June 11, 2015 Tim Halterman
|
|
|
- Vanessa Cummings
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 June 11, 2015 Tim Halterman
2 Defini&on Histologic change + loss of liver function Derives from Greek word kirrhos meaning yellow, tawny First named by Rene Laennec in 1819 Laennec s cirrhosis=alcoholic cirrhosis
3 Histologic changes
4 Other clues to diagnosis Physical exam stigmata Lab data Typical transaminase pattern Liver function tests Platelets Imaging studies Nodular liver, enlarged caudate lobe, enlarged portal vein, splenomegaly Ultrasound: sensitivity 30-89%, specificity % CT and MRI
5 Portal Hypertension Definition Hepatic venous pressure gradient (HVPG) >8
6 Portal Hypertension Causes Pre- hepatic (pre- sinusoidal) Intra- hepatic (sinusoidal) Post- hepatic (post- sinusoidal)
7 Complica&ons of Cirrhosis Varices (esophageal and gastric), portal hypertensive gastropathy Any melena, hematochezia, hematemesis? Ascites Any abdominal or leg swelling or significant weight gain? Hepatic encephalopathy Any confusion or difficulty thinking, trouble sleeping? Hepatocellular carcinoma
8 Esophageal Varices Rationale for screening Screening recommendations All patients with cirrhosis should undergo EGD Surveillance of esophageal varices Compensated cirrhosis and no varices on initial EGD Repeat EGD 2-3 years Decompensated cirrhosis Repeat EGD yearly unless already on prophylaxis Repeat EGD at first sign of decompensation
9 Esophageal varices Grading of varices: small versus large
10 Esophageal Varices Primary prophylaxis Small varices without red wale sign: no prophylaxis Small varices with red wale sign or Childs class B/C cirrhosis: endoscopic variceal ligation (EVL), nonselective beta- blocker Large varices: endoscopic variceal ligation (EVL) or non- selective beta- blocker Beta- blocker versus EVL
11 Esophageal varices Management of bleeding varices General measures: IV access, airway issues, resuscitation goals, antibiotics Pharmacologic therapy: octreotide Endoscopic therapy: EVL versus sclerotherapy Combination therapy: EVL + octreotide BEST strategy Recurrent bleeding: TIPS, Minnesota tube
12 Esophageal Varices Secondary prophylaxis Recurrent EVL + nonselective beta- blocker PPI twice daily to prevent post- banding ulcers
13 Gastric Varices Primary prophylaxis Nonselective beta- blockers Management of acute bleeding Cyanoacrylate injection versus TIPS EVL for GOV1 varices
14 Ascites Most common complication of cirrhosis 15% of pts with ascites die within one year, 45% within 5 years Causes Cirrhosis- 85% Liver related without cirrhosis: acute alcoholic hepatitis, Budd- Chiari, acute liver failure Other: cardiac, nephrotic syndrome, malignant, TB, pancreatitis, chylous
15 Ascites Paracentesis should be performed in any patient with new onset ascites, either inpatient or outpatient Paracentesis should be performed on any inpatient with symptoms suggestive of SBP, worsened renal function, encephalopathy, hypotension, hypothermia or acidosis
16 Ascites Routine peritoneal fluid tests Serum albumin ascites gradient Cell count and diff Albumin and total protein Specialized peritoneal fluid tests Cytology Amylase Triglycerides AFB bilirubin
17 Ascites Treatment Low sodium diet <2 grams per day Diuretics Spironolactone alone Spironolactone + furosemide Ratio of 100 mg spironolactone & 40 mg furosemide daily Max dose of 400 mg spironolactone & 160 mg furosemide Fluid restrict only if Na less than 125
18 Refractory ascites Management Large volume paracentesis If remove >5L, recommend albumin infusion TIPS Liver transplant Avoidance of non- selective beta- blockers, ACE/ARB, NSAIDs Midodrine
19 SBP Diagnosis 250 PMNs/mm 3 Culture negative v culture positive Treatment Third generation cephalosporin (preferably cefotaxime) for 5 days Oral ciprofloxacin for 7 days Albumin: 1.5 mg/kg day 1 and 1 mg/kg day 3 Conditions that require more broad- spectrum abx
20 SBP Prophylaxis Who benefits? History of SBP Low protein ascites (protein <1.5) + Cr >1.2 or bili >3 or Na <130 What to use? Norfloxacin 400 mg daily or cipro 500 mg daily Bactrim DS daily Cipro 750 mg weekly- not as effective PPIs and SBP
21 Hepatorenal Syndrome Diagnosis cirrhosis with ascites serum creatinine greater than 1.5 mg/dl no improvement of serum creatinine (decrease to a level of 1.5 mg/dl or less) after at least two days with diuretic withdrawal and volume expansion with albumin absence of shock no current or recent treatment with nephrotoxic drugs absence of parenchymal kidney disease Urinary neutrophil gelatinase- associated lipocalin
22 Hepatorenal Syndrome Treatment Albumin + midodrine/octreotide Albumin + norepinephrine (ICU patients) Liver transplant
23 Hepa&c encephalopathy West Haven grading criteria (Overt) Grade 1 - Trivial lack of awareness; euphoria or anxiety; shortened attention span; impaired performance of addition or subtraction Grade 2 - Lethargy or apathy; minimal disorientation for time or place; subtle personality change; inappropriate behaviour Grade 3 - Somnolence to semistupor, but responsive to verbal stimuli; confusion; gross disorientation Grade 4 - Coma (unresponsive to verbal or noxious stimuli) Minimal hepatic encephalopathy and covert HE
24 Hepa&c encephalopathy Altered sleep- wake cycle Physical Exam findings: asterixis, hyperreflexia Ammonia levels Remember to think about precipitants
25 Hepa&c encephalopathy Management Lactulose Titrate to 3 loose BMs per day Nonabsorbable antibiotics Xifaxin 550 mg twice daily- typically add on therapy Neomycin Metronidazole Others: zinc, BCAA, acarbose,?probiotics No benefit to protein restriction
26 Hepatocellular carcinoma Screening Good quality US every 6 months AFP not recommended by AASLD but supported by many experts CT/MRI not cost effective Who to screen? Anyone with cirrhosis Chronic hepatitis B- Asian M >40, Asian F >50, FHx, Africans >25 Uncertain benefit: HCV stage 3 fibrosis, NAFLD
27 Hepatocellular carcinoma Screening recommendations
28 AASLD Guidelines
Evaluation and Prognosis of Patients with Cirrhosis
 Evaluation and Prognosis of Patients with Cirrhosis Marion G. Peters, MD John V. Carbone, MD, Endowed Chair Professor of Medicine Chief of Hepatology Research University of California San Francisco Recorded
Evaluation and Prognosis of Patients with Cirrhosis Marion G. Peters, MD John V. Carbone, MD, Endowed Chair Professor of Medicine Chief of Hepatology Research University of California San Francisco Recorded
End Stage Liver Disease: What is New? Marion Peters MD UCSF Berlin 2012
 End Stage Liver Disease: What is New? Marion Peters MD UCSF Berlin 2012 Natural History of ESLD Increasing liver fibrosis Development of HCC Chronic liver disease Compensated cirrhosis Decompensated cirrhosis
End Stage Liver Disease: What is New? Marion Peters MD UCSF Berlin 2012 Natural History of ESLD Increasing liver fibrosis Development of HCC Chronic liver disease Compensated cirrhosis Decompensated cirrhosis
COMPLICATIONS OF CIRRHOSIS COMPLICATIONS OF CIRRHOSIS OBSERVATIONS OF AN AGING HEPATOLOGIST. Philip C. Delich, M.D.
