer within the fire service is one of the most dangerous threats to our firefighter s health & wellness. According to the latest studies firefighters are
Exercise and Breast Cancer: Things you can do! Cancer within the fire service is one of the most dangerous threats to our firefighter s health & wellness. According to the latest studies firefighters are
Standard Grade. Swimming. Name. Teacher. Class. P.E. Department Crieff High School. Miss Steele Jan 10 1
 Standard Grade Swimming Name Teacher Class P.E. Department Crieff High School Miss Steele Jan 10 1 Contents Tens Workbook Reference Swimming Section p87-92 and p127-128. Background Information Page 3 Stroke
Standard Grade Swimming Name Teacher Class P.E. Department Crieff High School Miss Steele Jan 10 1 Contents Tens Workbook Reference Swimming Section p87-92 and p127-128. Background Information Page 3 Stroke
Archery: Coaching Young Athletes. Developing Fundamental Movement Skills
 Archery: Coaching Young Athletes Developing Fundamental Movement Skills Make a long term commitment Long Term Athlete Development Long Term Athlete Development (LTAD) is a strategy for helping youngsters
Archery: Coaching Young Athletes Developing Fundamental Movement Skills Make a long term commitment Long Term Athlete Development Long Term Athlete Development (LTAD) is a strategy for helping youngsters
Performance Enhancing Substances in Sport
 Performance Enhancing Substances in Sport Program Support Notes by: Jo Basnett Bachelor Education (Human Movement and Health) Produced by: VEA Pty Ltd Commissioning Editor: Sandra Frerichs B.Ed, M.Ed.
Performance Enhancing Substances in Sport Program Support Notes by: Jo Basnett Bachelor Education (Human Movement and Health) Produced by: VEA Pty Ltd Commissioning Editor: Sandra Frerichs B.Ed, M.Ed.
Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors
 Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors Risk factors are traits and life-style habits that increase a person's chances of having coronary artery and vascular disease. Some risk factors cannot be changed or
Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors Risk factors are traits and life-style habits that increase a person's chances of having coronary artery and vascular disease. Some risk factors cannot be changed or
What Are the Health Benefits Associated with Strength Training?
 Strength Training Program Necessary Basic information to obtain results. -- Most of the information contained in this handout is based on information gathered, researched, and presented by the National
Strength Training Program Necessary Basic information to obtain results. -- Most of the information contained in this handout is based on information gathered, researched, and presented by the National
Patient Information. and Physical Activity Diary. Wythenshawe Hospital Cardiac Rehabilitation. Name:... The ticker club Registered Charity No.
 Wythenshawe Hospital Cardiac Rehabilitation Patient Information Remember : Lifelong regular physical activity - 0 minutes, five times per week is important for your general health. I feel so much better
Wythenshawe Hospital Cardiac Rehabilitation Patient Information Remember : Lifelong regular physical activity - 0 minutes, five times per week is important for your general health. I feel so much better
Animal Systems: The Musculoskeletal System
 Animal Systems: The Musculoskeletal System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Animal Systems: The Musculoskeletal System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Anaerobic and Aerobic Training Adaptations. Chapters 5 & 6
 Anaerobic and Aerobic Training Adaptations Chapters 5 & 6 Adaptations to Training Chronic exercise provides stimulus for the systems of the body to change Systems will adapt according to level, intensity,
Anaerobic and Aerobic Training Adaptations Chapters 5 & 6 Adaptations to Training Chronic exercise provides stimulus for the systems of the body to change Systems will adapt according to level, intensity,
Chapter 4. Vocabulary. Name Class Date
 Chapter 4 Vocabulary physical activity anaerobic exercise anabolic steroids physical fitness overload health screening sedentary lifestyle progression overexertion osteoporosis specificity heat cramps
Chapter 4 Vocabulary physical activity anaerobic exercise anabolic steroids physical fitness overload health screening sedentary lifestyle progression overexertion osteoporosis specificity heat cramps
