AACN PCCN Review. Gastrointestinal
|
|
|
- Samantha Miles
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AACN PCCN Review Gastrointestinal Presenter: Carol A. Rauen, RN, MS, CCNS, CCRN, PCCN, CEN Independent Clinical Nurse Specialist & Education Consultant
2 Gastrointestinal I. INTRODUCTION PCCN Test Plan Endocrine, Heme, GI, & Renal: 18% a. Functional GI Disorders (e.g., obstruction, ileus, diabetic gastroparesis, gastroesophageal reflux, irritable bowel syndrome) b. GI Bleed Lower Upper c. GI Infections d. Hepatic Failure e. Ischemic Bowel f. Malnutrition (e.g., failure to thrive, malabsorption disorders) g. Pancreatitis Structures/Function/Digestion a. Mouth b. Esophagus c. Stomach d. Small Intestine e. Pancreas f. Gallbladder g. Liver h. Spleen i. Portal Circulation j. Mesentery Circulation k. Large Intestine l. Digestive Hormones m. Digestive Enzymes Assessment a. Inspection b. Auscultation c. Palpation d. Percussion 1
3 II. THE HEPATIC SYSTEM Liver Function a. Metabolic Factory & Waste Disposal Plant b. Carbohydrate, Fat & Protein Metabolism c. Production of Bile Salts d. Production of Clotting Factors e. Bilirubin Metabolism f. Detoxification: Nutrients, Drugs, Toxins, Bacteria, Everything g. Vitamin & Mineral Storage: h. Blood Reservoir: 10% of Total Blood Volume Liver Function Tests Test Serum Proteins Serum Ammonia Bilirubin Coagulation Studies Hepatic Enzymes Liver Function Tests Results Total Protein: g/dl Serum Albumin: g/dl Serum Globulins: g/dL Pre-Albumin: mg/dl mcg/dl Total Bilirubin: mg/dl Unconjugated Bilirubin: mg/dl Conjugated Bilirubin: mg/dl Indirectly reflect liver function o PT o PTT o INR o Bleeding Time o ACT ALP: U/L GGT o Men: 0 85 U/L o Women: 0-70 U/L AST o Men: U/L o Women: 13-35U/L ALT o Men: 10-55U/L o Women: 7-30U/L 2
4 Liver Dysfunction & Failure Pathophysiology a. Liver Tissue (cells) are Destroyed and Replaced with Fibrotic Tissue b. Functions are Altered c. Organ Changes Shape d. Vascular Flow is Obstructed e. Portal Hypertension Cirrhosis A chronic progressive liver disease where diffuse fibrotic bands of connective tissue, distort the liver s normal architecture and functional ability. The liver loses its ability to regulate fluids, metabolize waste, regulate coagulation and nutrition. a. Causes Alcoholic, Laennec's Portal, or Fatty Post Necrotic: Toxic, Nodular, or Post Hepatic Biliary: Cholangitic or Obstructive Hepatitis Widespread Inflammation of Liver Cells a. Causes Primary Viral Most Common Hepatotoxins - Toxic or Drugs Secondary Viral, Low Mortality Clinical Presentation of Liver Dysfunction Hepatic Encephalopathy The liver is unable to perform its detoxification function and toxins build up. Primarily ammonia causing altered LOC, behavior and motor abilities. Confusion Coma Agitation Unsafe Behavior Asterixis: Flap like Tremor of Hands Apraxia: Inability to Perform Purposeful Acts Elevated Ammonia Limit Protein Intake Limit Hepatotoxic Drugs Lactulose & Neomycin Safe Environment 3
5 Malnutrition The liver is unable to perform its function of carbohydrate, protein and fat metabolism. This leads to malnutrition Need to tx the Cause of Liver Failure Parenteral Nutrition Limit Protein Intake Restrict Fluids Coagulopathy The liver is unable to synthesize fibrinogen, prothrombin and factors V, VII, IX, X, XI, XIII, fibrinolytic factors and Vit. K. These are needed to maintain the ability to clot. Platelet aggregation and adhesion are also effected by liver dysfunction. Bleeding Tendencies Nonspecific Bleeding Monitor Coagulation Studies & Platelet Ct Decrease Bleeding and Bruising Risk Administer Blood Products Portal Hypertension Increased pressure in the portal vein occurs secondary to flow obstruction from inflammation, bands, or fibrotic hepatic tissue. This retrograde pressure leads to formation of varices in the esophagus, stomach and rectal vault. Caput Medusae: dilated cutaneous veins radiating from the umbilical Spider angiomas commonly seen in Cirrhosis Upper GI Bleeding Surgical Shunting TIPSS - Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosytemic Stent Shunt Treat Bleeding Treat Cause Hepatorenal Syndrome A form of pre-renal failure caused by the liver dysfunction. Mortality of liver failure is very high once renal failure develops. S&S of Renal Dysfunction 4
6 Maintain Adequate Renal Perfusion Restrict Fluids Restrict Nephrotoxic Agents Continuous Renal Replacement Therapies Ascites Fluid accumulation in the peritoneal space secondary to decreased production of albumin, decreased systemic oncotic pressure, increased hepatic lymph production and increased capillary permeability. The fluid accumulation impacts the respiratory (diaphragm) and cardiac (hemodynamic) systems primarily as well as comfort and body image. Inc. Abdominal Girth Hypotension and Tachycardia Dyspnea, Orthopnea, Tachypnea S&S of Dehydration N&V Restrict PO Fluid Diuretics (if tolerated hemodynamically) Restrict Na Respiratory Support Paracentesis Peritoneovenous Shunt Surgery Infection One of the functions of the liver cells (Kuppfer cells) is to clean the blood of bacteria. With liver failure this function is not provided and bacteria builds up (primarily gram negative bugs) in the systemic circulation increasing the risk of infection. Poor Wound Healing Increased Risk of Infection Heightened Prevention Measures Abx Therapy w Caution 5
7 III. THE PANCREAS Function a. Endocrine Functions Synthesis & Release of Hormones: o Glycogen o Insulin o Gastrin b. Exocrine Functions Pancreatic Enzymes Break Down Protein, Starch & Fat. > 2L/day Bicarbonate Raise ph c. PNS, Gastrin & Hormones Regulate Secretions Pancreatic Enzymes a. Trypsin: Aids in Protein Digestion b. Amylase: Aids in Carbohydrate Digestion c. Lipase: Aids in Fat Digestion Acute Pancreatitis Pathophysiology a. Auto Digestion Tissue Damage Fat Necrosis Vascular Damage & Hemorrhage Increased Capillary Permeability Hypotension b. Forms/Types Edematous Hemorrhagic c. Classifications Acute Pancreatitis Recurrent Acute Recurrent Chronic Chronic Pancreatitis Cause (blocked enzyme release) a. Alcoholism b. Biliary Stones c. Hyperlipidemia d. Abd Trauma e. Infection (bacterial or viral) 6
8 f. Shock g. Drugs (Most Common: Cyclosporine, Acetaminophen, Cimetidine, Steroids, Salicylates, Furosemide, Thiazides, Estrogens) Clinical Presentation a. Pain b. Low Grade Fever c. N&V d. Distended/Tender/Rigid Abd e. Guarding with Rebound Tenderness f. Jaundice g. Hypoactive Bowel Sounds h. Steatorrhea: bulky, pale, foul-smelling stools i.? Ascites j. Hypovolemic Shock k. In Necrotizing Pancreatitis Cullen s Sign: o Bluish Discoloration Umbilical Grey Turner s Sign: o Bluish Discoloration Flanks Labs Underlined labs are the MOST diagnostic a. Hypocalcemia (classic sign) b. Low Ca, Mg, K c. Hyperglycemia d. Hyperbilirubinemia e. Hypertriglyceridemia f. Increased BUN & Creatinine g. Elevated Amylase h. Elevated Lipase i. Elevated LFTs j. Elevated WBC k. Decreased H/H l.? Increased H/H Treatment Options a. Fluid Resuscitation b. Rest the Pancreas: NPO, NGT c. Pain Management d. Monitor & Replace Electrolytes e. Tx Multisystem f. Nutritional Support g. Surgery 7