 1 COMPLICATIONS OF CIRRHOSIS OBSERVATIONS OF AN AGING HEPATOLOGIST COMPLICATIONS OF CIRRHOSIS Philip C. Delich, M.D. Faculty Disclosure Dr. Delich has indicated that he does not have any relevant financial
1 COMPLICATIONS OF CIRRHOSIS OBSERVATIONS OF AN AGING HEPATOLOGIST COMPLICATIONS OF CIRRHOSIS Philip C. Delich, M.D. Faculty Disclosure Dr. Delich has indicated that he does not have any relevant financial
MANAGEMENT OF LIVER CIRRHOSIS
 MANAGEMENT OF LIVER CIRRHOSIS Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What is cirrhosis? Cirrhosis is a result of long-term, continuous damage to the liver and may be due to many different
MANAGEMENT OF LIVER CIRRHOSIS Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What is cirrhosis? Cirrhosis is a result of long-term, continuous damage to the liver and may be due to many different
Liver Failure. Nora Aziz. www.3bv.org. Bones, Brains & Blood Vessels
 Liver Failure Nora Aziz www.3bv.org Bones, Brains & Blood Vessels Severe deterioration in liver function Looses ability to regenerate/repair decompensated Liver extensively damaged before it fails Equal
Liver Failure Nora Aziz www.3bv.org Bones, Brains & Blood Vessels Severe deterioration in liver function Looses ability to regenerate/repair decompensated Liver extensively damaged before it fails Equal
COMPLICATIONS OF CIRRHOSIS: CASES. Anil Seetharam, MD [email protected]
 COMPLICATIONS OF CIRRHOSIS: CASES Anil Seetharam, MD [email protected] Defining Cirrhosis Histological diagnosis Nodules of regenerating hepatocytes surrounded by fibrous tissue Common final
COMPLICATIONS OF CIRRHOSIS: CASES Anil Seetharam, MD [email protected] Defining Cirrhosis Histological diagnosis Nodules of regenerating hepatocytes surrounded by fibrous tissue Common final
Complications of Cirrhosis
 Complications of Cirrhosis What is Cirrhosis? Paul J. Gaglio, MD Center for Liver Disease and Transplantation Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons NAFLD 1 Decreased clearance of Estrogen
Complications of Cirrhosis What is Cirrhosis? Paul J. Gaglio, MD Center for Liver Disease and Transplantation Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons NAFLD 1 Decreased clearance of Estrogen
Complications of Chronic Liver Disease
 Complications of Chronic Liver Disease By Rima A. Mohammad, Pharm.D., BCPS Reviewed by Paulina Deming, Pharm.D.; Marisel Segarra-Newnham, Pharm.D., MPH, FCCP, BCPS; and Kelly S. Bobo, Pharm.D., BCPS Learning
Complications of Chronic Liver Disease By Rima A. Mohammad, Pharm.D., BCPS Reviewed by Paulina Deming, Pharm.D.; Marisel Segarra-Newnham, Pharm.D., MPH, FCCP, BCPS; and Kelly S. Bobo, Pharm.D., BCPS Learning
Presented by: Jean Yoo-Campbell, Matthew Konerman, Monica Konerman, Jean Yoo Campbell, Christian Gocke, Eunpi Cho Donald Lynch
 Bass N.M., et. al. N Engl J Med 2010; 362:1071-1081 Presented by: Jean Yoo-Campbell, Matthew Konerman, Monica Konerman, Jean Yoo Campbell, Christian Gocke, Eunpi Cho Donald Lynch Faculty Advisor: Dr. Fred
Bass N.M., et. al. N Engl J Med 2010; 362:1071-1081 Presented by: Jean Yoo-Campbell, Matthew Konerman, Monica Konerman, Jean Yoo Campbell, Christian Gocke, Eunpi Cho Donald Lynch Faculty Advisor: Dr. Fred
A CASE OF LIVER CIRRHOSIS & HEPATIC ENCEPHALOPATHY
 A CASE OF LIVER CIRRHOSIS & HEPATIC ENCEPHALOPATHY 2 1 Mr N.N. 56 yr old male. Admitted on 22/03/02. 1 month Hx of abdominal distention, confusion, inability to concentrate and dyspnoea Grade 111. Pmx:
A CASE OF LIVER CIRRHOSIS & HEPATIC ENCEPHALOPATHY 2 1 Mr N.N. 56 yr old male. Admitted on 22/03/02. 1 month Hx of abdominal distention, confusion, inability to concentrate and dyspnoea Grade 111. Pmx:
Oral Zinc Supplementation as an Adjunct Therapy in the Management of Hepatic Encephalopathy: A Randomized Controlled Trial
 Oral Zinc Supplementation as an Adjunct Therapy in the Management of Hepatic Encephalopathy: A Randomized Controlled Trial Marcus R. Pereira A. Study Purpose Hepatic encephalopathy is a common complication
Oral Zinc Supplementation as an Adjunct Therapy in the Management of Hepatic Encephalopathy: A Randomized Controlled Trial Marcus R. Pereira A. Study Purpose Hepatic encephalopathy is a common complication
CCHCS Care Guide: End Stage Liver Disease
 GOAL DIAGNOSE CIRRHOSIS EARLY DETERMINE COMPLICATIONS, IF PRESENT DELAY DECOMPENSATION ALERTS ABDOMINAL PAIN [CONSIDER SPONTANEOUS BACTERIAL PERITONITIS (SBP)] MENTAL STATUS CHANGES/COMA HEMATEMESIS/MELENA
GOAL DIAGNOSE CIRRHOSIS EARLY DETERMINE COMPLICATIONS, IF PRESENT DELAY DECOMPENSATION ALERTS ABDOMINAL PAIN [CONSIDER SPONTANEOUS BACTERIAL PERITONITIS (SBP)] MENTAL STATUS CHANGES/COMA HEMATEMESIS/MELENA
After the Cure: Long-Term Management of HCV Liver Disease Norah A. Terrault, MD, MPH