Strength Training For Runners
 Strength Training For Runners Be the strongest, fastest athlete you can be Agenda Why to strength train and the benefits Myths about runners and strength training What to do How often Example program About
Strength Training For Runners Be the strongest, fastest athlete you can be Agenda Why to strength train and the benefits Myths about runners and strength training What to do How often Example program About
ABOUT US. Why train using the ACTIV8 Program? - Restoration of movement. Performance Enhancement & Injury Prevention
 ABOUT US Mission Statement - ACTIV8 Strength and Conditioning Program is committed to providing training experience for each participant. Our focus is on building a strong and functionally fit human being
ABOUT US Mission Statement - ACTIV8 Strength and Conditioning Program is committed to providing training experience for each participant. Our focus is on building a strong and functionally fit human being
Muscle Fibres. Anatomy and Physiology Advanced Diploma Course Sample Pages Page 1
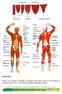 Muscle Fibres Muscles are composed of thousands of individual muscle fibres, which are held together by connective tissue. However, muscle fibres may differ in physiological makeup. Anatomy and Physiology
Muscle Fibres Muscles are composed of thousands of individual muscle fibres, which are held together by connective tissue. However, muscle fibres may differ in physiological makeup. Anatomy and Physiology
Anatomy and Physiology for Exercise and Health Level 3
 Anatomy and Physiology for Exercise and Health Level 3 A/600/9051 Mock Paper There are 25 questions within this paper To achieve a pass you will need to score 18 out of 25 marks All questions are multiple
Anatomy and Physiology for Exercise and Health Level 3 A/600/9051 Mock Paper There are 25 questions within this paper To achieve a pass you will need to score 18 out of 25 marks All questions are multiple
Interval Training. Interval Training
 Interval Training Interval Training More work can be performed at higher exercise intensities with same or less fatigue than in continuous training Fitness Weight Loss Competition Baechle and Earle, Essentials
Interval Training Interval Training More work can be performed at higher exercise intensities with same or less fatigue than in continuous training Fitness Weight Loss Competition Baechle and Earle, Essentials
Biomechanics, Psychology and Physical Training Instructions and answers for teachers These instructions should accompany the OCR resource
 Biomechanics, Psychology and Physical Training Instructions and answers for teachers These instructions should accompany the OCR resource Biomechanics, Psychology and Physical Training activity which supports
Biomechanics, Psychology and Physical Training Instructions and answers for teachers These instructions should accompany the OCR resource Biomechanics, Psychology and Physical Training activity which supports
Caring for the Client with Heart Failure
 Peak Development Resources, LLC P.O. Box 13267 Richmond, VA 23225 Phone: (804) 233-3707 Fax: (804) 233-3705 After reading the newsletter, the home health aide should be able to: 1. Define heart failure.
Peak Development Resources, LLC P.O. Box 13267 Richmond, VA 23225 Phone: (804) 233-3707 Fax: (804) 233-3705 After reading the newsletter, the home health aide should be able to: 1. Define heart failure.
Fit for Flight. Developing a Personal Fitness Program
 Fit for Flight Developing a Personal Fitness Program The purpose of this brochure is to provide you with basic guidelines for developing a balanced physical fitness program and customizing a workout to
Fit for Flight Developing a Personal Fitness Program The purpose of this brochure is to provide you with basic guidelines for developing a balanced physical fitness program and customizing a workout to
COACHING GUIDE. Preparing Athletes for Competition
 COACHING GUIDE Preparing Athletes for Competition Table of Contents Table of Contents Psychological Considerations Anxiety and Stress Management Winning and Losing Handling Grief Taking Athletes to Competition
COACHING GUIDE Preparing Athletes for Competition Table of Contents Table of Contents Psychological Considerations Anxiety and Stress Management Winning and Losing Handling Grief Taking Athletes to Competition
Low Blood Pressure. This reference summary explains low blood pressure and how it can be prevented and controlled.