9 IV. ACUTE GI HEMORRHAGE Lower GI Bleeding Not Typically Life Threatening a. Causes Diverticulitis Angiodysplasia Cancer Hemorrhoids Inflammatory Bowel Disease (Ulcerative Colitis; Crohn's Disease) Bowel Infarction Upper GI Bleeding a. Causes Peptic Ulcer Disease: Duodenal, Gastric and Stomal ulcers account for 50% bleeding episodes Gastritis or Esophagitis Esophageal Varices Mallory -Weiss Syndrome b. Clinical Presentation Hematemesis Melena PUD Distended & Tender Abd Hyperactive Bowel Sounds Hypovolemia Shock c. Assessment H & H Coags & Platelets Hemoconcentration Elevated BUN LFTs Endoscopy Angiography Raionuclide Scans d. Treatment NG Decompression/Lavage Room Temp vs Iced Fluid Resuscitation Blood Product Admin Endoscopic Sclerotherapy 8
10 Pharmacology Surgery o Vagotomy and Pyloroplasty o Oversew Ulcer or Tear o Total and Subtotal Gastric Resection o Billroth I: Vagotomy, Antrectomy, Anastomosis Stomach and Duodenum o Billroth II: Vagotomy, Antrectomy, Anastomosis Stomach and Jejunum o Whipple: Removal of the Distal 3 rd of Stomach, Entire Duodenum, Head of Pancreas, Gastrojejunotomy o Colon Resection Bleeding Esophageal Varices o TIPSS: Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosytemic Stent Shunt o Beta Blocker Decreases Pressure o Portal Caval Shunt V. DISORDERS OF THE BOWEL Bowel Infarction a. Etiology Embolic or Thrombotic Occlusion Typically from the Superior Mesenteric Artery b. Clinical Presentation Severe Epigastric Pain Rebound Tenderness Guarding & Rigidity Stimulated Sympathetic Response from Pain c. Treatment Options Angiography to Identify/Confirm Occlusion Surgery to Remove Occlusion & Dead Bowel Bowel Obstruction a. Etiology Internal Lumen Obstruction ex. Tumor External Lumen Obstruction ex. Adhesions Emboli: no blood flow Paralytic Ileus 9
11 b. Clinical Presentation Complete vs Partial Distended Edematous Bowel Fluid and Electrolytes Leaking from Bowel Elevated WBC Fever Small Intestine o Acute Pain w Sudden Onset o N & V (movement on both ends) o Wave-Like Hyperactive High Pitched Bowel Sounds o May Have Some Gas or Feces o Distention (mild) Large Intestine o Slow Onset Pain Progression Mild Severe, Lower Abd o No N & V (nothing moving) o No Stool o Low Pitched Bowel Sounds o Distention (large amount) Treatment Options o Diagnosis Obstruction by Hx, X-Ray, CT, Upper or Lower Barium Radiology Tests o Pain Management o IV Fluids o Decompress w NG, Rectal or Intestinal Tube o Abx o NPO and Time (rest the bowel) o Surgery Perforation/Peritonitis a. Etiology Gastric/Intestinal Contents Leak into Peritoneal Cavity Ulcer Perforation Diverticular Rupture Trauma Bowel Infarction b. Clinical Presentation Infection/Sepsis (all the S&S) Sudden Onset of Severe Pain Rigid Abdomen w Rebound Tenderness Hypoactive Bowel Sounds No Bowel Sounds 10
12 c. Treatment Options Surgery to Repair Cause & Clean Up ABX Fluids Tx of Sepsis Tx of MODS Functional GI Disorders a. Ileus b. Diabetic Gastroparesis c. Gastroesophageal Reflux d. Irritable Bowel Syndrome 11
Learning Objectives. Introduction to Medical Careers. Vocabulary: Chapter 16 FACTS. Functions. Organs. Digestive System Chapter 16
 Learning Objectives Introduction to Medical Careers Digestive System Chapter 16 Define at least 10 terms relating to the digestive Describe the four functions of the digestive Identify different structures
Learning Objectives Introduction to Medical Careers Digestive System Chapter 16 Define at least 10 terms relating to the digestive Describe the four functions of the digestive Identify different structures
GI Bleeding. Thomas S.Foster,Pharm.D. PHR 961 Integrated Therapeutics
 GI Bleeding Thomas S.Foster,Pharm.D. PHR 961 Integrated Therapeutics Overview Because GI bleeding is internal, it is possible for a person to have GI bleeding without symptoms. Important to recognize
GI Bleeding Thomas S.Foster,Pharm.D. PHR 961 Integrated Therapeutics Overview Because GI bleeding is internal, it is possible for a person to have GI bleeding without symptoms. Important to recognize
Gastrointestinal Bleeding
 Gastrointestinal Bleeding Introduction Gastrointestinal bleeding is a symptom of many diseases rather than a disease itself. A number of different conditions can cause gastrointestinal bleeding. Some causes
Gastrointestinal Bleeding Introduction Gastrointestinal bleeding is a symptom of many diseases rather than a disease itself. A number of different conditions can cause gastrointestinal bleeding. Some causes
Acute Abdominal Pain following Bariatric Surgery. Disclosure. Objectives 8/17/2015. I have nothing to disclose
 Acute Abdominal Pain following Bariatric Surgery Kathy J. Morris, DNP, APRN, FNP C, FAANP University of Nebraska Medical Center College of Nursing Disclosure I have nothing to disclose Objectives Pathophysiology
Acute Abdominal Pain following Bariatric Surgery Kathy J. Morris, DNP, APRN, FNP C, FAANP University of Nebraska Medical Center College of Nursing Disclosure I have nothing to disclose Objectives Pathophysiology
Diseases of peritoneum Lect. Al Qassim University, Faculty of Medicine Phase II Year III, CMD 332 Pathology Department 31-32
 Diseases of peritoneum Lect Al Qassim University, Faculty of Medicine Phase II Year III, CMD 332 Pathology Department 31-32 Describe the etiology, pathogenesis and types of peritonitis Define ascites and
Diseases of peritoneum Lect Al Qassim University, Faculty of Medicine Phase II Year III, CMD 332 Pathology Department 31-32 Describe the etiology, pathogenesis and types of peritonitis Define ascites and
NUTRITION IN LIVER DISEASES
 NUTRITION IN LIVER DISEASES 1. HEPATITIS: Definition: - Viral inflammation of liver cells. Types: a. HAV& HEV, transmitted by fecal-oral route. b. HBV & HCV, transmitted by blood and body fluids. c. HDV
NUTRITION IN LIVER DISEASES 1. HEPATITIS: Definition: - Viral inflammation of liver cells. Types: a. HAV& HEV, transmitted by fecal-oral route. b. HBV & HCV, transmitted by blood and body fluids. c. HDV
Introduction. Physiology of the Abdomen. Anatomy & Physiology. Abdominal Pain Introduction (2 of 2) Gastrointestional and Urologic Emergencies
 Gastrointestional and Urologic Emergencies Introduction Abdominal pain is a common complaint. Cause of abdominal pain is often difficult to determine. As an EMT: You do not need to determine exact cause.