 After the Cure: Long-Term Management of HCV Liver Disease Norah A. Terrault, MD, MPH Professor of Medicine Department of Gastroenterology Director, Viral Hepatitis Center University of California San Francisco
After the Cure: Long-Term Management of HCV Liver Disease Norah A. Terrault, MD, MPH Professor of Medicine Department of Gastroenterology Director, Viral Hepatitis Center University of California San Francisco
{ Rifaximin versus Nonabsorbable Disaccharides for the Treatment of Hepatic Encephalopathy: A Meta Analysis}
 { Rifaximin versus Nonabsorbable Disaccharides for the Treatment of Hepatic Encephalopathy: A Meta Analysis} {Dong Wu, Shu-Mei Wu, Jie Lu, Ying-Qun Zhou, Ling Xu, and Chuan-Yong Guo} Noor Al-Hakami, Pharm
{ Rifaximin versus Nonabsorbable Disaccharides for the Treatment of Hepatic Encephalopathy: A Meta Analysis} {Dong Wu, Shu-Mei Wu, Jie Lu, Ying-Qun Zhou, Ling Xu, and Chuan-Yong Guo} Noor Al-Hakami, Pharm
Perspective End-Stage Liver Disease in HIV Disease
 Perspective End-Stage Liver Disease in HIV Disease Liver disease is the most common non AIDS-related cause of mortality in HIV-infected patients. HIV-infected patients with chronic liver disease progress
Perspective End-Stage Liver Disease in HIV Disease Liver disease is the most common non AIDS-related cause of mortality in HIV-infected patients. HIV-infected patients with chronic liver disease progress
A 55 year old man with cirrhosis due to chronic hepatitis C (CHC) genotype 3a is referred for liver transplantation.
 A 55 year old man with cirrhosis due to chronic hepatitis C (CHC) genotype 3a is referred for liver transplantation. Three years ago he was treated with 24 weeks of peginterferon alfa-2a (180 µg/wk, PEGIFN)
A 55 year old man with cirrhosis due to chronic hepatitis C (CHC) genotype 3a is referred for liver transplantation. Three years ago he was treated with 24 weeks of peginterferon alfa-2a (180 µg/wk, PEGIFN)
REVIEW CLINICAL REVIEWS
 1802 CLINICAL S nature publishing group Management and Treatment of Patients With Cirrhosis and Portal Hypertension: Recommendations From the Department of Veterans Affairs Hepatitis C Resource Center
1802 CLINICAL S nature publishing group Management and Treatment of Patients With Cirrhosis and Portal Hypertension: Recommendations From the Department of Veterans Affairs Hepatitis C Resource Center
1802 CLINICAL REVIEWS
 1802 CLINICAL S nature publishing group Management and Treatment of Patients With Cirrhosis and Portal Hypertension: Recommendations From the Department of Veterans Affairs Hepatitis C Resource Center
1802 CLINICAL S nature publishing group Management and Treatment of Patients With Cirrhosis and Portal Hypertension: Recommendations From the Department of Veterans Affairs Hepatitis C Resource Center
rifaximin 550mg film-coated tablets (Targaxan ) SMC No. (893/13) Norgine Pharmaceuticals Ltd
 rifaximin 550mg film-coated tablets (Targaxan ) SMC No. (893/13) Norgine Pharmaceuticals Ltd 09 August 2013 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the above product and
rifaximin 550mg film-coated tablets (Targaxan ) SMC No. (893/13) Norgine Pharmaceuticals Ltd 09 August 2013 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the above product and
Hepatic Encephalopathy, Hyperammonemia, and Current Treatment in ICU Room
 Hepatic Encephalopathy, Hyperammonemia, and Current Treatment in ICU Room Assoc.Prof. Chan Sovandy Chairman by : Prof.So Saphy and Assoc Prof, Kim chhoung Hepatic Encephalopathy Hepatic (portal systemic
Hepatic Encephalopathy, Hyperammonemia, and Current Treatment in ICU Room Assoc.Prof. Chan Sovandy Chairman by : Prof.So Saphy and Assoc Prof, Kim chhoung Hepatic Encephalopathy Hepatic (portal systemic
Diabetic Nephropathy
 Diabetic Nephropathy Kidney disease is common in people affected by diabetes mellitus Definition Urinary albumin excretion of more than 300mg in a 24 hour collection or macroalbuminuria Abnormal renal
Diabetic Nephropathy Kidney disease is common in people affected by diabetes mellitus Definition Urinary albumin excretion of more than 300mg in a 24 hour collection or macroalbuminuria Abnormal renal
AASLD PRACTICE GUIDELINES Prevention and Management of Gastroesophageal Varices and Variceal Hemorrhage in Cirrhosis
 AASLD PRACTICE GUIDELINES Prevention and Management of Gastroesophageal Varices and Variceal Hemorrhage in Cirrhosis Guadalupe Garcia-Tsao, 1 Arun J. Sanyal, 2 Norman D. Grace, 3 William Carey, 4 and the
AASLD PRACTICE GUIDELINES Prevention and Management of Gastroesophageal Varices and Variceal Hemorrhage in Cirrhosis Guadalupe Garcia-Tsao, 1 Arun J. Sanyal, 2 Norman D. Grace, 3 William Carey, 4 and the
LIVER FUNCTION TESTS AND STATINS
 LIVER FUNCTION TESTS AND STATINS Philippe J. Zamor and Mark W. Russo Current Opinion in Cardiology 2011,26:338 341 SUMMARY Purpose of review: To discuss recent data on statins in patients with elevated