 Low Blood Pressure Introduction Low blood pressure, or hypotension, is when your blood pressure reading is 90/60 or lower. Some people have low blood pressure all of the time. In other people, blood pressure
Low Blood Pressure Introduction Low blood pressure, or hypotension, is when your blood pressure reading is 90/60 or lower. Some people have low blood pressure all of the time. In other people, blood pressure
Exercise Prescription Case Studies
 14 Exercise Prescription Case Studies 14 14 Exercise Prescription Case Studies Case 1 Risk Stratification CY CHAN is a 43-year-old man with known history of hypertension on medication under good control.
14 Exercise Prescription Case Studies 14 14 Exercise Prescription Case Studies Case 1 Risk Stratification CY CHAN is a 43-year-old man with known history of hypertension on medication under good control.
Chapter 16: Circulation
 Section 1 (The Body s Transport System) Chapter 16: Circulation 7 th Grade Cardiovascular system (the circulatory system) includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood carries needed substances to the cells
Section 1 (The Body s Transport System) Chapter 16: Circulation 7 th Grade Cardiovascular system (the circulatory system) includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood carries needed substances to the cells
This chapter presents
 Chapter 8 Aerobic Fitness Programs T This chapter presents programs for three levels of aerobic fitness: a starter program for low fit or previously sedentary individuals (fitness under 35 ml/kg min);
Chapter 8 Aerobic Fitness Programs T This chapter presents programs for three levels of aerobic fitness: a starter program for low fit or previously sedentary individuals (fitness under 35 ml/kg min);
Faculty of Physical Education University of Pune, Pune- 411043. Proposal. Diploma for Gym Instructor
 Faculty of Physical Education University of Pune, Pune- 411043 Proposal Diploma for Gym Instructor Diploma for Gym Instructor 1. General Objectives of the Course: 1. To enable student to become competent
Faculty of Physical Education University of Pune, Pune- 411043 Proposal Diploma for Gym Instructor Diploma for Gym Instructor 1. General Objectives of the Course: 1. To enable student to become competent
Final. Mark Scheme. Physical Education. (Specification 4890)
 Version 2 General Certificate of Secondary Education June 2013 Physical Education 48903 (Specification 4890) Unit 3: Knowledge and Understanding for the Active Participant (Full Course and Double Award)
Version 2 General Certificate of Secondary Education June 2013 Physical Education 48903 (Specification 4890) Unit 3: Knowledge and Understanding for the Active Participant (Full Course and Double Award)
LEVEL II DEVELOPING FITNESS PHYSIOLOGY. January 2008 Page 1
 DEVELOPING FITNESS January 2008 Page 1 DEVELOPING FITNESS There are many reasons why young hockey players should develop high levels of fitness; they will be less prone to injury; they will recover faster
DEVELOPING FITNESS January 2008 Page 1 DEVELOPING FITNESS There are many reasons why young hockey players should develop high levels of fitness; they will be less prone to injury; they will recover faster
2014-2015 Curriculum Blueprint Grade: 6/7 Course: M/J Comprehensive P.E. 6 th and 7 th Grade Unit 1: Safety and Fitness
 Unit 1: Safety and Fitness 15 days 1 Heat exhaustion, heat stroke, dehydration, frostbite, warm up, cool down, aerobic, anaerobic, resting heart rate, target heart rate, cardiovascular fitness, strength,
Unit 1: Safety and Fitness 15 days 1 Heat exhaustion, heat stroke, dehydration, frostbite, warm up, cool down, aerobic, anaerobic, resting heart rate, target heart rate, cardiovascular fitness, strength,
Basic Principles of Strength Training and Conditioning
 Basic Principles of Strength Training and Conditioning John M. Cissik, MS, CSCS Whether you are a recreational weight trainer, a weekend athlete, or a strength coach working with elite athletes, it is
Basic Principles of Strength Training and Conditioning John M. Cissik, MS, CSCS Whether you are a recreational weight trainer, a weekend athlete, or a strength coach working with elite athletes, it is
12-week Half Marathon Training Program By Ben Wisbey
 12-week Half Marathon Training Program By Ben Wisbey Introduction The half marathon is often the intermediate goal for those runners looking at doing their first marathon. It is also the longest distance
12-week Half Marathon Training Program By Ben Wisbey Introduction The half marathon is often the intermediate goal for those runners looking at doing their first marathon. It is also the longest distance
JAPANESE KINESIOLOGY COURSE DESCRIPTION. WEST LOS ANGELES COLLEGE 2014 2016 CATALOG (revised Fall 2015) 209. (Replaces Physical Education )
 JAPANESE 1 Elementary Japanese I (5) This course provides the fundamentals of the Japanese language with emphasis on the spoken word. The Japanese syllabary for Hiragana, Katakana and basic Kanji are introduced.