Gastrointestional and Urologic Emergencies Introduction Abdominal pain is a common complaint. Cause of abdominal pain is often difficult to determine. As an EMT: You do not need to determine exact cause.
MANAGEMENT OF LIVER CIRRHOSIS
 MANAGEMENT OF LIVER CIRRHOSIS Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What is cirrhosis? Cirrhosis is a result of long-term, continuous damage to the liver and may be due to many different
MANAGEMENT OF LIVER CIRRHOSIS Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What is cirrhosis? Cirrhosis is a result of long-term, continuous damage to the liver and may be due to many different
Upper Gastrointestinal Tract KNH 406
 Upper Gastrointestinal Tract KNH 406 Upper GI A&P GI tract long tube ~ 15 ft. Upper GI mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach Accessory organs pancreas, biliary system, liver Four basic functions: motility,
Upper Gastrointestinal Tract KNH 406 Upper GI A&P GI tract long tube ~ 15 ft. Upper GI mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach Accessory organs pancreas, biliary system, liver Four basic functions: motility,
Liver Function Tests. Dr Stephen Butler Paediatric Advance Trainee TDHB
 Liver Function Tests Dr Stephen Butler Paediatric Advance Trainee TDHB Introduction Case presentation What is the liver? Overview of tests used to measure liver function RJ 10 month old European girl
Liver Function Tests Dr Stephen Butler Paediatric Advance Trainee TDHB Introduction Case presentation What is the liver? Overview of tests used to measure liver function RJ 10 month old European girl
Amylase and Lipase Tests
 Amylase and Lipase Tests Also known as: Amy Formal name: Amylase Related tests: Lipase The Test The blood amylase test is ordered, often along with a lipase test, to help diagnose and monitor acute or
Amylase and Lipase Tests Also known as: Amy Formal name: Amylase Related tests: Lipase The Test The blood amylase test is ordered, often along with a lipase test, to help diagnose and monitor acute or
Bile Duct Diseases and Problems
 Bile Duct Diseases and Problems Introduction A bile duct is a tube that carries bile between the liver and gallbladder and the intestine. Bile is a substance made by the liver that helps with digestion.
Bile Duct Diseases and Problems Introduction A bile duct is a tube that carries bile between the liver and gallbladder and the intestine. Bile is a substance made by the liver that helps with digestion.
Liver, Gallbladder and Pancreas diseases. Premed 2 Pathophysiology
 Liver, Gallbladder and Pancreas diseases Premed 2 Pathophysiology Pancreas Pancreatitis Acute Pancreatitis Autodigestion of the pancreas due to activation of the enzymes Hemorrhagic fat necrosis, calcium
Liver, Gallbladder and Pancreas diseases Premed 2 Pathophysiology Pancreas Pancreatitis Acute Pancreatitis Autodigestion of the pancreas due to activation of the enzymes Hemorrhagic fat necrosis, calcium
Medical Nutrition Therapy for Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Disorders. By: Jalal Hejazi PhD, MSc.