LIVER FUNCTION TESTS AND STATINS Philippe J. Zamor and Mark W. Russo Current Opinion in Cardiology 2011,26:338 341 SUMMARY Purpose of review: To discuss recent data on statins in patients with elevated
CIRRHOSIS REFERRAL & MANAGEMENT GUIDELINES for the Southern Adelaide Local Health Network (SALHN)
 CIRRHOSIS REFERRAL & MANAGEMENT GUIDELINES for the Southern Adelaide Local Health Network (SALHN) Cirrhosis is severe scarring of the liver and can be diagnosed with ultrasound or CT or with clinical signs
CIRRHOSIS REFERRAL & MANAGEMENT GUIDELINES for the Southern Adelaide Local Health Network (SALHN) Cirrhosis is severe scarring of the liver and can be diagnosed with ultrasound or CT or with clinical signs
Nurse Practitioner Outcomes: The Integration & Future Directions of The Liver Transplant NP. Amanda Tinning MN NP October 13, 2011
 Nurse Practitioner Outcomes: The Integration & Future Directions of The Liver Transplant NP Amanda Tinning MN NP October 13, 2011 Overview Define clinical outcomes Discuss the contributions of the NP role
Nurse Practitioner Outcomes: The Integration & Future Directions of The Liver Transplant NP Amanda Tinning MN NP October 13, 2011 Overview Define clinical outcomes Discuss the contributions of the NP role
The most serious symptoms of this stage are:
 The Natural Progression of Hepatitis C The natural history of hepatitis C looks at the likely outcomes for people infected with the virus if there is no medical intervention. However, the process of trying
The Natural Progression of Hepatitis C The natural history of hepatitis C looks at the likely outcomes for people infected with the virus if there is no medical intervention. However, the process of trying
Surveillance for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
 Surveillance for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Marion G. Peters, MD John V. Carbone, MD, Endowed Chair Professor of Medicine Chief of Hepatology Research University of California San Francisco Recorded on April
Surveillance for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Marion G. Peters, MD John V. Carbone, MD, Endowed Chair Professor of Medicine Chief of Hepatology Research University of California San Francisco Recorded on April
CLINICAL CONSEQUENCES OF PORTAL HYPERTENSION
 Página 1 de 10 CLINICAL CONSEQUENCES OF PORTAL HYPERTENSION Part of "11 - PORTAL HYPERTENSION" The portal hypertensive syndrome is responsible for many of the manifestations of advanced, decompensated
Página 1 de 10 CLINICAL CONSEQUENCES OF PORTAL HYPERTENSION Part of "11 - PORTAL HYPERTENSION" The portal hypertensive syndrome is responsible for many of the manifestations of advanced, decompensated
Diabetic nephropathy is detected clinically by the presence of persistent microalbuminuria or proteinuria.
 Kidney Complications Diabetic Nephropathy Diabetic nephropathy is detected clinically by the presence of persistent microalbuminuria or proteinuria. The peak incidence of nephropathy is usually 15-25 years
Kidney Complications Diabetic Nephropathy Diabetic nephropathy is detected clinically by the presence of persistent microalbuminuria or proteinuria. The peak incidence of nephropathy is usually 15-25 years
Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)
 Abhishek Vadalia Introduction Chemoembolization is being used with increasing frequency in the treatment of solid hepatic tumors such as Hepatocellular Carinoma (HCC) & rare Cholangiocellular Carcinoma
Abhishek Vadalia Introduction Chemoembolization is being used with increasing frequency in the treatment of solid hepatic tumors such as Hepatocellular Carinoma (HCC) & rare Cholangiocellular Carcinoma
Study of Effects of Probiotic Lactobacilli in Preventing Major Complications in Patients of Liver Cirrhosis
 Research Article Study of Effects of Probiotic Lactobacilli in Preventing Major Complications in Patients of Liver Cirrhosis RR. Pawar*, ML. Pardeshi and BB. Ghongane Department of Pharmacology, B.J. Medical
Research Article Study of Effects of Probiotic Lactobacilli in Preventing Major Complications in Patients of Liver Cirrhosis RR. Pawar*, ML. Pardeshi and BB. Ghongane Department of Pharmacology, B.J. Medical
Date of preparation: March 2015. GL/XIF/0214/0011a(1)
 Date of preparation: March 2015. GL/XIF/0214/0011a(1) 1 This educational programme is funded by a grant from Norgine. Norgine has no involvement in the development of the content, which is developed independently
Date of preparation: March 2015. GL/XIF/0214/0011a(1) 1 This educational programme is funded by a grant from Norgine. Norgine has no involvement in the development of the content, which is developed independently
Cirrhosis and HCV. Jonathan Israel M.D.