JAPANESE 1 Elementary Japanese I (5) This course provides the fundamentals of the Japanese language with emphasis on the spoken word. The Japanese syllabary for Hiragana, Katakana and basic Kanji are introduced.
Exchange solutes and water with cells of the body
 Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
Sports Injury Treatment
 Sports Injury Treatment Participating in a variety of sports is fun and healthy for children and adults. However, it's critical that before you participate in any sport, you are aware of the precautions
Sports Injury Treatment Participating in a variety of sports is fun and healthy for children and adults. However, it's critical that before you participate in any sport, you are aware of the precautions
IMGPT: Exercise After a Heart Attack 610 944 8140 805 N. RICHMOND ST (Located next to Fleetwood HS) Why is exercise important following a heart
 Why is exercise important following a heart attack? Slow progression back into daily activity is important to strengthen the heart muscle and return blood flow to normal. By adding aerobic exercises, your
Why is exercise important following a heart attack? Slow progression back into daily activity is important to strengthen the heart muscle and return blood flow to normal. By adding aerobic exercises, your
MOCK PAPER Level 3 Anatomy and Physiology For Exercise and Health. Unit Accreditation Number A/600/9051
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number APEH 3.01 Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title Time allocation 60 minutes MOCK PAPER Level 3 Anatomy
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number APEH 3.01 Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title Time allocation 60 minutes MOCK PAPER Level 3 Anatomy
Calories. 23 calories from fat + 48 calories from carbohydrates + 32 calories from protein = 103 Calories in 1 cup of 1% milk
 Calories What's the magical formula to achieve your weight goals? Calorie needs are based on individual needs. In order for your weight to stay the same, the energy (or Calories) you consume must equal
Calories What's the magical formula to achieve your weight goals? Calorie needs are based on individual needs. In order for your weight to stay the same, the energy (or Calories) you consume must equal
GRADE 11F: Biology 3. UNIT 11FB.3 9 hours. Human gas exchange system and health. Resources. About this unit. Previous learning.
 GRADE 11F: Biology 3 Human gas exchange system and health UNIT 11FB.3 9 hours About this unit This unit is the third of six units on biology for Grade 11 foundation. The unit is designed to guide your
GRADE 11F: Biology 3 Human gas exchange system and health UNIT 11FB.3 9 hours About this unit This unit is the third of six units on biology for Grade 11 foundation. The unit is designed to guide your
GA-3 Disaster Medical Assistance Team. Physical Fitness Guide
 GA-3 Disaster Medical Assistance Team Physical Fitness Guide PURPOSE: The purpose of this Physical Fitness Guide is to provide physical fitness training information to the members of the GA-3 Disaster
GA-3 Disaster Medical Assistance Team Physical Fitness Guide PURPOSE: The purpose of this Physical Fitness Guide is to provide physical fitness training information to the members of the GA-3 Disaster
STAGE 5: Interacting Systems
 Stage 5: In this stage, students will explore how systems interact with each other to maintain healthy and optimal body functioning, including how the body responds to changes in the environment such as
Stage 5: In this stage, students will explore how systems interact with each other to maintain healthy and optimal body functioning, including how the body responds to changes in the environment such as
Strength Training for the Runner
 Strength Training for the Runner Strength Training for the Runner What? The goal of resistance training for runners is not necessarily adding muscle mass but 1. improving muscular strength, 2. improving
Strength Training for the Runner Strength Training for the Runner What? The goal of resistance training for runners is not necessarily adding muscle mass but 1. improving muscular strength, 2. improving
9-12 Physical Education and Leisure Curriculum Framework. Revised 2011
 9-12 Physical Education and Leisure Curriculum Framework Revised 2011 Course Title: Physical Education and Leisure Course/Unit Credit: 1 Course Number: 485000 Teacher Licensure: Please refer to the Course
9-12 Physical Education and Leisure Curriculum Framework Revised 2011 Course Title: Physical Education and Leisure Course/Unit Credit: 1 Course Number: 485000 Teacher Licensure: Please refer to the Course
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION
 CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
Provided by the American Venous Forum: veinforum.org
 CHAPTER 1 NORMAL VENOUS CIRCULATION Original author: Frank Padberg Abstracted by Teresa L.Carman Introduction The circulatory system is responsible for circulating (moving) blood throughout the body. The
CHAPTER 1 NORMAL VENOUS CIRCULATION Original author: Frank Padberg Abstracted by Teresa L.Carman Introduction The circulatory system is responsible for circulating (moving) blood throughout the body. The
Once the immune system is triggered, cells migrate from the blood into the joints and produce substances that cause inflammation.