 Medical Nutrition Therapy for Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Disorders By: Jalal Hejazi PhD, MSc. Digestive Disorders Common problem; more than 50 million outpatient visits per year Dietary habits and nutrition
Medical Nutrition Therapy for Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Disorders By: Jalal Hejazi PhD, MSc. Digestive Disorders Common problem; more than 50 million outpatient visits per year Dietary habits and nutrition
Evaluation and Prognosis of Patients with Cirrhosis
 Evaluation and Prognosis of Patients with Cirrhosis Marion G. Peters, MD John V. Carbone, MD, Endowed Chair Professor of Medicine Chief of Hepatology Research University of California San Francisco Recorded
Evaluation and Prognosis of Patients with Cirrhosis Marion G. Peters, MD John V. Carbone, MD, Endowed Chair Professor of Medicine Chief of Hepatology Research University of California San Francisco Recorded
June 11, 2015 Tim Halterman
 June 11, 2015 Tim Halterman Defini&on Histologic change + loss of liver function Derives from Greek word kirrhos meaning yellow, tawny First named by Rene Laennec in 1819 Laennec s cirrhosis=alcoholic
June 11, 2015 Tim Halterman Defini&on Histologic change + loss of liver function Derives from Greek word kirrhos meaning yellow, tawny First named by Rene Laennec in 1819 Laennec s cirrhosis=alcoholic
The digestive system. Medicine and technology. Normal structure and function Diagnostic methods Example diseases and therapies
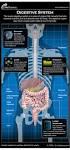 The digestive system Medicine and technology Normal structure and function Diagnostic methods Example diseases and therapies The digestive system An overview (1) Oesophagus Liver (hepar) Biliary system
The digestive system Medicine and technology Normal structure and function Diagnostic methods Example diseases and therapies The digestive system An overview (1) Oesophagus Liver (hepar) Biliary system
Hepatitis C. Laboratory Tests and Hepatitis C
 Hepatitis C Laboratory Tests and Hepatitis C If you have hepatitis C, your doctor will use laboratory tests to check your health. This handout will help you understand what the major tests are and what
Hepatitis C Laboratory Tests and Hepatitis C If you have hepatitis C, your doctor will use laboratory tests to check your health. This handout will help you understand what the major tests are and what
PATIENT CONSENT TO PROCEDURE - ROUX-EN-Y GASTRIC BYPASS
 As a patient you must be adequately informed about your condition and the recommended surgical procedure. Please read this document carefully and ask about anything you do not understand. Please initial
As a patient you must be adequately informed about your condition and the recommended surgical procedure. Please read this document carefully and ask about anything you do not understand. Please initial
Homeostatic Imbalances of the Digestive System
 Homeostatic Imbalances of the Digestive System Sign or Disease Description, Causes, Etc. 1 Abdominal Adhesions Fibrous bands that form between tissues and organs, often as a result of injury during surgery;
Homeostatic Imbalances of the Digestive System Sign or Disease Description, Causes, Etc. 1 Abdominal Adhesions Fibrous bands that form between tissues and organs, often as a result of injury during surgery;
GI Bleed. Steven Lichtenstein, D.O. Chief, Division of Gastroenterology Mercy Health System. Director, Endoscopy/GI Lab Mercy Fitzgerald Hospital
 October 3, 2015 GI Bleed Steven Lichtenstein, D.O. Chief, Division of Gastroenterology Mercy Health System Director, Endoscopy/GI Lab Mercy Fitzgerald Hospital Clinical Associate Professor of Medicine
October 3, 2015 GI Bleed Steven Lichtenstein, D.O. Chief, Division of Gastroenterology Mercy Health System Director, Endoscopy/GI Lab Mercy Fitzgerald Hospital Clinical Associate Professor of Medicine
Acute abdominal conditions Key Points
 7 Acute abdominal conditions Key Points 7.1 ASSESSMENT AND DIAGNOSIS Referred abdominal pain Fore gut pain (stomach, duodenum, gall bladder) is referred to the upper abdomen Mid gut pain (small intestine,
7 Acute abdominal conditions Key Points 7.1 ASSESSMENT AND DIAGNOSIS Referred abdominal pain Fore gut pain (stomach, duodenum, gall bladder) is referred to the upper abdomen Mid gut pain (small intestine,
Liver, Gallbladder, Exocrine Pancreas KNH 406
 Liver, Gallbladder, Exocrine Pancreas KNH 406 2007 Thomson - Wadsworth LIVER Anatomy - functions With disease blood flow becomes obstructed Bile All bile drains into common hepatic duct Liver Bile complex
Liver, Gallbladder, Exocrine Pancreas KNH 406 2007 Thomson - Wadsworth LIVER Anatomy - functions With disease blood flow becomes obstructed Bile All bile drains into common hepatic duct Liver Bile complex
Gastrointestinal bleeding
 Gastrointestinal bleeding..is the reason in 2 % of all admissions to hospital 85.000 cases/year in the US. The incidence of urgent upper GI bleeding: 145/100.000 inhabitant/year in Hungary ( Nagy Gy. MBA
Gastrointestinal bleeding..is the reason in 2 % of all admissions to hospital 85.000 cases/year in the US. The incidence of urgent upper GI bleeding: 145/100.000 inhabitant/year in Hungary ( Nagy Gy. MBA
The child with abnormal liver function tests
 The child with abnormal liver function tests Dr Jane Hartley Consultant Paediatric Hepatologist Birmingham Children s Hospital, UK 1 st Global Congress CIP, Paris 2011 Contents Over view of liver anatomy,
The child with abnormal liver function tests Dr Jane Hartley Consultant Paediatric Hepatologist Birmingham Children s Hospital, UK 1 st Global Congress CIP, Paris 2011 Contents Over view of liver anatomy,
Approach to Abnormal Liver Tests
 Approach to Abnormal Liver Tests Naga P. Chalasani, MD, FACG Professor of Medicine and Cellular & Integrative Physiology Director, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Indiana University School
Approach to Abnormal Liver Tests Naga P. Chalasani, MD, FACG Professor of Medicine and Cellular & Integrative Physiology Director, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Indiana University School
A CASE OF LIVER CIRRHOSIS & HEPATIC ENCEPHALOPATHY
 A CASE OF LIVER CIRRHOSIS & HEPATIC ENCEPHALOPATHY 2 1 Mr N.N. 56 yr old male. Admitted on 22/03/02. 1 month Hx of abdominal distention, confusion, inability to concentrate and dyspnoea Grade 111. Pmx:
A CASE OF LIVER CIRRHOSIS & HEPATIC ENCEPHALOPATHY 2 1 Mr N.N. 56 yr old male. Admitted on 22/03/02. 1 month Hx of abdominal distention, confusion, inability to concentrate and dyspnoea Grade 111. Pmx:
Adams Memorial Hospital Decatur, Indiana EXPLANATION OF LABORATORY TESTS
 Adams Memorial Hospital Decatur, Indiana EXPLANATION OF LABORATORY TESTS Your health is important to us! The test descriptions listed below are for educational purposes only. Laboratory test interpretation
Adams Memorial Hospital Decatur, Indiana EXPLANATION OF LABORATORY TESTS Your health is important to us! The test descriptions listed below are for educational purposes only. Laboratory test interpretation
Laparoscopic Surgery of the Colon and Rectum (Large Intestine) A Simple Guide to Help Answer Your Questions
 Laparoscopic Surgery of the Colon and Rectum (Large Intestine) A Simple Guide to Help Answer Your Questions What are the Colon and Rectum? The colon and rectum together make up the large intestine. After
Laparoscopic Surgery of the Colon and Rectum (Large Intestine) A Simple Guide to Help Answer Your Questions What are the Colon and Rectum? The colon and rectum together make up the large intestine. After
RN.com s Assessment Series: Focused Gastrointestinal Assessment
 RN.com s Assessment Series: Focused Gastrointestinal Assessment Presented by: RN.com 12400 High Bluff Drive San Diego, CA 92130 This course has been approved for one (1.0) contact hour. This course expires
RN.com s Assessment Series: Focused Gastrointestinal Assessment Presented by: RN.com 12400 High Bluff Drive San Diego, CA 92130 This course has been approved for one (1.0) contact hour. This course expires
Chapter 17 Digestive System. Alimentary Canal. Movements of the Tube
 Chapter 17 Digestive System Functions of Digestive System ingestion mechanical digestion chemical digestion propulsion absorption defecation Consists of the alimentary canal and accessory organs 1 Alimentary
Chapter 17 Digestive System Functions of Digestive System ingestion mechanical digestion chemical digestion propulsion absorption defecation Consists of the alimentary canal and accessory organs 1 Alimentary
Guide to Abdominal or Gastroenterological Surgery Claims
 What are the steps towards abdominal surgery? Investigation and Diagnosis It is very important that all necessary tests are undertaken to investigate the patient s symptoms appropriately and an accurate
What are the steps towards abdominal surgery? Investigation and Diagnosis It is very important that all necessary tests are undertaken to investigate the patient s symptoms appropriately and an accurate
TPN/ Enteral nutrition. Salsabil HADIRE Dietitian in Oncology Hematology Center of University Hospital Mohammed VI Marrakech-
 TPN/ Enteral nutrition Salsabil HADIRE Dietitian in Oncology Hematology Center of University Hospital Mohammed VI Marrakech- Work plan Part 1: Total Parenteral Nutrition (TPN) Part 2: Enteral Nutrition
TPN/ Enteral nutrition Salsabil HADIRE Dietitian in Oncology Hematology Center of University Hospital Mohammed VI Marrakech- Work plan Part 1: Total Parenteral Nutrition (TPN) Part 2: Enteral Nutrition
Liver Diseases. An Essential Guide for Nurses and Health Care Professionals
 Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/1047385/ Liver Diseases. An Essential Guide for Nurses and Health Care Professionals Description: Liver disease is a rapidly growing
Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/1047385/ Liver Diseases. An Essential Guide for Nurses and Health Care Professionals Description: Liver disease is a rapidly growing
The Acute Abdomen. Dr. Ed Snyder Dr. Melanie Walker Huntington Memorial Hospital
 The Acute Abdomen Dr. Ed Snyder Dr. Melanie Walker Huntington Memorial Hospital Causes of the Acute Abdomen Hemorrhage in the GI tract Blood vessel GU tract Perforation of the GI tract Ulcer Infection
The Acute Abdomen Dr. Ed Snyder Dr. Melanie Walker Huntington Memorial Hospital Causes of the Acute Abdomen Hemorrhage in the GI tract Blood vessel GU tract Perforation of the GI tract Ulcer Infection
What is the Sleeve Gastrectomy?