 Cirrhosis and HCV Jonathan Israel M.D. Outline Relationship of fibrosis and cirrhosisprevalence and epidemiology. Sequelae of cirrhosis Diagnosis of cirrhosis Effect of cirrhosis on efficacy of treatment
Cirrhosis and HCV Jonathan Israel M.D. Outline Relationship of fibrosis and cirrhosisprevalence and epidemiology. Sequelae of cirrhosis Diagnosis of cirrhosis Effect of cirrhosis on efficacy of treatment
Cirrhosis: Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention
 : Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention S. PAUL STARR, MD, and DANIEL RAINES, MD, Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center School of Medicine at New Orleans, New Orleans, Louisiana Cirrhosis is
: Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention S. PAUL STARR, MD, and DANIEL RAINES, MD, Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center School of Medicine at New Orleans, New Orleans, Louisiana Cirrhosis is
GI Bleeding. Thomas S.Foster,Pharm.D. PHR 961 Integrated Therapeutics
 GI Bleeding Thomas S.Foster,Pharm.D. PHR 961 Integrated Therapeutics Overview Because GI bleeding is internal, it is possible for a person to have GI bleeding without symptoms. Important to recognize
GI Bleeding Thomas S.Foster,Pharm.D. PHR 961 Integrated Therapeutics Overview Because GI bleeding is internal, it is possible for a person to have GI bleeding without symptoms. Important to recognize
NUTRITION IN LIVER DISEASES
 NUTRITION IN LIVER DISEASES 1. HEPATITIS: Definition: - Viral inflammation of liver cells. Types: a. HAV& HEV, transmitted by fecal-oral route. b. HBV & HCV, transmitted by blood and body fluids. c. HDV
NUTRITION IN LIVER DISEASES 1. HEPATITIS: Definition: - Viral inflammation of liver cells. Types: a. HAV& HEV, transmitted by fecal-oral route. b. HBV & HCV, transmitted by blood and body fluids. c. HDV
Management of Chronic Liver Disease. Dr Melissa Haines Gastroenterologist Waikato Hospital
 Management of Chronic Liver Disease Dr Melissa Haines Gastroenterologist Waikato Hospital Outline Recognising and diagnosing the patient with chronic liver disease Causes of chronic liver disease in NZ
Management of Chronic Liver Disease Dr Melissa Haines Gastroenterologist Waikato Hospital Outline Recognising and diagnosing the patient with chronic liver disease Causes of chronic liver disease in NZ
HCV/HIVCo-infection A case study by. Dominic Côté, Nurse Clinician B.Sc Chronic Viral Illness Services McGill University Health Centre
 HCV/HIVCo-infection A case study by Dominic Côté, Nurse Clinician B.Sc Chronic Viral Illness Services McGill University Health Centre Objectives By sharing a case study of a patient co-infected with HIV/HCV
HCV/HIVCo-infection A case study by Dominic Côté, Nurse Clinician B.Sc Chronic Viral Illness Services McGill University Health Centre Objectives By sharing a case study of a patient co-infected with HIV/HCV
Recanalized Umbilical Vein in the Presence of Cirrhosis-Induced Portal Hypertension
 Recanalized Umbilical Vein in the Presence of Cirrhosis-Induced Portal Hypertension Audrey Galey RDMS, RVT, Mary Grace Renfro RDSM, RVT, Lindsey Simon, RVT March 22, 2013 2 Abstract A recanalized umbilical
Recanalized Umbilical Vein in the Presence of Cirrhosis-Induced Portal Hypertension Audrey Galey RDMS, RVT, Mary Grace Renfro RDSM, RVT, Lindsey Simon, RVT March 22, 2013 2 Abstract A recanalized umbilical
Screening for Varices and Prevention of Bleeding
 Hepatitis C Online PDF created August 24, 2016, 3:30 am Screening for Varices and Prevention of Bleeding Module 3: Lesson 3: Contents: Management of Cirrhosis-Related Complications Screening for Varices
Hepatitis C Online PDF created August 24, 2016, 3:30 am Screening for Varices and Prevention of Bleeding Module 3: Lesson 3: Contents: Management of Cirrhosis-Related Complications Screening for Varices
Managing LFT s in General Practice
 Managing LFT s in General Practice Sulleman Moreea FRCP(Edin Edin) ) FRCS(Glasg Glasg) Consultant Gastroenterologist/Hepatologist Bradford Hospitals Trust The normal liver Managing LFT s History and examination
Managing LFT s in General Practice Sulleman Moreea FRCP(Edin Edin) ) FRCS(Glasg Glasg) Consultant Gastroenterologist/Hepatologist Bradford Hospitals Trust The normal liver Managing LFT s History and examination
GI Bleed. Steven Lichtenstein, D.O. Chief, Division of Gastroenterology Mercy Health System. Director, Endoscopy/GI Lab Mercy Fitzgerald Hospital
 October 3, 2015 GI Bleed Steven Lichtenstein, D.O. Chief, Division of Gastroenterology Mercy Health System Director, Endoscopy/GI Lab Mercy Fitzgerald Hospital Clinical Associate Professor of Medicine
October 3, 2015 GI Bleed Steven Lichtenstein, D.O. Chief, Division of Gastroenterology Mercy Health System Director, Endoscopy/GI Lab Mercy Fitzgerald Hospital Clinical Associate Professor of Medicine
The State of the Liver in the Adult Patient after Fontan Palliation
 The State of the Liver in the Adult Patient after Fontan Palliation Fred Wu, M.D. Boston Adult Congenital Heart Service Boston Children s Hospital/Brigham & Women s Hospital 7 th National Adult Congenital
The State of the Liver in the Adult Patient after Fontan Palliation Fred Wu, M.D. Boston Adult Congenital Heart Service Boston Children s Hospital/Brigham & Women s Hospital 7 th National Adult Congenital
NP/PA Clinical Hepatology Fellowship Summary of Year-Long Curriculum
 OVERVIEW OF THE FELLOWSHIP The goal of the AASLD NP/PA Fellowship is to provide a 1-year postgraduate hepatology training program for nurse practitioners and physician assistants in a clinical outpatient
OVERVIEW OF THE FELLOWSHIP The goal of the AASLD NP/PA Fellowship is to provide a 1-year postgraduate hepatology training program for nurse practitioners and physician assistants in a clinical outpatient
To give you a brief outline of this CME session I'm going to touch upon a little bit upon
 KAPIL CHOPRA, MD, DM, FACP, FASSSLD, AGAF 1 Today we are going to talk about an important topic in chronic liver disease, cirrhosis of the liver. This CME activity is titled Infection Challenges in the
KAPIL CHOPRA, MD, DM, FACP, FASSSLD, AGAF 1 Today we are going to talk about an important topic in chronic liver disease, cirrhosis of the liver. This CME activity is titled Infection Challenges in the
PRIOR AUTHORIZATION PROTOCOL FOR HEPATITIS C TREATMENT
 PRIOR AUTHORIZATION PROTOCOL FOR HEPATITIS C TREATMENT HARVONI (90mg ledipasvir/400mg sofosbuvir): tablet (PREFERRED AGENT) SOVALDI (sofosbuvir ): 400mg tablets (PREFERRED AGENT ) OLYSIO (simeprivir) PEG-INTRON
PRIOR AUTHORIZATION PROTOCOL FOR HEPATITIS C TREATMENT HARVONI (90mg ledipasvir/400mg sofosbuvir): tablet (PREFERRED AGENT) SOVALDI (sofosbuvir ): 400mg tablets (PREFERRED AGENT ) OLYSIO (simeprivir) PEG-INTRON
The Liver and Alpha-1. Antitrypsin Deficiency (Alpha-1) 1 ALPHA-1 FOUNDATION
 The Liver and Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency (Alpha-1) 1 ALPHA-1 FOUNDATION What Is Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency? Alpha-1 is a condition that may result in serious lung disease in adults and/or liver