 HealthExchange Points For Your Joints An Arthritis Talk Howard Epstein, MD Orthopaedic & Rheumatologic Institute Rheumatic & Immunologic Disease Cleveland Clinic Beachwood Family Health & Surgery Center
HealthExchange Points For Your Joints An Arthritis Talk Howard Epstein, MD Orthopaedic & Rheumatologic Institute Rheumatic & Immunologic Disease Cleveland Clinic Beachwood Family Health & Surgery Center
Milwaukee School of Engineering Gerrits@msoe.edu. Case Study: Factors that Affect Blood Pressure Instructor Version
 Case Study: Factors that Affect Blood Pressure Instructor Version Goal This activity (case study and its associated questions) is designed to be a student-centered learning activity relating to the factors
Case Study: Factors that Affect Blood Pressure Instructor Version Goal This activity (case study and its associated questions) is designed to be a student-centered learning activity relating to the factors
Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together.
 Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together. CLASSES OF JOINTS. 1. Joints are classified according to how the bones are held together. 2. The three types of
Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together. CLASSES OF JOINTS. 1. Joints are classified according to how the bones are held together. 2. The three types of
Chapter 6. Components of Elasticity. Musculotendinous Unit. Behavioral Properties of the Musculotendinous Unit. Biomechanics of Skeletal Muscle
 Chapter 6 Behavioral Properties of the Musculotendinous Unit 1) extensibility: ability to be stretched or to increase in length 2) elasticity: ability to return to normal resting length following a stretch
Chapter 6 Behavioral Properties of the Musculotendinous Unit 1) extensibility: ability to be stretched or to increase in length 2) elasticity: ability to return to normal resting length following a stretch
Personal Fitness Plan
 Personal Fitness Plan 7 th Grade 1 week plan/1 week food log Name Period 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Date When you complete this project, you will accomplish the following: Set specific short-term and long-term personal
Personal Fitness Plan 7 th Grade 1 week plan/1 week food log Name Period 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Date When you complete this project, you will accomplish the following: Set specific short-term and long-term personal
North Bergen School District Benchmarks
 Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
GRADE ONE. End of 1st 9 Weeks. Initial Evaluation. Scoring: Not attempted 0 points Attempted 1 point Performs most 2 points Mastery 3 points
 GRADE ONE Date 1. Demonstrate jumping and landing skills by using one- and two-foot take-off methods, balancing at varying levels on multiple body parts, and forming bridges using different body parts.
GRADE ONE Date 1. Demonstrate jumping and landing skills by using one- and two-foot take-off methods, balancing at varying levels on multiple body parts, and forming bridges using different body parts.