 What is the Sleeve Gastrectomy? The Sleeve Gastrectomy (also referred to as the Gastric Sleeve, Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy, Partial Gastrectomy, or Tube Gastrectomy) is a relatively new procedure for
What is the Sleeve Gastrectomy? The Sleeve Gastrectomy (also referred to as the Gastric Sleeve, Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy, Partial Gastrectomy, or Tube Gastrectomy) is a relatively new procedure for
The Whipple Procedure. Sally Hodges, Ph.D.(c) Given the length and difficulty of the procedure, regardless of the diagnosis, certain
 The Whipple Procedure Sally Hodges, Ph.D.(c) Preoperative procedures Given the length and difficulty of the procedure, regardless of the diagnosis, certain assurances must occur prior to offering a patient
The Whipple Procedure Sally Hodges, Ph.D.(c) Preoperative procedures Given the length and difficulty of the procedure, regardless of the diagnosis, certain assurances must occur prior to offering a patient
Understanding. Pancreatic Cancer
 Understanding Pancreatic Cancer Understanding Pancreatic Cancer The Pancreas The pancreas is an organ that is about 6 inches long. It s located deep in your belly between your stomach and backbone. Your
Understanding Pancreatic Cancer Understanding Pancreatic Cancer The Pancreas The pancreas is an organ that is about 6 inches long. It s located deep in your belly between your stomach and backbone. Your
LIVER FUNCTION TESTS
 LIVER FUNCTION TESTS University of PNG School of Medicine and Health Sciences, Division of Basic Medical Sciences, Discipline of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology VJ Temple 1 What are some of the functions
LIVER FUNCTION TESTS University of PNG School of Medicine and Health Sciences, Division of Basic Medical Sciences, Discipline of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology VJ Temple 1 What are some of the functions
Consent for Treatment/Procedure Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy
 Patient's Name: Today's Date: / / The purpose of this document is to confirm, in the presence of witnesses, your informed request to have Surgery for obesity. You are asked to read the following document
Patient's Name: Today's Date: / / The purpose of this document is to confirm, in the presence of witnesses, your informed request to have Surgery for obesity. You are asked to read the following document
CLINICAL CONSEQUENCES OF PORTAL HYPERTENSION
 Página 1 de 10 CLINICAL CONSEQUENCES OF PORTAL HYPERTENSION Part of "11 - PORTAL HYPERTENSION" The portal hypertensive syndrome is responsible for many of the manifestations of advanced, decompensated
Página 1 de 10 CLINICAL CONSEQUENCES OF PORTAL HYPERTENSION Part of "11 - PORTAL HYPERTENSION" The portal hypertensive syndrome is responsible for many of the manifestations of advanced, decompensated
OMG my LFT s! How to Interpret and Use Them. OMG my LFT s! OMG my LFT s!
 How to Interpret and Use Them René Romero, M.D. Clinical Director, Pediatric Hepatology CPG Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Emory University School of Medicine Objectives Understand the anatomy
How to Interpret and Use Them René Romero, M.D. Clinical Director, Pediatric Hepatology CPG Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Emory University School of Medicine Objectives Understand the anatomy
What to do with abnormal LFTs? Andrew M Smith Hepatobiliary Surgeon
 What to do with abnormal LFTs? Andrew M Smith Hepatobiliary Surgeon "it looks like there's something wrong.with your television set. Matt Groenig, creator of The Simpsons Probability of an abnormal screening
What to do with abnormal LFTs? Andrew M Smith Hepatobiliary Surgeon "it looks like there's something wrong.with your television set. Matt Groenig, creator of The Simpsons Probability of an abnormal screening
A Guide for Patients Living with a Biliary Metal Stent
 A Guide for Patients Living with a Biliary Metal Stent What is a biliary metal stent? A biliary metal stent (also known as a bile duct stent ) is a flexible metallic tube specially designed to hold your
A Guide for Patients Living with a Biliary Metal Stent What is a biliary metal stent? A biliary metal stent (also known as a bile duct stent ) is a flexible metallic tube specially designed to hold your
Eating, pooping, and peeing THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Ingested food is not technically in the body until it is absorbed so it needs to be: Mechanically and chemically reduced Transported by the blood to the cells Large portions are not
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Ingested food is not technically in the body until it is absorbed so it needs to be: Mechanically and chemically reduced Transported by the blood to the cells Large portions are not
The Top 20 ICD-10 Documentation Issues That Cause DRG Changes
 7th Annual Association for Clinical Documentation Improvement Specialists Conference The Top 20 ICD-10 Documentation Issues That Cause DRG Changes Donna Smith, RHIA Project Manager, Consulting Services
7th Annual Association for Clinical Documentation Improvement Specialists Conference The Top 20 ICD-10 Documentation Issues That Cause DRG Changes Donna Smith, RHIA Project Manager, Consulting Services
GI TRACT ORGANS ACCESSORY ORGANS
 Digestive System GI TRACT ORGANS Oral cavity Oropharynx Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large Intestine Anus ACCESSORY ORGANS Salivary glands Pancreas Liver Gall bladder GI TRACT LAYERS Mucosa Submucosa
Digestive System GI TRACT ORGANS Oral cavity Oropharynx Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large Intestine Anus ACCESSORY ORGANS Salivary glands Pancreas Liver Gall bladder GI TRACT LAYERS Mucosa Submucosa
Digestion. What we ll cover. Main stages of digestion. Digestion: A Closer Look. A Tour of the Human Digestive System. Mechanical digestion
 Digestion What we ll cover What are the digestive system structures and their functions? Where does carbohydrate, protein and fat digestion and absorption occur? What are the 3 accessory organs of digestion?