The Liver and Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency (Alpha-1) 1 ALPHA-1 FOUNDATION What Is Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency? Alpha-1 is a condition that may result in serious lung disease in adults and/or liver
Management of Adult Patients with Ascites Due to Cirrhosis: Update 2012
 PRACTICE Management of Adult Patients with Ascites Due to Cirrhosis: Update 2012 Bruce A. Runyon Jump to: Contents (click section title or page number) Recommendations and Rationales... 3 Full-text Guideline....56
PRACTICE Management of Adult Patients with Ascites Due to Cirrhosis: Update 2012 Bruce A. Runyon Jump to: Contents (click section title or page number) Recommendations and Rationales... 3 Full-text Guideline....56
Review Group: Mental Health Operational Medicines Management Group. Signature Signature Signature. Review Date: December 2014
 Mental Health NHS Grampian Mental Health Service Staff Guidance For The Prescribing Of Vitamin Supplementation During In-Patient Admission (Mental Health) For Alcohol Withdrawal Co-ordinators: Consultant
Mental Health NHS Grampian Mental Health Service Staff Guidance For The Prescribing Of Vitamin Supplementation During In-Patient Admission (Mental Health) For Alcohol Withdrawal Co-ordinators: Consultant
CARDIOVASCULAR DYSFUNCTION IN LIVER CIRRHOSIS
 LUCIAN BLAGA UNIVERSITY OF SIBIU VICTOR PAPILIAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE CARDIOVASCULAR DYSFUNCTION IN LIVER CIRRHOSIS Ph.D. THESIS SUMMARY COORDINATOR: PROF.DR. MANIŢIU IOAN Ph.D. STUDENT: LORENA MĂRIEŞ SIBIU
LUCIAN BLAGA UNIVERSITY OF SIBIU VICTOR PAPILIAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE CARDIOVASCULAR DYSFUNCTION IN LIVER CIRRHOSIS Ph.D. THESIS SUMMARY COORDINATOR: PROF.DR. MANIŢIU IOAN Ph.D. STUDENT: LORENA MĂRIEŞ SIBIU
Enoxaparin for long term anticoagulation in patients unsuitable for oral anticoagulants
 Enoxaparin for long term anticoagulation in patients unsuitable for oral anticoagulants Traffic light classification- Amber 2 Information sheet for Primary Care Prescribers Relevant Licensed Indications
Enoxaparin for long term anticoagulation in patients unsuitable for oral anticoagulants Traffic light classification- Amber 2 Information sheet for Primary Care Prescribers Relevant Licensed Indications
CMS Limitations Guide - Laboratory Services
 CMS Limitations Guide - Laboratory Services Starting October 1, 2015, CMS will update their exisiting medical necessity limitations on tests and procedures to correspond to ICD-10 codes. This limitattions
CMS Limitations Guide - Laboratory Services Starting October 1, 2015, CMS will update their exisiting medical necessity limitations on tests and procedures to correspond to ICD-10 codes. This limitattions
Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Guide to Screening and Diagnosis
 February 2012 Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Guide to Screening and Diagnosis Reid Merryman, Harvard Medical School Year III Agenda Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) introduction Index patient: clinical presentation
February 2012 Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Guide to Screening and Diagnosis Reid Merryman, Harvard Medical School Year III Agenda Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) introduction Index patient: clinical presentation
What is Cirrhosis of the Liver?
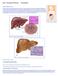 Liver Transplant Workup: Introduction What is Cirrhosis of the Liver? Cirrhosis of the liver is the end result of chronic injury to the liver from various causes. A cirrhotic liver is shrunken and fibrosed
Liver Transplant Workup: Introduction What is Cirrhosis of the Liver? Cirrhosis of the liver is the end result of chronic injury to the liver from various causes. A cirrhotic liver is shrunken and fibrosed
Chronic Kidney Disease and the Electronic Health Record. Duaine Murphree, MD Sarah M. Thelen, MD
 Chronic Kidney Disease and the Electronic Health Record Duaine Murphree, MD Sarah M. Thelen, MD Definition of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Defined by the National Kidney Foundation Either a decline in
Chronic Kidney Disease and the Electronic Health Record Duaine Murphree, MD Sarah M. Thelen, MD Definition of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Defined by the National Kidney Foundation Either a decline in
Lamivudine for Patients with hronic Hepatitis B and Advanced Liver Disease. From : New England Journal of Medicine
 Lamivudine for Patients with hronic Hepatitis B and Advanced Liver Disease From : New England Journal of Medicine Volume 351:1521-1531, Number 15, Oct 7, 2004 馬 偕 紀 念 醫 院 一 般 內 科, 肝 膽 腸 胃 科 新 竹 分 院 陳 重
Lamivudine for Patients with hronic Hepatitis B and Advanced Liver Disease From : New England Journal of Medicine Volume 351:1521-1531, Number 15, Oct 7, 2004 馬 偕 紀 念 醫 院 一 般 內 科, 肝 膽 腸 胃 科 新 竹 分 院 陳 重
Figure 1. Location of liver in the body. Figure 2. Clinical manifestations of portal hypertension
 Portal Hypertension: Introduction As early as the 17th century, it was realized that structural changes in the portal circulation could cause gastrointestinal bleeding. In 1902, Gilbert and Carnot introduced
Portal Hypertension: Introduction As early as the 17th century, it was realized that structural changes in the portal circulation could cause gastrointestinal bleeding. In 1902, Gilbert and Carnot introduced
HEPATOLOGY CLERKSHIP
 College of Osteopathic Medicine HEPATOLOGY CLERKSHIP Office for Clinical Affairs 515-271-1629 FAX 515-271-1727 Elective Rotation General Description This elective rotation is a four (4) week introductory,
College of Osteopathic Medicine HEPATOLOGY CLERKSHIP Office for Clinical Affairs 515-271-1629 FAX 515-271-1727 Elective Rotation General Description This elective rotation is a four (4) week introductory,
CANCER OF THE LIVER HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA
 CANCER OF THE LIVER HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA WHAT IS CANCER OF THE LIVER? Hepatocellular carcinoma is the most common form and it comes from the main type of liver cell, the hepatocyte. About 3 out 4
CANCER OF THE LIVER HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA WHAT IS CANCER OF THE LIVER? Hepatocellular carcinoma is the most common form and it comes from the main type of liver cell, the hepatocyte. About 3 out 4
Liver Cirrhosis: A Toolkit for Patients
 Liver Cirrhosis: A Toolkit for Patients Bring this book to every appointment Table of Contents: Welcome and Phone numbers...2 What is the liver?...2 What is liver cirrhosis...4 Treating the complications
Liver Cirrhosis: A Toolkit for Patients Bring this book to every appointment Table of Contents: Welcome and Phone numbers...2 What is the liver?...2 What is liver cirrhosis...4 Treating the complications
HEPATIC ENCEPHALOPATHY