Personal Trainer Knowledge, Skills, and Abilities (1/01/12)
 1. Core Knowledge A. Kinesiology: Anatomy and Biomechanics B. Exercise Physiology C. Basic Nutrition and Weight Management D. Human Behavior 2. Health and Medical Review; and Fitness Assessment A. Health
1. Core Knowledge A. Kinesiology: Anatomy and Biomechanics B. Exercise Physiology C. Basic Nutrition and Weight Management D. Human Behavior 2. Health and Medical Review; and Fitness Assessment A. Health
About High Blood Pressure
 About High Blood Pressure Your Treatment & You: working together to help manage your health Glaxo- Blood Pressure Booklet (ASK) EN.indd 1 10/7/2014 4:49:14 PM Glaxo- Blood Pressure Booklet (ASK) EN.indd
About High Blood Pressure Your Treatment & You: working together to help manage your health Glaxo- Blood Pressure Booklet (ASK) EN.indd 1 10/7/2014 4:49:14 PM Glaxo- Blood Pressure Booklet (ASK) EN.indd
Important Concepts of Physical Activity and Physical Fitness. To introduce important concepts and terms regarding physical activity and physical
 Chapter 1 Important Concepts of Physical Activity and Physical Fitness Chapter objectives: To introduce important concepts and terms regarding physical activity and physical fitness. To describe different
Chapter 1 Important Concepts of Physical Activity and Physical Fitness Chapter objectives: To introduce important concepts and terms regarding physical activity and physical fitness. To describe different
Aerobics: Knowledge and Practice
 Aerobics: Knowledge and Practice Brought to you by the Wellness Center and Vanderbilt Recreation Group Fitness Program Overview The goal of this self-study course is to provide aspiring aerobics instructors
Aerobics: Knowledge and Practice Brought to you by the Wellness Center and Vanderbilt Recreation Group Fitness Program Overview The goal of this self-study course is to provide aspiring aerobics instructors
CARDIAC REHABILITATION HOME EXERCISE ADVICE
 CARDIAC REHABILITATION HOME EXERCISE ADVICE Introduction Exercise is a very important as part of your rehabilitation and your future health. You will need to exercise at least three times per week, minimum,
CARDIAC REHABILITATION HOME EXERCISE ADVICE Introduction Exercise is a very important as part of your rehabilitation and your future health. You will need to exercise at least three times per week, minimum,
UNIVERSAL FITNESS NETWORK, Inc. 2315 West Monica Dunlap, IL 61525 (309)-360-5615 bahenso@comcast.net FACTS ABOUT THE PHYSICAL FITNESS ASSESSMENT TESTS
 UNIVERSAL FITNESS NETWORK, Inc. 2315 West Monica Dunlap, IL 61525 (309)-360-5615 bahenso@comcast.net FACTS ABOUT THE PHYSICAL FITNESS ASSESSMENT TESTS Universal Fitness Network, Inc. specializes in physical
UNIVERSAL FITNESS NETWORK, Inc. 2315 West Monica Dunlap, IL 61525 (309)-360-5615 bahenso@comcast.net FACTS ABOUT THE PHYSICAL FITNESS ASSESSMENT TESTS Universal Fitness Network, Inc. specializes in physical
High Blood Pressure and Chronic Kidney Disease. For People With CKD Stages 1 4
 High Blood Pressure and Chronic Kidney Disease For People With CKD Stages 1 4 National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative (NKF-KDOQI ) The National Kidney Foundation s Kidney
High Blood Pressure and Chronic Kidney Disease For People With CKD Stages 1 4 National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative (NKF-KDOQI ) The National Kidney Foundation s Kidney
The Body s Transport System
 Circulation Name Date Class The Body s Transport System This section describes how the heart, blood vessels, and blood work together to carry materials throughout the body. Use Target Reading Skills As
Circulation Name Date Class The Body s Transport System This section describes how the heart, blood vessels, and blood work together to carry materials throughout the body. Use Target Reading Skills As
Clinical Care Program
 Clinical Care Program Therapy for the Cardiac Patient What s CHF? Not a kind of heart disease o Heart disease is called cardiomyopathy o Heart failure occurs when the heart can t pump enough blood to meet
Clinical Care Program Therapy for the Cardiac Patient What s CHF? Not a kind of heart disease o Heart disease is called cardiomyopathy o Heart failure occurs when the heart can t pump enough blood to meet
Our Human Body On-site student activities Years 5 6
 Our Human Body On-site student activities Years 5 6 Our Human Body On-site student activities: Years 5-6 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to
Our Human Body On-site student activities Years 5 6 Our Human Body On-site student activities: Years 5-6 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to
Engage: Brainstorming Body Systems. Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below.