Digestion What we ll cover What are the digestive system structures and their functions? Where does carbohydrate, protein and fat digestion and absorption occur? What are the 3 accessory organs of digestion?
Adult CCRN/CCRN E/CCRN K Certification Review Course: Endocrine 12/2015. Endocrine 1. Disclosures. Nothing to disclose
 Adult CCRN/CCRN E/CCRN K Certification Review Course: Carol Rauen RN BC, MS, PCCN, CCRN, CEN Disclosures Nothing to disclose 1 Body Harmony disorders and emergencies Body Harmony (cont) Introduction Disorders
Adult CCRN/CCRN E/CCRN K Certification Review Course: Carol Rauen RN BC, MS, PCCN, CCRN, CEN Disclosures Nothing to disclose 1 Body Harmony disorders and emergencies Body Harmony (cont) Introduction Disorders
Lab 18 The Digestive System
 Lab 18 The Digestive System Laboratory Objectives Identify on a diagram, model or cadaver the parts of the digestive system and accessory organs. Describe the general histology of the digestive system.
Lab 18 The Digestive System Laboratory Objectives Identify on a diagram, model or cadaver the parts of the digestive system and accessory organs. Describe the general histology of the digestive system.
The Digestive System
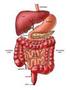 School of Social Work The Digestive System Undergraduate researcher: Nancy D. Bergerson (2010). 1 The Digestive System breaks down and absorbs food. When food is eaten, it is not in a form the body can
School of Social Work The Digestive System Undergraduate researcher: Nancy D. Bergerson (2010). 1 The Digestive System breaks down and absorbs food. When food is eaten, it is not in a form the body can
Acute Abdominal Pain: Other causes
 Acute Abdominal Pain: Other causes Vishal Gupta, MCh Associate Professor Deptt Surg. Gastroenterology KGMU Definition Acute abdominal pain: Presentation of previously undiagnosed abdominal pain Lasting
Acute Abdominal Pain: Other causes Vishal Gupta, MCh Associate Professor Deptt Surg. Gastroenterology KGMU Definition Acute abdominal pain: Presentation of previously undiagnosed abdominal pain Lasting
Types of Bariatric Procedures. Tejal Brahmbhatt, MD General Surgery Teaching Conference April 18, 2012
 Types of Bariatric Procedures Tejal Brahmbhatt, MD General Surgery Teaching Conference April 18, 2012 A Brief History of Bariatric Surgery First seen in pts with short bowel syndrome weight loss First
Types of Bariatric Procedures Tejal Brahmbhatt, MD General Surgery Teaching Conference April 18, 2012 A Brief History of Bariatric Surgery First seen in pts with short bowel syndrome weight loss First
Viral Liver Disease. The Liver and Its Functions
 Viral Liver Disease The Liver and Its Functions The liver, the body's largest organ weighing about three pounds, is located on the right side of the abdomen, protected by the lower rib cage. It is responsible
Viral Liver Disease The Liver and Its Functions The liver, the body's largest organ weighing about three pounds, is located on the right side of the abdomen, protected by the lower rib cage. It is responsible
The Vertebrate (mostly human) Digestive System
 The Vertebrate (mostly human) Digestive System Mouth - mastication, lubrication, digestion Pharynx and Esophagus - swallowing Stomach - some digestion Small intestine - most digestion and absorption Large
The Vertebrate (mostly human) Digestive System Mouth - mastication, lubrication, digestion Pharynx and Esophagus - swallowing Stomach - some digestion Small intestine - most digestion and absorption Large
Cardiovascular diseases. pathology
 Cardiovascular diseases pathology Atherosclerosis Vascular diseases A disease that results in arterial wall thickens as a result of build- up of fatty materials such cholesterol, resulting in acute and
Cardiovascular diseases pathology Atherosclerosis Vascular diseases A disease that results in arterial wall thickens as a result of build- up of fatty materials such cholesterol, resulting in acute and
Whipple Procedure: A guide for patients and families UHN
 Whipple Procedure: A guide for patients and families UHN Please visit the UHN Patient Education website for more health information: www.uhnpatienteducation.ca 2014 University Health Network. All rights
Whipple Procedure: A guide for patients and families UHN Please visit the UHN Patient Education website for more health information: www.uhnpatienteducation.ca 2014 University Health Network. All rights
37 2 Blood and the Lymphatic System Slide 1 of 34
 1 of 34 Blood is a connective tissue that contains both dissolved substances and specialized cells. 2 of 34 The functions of blood include: collecting oxygen from the lungs, nutrients from the digestive
1 of 34 Blood is a connective tissue that contains both dissolved substances and specialized cells. 2 of 34 The functions of blood include: collecting oxygen from the lungs, nutrients from the digestive
Functions of the GI Tract. Chapter 18. Functions of the GI Tract (continued)
 Functions of the GI Tract Chapter 18 The Digestive System Motility: Movement of of food through the GI tract. Ingestion: Taking food into the mouth. Mastication: Chewing the food and mixing it with saliva.
Functions of the GI Tract Chapter 18 The Digestive System Motility: Movement of of food through the GI tract. Ingestion: Taking food into the mouth. Mastication: Chewing the food and mixing it with saliva.
United States Department of Transportation National Highway Traffic Safety Administration Paramedic: National Standard Curriculum 1
 UNIT TERMINAL OBJECTIVE 4-8 At the completion of this unit, the paramedic student will be able to integrate pathophysiologic principles and the assessment findings to formulate a field impression and implement
UNIT TERMINAL OBJECTIVE 4-8 At the completion of this unit, the paramedic student will be able to integrate pathophysiologic principles and the assessment findings to formulate a field impression and implement
The Anorexic Cat For this reason, any cat that stops eating for any reason is considered an emergency situation.