 HEPATIC ENCEPHALOPATHY Jan Albrecht Department of Neurotoxicology, Medical Research Centre, Polish Academy of Sciences, Warsaw, Poland Brussels, July 14, 2009 DEFINITIONS: - HEPATIC ENCEPHALOPATHY (HE)
HEPATIC ENCEPHALOPATHY Jan Albrecht Department of Neurotoxicology, Medical Research Centre, Polish Academy of Sciences, Warsaw, Poland Brussels, July 14, 2009 DEFINITIONS: - HEPATIC ENCEPHALOPATHY (HE)
Albumin. Prothrombin time. Total protein
 Hepatitis C Fact Sheet February 2016 www.hepatitis.va.gov Laboratory Tests and Hepatitis If you have hepatitis C, your doctor will use laboratory tests to about learn more about your individual hepatitis
Hepatitis C Fact Sheet February 2016 www.hepatitis.va.gov Laboratory Tests and Hepatitis If you have hepatitis C, your doctor will use laboratory tests to about learn more about your individual hepatitis
HERTFORDSHIRE MEDICINES MANAGEMENT COMMITTEE (HMMC) RIVAROXABAN RECOMMENDED see specific recommendations for licensed indications below
 Name: generic (trade) Rivaroxaban (Xarelto ) HERTFORDSHIRE MEDICINES MANAGEMENT COMMITTEE (HMMC) RIVAROXABAN RECOMMENDED see specific recommendations for licensed indications below What it is Indications
Name: generic (trade) Rivaroxaban (Xarelto ) HERTFORDSHIRE MEDICINES MANAGEMENT COMMITTEE (HMMC) RIVAROXABAN RECOMMENDED see specific recommendations for licensed indications below What it is Indications
Diagnostics: Page 2 of 5
 Proteinuria Proteinuria is a condition in which there are increased amounts of protein in the urine. There are a number of different diseases which can result in proteinuria. In the early stages of the
Proteinuria Proteinuria is a condition in which there are increased amounts of protein in the urine. There are a number of different diseases which can result in proteinuria. In the early stages of the
1 ALPHA-1. The Liver and Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency (Alpha-1) FOUNDATION FOUNDATION. A patient s guide to Alpha-1 liver disease
 The Liver and Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency (Alpha-1) 1 ALPHA-1 FOUNDATION The Alpha-1 Foundation is committed to finding a cure for Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency and to improving the lives of people
The Liver and Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency (Alpha-1) 1 ALPHA-1 FOUNDATION The Alpha-1 Foundation is committed to finding a cure for Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency and to improving the lives of people
Liver Diseases. An Essential Guide for Nurses and Health Care Professionals
 Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/1047385/ Liver Diseases. An Essential Guide for Nurses and Health Care Professionals Description: Liver disease is a rapidly growing
Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/1047385/ Liver Diseases. An Essential Guide for Nurses and Health Care Professionals Description: Liver disease is a rapidly growing
Management of hepatitis C: pre- and post-liver transplantation. Piyawat Komolmit Bangkok
 Management of hepatitis C: pre- and post-liver transplantation Piyawat Komolmit Bangkok Liver transplantation and CHC Cirrhosis secondary to HCV is the leading cause of liver transplantation in the US
Management of hepatitis C: pre- and post-liver transplantation Piyawat Komolmit Bangkok Liver transplantation and CHC Cirrhosis secondary to HCV is the leading cause of liver transplantation in the US
DENOMINATOR: All patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of chronic hepatitis C cirrhosis
 Measure #401: Hepatitis C: Screening for Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) in Patients with Cirrhosis National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY
Measure #401: Hepatitis C: Screening for Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) in Patients with Cirrhosis National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY
Ascites refers to the pathologic accumulation of fluid within the peritoneal cavity. It is important
 Approach to the Patient with Ascites Differential Diagnosis Ascites refers to the pathologic accumulation of fluid within the peritoneal cavity. It is important to establish a cause for its development
Approach to the Patient with Ascites Differential Diagnosis Ascites refers to the pathologic accumulation of fluid within the peritoneal cavity. It is important to establish a cause for its development
PERITONEAL (ABDOMINAL) PARACENTESIS
 PERITONEAL (ABDOMINAL) PARACENTESIS Indications 1. To determine the cause of ascites. 2. To determine if ascites is infected. 3. For therapeutic removal of fluid: (a) (b) When distention is pronounced
PERITONEAL (ABDOMINAL) PARACENTESIS Indications 1. To determine the cause of ascites. 2. To determine if ascites is infected. 3. For therapeutic removal of fluid: (a) (b) When distention is pronounced
Patterns of abnormal LFTs and their differential diagnosis
 Patterns of abnormal LFTs and their differential diagnosis Professor Matthew Cramp South West Liver Unit and Peninsula Schools of Medicine and Dentistry, Plymouth Summary liver function / liver function
Patterns of abnormal LFTs and their differential diagnosis Professor Matthew Cramp South West Liver Unit and Peninsula Schools of Medicine and Dentistry, Plymouth Summary liver function / liver function
CASE REPORT. T. L. Krishnamoorthy 1, M. Taneja 2 & P. E. Chang 1. Key Clinical Message
 CASE REPORT Symptomatic hepatic hydrothorax successfully treated with transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) role of titration of portosystemic gradient reduction to avoid post- TIPS encephalopathy
CASE REPORT Symptomatic hepatic hydrothorax successfully treated with transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) role of titration of portosystemic gradient reduction to avoid post- TIPS encephalopathy
Living With Advanced Liver Disease
 2014 Living With Advanced Liver Disease This book belongs to: repared by: Multi Organ Transplant rogram QEII Health Sciences Centre Halifax, NS Tel 902-473-1256 Fax 902-473-5898 Website: www.mydoctor.ca
2014 Living With Advanced Liver Disease This book belongs to: repared by: Multi Organ Transplant rogram QEII Health Sciences Centre Halifax, NS Tel 902-473-1256 Fax 902-473-5898 Website: www.mydoctor.ca
Living With Hepatic Encephalopathy (HE)
 Living With Hepatic Encephalopathy (HE) What is hepatic encephalopathy (HE)? HE is a condition that occurs in people with advanced cirrhosis or severe liver damage. The damaged liver cannot remove the
Living With Hepatic Encephalopathy (HE) What is hepatic encephalopathy (HE)? HE is a condition that occurs in people with advanced cirrhosis or severe liver damage. The damaged liver cannot remove the
Optimal Management of Splenic/Portal Vein Thrombosis. David Mauchley University of Colorado
 Optimal Management of Splenic/Portal Vein Thrombosis David Mauchley University of Colorado Overview Portal Vein Thrombosis (PVT) Etiology Presentation/Clinical Aspects Diagnosis Management Cirrhotic vs.