 Engage: Brainstorming Body s Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below. Body Nervous Circulatory Excretory Immune Digestive Respiratory Skeletal Muscular Endocrine Integumentary
Engage: Brainstorming Body s Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below. Body Nervous Circulatory Excretory Immune Digestive Respiratory Skeletal Muscular Endocrine Integumentary
Eating Disorders. 1995-2012, The Patient Education Institute, Inc. www.x-plain.com mhf70101 Last reviewed: 06/29/2012 1
 Eating Disorders Introduction Eating disorders are illnesses that cause serious changes in a person s daily diet. This can include not eating enough food or overeating. Eating disorders affect about 70
Eating Disorders Introduction Eating disorders are illnesses that cause serious changes in a person s daily diet. This can include not eating enough food or overeating. Eating disorders affect about 70
Basic Training Methodology. Editors: Thor S. Nilsen (NOR), Ted Daigneault (CAN), Matt Smith (USA)
 4 Basic Training Methodology Editors: Thor S. Nilsen (NOR), Ted Daigneault (CAN), Matt Smith (USA) 58 4. BASIC TRAINING METHODOLOGY 1.0 INTRODUCTION The role of the coach in the development of athletic
4 Basic Training Methodology Editors: Thor S. Nilsen (NOR), Ted Daigneault (CAN), Matt Smith (USA) 58 4. BASIC TRAINING METHODOLOGY 1.0 INTRODUCTION The role of the coach in the development of athletic
Heart Rate and Physical Fitness
 Heart Rate and Physical Fitness The circulatory system is responsible for the internal transport of many vital substances in humans, including oxygen, carbon dioxide, and nutrients. The components of the
Heart Rate and Physical Fitness The circulatory system is responsible for the internal transport of many vital substances in humans, including oxygen, carbon dioxide, and nutrients. The components of the
Men s Basketball STRENGTH & CONDITIONING PROGRAM. Developed by: Chad Kish, PhD
 Men s Basketball STRENGTH & CONDITIONING PROGRAM Developed by: Chad Kish, PhD PURPOSE The purpose of the Cardinals strength and conditioning manual is to provide the athlete with a general overview of
Men s Basketball STRENGTH & CONDITIONING PROGRAM Developed by: Chad Kish, PhD PURPOSE The purpose of the Cardinals strength and conditioning manual is to provide the athlete with a general overview of
Physical Activity and Weight Control
 Physical Activity and Weight Control WIN Weight-control Information Network U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH Physical Activity and Weight Control Physical activity
Physical Activity and Weight Control WIN Weight-control Information Network U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH Physical Activity and Weight Control Physical activity
SISSRGU203A Participate in conditioning for Rugby Union
 SISSRGU203A Participate in conditioning for Rugby Union Release: 2 SISSRGU203A Participate in conditioning for Rugby Union Modification History Not Applicable Unit Descriptor This unit describes the performance
SISSRGU203A Participate in conditioning for Rugby Union Release: 2 SISSRGU203A Participate in conditioning for Rugby Union Modification History Not Applicable Unit Descriptor This unit describes the performance
Chapter 11. What are the functions of the skeletal system? More detail on bone
 Skeletal System Chapter 11 11.1 Overview of the skeletal system What are the functions of the skeletal system? 1. Supports the body 2. Protects the soft body parts 3. Produces blood cells 4. Stores minerals
Skeletal System Chapter 11 11.1 Overview of the skeletal system What are the functions of the skeletal system? 1. Supports the body 2. Protects the soft body parts 3. Produces blood cells 4. Stores minerals