 The Anorexic Cat Introduction Any cat that stops eating (anorexic) or begins to eat much less than their normal amount should be seen by a veterinarian right away. The primary reason why a cat stops eating
The Anorexic Cat Introduction Any cat that stops eating (anorexic) or begins to eat much less than their normal amount should be seen by a veterinarian right away. The primary reason why a cat stops eating
Liver Failure. Nora Aziz. www.3bv.org. Bones, Brains & Blood Vessels
 Liver Failure Nora Aziz www.3bv.org Bones, Brains & Blood Vessels Severe deterioration in liver function Looses ability to regenerate/repair decompensated Liver extensively damaged before it fails Equal
Liver Failure Nora Aziz www.3bv.org Bones, Brains & Blood Vessels Severe deterioration in liver function Looses ability to regenerate/repair decompensated Liver extensively damaged before it fails Equal
Dogs and cats with pancreatitis can have a wide variety of signs, which include, but are not limited to the following:
 Pancreatitis is defined as inflammation of the pancreas and can be caused by a number of inciting factors. The pancreas is responsible for tasks such as glucose regulation and aids in the digestion of
Pancreatitis is defined as inflammation of the pancreas and can be caused by a number of inciting factors. The pancreas is responsible for tasks such as glucose regulation and aids in the digestion of
Patterns of abnormal LFTs and their differential diagnosis
 Patterns of abnormal LFTs and their differential diagnosis Professor Matthew Cramp South West Liver Unit and Peninsula Schools of Medicine and Dentistry, Plymouth Summary liver function / liver function
Patterns of abnormal LFTs and their differential diagnosis Professor Matthew Cramp South West Liver Unit and Peninsula Schools of Medicine and Dentistry, Plymouth Summary liver function / liver function
A.P. Chen, MD Director, Developmental Therapeutics Clinic Division of Cancer Treatment and Diagnosis National Cancer Institute
 A.P. Chen, MD Director, Developmental Therapeutics Clinic Division of Cancer Treatment and Diagnosis National Cancer Institute Click to view Biosketch and Presentation Abstract or page down to review presentation
A.P. Chen, MD Director, Developmental Therapeutics Clinic Division of Cancer Treatment and Diagnosis National Cancer Institute Click to view Biosketch and Presentation Abstract or page down to review presentation
Digestive System AKA. GI System. Overview. GI Process Process Includes. G-I Tract Alimentary Canal
 Digestive System AKA G-I Tract Alimentary Canal Overview GI System Consists of Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, anus About 30 in length Accessory Organs Teeth, tongue,
Digestive System AKA G-I Tract Alimentary Canal Overview GI System Consists of Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, anus About 30 in length Accessory Organs Teeth, tongue,
Topic 4: Digestion and Nutrition
 Topic 4: Digestion and Nutrition THE CONTENTS OF FOOD Food contains nutrients: Nutrients include: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Nutrients must be small enough to enter our cells. If they are too large they must be digested
Topic 4: Digestion and Nutrition THE CONTENTS OF FOOD Food contains nutrients: Nutrients include: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Nutrients must be small enough to enter our cells. If they are too large they must be digested
COMPLICATIONS OF CIRRHOSIS COMPLICATIONS OF CIRRHOSIS OBSERVATIONS OF AN AGING HEPATOLOGIST. Philip C. Delich, M.D.
 1 COMPLICATIONS OF CIRRHOSIS OBSERVATIONS OF AN AGING HEPATOLOGIST COMPLICATIONS OF CIRRHOSIS Philip C. Delich, M.D. Faculty Disclosure Dr. Delich has indicated that he does not have any relevant financial
1 COMPLICATIONS OF CIRRHOSIS OBSERVATIONS OF AN AGING HEPATOLOGIST COMPLICATIONS OF CIRRHOSIS Philip C. Delich, M.D. Faculty Disclosure Dr. Delich has indicated that he does not have any relevant financial
Interpretation of Laboratory Values
 Interpretation of Laboratory Values Konrad J. Dias PT, DPT, CCS Overview Electrolyte imbalances Renal Function Tests Complete Blood Count Coagulation Profile Fluid imbalance Sodium Electrolyte Imbalances
Interpretation of Laboratory Values Konrad J. Dias PT, DPT, CCS Overview Electrolyte imbalances Renal Function Tests Complete Blood Count Coagulation Profile Fluid imbalance Sodium Electrolyte Imbalances
Colocutaneous Fistula. Disclosures
 Colocutaneous Fistula Madhulika G. Varma MD Associate Professor Chief, Colorectal Surgery University of California, San Francisco Honoraria Applied Medical Covidien Disclosures 1 Colocutaneous Fistula
Colocutaneous Fistula Madhulika G. Varma MD Associate Professor Chief, Colorectal Surgery University of California, San Francisco Honoraria Applied Medical Covidien Disclosures 1 Colocutaneous Fistula
SMALL AND LARGE INTESTINE SECRETIONS
 SMALL AND LARGE INTESTINE SECRETIONS Objectives At the end of lecture student should be able to know, Digestive system Digestive system secretions Small intestine Component of small intestine Intestinal
SMALL AND LARGE INTESTINE SECRETIONS Objectives At the end of lecture student should be able to know, Digestive system Digestive system secretions Small intestine Component of small intestine Intestinal
Chapter 48. Nutrients in Food. Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids. Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids, continued
 Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids The three nutrients needed by the body in the greatest amounts are carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Nutrients in Food All of these nutrients are called organic compounds,
Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids The three nutrients needed by the body in the greatest amounts are carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Nutrients in Food All of these nutrients are called organic compounds,
AORTOENTERIC FISTULA. Mark H. Tseng MD Brooklyn VA Hospital February 11, 2005
 AORTOENTERIC FISTULA Mark H. Tseng MD Brooklyn VA Hospital February 11, 2005 AORTOENTERIC FISTULA diagnosis and management Mark H. Tseng MD Brooklyn VA Hospital February 11, 2005 AORTOENTERIC FISTULA Aortoenteric
AORTOENTERIC FISTULA Mark H. Tseng MD Brooklyn VA Hospital February 11, 2005 AORTOENTERIC FISTULA diagnosis and management Mark H. Tseng MD Brooklyn VA Hospital February 11, 2005 AORTOENTERIC FISTULA Aortoenteric
Digestive System Notes
 Digestive System Notes Structure Function Relation Mouth cavity Mechanical digestion by teeth; chemical digestion of starch by saliva. Salivary glands Three pairs of glands which secrete saliva containing
Digestive System Notes Structure Function Relation Mouth cavity Mechanical digestion by teeth; chemical digestion of starch by saliva. Salivary glands Three pairs of glands which secrete saliva containing
Emergencies in Post- Bariatric Surgery Patients
 Emergencies in Post- Patients Disclosures Dr. Birnbaumer has no financial disclosures Diane M. Birnbaumer, M.D., FACEP Professor of Medicine University of California, Los Angeles Senior Clinical Educator
Emergencies in Post- Patients Disclosures Dr. Birnbaumer has no financial disclosures Diane M. Birnbaumer, M.D., FACEP Professor of Medicine University of California, Los Angeles Senior Clinical Educator
Marginal Ulcers. Marginal Ulcers. Gastric Remnant Ulcers. Double Balloon Enteroscopy. Marginal Ulcer. Gastrojejunal Stricture.