Optimal Management of Splenic/Portal Vein Thrombosis David Mauchley University of Colorado Overview Portal Vein Thrombosis (PVT) Etiology Presentation/Clinical Aspects Diagnosis Management Cirrhotic vs.
LCD for Viral Hepatitis Serology Tests
 LCD for Viral Hepatitis Serology Tests Applicable CPT Code(s): 86692 Antibody; Hepatitis, Delta Agent 86704 Hepatitis B Core Antibody (HBcAb); Total 86705 Hepatitis B Core Antibody (HBcAb); IgM Antibody
LCD for Viral Hepatitis Serology Tests Applicable CPT Code(s): 86692 Antibody; Hepatitis, Delta Agent 86704 Hepatitis B Core Antibody (HBcAb); Total 86705 Hepatitis B Core Antibody (HBcAb); IgM Antibody
Liver, Gallbladder and Pancreas diseases. Premed 2 Pathophysiology
 Liver, Gallbladder and Pancreas diseases Premed 2 Pathophysiology Pancreas Pancreatitis Acute Pancreatitis Autodigestion of the pancreas due to activation of the enzymes Hemorrhagic fat necrosis, calcium
Liver, Gallbladder and Pancreas diseases Premed 2 Pathophysiology Pancreas Pancreatitis Acute Pancreatitis Autodigestion of the pancreas due to activation of the enzymes Hemorrhagic fat necrosis, calcium
LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS
 LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS Healthy Liver Cirrhotic Liver Tumour What causes liver cancer? Many factors may play a role in the development of cancer. Because the liver filters blood
LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS Healthy Liver Cirrhotic Liver Tumour What causes liver cancer? Many factors may play a role in the development of cancer. Because the liver filters blood
HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA (HCC) RESECTION VERSUS TRANSPLANTATION. Francis Yao, M.D.
 UCSF TRANSPLANT CONFERENCE - 9/28/2012 HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA (HCC) RESECTION VERSUS TRANSPLANTATION Francis Yao, M.D. Professor of Clinical Medicine and Surgery Medical Director, Liver Transplantation
UCSF TRANSPLANT CONFERENCE - 9/28/2012 HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA (HCC) RESECTION VERSUS TRANSPLANTATION Francis Yao, M.D. Professor of Clinical Medicine and Surgery Medical Director, Liver Transplantation
S0140-6736(14)60121-5
 Liver cirrhosis Emmanuel A Tsochatzis, Jaime Bosch, Andrew K Burroughs Cirrhosis is an increasing cause of morbidity and mortality in more developed countries, being the 14th most common cause of death
Liver cirrhosis Emmanuel A Tsochatzis, Jaime Bosch, Andrew K Burroughs Cirrhosis is an increasing cause of morbidity and mortality in more developed countries, being the 14th most common cause of death
GASTROENTEROLOGY FELLOWSHIP HEPATOLOGY ROTATION GOALS AND OBJECTIVES University of Toledo
 GASTROENTEROLOGY FELLOWSHIP HEPATOLOGY ROTATION GOALS AND OBJECTIVES University of Toledo Educational Purpose: The Hepatology Rotation introduces the fellow to the management of outpatients and inpatients
GASTROENTEROLOGY FELLOWSHIP HEPATOLOGY ROTATION GOALS AND OBJECTIVES University of Toledo Educational Purpose: The Hepatology Rotation introduces the fellow to the management of outpatients and inpatients
Alcoholic liver disease
 Alcoholic liver disease Introduction Harmful drinking Harmful drinking means drinking alcohol at levels that lead to significant harm to physical and mental health, and that may cause harm to others. Women
Alcoholic liver disease Introduction Harmful drinking Harmful drinking means drinking alcohol at levels that lead to significant harm to physical and mental health, and that may cause harm to others. Women
Clinical Practice Guidelines for Hepatocellular Carcinoma, List of Clinical Questions/Recommendations. Chapter. Grade. CQ No. 1 Interferon Therapy
 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Hepatocellular Carcinoma, List of Clinical Questions/Recommendations Chapter Chapter 1 Prevention Sectio n CQ No. 1 Interferon Therapy Clinical Question 1 Does interferon
Clinical Practice Guidelines for Hepatocellular Carcinoma, List of Clinical Questions/Recommendations Chapter Chapter 1 Prevention Sectio n CQ No. 1 Interferon Therapy Clinical Question 1 Does interferon
HYPERTENSION ASSOCIATED WITH RENAL DISEASES
 RENAL DISEASE v Patients with renal insufficiency should be encouraged to reduce dietary salt and protein intake. v Target blood pressure is less than 135-130/85 mmhg. If patients have urinary protein
RENAL DISEASE v Patients with renal insufficiency should be encouraged to reduce dietary salt and protein intake. v Target blood pressure is less than 135-130/85 mmhg. If patients have urinary protein
Department of Veterans Affairs VHA HANDBOOK 1140.5. Washington, DC 20420 March 1, 2005 COMMUNITY HOSPICE CARE: REFERRAL AND PURCHASE PROCEDURES
 Department of Veterans Affairs VHA HANDBOOK 1140.5 Veterans Health Administration Transmittal Sheet Washington, DC 20420 March 1, 2005 COMMUNITY HOSPICE CARE: REFERRAL AND PURCHASE PROCEDURES 1. REASON
Department of Veterans Affairs VHA HANDBOOK 1140.5 Veterans Health Administration Transmittal Sheet Washington, DC 20420 March 1, 2005 COMMUNITY HOSPICE CARE: REFERRAL AND PURCHASE PROCEDURES 1. REASON
Calculating the stage of Renal Disease
 Calculating the stage of Renal Disease When the Refresh Template/Check Labs button is depressed, the box next to MDRD, will be automatically checked. In order to use this in the calculation of the stage
Calculating the stage of Renal Disease When the Refresh Template/Check Labs button is depressed, the box next to MDRD, will be automatically checked. In order to use this in the calculation of the stage