 Upper Abdominal Pain in the Bariatric Surgery Patient Martin L. Freeman, M.D., FASGE,FACG Professor of Medicine Director, Pancreaticobiliary Endoscopy Fellowship Interim Director, Division of GI, Hepatology
Upper Abdominal Pain in the Bariatric Surgery Patient Martin L. Freeman, M.D., FASGE,FACG Professor of Medicine Director, Pancreaticobiliary Endoscopy Fellowship Interim Director, Division of GI, Hepatology
Digestive System (continued) Digestive System. Stomach. Peptic Ulcer Disease
 Digestive System Digestive System (continued) Responsible for breaking down food, absorbing nutrients, eliminating wastes Alimentary canal Also known as gastrointestinal tract Reaches from mouth to anus
Digestive System Digestive System (continued) Responsible for breaking down food, absorbing nutrients, eliminating wastes Alimentary canal Also known as gastrointestinal tract Reaches from mouth to anus
Albumin. Prothrombin time. Total protein
 Hepatitis C Fact Sheet February 2016 www.hepatitis.va.gov Laboratory Tests and Hepatitis If you have hepatitis C, your doctor will use laboratory tests to about learn more about your individual hepatitis
Hepatitis C Fact Sheet February 2016 www.hepatitis.va.gov Laboratory Tests and Hepatitis If you have hepatitis C, your doctor will use laboratory tests to about learn more about your individual hepatitis
ABThera Open Abdomen Negative Pressure Therapy for Active Abdominal Therapy. Case Series
 ABThera Open Abdomen Negative Pressure Therapy for Active Abdominal Therapy Case Series Summary of Cases: USER EXPERIENCE The ABThera OA NPT system was found by surgeons to be a convenient and effective
ABThera Open Abdomen Negative Pressure Therapy for Active Abdominal Therapy Case Series Summary of Cases: USER EXPERIENCE The ABThera OA NPT system was found by surgeons to be a convenient and effective
Preoperative Laboratory and Diagnostic Studies
 Preoperative Laboratory and Diagnostic Studies Preoperative Labratorey and Diagnostic Studies The concept of standardized testing in all presurgical patients regardless of age or medical condition is no
Preoperative Laboratory and Diagnostic Studies Preoperative Labratorey and Diagnostic Studies The concept of standardized testing in all presurgical patients regardless of age or medical condition is no
TOTAL PARENTERAL NUTRITION (TPN) Revised January 2013
 TOTAL PARENTERAL NUTRITION (TPN) Revised January 2013 OBJECTIVES Definition Indications for TPN administration Composition of TPN solutions Access routes for TPN administration Monitoring TPN administration
TOTAL PARENTERAL NUTRITION (TPN) Revised January 2013 OBJECTIVES Definition Indications for TPN administration Composition of TPN solutions Access routes for TPN administration Monitoring TPN administration
EXECUTIVE BLOOD WORK PANEL
 EXECUTIVE BLOOD WORK PANEL Below is a list of all blood and urine testing done on the day of your Executive Medical. MALE Serum Glucose Random Serum Glucose Fasting Creatinine Uric Acid Sodium Potassium
EXECUTIVE BLOOD WORK PANEL Below is a list of all blood and urine testing done on the day of your Executive Medical. MALE Serum Glucose Random Serum Glucose Fasting Creatinine Uric Acid Sodium Potassium
HEPATOLOGY CLERKSHIP
 College of Osteopathic Medicine HEPATOLOGY CLERKSHIP Office for Clinical Affairs 515-271-1629 FAX 515-271-1727 Elective Rotation General Description This elective rotation is a four (4) week introductory,
College of Osteopathic Medicine HEPATOLOGY CLERKSHIP Office for Clinical Affairs 515-271-1629 FAX 515-271-1727 Elective Rotation General Description This elective rotation is a four (4) week introductory,
Digestion, Absorption. How & where?
 Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
Liver Function Essay
 Liver Function Essay Name: Quindoline Ntui Date: April 20, 2009 Professor: Dr. Danil Hammoudi Class: Anatomy and Physiology 2 Liver function The human body consist of many highly organize part working
Liver Function Essay Name: Quindoline Ntui Date: April 20, 2009 Professor: Dr. Danil Hammoudi Class: Anatomy and Physiology 2 Liver function The human body consist of many highly organize part working
COMPLICATIONS OF CIRRHOSIS: CASES. Anil Seetharam, MD [email protected]
 COMPLICATIONS OF CIRRHOSIS: CASES Anil Seetharam, MD [email protected] Defining Cirrhosis Histological diagnosis Nodules of regenerating hepatocytes surrounded by fibrous tissue Common final
COMPLICATIONS OF CIRRHOSIS: CASES Anil Seetharam, MD [email protected] Defining Cirrhosis Histological diagnosis Nodules of regenerating hepatocytes surrounded by fibrous tissue Common final
Digestion, Absorption. How & where?
 Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones. Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke
 Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke Nephrology vs. Urology Nephrologist a physician who has been trained in the diagnosis
Open the Flood Gates Urinary Obstruction and Kidney Stones Dr. Jeffrey Rosenberg Dr. Emilio Lastarria Dr. Richard Kasulke Nephrology vs. Urology Nephrologist a physician who has been trained in the diagnosis
CIRRHOSIS REFERRAL & MANAGEMENT GUIDELINES for the Southern Adelaide Local Health Network (SALHN)
 CIRRHOSIS REFERRAL & MANAGEMENT GUIDELINES for the Southern Adelaide Local Health Network (SALHN) Cirrhosis is severe scarring of the liver and can be diagnosed with ultrasound or CT or with clinical signs
CIRRHOSIS REFERRAL & MANAGEMENT GUIDELINES for the Southern Adelaide Local Health Network (SALHN) Cirrhosis is severe scarring of the liver and can be diagnosed with ultrasound or CT or with clinical signs
Complications of Cirrhosis
 Complications of Cirrhosis What is Cirrhosis? Paul J. Gaglio, MD Center for Liver Disease and Transplantation Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons NAFLD 1 Decreased clearance of Estrogen
Complications of Cirrhosis What is Cirrhosis? Paul J. Gaglio, MD Center for Liver Disease and Transplantation Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons NAFLD 1 Decreased clearance of Estrogen
